WO2017118315A1 - 一种智能卡应用安全验证方法及装置 - Google Patents
一种智能卡应用安全验证方法及装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017118315A1 WO2017118315A1 PCT/CN2016/112265 CN2016112265W WO2017118315A1 WO 2017118315 A1 WO2017118315 A1 WO 2017118315A1 CN 2016112265 W CN2016112265 W CN 2016112265W WO 2017118315 A1 WO2017118315 A1 WO 2017118315A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- smart card
- related data
- current service
- application
- security
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q20/00—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols
- G06Q20/38—Payment protocols; Details thereof
- G06Q20/40—Authorisation, e.g. identification of payer or payee, verification of customer or shop credentials; Review and approval of payers, e.g. check credit lines or negative lists
- G06Q20/409—Device specific authentication in transaction processing
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F21/00—Security arrangements for protecting computers, components thereof, programs or data against unauthorised activity
- G06F21/30—Authentication, i.e. establishing the identity or authorisation of security principals
- G06F21/31—User authentication
- G06F21/34—User authentication involving the use of external additional devices, e.g. dongles or smart cards
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F21/00—Security arrangements for protecting computers, components thereof, programs or data against unauthorised activity
- G06F21/30—Authentication, i.e. establishing the identity or authorisation of security principals
- G06F21/44—Program or device authentication
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q20/00—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols
- G06Q20/30—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols characterised by the use of specific devices or networks
- G06Q20/32—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols characterised by the use of specific devices or networks using wireless devices
- G06Q20/327—Short range or proximity payments by means of M-devices
- G06Q20/3278—RFID or NFC payments by means of M-devices
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q20/00—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols
- G06Q20/30—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols characterised by the use of specific devices or networks
- G06Q20/34—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols characterised by the use of specific devices or networks using cards, e.g. integrated circuit [IC] cards or magnetic cards
- G06Q20/341—Active cards, i.e. cards including their own processing means, e.g. including an IC or chip
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q20/00—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols
- G06Q20/30—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols characterised by the use of specific devices or networks
- G06Q20/34—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols characterised by the use of specific devices or networks using cards, e.g. integrated circuit [IC] cards or magnetic cards
- G06Q20/352—Contactless payments by cards
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q20/00—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols
- G06Q20/38—Payment protocols; Details thereof
- G06Q20/40—Authorisation, e.g. identification of payer or payee, verification of customer or shop credentials; Review and approval of payers, e.g. check credit lines or negative lists
- G06Q20/401—Transaction verification
- G06Q20/4016—Transaction verification involving fraud or risk level assessment in transaction processing
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W12/00—Security arrangements; Authentication; Protecting privacy or anonymity
- H04W12/12—Detection or prevention of fraud
- H04W12/126—Anti-theft arrangements, e.g. protection against subscriber identity module [SIM] cloning
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/80—Services using short range communication, e.g. near-field communication [NFC], radio-frequency identification [RFID] or low energy communication
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W12/00—Security arrangements; Authentication; Protecting privacy or anonymity
- H04W12/60—Context-dependent security
- H04W12/61—Time-dependent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W12/00—Security arrangements; Authentication; Protecting privacy or anonymity
- H04W12/60—Context-dependent security
- H04W12/63—Location-dependent; Proximity-dependent
Definitions
- the present application relates to the field of information security technologies, and in particular, to a smart card application security verification method and apparatus.
- a smart card application security verification method and device are proposed, which are used to limit the use of the smart card application according to the user setting or the user's usage habits. This ensures the security of the smart card application.
- the embodiment of the present application specifically provides a smart card application security verification method, including
- the embodiment of the present application further provides a smart card application security verification apparatus, including
- An obtaining unit configured to acquire current service related data during a process in which the smart card application performs business with the outside world
- a determining unit configured to determine the current service related data and security parameters
- the processing unit is configured to terminate the current service if the current service related data does not meet the security parameter.
- the geographical location, time, and transaction letter when the service is performed can further ensure the security when using the smart card application for business; and according to different types of smart card applications (eSE chip or HCE, etc.), a security verification method suitable for different types of smart card applications is designed. For example, the business process between the smart card application and the communication module in the eSE chip is obtained, thereby performing verification, or performing security verification on the service through a security verification method built in the HCE smart card application.
- FIG. 1 is a flowchart of a smart card application security verification method according to an embodiment of the present application
- FIG. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of a smart card application security verification apparatus according to an embodiment of the present application
- FIG. 3 is a specific flowchart of a smart card application security verification method according to an embodiment of the present application
- FIG. 4 is a structural diagram of a system for installing a smart card application into an eSE chip according to an embodiment of the present application
- FIG. 5 is a specific flowchart of another smart card application security verification method according to an embodiment of the present application.
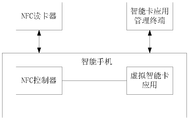
- FIG. 6 is a structural diagram of a system for installing a smart card application into a smart phone according to an embodiment of the present application.
- the embodiment of the present application provides a smart card application security verification method and device.
- the smart card application in the present application includes applications such as access control, transportation card, bank card, etc., and an eSE chip (embedded secure element) is set in the smart terminal, and the smart card application is placed in the eSE chip, or through the HCE (The card analog technology is used to implement the smart card application.
- applications such as access control, transportation card, bank card, etc.
- an eSE chip embedded secure element
- HCE The card analog technology is used to implement the smart card application.
- FIG. 1 is a flowchart of a smart card application security verification method according to an embodiment of the present application.
- the intelligent terminal determines whether the current service is secure according to the determination rule, and if the security is not secure, the service is interrupted, otherwise the service is allowed to continue, and the determination rule may be based on the location information and the time information.
- the judgment of the information such as the service content can be set by the user, or the system can be statistically analyzed and then sent to the intelligent terminal.
- the smart card application can be securely controlled by the above method to prevent the harm of the smart terminal after being lost.
- the figure specifically includes a step 101 of acquiring current service related data in a process in which the smart card application performs a service with the outside world.
- Step 102 Determine the current service related data and security parameters.
- Step 103 If the current service related data does not meet the security parameter, terminate the current service.
- the method further includes allowing the current service to continue if the current service related data meets the security parameter.
- the current service can be interrupted or authorized, so that the security of the current service performed by the smart card application can be further ensured.
- the current service related data includes at least a combination of one or more of current location information, current time information, and transaction information.
- the current location information may be determined with the location information set in the security parameter, and if the location range set in the security parameter is exceeded, the service should not be allowed to continue, for example, when the smart card application is in service The current location is Tianjin, and the location range in the security parameters set by the user is Beijing. It is considered that the service performed by the smart card application is not secure; or, when the smart card application is conducting business transactions, the payment is 1000 yuan, and If the transaction information of the security parameter set by the user is 800 yuan, it is considered that the current service performed by the smart card application is not secure.
- the current service related data may obtain current location information through a GPS module of the smart terminal or a positioning manner of the base station, obtain current time information through a system clock or a network clock, and obtain transaction information through a transaction order.
- a GPS module of the smart terminal or a positioning manner of the base station
- current time information may also be referred to the specific solution in the prior art, and details are not described herein again.
- the acquiring current service related data further includes a smart card application and an NFC (near field communication) embedded in the eSE chip (embedded secure component).
- NFC near field communication
- the communication process of the controller monitors the communication process of both parties and obtains current business related data.
- the method in the embodiment of the present application may be implemented in a software manner or in a hardware module manner, and the method for acquiring current service related data and subsequent judgment analysis and the like is to monitor the eSE chip.
- Smart card application and NFC controller (or similar communication module used by other smart card applications) The communication process is activated, or the NFC controller can notify the security verification application of the present application in a certain service process, that is, the security verification method of the embodiment of the present application monitors the smart card application and the NFC control in the eSE chip. Whether service processing is in progress between the devices, and if there is business processing, security verification is started.
- This embodiment can also obtain current service related data and subsequent steps in any process in which the smart card application communicates with the NFC controller, for example, performing security verification before the NFC controller forwards the service instruction to the smart card application.
- acquiring the current service related data further includes: in the process of the virtual smart card application (HCE) and the NFC controller, in the virtual smart card
- HCE virtual smart card application
- NFC controller in the virtual smart card The application monitors the communication process of both parties and obtains current business related data.
- the security verification method of the present application may be added to the application, and the application may be performed in the application of the simulated smart card.
- the security verification method of the embodiment of the present application is performed before or after any step, and when the security verification is passed, the business process can be continued, otherwise the business process will be interrupted.
- the method before determining the current service related data and the security parameter, the method further includes: receiving and saving a security parameter input by the user;
- the security parameter may be set by the user, or may be determined by the server based on the analysis of the historical behavior of the user, for example, by statistically analyzing the user to appear in the A area, and the location information of the current service is A. In the area, the service may be considered to be a security risk, and the user's current service may be rejected.
- the service is access control authentication
- the user never requests to enter the A area, and the request is to enter the A area. It may be due to the loss of the mobile phone with the access control smart card application and the behavior of being picked up.
- the judgment of the geographical location, time, transaction information and the like of the service may further ensure the security when using the smart card application for business; and according to different types of smart card applications (eSE chips) Or HCE, etc., designed a security verification method suitable for different types of smart card applications, such as obtaining a business process between a smart card application and a communication module in an eSE chip, thereby performing verification, or performing security verification built in an HCE smart card application.
- the method is to perform security verification on the business.
- FIG. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of a smart card application security verification apparatus according to an embodiment of the present application.
- the apparatus in this embodiment may be built in and run on a smart terminal, where the smart terminal includes, for example, a smart phone, a tablet computer, and the like.
- the smart card application verification device may be implemented by a dedicated chip such as a programmable logic device (FPGA) or by software in an analog smart card application (HCE).
- FPGA programmable logic device
- HCE analog smart card application
- the figure specifically includes an obtaining unit 201, which is used in the process of processing a smart card application with the outside world. Take current business related data.
- the determining unit 202 is configured to determine the current service related data and the security parameter.
- the processing unit 203 is configured to terminate the current service if the current service related data does not meet the security parameter.
- the processing unit is further configured to allow the current service to continue if the current service related data meets the security parameter.
- the current service related data includes at least a combination of one or more of current location information, current time information, and transaction information.
- the current location information may be obtained by a GPS module inside the smart terminal, and the current time information may be obtained by using a network communication module, or obtained by a clock crystal inside the smart terminal, and the transaction information may be through a transaction order of the smart terminal. obtain.
- the acquisition unit monitors a communication process of a smart card application built in an eSE chip (embedded secure element) and an NFC (Near Field Communication Unit) controller, and acquires current service related data.
- eSE chip embedded secure element
- NFC Near Field Communication Unit
- the acquiring unit is built in an application of the virtual smart card, and acquires current service related data in a communication process between the application (HCE) of the virtual smart card and the NFC controller.
- a security parameter receiving unit 204 is further included, configured to receive and save a security parameter input by the user;
- the judgment of the geographical location, time, transaction information and the like of the service may further ensure the security when using the smart card application for business; and according to different types of smart card applications (eSE chips) Or HCE, etc., designed a security verification method suitable for different types of smart card applications, such as obtaining a business process between a smart card application and a communication module in an eSE chip, thereby performing verification, or performing security verification built in an HCE smart card application.
- the method is to perform security verification on the business.
- FIG. 3 is a specific flowchart of a smart card application security verification method according to an embodiment of the present application.
- the smart card application in the figure is built in an eSE security chip, and the smart terminal in this embodiment may be a smart phone.
- the card device can be an NFC card reader installed on the POS machine, and the NFC controller is hardware on the smart phone for communicating with the NFC card reader on the POS machine to complete the payment service.
- the device in the embodiment of the present application or the method running in software is built in the smart phone, and the payment service processing process between the smart card application and the NFC controller is monitored, thereby achieving the purpose of performing security verification on the payment service.
- the method includes the following steps: the payment application built in the eSE chip is registered on the NFC controller, and is in the NFC. A payment application ID is recorded in the controller.
- the smart card application can be installed into the eSE chip through the smart card application management terminal, or installed into the eSE chip through the network through the air card issuing unit (which can be built in the eSE chip of the smart phone), and the specific system structure diagram can be as shown in the figure. 4, wherein the NFC card reader on the POS communicates with the NFC controller of the smart phone by means of near field communication, and the smart card application management terminal also installs the smart card application to the eSE chip of the smart phone through the near field communication method.
- the smart card application can also be installed in the eSE chip through the air card issuing unit.
- the security verification application in the present application is also built in the smart phone, and the communication between the eSE chip and the NFC controller is monitored.
- the application can also monitor communication between the eSE chip and the NFC controller through a communication interface in the NFC controller.
- the user can input security parameters in the security verification application of the present application embedded in the smart phone through the input device of the smart phone, such as a touch screen, a button, etc., wherein the security parameter is in the smart card.
- the payment application may be, for example, a location location or a range, a transaction amount threshold, or the like, or may increase or decrease the setting of the security parameter according to actual needs.
- the location is defined as area A, area B, and C.
- the region and the three areas along the way are payment applications that allow the use of smart cards.
- the payment application is prohibited in other regions.
- the transaction amount threshold can be, for example, 1000 pieces, that is, no more than 1000 is allowed in any area.
- Step 302 The NFC card reader of the POS machine communicates with the NFC controller of the smart phone to perform a payment service.
- the payment service processing procedure between the NFC card reader and the NFC controller can refer to the solution in the prior art.
- the NFC card reader selects the payment application ID registered in the NFC controller, and then executes the corresponding Smart card payment business process.
- Step 303 The NFC controller sends a prompt for the payment service to the security verification application to start the security verification application.
- Step 304 The security verification application built in the smart phone acquires payment service related data.
- the security verification application can obtain payment service related data through the interface of the NFC controller, and the payment application does not obtain the payment service related data.
- the payment service related data includes current location information and current transaction amount.
- the security verification application The current location information is obtained by using the GPS module in the smart phone, or the current location information can be obtained by way of base station positioning or network positioning, and the transaction amount can be obtained by the intercepted service processing result.
- Step 305 Verify the current location information and the current transaction amount according to the security parameters.
- the intercepted location information is the D area
- the transaction amount is 2000 yuan
- the payment service related data is compared with the limited position and the transaction amount threshold in the security parameter, and the judgment result is that the security parameter is not met.
- Step 306 The security verification application terminates the payment service, and sends the execution result of the failure of the payment service to the NFC controller.
- the result of the security verification can also be prompted to the user through the screen of the smartphone.
- the payment service is allowed to continue (ie, does not act), and does not interfere with the payment service process performed by the smart card application in the NFC controller and the eSE chip, which is dotted in the figure.
- the mode displays a process of allowing the payment application to perform service processing when the payment service is continued, and the NFC controller forwards the payment service instruction to the payment application built in the eSE chip, the payment application performs business processing, and passes the NFC controller to the NFC card reader.
- the service processing result is returned, and the payment application may have multiple communications with the NFC card reader, so that the payment service process runs smoothly, but this part of the content is not described in the prior art as in the prior art.
- Step 307 The NFC controller sends the execution result of the failure of the payment service to the POS machine NFC card reader, and the payment fails.
- the technical solution of the present application can control the smart card application according to the security parameter set by the user, and when the service is not authorized (that is, other than the security parameter), the service processing of the unsecure smart card application is terminated in time.
- the security of the user's property and information is guaranteed, and the loss caused by the malicious use of the smart terminal after being lost by others is avoided.
- FIG. 5 is a specific flowchart of another smart card application security verification method according to an embodiment of the present application.
- a virtual smart card application is taken as an example to introduce the technical solution of the present application.
- the virtual smart card is mainly for some without built-in eSE.
- the smart terminal of the chip enables the smart terminal to support the smart card application.
- the security verification method or device of the present application can be built in the virtual smart card application, so that the virtual smart card application can be securely verified.
- the payment service is used as a description
- the smart terminal is a smart phone
- the POS machine card reader is an NFC card reader
- the smart phone communicates with the NFC card reader through the NFC controller.
- Other modes of near field communication technology can also be used for communication, which is not limited herein.
- step 501 the virtual smart card application registers the payment application ID in the NFC controller.
- the virtual smart card application can be installed into the storage of the smart phone through the smart card application management terminal.
- the specific system structure diagram can be as shown in FIG. 6, wherein the NFC card reader on the POS machine communicates with the NFC controller of the smart phone through near field communication, and the smart card application management terminal also passes the near field communication mode.
- the virtual smart card application is installed in the memory of the smart phone, or the virtual smart card application can be installed in the smart phone through the networking function of the smart phone.
- the security verification application of the present application can be built in the virtual smart card application.
- Step 502 the NFC card reader of the POS machine communicates with the NFC controller, and selects the virtual smart card application ID to perform the payment service.
- Step 503 The NFC controller sends an instruction to perform a payment service to the virtual smart card application.
- Step 504 The security verification application in the virtual smart card application can obtain current location information and current time information.
- the current location information may be obtained by using a GPS module in the smart phone, or the current location information may be obtained by means of a base station positioning manner or a network positioning manner; the current time information may be obtained through a system time of the smart phone. Or you can get it from the Internet through the networking function of your smartphone.
- Step 505 Obtain the security parameter of the user from the remote server by using a communication module of the smart phone.
- the security parameters in this step are obtained from the remote server through the Internet, and the remote server obtains corresponding security parameters by analyzing the historical data of the user, or by analyzing the big data related to the user, for example, by using the security parameter.
- the user's daily payment transaction habits, amount, location, time, product category and other data are analyzed to obtain the user security parameters.
- the security risk of the transaction is determined in the electronic transaction field.
- the specific safety parameter calculation method involved can refer to the content in the prior art, and only the prior art of this part is utilized here.
- the method for obtaining the security parameter in the embodiment and the method for setting the security parameter by the user in the embodiment shown in FIG. 3 are interchangeable.
- Step 506 Verify current location information and current time information of the current payment service according to the security parameter.
- the user If the location information in the security parameter is different from the current location information, and the time information in the security parameter is different from the current time information, the user usually does not perform the payment service at the current time and the current location, and the payment service may not be the user himself. Implementation, there may be risks.
- step 507 the payment service is terminated, and the corresponding service processing result is generated and transmitted to the NFC controller.
- step 506 If the result of the above step 506 is a secure payment service, the payment service flow of the virtual smart card application is continued, and the NFC controller may perform one or several communication with the POS-level NFC card reader during the period, and the payment service flow has been completed.
- Step 508 The NFC controller sends the payment service processing result to the NFC card reader of the POS machine.
- the method and the device in the foregoing embodiments of the present application determine the location, time, transaction information and the like of the service, and can further ensure the security when using the smart card application for service; and according to the smart card application.
- Types eSE chips or HCE, etc.
- Security verification method to securely verify the business.
- PLD Programmable Logic Device
- FPGA Field Programmable Gate Array
- HDL Hardware Description Language
- the controller can be implemented in any suitable manner, for example, the controller can take the form of, for example, a microprocessor or processor and a computer readable medium storing computer readable program code (eg, software or firmware) executable by the (micro)processor.
- computer readable program code eg, software or firmware
- examples of controllers include, but are not limited to, the following microcontrollers: ARC 625D, Atmel AT91SAM, Microchip PIC18F26K20 and Silicone Labs C8051F320,
- the memory controller can also be implemented as part of the control logic of the memory.
- the controller can be logically programmed by means of logic gates, switches, ASICs, programmable logic controllers, and embedding.
- Such a controller can therefore be considered a hardware component, and the means for implementing various functions included therein can also be considered as a structure within the hardware component.
- a device for implementing various functions can be considered as a software module that can be both a method of implementation and a structure within a hardware component.
- the system, device, module or unit illustrated in the above embodiments may be implemented by a computer chip or an entity, or by a product having a certain function.
- the present application can be implemented by means of software plus a necessary general hardware platform. Based on such understanding, the technical solution of the present application may be embodied in the form of a software product in essence or in the form of a software product, which may be stored in a storage medium such as a ROM/RAM or a disk. , an optical disk, etc., includes instructions for causing a computer device (which may be a personal computer, server, or network device, etc.) to perform the methods described in various embodiments of the present application or portions of the embodiments.
- a computer device which may be a personal computer, server, or network device, etc.
- This application can be used in a variety of general purpose or special purpose computer system environments or configurations.
- the application can be described in the general context of computer-executable instructions executed by a computer, such as a program module.
- program modules include routines, programs, objects, components, data structures, and the like that perform particular tasks or implement particular abstract data types.
- the present application can also be practiced in distributed computing environments where tasks are performed by remote processing devices that are connected through a communication network.
- program modules can be located in both local and remote computer storage media including storage devices.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Accounting & Taxation (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Finance (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Telephone Function (AREA)
- Financial Or Insurance-Related Operations Such As Payment And Settlement (AREA)
- Storage Device Security (AREA)
Priority Applications (7)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP16883440.6A EP3401823B1 (en) | 2016-01-05 | 2016-12-27 | Security verification method and device for smart card application |
| SG11201805753QA SG11201805753QA (en) | 2016-01-05 | 2016-12-27 | Security verification method and device for smart card application |
| JP2018535112A JP2019501461A (ja) | 2016-01-05 | 2016-12-27 | スマートカードアプリケーションのためのセキュリティ検証方法及びデバイス |
| KR1020187022639A KR102125159B1 (ko) | 2016-01-05 | 2016-12-27 | 스마트 카드 응용을 위한 보안 검증 방법 및 디바이스 |
| MYPI2018702345A MY197570A (en) | 2016-01-05 | 2016-12-27 | Security verification method and device for smart card application |
| US16/027,083 US11127019B2 (en) | 2016-01-05 | 2018-07-03 | Security verification method and device for smart card application |
| PH12018501427A PH12018501427A1 (en) | 2016-01-05 | 2018-07-04 | Security verification method and device for smart card application |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201610006062.2A CN106940767A (zh) | 2016-01-05 | 2016-01-05 | 一种智能卡应用安全验证方法及装置 |
| CN201610006062.2 | 2016-01-05 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/027,083 Continuation US11127019B2 (en) | 2016-01-05 | 2018-07-03 | Security verification method and device for smart card application |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017118315A1 true WO2017118315A1 (zh) | 2017-07-13 |
Family
ID=59273243
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2016/112265 Ceased WO2017118315A1 (zh) | 2016-01-05 | 2016-12-27 | 一种智能卡应用安全验证方法及装置 |
Country Status (10)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11127019B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP3401823B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP2019501461A (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR102125159B1 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN106940767A (enExample) |
| MY (1) | MY197570A (enExample) |
| PH (1) | PH12018501427A1 (enExample) |
| SG (1) | SG11201805753QA (enExample) |
| TW (1) | TWI744267B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2017118315A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN119255211A (zh) * | 2024-09-30 | 2025-01-03 | 支付宝(杭州)信息技术有限公司 | 交通工具搭乘业务处理方法、装置以及设备 |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11704663B2 (en) * | 2017-03-31 | 2023-07-18 | Vijay Madisetti | Method and system for blockchain-based vehicle identifiers and wallets for decentralized payments |
| CN108734005B (zh) * | 2018-02-09 | 2021-02-09 | 深圳市微付充科技有限公司 | 一种安全/身份验证方法、移动设备及存储装置 |
| US11196737B2 (en) | 2019-04-30 | 2021-12-07 | Bank Of America Corporation | System for secondary authentication via contactless distribution of dynamic resources |
| US10998937B2 (en) | 2019-04-30 | 2021-05-04 | Bank Of America Corporation | Embedded tag for resource distribution |
| US11234235B2 (en) * | 2019-04-30 | 2022-01-25 | Bank Of America Corporation | Resource distribution hub generation on a mobile device |
| WO2021022204A1 (en) * | 2019-07-31 | 2021-02-04 | Iigc, Inc. | Image-based authorization and transmission of stored value or sim cards |
| TWI726488B (zh) * | 2019-11-19 | 2021-05-01 | 元太科技工業股份有限公司 | 非接觸式智慧卡及其操作方法 |
| CN111682883A (zh) * | 2020-06-05 | 2020-09-18 | 桂林微网互联信息技术有限公司 | 独立安全卡以及用于使用独立安全卡的终端设备 |
| CN114726407B (zh) * | 2022-05-17 | 2022-08-26 | 北京紫光青藤微系统有限公司 | 用于获取异常信息的方法、装置、控制器及存储介质 |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20100145819A1 (en) * | 2004-11-08 | 2010-06-10 | Pantech Co., Ltd. | Wireless communication terminal suspending interrupt during rf payment and method thereof |
| CN102855560A (zh) * | 2011-06-29 | 2013-01-02 | 国民技术股份有限公司 | 一种移动支付方法及系统 |
| CN103065240A (zh) * | 2013-01-11 | 2013-04-24 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 一种移动支付处理方法和系统 |
| CN104504568A (zh) * | 2014-12-26 | 2015-04-08 | 网易宝有限公司 | 支付模式控制方法和设备 |
| CN104751329A (zh) * | 2015-02-28 | 2015-07-01 | 深圳市中兴移动通信有限公司 | 一种移动支付终端、移动支付系统及移动支付方法 |
Family Cites Families (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4899274B2 (ja) * | 2001-08-30 | 2012-03-21 | 富士通株式会社 | 携帯型端末及び機能抑制方法 |
| US10176476B2 (en) * | 2005-10-06 | 2019-01-08 | Mastercard Mobile Transactions Solutions, Inc. | Secure ecosystem infrastructure enabling multiple types of electronic wallets in an ecosystem of issuers, service providers, and acquires of instruments |
| FR2934910B1 (fr) * | 2008-08-05 | 2013-08-16 | Inside Contactless | Procede de securisation d'une transaction executee au moyen d'un dispositif portable programmable. |
| CN101789151A (zh) * | 2009-12-31 | 2010-07-28 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 移动终端电子钱包的应用方法及移动终端 |
| JP2012088952A (ja) * | 2010-10-20 | 2012-05-10 | Nec Casio Mobile Communications Ltd | 携帯端末、決済システム、決済方法、およびプログラム |
| US20120166332A1 (en) * | 2010-12-22 | 2012-06-28 | Ebay Inc. | Bill splitting system |
| US20120197793A1 (en) * | 2011-01-31 | 2012-08-02 | Bank Of America Corporation | Dependent notification alert |
| TWI483627B (zh) * | 2011-05-19 | 2015-05-01 | Chi Mei Comm Systems Inc | 具有nfc保護功能之移動設備及其保護方法 |
| US11232447B2 (en) * | 2013-03-15 | 2022-01-25 | Allowify Llc | System and method for enhanced transaction authorization |
| CN105339965A (zh) * | 2013-04-25 | 2016-02-17 | 奥夫拉自我安全有限公司 | 自认证 |
| CN104182870B (zh) * | 2013-05-24 | 2017-12-15 | 中国银联股份有限公司 | 一种基于手机钱包的安全支付方法以及支付系统 |
| US9811830B2 (en) * | 2013-07-03 | 2017-11-07 | Google Inc. | Method, medium, and system for online fraud prevention based on user physical location data |
| US9390242B2 (en) * | 2014-02-07 | 2016-07-12 | Bank Of America Corporation | Determining user authentication requirements based on the current location of the user being within a predetermined area requiring altered authentication requirements |
| CN104132870B (zh) | 2014-07-10 | 2017-03-15 | 上海大学 | 表面张力和表面面积粘性测定装置 |
| CN104794615A (zh) * | 2015-05-11 | 2015-07-22 | 易联支付有限公司 | 一种手机支付安全验证方法 |
-
2016
- 2016-01-05 CN CN201610006062.2A patent/CN106940767A/zh active Pending
- 2016-12-19 TW TW105142083A patent/TWI744267B/zh not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2016-12-27 MY MYPI2018702345A patent/MY197570A/en unknown
- 2016-12-27 SG SG11201805753QA patent/SG11201805753QA/en unknown
- 2016-12-27 JP JP2018535112A patent/JP2019501461A/ja active Pending
- 2016-12-27 KR KR1020187022639A patent/KR102125159B1/ko active Active
- 2016-12-27 EP EP16883440.6A patent/EP3401823B1/en active Active
- 2016-12-27 WO PCT/CN2016/112265 patent/WO2017118315A1/zh not_active Ceased
-
2018
- 2018-07-03 US US16/027,083 patent/US11127019B2/en active Active
- 2018-07-04 PH PH12018501427A patent/PH12018501427A1/en unknown
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20100145819A1 (en) * | 2004-11-08 | 2010-06-10 | Pantech Co., Ltd. | Wireless communication terminal suspending interrupt during rf payment and method thereof |
| CN102855560A (zh) * | 2011-06-29 | 2013-01-02 | 国民技术股份有限公司 | 一种移动支付方法及系统 |
| CN103065240A (zh) * | 2013-01-11 | 2013-04-24 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 一种移动支付处理方法和系统 |
| CN104504568A (zh) * | 2014-12-26 | 2015-04-08 | 网易宝有限公司 | 支付模式控制方法和设备 |
| CN104751329A (zh) * | 2015-02-28 | 2015-07-01 | 深圳市中兴移动通信有限公司 | 一种移动支付终端、移动支付系统及移动支付方法 |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN119255211A (zh) * | 2024-09-30 | 2025-01-03 | 支付宝(杭州)信息技术有限公司 | 交通工具搭乘业务处理方法、装置以及设备 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20180315048A1 (en) | 2018-11-01 |
| KR102125159B1 (ko) | 2020-06-22 |
| EP3401823A1 (en) | 2018-11-14 |
| MY197570A (en) | 2023-06-26 |
| JP2019501461A (ja) | 2019-01-17 |
| TW201730804A (zh) | 2017-09-01 |
| TWI744267B (zh) | 2021-11-01 |
| EP3401823B1 (en) | 2022-10-12 |
| PH12018501427A1 (en) | 2019-01-28 |
| EP3401823A4 (en) | 2018-11-14 |
| CN106940767A (zh) | 2017-07-11 |
| KR20180109919A (ko) | 2018-10-08 |
| US11127019B2 (en) | 2021-09-21 |
| SG11201805753QA (en) | 2018-08-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2017118315A1 (zh) | 一种智能卡应用安全验证方法及装置 | |
| US11316702B2 (en) | Verification-based service authorization | |
| KR102216877B1 (ko) | 전자장치에서 생체 정보를 이용한 인증 방법 및 장치 | |
| CN107278313B (zh) | 支付手段操作支持方法和用于支持该方法的电子设备 | |
| CN105894268B (zh) | 支付处理方法及支付其的电子设备 | |
| KR102388512B1 (ko) | 통신 소프트웨어에서 음성으로 비즈니스를 활성화하는 방법 및 대응 장치 | |
| US10572007B2 (en) | Preventing unintended input | |
| US20170103382A1 (en) | Method of providing payment service and electronic device for implementing same | |
| KR101654778B1 (ko) | 하드웨어 강제 액세스 보호 | |
| US20210240807A1 (en) | Authentication method for mobile terminal and mobile terminal | |
| CN104424028A (zh) | 终端设备以及切换方法 | |
| WO2015117332A1 (zh) | 一种usb调试模式接口启动的方法、装置及终端 | |
| CN103870336A (zh) | 数据处理设备的基于优先级的应用运行方法及装置 | |
| TWI706288B (zh) | 穿戴式設備、解鎖控制系統及解鎖控制方法 | |
| CN108305065A (zh) | 数据处理方法、终端设备和数据处理系统 | |
| CN108319826A (zh) | 一种身份验证的方法、装置及设备 | |
| WO2017161735A1 (zh) | 用户管理方法、用户管理系统和用户终端 | |
| CN104427097A (zh) | 终端设备以及切换方法 | |
| KR20180040904A (ko) | 전자 장치 및 그의 동작 방법 | |
| HK1238741A1 (en) | Security verification method and device for smart card application | |
| HK1238741A (en) | Security verification method and device for smart card application | |
| CN107124388B (zh) | 一种业务与算法解耦的方法、装置及系统 | |
| WO2014169036A1 (en) | Detecting physical gestures for mobile device security | |
| CN112740204A (zh) | 在密码输入中的数据处理方法、数据处理装置及电子设备 | |
| CN106295268A (zh) | 信息处理方法和电子设备 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 16883440 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 11201805753Q Country of ref document: SG Ref document number: 12018501427 Country of ref document: PH |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2018535112 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20187022639 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2016883440 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2016883440 Country of ref document: EP Effective date: 20180806 |