WO2022034879A1 - 3次元人物モデル生成装置およびプログラム - Google Patents
3次元人物モデル生成装置およびプログラム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2022034879A1 WO2022034879A1 PCT/JP2021/029511 JP2021029511W WO2022034879A1 WO 2022034879 A1 WO2022034879 A1 WO 2022034879A1 JP 2021029511 W JP2021029511 W JP 2021029511W WO 2022034879 A1 WO2022034879 A1 WO 2022034879A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- person model
- dimensional
- information
- person
- evaluation
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
- G06N3/094—Adversarial learning
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
- G06N3/0475—Generative networks
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
- G06N3/09—Supervised learning
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T17/00—Three dimensional [3D] modelling, e.g. data description of 3D objects
- G06T17/20—Finite element generation, e.g. wire-frame surface description, tesselation
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T19/00—Manipulating 3D models or images for computer graphics
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to a three-dimensional person model generator, more specifically, a device capable of generating a desired three-dimensional person model with little effort by a designer involved in computer graphics.
- Patent Document 1 In the generation of a 3D person model, it is important that the designer can easily generate a 3D person model that meets the needs of the orderer according to the attributes and shapes required by the orderer to the designer.
- the technique of Patent Document 1 is limited to automatically generating data related to the color and texture of the surface of the three-dimensional model data, and there is still room for improvement in terms of automation to meet the needs of the ordering party.
- the designer prepares the training data as a model.
- a neural network that generates a 3D person model with the attributes desired by the orderer to the designer requires training data corresponding to each of the attributes desired by the orderer. For this reason, the designer requires a great deal of effort to prepare a large amount of training data. In order for the designer to generate the desired 3D person model with little effort, it is important to reduce the effort required for learning the neural network.
- the present disclosure has been made in view of such circumstances, and the purpose is to generate a 3D person model desired by the orderer with as little effort as possible by a designer involved in computer graphics. It is to provide a model generator.
- the inventor of the present application has found that the above object can be achieved by performing unsupervised learning of a neural network, and has completed the present disclosure. Specifically, the present disclosure provides:
- the first disclosure includes person model configuration information capable of constructing a three-dimensional person model, evaluation information regarding each of a plurality of types of three-dimensional person models composed of the person model configuration information, and the plurality of types of three-dimensional person models.
- An evaluation learning unit that allows the first neural network to machine-learn the evaluation criteria of the plurality of types of three-dimensional person models using the attribute information of the above, and a plurality of types using the second neural network and the attribute information.
- a generation unit capable of generating a generated 3D person model, an evaluation unit capable of evaluating the plurality of types of generated 3D person models using the evaluation criteria and the attribute information, and the plurality of types of generated 3 Among the dimensional person models, an output unit capable of outputting a single type of output 3D person model evaluated by the evaluation unit or a plurality of types of output 3D person models evaluated by the evaluation unit, and the output unit 3 Regarding the dimensional person model, an update that enables the person model configuration information to be updated by the receiving unit capable of receiving user evaluation information and the output three-dimensional person model, and the evaluation information can be updated by the user evaluation information.
- a three-dimensional person model generation device including a unit and a machine learning unit capable of performing machine learning by unsupervised learning for at least the second neural network.
- the generation unit can generate a plurality of generated 3D person models having the attributes required by the user in the 3D person model. Then, the output unit satisfies the evaluation criteria regarding the attributes from the plurality of generated 3D person models generated by the generation unit, that is, a plurality of types of output 3D persons recognized as a desired 3D person model. Models can be selected and output. Since a series of processes related to the output of the output 3D person model are automatically performed, the designer can output the 3D person model desired by the user (orderer) with less effort.
- the person model composition information, evaluation information, and attribute information play the role of training data that serves as a model for machine learning. Since the update unit can update the person model configuration information and the evaluation information, the designer can prepare the training data with less effort. That is, the designer can obtain an evaluation standard that further reflects the attributes required by the user (orderer to the designer) in the three-dimensional person model with less effort. As a result, the designer can output the three-dimensional person model desired by the user (orderer) with less effort.
- the generation unit can generate the three-dimensional person model desired by the user (orderer to the designer) in a more vivid state by using the machine-learned second neural network.
- Machine learning by unsupervised learning can be executed without external training data as a model, so the 3D person model desired by the user (orderer) can be made more vivid without increasing the labor of the designer. Can be generated in a state of being.
- a three-dimensional person model generator capable of generating a three-dimensional person model desired by a user (orderer) with as little effort as possible by a designer involved in computer graphics.
- the machine learning unit can execute the machine learning by the unsupervised learning for both the first neural network and the second neural network.
- a dimensional person model generator is provided.
- the evaluation learning department in order to perform machine learning by unsupervised learning, has an evaluation standard based on the updated person model composition information and evaluation information even without the training data given by the designer. Can be machine-learned by the first neural network. Therefore, the three-dimensional person model desired by the user (orderer) can be output in a more vivid state without increasing the labor of the designer.
- the third disclosure in addition to the first disclosure or the second disclosure, provides a three-dimensional person model generator in which the unsupervised learning is learning by a hostile generation network.
- machine learning can be performed by a hostile generation network in which the second neural network is used as the generator of the hostile generation network and the first neural network is used as the classifier of the hostile generation network.
- the generator In machine learning with a hostile generation network, the generator generates the data and the classifier identifies the generated data. Then, the generator performs machine learning for the purpose of being identified by the classifier as the generated data being correct data.
- the generator is the second neural network for the generation of the generated 3D person model
- the discriminator is the first neural network that machine-learns the evaluation criteria of the 3D person model.
- the user uses the generated 3D person model generated in the second neural network by the first neural network that machine-learned the evaluation criteria. It corresponds to evaluating it as a three-dimensional person model having the desired attributes. That is, the second neural network performs machine learning for the purpose of generating a generated three-dimensional person model that is evaluated by the first neural network as having the attributes required by the user (orderer).
- the generation unit using the second neural network can generate a desired three-dimensional person model in a more vivid state.
- Machine learning by the above-mentioned hostile generation network is unsupervised learning, so it does not increase the effort of the designer. Therefore, according to the third disclosure, it is possible to provide a three-dimensional person model generation device capable of generating a three-dimensional person model desired by a user (orderer) with little effort by a designer involved in computer graphics.
- the fourth disclosure is any one of the first to the third disclosures, wherein the attribute information provides a three-dimensional person model generation device including information on a person's characteristics.
- the first neural network machine-learn the evaluation criteria regarding the characteristics of the person desired by the user (orderer).
- the first neural network sets the evaluation criteria of the 3D person model to the part corresponding to the characteristics of the person required by the user who uses the 3D person model (the orderer who orders the 3D person model from the designer).
- Machine learning can be done to pay attention and evaluate.
- the designer can easily generate and output a 3D person model that captures the characteristics of the person desired by the user (orderer) of the 3D person model through the information on the characteristics of the person included in the attribute information. Can be done.
- the fifth disclosure is any one of the first to the fourth disclosures, wherein the attribute information provides a three-dimensional person model generation device including information regarding a purpose of use of the three-dimensional person model.
- the generation unit can generate a generated three-dimensional person model according to the purpose of use. Therefore, the designer can generate the 3D person model desired by the user (orderer) simply by specifying the purpose of use without the labor of specifying the attribute information of the 3D person model according to the purpose of use. be able to. Therefore, the designer involved in computer graphics can generate the three-dimensional person model desired by the user (orderer) with less effort.
- the sixth disclosure is any one of the first to fifth disclosures, wherein the attribute information makes it possible to identify the singular type of output 3D person model or a plurality of types of output 3D person models.
- a three-dimensional person model generator including identification information is provided.
- the evaluation information updated by the user evaluation information is associated with the output three-dimensional person model by the identification information included in the attribute information. Can be done.
- the first neural network can be machine-learned about the evaluation criteria for the output three-dimensional model without updating the person model configuration information. If the person model composition information is not updated, the designer will not have to wait due to the update of the person model composition information, and the effort of the designer can be reduced.
- the seventh disclosure is a change in the category of the configuration pertaining to the first disclosure.
- a three-dimensional person model generator capable of generating a three-dimensional person model desired by a user (orderer) of the three-dimensional person model with as little effort as possible by a designer involved in computer graphics. ..
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an example of the configuration of the three-dimensional person model generation device 1 (hereinafter, also simply referred to as “generation device 1”) of the present embodiment.
- the generation device 1 includes at least a control unit 11, a storage unit 12, a display unit 13, and an input unit 14.
- the control unit 11 includes a CPU (Central Processing Unit), a RAM (Random Access Memory), a ROM (Read Only Memory), and the like.
- a CPU Central Processing Unit
- RAM Random Access Memory
- ROM Read Only Memory
- the control unit 11 reads a predetermined program, and the storage unit 12, the display unit 13, and the input unit 14 cooperate with each other as necessary to generate the evaluation learning unit 111, which is an element of the software configuration in the generation device 1.
- a unit 112, an evaluation unit 113, an output unit 114, a receiving unit 115, an updating unit 116, a machine learning unit 117, and the like are realized.
- the storage unit 12 is a device for storing data and files, and has a data storage unit such as a hard disk, a semiconductor memory, a recording medium, and a memory card.
- the storage unit 12 has a mechanism that enables connection with a storage device such as NAS (Network Area Network), SAN (Storage Area Network), cloud storage, a file server, a distributed file system, or a storage system via a network. You may.
- the storage unit 12 stores a control program executed by a microcomputer, a person model information table 121, a neural network table 122, and the like. Signals and information are input to the storage unit 12 from the output unit 114 of the control unit 11. Further, signals and information are transmitted from the storage unit 12 to the receiving unit 115 of the control unit 11.
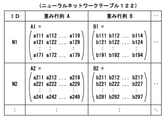
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing an example of the person model information table 121.
- the person model information table 121 shown in FIG. 2 has an “ID” that identifies the person model information, a shape of the three-dimensional person model, a texture of the surface of the three-dimensional person model, and a color of the surface of the three-dimensional person model.
- Information that associates "configuration information", "evaluation information” about a three-dimensional person model composed of person model configuration information, and "attribute information" of a three-dimensional person model is stored.
- the person model information table 121 is configured so that information associated with an ID, a person model configuration information, and an attribute information can be added. Since the person model information table 121 is configured so that information can be added, the update unit 116 can update the person model configuration information by the output three-dimensional person model.
- the person model configuration information is information that can configure a three-dimensional person model.
- the three-dimensional person model is not particularly limited as long as it is a three-dimensional model for visually expressing a person or a part of the person.
- the three-dimensional person model may be either male or female, and may include at least one of three-dimensional models of clothing, ornaments, and props worn by the person.
- the format of the person model composition information is not particularly limited, and the person model composition information in the format of the prior art can be stored.
- the person model configuration information preferably includes at least one of information regarding the three-dimensional shape of the three-dimensional person model, information regarding the texture of the surface of the three-dimensional person model, and information regarding the color of the surface of the three-dimensional person model. ..
- the person model configuration information preferably includes at least one of information regarding the three-dimensional shape of the three-dimensional person model, information regarding the texture of the surface of the three-dimensional person model, and information regarding the color of the surface of the three-dimensional person model. ..
- the first neural network N1 is machine-learned about the evaluation criteria for at least one of the three-dimensional shape of the three-dimensional person model, the surface color of the three-dimensional person model, and the surface color of the three-dimensional person model. Can be done.
- the person model information table 121 can provide training data as a model to the second neural network N2 described later.
- the second neural network N2 can machine-learn the generation algorithm for at least one of the three-dimensional shape of the three-dimensional person model, the surface color of the three-dimensional person model, and the surface color of the three-dimensional person model.
- a person model configuration constituting a three-dimensional person model in which the shape is an elongated face and the surface color and texture are light-colored hair, beard, and light-colored skin. Information is stored.
- the person model configuration information may include information that can configure the output three-dimensional person model output by the output unit 114, which will be described later.
- the information that can configure the output 3D person model is not particularly limited as long as the output 3D person model can be configured, and the output 3D person model in the conventional format is used in the same manner as the person model configuration information.
- evaluation information is user's evaluation information performed on a three-dimensional person model composed of person model configuration information.
- evaluation information indicating the ratio of matching the evaluation criteria for the three-dimensional person model required by the user on a scale of 100 points is stored as evaluation information.
- the format of the evaluation information is not limited to the evaluation showing the ratio of matching the evaluation criteria on a scale of 100 points.
- information on the score evaluated by the user of the 3D person model and the attributes of the 3D person model are listed. It may include information, information listing attributes that the 3D person model does not have, and the like.
- the evaluation criteria may include the history of the three-dimensional person model purchased by the user after placing an order.
- the route in which the user's evaluation is input to the receiving unit 115 includes a route input from the input unit 14 to the receiving unit 115 and a route input to the receiving unit 115 via the external device 120 and the communication unit 15. including.
- the user is an orderer who orders a 3D person model from a designer.
- the attribute information is the attribute information of the three-dimensional person model composed of the person model configuration information.
- the format of the attribute information is not particularly limited, and may include arbitrary information regarding the attributes of the three-dimensional person model.
- the attribute information includes information on "characteristics of the person desired by the user".
- information on the characteristics of a person such as "bright-colored hair", “slender face”, and “beard” is stored as attribute information associated with the ID "M1".
- the first neural network N1 described later can machine-learn the evaluation criteria on the characteristics of the person requested by the user (orderer).
- the first neural network N1 pays attention to and evaluates the part corresponding to the characteristics of the person desired by the user who uses the 3D person model (the orderer who orders the 3D person model from the designer).
- Machine learning can be performed on the evaluation criteria of a 3D person model.
- the designer can easily generate and output a 3D person model that captures the characteristics of the person desired by the user (orderer) of the 3D person model through the information on the characteristics of the person included in the attribute information. Can be done.
- the attribute information includes information on the purpose of use of the three-dimensional person model.
- information on the purpose of use of the three-dimensional person model "for advertising in the North American region” is stored as the attribute information associated with the ID "M1".
- the purpose of use includes advertising areas such as "for advertising in North America", “for advertising in Asia”, “for advertising in Europe”, and "for advertising in Africa".
- the first neural network N1 pays attention to whether or not the user who uses the 3D person model (the orderer who orders the 3D person model from the designer) is suitable for the purpose of using the 3D person model. You can machine-learn the evaluation criteria of the 3D person model so that you can evaluate it.
- the designer obtains a 3D person model suitable for the purpose of use of the 3D person model requested by the user (orderer) of the 3D person model through the information regarding the purpose of use of the 3D person model included in the attribute information. It can be easily generated and output.
- the generation device 1 can receive the purpose of use of the three-dimensional person model via the attribute information. Therefore, the designer can generate the generated 3D person model according to the purpose of use only by specifying the purpose of use without requiring the labor of specifying the attribute information of the 3D person model according to the purpose of use one by one. Therefore, the designer involved in computer graphics can generate the three-dimensional person model desired by the user (orderer) with less effort.
- the attribute information includes identification information that makes the output 3D person model identifiable.
- the information "output 3D person model: P1" that enables the output 3D person model to be identified is stored.
- the evaluation information updated by the user evaluation information can be associated with the output three-dimensional person model by the identification information included in the attribute information.
- the first neural network N1 can be machine-learned about the evaluation criteria for the generated three-dimensional model without updating the person model configuration information stored in the person model information table 121. If the person model composition information is not updated, the designer will not have to wait due to the update of the person model composition information, and the effort of the designer can be reduced.
- the information stored in the person model information table 121 can be easily acquired and updated. Since the evaluation information is stored, it is possible to provide training data as a model to the first neural network N1 described later. As a result, the first neural network N1 can be machine-learned about the evaluation criteria of the three-dimensional person model. Since the attribute information is stored, the evaluation learning unit 111 sets the evaluation criteria regarding the attributes required for the 3D person model by the orderer to the graphic designer who is the user of the 3D person model in the first neural network N1. Can be learned.
- the generation unit 112 can generate a plurality of generated 3D person models having the attributes required by the user in the 3D person model. Then, the output unit 114 satisfies the evaluation criteria regarding the attributes from the plurality of generated three-dimensional person models generated by the generation unit 112, that is, a plurality of types of output units 3 recognized as a desired three-dimensional person model. Dimensional person models can be selected and output.
- a person model configuration constituting a three-dimensional person model in which the shape is an elongated face and the surface color and texture are light-colored hair, whiskers, and light-colored skin.
- "Bearded”, "light-colored skin”, and “for advertising in the North American region” are associated and memorized.
- the person model information table 121 can store the person model configuration information, the evaluation information, and the attribute information in association with each other.
- FIG. 3 is a diagram showing an example of the neural network table 122.
- the neural network table 122 includes at least a first neural network N1 (corresponding to ID “N1”) relating to the evaluation criteria of the three-dimensional person model and a second neural network N2 (corresponding to ID “N2”) relating to the generation of the three-dimensional person model. ) Is memorized.
- the format of the first neural network N1 and the second neural network N2 is not particularly limited, and activation that determines the presence or absence of a signal output by an artificial neuron (also referred to as a node) of the neural network or the strength of the signal.
- a data structure containing information on a bias vector that gives a reference weight (also referred to as a bias parameter or simply bias) to a signal input to an artificial neuron in a neural network, information on the connection relationship between artificial neurons of a neural network, and the like. May include.
- the types of the first neural network N1 and the second neural network N2 stored in the neural network table 122 are not particularly limited, and are, for example, a forward propagation type neural network (also referred to as a feed-forward neural network or FFNN) and a convolution.
- Neural network also referred to as Convolutional neural network, CNN, or ConvNet
- Deep stacking network also referred to as DSN
- RBF network also referred to as Radial basefaction network
- regression type Various conventional neural networks such as a recurrent neural network, or RNN), a modular neural network, etc. are referred to as a first neural network N1 and a second neural network N2. It can be stored in the table 122.
- the neural network table 122 shown in FIG. 3 stores the "ID" that identifies the neural network and the weight matrices A and B of the neural network in association with each other. There is. By storing the ID, it becomes easy to acquire and update the information stored in the neural network table 122. By storing the weight matrices A and B of the neural network, it is possible to perform generation or evaluation using the neural network and to make the neural network perform machine learning.
- the first neural network N1 represented by the weight matrix A1 (matrix including elements a111 to a179) and the weight matrix B1 (matrix including elements b111 to b194) is included. It is stored.
- the evaluation learning unit 111 can make the first neural network N1 machine-learn the evaluation criteria. Further, by storing the weight matrix A1 and the weight matrix B1, the evaluation unit 113 can evaluate the generated three-dimensional person model.
- a second neural network N2 represented by a weight matrix A2 (a matrix containing elements a211 to a249) and a weight matrix B2 (a matrix containing elements b211 to b297) is included. It is stored.
- the generation unit 112 can generate the generated three-dimensional person model. Further, by storing the weight matrix A2 and the weight matrix B2, the machine learning unit 117 can execute machine learning regarding the second neural network N2.
- the evaluation learning unit 111 can make the first neural network N1 learn the evaluation criteria of the three-dimensional person model.
- the generation unit 112 can generate a plurality of types of generated three-dimensional models.
- the machine learning unit 117 can execute machine learning by unsupervised learning on the second neural network N2.
- Machine learning is a method of learning without giving a correct answer to the learning data.
- Display unit 13 The type of the display unit 13 is not particularly limited. Examples of the display unit 13 include a monitor, a touch panel, a projector, a video card for displaying an output three-dimensional person model on an external device 120, and the like. Signals and information output from the output unit 114 of the control unit 11 are input to the display unit 13.
- the type of the input unit 14 is not particularly limited. Examples of the input unit 14 include a keyboard, a mouse, a touch panel, a communication device that receives input from an external device 120, and the like. The signals and information input from the input unit 14 are input to the receiving unit 115 of the control unit 11. The user's order information input to the input unit 14 is sent to the receiving unit 115.
- the generation device 1 may include a communication unit 15 that communicates between the generation device 1 and the external device 120.
- the communication unit 15 and the external device 120 are connected via the network 123.
- the network 123 may be constructed either wirelessly or wiredly. Further, the external device 120 may be singular or plural.
- the generation device 1 can transmit the output three-dimensional person model output by the output unit 114 to the external device 120.
- the generation device 1 can receive a command regarding generation of the three-dimensional person model from the external device 120.
- the generation device 1 can receive and use the person model configuration information, the evaluation information, the attribute information, the user evaluation information, and the like from the external device 120.
- the external device 120 may be either a portable terminal or a fixed terminal.
- the external device 120 is operated by a user and has a control circuit 125, an input unit 126, a display unit 127, a storage unit 128, and a communication unit 129.
- the control circuit 125 is a computer having an input port, an output port, and a central arithmetic processing circuit.
- the control circuit 125 is connected to the input unit 126, the display unit 127, the storage unit 128, and the communication unit 129 so as to be able to transmit and receive signals.
- Examples of the input unit 126 include a keyboard, a mouse, a touch panel, a communication device that receives input from an external device 120, and the like.
- Examples of the display unit 127 include a monitor, a touch panel, a projector, a video card for displaying an output three-dimensional person model on an external device 120, and the like.
- the storage unit 128 is a device for storing data and files, and has a data storage unit such as a hard disk, a semiconductor memory, a recording medium, and a memory card.
- the communication unit 129 is connected to the network 123.
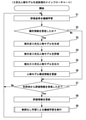
- FIG. 4 is an example of a main flowchart showing the procedure of the generation process in this modification.
- a preferred procedure for the generation process performed by the generation device 1 will be described with reference to FIG.
- Step S1 Machine learning of evaluation criteria
- the control unit 11 executes the evaluation learning unit 111 in cooperation with the storage unit 12, refers to the person model information table 121, and sets the evaluation criteria of a plurality of types of three-dimensional person models to the first neural network N1.
- the process of learning is executed (step S1).
- the algorithm for machine learning the evaluation criteria in step S1 is not particularly limited, and is a probabilistic gradient descent method such as an error back propagation method, a Widrow-Hoff method (also referred to as a delta rule), a gradient descent method, online learning, and the like.
- Machine learning algorithms for supervised learning of known neural networks using one or more of batch learning, logistic functions, sigmoid functions, maximum value functions, etc. can be used.
- the control unit 11 executes the evaluation learning unit 111 and acquires the person model configuration information, the evaluation information, and the attribute information from the person model information table 121. Then, the control unit 11 causes the first neural network N1 stored in the neural network table 122 to machine-learn the evaluation criteria using the person model configuration information, the evaluation information, and the attribute information, and stores the evaluation criteria in the neural network table 122. The first neural network N1 is updated. In other words, the control unit 11 acquires the person model configuration information, the evaluation information, and the attribute information from the person model information table 121, and serves as a model for the person model configuration information, the evaluation information, and the attribute information in the first neural network N1. Machine-learn evaluation criteria using as training data.
- the first neural network N1 can be machine-learned about the evaluation criteria regarding the attributes required by the graphic designer who is the user of the 3D person model.
- the control unit 11 finishes the process of step S1, the control unit 11 makes a determination of step S2.
- Step S2 Determine whether or not attribute information has been received
- the control unit 11 executes the generation unit 112 in cooperation with the storage unit 12 and the input unit 14, and determines whether or not the reception unit 115 has received the attribute information (step S2).
- the control unit 11 determines Yes in step S2, and performs the processing in step S3. If the control unit 11 has not received the attribute information, it determines No in step S2 and determines in step S7.
- Step S3 Generate a generated 3D person model
- the control unit 11 executes the generation unit 112 in cooperation with the storage unit 12 to acquire the second neural network N2 stored in the neural network table 122. Then, the control unit 11 generates a plurality of types of generated three-dimensional person models by using the attribute information received in step S2 and the second neural network N2 (step S3).
- the generation unit 112 can generate a plurality of random three-dimensional person models by using the attribute information received in step S2 and the second neural network N2 represented by the weight matrices A2 and B2. As a result, the designer can generate a plurality of generated 3D person models having the attributes required by the user (orderer) of the 3D person model in the 3D person model with little effort.
- the control unit 11 proceeds to step S4 after the processing of step S3.
- Step S4 Evaluate the generated 3D person model
- the control unit 11 executes the evaluation unit 113 in cooperation with the storage unit 12 and acquires the first neural network N1 stored in the neural network table 122. Then, the control unit 11 evaluates a plurality of types of generated three-dimensional person models generated in step S3 using the attribute information received in step S2 and the first neural network N1 (step S4).
- control unit 11 uses the attribute information received in step S2 and the first neural network N1 whose evaluation criteria are machine-learned in step S1 to generate a plurality of types of generated three dimensions in step S3. Evaluate the person model. Therefore, the plurality of types of generated three-dimensional person models generated by the generation unit 112 are given an evaluation regarding the attributes indicated by the attribute information received in step S2. The control unit 11 proceeds to step S5 after the processing of step S4.
- Step S5 Output the output 3D person model
- the control unit 11 executes the output unit 114 in cooperation with the storage unit 12 and the display unit 13, and among the plurality of types of generated three-dimensional person models generated in step S3, a predetermined evaluation is made in step S4.
- the generated 3D person model is output as the output 3D person model (step S5).
- the output unit 114 can select and output the output three-dimensional person model for which a predetermined evaluation has been made with respect to the attribute indicated by the attribute information received in step S2. Since a series of processes related to the output of the output 3D person model are automatically performed, the designer can output the 3D person model desired by the user (orderer) with less effort.
- the control unit 11 proceeds to step S6 after the processing of step S5.
- Step S6 Update the person model configuration information
- the control unit 11 executes the update unit 116 in cooperation with the storage unit 12, and includes a new ID and information that can configure the output three-dimensional person model output in step S5, and the person model configuration information and the subject.
- Output Three-dimensional person model is added to the person model information table 121 by associating it with attribute information including identifiable information (step S6).
- the update unit 116 links the new ID and the person model configuration information including the information that can configure the output 3D person model output in step S5 and the attribute information including the information that can identify the output 3D person model.
- the person model configuration information stored in the person model information table 121 is updated.
- the designer can prepare training data as a model used in the process executed in step S1 and the process executed in step S9 described later with little effort. That is, the designer can obtain an evaluation standard that further reflects the attributes required by the user (orderer to the designer) in the three-dimensional person model with less effort. As a result, the designer can output the three-dimensional person model desired by the user (orderer) with less effort.
- control unit 11 determines in step S2 whether or not the attribute information has been received, and performs subsequent processing.
- the control unit 11 can skip the processes executed in steps S3 to S5 for generating, evaluating, and outputting the three-dimensional person model according to the attribute information.
- the control unit 11 can skip step S6 relating to the update of the person model configuration information. As a result, the amount of processing executed by the control unit 11 can be reduced.
- the control unit 11 proceeds to step S7 after the processing of step S6.
- Step S7 Determine whether or not evaluation information has been received from the user
- the control unit 11 executes the reception unit 115 in cooperation with the storage unit 12 and the input unit 14, and determines whether or not the evaluation information has been received from the user (step S7).
- the control unit 11 determines Yes in step S7 and proceeds to step S8. If the control unit 11 has not received the evaluation information from the user, the control unit 11 determines No in step S7 and returns to step S1.
- Step S8 Update evaluation information
- the control unit 11 executes the update unit 116 in cooperation with the storage unit 12, and the output three-dimensional person model output in S5 stored in the person model information table 121 according to the evaluation information received from the user.
- the evaluation information regarding the above is updated (step S8).
- the designer can use the training data as a model used in the process executed in step S1 and the process executed in step S9 described later. Can be prepared with little effort. That is, the designer can obtain an evaluation standard that further reflects the attributes required by the user (orderer to the designer) in the three-dimensional person model with less effort. As a result, the designer can output the three-dimensional person model desired by the user (orderer) with less effort.
- the control unit 11 proceeds to step S9 after the processing of step S8.
- Step S9 Perform machine learning by unsupervised learning
- the control unit 11 executes the machine learning unit 117 in cooperation with the storage unit 12, and acquires the person model configuration information, the evaluation information, and the attribute information from the person model information table 121. Then, using the person model configuration information, evaluation information, and attribute information, the second neural network N2 stored in the neural network table 122 is machine-learned to generate a three-dimensional person model by unsupervised learning, and the neural network table 122 is used. The second neural network N2 stored in is updated (step S9).
- the algorithm for performing machine learning in step S9 is not particularly limited as long as it is unsupervised learning, and is also referred to as cluster analysis, principal component analysis, vector quantization, self-organizing mapping, genomic adversarial network, or GAN.
- a machine learning algorithm for unsupervised learning of known neural networks using one or more of deep belief network (also referred to as DBN), Heb's law, etc. can be used.
- the machine learning executed in step S9 enables the second neural network N2 to generate a three-dimensional person model related to attribute information in a more vivid state.
- the generation unit 112 can generate the three-dimensional person model desired by the user (orderer to the designer) in a more vivid state by using the second neural network N2 in which machine learning has been performed. Since the machine learning by unsupervised learning executed in step S9 can be executed without being given training data as a model from the outside, the generator 1 can be used by the user (orderer) without increasing the labor of the designer. ) Can generate the desired three-dimensional person model in a more vivid state.
- the 3D person model generator capable of generating the 3D person model desired by the user (orderer) with as little effort as possible by the designer involved in computer graphics. 1 can be provided.
- the control unit 11 returns to step S1 after the processing of step S9.
- control unit 11 determines whether or not the evaluation information has been received from the user, and when the control unit 11 receives the evaluation information from the user, the control unit 11 performs "machine learning by unsupervised learning". be able to. "Machine learning by unsupervised learning” will be described later. Further, the control unit 11 can repeat the three-dimensional person model generation process without performing "machine learning by unsupervised learning" when the evaluation information is not received from the user.
- the algorithm that performs machine learning in step S9 can suppress variations in the output from the neural network with respect to the input to the neural network, and also performs various functions on the neural network, including generation and evaluation of a three-dimensional person model. It is preferable to include a hostile generation network because it is feasible in.
- the received attribute information corresponds to the input to the 2nd neural network N2
- the generated 3D person model is the 2nd neural network N2.
- the second neural network N2 generates only the desired 3D person model in a vivid state with respect to the received attribute information, and the desired 3D person model. It is possible not to generate a non-three-dimensional person model similar to. That is, it becomes possible to generate a three-dimensional person model related to attribute information in a more vivid state.
- FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing an example of the flow of machine learning processing when the hostile generation network executed in step S9 is used.
- a preferable procedure of the machine learning process executed in step S9 of FIG. 4 will be described by taking as an example the case where the algorithm for performing machine learning includes a hostile generation network.
- Step S11 Acquire attribute information
- the control unit 11 executes the machine learning unit 117 in cooperation with the storage unit 12, and sets the update count indicating the number of updates of the second neural network N2 to 0.
- the control unit 11 further acquires the attribute information (step S11).
- step S11 By setting the update number to 0 by the control unit 11, machine learning can be continuously executed a predetermined number of times.
- the control unit 11 can execute machine learning according to the attribute information.
- the control unit 11 proceeds to step S12 after the processing of step S11.
- Step S12 Generate a generated 3D person model
- the control unit 11 executes the machine learning unit 117 in cooperation with the storage unit 12 and generates a generated person model using the second neural network N2 (step S12).
- a generator In machine learning with a hostile generation network, a generator generates data and a discriminator identifies the generated data. Then, the generator performs machine learning for the purpose of being identified by the classifier as the generated data being correct data.
- the control unit 11 can make the second neural network N2 a generator in the hostile generation network. The control unit 11 proceeds to step S13 after the processing of step S12.
- Step S13 Evaluate the generated 3D person model
- the control unit 11 executes the machine learning unit 117 in cooperation with the storage unit 12, and evaluates the generated person model generated in step S12 using the first neural network N1 (step S13).
- the machine learning unit 117 uses the first neural network N1 to evaluate the generated person model generated in step S12 by the control unit 11 in step S13. Therefore, the first neural network N1 can be a discriminator in a hostile generation network. Therefore, the machine learning unit 117 can execute machine learning by a hostile generation network in which the second neural network N2 is used as a generator in the hostile generation network and the first neural network N1 is used as a discriminator in the hostile generation network.
- the control unit 11 determines in step S14 after the processing in step S13.
- Step S14 Determining whether or not the evaluation criteria for attributes are satisfied
- the control unit 11 executes the machine learning unit 117 in cooperation with the storage unit 12, and determines whether or not the generated three-dimensional person model generated in step S12 satisfies the evaluation criteria regarding the attributes (step S14). .. If the control unit 11 satisfies the evaluation criteria regarding the attributes, the control unit 11 determines Yes in step S14, and proceeds to step S15. If the control unit 11 does not satisfy the evaluation criteria for the attribute, the control unit 11 determines No in step S14 and proceeds to step S16.
- Step S15 Update the second neural network N2 to generate more similar 3D person models to be generated
- the control unit 11 executes the machine learning unit 117 in cooperation with the storage unit 12 to generate more generated three-dimensional person models similar to the generated person model generated in step S12. Update network N2 (step S15).
- step S12 Generation using the second neural network N2 by updating the second neural network N2 so that the machine learning unit 117 generates more generated three-dimensional person models similar to the generated person model generated in step S12.
- the unit 112 will generate more generated 3D person models similar to the generated 3D person model obtained the predetermined evaluation in step S13. That is, the generation unit 112 can generate the three-dimensional person model desired by the user (orderer) in a more vivid state.
- the control unit 11 proceeds to step S17 after the processing of step S15.
- Step S16 Update the second neural network N2 to generate less similar 3D person models to be generated
- the control unit 11 executes the machine learning unit 117 in cooperation with the storage unit 12 to generate less generated three-dimensional person models similar to the generated person model generated in step S12. Update network N2 (step S16).
- Unit 112 will generate fewer generated 3D person models that are similar to the generated 3D person model for which the predetermined evaluation was not obtained in step S13. That is, the generation unit 112 can generate the three-dimensional person model desired by the user (orderer) in a more vivid state.
- control unit 11 determines in step S14 whether or not the generated three-dimensional person model generated in step S12 satisfies the evaluation criteria regarding the attributes. Then, the machine learning unit 117 can update the second neural network N2 so as to change the ratio of generation of similar three-dimensional person models to be generated depending on whether or not the evaluation criteria for attributes are satisfied. The control unit 11 proceeds to step S17 after the processing of step S15 or after the processing of step S16.
- Step S17 Increase the number of updates by 1
- the control unit 11 executes the machine learning unit 117 in cooperation with the storage unit 12 and increases the number of updates by 1 (step S17). By increasing the number of updates by 1, the number of times the second neural network N2 has been updated can be reflected in the number of updates.
- the control unit 11 proceeds to step S18 after the processing of step S17.
- Step S18 Determining whether or not the number of updates is a predetermined number or more
- the control unit 11 executes the machine learning unit 117 in cooperation with the storage unit 12, and determines whether or not the number of updates is equal to or greater than a predetermined number (step S18). If the number of updates is less than the predetermined number, the control unit 11 determines No in step S18, and determines that the number of updates is less than the predetermined number. Return to step S12. If the number of updates is equal to or greater than a predetermined number, the control unit 11 determines Yes in step S18, and returns to step S1 in FIG.
- control unit 11 determines whether or not the number of updates is equal to or greater than the predetermined number of times, and changes the process to perform machine learning using the hostile generation network exactly the same number of times as the predetermined number of times. Only can be executed continuously.
- the machine learning unit 117 uses the second neural network N2 as the generator of the hostile generation network and the first neural network N1 as the identification of the hostile generation network.
- Machine learning can be performed using a hostile generation network as a vessel.
- the generator In machine learning with a hostile generation network, the generator generates the data and the classifier identifies the generated data. Then, the generator performs machine learning for the purpose of being identified by the classifier as the generated data being correct data.
- the generator is the second neural network N2 for the generation of the generated 3D person model and the classifier is the first neural network N1 for machine learning the evaluation criteria of the 3D person model.
- the first neural network N1 machine-learned the evaluation criteria uses the generated three-dimensional person model generated in the second neural network N2. It corresponds to evaluating that it is a three-dimensional person model having the attributes required by the orderer). That is, the second neural network N2 performs machine learning for the purpose of generating a generated three-dimensional person model that is evaluated by the first neural network N1 as having the attributes required by the user (orderer). ..
- the generation unit 112 using the second neural network N2 can generate a desired three-dimensional person model in a more vivid state.
- Machine learning by the above-mentioned hostile generation network is unsupervised learning, so it does not increase the effort of the designer. Therefore, it is possible to provide a three-dimensional person model generation device 1 that allows a designer involved in computer graphics to generate a three-dimensional person model desired by a user (orderer) with little effort.
- the designer who has been ordered by the user (orderer) to generate a three-dimensional person model having a desired attribute causes the generation device 1 to execute the three-dimensional person model generation process.
- the generation device 1 executes the evaluation learning unit 111, and causes the first neural network N1 to machine-learn the evaluation criteria by using the person model configuration information, the evaluation information, and the attribute information stored in the person model information table 121.
- FIG. 2 an example of the evaluation criteria for making the first neural network N1 machine learn will be described.
- the person model information table 121 shown in FIG. 2 regarding the attribute information regarding the shape of the three-dimensional person model, the person model configuration information M1 and M3 having the attribute information "elongated face” and the person having the attribute information "wide face”.
- Model configuration information M2 and M4 are stored.
- the evaluation learning unit 111 uses the "elongated face” and "light-colored skin”, which are the features of the person model composition information common to the person model composition information M1 and M3, as the evaluation criteria for the attribute information "elongation face” as the first neural network.
- N1 perform machine learning
- the attribute information "wide face”, “dark skin”, “no whiskers”, and “dark hair” which are the features of the person model composition information common to the person model composition information M2 and M4 are used.
- the first neural network N1 perform machine learning as an evaluation criterion for "a wide face”.
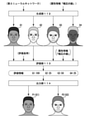
- FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of generating a three-dimensional person model using attribute information.
- the designer transmits (inputs) the attribute desired by the user (orderer) to the generation device 1 as attribute information.
- the attribute desired by the user is described as assuming that the attribute information "wide face" is used.
- the generation device 1 executes the generation unit 112 in step S2 of FIG. 4 and receives the attribute information “wide face” transmitted by the designer.
- the generation unit 112 generates G4 from a random generated three-dimensional model G1 by using the second neural network N2 and the attribute information “wide face”.
- the evaluation unit 113 evaluates each of the generated three-dimensional models G1 to G4 using the evaluation criteria machine-learned by the first neural network N1 and the attribute information "wide face".
- the generated 3D model G1 meets four of the four evaluation criteria for "wide face”: “wide face”, “dark skin”, “no beard”, and “dark hair”. , Get a high evaluation of "100” out of 100 points.
- the generated 3D model G3 has a high evaluation of "50” because it satisfies two of the four evaluation criteria for "wide face”, “wide face” and “dark hair”. To get.
- the generated 3D model G2 receives a low evaluation of "25” because it satisfies only "no mustache” among the four evaluation criteria for "wide face”. Further, since the generated three-dimensional model G4 satisfies only "dark skin” among the four evaluation criteria for "wide face", it gets a low evaluation of "25" points.
- the output unit 114 outputs the generated three-dimensional models G1 and G3 that have obtained a predetermined evaluation as the output three-dimensional person models P1 and P2.
- a generated 3D model having the attribute information "wide face" is generated by the generation unit 112, and the generated 3D models G1 and G3 that have been evaluated by the evaluation unit 113 and obtained a predetermined evaluation are output.
- output 3D person models P1 and P2 which are desired 3D person models with wide facial features, are output.
- the designer can create a 3D person model having the attribute information "wide face" desired by the user (orderer). It can be output with less effort.
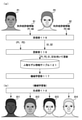
- FIG. 7 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of machine learning using user evaluation information.
- Machine learning using user evaluation information will be described with reference to the example shown in FIG.
- the user (ordering party) transmits (inputs) the evaluation of the output three-dimensional person models P1 and P2 to the generation device 1 as user evaluation information.
- the user (orderer) gave the output 3D person model P1 a rating of "80" and the output 3D person model P1 a rating of "90". That is, the user (orderer) performed an evaluation different from the evaluation using the evaluation criteria, which gives a higher evaluation to the output three-dimensional person model P2 having a wider face shape.
- the user (ordering party) transmitted those evaluations to the generation device 1 as user evaluation information S1 and S2.
- the generation device 1 executes the reception unit 115 and the update unit 116 to receive the user evaluation information and update the person model information table 121.
- the generation device 1 executes the machine learning unit 117, and causes machine learning of the generation of the three-dimensional person model for the second neural network N2 by unsupervised learning. Then, the machine learning unit 117 updates the second neural network N2 stored in the neural network table 122.
- the evaluation unit 113 is higher than the output 3D person model P2 with respect to the output 3D person model P1 based on the information stored in the initial person model information table 121 shown in FIG. Gave a rating.
- the generator 1 received the user evaluation information S1 that gives the output 3D person model P1 an evaluation of "80" points, and the output 3D person model. It is the user evaluation information S2 that gives P1 an evaluation of "90” points. That is, the user (orderer) performed an evaluation different from the evaluation using the evaluation criteria, which gives a higher evaluation to the output three-dimensional person model P2 having a wider face shape.
- the evaluation criteria by machine learning using the original person model information table 121 shown in FIG. 2 is a feature of the three-dimensional person model composition information that is not directly related to the "wide face", “dark skin” and "”. This is because "no beard” and "dark hair” were included in the evaluation criteria for the attribute information "wide face”.
- the update unit 116 updates the person model information table 121 using the output three-dimensional person models P1 and P2 and the user evaluation information S1 and S2. Then, the machine learning unit 117 executes machine learning by unsupervised learning for the second neural network N2 by using the updated person model information table 121. As a result, the second neural network N2 machine-learns the characteristics of the three-dimensional person model regarding the attribute information "wide face” based on the above evaluation. Then, the second neural network N2 becomes a neural network in which the characteristics of the three-dimensional person model configuration information regarding the "wide face" are learned more deeply.
- the generation unit 112 after machine learning includes generated three-dimensional person models G11 and G12 having various skin colors, the presence or absence of whiskers, hair color, and a wide face. , G13 and G14. That is, by machine learning by unsupervised learning executed by the machine learning unit 117, it becomes possible to generate a three-dimensional person model desired by a user (orderer to a designer) in a more vivid state. Since machine learning by unsupervised learning can be executed without externally given training data as a model, the generator 1 has the three dimensions desired by the user (orderer) without increasing the labor of the designer. A person model can be generated in a more vivid state.
- the designer involved in computer graphics can generate the three-dimensional person model desired by the user (orderer) with as little effort as possible.
- the attribute information stored in the person model information table 121 may include information next.
- the person model information table 121 can store, for example, the body shape of the three-dimensional person model desired by the user. Further, when the three-dimensional person model requested by the user is displayed on the display unit 13 or the display unit of the external device 120, the person model information table 121 stores background information suitable for the three-dimensional person model requested by the user. can.
- the person model information table 121 can store clothes types, clothes designs, clothes colors, clothes patterns, etc. suitable for the three-dimensional person model desired by the user. Further, the person model information table 121 can store the type of bag suitable for the three-dimensional person model desired by the user, the design of the bag, and the like.
- the person model information table 121 can store the type of accessory and the color of the accessory suitable for the three-dimensional person model desired by the user. Furthermore, the person model information table 121 can store hair makeup suitable for the three-dimensional person model desired by the user. Further, the person model information table 121 can store footwear suitable for the body shape, clothes, etc. of the three-dimensional person model desired by the user. Footwear includes shoes, clogs, sandals, boots, pumps, mules, sandals and the like. Further, the person model information table 121 can store the facial expression, age, gender of a man or woman, and the angle of the face or body of the three-dimensional person model requested by the user. Gender information may include a masculine element or a feminine element. The angle of the face includes, for example, the angle of the centerline of the face with respect to the centerline of the torso. Body angles include, for example, posing.
- the body shape of the three-dimensional person model includes, for example, a thin shape, a standard shape, a thick shape, and the like.
- the background of the three-dimensional person model includes, for example, mountains, the sea, urban areas, indoors, outdoors, the sky, and the like.
- the types of clothing worn by portrait models include shirts, blouses, sweaters, knits, jackets, skirts, cardigans, vests, pants and the like.
- Accessories include necklaces, earrings, bracelets, sunglasses, hats and the like.
- Hair make includes shortcuts, bobs, longs, perms, straights, etc.
- Types of clothes worn by 3D figures clothes designs, colors of clothes, patterns of clothes, types of bags held by 3D figures, designs of bags, types of accessories worn by 3D figures, colors of accessories 3D person model hair makeup, clothing, 3D person model facial expression, age, gender of male or female, face and body angle, etc. can be created by a person using apparel 3D.
- apparel 3D a person analyzes an ordered 3D person model, and a 3D person model is generated by switching and changing various patterns prepared in advance for the basic model.
- the facial expression, age, gender of male or female, face or body angle, etc. may be created by the AI system.
- the AI system is a system that analyzes an ordered three-dimensional person model and generates an image of clothes or the like having a design that matches the orderer's taste.
- the apparel 3D system and the AI system may be constructed by the three-dimensional person model generation device 1 or may be constructed by using the external device 120.
- Step S1 in FIG. 4 is a machine learning step.
- Step S6 is an update step. Determining Yes in step S7 is the receiving step.
- Step S5 is an output step.
- Step S3 is a generation step.
- Step S4 is an evaluation step.
- Step S1 is an evaluation learning step.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Computer Graphics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Image Generation (AREA)
- Processing Or Creating Images (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021559614A JP7007780B1 (ja) | 2020-08-13 | 2021-08-10 | 3次元人物モデル生成装置およびプログラム |
| JP2021212791A JP7784082B2 (ja) | 2020-08-13 | 2021-12-27 | 3次元人物モデル出力装置、プログラム、及び3次元人物モデル出力方法 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020-136828 | 2020-08-13 | ||
| JP2020136828 | 2020-08-13 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2022034879A1 true WO2022034879A1 (ja) | 2022-02-17 |
Family
ID=80247916
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2021/029511 Ceased WO2022034879A1 (ja) | 2020-08-13 | 2021-08-10 | 3次元人物モデル生成装置およびプログラム |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (2) | JP7007780B1 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2022034879A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2024072165A (ja) * | 2022-11-15 | 2024-05-27 | 株式会社Pbadao | データ端末装置およびコンテンツ販売システム |
| KR20250140379A (ko) * | 2024-03-18 | 2025-09-25 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 이미지를 처리하는 전자 장치 및 그 동작 방법 |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6448839B1 (ja) * | 2018-06-20 | 2019-01-09 | 株式会社 ディー・エヌ・エー | 画像生成装置、画像生成器、画像識別器、画像生成プログラム、及び、画像生成方法 |
-
2021
- 2021-08-10 WO PCT/JP2021/029511 patent/WO2022034879A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2021-08-10 JP JP2021559614A patent/JP7007780B1/ja active Active
- 2021-12-27 JP JP2021212791A patent/JP7784082B2/ja active Active
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6448839B1 (ja) * | 2018-06-20 | 2019-01-09 | 株式会社 ディー・エヌ・エー | 画像生成装置、画像生成器、画像識別器、画像生成プログラム、及び、画像生成方法 |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| ASAHIKO KAI: "AI to automatically generate the whole body of a non-existent fashion model, venture development from Kyoto University", 10 May 2019 (2019-05-10), pages 1 - 4, XP055900326, Retrieved from the Internet <URL:https://www.itmedia.co.jp/news/articles/1905/10/news106.html> [retrieved on 20220311] * |
| ITnews. AIが自動生成する顔写真DBの「GENERATED PHOTOS」がAPIを公開! [online], 11 February 2020, Internet: <URL: https://itnews.org/news_contents/product-generated-photos> [retrieved on 14 September 2021], non-official translation ("GENERATED PHOTOS", the Database for Automatically-Generated AI Photos, Announces API.) * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP7784082B2 (ja) | 2025-12-11 |
| JP7007780B1 (ja) | 2022-01-25 |
| JPWO2022034879A1 (enExample) | 2022-02-17 |
| JP2022033237A (ja) | 2022-02-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102045017B1 (ko) | 이미지/텍스트 기반 디자인 생성 장치 및 방법 | |
| US11809985B2 (en) | Algorithmic apparel recommendation | |
| CN107066628A (zh) | 穿衣推荐方法及装置 | |
| JP7007780B1 (ja) | 3次元人物モデル生成装置およびプログラム | |
| KR102211400B1 (ko) | 이미지/텍스트 기반 디자인 생성 장치 및 방법 | |
| CN105527946A (zh) | 一种基于工业互联网的快速成衣系统及其方法 | |
| CN107451894A (zh) | 数据处理方法、装置和计算机可读存储介质 | |
| CN109242593B (zh) | 一种基于案例推理的服装推荐方法、装置和存储介质 | |
| CN113988174A (zh) | 基于知识图谱的服装样板匹配方法、系统以及设备 | |
| CN111767817B (zh) | 一种服饰搭配方法、装置、电子设备及存储介质 | |
| CN108109049A (zh) | 服饰搭配预测方法、装置、计算机设备及存储介质 | |
| US12417481B2 (en) | Systems and methods for automating clothing transaction | |
| CN110569593A (zh) | 着装人体三维尺寸测量方法、系统、存储介质及电子设备 | |
| CN113988978A (zh) | 基于知识图谱的服装搭配推荐方法、系统以及设备 | |
| Yan et al. | RETRACTED: Garment Design Models Combining Bayesian Classifier and Decision Tree Algorithm | |
| US20210174603A1 (en) | Body shape display method for modeling of clothing | |
| KR102429572B1 (ko) | 인공지능 기반 사용자 맞춤형 의류 및 스타일링 추천 방법, 장치 및 시스템 | |
| JP6744633B2 (ja) | 物品判定装置、システム、学習方法及びプログラム | |
| KR102230507B1 (ko) | 패션 제품 제조 플랫폼 서비스 제공 방법, 장치 및 시스템 | |
| CN111523978A (zh) | 一种定制旗袍样板生成方法 | |
| WO2020050287A1 (ja) | 情報処理装置及びプログラム | |
| Mok et al. | Fashion sketch design by interactive genetic algorithms | |
| JP7106085B1 (ja) | デザイン生成システム及びデザイン生成方法 | |
| CN112669203B (zh) | 图像中的人物性转方法、电子设备和存储介质 | |
| KR102626945B1 (ko) | 인공지능 모델 기반 3d 의류 데이터 변환 방법 및 장치 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2021559614 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 21855958 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 21855958 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |