WO2023085262A1 - 消化管表層微小血管の血流速度測定内視鏡システム - Google Patents
消化管表層微小血管の血流速度測定内視鏡システム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2023085262A1 WO2023085262A1 PCT/JP2022/041538 JP2022041538W WO2023085262A1 WO 2023085262 A1 WO2023085262 A1 WO 2023085262A1 JP 2022041538 W JP2022041538 W JP 2022041538W WO 2023085262 A1 WO2023085262 A1 WO 2023085262A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- blood flow
- frame
- moving image
- microvessels
- endoscope
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/10—Segmentation; Edge detection
- G06T7/11—Region-based segmentation
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/00002—Operational features of endoscopes
- A61B1/00004—Operational features of endoscopes characterised by electronic signal processing
- A61B1/00009—Operational features of endoscopes characterised by electronic signal processing of image signals during a use of endoscope
- A61B1/000094—Operational features of endoscopes characterised by electronic signal processing of image signals during a use of endoscope extracting biological structures
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/04—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor combined with photographic or television appliances
- A61B1/045—Control thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/273—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor for the upper alimentary canal, e.g. oesophagoscopes, gastroscopes
- A61B1/2736—Gastroscopes
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/02—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the cardiovascular system, e.g. pulse, heart rate, blood pressure or blood flow
- A61B5/026—Measuring blood flow
- A61B5/0261—Measuring blood flow using optical means, e.g. infrared light
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/0002—Inspection of images, e.g. flaw detection
- G06T7/0012—Biomedical image inspection
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/20—Analysis of motion
- G06T7/246—Analysis of motion using feature-based methods, e.g. the tracking of corners or segments
- G06T7/248—Analysis of motion using feature-based methods, e.g. the tracking of corners or segments involving reference images or patches
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/90—Determination of colour characteristics
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/10—Image acquisition modality
- G06T2207/10016—Video; Image sequence
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/10—Image acquisition modality
- G06T2207/10068—Endoscopic image
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/30—Subject of image; Context of image processing
- G06T2207/30004—Biomedical image processing
- G06T2207/30028—Colon; Small intestine
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/30—Subject of image; Context of image processing
- G06T2207/30004—Biomedical image processing
- G06T2207/30096—Tumor; Lesion
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/30—Subject of image; Context of image processing
- G06T2207/30004—Biomedical image processing
- G06T2207/30101—Blood vessel; Artery; Vein; Vascular
- G06T2207/30104—Vascular flow; Blood flow; Perfusion
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an endoscope system for measuring the blood flow velocity of microvessels on the surface of the gastrointestinal tract.
- the present inventors measured the blood flow velocity of the gastric surface microvessels using a magnifying endoscope, and found that the blood flow velocity of the gastric surface microvessels is useful for qualitative diagnosis in the magnifying endoscopic diagnosis of early gastric cancer. We have found and reported that (Non-Patent Documents 1 to 4).
- an object of the present invention is to provide an endoscope system that measures the blood flow velocity of microvessels on the surface of the gastrointestinal tract in real time.
- the present inventors studied the real-time measurement of the blood flow velocity of the surface microvessels of the gastrointestinal tract.
- the inventors have found that the blood flow velocity of microvessels on the surface of the gastrointestinal tract can be measured in real time by measuring the change in the red color component, which indicates the movement of red blood cells in the moving image, and completed the present invention.
- an endoscopic system for measuring the blood flow velocity of microtubules in the surface layer of the gastrointestinal tract comprising a magnifying endoscope and a blood flow moving image data processing section obtained by the magnifying endoscope, (A) the magnifying endoscope captures a blood flow moving image of microvessels on the surface of the gastrointestinal tract and sends it to the blood flow moving image data processing unit; (B) An endoscope for measuring the blood flow velocity of gastrointestinal superficial microvessels, wherein the blood flow moving image data processing unit that receives the blood flow moving image performs the following data processing (B1) to (B5). system.
- the endoscope system according to [2] further performs a process of comparing the obtained blood flow velocity of the gastrointestinal superficial microvessels with the normal blood flow velocity of the gastrointestinal superficial microvessels.
- the endoscope system according to any one of [1] to [4], wherein the process of calculating the difference using the red component detects movement of red blood cells.
- the endoscope system according to any one of [1] to [5], wherein the regions generated by the regionization are regions through which red blood cells have passed between frames 1 and 2.
- a method for measuring the blood flow velocity of surface microvessels of the gastrointestinal tract comprising: using a magnifying endoscope to capture a video of the blood flow in the surface microvessels of the gastrointestinal tract; decomposing the obtained blood flow movie into frames; comparing the image of frame 1 with the next image of frame 2 to remove translation components; calculating the difference with the red component of the image with the translation component removed; a step of regionalizing the portion for which the difference of the red component is calculated;
- a method for measuring blood flow velocity in gastrointestinal superficial microvessels comprising the step of calculating a region size of obtained region data.
- the measurement method according to [9], wherein the moving image of blood flow is a moving image of blood flow of microvessels at a site suspected of having an abnormality in the surface layer of the gastrointestinal tract obtained by a magnifying endoscope.
- the measuring method according to [10] further comprising the step of comparing the obtained blood flow velocity in the gastrointestinal tract superficial microvessels with normal blood flow velocity in the gastrointestinal superficial microvessels.
- the measurement method according to any one of [9] to [11], wherein the step of removing the translation component is a step of detecting differences between frames caused by blood flow.
- the measuring method according to any one of [9] to [12], wherein the step of calculating the difference with the red component detects movement of red blood cells.
- a magnifying endoscope can be used to measure the blood flow velocity of microvessels on the surface of the gastrointestinal tract in real time.
- inflammatory bowel disease inflammatory and functional diseases related to the gastrointestinal tract
- allergic gastrointestinal diseases inflammatory and functional diseases related to the gastrointestinal tract
- abnormal gastrointestinal blood flow due to lifestyle-related diseases other than gastrointestinal diseases.
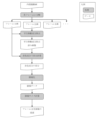
- FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a flow of obtaining blood flow velocities from frame 2 and frame 1 to frame 2 of the endoscope moving image by the endoscope system of the present invention;
- gray portions indicate processing means, and white portions indicate data.
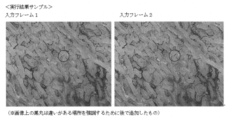
- FIG. 3 is a diagram in which translation components are removed from frames 1 and 2; It is a figure which shows the difference of a red component.
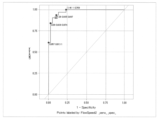
- ROC analysis results for blood flow velocities in early stage gastric cancer and mean blood flow velocities in normal gastric superficial microvessels are shown.
- One aspect of the present invention is an endoscopic system for measuring the blood flow velocity of gastrointestinal surface microtubules, comprising a magnifying endoscope and a blood flow moving image data processing unit obtained by the magnifying endoscope, (A) the magnifying endoscope captures a blood flow moving image of microvessels on the surface of the gastrointestinal tract and sends it to the blood flow moving image data processing unit; (B) An endoscope for measuring the blood flow velocity of gastrointestinal superficial microvessels, wherein the blood flow moving image data processing unit that receives the blood flow moving image performs the following data processing (B1) to (B5). System.
- Another aspect of the present invention is a method for measuring the blood flow velocity of microvessels in the surface layer of the gastrointestinal tract in real time from microvessel moving images of the surface layer of the gastrointestinal tract, comprising the following step (a): (f).
- the magnifying endoscope captures a blood flow moving image of microvessels on the surface of the gastrointestinal tract and sends it to the blood flow moving image data processing unit; All of the steps of capturing a moving image of blood flow in microvessels on the surface of the gastrointestinal tract using a magnifying endoscope are processes performed by the magnifying endoscope.
- This magnifying endoscope may be any endoscope that can measure blood flow in microvessels. Commercially available magnifying endoscopes have a moving image capturing function.
- FIG. 1 shows an example of a specific processing flow.
- Step (a) of the present invention is a step of capturing a moving image of blood flow in microvessels at a site suspected of having an abnormality in the surface layer of the gastrointestinal tract obtained by a magnifying endoscope.
- This magnifying endoscope may be any endoscope that can measure blood flow in microvessels.
- Commercially available magnifying endoscopes have a moving image capturing function.
- Steps (b) to (f) of the present invention can be performed in real time by a computer that receives blood flow moving images obtained by a magnifying endoscope.
- Known software can be used as the framework used for the image processing of the present invention. For example, OpenCV, dlib, etc. can be used. In addition, development languages such as c/c++, Python, and JavaScript can be used.
- Step (b) is a step of decomposing the obtained magnified endoscopic blood flow moving image into frames.
- This step is a step of designating a moving image file captured by a magnifying endoscope to be analyzed, and decomposing the moving image into frames.
- the moving image is decomposed into an image of frame 1, an image of frame 2, an image of frame 3, and so on, as shown in FIG.
- Step (c) is a step of comparing the image of frame 1 with the image of next frame 2 to remove the translation component.
- an image from which the translation component between the image of frame 1 and the image of frame 2 is removed is obtained (see FIG. 1).
- This step detects the difference between the frame 1 image and the frame 2 image, that is, the difference between the frames caused by the blood flow (see FIG. 2).
- Step (d) is a step of calculating the difference with the red component of the image from which the translation component has been removed.
- This step is to calculate the difference between the images of frame 1 and frame 2, ie, the difference between the frames caused by the blood flow, in the red component. Since the movement of the red component is the movement of red blood cells in blood, the movement of red blood cells can be detected by calculating the difference with the red component.
- Step (e) is a step of regionalizing the portion where the difference of the red component is calculated. This step measures the area traversed by the red blood cells between frame 1 and frame 2.
- Step (f) is a step of calculating the region size of the obtained region data. This step measures the minor and major diameters of the region size.
- the blood flow velocity in each region of Frame 2 can be measured. Also, as shown in Table 2, the blood flow velocity in each region in the other frame images of the obtained moving image can also be measured.
- this blood flow rate with the normal blood flow rate of microvessels in the surface layer of the gastrointestinal tract, it is possible to diagnose whether or not a disease such as early cancer exists in the surface layer of the gastrointestinal tract.
- the comparison of these blood flow velocities can also be performed by a computer that performs the steps (b) to (f).
- the gastrointestinal tract includes the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, small intestine, large intestine and rectum.
- gastrointestinal diseases include neoplastic lesions such as esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, duodenal cancer, colon cancer and rectal cancer; non-neoplastic lesions such as gastric polyps and colon polyps; Inflammatory and functional diseases such as intestinal disease, esophagitis, gastritis, functional dyspepsia, irritable bowel syndrome, chronic constipation, diarrhea, and bowel movements, allergic gastrointestinal diseases, lifestyle-related diseases other than gastrointestinal diseases Abnormal gastrointestinal blood flow due to Here, for example, blood flow velocities in early gastric cancer were statistically significantly slower and narrower than those in normal gastric superficial microvessels, even when intra-individual variability was taken into account. . Furthermore, when ROC analysis was performed for each average, the cutoff value was 1.09 as shown in FIG. 4 (sensitivity 90.3%, specificity 89.7%
- Example 1 Using Python as a development language and OpenCV as an image processing framework, three arguments in Table 1 were specified, and a magnified endoscopic video of the gastric mucosa was processed according to the flow in FIG.
- the magnified endoscopic video was captured using a LASEREO 7000 series (FUJIFILM) endoscope system and an EG-L600ZW7 (FUJIFILM) scope.
- the parallel movement component-removed image shown in FIG. 2 was obtained, and the difference of the red component shown in FIG. 3 was detected.
- the blood flow velocity could be measured from the blood flow moving image of the microvessels on the surface of the gastrointestinal tract obtained by the magnifying endoscope.
- Table 2 shows the region size in each frame and the measurement results of the blood flow velocity in that region.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Gastroenterology & Hepatology (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Measuring Pulse, Heart Rate, Blood Pressure Or Blood Flow (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023559636A JPWO2023085262A1 (enExample) | 2021-11-09 | 2022-11-08 | |
| US18/708,089 US20250169707A1 (en) | 2021-11-09 | 2022-11-08 | Endoscope system for measuring blood flow velocity in gastrointestinal superficial small blood vessel |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021182768 | 2021-11-09 | ||
| JP2021-182768 | 2021-11-09 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2023085262A1 true WO2023085262A1 (ja) | 2023-05-19 |
Family
ID=86336130
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2022/041538 Ceased WO2023085262A1 (ja) | 2021-11-09 | 2022-11-08 | 消化管表層微小血管の血流速度測定内視鏡システム |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20250169707A1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JPWO2023085262A1 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2023085262A1 (enExample) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0417076A (ja) * | 1990-05-10 | 1992-01-21 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | 内視鏡用画像処理装置 |
| JP2014004329A (ja) * | 2012-06-01 | 2014-01-16 | Sony Corp | 歯用装置、医療用装置及び算出方法 |
| WO2016121811A1 (ja) * | 2015-01-29 | 2016-08-04 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 画像処理装置及び画像処理方法、並びに内視鏡システム |
| WO2017061256A1 (ja) * | 2015-10-07 | 2017-04-13 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 内視鏡システム及び内視鏡システムの作動方法 |
| JP2019520879A (ja) * | 2016-05-23 | 2019-07-25 | ライカ インストゥルメンツ (シンガポール) プライヴェット リミテッドLeica Instruments (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | 顕微鏡または内視鏡等の医療用観察装置ならびに時間変調および/または空間変調を有する疑似カラーパターンを用いる方法 |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012053306A1 (ja) * | 2010-10-22 | 2012-04-26 | 学校法人 福岡大学 | 胃上皮性腫瘍(腺腫・胃癌)の診断に有用な白色不透明物質を応用した内視鏡観察法および診断能改善組成物 |
| JP6850225B2 (ja) * | 2017-09-01 | 2021-03-31 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 医療画像処理装置、内視鏡装置、診断支援装置、及び、医療業務支援装置 |
| CN120392163A (zh) * | 2020-02-14 | 2025-08-01 | 富士胶片株式会社 | 超声波诊断装置 |
-
2022
- 2022-11-08 JP JP2023559636A patent/JPWO2023085262A1/ja active Pending
- 2022-11-08 US US18/708,089 patent/US20250169707A1/en active Pending
- 2022-11-08 WO PCT/JP2022/041538 patent/WO2023085262A1/ja not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0417076A (ja) * | 1990-05-10 | 1992-01-21 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | 内視鏡用画像処理装置 |
| JP2014004329A (ja) * | 2012-06-01 | 2014-01-16 | Sony Corp | 歯用装置、医療用装置及び算出方法 |
| WO2016121811A1 (ja) * | 2015-01-29 | 2016-08-04 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 画像処理装置及び画像処理方法、並びに内視鏡システム |
| WO2017061256A1 (ja) * | 2015-10-07 | 2017-04-13 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 内視鏡システム及び内視鏡システムの作動方法 |
| JP2019520879A (ja) * | 2016-05-23 | 2019-07-25 | ライカ インストゥルメンツ (シンガポール) プライヴェット リミテッドLeica Instruments (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | 顕微鏡または内視鏡等の医療用観察装置ならびに時間変調および/または空間変調を有する疑似カラーパターンを用いる方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20250169707A1 (en) | 2025-05-29 |
| JPWO2023085262A1 (enExample) | 2023-05-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Wu et al. | A deep neural network improves endoscopic detection of early gastric cancer without blind spots | |
| Rex et al. | High-definition colonoscopy versus Endocuff versus EndoRings versus full-spectrum endoscopy for adenoma detection at colonoscopy: a multicenter randomized trial | |
| Hoffman et al. | High-definition endoscopy with i-Scan and Lugol’s solution for more precise detection of mucosal breaks in patients with reflux symptoms | |
| Cho et al. | Comparison of convolutional neural network models for determination of vocal fold normality in laryngoscopic images | |
| Wu et al. | Real-time artificial intelligence for detecting focal lesions and diagnosing neoplasms of the stomach by white-light endoscopy (with videos) | |
| Fernández-Esparrach et al. | Exploring the clinical potential of an automatic colonic polyp detection method based on the creation of energy maps | |
| Galmiche et al. | Screening for esophagitis and Barrett's esophagus with wireless esophageal capsule endoscopy: a multicenter prospective trial in patients with reflux symptoms | |
| JP2024045234A (ja) | 腸の病理学のための画像スコアリング | |
| JP7034102B2 (ja) | 対象の消化管における粘膜疾患の評価及び監視のためのシステム及び方法 | |
| Cammarota et al. | Emerging technologies in upper gastrointestinal endoscopy and celiac disease | |
| Brodersen et al. | Artificial intelligence-assisted analysis of pan-enteric capsule endoscopy in patients with suspected Crohn’s disease: A study on diagnostic performance | |
| WO2019245009A1 (ja) | 消化器官の内視鏡画像による疾患の診断支援方法、診断支援システム、診断支援プログラム及びこの診断支援プログラムを記憶したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体 | |
| CN104054092A (zh) | 用于显示体内图像流中的活动力事件的系统和方法 | |
| Yoon et al. | Lesion-based convolutional neural network in diagnosis of early gastric cancer | |
| WO2020215810A1 (zh) | 一种基于图像识别的结肠镜手术中窄带成像检测方法 | |
| JP2022002701A (ja) | 内視鏡観察法、内視鏡観察システム、およびソフトウェアプログラム製品 | |
| WO2023085262A1 (ja) | 消化管表層微小血管の血流速度測定内視鏡システム | |
| Honzawa et al. | A novel endoscopic imaging system for quantitative evaluation of colonic mucosal inflammation in patients with quiescent ulcerative colitis | |
| Aoyama et al. | Effects of artificial intelligence assistance on endoscopist performance: Comparison of diagnostic performance in superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma detection using video‐based models | |
| JP2023079866A (ja) | 超拡大内視鏡による胃癌の検査方法、診断支援方法、診断支援システム、診断支援プログラム、学習済みモデル及び画像診断支援装置 | |
| CN119091206A (zh) | 一种基于人工智能的肠镜合格退镜时间评估方法及系统 | |
| Capela et al. | TOP 100 and detection of colorectal lesions in colon capsule endoscopy: more than meets the eye | |
| Rondonotti et al. | Capsule endoscopy in portal hypertension | |
| Ebigbo et al. | Application of Artificial Intelligence in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | |
| An et al. | Improving Gastric Lesion Detection by using Specular Highlights Removal Algorithm and Deep Learning Approach |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 22892760 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2023559636 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 22892760 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWP | Wipo information: published in national office |
Ref document number: 18708089 Country of ref document: US |