WO2018133703A1 - R228060 盐酸盐的晶型及其制备方法和用途 - Google Patents
R228060 盐酸盐的晶型及其制备方法和用途 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2018133703A1 WO2018133703A1 PCT/CN2018/071889 CN2018071889W WO2018133703A1 WO 2018133703 A1 WO2018133703 A1 WO 2018133703A1 CN 2018071889 W CN2018071889 W CN 2018071889W WO 2018133703 A1 WO2018133703 A1 WO 2018133703A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- crystalline form
- crystal form
- hydrochloride
- preparation
- ray powder
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C269/00—Preparation of derivatives of carbamic acid, i.e. compounds containing any of the groups, the nitrogen atom not being part of nitro or nitroso groups
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C271/00—Derivatives of carbamic acids, i.e. compounds containing any of the groups, the nitrogen atom not being part of nitro or nitroso groups
- C07C271/06—Esters of carbamic acids
- C07C271/08—Esters of carbamic acids having oxygen atoms of carbamate groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms
- C07C271/10—Esters of carbamic acids having oxygen atoms of carbamate groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms with the nitrogen atoms of the carbamate groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms
- C07C271/12—Esters of carbamic acids having oxygen atoms of carbamate groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms with the nitrogen atoms of the carbamate groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms to hydrogen atoms or to carbon atoms of unsubstituted hydrocarbon radicals
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/13—Amines
- A61K31/132—Amines having two or more amino groups, e.g. spermidine, putrescine
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/13—Amines
- A61K31/135—Amines having aromatic rings, e.g. ketamine, nortriptyline
- A61K31/137—Arylalkylamines, e.g. amphetamine, epinephrine, salbutamol, ephedrine or methadone
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/21—Esters, e.g. nitroglycerine, selenocyanates
- A61K31/215—Esters, e.g. nitroglycerine, selenocyanates of carboxylic acids
- A61K31/22—Esters, e.g. nitroglycerine, selenocyanates of carboxylic acids of acyclic acids, e.g. pravastatin
- A61K31/223—Esters, e.g. nitroglycerine, selenocyanates of carboxylic acids of acyclic acids, e.g. pravastatin of alpha-aminoacids
Definitions
- the invention relates to the field of pharmaceutical crystal technology. Specifically, the crystal form involving R228060 hydrochloride, a preparation method thereof and use thereof belong to the field of medicine.
- Excessive Daytime Sleepiness or pathological sleepiness refers to excessive daytime sleep associated with various sleep and wakefulness conditions. These conditions can be caused by underlying sleep conditions or some other medical condition that has side effects on sleep. Excessive sleep during the day, also known as narcolepsy, is the main patient disease seen in sleep clinics, affecting 12% of the general population. Patients with EDS may be mentally distressed, have poor work or study performance, and increase the risk of accidents. The effects of EDS can make people weak or even life-threatening.
- R228060 also known as JZP-110, is a selective dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor originally developed by SK Biopharma, Korea. In 2014, jazz Pharmaceutical acquired the ownership of the compound. R228060 has the potential to treat narcolepsy and sleep apnea syndrome, and has achieved major research endpoints in two global multicenter, phase 3 studies with positive results that significantly improved adult obstructive sleep apnea patients. Excessive sleepiness and excessive sleep problems in patients with narcolepsy.
- R228060 chemical name is O-carbamoyl-(D)-phenylalaninol, and its structural formula is as shown in formula (I):
- a suitable drug salt type can improve the solubility of the drug, increase the physical and chemical stability, and improve the physical properties such as melting point, hygroscopicity, and crystallization type after the salt is formed into a salt, and further develop the pharmaceutical dosage form. Has an important role.
- R228060 hydrochloride and its preparation are disclosed in the patent document WO1996007637A1, and a white solid having a melting point of 172-174 ° C is obtained, and other characteristic data of the solid are not given in the text. Furthermore, the inventors of the present application have not found other crystal form patents or literature reports on R228060 hydrochloride. Therefore, there is a need in the art to systematically develop a crystalline form of R228060 hydrochloride to find a crystal form suitable for development.
- the inventors of the present application have conducted a large number of experimental studies and found that the crystalline form CS1 and the crystalline form CS2 of R228060 hydrochloride have a melting point of 183 ° C, and the melting point is much higher than the solid disclosed in the prior art. It provides a better choice for the preparation of pharmaceutical preparations containing R228060 and is of great significance for drug development.
- the main object of the present invention is to provide a crystal form of R228060 hydrochloride and a preparation method and use thereof.
- the present invention provides a crystalline form CS1 of R228060 hydrochloride (hereinafter referred to as "crystalline form CS1") which is a hydrate.
- the X-ray powder diffraction of the crystal form CS1 has characteristic peaks at diffraction angle 2 ⁇ values of 22.9° ⁇ 0.2°, 27.3° ⁇ 0.2°, and 20.9° ⁇ 0.2°.
- the X-ray powder diffraction of the crystal form CS1 has a characteristic peak at one or two or three points in the diffraction angle 2 ⁇ value of 24.1° ⁇ 0.2°, 21.6° ⁇ 0.2°, and 26.1° ⁇ 0.2°.
- the X-ray powder diffraction of the crystalline form CS1 has characteristic peaks at diffraction angle 2 ⁇ values of 24.1° ⁇ 0.2°, 21.6° ⁇ 0.2°, and 26.1° ⁇ 0.2°.
- the X-ray powder diffraction of the crystal form CS1 has a characteristic peak at one or two or three of the diffraction angle 2 ⁇ values of 17.1° ⁇ 0.2°, 13.5° ⁇ 0.2°, and 6.9 ⁇ 0.2°.
- the X-ray powder diffraction of the crystal form CS1 has characteristic peaks at diffraction angle 2 ⁇ values of 17.1° ⁇ 0.2°, 13.5° ⁇ 0.2°, and 6.9° ⁇ 0.2°.
- the X-ray powder diffraction of the crystalline form CS1 has a diffraction angle 2 ⁇ of 22.9° ⁇ 0.2°, 27.3° ⁇ 0.2°, 20.9° ⁇ 0.2°, 24.1° ⁇ 0.2°, 21.6°. There are characteristic peaks at ⁇ 0.2°, 26.1° ⁇ 0.2°, 17.1° ⁇ 0.2°, 13.5° ⁇ 0.2°, and 6.9° ⁇ 0.2°.
- the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form CS1 is shown in FIG.
- the crystal form CS1 provided by the present invention when subjected to differential scanning calorimetry, is heated to a temperature near 76 ° C to start the first endothermic peak, which is a crystal form.
- the dehydration endothermic peak of CS1 starts to show a second endothermic peak near 183 °C, and its DSC chart is shown in Fig. 2.
- the present invention also provides a process for the preparation of crystalline form CS1 of R228060 hydrochloride, characterized in that it comprises: R228060 free base solids with esters or alkanes or aromatic hydrocarbons or halogenated hydrocarbons The solvent is mixed, then concentrated hydrochloric acid is added, and the mixture is stirred at room temperature to obtain a crystal form CS1.
- the esters comprise ethyl acetate, the alkane comprises cyclohexane and n-heptane, the aromatic hydrocarbons comprise toluene, and the halogenated hydrocarbons comprise chloroform.
- the present invention also provides a crystalline form CS2 of R228060 hydrochloride (hereinafter referred to as "Form CS2”), which is an anhydride.
- the X-ray powder diffraction of the crystal form CS2 has characteristic peaks at diffraction angle 2 ⁇ values of 24.7° ⁇ 0.2°, 23.8° ⁇ 0.2°, and 19.8° ⁇ 0.2°.
- the X-ray powder diffraction of the crystal form CS2 has a characteristic peak at one or two or three points of the diffraction angle 2 ⁇ value of 29.3° ⁇ 0.2°, 20.4° ⁇ 0.2°, and 26.3° ⁇ 0.2°.
- the X-ray powder diffraction of the crystalline form CS2 has characteristic peaks at diffraction angle 2 ⁇ values of 29.3° ⁇ 0.2°, 20.4° ⁇ 0.2°, and 26.3° ⁇ 0.2°.
- the X-ray powder diffraction of the crystal form CS2 has a characteristic peak at one or two or three points in the diffraction angle 2 ⁇ value of 16.0° ⁇ 0.2°, 6.7° ⁇ 0.2°, and 12.3° ⁇ 0.2°.
- the X-ray powder diffraction of the crystalline form CS2 has characteristic peaks at diffraction angle 2 ⁇ values of 16.0° ⁇ 0.2°, 6.7° ⁇ 0.2°, and 12.3° ⁇ 0.2°.
- the X-ray powder diffraction of the crystalline form CS2 has a diffraction angle 2 ⁇ of 24.7° ⁇ 0.2°, 23.8° ⁇ 0.2°, 19.8° ⁇ 0.2°, 29.3° ⁇ 0.2°, 20.4°. Characteristic peaks are present at ⁇ 0.2°, 26.3° ⁇ 0.2°, 16.0° ⁇ 0.2°, 6.7° ⁇ 0.2°, 12.3° ⁇ 0.2°, 13.2° ⁇ 0.2°, and 31.0° ⁇ 0.2°.
- the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form CS2 is shown in FIG.
- the crystal form CS2 provided by the present invention when subjected to differential scanning calorimetry, is heated to a temperature near 183 ° C to start an endothermic peak, which is the melting point of the crystalline form CS2.
- the DSC chart is shown in Figure 5.
- the present invention also provides a process for the preparation of the crystalline form CS2 of R228060 hydrochloride, characterized in that the method is 1), 2) or 3):
- the heating temperature is 110 ° C;
- the alcohol comprises methanol
- the ether comprises methyl tert-butyl ether
- the ketone comprises acetone and methyl ethyl ketone, the nitrile comprising acetonitrile.
- the "room temperature” comprises 15 to 30 ° C;
- the “stirring” is carried out by a conventional method in the art, such as magnetic stirring or mechanical stirring, and the stirring speed is 50 to 1800 rpm, preferably 300 to 900 rpm.
- crystal or “polymorph” means confirmed by the X-ray diffraction pattern characterization shown.
- X-ray diffraction pattern will generally vary with the conditions of the instrument. It is particularly important to note that the relative intensities of the X-ray diffraction patterns may also vary with experimental conditions, so the order of peak intensities cannot be the sole or decisive factor. In fact, the relative intensity of the diffraction peaks in the XRPD pattern is related to the preferred orientation of the crystal.
- the peak intensities shown here are illustrative and not for absolute comparison.
- the experimental error of the peak angle is usually 5% or less, and the error of these angles should also be taken into account, and an error of ⁇ 0.2° is usually allowed.
- the overall offset of the peak angle is caused, and a certain offset is usually allowed.
- the X-ray diffraction pattern of one crystal form in the present invention is not necessarily identical to the X-ray diffraction pattern in the example referred to herein, and the "XRPD pattern is the same" as used herein does not mean absolutely the same.
- the same peak position can differ by ⁇ 0.2° and the peak intensity allows for some variability.
- Any crystal form having a map identical or similar to the characteristic peaks in these maps is within the scope of the present invention.
- One skilled in the art will be able to compare the maps listed herein with a map of an unknown crystal form to verify whether the two sets of maps reflect the same or different crystal forms.
- the crystalline form CS1 and crystalline form CS2 of the present invention are pure, unitary, and substantially free of any other crystalline form.
- substantially free when used to refer to a new crystalline form means that the crystalline form contains less than 20% by weight of other crystalline forms, especially less than 10% by weight of other crystalline forms, more Other crystal forms of 5% by weight, more preferably less than 1% by weight of other crystal forms.
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically and/or prophylactically effective amount of the crystalline form CS1, crystalline form CS2 of the present invention, and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, diluent or Shape agent.
- the present invention provides the use of the crystalline form CS1, crystalline form CS2 of R228060 hydrochloride for the preparation of a pharmaceutical preparation for treating central nervous system diseases.
- the present invention provides the use of the crystalline form CS1, crystalline form CS2 of R228060 hydrochloride for the preparation of a pharmaceutical preparation for treating narcolepsy and sleep apnea syndrome.
- the crystalline form CS1 and the crystalline form CS2 of the present invention have good stability, including high temperature stability, long-term stability, and mechanical stability.
- the melting points of the crystalline form CS1 and the crystalline form CS2 are all around 183 ° C, which is much higher than the melting point of the solid (172-174 ° C) in the prior patent, and has better high temperature stability.
- the crystalline form CS1 and the crystalline form CS2 are stable for at least one month at 25 ° C / 60% RH or / and 40 ° C / 75% RH, preferably at least for six months, preferably at least one year.
- the crystalline form CS1 and the crystalline form CS2 have good stability, can ensure that the drug does not undergo crystal transformation during the preparation, transportation, storage and preservation process, which affects the quality of the drug, guarantees the efficacy and safety of the drug, and prevents the drug from being defective.
- the occurrence of the reaction is of great significance.
- the crystal form CS1 and the form CS2 were manually ground for 30 minutes, and the crystal form and crystallinity did not change significantly, indicating that the crystal form CS1 and the form CS2 of the present invention have outstanding mechanical stability, and the grinding of the raw material medicine is often required in the preparation process.
- the pulverization and high mechanical stability can reduce the risk of crystallinity change and crystal transformation of the drug substance during the processing of the preparation.
- the crystalline form CS1 and the crystalline form CS2 provided by the invention have excellent solubility and high dissolution rate, and the solubility in water is more than 10 mg/mL, and the amount of dissolution in the form of a capsule preparation after 10 minutes in water is prepared. Up to 60% or more.
- the rapid dissolution rate of the drug can accelerate the rapid dissolution in the body after the administration of the drug, and the drug can be controlled to act at a specific site to improve the onset rate of the drug by adjusting the auxiliary material.
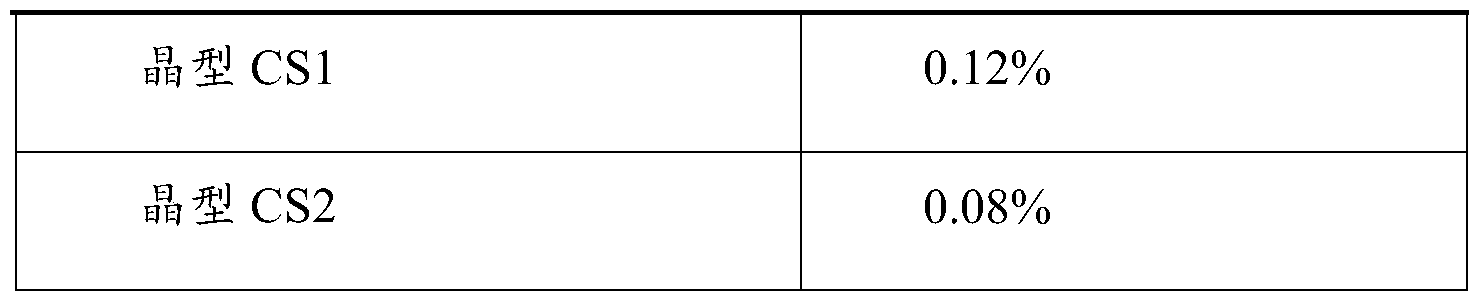
- the crystalline form CS1 and the crystalline form CS2 provided by the present invention have almost no hygroscopicity, and the weight gain at 80% relative humidity is 0.12% and 0.08%, respectively, and the crystal form does not change before and after the wettability.
- the almost non-hygroscopic crystal form does not need to control the environmental humidity during the preparation process, and has no special requirements for packaging and storage conditions, cost saving, easy industrial production and long-term storage of medicines. Because the storage conditions are not demanding, the material storage and quality control costs will be greatly reduced, and it has strong economic value and is more suitable for medicinal use.
- the crystalline form CS1 and the crystalline form CS2 provided by the present invention have good formulation stability, and the crystalline form can be stably placed in the formulation for at least two weeks. There was no significant change in the crystal form and single impurity content for a period of time, which is of great significance for ensuring the safety and efficacy of the preparation.
- Figure 1 is an XRPD pattern of a crystal form CS1 obtained according to Example 1 of the present invention.
- Example 2 is a DSC chart of a crystal form CS1 obtained according to Example 1 of the present invention.
- Figure 3 is a TGA diagram of a crystalline form CS1 obtained in accordance with Example 1 of the present invention.
- Example 4 is an XRPD pattern of a crystal form CS2 obtained according to Example 3 of the present invention.
- Figure 5 is a DSC chart of a crystalline form CS2 obtained in accordance with Example 3 of the present invention.
- Figure 6 is a TGA diagram of a crystalline form CS2 obtained in accordance with Example 3 of the present invention.
- Fig. 7 is an XRPD overlay of the crystal form CS1 placed at 25 ° C / 60% RH for one month before and after the embodiment 6 of the present invention.
- Fig. 8 is an XRPD overlay of the crystal form CS1 placed at 40 ° C / 75% RH for one month before and after the embodiment 6 of the present invention.
- Fig. 9 is an XRPD diagram of the crystal form CS2 placed at 25 ° C / 60% RH for one month before and after the embodiment 6 of the present invention.
- Figure 10 is an XRPD overlay of the crystal form CS1 before and after polishing in Example 7 of the present invention.
- Figure 11 is an XRPD overlay of the crystal form CS2 before and after polishing in Example 7 of the present invention.
- Figure 12 is a DVS diagram of the crystal form CS1 in the eighth embodiment of the present invention.
- Figure 13 is a DVS diagram of a crystal form CS2 in Example 8 of the present invention.
- the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of the present invention was collected on a Panalytical Empyrean X-ray powder diffractometer.
- the method parameters of the X-ray powder diffraction described in the present invention are as follows:
- Scan range: from 3.0 to 40.0 degrees
- the differential thermal analysis (DSC) data was taken from the TA Instruments Q200MDSC, the instrument control software was Thermal Advantage, and the analysis software was Universal Analysis.
- Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) data was taken from the TA Instruments Q500TGA, the instrument control software was Thermal Advantage, and the analysis software was Universal Analysis.
- the dynamic moisture adsorption (DVS) pattern of the present invention was collected on an Intrinsic dynamic moisture adsorber manufactured by SMS Corporation (Surface Measurement Systems Ltd.).
- the instrument control software is DVS-Intrinsic control software
- the analysis software is DVS-Intrinsic Analysis software.
- the method parameters of the dynamic moisture adsorber are as follows:
- Relative humidity range 0%RH-95%RH
- HPLC high performance liquid chromatography
- the elution gradient is as follows:
- the dissolution data was measured from Sotax AT7Smart.
- R228060 free base and R228060 hydrochloride used in the following examples were prepared according to the method described in WO1996007637A1.
- the DSC of the crystal form CS1 is as shown in Fig. 2, and the first endothermic peak starts to appear near the temperature of 76 ° C, and the second endothermic peak starts to appear at 183 ° C.
- the TGA of the crystal form CS1 is as shown in Fig. 3, and when heated to 100 ° C, it has a mass loss of about 3.4%.
- the crystal form CS1 of 10.2 mg R228060 was heated to 110 ° C, and the obtained solid was detected as the crystal form CS2, the XRPD data thereof is shown in Table 4, and the XRPD pattern is shown in Fig. 4.
- the DSC of the crystal form CS2 starts to have a melting endothermic peak near the temperature of 183 ° C, which is the melting point of the crystal form CS2.
- the TGA of the crystal form CS2 is as shown in Fig. 6, and when heated to 150 ° C, it has a mass loss of about 0.2%.
- FIG. 7 is the XRPD pattern before the crystal form CS1 is placed, and the lower graph is the XRPD pattern placed at 25 °C/60% RH for one month;
- the upper graph in Figure 8 is the XRPD pattern before the crystal form CS1 is placed, the bottom view is the XRPD pattern placed at 40 °C / 75% RH for one month;
- the upper view in Fig. 9 is the XRPD pattern before the crystal form CS2 is placed.
- the figure below shows the XRPD pattern placed at 25 ° C / 60% RH for 1 month.
- Deliquescence absorbs enough water to form a liquid.
- the wetting weight gain is not less than 15%.
- the wetting weight gain is less than 15% but not less than 2%.
- wetting gain is less than 0.2%.
- the crystal form CS1 and the form CS2 of the present invention have low hygroscopicity, and can well prevent problems such as crystal instability in the process of pharmaceutical preparation and/or storage, and unworkability of the preparation caused by external factors such as environmental moisture. Conducive to accurate quantification in the preparation of the preparation and later transportation and storage.
- the crystalline form CS1 or the crystalline form CS2, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium and 3 mg of magnesium stearate in the amounts listed in the table below were weighed and mixed for 2 minutes. It was pressed into a piece by a manual tableting machine, and a circular die having a diameter of 20 mm was pressed at a pressure of 5 kN ⁇ 1 kN. Manually passed through a 20 mesh screen, and then added 3 mg of magnesium stearate for 1 minute. The above mixture was placed in a 0# gelatin capsule shell. Packed in 35cc HDPE (high density polyethylene) bottles (one per bottle), each bottle contains 1g desiccant and sealed with a sealing machine. The prescription of the capsule (per 300 mg) is shown in Table 9 below. After the drug was left for one month, the crystal form CS1 and the form CS2 were not changed in the capsule form and purity.
- Capsule composition Dosage (mg / capsule) Crystal Form CS1 or Form CS2 75 Microcrystalline cellulose 204 Croscone sodium 15 Magnesium stearate 6
- Dissolution medium water
- Dissolution method slurry method
- the dissolution rate of the crystalline form CS1 and the crystalline form CS2 showed that both the crystalline form CS1 and the crystalline form CS2 had a faster dissolution rate, and the dissolution amount at 10 minutes could be more than 60%.
- the rapid dissolution rate of the drug can accelerate the rapid dissolution in the body after the drug is taken, and the auxiliary agent can be adjusted to control the rapid action of the drug in a specific part and improve the onset rate of the drug.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
本发明涉及R228060盐酸盐的晶型及其制备方法和用途。本发明提供的R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS1和晶型CS2稳定性好、溶解度高、熔点高、结晶度好、引湿性低、制备方法简单,适合药物开发,R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS1和晶型CS2的发现为含R228060盐酸盐的药物制剂的制备提供了更好的选择,对于药物开发具有非常重要的意义。
Description
本发明涉及药物晶体技术领域。具体而言,涉及R228060盐酸盐的晶型及其制备方法和用途,属于医药领域。
白天睡眠过多(Excessive Daytime Sleepiness,EDS)或病理性嗜睡指与各种睡眠和清醒病症相关的白天睡眠过多。这些病症可以是基础睡眠病症或者对睡眠有副作用的一些其它医学病症所致。白天睡眠过多,又称为嗜睡症,是睡眠诊所中所见的主要患者疾病,其影响占普通人群的12%。EDS患者可能会表现为精神苦恼、工作或学习表现欠佳,增加了发生事故的风险,EDS的影响可使人衰弱,甚至威胁生命。
R228060,又名JZP-110,是一种选择性多巴胺和去甲肾上腺素再摄取抑制剂,最初由韩国SK生物制药公司研发,2014年爵士制药获得该化合物的所有权。R228060具有治疗嗜睡症和睡眠呼吸暂停综合症的潜力,在两项全球多中心3期研究中均达到了主要研究终点,取得了积极的效果,显着的改善了成人阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停患者的过度嗜睡和嗜睡症患者过度睡眠问题。
R228060化学名称为O-氨基甲酰基-(D)-苯丙氨醇,其结构式如式(I)所示:
固体化学药物晶型不同,可造成其溶解度和稳定性不同,从而影响药物的吸收和生物利用度,并且会导致临床药效的差异。通过成盐方式提高候选化合物的溶解度已成为药物研发中的重要手段。与药物的游离形式相比,适宜的药物盐型能提高药物的溶解度,增加物理化学稳定性,而且药物成盐后还可改善其熔点、吸湿性、结晶类型等物理性质,对进一步开发药物剂型具有重要作用。专利文献WO1996007637A1中公开了R228060盐酸盐及其制备方法,并得到了一种熔点为172-174℃白色固体,文本中未给出该固体的其他特征数据。此外,本申请发明人未发现其他有关R228060盐酸盐的晶型专利或文献报道。因此, 本领域需要系统全面的开发R228060盐酸盐的晶型,以发现适合开发的晶型。本申请发明人经过了大量的实验研究,发现了R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS1和晶型CS2,晶型CS1和晶型CS2的熔点为183℃,熔点远高于现有技术公开的固体。为含R228060的药物制剂的制备提供了更好的选择,对于药物开发具有非常重要的意义。
发明内容
针对现有技术存在的不足和空白,本发明的主要目的是提供R228060盐酸盐的晶型及其制备方法和用途。
根据本发明的目的,本发明提供R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS1(以下称作“晶型CS1”),所述晶型CS1为水合物。
使用Cu-Kα辐射,所述晶型CS1的X射线粉末衍射在衍射角2θ值为22.9°±0.2°、27.3°±0.2°、20.9°±0.2°处有特征峰。
进一步的,所述晶型CS1的X射线粉末衍射在衍射角2θ值为24.1°±0.2°、21.6°±0.2°、26.1°±0.2°中的一处或两处或三处有特征峰。优选的,所述晶型CS1的X射线粉末衍射在衍射角2θ值为24.1°±0.2°、21.6°±0.2°、26.1°±0.2°处均有特征峰。
进一步的,所述晶型CS1的X射线粉末衍射在衍射角2θ值为17.1°±0.2°、13.5°±0.2°、6.9±0.2°中的一处或两处或三处有特征峰。优选的,所述晶型CS1的X射线粉末衍射在衍射角2θ值为17.1°±0.2°、13.5°±0.2°、6.9°±0.2°处均有特征峰。
在一个优选的实施方案中,所述晶型CS1的X射线粉末衍射在衍射角2θ值为22.9°±0.2°、27.3°±0.2°、20.9°±0.2°、24.1°±0.2°、21.6°±0.2°、26.1°±0.2°、17.1°±0.2°、13.5°±0.2°、6.9°±0.2°处有特征峰。
非限制性地,在本发明的一个具体实施方案中,晶型CS1的X射线粉末衍射谱图如图1所示。
非限制性地,在本发明的一个具体实施方案中,本发明提供的晶型CS1,当进行差示扫描量热分析时,加热至76℃附近开始出现第一个吸热峰,为晶型CS1的脱水吸热峰,加热在183℃附近开始出现第二个吸热峰,其DSC图如图2所示。
根据本发明的目的,本发明还提供R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS1的制备方法,其特征在于,所述方法包含:将R228060游离碱固体与酯类或烷烃类或芳香烃类或卤代烃类溶剂混合,然后加入浓盐酸,室温下搅拌制得晶型CS1。
所述酯类包含乙酸乙酯,所述烷烃类包含环己烷和正庚烷,所述芳香烃类包括甲苯,所述卤代烃类包含氯仿。
根据本发明的目的,本发明还提供R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS2(以下称作“晶型CS2”), 所述晶型CS2为无水物。
使用Cu-Kα辐射,所述晶型CS2的X射线粉末衍射在衍射角2θ值为24.7°±0.2°、23.8°±0.2°、19.8°±0.2°处有特征峰。
进一步的,所述晶型CS2的X射线粉末衍射在衍射角2θ值为29.3°±0.2°、20.4°±0.2°、26.3°±0.2°中的一处或两处或三处有特征峰。优选的,所述晶型CS2的X射线粉末衍射在衍射角2θ值为29.3°±0.2°、20.4°±0.2°、26.3°±0.2°处均有特征峰。
进一步的,所述晶型CS2的X射线粉末衍射在衍射角2θ值为16.0°±0.2°、6.7°±0.2°、12.3°±0.2°中的一处或两处或三处有特征峰。优选的,所述晶型CS2的X射线粉末衍射在衍射角2θ值为16.0°±0.2°、6.7°±0.2°、12.3°±0.2°处均有特征峰。
在一个优选的实施方案中,所述晶型CS2的X射线粉末衍射在衍射角2θ值为24.7°±0.2°、23.8°±0.2°、19.8°±0.2°、29.3°±0.2°、20.4°±0.2°、26.3°±0.2°、16.0°±0.2°、6.7°±0.2°、12.3°±0.2°、13.2°±0.2°、31.0°±0.2°处有特征峰。
非限制性地,在本发明的一个具体实施方案中,晶型CS2的X射线粉末衍射谱图如图4所示。
非限制性地,在本发明的一个具体实施方案中,本发明提供的晶型CS2,当进行差示扫描量热分析时,加热至183℃附近开始出现吸热峰,为晶型CS2的熔点,其DSC图如图5所示。
根据本发明的目的,本发明还提供R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS2的制备方法,其特征在于,所述方法为1)、2)或者3):
1)将R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS1加热到80~180℃,得到晶型CS2。
优选地,所述加热温度为110℃;
2)将R228060盐酸盐固体与醇类溶剂混合,然后滴加醚类溶剂,室温搅拌至有固体析出,得到晶型CS2;
优选地,所述醇类包含甲醇,所述醚类包含甲基叔丁基醚;
3)将R228060游离碱固体与酮类或腈类溶剂混合,然后加入浓盐酸,室温下搅拌制得晶型CS2;
优选地,所述酮类包含丙酮和甲基乙基酮,所述腈类包含乙腈。
在本发明的晶型的制备方法中:
所述“室温”包含15~30℃;
所述“搅拌”,采用本领域的常规方法完成,例如磁力搅拌或机械搅拌,搅拌速度为50~1800转/分钟,优选300~900转/分钟。
本发明中,“晶体”或“多晶型”指的是被所示的X射线衍射图表征所证实的。本领域技术人员能够理解,这里所讨论的理化性质可以被表征,其中的实验误差取决于仪器的条件、样品的准备和样品的纯度。特别是,本领域技术人员公知,X射线衍射图通常会随着仪器的条件而有所改变。特别需要指出的是,X射线衍射图的相对强度也可能随着实验条件的变化而变化,所以峰强度的顺序不能作为唯一或决定性因素。事实上,XRPD图谱中衍射峰的相对强度与晶体的择优取向有关,本文所示的峰强度为说明性而非用于绝对比较。另外,峰角度的实验误差通常在5%或更少,这些角度的误差也应该被考虑进去,通常允许有±0.2°的误差。另外,由于样品高度等实验因素的影响,会造成峰角度的整体偏移,通常允许一定的偏移。因而,本领域技术人员可以理解的是,本发明中一个晶型的X射线衍射图不必和这里所指的例子中的X射线衍射图完全一致,本文所述“XRPD图相同”并非指绝对相同,相同峰位置可相差±0.2°且峰强度允许一定可变性。任何具有和这些图谱中的特征峰相同或相似的图的晶型均属于本发明的范畴之内。本领域技术人员能够将本发明所列的图谱和一个未知晶型的图谱相比较,以证实这两组图谱反映的是相同还是不同的晶型。
在一些实施方案中,本发明的晶型CS1和晶型CS2是纯的、单一的,基本没有混合任何其他晶型。本发明中,“基本没有”当用来指新晶型时指这个晶型含有少于20%(重量)的其他晶型,尤其指少于10%(重量)的其他晶型,更指少于5%(重量)的其他晶型,更指少于1%(重量)的其他晶型。
需要说明的是,本发明中提及的数值及数值范围不应被狭隘地理解为数值或数值范围本身,本领域技术人员应当理解其可以根据具体技术环境的不同,在不背离本发明精神和原则的基础上围绕具体数值有所浮动,本发明中,这种本领域技术人员可预见的浮动范围多以术语“约”来表示。
此外,本发明提供一种药物组合物,所述药物组合物包含治疗和/或预防有效量的本发明晶型CS1、晶型CS2,以及至少一种药学上可接受的载体、稀释剂或赋形剂。
进一步的,本发明提供R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS1、晶型CS2在制备治疗中枢神经系统疾病药物制剂中的用途。
进一步的,本发明提供R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS1、晶型CS2在制备治疗嗜睡症和睡眠呼吸暂停综合症药物制剂中的用途。
本发明晶型CS1和晶型CS2的有益效果:
1)本发明的晶型CS1和晶型CS2具有较好的稳定性,包含高温稳定性、长期稳定性和机械稳定性。晶型CS1和晶型CS2的熔点均在183℃附近,远高于现有专利中的固体(172-174℃)的熔点,具有更好的高温稳定性。晶型CS1和晶型CS2在25℃/60%RH或/ 和40℃/75%RH至少可稳定放置一个月,优选的至少可稳定放置六个月,优选的至少可稳定放置一年。晶型CS1和晶型CS2具有较好的稳定性,能够保证药品在制备、运输、贮藏及保存过程中不会发生转晶现象而影响到药品质量,对保证药物疗效和安全性,防止药物不良反应的发生具有重要意义。将晶型CS1和晶型CS2手动研磨30分钟,晶型和结晶度均未发生明显变化,说明本发明晶型CS1和晶型CS2具有突出的机械稳定性,制剂加工过程中常需要原料药的研磨粉碎,高的机械稳定性能够减小制剂加工过程中发生原料药晶型结晶度改变和转晶的风险。
2)本发明提供的晶型CS1和晶型CS2具有优异的溶解性和较高的溶出速率,在水中的溶解度大于10mg/mL,晶型制备成胶囊制剂后,在水中10min时的溶出量即可达60%以上。在制剂开发中,药物具有快速的溶出速率可加快药物服用后在体内快速溶解,可通过调整辅料,控制药物在特定部位快速发挥作用,提高药物的起效速率。
3)本发明提供的晶型CS1和晶型CS2几乎无引湿性,80%相对湿度下增重分别为0.12%和0.08%,且引湿性前后晶型未发生改变。几乎无引湿性的晶型在制剂过程中可不必控制环境湿度,对包装和贮存条件无特殊苛刻要求,节约成本,易于工业化生产和药品的长期贮存。由于对储存条件要求不苛刻,将大大降低物料储存以及质量控制成本,具有很强的经济价值,更适合药用。
4)本发明提供的晶型CS1和晶型CS2具有良好的制剂稳定性,晶型在制剂中至少可稳定放置两周。放置一段时间晶型和单杂含量均未发生明显变化,对保证制剂安全和疗效具有重要意义。
图1为根据本发明实施例1所得晶型CS1的XRPD图。
图2为根据本发明实施例1所得晶型CS1的DSC图。
图3为根据本发明实施例1所得晶型CS1的TGA图。
图4为根据本发明实施例3所得晶型CS2的XRPD图。
图5为根据本发明实施例3所得晶型CS2的DSC图。
图6为根据本发明实施例3所得晶型CS2的TGA图。
图7为本发明实施例6中晶型CS1放置在25℃/60%RH一个月前后的XRPD叠图。
图8为本发明实施例6中晶型CS1放置在40℃/75%RH一个月前后的XRPD叠图。
图9为本发明实施例6中晶型CS2放置在25℃/60%RH一个月前后的XRPD图。
图10为本发明实施例7中晶型CS1研磨前后的XRPD叠图。
图11为本发明实施例7中晶型CS2研磨前后的XRPD叠图。
图12为本发明实施例8中晶型CS1的DVS图。
图13为本发明实施例8中晶型CS2的DVS图。
本发明进一步参考以下实施例限定,所述实施例详细描述本发明的晶型的制备和使用方法。对本领域技术人员显而易见的是,对于材料和方法两者的许多改变可在不脱离本发明范围的情况下实施。
本发明中所用到的名词解释如下:
XRPD:X射线粉末衍射
HPLC:高效液相色谱
DSC:差示扫描量热
TGA:热重分析
1H NMR:核磁共振氢谱
RH:相对湿度
采集数据所用的仪器及方法:
本发明所述的X射线粉末衍射图在Panalytical Empyrean X射线粉末衍射仪上采集。本发明所述的X射线粉末衍射的方法参数如下:
X射线反射参数:Cu,Kα
Kα2/Kα1强度比例:0.50
电压:45仟伏特(kV)
电流:40毫安培(mA)
扫描范围:自3.0至40.0度
差热分析(DSC)数据采自于TA Instruments Q200MDSC,仪器控制软件是Thermal Advantage,分析软件是Universal Analysis。
扫描速率:10℃/min
保护气体:氮气
热重分析(TGA)数据采自于TA Instruments Q500TGA,仪器控制软件是Thermal Advantage,分析软件是Universal Analysis。
扫描速率:10℃/min
保护气体:氮气
本发明所述动态水分吸附(DVS)图在由SMS公司(Surface Measurement Systems Ltd.) 生产的Intrinsic动态水分吸附仪上采集。仪器控制软件是DVS-Intrinsic control software,分析软件是DVS-Intrinsic Analysis software。所述的动态水分吸附仪的方法参数如下:
温度:25℃
载气,流速:N
2,200毫升/分钟
单位时间质量变化:0.002%/分钟
相对湿度范围:0%RH-95%RH
本发明中高效液相色谱(HPLC)数据采自于安捷伦1260,所用检测器为紫外可变波长检测器(VWD)。本发明所述的测试纯度的HPLC方法参数如下:
1、色谱柱:Waters Xbridge C18,150×4.6mm,5μm
2、流动相:A:2mmol/L正庚烷磺酸钠(pH=3.0)
B:甲醇
洗脱梯度如下:
| Time(min) | %B |
| 0.0 | 15 |
| 3.0 | 15 |
| 20.0 | 35 |
| 23.0 | 35 |
| 26.0 | 15 |
| 35.0 | 15 |
3、流速:1.0mL/min
4、进样量:10μL
5、检测波长:210nm
6、柱温:40℃
7、稀释剂:水
本发明中溶出度数据测定采自于Sotax AT7Smart。
除非特殊说明,以下实施例均在室温条件下操作。
以下实施例中所使用的R228060游离碱和R228060盐酸盐根据WO1996007637A1专利文献所记载的方法制备。
实施例1
晶型CS1的制备:
称将11.3mg R228060游离碱加入到1.0mL乙酸乙酯中,然后加入2μL浓盐酸(12 mol/L),室温下搅拌24小时,离心取下层固体,室温下干燥,经过检测,所得固体为晶型CS1,其XRPD数据如表1所示,XRPD图如图1所示。
表1
| 衍射角2θ | d值 | 强度% |
| 6.91 | 12.80 | 17.51 |
| 11.07 | 7.99 | 2.55 |
| 12.18 | 7.27 | 1.58 |
| 12.60 | 7.03 | 1.45 |
| 13.46 | 6.58 | 22.56 |
| 16.12 | 5.50 | 14.86 |
| 17.10 | 5.19 | 32.24 |
| 17.39 | 5.10 | 43.52 |
| 17.71 | 5.01 | 11.40 |
| 18.42 | 4.82 | 13.51 |
| 20.86 | 4.26 | 60.78 |
| 21.61 | 4.11 | 39.50 |
| 22.57 | 3.94 | 49.19 |
| 22.88 | 3.89 | 100.00 |
| 23.28 | 3.82 | 5.00 |
| 24.05 | 3.70 | 50.90 |
| 24.40 | 3.65 | 12.16 |
| 25.87 | 3.44 | 26.93 |
| 26.15 | 3.41 | 34.24 |
| 26.82 | 3.32 | 10.07 |
| 27.30 | 3.27 | 70.97 |
| 27.94 | 3.19 | 17.38 |
| 29.45 | 3.03 | 3.61 |
| 30.04 | 2.97 | 2.61 |
| 30.49 | 2.93 | 4.98 |
| 30.99 | 2.89 | 6.26 |
| 31.35 | 2.85 | 14.44 |
| 31.87 | 2.81 | 23.05 |
| 32.27 | 2.77 | 15.23 |
| 32.61 | 2.75 | 13.37 |
| 33.19 | 2.70 | 19.01 |
晶型CS1的DSC如图2所示,加热至76℃附近开始出现第一个吸热峰,在183℃处开始出现第二个吸热峰。
晶型CS1的TGA如图3所示,其加热至100℃时,具有约3.4%的质量损失。
实施例2
晶型CS1的制备:
称取一定质量的R228060游离碱加入到表2中的溶剂中,然后加入2μL浓盐酸(12mol/L),室温下搅拌24小时,离心取下层固体,室温下干燥。经检测,所得固体均为晶型CS1,其中样品2-a的XRPD数据如表3所示。
表2
表3
| 衍射角2θ | d值 | 强度% |
| 6.91 | 12.79 | 20.80 |
| 13.52 | 6.55 | 26.64 |
| 16.13 | 5.49 | 10.67 |
| 17.12 | 5.18 | 41.19 |
| 17.38 | 5.10 | 21.29 |
| 17.73 | 5.00 | 6.99 |
| 18.45 | 4.81 | 8.73 |
| 20.88 | 4.25 | 51.97 |
| 21.64 | 4.11 | 16.66 |
| 22.60 | 3.93 | 22.48 |
| 22.86 | 3.89 | 100.00 |
| 24.05 | 3.70 | 29.84 |
| 24.48 | 3.64 | 7.37 |
| 25.93 | 3.44 | 14.13 |
| 26.18 | 3.40 | 17.81 |
| 27.31 | 3.27 | 35.48 |
| 28.00 | 3.19 | 10.61 |
| 33.26 | 2.69 | 10.26 |
| 34.13 | 2.63 | 8.29 |
| 37.29 | 2.41 | 8.45 |
| 37.88 | 2.38 | 10.38 |
实施例3
晶型CS2的制备:
将10.2mg R228060的晶型CS1加热到110℃,所得固体经检测为晶型CS2,其XRPD数据如表4所示,XRPD图如图4所示。
表4
| 衍射角2θ | d值 | 强度% |
| 6.68 | 13.22 | 15.35 |
| 12.34 | 7.17 | 14.47 |
| 13.15 | 6.73 | 15.37 |
| 15.37 | 5.77 | 12.95 |
| 16.03 | 5.53 | 27.91 |
| 16.27 | 5.45 | 20.09 |
| 17.36 | 5.11 | 9.98 |
| 19.30 | 4.60 | 18.63 |
| 19.82 | 4.48 | 69.91 |
| 20.23 | 4.39 | 24.67 |
| 20.36 | 4.36 | 28.54 |
| 21.35 | 4.16 | 29.07 |
| 22.32 | 3.98 | 11.23 |
| 22.86 | 3.89 | 21.26 |
| 23.81 | 3.73 | 56.01 |
| 23.93 | 3.72 | 72.51 |
| 24.01 | 3.71 | 54.59 |
| 24.69 | 3.60 | 100.00 |
| 26.34 | 3.38 | 28.09 |
| 26.94 | 3.31 | 6.33 |
| 28.67 | 3.11 | 29.67 |
| 29.28 | 3.05 | 46.59 |
| 30.12 | 2.97 | 6.18 |
| 30.96 | 2.89 | 25.69 |
| 31.47 | 2.84 | 8.52 |
| 32.57 | 2.75 | 19.96 |
| 33.59 | 2.67 | 8.88 |
| 34.15 | 2.62 | 11.74 |
| 34.57 | 2.59 | 9.46 |
晶型CS2的DSC如图5所示,加热至183℃附近开始出现一个熔化吸热峰,为晶型CS2的熔点。
晶型CS2的TGA如图6所示,加热至150℃时,具有约0.2%的质量损失。
实施例4
晶型CS2的制备:
将10.2mg R228060盐酸盐加入到0.1mL甲醇中,然后逐滴加入1.2mL甲基叔丁基醚,室温搅拌至析晶,离心取下层固体,室温下干燥,经检测,所得固体为晶型CS2,其XRPD数据如表5所示。
表5
| 衍射角2θ | d值 | 强度% |
| 6.56 | 13.47 | 29.28 |
| 12.31 | 7.19 | 23.06 |
| 13.13 | 6.74 | 34.18 |
| 15.55 | 5.70 | 14.85 |
| 16.05 | 5.52 | 22.80 |
| 17.34 | 5.12 | 4.96 |
| 19.22 | 4.62 | 14.16 |
| 19.74 | 4.50 | 83.41 |
| 20.24 | 4.39 | 32.86 |
| 21.32 | 4.17 | 17.42 |
| 22.87 | 3.89 | 18.70 |
| 23.81 | 3.74 | 76.83 |
| 24.61 | 3.62 | 100.00 |
| 26.26 | 3.39 | 39.81 |
| 28.60 | 3.12 | 17.06 |
| 29.28 | 3.05 | 40.76 |
| 30.94 | 2.89 | 36.35 |
| 32.46 | 2.76 | 22.32 |
| 36.23 | 2.48 | 21.83 |
实施例5
晶型CS2的制备:
称取一定质量的R228060游离碱加入到表6中的溶剂中,然后加入2μL浓盐酸(12mol/L),室温下搅拌24小时,离心取下层固体,室温下干燥,经检测,所得固体均为晶型CS2。其中样品5-a所得固体的XRPD数据如表7所示。
表6
表7
| 衍射角2θ | d值 | 强度% |
| 6.64 | 13.31 | 51.03 |
| 12.39 | 7.14 | 17.24 |
| 13.23 | 6.69 | 20.02 |
| 15.50 | 5.72 | 21.24 |
| 16.08 | 5.51 | 43.31 |
| 17.30 | 5.13 | 14.18 |
| 19.20 | 4.62 | 32.85 |
| 19.76 | 4.49 | 86.44 |
| 20.31 | 4.37 | 63.05 |
| 21.32 | 4.17 | 39.49 |
| 22.30 | 3.99 | 13.03 |
| 22.88 | 3.89 | 29.27 |
| 23.84 | 3.73 | 100.00 |
| 24.68 | 3.61 | 87.04 |
| 26.30 | 3.39 | 32.74 |
| 27.44 | 3.25 | 13.35 |
| 28.60 | 3.12 | 23.25 |
| 29.29 | 3.05 | 43.90 |
| 31.03 | 2.88 | 34.13 |
| 32.46 | 2.76 | 24.09 |
| 36.25 | 2.48 | 25.06 |
| 39.05 | 2.31 | 14.46 |
实施例6
长期稳定性研究:
取R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS1和晶型CS2样品分别置于25℃/60%RH和/或40℃/75%RH的恒温恒湿箱中敞口放置,1个月后取样测XRPD和纯度。XRPD结果如图7、如图8和图9所示,图7中上图为晶型CS1放置前的XRPD图,下图为放置于25℃/60%RH条件下1个月的XRPD图;图8中上图为晶型CS1放置前的XRPD图,下图为放置于40℃/75%RH条件下1个月的XRPD图;图9中上图为晶型CS2放置前的XRPD图,下图为放置于25℃/60%RH条件下1个月的XRPD图。
结果表明,R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS1和晶型CS2在25℃/60%RH和/或40℃/75%RH放置1个月晶型保持不变,且纯度也未见明显变化。说明R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS1和晶型CS2具有优异的稳定性。晶型CS1和晶型CS2具有较好的长期稳定性,能够保证药品在制备、运输、贮藏及保存过程中不会发生转晶现象而影响到药品质量,对保证药物疗效和安全性,防止药物不良反应的发生具有重要意义。
实施例7
机械稳定性研究:
将本发明的R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS1和晶型CS2样品置于研钵中,手动研磨30分钟,测试固体XRPD。结果如图10(CS1研磨前后XRPD对比图,上图为研磨前,下图为研磨后)和图11(CS2研磨前后XRPD对比图,上图为研磨前,下图为研磨后)所示。
结果表明,在一定机械应力的作用下,本发明的R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS1和晶型CS2的晶型和结晶度均未发生明显变化,仍可保持稳定的物理化学性质,适合成药和储存。制剂加工过程中常需要原料药的研磨粉碎,高的研磨稳定性能够减小制剂加工过程中发生原料药晶型结晶度改变和转晶的风险。
实施例8
引湿性研究:
称取R228060盐酸盐晶型CS1和晶型CS2约10mg采用动态水分吸附(DVS)仪测试其引湿性,实验结果如表8所示,晶型CS1和晶型CS2的DVS图分别如图12和图13所示。
表8
关于引湿性特征描述与引湿性增重的界定(中国药典2015年版通则9103药物引湿性试验指导原则,实验条件:25℃±1℃,80%相对湿度):
引湿性特征描述与引湿性增重的界定:
潮解:吸收足量水分形成液体。
极具引湿性:引湿增重不小于15%。
有引湿性:引湿增重小于15%但不小于2%。
略有引湿性:引湿增重小于2%但不小于0.2%。
无或几乎无引湿性:引湿增重小于0.2%。
结果表明,本发明的晶型CS1和晶型CS2在80%湿度下平衡后增重分别为0.12%和0.08%,根据引湿性增重的界定标准,两个晶型均属于几乎无引湿性。本发明晶型CS1和晶型CS2的引湿性低,能够很好地对抗药物制剂和/或存储等过程中晶型不稳定以及由环境湿气等外来因素所引起的制剂不可加工等问题,有利于制剂制备中的准确定量和后期的运输和储存。
实施例9
制剂研究:
称量下表中所列含量的晶型CS1或晶型CS2、微晶纤维素、交联羧甲基纤维素钠和3mg硬脂酸镁,混合2分钟。用手动压片机压制成片,直径20mm圆形冲模,压力5kN±1kN。手工过20目筛网,再加入3mg硬脂酸镁,混合1分钟。将上述混合物装入0#明胶胶囊壳。用35cc HDPE(高密度聚乙烯)瓶包装(每瓶一粒),每瓶含有1g干燥剂,用封口机封口。胶囊的处方(每300mg)如下表9,药品放置一个月后,经检测,晶型CS1和晶型CS2在胶囊中未发生晶型和纯度的改变。
表9
| 胶囊成分 | 用量(mg/胶囊) |
| 晶型CS1或晶型CS2 | 75 |
| 微晶纤维素 | 204 |
| 交联羧甲基纤维素钠 | 15 |
| 硬脂酸镁 | 6 |
将获得的胶囊测试溶出情况,溶出度的测定按照中国药典2015年版0931溶出度与释 放度测定法,条件如下:
溶出介质:水
溶出方法:浆法
介质体积:500mL
转速:50rpm
介质温度:37℃
晶型CS1和晶型CS2的溶出速率结果表明晶型CS1和晶型CS2均具有较快的溶出速率,10min时的溶出量即可达60%以上。在制剂开发中,药物具有快速的溶出速率可加快药物服用后在体内快速溶解,可通过调整辅料,来控制药物在特定部位快速发挥作用,提高药物的起效速率。
上述实施例只为说明本发明的技术构思及特点,其目的在于让熟悉此项技术的人士能够了解本发明的内容并据以实施,并不能以此限制本发明的保护范围。凡根据本发明精神实质所作的等效变化或修饰,都应涵盖在本发明的保护范围之内。
Claims (13)
- 一种R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS1,其特征在于,其X射线粉末衍射图在2θ值为22.9°±0.2°、27.3°±0.2°、20.9°±0.2°处具有特征峰。
- 根据权利要求1所述的晶型CS1,其特征还在于,其X射线粉末衍射图在2θ值为24.1°±0.2°、21.6°±0.2°、26.1°±0.2°中的一处或两处或三处具有特征峰。
- 根据权利要求1或2所述的晶型CS1,其特征还在于,其X射线粉末衍射图在2θ值为17.1°±0.2°、13.5°±0.2°、6.9°±0.2°中的一处或两处或三处具有特征峰。
- 一种权利要求1中所述晶型CS1的制备方法,其特征在于,将R228060游离碱固体与酯类或烷烃类或芳香烃类或卤代烃类溶剂混合,然后加入浓盐酸,室温下搅拌得到晶型CS1。
- 根据权利要求4所述的制备方法,其特征在于,所述酯类包含乙酸乙酯,所述烷烃类包含环己烷和正庚烷,所述芳香烃类包含甲苯,所述卤代烃类包含氯仿。
- 一种R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS2,其特征在于,其X射线粉末衍射图在2θ值为24.7°±0.2°、23.8°±0.2°、19.8°±0.2°处具有特征峰。
- 根据权利要求6所述的晶型CS2,其特征还在于,其X射线粉末衍射图在2θ值为29.3°±0.2°、20.4°±0.2°、26.3°±0.2°中的一处或两处或三处具有特征峰。
- 根据权利要求6或7所述的晶型CS2,其特征还在于,其X射线粉末衍射图在2θ值为16.0°±0.2°、6.7°±0.2°、12.3°±0.2°中的一处或两处或三处具有特征峰。
- 一种权利要求6所述晶型CS2的制备方法,其特征在于,所述方法为1)、2)或3):1)将R228060盐酸盐的晶型CS1加热到80~180℃,得到晶型CS2;2)将R228060盐酸盐固体与醇类溶剂混合,然后滴加醚类溶剂,室温搅拌至有固体析出,得到晶型CS2;3)将R228060游离碱固体与酮类或腈类溶剂混合,然后加入浓盐酸,室温下搅拌制得晶型CS2。
- 根据权利要求9所述的制备方法,其特征在于:方法1)中所述加热温度为110℃;方法2)中所述醇类包含甲醇,所述醚类包含甲基叔丁基醚。方法3)中所述酮类包含丙酮和甲基乙基酮,所述腈类包含乙腈
- 一种药物组合物,所述药物组合物包含有效治疗量的权利要求1所述的晶型CS1、权利要求6所述的晶型CS2及药学上可接受的载体、稀释剂或赋形剂。
- 权利要求1所述的晶型CS1、权利要求6所述的晶型CS2在制备治疗中枢神经系统疾病 药物中的用途。
- 权利要求1所述的晶型CS1、权利要求6所述的晶型CS2在制备治疗嗜睡症和睡眠呼吸暂停综合症药物中的用途。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710047910.9 | 2017-01-20 | ||
| CN201710047910 | 2017-01-20 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2018133703A1 true WO2018133703A1 (zh) | 2018-07-26 |
Family
ID=62907684
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2018/071889 WO2018133703A1 (zh) | 2017-01-20 | 2018-01-09 | R228060 盐酸盐的晶型及其制备方法和用途 |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| WO (1) | WO2018133703A1 (zh) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2021001457A1 (en) | 2019-07-04 | 2021-01-07 | Sandoz Ag | Crystalline (r)-2-amino-3-phenylpropylcarbamate acid addition salts |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1135209A (zh) * | 1994-09-09 | 1996-11-06 | 株式会社油公 | 新的氨基甲酸苯基烷基氨基醇酯及其制备方法 |
| CN1867542A (zh) * | 2003-10-08 | 2006-11-22 | Sk株式会社 | 在活性胺基存在下制备o-氨基甲酰基化合物的方法 |
-
2018
- 2018-01-09 WO PCT/CN2018/071889 patent/WO2018133703A1/zh active Application Filing
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1135209A (zh) * | 1994-09-09 | 1996-11-06 | 株式会社油公 | 新的氨基甲酸苯基烷基氨基醇酯及其制备方法 |
| CN1867542A (zh) * | 2003-10-08 | 2006-11-22 | Sk株式会社 | 在活性胺基存在下制备o-氨基甲酰基化合物的方法 |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2021001457A1 (en) | 2019-07-04 | 2021-01-07 | Sandoz Ag | Crystalline (r)-2-amino-3-phenylpropylcarbamate acid addition salts |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2021136477A1 (zh) | 化合物i二盐酸盐的共晶及其制备方法和用途 | |
| WO2018108101A1 (zh) | {[5-(3-氯苯基)-3-羟基吡啶-2-羰基]氨基}乙酸的新晶型及其制备方法 | |
| CN111094290B (zh) | 瑞博西尼的单琥珀酸盐晶型及其制备方法和用途 | |
| WO2019052133A1 (zh) | Gsk1278863的晶型及其制备方法和制药用途 | |
| CN110799501B (zh) | 一种食欲素受体拮抗剂的晶型及其制备方法和用途 | |
| WO2018103726A1 (zh) | 一种溴结构域蛋白抑制剂药物的晶型及其制备方法和用途 | |
| JP2021528487A (ja) | モルホリノキナゾリン系化合物の結晶形、その製造方法及び使用 | |
| WO2016155670A1 (zh) | 一种cdk抑制剂和mek抑制剂的共晶及其制备方法 | |
| WO2019042219A1 (zh) | 奥扎莫德盐酸盐的晶型及其制备方法 | |
| WO2020057622A1 (zh) | 卡博替尼苹果酸盐晶型及其制备方法和用途 | |
| WO2020063939A1 (zh) | 一种Upadacitinib的晶型及其制备方法和用途 | |
| WO2018133703A1 (zh) | R228060 盐酸盐的晶型及其制备方法和用途 | |
| WO2021129465A1 (zh) | 一种Resmetirom晶型及其制备方法和用途 | |
| WO2018233437A1 (zh) | 巴瑞克替尼的晶型及其制备方法 | |
| WO2019134455A1 (zh) | Acalabrutinib的新晶型及其制备方法和用途 | |
| WO2019205812A1 (zh) | Acalabrutinib的新晶型及其制备方法和用途 | |
| WO2016078587A1 (zh) | Lu AE58054的盐酸盐晶型A及其制备方法和用途 | |
| WO2018157741A1 (zh) | Sb-939的盐的晶型及其制备方法和用途 | |
| WO2019105359A1 (zh) | Acalabrutinib的晶型及其制备方法和用途 | |
| US10544129B2 (en) | Crystalline forms of AP26113, and preparation method thereof | |
| WO2019149262A1 (zh) | Sb-939的晶型及其制备方法和用途 | |
| WO2023078424A1 (zh) | Kras突变体抑制剂的晶型、其制备方法及其应用 | |
| WO2016155631A1 (zh) | 托吡司他的新晶型及其制备方法 | |
| US9981912B2 (en) | Cocrystal of lorcaserin, preparation methods, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof | |
| WO2017076358A1 (zh) | 咪唑基联苯基化合物盐的新晶型及其制备方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 18742091 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 18742091 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |