WO2009116198A1 - 広告媒体決定装置および広告媒体決定方法 - Google Patents
広告媒体決定装置および広告媒体決定方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2009116198A1 WO2009116198A1 PCT/JP2008/067493 JP2008067493W WO2009116198A1 WO 2009116198 A1 WO2009116198 A1 WO 2009116198A1 JP 2008067493 W JP2008067493 W JP 2008067493W WO 2009116198 A1 WO2009116198 A1 WO 2009116198A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- search
- advertisement
- searcher
- medium
- word
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q30/00—Commerce
- G06Q30/02—Marketing; Price estimation or determination; Fundraising
- G06Q30/0241—Advertisements
- G06Q30/0242—Determining effectiveness of advertisements
- G06Q30/0245—Surveys
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/22—Indexing; Data structures therefor; Storage structures
- G06F16/2282—Tablespace storage structures; Management thereof
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/24—Querying
- G06F16/245—Query processing
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q30/00—Commerce
- G06Q30/02—Marketing; Price estimation or determination; Fundraising
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q30/00—Commerce
- G06Q30/02—Marketing; Price estimation or determination; Fundraising
- G06Q30/0241—Advertisements
- G06Q30/0251—Targeted advertisements
- G06Q30/0254—Targeted advertisements based on statistics
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q30/00—Commerce
- G06Q30/02—Marketing; Price estimation or determination; Fundraising
- G06Q30/0241—Advertisements
- G06Q30/0251—Targeted advertisements
- G06Q30/0255—Targeted advertisements based on user history
- G06Q30/0256—User search
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an advertisement medium determination device, and more particularly to an advertisement medium determination process using a search history.
- attribute questionnaires such as “very sensitive to fashion”, “sensitive to fashion”, and “not sensitive to fashion” are taken in advance and an advertising plan for an advertising medium is created with reference to this questionnaire.
- An object of the present invention is to provide an advertisement medium determining apparatus that can objectively determine an advertisement medium or its advertisement time by using a search result using a search engine on the Internet.
- the advertising medium determination device includes: 1) target specifying information storage means for storing target attribute specifying information including information transmitting medium specifying information for specifying a contact target information transmitting medium in association with a searcher ID. 2) Search word storage means for storing the searcher ID, search time, and search word in association with each other; 3) When a search word as a search condition is given, the search word storage means stores the search word For each searcher ID, extracting means for extracting the searcher ID in each section by dividing the extracted search time into a predetermined number in time series, 4) stored in the target specific information storage means The candidate information transmission medium in each section is extracted from the extracted searcher ID using the target identification information, and one or more representative candidate information transmissions are extracted from the extracted candidate information transmission medium.
- Advertisement medium data determining means for determining a medium, and thereby determining the representative candidate information transmission medium arranged in the time-series order of each section as advertisement medium data in the advertisement target name given corresponding to the search term It has. Therefore, the searchers can be classified according to the search times of past search terms, and the searchers belonging to each category can determine the time series order of the advertising media based on the information transmission medium to be contacted.
- the advertisement medium determination device when a word corresponding to an advertisement target name is given, gives the advertisement medium data determination means, specifies a search word corresponding to the advertisement target name, and gives it to the extraction means A search term specifying means is provided. Therefore, when a word corresponding to the advertisement target name is given, a search word corresponding to the advertisement target name can be given to the extraction means.
- the search terms stored in the search term storage unit are classified into categories, and the search term identification unit includes a category to which a word corresponding to the advertisement target name belongs. Identify search terms for. Therefore, the search term of the category to which the word corresponding to the advertisement target name belongs can be given.
- the advertisement medium determining apparatus further includes a search number fluctuation history calculating means for calculating a search number fluctuation history representing a time-series fluctuation of the search number for each search word stored in the search word storage means, And a search number fluctuation history storage means for storing the calculated search number fluctuation history, wherein the search word specifying means displays the search number fluctuation history of each search word, and when any one is selected, Identify search terms. Therefore, the operator can select a search term by referring to the search number fluctuation history. In addition, the extraction is performed by such a search term.
- the advertisement medium determination device provides the advertisement object name to the advertisement medium data determination means and a search corresponding to the advertisement object name when an advertisement object name and a search word corresponding to the advertisement object name are given.
- a search word specifying means for giving a word to the extracting means is provided. Therefore, the extraction is performed by a given search word.
- the advertisement medium determining device includes a segment determining unit that stores the segment determining rule for segmenting into the predetermined number, and the extracting unit uses the segment determining rule given from the segment determining unit.
- the searcher ID is extracted. Therefore, the searcher of each division is specified based on the division determination rule.
- the advertisement medium determining device further includes: 1) a search number fluctuation history calculating means for calculating a search number fluctuation history representing a time-series fluctuation of the search number for the search words stored in the search word storage means. 2) a search number fluctuation history storage means for storing the calculated search number fluctuation history, 3) a classification determination means for determining a classification based on the shape of the search number fluctuation history, and 4) the extraction means. Extracts the searcher ID using the category given by the category determining means. Accordingly, the classification is determined based on the shape of the search number fluctuation history.
- the category determining means determines that the category is a new category when the shape change rate of the search number change history changes more than a predetermined value, and determines the category. To do. Accordingly, when the shape change rate of the search number change history changes more than a predetermined value, the classification is automatically determined.
- the category determining means displays the search number fluctuation history and determines the category using the given category data. Therefore, the operator can determine the category with reference to the displayed search number fluctuation history.
- the search terms stored in the search term storage means are classified into categories, and the category is determined by the category of the search terms of the category to which the search term belongs.
- Classification determining means is provided. Accordingly, the category is determined by the search terms of the same category.
- a search number fluctuation history calculating means for each search word stored in the search word storage means, a search number fluctuation history calculating means for calculating a search number fluctuation history representing a time-series fluctuation of the search number;
- the search number fluctuation history storage means for storing the calculated search number fluctuation history is provided, and when the advertisement target name is input as a correction target, the search word specifying means stores the input advertisement target name.
- a search term including a search number fluctuation history similar to the search number fluctuation history is specified, and the specified search word is given to the advertisement medium data determination means as a word corresponding to the advertisement target name. Therefore, it is possible to change by a search term including a search number fluctuation history similar to the search number fluctuation history of the input advertisement target name.
- a search number fluctuation history calculating means for calculating a search number fluctuation history representing a time-series fluctuation of the search number, and
- the search number fluctuation history storage means for storing the calculated search number fluctuation history is provided, and when the advertisement target name is input as a correction target, the search word specifying means stores the input advertisement target name.
- a search term including a search number fluctuation history similar to the search number fluctuation history is specified, a search number fluctuation history of the specified search word is displayed, and when any one is selected, the selected search word is designated as the advertisement target name. Is given to the advertisement medium data determination means. Therefore, it is possible to change according to the selected search word among the search words including the similar search number fluctuation history.
- the search term as the search condition is a plurality of search terms in which either or both of logical product and logical sum are combined
- the extraction means includes each search term A period from the search start time to the search end time is obtained for the word, and a calculation based on the search condition is performed to extract a searcher ID belonging to each category. Therefore, the searcher ID of each section can be extracted by the calculation based on the search conditions using a plurality of search terms.
- the operation based on the search condition is a given logical product operation. Therefore, the searcher ID of each section can be extracted by an operation based on the logical product operation.
- the advertising medium determination device determines whether the advertising medium is based on the search condition. If the logical product operation obtains the maximum value of the period. Therefore, a value matching the search condition can be obtained.
- the advertising medium determination device determines whether the advertising medium is based on the search condition.
- the logical product operation obtains an average value of the periods. Therefore, even when the search result for a part of the conditions changes significantly, it is possible to perform the arithmetic processing that matches the search conditions.
- the extraction means performs the calculation after normalizing the period for each obtained search word for each search word. Therefore, calculation is possible by relative evaluation of the period by each search term.
- the normalization is performed by dividing the search start time to the search end time into a predetermined number for each search word, and determining the logical product operation according to which of the search words belongs. I do. Therefore, a separate normalization process becomes unnecessary.
- the advertisement medium determination device when the data to be subjected to the logical product operation is separated from other data by a predetermined threshold or more among the normalized data of the respective search terms, the normalization is performed. Performs logical AND operation ignoring data. Therefore, because some search conditions are separated from other data by a predetermined threshold or more, even a searcher who is not an extraction target can extract without changing the search conditions.
- the distance from the predetermined threshold is a case where there is no search time. Therefore, since there are no search results for some search conditions, even a searcher who is not an extraction target can extract without changing the search conditions.
- the advertisement medium determination device determines whether there is a search word that does not have a search time for a search word that performs a logical product operation, if the search word is less than a predetermined number, the search word is ignored. Perform product operation. Therefore, since there are no search results for some search conditions, even a searcher who is not an extraction target can extract without changing the search conditions.
- the computer 1) matches the searcher ID with the target attribute specifying information including the information transmitting medium specifying information for specifying the information transmitting medium to be contacted; and 2)
- the searcher ID, the search time, and the search word data associated with the search word are stored, and the computer searches the search word storage unit for the search word when given a search word.
- the time is extracted for each searcher ID, the extracted search times are divided into a predetermined number in chronological order, the searcher ID in each division is extracted, and the computer uses the stored target identification information, Candidate information transmission media in each category are extracted from the extracted searcher ID, and one or more representative candidate information transmission media are determined from the extracted candidate information transmission media
- the representative candidate information transmission medium arranged in the time series of the respective sections is determined as the advertisement medium data in the advertisement target name given corresponding to the search word.
- the searchers can be classified according to the search time of the past search terms, and the searchers belonging to each category can determine the time series order of the advertising media based on the information transmission medium to be contacted.
- the advertisement medium determining device is as follows: 1) When a search word is given, the search result data storage device storing the searcher ID, the search time, and the search word corresponding to the search is stored. Extraction means for extracting a search time of a word for each searcher ID, dividing the extracted search time into a predetermined number in time-series order from a search start time to a search end time, and extracting a searcher ID in each division; 2 ) Candidate information in each section from the extracted searcher ID using target attribute specifying information including information transfer medium specifying information for specifying a contact target information transfer medium stored in association with the searcher ID A transmission medium is extracted, and one or more representative candidate information transmission media are determined from the extracted candidate information transmission medium, whereby representative candidate information transmission arranged in chronological order of each section is performed. Advertisement medium data determining means for determining a medium as advertisement medium data in an advertisement target name given corresponding to the search term is provided.
- the searchers can be classified according to the search time of the past search terms, and the searchers belonging to each category can determine the time series order of the advertising media based on the information transmission medium to be contacted.
- the program according to the present invention causes a computer to execute the following steps 1) and 2). 1) When a search word is given, the searcher ID for which the search was performed, the search time, and the search time of the search word are extracted for each searcher ID from the search result data storage device that stores the search word in association with each other.
- the searchers can be classified according to the search time of the past search terms, and the searchers belonging to each category can determine the time series order of the advertising media based on the information transmission medium to be contacted.
- a method for determining an advertising medium includes: A) a first computer, 1) target attribute specifying information including information transmitting medium specifying information for specifying an information transmitting medium to be contacted in association with a searcher ID. 2) The searcher ID, the search time, and the search word data associated with the search word are stored, and B) the second computer receives the search word when given a search word.
- the search term of the search term is extracted from each computer for each searcher ID, the extracted search times are divided into a predetermined number in time series, and the searcher ID in each division is extracted, and C) the second computer Extracts the candidate information transmission medium in each section from the extracted searcher ID using the stored target identification information, and one or more representatives from the extracted candidate information transmission medium Determining the auxiliary information transmitting medium, thereby, the representative candidate information transmitting medium arranged in chronological order of each segment is determined as an advertising medium data in the advertisement object name given in correspondence with the search word.
- the searchers can be classified according to the search time of the past search terms, and the searchers belonging to each category can determine the time series order of the advertising media based on the information transmission medium to be contacted.
- target attribute specifying information refers to information for specifying attributes as targets such as preferences and owned products for each searcher. Moreover, information transmission medium specific information is included.
- the “information transmission medium specifying information” is information for specifying an information transmission medium with which a searcher contacts.
- a magazine name as an advertising medium is applicable, but in addition, a newspaper name, a TV program name, the Internet Including the site name.
- extract search term of search term for each searcher ID means that when the same searcher ID is searched a plurality of times, the earliest search time is extracted for the searcher.
- first means the oldest search time when the search start time is not specified, and the oldest after the specified search time when the search start time is specified. It means search time. For example, for searcher X, if there are three search periods 2008/1/10, 2008/2/16, 2008/3/1 for a certain search term, the search start period is specified as 2008/1/15 If the search start time is not specified as 2008/1/15, 2008/1/10 is extracted as the earliest search time.
- the data for which the logical product operation is performed is separated from other data by a predetermined threshold or more” includes the case where the search result does not exist and is a missing value.
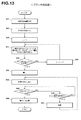
- FIG. 2 is an example of a hardware configuration of an advertisement medium determination device 1. It is a figure which shows the data structure of a search word memory
- FIG. 2 is an example of a hardware configuration of a questionnaire result analysis support apparatus 100. It is a figure which shows the data structure of a search word memory
- Advertising medium determination device 23 ... CPU 27 ... Memory
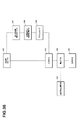
- the advertisement medium determination device 1 includes a target identification information storage unit 2, a search term storage unit 3, an extraction unit 4, an advertisement medium data determination unit 5, a search term identification unit 6, a search number variation history calculation unit 7, and a search number variation history storage. Means 8 are provided.
- the target specifying information storage unit 2 stores target attribute specifying information including information transmitting medium specifying information for specifying the information transmitting medium to be contacted in association with the searcher ID.
- the search word storage means 3 stores the searcher ID, the search time, and the search word that have been searched in association with each other.
- the extraction means 4 extracts the search time of the search word for each searcher ID from the search word storage means, and sets the search time for each extracted searcher ID in chronological order. A searcher ID belonging to each division is extracted by dividing into a predetermined number.
- the advertisement medium data determining means 5 extracts the candidate information transmission medium in each section from the extracted searcher ID using the target identification information stored in the target identification information storage means 2, and extracts the extracted candidate information transmission One or two or more representative candidate information transmission media are determined from the medium, whereby the representative candidate information transmission media arranged in chronological order of each of the categories are given advertisement target names corresponding to the search terms To be determined as advertisement medium data.
- the determined advertisement medium data is stored in the result storage means 9.
- the search word specifying means 6 gives the advertisement target name to the advertisement medium data determining means 5 and extracts the search word corresponding to the advertisement target name. To give.
- the search number fluctuation history calculation means 7 calculates a search number fluctuation history representing the time-series fluctuation of the search number for each search word stored in the search word storage means 3.
- the search number fluctuation history storage means 8 stores the calculated search number fluctuation history.
- the search word specifying unit 6 specifies a search term including a search number variation history similar to the search number variation history of the input advertisement target name.
- the search number fluctuation history of the search term is displayed, and when any one is selected, the selected search term is given to the advertisement medium data determining means 5 as a word corresponding to the advertisement target name.
- the extraction means 4 determines the period from the search start time to the search end time for each search word. The calculation is performed based on the search condition, and the searcher ID of each category is extracted.
- the category determining means 11 determines the category based on the shape of the search number fluctuation history.
- the extracting unit 4 extracts the searcher ID using the category given from the category determining unit 11.
- the target specifying information storage unit 2 and the search word storage unit 3 are stored in one advertising medium determination device, but these are stored in another computer. Alternatively, it may be read from the other computer.
- FIG. 2 is an example of a hardware configuration of the advertisement medium determination device 1 configured using a CPU.
- the advertising medium determination device 1 includes a CPU 23, a memory 27, a hard disk 26, a monitor 30, an optical drive 25, a mouse 28, a keyboard 31, and a bus line 29.
- the CPU 23 controls each unit via the bus line 29 according to each program stored in the hard disk 26.
- the hard disk 26 includes an operating system program (hereinafter abbreviated as OS) 26o, an advertisement medium determination program 26p, a search word storage unit 26k, a target data storage unit 26t, a search number variation history storage unit 26h, and an advertisement medium determination data storage unit 26b. .
- OS operating system program
- advertisement medium determination program 26p advertisement medium determination program
- search word storage unit 26k search word storage unit
- target data storage unit 26t target data storage unit 26t
- search number variation history storage unit 26h a search number variation history storage unit 26h
- advertisement medium determination data storage unit 26b advertisement medium determination data storage unit 26b.
- the search word storage unit 26k stores a user ID and a search time as a searcher ID for performing a search for each search word.
- the search date and time are stored as the search time, but only the search date may be stored.
- the search time and the user ID for each search word are stored, for example, for a search using a search engine on the Internet for each user who logs in to a certain portal site. That's fine.
- target attribute specifying information including advertising medium specifying information for specifying an advertising medium with which the user contacts is stored for each user.
- advertising medium specifying information for specifying an advertising medium with which the user contacts
- a user with a user ID 10001 has magazine B and television programs A and B as advertising media to be contacted, and the target attribute of the user is “a person who cares about fashion” or “a person who is sensitive to fashion” Is stored.
- a product for example, “Computer A”, “Drink A” owned by the user is stored.
- data such as purchase experience, purchase intention, and number of purchases may be handled.
- the target attribute for each user may be acquired at the time of new registration or by a subsequent questionnaire or the like.
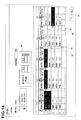
- the search number fluctuation history storage unit 26h aggregates each search word stored in the search word storage unit 26k and obtains a search number fluctuation history representing the time-series fluctuation of the search number for each search word. "Date and time”, “Number of search respondents”, and “Respondent ID” are stored. For example, in the case of the search word shown in FIG. 5, the search is performed once on 2007/4/2, and the searcher is one of “10011”. Further, the search was performed three times on April 4, 2007, and the number of searchers is 12303, 10013, 10024 ". In this way, the search number fluctuation history storage unit 26h is in chronological order. A search number fluctuation history is stored.
- the advertisement medium determination data storage unit 26b As shown in FIG. 6, the advertisement medium determination data created by the advertisement medium determination program 26p described later is stored. A specific data structure of each advertisement medium determination data is shown in FIG. As described above, the advertisement medium determination data defines an advertisement medium for each advertisement period.
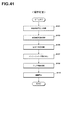
- the advertisement medium determination program 26p creates the advertisement medium determination data shown in FIGS. 6 and 7 by the aggregation process (step S2), the division determination process (step S3), and the plan creation process (step S5) shown in FIG. Details will be described later.
- Windows Vista registered trademark or trademark
- OS operating system program
- Each program is read from the CD-ROM 25a storing the program via the optical drive 25 and installed in the hard disk 26.
- a program such as a flexible disk (FD) or an IC card may be installed on a hard disk from a computer-readable recording medium. Furthermore, it may be downloaded using a communication line.
- FD flexible disk
- IC card integrated circuit card
- the program stored in the CD-ROM is indirectly executed by the computer by installing the program from the CD-ROM to the hard disk 26.
- the present invention is not limited to this, and the program stored in the CD-ROM may be directly executed from the optical drive 25.
- programs that can be executed by a computer are not only programs that can be directly executed by being installed as they are, but also programs that need to be converted into other forms (for example, those that have been compressed) In addition, those that can be executed in combination with other module parts are also included.
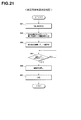
- the CPU 23 performs an input process of an advertisement target name, a history use search term, and a campaign start time (step S1). Such processing may be performed by the CPU 23 prompting an input by displaying a dialog as shown in FIG. 9 on the monitor.
- FIG. 9A when an advertisement target name is input in the area 31 and the button 32 is selected, the advertisement target name is determined.
- B of FIG. 9 when a search word is input in the area 33 and the button 34 is selected, the advertisement target name is determined.
- the campaign start time may be input in the areas 35 to 37. In the following, it is assumed that “Shampoo X” is input as the advertisement target name, “TSUBAKI” is input as the history use search term, and “May 1, 2008” is input as the campaign start time.
- the CPU 23 determines whether or not a history use search word (hereinafter referred to as a search word) is input (step S11 in FIG. 10). When the search word is input, all records in which the search word is searched are displayed. Extract (step S13). In this case, since the search term is “TSUBAKI”, the CPU 23 searches the searcher ID “10011”, the search date and time “2007/4/2 06:01”, the search term “TSUBAKI”, and the searcher ID “12303”.
- a search word hereinafter referred to as a search word
- the CPU 23 identifies the record retrieved at the earliest time among the extracted records (step S15).
- the CPU 23 sets the date and time searched at the earliest time as the population search date and time of the search word (step S17).
- the population search date of the search term “TSUBAKI” is “2007/4/2 06:01”.
- the population search date may be quite old.
- the population search date and time calculated in step S7 is displayed on the monitor, and the operator is asked, “The population search date and time is ⁇ year ⁇ month ⁇ day, is this day OK?” Any date and time may be input.
- the CPU 23 For each ID of the extracted record, the CPU 23 extracts the record with the earliest date and time after the population search date, calculates the personal search time difference for each ID, and stores this (step S19 in FIG. 10). .
- the number of days is adopted as the individual search time difference. For example, in the case of FIG. 3, as shown in FIG. 5, the search date / time 2007/4/2, the number of respondents “1”, and the searcher ID “10011” , Search date “2007/4/5, ⁇ number of respondents“ 3 ”, searcher IDs“ 12303 ”,“ 10013 ”,“ 10024 ”are obtained. (For example, in units of 3 hours) may be arbitrarily input.
- the earliest date becomes the earliest search date and time of the user
- the difference between the earliest search date and the population search date and time becomes the personal search time difference of the user
- the CPU 23 performs a classification determination process (step S3 in FIG. 8).
- the search number change history is displayed for the search term for which the search number change history data is created, and the operator refers to this and sets the search number to a predetermined number in time series using the search time as a key.
- the search term is divided into a predetermined number from the search start time to the search end time, and user IDs belonging to the respective categories are extracted. Such processing will be described.
- the CPU 23 displays a line graph on the monitor based on the search number fluctuation history data.
- the horizontal axis is the date (individual search time difference)
- the vertical axis is the number of searches.
- the aggregated distribution as shown in FIG. 11 is displayed.
- the operator refers to such distribution and designates the classification method and the number of classifications. Thereby, the number of divisions is determined.
- the number of divisions is specified by the division by quantile.
- the division by quantile means that the total number of searches is equally divided by a predetermined number of divisions. In this case, since the number of divisions is “5”, the total number of searches is divided into five, with 20% as one division.
- An example of data after classification is shown in FIG.
- the CPU 23 performs a plan creation process (step S5 in FIG. 8).
- the plan creation process the user belonging to the category obtained in step S3 is identified, and the candidate information transmission medium in each category is extracted using the target identification information of each user. Further, one or more representative candidate information transmission media are determined from the extracted candidate information transmission media, whereby the representative candidate information transmission media arranged in the time series of the respective sections correspond to the search terms. It is determined as the advertisement medium data in the given advertisement target name.
- the CPU 23 displays the search number fluctuation history (step S21).
- the CPU 23 reads out the number of sections determined in step S3 in FIG. 8 (step S23 in FIG. 13). In this case, the division number “5” is read.
- the medium contact rate of the magazine A is 12.3%. In this way, the medium contact rate in the category is obtained for all advertising media.
- the CPU 23 determines whether or not all the sections have been processed (step S29). In this case, since the processing has not been completed, the processing target section j is incremented (step S30), and the processes after step S27 are repeated.
- step S31 When processing is completed for all categories, the results are totaled (step S31). Further, the CPU 23 determines and displays candidate advertisement media (step S33). A display example is shown in FIG.
- the media contact ratios in the category of advertisement media are arranged in descending order, and among them, the media contact rate in the category is specified as a candidate that is higher than the average media contact rate in all categories by a predetermined value or more.
- Highlight display as special display.
- the present invention is not limited to this, and the medium with the highest medium contact rate may be determined as a candidate.
- the special display various displays such as changing the color scheme, displaying at a position different from other media, and changing the size of characters can be considered. Special display is optional.
- the user looks at the displayed candidates and, if he / she wishes to change, the user can select the selection area of the corresponding advertisement medium with the pointing device. For example, in FIG. 14, those that are 3% or higher than the average medium contact rate are specially displayed as candidates. In category C4, magazine K and magazine M are not highlighted because they are not 3% or more higher than the overall average medium contact rate. The same applies to the magazine K and the magazine M in the section C5. If the operator selects these advertisement media, the region 53, 54, 55, 56 may be clicked.
- the CPU 23 determines whether or not there is a change instruction (step S36), and when there is a change instruction, the display of the candidate is changed (step S37).
- FIG. 15 shows a state after the candidate display is changed with the areas 53, 54, 55, and 56 being clicked.
- step S37 the CPU 23 determines whether or not the button 51 is selected (step S35 in FIG. 13).
- step S35 the button 51 is selected, it is stored as a decision plan. About a plan name, what is necessary is just to make it input into the area
- FIG. 17 shows an outline of the determined plan A.
- the search time for the search term is appropriately classified, the respondent belonging to the category is determined, and the answer medium with which the respondent has many opportunities to contact was extracted and a media plan draft was created.
- a media plan proposal corresponding to a past search tendency for a specific search word.
- the degree of interest in a specific search term can be considered to have a certain relationship with the degree of interest in a new product. Since the search time for a specific search word can be correlated with the sensitivity to the fashion, a media plan draft that does not depend on the user's subjectivity can be created.
- the number of days actually searched for is also used as the number of days in each section, but is not limited to this.
- the “plan A” related to “shampoo X” created in this way is a plan plan on the assumption that attention will be paid in the same way as a certain search term in the past.
- This advertisement target name “shampoo X” is also newly searched as a search term.
- the search history may be completely different from the search term “TSUBAKI”.
- the created media plan proposal is changed according to the actual search history using the history of another search term. Thereby, it can be set as the media plan proposal according to the actual search history about an advertisement object name.
- the CPU 23 performs an input process of the correction target plan (step S41). For example, the dialog shown in FIG. 19 may be displayed to prompt input. The operator inputs “shampoo X” in area 61. The CPU 23 displays the shampoo X plan in the area 63. In this case, since “plan A” exists, plan A is displayed in area 63.
- a plurality of plans may be stored for one advertisement target name. In this case, a plurality of plans are displayed in the area 63.
- the CPU 23 aggregates the search history using “shampoo X” as a search word and using the search results stored in the search word storage unit (step S43 in FIG. 18). Since this aggregation process is the same as step S2 in FIG. 8, a description thereof will be omitted. As a result, a search history from 5/1 to 6/19 is obtained for the search word “shampoo X” as shown in FIG.
- the CPU 23 uses the search history for the search word “shampoo X” to determine a search word having a similar search number fluctuation history as a search word for correction (step S45). Details of step S45 will be described with reference to FIG.
- CPU 23 performs a range designation process (step S51).
- a definition file defined in the hard disk 26 (see FIG. 2) is stored with the subcategory to which the search term belongs, the major classification to which the subcategory belongs, and a hierarchical structure. Specified the range of search terms for similarity judgment.
- an operator can designate a range by displaying a dialog as shown in FIG. 23 on the screen. If the genre is determined, the operator may select the determination button 71. Further, in the case where the similarity determination is performed only for a part of the search terms in the small classification, a dialog as shown in FIG. 24 may be displayed to allow the operator to select.
- buttons 74 and 76 When the button 74 is selected for the search word displayed in the area 73, it is displayed in the area 75. When all selections are completed, the operator selects the button 76. In this case, it is assumed that shampoos Y1, Y5, and Y6 are selected.
- the CPU 23 performs an aggregation process and a search history calculation process for the search words in the specified range (step S53 in FIG. 21). Since the counting process and the history calculation process are the same as described above, the description thereof is omitted. Thereby, the search number history variation of the shampoos Y1, Y5, Y6 is obtained.
- the CPU 23 calculates the search history of 50 days from 5/1 to 6/19 and the similarity of the search number history fluctuation in the first 50 days in the shampoos Y1, Y5, Y6, A list is displayed (step S55 in FIG. 21).
- FIG. 25 shows the state displayed as a list.
- the correlation coefficient between the two search histories is used as a method for calculating the similarity between the two search histories.
- the similarity of the line graph can be determined, such as the Euclidean distance or the sum of squares. It can be anything.
- a plurality of calculation methods can be combined.
- shampoo Y6 since shampoo Y6 has a high similarity of 0.88, the operator selects shampoo Y6 as a search term for correcting “plan A” related to “shampoo X” and presses the enter button.
- the CPU 23 determines whether or not the determination button has been selected (step S57). When the determination button is selected, the search number history fluctuation before correction and the search number history fluctuation after correction are displayed in an overlapping manner. A display example is shown in FIG.
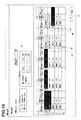
- step S45 in FIG. 18 the plan A is corrected with the determined search word (step S47). Since this process is the same as step S3 and step S5 in FIG. In step S3 of FIG. 8, the number of sections does not completely match before and after the change. In particular, some categories have already been completed by performing actual advertisements. Therefore, we revised the plans after the date of revision.
- advertisements are contracted with advertising media providers for a certain period of time. Therefore, there is a case where an already ordered advertisement can no longer be changed even if the plan is changed. For example, in this example, the correction was made on June 19, 2008. However, in Category C2, magazine C has been determined as the advertising medium until June 30, 2008, and it has already been ordered to advertise to magazine C. is there. Therefore, this cannot be canceled. However, since it may be desirable to make the effect of the correction earlier, in the present embodiment, advertisements are made to overlap for some periods. In this example, magazines H and C are determined as advertising media from 6/20 to 7/30. As a result, the advertising media overlap during the period 6/20 to 6/30. In this example, the classification after 6/20 is two.
- FIG. 27 shows an example of plans before and after correction
- FIG. 28 shows an example of a plan in which these are displayed together.
- the sections C2 and C2 ' may be displayed together.
- the search terms may be classified into categories so that search terms belonging to the same category can be selected. Specifically, the definition file shown in FIG. 22 is stored, and dialogs as shown in FIGS. 23 and 24 are displayed so that the operator can specify the classification or search term to which the advertisement target name belongs. Good.
- the search number fluctuation history of the search word is calculated and displayed so that the operator can specify the search word when creating a plan from the search number fluctuation history. May be.
- Identification of Category the operator specifies the number of categories.
- the candidate for classification can be automatically determined by the computer. The automatic determination division process will be described with reference to FIG. In this process, when the search history rises or falls, it is assumed that it is one division.
- the CPU 23 reads data to be processed (step S71 in FIG. 29).
- the CPU 23 performs aggregation unit setting, condition setting regarding ascending / descending points, and calculation method specifying processing for the given search number variation history (step S72).
- the dialog shown in FIG. 31 is displayed to allow the operator to input necessary data.
- the aggregation unit is set to “week”
- the rising point condition is set to “3 weeks continuous increase” and “overall increase of 0.5% or more as a whole”.
- the moving average “Yes” and “Previous 4-week average” are set.
- the descending point is the same as the ascending point.
- the CPU 23 calculates the moving average value and the total cumulative distribution number (step S73). The calculation result is shown in FIG.
- CPU 23 extracts ascending point candidates and descending point candidates that satisfy the conditions specified in step S72 (step S74).
- the 10th to 16th weeks and the 22nd to 25th weeks are extracted as the rising point candidates
- the 17th to 21st weeks and the 26th to 28th weeks are extracted as the lowering point candidates.
- the CPU 23 excludes the last ascending point candidate from the candidates until it does not exist continuously, and the descending point candidates continue. If it exists, the first descending point candidate is excluded from the candidates until it does not exist continuously (step S75). This excludes weeks 11-15, 21-25, 17-20, and 26-27.
- the CPU 23 defines as an ascending point when the ascending point candidates are not consecutive and as a descending point when the descending point candidates do not exist continuously (step S76).
- week 10 and week 22 are defined as rising points
- week 21 and week 28 are defined as falling points.
- CPU 23 displays the period between each point (ascending point or descending point) and the number of searches (step S77). In this case, a total of five ascent and descent points as shown in FIG. 33 are defined, and the sections C1 to C4 are displayed by the five points.
- the operator refers to the display and performs an ascending point and descending point specifying process (step S78). Specifically, if the time period is too short, the selection may be made such that the time period is combined with one before or after the time period. In this case, since the section C3 is only the 21st week and the search rate is as low as 0.1%, it is assumed that the section C3 is merged with the subsequent section C4.
- FIG. 34 shows a screen example after combining. Thus, by displaying the number of searches, the operator can exclude a category with a small number of searches.
- the CPU 23 displays the period for each category and the number of searches based on the specified rising and falling points (step S79 in FIG. 29). A display example is shown in FIG.
- the numerical value list is displayed on the screen and the correction is performed.
- the line graph and the boundary line shown in FIG. 35 are displayed, and the boundary line is added or deleted, thereby specifying the step S78. Processing may be performed. Moreover, you may make it display both.
- the boundary of the classification can be automatically determined from the shape of the search number fluctuation history. Therefore, since the boundary candidates for the category are displayed, even an operator who is not familiar with the method of classifying the search number variation history can define the category according to the shape of the search number variation history.
- candidates are displayed, but may be determined automatically.
- a boundary line for dividing a segment is defined using a moving average of the search number history fluctuation. Therefore, it is possible to detect an upward trend including the exclusion of the second week in which a short-term increase is observed and the 11th week in which a short-term decrease is observed.
- search word A and (search word B or search word C) an ID that satisfies the condition may be extracted as it is. Specifically, the search word B or the search word C is searched, and the person who also searched the search word A is extracted. For the evaluation of the searcher, each ID uses “date when search word B or search word C is searched and search word A is searched”. The earliest date among all IDs, “search word B or search word C is searched and search word A is searched” may be set as the population search date.
- Such a search condition is effective when it is desired to extract and classify people who searched a plurality of search terms at the same time.
- the personal search time difference may be calculated for each search term, and the personal search time difference may be calculated according to the conditions.
- the AND condition calculates the maximum value
- Such a technique is effective when it is desired to detect and classify a person who has always searched a plurality of search terms of the same genre at an early timing.
- the normalization method is not limited to the case of classification into the above-described categories, and a general normalization method may be adopted.
- the search condition when the search condition is a logical product operation, the search result may not exist, or even if it exists, it may be significantly different from other search conditions.
- the evaluation can be performed in the above-described manner, but it is also possible to relax and evaluate some conditions as follows.
- the following reason can be considered when there is no search result for a certain search word among the search words designated to perform a logical product operation.
- One is when the user has low information sensitivity for the search term.
- the other is not related to information sensitivity, such as not knowing the search term and not searching, or accidentally not interested in the search term.
- the user has low information sensitivity for the search term, it is not necessary to be a user to be extracted, but in the latter case, it is preferable to be a target for extraction. Therefore, such a user may be extracted as follows.
- search word w1 and search word w2 and search word w3 and search word w4 and search word w5 is given as a search word, and the following is obtained as a search result.
- search term w1 to search term w5 all C1
- User U2 search word w1 to search word w5: all C5
- User U3 Search term w1 to search term w4: All C1
- search term w5 C5
- the search terms w1 to w4 belong to the category C1
- some search terms belong to the other category C5. Determination based on a value, an average value, a mode value, and a threshold value (for example, when a predetermined number or more of categories are included, it is recognized as the category) is possible.
- search term w3 has no search record.
- the individual search time difference of the individual i with respect to the search word j is set to NA when there is a missing value, and each search time difference t (ij) for each search word when there is no missing value.
- the and condition is NA
- the ave condition is NA
- the or condition is the minimum value (however, NA is all NA).
- the and condition is the maximum value excluding NA (however, all NA is NA)
- the ave condition is the average value excluding NA. Yes (NA for all NA), or condition is the minimum value excluding NA (NA for all NA).
- the personal search time difference calculated according to the condition is set as T (i), and after setting the personal search time difference category using T (i), the time difference category is performed in the same manner as when one search word is selected.
- the and condition When calculating for data that includes missing values, the and condition is NA, the ave condition is NA, and the or condition is the minimum value (however, NA is all NA).
- the and condition when calculating with data that includes missing values excluded, the and condition is the maximum value excluding NA (however, all NA is NA), and the ave condition is the average value excluding NA (however, all If NA, NA) rounds to a positive integer.
- the or condition is the minimum value excluding NA (however, if all are NA).
- the personal time difference classification calculated according to the condition is C (i), and the summation may be performed using C (i).
- the target attribute specifying information and the search term data are stored as examples in the advertisement medium determining device.
- either or both of them are stored in another computer (for example, a center server).
- Data may be stored and read out via a network.
- a history storage program for using a search engine is installed in the user's personal computer, and the search term and the search time are stored each time a search is performed. You may make it transmit to a center server regularly or irregularly. In this way, a known technique can be adopted as a collection method for the search result.
- the operator inputs the search term.
- the search term is classified and stored in a category, and the search term of the category to which the word corresponding to the advertisement target name belongs is automatically set. It may be determined. Alternatively, it may be displayed as a candidate so that either can be selected.
- search number fluctuation history may be stored for each search word, displayed to the operator, and when any one is selected, the search word may be specified.
- a classification determination rule for dividing into a predetermined number may be stored, and the classification may be determined using this rule.
- the search terms may be classified into categories and stored, and the category may be determined according to the category of the search term of the category to which the search term belongs.
- the search term specifying means may automatically specify a search term including a search number variation history similar to the search number variation history of the input advertisement target name. Good. Further, instead of automatic identification, a history of fluctuations in the number of searches for the specified search terms is displayed, and when any one is selected, the selected search terms are given to the advertising medium data determining means as terms corresponding to the advertisement target names. You may do it.
- the various periods are based on the day, but can be arbitrarily applied, such as week, month, morning or afternoon, or time (for example, in units of 3 hours).
- any time segment for example, one month, etc. may be set for the total category.
- the candidate is determined based on the medium contact rate in step S33 in FIG. 13, but the candidate may be determined based on a value that considers the advertising cost.
- the advertising cost may be stored in advance for each advertising medium, and the medium contact rate per unit price (a value obtained by dividing the medium contact rate by the advertising cost) may be arranged in descending order.
- the medium contact rate is 12.3% for magazine A, 10.5% for magazine B, 7.5% for magazine C, 4.5% for magazine D, and 2.5% for magazine E. %.
- the unit price The hit medium contact rate is 0.12 for magazine A, 0.15 for magazine B, 1.0 for magazine C, 0.075 for magazine D and 0.083 for magazine E. Magazine B, Magazine A, Magazine C, Magazine E, Magazine D are in this order.
- the advertising cost per unit medium contact rate (a value obtained by dividing the advertising cost by the medium contact rate) may be calculated and arranged in ascending order.
- candidates may be determined by the content rate.
- candidates may be determined by combining the medium contact rate and / or the content rate, and further adding a cost to these values.
- the combination may be to obtain a simple and condition or or condition, or to obtain a total point by multiplying by a predetermined coefficient.
- a CPU in order to realize each function, a CPU is used and this is realized by software. However, some or all of them may be realized by hardware such as a logic circuit.
- OS operating system
- FIG. 36 shows a functional block diagram of the questionnaire result analysis support apparatus 100.
- the questionnaire result analysis support apparatus 100 includes an answer information storage unit 102, a search word storage unit 103, a determination unit 104, a totaling unit 105, a generation unit 106, a search number variation history calculation unit 107, a search number variation history storage unit 108, and a category determination. Means 109 are provided.
- the response information storage unit 102 stores questionnaire response information in which relevant or non-relevant responses are made for a plurality of items in association with the respondent ID.
- the search word storage means 103 stores the search term searched at a specific search site in association with the search time and the searcher ID that performed the search.
- the determination unit 104 extracts the search time of the search word from the search word storage unit 103 for each searcher ID, and classifies the extracted search time into a predetermined number in time series. Then, the user specified by the respondent ID associated with the searcher ID is determined as the user in each category.
- Aggregating means 105 arranges the respective sections in the first axis direction in the cross tabulation for the items for which the corresponding answer is made in the questionnaire answer information stored in the answer information storage means 2, and The items of the questionnaire response information are arranged in the direction of the two axes, and the number of the items in each category is cross-tabulated.
- the generating unit 106 extracts one or more items designated by the operator from the items arranged in the first axial direction or the items arranged in the second axial direction from the total result. Then, display data in which cells belonging to the extracted item are arranged is generated.
- the generation unit 106 compares the cell value of the item arranged in the first axial direction with the same item in the second axial direction, and easily distinguishes the cell with a unique value from other cells. Emphasized item processing data is generated. Therefore, among the cells belonging to the specific item arranged in the first axial direction, it is possible to perform highlighting that makes it easy to distinguish a cell having a unique value from other cells. Further, when two or more items are extracted, it becomes easy to analyze the characteristics between users having different search times in different items.
- the search number fluctuation history calculating means 107 calculates a search number fluctuation history representing a time-series fluctuation of the search number for each search word stored in the search word storage means 103.
- the search number fluctuation history storage means 108 stores the calculated search number fluctuation history.
- the classification determination unit 109 determines the classification based on the shape of the search number variation history.
- the determination unit 104 extracts the searcher ID using the category given from the category determination unit 109.
- the questionnaire result data storage means 102 and the search word storage means 103 are stored in one questionnaire result analysis support apparatus. However, these are stored in separate computers. Alternatively, it may be read from the other computer. Further, the questionnaire result data storage unit 102 and the search word storage unit 103 may be realized by one computer.
- the hardware configuration of the questionnaire result analysis support apparatus 100 is substantially the same as that of the advertisement medium determination apparatus 1 shown in FIG. 2 except for the program and data stored in the hard disk 26. As shown in FIG. 37, the hard disk 26 of the questionnaire result analysis support apparatus 100 stores an analysis program 126p, a search word storage unit 126k, a questionnaire data storage unit 126t, and a search number fluctuation history storage unit 126h.
- a user ID and a search time are stored as a searcher ID for performing a search for each search word.
- the table format is grouped for each user ID.
- the search date is stored as the search time, but the search date and the search time may be stored.
- the search time and the user ID for each search word are stored, for example, for a search using a search engine on the Internet for each user who logs in to a certain portal site. That's fine.
- questionnaire result data is stored in the questionnaire data storage unit 126t for each user.
- the user ID 10001 has the following questionnaire response items: “A person who cares for hair care”, “A person who cares about the roughness of hair”, “A person who cares about fashion”, “ “Sensitive one” is defined as “yes”.
- “Magazine B”, “TV Program A”, “TV Program B”, etc. are applicable (yes) and “Magazine A” is not applicable (No).
- “shampoo A television advertisement”, “shampoo A banner advertisement”, “shampoo A homepage” are applicable as the recognized advertisements that are actually recognized (yes), and “Shampoo C” is already purchased. Answered yes (yes).
- each search word stored in the search word storage unit 126k is aggregated, and a search number fluctuation history representing the time-series fluctuation of the search number is obtained for each search word.
- “Date and time”, “number of search respondents”, and “user ID” are stored.
- the search is performed once on May 1, 2008, and the searcher is one person of “10011”. Further, the search was performed three times on May 2, 2008, and there are three searchers 12303, 10013, and 10024 ". In this way, the search number fluctuation history storage unit 126h is in chronological order. A search number fluctuation history is stored.
- the questionnaire result analysis process will be described with reference to FIG.
- the CPU 23 performs a search target word input process that is one axis in the case of cross tabulation (step S101). Such processing may be performed by the CPU 23 prompting input by displaying a dialog as shown in FIG. 42 on the monitor.
- search target word is determined. In the following, it is assumed that “shampoo A” is input as a search target word.
- CPU 23 performs a search history totaling process for the specified search term (step S102). Details of the counting process are shown in FIG.
- CPU23 extracts all the records from which the said search term was searched (step S113).
- the CPU 23 searches the searcher ID “10001”, the search date “2008/8/5”, the searcher ID “10002”, the search date “2008/6”. / 1, searcher ID "10003”, search date "2008/7/16”, searcher ID "10004", search date "2008/9/1”, searcher ID "10005", search date "2008/6 / 24 "... is extracted.
- the CPU 23 identifies the record retrieved at the earliest time among the extracted records (step S115).
- the CPU 23 sets the date and time searched at the earliest time as the population search date and time of the search word (step S117). For example, in the example of FIG. 38A, the population search date of the search term “shampoo A” is “2008/5/1”.
- the population search date may be quite old.
- the population search date and time calculated in step S117 is displayed on the monitor, and the operator confirms that “the population search date and time is ⁇ year ⁇ month ⁇ day, is this date OK?” Any date and time may be input.
- the CPU 23 For each ID of the extracted record, the CPU 23 extracts the record with the earliest date and time after the population search date, calculates the personal search time difference for each ID, and stores this (step S119 in FIG. 43). .
- the number of days is adopted as the individual search time difference.
- the search date 2008/5/1, the number of respondents “1”, and the searcher ID “10011” Search date “2008/5/2, ⁇ number of respondents“ 3 ”, searcher ID“ 12303 ”,“ 10013 ”,“ 10024 ”, etc.
- the unit of aggregation is week, month or morning In the afternoon, time (for example, in units of 3 hours) may be arbitrarily input.
- the earliest date becomes the earliest search date and time of the user
- the difference between the earliest search date and the population search date and time becomes the personal search time difference of the user
- the CPU 23 performs a classification determination process (step S105 in FIG. 41).
- the search number change history is displayed for the search term for which the search number change history data is created, and the operator refers to this and sets the search number to a predetermined number in time series using the search time as a key.
- the search term is divided into a predetermined number from the search start time to the search end time, and user IDs belonging to the respective categories are extracted. Such processing will be described.
- the CPU 23 displays a line graph on the monitor based on the search number fluctuation history data.
- the horizontal axis is the date (individual search time difference)
- the vertical axis is the number of searches.
- the total distribution as shown in FIG. 44 is displayed.
- the operator refers to such distribution and designates the classification method and the number of classifications. Thereby, the number of divisions is determined.
- the number of divisions is specified by the division by quantile.
- the division by quantile means that the total number of searches is equally divided by a predetermined number of divisions. In this case, since the number of divisions is “5”, the total number of searches is divided into five, with 20% as one division.
- An example of data after classification is shown in FIG.
- the CPU 23 reads the questionnaire result data (step S107 in FIG. 41). In this case, it is assumed that the questionnaire result data shown in FIG. 39 has been read.
- the CPU 23 classifies a plurality of items in the questionnaire result data according to the category determined in step S105, and performs a cross tabulation process using the questionnaire items as another axis. (Step S109).
- the conventional tabulation method is possible.
- the above-mentioned classification is taken as the head (column)
- the questionnaire items are front side (rows)
- the vertical% tabulation indicating the number distribution is performed as a percentage.
- the value of each item is expressed as a percentage divided by the total number in the vertical direction.
- the ratio of recognizing the TV advertisement of shampoo A is 42.5%
- the ratio of recognizing the TV advertisement of shampoo A is 54.
- the result of analysis is .6%.
- non-searchers are also placed at the top of the table and cross tabulated (see FIG. 46). As a result, analysis in consideration of the characteristics of the non-searcher is possible.
- the CPU 23 highlights a cell having a unique value (step S110 in FIG. 41).
- emphasized item processing data is generated so that it can be easily distinguished from other items when displayed.
- FIG. 1 A part of the display example is shown in FIG.
- the average of the users belonging to the sections C1 to C5 is 40.2%, and the users belonging to the section C2 is 54.6%.
- FIG. 48 shows an overall display example in which each item is highlighted.
- Questionnaire analysts refer to this, for example, those who search for “shampoo A” at an early stage are “teens”, “care for hair care”, “worried about the hairiness”
- the contact rate of “Magazine B” and “TV program B” is high as contact media. Therefore, for example, it is possible to obtain an analysis result indicating that an advertisement may be placed on “Magazine B” or “Television Program B” to appeal the problem of hair care or hairiness.
- a marketing strategy corresponding to that can be devised.
- the person who searches for the product is a person who is highly involved in the product, it is possible to grasp the time when the person who is highly involved in the product has been involved in the product. Moreover, considering the percentage of people currently searching on the Internet, the representativeness of the population is also excellent, and since it has search history data, it is possible to grasp the exact search time. Furthermore, the already purchased products can be supplemented by asking questions in a questionnaire survey.
- a searcher who searches for a certain search term is used as one axis of cross tabulation. Therefore, it is possible to conduct a questionnaire assuming the prospective purchasers in the case of newly released products, and it is possible to efficiently secure a large number of samples even for products with few buyers. Further, conventionally, there is a problem that it is very difficult to specify “purchase time” unless there is POS data / personal purchase history data such as a distribution chain. Furthermore, the surveys and tabulations associated with the POS data / personal purchase history data of the distribution chain, etc., have a problem in that the distribution chain area, etc. are limited, and a sufficient number of samples cannot be secured or the samples are biased. It was. In the present invention, it is possible to solve such a problem and perform analysis in consideration of information sensitivity and the like.
- extraction condition means that, for example, if extraction is limited to respondents of “age teenage” among the front side items, the operator selects “conditional” and selects from the pull-down menu. , “Age teenage” may be specified.
- “Table type” is the display of the value of each cell. If you want to display the absolute number of people, the “frequency” is the ratio of the national population and the total number of respondents (matrix). If you want to get an estimate of how much you have in the whole country, if you want to display "Estimated number of people",% including non-searchers, or "Total%”, if you want to get item ranking For example, “ranking display” is selected, and the criteria for ranking (numerical value, difference from overall average, difference from searcher average, squared value, etc.) may be selected from a pull-down menu. “Horizontal%” is a case where the display is performed at a ratio when the sum of specific items arranged on the front side is 100.
- “Items to be used for the front” and “Items to be used for the front” may be selected from the pull-down menus.
- “items used for the front” is the search time
- “items used for the front” are questionnaire items such as sex, age,.
- a criterion and a threshold value for highlighting as shown in FIG. 48 are input. Any one may be selected, and “more” or “less” may be selected as a threshold value in addition to the numerical value.
- the CPU 23 inputs each instruction (“extraction condition”, “table type”, “item used at the front”, “item used at the front”, “average”, “marking” entered on the input screen shown in FIG. About “)”, the instructed condition is stored, and the output display of the tabulation table may be determined before step S109 in FIG.
- FIG. 50 is an example in which the items are rearranged in descending order of the average value subtracted in the sections C1 and C2 when the tabulation result of FIG. 48 is obtained.
- FIG. 51 shows an example in which only the items are rearranged for the sections C1 to C5.
- the results of the questionnaire for all the members are grouped according to the above search time for each user and tabulated, but only users belonging to a specific group from the beginning are targeted for the questionnaire, You may make it total a result.
- the users belonging to the category C1 are people who searched at an early stage when the products are not yet well known, there are cases where it is desired to conduct a questionnaire only for these users. In such a case, since a population can be narrowed down compared with conducting a questionnaire for all users, a more efficient questionnaire can be implemented.
- target attribute specifying information and search word data are stored in the questionnaire result analysis support apparatus.
- either or both may be stored in another computer (for example, a center server). These data may be stored and read out via a network.
- the center server can be divided into two and realized as a computer system constituted by three computers.
- a history storage program for using a search engine is installed in the user's personal computer, and the search term and the search time are stored each time a search is performed. You may make it transmit to a center server regularly or irregularly. In this way, a known technique can be adopted as a collection method for the search result.
- the search term is input by the operator, but the search term is classified and stored in a category so that the search term belonging to the category to which the search term belongs can be automatically specified. Also good. Alternatively, it may be displayed as a candidate so that either can be selected.
- search number fluctuation history may be stored for each search word, displayed to the operator, and when any one is selected, the search word may be specified.
- classification determination rules for dividing into a predetermined number and determine the classification using this rule.
- the search terms may be classified into categories and stored, and the category may be determined according to the category of the search term of the category to which the search term belongs.
- the search term specifying means may automatically specify a search term including a search number variation history similar to the search number variation history of the input advertisement target name. Furthermore, instead of automatic identification, a history of the number of searches of the specified search terms is displayed, and when any one is selected, the selected search terms are given to the search term specifying means as words corresponding to the advertisement target names. It may be.
- the various periods are based on the day, but can be arbitrarily applied, such as week, month, morning or afternoon, or time (for example, in units of 3 hours).
- any time category for example, one month may be set.
- the questionnaire result analysis support device includes: 1) answer information storage means for storing questionnaire answer information in which relevant or non-relevant answers are made for a plurality of items in association with the respondent ID; Search term storage means that stores the search term searched in the search site in association with the search time and the searcher ID that performed the search, and 3) given a search term as a search condition, The search term of the search term is extracted for each searcher ID from the search term storage means, and the extracted search time is divided into a predetermined number in time-series order and specified by the respondent ID associated with the searcher ID.
- cross-tabulation of questionnaire results can be performed based on the search time of a certain search term.
- the counting unit further arranges a user who did not perform the search among the respondents as a non-search user classification in the first axial direction. And cross tabulate. Therefore, cross-tabulation of questionnaire results can be performed based on the search time of a certain search term in comparison with non-search users.
- the counting unit includes cells belonging to a specific item among items arranged in the first axis direction among the cells in the cross-tabulated table. Is normalized based on the value of the cell belonging to the item. Therefore, it is possible to compare values of cells belonging to a specific item arranged in the first axial direction. In addition, by performing a plurality of specific items arranged in the first axial direction, it is possible to analyze characteristics between users at different search times.
- the counting unit includes cells belonging to a specific item among items arranged in the second axis direction among the cells in the cross-tabulated table. Is normalized based on the value of the cell belonging to the item. Therefore, the values of cells belonging to a specific item arranged in the second axial direction can be compared. In addition, by performing a plurality of specific items arranged in the second axial direction, it is possible to analyze characteristics between users with different search times in different items.
- the generating means operates, among the items arranged in the first axial direction or the items arranged in the second axial direction with respect to the aggregation result, One or more items designated by the user are extracted, and display data in which cells belonging to the extracted items are arranged is generated. Therefore, it is possible to display the items that the analyst wishes to analyze.
- one or more items designated by the operator are extracted from the items arranged in the first axial direction with respect to the total result
- a generating unit configured to generate display data in which cells belonging to the extracted item are arranged, wherein the generating unit sets the cell value of the item arranged in the first axial direction to the same item in the second axial direction;
- the emphasis item processing data that makes it easy to distinguish a cell having a unique value from other cells is generated. Therefore, among the cells belonging to the specific item arranged in the first axial direction, it is possible to perform highlighting that makes it easy to distinguish a cell having a unique value from other cells. Further, when two or more items are extracted, it becomes easy to analyze the characteristics between users having different search times in different items.
- one or more items designated by the operator are extracted from the items arranged in the first axial direction with respect to the total result
- a generating unit configured to generate display data in which cells belonging to the extracted item are arranged, wherein the generating unit sets the cell value of the item arranged in the first axial direction to the same item in the second axial direction;
- the ranking process data arranged in the order of unique values is generated. Therefore, a cell having a unique value among cells belonging to a specific item arranged in the first axial direction can be displayed. Further, when two or more items are extracted, it becomes easy to analyze the characteristics between users having different search times in different items.
- one or more items designated by the operator are extracted from the items arranged in the second axis direction with respect to the total result
- a generating unit configured to generate display data in which cells belonging to the extracted item are arranged, wherein the generating unit sets the cell value of the item arranged in the second axial direction to the same item in the first axial direction;
- the emphasis item processing data that makes it easy to distinguish a cell having a unique value from other cells is generated. Therefore, among the cells belonging to the specific item arranged in the second axis direction, it is possible to perform highlighting that makes it easy to distinguish a cell having a unique value from other cells. Further, when two or more items are extracted, it becomes easy to analyze the characteristics between users having different search times in different items.
- one or more items designated by the operator are extracted from the items arranged in the second axis direction with respect to the total result
- a generating unit configured to generate display data in which cells belonging to the extracted item are arranged, wherein the generating unit sets the cell value of the item arranged in the second axial direction to the same item in the first axial direction;
- the ranking process data arranged in the order of unique values is generated. Therefore, a cell having a unique value among cells belonging to a specific item arranged in the second axial direction can be displayed. Further, when two or more items are extracted, it becomes easy to analyze the characteristics between users having different search times in different items.
- the computer-aided questionnaire result analysis method is based on questionnaire response information in which relevant or non-relevant answers have been made for a plurality of items in association with respondent IDs on a computer, and a specific search site.
- the search term and the searcher ID that performed the search are associated with each other and stored in the storage unit, and when the search term is given as a search condition, the computer stores the search term in the storage unit.
- the search time of the stored search term is extracted for each searcher ID, the extracted search time is divided into a predetermined number in time series, and the user identified by the respondent ID associated with the searcher ID Is determined as a user in each category, and among the questionnaire response information stored in the storage unit, the item for which the corresponding response is made, Said each divided into a first axial direction disposed in the loss aggregates, each item of the questionnaire information to the second axial disposed in the cross tabulation, cross tabulation the number of each item in each segment.
- the questionnaire results can be cross tabulated based on the search time of a certain search term.
- a questionnaire result analysis program is a program for causing a computer to execute the following steps 1) to 3). 1) Corresponding to the respondent ID, the search time and search were performed for the questionnaire response information in which the corresponding or non-applicable responses were made for multiple items and the search terms searched for on a specific search site. A step of associating a searcher ID with the storage unit and storing it in the storage unit. 2) When a search term is given as a search condition, the search term of the search term stored in the storage unit is extracted for each searcher ID and extracted.
- a questionnaire result analysis system stores, in a first computer, questionnaire response information in which a corresponding or non-applicable answer is made for a plurality of items in association with a respondent ID, and a second computer
- the search term searched for at a specific search site is stored in association with the search time and the searcher ID that performed the search, and connected to the first and second computers.
- the computer of No. 3 extracts the search time of the search word for each searcher ID from the second computer, and divides the extracted search time into a predetermined number in chronological order.
- the user identified by the respondent ID associated with the searcher ID is determined as the user in each category, and the first computer Among the questionnaire response information stored in the data, the respective categories are arranged in the first axis direction in the cross tabulation and the questionnaire response information in the second axis direction in the cross tabulation. Are arranged, and the number of each item in each section is cross-tabulated.
- the questionnaire results can be cross tabulated based on the search time of a certain search term.
- a questionnaire questionnaire target person determination device includes: 1) answer information storage means for storing questionnaire answer information in which relevant or non-relevant answers have been made for a plurality of items in association with the respondent ID; 2) With respect to a search term searched on a specific search site, search term storage means for storing the search time and the searcher ID that performed the search in association with each other, and 3) given a search term as a search condition, The search term of the search term is extracted for each searcher ID from the search term storage means, and the extracted search times are divided into a predetermined number in time-series order and specified by the respondent ID associated with the searcher ID. Determining means for determining a user to be selected as a user in each category; 4) when any of the categories is specified, a searcher ID belonging to the category is determined as a survey target person And it includes a questionnaire subject determining means.
- cells having unique values means, for example, a value indicating whether or not the items of the aggregated cross tabulation results are statistically significant, and the average value of each section is subtracted from the numerical value of each cell. The case where the obtained value is larger than other cells is also included. Furthermore, it refers to a cell having a large chi-square value for the item of the cross tabulation result.
Abstract
Description
23・・・CPU
27・・・メモリ
図1に、本件発明にかかる広告媒体決定装置1の機能ブロック図を示す。広告媒体決定装置1は、ターゲット特定情報記憶手段2、検索語記憶手段3、抽出手段4、広告媒体データ決定手段5、検索語特定手段6、検索数変動履歴演算手段7、検索数変動履歴記憶手段8を備えている。
広告媒体決定装置1のハードウェア構成について、説明する。図2は、CPUを用いて構成した広告媒体決定装置1のハードウェア構成の一例である。
以下、広告媒体決定処理について図8を用いて説明する。CPU23は、広告対象名、履歴利用検索語、およびキャンペーン開始時期の入力処理を行う(ステップS1)。かかる処理は、CPU23が図9のようなダイアログをモニタに表示して入力を促せばよい。図9のAでは、領域31に広告対象名を入力し、ボタン32を選択すると、広告対象名が決定される。図9のBでは、領域33に検索語を入力し、ボタン34を選択すると、広告対象名が決定される。図9のCでは、領域35~37にキャンペーン開始時期を入力すればよい。以下では、広告対象名として"シャンプーX"が、履歴利用検索語として"TSUBAKI"が、キャンペーン開始時期として"2008年5月1日"が入力されたものとする。
CPU23は、集計処理を行う(図8ステップS1)。集計処理の詳細を図10に示す。
集計処理が完了すると、CPU23は区分け決定処理を行う(図8ステップS3)。本実施形態においては、上記検索数変動履歴データが作成された検索語について、検索数変動履歴を表示して、操作者がこれを参照して、検索時期をキーとして、時系列順に所定数に区分して、当該検索語について検索開始時期から検索終了時期までを所定数に区分して、各区分に属するユーザIDを抽出する。かかる処理について説明する。
3)〔プラン作成処理〕
次に、CPU23は、プラン作成処理を行う(図8ステップS5)。プラン作成処理では、ステップS3にて得られた区分に属するユーザを特定し、各ユーザのターゲット特定情報を用いて、前記各区分における候補情報伝達媒体が抽出される。さらに、抽出した候補情報伝達媒体から、1または2以上の代表候補情報伝達媒体が決定され、これにより、前記各区分の時系列順に並べられた代表候補情報伝達媒体が、前記検索語に対応して与えられた広告対象名称における広告媒体データとして決定される。
このようにして作成された"シャンプーX"の関する”プランA"は、あくまでも、過去のある検索語と同じような注目がされると想像した上のプラン案である。この広告対象名"シャンプーX"についても、新たに検索語として検索される。その結果、検索語"TSUBAKI"とは、検索履歴が全く異なる場合もありうる。この実施形態では、作成したメディアプラン案を実際の検索履歴に応じて、さらに別の検索語の履歴を用いて変更する。これにより、広告対象名についての実際の検索履歴に応じたメディアプラン案とすることができる。
上記実施形態においては、当初プランを作成するに当たっては、どの検索語を用いるのか操作者が特定する必要がある。かかる決定は経験が豊かな操作者でも適切に行うことは困難な場合がある。そこで、かかる問題を解決するために、検索語をカテゴリー別に分類しておき、同じ分類に属する検索語から選択できるようにしてもよい。具体的には、図22に示す定義ファイルを記憶しておき、図23,図24に示すようなダイアログを表示し、操作者に広告対象名が属する分類または検索語を特定させるようにしてもよい。
本実施形態においては、区分数を操作者が指定するようにした。これに対してコンピュータによって自動的に区分候補を決定することもできる。自動決定区分処理について図29を用いて説明する。この処理では、検索履歴が上昇または下降する場合に1つの区分であるとしている。
上記実施形態においては検索語を1つだけ指定する場合を例として説明したが、複数の検索語について論理和(or)およびまたは論理積(and)演算を行うように指定した検索語を与えることもできる。
個人時間差区分は、MAX[1、MIN(1、2)]=1となり、個人時間差区分はC1となる。
ユーザU2:検索語w1~検索語w5:全てC5、
ユーザU3:検索語w1~検索語w4:全てC1、検索語w5:C5
このように、ユーザU3のように、検索語w1~検索語w4については区分C1に属すが、一部の検索語については他の区分C5に属する場合、評価としては、これらの最大値、最小値、平均値、最頻値、閾値による判定(例えば、所定個数以上ある区分に属した場合は当該区分と認定するなど)が可能である。
本実施形態においては、既にインターネット上の検索エンジンを用いた検索結果が記憶されている場合について説明したが、前記修正処理をする場合には、修正処理を開始する時までの検索結果を記憶しておけばよい。
アンケート結果解析支援装置100のハードウェア構成は、ハードディスク26に記憶されているプログラムおよびデータを除き、図2に示す広告媒体決定装置1とほぼ同様である。アンケート結果解析支援装置100のハードディスク26には、図37に示すように、解析プログラム126p、検索語記憶部126k、アンケートデータ記憶部126t、検索数変動履歴記憶部126hが記憶されている。
アンケート結果の解析処理について図41を用いて説明する。CPU23は、クロス集計する場合の1つの軸となる検索対象語の入力処理を行う(ステップS101)。かかる処理は、CPU23が図42のようなダイアログをモニタに表示して入力を促せばよい。領域133に検索語を入力し、ボタン134を選択すると、検索対象語が決定される。以下では、検索対象語として"シャンプーA"が入力されたものとする。
つぎに、CPU23は、アンケート結果データを読み出す(図41ステップS107)。この場合、図39に示すアンケート結果データが読み出されたものとする。
上記実施形態においては、クロス集計として縦%を求め、かつ、特異な値を有するセルについて強調表示を行うようにした場合について説明したが、集計タイプ、強調表示などのマーキングについては、操作者が選択できるようにしてもよい。たとえば、図41ステップS109の前までに、図49に示すような集計指示入力画面を表示し、操作者に入力させるようにすればよい。
Claims (25)
- 検索者IDに対応づけて、接触対象の情報伝達媒体を特定する情報伝達媒体特定情報を含むターゲット属性特定情報を記憶するターゲット特定情報記憶手段、
検索を行った検索者ID、検索時期、および検索語を対応づけて記憶する検索語記憶手段、
検索条件としての検索語が与えられると、前記検索語記憶手段から当該検索語の検索時期を検索者ID毎に抽出し、抽出した検索時期を時系列順に所定数に区分して、各区分に属する検索者IDを抽出する抽出手段、
前記ターゲット特定情報記憶手段に記憶されたターゲット特定情報を用いて、前記抽出した検索者IDから、前記各区分における候補情報伝達媒体を抽出し、抽出した候補情報伝達媒体から、1または2以上の代表候補情報伝達媒体を決定し、これにより、前記各区分の時系列順に並べられた代表候補情報伝達媒体を、前記検索語に対応して与えられた広告対象名称における広告媒体データとして決定する広告媒体データ決定手段、
を備えたことを特徴とする広告媒体決定装置。 - 請求項1の広告媒体決定装置において、
広告対象名称に対応する語が与えられると前記広告媒体データ決定手段に与えるとともに、前記広告対象名称に対応する検索語を特定し前記抽出手段に与える検索語特定手段を備えたこと、
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項2の広告媒体決定装置において、
前記検索語記憶手段に記憶された検索語は、カテゴリーに分類されており、
前記検索語特定手段は、前記広告対象名称に対応する語が属するカテゴリーの検索語を特定すること、
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項2の広告媒体決定装置において、
前記検索語記憶手段に記憶された各検索語について、検索数の時系列変動を表す検索数変動履歴を演算する検索数変動履歴演算手段、
前記演算された検索数変動履歴を記憶する検索数変動履歴記憶手段、
を備え、
前記検索語特定手段は、前記各検索語の検索数変動履歴を表示し、いずれかが選択されると、その検索語を特定すること、
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項1の広告媒体決定装置において、
広告対象名称およびこれに対応する検索語が与えられると、前記広告対象名称を前記広告媒体データ決定手段に与えるとともに、前記広告対象名称に対応する検索語を前記抽出手段に与える検索語特定手段を備えたこと、
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項1、請求項2、または請求項5の広告媒体決定装置において、
前記所定数に区分する区分決定規則を記憶する区分決定手段を備え、
前記抽出手段は、前記区分決定手段から与えられた区分決定規則を用いて前記検索者IDを抽出すること、
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項1、請求項2、または請求項5の広告媒体決定装置において、
前記検索語記憶手段に記憶された検索語について、検索数の時系列変動を表す検索数変動履歴を演算する検索数変動履歴演算手段、
前記演算された検索数変動履歴を記憶する検索数変動履歴記憶手段、
前記検索数変動履歴の形状に基づいて、区分を決定する区分決定手段、
を備え、
前記抽出手段は、前記区分決定手段から与えられた区分を用いて前記検索者IDを抽出すること、
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項7の広告媒体決定装置において、
前記区分決定手段は、前記検索数変動履歴の形状変化率が所定以上変化する場合には、新たな区分であると判断して、区分を決定すること、
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項7の広告媒体決定装置において、
前記区分決定手段は、前記検索数変動履歴を表示し、与えられた区分データを用いて、区分を決定すること、
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項1、請求項2、または請求項5の広告媒体決定装置において、
前記検索語記憶手段に記憶された検索語は、カテゴリーに分類されており、
前記検索語が属するカテゴリーの検索語の区分で、区分を決定する区分決定手段を備えていること、
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項2または請求項5の広告媒体決定装置において、
前記検索語記憶手段に記憶された各検索語について、検索数の時系列変動を表す検索数変動履歴を演算する検索数変動履歴演算手段、
前記演算された検索数変動履歴を記憶する検索数変動履歴記憶手段、
を備えており、
前記検索語特定手段は、修正対象として広告対象名称が入力された場合には、入力された広告対象名称の検索数変動履歴と類似する検索数変動履歴を含む検索語を特定し、特定した検索語が前記広告対象名称に対応する語として、前記広告媒体データ決定手段に与えること
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項2または請求項5の広告媒体決定装置において、
前記検索語記憶手段に記憶された各検索語について、検索数の時系列変動を表す検索数変動履歴を演算する検索数変動履歴演算手段、
前記演算された検索数変動履歴を記憶する検索数変動履歴記憶手段、
を備えており、
前記検索語特定手段は、修正対象として広告対象名称が入力された場合には、入力された広告対象名称の検索数変動履歴と類似する検索数変動履歴を含む検索語を特定し、特定した検索語の検索数変動履歴を表示し、いずれかが選択されると、選択された検索語を前記広告対象名称に対応する語として、前記広告媒体データ決定手段に与えること
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項2、請求項5、請求項11または、請求項12の広告媒体決定装置において、
前記検索条件としての検索語は、論理積および論理和のいずれかまたは双方が組み合わされた複数の検索語であり、
前記抽出手段は、各検索語について検索開始時期から検索終了時期までの期間を求め、前記検索条件に基づいた演算を行い、各区分に属する検索者IDを抽出すること、
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項13の広告媒体決定装置において、
前記検索条件に基づいた演算は、与えられた論理積演算であること、
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項13の広告媒体決定装置において、
前記検索条件に基づいた演算のうち、論理積演算は、期間の最大値を求めること、
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項13の広告媒体決定装置において、
前記検索条件に基づいた演算のうち、論理積演算は、期間の平均値を求めること、
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項13~請求項16のいずれかの広告媒体決定装置において、
前記抽出手段は、前記求めた各検索語についての期間を検索語毎に正規化してから、前記演算を行うこと、
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項17の広告媒体決定装置において、
前記正規化は、検索開始時期から検索終了時期までを前記検索語毎に所定数に区分して、いずれの区分に属するかで前記論理積演算を行うこと、
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項18の広告媒体決定装置において、
前記各検索語の正規化データのうち、論理積演算を行うデータが、他のデータと所定の閾値以上離れている場合には、当該正規化データを無視して論理積演算を行うこと、
を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項19の広告媒体決定装置において、
前記所定の閾値以上離れているとは、検索時期が存在しない場合であること、 を特徴とするもの。 - 請求項13~請求項16のいずれかの広告媒体決定装置において、
論理積演算を行う検索語について検索時期が存在しない検索語が存在する場合、それが所定数以下であれば、当該検索語を無視して論理積演算を行うこと、
を特徴とするもの。 - コンピュータに、1)検索者IDに対応づけて、接触対象の情報伝達媒体を特定する情報伝達媒体特定情報を含むターゲット属性特定情報、および2)検索を行った検索者ID、検索時期、および検索語を対応づけた検索語データを記憶させておき、
前記コンピュータは、ある検索語が与えられると、前記検索語記憶手段から当該検索語の検索時期を検索者ID毎に抽出し、抽出した検索時期を時系列順に所定数に区分して、各区分における検索者IDを抽出し、
前記コンピュータは、前記記憶されたターゲット特定情報を用いて、前記抽出した検索者IDから、前記各区分における候補情報伝達媒体を抽出し、抽出した候補情報伝達媒体から、1または2以上の代表候補情報伝達媒体を決定し、これにより、前記各区分の時系列順に並べられた代表候補情報伝達媒体を、前記検索語に対応して与えられた広告対象名称における広告媒体データとして決定すること、
を特徴とするコンピュータによる広告媒体決定方法。 - 検索語が与えられると、検索を行った検索者ID、検索時期、および検索語を対応づけて記憶させた検索結果データ記憶装置から当該検索語の検索時期を検索者ID毎に抽出し、抽出した検索時期を抽出した検索時期について、検索開始時期から検索終了時期まで時系列順に所定数に区分して、各区分における検索者IDを抽出する抽出手段、
検索者IDに対応づけて記憶された、接触対象の情報伝達媒体を特定する情報伝達媒体特定情報を含むターゲット属性特定情報を用いて、前記抽出した検索者IDから、前記各区分における候補情報伝達媒体を抽出し、抽出した候補情報伝達媒体から、1または2以上の代表候補情報伝達媒体を決定し、これにより、前記各区分の時系列順に並べられた代表候補情報伝達媒体を、前記検索語に対応して与えられた広告対象名称における広告媒体データとして決定する広告媒体データ決定手段、
を備えたことを特徴とする広告媒体決定装置。 - コンピュータに以下のステップ1)、2)を実行させるためのプログラム。
1)検索語が与えられると、検索を行った検索者ID、検索時期、および検索語を対応づけて記憶させた検索結果データ記憶装置から当該検索語の検索時期を検索者ID毎に抽出し、抽出した検索時期を時系列順に所定数に区分して、当該検索語について検索開始時期から検索終了時期までを所定数に区分して、各区分における検索者IDを抽出する抽出ステップ、
2)検索者IDに対応づけて記憶された、接触対象の情報伝達媒体を特定する情報伝達媒体特定情報を含むターゲット属性特定情報を用いて、前記抽出した検索者IDから、前記各区分における候補情報伝達媒体を抽出し、抽出した候補情報伝達媒体から、1または2以上の代表候補情報伝達媒体を決定し、これにより、前記各区分の時系列順に並べられた代表候補情報伝達媒体を、前記検索語に対応して与えられた広告対象名称における広告媒体データとして決定する広告媒体データ決定ステップ。 - 第1のコンピュータに、1)検索者IDに対応づけて、接触対象の情報伝達媒体を特定する情報伝達媒体特定情報を含むターゲット属性特定情報、および2)検索を行った検索者ID、検索時期、および検索語を対応づけた検索語データを記憶させておき、
第2のコンピュータは、ある検索語が与えられると、前記第1のコンピュータから当該検索語の検索時期を検索者ID毎に抽出し、抽出した検索時期を時系列順に所定数に区分して、各区分における検索者IDを抽出し、
前記第2のコンピュータは、前記記憶されたターゲット特定情報を用いて、前記抽出した検索者IDから、前記各区分における候補情報伝達媒体を抽出し、抽出した候補情報伝達媒体から、1または2以上の代表候補情報伝達媒体を決定し、これにより、前記各区分の時系列順に並べられた代表候補情報伝達媒体を、前記検索語に対応して与えられた広告対象名称における広告媒体データとして決定すること、
を特徴とするコンピュータによる広告媒体決定方法。
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/518,817 US8103663B2 (en) | 2008-03-21 | 2008-09-26 | Advertising medium determination device and method therefor |
| JP2009525841A JP4896227B2 (ja) | 2008-03-21 | 2008-09-26 | 広告媒体決定装置および広告媒体決定方法 |
| US13/312,509 US8423539B2 (en) | 2008-03-21 | 2011-12-06 | Advertising medium determination device method therefor |
| US13/834,635 US20130204702A1 (en) | 2008-03-21 | 2013-03-15 | Advertising Medium Determination Device and Method Therefor |
| US14/856,700 US20160005069A1 (en) | 2008-03-21 | 2015-09-17 | Advertising Medium Determination Device and Method Therefor |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008073222 | 2008-03-21 | ||
| JP2008-073222 | 2008-03-21 |
Related Child Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/518,817 A-371-Of-International US8103663B2 (en) | 2008-03-21 | 2008-09-26 | Advertising medium determination device and method therefor |
| US13/312,509 Division US8423539B2 (en) | 2008-03-21 | 2011-12-06 | Advertising medium determination device method therefor |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2009116198A1 true WO2009116198A1 (ja) | 2009-09-24 |
Family
ID=41090615
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2008/067493 WO2009116198A1 (ja) | 2008-03-21 | 2008-09-26 | 広告媒体決定装置および広告媒体決定方法 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (4) | US8103663B2 (ja) |
| JP (2) | JP4896227B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2009116198A1 (ja) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011107901A (ja) * | 2009-11-16 | 2011-06-02 | Video Research:Kk | 調査システム及び調査方法 |
| JP2015501990A (ja) * | 2011-12-10 | 2015-01-19 | フェイスブック,インク. | 広告キャンペーンの支援調整 |
| JP2016042213A (ja) * | 2014-08-13 | 2016-03-31 | ヤフー株式会社 | 抽出装置、検索サーバ、情報処理装置、抽出システム、抽出方法及び抽出プログラム |
| JP2018195146A (ja) * | 2017-05-18 | 2018-12-06 | ヤフー株式会社 | 生成装置、生成方法および生成プログラム |
| JP7368428B2 (ja) | 2021-09-15 | 2023-10-24 | ヤフー株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、および情報処理プログラム |
Families Citing this family (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10600073B2 (en) * | 2010-03-24 | 2020-03-24 | Innovid Inc. | System and method for tracking the performance of advertisements and predicting future behavior of the advertisement |
| US9626441B2 (en) * | 2011-05-13 | 2017-04-18 | Inolex Group, Inc. | Calendar-based search engine |
| US9697695B2 (en) | 2011-06-15 | 2017-07-04 | Longitude Llc | Enhanced parimutuel wagering filter |
| US8532798B2 (en) * | 2011-08-23 | 2013-09-10 | Longitude Llc | Predicting outcomes of future sports events based on user-selected inputs |
| JP5449466B2 (ja) * | 2012-06-29 | 2014-03-19 | 楽天株式会社 | 情報処理システム、類似カテゴリ特定方法、およびプログラム |
| US9460407B2 (en) * | 2013-05-03 | 2016-10-04 | Sap Se | Generating graphical representations of data |
| US20150186924A1 (en) | 2013-12-31 | 2015-07-02 | Anto Chittilappilly | Media spend optimization using a cross-channel predictive model |
| US10558987B2 (en) * | 2014-03-12 | 2020-02-11 | Adobe Inc. | System identification framework |
| WO2016013157A1 (ja) * | 2014-07-23 | 2016-01-28 | 日本電気株式会社 | テキスト処理システム、テキスト処理方法およびテキスト処理プログラム |
| US10042514B2 (en) * | 2014-10-30 | 2018-08-07 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Typeahead features |
| US10679260B2 (en) | 2016-04-19 | 2020-06-09 | Visual Iq, Inc. | Cross-device message touchpoint attribution |
| JP6779045B2 (ja) * | 2016-06-13 | 2020-11-04 | ヤフー株式会社 | クエリ抽出装置、検索システム、広告配信システム、クエリ抽出方法、およびクエリ抽出プログラム |
| US10068188B2 (en) | 2016-06-29 | 2018-09-04 | Visual Iq, Inc. | Machine learning techniques that identify attribution of small signal stimulus in noisy response channels |
| CN107038224B (zh) * | 2017-03-29 | 2022-09-30 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | 数据处理方法及数据处理装置 |
| JP7206603B2 (ja) * | 2018-03-16 | 2023-01-18 | 富士フイルムビジネスイノベーション株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理システムおよびプログラム |
| JP7184947B2 (ja) * | 2021-03-18 | 2022-12-06 | ヤフー株式会社 | 特定装置、特定方法及び特定プログラム |
| JP7079867B1 (ja) | 2021-03-19 | 2022-06-02 | ヤフー株式会社 | 生成装置、生成方法及び生成プログラム |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003196301A (ja) * | 2001-12-28 | 2003-07-11 | Nri & Ncc Co Ltd | キーワード分析システム |
| WO2005064511A1 (ja) * | 2003-12-26 | 2005-07-14 | Dentsu Inc. | キャンペーン動的適正化システム及びその方法又はその方法を記録した記録媒体及びその方法を伝送する伝送媒体 |
Family Cites Families (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002083116A (ja) * | 2000-06-20 | 2002-03-22 | Disparce Inc | ネットワークを利用した顧客情報収集方法、顧客情報提供方法、ポイント付与方法、商品情報提供方法、顧客情報収集装置 |
| US20050108095A1 (en) * | 2000-08-09 | 2005-05-19 | Adicus Media. Inc. | System and method for electronic advertising, advertisement play tracking and method of payment |
| US7146416B1 (en) * | 2000-09-01 | 2006-12-05 | Yahoo! Inc. | Web site activity monitoring system with tracking by categories and terms |
| JP4686870B2 (ja) * | 2001-02-28 | 2011-05-25 | ソニー株式会社 | 携帯型情報端末装置、情報処理方法、プログラム記録媒体及びプログラム |
| US7899862B2 (en) * | 2002-11-18 | 2011-03-01 | Aol Inc. | Dynamic identification of other users to an online user |
| WO2005033995A1 (ja) * | 2003-09-30 | 2005-04-14 | Sony Corporation | サービス宣伝情報の受信装置及び管理装置 |
| KR100497643B1 (ko) * | 2004-09-21 | 2005-07-01 | 엔에이치엔(주) | 키워드 광고에서 광고주의 계정 잔액을 조정하는 방법 및계정 잔액 조정 시스템 |
| US8812369B2 (en) * | 2004-11-02 | 2014-08-19 | Yong-Seok Jeong | Method and apparatus for requesting service using multi-dimensional code |
| AU2006283553B9 (en) * | 2005-08-19 | 2012-12-06 | Fourthwall Media, Inc. | System and method for recommending items of interest to a user |
| US8032425B2 (en) * | 2006-06-16 | 2011-10-04 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Extrapolation of behavior-based associations to behavior-deficient items |
| US7613691B2 (en) * | 2006-06-21 | 2009-11-03 | Microsoft Corporation | Dynamic insertion of supplemental video based on metadata |
| US20080052166A1 (en) * | 2006-08-22 | 2008-02-28 | Warmus James L | System and method for placement of local advertisements in national publications |
| US8271326B1 (en) * | 2006-09-07 | 2012-09-18 | Newtek Business Services, Inc. | Referral processing and tracking system |
| WO2008095174A2 (en) * | 2007-02-01 | 2008-08-07 | Invidi Technologies Corporation | Verifying and encouraging asset consumption in a communications network |
| US8145677B2 (en) * | 2007-03-27 | 2012-03-27 | Faleh Jassem Al-Shameri | Automated generation of metadata for mining image and text data |
| WO2009070573A1 (en) * | 2007-11-30 | 2009-06-04 | Data Logix, Inc. | Targeting messages |
| US20090171721A1 (en) * | 2007-12-28 | 2009-07-02 | Lebaron Matt | Bidding system for search engine marketing |
| US8086625B2 (en) * | 2008-07-31 | 2011-12-27 | Simply Hired, Inc. | Automated method for re-attracting job seekers to job match site at more opportune times |
| JPWO2010109581A1 (ja) * | 2009-03-23 | 2012-09-20 | 富士通株式会社 | コンテンツ推奨方法、推奨情報作成方法、コンテンツ推奨プログラム、コンテンツ推奨サーバおよびコンテンツ提供システム |
| US20110173130A1 (en) * | 2010-01-13 | 2011-07-14 | Schaefer Iv William Benjamin | Method and system for informing a user by utilizing time based reviews |
-
2008
- 2008-09-26 JP JP2009525841A patent/JP4896227B2/ja active Active
- 2008-09-26 US US12/518,817 patent/US8103663B2/en active Active
- 2008-09-26 WO PCT/JP2008/067493 patent/WO2009116198A1/ja active Application Filing
-
2011
- 2011-12-06 US US13/312,509 patent/US8423539B2/en active Active
- 2011-12-20 JP JP2011278719A patent/JP5292454B2/ja active Active
-
2013
- 2013-03-15 US US13/834,635 patent/US20130204702A1/en not_active Abandoned
-
2015
- 2015-09-17 US US14/856,700 patent/US20160005069A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003196301A (ja) * | 2001-12-28 | 2003-07-11 | Nri & Ncc Co Ltd | キーワード分析システム |
| WO2005064511A1 (ja) * | 2003-12-26 | 2005-07-14 | Dentsu Inc. | キャンペーン動的適正化システム及びその方法又はその方法を記録した記録媒体及びその方法を伝送する伝送媒体 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| MITSUYOSHI HANAKI: "PART3 Jisedai no Kokino Engine de Nani ga Dekiru?", KENSAKU TECHNOLOGY NO MIRAI O SAGURU, COMPUTERWORLD, vol. 2, no. 6, 1 June 2005 (2005-06-01), pages 70 - 77 * |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011107901A (ja) * | 2009-11-16 | 2011-06-02 | Video Research:Kk | 調査システム及び調査方法 |
| JP2015501990A (ja) * | 2011-12-10 | 2015-01-19 | フェイスブック,インク. | 広告キャンペーンの支援調整 |
| JP2016042213A (ja) * | 2014-08-13 | 2016-03-31 | ヤフー株式会社 | 抽出装置、検索サーバ、情報処理装置、抽出システム、抽出方法及び抽出プログラム |
| JP2018195146A (ja) * | 2017-05-18 | 2018-12-06 | ヤフー株式会社 | 生成装置、生成方法および生成プログラム |
| JP7368428B2 (ja) | 2021-09-15 | 2023-10-24 | ヤフー株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、および情報処理プログラム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2012089156A (ja) | 2012-05-10 |
| US20130204702A1 (en) | 2013-08-08 |
| JPWO2009116198A1 (ja) | 2011-07-21 |
| US8103663B2 (en) | 2012-01-24 |
| JP5292454B2 (ja) | 2013-09-18 |
| US20120095832A1 (en) | 2012-04-19 |
| US20110035400A1 (en) | 2011-02-10 |
| JP4896227B2 (ja) | 2012-03-14 |
| US20160005069A1 (en) | 2016-01-07 |
| US8423539B2 (en) | 2013-04-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4896227B2 (ja) | 広告媒体決定装置および広告媒体決定方法 | |
| US7725414B2 (en) | Method for developing a classifier for classifying communications | |
| CN107590675B (zh) | 一种基于大数据的用户购物行为识别方法、储存设备及移动终端 | |
| US7653568B2 (en) | System and method of identifying individuals of influence | |
| US20080065491A1 (en) | Automated advertising optimizer | |
| US20110161144A1 (en) | Information extraction system, information extraction method, information extraction program, and information service system | |
| WO2007001770A2 (en) | Automatic ad placement | |
| US20150120634A1 (en) | Information processing device, information processing method, and program | |
| Tama | DATA MINING FOR PREDICTING CUSTOMER SATISFACTION IN FAST-FOOD RESTAURANT. | |
| KR20220101326A (ko) | 오픈마켓 상품판매 증대 및 효율적인 운영을 위한 시스템 | |
| CN115760202A (zh) | 一种基于人工智能的产品运营管理系统及方法 | |
| US20190050890A1 (en) | Video dotting placement analysis system, analysis method and storage medium | |
| JP4827900B2 (ja) | アンケート結果解析支援装置およびその方法 | |
| JP2007140841A (ja) | 情報処理装置及びその制御方法 | |
| US20150046255A1 (en) | Asset maps | |
| US20150142782A1 (en) | Method for associating metadata with images | |
| Foedermayr et al. | Exploring the construct of segmentation effectiveness: Insights from international companies and experts | |
| JP6031165B1 (ja) | 有望顧客予測装置、有望顧客予測方法及び有望顧客予測プログラム | |
| JP5015978B2 (ja) | 情報提供装置及び情報提供方法並びに情報提供装置用プログラム | |
| JP4928101B2 (ja) | メディア・プランニング・システム | |
| KR100698880B1 (ko) | 통신망을 통해 제공되는 매스미디어 정보에 대한 고객열람현황 분석정보 서비스 방법 및 그에 따른 분석정보서비스 장치 | |
| CN113139124B (zh) | 基于互联网用户兴趣自主分析自媒体内容的方法及终端 | |
| TWI818213B (zh) | 商品推薦系統與方法及電腦可讀媒介 | |
| Phua et al. | Customer information system for product and service management: Towards knowledge extraction from textual and mixed-format data | |
| Prasad et al. | Targeted advertising in the online video space |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 12518817 Country of ref document: US |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2009525841 Country of ref document: JP |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 08873460 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 08873460 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |