WO2016134551A1 - 一种无机胶凝材料及其制备方法 - Google Patents
一种无机胶凝材料及其制备方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2016134551A1 WO2016134551A1 PCT/CN2015/073568 CN2015073568W WO2016134551A1 WO 2016134551 A1 WO2016134551 A1 WO 2016134551A1 CN 2015073568 W CN2015073568 W CN 2015073568W WO 2016134551 A1 WO2016134551 A1 WO 2016134551A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- parts
- fly ash
- steaming
- lime
- gypsum
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C04—CEMENTS; CONCRETE; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES
- C04B—LIME, MAGNESIA; SLAG; CEMENTS; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF, e.g. MORTARS, CONCRETE OR LIKE BUILDING MATERIALS; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES; TREATMENT OF NATURAL STONE
- C04B7/00—Hydraulic cements
- C04B7/24—Cements from oil shales, residues or waste other than slag
- C04B7/26—Cements from oil shales, residues or waste other than slag from raw materials containing flue dust, i.e. fly ash
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02P—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE PRODUCTION OR PROCESSING OF GOODS
- Y02P40/00—Technologies relating to the processing of minerals
- Y02P40/10—Production of cement, e.g. improving or optimising the production methods; Cement grinding
Definitions
- the invention relates to the technical field of building materials, in particular to a fast setting high-strength inorganic cementing material using fly ash, lime and a small amount of Portland cement or cement clinker as main raw materials and a preparation method thereof.
- fly ash discharged from the dry process of power plants has been utilized in recent years, the large amount of fly ash discharged by the wet method before the 1980s and 1990s is relatively coarse and has a high carbon content.
- the physical properties and reactivity cannot meet the requirements of cement admixtures and concrete admixtures, and cannot be directly applied to cement and concrete and other building materials, so they have not been effectively utilized and have been stored for a long time. Long-term storage of fly ash not only occupies a large amount of land, but also seriously pollutes the surrounding environment, so its effective resource utilization is an urgent problem to be solved.
- fly ash as the main raw material for the preparation of inorganic cementitious materials not only saves non-renewable resources, but also saves energy and protects the environment.
- the existing technology for preparing inorganic cementitious materials from fly ash has the problems of less consumption of fly ash, high quality requirements for fly ash and poor product performance.
- the technical problem to be solved by the present invention is to provide a quick-setting inorganic cementitious material which can utilize a large amount of low-quality fly ash as a main raw material in view of the problems existing in the prior art mentioned above.
- Another object of the present invention is to provide a process for the preparation of such a fast setting high strength inorganic cementitious material.
- the present invention provides an inorganic cementitious material which is composed of 65-80 parts by mass of fly ash, 20-35 parts of lime as effective CaO, and 0.5-2 of an activator. And 15 to 50 parts of the obtained material or pellets are prepared by steaming and calcining 60-70 parts of the synthetic material, 20-30 parts of Portland cement and 5-10 parts of gypsum.
- the fly ash is fly ash which meets the technical index of grade III or higher of fly ash in cement and concrete according to GBT 1596;
- the lime is calcareous lime which satisfies the technical index of JC/T 479 building lime and meets JC/ Calcium slaked lime which is a technical indicator of slaked lime;
- the gypsum is a combination of one or more of dihydrate gypsum, hemihydrate gypsum and anhydrite;
- the activator is alkali metal hydroxide, alkali metal carbon A combination of one or more of an acid salt and an alkali metal sulfate.
- the present invention also provides a method for preparing an inorganic cementing material, the main steps of which are as follows:
- Step (1) mixing fly ash, lime and activator in proportion, and grinding together to a batch with a fineness of 45 ⁇ m and a sieve residue of less than 10%;
- Step (2) uniformly mixing the batch with water, aging for 2 to 3 hours, forming a block having a maximum size of 10-240 mm or a ball having a diameter of 8-16 mm;
- Step (3) steaming the pellets at a temperature of 90 to 98 ° C for 8 to 16 hours to obtain a steaming nutrient
- Step (4) the steaming material is calcined at 750-1000 ° C for 15-90 min, then air-cooled or cooled in air to obtain a synthetic material.
- Step (5) 60-70 parts of the synthetic material, 20-30 parts of Portland cement and 5-10 parts of gypsum are ground together to a specific surface area of 350-450 m 2 /kg to prepare an inorganic cementing material. .
- the invention utilizes steam curing to react lime and activated silica in the fly ash to form hydrated calcium silicate and calcium hydrated calcium aluminate, and calcined at a lower temperature to form dicalcium silicate and heptaluminate.
- the activator in the invention can react with the aluminosilicate glass body in the fly ash, destroy the vitreous network structure, reduce the polymerization degree of the vitreous network structure, greatly improve the reaction rate of the silicon oxide and the alumina with the lime and the hydrated silicic acid.
- the formation rate of calcium and hydrated calcium aluminate further increases the content of dicalcium silicate and heptaluminate in the inorganic cementitious material, and improves the gelation of the inorganic cementitious material.
- the high hydration activity of heptaluminate can impart fast setting and fast-hardening properties to inorganic cementitious materials.
- Portland cement or Portland cement clinker can ensure sufficient alkalinity and ensure glue after hydration of inorganic cementitious materials.
- the condensed material has good carbonation resistance after hardening.
- Figure 1 is a flow chart of the production process of the present invention.
- the batch material contains the following ingredients in parts by mass:
- the batch contains the following ingredients in parts by mass:
- a synthetic material was obtained; a composite material of 68 parts, 25 parts of Portland cement and 7 parts of dihydrate gypsum was ground to a specific surface area of 415 m 2 /kg to prepare a fast-setting high-strength inorganic cementitious material.
- the batch contains the following ingredients in parts by mass:
- the composite material was crushed into particles of less than 16 mm by a crusher, and 67 parts of synthetic material, 25 parts of Portland cement and 8 parts of hemihydrate gypsum were ground together to a specific surface area of 425 m 2 /kg to prepare a fast coagulation. High-strength inorganic cementitious materials.
- the batch contains the following ingredients in parts by mass:
- fly ash, quicklime and anhydrous sodium sulfate were weighed and ground to a batch with a fineness of 45 ⁇ m and a 8.1% residue; the batch was poured into a mixer, and 50 parts of water was added and stirred for 3 minutes. After 3 hours of aging, it is extruded into a 50 mm ⁇ 50 mm ⁇ 30 mm block; the material is steamed in a steaming box at 98 ° C for 12 h to obtain a steaming nutrient, and the steaming material is calcined in a small kiln at 800 ° C for 45 min and then naturally cooled in the air.
- the synthetic material is obtained; after the synthetic material is crushed into particles of less than 16 mm by a crusher, 65 parts of 95 parts of synthetic materials, 30 parts of Portland cement and 5 parts of hemihydrate gypsum are ground together to a specific surface area of 440 m 2 /kg. A fast-setting high-strength inorganic cementitious material is obtained.
- the batch contains the following ingredients in parts by mass:
- the composite material is naturally cooled in the air; 67 parts of synthetic material, 25 parts of Portland cement, 4 parts of anhydrite and 3 parts of hemihydrate gypsum are ground together to a specific surface area of 370 m 2 /kg to obtain a fast-setting high strength. Inorganic cementitious materials.
- the batch contains the following ingredients in parts by mass:
- a synthetic material was obtained; 67 parts of synthetic material, 25 parts of Portland cement and 8 parts of dihydrate gypsum were ground together to a specific surface area of 385 m 2 /kg to prepare a fast-setting high-strength inorganic cementing material.
- the batch contains the following ingredients in parts by mass:
- the composite material was cooled; 64 parts of synthetic material, 30 parts of Portland cement and 6 parts of dihydrate gypsum were ground together to a specific surface area of 445 m 2 /kg to prepare a fast-setting high-strength inorganic cementitious material.
- the batch contains the following ingredients in parts by mass:
- the small kiln is calcined at 900 °C for 30 min to cool the synthetic material; 66 parts of synthetic material, 27 parts of Portland cement and 7 parts of hemihydrate gypsum are ground together to a specific surface area of 440 m2/kg to prepare a fast-setting high-strength inorganic rubber. Condensate material.
- the inorganic cementitious material of the invention can be made of low-quality fly ash with high carbon content as raw material, and the utilization rate of fly ash is large, and the utilization of the stored fly ash can be realized, the occupation of land is reduced, and natural resources are saved. ,Improve the environment;
- the invention uses an alkaline activator to accelerate the reaction between the components in the steaming process block or the ball, accelerates the acceleration and complete completion of the reaction, reduces the steaming heat consumption, shortens the steaming time, and improves the production efficiency and Equipment use efficiency;
- the preparation method of the inorganic cementing material of the invention is simple, no large equipment is needed, the calcination temperature is low, the greenhouse gas emission is small, the composition and performance are flexible and adjustable, easy to control, and the applicability is good;
- the inorganic cementing material of the invention has the characteristics of fast setting, fast hardness, high strength and good resistance to sulfate attack, and is particularly suitable for tunnels, underwater, saline-alkali zones and coastal areas.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Curing Cements, Concrete, And Artificial Stone (AREA)
- Processing Of Solid Wastes (AREA)
Abstract
提供一种无机胶凝材料及其制备方法,其中,胶凝材料是由按质量份计粉煤灰65-80份、石灰以有效CaO计20-35份、激发剂0.5-2份和水15-50份制得的料块或料球经蒸养和煅烧所得的合成料60-70份、硅酸盐水泥20-30份和石膏5-10份共同粉磨制得。该无机胶凝材料用含碳量高的低品质粉煤灰为主要原料,煅烧温度和热耗低。
Description
本发明涉及一种建筑材料技术领域,特别是一种利用粉煤灰、石灰和少量硅酸盐水泥或水泥熟料为主要原料的快凝高强无机胶凝材料及其制备方法。
水泥作为土木、水利和交通建筑工程用量巨大的胶凝材料,其生产过程的高资源和高能源消耗及高温室气体排放等问题日益为人们所关注,材料工作者一直致力于寻求新的原材料资源和可替代的或者可作为补充的新的胶凝材料的制备方法。同时,随着建设开发的地区和领域的不断扩大,处于特殊自然环境的建筑工程也对无机胶凝材料的性能提出了不同的新的要求,具有特殊性能的无机胶凝材料的需求日益增加。另一方面,各类工业废渣对环境的不利影响和有效处置仍是一个尚未彻底解决的问题,其中包括火力发电企业排出的粉煤灰。尽管近年来电厂干法排出的粉煤灰一大部分已被利用,但上世纪八、九十年代以前湿法排放的大量粉煤灰,由于其一般粒度较粗,含碳量较高,其物理性质和反应活性不能满足作为水泥混合材和混凝土掺合料的要求,不能直接大量地应用于水泥与混凝土和其它建材制品中,因此尚未能被有效利用而被长期堆存。长期堆存的粉煤灰不仅占有大量的土地,还严重污染周围环境,因此其有效资源化利用是一亟待解决的问题。用堆存粉煤灰为主要原料制备无机胶凝材料,不仅可以节省不可再生资源,而且节能、环保。但现有用粉煤灰制备无机胶凝材料的技术存在粉煤灰用量少、对粉煤灰品质要求高和产品性能较差的问题。
发明公开
本发明所要解决的技术问题是针对上述现有技术存在的问题,提供一种可以大量利用堆存低品质粉煤灰为主要原料的快凝无机胶凝材料。
本发明的另一目的是提供这种快凝高强无机胶凝材料的制备方法。
为了实现上述目的,本发明提供了一种无机胶凝材料,该胶凝材料是由用按质量份计粉煤灰65-80份、石灰以有效CaO计20-35份、激发剂0.5-2份和
水15-50份制得的料块或料球经蒸养和煅烧所得的合成料60-70份、硅酸盐水泥20-30份与石膏5-10份共同粉磨制得。所述粉煤灰为符合GBT 1596用于水泥和混凝土中的粉煤灰III级以上技术指标的粉煤灰;所述石灰为满足JC/T 479建筑生石灰技术指标的钙质石灰和满足JC/T 481建筑消石灰技术指标的钙质消石灰;所述石膏为二水石膏、半水石膏和无水石膏中的一种或几种的组合;所述激发剂为碱金属氢氧化物、碱金属碳酸盐和碱金属硫酸盐的一种或几种的组合。
为了更好地实现上述目的,本发明还提供了一种无机胶凝材料的制备方法,其主要步骤如下:
步骤(1):将粉煤灰、石灰、激发剂按比例配合,共同粉磨至细度为45μm筛余小于10%的配合料;
步骤(2):将所述配合料与水均匀混合后,陈化2~3h,成型成最大尺寸为10-240mm的料块或直径为8-16mm的料球;
步骤(3):将所述料块料球在90~98℃蒸汽养护8~16h得蒸养料;
步骤(4):将所述蒸养料在750~1000℃下煅烧15-90min后风冷或在空气中冷却得合成料。
步骤(5):将所述合成料60-70份、硅酸盐水泥20-30份与石膏5-10份共同粉磨至比表面积为350-450m2/kg制得一种无机胶凝材料。
本发明通过蒸汽养护使得石灰与粉煤灰中活性氧化硅和活性氧化铝反应形成水化硅酸钙和水化铝酸钙,在较低温度下煅烧后形成硅酸二钙和七铝十二钙,其中七铝十二钙有很高的水化活性,硅酸二钙也由于在较低的温度下形成,存在大量结构缺陷,因此也具有很高的水化活性,容易与水反应形成具有高胶凝性的水化产物。
本发明中激发剂可以与粉煤灰中的铝硅酸盐玻璃体反应,破坏玻璃体网络结构,降低玻璃体网络结构的聚合程度,大大提高其中氧化硅和氧化铝与石灰的反应速率及水化硅酸钙和水化铝酸钙的形成率,进而提高无机胶凝材料中硅酸二钙和七铝十二钙的含量,提高无机胶凝材料的胶凝性。
七铝十二钙的高水化活性可以赋予无机胶凝材料快凝快硬特性,硅酸盐水泥或硅酸盐水泥熟料可以保准无机胶凝材料水化后具有足够的碱度、保证胶凝材料硬化后具有良好的抗碳化性能。
以下结合附图和具体实施例对本实用新型进行详细描述,但不作为对本实用新型的限定。
附图简要说明
图1为本发明的生产工艺流程图。
实现本发明的最佳方式
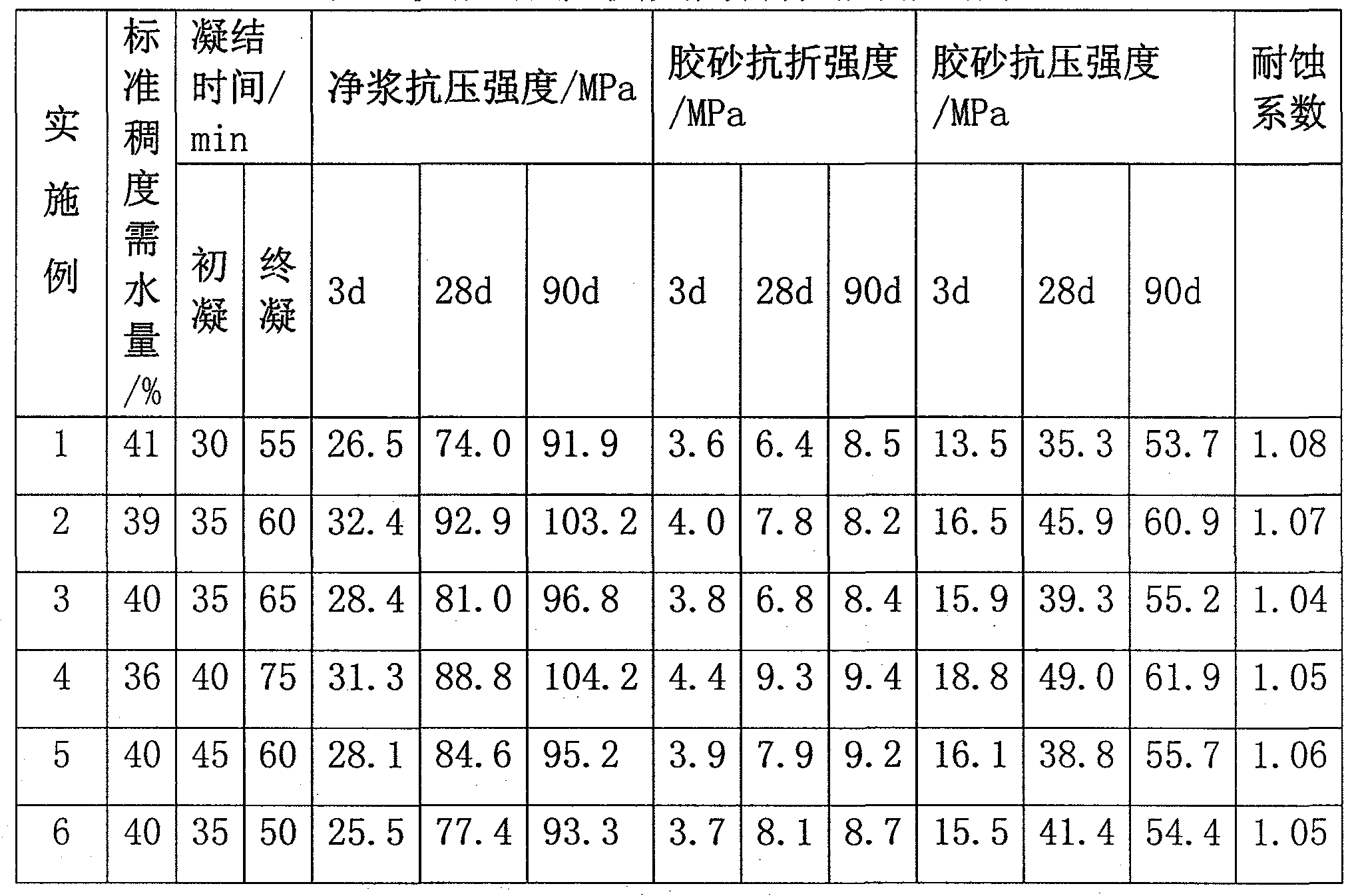
下面通过实施例的方式对本发明技术方案进行详细说明,但是本发明的保护范围不局限于所述实施例。各实施例快凝高强无机胶凝材料的凝结时间、净浆抗压强度、标准胶砂强度和耐硫酸盐侵蚀系数检测结果见表1。
实施例1
配合料按质量份)含有以下成分:
粉煤灰 80份
生石灰以CaO计 20份
氢氧化钠 0.5份
按上述质量比称取粉煤灰、生石灰、氢氧化钠,共同粉磨至细度为45μm筛余为5.2%的配合料;将配合料倒入搅拌机中,加入35份水后搅拌3min,陈化2h后用成球盘成型成直径为8-16mm的料球;将料球在蒸养箱中90℃蒸养10h得蒸养料,将蒸养料用小型窑炉750℃煅烧90min后吹风冷却得合成料;取合成料70份、硅酸盐水泥20份与无水石膏10份共同粉磨至比表面积为350m2/kg制得一种快凝高强无机胶凝材料。
实施例2
配合料按质量份计含有以下成分:
粉煤灰 70份
生石灰以CaO计 30份
氢氧化钠 1.0份
按上述质量比称取粉煤灰、生石灰、氢氧化钠,共同粉磨至细度为45μm筛余为5.8%的配合料;将配合料倒入搅拌机中,加入45份水后搅拌2min,陈化2.5h后用成球盘成型成直径为8-16mm的料球;将料球在蒸养箱中95℃蒸养8h得蒸养料,将蒸养料用小型窑炉800℃煅烧60min后吹风冷却得合成料;取合
成料68份、硅酸盐水泥25份与二水石膏7份共同粉磨至比表面积为415m2/kg制得一种快凝高强无机胶凝材料。
实施例3
配合料按质量份计含有以下成分:
粉煤灰 75份
生石灰以CaO计 25份
碳酸钠 1.4份
按上述质量比称取粉煤灰、生石灰、碳酸钠,共同粉磨至细度为45μm筛余为9.8%的配合料;将配合料倒入搅拌机中,加入40份水后搅拌3min,陈化3h后挤压成240mm×115mm×53mm的料块,将料块在蒸养箱中90℃蒸养16h得蒸养料,将蒸养料用小型窑炉750℃煅烧75min后在空气中自然冷却得合成料;将合成料用破碎机破碎成小于16mm的颗粒,取合成料67份、硅酸盐水泥25份与半水石膏8份共同粉磨至比表面积为425m2/kg制得一种快凝高强无机胶凝材料。
实施例4
配合料按质量份计含有以下成分:
粉煤灰 65份
生石灰以CaO计 35份
无水硫酸钠 2.0份
按上述质量比称取粉煤灰、生石灰、无水硫酸钠,共同粉磨至细度为45μm筛余为8.1%的配合料;将配合料倒入搅拌机中,加入50份水后搅拌3min,陈化3h后挤压成50mm×50mm×30mm的料块;将料块在蒸养箱中98℃蒸养12h得蒸养料,将蒸养料用小型窑炉800℃煅烧45min后在空气中自然冷却得合成料;将合成料用破碎机破碎成小于16mm的颗粒后,取合成料95份65份、硅酸盐水泥30份与半水石膏5份共同粉磨至比表面积为440m2/kg制得一种快凝高强无机胶凝材料。
实施例5
配合料按质量份计含有以下成分:
粉煤灰 75份
消石灰以CaO计 25份
碳酸钾 1.5份
按上述质量比称取粉煤灰、消石灰、碳酸钾,共同粉磨至细度为45μm方孔筛筛余为4.3%的配合料;将配合料倒入搅拌机中,加入20份水后搅拌3min,陈化2h后用成球盘成型成直径为8-16mm的料球;将料球在蒸养箱中90℃蒸养8h得蒸养料,将蒸养料用小型窑炉800℃煅烧50min在后空气中自然冷却得合成料;取合成料67份、硅酸盐水泥25份、无水石膏4份和半水石膏3份共同粉磨至比表面积为370m2/kg制得一种快凝高强无机胶凝材料。
实施例6
配合料按质量份计含有以下成分:
粉煤灰 80份
消石灰以CaO计 20份
氢氧化钾 1.3份
按上述质量比称取粉煤灰、消石灰、氢氧化钾,共同粉磨至细度为45μm筛余为3.5%的配合料;将配合料倒入搅拌机中,加入15份水后搅拌3min,陈化3h后挤压成直径10mm、厚6mm的料块;将料块在蒸养箱中98℃蒸养12h得蒸养料,将蒸养料,用小型窑炉800℃煅烧60min后在空气中自然冷却得合成料;取合成料67份、硅酸盐水泥25份与二水石膏8份共同粉磨至比表面积为385m2/kg制得一种快凝高强无机胶凝材料。
实施例7
配合料按质量份计含有以下成分:
粉煤灰 70份
消石灰以CaO计 30份
氢氧化钠 1.2份
按上述质量比称取粉煤灰、消石灰、氢氧化钠,共同粉磨至细度为45μm方孔筛筛余为7.6%的配合料;将配合料倒入搅拌机中,加入25份水后搅拌3min,陈化3h后用成球盘成型成直径为-16mm的料球;将料球在蒸养箱中90℃蒸养10h得蒸养料,将蒸养料用小型窑炉1000℃煅烧15min后吹风冷却得合成料;取合成料64份、硅酸盐水泥30份与二水石膏6份共同粉磨至比表面积为445m2/kg制得一种快凝高强无机胶凝材料。
实施例8
配合料按质量份计含有以下成分:
按上述质量比称取粉煤灰、消石灰、氢氧化钠和无水硫酸钠,共同粉磨至细度为45μm方孔筛筛余为6.2%的配合料;将配合料倒入搅拌机中,加入25份水后搅拌3min,陈化3h后用成球盘成型成直径为(8-16)mm的料球;将料球在蒸养箱中95℃蒸养14h得蒸养料,将蒸养料用小型窑炉900℃煅烧30min吹风冷却得合成料;取合成料66份、硅酸盐水泥27份与半水石膏7份共同粉磨至比表面积为440m2/kg制得一种快凝高强无机胶凝材料。
参照GBT 1346-2011水泥标准稠度用水量、凝结时间、安定性检验方法测得实施例1-8无机胶凝材料的标准稠度需水量、凝结时间,及标准稠度水泥净浆试体各龄期的抗压强度,按GBT 17671-1999水泥胶砂强度试验方法测得各无机胶凝材料标准胶砂强度,按GBT749-2008水泥抗硫酸盐侵蚀试验方法测得各无机胶凝材料耐硫酸盐侵蚀系数,结果见表1。
表1快凝高强无机胶凝材料性能测定结果
当然,本发明还可有其它多种实施例,在不背离本发明精神及其实质的情况下,熟悉本领域的技术人员当可根据本发明作出各种相应的改变和变形,但这些相应的改变和变形都应属于本发明所附的权利要求的保护范围。
工业应用性
本发明的有益效果为:
(1)本发明无机胶凝材料可以用含碳量高的低品质粉煤灰为原料,粉煤灰利用率大,可以实现堆存粉煤灰资源化利用,减少土地的占用,节约自然资源,改善环境;
(2)本发明采用碱性激发剂加速蒸养过程料块或料球中各组分间的反应,促进反应的加速和彻底完成,降低蒸养热耗,缩短蒸养时间,提高生产效益和设备使用效率;
(3)本发明无机胶凝材料的制备方法简单,无需大型的设备、煅烧温度低,温室气体排放量少,其组成和性能灵活可调,易于控制,适用性好;
(4)本发明无机胶凝材料具有快凝快硬、强度高、耐硫酸盐侵蚀性好的特性,特别适用于坑道、水下、盐碱地带和沿海地区工程。
Claims (6)
- 一种无机胶凝材料,其特征在于该胶凝材料是由用按质量份计粉煤灰65~80份、石灰以有效CaO计20~35份、激发剂0.5~2.0份和水15-50份制得的料块或料球经蒸养和煅烧所得的合成料60-70份、硅酸盐水泥20-30份与石膏5-10份共同粉磨制得。
- 根据权利要求1所述的无机胶凝材料,其特征在于,所述粉煤灰符合GBT 1596用于水泥和混凝土中的粉煤灰III级以上技术指标的粉煤灰;所述石灰为满足JC/T 479建筑生石灰技术指标的钙质石灰和满足JC/T 481建筑消石灰技术指标的钙质消石灰;所述石膏为二水石膏、半水石膏和无水石膏中的一种或几种的组合。
- 根据权利要求1所述的无机胶凝材料,其特征在于,所述激发剂为碱金属氢氧化物、碱金属碳酸盐和碱金属硫酸盐的一种或几种的组合。
- 一种根据权利要求1所述的无机胶凝材料的制备方法,其特征在于,该方法的步骤如下:第一步:将粉煤灰、石灰、激发剂按比例配合,共同粉磨至细度为45μm筛余小于10%的配合料;第二步:将所述配合料与水后搅拌混合,陈化2~3h后成型得料块或料球;第三步:将所述料块或料球蒸汽养护8~16h得蒸养料;第四步:将所述蒸养料在设定煅烧温度下煅烧15-90min后风冷或在空气中冷却得合成料;第五步:将所述合成料60-70份、硅酸盐水泥20-30份与石膏5-10份共同粉磨至比表面积为350-450m2/kg制得一种快凝高强无机胶凝材料。
- 根据权利要求4所述的无机胶凝材料的制备方法,其特征在于,所述蒸养料的蒸汽养护温度为90-98℃。
- 根据权利要求4所述的无机胶凝材料的制备方法,其特征在于,所述蒸养料的煅烧温度为750-1000℃。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201510088879.4A CN105985039B (zh) | 2015-02-26 | 2015-02-26 | 一种无机胶凝材料及其制备方法 |
| CN201510088879.4 | 2015-02-26 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2016134551A1 true WO2016134551A1 (zh) | 2016-09-01 |
Family
ID=56787752
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2015/073568 WO2016134551A1 (zh) | 2015-02-26 | 2015-03-03 | 一种无机胶凝材料及其制备方法 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN105985039B (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2016134551A1 (zh) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109851287A (zh) * | 2019-03-19 | 2019-06-07 | 扬州云龙环保建材有限公司 | 一种粉煤灰蒸压砖加工工艺流程 |
| CN115466065A (zh) * | 2022-09-19 | 2022-12-13 | 一夫科技股份有限公司 | 一种磷基ⅱ型无水石膏胶凝材料及其活化方法 |
| CN115594481A (zh) * | 2022-10-09 | 2023-01-13 | 盐城工学院(Cn) | 一种适用于管桩的免蒸养免蒸压高强复合胶凝材料及其制备方法 |
| CN116023077A (zh) * | 2022-12-27 | 2023-04-28 | 武汉大学 | 一种耐冻融循环损伤的碱激发胶凝材料及其制备方法 |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2019232687A1 (zh) * | 2018-06-05 | 2019-12-12 | 华智节能(香港)有限公司 | 超快硬特种无机胶凝材料及其制备方法 |
| CN110482986A (zh) * | 2019-09-18 | 2019-11-22 | 贵州中能高新材料有限公司 | 一种石膏复合胶凝材料的加工方法 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1030217A (zh) * | 1987-12-04 | 1989-01-11 | 淮南发电总厂 | 从粉煤灰提氧化铝同时生成β-C2S胶凝材料法 |
| CN1068555A (zh) * | 1992-08-06 | 1993-02-03 | 登封电厂 | 粉煤灰水泥的配方及其生产工艺 |
| CN1072159A (zh) * | 1992-11-15 | 1993-05-19 | 四川建筑材料工业学院 | 一种低温煅烧水泥熟料工艺 |
| CN101372403A (zh) * | 2008-10-15 | 2009-02-25 | 登电集团水泥有限公司 | 一种粉煤灰水泥的制备方法 |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1037506C (zh) * | 1993-07-13 | 1998-02-25 | 武汉工业大学 | 高活性粉煤灰混合材 |
| CN1115309C (zh) * | 2000-05-31 | 2003-07-23 | 蒋兆广 | 粉煤灰的处理方法 |
| CN102249625A (zh) * | 2010-12-17 | 2011-11-23 | 范会生 | 一种复合胶凝材料及其制备方法 |
| CN104370484A (zh) * | 2013-08-16 | 2015-02-25 | 山西华通蓝天环保有限公司 | 早强型高掺活化超细粉煤灰水泥 |
-
2015
- 2015-02-26 CN CN201510088879.4A patent/CN105985039B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2015-03-03 WO PCT/CN2015/073568 patent/WO2016134551A1/zh active Application Filing
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1030217A (zh) * | 1987-12-04 | 1989-01-11 | 淮南发电总厂 | 从粉煤灰提氧化铝同时生成β-C2S胶凝材料法 |
| CN1068555A (zh) * | 1992-08-06 | 1993-02-03 | 登封电厂 | 粉煤灰水泥的配方及其生产工艺 |
| CN1072159A (zh) * | 1992-11-15 | 1993-05-19 | 四川建筑材料工业学院 | 一种低温煅烧水泥熟料工艺 |
| CN101372403A (zh) * | 2008-10-15 | 2009-02-25 | 登电集团水泥有限公司 | 一种粉煤灰水泥的制备方法 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| HAN, HUAIQIANG ET AL., FLY ASH UTILIZATION TECHNIQUES, 31 January 2001 (2001-01-31) * |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109851287A (zh) * | 2019-03-19 | 2019-06-07 | 扬州云龙环保建材有限公司 | 一种粉煤灰蒸压砖加工工艺流程 |
| CN115466065A (zh) * | 2022-09-19 | 2022-12-13 | 一夫科技股份有限公司 | 一种磷基ⅱ型无水石膏胶凝材料及其活化方法 |
| CN115466065B (zh) * | 2022-09-19 | 2023-08-29 | 一夫科技股份有限公司 | 一种磷基ⅱ型无水石膏胶凝材料及其活化方法 |
| CN115594481A (zh) * | 2022-10-09 | 2023-01-13 | 盐城工学院(Cn) | 一种适用于管桩的免蒸养免蒸压高强复合胶凝材料及其制备方法 |
| CN115594481B (zh) * | 2022-10-09 | 2023-09-22 | 盐城工学院 | 一种适用于管桩的免蒸养免蒸压高强复合胶凝材料及其制备方法 |
| CN116023077A (zh) * | 2022-12-27 | 2023-04-28 | 武汉大学 | 一种耐冻融循环损伤的碱激发胶凝材料及其制备方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN105985039A (zh) | 2016-10-05 |
| CN105985039B (zh) | 2019-03-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2016134551A1 (zh) | 一种无机胶凝材料及其制备方法 | |
| WO2016134552A1 (zh) | 一种无机胶凝材料及其制备方法 | |
| CN102910889B (zh) | 一种含有江河淤泥沙的加气混凝土墙材及其制备方法 | |
| KR101809485B1 (ko) | 초속경 고강도 방수 방충 몰탈 조성물 | |
| CN109485278B (zh) | 一种以煤矸石为原料的胶凝材料及其制备方法 | |
| CN112266264B (zh) | 基于碱激发与加速碳化协同作用的加气混凝土及制备方法 | |
| CN103241966B (zh) | 无熟料钢渣再生微粉复合水泥 | |
| CN108658485B (zh) | 一种水硬性水泥熟料及其制备方法、水硬性水泥及其应用 | |
| CN103803918A (zh) | 一种掺有瓷粉废料的水泥基微膨胀裂缝修补砂浆及使用方法 | |
| CN104556909B (zh) | 一种以粉煤灰为原料的快凝耐蚀水泥及其制备方法 | |
| CN112266193A (zh) | 人造钢渣骨料及其制备方法和应用 | |
| CN105174887A (zh) | 一种改性脱硫石膏基母料及其制备方法 | |
| CN110041035B (zh) | 一种低胶材用量的c30高抗渗混凝土及其制备方法 | |
| CN112159187B (zh) | 一种环保脱硫石膏加气砌块及其生产工艺 | |
| CN112794683B (zh) | 一种废弃混凝土基再生胶凝材料及其制备方法 | |
| CN114988791B (zh) | 一种掺富硫锂渣的烟道灌浆料及其制备方法和应用 | |
| CN107746215A (zh) | 一种矿物聚合物泡沫混凝土及制备方法 | |
| CN108083671A (zh) | 粒化高炉矿渣激发剂及其制备方法与用途 | |
| CN112521113B (zh) | 一种低温水化硬化凝胶材料及其制备方法和应用 | |
| WO2019232687A1 (zh) | 超快硬特种无机胶凝材料及其制备方法 | |
| CN111285654A (zh) | 一种脱硫建筑石膏基复合胶凝材料的制备方法 | |
| CN110963764A (zh) | 一种防水混凝土及其制备方法 | |
| CN113880516A (zh) | 一种免蒸压粉煤灰加气混凝土保温砌块及其制备方法 | |
| CN110845168A (zh) | 一种活性掺和料、活性掺和料的制备方法、应用及混凝土 | |
| CN113979679B (zh) | 一种自修复地聚合物基渗透结晶防水材料及其制备方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 15882989 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 15882989 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |