WO2017158999A1 - 関心度推定装置、関心度推定方法、プログラムおよび記録媒体 - Google Patents
関心度推定装置、関心度推定方法、プログラムおよび記録媒体 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017158999A1 WO2017158999A1 PCT/JP2017/000048 JP2017000048W WO2017158999A1 WO 2017158999 A1 WO2017158999 A1 WO 2017158999A1 JP 2017000048 W JP2017000048 W JP 2017000048W WO 2017158999 A1 WO2017158999 A1 WO 2017158999A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- pulse
- crowd
- person
- interest
- interest level
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/02—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the cardiovascular system, e.g. pulse, heart rate, blood pressure or blood flow
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/02—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the cardiovascular system, e.g. pulse, heart rate, blood pressure or blood flow
- A61B5/024—Measuring pulse rate or heart rate
- A61B5/02405—Determining heart rate variability
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/02—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the cardiovascular system, e.g. pulse, heart rate, blood pressure or blood flow
- A61B5/024—Measuring pulse rate or heart rate
- A61B5/02416—Measuring pulse rate or heart rate using photoplethysmograph signals, e.g. generated by infrared radiation
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/103—Measuring devices for testing the shape, pattern, colour, size or movement of the body or parts thereof, for diagnostic purposes
- A61B5/1032—Determining colour of tissue for diagnostic purposes
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/16—Devices for psychotechnics; Testing reaction times ; Devices for evaluating the psychological state
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/16—Devices for psychotechnics; Testing reaction times ; Devices for evaluating the psychological state
- A61B5/165—Evaluating the state of mind, e.g. depression, anxiety
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q30/00—Commerce
- G06Q30/02—Marketing; Price estimation or determination; Fundraising
- G06Q30/0201—Market modelling; Market analysis; Collecting market data
- G06Q30/0203—Market surveys; Market polls
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H50/00—ICT specially adapted for medical diagnosis, medical simulation or medical data mining; ICT specially adapted for detecting, monitoring or modelling epidemics or pandemics
- G16H50/30—ICT specially adapted for medical diagnosis, medical simulation or medical data mining; ICT specially adapted for detecting, monitoring or modelling epidemics or pandemics for calculating health indices; for individual health risk assessment
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B2503/00—Evaluating a particular growth phase or type of persons or animals
- A61B2503/12—Healthy persons not otherwise provided for, e.g. subjects of a marketing survey
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B2560/00—Constructional details of operational features of apparatus; Accessories for medical measuring apparatus
- A61B2560/02—Operational features
- A61B2560/0242—Operational features adapted to measure environmental factors, e.g. temperature, pollution
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H30/00—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images
- G16H30/20—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images for handling medical images, e.g. DICOM, HL7 or PACS
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an interest level estimation device, and more particularly, to an interest level estimation device and an interest level estimation method for evaluating the interest level of a crowd with respect to an object such as an event.
- the present invention also relates to a program for causing a computer to execute such an interest level estimation method.
- the present invention also relates to a computer-readable recording medium recording such a program.
- Patent Document 1 Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2009-24775
- Devices and methods for estimating degrees are known.
- the interest level estimation apparatus disclosed in Patent Document 1 is not suitable for collectively evaluating the interest level of a crowd because it is necessary to attach electrodes to human skin. Also, if each person's measurement results are statistically processed as they are to obtain statistical processing values (average values, etc.), the statistical processing values obtained will vary in individual differences during normal times (when no stimulus is received from the subject). It is considered that the estimation accuracy is not good.
- the interest level estimation device of the present invention provides: An interest estimation device that evaluates a crowd's interest in a subject, A video input unit for inputting a video in which a crowd receiving stimulation from the target is captured; A person recognition unit for recognizing the presence of each person constituting the crowd based on the video, Based on the brightness change of the skin of each person in the video, a pulse acquisition unit that obtains the pulse of each person, An attribute recognition unit for recognizing the attributes of each person in the video; A first pulse correction unit that corrects each person's pulse so as to eliminate the pulse difference depending on the attribute; Statistical processing of the corrected pulse of each person to obtain a statistical processing value of the crowd pulse, An interest level output unit that outputs a numerical index corresponding to the statistical processing value of the crowd pulse as an interest level.
- object refers to an object that the crowd is interested in, such as an event.
- “Receiving a stimulus” from a subject means receiving a stimulus through at least one of the five senses, that is, visual, auditory, olfactory, taste, and tactile.
- Video input unit means, for example, an input interface for inputting a video.
- pulse means the pulse rate per unit time, for example, the pulse rate per minute, that is, [beats / minute] (or also expressed as [bpm]).
- Statistical processing refers to processing for obtaining average values and variances.
- the moving image input unit inputs a moving image in which a crowd receiving a stimulus from a target is photographed.
- a person recognition unit recognizes the presence of each person making up the crowd based on the moving image.
- a pulse acquisition part calculates
- An attribute recognition unit recognizes the attribute of each person in the moving image.
- the first pulse correction unit corrects each person's pulse so as to eliminate the pulse difference depending on the attribute.
- the corrected pulse of each person is stimulated from the subject with respect to the pulse of each person's normal time (when no stimulus is received from the target) in a state where variations due to attributes are eliminated. It represents the change in the pulse when receiving.
- a statistical processing unit statistically processes the corrected pulse of each person to obtain a statistical processing value of the crowd pulse.
- the statistical processing value of the pulse of the crowd represents the amount of change in the pulse when receiving the stimulus from the target with respect to the pulse of the crowd in a state where the variation due to the attribute is eliminated Become.
- the interest level output unit outputs a numerical index corresponding to the statistical processing value of the crowd pulse as the interest level. In this way, according to the interest level estimation apparatus, the interest level of the crowd with respect to the target can be appropriately evaluated.
- the statistical processing unit obtains the statistical processing value of the pulse of the first crowd and the statistical processing value of the pulse of the second crowd at a certain time, and the interest output unit outputs the statistical processing value of the pulse of the first crowd.
- a numerical index corresponding to the difference between the statistical processing value of the pulse of and the statistical processing value of the pulse of the second crowd is output as the degree of interest.
- the statistical processing unit obtains the statistical processing value of the pulse at the first time point and the statistical processing value of the pulse at the second time point for a certain crowd, and the interest level output unit outputs the statistical processing value of the pulse at the first time point.
- a numerical index corresponding to the difference between the statistical processing value of the pulse and the statistical processing value of the pulse at the second time point is output as the degree of interest.
- An environment information input unit for inputting environment information representing the environment around the crowd that has been photographed;
- a second pulse correction unit that corrects the statistical processing value of the crowd pulse so as to eliminate the pulse difference depending on the environment based on the environment information obtained by the environment information input unit; It is characterized by.
- environmental information refers to the temperature around the crowd, for example.
- the environment information input unit inputs environment information representing the environment around the crowd that has been photographed.
- the second pulse correction unit corrects the statistical processing value of the crowd pulse so as to eliminate the pulse difference depending on the environment based on the environment information obtained by the environment information input unit.
- the corrected statistical processing value is obtained by eliminating the variation depending on the environment.
- the interest level output unit outputs a numerical index corresponding to the statistical processing value of the crowd pulse as the interest level. Therefore, according to the interest level estimation device, the interest level of the crowd with respect to the target can be more appropriately evaluated.
- the attribute of each person is at least one of age or sex.
- the pulse of each person corrected by the first pulse correction unit is in a state in which variation due to at least one of age or sex is eliminated.
- the degree of interest of the crowd with respect to the object can be appropriately evaluated.
- the first pulse correction unit may determine the age of each person recognized by the attribute recognition unit or the pulse of each person obtained by the pulse acquisition unit. According to at least one of the sexes, the correction is performed by multiplying a pulse correction coefficient by a predetermined age and a pulse correction coefficient by gender.
- the first pulse correction unit is configured to recognize the age of each person recognized by the attribute recognition unit with respect to the pulse of each person obtained by the pulse acquisition unit. Or according to at least one of sex, it correct
- the interest level estimation device includes an imaging unit that captures a crowd receiving a stimulus from the target and acquires a moving image.
- the imaging unit captures a crowd receiving a stimulus from the target and acquires a moving image.
- the interest level estimation method of the present invention comprises: An interest estimation method that evaluates the interest of a crowd to a subject, Enter a video shot of a crowd inspired by the above subjects, Recognize the presence of each person in the crowd based on the video, Based on the change in brightness of each person's skin in the video, find the person's pulse, Recognize each person ’s attributes in the video, Correct each person's pulse so as to eliminate the pulse difference depending on the attribute, Statistically processing the corrected pulse of each person to obtain a statistical processing value of the crowd pulse, A numerical index corresponding to the statistical processing value of the crowd pulse is output as an interest level.
- the corrected pulse of each person varies depending on the attribute by the process of “correcting the pulse of each person so as to eliminate the pulse difference depending on the attribute”.
- the change in pulse when the stimulus is received from the subject relative to the normal pulse of each person is represented.
- the statistical processing value of the crowd pulse obtained by the process of “statistically processing the corrected pulse of each person to obtain the statistical processing value of the crowd pulse” eliminates variation due to attributes.
- the change of the pulse when the stimulus is received from the object with respect to the normal pulse of the crowd is represented.
- a numerical index corresponding to the statistical processing value of the crowd pulse is output as the degree of interest. In this way, according to this interest level estimation method, the interest level of the crowd with respect to the target can be appropriately evaluated.
- process of “obtaining the pulse of each person based on the luminance change of the skin of each person in the video” and the process of “recognizing the attribute of each person in the video” may be executed first, or both processes may be executed in parallel.
- the program of the present invention is a program for causing a computer to execute the interest level estimation method of the present invention.
- the interest level estimation method of the present invention can be executed by a computer.
- the recording medium of the present invention is a computer-readable recording medium recording the program of the present invention.
- the program recorded on the recording medium of the present invention is installed in a computer, the interest level estimation method of the above invention can be executed by the computer.
- the interest level estimation device and the interest level estimation method of the present invention the interest level of the crowd with respect to the target can be appropriately evaluated.
- the interest level estimation method of the said invention can be performed by a computer.
- the computer can execute the interest level estimation method of the present invention.
- FIG. 1 shows the block structure of the interest level estimation apparatus of one Embodiment of this invention. It is a figure which shows the whole processing flow of the interest level estimation method which the said interest level estimation apparatus performs. It is a figure which shows one example of step S9 which compares the average pulse value of the crowd in FIG. It is a figure which shows the pulse average value B11 of 1st crowd B1 and the pulse average value B21 of 2nd crowd B2 in a certain time t1. It is a figure which shows another example of step S9 which compares the average pulse value of the crowd in FIG. It is a figure which shows the time passage of the pulse average value about crowd C1, C2, respectively.
- FIG. 5 is a diagram showing a flow of a modified example of steps S9 to S10 in FIG.
- FIG. 8A is a diagram showing pulse distributions for the crowds D1 and D2.
- FIG. 8B is a diagram showing pulse distributions for the crowds D1 and D2 '.
- FIG. 9 is a diagram showing a flow of another modification example of steps S9 to S10 in FIG.
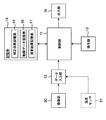
- FIG. 1 shows a block configuration of an interest level estimation apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- This interest level estimation device includes a control unit 11, a data input unit 12, an operation unit 13, a storage unit 14, and an output unit 18.
- the imaging unit 30 is connected to the data input unit 12.
- the imaging unit 30 captures a crowd receiving a stimulus from the target and acquires a moving image.
- the imaging unit 30 includes a commercially available photographing camera, but is not limited thereto.
- the control unit 11 includes a CPU (Central Processing Unit) that is operated by software, and executes various processes described later.
- CPU Central Processing Unit
- the data input unit 12 includes a known input interface, and sequentially inputs the moving image data acquired by the imaging unit 30 in real time in this example.
- the operation unit 13 includes a known keyboard and mouse, and functions to input commands and various information from the user.
- the command includes a command for instructing start of processing, a command for instructing recording of the operation result, and the like.
- the input information includes the time (year / month / day and time) when the moving image was shot, information for identifying each of the plurality of input moving image data, and the like.
- the storage unit 14 includes a hard disk drive or EEPROM (electrically rewritable non-volatile memory) capable of storing data non-temporarily, and includes a correction coefficient storage unit 15, a moving image data storage unit 16, And a calculation result storage unit 17.
- EEPROM electrically rewritable non-volatile memory
- the correction coefficient storage unit 15 stores a pulse correction coefficient for correcting the pulse of each person so as to eliminate the difference in pulse depending on the attribute of each person constituting the crowd.
- the “pulse correction coefficient table by age” shown in the following Table 1 and the “pulse correction coefficient table by sex” shown in Table 2 are stored. These pulse correction factors indicate that the average pulse rate in normal children (when no stimulus is received from the subject) tends to be higher than the average pulse rate in normal adults. Is set so as to eliminate the variation between the average values of the pulses based on general knowledge such as the tendency to be high and the elderly having a low maximum pulse rate.
- the age-related pulse correction coefficient ⁇ in Table 1 is based on the average pulse value of adults (19 to 59 years old), and is a non-adult person (0 to 6 years old infants, 7 to 12 years old children) (This includes elementary school students, 13-18 year old middle and high school students, and elderly people over 60 years old.) This is equivalent to a factor for aligning the average pulse rate with that of adults.
- the gender-related pulse correction coefficient ⁇ in Table 2 corresponds to a factor for aligning the female pulse average value with the male pulse average value based on the male pulse average value.
- the moving image data storage unit 16 in FIG. 1 stores moving image data input via the data input unit 12 in association with the identification number of the moving image for each moving image.
- the calculation result storage unit 17 stores, for each moving image, a numerical index representing the degree of interest of the crowd with respect to a target obtained by processing described later in association with the identification number of the moving image.
- the output unit 18 is composed of an LCD (liquid crystal display element) in this example, and displays various information such as a calculation result by the control unit 11. Note that the output unit 18 may include a printer (driver), print out on paper, and output the calculation result.
- LCD liquid crystal display element
- the temperature sensor 31 is an optional additional element that is not essential, and detects the temperature [° C.] as environmental information indicating the environment around the photographed crowd.
- the detected temperature [° C.] is input to the control unit 11 by the data input unit 12 acting as an environment information input unit.
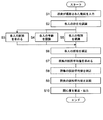
- This degree-of-interest estimation apparatus operates as a whole according to the processing flow shown in FIG. 2 under the control of the control unit 11.
- step S ⁇ b> 1 in FIG. 2 the control unit 11 inputs data of a moving image captured by the imaging unit 30 via the data input unit 12.
- the video shows a crowd receiving a stimulus from the subject.
- a crowd watching an event such as an exhibition or lecture is being filmed.
- moving image data captured by the image capturing unit 30 is sequentially input in real time via the data input unit 12, and the moving image data storage unit 16 is associated with the moving image identification number under the control of the control unit 11. Is remembered.
- the moving image data is sequentially captured by the imaging unit 30, but is not limited thereto.
- the data input unit 12 may receive and input moving image data acquired in advance outside the interest level estimation apparatus sequentially or substantially simultaneously via a network (not shown) such as the Internet.
- control part 11 works as a person recognition part, and as shown to step S2 in FIG. 2, it recognizes the presence of each person who comprises a crowd based on a moving image.
- the recognition of the presence of each person is performed by, for example, Paul Viola et al. “Rapid Object Detection using a Boosted Cascade of Simple Features”, Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2001. CVPR 2001. Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on 2001, p. I-511-I-518 vol. This is performed by a known method as disclosed in 1.
- the control unit 11 works as a pulse acquisition unit, and, as shown in step S3 in FIG. 2, the pulse of each person is calculated based on the luminance change of each person's skin in the moving image.
- the pulse of each person is obtained based on the luminance change of the green component of each person's skin by a known method as disclosed in Japanese Patent No. 4264-4271.
- the No. The pulse of each person from 1 to 6 is assumed to be 110 [bpm], 90 [bpm], 75 [bpm], 63 [bpm], 75 [bpm], and 70 [bpm], respectively.
- control unit 11 works as an attribute recognition unit, and as shown in step S4 in FIG.
- the age of each person in the moving image is recognized by a known method.
- control unit 11 works as an attribute recognition unit.
- the age of each person in the moving image is recognized by a known method as disclosed.
- any of the processes (3) to (5) may be performed first or in parallel with each other.
- control part 11 works as a 1st pulse correction part, and as shown to step S6 in FIG. 2, each person's calculated
- each person's pulse obtained by the process of (3) above (referred to as “original pulse”) is n 0 [bpm], and the corrected pulse of each person is n 1 [bpm].
- n 1 n 0 ⁇ ⁇ ⁇ ⁇ (EQ1)
- ⁇ represents the pulse correction coefficient according to the age shown in Table 1.
- ⁇ represents a pulse correction coefficient according to gender shown in Table 2.
- the pulse correction coefficient ⁇ according to age is 0.583333333.
- the pulse correction coefficient ⁇ according to age is 0.777777778.
- person 3 belongs to the group of junior high and high school students (13 to 18 years old), the pulse correction coefficient ⁇ according to age is 0.875.
- the pulse correction coefficient ⁇ 1 according to age.
- the pulse correction coefficient ⁇ 1 according to age.
- no. The sex of each person from 1 to 6 is male, female, female, male, female and male, respectively.
- no. No. 1 no. No. 4, no.
- the pulse correction coefficient ⁇ 1 according to gender.
- No. No. 2 no. No. 3, no.
- the pulse correction coefficient ⁇ by gender is 0.928571429.
- the pulse correction coefficient ⁇ according to age in Table 1 is based on the average pulse value of adults (19-59 years old), and non-adults (0-6 years old infants, 7-12 years old infants) (Including children / elementary school students, 13-18 year old middle and high school students, and elderly people over 60 years old).
- the gender-related pulse correction coefficient ⁇ in Table 2 corresponds to a factor for aligning the female pulse average value with the male pulse average value based on the male pulse average value. Therefore, by multiplying the original pulse n 0 by the pulse correction coefficient ⁇ by age and the pulse correction coefficient ⁇ by gender, the corrected pulse n 1 of each person is given the age and gender as in Equation EQ1. In a state in which the variation due to the above is eliminated, the change in the pulse when the stimulus is received from the subject is expressed with respect to the pulse of each person at normal times (when the stimulus is not received from the subject). This makes it possible to easily correct the pulse.
- each person's pulse correction method may be a method of adding or subtracting a predetermined pulse rate for correction instead of multiplying the correction coefficient ⁇ by age and the correction coefficient ⁇ by gender. .
- the control unit 11 works as a statistical processing unit, and as shown in step S7 in FIG. statistically processing the pulse n 1 of human, seek statistically processed value of the pulse of the crowd.
- an average value is obtained as a statistical processing value.
- the obtained average value is referred to as “crowd pulse average value” (represented by the symbol N 1 , the unit is [bpm]).
- step S8 the control unit 11 works as a second pulse correction unit, and the crowd value obtained in the process (7) is correcting the pulse mean value N 1.
- step S8 is an optional additional step that is not essential, and the frame of step S8 is indicated by a broken line to indicate that.
- control unit 11 receives the temperature [° C.] as environment information representing the environment around the crowd detected by the temperature sensor 31 via the data input unit 12. Then, the control unit 11 functions as a second pulse correction unit, and is disclosed in, for example, Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 8-080287 (corrects the influence of the pulse rate on temperature and displays the pulse rate under a certain condition). by a known method such as is, to eliminate the difference between the pulse which depends on the temperature [° C.], it corrects the pulse mean value N 1 of the crowd.
- oxygen concentration may be employed as environmental information representing the environment around the crowd instead of or in addition to the air temperature. In that case, so as to eliminate the difference between the pulse dependent on the oxygen concentration to correct the pulse mean value N 1 of the crowd.
- pulse mean value N 2 of the corrected crowd is equal to the pulse mean value N 1 of the crowd without correction.
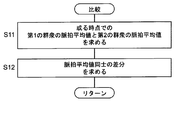
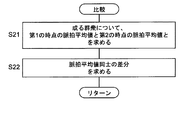
- step S9 in FIG. 2 the control unit 11 compares the pulse mean value N 2 of the crowd obtained in process (8).
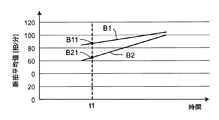
- the control unit 11 obtains the pulse average value B11 of the first crowd and the pulse average value B21 of the second crowd at the time t1.
- a difference between these pulse average values (represented by a symbol ⁇ N) is obtained.
- the subtraction direction is set so that the sign of ⁇ N is positive.
- step S21 in FIG. 5 the control unit 11 first obtains the pulse average value C11 at the first time point t1 and the pulse average value C12 at the second time point t2 for the crowd C1.
- step S22 a difference ⁇ N between the pulse average values is obtained.
- control unit 11 and the output unit 18 function as the interest level output unit, and as shown in step S10 in FIG. 2, the pulse obtained by the process (9) above.
- a numerical index corresponding to the difference ⁇ N between the average values is output as the degree of interest of the crowd with respect to the object (this is represented by the symbol X).
- a correspondence table in which the difference ⁇ N between the pulse average values and the degree of interest X are associated is prepared in advance (for example, in the storage unit 14 in FIG. 1).
- the pulse mean value N 2 of the first multitude B1 pulse mean value N 2 of the second multitude B2 is, were respectively B11, B21.
- the interest level X of the first crowd B1 is evaluated as being 3 higher than the interest level of the second crowd B2 at the time t1.
- pulse mean value N 2 of the first time point t1 the pulse mean value N 2 of the second time point t2, were respectively C11, C12.
- the interest level X at the first time point t1 is higher by 3 than the interest level at the second time point t2 for the crowd C1 according to the correspondence table of Table 4.
- the interest level of the crowd with respect to the target can be appropriately evaluated.
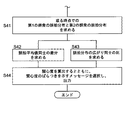
- FIG. 7 shows a flow of a modified example of steps S9 to S10 in FIG.
- the control unit 11 first obtains a pulse average value at a first time point and a pulse average value at a later time point for a certain crowd.
- a difference ⁇ N between these pulse average values is obtained.
- time-series information of the difference ⁇ N between the pulse average values is accumulated for the crowd.
- the interest level X and its change tendency are obtained and output for the crowd.
- the interest level X at the second time point t2 is 3 lower than the interest level at the first time point t1.
- the interest level X at the second time point t2 is higher by 3 than the interest level at the third time point t3.
- the interest level X at the third time point t3 is lower by 3 than the interest level at the second time point t2.
- the crowd C1 it can be seen that the degree of interest tends to decrease (being tired) over time.
- pulse mean value N 2 of the first time point t1 the pulse mean value N 2 of the second time point t2
- control unit 11 outputs the degree of interest X thus obtained and the change tendency thereof. Therefore, the degree of interest of the crowd with respect to the object can be more appropriately evaluated.
- FIG. 9 shows a flow of another modified example of steps S9 to S10 in FIG.
- step S7 in FIG. 2 not only the pulse average value but also the pulse distribution is obtained as a statistical processing value of the pulse of the crowd.
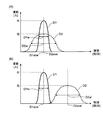
- the pulse distribution is, for example, a distribution of the crowds D1 and D2 shown in FIG. 8A when the horizontal axis represents each person's pulse [beats / minute] and the vertical axis represents the frequency [person].
- the size (number of people) of the crowds D1 and D2 is sufficiently large, and that each pulse distribution is regarded as a normal distribution.
- the shape of each pulse distribution is specified by the pulse average values D1ave and D2ave and the normalized spread (half width / frequency) of the pulse distribution.
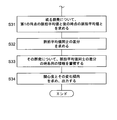
- step S41 in FIG. 9 the control unit 11 first obtains the pulse distribution of the first crowd and the pulse distribution of the second crowd at a certain time point.
- step S42 a difference ⁇ N between the pulse average values is obtained.
- step S43 a ratio between the normalized spreads of the pulse distribution is obtained.
- step S44 the interest level X is calculated, and a message indicating the variation in the interest level is selected and output.
- the pulse average value D2ave ′ is larger than the crowd D2 in FIG. 8A, and the normalized spread of the pulse distribution (D2w ′ / f2) ') Is an example of equality.
- the degree of interest X is displayed to the crowd D1, and a message “the degree of interest varies greatly” is output.
- the pulse correction coefficient ⁇ by age and the pulse correction coefficient ⁇ by gender are set independently of each other so as to eliminate the difference in pulse depending on age and sex as attributes, but the present invention is not limited to this. Absent.
- the pulse correction coefficient may be set as an element of a matrix in which age is taken in the row direction, gender is taken in the column direction, and age and gender are combined. In such a case, for example, it is possible to correct a specific tendency that combines age and gender, such that a woman who is 50 years or older is likely to have a pulse. That is, for a woman over 50 years old, if the correction is made to reduce the rise of the pulse, the difference in pulse depending on age and sex as attributes can be eliminated.
- the movie is obtained by shooting, but the present invention is not limited to this.
- the captured video may be input and acquired via a network such as the Internet or a local area network.
- the above-described interest level estimation method can be recorded as application software (computer program) on a recording medium capable of temporarily storing data, such as a CD (compact disc), a DVD (digital universal disc), or a flash memory.
- a substantial computer device such as a personal computer, a PDA (Personal Digital Assistance), or a smartphone
- the above-described degree of interest estimation is performed on the computer device. The method can be performed.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Accounting & Taxation (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Finance (AREA)
- Development Economics (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation (AREA)
- Psychiatry (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Psychology (AREA)
- Social Psychology (AREA)
- Hospice & Palliative Care (AREA)
- Educational Technology (AREA)
- Developmental Disabilities (AREA)
- Child & Adolescent Psychology (AREA)
- Game Theory and Decision Science (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Dentistry (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE112017000075.0T DE112017000075T5 (de) | 2016-03-15 | 2017-01-04 | Vorrichtung zur Schätzung des Grads des Interesses, Verfahren zur Schätzung des Grads des Interesses, Programm und Speichermedium |
| CN201780002665.8A CN107847195B (zh) | 2016-03-15 | 2017-01-04 | 关心度估计装置、关心度估计方法以及记录介质 |
| US15/753,203 US20180368748A1 (en) | 2016-03-15 | 2017-01-04 | Degree-of-interest estimation device, degree-of-interest estimation method, program, and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016-051481 | 2016-03-15 | ||
| JP2016051481A JP6686576B2 (ja) | 2016-03-15 | 2016-03-15 | 関心度推定装置、関心度推定方法、プログラムおよび記録媒体 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017158999A1 true WO2017158999A1 (ja) | 2017-09-21 |
Family
ID=59850450
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/000048 Ceased WO2017158999A1 (ja) | 2016-03-15 | 2017-01-04 | 関心度推定装置、関心度推定方法、プログラムおよび記録媒体 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20180368748A1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6686576B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN107847195B (enExample) |
| DE (1) | DE112017000075T5 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2017158999A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109828662A (zh) * | 2019-01-04 | 2019-05-31 | 杭州赛鲁班网络科技有限公司 | 一种心仪商品的感知和计算系统 |
| JP7707630B2 (ja) | 2021-04-27 | 2025-07-15 | オムロン株式会社 | 脈波検出装置および脈波検出方法、脈波検出プログラム |
| JP2023137778A (ja) * | 2022-03-18 | 2023-09-29 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 検出システム、検出方法、及び、検出プログラム |
| JP2023137776A (ja) * | 2022-03-18 | 2023-09-29 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 検出システム、検出方法、及び、検出プログラム |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005198828A (ja) * | 2004-01-15 | 2005-07-28 | Seiko Epson Corp | 生体情報解析装置、生体情報解析方法、制御プログラムおよび記録媒体 |
| JP2008272019A (ja) * | 2007-04-25 | 2008-11-13 | Oki Electric Ind Co Ltd | 集団感情認識支援システム |
Family Cites Families (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SU1171010A1 (ru) * | 1984-02-27 | 1985-08-07 | Донецкий Научно-Исследовательский Институт Гигиены Труда И Профессиональных Заболеваний | Устройство дл психологических исследований |
| JP3053455B2 (ja) * | 1991-05-17 | 2000-06-19 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 快適性評価システム及び快適性評価・制御システム |
| JPH0880287A (ja) * | 1994-09-13 | 1996-03-26 | Seiko Epson Corp | 携帯用小型電子機器 |
| JP3613278B2 (ja) * | 2003-08-06 | 2005-01-26 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | 在席装置 |
| JP4303092B2 (ja) * | 2003-11-12 | 2009-07-29 | 株式会社国際電気通信基礎技術研究所 | 年齢推定装置、年齢推定方法および年齢推定プログラム |
| JP2006085440A (ja) * | 2004-09-16 | 2006-03-30 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | 情報処理システム及び情報処理方法、並びにコンピュータ・プログラム |
| WO2007091199A2 (en) * | 2006-02-09 | 2007-08-16 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics, N.V. | Assessment of attention span or lapse thereof |
| JP4367663B2 (ja) * | 2007-04-10 | 2009-11-18 | ソニー株式会社 | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法、プログラム |
| JP4930786B2 (ja) | 2007-07-19 | 2012-05-16 | 日本精工株式会社 | クラッチレリーズ軸受装置 |
| JP2010033474A (ja) | 2008-07-31 | 2010-02-12 | Omron Corp | 属性別人数集計装置、属性別人数集計方法、および属性別人数集計システム |
| WO2010106435A1 (en) * | 2009-03-20 | 2010-09-23 | Pub Company S.R.L. | Video game hardware systems and software methods using electroencephalography |
| CN101658425B (zh) * | 2009-09-11 | 2011-06-01 | 西安电子科技大学 | 基于心率变异分析的注意力集中程度的检测装置及方法 |
| JP2014012072A (ja) * | 2012-07-04 | 2014-01-23 | Sony Corp | 計測装置、計測方法、プログラム、記憶媒体及び計測システム |
| JP2014036801A (ja) * | 2012-08-20 | 2014-02-27 | Olympus Corp | 生体状態観察システム、生体状態観察方法、およびプログラム |
| US9640218B2 (en) * | 2012-12-07 | 2017-05-02 | Intel Corporation | Physiological cue processing |
| KR101534809B1 (ko) * | 2013-01-30 | 2015-07-08 | 한국표준과학연구원 | 다차원 생체신호 측정기반 집중력 향상용 시청각콘텐츠의 효능 평가 방법 |
| US10052038B2 (en) * | 2013-03-14 | 2018-08-21 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Device and method for determining vital signs of a subject |
| US20140330132A1 (en) * | 2013-05-02 | 2014-11-06 | Aza Raskin | Physiological characteristic detection based on reflected components of light |
| CN204049620U (zh) * | 2014-07-29 | 2014-12-31 | 衢州亿龙信息技术有限公司 | 一种反射式光电脉搏测量装置 |
| CN104688199B (zh) * | 2015-03-20 | 2017-03-08 | 杭州师范大学 | 一种基于皮肤色素浓度差分的非接触式脉搏测量方法 |
-
2016
- 2016-03-15 JP JP2016051481A patent/JP6686576B2/ja active Active
-
2017
- 2017-01-04 WO PCT/JP2017/000048 patent/WO2017158999A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2017-01-04 US US15/753,203 patent/US20180368748A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2017-01-04 DE DE112017000075.0T patent/DE112017000075T5/de active Pending
- 2017-01-04 CN CN201780002665.8A patent/CN107847195B/zh active Active
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005198828A (ja) * | 2004-01-15 | 2005-07-28 | Seiko Epson Corp | 生体情報解析装置、生体情報解析方法、制御プログラムおよび記録媒体 |
| JP2008272019A (ja) * | 2007-04-25 | 2008-11-13 | Oki Electric Ind Co Ltd | 集団感情認識支援システム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN107847195A (zh) | 2018-03-27 |
| DE112017000075T5 (de) | 2018-04-19 |
| JP2017164215A (ja) | 2017-09-21 |
| CN107847195B (zh) | 2020-06-12 |
| US20180368748A1 (en) | 2018-12-27 |
| JP6686576B2 (ja) | 2020-04-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6467966B2 (ja) | 健康管理補助装置及び健康管理補助方法 | |
| CN104221054B (zh) | 人物属性推定系统及学习用数据生成装置 | |
| US10810438B2 (en) | Setting apparatus, output method, and non-transitory computer-readable storage medium | |
| US20130102854A1 (en) | Mental state evaluation learning for advertising | |
| WO2017158999A1 (ja) | 関心度推定装置、関心度推定方法、プログラムおよび記録媒体 | |
| WO2012132418A1 (ja) | 属性推定装置 | |
| US12272159B2 (en) | Driving analysis device and driving analysis method for analyzing driver tendency | |
| CN114882570B (zh) | 一种远程考试异常状态预判方法、系统、设备及存储介质 | |
| CN113691721B (zh) | 一种缩时摄影视频的合成方法、装置、计算机设备和介质 | |
| Booth et al. | A novel method for human bias correction of continuous-time annotations | |
| CN108875931A (zh) | 神经网络训练及图像处理方法、装置、系统 | |
| JP7176616B2 (ja) | 画像処理システム、画像処理装置、画像処理方法、及び画像処理プログラム | |
| JP7211495B2 (ja) | 教師データ生成装置 | |
| US12159371B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image forming system, image processing method, and non-transitory computer-readable storage medium | |
| JP2023100112A (ja) | 画像選択システム | |
| JP6318451B2 (ja) | 顕著度画像生成装置、方法、及びプログラム | |
| Yin et al. | Hearing loss detection from facial expressions in one-on-one conversations | |
| JP5941764B2 (ja) | コンテンツ評価データ生成システム、コンテンツ評価データ生成方法、およびプログラム | |
| CN110941733A (zh) | 一体化界面信息多重融合展示方法 | |
| JP2020126563A (ja) | 視認性評価装置、視認性評価プログラムおよび視認性評価方法 | |
| CN114913573A (zh) | 一种表情识别方法、装置、存储介质及设备 | |
| JP7534913B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、システム、情報処理装置の制御方法、及び、プログラム | |
| JP2020184155A (ja) | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法及びプログラム | |
| KR101971602B1 (ko) | 영상분석을 이용한 공감 감성 추론 방법 및 시스템 | |
| CN109409325A (zh) | 一种识别方法和电子设备 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 112017000075 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 17766007 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 17766007 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |