WO2019159593A1 - 電子制御装置及び通信システム - Google Patents
電子制御装置及び通信システム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2019159593A1 WO2019159593A1 PCT/JP2019/001320 JP2019001320W WO2019159593A1 WO 2019159593 A1 WO2019159593 A1 WO 2019159593A1 JP 2019001320 W JP2019001320 W JP 2019001320W WO 2019159593 A1 WO2019159593 A1 WO 2019159593A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- electronic control
- message
- control device
- key
- side electronic
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R25/00—Fittings or systems for preventing or indicating unauthorised use or theft of vehicles
- B60R25/20—Means to switch the anti-theft system on or off
- B60R25/24—Means to switch the anti-theft system on or off using electronic identifiers containing a code not memorised by the user
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/32—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols including means for verifying the identity or authority of a user of the system or for message authentication, e.g. authorization, entity authentication, data integrity or data verification, non-repudiation, key authentication or verification of credentials
- H04L9/3236—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols including means for verifying the identity or authority of a user of the system or for message authentication, e.g. authorization, entity authentication, data integrity or data verification, non-repudiation, key authentication or verification of credentials using cryptographic hash functions
- H04L9/3242—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols including means for verifying the identity or authority of a user of the system or for message authentication, e.g. authorization, entity authentication, data integrity or data verification, non-repudiation, key authentication or verification of credentials using cryptographic hash functions involving keyed hash functions, e.g. message authentication codes [MACs], CBC-MAC or HMAC
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/14—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols using a plurality of keys or algorithms
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/32—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols including means for verifying the identity or authority of a user of the system or for message authentication, e.g. authorization, entity authentication, data integrity or data verification, non-repudiation, key authentication or verification of credentials
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L2209/00—Additional information or applications relating to cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communication H04L9/00
- H04L2209/84—Vehicles
Definitions
- This application relates to selection and switching of an encryption key for ensuring the security of an electronic control unit (ECU: Electric Control Unit), and is mainly used for an in-vehicle electronic control unit.
- ECU Electric Control Unit
- a message authentication code In communication between electronic control units, a message authentication code (MAC) is used to check the integrity of a message, that is, tampering or spoofing.
- MAC message authentication code
- the transmission side electronic control device and the reception side electronic control device use a shared key, which is a common key. And since the authenticity of a message increases by having a plurality of shared keys and periodically switching them, a method of switching a plurality of keys between the transmitting side and the receiving side has been proposed.
- Patent Document 1 describes that a key is updated by transmitting an update frame on condition that the state of the vehicle is a predetermined state. Further, Patent Document 2 describes that keys are collectively updated by transmitting a device key update command from a key management server to a plurality of terminals.
- the techniques described in any of the patent documents transmit a dedicated synchronization signal when updating the key between devices.
- key switching and message transmission / reception are not performed sequentially.
- a message authenticated using the key after switching may be sent from the transmission-side electronic control device.
- key switching fails because a dedicated synchronization signal cannot be received.
- the reception-side electronic control device determines that the authentication of the received message is NG and discards it.
- An object of the present disclosure is to switch keys between transmission and reception that can occur when a dedicated synchronization signal is used by switching keys of the transmission side electronic control device and the reception side electronic control device without using a dedicated synchronization signal. It is intended to reduce the failure of communication due to misalignment or key switching failure.
- An electronic control device is a transmission-side electronic control device of a communication system including a transmission-side electronic control device that transmits a message and a reception-side electronic control device that receives the message, A key table unit having a key, and a key selection unit that selects one key from the key table based on synchronization information that is information synchronized between the transmission-side electronic control device and the reception-side electronic control device; A message generation unit that generates the message, a MAC generation unit that generates a message authentication code (MAC) using the key selected by the key selection unit and the message, and gives the message authentication code to the message And a transmitting unit for transmitting the data.
- MAC message authentication code
- An electronic control device is the reception-side electronic control device of a communication system including a transmission-side electronic control device that transmits a message and a reception-side electronic control device that receives the message, A receiving unit that receives the message transmitted from the transmission-side electronic control device and a message authentication code (MAC) attached to the message, a key table unit having a plurality of keys, the reception-side electronic control device, and the transmission Based on synchronization information, which is information synchronized in communication with the side electronic control unit, using a key selection unit that selects one key from the key table unit, a key selected by the key selection unit, and the message A verification MAC generation unit for generating a verification message authentication code (MAC), the message authentication code and the verification message authentication code; A verification unit for verifying the identity of de, the.
- MAC message authentication code
- a communication system is a communication system including a transmission-side electronic control device that transmits a message and a reception-side electronic control device that receives the message, the transmission-side electronic control device and the reception
- Each of the side electronic control units is based on the key table unit having a plurality of keys, and synchronization information that is information synchronized in communication between the transmission side electronic control unit and the reception side electronic control unit.
- a key selection unit that selects one key, and the transmission-side electronic control device uses the message generation unit that generates the message, the key selected by the key selection unit, and the message to authenticate the message.
- a MAC generation unit that generates a code (MAC), and a transmission unit that transmits the message with the message authentication code attached thereto
- the transmission-side electronic control device includes: a reception unit that receives the message transmitted from the transmission-side electronic control device and a message authentication code (MAC) attached to the message; the key selected by the key selection unit; A verification MAC generation unit that generates a verification message authentication code (MAC) using the message; and a verification unit that verifies the identity of the message authentication code and the verification message authentication code.
- MAC message authentication code
- a key selection device is a key selection device used in a communication system including a transmission-side electronic control device that transmits a message and a reception-side electronic control device that receives the message.
- a key table unit having a key, and a key selection unit that selects one key from the key table unit based on synchronization information that is information synchronized in communication between the transmission-side electronic control device and the reception-side electronic control device And an output unit for outputting the one key selected by the key selection unit.
- a message transmission method includes a message executed by the transmission-side electronic control device of a communication system including a transmission-side electronic control device that transmits a message and a reception-side electronic control device that receives the message.
- the transmission method based on synchronization information that is information synchronized in communication between the transmission-side electronic control device and the reception-side electronic control device, one key is selected from a key table unit having a plurality of keys, and A message is generated, a message authentication code (MAC) is generated using the selected one key and the message, and the message authentication code is added to the message for transmission.
- MAC message authentication code
- a message reception method includes a message executed by the reception-side electronic control device of a communication system including a transmission-side electronic control device that transmits a message and a reception-side electronic control device that receives the message.
- a receiving method for receiving the message transmitted from the transmitting-side electronic control device and a message authentication code (MAC) attached to the message, and for receiving the receiving-side electronic control device and the transmitting-side electronic control device.
- MAC message authentication code
- a key selection method is a key selection method used in a communication system including a transmission-side electronic control device that transmits a message and a reception-side electronic control device that receives the message.
- One key is selected from the key table unit having a plurality of keys based on synchronization information that is information synchronized in communication between the side electronic control device and the reception side electronic control device, and the selected one key Is output.
- a computer-executable message transmission program includes a transmission-side electronic control of a communication system including a transmission-side electronic control device that transmits a message and a reception-side electronic control device that receives the message.
- a message transmission program executed by a device, based on synchronization information, which is information synchronized in communication between the transmission-side electronic control device and the reception-side electronic control device, from a key table unit having a plurality of keys. Selecting one key, generating the message, generating a message authentication code (MAC) using the selected one key and the message, and sending the message with the message authentication code attached thereto;
- MAC message authentication code
- a computer-executable message receiving program includes a transmission-side electronic control device that transmits a message and a reception-side electronic control of a communication system that includes the reception-side electronic control device that receives the message.
- a message reception program executed by a device that receives the message transmitted from the transmission-side electronic control device and a message authentication code (MAC) attached to the message, and that receives the reception-side electronic control device and the transmission
- a key is selected from a key table unit having a plurality of keys based on synchronization information that is synchronized in communication with a side electronic control unit, and the verification is performed using the selected one key and the message.
- a message authentication code (MAC) is generated, and the message authentication code and the verification message Possible to verify the identity of the witness code, with a.
- a key selection program executable by a computer is a key selection program used in a communication system including a transmission-side electronic control device that transmits a message and a reception-side electronic control device that receives the message. And selecting one key from the key table unit having a plurality of keys based on synchronization information that is information synchronized in communication between the transmission-side electronic control device and the reception-side electronic control device. Outputting said one key.
- An electronic control device is the transmission-side electronic control device of a communication system including a transmission-side electronic control device that transmits an encrypted message and a reception-side electronic control device that receives the encrypted message.
- a key table unit having a plurality of keys, and one key from the key table unit based on synchronization information which is information synchronized in communication between the transmission-side electronic control device and the reception-side electronic control device.
- a key selection unit to select; a message generation unit to generate a message; an encryption unit to generate the encrypted message using the key selected by the key selection unit and the message; and transmit the encrypted message And a transmission unit.
- An electronic control device is the reception-side electronic control device of a communication system including a transmission-side electronic control device that transmits an encrypted message and a reception-side electronic control device that receives the encrypted message.
- the synchronization information which is information synchronized in the communication between the reception unit that receives the encrypted message, the key table unit having a plurality of keys, and the reception-side electronic control device and the transmission-side electronic control device.
- a key selection unit that selects one key from the key table unit; and a decryption unit that decrypts the encrypted message using the key selected by the key selection unit.
- An electronic control device a communication system, a key selection device, a message transmission method, a message reception method, a key selection method, a message transmission program, a message reception program, and a key selection program (hereinafter collectively referred to as an electronic control device) According to this, it is possible to reduce the failure of communication due to a shift in key switching timing between transmission and reception and a key switching failure that may occur when a dedicated synchronization signal is used.
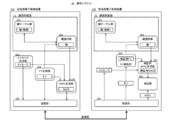
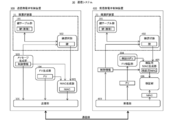
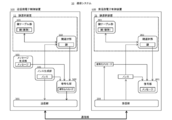
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram illustrating configurations of a communication system and an electronic control device according to the first embodiment.
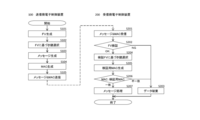
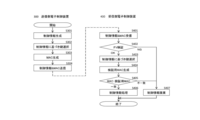
- FIG. 2 is a flowchart for explaining the operation (message transmission method, message reception method, message transmission program, message reception program) of the communication system and the electronic control device according to the first embodiment.
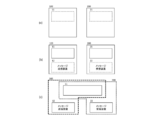
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram illustrating an aspect of the key selection device according to the first embodiment.
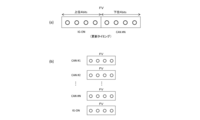
- FIG. 4 is an explanatory diagram illustrating a key selection method in the key selection unit according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 5 is a block diagram illustrating configurations of a communication system and an electronic control device according to the second embodiment.
- FIG. 6 is a flowchart for explaining the operations (message transmission method, message reception method, message transmission program, message reception program) of the communication system and the electronic control device according to the second embodiment.
- FIG. 7 is a block diagram illustrating configurations of a communication system and an electronic control device according to the third embodiment.
- the effect described in the embodiment is an effect when the configuration of the exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure is provided, and is not necessarily the effect that the present disclosure has.
- the configuration disclosed in each embodiment is not closed only by each embodiment, and can be combined across the embodiments.
- the configuration disclosed in one embodiment may be combined with another embodiment.
- the problem described in the present disclosure is not a known problem, but has been independently found by the present inventor, and is a fact that confirms the inventive step together with the configuration and method of the present disclosure.
- a communication system 10 includes a plurality of electronic control devices, that is, a transmission-side electronic control device 100 that transmits a message, a reception-side electronic control device 200 that receives the message, and It consists of a communication path that connects them.
- the “electronic control device” of the present disclosure may be any device that can acquire or process information and can transmit or receive information to or from other devices.
- a computer personal computer, embedded microcomputer, etc.
- a display device television, stereo, stereo, etc.
- BD recording / reproducing device
- SD card reader etc.
- a communication device mobile phone
- Smart phones tablets, base stations, etc.
- circuit boards semiconductor modules, semiconductors, and the like, and include all forms of finished products, semi-finished products, and parts.
- the transmission-side electronic control device 100 of this embodiment includes a key table unit 101, a key selection unit 102, a message generation unit 103, an FV generation unit 104, a MAC generation unit 105, and a transmission unit 106.
- the transmission-side electronic control device 100 and the individual functional blocks constituting the transmission-side electronic control device 100 may be realized by a dedicated or general-purpose central processing unit, a memory, a bus, and a program developed and executed in the memory, or a semiconductor It may be realized by dedicated hardware such as a module or a circuit board. The same applies to a receiving-side electronic control device 200 described later.
- the key table unit 101 has a plurality of keys, and is composed of, for example, a memory.
- the key is assumed to be a normal common key, but other keys may be used, and a session key may be used.
- the key selection unit 102 selects one key from a plurality of keys stored in the key table unit 101 based on a freshness value (FV: Freshness Value) (corresponding to synchronization information) generated by the FV generation unit 104 described later. To do. Such selection is performed according to a predetermined key selection rule.
- the key selection rule can be realized by, for example, developing in a memory and executing it. A specific example of the key selection method will be described later.
- One selected key is output to the MAC generation unit 105.
- the “one key” of the present disclosure may be a key that is used or that is scheduled to be used next time after a predetermined time. In addition to this, a spare key or a next key is scheduled to be used. Of course, the case where the key to be selected is selected is also included.
- the key table unit 101 and the key selection unit 102 constitute the key selection device 11.
- the selected key is output to the MAC generation unit 105 from the output unit of the key selection device 11.
- the message generation unit 103 generates a message to be transmitted to the reception-side electronic control device 200.
- Specific examples of the message include various control information for controlling the vehicle in the case of an in-vehicle electronic control device mounted on the vehicle. The control information will be described in the second embodiment.
- detection data detected by a sensor or the like text data, audio data, image data, and the like can be mentioned.
- the FV generation unit 104 generates a freshness value according to the number of transmissions of the message generated by the message generation unit 103 and transmitted by the transmission unit 106 described later.
- a counter is mainly described among the freshness values.
- a freshness value is generated by counting the number of transmissions for each CANID assigned according to the type of generated control information. For example, when the control information to which CAN # 1 is assigned is transmitted four times, the freshness value of CAN # 1 is 4.
- the “freshness value (FV)” of the present disclosure is a value having a property of determining whether it is a value used in the past, and includes, for example, a counter, time information, and nonce.
- the counter is a value indicating the number of times that a specific message has been transmitted from the transmission-side electronic control device or the number of times that the reception-side electronic control device has been received, and is a concept including a sequence number.
- a relative value obtained by setting a certain reference and counting from the reference is also included.
- the freshness value is generated by counting the number of receptions for each CANID in the receiving-side electronic control device 200 as described later. Accordingly, since the freshness value is the same in the transmission-side electronic control device 100 and the reception-side electronic control device 200, the freshness value is information synchronized in communication between the transmission-side electronic control device 100 and the reception-side electronic control device 200. Is the synchronization information.
- the “synchronized information” of the present disclosure refers to the same information that can be contacted by both the transmission-side electronic control device and the reception-side electronic control device at substantially the same time, or even different information. Any information that can derive the same attribute and the same property from the information may be used. In addition, when viewed in information units, the information may be a part of the information in addition to the entire information. Further, in addition to the case where the content of the information itself is used, it may be the attribute or property of the information, for example, the number of times of transmission / reception of the information or the transmission / reception of the information under a predetermined condition.
- the MAC generation unit 105 uses a key selected by the key selection unit 102, a message generated by the message generation unit 103, and a freshness value generated by the FV generation unit 104 to generate a message authentication code (MAC: Message Authentication Code). Is generated.
- MAC Message Authentication Code
- the message authentication code is generated by calculating based on the MAC algorithm using the selected key for the data in which the freshness value is inserted or added to the message.
- the transmission unit 106 adds the message authentication code generated by the MAC generation unit 105 to the data generated by the FV generation unit 104 and adds the message authentication code generated by the MAC generation unit 105 to the data generated by the message generation unit 103 and transmits the data. It may be transmitted by designating a specific receiving-side electronic control device 200 as a transmission destination, but may be transmitted by broadcast without designating the transmission destination, and can be received by the receiving-side electronic control device 200 as a result. If it is.
- the receiving-side electronic control device 200 includes a key table unit 201, a key selection unit 202, a receiving unit 203, an FV verification unit 204, a verification MAC generation unit 205, and a verification unit 206. .
- the receiving unit 203 receives data in which a freshness value is inserted or added to a message transmitted from the transmission-side electronic control device 100, and a message authentication code attached to the data.
- the FV verification unit 204 verifies the identity between the freshness value received by the reception unit 203 and the verification freshness value generated by the reception-side electronic control device 200. For example, in the case of a CAN that is an in-vehicle network, the verification freshness value is generated by counting the number of receptions for each CAN ID assigned to the control information included in the received message. If the freshness value received by the reception unit 203 matches the verification freshness value, the verification freshness value is output to a key selection unit 202 and a verification MAC generation unit 205 described later. If they do not match, the received data is discarded.
- the FV verification unit 204 may perform the following operation instead of the above operation.
- the freshness value for verification is a freshness value recorded for each CANID included in the most recently received message, and the FV verification unit 204 receives the freshness value received by the receiving unit 203 from the freshness value for verification. Verify that it is large. If it is larger, the freshness value received by the receiving unit 203 is output as a new verification freshness value to the key selection unit 202 and the verification MAC generation unit 205 described later. In this case, since a configuration for counting the number of receptions is not required, the circuit scale can be reduced.
- the key table unit 201 has the same configuration as the key table unit 101 of the transmission-side electronic control device 101.
- the key selection unit 202 has the same configuration as the key selection unit 102 of the transmission-side electronic control device 100. Then, the key selection unit 202 selects one key from a plurality of keys stored in the key table unit 201 based on the verification freshness value (corresponding to synchronization information) generated by the FV verification unit 204. Such selection is performed according to a predetermined key selection rule similar to that of the key selection unit 102. One selected key is output to the verification MAC generation unit 205. Similar to the transmission-side electronic control device 100, the key table unit 201 and the key selection unit 202 constitute the key selection device 21. In this case, the selected key is output from the output unit of the key selection device 21 to the verification MAC generation unit 205.
- the verification MAC generation unit 205 generates a verification message authentication code using the key selected by the key selection unit 202, the message received by the reception unit 203, and the verification freshness value output from the FV verification unit 204. To do.
- a verification message authentication code is generated by performing calculation based on the MAC algorithm using a selected key for data in which a verification freshness value is inserted or added to a message.
- the verification unit 206 verifies the identity of the message authentication code received by the reception unit 203 and the verification message authentication code generated by the verification MAC generation unit 205. If the message authentication code matches the verification message authentication code, the received message is processed. If they do not match, the received message is discarded.
- the transmission-side electronic control device 100 and the reception-side electronic control device 200 of the present embodiment described above the above-described effects of the present disclosure are exhibited, and the freshness value is used as synchronization information.
- the transmission side electronic control device 100 and the reception side electronic control device 200 can select the same key regardless of whether or not the freshness value itself is transmitted as well as the transmission of the synchronization signal is not necessary.
- a message transmission method, a message reception method, and a program for executing the method A message transmission method executed by the transmission-side electronic control device 100 and a message reception method executed by the reception-side electronic control device 200 will be described with reference to FIG. explain. Note that the order of the processes in FIG. 2 can be appropriately changed unless a certain process is a precondition for the next process. The same applies to any of the following embodiments.
- the transmission-side electronic control device 100 executes the following steps.
- a freshness value as synchronization information is generated (S101). Based on the freshness value, one key is selected from a plurality of keys stored in the key table unit 101 (S102).
- a message to be transmitted to the reception-side electronic control device 200 is generated (S103).
- a message authentication code is generated using the key selected in S102, the message generated in S103, and the freshness value generated in S101 (S104).
- the message authentication code generated in S104 is added to the data composed of the message generated in S103 and the freshness value generated in S101, and transmitted (S105).
- the reception-side electronic control device 200 executes the following steps. Data including the message and freshness value transmitted from the transmission-side electronic control device 100 and a message authentication code assigned to the data are received (S201). The freshness value received in S201 is compared (verified) with the verification freshness value generated by the receiving-side electronic control device 200 (S202). If no match or condition is met, the received data is discarded (S203). If a match or a condition is satisfied in S202, one key is selected from a plurality of keys stored in the key table unit 201 based on the verification freshness value (S204). A verification message authentication code is generated using the key selected in S204, the message received in S201, and the verification freshness value (S205). The identity of the message authentication code received in S201 and the verification message authentication code generated in S205 is verified (S206). If they match, the message is processed (S207). If they do not match, the data is discarded (S203).
- the “computer” of the present disclosure only needs to include at least an arithmetic circuit and a memory, and may be used for general purpose or dedicated use. Moreover, the form is not ask
- the above-described effects of the present disclosure are exhibited, and the freshness value is verified prior to the verification of the message authentication code. Can be increased.
- the key selection device 11 and the key selection device 21 are replaced with the transmission-side electronic control device 100 and the reception-side electronic control device 200. Configured as component parts. In this case, the key selection device 11 and the key selection device 21 are configured as semiconductor modules or semiconductors as components, for example.
- the key selection device 11 and the key selection device 22 are configured as independent electronic control devices, and the message generation unit 103, the FV generation unit 104, the MAC generation unit 105, and the transmission unit 106 And the message receiving device 22 including the receiving unit 203, the FV verification unit 204, the verification MAC generation unit 205, and the verification unit 206.
- the receiving-side electronic control device 200 may be used.
- the key selection device 11 and the key selection device 21 can be configured as a semiconductor module or a semiconductor as a component, or an electronic control device or a circuit board as a finished product or a semi-finished product.
- the key selection device 11 may be shared by the message transmission device 12 and the message reception device 22. Also in this case, the key selection device 11 can be configured as a part, a finished product, or a semi-finished product.
- the key selection method executed by the key selection device 11 and the key selection device 21 may be realized in the form of a key selection program that can be executed by a computer.
- the “key selection device” of the present disclosure only needs to be able to select one key from a plurality of keys in accordance with an input, and may be in any form. That is, it includes any of finished products, semi-finished products, and parts such as electronic control devices, circuit boards, semiconductor modules, and semiconductors.
- 3A, 3B, and 3C all constitute the communication system 10. Further, as shown in FIG. 3C, when the key selection device 11 including the key table unit 101 and the key selection unit 102 is shared between the transmission side and the reception side, the key table unit 101 and the key selection in FIG. The unit 102 can be understood as the key table units 101 and 201 and the key selection units 102 and 202 of the transmission side electronic control device 100 and the reception side electronic control device 200, respectively.
- Key selection method In this embodiment, the freshness value is used as the synchronization information used for key selection by the key selection unit 102 and the key selection unit 202, but the key selection method (key selection rule) will be described in more detail. In this section, the description is based on the assumption that there are two keys (key 1 and key 2) included in the key table, but the number of keys may be two or more.
- Counter FIG. 4A shows an example of a counter that is an example of a freshness value.
- the counter consists of 8 bits. The upper 4 bits count the number of times the ignition is turned on, and the lower 4 bits count the number of times of transmission / reception of a message having a specific CANID.
- the key selection rule consider a case where the key 1 is selected when the least significant bit of the upper 4 bits of the counter is 0, and the key 2 is selected when it is 1. In this case, the key can be switched every time the ignition is turned on. As another example, consider a case in which the key 1 is selected when the most significant bit of the upper 4 bits of the counter is 0, and the key 2 is selected when it is 1. In this case, the key can be switched every time the ignition ON is executed eight times. As another example, consider the case where the key 1 is selected when the most significant bit of the lower 4 bits of the counter is 0, and the key 2 is selected when it is 1. In this case, the key can be switched every time a specific CANID transmission / reception is executed eight times. Furthermore, these examples may be combined or a plurality of bits may be used. According to this configuration, it is possible to design various key switching timings.
- a freshness value for each CANID as shown in FIG. 4B may be used instead of the counter of FIG. 4A.
- a CANID is assigned for each type of control information.
- a key selection rule can be provided for each CANID.
- a rule may be considered in which a message with CAN # 1 is assigned with the least significant bit and a message with CAN # 2 assigned with a key is changed according to the value of the most significant bit.
- the key switching timing can be determined according to the importance of the control information handled by the electronic control device. The higher the importance of the control information, the more the key switching. It is possible to speed up the timing.
- the key selection unit 102 and the key selection unit 202 select one key from the key table unit 101 and the key table unit 201 based on the specific bits constituting the freshness value.
- the “specific bit” of the present disclosure includes a specific plurality of bits in addition to a specific one bit.
- upper 2 bits, lower 4 bits and the like can be mentioned.
- Time information generated by the transmission-side electronic control device and the reception-side electronic control device which is an example of a freshness value, may be used as the synchronization information.
- the timers of the transmission-side electronic control device 100 and the reception-side electronic control device 200 may be synchronized, and the key may be switched based on each time information or time information transmitted from the transmission-side electronic control device 100.
- time information is information indicating time, and includes, for example, a time, a time stamp, an elapsed time from a reference time, and the like.
- the time includes the date and year information or the date and year information alone.
- Nonce Nonce which is an example of a freshness value, may be used as the synchronization information.
- the nonce is a disposable random value transmitted from the transmission-side electronic control device 100 to the reception-side electronic control device 200. Then, for example, the key may be switched based on a specific nonce bit.
- FIG. 5 shows the transmission-side electronic control device 300 and the reception-side electronic control device 400 that constitute the communication system 30 of the present embodiment.
- the same figure number is used for the structure similar to Embodiment 1.
- FIG. It is assumed that the communication system 30 of this embodiment and the transmission-side electronic control device 300 and the reception-side electronic control device 400 that constitute the communication system 30 are mounted on a vehicle.
- a transmission-side electronic control device 300 according to the present embodiment has the same configuration as that of the transmission-side electronic control device 100 according to the first embodiment.
- the function of each block is as follows.
- the message generator 103 generates control information for controlling the vehicle as a message.
- the key selection unit 302 selects one key from a plurality of keys stored in the key table unit 101 based on the control information. That is, in this embodiment, the control information for controlling the vehicle corresponds to the synchronization information.
- control the vehicle is not limited to the case of controlling the behavior of the entire vehicle, but to the case of controlling parts (for example, a door, a mirror, an airbag, a wiper, etc.) constituting the vehicle. This includes the case of controlling various devices (air conditioner, navigation system, audio player, etc.).
- control information includes, but is not limited to, information regarding speed, door opening / closing, information regarding mirror angle adjustment, information regarding sheet position adjustment, and information regarding ignition ON / OFF, for example. .
- the MAC generation unit 305 uses the message authentication code (MAC : Message Authentication Code).
- the transmission unit 306 adds the message authentication code generated by the MAC generation unit 305 to the data obtained by inserting or adding the freshness value generated by the FV generation unit 104 to the control information generated by the message generation unit 103, and transmits the data.
- a receiving-side electronic control device 400 of this embodiment has the same configuration as that of the receiving-side electronic control device 200 of the first embodiment.
- the function of each block is as follows.
- the receiving unit 403 receives data obtained by inserting or adding a freshness value to the control information transmitted from the transmission-side electronic control device 100, and a message authentication code attached to the data.
- the key selection unit 402 selects one key from a plurality of keys stored in the key table unit 201 based on the received control information.
- the verification MAC generation unit 405 uses the key selected by the key selection unit 402, the control information received by the reception unit 403, and the verification freshness value output from the FV verification unit 204 to generate a verification message authentication code. Generate.
- a message transmission method, a message reception method, and a program for executing the method A message transmission method executed by the transmission-side electronic control device 300 and a message reception method executed by the reception-side electronic control device 400 will be described with reference to FIG. explain.
- the transmission-side electronic control device 300 executes the following steps. Control information that is a message to be transmitted to the reception-side electronic control device 400 is generated (S301). Based on the control information generated in S301, one key is selected from a plurality of keys stored in the key table unit 101 (S302). A message authentication code is generated using the key selected in S302, the control information generated in S301, and the freshness value (S303). The message authentication code generated in S303 is added to the control information and freshness value generated in S301 and transmitted (S304).
- the reception-side electronic control device 400 executes the following steps.
- the control information and freshness value transmitted from the transmission-side electronic control device 300 and the message authentication code assigned to the control information and freshness value are received (S401).
- the freshness value received in S401 is compared (verified) with the verification freshness value generated by the receiving-side electronic control device 400 (S402). If no match or condition is satisfied, the received control information is discarded (S407).
- one key is selected from a plurality of keys stored in the key table unit 201 based on the control information (S403).
- a verification message authentication code is generated using the key selected in S403, the control information received in S401, and the verification freshness value (S404).
- the identity of the message authentication code received in S401 and the verification message authentication code generated in S404 is verified (S405). If they match, the control information is processed (S406). If they do not match, the control information is discarded (S407).
- Key selection method In the present embodiment, control information for controlling the vehicle is used as synchronization information used for key selection by the key selection unit 302 and the key selection unit 402, but a key selection method (key selection rule) will be described in more detail. In this section, the description is based on the assumption that there are two keys (key 1 and key 2) included in the key table, but the number of keys may be two or more.
- the key 1 may be selected when the speed becomes a certain value or higher, and the key 2 may be selected when the speed becomes a certain value or less. By selecting and changing the key according to the speed, the key can be switched according to the danger of the vehicle.
- the door 1 may be switched between the key 1 and the key 2 every predetermined number of times. Since the vehicle is stopped when the door is opened and closed, the key can be switched when the vehicle is in a safe state and the in-vehicle network is less congested.
- the key 1 and the key 2 are switched when the mirror adjustment is performed or when the sheet position is adjusted. Also good. Since these operations are often performed when the driver is changed, the key can be changed virtually for each driver.
- the “transmission frequency” of the present disclosure refers to the frequency of control information transmitted in a predetermined time, and is indicated by the number of times, the period, the time, and the like.
- the above-described effects of the present disclosure are achieved and the control information is used as synchronization information.
- the control information is used as synchronization information.
- FIG. 7 shows a transmission-side electronic control device 500 and a reception-side electronic control device 600 that constitute the communication system 50 of the present embodiment.
- the same figure number is used for the structure similar to Embodiment 1.
- FIG. 7 shows a transmission-side electronic control device 500 and a reception-side electronic control device 600 that constitute the communication system 50 of the present embodiment.
- the same figure number is used for the structure similar to Embodiment 1.
- FIG. 7 shows a transmission-side electronic control device 500 and a reception-side electronic control device 600 that constitute the communication system 50 of the present embodiment.
- the same figure number is used for the structure similar to Embodiment 1.
- FIG. in the first and second embodiments an example of message authentication is disclosed, and an example in which a key is used to generate a message authentication code has been shown.
- an example of encryption is disclosed, and an example in which a key is used to encrypt a message to be transmitted and to decrypt the encrypted message is shown. Note that the matters described in the first and second embodiments can be combined
- the transmission-side electronic control device 500 of this embodiment includes a key table unit 101, a key selection unit 102, a message generation unit 103, a nonce generation unit 501, an encryption unit 502, and a transmission unit 106. .
- the nonce generation unit 501 generates a nonce that is a disposable random value.
- the nonce is the synchronization information that is the synchronized information of the present disclosure, but is not limited thereto.
- the key selection unit 102 selects one key from a plurality of keys stored in the key table unit 101 based on the nonce generated by the nonce generation unit 501.
- the encryption unit 502 encrypts the message generated by the message generation unit 103 using the key selected by the key selection unit 102 and generates an encrypted message.
- the encryption method is arbitrary. Note that a message including a nonce may be encrypted.
- the transmission unit 106 transmits the encrypted message generated by the encryption unit 502 and the nonce.
- a reception-side electronic control device 600 includes a reception unit 203, a key table unit 201, a key selection unit 202, and a decryption unit 601.
- the key selection unit 202 selects one key from a plurality of keys stored in the key table unit 201 based on the nonce received by the reception unit 203.
- the decryption unit 601 decrypts the encrypted message using the key selected by the key selection unit 202, and generates a message.
- the decryption method is arbitrary as in the case of encryption. Note that a message including a nonce may be decoded.
- the above-described effects of the present disclosure can be achieved and the confidentiality of the message can be ensured.
- the electronic control device and the like in each embodiment of the present disclosure have been described above.
- the present disclosure can be realized in the form of a program executed on a computer, a storage area in an exclusive or general-purpose hardware (external storage device (hard disk, USB memory, etc.), internal storage device (RAM, ROM, etc.))
- the program stored in can be provided to the above-described dedicated or general-purpose hardware (corresponding to a computer) through a recording medium or via a communication line from a server without using a recording medium.
- the latest functions can always be provided through program upgrades.
- the electronic control device and the like of the present disclosure have been described with the electronic control device mounted on the automobile in mind in each embodiment, but can be applied to all moving mobile objects such as motorcycles, ships, railroads, and airplanes. It is possible and includes these. Moreover, it is applicable not only to a mobile body but to all products including a computer.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Small-Scale Networks (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE112019000765.3T DE112019000765T5 (de) | 2018-02-13 | 2019-01-17 | Elektronische Steuerungseinheit und Kommunikationssystem |
| US16/990,693 US20200369242A1 (en) | 2018-02-13 | 2020-08-11 | Electronic control unit and communication system |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018-023447 | 2018-02-13 | ||
| JP2018023447A JP2019140577A (ja) | 2018-02-13 | 2018-02-13 | 電子制御装置及び通信システム |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/990,693 Continuation US20200369242A1 (en) | 2018-02-13 | 2020-08-11 | Electronic control unit and communication system |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2019159593A1 true WO2019159593A1 (ja) | 2019-08-22 |
Family
ID=67619301
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2019/001320 Ceased WO2019159593A1 (ja) | 2018-02-13 | 2019-01-17 | 電子制御装置及び通信システム |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20200369242A1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP2019140577A (enExample) |
| DE (1) | DE112019000765T5 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2019159593A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11263308B2 (en) * | 2019-03-25 | 2022-03-01 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Run-time code execution validation |
| JP7176456B2 (ja) | 2019-03-29 | 2022-11-22 | 株式会社デンソー | メッセージ監視システム、メッセージ送信電子制御装置、および監視用電子制御装置 |
| US11750399B2 (en) * | 2019-12-06 | 2023-09-05 | Motional Ad Llc | Cyber-security protocol |
| CN119696763A (zh) * | 2020-01-10 | 2025-03-25 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种通信方法及装置 |
| JP2022086355A (ja) * | 2020-11-30 | 2022-06-09 | 株式会社東海理化電機製作所 | 送信機、受信機、通信システム、およびプログラム |
| CN115175137A (zh) * | 2020-12-28 | 2022-10-11 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种数据传输方法及装置 |
| JP7400744B2 (ja) | 2021-01-14 | 2023-12-19 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 車両制御システム |
| US11727733B2 (en) * | 2021-05-11 | 2023-08-15 | Ford Global Technologies, Llc | Enabling operator controls for machine operation |
| CN117413545A (zh) * | 2021-05-27 | 2024-01-16 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种车内通信方法及装置 |
| US11792644B2 (en) | 2021-06-21 | 2023-10-17 | Motional Ad Llc | Session key generation for autonomous vehicle operation |
| US20220407716A1 (en) * | 2021-06-21 | 2022-12-22 | Motional Ad Llc | Authenticated point cloud data |
| US12130903B2 (en) * | 2022-03-17 | 2024-10-29 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | Soft part authentication for electronic control unit |
| JPWO2023187896A1 (enExample) * | 2022-03-28 | 2023-10-05 | ||
| CN116781263B (zh) * | 2023-08-23 | 2023-10-20 | 合肥工业大学 | 车内ecu间身份认证及密钥自更新方法、可读存储介质 |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0698179A (ja) * | 1992-05-29 | 1994-04-08 | Nec Corp | ファクシミリ装置 |
| JP2003101528A (ja) * | 2001-09-19 | 2003-04-04 | Nagano Fujitsu Component Kk | 暗号化データ送受信方法及びその方法を行うためのシステム、送信機 |
| JP2003272285A (ja) * | 2002-03-13 | 2003-09-26 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 情報記録再生装置、情報送信装置、情報受信装置、情報受信記録再生装置、情報送受信システム |
| WO2011145353A1 (ja) * | 2010-05-19 | 2011-11-24 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 基地局装置 |
| US20170302452A1 (en) * | 2016-04-18 | 2017-10-19 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | Message authentication library |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07250085A (ja) * | 1994-03-10 | 1995-09-26 | Fujitsu Ltd | データ通信装置におけるバスの負荷分散方法及びデータ通信装置用バス切替制御装置 |
| JP4089309B2 (ja) * | 2002-06-26 | 2008-05-28 | ソニー株式会社 | オブジェクト利用管理システム、オブジェクトを利用し又は提供する情報処理装置又は情報処理方法、並びにコンピュータ・プログラム |
| JP4363471B2 (ja) * | 2007-08-03 | 2009-11-11 | 株式会社デンソー | 故障コード記憶管理装置、及び記憶管理装置 |
| JP5692244B2 (ja) * | 2011-01-31 | 2015-04-01 | 富士通株式会社 | 通信方法、ノード、およびネットワークシステム |
| US20160125020A1 (en) * | 2014-10-29 | 2016-05-05 | Vonage Network Llc | Systems and methods for managing contact information |
| JP6181032B2 (ja) * | 2014-11-18 | 2017-08-16 | 株式会社東芝 | 通信システム及び通信装置 |
| JP6512023B2 (ja) * | 2015-08-07 | 2019-05-15 | 株式会社デンソー | 通信システム、送信ノード、及び受信ノード |
| EP3337120B1 (en) * | 2016-12-14 | 2021-04-21 | Nxp B.V. | Network message authentication and verification |
| US10785193B2 (en) * | 2017-03-30 | 2020-09-22 | Seagate Technology Llc | Security key hopping |
-
2018
- 2018-02-13 JP JP2018023447A patent/JP2019140577A/ja active Pending
-
2019
- 2019-01-17 DE DE112019000765.3T patent/DE112019000765T5/de active Pending
- 2019-01-17 WO PCT/JP2019/001320 patent/WO2019159593A1/ja not_active Ceased
-
2020
- 2020-08-11 US US16/990,693 patent/US20200369242A1/en active Pending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0698179A (ja) * | 1992-05-29 | 1994-04-08 | Nec Corp | ファクシミリ装置 |
| JP2003101528A (ja) * | 2001-09-19 | 2003-04-04 | Nagano Fujitsu Component Kk | 暗号化データ送受信方法及びその方法を行うためのシステム、送信機 |
| JP2003272285A (ja) * | 2002-03-13 | 2003-09-26 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 情報記録再生装置、情報送信装置、情報受信装置、情報受信記録再生装置、情報送受信システム |
| WO2011145353A1 (ja) * | 2010-05-19 | 2011-11-24 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 基地局装置 |
| US20170302452A1 (en) * | 2016-04-18 | 2017-10-19 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | Message authentication library |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2019140577A (ja) | 2019-08-22 |
| DE112019000765T5 (de) | 2020-10-22 |
| US20200369242A1 (en) | 2020-11-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2019159593A1 (ja) | 電子制御装置及び通信システム | |
| CN107085870B (zh) | 使用加密方法调节车辆访问 | |
| US11228438B2 (en) | Security device for providing security function for image, camera device including the same, and system on chip for controlling the camera device | |
| US9269203B2 (en) | Vehicle component identification and configuration registry reporting system | |
| JP5949732B2 (ja) | プログラム更新システム及びプログラム更新方法 | |
| CN105827586B (zh) | 一种v2x通信设备、系统及非易失性存储器 | |
| US9053332B2 (en) | Policy for secure packet transmission using required node paths and cryptographic signatures | |
| US11212080B2 (en) | Communication system, vehicle, server device, communication method, and computer program | |
| JP6065113B2 (ja) | データ認証装置、及びデータ認証方法 | |
| US9992178B2 (en) | Method, apparatus and system for dynamically controlling secure vehicle communication based on ignition | |
| US20140301550A1 (en) | Method for recognizing a manipulation of a sensor and/or sensor data of the sensor | |
| US20180205729A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for encryption, decryption and authentication | |
| Boudguiga et al. | A simple intrusion detection method for controller area network | |
| WO2009147734A1 (ja) | 車両、メンテナンス装置、メンテナンスサービスシステム及びメンテナンスサービス方法 | |
| KR101269086B1 (ko) | 차량용 데이터의 인증 및 획득 방법 및 시스템 | |
| KR102393555B1 (ko) | 차량과 외부 서버 사이의 보호된 통신을 위한 방법, 이러한 방법에서 키 유도를 수행하기 위한 장치 및 차량 | |
| US20180310173A1 (en) | Information processing apparatus, information processing system, and information processing method | |
| EP4080818B1 (en) | Communication method and device, ecu, vehicle and storage medium | |
| WO2017115751A1 (ja) | 車載コンピュータシステム、車両、管理方法、及びコンピュータプログラム | |
| US12028350B2 (en) | Apparatus for electronic control of vehicle, apparatus for gateway and vehicle including the same | |
| KR20180012221A (ko) | 적어도 2개의 통신 파트너 사이에서 인증된 접속을 제공하는 방법 | |
| Giri et al. | An integrated safe and secure approach for authentication and secret key establishment in automotive cyber-physical systems | |
| CN114999029B (zh) | 一种车辆解锁方法及系统 | |
| KR102236282B1 (ko) | 차량용 통신 데이터 인증 방법 및 시스템 | |
| JP6203798B2 (ja) | 車載制御システム、車両、管理装置、車載コンピュータ、データ共有方法、及びコンピュータプログラム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 19755044 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 19755044 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |