EP0354121B1 - Elektromagnetische Leistungsspule - Google Patents
Elektromagnetische Leistungsspule Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0354121B1 EP0354121B1 EP19890402191 EP89402191A EP0354121B1 EP 0354121 B1 EP0354121 B1 EP 0354121B1 EP 19890402191 EP19890402191 EP 19890402191 EP 89402191 A EP89402191 A EP 89402191A EP 0354121 B1 EP0354121 B1 EP 0354121B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- turns
- turn
- winding
- constituting
- primary
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 claims description 32
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 13
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000002470 thermal conductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000009466 transformation Effects 0.000 description 2
- PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium oxide Inorganic materials [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Al+3] PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000615 nonconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007650 screen-printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000002105 tongue Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229910000859 α-Fe Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F27/00—Details of transformers or inductances, in general
- H01F27/28—Coils; Windings; Conductive connections
- H01F27/2804—Printed windings
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F27/00—Details of transformers or inductances, in general
- H01F27/06—Mounting, supporting or suspending transformers, reactors or choke coils not being of the signal type
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F27/00—Details of transformers or inductances, in general
- H01F27/06—Mounting, supporting or suspending transformers, reactors or choke coils not being of the signal type
- H01F2027/065—Mounting on printed circuit boards
Definitions
- the present invention relates to electromagnetic power windings and transformers comprising such windings generally used in electronic power circuits and in particular in electrical supplies of electronic circuits.
- the patent D2 describes windings formed of turns comprising "two tongues forming an outward protrusion of the stack of turns constituting the winding, these tabs making it possible to easily make the electrical connection in parallel or in series of the turns" (page 3 lines 14-18 of document D2).
- the D1 patent describes an arrangement of turns comprising such tabs arranged on a support so as to better evacuate the heat released in circuits comprising these turns.
- the winding comprises a support on which rests a set of conductive, independent, contiguous turns, covered with an insulating sheath and inside which a magnetic circuit can be introduced and on which are printed conductive tracks to achieve electrical continuity between each turn.
- These conductive turns are bent on themselves towards the inside or the outside, depending on whether it is a self-inductance or a transformer, so as to form a box in which the circuit can be introduced.
- magnetic for example a ferrite.
- each of these conductive turns are located opposite one another and are produced so as to be able to rest on the support comprising an insulating and thermal conductive substrate; these ends also provide electrical continuity and conduction thermal with the insulating substrate to dissipate the heat transmitted by the turns during the passage of a current inside the winding.
- the object of the invention is to remedy these drawbacks by modifying the shape of the turns and by proposing a particular interlacing of these turns.
- the present invention relates to an electromagnetic power winding comprising conductive turns, each turn being independent and having two ends, a first and a second, the turns being aligned along the same axis, the winding consisting of a first set of turns. forming a primary winding and a second set of turns forming a secondary winding thus constituting a transformer, the electrical continuity between the turns of each set and the evacuation of the heat transmitted by the turns being ensured by the fact that each of the ends of each turn rests on a conductive track printed on an electrically insulating and thermally conductive substrate, characterized in that each turn is coated with an electrical insulating deposit to isolate it from the other turns, the turns constituting the primary and those constituting the secondary are alternated, the first and second ex end of each turn are placed side by side and arranged on the same side with respect to a median plane perpendicular to the plane of the turn and distant from it, the turns constituting the primary being pivoted by 180 ° relative to the turns constituting the secondary so that the ends of the turns
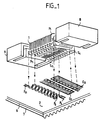
- FIG. 1 there is shown a first application of the winding according to the invention. It concerns a first application of this winding as a transformer.
- the winding comprises two sets of turns P1 to P n and S1 to S n positioned on the same axis, a magnetic circuit and a support.
- the coil is constituted, on the one hand, by a first set of conductive turns P1 to P n connected in series by the support and on the other hand, by a second set of conductive turns S1 to S n connected in parallel by the support .
- the winding behaves like a step-down or step-up transformer, the primary being for example constituted by the turns P1 to P n and the secondary by the turns S1 to S n .
- These turns P1 to P n and S1 to S n are not obtained in a conventional manner by winding a single conductive wire around a core. They are produced by a set of conductors P1 to P n and S1 to S n all identical.
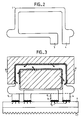
- a turn 1 is shown in Figure 2. Each of these turns is curved on itself, so as to form, for example, a rectangle inside which can be introduced a magnetic circuit.
- each of turns 3 and 4 are placed side by side and are made so that they can rest on the support to establish thermal and electrical contact.
- the ends of each turn 3 and 4 are connected to the support 2 of Figure 1 so as to allow an electrical connection, for example it is a weld.
- the shape and arrangement of the turns P1 to P n and S1 to S n have been designed so as to obtain a maximum insulation voltage by moving the ends of the primary and secondary turns away.
- the assembly of the turns P1 to P n and S1 to S n allowing the constitution of the coil of the electromagnetic power winding, is carried out in the following manner: a turn is previously taken up with a deposit of electrical insulator, as shown in Figure 2, we juxtapose a second turn that we will have rotated 180 ° so that the ends of the second turn are opposite the ends of the first turn, we then take a third turn positioned behind the second but whose ends are found opposite the ends of the first turn. These turns are alternated until the winding is formed.
- the support 2 comprises a substrate or printed circuit 6 and a cooling system, for example a radiator 7.
- the substrate or printed circuit 6 is placed on the radiator and is integral therewith, it is an electrical insulating substrate, good thermal conductor.
- a set of conductive tracks F1 to F n and G1 to G2 is printed or screen printed on the substrate 6 so that, when the coil is fixed on this substrate 6 and supplied, the current can flow through it. Indeed, at a given instant, the current arrives on the track F1, follows the first turn P1, then successively traverses the second track F2 and the turn P2 until the turn P n and the track F n .
- the winding comprising a magnetic circuit, a current also passes through each of the turns S1 to S n ; these turns being mounted in parallel thanks to the conductors G1 and G2, one recovers on the conductors a current depending on the chosen transformation ratio.
- the heat released by each turn S1 to S n and P1 to P n and by the magnetic circuit is transmitted to the substrate 6 longitudinally along these turns.
- the substrate 6 is designed to allow the electrical connection between the turns and to advantageously capture the heat given off by the winding and transmit it to the radiator 7.
- the electrical conductor that constitutes the turn also serves as a thermal conductor.
- the substrate 6 is in this particular embodiment an alumina plate a few hundred microns thick.
- the radiator 7 is known per se, it makes it possible to dissipate the heat released and thus to allow permanent cooling of the winding.
- the magnetic circuit 8, 9 consists in our particular embodiment, of two boxes able to be introduced inside the winding and to wrap the turns when they are joined in order to capture the maximum flux.
- FIG. 3 represents a sectional view of the circuit according to the invention. It makes it possible to show the movement of the heat flow over a turn via the arrows, represented in this figure, which indicate the movement of the flow during the passage of a current.
- the present invention applies to any support for any surface mounting.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Coils Of Transformers For General Uses (AREA)
- Coils Or Transformers For Communication (AREA)
Claims (2)
- Elektromagnetische Leistungswicklung mit Leiterwindungen, wobei jede Windung unabhängig ist und Zwei Enden, ein erstes (3) und ein zweites (4), aufweist, wobei die Windungen auf dieselbe Achse ausgerichtet sind, wobei die Wicklung aus einer ersten Gruppe von Windungen (P₁ bis Pn), die eine Primärwicklung bildet, sowie aus einer zweiten Gruppe von Windungen (S₁ bis Sn), die eine Sekundärwicklung bildet, aufgebaut ist und somit einen Transformator bildet, wobei die elektrische Verbindung zwischen den Windungen einer jeden Gruppe und die Abführung der von den Windungen übertragenen Wärme durch die Tatsache gewährleistet sind, daß jedes der Enden (3, 4) einer jeden Windung auf einer Leiterbahn (F₁, Fn, G₁, Gn) aufruht, die auf ein elektrisch isolierendes und thermisch leitendes Substrat (6) gedruckt ist, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß jede Windung (1) mit einer elektrisch isolierenden Beschichtung überzogen ist, um sie von den anderen Windungen (1) zu isolieren, wobei die die Primärwicklung bildenden Windungen (P₁ bis Pn) und diejenigen (S₁ bis Sn), die die Sekundärwicklung bilden, abwechseln, wobei das erste (3) und das zweite (4) Ende einer jeden Windung (1) nebeneinander und in bezug auf eine Mittelebene, die zur Ebene der Windung senkrecht ist, auf derselben Seite und von dieser entfernt angeordnet sind, wobei die die Primärwicklung bildenden Windungen (P₁ bis Pn) in bezug auf die die Sekundärwicklung bildenden Windungen (S₁ bis Sn) um 180° gedreht sind, derart, daß sich die Enden (3, 4) der Windungen (P₁ bis Pn) der Primärwicklung und die Enden (3, 4) der Windungen der Sekundärwicklung beiderseits der Mittelebene der Windungen befinden, wobei die ersten (3) bzw. die zweiten Enden der Windungen eines jeden Wicklungstyps auf entsprechende Achsen ausgerichtet sind.
- Elektromagnetische Spule gemäß Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Form einer jeden der Leiterwindungen (P₁ bis Pn, S₁ bis Sn) ein Rechteck ist.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR8810614 | 1988-08-05 | ||
| FR8810614A FR2635225A1 (fr) | 1988-08-05 | 1988-08-05 | Bobinage electromagnetique de puissance |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0354121A1 EP0354121A1 (de) | 1990-02-07 |
| EP0354121B1 true EP0354121B1 (de) | 1993-11-10 |
Family
ID=9369154
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19890402191 Expired - Lifetime EP0354121B1 (de) | 1988-08-05 | 1989-08-02 | Elektromagnetische Leistungsspule |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0354121B1 (de) |
| DE (1) | DE68910606T2 (de) |
| FR (1) | FR2635225A1 (de) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE69619420T2 (de) * | 1995-03-29 | 2002-10-31 | Valeo Electronique, Creteil | Transformatoreinrichtung, insbesondere für eine Versorgungseinrichtung von Entladungslampen in Kraftfahrzeugen |
| FR2752642B1 (fr) * | 1996-08-20 | 1998-11-06 | Thomson Csf | Transformateur-redresseur t.h.t. pour montage en surface |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR1184248A (fr) * | 1956-10-12 | 1959-07-17 | American Mach & Foundry | Inducteur à plusieurs bobines |
| FR2476898B1 (fr) * | 1980-02-22 | 1985-06-28 | Mini Informatiq System Ste Eur | Bobinage electromagnetique comportant des elements discrets et dispositif d'alimentation electrique comportant de tels bobinages |
| FR2556493B1 (fr) * | 1983-12-09 | 1987-05-29 | Inf Milit Spatiale Aeronaut | Bobinage electromagnetique et transformateur comportant un tel bobinage |
-
1988
- 1988-08-05 FR FR8810614A patent/FR2635225A1/fr active Granted
-
1989
- 1989-08-02 EP EP19890402191 patent/EP0354121B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1989-08-02 DE DE1989610606 patent/DE68910606T2/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| FR2635225A1 (fr) | 1990-02-09 |
| DE68910606T2 (de) | 1994-03-17 |
| FR2635225B1 (de) | 1995-04-07 |
| DE68910606D1 (de) | 1993-12-16 |
| EP0354121A1 (de) | 1990-02-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0523588B1 (de) | Transformatorwicklung bestehend aus einem Isolierband mit elektrisch leitfähigen Mustern zum Parallelschalten von den Mustern beim zickzackförmigen Falten dieses Isolierbandes | |
| EP0053968A1 (de) | Elektrische Verbindungsvorrichtung mit hoher Kontaktdichte | |
| EP0683547A1 (de) | Verbindungsvorrichtung zur Sicherstellung der Verbindung zwischen einen coaxial Kabel und eine gedrückte Schaltung und gedrückte Schaltung mit solchen ausgestatte Vorrichtung | |
| EP1042768B1 (de) | Wicklung für planartransformator | |
| JPH05506743A (ja) | 高密度の多極挿入コネクタ | |
| WO1990016096A1 (fr) | Connecteur electrique pour le raccordement d'un cable multiconducteur blinde a un ensemble electrique place a l'interieur d'un chassis | |
| EP3682531A1 (de) | Verbindungssystem für eine elektrische maschine | |
| EP0197888B1 (de) | Elektrischer Gleichstrommotor | |
| EP0354121B1 (de) | Elektromagnetische Leistungsspule | |
| FR2556493A1 (fr) | Bobinage electromagnetique et transformateur comportant un tel bobinage | |
| EP1022750A1 (de) | Diskretes elektronisches induktives Bauteil, und Herstellungsverfahren solcher Bauteile | |
| FR2535905A1 (fr) | Circuit de couplage a haute frequence notamment pour double amplificateur equilibre | |
| EP0392422A1 (de) | Verfahren zum Abzweigen und Festklemmen eines mehradrigen, abgeschirmten elektrischen Kabelstranges und Verbinder hierfür | |
| CA1155506A (fr) | Conducteur supraconducteur multibrins plat avec separateur | |
| EP0860835A1 (de) | Lackierter Draht mit hoher Teilentladungsfestigkeit | |
| EP0335788A1 (de) | Mikrowellenphasenschieber | |
| EP0450996B1 (de) | Anordnung zum Fixieren eines Koaxialkabels und zum Verbinden mit der Masse einer gedruckten Leiterplatte | |
| EP0033723A2 (de) | Verstellbarer elektrischer Steckverbinder für die Anpassung an unterschiedliche Steckdosen | |
| EP0070752B1 (de) | Sicherheitstransformator mit konzentrischen Wicklungen | |
| EP0858668A1 (de) | Eht-gleichrichtertransformator für oberflächenmontage | |
| FR2623030A1 (fr) | Dispositif d'alimentation electrique d'un support pour la fixation de materiel electrique et/ou electronique a un rail | |
| JPH10241955A (ja) | コイル装置 | |
| EP0095957B1 (de) | Elektrischer Verbinder für isolierte Leiter | |
| FR2762145A1 (fr) | Procede et dispositif de mise en contact d'une patte avec un ruban conducteur | |
| WO2021234320A1 (fr) | Système de connexion pour l'échange de signaux électriques à connecteurs symétriques magnétiques |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): DE GB IT NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19900703 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19920910 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE GB IT NL SE |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 68910606 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19931216 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 19931217 |
|
| RAP2 | Party data changed (patent owner data changed or rights of a patent transferred) |
Owner name: THOMSON-CSF |
|
| NLT2 | Nl: modifications (of names), taken from the european patent patent bulletin |
Owner name: THOMSON-CSF TE PARIJS, FRANKRIJK. |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| EAL | Se: european patent in force in sweden |
Ref document number: 89402191.4 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20010723 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20010724 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20010726 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20010727 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20020802 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20020803 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030301 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030301 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20020802 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed | ||
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 20030301 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 20050802 |