WO2015064319A1 - 画像処理装置及び画像処理方法 - Google Patents
画像処理装置及び画像処理方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015064319A1 WO2015064319A1 PCT/JP2014/076922 JP2014076922W WO2015064319A1 WO 2015064319 A1 WO2015064319 A1 WO 2015064319A1 JP 2014076922 W JP2014076922 W JP 2014076922W WO 2015064319 A1 WO2015064319 A1 WO 2015064319A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- information
- lens
- assist information
- image
- assist
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N23/00—Cameras or camera modules comprising electronic image sensors; Control thereof
- H04N23/60—Control of cameras or camera modules
- H04N23/64—Computer-aided capture of images, e.g. transfer from script file into camera, check of taken image quality, advice or proposal for image composition or decision on when to take image
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N23/00—Cameras or camera modules comprising electronic image sensors; Control thereof
- H04N23/60—Control of cameras or camera modules
- H04N23/63—Control of cameras or camera modules by using electronic viewfinders
- H04N23/633—Control of cameras or camera modules by using electronic viewfinders for displaying additional information relating to control or operation of the camera
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03B—APPARATUS OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR TAKING PHOTOGRAPHS OR FOR PROJECTING OR VIEWING THEM; APPARATUS OR ARRANGEMENTS EMPLOYING ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ACCESSORIES THEREFOR
- G03B17/00—Details of cameras or camera bodies; Accessories therefor
- G03B17/02—Bodies
- G03B17/12—Bodies with means for supporting objectives, supplementary lenses, filters, masks, or turrets
- G03B17/14—Bodies with means for supporting objectives, supplementary lenses, filters, masks, or turrets interchangeably
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03B—APPARATUS OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR TAKING PHOTOGRAPHS OR FOR PROJECTING OR VIEWING THEM; APPARATUS OR ARRANGEMENTS EMPLOYING ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ACCESSORIES THEREFOR
- G03B17/00—Details of cameras or camera bodies; Accessories therefor
- G03B17/18—Signals indicating condition of a camera member or suitability of light
- G03B17/20—Signals indicating condition of a camera member or suitability of light visible in viewfinder
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an image processing apparatus and image processing method for presenting assist information for assisting imaging.
- Japanese Patent Application Publication No. 2009-521134 searches an image having an image feature amount similar to an image feature amount extracted from an image obtained by photographing from a database, and an image retrieved Information indicating the direction in which the imaging device should be moved to approach the same composition as the composition of is presented to the user as assist information.
- the present invention has been made in view of the above-described circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to provide an image processing apparatus and an image processing method capable of presenting information on a lens according to shooting information as assist information.
- an image processing apparatus comprises an image acquisition unit for acquiring image data, a photographing information acquisition unit for acquiring photographing information related to the image data, and the photographing information
- a scene / subject discrimination unit for discriminating a shooting scene or subject in the image data based on the image data
- an assist information search unit for searching assist information on a lens according to the shooting scene or subject discrimination result, and the searched assist And a display unit for displaying information.
- an image processing method of a second aspect of the present invention acquiring image data, acquiring imaging information regarding the image data, and the image based on the imaging information Determining a shooting scene or subject in the data, searching assist information on a lens according to the shooting scene or subject determination result, and displaying the searched assist information on a display unit .
- an image processing apparatus and an image processing method capable of presenting information related to a lens according to imaging information as assist information.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an entire configuration of an imaging device according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 2 is a flowchart showing the procedure of displaying assist information according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 3 is a view showing a display example of assist information according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a first example of a screen displayed when assist information is selected.
- FIG. 5 is a view showing a second example of the screen displayed when the assist information is selected.
- FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing an entire configuration of an imaging apparatus according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing a procedure of displaying assist information according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an entire configuration of an imaging device according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 2 is a flowchart showing the procedure of displaying assist information according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 8 is a block diagram showing an entire configuration of an imaging apparatus according to a third embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 9 is a flowchart showing a procedure of displaying assist information according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 10 is a view showing a first display example of assist information according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 11 is a view showing a second display example of the assist information according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 12 is a block diagram showing an entire configuration of an imaging apparatus according to a fourth embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an entire configuration of an imaging apparatus as an application example of an image processing apparatus according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
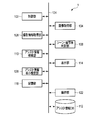
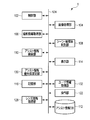
- the imaging device 1 illustrated in FIG. 1 can be applied to various types of mobile terminal devices such as, for example, a digital camera, a mobile phone with a camera, and a smartphone.
- the imaging apparatus 1 includes a control unit 102, an image acquisition unit 104, an imaging information acquisition unit 106, an imaging scene / subject determination unit 108, an assist information search unit 110, an assist information database (DB) 112, and a display.
- DB assist information database
- a unit 114, a storage unit 116, and an operation unit 122 are included. Further, as shown in FIG. 1, the control unit 102, the image acquisition unit 104, the photographing information acquisition unit 106, the photographing scene / subject discrimination unit 108, the assist information search unit 110, the assist information DB 112, the display unit
- the memory 114, the storage unit 116, and the operation unit 122 are communicably connected to one another via a bus 124.
- the control unit 102 has, for example, a CPU, and controls the overall operation of the imaging device 1. For example, the control unit 102 controls an image acquisition operation by the image acquisition unit 104, or causes the display unit 114 to display an image based on image data acquired by the image acquisition unit 104. Furthermore, the control unit 102 performs image processing on the image data acquired by the image acquisition unit 104 to create an image file, and causes the storage unit 116 to store the created image file.
- the image acquisition unit 104 acquires image data.
- the image acquisition unit 104 is an imaging unit having, for example, a lens, an aperture, a shutter, an imaging element, an A / D conversion circuit, and the like.
- the lens in the present embodiment is, for example, an interchangeable lens configured to be detachable from the main body of the imaging device 1.
- the image acquisition unit 104 converts an optical image of a subject incident through a lens into an analog electrical signal in the imaging device, and converts the analog electrical signal into digital in an A / D conversion circuit. Image data is acquired by converting into a signal.
- the imaging information acquisition unit 106 acquires imaging information regarding the image data acquired by the image acquisition unit 104.
- the shooting information here includes the subject distance at the time of shooting, the brightness of the image data, the color, the image feature amount, and the amount of movement of the subject or the imaging device 1.
- the image feature amount for example, Local Binary Pattern (LBP), Scale-Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT), Speeded Up Robust Features (SURF), Oriented FAST and Rotated Brief (ORB), an HSV histogram or the like is used.
- LBP Local Binary Pattern
- SIFT Scale-Invariant Feature Transform
- SURF Speeded Up Robust Features
- ORB Rotated Brief
- the shooting scene / subject determination unit 108 determines a shooting scene of the image data and the main subject based on the shooting information acquired by the shooting information acquisition unit 106. For example, when the brightness of the background area is low, the shooting scene / subject determining unit 108 determines that the scene is a night scene shooting scene, and determines that the scene is a sunset shooting scene if there are many red components in the background area. When the brightness of the background area is higher than that of the background area, it is determined that the scene is a backlit image. Further, when the subject distance corresponds to a macro area set for each lens, the shooting scene / subject determination unit 108 determines that the scene is a macro shooting scene. Furthermore, the shooting scene / subject determination unit 108 compares the similarity between the image feature quantity extracted as shooting information from the image data and the image feature quantity for each subject stored in advance in the storage unit 116, for example. Determine the main subject.
- the assist information search unit 110 searches the assist information DB 112 for assist information on a lens according to the determination result of the shooting scene or the main subject in the shooting scene / subject determination unit 108.
- the assist information DB 112 stores assist information on the lens in association with the type of shooting scene and the type of subject.
- the assist information is information including an image (sample image) indicating an example of various photographs and lens-related assist information used to capture each sample image.
- sample image an image
- a different subject or a different photographed scene is photographed using the same lens as a sample image obtained by photographing the same subject or the same photographing scene using different lenses.
- lens-related assist information includes the lens name (may be model number etc.), lens specs (focal length and open aperture value etc.), and settings related to the lens at the time of shooting the sample image (focal length setting, aperture value Setting etc.).
- lens-related assist information is used to explain the setting (shutter speed, image processing setting, etc.) of the imaging device 1 at the time of shooting a sample image and various points for shooting an image equivalent to the sample image to the user. Guide information etc. may be included.
- the assist information stored in the assist information DB 112 be sequentially updated, for example, when the imaging device 1 is connected to the network.
- the display unit 114 is a display unit such as a liquid crystal display or an organic EL display, and displays various images under the control of the control unit 102.
- the display unit 114 also displays the assist information searched by the assist information search unit 110.
- the storage unit 116 includes, for example, a ROM and a RAM, and stores image data obtained by shooting and image feature quantities for each subject used in subject determination in the shooting scene / subject determination unit 108.
- image feature quantity for each subject be successively updated by machine learning using, for example, SVM (Support Vector Machine) or the like.
- the storage unit 116 records various programs executed by the control unit 102 and various parameters used when the programs are executed.
- the storage unit 116 temporarily stores various data such as image data obtained by the image acquisition unit 104 and image data during image processing in the control unit 102.
- the operation unit 122 is an operation unit for the user to perform various operations of the imaging apparatus 1.
- the operation unit 122 may be a mechanical operation unit such as a button or an operation unit using a touch panel.
- an instruction to execute a shooting operation is made, and various settings such as a shooting scene mode are made.
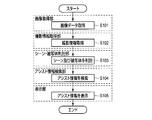
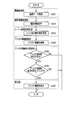
- FIG. 2 is a flowchart showing a procedure of displaying assist information as an image processing method according to the present embodiment.
- FIG. 2 shows a procedure for displaying assist information during live view display before shooting. Further, the processing of the flowchart in FIG. 2 is mainly performed by the control unit 102.
- the control unit 102 causes the image acquisition unit 104 to acquire image data (step S101).
- the image acquisition unit 104 drives an imaging element to capture an object.
- An image signal obtained by the imaging device is converted into a digital signal in an A / D conversion circuit.
- the image data as the digital signal is stored in the storage unit 116.
- control unit 102 After acquiring the image data, the control unit 102 causes the imaging information acquisition unit 106 to acquire imaging information (step S102). After obtaining the shooting information, the control unit 102 causes the shooting scene / subject determination unit 108 to determine the shooting scene of the image data and the main subject (step S103).
- the control unit 102 After determining the shooting scene and the main subject, the control unit 102 causes the assist information search unit 110 to search for assist information (step S104). After searching for the assist information, the control unit 102 causes the display unit 114 to display the through image on the basis of the image data acquired in step S101, and causes the display unit 114 to display the assist information searched in step S104 (step S105). Thereafter, the control unit 102 ends the process of FIG.
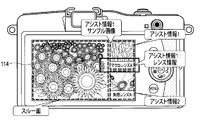
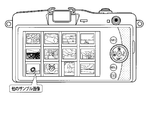
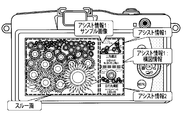
- FIG. 3 is a view showing a display example of assist information according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 3 shows a display example of assist information when it is determined in the shooting scene / subject determination unit 108 that the main subject is “sunflower (flower)”.
- the sample image of the sunflower photographed using a plurality of different lenses is the lens of the lens used to photograph the sample image. It is displayed on the display unit 114 together with the related assist information.
- FIG. 3 shows an example in which the sample image is displayed on the right side of the display unit 114.
- the display position of the sample image may be the upper side, the lower side, or the left side of the display unit 114.
- FIG. 3 shows an example in which two sample images are displayed on the display unit 114 at one time. On the other hand, three or more sample images may be displayed at one time. If many sample images can not be displayed at one time because the area of the display screen of the display unit 114 is limited or the like, the sample image displayed on the display unit 114 by a scroll operation or the like by the user May be changed.
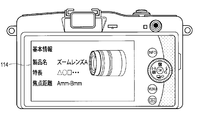
- FIG. 4 is a view showing a first example of a screen displayed when any one of assist information of the assist information displayed on the display unit 114 as shown in FIG. 3 is selected.
- the first example when assist information is selected, detailed information of the lens associated with the selected assist information is displayed.
- FIG. 4 shows an example in which the product name of the lens, the information indicating the main features, and the information indicating the specification of the lens (focal length in FIG. 4) are displayed as the detailed information of the lens.
- Detailed information of the lens to be displayed as the first example can be set as appropriate.
- the type of information to be displayed may be set by the user.
- FIG. 5 is a view showing a second example of a screen displayed when any assist information of the assist information displayed on the display unit 114 as shown in FIG. 3 is selected.
- the assist information including other sample images captured using the lens associated with the selected assist information is displayed.
- Another sample image displayed as the second example may be an image in which a subject different from the determination result by the shooting scene / subject determination unit 108 is captured.
- Whether the transition to the screen of FIG. 4 or the screen of FIG. 5 is made when assist information is selected while the screen of FIG. 3 is displayed is set by, for example, the operation of the operation unit 122 of the user.
- the display of the screen in FIG. 3 is set as the display screen of the assist information of the first hierarchy, and any assist information is selected on the display screen of the assist information of the first hierarchy.
- the display screen of FIG. 4 as the display screen of the assist information of the second hierarchy is displayed, and the assist information of the third hierarchy is displayed when any operation is further performed on the display screen of the assist information of the second hierarchy. It is also possible to control the transition of the display screen such as displaying the screen of FIG. 5 as a screen.
- assist information related to a lens according to a shooting scene or subject that is considered to be of interest to the user according to the shooting scene or subject condition during live view display Is presented to the user.
- assist information on such a lens to the user it is possible to notify the user that the range of expression at the time of photographing can be expanded by lens replacement.
- assist information including sample images obtained by photographing the same subject or the same shooting scene with different lenses it is possible to notify the user of differences in expression due to differences in lenses.
- assist information including sample images obtained by shooting different subjects or shooting scenes with the same lens to the user it is possible to shoot other subjects or shooting scenes using the same lens.
- the interest can be given to the user.
- FIG. 2 shows an example in which assist information is displayed at the time of through image display.
- the assist information may be displayed at the time of confirmation of the imaging result after execution of imaging or during reproduction of the image.
- the process of step S101 is a process of merely inputting image data.
- the process of step S102 is changed to a process of acquiring shooting information when the image being reproduced is actually shot. As shooting information acquired in this case, the one recorded in the header or the like of the image file is used. Further, in the process of step S103, the image once determined is read in the header or the like to the image file, and thus read out.
- the assist information to be displayed on the display unit 114 may be acquired via the network. By doing this, the user can obtain the latest information because the information of the new lens is displayed when saving the capacity of the assist information DB 112 or when the manufacturer releases the latest lens. is there.
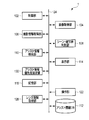
- FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing an entire configuration of an imaging apparatus as an application example of the image processing apparatus according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
- the imaging device 1 in the second embodiment further includes an assist information display setting unit 126.
- the assist information display setting unit 126 sets conditions for displaying assist information in response to, for example, an operation of the operation unit 122 by the user.
- This condition is, for example, a condition as to whether or not the assist information is to be displayed, and a condition as to when the assist information is to be displayed.
- the timing for displaying assist information is, for example, when the shutter button, which is an operation unit for instructing to execute shooting, is pressed halfway, and when the shooting result is confirmed when the shutter button is fully pressed, the playback button is pressed. It is at the time of viewing the case image.
- FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing the procedure of displaying assist information as the image processing method according to the present embodiment.
- the description of the processing common to FIG. 2 will be omitted. That is, since the processing of steps S201 to S204 is the same processing as steps S101 to S104, the description will be omitted.
- step S205 determines whether the assist information display setting unit 126 is set to display assist information.
- the control unit 102 ends the process of FIG. 7. In this case, the assist information is not displayed. Note that the processing such as through image display is continued regardless of the presence or absence of the display of the assist information.
- step S205 When it is determined in step S205 that the assist information display setting unit 126 is set to display assist information, the control unit 102 displays the display timing of the assist information currently set in the assist information display setting unit 126. It is determined whether or not (step S206). If it is determined in step S206 that the present time is not the display timing of the assist information set in the assist information display setting unit 126, the control unit 102 ends the process of FIG. Also in this case, the assist information is not displayed. That is, even if the assist information is set to be displayed, the assist information is not displayed when it is not the display timing of the assist information. As in step S205, the processing such as through image display is continued regardless of the presence or absence of the display of the assist information.
- step S206 When it is determined in step S206 that the present time is the display timing of the assist information, the control unit 102 causes the display unit 114 to display an image corresponding to the image data acquired in step S201 as a through image. The searched assist information is displayed on the display unit 114 (step S207). Thereafter, the control unit 102 ends the process of FIG.
- the user can arbitrarily set whether or not to make the assist information, and at which timing the display is made, the display is made. This makes it possible to improve the usability for the user.
- FIG. 8 is a block diagram showing an entire configuration of an imaging apparatus as an application example of the image processing apparatus according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
- the imaging device 1 according to the third embodiment further includes a lens information acquisition unit 128 and an assist information priority setting unit 130.
- the lens information acquisition unit 128 acquires lens information.
- the lens information is information used to set the priority of the assist information, and is information indicating the relationship between the corresponding lens and the user.
- the lens information includes information indicating whether the user holds the corresponding lens.
- the lens information further includes information indicating the purchase time of the corresponding lens.
- the lens information is photographed using the information indicating the time when the corresponding lens is mounted for the first time and the corresponding lens It further includes information indicating the number of images.
- Information indicating the mounting time is acquired by communication between the imaging device 1 and the lens when the lens is mounted on the imaging device 1 and stored in the storage unit 116.
- the corresponding lens is used for the information indicating whether the user holds the corresponding lens and the information indicating whether the user has attached the corresponding lens to the imaging apparatus 1 in the initial state.
- Information indicating that the user does not hold the information and information indicating that the user has not attached the corresponding lens to the imaging apparatus 1 are stored in the storage unit 116.
- the information indicating that the user does not hold the corresponding lens is updated to the information indicating that the user holds the corresponding lens.
- information indicating the lens purchase time is also stored in the storage unit 116.
- the information is updated to information indicating that the user has attached the corresponding lens to the imaging device 1.
- information indicating when the corresponding lens is attached for the first time is also stored in the storage unit 116.
- the information indicating the number of shots is updated.
- the assist information priority setting unit 130 sets priorities among pieces of assist information recorded in the assist information DB 112 using the lens information acquired by the lens information acquisition unit 128. For example, the assist information priority setting unit 130 sets the priority so that the assist information of the lens currently attached to the imaging device 1 is displayed preferentially.
- FIG. 9 is a flowchart showing the procedure of displaying assist information as the image processing method according to the present embodiment.
- the description of the process common to FIG. 2 will be omitted. That is, since the process of steps S301 to S304 is the same process as steps S101 to S104, the description will be omitted.
- the control unit 102 After the assist information search unit 110 searches for assist information, the control unit 102 causes the lens information acquisition unit 128 to acquire lens information (step S305). After acquiring the lens information, the control unit 102 causes the assist information priority setting unit 130 to set the priority of the assist information (step S306).
- the priority of the assist information of the lens currently attached to the imaging apparatus 1 is increased, the priority of the assist information of the lens having the latest purchase time is increased, Increase the priority of assist information for lenses with a large number of images, increase the priority of assist information for lenses that have not been mounted, and increase the priority of assist information for lenses held by the user
- Various setting conditions can be considered such as increasing the priority of the assist information of the lens not held by the user, and making the priorities of the respective assist information the same. It is determined by the user, for example, based on which of these setting conditions the priority is to be set.
- control unit 102 After setting the priority, the control unit 102 causes the display unit 114 to display an image corresponding to the image data acquired in step S301 as a through image, and sets the assist information searched in step S304 to the assist information priority setting unit It is displayed on the display unit 114 according to the priority set by 130 (step S307). Thereafter, the control unit 102 ends the process of FIG.
- FIG. 10 is a view showing a first display example of assist information according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
- the first display example is a display example when the priority setting condition is set so as to increase the priority of the lens information of the currently mounted lens.
- the assist information of the currently mounted lens is preferentially displayed on the display unit 114.
- the user can view the assist information of the lens most closely associated with the current imaging condition. For example, information on the distance between the camera and the subject, composition information such as an angle, and assist information such as color and brightness settable on the camera, and iris information can be used as a method of taking maximum advantage of the mounted lens. be able to.
- FIG. 11 is a view showing a second display example of the assist information according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
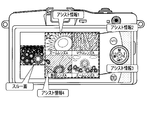
- the second display example is a display example when the setting condition of the priority is set so as to make the priority of the assist information the same.
- the assist information related to the “Japanese sunflower” searched in step S304 the assist information of the lens currently attached to the imaging device 1, the assist information of the lens attached to the imaging device 1, and imaging
- the display unit 114 displays the assist information of the lens that has not been attached to the device 1 and the assist information of the lens that the user does not hold.
- each piece of assist information displayed on the display unit 114 is the assist information displayed based on which lens information.
- a sample image taken with a lens not held by the user is displayed, for example, converted to gray scale or a gray image superimposed on the background of a color image.
- the sample image of the assist information 2 and the sample image of the assist information 4 are sample images captured by a lens not held by the user.
- a star mark is attached to a sample image photographed with a lens recently purchased by the user.
- the sample image of assist information 1 is a sample image captured by a lens recently purchased by the user.
- information desired by the user can be appropriately presented by setting the priority of the assist information according to the lens information.
- the lens replacement is provided to the user by presenting not only the assist information of the currently mounted lens, but also the assist information of the lens which is held or not, and the assist information of the lens which is not held. And can encourage lens purchase.
- the assist device can be provided with the assist information according to the lens information as described in the third embodiment by causing the imaging apparatus 1 in the third embodiment to have the assist information display setting unit 126 described in the second embodiment.
- the information may be displayed at the timing desired by the user.
- FIG. 12 is a block diagram showing an entire configuration of an imaging apparatus as an application example of the image processing apparatus according to the fourth embodiment of the present invention.
- the imaging device 1 in the fourth embodiment further includes a user information acquisition unit 132.
- the user information acquisition unit 132 acquires user information.
- the user information is various information for specifying a person who is currently using the imaging device 1 and is, for example, information indicating an attribute of the user (gender, area where he / she lives, etc.), preference of the user (each sample image)
- the information includes a degree of interest in the user, a selection history of assist information, information indicating a subject that is often photographed, a photographing scene, etc., and information indicating a photographing skill (number of photographs using each lens, photographing period).
- Fingerprint authentication, face authentication or the like can be used for user authentication, and the user information acquisition unit 132 acquires information corresponding to the authentication result. Also, the user may input the user information by himself.
- the assist information priority setting unit 130 sets the priority in consideration of not only the lens information but also the user information. For example, it is known that Japanese women (especially women in their twenties and thirties) tend to prefer blurry, fluffy examples. Therefore, when the user is a Japanese woman, assist information priority setting unit 130 is not so long as to be easily carried around, and a bright lens that can take a picture with blur and a soft atmosphere taken with that lens The priority of assist information including a sample image is increased. It is also known that Western men (especially in their thirties) tend to prefer vivid and sharp examples.
- the assist information priority setting unit 130 detects high-resolution lens information and a high-sharpness sample image (for example, a high-resolution lens MTF). Priority is given to assist information including sample images.
- the assist information priority setting unit 130 is frequently photographed, such as a history of browsing information of a lens by a user in online shopping etc, a history of selection of presented examples, and a history of browsing of a user by a photo sharing site.
- the priority of assist information is changed based on preference information such as a shooting scene and a subject.
- the assist information priority setting unit 130 changes the priority of the assist information based on information such as how long the user is photographing with each lens, how long the photographing period is, and how much the photographing skill is .
- assist information as described in the fourth embodiment is desired by the user. It may be displayed at the timing. Further, in the fourth embodiment, the priority may be set only from the user information.
- each process according to the above-described embodiment can be stored as a program that can be executed by the control unit 102.
- it can be stored and distributed in a storage medium of an external storage device such as a memory card (ROM card, RAM card, etc.), magnetic disk (hard disk, etc.), optical disk (CD-ROM, DVD, etc.), semiconductor memory, etc. .
- the control unit 102 can read the program stored in the storage medium of the external storage device, and can execute the above-described processing by controlling the operation by the read program.
- the embodiments described above include inventions of various stages, and various inventions can be extracted by appropriate combinations of a plurality of disclosed constituent features. For example, even if some of the configuration requirements are removed from all the configuration requirements shown in the embodiment, the configuration requirements can be solved if the problems as described above can be solved and the effects as described above can be obtained. The configuration can also be extracted as an invention.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
- Indication In Cameras, And Counting Of Exposures (AREA)
- Exposure Control For Cameras (AREA)
- Structure And Mechanism Of Cameras (AREA)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/133,923 US10116859B2 (en) | 2013-10-28 | 2016-04-20 | Image processing apparatus and image processing method that present assist information to assist photographing |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013223753A JP6381892B2 (ja) | 2013-10-28 | 2013-10-28 | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法及び画像処理プログラム |
| JP2013-223753 | 2013-10-28 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/133,923 Continuation US10116859B2 (en) | 2013-10-28 | 2016-04-20 | Image processing apparatus and image processing method that present assist information to assist photographing |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015064319A1 true WO2015064319A1 (ja) | 2015-05-07 |
Family
ID=53003930
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/076922 Ceased WO2015064319A1 (ja) | 2013-10-28 | 2014-10-08 | 画像処理装置及び画像処理方法 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10116859B2 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6381892B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2015064319A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5830512B2 (ja) * | 2013-10-24 | 2015-12-09 | オリンパス株式会社 | 画像表示端末、画像表示方法、およびプログラム |
| JP6685188B2 (ja) * | 2016-06-29 | 2020-04-22 | キヤノン株式会社 | 撮像装置、画像処理装置及びそれらの制御方法、プログラム |
| JP2018036415A (ja) * | 2016-08-30 | 2018-03-08 | オリンパス株式会社 | カメラシステム、交換レンズ、カメラシステムの制御方法、及びカメラシステムの制御プログラム |
| US11048745B2 (en) | 2018-06-22 | 2021-06-29 | International Business Machines Corporation | Cognitively identifying favorable photograph qualities |
| US10972656B2 (en) | 2018-06-22 | 2021-04-06 | International Business Machines Corporation | Cognitively coaching a subject of a photograph |
| JP7612338B2 (ja) | 2020-03-26 | 2025-01-14 | キヤノン株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理システムおよび情報処理方法 |
| US11509819B2 (en) * | 2021-01-19 | 2022-11-22 | Adobe Inc. | Providing contextual augmented reality photo pose guidance |
| WO2025211547A1 (en) * | 2024-04-04 | 2025-10-09 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method and system for reconstructing multi-dimensional extended reality scene |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006352712A (ja) * | 2005-06-17 | 2006-12-28 | Olympus Imaging Corp | 撮影アドバイス装置、撮影アドバイス方法、及びプログラム |
| JP2010268031A (ja) * | 2009-05-12 | 2010-11-25 | Olympus Corp | デジタルカメラ |
| JP2011170194A (ja) * | 2010-02-19 | 2011-09-01 | Olympus Imaging Corp | 撮影装置及び撮影制御方法 |
| JP2013128251A (ja) * | 2011-12-19 | 2013-06-27 | Nikon Corp | 撮像装置およびプログラム |
| JP2013197739A (ja) * | 2012-03-16 | 2013-09-30 | Canon Inc | 撮像装置及びその制御方法、並びにプログラム |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1964392A1 (en) | 2005-12-22 | 2008-09-03 | Olympus Corporation | Photographing system and photographing method |
| CN101772952B (zh) * | 2007-07-23 | 2013-04-24 | 松下电器产业株式会社 | 摄像装置 |
| RU2462757C2 (ru) * | 2008-09-08 | 2012-09-27 | Сони Корпорейшн | Устройство и способ обработки изображений, устройство ввода изображений и программа |
| JP2010181725A (ja) * | 2009-02-06 | 2010-08-19 | Nikon Corp | デジタルカメラおよびプログラム |
| US8228413B2 (en) * | 2009-09-01 | 2012-07-24 | Geovector Corp. | Photographer's guidance systems |
-
2013
- 2013-10-28 JP JP2013223753A patent/JP6381892B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2014
- 2014-10-08 WO PCT/JP2014/076922 patent/WO2015064319A1/ja not_active Ceased
-
2016
- 2016-04-20 US US15/133,923 patent/US10116859B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006352712A (ja) * | 2005-06-17 | 2006-12-28 | Olympus Imaging Corp | 撮影アドバイス装置、撮影アドバイス方法、及びプログラム |
| JP2010268031A (ja) * | 2009-05-12 | 2010-11-25 | Olympus Corp | デジタルカメラ |
| JP2011170194A (ja) * | 2010-02-19 | 2011-09-01 | Olympus Imaging Corp | 撮影装置及び撮影制御方法 |
| JP2013128251A (ja) * | 2011-12-19 | 2013-06-27 | Nikon Corp | 撮像装置およびプログラム |
| JP2013197739A (ja) * | 2012-03-16 | 2013-09-30 | Canon Inc | 撮像装置及びその制御方法、並びにプログラム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6381892B2 (ja) | 2018-08-29 |
| US20160234432A1 (en) | 2016-08-11 |
| US10116859B2 (en) | 2018-10-30 |
| JP2015088801A (ja) | 2015-05-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6381892B2 (ja) | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法及び画像処理プログラム | |
| CN105052123B (zh) | 摄像装置、构图辅助装置、构图辅助方法及存储介质 | |
| JP6861342B2 (ja) | 撮像装置および撮像装置とサーバとを含むシステム | |
| JP5713055B2 (ja) | 撮像装置、撮像方法及びプログラム | |
| US9843721B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus | |
| WO2015098313A1 (ja) | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法及び画像処理プログラムを記憶した記憶媒体 | |
| CN108900764A (zh) | 拍摄方法和电子装置以及拍摄控制方法和服务器 | |
| JP2019146022A (ja) | 撮像装置及び撮像方法 | |
| US9497384B2 (en) | Template photography and methods of using the same | |
| JP2016127431A (ja) | 撮像装置、撮像制御方法及びプログラム | |
| JP6230386B2 (ja) | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法及び画像処理プログラム | |
| JP2015198300A (ja) | 情報処理装置、撮像装置、画像管理システム | |
| KR102146856B1 (ko) | 렌즈 특성 기반의 촬영 모드 제시 방법, 상기 방법을 기록한 컴퓨터 판독 가능 저장매체 및 디지털 촬영 장치. | |
| JP6594666B2 (ja) | 撮像補助装置、撮像装置および撮像補助方法 | |
| US9767587B2 (en) | Image extracting apparatus, image extracting method and computer readable recording medium for recording program for extracting images based on reference image and time-related information | |
| CN114342350B (zh) | 成像控制装置、成像控制方法、程序以及成像设备 | |
| CN107431756B (zh) | 自动图像帧处理可能性检测的方法和装置 | |
| JP2016103807A (ja) | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法、およびプログラム | |
| JP2005057623A (ja) | 画像データ処理装置 | |
| TWI380225B (en) | Imaging processing device and method thereof | |
| US10659696B2 (en) | Electronic device, control method of electronic device, and storage medium | |
| WO2022158201A1 (ja) | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法、プログラム | |
| KR20140094331A (ko) | 촬영자 식별 장치 및 방법 | |
| JP2016015543A (ja) | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法及びプログラム | |
| JP2012034296A (ja) | 撮像装置及びその制御方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14857953 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 14857953 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |