WO2017138220A1 - 情報処理方法および情報処理装置 - Google Patents
情報処理方法および情報処理装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017138220A1 WO2017138220A1 PCT/JP2016/085025 JP2016085025W WO2017138220A1 WO 2017138220 A1 WO2017138220 A1 WO 2017138220A1 JP 2016085025 W JP2016085025 W JP 2016085025W WO 2017138220 A1 WO2017138220 A1 WO 2017138220A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- information
- neural network
- information processing
- processing method
- statistical information
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F8/00—Arrangements for software engineering
- G06F8/30—Creation or generation of source code
- G06F8/34—Graphical or visual programming
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F17/00—Digital computing or data processing equipment or methods, specially adapted for specific functions
- G06F17/10—Complex mathematical operations
- G06F17/18—Complex mathematical operations for evaluating statistical data, e.g. average values, frequency distributions, probability functions, regression analysis
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/01—Input arrangements or combined input and output arrangements for interaction between user and computer
- G06F3/048—Interaction techniques based on graphical user interfaces [GUI]
- G06F3/0481—Interaction techniques based on graphical user interfaces [GUI] based on specific properties of the displayed interaction object or a metaphor-based environment, e.g. interaction with desktop elements like windows or icons, or assisted by a cursor's changing behaviour or appearance
- G06F3/0482—Interaction with lists of selectable items, e.g. menus
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/01—Input arrangements or combined input and output arrangements for interaction between user and computer
- G06F3/048—Interaction techniques based on graphical user interfaces [GUI]
- G06F3/0484—Interaction techniques based on graphical user interfaces [GUI] for the control of specific functions or operations, e.g. selecting or manipulating an object, an image or a displayed text element, setting a parameter value or selecting a range
- G06F3/04845—Interaction techniques based on graphical user interfaces [GUI] for the control of specific functions or operations, e.g. selecting or manipulating an object, an image or a displayed text element, setting a parameter value or selecting a range for image manipulation, e.g. dragging, rotation, expansion or change of colour
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
- G06N3/045—Combinations of networks
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
- G06N3/0464—Convolutional networks [CNN, ConvNet]
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
- G06N3/0499—Feedforward networks
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/06—Physical realisation, i.e. hardware implementation of neural networks, neurons or parts of neurons
- G06N3/063—Physical realisation, i.e. hardware implementation of neural networks, neurons or parts of neurons using electronic means
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
- G06N3/084—Backpropagation, e.g. using gradient descent
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/10—Interfaces, programming languages or software development kits, e.g. for simulating neural networks
- G06N3/105—Shells for specifying net layout
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F11/00—Error detection; Error correction; Monitoring
- G06F11/30—Monitoring
- G06F11/34—Recording or statistical evaluation of computer activity, e.g. of down time, of input/output operation ; Recording or statistical evaluation of user activity, e.g. usability assessment
- G06F11/3452—Performance evaluation by statistical analysis
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F8/00—Arrangements for software engineering
- G06F8/30—Creation or generation of source code
- G06F8/35—Creation or generation of source code model driven
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F8/00—Arrangements for software engineering
- G06F8/30—Creation or generation of source code
- G06F8/36—Software reuse
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F8/00—Arrangements for software engineering
- G06F8/30—Creation or generation of source code
- G06F8/38—Creation or generation of source code for implementing user interfaces
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/44—Arrangements for executing specific programs
- G06F9/451—Execution arrangements for user interfaces
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/44—Arrangements for executing specific programs
- G06F9/451—Execution arrangements for user interfaces
- G06F9/453—Help systems
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/46—Multiprogramming arrangements
- G06F9/50—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU]
- G06F9/5005—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU] to service a request
- G06F9/5011—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU] to service a request the resources being hardware resources other than CPUs, Servers and Terminals
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/46—Multiprogramming arrangements
- G06F9/50—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU]
- G06F9/5083—Techniques for rebalancing the load in a distributed system
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/10—Interfaces, programming languages or software development kits, e.g. for simulating neural networks
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to an information processing method and an information processing apparatus.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a software generation method using a visual programming language.
- the present disclosure proposes an information processing method and an information processing apparatus capable of presenting information that improves the development efficiency of the neural network to the user.
- a processor provides a form for creating a program for constructing a neural network based on a component to be arranged and properties set in the component; Presenting such statistical information, an information processing method is provided.
- a form control unit that provides a form for creating a program for constructing a neural network based on a component to be arranged and a property set in the component;
- the form control unit is provided with an information processing apparatus that presents statistical information related to the neural network.
- the program creation unit includes a program creation unit that creates a program for constructing a neural network based on a component arranged on a form and a property set in the component. Provides an information processing device for calculating statistical information related to the neural network.
- FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a system configuration example according to an embodiment of the present disclosure.
- FIG. It is a functional block diagram of the information processing terminal according to the embodiment. It is a functional block diagram of the server concerning the embodiment. It is a figure for demonstrating the form which concerns on the same embodiment. It is an example of a property display according to the embodiment. It is a display example of statistical information according to the embodiment. It is a figure for demonstrating the change of the layer structure which concerns on the embodiment. It is a figure for demonstrating the real-time update of the statistical information which concerns on the embodiment. It is a figure for demonstrating the calculation method peculiar to the Affine layer concerning the embodiment.
- a neural network is a model that imitates the human cranial nerve circuit, and is a technique for realizing the learning ability of a human on a computer. As described above, one of the features of the neural network is that it has learning ability.
- an artificial neuron node
- an artificial neuron node
- the neural network can automatically infer a solution rule for a problem by repeating learning.
- Examples of learning using a neural network include image recognition and voice recognition.
- the neural network for example, it is possible to classify input image information into any of numbers 0 to 9 by repeatedly learning a handwritten number pattern.
- the learning ability of the neural network as described above is attracting attention as a key for promoting the development of artificial intelligence.
- the pattern recognition ability of neural networks is expected to be applied in various industrial fields.
- the information processing method and information processing apparatus have been conceived by focusing on the neural network development method as described above, and can improve development efficiency in neural network visual programming. It is.
- visual programming refers to a technique for creating program code using visual objects without describing text in software development.
- a program can be created by manipulating an object on a GUI (Graphical User Interface).
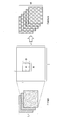
- FIG. 1 is an image diagram of visual programming according to the present disclosure.
- FIG. 1 shows a product generated based on an object (component) arranged on the GUI.
- the components 1 to 3 are arranged so as to be processed in order.
- the components 1 to 3 may be components that mean, for example, data acquisition, data processing, and data output, respectively.
- a setting file, an XML file, or the like may be generated in addition to the source code.
- the information processing method and the information processing apparatus according to the present disclosure can improve the development efficiency in the visual programming of the neural network.
- the effects of the features will be described with reference to the features of the information processing method and the information processing apparatus according to the present disclosure.
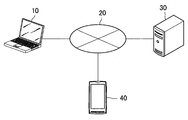
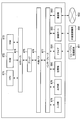
- the system for performing the information processing method according to this embodiment includes an information processing terminal 10, a server 30, and a device 40.
- the information processing terminal 10, the server 30, and the device 40 are connected via the network 20 so that they can communicate with each other.
- the information processing terminal 10 is an information processing apparatus for performing visual programming of a neural network.
- the server 30 is an information processing apparatus that provides the information processing terminal 10 with a form for visual programming and creates a program related to the neural network based on components arranged on the form.
- the device 40 is hardware that executes a neural network program created by the server 30.
- the device 40 may be, for example, a smartphone, a tablet, or a PC (Personal Computer).
- the network 20 may be a public line network such as the Internet, a telephone line network, or a satellite communication network, or may include a dedicated line network such as an IP-VPN (Internet Protocol-Virtual Private Network).
- IP-VPN Internet Protocol-Virtual Private Network
- a form for creating a program for constructing a neural network is provided based on the components to be arranged and the properties set in the components.
- the information processing method according to the present embodiment is characterized by presenting statistical information (hereinafter also simply referred to as statistical information) related to the neural network. Further, the statistical information may be calculated in real time based on a change in a component or a property set in the component. As a result, the user can perform visual programming while checking the statistical information related to the neural network in real time.
- the information processing terminal 10 according to the present embodiment has a function of providing a user with a form relating to visual programming of a neural network.
- the information processing terminal 10 has a function of presenting statistical information related to the created neural network to the user.
- the statistical information related to the neural network may include the number of output units in the neural network, the number of parameters to be processed, the amount of calculation for each calculation type, and the like. Further, as described above, the statistical information may be information calculated in real time based on the change of the component or property.
- the information processing terminal 10 includes a display unit 110, an input unit 120, a form control unit 130, and a server communication unit 140.
- a display unit 110 the information processing terminal 10 according to the present embodiment includes a display unit 110, an input unit 120, a form control unit 130, and a server communication unit 140.
- a server communication unit 140 the server communication unit 140.
- the display unit 110 has a function of displaying information controlled by each configuration of the information processing terminal 10. In this embodiment, in particular, a function for displaying a form for visual programming of a neural network may be provided.
- the above functions may be realized by, for example, a CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) display device, a liquid crystal display (LCD) device, or an OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) device.
- the display unit 110 may have a function as an input unit that receives information input from the user.
- the function as the input unit can be realized by a touch panel, for example.
- the input unit 120 has a function of accepting information input from a user and delivering input information to each component of the information processing terminal 10.
- it may have a function of accepting a user operation on a form related to visual programming and passing input information based on the operation to a form control unit 130 described later.
- the above function may be realized by a keyboard or a mouse, for example.
- the form control unit 130 has a function of controlling a form related to visual programming of the neural network. Specifically, the form control unit 130 can control components on the form and values of the components based on information acquired from the input unit 120. In addition, the form control unit 130 has a function of controlling the contents displayed on the display unit 110 based on information acquired from the server 30 via the server communication unit 140 described later.
- the server communication unit 140 has a function of performing information communication with the server 30 via the network 20. Specifically, the server communication unit 140 transmits information on the form to the server 30 based on the control of the form control unit 130. In addition, the server communication unit 140 delivers the information acquired from the server 30 to the form control unit 130.
- the server 30 according to the present embodiment is an information processing apparatus that creates a program for constructing a neural network based on components arranged on a form and properties set in the components.
- the server 30 has a function of calculating statistical information related to the neural network.
- the server 30 can cause the emulator or device 40 to execute the created neural network.
- the server 30 includes a program creation unit 310, an emulator unit 320, and a terminal communication unit 330.
- a program creation unit 310 the server 30
- an emulator unit 320 the server 30
- a terminal communication unit 330 the server 30
- each structure with which the server 30 is provided is demonstrated.
- the program creation unit 310 has a function of creating a program for constructing a neural network based on information acquired from the information processing terminal 10 via the terminal communication unit 330 described later. Further, the program creation unit 310 has a function of calculating statistical information related to the neural network in real time based on information acquired from the information processing terminal 10.
- the information acquired from the information processing terminal 10 may be information relating to components arranged on the form and properties set to the components. Further, as described above, the statistical information may be the number of output units in the neural network, the number of parameters to be processed, the amount of calculation for each calculation type, and the like.
- the program creation unit 310 can calculate execution prediction information when processing by a neural network is executed on hardware.
- the program creation unit 310 can calculate execution prediction information based on statistical information and preset hardware profile information.
- the execution prediction information may include the execution time of the processing by the neural network, the memory usage, the power consumption, and the calculation amount. Further, the execution prediction information may be information calculated in real time based on a change in statistical information. Note that the above hardware may be different hardware from the device 40 connected via the network 20.
- the program creation unit 310 can calculate estimation information related to computing resources on the cloud for executing processing by the created neural network.
- the program creation unit 310 can calculate estimation information based on statistical information and information acquired from a cloud service that provides computing resources.
- the estimation information may include the type of instance, the number of instances, the amount of computing resources, the processing time by the neural network, and the like. Further, the estimate information may be information calculated in real time based on a change in statistical information.
- the emulator unit 320 has a function of executing a program for constructing the neural network created by the program creation unit 310 on the emulator and obtaining an execution result.
- the emulator unit 320 may include a plurality of emulators related to hardware on which the neural network is mounted. Further, the emulator unit 320 may cause an emulator connected to the server 30 via the network 20 to execute a program and obtain an execution result.
- the emulator unit 320 has a function of causing the device 40 to execute the program created by the program creation unit 310 and acquiring the execution result.
- the execution result of the neural network on the emulator or device 40 may include processing execution time, memory usage, power consumption, calculation amount, and the like.
- the terminal communication unit 330 has a function of performing information communication with the information processing terminal 10 and the device 40 via the network 20. Specifically, the terminal communication unit 330 transmits information calculated by the program creation unit 310 to the information processing terminal 10. Here, the information calculated by the program creation unit 310 may include statistical information, execution prediction information on hardware, and cloud resource estimation information. In addition, the terminal communication unit 330 transmits information acquired by the emulator unit 320 to the information processing terminal 10. Here, the information acquired by the emulator unit 320 may include an execution result of the neural network on the emulator or hardware.
- the form according to the present embodiment may be displayed on the display unit 110 of the information processing terminal 10.
- the user can construct a neural network by performing operations on the above-described form.
- FIG. 5 is a diagram showing a configuration example of the form according to the present embodiment.
- the form F1 according to the present embodiment includes pallets P1 to P3.
- the palette P1 may be an area for displaying a list of components.
- the palette P2 may be an area for editing a component and constructing a neural network.
- the palette P3 may be an area for displaying various types of information related to the neural network.
- the components according to the present embodiment correspond to layers constituting the neural network. For this reason, in the following description, the component and the layer are treated as the same thing, and are unified by the name of layer.
- the palette P1 is an area for displaying a list of layers. As an example illustrated in FIG. 5, layers may be displayed for each classification on the palette P ⁇ b> 1. Moreover, the list of layers for each category may be controlled to be expanded by clicking the category name. Referring to FIG. 5, the palette P1 displays a list of layers classified into input / output layers, intermediate layers, activation functions, and the like. The user can add a corresponding layer to the palette P2 by dragging the layer displayed on the palette P1. Alternatively, a corresponding layer may be added to the palette P2 by selecting a layer displayed on the palette P1. Note that the layers shown in FIG. 5 and subsequent figures are well known, and thus detailed description thereof is omitted.
- the palette P2 is an area for editing a layer and constructing a neural network.
- the processing flow in the neural network is constructed by connecting the layers with lines.
- a user can visually construct a neural network by moving, adding or deleting layers.
- the layer selected by the user may be displayed in a display format different from other layers.
- An example of FIG. 5 illustrates a state where the layer “Affine # 2” is selected.
- the palette P3 is an area for displaying various information related to the neural network. Referring to FIG. 5, in the palette P3, property information related to the layer selected in the palette P2 is displayed as information i1. In addition, the neural network statistical information based on the layers arranged on the palette P2 is displayed on the palette P3 as information i2. In addition to property information and statistical information, the palette P3 may display execution prediction information on hardware, cloud resource estimation information, execution results on the emulator or device 40, and the like.
- FIG. 6 is an example of property information displayed on the palette P3.
- FIG. 6 shows an example of property information when the layer “Affine # 2” is selected in the palette P2 of FIG.
- the property information includes basic information related to the layer such as “Name” indicating the layer name, information automatically calculated according to the connection status between the layers and the characteristics of the layer, and unique to each layer type. The setting value of is included.
- “Input” and “Output” are values indicating the input / output size of the layer. Further, “CostAdd” and “CostMultipleAdd” may be information relating to the calculation amount in the layer. “CostParameter” is a value indicating the number of parameters (memory amount) included in the layer. Each item listed above may be an item that is automatically calculated based on a connection state between layers and a setting value to be described later. The user can grasp the memory amount and the calculation amount in each layer without manually calculating by checking each item described above. The detailed description of “CostAdd” and “CostMultipleAdd” will be described later.
- “OutShape” is an item for designating the number of output neurons of the Affine layer.
- the property information may include a setting value unique to each layer type.
- items other than “OutShape” may be included in the setting values unique to each layer type.
- the property information may include items for specifying the presence / absence of a bias term and various items regarding the weight.
- the statistical information displayed on the palette P3 is information calculated in real time based on the layer arranged on the form and the property of the layer being changed. Further, the statistical information according to the present embodiment may be the sum of the memory amount and the calculation amount calculated for each layer.
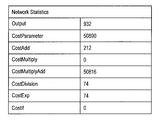
- FIG. 7 is a diagram showing statistical information when a layer is arranged on the palette P2 in FIG.
- the statistical information includes “Output” and “CostParameter”.
- Output may be a value indicating the total number of output units related to the entire neural network. That is, “Output” means the number of intermediate calculation values (buffers) held in the calculation process.
- CostParameter may be the total number of parameters related to the entire neural network.
- the statistical information further includes “CostAdd”, “CostMultiple”, “CostMultipleAdd”, “CostDivision”, “CostExp”, and “CostIf”.
- Each of the above items indicates the total amount of computation for each computation type processed by the neural network.
- Each of the above items may be a value indicating the number of additions, the number of multiplications, the number of multiplications and additions, the number of divisions, the number of exponent calculations, or the number of conditional branch determinations. In the example illustrated in FIG. 7, the value of “CostMultiple” is 0 because the number of multiplications is included in the number of multiplications and additions.
- FIG. 8 is a diagram showing that the layer configuration related to the neural network is changed on the palette P2.
- layers “Tanh # 2” and “Affine # 3” are newly added to the layer configuration illustrated in FIG. 5.
- each layer on the palette P2 does not need to be arranged linearly.
- FIG. 9 is a diagram showing statistical information at the time of layer configuration shown in FIG. That is, FIG. 9 shows updated statistical information based on the change in the layer configuration.
- each item indicated by the statistical information is updated from the state shown in FIG. Specifically, in the statistical information illustrated in FIG. 9, the values of “Output” and “CostParameter” are increased as compared with the statistical information illustrated in FIG. 7. In addition, in the statistical information illustrated in FIG. 9, the values of “CostAdd”, “CostMultipleAdd”, “CostDivision”, and “CostExp” are increased as compared with the statistical information illustrated in FIG. 7.
- statistical information can be calculated in real time based on a change in a layer or a property set in the layer. That is, the program creation unit 310 of the server 30 can calculate the statistical information in real time based on the change of the layer configuration on the form displayed on the information processing terminal 10. In the example described with reference to FIGS. 8 and 9, the program creation unit 310 updates the value of the statistical information based on the addition of the layers “Tanh # 2” and “Affine # 3” on the form. is doing.
- the program creation unit 310 updates the statistical information even when the layer is deleted or the property of the layer is changed.
- the program creation unit 310 can update the statistical information based on a change in the value of “OutShape” in the properties of the Affine layer.
- the program creation unit 310 updates the statistical information in real time based on the change in the layer configuration, so that the user can perform visual programming of the neural network while checking the latest statistical information.
- the statistical information according to the present embodiment is the total number of parameters and calculation amount calculated for each layer.
- the program creation unit 310 according to the present embodiment can update the value of the statistical information by recalculating the number of parameters and the calculation amount related to each layer.
- a method for calculating the number of parameters and the calculation amount in the layer will be described with examples.
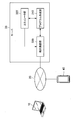
- FIG. 10 is a diagram for explaining a method for calculating the number of parameters and the calculation amount in the Affine layer.
- the weight W is shown, and in this example, the weights W 1,1 to W 3,4 are shown. That is, the number of weights W in the Affine layer can be calculated by multiplying Input and Output. For this reason, the number of parameters in the Affine layer can be calculated by the following formula (1).
- Equation (1) b represents a bias term.
- the weight W can be calculated
- FIG. 11 is a diagram for explaining a method of calculating the number of parameters and the amount of calculation in the conversion layer. It is.
- the input map is indicated as L and the output Map is indicated as M.
- the weight W can be calculated by a ⁇ b, and indicates a single convolution calculation amount.
- the value of Output can be calculated by a ⁇ b ⁇ L ⁇ M. That is, in the Convolution layer, it is possible to calculate the number of parameters and the calculation amount by using the following formula (3).
- the method for calculating the number of parameters and the amount of calculation in the layer has been described with examples.
- the Affine layer and the Convolution layer that are often used as the configuration of the neural network have been described.
- the number of parameters and the amount of calculation can be calculated by a layer-specific method.
- the value of the statistical information related to the neural network is updated by recalculating the number of parameters and the calculation amount for each layer based on the change in the layer configuration. Is possible.
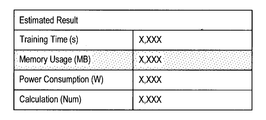
- FIG. 12 is a diagram illustrating an example of execution prediction information of a neural network on hardware.
- the execution prediction information according to the present embodiment may be a value calculated by the program creation unit 310 of the server 30 based on statistical information and a hardware profile.
- the hardware profile may include hardware specifications of the hardware, restriction information related to execution of the neural network, and the like.
- the execution prediction information according to the present embodiment may be displayed on the palette P3 on the form F1 shown in FIG.
- the execution prediction information includes learning time, memory usage, power consumption, and calculation amount by the neural network.
- the program creation unit 310 can calculate the above items in real time according to the update of the statistical information calculated based on the layer configuration.
- the program creation unit 310 can generate alert information based on the fact that the statistical information deviates from the range of restriction information included in the hardware profile. In the example shown in FIG. 12, the program creation unit 310 generates alert information based on the fact that the statistical information deviates from the limit related to the memory usage of hardware.
- the form control unit 130 of the information processing terminal 10 receives the above alert information, and controls the display format of the execution prediction information shown on the palette P3 based on the information. The display control by the form control unit 130 may emphasize the background of items that deviate from the limitation, as shown in FIG. 12, for example. In addition, the form control unit 130 may display a message related to the alert on the form.
- the execution prediction information according to the present embodiment may be information calculated in real time based on the update of statistical information.
- the user can perform visual programming so as not to deviate from the restriction information of the hardware that implements the neural network.
- the execution prediction information according to the present embodiment may be presented in comparison with hardware restriction information.
- the user can construct a neural network while confirming the upper limit value of each item related to hardware restrictions.
- FIG. 13 is a diagram illustrating an example of estimation information related to a cloud resource for executing processing by a neural network.
- the estimate information according to the present embodiment may be a value calculated by the program creation unit 310 of the server 30 based on statistical information and information acquired from the cloud service.
- the information acquired from the cloud service may include specifications of the provided instances and monetary information.
- the instance specification may include information such as a GPU (GraPics Processing Unit) and a CPU (Central Processing Unit) used for the instance.
- the estimation information according to the present embodiment may be displayed on the palette P3 on the form F1 shown in FIG.
- the estimate information according to the present embodiment includes the type of instance to be provided, the number of instances, amount information, and learning time by a neural network.
- the program creation unit 310 can calculate the above items in real time according to the update of the statistical information calculated based on the layer configuration.
- the estimation information according to the present embodiment may be calculated using the following mathematical formula (4).
- f and g may be arbitrary functions.
- z indicates the instance type
- y indicates the number of instances, the amount, and the learning time.
- x represents statistical information, the number of input data, and the number of classes in the identification problem.
- the first term is a categorical cross entropy, and may be an error function with respect to z that is a category value.
- the second term is a square error term and may be an error function for continuous values. Note that the number of classes and the functions f and g in the identification problem may be obtained by learning using a neural network.
- each item in the calculated estimate information can be treated as a variable, and the value of each item can be changed.
- the program creation unit 310 can recalculate the value of another item based on the change of the value of the item. For example, when the amount value is changed by the user, the program creation unit 310 recalculates the instance type, the number of instances, and the learning time value based on the changed amount value in the estimation information. .
- the value of each item may be calculated by the following mathematical formula (5). For items specified by the user, values specified by the user are used instead of the corresponding estimation functions.
- f, g, and h may be arbitrary functions.
- Y 1 to y 4 indicate an instance type, the number of instances, an amount of money, and a learning time, respectively.
- the values represented by y, backslash, and j (1 to 4) mean all y except for the jth objective variable following the backslash. Yes. Thereby, it is possible to perform calculation without including the objective variable in the explanatory variable.
- x represents the statistical information, the number of input data, and the number of classes in the identification problem.
- the first term is a categorical cross entropy, and may be an error function for y backslash 1 that is a category value.
- the second term, the third term, and the fourth term are square error terms, and may be error functions for continuous values. Note that the number of classes and the functions f, g, and h in the identification problem may be obtained by learning using a neural network. That is, it is expected that the accuracy of the mathematical formula (5) is improved by accumulating data by learning.
- the estimation information according to the present embodiment may be information calculated in real time based on the update of statistical information. Furthermore, in the information processing method according to the present embodiment, based on the value of an arbitrary item included in the estimate information being designated, the values of other items other than the item may be recalculated and presented. Thereby, the user can perform visual programming while determining the trade-off between the amount information of the cloud resource and the learning time by the neural network.
- FIG. 14 is a diagram for explaining the relationship between properties, statistical information, and estimation information according to this embodiment.
- the statistical information can be dynamically changed based on the change of the property value.
- the estimate information may be further changed based on the dynamically changed statistical information.
- the statistical information may be dynamically changed based on the change of the estimate information.
- the property value may be further changed based on the dynamically changed statistical information.
- each item of the statistical information is treated as a variable, and a value may be designated by the user.
- the change of the property value based on the change of the statistical information may be performed according to the contribution rate of each layer.
- a description will be given assuming a neural network in which processing is performed in the order of each layer of Input, Convolution, Affine, and Output.
- the layer contribution ratios can be calculated as 4.85 and 95.15, respectively.
- the program creation unit 310 distributes the number of parameters of the changed statistical information to the Convolution and Affine layers according to the contribution rate calculated by the above method, and dynamically assigns the value of each layer. Can be changed.
- the values of statistical information, properties, and estimation information can be dynamically linked. Therefore, a user's burden can be reduced and the efficiency which concerns on development of a neural network can be improved further.
- FIG. 15 is a diagram illustrating a display example of comparison information according to the present embodiment.
- FIG. 15 shows an example in which “CostParameter” is selected in the statistical information I2 displayed on the palette P3.
- the palette P2 displays a plurality of numerical values and bars in addition to the layer configuration.
- the numerical value and the bar may be comparison information of each layer related to the selected statistical information item. That is, in FIG. 15, the value of “CostParameter” in each layer is indicated by a numerical value and a bar.
- “CostParameter” in the “Convolution # 1” layer is 416.
- “CostParameter” in the Convolution # 2 layer is 6416.
- the bar included in the comparison information may be an indicator that indicates the size of the item value. That is, the bar included in the comparison information may be displayed longer as the value of the item is larger. At this time, the length of the bar may be determined by the absolute value of the value, or may be determined by the relative value with the value in each layer.
- the information processing method it is possible to present the comparison information of each layer constituting the statistical information to the user. Thereby, the user can intuitively perceive the calculation amount of each layer, and can be used as a reference when changing the layer configuration of the neural network.
- the emulator unit 320 can execute a program related to the neural network created by the program creation unit 310 on the emulator and obtain an execution result. Further, the emulator unit 320 can cause the device 40 to execute the program related to the neural network created by the program creation unit 310 and acquire the execution result.
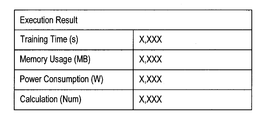
- FIG. 16 is a diagram illustrating an example of an execution result according to the present embodiment.
- the execution result according to the present embodiment includes learning time by the neural network, memory usage, power consumption, and calculation amount.
- the execution result according to the present embodiment may be displayed on the palette P3 on the form F1 shown in FIG.
- the execution result of the neural network executed on the emulator or the device 40 can be presented to the user. Thereby, the user can confirm the execution result of the created neural network on the development screen.
- FIG. 17 is a block diagram illustrating a hardware configuration example of the information processing terminal 10, the server 30, and the device 40 according to the present disclosure.
- the information processing terminal 10, the server 30, and the device 40 include, for example, a CPU 871, a ROM 872, a RAM 873, a host bus 874, a bridge 875, an external bus 876, an interface 877, and an input unit. 878, an output unit 879, a storage unit 880, a drive 881, a connection port 882, and a communication unit 883.
- the hardware configuration shown here is an example, and some of the components may be omitted. Moreover, you may further include components other than the component shown here.
- the CPU 871 functions as, for example, an arithmetic processing unit or a control unit, and controls all or part of the operation of each component based on various programs recorded in the ROM 872, RAM 873, storage unit 880, or removable recording medium 901. .
- the ROM 872 is a means for storing programs read by the CPU 871, data used for calculations, and the like.
- the RAM 873 for example, a program read by the CPU 871, various parameters that change as appropriate when the program is executed, and the like are temporarily or permanently stored.
- the CPU 871, the ROM 872, and the RAM 873 are connected to each other via, for example, a host bus 874 capable of high-speed data transmission.
- the host bus 874 is connected to an external bus 876 having a relatively low data transmission speed via a bridge 875, for example.
- the external bus 876 is connected to various components via an interface 877.
- Input unit 8708 For the input unit 878, for example, a mouse, a keyboard, a touch panel, a button, a switch, a lever, or the like is used. Furthermore, as the input unit 878, a remote controller (hereinafter referred to as a remote controller) that can transmit a control signal using infrared rays or other radio waves may be used.
- a remote controller hereinafter referred to as a remote controller
- a remote controller that can transmit a control signal using infrared rays or other radio waves may be used.
- Output unit 879 In the output unit 879, for example, a display device such as a CRT (Cathode Ray Tube), LCD, or organic EL, an audio output device such as a speaker or a headphone, a printer, a mobile phone, or a facsimile, etc. It is a device that can notify visually or audibly.
- a display device such as a CRT (Cathode Ray Tube), LCD, or organic EL
- an audio output device such as a speaker or a headphone, a printer, a mobile phone, or a facsimile, etc. It is a device that can notify visually or audibly.
- the storage unit 880 is a device for storing various data.
- a magnetic storage device such as a hard disk drive (HDD), a semiconductor storage device, an optical storage device, a magneto-optical storage device, or the like is used.
- the drive 881 is a device that reads information recorded on a removable recording medium 901 such as a magnetic disk, an optical disk, a magneto-optical disk, or a semiconductor memory, or writes information to the removable recording medium 901.
- a removable recording medium 901 such as a magnetic disk, an optical disk, a magneto-optical disk, or a semiconductor memory
- the removable recording medium 901 is, for example, a DVD medium, a Blu-ray (registered trademark) medium, an HD DVD medium, or various semiconductor storage media.
- the removable recording medium 901 may be, for example, an IC card on which a non-contact IC chip is mounted, an electronic device, or the like.
- connection port 882 is a port for connecting an external connection device 902 such as a USB (Universal Serial Bus) port, an IEEE 1394 port, a SCSI (Small Computer System Interface), an RS-232C port, or an optical audio terminal. is there.
- an external connection device 902 such as a USB (Universal Serial Bus) port, an IEEE 1394 port, a SCSI (Small Computer System Interface), an RS-232C port, or an optical audio terminal. is there.
- the external connection device 902 is, for example, a printer, a portable music player, a digital camera, a digital video camera, or an IC recorder.
- the communication unit 883 is a communication device for connecting to the network 903.
- the information processing method according to the present disclosure provides a form for creating a program for constructing a neural network based on a layer to be arranged and a property set in the layer. Can do. Moreover, in the information processing method according to the present disclosure, it is possible to present statistical information related to the neural network. According to this configuration, it is possible to present information that improves the development efficiency of the neural network to the user.
- the server 30 calculates the statistical information in real time based on the change in the layer configuration
- the present technology is not limited to such an example.
- the calculation of statistical information based on the change in the layer configuration may be realized by the information processing terminal 10.
- the form control unit 130 of the information processing terminal 10 can calculate statistical information in real time based on the change of the layer configuration.
- the update of the statistical information is not necessarily performed in real time.
- the program creation unit 310 may update the statistical information based on the fact that the process for confirming the editing of the layer configuration has been performed by the user.
- a processor providing a form for creating a program for building a neural network based on the components to be placed and the properties set on the components; Presenting statistical information relating to the neural network; Including an information processing method.
- the statistical information includes at least one of the number of output units in the neural network, the number of parameters to be processed, or the calculation amount for each calculation type.
- the information processing method according to (1) (3) Presenting in real time the statistical information calculated based on a change in the component placed on the form or a property set in the component; The information processing method according to (1) or (2).
- the execution prediction information includes at least one of execution time of the processing by the neural network, memory usage, power consumption, or calculation amount.
- the information processing method according to (4). Presenting alert information generated based on the statistical information deviating from the restriction information in the hardware; Further including The information processing method according to (4) or (5).
- the estimate information related to the computing resource includes at least one of an instance type, the number of instances, an amount, or a processing time by the neural network implemented on the computing resource.
- the information processing method according to (7). (9) Accepting a user's operation to change the value of the statistical information, and presenting the property value of the component to be changed based on the operation and the estimate information relating to the computing resource in real time; Further including The information processing method according to (7) or (8). (10) Accepting a user operation to change the value of the estimate information related to the computing resource, and presenting the property value of the component and the statistical information to be changed based on the operation in real time; Further including The information processing method according to any one of (7) to (9).
- the execution result includes at least one of execution time, memory usage, power consumption, or calculation amount of processing by the neural network.
- a form control unit that provides a form for creating a program for constructing a neural network based on the components to be arranged and the properties set in the components; With The form control unit presents statistical information relating to the neural network; Information processing device.
- a program creation unit for creating a program for constructing a neural network based on the components arranged on the form and the properties set in the components; With The program creation unit calculates statistical information related to the neural network; Information processing device.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Mathematical Optimization (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Computational Mathematics (AREA)
- Pure & Applied Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Analysis (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Computational Biology (AREA)
- Operations Research (AREA)
- Probability & Statistics with Applications (AREA)
- Evolutionary Biology (AREA)
- Algebra (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Stored Programmes (AREA)
- User Interface Of Digital Computer (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017566526A JP6516025B2 (ja) | 2016-02-12 | 2016-11-25 | 情報処理方法および情報処理装置 |
| US15/774,318 US10942711B2 (en) | 2016-02-12 | 2016-11-25 | Information processing method and information processing apparatus |
| EP16889921.9A EP3416105A4 (en) | 2016-02-12 | 2016-11-25 | INFORMATION PROCESSING METHOD AND INFORMATION PROCESSING DEVICE |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016-024545 | 2016-02-12 | ||
| JP2016024545 | 2016-02-12 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017138220A1 true WO2017138220A1 (ja) | 2017-08-17 |
Family
ID=59563307
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2016/085025 Ceased WO2017138220A1 (ja) | 2016-02-12 | 2016-11-25 | 情報処理方法および情報処理装置 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10942711B2 (OSRAM) |
| EP (1) | EP3416105A4 (OSRAM) |
| JP (2) | JP6516025B2 (OSRAM) |
| WO (1) | WO2017138220A1 (OSRAM) |
Cited By (24)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2019187542A1 (ja) | 2018-03-28 | 2019-10-03 | ソニー株式会社 | 情報処理方法、情報処理装置、およびプログラム |
| WO2020110766A1 (ja) * | 2018-11-30 | 2020-06-04 | キヤノン株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及びプログラム |
| KR20200080819A (ko) * | 2018-12-27 | 2020-07-07 | (주)아크릴 | 인공 신경망의 상용화 서비스 제공 방법 |
| WO2020166084A1 (ja) * | 2019-02-15 | 2020-08-20 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム |
| WO2020166641A1 (ja) * | 2019-02-15 | 2020-08-20 | ソニー株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法およびプログラム |
| CN111736836A (zh) * | 2020-07-22 | 2020-10-02 | 平安国际智慧城市科技股份有限公司 | 基于关系图的组件配置方法、装置及计算机可读存储介质 |
| CN111832737A (zh) * | 2019-04-18 | 2020-10-27 | 中科寒武纪科技股份有限公司 | 一种数据处理方法及相关产品 |
| JP2022539290A (ja) * | 2019-06-28 | 2022-09-08 | マイクロソフト テクノロジー ライセンシング,エルエルシー | ディープラーニングのためのビジュアルプログラミング |
| JP2022540872A (ja) * | 2019-07-08 | 2022-09-20 | ヴィアナイ システムズ, インコーポレイテッド | ニューラルネットワークの動作を変更するための手法 |
| JP2022547668A (ja) * | 2019-09-12 | 2022-11-15 | ヴィアナイ システムズ, インコーポレイテッド | 機械学習モデルの視覚的作成及び監視 |
| US11544059B2 (en) | 2018-12-28 | 2023-01-03 | Cambricon (Xi'an) Semiconductor Co., Ltd. | Signal processing device, signal processing method and related products |
| US11609760B2 (en) | 2018-02-13 | 2023-03-21 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Computing device and method |
| US11620130B2 (en) | 2018-02-13 | 2023-04-04 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Computing device and method |
| US11630666B2 (en) | 2018-02-13 | 2023-04-18 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Computing device and method |
| US11640539B2 (en) | 2019-07-08 | 2023-05-02 | Vianai Systems, Inc. | Techniques for visualizing the operation of neural networks using samples of training data |
| US11681925B2 (en) | 2019-07-08 | 2023-06-20 | Vianai Systems, Inc. | Techniques for creating, analyzing, and modifying neural networks |
| US11703939B2 (en) | 2018-09-28 | 2023-07-18 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Signal processing device and related products |
| US11847554B2 (en) | 2019-04-18 | 2023-12-19 | Cambricon Technologies Corporation Limited | Data processing method and related products |
| US11966583B2 (en) | 2018-08-28 | 2024-04-23 | Cambricon Technologies Corporation Limited | Data pre-processing method and device, and related computer device and storage medium |
| EP4290428A4 (en) * | 2021-02-03 | 2024-07-10 | Sony Group Corporation | SERVER DEVICE, GENERATION METHOD, ELECTRONIC EQUIPMENT GENERATION METHOD, DATABASE GENERATION METHOD, AND ELECTRONIC EQUIPMENT |
| US12205003B2 (en) | 2019-08-26 | 2025-01-21 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Data processing method and apparatus, and related product |
| US12314866B2 (en) | 2018-07-17 | 2025-05-27 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Parallel processing of network model operations |
| US12333671B2 (en) | 2020-02-24 | 2025-06-17 | Cambricon Technologies Corporation Limited | Data quantization processing method and apparatus, electronic device and storage medium |
| US12504951B2 (en) | 2020-03-17 | 2025-12-23 | Anhui Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Computing device and method for processing multi-bit width data |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6799197B2 (ja) * | 2018-05-10 | 2020-12-09 | ヌヴォトンテクノロジージャパン株式会社 | ニューラルネットワーク構築装置、情報処理装置、ニューラルネットワーク構築方法及びプログラム |
| KR102142205B1 (ko) * | 2019-01-04 | 2020-08-06 | 에스케이 주식회사 | 설명 가능한 인공지능 모델링 및 시뮬레이션 시스템 및 방법 |
| CN113966494A (zh) * | 2019-08-27 | 2022-01-21 | 西门子股份公司 | 支持基于神经元块图形编程的系统、方法及存储介质 |
| JP7475164B2 (ja) * | 2020-03-05 | 2024-04-26 | キヤノン株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法およびプログラム |
| EP3968108A1 (de) * | 2020-09-15 | 2022-03-16 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Steuerung eines technischen systems mit einer recheneinheit für künstliche intelligenz |
| KR20230002041A (ko) * | 2021-06-29 | 2023-01-05 | 주식회사 에너자이(ENERZAi) | 이미지 처리를 위한 인공 신경망 모델 학습 방법 및 시스템 |
| US20250110713A1 (en) * | 2023-09-28 | 2025-04-03 | Oracle International Corporation | Defining And Using Reusable Modules To Generate Form Control Code |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04153866A (ja) * | 1990-10-18 | 1992-05-27 | Fujitsu Ltd | ネットワーク編集方式 |
| JPH04190461A (ja) * | 1990-11-26 | 1992-07-08 | Fujitsu Ltd | ニューラルネットワークの構築表示方法 |
| JP2001282574A (ja) * | 2000-03-30 | 2001-10-12 | Oki Electric Ind Co Ltd | 処理時間情報を含む図式表現プログラムの表現方法 |
| JP2002268883A (ja) | 2001-03-13 | 2002-09-20 | Sony Corp | プログラム、記録媒体、ソフトウエア生成方法並びに情報処理装置 |
| JP2003029973A (ja) * | 1996-05-31 | 2003-01-31 | Toshiba Corp | システム構築装置 |
| WO2014139374A1 (en) * | 2013-03-15 | 2014-09-18 | International Business Machines Corporation | Quantized congestion notification in a virtual networking system |
Family Cites Families (68)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0349820B1 (de) * | 1988-07-05 | 1995-04-19 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Netzwerk -Baustein und Architektur für die programmierbare Emulation künstlicher neuronaler Netze mit digitaler Arbeitsweise |
| JP2691022B2 (ja) | 1989-06-30 | 1997-12-17 | 株式会社日立製作所 | ニューラルネットを用いた画像認識システム |
| US5875108A (en) * | 1991-12-23 | 1999-02-23 | Hoffberg; Steven M. | Ergonomic man-machine interface incorporating adaptive pattern recognition based control system |
| US6081750A (en) * | 1991-12-23 | 2000-06-27 | Hoffberg; Steven Mark | Ergonomic man-machine interface incorporating adaptive pattern recognition based control system |
| US6418424B1 (en) * | 1991-12-23 | 2002-07-09 | Steven M. Hoffberg | Ergonomic man-machine interface incorporating adaptive pattern recognition based control system |
| US6400996B1 (en) * | 1999-02-01 | 2002-06-04 | Steven M. Hoffberg | Adaptive pattern recognition based control system and method |
| US5903454A (en) * | 1991-12-23 | 1999-05-11 | Hoffberg; Linda Irene | Human-factored interface corporating adaptive pattern recognition based controller apparatus |
| US10361802B1 (en) * | 1999-02-01 | 2019-07-23 | Blanding Hovenweep, Llc | Adaptive pattern recognition based control system and method |
| US20070061735A1 (en) * | 1995-06-06 | 2007-03-15 | Hoffberg Steven M | Ergonomic man-machine interface incorporating adaptive pattern recognition based control system |
| JPH09160949A (ja) * | 1995-12-07 | 1997-06-20 | Hitachi Ltd | ハードウエアとソフトウエアの混在システムの設計支援方法 |
| JP3315890B2 (ja) * | 1996-05-31 | 2002-08-19 | 株式会社東芝 | データ処理システム |
| GB2321363A (en) * | 1997-01-21 | 1998-07-22 | Northern Telecom Ltd | Telecommunications |
| GB2321362A (en) * | 1997-01-21 | 1998-07-22 | Northern Telecom Ltd | Generic processing capability |
| US6678640B2 (en) * | 1998-06-10 | 2004-01-13 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Method and apparatus for parameter estimation, parameter estimation control and learning control |
| US7124101B1 (en) * | 1999-11-22 | 2006-10-17 | Accenture Llp | Asset tracking in a network-based supply chain environment |
| US7130807B1 (en) * | 1999-11-22 | 2006-10-31 | Accenture Llp | Technology sharing during demand and supply planning in a network-based supply chain environment |
| US7716077B1 (en) * | 1999-11-22 | 2010-05-11 | Accenture Global Services Gmbh | Scheduling and planning maintenance and service in a network-based supply chain environment |
| US8032409B1 (en) * | 1999-11-22 | 2011-10-04 | Accenture Global Services Limited | Enhanced visibility during installation management in a network-based supply chain environment |
| US7167844B1 (en) * | 1999-12-22 | 2007-01-23 | Accenture Llp | Electronic menu document creator in a virtual financial environment |
| US7610233B1 (en) * | 1999-12-22 | 2009-10-27 | Accenture, Llp | System, method and article of manufacture for initiation of bidding in a virtual trade financial environment |
| US7069234B1 (en) * | 1999-12-22 | 2006-06-27 | Accenture Llp | Initiating an agreement in an e-commerce environment |
| US6704718B2 (en) * | 2001-06-05 | 2004-03-09 | Microsoft Corporation | System and method for trainable nonlinear prediction of transform coefficients in data compression |
| JP3676296B2 (ja) * | 2001-12-20 | 2005-07-27 | 日本水産株式会社 | 米糠水抽出物およびその練製品添加物への使用 |
| US9170812B2 (en) * | 2002-03-21 | 2015-10-27 | Pact Xpp Technologies Ag | Data processing system having integrated pipelined array data processor |
| US7483868B2 (en) * | 2002-04-19 | 2009-01-27 | Computer Associates Think, Inc. | Automatic neural-net model generation and maintenance |
| US20050086635A1 (en) * | 2003-10-20 | 2005-04-21 | Pegasus Technologies, Inc. | Visual programming system and method |
| JP4525477B2 (ja) * | 2005-02-23 | 2010-08-18 | ソニー株式会社 | 学習制御装置および学習制御方法、並びに、プログラム |
| US20070016389A1 (en) * | 2005-06-24 | 2007-01-18 | Cetin Ozgen | Method and system for accelerating and improving the history matching of a reservoir simulation model |
| US7502763B2 (en) | 2005-07-29 | 2009-03-10 | The Florida International University Board Of Trustees | Artificial neural network design and evaluation tool |
| EP1946612B1 (fr) * | 2005-10-27 | 2012-11-14 | France Télécom | Individualisation de hrtfs utilisant une modelisation par elements finis couplee a un modele correctif |
| US9600767B1 (en) * | 2006-10-06 | 2017-03-21 | Hrl Laboratories, Llc | System, method, and computer program product for generating a single software code based on a description of a distributed architecture |
| US8504342B2 (en) * | 2007-02-02 | 2013-08-06 | Exxonmobil Upstream Research Company | Modeling and designing of well drilling system that accounts for vibrations |
| WO2009029496A1 (en) * | 2007-08-24 | 2009-03-05 | Yiping Ding | Virtualization planning system |
| JP4840426B2 (ja) * | 2008-09-24 | 2011-12-21 | ソニー株式会社 | 電子機器、ぼけ画像選別方法及びプログラム |
| EP3236384B1 (en) * | 2008-11-21 | 2018-12-05 | Exxonmobil Upstream Research Company | Methods and systems for modeling, designing, and conducting drilling operations that consider vibrations |
| US8311961B2 (en) * | 2009-05-29 | 2012-11-13 | International Business Machines Corporation | Effort estimation using text analysis |
| US8200593B2 (en) * | 2009-07-20 | 2012-06-12 | Corticaldb Inc | Method for efficiently simulating the information processing in cells and tissues of the nervous system with a temporal series compressed encoding neural network |
| US8442927B2 (en) * | 2009-07-30 | 2013-05-14 | Nec Laboratories America, Inc. | Dynamically configurable, multi-ported co-processor for convolutional neural networks |
| US8999721B2 (en) * | 2009-10-23 | 2015-04-07 | Therabrake, Inc. | Method and system to provide personalized pharmaceutical compositions and dosages |
| US7996723B2 (en) * | 2009-12-22 | 2011-08-09 | Xerox Corporation | Continuous, automated discovery of bugs in released software |
| WO2012109407A1 (en) * | 2011-02-09 | 2012-08-16 | The Trustees Of Columbia University In The City Of New York | Encoding and decoding machine with recurrent neural networks |
| US9063818B1 (en) * | 2011-03-16 | 2015-06-23 | Google Inc. | Automated software updating based on prior activity |
| US8880450B2 (en) * | 2011-05-26 | 2014-11-04 | World Heart Corporation | Systems and methods for predicting characteristics of an artificial heart using an artificial neural network |
| US9916538B2 (en) * | 2012-09-15 | 2018-03-13 | Z Advanced Computing, Inc. | Method and system for feature detection |
| US9153230B2 (en) * | 2012-10-23 | 2015-10-06 | Google Inc. | Mobile speech recognition hardware accelerator |
| US9147153B2 (en) * | 2012-11-06 | 2015-09-29 | Rockwell Automation Technologies, Inc. | Empirical modeling with globally enforced general constraints |
| US9235801B2 (en) * | 2013-03-15 | 2016-01-12 | Citrix Systems, Inc. | Managing computer server capacity |
| US10832289B2 (en) * | 2013-06-14 | 2020-11-10 | Oath Inc. | Systems and methods for providing and using an internet sentiment index |
| WO2015108748A1 (en) * | 2014-01-17 | 2015-07-23 | Fair Isaac Corporation | Cloud-based decision management platform |
| US9324022B2 (en) * | 2014-03-04 | 2016-04-26 | Signal/Sense, Inc. | Classifying data with deep learning neural records incrementally refined through expert input |
| US20150262061A1 (en) * | 2014-03-14 | 2015-09-17 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Contextual real-time feedback for neuromorphic model development |
| GB2541625A (en) * | 2014-05-23 | 2017-02-22 | Datarobot | Systems and techniques for predictive data analytics |
| US11094015B2 (en) * | 2014-07-11 | 2021-08-17 | BMLL Technologies, Ltd. | Data access and processing system |
| US10686869B2 (en) * | 2014-09-29 | 2020-06-16 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Tool for investigating the performance of a distributed processing system |
| SG10201406215YA (en) * | 2014-09-30 | 2016-04-28 | Mentorica Technology Pte Ltd | Systems and methods for automated data analysis and customer relationship management |
| US20160162779A1 (en) * | 2014-12-05 | 2016-06-09 | RealMatch, Inc. | Device, system and method for generating a predictive model by machine learning |
| US20160210550A1 (en) * | 2015-01-20 | 2016-07-21 | Nomizo, Inc. | Cloud-based neural networks |
| US9910481B2 (en) * | 2015-02-13 | 2018-03-06 | Intel Corporation | Performing power management in a multicore processor |
| CA2980166C (en) * | 2015-03-27 | 2023-10-10 | Equifax, Inc. | Optimizing neural networks for risk assessment |
| US9786036B2 (en) * | 2015-04-28 | 2017-10-10 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Reducing image resolution in deep convolutional networks |
| US11423311B2 (en) * | 2015-06-04 | 2022-08-23 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Automatic tuning of artificial neural networks |
| US10540588B2 (en) * | 2015-06-29 | 2020-01-21 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Deep neural network processing on hardware accelerators with stacked memory |
| US10664743B2 (en) * | 2015-10-28 | 2020-05-26 | International Business Machines Corporation | Modeling a subject process by machine learning with adaptive inputs |
| US9953217B2 (en) * | 2015-11-30 | 2018-04-24 | International Business Machines Corporation | System and method for pose-aware feature learning |
| US11715025B2 (en) * | 2015-12-30 | 2023-08-01 | Nutanix, Inc. | Method for forecasting distributed resource utilization in a virtualization environment |
| US10282822B2 (en) * | 2016-12-01 | 2019-05-07 | Almalence Inc. | Digital correction of optical system aberrations |
| WO2018125250A1 (en) * | 2016-12-31 | 2018-07-05 | Intel Corporation | Systems, methods, and apparatuses for heterogeneous computing |
| US20180315141A1 (en) * | 2017-04-26 | 2018-11-01 | Clause, Inc. | System and method for business intelligence through data-driven contract analysis |
-
2016
- 2016-11-25 EP EP16889921.9A patent/EP3416105A4/en not_active Ceased
- 2016-11-25 WO PCT/JP2016/085025 patent/WO2017138220A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2016-11-25 US US15/774,318 patent/US10942711B2/en active Active
- 2016-11-25 JP JP2017566526A patent/JP6516025B2/ja active Active
-
2019
- 2019-04-17 JP JP2019078617A patent/JP6852748B2/ja active Active
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04153866A (ja) * | 1990-10-18 | 1992-05-27 | Fujitsu Ltd | ネットワーク編集方式 |
| JPH04190461A (ja) * | 1990-11-26 | 1992-07-08 | Fujitsu Ltd | ニューラルネットワークの構築表示方法 |
| JP2003029973A (ja) * | 1996-05-31 | 2003-01-31 | Toshiba Corp | システム構築装置 |
| JP2001282574A (ja) * | 2000-03-30 | 2001-10-12 | Oki Electric Ind Co Ltd | 処理時間情報を含む図式表現プログラムの表現方法 |
| JP2002268883A (ja) | 2001-03-13 | 2002-09-20 | Sony Corp | プログラム、記録媒体、ソフトウエア生成方法並びに情報処理装置 |
| WO2014139374A1 (en) * | 2013-03-15 | 2014-09-18 | International Business Machines Corporation | Quantized congestion notification in a virtual networking system |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| "IBM SPSS Neural Networks 21", IBM CORPORATION, 2012, XP055519659, [retrieved on 20161219] * |
| See also references of EP3416105A4 |
Cited By (54)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11740898B2 (en) | 2018-02-13 | 2023-08-29 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Computing device and method |
| US11620130B2 (en) | 2018-02-13 | 2023-04-04 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Computing device and method |
| US11630666B2 (en) | 2018-02-13 | 2023-04-18 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Computing device and method |
| US11663002B2 (en) | 2018-02-13 | 2023-05-30 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Computing device and method |
| US11609760B2 (en) | 2018-02-13 | 2023-03-21 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Computing device and method |
| US11704125B2 (en) | 2018-02-13 | 2023-07-18 | Cambricon (Xi'an) Semiconductor Co., Ltd. | Computing device and method |
| US12073215B2 (en) | 2018-02-13 | 2024-08-27 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Computing device with a conversion unit to convert data values between various sizes of fixed-point and floating-point data |
| US11709672B2 (en) | 2018-02-13 | 2023-07-25 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Computing device and method |
| US11720357B2 (en) | 2018-02-13 | 2023-08-08 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Computing device and method |
| JP7279705B2 (ja) | 2018-03-28 | 2023-05-23 | ソニーグループ株式会社 | 情報処理方法、情報処理装置、およびプログラム |
| WO2019187542A1 (ja) | 2018-03-28 | 2019-10-03 | ソニー株式会社 | 情報処理方法、情報処理装置、およびプログラム |
| JPWO2019187542A1 (ja) * | 2018-03-28 | 2021-04-15 | ソニー株式会社 | 情報処理方法、情報処理装置、およびプログラム |
| US12314866B2 (en) | 2018-07-17 | 2025-05-27 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Parallel processing of network model operations |
| US11966583B2 (en) | 2018-08-28 | 2024-04-23 | Cambricon Technologies Corporation Limited | Data pre-processing method and device, and related computer device and storage medium |
| US11703939B2 (en) | 2018-09-28 | 2023-07-18 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Signal processing device and related products |
| US12112462B2 (en) | 2018-11-30 | 2024-10-08 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and storage medium |
| WO2020110766A1 (ja) * | 2018-11-30 | 2020-06-04 | キヤノン株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及びプログラム |
| KR102190103B1 (ko) * | 2018-12-27 | 2020-12-11 | (주)아크릴 | 인공 신경망의 상용화 서비스 제공 방법 |
| KR20200080819A (ko) * | 2018-12-27 | 2020-07-07 | (주)아크릴 | 인공 신경망의 상용화 서비스 제공 방법 |
| US11544059B2 (en) | 2018-12-28 | 2023-01-03 | Cambricon (Xi'an) Semiconductor Co., Ltd. | Signal processing device, signal processing method and related products |
| JPWO2020166084A1 (ja) * | 2019-02-15 | 2021-03-11 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム |
| WO2020166641A1 (ja) * | 2019-02-15 | 2020-08-20 | ソニー株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法およびプログラム |
| WO2020166084A1 (ja) * | 2019-02-15 | 2020-08-20 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及び情報処理プログラム |
| JP2021165867A (ja) * | 2019-04-18 | 2021-10-14 | カンブリコン テクノロジーズ コーポレーション リミテッドCambricon Technologies Corporation Limited | データ処理方法および関連製品 |
| JP2021182176A (ja) * | 2019-04-18 | 2021-11-25 | カンブリコン テクノロジーズ コーポレーション リミテッドCambricon Technologies Corporation Limited | データ処理方法および関連製品 |
| CN111832739B (zh) * | 2019-04-18 | 2024-01-09 | 中科寒武纪科技股份有限公司 | 一种数据处理方法及相关产品 |
| CN111832737A (zh) * | 2019-04-18 | 2020-10-27 | 中科寒武纪科技股份有限公司 | 一种数据处理方法及相关产品 |
| US11847554B2 (en) | 2019-04-18 | 2023-12-19 | Cambricon Technologies Corporation Limited | Data processing method and related products |
| US11762690B2 (en) | 2019-04-18 | 2023-09-19 | Cambricon Technologies Corporation Limited | Data processing method and related products |
| JP7106513B2 (ja) | 2019-04-18 | 2022-07-26 | カンブリコン テクノロジーズ コーポレーション リミテッド | データ処理方法および関連製品 |
| KR102544522B1 (ko) * | 2019-04-18 | 2023-06-15 | 캠브리콘 테크놀로지스 코퍼레이션 리미티드 | 데이터 처리방법 및 관련제품 |
| CN111832739A (zh) * | 2019-04-18 | 2020-10-27 | 中科寒武纪科技股份有限公司 | 一种数据处理方法及相关产品 |
| US11934940B2 (en) | 2019-04-18 | 2024-03-19 | Cambricon Technologies Corporation Limited | AI processor simulation |
| JP7045357B2 (ja) | 2019-04-18 | 2022-03-31 | カンブリコン テクノロジーズ コーポレーション リミテッド | データ処理方法および関連製品 |
| JP7044808B2 (ja) | 2019-04-18 | 2022-03-30 | カンブリコン テクノロジーズ コーポレーション リミテッド | データ処理方法および関連製品 |
| KR20210142784A (ko) * | 2019-04-18 | 2021-11-26 | 캠브리콘 테크놀로지스 코퍼레이션 리미티드 | 데이터 처리방법 및 관련제품 |
| CN111832737B (zh) * | 2019-04-18 | 2024-01-09 | 中科寒武纪科技股份有限公司 | 一种数据处理方法及相关产品 |
| JP2021521500A (ja) * | 2019-04-18 | 2021-08-26 | カンブリコン テクノロジーズ コーポレーション リミテッドCambricon Technologies Corporation Limited | データ処理方法および関連製品 |
| JP2022539290A (ja) * | 2019-06-28 | 2022-09-08 | マイクロソフト テクノロジー ライセンシング,エルエルシー | ディープラーニングのためのビジュアルプログラミング |
| US12079600B2 (en) | 2019-06-28 | 2024-09-03 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Visual programming for deep learning |
| JP7571056B2 (ja) | 2019-06-28 | 2024-10-22 | マイクロソフト テクノロジー ライセンシング,エルエルシー | ディープラーニングのためのビジュアルプログラミング |
| US11681925B2 (en) | 2019-07-08 | 2023-06-20 | Vianai Systems, Inc. | Techniques for creating, analyzing, and modifying neural networks |
| JP7301210B2 (ja) | 2019-07-08 | 2023-06-30 | ヴィアナイ システムズ, インコーポレイテッド | ニューラルネットワークの動作を変更するための手法 |
| US11615321B2 (en) | 2019-07-08 | 2023-03-28 | Vianai Systems, Inc. | Techniques for modifying the operation of neural networks |
| US11640539B2 (en) | 2019-07-08 | 2023-05-02 | Vianai Systems, Inc. | Techniques for visualizing the operation of neural networks using samples of training data |
| JP2022540872A (ja) * | 2019-07-08 | 2022-09-20 | ヴィアナイ システムズ, インコーポレイテッド | ニューラルネットワークの動作を変更するための手法 |
| US12205003B2 (en) | 2019-08-26 | 2025-01-21 | Shanghai Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Data processing method and apparatus, and related product |
| JP7439242B2 (ja) | 2019-09-12 | 2024-02-27 | ヴィアナイ システムズ, インコーポレイテッド | 機械学習モデルの視覚的作成及び監視 |
| JP2022547668A (ja) * | 2019-09-12 | 2022-11-15 | ヴィアナイ システムズ, インコーポレイテッド | 機械学習モデルの視覚的作成及び監視 |
| US12333671B2 (en) | 2020-02-24 | 2025-06-17 | Cambricon Technologies Corporation Limited | Data quantization processing method and apparatus, electronic device and storage medium |
| US12504951B2 (en) | 2020-03-17 | 2025-12-23 | Anhui Cambricon Information Technology Co., Ltd | Computing device and method for processing multi-bit width data |
| CN111736836B (zh) * | 2020-07-22 | 2020-11-17 | 平安国际智慧城市科技股份有限公司 | 基于关系图的组件配置方法、装置及计算机可读存储介质 |
| CN111736836A (zh) * | 2020-07-22 | 2020-10-02 | 平安国际智慧城市科技股份有限公司 | 基于关系图的组件配置方法、装置及计算机可读存储介质 |
| EP4290428A4 (en) * | 2021-02-03 | 2024-07-10 | Sony Group Corporation | SERVER DEVICE, GENERATION METHOD, ELECTRONIC EQUIPMENT GENERATION METHOD, DATABASE GENERATION METHOD, AND ELECTRONIC EQUIPMENT |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3416105A4 (en) | 2019-02-20 |
| EP3416105A1 (en) | 2018-12-19 |
| US20200257506A1 (en) | 2020-08-13 |
| JPWO2017138220A1 (ja) | 2018-11-29 |
| JP6516025B2 (ja) | 2019-05-22 |
| JP6852748B2 (ja) | 2021-03-31 |
| US10942711B2 (en) | 2021-03-09 |
| JP2019139792A (ja) | 2019-08-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6852748B2 (ja) | 情報処理方法および情報処理装置 | |
| JP6574942B2 (ja) | 情報処理方法および情報処理装置 | |
| CN112424769B (zh) | 用于地理位置预测的系统和方法 | |
| US11367050B2 (en) | Digital processing systems and methods for customized chart generation based on table data selection in collaborative work systems | |
| JP6922945B2 (ja) | 情報処理方法 | |
| EP3623961A1 (en) | Predictive modeling with machine learning in data management platforms | |
| US20190057309A1 (en) | Information processing apparatus and information processing method | |
| CN108604314A (zh) | 使用强化学习选择动作名单 | |
| WO2019035364A1 (ja) | プログラム、情報処理方法、および情報処理装置 | |
| CN113490955B (zh) | 用于产生金字塔层的架构的系统和方法 | |
| TW202338648A (zh) | 建築環境中計算模擬及擴增/虛擬實境系統與方法 | |
| US12159364B2 (en) | User-interactivity enabled search filter tool optimized for virtualized worlds | |
| JP2025134676A (ja) | ポインティングデバイスおよびキーボードアクションを使用する学習されたコンピュータ制御 | |
| Amiri et al. | The Patterns of Life Human Mobility Simulation | |
| Nguyen et al. | A Web-based System for Business Process Discovery: Leveraging the SICN-Oriented Process Mining Algorithm with Django, Cytoscape, and Graphviz. | |
| CN110263250B (zh) | 一种推荐模型的生成方法及装置 | |
| CN113572679B (zh) | 账户亲密度的生成方法、装置、电子设备和存储介质 | |
| JPWO2019187542A1 (ja) | 情報処理方法、情報処理装置、およびプログラム | |
| CN117744808A (zh) | 一种基于因果效应估计模型的决策方法、装置及相关设备 | |
| CN109726232A (zh) | 一种模型可视化计算方法及系统 | |
| CN114240172A (zh) | 一种辅助决策方法、装置、设备及介质 | |
| Liu | [Retracted] Fractal Art Pattern Generation Based on Genetic Algorithm | |
| CN109313718A (zh) | 交互网络 | |
| Xue | Research on cultivating students’ creative thinking ability in art design teaching based on machine learning | |
| Halıcı et al. | AI-based augmented reality for architectural mass study |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 16889921 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2017566526 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2016889921 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2016889921 Country of ref document: EP Effective date: 20180912 |