WO2016180369A1 - 数据发送和接收方法以及数据发送和接收设备 - Google Patents
数据发送和接收方法以及数据发送和接收设备 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2016180369A1 WO2016180369A1 PCT/CN2016/082096 CN2016082096W WO2016180369A1 WO 2016180369 A1 WO2016180369 A1 WO 2016180369A1 CN 2016082096 W CN2016082096 W CN 2016082096W WO 2016180369 A1 WO2016180369 A1 WO 2016180369A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- predetermined number
- symbol
- stream
- code division
- data
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04J—MULTIPLEX COMMUNICATION
- H04J13/00—Code division multiplex systems
- H04J13/0003—Code application, i.e. aspects relating to how codes are applied to form multiplexed channels
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/08—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by repeating transmission, e.g. Verdan system
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L27/00—Modulated-carrier systems
- H04L27/32—Carrier systems characterised by combinations of two or more of the types covered by groups H04L27/02, H04L27/10, H04L27/18 or H04L27/26
- H04L27/34—Amplitude- and phase-modulated carrier systems, e.g. quadrature-amplitude modulated carrier systems
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/70—Services for machine-to-machine communication [M2M] or machine type communication [MTC]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W72/00—Local resource management
- H04W72/20—Control channels or signalling for resource management
- H04W72/23—Control channels or signalling for resource management in the downlink direction of a wireless link, i.e. towards a terminal
Definitions
- the present invention relates to the field of wireless communications, and in particular to a data transmitting method and data receiving method and a data transmitting device and a data receiving device that can be used in a wireless communication system, particularly a machine type communication (MTC) system.
- MTC machine type communication
- Machine-like communication is a machine-to-machine (M2M) communication technology for data transmission over a wireless network, which can be applied to smart grids, intelligent transportation, and the like.
- MTC Machine-like communication
- 3GPP 3rd Generation Partnership Project
- CE coverage enhancement
- a data transmitting method comprising: modulating the data in a first modulation manner to generate a first symbol stream; and decomposing the first symbol stream into a predetermined number a second symbol stream, each second symbol stream being modulated in a modulation manner having a lower modulation order than the first modulation mode; processing the predetermined number of second symbol streams to generate a code division a multiplexed data stream; and processing the code-multiplexed data stream to transmit the processed data stream.
- a data receiving method comprising: receiving the data and processing the received data to obtain a code division multiplexed data stream; The data stream is processed to generate a predetermined number of first symbol streams; the predetermined number of first symbol streams are combined into a second symbol stream, wherein the second symbol stream is Modulating the first symbol stream in a modulation mode with a high modulation order; and demodulating the second symbol stream, To generate a demodulated data stream.
- a data transmitting apparatus comprising: modulating means configured to modulate the data in a first modulation manner to generate a first symbol stream; and decompose means configured To decompose the first symbol stream into a predetermined number of second symbol streams, each second symbol stream is modulated in a modulation manner having a lower modulation order than the first modulation mode; the processing device is Configuring to process the predetermined number of second symbol streams to generate a code division multiplexed data stream; the communication device configured to process the code division multiplexed data stream to transmit the processed data stream.
- a data receiving apparatus comprising: communication means configured to receive the data and process the received data to obtain a code division multiplexed data stream; Configuring to process the code division multiplexed data stream to generate a predetermined number of first symbol streams; combining means configured to combine the predetermined number of first symbol streams into a second code a stream of cells, wherein the second symbol stream is modulated in a modulation manner having a modulation order higher than a modulation pattern of each of the first symbol streams; and a demodulation device configured to: the second code The stream is demodulated to produce a demodulated data stream.
- a symbol stream modulated in a high-order modulation manner can be decomposed into a plurality of symbol streams modulated in a low-order modulation manner, and then transmitted using code division multiplexing.
- a plurality of symbol streams are described, thereby improving the reliability of data transmission, thereby reducing the number of repeated transmissions.
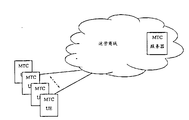
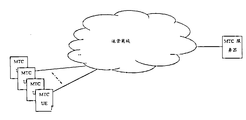
- FIG. 1A and 1B illustrate an example of a machine type communication (MTC) system to which an embodiment of the present invention can be applied.
- MTC machine type communication
- FIG. 2 shows a flow chart of a data transmitting method according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- Figure 3 shows a schematic diagram of generating a repeating symbol stream from a second symbol stream.
- FIG. 4 shows an example of a data stream of a plurality of code division multiplexing layers obtained when a repeating unit is a symbol.
- FIG. 5 shows an example of a data stream of a plurality of code division multiplexing layers obtained when a repeating unit is a subframe.
- 6A and 6B are diagrams showing a method of transmitting an indication bit indicating whether to perform code division multiplexing through a PDCCH.
- FIG. 7 shows a flow chart of a data receiving method according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 8 shows a block diagram of a data transmitting device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 9 shows a block diagram of a data receiving device in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIGS. 1A and 1B An example of an MTC system to which an embodiment of the present invention can be applied will be described with reference to FIGS. 1A and 1B.
- An example of the MTC system shown in FIG. 1A includes an MTC server (or base station) and an MTC User Equipment (UE), wherein the MTC server is located in a domain controlled by the communication carrier, and communicates with the UE through a wireless network or other network provided by the operator.
- An example of the MTC system shown in FIG. 1B includes an MTC server and a UE, wherein the MTC server is located outside the domain controlled by the communication carrier and communicates with the UE through a wireless network or other network provided by the operator.
- the UE may send a Physical Uplink Shared Channel (PUSCH) to the MTC server and a Physical Downlink Shared Channel (PDSCH) from the MTC server through the network.
- PUSCH Physical Uplink Shared Channel
- PDSCH Physical Downlink Shared Channel
- the method can be performed by the UE or by the MTC server.
- the method is described by the UE as an example to describe the embodiment of the present invention, however, the description can also be applied to the MTC server after appropriate adjustment.
- the data may be modulated in a first modulation manner to generate a first symbol stream.
- the data described herein may be data generated by scrambling MTC service data to be transmitted, or may be other data.
- the first modulation mode may be a high-order modulation mode, for example, a modulation mode with a modulation order greater than 2, and may be, for example, QPSK, 16QAM, or 64QAM.
- the first modulation mode may be selected according to a channel quality between the MTC server and the UE. For example, when the channel quality is good, a higher order modulation scheme, such as 16QAM or 64QAM, may be selected, and when the channel quality is not good, You can choose a lower order modulation method, such as QPSK. It is also possible to select an appropriate modulation method as the first modulation method according to actual needs or other factors.
- the selection of the first modulation mode may be performed by the UE and notified to the MTC server, or may be performed by the MTC server and notified to the UE. Alternatively, the first modulation mode may be preset in the MTC server and the UE.
- the first symbol stream may be decomposed into a predetermined number of second symbol streams.
- Each second symbol stream is modulated in a modulation manner having a lower modulation order than the first modulation scheme. That is, a high-order modulated symbol stream (first symbol stream) can be decomposed into a plurality of low-order modulated symbol streams (second symbol streams).
- the predetermined number is represented by N, N>1.
- the predetermined number N may be determined according to a modulation order and/or design requirements of the first modulation mode. N is less than or equal to the modulation order of the first modulation mode. For example, if the first modulation mode is 16QAM and the modulation order is 4, then N may be 2 or 4. If the first modulation mode is 64QAM and the modulation order is 6, then N may be 3 or 2. N may be determined by the MTC server, and information indicating N is transmitted to the UE through semi-static signaling or other signaling such as Radio Resource Control (RRC) signaling, such that the UE receives the information indicating N by RRC signaling. Alternatively, N may be determined by the UE and notified to the MTC server by appropriate signaling.
- RRC Radio Resource Control
- the modulation scheme of each of the second symbol streams can be determined according to the modulation order of the first modulation scheme and N and/or other factors. Briefly, the sum of the modulation orders of the modulation modes of the respective second symbol streams is equal to the modulation order of the first modulation mode.
- the modulation scheme of each of the second symbol streams may be the same.
- the modulation mode of each second symbol stream can be determined as QPSK, so that the 16QAM symbol stream as the first symbol stream can be decomposed into the first
- the two QPSK symbol streams of the two symbol streams may also determine the modulation mode of each second symbol stream as BPSK, so that the 16QAM symbol stream as the first symbol stream may be decomposed into the second symbol stream. 4 BPSK symbol streams.
- the modulation mode of each second symbol stream can be determined as QPSK, so that the 64QAM symbol stream as the first symbol stream can be decomposed into the second code.
- Three QPSK symbol streams of the stream are examples of the stream.
- the modulation of each of the second symbol streams may also be different.
- the modulation mode of one second symbol stream can be determined as QPSK, and the modulation mode of the other second symbol stream is determined to be 16QAM, so that it can be used as
- the 64QAM symbol stream of the first symbol stream is decomposed into a QPSK symbol as a second symbol stream Stream and a 16QAM symbol stream.
- the modulation scheme of each of the second symbol streams may be determined by the MTC server and notified to the UE by various signaling such as RRC signaling.
- the modulation mode of each of the second symbol streams may also be determined by the UE and notified to the MTC server by signaling.
- the UE may perform decomposition of the first symbol stream according to the predetermined number N and modulation modes of the respective second symbol streams. For example, in the case of decomposing a 16QAM symbol stream as a first symbol stream into two QPSK symbol streams as a second symbol stream, since each symbol of the 16QAM symbol stream corresponds to 4 bits, Each symbol of the QPSK symbol stream corresponds to 2 bits, so the first two bits of every four bits of the 16QAM symbol stream can be extracted as two bits of the first QPSK symbol stream, and the four are extracted. The last two bits of the bit are used as two bits of the second QPSK symbol stream until all bits of the 16QAM symbol stream are extracted.
- each symbol of the 64QAM symbol stream corresponds to 6 bits
- the QPSK symbol stream Each symbol corresponds to 2 bits
- each symbol of the 16QAM symbol stream corresponds to 4 bits, so the first two bits of every six bits of the 64QAM symbol stream can be extracted as two of the QPSK symbol streams.
- Bits, and the last four of the six bits are extracted as 4 bits of the 16QAM symbol stream until all bits of the 64QAM symbol stream are extracted.
- the first four bits out of every six bits of the 64QAM symbol stream can also be extracted as 4 bits of the 16QPSK symbol stream, and the last two bits of the six bits are extracted as QPSK. 2 bits of the symbol stream until all bits of the 64QAM symbol stream are extracted.
- the transmission power may be allocated to each of the second symbol streams, and the total transmission power of each of the second symbol streams is the same as the transmission power of the first symbol stream, and the transmission power of each of the second symbol streams may be the same or different.
- the transmission power of each QPSK symbol stream may be the same, and is half the transmission power of the 16QAM symbol stream, respectively.
- the transmission power of the QPSK symbol stream may be the same as the transmission power of the 16QAM symbol stream and is the transmission power of the 64QAM symbol stream.
- the N second symbol streams can be processed to produce a code division multiplexed data stream.
- Each second symbol stream corresponds to one layer of code division multiplexing.
- the processing may include repetition and code division multiplexing.
- the N second symbol streams may be repeated a predetermined number of times in units of predetermined units to generate N repeated symbol streams.
- the N repeated symbol streams can then be code division multiplexed to produce the code division multiplexed data stream.
- each of the second symbol streams may be repeated a predetermined number of times in units of predetermined units to generate a corresponding one of the repeated symbol streams.
- the predetermined unit may also be referred to as a predetermined repeating unit, and the predetermined number of times may also be referred to as a predetermined number of repetitions.
- N R the predetermined number of repetitions
- N R the predetermined number of repetitions at each repetition symbol streams
- N R units forming a repeating predetermined repeating group.
- the predetermined repeating unit may be a symbol, that is, repeated for each second symbol stream in units of symbols.
- the predetermined repeating unit may also be a subframe, that is, repeating for each second symbol stream in units of subframes.
- each symbol can be repeated three times to form a repeated symbol stream corresponding to the Each repeating group of the repeated symbol stream includes 3 symbols.
- Figure 3 shows this example.
- the corresponding repeated symbol streams are A 1 , A 1 , A 1 , A 1 , A 2 , A 2 , A 2 , . ..A M , A M , A M , ie, each symbol is repeated 3 times to form a repeating group.
- the repeating unit is a predetermined subframe, and N R 5, for each of the second symbol stream may correspond to the symbols in each subframe is repeated five times, thereby forming the corresponding repeat A symbol stream, a repeating group of the repeated symbol stream comprising 5 subframes. Repetition is performed in units of sub-frames, and only a small number of symbols need to be stored in units of symbols, requiring a smaller buffer length.
- the predetermined repeating unit and/or the predetermined number of repetitions may be determined by the MTC server and notified to the UE.
- the predetermined repeating unit may be determined according to actual needs or other factors, and the predetermined number of repetitions may be determined according to actual needs or other factors such as reliability or coverage to be achieved. Then, the MTC server may notify the UE of information indicating the predetermined repeating unit and/or information indicating the predetermined number of repetitions by semi-static signaling or other signaling such as RRC signaling. Alternatively, the predetermined repeating unit and/or the predetermined number of repetitions may be determined by the UE and signaled to the MTC server. Alternatively, the predetermined repeating unit and/or the predetermined number of repetitions may be preset in the MTC server and the UE.
- the N repeated symbol streams may be code division multiplexed to generate the code division multiplexed data stream.
- each repeating unit in the repeating group in each repeated symbol stream may be multiplied by a corresponding spreading sequence to generate a data stream of the corresponding code division multiplexing layer.
- the spreading sequence corresponding to each repeating unit in the repeating group in each repeated symbol stream can be determined according to the following formula (1):
- n layer represents the number of each repeated symbol stream (or corresponding second symbol stream), that is, the number of the code division multiplexing layer corresponding to each repeated symbol stream, where n layer ⁇ N ⁇ N R , n repunit indicates the number of the repeating unit in the repeating group, then Represents n repunit repeating units corresponding to the spreading sequence is repeated in the repeating group of symbol streams th n layer.
- N repeated symbol streams the following matrix of spreading sequences can be determined using the above equation (1):
- each repeating unit in each repeating group of the first repeated symbol stream can be multiplied by the corresponding spreading sequence of the first row in the matrix, thereby generating a data stream of the first code division multiplexing layer, which will
- Each repeating unit in each repeating group of the second repeated symbol stream is multiplied by a corresponding spreading sequence of the second row in the matrix, thereby generating a data stream of the second code division multiplexing layer, and so on.
- FIG 4 shows that when the repeating unit is N R symbols and a plurality of sample data is obtained when the 6 code division multiplexing layer flow.
- Figure 5 shows that when the subframe and the repeating unit is N R sample data stream with a plurality of code layers obtained when the 3-division multiplexing, frequency hopping is applied in this example.
- the data streams of the N code division multiplexing layers thus obtained can be added to generate the code division multiplexed data stream.
- the code division multiplexed data stream is processed to transmit the processed data stream.
- the processing may include mapping the code-multiplexed data stream to a resource unit mapping process of the resource unit and/or generating a single carrier frequency division multiple access (SC-FDMA) signal for transmission.
- SC-FDMA single carrier frequency division multiple access
- the process may also include other types of processing as needed.
- a symbol stream modulated in a high-order modulation manner can be converted into a plurality of symbol streams modulated in a low-order modulation manner, and then the plurality of symbol streams can be transmitted using code division multiplexing. Since the symbol stream of the low-order modulation is more reliable than the symbol stream of the high-order modulation, and the orthogonality is introduced by the orthogonal spreading sequence in the code division multiplexing, the reliability of data transmission can be improved. , then reduce the number of repeated transmissions and increase the coverage.
- the UE may decide whether to perform the operations of steps S202-S204 above for the first symbol stream according to the notification of the MTC server.
- the notification can be explicit or implicit.
- the MTC server may send information to the UE indicating whether to perform code division multiplexing.
- the UE may perform the above operation upon receiving the information indicating the code division multiplexing, and does not perform the above operation upon receiving the information indicating that the code division multiplexing is not performed.
- information indicating whether to perform code division multiplexing may be included in a Physical Downlink Control Channel (PDCCH).
- the information may be included in downlink control information (DCI) of the PDCCH (eg, DCI format 0, UL grant).
- DCI downlink control information
- an indication bit for example, 1 bit
- unnecessary bits for example, transmission power
- the control bit is replaced with the indication bit as shown in FIG. 6B.
- the MTC server does not transmit the information indicating whether to perform code division multiplexing, and uses the modulation and coding scheme (MCS) index transmitted from the MTC server to the UE to notify whether or not to perform code division multiplexing.
- MCS modulation and coding scheme
- the UE can determine the modulation order to be adopted according to the index, and then determine whether to perform the operations of the above steps S202-S204 according to the modulation order. For example, when the modulation order corresponding to the MCS index is greater than a certain value (for example, 2), the UE may determine to perform the operations of the above steps S202-S204, and vice versa, do not perform the operations of the above steps S202-S204. Without performing the above operation, processing such as resource unit mapping processing and/or generation of SC-FDMA signals may be performed on the first symbol stream, and the thus generated data stream is transmitted.
- a certain value for example, 2
- the method can also be performed by an MTC server.
- the MTC server can process the data to be transmitted in the same manner as described with reference to FIG. 2, thereby generating a code-multiplexed data stream, and multiplexing the code-multiplexed
- the processed data stream is processed after the data stream is processed.
- the UE will perform the corresponding
- the data receiving method is to recover the data sent by the MTC server from the received data.
- step S701 the data may be received and the received data processed to obtain a code division multiplexed data stream.
- the processing may be an inverse processing corresponding to the processing performed in step S204, and may include, for example, OFDM demodulation or resource unit demapping or the like. If the processing is not performed in step S204, but the code-multiplexed data stream is directly transmitted, in step S701, the processing may not be performed, but the received data may be directly used as the code-multiplexed data stream.
- the UE may determine whether the received data is generated from the code division multiplexed bit stream according to the notification of the MTC server, thereby determining whether each step described below should be performed.
- the notification can be explicit or implicit.
- the MTC server may send information indicating whether code division multiplexing is performed to the UE, so that the UE determines that the received data is generated in the code division when receiving the information indicating that the code division multiplexing is performed.
- the bit stream is used to determine that the following steps are performed, and the following steps are not performed when receiving information indicating that no code division multiplexing is performed.
- information indicating whether code division multiplexing is performed may be included in the PDCCH, for example, information indicating whether code division multiplexing is performed may be included in DCI of the PDCCH (eg, DCI format 1A, DL grant) in.
- the UE may determine whether the received data is generated from the code division multiplexed bit stream according to the MCS index notified by the MTC server. For example, when the modulation order corresponding to the MCS index is greater than a certain value (for example, 2), the UE may determine that the received data is generated in a code division multiplexed bit stream. In case the received data is not generated by the code division multiplexed bit stream, the UE can process the data in a conventional manner.
- a certain value for example, 2
- the code division multiplexed data stream may be processed to generate a predetermined number of symbol streams (hereinafter referred to as a third symbol stream for convenience of description).
- the predetermined number is still expressed as N.
- the code-multiplexed data stream may be demultiplexed to generate N demultiplexed data streams, which may then be extracted from the N demultiplexed data streams as predetermined units (The predetermined repeating unit) repeats the symbol stream of the predetermined number of times (predetermined number of repetitions, N R ) as N third symbol streams.
- UE information may be information indicating N N R & lt receiving indication from the base station via RRC signaling.
- the predetermined unit can be known in the manner described above. As described above, the predetermined unit may be a symbol or a subframe.
- the code-multiplexed data stream may be demultiplexed to generate N demultiplexed data streams.
- the code division multiplexed bit stream may be multiplied by a spreading sequence generated in the manner described above (ie, each spreading sequence in the matrix described above), thereby generating N solutions. Use bitstream.
- a symbol stream that has been repeated N R times as a predetermined repeating unit can be extracted from each of the demultiplexed data streams as a corresponding one of the third symbol streams.
- the inverse of the repetition can be performed to extract the code. Metaflow to eliminate duplicate data. For example, data for each N R repeating units (corresponding to one repeating group) in the demultiplexed data stream can be extracted.
- the data of the repeated group can be averaged with respect to N R to determine data as a basic unit of the repeated group, and then the data of the basic unit of each repeated group is combined, thereby obtaining a symbol stream, that is, The third symbol stream corresponding to the demultiplexed data stream.
- step S703 the N third symbol streams are combined into a fourth symbol stream, wherein the fourth symbol stream is higher in modulation mode than each third symbol stream.
- the modulation order of the modulation order is modulated.
- the N low order modulated symbol streams are combined into one higher order modulated symbol stream.
- the combination operation may be performed according to a modulation method of each third symbol stream and a modulation method of the fourth symbol stream.
- the UE may learn the modulation mode of each third symbol stream and the modulation manner of the fourth symbol stream in the manner described above with respect to FIG. 2, and details are not described herein again.
- the modulation of the fourth symbol stream is 16QAM
- the first two bits can be extracted from the first QPSK symbol stream, and The first two bits are extracted from the second QPSK symbol stream and the four bits are combined as bits of the first symbol of the fourth symbol stream.
- the 3-4th bit can be extracted from the first QPSK symbol stream, and the 3-4th bit is extracted from the second QPSK symbol stream, and the four bits are combined as the fourth code.
- the bits of the second symbol of the stream are, and so on, until all bits of the first QPSK symbol stream and the second QPSK symbol stream are extracted.
- the fourth symbol stream may be demodulated to generate a demodulated data stream.
- the demodulated data may be descrambled or the like if necessary to recover data transmitted from the MTC server.
- a data transmitting method and a data receiving method are described in the context of an MTC system. It should be appreciated that this is merely illustrative, and the data transmission method and data reception method can also be applied to a non-MTC system (in this case, the MTC server is replaced by a base station).
- the operations of step S202 and step S703 are slightly different, and other steps may remain unchanged. Specifically, in this case, the above-described operation of repeating the operation (sending) of the data and the operation of eliminating the repeated data (reception) may not be performed.
- the differences will be described, and the description of the same contents will be omitted.
- the processing may include code division multiplexing without This includes repeating the operation of the data.
- the N second symbol streams may be code division multiplexed to generate the code division multiplexed data stream.
- the N second symbol streams may be respectively multiplied by mutually orthogonal spreading sequences to generate N code sequences, and then the N code sequences are combined to generate the code division multiplexed data stream.
- the processing may include a demultiplexing operation without including the above elimination.
- the operation of the data is repeated, that is, the code-multiplexed data stream can be demultiplexed to directly obtain N symbol streams.
- the code division multiplexed data can be multiplied by the spreading sequence described above to produce N symbol streams.
- the data transmitting device can perform the data transmitting method described above.
- the data transmitting device may be located in the UE or may be located in the MTC server or the base station.
- description will be made with the data transmitting device located in the UE.
- the operation performed by the data transmitting device is substantially identical to the data transmitting method described above, the description of the same content is omitted here to avoid duplication, and for the same content, the description given above can be referred to.
- the data transmitting device 800 includes a modulating device 801, a disassembling device 802, a processing device 803, and a communication device 804, wherein the communication device 804 can communicate with an MTC server to receive/send various information and / or data stream.
- Modulation device 801 can modulate the data in a first modulation manner to produce a first symbol stream.
- the data described herein may be a number generated by scrambling the MTC service data to be transmitted. According to this, in this case, a scrambling device (not shown) can be provided in the data transmitting device 800.
- the data can also be other types of data.
- the first modulation mode may be a high-order modulation mode, for example, a modulation mode with a modulation order greater than 2, and may be, for example, QPSK, 16QAM, or 64QAM.
- the selection of the first modulation mode may be performed by the data transmitting device 800 (specifically, the modulating device 801) and notified to the MTC server by the communication device 804, or may be executed by the MTC server and notified to the data transmitting device 800.
- the first modulation mode may be preset in the MTC server and the UE.
- the decomposition device 802 can decompose the first symbol stream into a predetermined number (N) of second symbol streams. Each second symbol stream is modulated in a modulation manner having a lower modulation order than the first modulation scheme.
- N can be determined in the manner described above. Further, N may be determined by the MTC server, and information indicating N is transmitted to the data transmitting device 800 by semi-static signaling such as RRC signaling or other signaling, so that the data transmitting device 800 (specifically, the communication device 804) passes The RRC signaling receives the information indicating the N. Alternatively, N may be determined by the data transmitting device 800 and notified to the MTC server by appropriate signaling.
- the modulation modes of the respective second symbol streams may be determined in the manner described above, wherein the modulation manners of the respective second symbol streams may be the same or different.
- the modulation scheme of each of the second symbol streams may be determined by the MTC server and notified to the data transmitting device 800 by various signaling such as RRC signaling.
- the modulation mode of each of the second symbol streams may also be determined by the data transmitting device 800 (specifically, the decomposing device 802) and notified to the MTC server by signaling.
- the decomposition device 802 can perform decomposition of the first symbol stream according to the predetermined number N and modulation modes of the respective second symbol streams.
- the decomposition device 802 can perform the decomposition in the manner described above with reference to FIG. 2, and a detailed description thereof is omitted herein for the sake of simplicity.
- Processing device 803 can process the N second symbol streams to produce a code division multiplexed data stream.
- Each second symbol stream corresponds to one layer of code division multiplexing.
- the processing may include repetition and code division multiplexing.
- the processing means 803 may repeat the predetermined number of times for the N second symbol streams in predetermined units to generate N repeated symbol streams.
- the N repeated symbol streams can then be code division multiplexed to produce the code division multiplexed data stream.
- the processing device 803 may repeat each predetermined number of times (ie, a predetermined number of repetitions N R ) for each second symbol stream in units of predetermined units (ie, predetermined repeating units) to generate a corresponding one of the repeated symbol streams.
- the predetermined repeating unit may be a symbol or a subframe.
- N R repeating units form a repeating group.
- the predetermined repeating unit and/or the predetermined number of repetitions N R may be determined by the MTC server, and the predetermined repeating unit may be indicated by semi-static signaling or other signaling such as RRC signaling.
- Information and/or information indicating the predetermined number of repetitions is notified to the data transmitting device 800 such that the data transmitting device 800 (specifically, the communication device 804) receives information indicating the predetermined repeating unit and/or an indication through the signaling.
- the predetermined repeating unit and/or the predetermined number of repetitions may be determined by the data transmitting device 800 (specifically, the processing device 803) and signaled to the MTC server.
- the predetermined repeating unit and/or the predetermined number of repetitions may be preset in the MTC server and the data transmitting device 800.
- processing device 803 can code-multiplex the N repeated symbol streams to produce the code division multiplexed data stream. Specifically, the processing device 803 may multiply each repeating unit in the repeated group in each repeated symbol stream by a corresponding spreading sequence to generate a data stream of the corresponding code division multiplexing layer, and then divide the respective code points. The data streams of the multiplexing layer are combined to produce the code division multiplexed data stream.
- the spreading sequence corresponding to each repeating unit within the repeating group in each repeated symbol stream can be determined in the manner described above, and a detailed description thereof is omitted herein to avoid redundancy.
- Communication device 804 can communicate with the MTC server to transmit or receive information/data. For example, communication device 804 can receive information indicative of the first modulation scheme and information indicative of a modulation scheme for each of the second symbol streams. The communication device 804 may also receive information indicating the predetermined number N and/or information indicating the number of repetitions N R through RRC signaling or other signaling.
- the communication device 804 can also process the code-multiplexed data stream to transmit the processed data stream.
- the processing to be performed may be selected according to actual needs, such as resource unit mapping processing and/or processing for generating SC-FDMA signals, and the like.
- corresponding units may be provided at the communication device 804 to perform these processes.
- the data transmitting device 800 (specifically, each of the devices therein) can decide whether or not to perform the above operation on the first symbol stream based on the notification of the MTC server.
- the notification can be explicit or implicit.
- the MTC server may transmit information indicating whether to perform code division multiplexing to the data transmitting device 800.
- the communication unit 804 can receive the information indicating whether to perform code division multiplexing.
- the data transmitting device 800 can perform the above operation upon receiving the information indicating that the code division multiplexing is performed, and does not perform the code division upon receiving the indication. The above operation is not performed when using the information.
- information indicating whether to perform code division multiplexing may be included in the PDCCH.
- the information may be included in the DCI of the PDCCH (eg, DCI format 0, UL grant).
- the data transmitting device 800 may notify whether or not to perform code division multiplexing using the MCS index transmitted by the MTC server to the UE as described above.
- a symbol stream modulated in a high-order modulation manner may be converted into a plurality of symbol streams modulated in a low-order modulation manner, and then the plurality of symbol streams may be transmitted using a code division multiplexing manner. Since the symbol stream of the low-order modulation is more reliable than the symbol stream of the high-order modulation, and the orthogonality is introduced by the orthogonal spreading sequence in the code division multiplexing, the reliability of data transmission can be improved. , reduce the number of repeated transmissions.
- the MTC server can execute the data transmission method described with reference to FIG. 2 to process the data to be transmitted, generate a code division multiplexed data stream, and transmit the processing after processing the code division multiplexed data stream. After the data stream.
- the data receiving device can be set in the UE to recover the data transmitted by the MTC server from the received data.
- a data receiving apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG.
- the description is made by taking the receiving device in the UE as an example.
- the data receiving device can also be applied to the MTC server after appropriate adjustment.
- the data receiving device 900 includes a communication device 901, a processing device 902, a combining device 903, and a demodulating device 904.
- the communication device 901 can receive the data and process the received data to obtain a code division multiplexed data stream.
- the processing may include OFDM demodulation or resource unit demapping or the like.
- a corresponding unit (not shown) may be provided in the communication device 901 to perform these processes.
- the data receiving device 900 can determine whether the received data is generated from the code-multiplexed bit stream according to the notification of the MTC server, thereby determining whether each operation described below should be performed.
- the notification can be explicit or implicit.
- the MTC server may transmit information indicating whether or not code division multiplexing has been performed to the UE (specifically, the data receiving device 900).
- the communication device 901 can receive the information.
- the data receiving apparatus 900 may determine that the received data is generated in the code division multiplexed bit stream, thereby determining to perform the following operation, and not receiving the code division upon receiving the indication Reusable information The following operations are not performed.
- information indicating whether code division multiplexing is performed may be included in the PDCCH, for example, information indicating whether code division multiplexing is performed may be included in DCI of the PDCCH (eg, DCI format 1A, DL grant) in.
- the data receiving device 900 can determine whether the received data is generated in the code division multiplexed bit stream according to the MCS index notified by the MTC server in the manner described above.
- Processing device 902 can process the code division multiplexed data stream to produce a predetermined number (N) of third symbol streams. Briefly, the processing device 902 can demultiplex the code-multiplexed data stream to generate N demultiplexed data streams, which can then be extracted from the N demultiplexed data streams respectively.
- the predetermined unit (predetermined repeating unit) repeats the symbol stream of the predetermined number of times (predetermined number of repetitions, N R ) as N third symbol streams.
- the data reception apparatus 900 (specifically, the communication device 901) information may be information indicating N N R & lt receiving indication from the base station via RRC signaling. Further, the data receiving device 900 can learn the predetermined unit in the manner described above. As described above, the predetermined unit may be a symbol or a subframe.
- the processing device 902 can demultiplex the code-multiplexed data stream to generate N demultiplexed data streams.
- the code division multiplexed bit stream may be multiplied by a spreading sequence generated in the manner described above (ie, each spreading sequence in the matrix described above), thereby generating N solutions. Use bitstream.
- the processing device 902 can extract, from each of the demultiplexed data streams, a symbol stream that is repeated NR times as a predetermined repeating unit, as a corresponding third code, in the manner described above with reference to FIG. Yuan stream.
- processing device 902 may extract the demultiplexed data (corresponding to a repeating group) with each of N R repeating units in the data stream, the data with respect to the repeating group N R averaged to determine as to the replicate group of The data of the basic unit is then combined with the data of the basic unit of each repeated group to obtain a symbol stream, that is, a third symbol stream corresponding to the demultiplexed data stream.
- the combining means 903 may combine the N third symbol streams into a fourth symbol stream, wherein the fourth symbol stream is modulated with a modulation order higher than that of each third symbol stream Mode modulated. In other words, the N low order modulated symbol streams are combined into one higher order modulated symbol stream. Specifically, the combining means 903 can perform the above-described combining operation according to the modulation method of each of the third symbol streams and the modulation mode of the fourth symbol stream in the manner described above.
- Demodulation device 904 can demodulate the fourth symbol stream to produce a demodulated data stream. For the demodulated data, if necessary, it can also be descrambled and the like to recover from the MTC. The data sent by the server. In this case, a corresponding unit (not shown) may be provided in the demodulating device 904 to perform the processing.
- the above-described data transmitting device and data receiving device described in the background of the MTC system can also be applied to a non-MTC system.
- the operations performed by the processing device 803 of the above data transmitting device and the processing device 902 of the data receiving device are slightly different, while other devices may remain unchanged. In the following, only the differences will be described, and the description of the same content will be omitted.
- processing device 803 when processing device 803 processes the N second symbol streams to produce a code division multiplexed data stream, the processing may include code division multiplexing without including operations to repeat the data. In this case, processing device 803 can code division multiplex the N second symbol streams to produce the code division multiplexed data stream.
- the processing device 902 when the processing device 902 processes the code-multiplexed data stream to generate N symbol streams, the processing may include a demultiplexing operation without including the above-described operation of eliminating duplicate data, ie, The processing device 902 can demultiplex the code-multiplexed data stream to directly obtain N symbol streams.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
- Detection And Prevention Of Errors In Transmission (AREA)
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/574,111 US10594429B2 (en) | 2015-05-14 | 2016-05-13 | Data sending and receiving method, and data sending and receiving device |
| EP16792219.4A EP3297188B1 (en) | 2015-05-14 | 2016-05-13 | Data sending and receiving method, and data sending and receiving device |
| CN201680027892.1A CN107534631B (zh) | 2015-05-14 | 2016-05-13 | 数据发送和接收方法以及数据发送和接收设备 |
| JP2017559549A JP6847860B2 (ja) | 2015-05-14 | 2016-05-13 | データ送受信方法及びデータ送受信装置 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201510246653.2A CN106301662A (zh) | 2015-05-14 | 2015-05-14 | 数据发送和接收方法以及数据发送和接收设备 |
| CN201510246653.2 | 2015-05-14 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2016180369A1 true WO2016180369A1 (zh) | 2016-11-17 |
Family
ID=57247726
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2016/082096 Ceased WO2016180369A1 (zh) | 2015-05-14 | 2016-05-13 | 数据发送和接收方法以及数据发送和接收设备 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10594429B2 (cg-RX-API-DMAC7.html) |
| EP (1) | EP3297188B1 (cg-RX-API-DMAC7.html) |
| JP (1) | JP6847860B2 (cg-RX-API-DMAC7.html) |
| CN (2) | CN106301662A (cg-RX-API-DMAC7.html) |
| WO (1) | WO2016180369A1 (cg-RX-API-DMAC7.html) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107623565B (zh) * | 2016-07-15 | 2020-08-14 | 华为技术有限公司 | 基于多信道传输信号的方法和装置 |
| CN109391394B (zh) * | 2017-08-09 | 2021-07-27 | 北京紫光展锐通信技术有限公司 | Prg隐式指示方法及装置、存储介质、终端、基站 |
| CN110011692A (zh) * | 2017-12-29 | 2019-07-12 | 株式会社Ntt都科摩 | 一种扩频通信方法、用户设备和基站 |
| WO2019136741A1 (en) * | 2018-01-15 | 2019-07-18 | Zte Corporation | Methods and computing device for facilitating multiple access in a wireless communication network |
| CN115378472A (zh) * | 2021-05-19 | 2022-11-22 | 北京小米移动软件有限公司 | 通信方法、装置、电子设备及存储介质 |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20060291582A1 (en) * | 2001-05-17 | 2006-12-28 | Walton Jay R | Method and apparatus for processing data for transmission in a multi-channel communication system using selective channel inversion |
| CN101483463A (zh) * | 2008-01-11 | 2009-07-15 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种基于多分集的数据发送方法及装置 |
| CN101521529A (zh) * | 2008-02-27 | 2009-09-02 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种分集发射方法、系统和装置 |
| US20100046681A1 (en) * | 2008-08-20 | 2010-02-25 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Uplink sdma pilot estimation |
| CN101834694A (zh) * | 2009-03-11 | 2010-09-15 | 富士通株式会社 | 数据发送装置及其方法、数据接收装置及其方法 |
| US20130142160A1 (en) * | 2010-08-13 | 2013-06-06 | Panasonic Corporation | Terminal device, base station device, retransmission method, and resource allocation method |
| CN104038624A (zh) * | 2013-03-07 | 2014-09-10 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 实现终端情景模式设置的方法、装置及移动终端 |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6678311B2 (en) * | 1996-05-28 | 2004-01-13 | Qualcomm Incorporated | High data CDMA wireless communication system using variable sized channel codes |
| DE60238225D1 (de) * | 2001-03-21 | 2010-12-23 | Lg Electronics Inc | Wiederübertragung von daten durch eine Rückwärtsverbindung in einem Paketdatenübertragungssystem mit automatischer Wiederholungsaufforderung |
| BR0116961A (pt) * | 2001-04-05 | 2005-01-11 | Nortel Networks Ltd | Transmissor para um sistema de comunicações sem fio usando códigos múltiplos e antenas múltiplas |
| KR100450968B1 (ko) * | 2001-06-27 | 2004-10-02 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 부호분할다중접속 이동통신시스템에서 데이터 송/수신장치 및 방법 |
| US8885628B2 (en) * | 2005-08-08 | 2014-11-11 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Code division multiplexing in a single-carrier frequency division multiple access system |
| JP4783217B2 (ja) * | 2006-06-13 | 2011-09-28 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | 符号分割多重通信システム、符号分割多重通信方法および送信装置ならびに受信装置 |
| US20080137775A1 (en) * | 2006-12-07 | 2008-06-12 | Tae Hoon Kim | Method and apparatus for hierarchical modulation and demodulation in digital broadcasting system |
| WO2011086525A1 (en) * | 2010-01-15 | 2011-07-21 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Methods and apparatus for contention-based granting in a wireless communication network |
| CN101827444B (zh) * | 2010-03-31 | 2015-03-25 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 一种测量参考信号的信令配置系统及方法 |
| WO2013056741A1 (en) * | 2011-10-20 | 2013-04-25 | Nokia Siemens Networks Oy | Timeslot allocation in uplink cdma |
| CN104038324A (zh) * | 2013-03-04 | 2014-09-10 | 夏普株式会社 | 混合自动重传请求指示信道的发送方法以及基站 |
-
2015
- 2015-05-14 CN CN201510246653.2A patent/CN106301662A/zh active Pending
-
2016
- 2016-05-13 JP JP2017559549A patent/JP6847860B2/ja active Active
- 2016-05-13 US US15/574,111 patent/US10594429B2/en active Active
- 2016-05-13 EP EP16792219.4A patent/EP3297188B1/en active Active
- 2016-05-13 WO PCT/CN2016/082096 patent/WO2016180369A1/zh not_active Ceased
- 2016-05-13 CN CN201680027892.1A patent/CN107534631B/zh active Active
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20060291582A1 (en) * | 2001-05-17 | 2006-12-28 | Walton Jay R | Method and apparatus for processing data for transmission in a multi-channel communication system using selective channel inversion |
| CN101483463A (zh) * | 2008-01-11 | 2009-07-15 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种基于多分集的数据发送方法及装置 |
| CN101521529A (zh) * | 2008-02-27 | 2009-09-02 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种分集发射方法、系统和装置 |
| US20100046681A1 (en) * | 2008-08-20 | 2010-02-25 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Uplink sdma pilot estimation |
| CN101834694A (zh) * | 2009-03-11 | 2010-09-15 | 富士通株式会社 | 数据发送装置及其方法、数据接收装置及其方法 |
| US20130142160A1 (en) * | 2010-08-13 | 2013-06-06 | Panasonic Corporation | Terminal device, base station device, retransmission method, and resource allocation method |
| CN104038624A (zh) * | 2013-03-07 | 2014-09-10 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 实现终端情景模式设置的方法、装置及移动终端 |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| "3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); Multiplexing and channel coding (Release 12", 3GPP TS 36. 212. 4. 0., 31 March 2015 (2015-03-31), pages 57 - 83, XP055329532 * |
| See also references of EP3297188A4 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN106301662A (zh) | 2017-01-04 |
| EP3297188A4 (en) | 2019-02-13 |
| JP2018524847A (ja) | 2018-08-30 |
| EP3297188A1 (en) | 2018-03-21 |
| CN107534631A (zh) | 2018-01-02 |
| US20180351681A1 (en) | 2018-12-06 |
| JP6847860B2 (ja) | 2021-03-24 |
| EP3297188B1 (en) | 2020-03-18 |
| US10594429B2 (en) | 2020-03-17 |
| CN107534631B (zh) | 2020-08-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3560253B1 (en) | Physical downlink control channel design for 5g new radio | |
| CN103004163B (zh) | 用于复用应答信号和声探参考信号的方法和系统 | |
| JP5746303B2 (ja) | 無線通信システムにおける情報送信方法及び装置 | |
| EP2495905B1 (en) | Wireless communication system, base station device, mobile station device, wireless communication method, and integrated circuit | |
| CN103947246B (zh) | 移动台装置、基站装置、无线通信系统、无线通信方法以及集成电路 | |
| KR102473793B1 (ko) | 통신 단말 및 송신 방법 | |
| KR102567076B1 (ko) | 통신 장치, 통신 방법 및 집적 회로 | |
| US9042299B2 (en) | Mobile terminal apparatus and radio communication method | |
| CN105471543B (zh) | 发送装置和发送方法 | |
| JP2012514876A (ja) | 複数コンポーネント・キャリアofdma通信システム | |
| CN107534631B (zh) | 数据发送和接收方法以及数据发送和接收设备 | |
| WO2015170435A1 (ja) | 端末、基地局、送信方法及び受信方法 | |
| WO2017193975A1 (zh) | 一种信道状态信息反馈方法和装置 | |
| CN107872304A (zh) | 一种上行控制信号的传输方法、网络侧设备及终端设备 | |
| US9913260B2 (en) | Terminal device, base station device, and communication method | |
| US20220295525A1 (en) | Terminal, base station, transmission method, and reception method | |
| CN102017559A (zh) | 在无线通信系统中传送控制信号的方法 | |
| CN105634665B (zh) | 数据发送方法、接收方法和装置 | |
| WO2026002454A1 (en) | Apparatus, method, and computer program for pilot transmission | |
| WO2026002453A1 (en) | Apparatus, method, and computer program for pilot transmission |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 16792219 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2017559549 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |