WO2015060200A1 - 劣化関数算出装置、劣化率推定装置、劣化率推定システム、劣化関数算出方法、劣化率推定方法、及びプログラム - Google Patents
劣化関数算出装置、劣化率推定装置、劣化率推定システム、劣化関数算出方法、劣化率推定方法、及びプログラム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015060200A1 WO2015060200A1 PCT/JP2014/077604 JP2014077604W WO2015060200A1 WO 2015060200 A1 WO2015060200 A1 WO 2015060200A1 JP 2014077604 W JP2014077604 W JP 2014077604W WO 2015060200 A1 WO2015060200 A1 WO 2015060200A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- equivalent
- operation time
- deterioration
- secondary battery
- deterioration rate
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01R—MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES
- G01R31/00—Arrangements for testing electric properties; Arrangements for locating electric faults; Arrangements for electrical testing characterised by what is being tested not provided for elsewhere
- G01R31/36—Arrangements for testing, measuring or monitoring the electrical condition of accumulators or electric batteries, e.g. capacity or state of charge [SoC]
- G01R31/392—Determining battery ageing or deterioration, e.g. state of health
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01R—MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES
- G01R31/00—Arrangements for testing electric properties; Arrangements for locating electric faults; Arrangements for electrical testing characterised by what is being tested not provided for elsewhere
- G01R31/36—Arrangements for testing, measuring or monitoring the electrical condition of accumulators or electric batteries, e.g. capacity or state of charge [SoC]
- G01R31/3644—Constructional arrangements
- G01R31/3648—Constructional arrangements comprising digital calculation means, e.g. for performing an algorithm
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M10/00—Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M10/42—Methods or arrangements for servicing or maintenance of secondary cells or secondary half-cells
- H01M10/48—Accumulators combined with arrangements for measuring, testing or indicating the condition of cells, e.g. the level or density of the electrolyte
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02J—CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS OR SYSTEMS FOR SUPPLYING OR DISTRIBUTING ELECTRIC POWER; SYSTEMS FOR STORING ELECTRIC ENERGY
- H02J7/00—Circuit arrangements for charging or depolarising batteries or for supplying loads from batteries
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M10/00—Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M10/42—Methods or arrangements for servicing or maintenance of secondary cells or secondary half-cells
- H01M10/48—Accumulators combined with arrangements for measuring, testing or indicating the condition of cells, e.g. the level or density of the electrolyte
- H01M10/486—Accumulators combined with arrangements for measuring, testing or indicating the condition of cells, e.g. the level or density of the electrolyte for measuring temperature
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a deterioration function calculating device, a deterioration function calculating method and program for calculating a deterioration function related to a deterioration rate of a secondary battery, a deterioration rate estimating device, a deterioration rate estimating system, and a deterioration for estimating deterioration of a secondary battery.
- the present invention relates to a rate estimation method and a program.
- the secondary battery catalog may show a deterioration curve indicating the relationship between the operating time and the deterioration rate of the secondary battery when operated in a general manner.
- a deterioration curve can be referred to, the life of the secondary battery can be estimated by comparing with the cycle rate in the current operation of the secondary battery.
- the mode shown in the catalog and the actual usage mode are different, there is a difference between the relationship between the actual operation time and the deterioration rate and the deterioration curve shown in the catalog.
- Patent Document 1 provides secondary battery current / temperature / SOC (State Of Charge) operation upper limit thresholds, and uses the number of times the operation upper limit threshold has been exceeded as a parameter to estimate the secondary battery's deterioration state and remaining life. Techniques to do this are disclosed.
- SOC State Of Charge
- the technique described in Patent Document 1 predicts the lifetime of a secondary battery using an estimation formula for a deterioration state generated based on the shape and items of different formulas. For this reason, the technique described in Patent Document 1 generates a deterioration prediction formula based on historical information on the operation of the secondary battery with the same load pattern in the past, and predicts the deterioration of the secondary battery operated with the same load pattern. Can accurately predict degradation. However, the technique described in Patent Document 1 may not be able to accurately predict deterioration when predicting deterioration of a secondary battery that operates with an unknown load pattern.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a deterioration function calculating device, a deterioration rate estimating device, a deterioration rate estimating system, a deterioration function calculating method, a deterioration for accurately estimating a deterioration rate even when a secondary battery is operated in an unknown operation mode. It is to provide a rate estimation method and program.
- a first aspect of the present invention is a deterioration function calculation device including a storage unit, an equivalent coefficient calculation unit, an equivalent operation time calculation unit, and a deterioration function calculation unit.
- the storage unit associates and stores the operating time of the secondary battery in the operation and the deterioration rate of the secondary battery in the operating time.
- the equivalent coefficient calculation unit calculates an equivalent coefficient that normalizes the operation time based on a value related to the operation.
- the equivalent operation time calculation unit normalizes each operation time stored in association with each operation and each deterioration rate by the storage unit based on the operation time and the equivalent coefficient related to the operation related to the operation time. The equivalent operating time that is the operating time thus calculated is calculated.
- the deterioration function calculation unit calculates the relationship between the equivalent operation time and the deterioration rate based on the equivalent operation time and the deterioration rate stored in the storage unit in association with the operation time used to calculate the equivalent operation time.
- the degradation function shown is calculated.
- the equivalent coefficient calculation unit calculates an equivalent operation time calculated based on a deterioration rate stored in the storage unit and an operation time associated with the deterioration rate.
- a deterioration function calculating device that generates the equivalent coefficient so that the degree of dispersion between the deterioration rate obtained from the deterioration function and the deterioration rate is reduced.
- the equivalent operation time calculation unit divides the operation time into partial operation times for each operation state, and according to the operation state for each partial operation time. It is a deterioration function calculating device that calculates the equivalent operating time by multiplying an equivalent coefficient and calculating the total sum.
- a fourth aspect of the present invention is a deterioration rate estimation device including an input unit, an equivalent coefficient calculation unit, an equivalent operation time calculation unit, and a deterioration rate estimation unit.
- the input unit accepts input of values relating to the operation time of the secondary battery and the operation of the secondary battery.
- the equivalent coefficient calculation unit calculates an equivalent coefficient that normalizes the operation time based on a value related to an operation that has received an input.
- the equivalent operation time calculation unit calculates an equivalent operation time that is a normalized operation time based on the operation time that has received the input and the equivalent coefficient.
- the deterioration rate estimation unit estimates the deterioration rate of the secondary battery based on the deterioration function indicating the relationship between the equivalent operation time and the deterioration rate of the secondary battery and the calculated equivalent operation time.
- the deterioration rate estimation unit calculates the deterioration function calculated by the deterioration function calculation unit of the deterioration function calculation device according to any one of the first to third aspects.
- the deterioration rate estimation device estimates the deterioration rate of the secondary battery based on the calculated equivalent operation time.
- a sixth aspect of the present invention is a deterioration function calculating method for calculating a deterioration function used for estimating a deterioration rate of a secondary battery.
- the degradation function calculation method includes a step in which the degradation function calculation device calculates an equivalent coefficient for normalizing the operation time based on a value related to the operation for each past operation of the secondary battery.
- the degradation function calculation device is configured so that, for each operation time stored in the storage unit in association with each operation and each deterioration rate, the operation time and the equivalent of the operation related to the operation time. And calculating an equivalent operation time which is the normalized operation time based on the coefficient.
- the storage unit For each past operation of the secondary battery, the storage unit associates and stores the operating time of the secondary battery in the operation and the deterioration rate of the secondary battery in the operating time.
- the degradation function calculation method is based on the equivalent operation time based on the equivalent operation time and the deterioration rate stored in the storage unit in association with the operation time used to calculate the equivalent operation time.
- the seventh aspect of the present invention is a secondary battery deterioration rate estimation method.
- the degradation rate estimation method includes a step in which the degradation rate estimation device receives input of an operation time of a secondary battery and values relating to operation of the secondary battery.
- the degradation rate estimation method includes a step in which the degradation rate estimation apparatus calculates an equivalent coefficient that normalizes the operation time based on a value relating to an operation that has received an input.
- the deterioration rate estimation method includes a step in which the deterioration rate estimation device calculates an equivalent operation time that is a normalized operation time based on an operation time that has received an input and the equivalent coefficient.
- the degradation rate estimation apparatus is configured to determine whether or not the secondary battery is based on a degradation function indicating a relationship between an equivalent operation time and a degradation rate of the secondary battery, and the calculated equivalent operation time. A step of estimating a deterioration rate.
- the 8th aspect of this invention is a program for functioning a computer as a memory
- the storage unit associates and stores the operating time of the secondary battery in the operation and the deterioration rate of the secondary battery in the operating time.
- the equivalent coefficient calculation unit calculates an equivalent coefficient that normalizes the operation time based on a value related to the operation.
- the equivalent operation time calculation unit normalizes each operation time stored in association with each operation and each deterioration rate by the storage unit based on the operation time and the equivalent coefficient related to the operation related to the operation time. The equivalent operating time that is the operating time thus calculated is calculated.
- the deterioration function calculation unit calculates the relationship between the equivalent operation time and the deterioration rate based on the equivalent operation time and the deterioration rate stored in the storage unit in association with the operation time used to calculate the equivalent operation time.
- the degradation function shown is calculated.
- a ninth aspect of the present invention is a program for causing a computer to function as an input unit, an equivalent coefficient calculation unit, an equivalent operation time calculation unit, and a deterioration rate estimation unit.
- the input unit accepts input of values relating to the operation time of the secondary battery and the operation of the secondary battery.
- the equivalent coefficient calculation unit calculates an equivalent coefficient that normalizes the operation time based on a value related to an operation that has received an input.
- the equivalent operation time calculation unit calculates an equivalent operation time that is a normalized operation time based on the operation time that has received the input and the equivalent coefficient.
- the deterioration rate estimation unit estimates the deterioration rate of the secondary battery based on the deterioration function indicating the relationship between the equivalent operation time and the deterioration rate of the secondary battery and the calculated equivalent operation time.
- the tenth aspect includes a storage unit, a first equivalent coefficient calculation unit, a first equivalent operating time calculation unit, a deterioration function calculation unit, an input unit, a second equivalent coefficient calculation unit, A deterioration rate estimation system including a second equivalent operation time calculation unit and a deterioration rate estimation unit.
- the storage unit associates and stores the operating time of the secondary battery in the operation and the deterioration rate of the secondary battery in the operating time.
- the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit calculates an equivalent coefficient that normalizes the operation time based on a value related to the operation.
- the first equivalent operation time calculation unit includes the operation time and the equivalent coefficient calculated by the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit for each operation time stored in association with each operation and each deterioration rate by the storage unit. Based on the above, an equivalent operating time which is the normalized operating time is calculated.
- the deterioration function calculation unit is based on the equivalent operation time calculated by the first equivalent operation time calculation unit and the deterioration rate stored in the storage unit in association with the operation time used to calculate the equivalent operation time. Then, a deterioration function indicating the relationship between the equivalent operation time and the deterioration rate is calculated.
- the second equivalent coefficient calculation unit normalizes the operation time based on an input unit that receives input of an operation time of the secondary battery and a value related to the operation of the secondary battery, and a value related to the operation that received the input
- the equivalent coefficient is calculated.
- the second equivalent operation time calculation unit calculates an equivalent operation time that is a normalized operation time based on the operation time that has received the input and the equivalent coefficient calculated by the second equivalent coefficient calculation unit. To do.
- the deterioration rate estimation unit estimates the deterioration rate of the secondary battery based on the deterioration function calculated by the deterioration function calculation unit and the equivalent operation time calculated by the second equivalent operation time calculation unit.
- the deterioration function calculating apparatus can calculate a deterioration function for accurately estimating the deterioration rate even when the secondary battery is operated in an unknown operation aspect.
- the deterioration rate estimation device can accurately estimate the deterioration rate even when the secondary battery is operated in an unknown operation aspect.
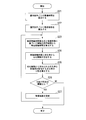
- FIG. 1 is a schematic block diagram showing a configuration of a deterioration rate estimation system 100 according to the first embodiment.
- the deterioration rate estimation system 100 estimates the deterioration rate of the secondary battery.
- the degradation rate estimation system 100 includes a degradation function calculation device 110 and a degradation rate estimation device 120.
- the deterioration function calculation device 110 calculates a deterioration function used for estimating the deterioration rate of the secondary battery.
- the deterioration curve is an aspect of the deterioration function. By representing the degradation function in a graph, a degradation curve can be obtained.
- the deterioration function calculation device 110 includes a storage unit 111, a first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 112, a first equivalent operation time calculation unit 113, a deterioration function calculation unit 114, and a deterioration function evaluation unit 115.
- the storage unit 111 includes the operation time of the secondary battery in the operation, the value related to the operation of the secondary battery when the operation time has elapsed, and the operation time has elapsed.
- storage part 111 memorize
- 1st equivalent coefficient calculation part 112 calculates the equivalent coefficient which normalizes operation time based on the value concerning the operation of the secondary battery which storage part 111 memorizes. Specifically, when the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 112 calculates an equivalent coefficient for a certain elapsed time stored in the storage unit 111, the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 112 performs the operation from the start of operation of the secondary battery until the operation time elapses. A plurality of such values are acquired from the storage unit 111, and based on this, an operation pattern such as a charging rate usage range, a charging rate change rate, and a maximum current value is specified. The operation pattern is also an example of values related to the operation of the secondary battery.
- the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 112 calculates the equivalent coefficient by substituting the identified operation pattern into a predetermined equivalent coefficient calculation formula. Note that the equivalent coefficient calculated by the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 112 is not limited to one. When the equivalent operation time calculation formula used for calculating the equivalent operation time uses a plurality of equivalent coefficients, the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 112 calculates a plurality of equivalent coefficients. The equivalent coefficient calculation formula is updated as appropriate during the process of calculating the deterioration function. The type of the equivalent coefficient calculation formula and the initial value of the dependent variable are determined in advance before the deterioration function calculation processing.
- the first equivalent operation time calculation unit 113 calculates an equivalent operation time that is a normalized operation time based on the operation time and the equivalent coefficient stored in the storage unit 111. Specifically, the first equivalent operation time calculation unit 113 identifies an operation associated with the operation time, and substitutes an equivalent coefficient corresponding to the operation and the operation time into a predetermined equivalent operation time calculation formula. Thus, the equivalent operation time is calculated.
- the type of the equivalent operation time calculation formula is determined in advance in the stage before the deterioration function calculation processing.
- the deterioration function calculation unit 114 calculates a deterioration function indicating the relationship between the equivalent operation time and the deterioration rate based on the equivalent operation time and the deterioration rate calculated by the first equivalent operation time calculation unit 113. Specifically, the deterioration function calculation unit 114 reads out the deterioration rate associated with the operation time used to calculate the equivalent operation time from the storage unit 111, and generates a plurality of combinations of the equivalent operation time and the deterioration rate. The deterioration function calculation unit 114 calculates a deterioration function by performing curve fitting based on the combination.
- the degradation function evaluation unit 115 calculates the variance between the degradation function calculated by the degradation function calculation unit 114 and the degradation rate, and determines that the degradation function is appropriate when the variance is less than a predetermined threshold.
- the degradation function evaluation unit 115 describes a case where the degradation function is evaluated based on the variance of the degradation rate, but is not limited thereto. In other embodiments, for example, the deterioration function may be evaluated based on the degree of dispersion other than dispersion, such as standard deviation or range.
- the deterioration rate estimation device 120 estimates the deterioration rate of the secondary battery using the deterioration function calculated by the deterioration function calculation device 110.
- the deterioration rate estimation device 120 includes an input unit 121, a second equivalent coefficient calculation unit 122, a second equivalent operation time calculation unit 123, and a deterioration rate estimation unit 124.
- the input unit 121 receives an input of a load pattern and an operation time of a secondary battery that is an estimation target of the deterioration rate.
- the load pattern that the input unit 121 receives input is defined by values related to operation used for calculating the equivalent coefficient.
- the second equivalent coefficient calculation unit 122 calculates an equivalent coefficient from the load pattern received by the input unit 121 based on the equivalent coefficient calculation formula used by the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 112 to calculate the equivalent coefficient.
- the second equivalent operation time calculation unit 123 substitutes the equivalent coefficient calculated by the second equivalent coefficient calculation unit 122 and the operation time received by the input unit 121 into the equivalent operation time calculation formula. Calculate the operating time.
- the deterioration rate estimation unit 124 estimates the deterioration rate of the secondary battery to be estimated from the operation time calculated by the second equivalent operation time calculation unit 123 based on the deterioration function calculated by the deterioration function calculation device 110.
- the degradation function calculation device 110 and the degradation rate estimation device 120 can reduce the estimation error due to the difference in the load pattern by using the equivalent operation time obtained by normalizing the operation time according to the different load patterns. it can.
- FIG. 2 is a flowchart illustrating the deterioration function calculation method according to the first embodiment.
- the storage unit 111 records the relationship between the operation time and the deterioration rate related to the past operation of the secondary battery having the same performance as the secondary battery whose deterioration rate is to be estimated. The For example, experimental data, actual operation data, and the like of the same type of secondary battery are recorded in the storage unit 111.
- the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 112 specifies a load pattern related to the operation time for each operation time stored in the storage unit 111 (step S1). Specifically, the equivalent coefficient calculation unit identifies a load pattern by reading values related to operations associated with each operation time before the operation time and collecting the values related to the read operations.
- the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 112 calculates the equivalent coefficient by substituting the specified load pattern into the equivalent coefficient calculation formula (step S2).
- the first equivalent operation time calculation unit 113 calculates the equivalent operation time for each operation time stored in the storage unit 111 based on the equivalent coefficient corresponding to the operation related to the operation time and the equivalent operation time calculation formula. Is calculated (step S3).
- the deterioration function calculation unit 114 is based on a combination of the equivalent operation time calculated by the first equivalent operation time calculation unit 113 and the deterioration rate associated with the operation time used for calculating the equivalent operation time. Curve fitting is performed to calculate a deterioration function (step S4).
- the curve fitting can be performed by polynomial approximation, for example.
- the deterioration function evaluation unit 115 calculates a variance between the deterioration function calculated by the deterioration function calculation unit 114 and the deterioration degree stored in the storage unit 111 (step S5). Specifically, the variance between the degree of deterioration stored in the storage unit 111 and the degree of deterioration obtained by substituting the equivalent operating time combined with the degree of deterioration into the deterioration function is calculated. Note that dispersion is an example of the degree of dispersion.
- the degradation function evaluation unit 115 determines whether or not the variance is greater than or equal to a predetermined threshold (step S6).
- the degradation function evaluation unit 115 determines that the accuracy of the equivalent coefficient calculation formula and the degradation function is not sufficient when the calculated variance is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold (step S6: YES).
- the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 112 updates the dependent variable of the equivalent coefficient calculation formula so that the variance calculated by the deterioration function evaluation unit 115 is reduced (step S7).
- the equivalent coefficient is calculated using the updated equivalent coefficient calculation formula. That is, the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 112 calculates the deterioration rate stored in the storage unit 111 and the deterioration rate obtained from the equivalent operation time and the deterioration function calculated based on the operation time associated with the deterioration rate. Equivalent coefficients are generated so that the degree of dispersion between them becomes small. Thereby, the precision of the deterioration function which the deterioration function calculation part 114 calculates can be ensured more than fixed.
- step S6 determines that the equivalent coefficient calculation formula and the accuracy of the degradation function are sufficient, and performs the degradation function calculation processing. finish. Thereby, the degradation function calculation apparatus 110 can generate the degradation function showing the relationship between the equivalent operation time and the degradation rate with high accuracy. As a result, the degradation function calculation apparatus 110 determines an equivalent coefficient calculation formula for calculating the equivalent coefficient.
- FIG. 3 is a flowchart illustrating the deterioration rate estimation method according to the first embodiment.
- the deterioration rate estimation device 120 estimates the deterioration rate of the secondary battery when the deterioration function is calculated by the deterioration function calculation device 110.
- the input unit 121 receives an input of a load pattern and an operating time of the secondary battery from an administrator of the secondary battery to be estimated for the deterioration rate (step S8).
- the second equivalent coefficient calculation unit 122 calculates an equivalent coefficient using the equivalent coefficient calculation formula used by the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 112 based on the load pattern received by the input unit 121 (Step S1). S9). That is, the second equivalent coefficient calculation unit 122 calculates the equivalent coefficient using the equivalent coefficient calculation formula determined by the deterioration function evaluation unit 115 that the accuracy is sufficient.
- the second equivalent operation time calculation unit 123 calculates the equivalent operation from the operation time received by the input unit 121. Time is calculated (step S10).
- the equivalent operation time calculation formula used by the second equivalent operation time calculation unit 123 is the same as the equivalent operation time calculation formula used by the first equivalent operation time calculation unit 113.
- the deterioration rate estimation unit 124 is calculated by the second equivalent operation time calculation unit 123 based on the deterioration function calculated by the deterioration function calculation device 110 and the equivalent operation time calculated by the second equivalent operation time calculation unit 123.
- the deterioration rate of the secondary battery to be estimated is estimated from the operated time (step S11).
- the deterioration rate estimation system 100 calculates the deterioration function and estimates the deterioration rate using the equivalent operation time obtained by normalizing the operation time based on the load pattern related to operation. Do. Thereby, the degradation rate estimation system 100 can estimate the degradation rate regardless of the load pattern related to operation. That is, according to the deterioration rate estimation system 100 of the present embodiment, the deterioration rate of the secondary battery can be accurately estimated even when the secondary battery is operated with an unknown load pattern.
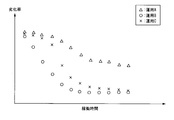
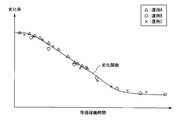
- FIG. 4A and 4B are diagrams illustrating an example of the degradation function calculation method according to the first embodiment.
- the storage unit 111 associates the operating time and the deterioration rate of the secondary battery in the operation for each past operation of the secondary battery.
- the first equivalent operation time calculation unit 113 calculates the equivalent operation time from the operation time shown in FIG. 4A. Thereby, as shown to FIG. 4B, the relationship between equivalent operation time and a deterioration rate can be obtained.
- the degradation function calculation part 114 can obtain the degradation function (degradation curve) shown in FIG. 4B by performing curve fitting based on the relationship between the equivalent operation time and the degradation rate shown in FIG. 4B.
- Second Embodiment When a secondary battery is operated on a real machine, there is a possibility that the types of values related to the operation that can be acquired and the sampling cycle are limited as compared with the case where a measurement test is performed in a laboratory. For example, in a measurement test, a sampling period of seconds can be taken, whereas in an actual machine, there is a possibility that it can be taken only in minutes. In the measurement test, current, voltage, temperature, and charging rate can be acquired as values related to operation, whereas only the temperature and charging rate may be acquired in an actual machine.
- the degradation rate estimation system 200 of the second embodiment calculates an appropriate degradation function even under limited conditions, and estimates the degradation rate with high accuracy.
- FIG. 5 is a schematic block diagram showing the configuration of the deterioration rate estimation system 200 according to the second embodiment.
- the deterioration function calculation device 210 includes an accumulated time calculation unit 216 in addition to the configuration of the first embodiment.
- the deterioration rate estimation system 200 of the second embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment, the information that the input unit 221 receives input, the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 212, the first equivalent operating time calculation unit 213, and the second The equivalent coefficient calculating unit 222 and the second equivalent operating time calculating unit 223 are different in processing.
- the accumulated time calculation unit 216 calculates the accumulated operation time (partial operation time) for each operation condition from the operation start to the operation time for each operation time stored in the storage unit 211.
- the cumulative time calculation unit 216 includes a cumulative time when the charging rate of the secondary battery is less than 20% from the start of operation of the secondary battery to the operating time, and a charging rate of the secondary battery of 20% or more 40
- the cumulative time when the charge rate of the secondary battery was 40% or more and less than 60%, the cumulative time when the charge rate of the secondary battery was 60% or more and less than 80%,
- the accumulated time when the charging rate of the secondary battery is 80% or more is calculated.
- the usage range of the charging rate of the secondary battery is an example of operation conditions.
- the accumulated time calculation unit 216 similarly calculates the accumulated time for other operating conditions such as the range of the change rate of the charging rate and the range of the temperature.
- the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 212 calculates an equivalent coefficient for each operation condition.
- the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 212 may calculate the equivalent coefficient of the operation condition based on a predetermined mathematical formula, or may calculate based on a predetermined probability regardless of the mathematical formula.
- the first equivalent operation time calculation unit 213 calculates, for each operation time, a total sum of values obtained by multiplying the accumulation time calculated by the accumulation time calculation unit 216 by the equivalent coefficient calculated by the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 212. Calculate as time.
- the input unit 221 receives an input of accumulated time for each operation condition from the start of operation to the present time of the secondary battery whose deterioration rate is to be estimated.
- the second equivalent coefficient calculation unit 222 calculates the same equivalent coefficient as the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 212 for each operation condition.
- the second equivalent operation time calculation unit 223 calculates, for each operation time, a sum of values obtained by multiplying the accumulation time calculated by the second accumulation time calculation unit 216 by the equivalent coefficient calculated by the second equivalent coefficient calculation unit 222. The equivalent operating time is calculated.
- FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing a deterioration function calculation method according to the second embodiment.
- the accumulated time calculation unit 216 calculates the accumulated operation time for each operation condition from the operation start to the operation time for each operation time stored in the storage unit 211 (step S21).
- the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 212 calculates an equivalent coefficient for each operation condition (step S22).
- the first equivalent operation time calculation unit 213 uses the sum of values obtained by multiplying the accumulation time calculated by the accumulation time calculation unit 216 by the equivalent coefficient calculated by the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 212 as the equivalent operation time.
- the deterioration function calculation unit 114 is based on a combination of the equivalent operation time calculated by the first equivalent operation time calculation unit 213 and the deterioration rate associated with the operation time used to calculate the equivalent operation time. Curve fitting is performed to calculate a deterioration function (step S24).
- the deterioration function evaluation unit 115 calculates the variance between the deterioration function calculated by the deterioration function calculation unit 114 and the deterioration degree stored in the storage unit 211 (step S25). The degradation function evaluation unit 115 determines whether or not the variance is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold (step S26).
- the degradation function evaluation unit 115 determines that the accuracy of the equivalent coefficient and the degradation function is not sufficient when the calculated variance is greater than or equal to a predetermined threshold (step S26: YES).
- the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 212 updates each equivalent coefficient so that the variance calculated by the deterioration function evaluation unit 115 becomes small (step S27), and returns to step S23.
- step S26 NO
- the degradation function evaluation unit 115 determines that the equivalent coefficient calculation formula and the accuracy of the degradation function are sufficient, and performs the degradation function calculation process. finish.
- the degradation function calculation device 210 can accurately generate a degradation function indicating the relationship between the equivalent operation time and the degradation rate.
- the degradation function calculation apparatus 210 determines an equivalent coefficient.
- FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing a deterioration rate estimation method according to the second embodiment.
- the deterioration rate estimation device 220 estimates the deterioration rate of the secondary battery when the deterioration function is calculated by the deterioration function calculation device 210.
- the input unit 221 receives an input of an accumulated time for each operating condition of the secondary battery from a user such as an administrator of the secondary battery to be estimated for the deterioration rate (step S28).
- the second equivalent coefficient calculation unit 222 calculates the equivalent coefficient last calculated by the first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 212 as an equivalent coefficient used for estimation of the deterioration rate (step S29).
- the second equivalent operation time calculation unit 223 Based on the equivalent coefficient calculated by the second equivalent coefficient calculation unit 222 and a predetermined equivalent operation time calculation formula, the second equivalent operation time calculation unit 223 accumulates for each operation condition for which the input unit 221 has received an input. The equivalent operation time is calculated from the time (step S30).
- the equivalent operation time calculation formula used by the second equivalent operation time calculation unit 223 is the same as the equivalent operation time calculation formula used by the first equivalent operation time calculation unit 213.
- the deterioration rate estimation unit 124 is calculated by the second equivalent operation time calculation unit 223 based on the deterioration function calculated by the deterioration function calculation device 210 and the equivalent operation time calculated by the second equivalent operation time calculation unit 223.
- the deterioration rate of the secondary battery to be estimated is estimated from the operated time (step S31).
- the deterioration rate estimation system 200 calculates the accumulated time for a plurality of operating conditions from limited data, and calculates the equivalent operating time from the accumulated time. Thereby, even if the value which concerns on the operation
- the deterioration rate estimation system 200 can estimate a deterioration rate appropriately.
- the current, voltage Compared with the case where values related to operation such as the charging rate and temperature are stored, the amount of data can be reduced.
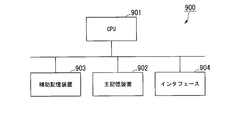
- FIG. 8 is a schematic block diagram illustrating a configuration of a computer 900 according to at least one embodiment.
- the computer 900 includes a CPU 901, a main storage device 902, an auxiliary storage device 903, and an interface 904.
- the above-described deterioration rate estimation systems 100 and 200 are implemented in a computer 900.
- the operation of each processing unit described above is stored in the auxiliary storage device 903 in the form of a program.
- the CPU 901 reads a program from the auxiliary storage device 903, develops it in the main storage device 902, and executes the above processing according to the program. Further, the CPU 901 secures a storage area corresponding to the storage units 111 and 211 described above in the main storage device 902 according to the program.
- the auxiliary storage device 903 is an example of a tangible medium that is not temporary.
- Other examples of the non-temporary tangible medium include a magnetic disk, a magneto-optical disk, a CD-ROM, a DVD-ROM, and a semiconductor memory connected via the interface 904.
- the program may be for realizing a part of the functions described above. Further, the program may be a so-called difference file (difference program) that realizes the above-described function in combination with another program already stored in the auxiliary storage device 903.
- difference file difference program
- the deterioration function calculating device and the deterioration rate estimating device may be mounted on separate computers 900.
- the deterioration function calculating device can calculate a deterioration function for accurately estimating the deterioration rate even when the secondary battery is operated in an unknown operation mode.
- the deterioration rate estimation device can accurately estimate the deterioration rate even when the secondary battery is operated in an unknown operation mode.
- DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 100 Degradation rate estimation system 110 Degradation function calculation apparatus 111 Storage part 112 1st equivalent coefficient calculation part 113 1st equivalent operation time calculation part 114 Deterioration function calculation part 115 Degradation function evaluation part 120 Degradation function estimation apparatus 121 Input part 122 second equivalent coefficient calculation unit 123 second equivalent operation time calculation unit 124 deterioration rate estimation unit 200 deterioration rate estimation system 210 deterioration function calculation device 211 storage unit 212 first equivalent coefficient calculation unit 213 first equivalent operation time Calculation unit 216 Cumulative time calculation unit 220 Deterioration rate estimation device 221 Input unit 222 Second equivalent coefficient calculation unit 223 Second equivalent operation time calculation unit
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Electrochemistry (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Secondary Cells (AREA)
- Tests Of Electric Status Of Batteries (AREA)
- Charge And Discharge Circuits For Batteries Or The Like (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| SG11201602054QA SG11201602054QA (en) | 2013-10-22 | 2014-10-16 | Deterioration function calculation device, deterioration rate estimation device, deterioration rate estimation system, deterioration function calculation method, deterioration rate estimation method, and program |
| US15/022,289 US20160231389A1 (en) | 2013-10-22 | 2014-10-16 | Deterioration function calculation device, deterioration rate estimation device, deterioration rate estimation system, deterioration function calculation method, deterioration rate estimation method, and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013219352A JP6222822B2 (ja) | 2013-10-22 | 2013-10-22 | 劣化関数算出装置、劣化率推定システム、劣化関数算出方法、及びプログラム |
| JP2013-219352 | 2013-10-22 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015060200A1 true WO2015060200A1 (ja) | 2015-04-30 |
Family
ID=52992798
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/077604 Ceased WO2015060200A1 (ja) | 2013-10-22 | 2014-10-16 | 劣化関数算出装置、劣化率推定装置、劣化率推定システム、劣化関数算出方法、劣化率推定方法、及びプログラム |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20160231389A1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6222822B2 (enExample) |
| SG (1) | SG11201602054QA (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2015060200A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR3009093B1 (fr) * | 2013-07-29 | 2017-01-13 | Renault Sa | Estimation de l'etat de vieillissement d'une batterie electrique |
| JP6222841B2 (ja) * | 2014-03-25 | 2017-11-01 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 運行管理装置、列車制御方法及びプログラム |
| CN109784510A (zh) * | 2019-01-21 | 2019-05-21 | 上海船舶研究设计院(中国船舶工业集团公司第六0四研究院) | 船舶设备健康维护方法及系统 |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002354708A (ja) * | 2001-05-24 | 2002-12-06 | Shin Kobe Electric Mach Co Ltd | 無停電電源装置 |
| JP2007055450A (ja) * | 2005-08-24 | 2007-03-08 | Fuji Heavy Ind Ltd | 蓄電デバイスの劣化状態推定システム |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20070055450A1 (en) * | 2005-09-08 | 2007-03-08 | Searete Llc, A Limited Liability Corporation Of State Of Delaware | Data techniques related to tissue coding |
| EP2565660A1 (en) * | 2010-04-26 | 2013-03-06 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Degradation estimation device and degradation estimation method for storage battery device |
| WO2011160258A1 (zh) * | 2010-06-24 | 2011-12-29 | 松下电器产业株式会社 | 获取电池的劣化度的方法和系统 |
-
2013
- 2013-10-22 JP JP2013219352A patent/JP6222822B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2014
- 2014-10-16 US US15/022,289 patent/US20160231389A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2014-10-16 WO PCT/JP2014/077604 patent/WO2015060200A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2014-10-16 SG SG11201602054QA patent/SG11201602054QA/en unknown
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002354708A (ja) * | 2001-05-24 | 2002-12-06 | Shin Kobe Electric Mach Co Ltd | 無停電電源装置 |
| JP2007055450A (ja) * | 2005-08-24 | 2007-03-08 | Fuji Heavy Ind Ltd | 蓄電デバイスの劣化状態推定システム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| SG11201602054QA (en) | 2016-04-28 |
| US20160231389A1 (en) | 2016-08-11 |
| JP6222822B2 (ja) | 2017-11-01 |
| JP2015082387A (ja) | 2015-04-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5036733B2 (ja) | 推定バッテリー状態ベクトルと推定バッテリーパラメータベクトルとを定めるシステム及び方法 | |
| US11366170B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for correcting SOC, battery management system and storage medium | |
| JP4920696B2 (ja) | 推定バッテリーパラメータベクトルを定めるシステムと方法及びその製造物 | |
| JP4772871B2 (ja) | バッテリと関連する状態ベクトルを推定するシステム及び方法 | |
| JP6495469B2 (ja) | バッテリパラメータの推定 | |
| CN113015918B (zh) | 用于确定二次电池的健康状态的方法和电池管理系统 | |
| JP2020180820A (ja) | 電池評価システム、電池評価方法及びプログラム | |
| KR101777334B1 (ko) | 배터리 soh 추정 장치 및 방법 | |
| JP2015059924A (ja) | 蓄電池性能評価装置およびその方法 | |
| JP6213333B2 (ja) | 推定プログラム、推定方法および推定装置 | |
| JP2014044074A (ja) | 電池状態推定装置、電池制御装置、電池システム、電池状態推定方法 | |
| JP6110771B2 (ja) | 劣化量算出装置、劣化量算出方法及びプログラム | |
| JP2018141665A (ja) | 電池管理方法、電池管理装置、及びコンピュータプログラム | |
| CN106933618B (zh) | 基于系统参数相关系数的系统升级评估方法 | |
| JP6299187B2 (ja) | 推定プログラム、推定方法および推定装置 | |
| KR20120068852A (ko) | 전지의 제어 방법 및 그 방법을 구현하기 위한 장치 | |
| KR20200056716A (ko) | 배터리 soh 산출 시스템 및 방법 | |
| KR20170134193A (ko) | 배터리의 충전 상태를 추정하는 방법 및 그 방법을 실행하는 배터리 관리 시스템 | |
| KR20160107093A (ko) | 배터리의 잔존 유효 수명을 예측하는 방법 및 시스템 | |
| JP6222822B2 (ja) | 劣化関数算出装置、劣化率推定システム、劣化関数算出方法、及びプログラム | |
| JP2017015594A (ja) | バッテリー、電源管理装置、及び電源管理方法 | |
| JP5461668B1 (ja) | 二次電池管理装置、満充電容量算出方法、及びプログラム | |
| KR101906928B1 (ko) | 배터리의 수명 추정 장치 및 방법 | |
| JP6130779B2 (ja) | 容量推定装置、容量推定方法及びプログラム | |
| TWI611196B (zh) | 鉛電池之劣化程度檢測方法及鉛電池之充電控制方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14856346 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15022289 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 14856346 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |