RU2233918C2 - Woven carcass of conveyor belt - Google Patents
Woven carcass of conveyor belt Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2233918C2 RU2233918C2 RU2002119322/12A RU2002119322A RU2233918C2 RU 2233918 C2 RU2233918 C2 RU 2233918C2 RU 2002119322/12 A RU2002119322/12 A RU 2002119322/12A RU 2002119322 A RU2002119322 A RU 2002119322A RU 2233918 C2 RU2233918 C2 RU 2233918C2
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- woven
- weft
- warp
- threads
- layer
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
Изобретение относится к текстильной промышленности и может быть использовано для изготовления одно- и двухпрокладочных конвейерных лент с эластомерным покрытием, преимущественно резинотканевых конвейерных лент, используемых при транспортировке горной массы.The invention relates to the textile industry and can be used for the manufacture of single and double gasket conveyor belts with an elastomeric coating, mainly rubber fabric conveyor belts used in the transportation of rock mass.
В настоящее время требования к показателям качества и безопасности работы конвейеров для транспортировки горной массы значительно ужесточены. В связи с этим основными техническими требованиями, предъявляемыми к тканым каркасам одно- и двухпрокладочных конвейерных лент с эластомерным покрытием для транспортировки горной массы являются: высокая разрывная нагрузка (от 600 до 2000 кгс/см по основе и соответственно от 200 до 660 кгс/см по утку), минимальное (не более 4,5%) деформационное удлинение в зоне рабочих нагрузок, достаточная (не менее 4,8 кгс/см) прочность связи поверхности каркаса с эластомерным материалом, преимущественно резиной.Currently, the requirements for indicators of quality and safety of conveyors for transporting rock mass are significantly tightened. In this regard, the main technical requirements for woven frames of one- and two-laying conveyor belts with an elastomeric coating for transporting rock mass are: high breaking load (from 600 to 2000 kgf / cm on the basis and, accordingly, from 200 to 660 kgf / cm on duck), minimal (not more than 4.5%) strain elongation in the area of workloads, sufficient (not less than 4.8 kgf / cm) bond strength of the frame surface with an elastomeric material, mainly rubber.
Известен тканый каркас конвейерной ленты, содержащий две параллельно наложенные друг на друга многослойные тканые конструкции одинакового переплетения и соединенные воедино системой дополнительных перевязочных основных нитей [Патент Великобритании №1559380, МКИ D 03 D 15/00, опубл. 16.01.1980 г.].Known woven frame conveyor belt containing two parallel stacked on top of each other multilayer woven designs of the same weave and connected together by a system of additional dressing main threads [British Patent No. 1559380, MKI D 03
Недостатком известного тканого каркаса является повышенная жесткость на изгиб, обусловленная наличием перевязочных нитей основы, придающих ткани повышенную продольную жесткость. Кроме того, наличие в нем двух разнопереплетающихся систем основных нитей: основных нитей, несущих нагрузку, и дополнительных перевивочных нитей, не несущих нагрузку, приводит к нерациональному увеличению поверхностной плотности, что в итоге приводит к ухудшению технико-экономических показателей производства и эксплуатации конвейерных лент на его основе.A disadvantage of the known woven frame is the increased bending stiffness due to the presence of dressings warp threads, giving the fabric increased longitudinal stiffness. In addition, the presence in it of two differently interlocking systems of warp threads: warp threads, and additional leno threads, not carrying load, leads to an irrational increase in surface density, which ultimately leads to a deterioration in the technical and economic indicators of production and operation of conveyor belts on its basis.
Известен также многослойный тканый каркас, содержащий, по меньшей мере, две параллельно наложенные друг на друга двухслойные тканые конструкции одинакового переплетения и соединенные воедино посредством нитей основы и одного из периферийных слоев утка каждой из двух конструкций, объединенных в один общий центральный слой. Каждая из, как минимум, двух одинаковых составных двухслойных конструкций дополнительно содержит наполнительный уток и наполнительную основу, расположенные почти прямолинейно. Раппорт переплетения нитей основы по центральному уточному слою равен 4-6 [Патент США №4922969, МКИ5 D 03 D 11/00, 13/00, 15/00, опубл. 05.08.1990 г.].Also known is a multilayer woven frame, containing at least two parallel two-layer woven structures of the same weave and connected together by warp threads and one of the peripheral weft layers of each of the two structures combined into one common central layer. Each of at least two identical composite two-layer structures additionally contains filling ducks and filling base, located almost rectilinearly. The report of the interweaving of warp threads along the central weft layer is 4-6 [US Patent No. 4922969, MKI 5 D 03
Наличие в переплетении этого тканого материала наполнительных нитей утка в качестве среднего слоя каждой из составных двухслойных тканей существенно повышает его поперечную жесткость, что является положительным, однако наличие в промежутках уточных слоев почти прямолинейно расположенных наполнительных нитей основы, не переплетающихся с нитями утка, придает тканому материалу дополнительную продольную жесткость, что является крайне отрицательным. Кроме того, шаг зигзагообразного изгиба нитей основы, перекрывающий всего три уточные нити центрального нейтрального слоя, не может обеспечить низкого (не более 4,2%) деформационного удлинения в зоне рабочих нагрузок, а наличие в ней двух разнопереплетающихся систем основных нитей: основных нитей, несущих нагрузку и перевивочных нитей, не несущих нагрузку, обусловливает нерациональное использование сырья.The presence in the interweaving of this woven material of weft filling threads as the middle layer of each of the composite bilayer fabrics significantly increases its transverse stiffness, which is positive, however, the presence of almost straight-spaced filling warp threads that are not interwoven with weft yarns gives the woven material additional longitudinal stiffness, which is extremely negative. In addition, the step of a zigzag bending of the warp threads, covering only three weft threads of the central neutral layer, cannot provide low (not more than 4.2%) strain elongation in the area of workloads, and the presence of two differently interlocking systems of warp threads: main threads, bearing load and leno threads, not carrying load, determines the irrational use of raw materials.
Наиболее близким по технической сущности и достигаемому результату является тканый каркас конвейерной ленты, содержащий две параллельно расположенные относительно друг друга тканые конструкции одинакового переплетения слойностью не менее двух, соединенные воедино всеми нитями основы каждой тканой конструкции, в чередующемся порядке переходящими из верхнего слоя в нижний и обратно, и одним из периферийных слоев уточных нитей каждой из двух тканых конструкций, объединенных в один общий центральный слой.The closest in technical essence and the achieved result is a woven frame of a conveyor belt containing two woven structures parallel to each other with the same weaving of at least two layers, joined together by all the warp threads of each woven structure, alternating from one upper layer to the lower one and vice versa , and one of the peripheral layers of the weft yarns of each of the two woven structures combined into one common central layer.
Центральный слой, помимо соединительных уточных нитей, содержит армирующие нити утка. В каждой из двух составных тканых конструкций могут содержаться нити наполнительного утка. При этом раппорт переплетения нитей основы по центральному уточному слою равен 8-12, а заполнение центрального слоя по утку вдвое больше заполнения остальных уточных слоев при соотношении линейных плотностей нитей основы и утка тканого каркаса в пределах от 0,5-1,0 [Патент РФ на изобретение №2135654, D 03 D 11/00, опубл. 27.08.1999 г., БИ №24].The central layer, in addition to connecting weft threads, contains weft reinforcing threads. Each of the two composite woven structures may contain filament weft threads. Moreover, the rapport of the weaving of warp yarns along the central weft layer is 8-12, and the filling of the central weft layer is twice that of the remaining weft layers with a linear density ratio of warp and weft woven frames ranging from 0.5-1.0 [RF Patent for the invention No. 2135654, D 03
Данный тканый каркас в основном соответствует своему целевому назначению по основным показателям, однако обладает существенными недостатками - высоким (до 4,5%) удлинением в режиме рабочих нагрузок конвейера, приводящим к необходимости их перестыковки и недостаточной (до 4,5 кгс/см) степенью связи к эластомерному покрытию, обусловленной недостаточно рельефной опорной поверхностью, что в некоторых случаях приводит к отслоению эластомерного покрытия от поверхности тканого каркаса. Кроме того, изготовление данного тканого каркаса на ткацком станке технологически затруднено, так как при зевообразовании и формировании периферийных слоев составных тканых конструкций соотношение количества нитей основы в ветвях зева нерационально и составляет 1/7 (7/1), 1/9 (9/1) или 1/11 (11/1) и обуславливает перепад числа нитей в ветвях зева от 7 до 11 раз.This woven frame mainly meets its intended purpose for the main indicators, however, it has significant drawbacks - high (up to 4.5%) elongation in the mode of conveyor workloads, which leads to the need for their reflowing and insufficient (up to 4.5 kgf / cm) degree connection to the elastomeric coating, due to insufficiently embossed supporting surface, which in some cases leads to delamination of the elastomeric coating from the surface of the woven frame. In addition, the manufacture of this woven frame on a loom is technologically difficult, since when yawning and the formation of peripheral layers of composite woven structures, the ratio of the number of warp threads in the branches of the throat is irrational and is 1/7 (7/1), 1/9 (9/1 ) or 1/11 (11/1) and causes a difference in the number of threads in the branches of the throat from 7 to 11 times.
Задачей изобретения является создание структуры тканого каркаса однопрокладочных конвейерных лент для транспортировки горной массы, обладающей разрывной нагрузкой по основе не менее 600-2000 кгс/см, деформационными удлинениями в зоне рабочих нагрузок не более 4,2%, прочностью связи поверхности каркаса с эластомерным материалом, преимущественно резиной, не менее 4,8 кгс/см. При этом структура каркаса должна быть технологична, т.е. при зевообразовании и формировании его на ткацком станке перепад числа нитей основы в ветвях зева не должен превышать 4 раз.The objective of the invention is to create a woven frame structure of single-lay conveyor belts for transporting rock mass, having a breaking load of at least 600-2000 kgf / cm on the base, strain elongations in the area of working loads of not more than 4.2%, bond strength of the frame surface with elastomeric material, mainly rubber, not less than 4.8 kgf / cm. In this case, the structure of the frame must be technologically advanced, i.e. when yawning and forming it on a loom, the difference in the number of warp threads in the branches of the throat should not exceed 4 times.
Данная задача решена таким образом, что предлагаемый тканый каркас содержит две параллельно расположенные относительно друг друга тканые конструкции одинакового переплетения слойностью не менее двух и соединенные воедино нитями основы, в чередующемся порядке переходящими из верхнего слоя в нижний и обратно, и периферийными слоями уточных нитей каждой из двух тканых конструкций, объединенных в один общий центральный слой. Соединяемые тканые конструкции расположены в двух уровнях со смещением друг относительно друга по вертикали на уровень, равный от 1 до 3 горизонтальных слоев уточных нитей. Каждая нить основы в центральном слое перекрывает одну уточную нить, а в периферийном слое от 2 до (R01-2) уточные нити, где R01 - раппорт по основе исходной тканой конструкции. В центральном соединительном слое дополнительно содержатся армирующие нити утка. При этом заполнение центрального слоя по утку вдвое больше заполнения остальных уточных слоев. В каждой из двух составных тканых конструкций могут содержаться нити наполнительного утка.This problem is solved in such a way that the proposed woven frame contains two woven structures parallel to each other of the same weave with a layer of at least two and joined together by warp threads, alternating from one upper layer to the lower one and vice versa, and with peripheral layers of weft yarns of each two woven designs combined into one common central layer. The connected woven structures are located at two levels with vertical displacement relative to each other by a level equal to 1 to 3 horizontal layers of weft threads. Each warp thread in the central layer overlaps one weft thread, and in the peripheral layer from 2 to (R 01 -2) weft threads, where R 01 is rapport based on the original woven structure. The reinforcing weft threads are additionally contained in the central connecting layer. In this case, the filling of the central layer by duck is twice as large as the filling of the remaining weft layers. Each of the two composite woven structures may contain filament weft threads.
В некоторых случаях для повышения адгезии поверхности тканого каркаса к эластомерному материалу, а следовательно, увеличения прочности связи с покрытием соединение исходных тканых конструкций производится не в чередующемся порядке нитей основы, а по-раппортно. При этом каждая соединяемая тканая конструкция одного уровня может содержать в себе от 1 до 3 полных раппортов по основе исходного переплетения и образует на верхней и нижней поверхностях тканого каркаса равномерно расположенные в чередующемся порядке отрезки прямолинейно расположенных уточных нитей, не переплетенных с основой и обеспечивающих тканому каркасу дополнительную когезионную связь с эластомерным покрытием конвейерной ленты.In some cases, in order to increase the adhesion of the surface of the woven frame to the elastomeric material, and therefore, to increase the bond strength with the coating, the connection of the initial woven structures is carried out not in alternating order of warp threads, but in a different manner. Moreover, each connected woven structure of one level can contain from 1 to 3 full rapports based on the initial weave and forms, on the upper and lower surfaces of the woven frame, segments of straight-line weft threads uniformly arranged in alternating order that are not interwoven with the warp and provide the woven frame additional cohesive bond with the elastomeric coating of the conveyor belt.
Основные нити выполнены из синтетических, преимущественно из полиэфирных комплексных нитей, а уточные нити - из полиамидных комплексных нитей или комбинированных нитей (полиамид плюс хлопок). Раппорт переплетения нитей основы по центральному уточному слою равен 8-12, а заполнение центрального слоя по утку вдвое больше заполнения остальных уточных слоев. Отношение линейных плотностей нитей основы и утка тканого каркаса находится в пределах от 1,0 до 4.0.The warp yarns are made of synthetic, mainly polyester multifilament yarns, and the weft yarns are made of polyamide multifilament yarn or combination yarn (polyamide plus cotton). The interweaving of the warp yarns along the central weft layer is 8-12, and the filling of the central weft layer is twice that of the remaining weft layers. The ratio of linear densities of warp and weft of the woven frame is in the range from 1.0 to 4.0.
На фиг.1 приведена схема разреза вдоль нитей основы тканого каркаса, образованного двумя двухслойными ткаными конструкциями, в которых каждая нить основы перекрывает одновременно 2 уточные нити периферийного слоя.Figure 1 shows the cut along the warp yarns of the woven frame formed by two two-layer woven structures in which each warp yarn overlaps simultaneously 2 weft yarns of the peripheral layer.
На фиг.2 приведена схема разреза вдоль нитей основы тканого каркаса, образованного двумя 2,5-слойными ткаными конструкциями, в которых каждая нить основы перекрывает одновременно 2 уточные нити периферийного слоя.Figure 2 shows a sectional diagram along the warp yarns of the woven frame formed by two 2.5-ply woven structures in which each warp yarn overlaps simultaneously 2 weft yarns of the peripheral layer.
На фиг.3 приведена схема разреза вдоль нитей основы тканого каркаса, образованного двумя 2,5-слойными ткаными конструкциями, в которых каждая нить основы перекрывает одновременно 3 уточные нити периферийного слоя.Figure 3 shows a sectional diagram along the warp yarns of the woven frame formed by two 2.5-layer woven structures in which each warp yarn overlaps 3 weft yarns of the peripheral layer simultaneously.
На фиг.4 приведена схема разреза вдоль нитей основы тканого каркаса, образованного двумя трехслойными ткаными конструкциями, в которых каждая нить основы перекрывает одновременно 2 уточные нити периферийного слоя.Figure 4 shows a sectional diagram along the warp yarns of the woven frame formed by two three-layer woven structures in which each warp yarn overlaps 2 weft yarns of the peripheral layer simultaneously.
На фиг.5 приведена схема разреза вдоль нитей основы тканого каркаса, образованного двумя трехслойными ткаными конструкциями, в которых каждая нить основы перекрывает одновременно 3 уточные нити периферийного слоя.Figure 5 shows a sectional diagram along the warp yarns of the woven frame formed by two three-layer woven structures in which each warp yarn overlaps 3 weft yarns of the peripheral layer at the same time.
На фиг.6 приведена схема разреза вдоль нитей основы тканого каркаса, образованного двумя трехслойными ткаными конструкциями, в которых каждая нить основы перекрывает одновременно 4 уточные нити периферийного слоя.Figure 6 shows a sectional diagram along the warp yarns of the woven frame formed by two three-layer woven structures in which each warp yarn simultaneously overlays 4 weft yarns of the peripheral layer.
На фиг.7 приведена схема разреза вдоль нитей основы тканого каркаса, образованного двумя трехслойными ткаными конструкциями с четырьмя рядами наполнительных уточных нитей, в которых каждая нить основы перекрывает одновременно 4 уточные нити периферийного слоя.7 is a diagram of a section along the warp yarns of the woven frame formed by two three-layer woven structures with four rows of filler weft yarns, in which each warp yarn overlaps at the
На фиг.8 приведен рисунок раппорта переплетения и совмещенные с ним схемы расположения нитей в продольном и поперечном сечениях тканого каркаса без наполнительных уточных нитей, образованного соединением в чередующемся порядке нитей основы двух двухслойных тканых конструкций, в которых каждая нить основы перекрывает одновременно 2 уточные нити периферийного слоя.Fig. 8 shows a drawing of the weaving pattern and the matching patterns of the yarn arrangement in the longitudinal and transverse sections of the woven fabric without filling weft threads, formed by alternating the warp threads of two two-layer woven structures in which each warp thread overlaps 2 peripheral weft threads simultaneously layer.
На фиг.9 приведен рисунок раппорта переплетения и совмещенные с ним схемы расположения нитей в продольном и поперечном сечениях тканого каркаса с наполнительными нитями утка, образованного соединением в чередующемся порядке нитей основы двух двухслойных тканых конструкций, в которых каждая нить основы перекрывает одновременно 2 уточные нити периферийного слоя.Figure 9 shows the pattern of weaving and the matching patterns of the arrangement of threads in the longitudinal and cross sections of the woven frame with the filament weft, formed by joining in the alternating order of the warp threads of two two-layer woven structures, in which each warp thread overlaps 2 peripheral weft threads at the same time layer.
На фиг.10 приведен рисунок раппорта переплетения и совмещенная с ним схема расположения нитей в продольном сечении тканого каркаса без наполнительных нитей утка, образованного соединением в чередующемся порядке нитей основы двух 2,5-слойных тканых конструкций, в которых каждая нить основы перекрывает одновременно 2 уточные нити периферийного слоя.Figure 10 shows the pattern of weaving and the alignment of the threads in the longitudinal section of the woven carcass without filler weft formed by alternately joining the warp threads of two 2.5-ply woven structures in which each warp thread overlaps 2 weft threads simultaneously filaments of the peripheral layer.
На фиг.11 приведен рисунок раппорта переплетения и совмещенная с ним схема расположения нитей в продольном сечении тканого каркаса с наполнительными нитями утка, образованного соединением в чередующемся порядке нитей основы двух 2,5-слойных тканых конструкций, в которых каждая нить основы перекрывает одновременно 3 уточные нити периферийного слоя.Figure 11 shows the pattern of weaving and the alignment of the threads in the longitudinal section of the woven carcass with the filament weft, formed by joining in the alternating order of warp threads of two 2.5-ply woven structures, in which each warp thread overlaps 3 weft filaments of the peripheral layer.
На фиг.12 приведен рисунок раппорта переплетения и совмещенная с ним схема расположения нитей в продольном сечении тканого каркаса, образованного соединением в чередующемся порядке нитей основы двух 2,5-слойных тканых конструкций, в которых каждая нить основы перекрывает одновременно 2 наполнительные уточные нити периферийного слоя и 3 тканеформирующие уточные нити.Fig. 12 shows a drawing of the weaving pattern and the alignment pattern of the threads in the longitudinal section of the woven carcass formed by alternately joining the warp threads of two 2.5-ply woven structures in which each warp thread overlaps at the
На фиг.13 приведен рисунок раппорта переплетения и совмещенные с ним схемы расположения нитей в продольном и поперечном сечениях тканого каркаса без наполнительных нитей утка, образованного пораппортным соединением двух двухслойных тканых конструкций.Figure 13 shows the pattern of weaving and the matching patterns of the arrangement of threads in the longitudinal and transverse sections of the woven frame without filling weft threads formed by the joining of two two-layer woven structures.
На фиг.14 приведен рисунок раппорта переплетения и совмещенные с ним схемы расположения нитей в продольном и поперечном сечениях тканого каркаса с наполнительными нитями утка, образованного пораппортным соединением двух двухслойных тканых конструкций.Fig. 14 shows a drawing of a weaving pattern and alignment patterns of threads in longitudinal and transverse sections of a woven frame with filler weft threads formed by a post-joining of two two-layer woven structures.
На фиг.1-7 приняты следующие условные обозначения уточных нитей тканого каркаса: 1 - нити тканеформирующего утка периферийных слоев; 2 - соединительные нити утка центрального слоя; 3 - армирующие нити утка центрального слоя; 4 - наполнительные нити утка.Figure 1-7 adopted the following conventions of the weft threads of the woven frame: 1 - yarn tissue-forming weft of the peripheral layers; 2 - connecting thread weft of the Central layer; 3 - reinforcing thread weft of the Central layer; 4 - filling threads duck.
На фиг.8-14 приняты следующие условные обозначения нитей: O1-O12 - нити основы с порядковым номером от 1 до 12; У1-У24 - нити утка с порядковым номером от 1 до 24.In Fig.8-14, the following conventions of the threads are adopted: O 1 -O 12 - warp threads with a serial number from 1 to 12; At 1 -U 24 - weft threads with a serial number from 1 to 24.
Нити основы [(O1-O8), (O1-О10), (O1-O12)] обеих тканых конструкций огибают не менее двух нитей утка (1) в периферийных слоях и переходят в центральный слой, огибая соответствующий уток (2), тем самым образуя соединительный слой указанных тканых конструкций. В центральном слое между нитями утка (2) в вертикальной плоскости расположены армирующие нити утка (3). В промежутках между периферийными и центральным слоями в вертикальной плоскости могут располагаться наполнительные нити утка (4).Warp threads [(O 1 -O 8 ), (O 1 -O 10 ), (O 1 -O 12 )] of both woven structures bend around at least two weft threads (1) in the peripheral layers and pass into the central layer, enveloping the corresponding weft (2), thereby forming a connecting layer of these woven structures. In the central layer between the weft threads (2) in a vertical plane are the reinforcing weft threads (3). In the spaces between the peripheral and central layers in the vertical plane can be placed filament weft (4).
Предлагаемую ткань изготавливают на челночных или рапирных ткацких станках, оснащенных зевообразовательными каретками.The proposed fabric is made on shuttle or rapier weaving machines equipped with shedding carriages.
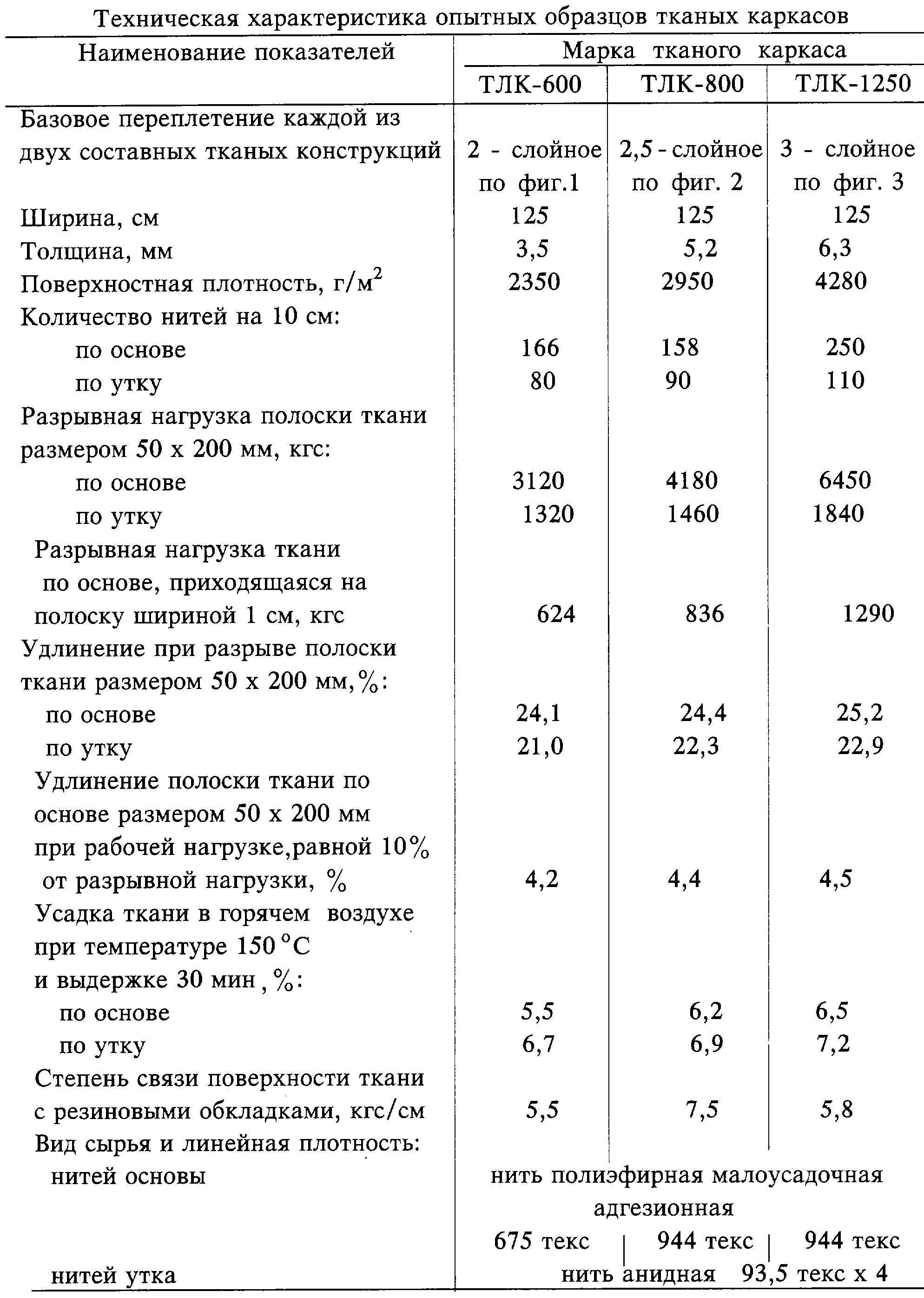
Для подтверждения технического результата изобретения было изготовлено три экспериментальных образца тканого каркаса предложенной конструкции. Технические характеристики изготовленных тканых каркасов марок ТЛК-600, ТЛК-800, ТЛК-1250 приведены в таблице. Данные таблицы показывают, что заявляемый тканый каркас в сравнении с аналогом имеет: более высокую прочность связи с покрытием, в частности с резиной, 5,5-7,2 кгс/см против 4,6 кгс/см, а по остальным показателям соответствует требованиям, предъявляемым к цельнотканым каркасам однопрокладочных конвейерных лент. Кроме того, при выработке опытных образцов тканого каркаса на ткацком станке технологических затруднений и отказов не наблюдалось.To confirm the technical result of the invention, three experimental samples of the woven frame of the proposed design were made. Technical characteristics of the fabricated woven frames of the brands TLK-600, TLK-800, TLK-1250 are shown in the table. The data in the table show that the inventive woven frame in comparison with the analogue has: higher bond strength with the coating, in particular with rubber, 5.5-7.2 kgf / cm vs 4.6 kgf / cm, and according to other indicators meets the requirements presented to solid-woven frames of single-laying conveyor belts. In addition, during the development of prototypes of the woven frame on a loom, technological difficulties and failures were not observed.
Claims (2)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2002119322/12A RU2233918C2 (en) | 2002-07-17 | 2002-07-17 | Woven carcass of conveyor belt |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2002119322/12A RU2233918C2 (en) | 2002-07-17 | 2002-07-17 | Woven carcass of conveyor belt |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU2002119322A RU2002119322A (en) | 2004-02-10 |
| RU2233918C2 true RU2233918C2 (en) | 2004-08-10 |
Family
ID=33412665
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2002119322/12A RU2233918C2 (en) | 2002-07-17 | 2002-07-17 | Woven carcass of conveyor belt |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2233918C2 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2655296C1 (en) * | 2017-05-04 | 2018-05-24 | Открытое акционерное общество "Научно-исследовательский институт технических тканей" | Woven gasket for elastomer coated conveyor belts |
| RU223958U1 (en) * | 2023-04-24 | 2024-03-11 | Общество с ограниченной ответственностью "Сурский комбинат технических сукон" | SOLID WOVEN FRAME WITH ADHESIVE IMPREGNATION |
-
2002
- 2002-07-17 RU RU2002119322/12A patent/RU2233918C2/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| КУТЕПОВ О.С. Строение и проектирование тканей. - М.: Легпромбытиздат, 1988, с.88. * |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2655296C1 (en) * | 2017-05-04 | 2018-05-24 | Открытое акционерное общество "Научно-исследовательский институт технических тканей" | Woven gasket for elastomer coated conveyor belts |
| RU223958U1 (en) * | 2023-04-24 | 2024-03-11 | Общество с ограниченной ответственностью "Сурский комбинат технических сукон" | SOLID WOVEN FRAME WITH ADHESIVE IMPREGNATION |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| RU2002119322A (en) | 2004-02-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| FI77488B (en) | KOMPOUNDVAEV SOM BAERANDE PLAN FOER PAPPERFORMNINGSOMRAODET VID EN PAPPERSMASKIN. | |
| JP2563842B2 (en) | Fabric for papermaking | |
| US7306014B2 (en) | Industrial two-layer fabric | |
| US3296062A (en) | Belt fabric | |
| KR960007934A (en) | Triple layered paper fabric with improved fibrous support | |
| US4839220A (en) | Conveyor belt, in particular for a through conveyor | |
| US20060040578A1 (en) | Industrial two-layer fabric | |
| JPH03503397A (en) | conveyor belt | |
| ATE267911T1 (en) | COMPOSITE FABRIC | |
| FI87667B (en) | BEKLAEDNAD FOER EN ARKFORMNINGSDEL VID EN PAPPERSMASKIN | |
| US6837366B2 (en) | Reinforcing band for conveyor belts, and conveyor belt using the same | |
| RU2233918C2 (en) | Woven carcass of conveyor belt | |
| EP0911444B1 (en) | A shoe press jacket and method for its production | |
| RU2724657C1 (en) | Woven frame of single-piece conveyor belt with elastomer coating | |
| CN102373527A (en) | Plain weave three-dimensional multilayer cylindrical or cylindrical special-shaped braided fabric | |
| RU2135654C1 (en) | Woven frame of conveyor belt | |
| AU677075B2 (en) | Rubberline belting | |
| RU2655296C1 (en) | Woven gasket for elastomer coated conveyor belts | |
| RU2507324C1 (en) | Two-layer reinforcing fabric for elastomeric coating | |
| US3595730A (en) | Lenoweave substrate construction | |
| CN217803701U (en) | Multi-layer ventilation plate | |
| CN100491615C (en) | Strip with fabric having exactly two layers of fabric | |
| RU2676810C1 (en) | Woven frame of conveyor belt with elastomeric coating | |
| JPS6350472B2 (en) | ||
| RU2202014C2 (en) | Duck fabric for polymeric covering |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MM4A | The patent is invalid due to non-payment of fees |
Effective date: 20060718 |