KR20200116168A - Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment - Google Patents
Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20200116168A KR20200116168A KR1020207027527A KR20207027527A KR20200116168A KR 20200116168 A KR20200116168 A KR 20200116168A KR 1020207027527 A KR1020207027527 A KR 1020207027527A KR 20207027527 A KR20207027527 A KR 20207027527A KR 20200116168 A KR20200116168 A KR 20200116168A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- gel
- composition
- months
- vitamin
- skin
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L27/00—Materials for grafts or prostheses or for coating grafts or prostheses
- A61L27/14—Macromolecular materials
- A61L27/20—Polysaccharides
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/54—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an organic compound
- A61K47/545—Heterocyclic compounds
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K8/00—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations
- A61K8/18—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition
- A61K8/30—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic compounds
- A61K8/67—Vitamins
- A61K8/676—Ascorbic acid, i.e. vitamin C
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K8/00—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations
- A61K8/18—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition
- A61K8/72—Cosmetics or similar toiletry preparations characterised by the composition containing organic macromolecular compounds
- A61K8/73—Polysaccharides
- A61K8/735—Mucopolysaccharides, e.g. hyaluronic acid; Derivatives thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L27/00—Materials for grafts or prostheses or for coating grafts or prostheses
- A61L27/50—Materials characterised by their function or physical properties, e.g. injectable or lubricating compositions, shape-memory materials, surface modified materials
- A61L27/505—Stabilizers
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L27/00—Materials for grafts or prostheses or for coating grafts or prostheses
- A61L27/50—Materials characterised by their function or physical properties, e.g. injectable or lubricating compositions, shape-memory materials, surface modified materials
- A61L27/54—Biologically active materials, e.g. therapeutic substances
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61Q—SPECIFIC USE OF COSMETICS OR SIMILAR TOILETRY PREPARATIONS
- A61Q19/00—Preparations for care of the skin
- A61Q19/08—Anti-ageing preparations
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08B—POLYSACCHARIDES; DERIVATIVES THEREOF
- C08B37/00—Preparation of polysaccharides not provided for in groups C08B1/00 - C08B35/00; Derivatives thereof
- C08B37/006—Heteroglycans, i.e. polysaccharides having more than one sugar residue in the main chain in either alternating or less regular sequence; Gellans; Succinoglycans; Arabinogalactans; Tragacanth or gum tragacanth or traganth from Astragalus; Gum Karaya from Sterculia urens; Gum Ghatti from Anogeissus latifolia; Derivatives thereof
- C08B37/0063—Glycosaminoglycans or mucopolysaccharides, e.g. keratan sulfate; Derivatives thereof, e.g. fucoidan
- C08B37/0072—Hyaluronic acid, i.e. HA or hyaluronan; Derivatives thereof, e.g. crosslinked hyaluronic acid (hylan) or hyaluronates
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J3/00—Processes of treating or compounding macromolecular substances
- C08J3/24—Crosslinking, e.g. vulcanising, of macromolecules
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L5/00—Compositions of polysaccharides or of their derivatives not provided for in groups C08L1/00 or C08L3/00
- C08L5/08—Chitin; Chondroitin sulfate; Hyaluronic acid; Derivatives thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K2800/00—Properties of cosmetic compositions or active ingredients thereof or formulation aids used therein and process related aspects
- A61K2800/80—Process related aspects concerning the preparation of the cosmetic composition or the storage or application thereof
- A61K2800/91—Injection
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L2300/00—Biologically active materials used in bandages, wound dressings, absorbent pads or medical devices
- A61L2300/40—Biologically active materials used in bandages, wound dressings, absorbent pads or medical devices characterised by a specific therapeutic activity or mode of action
- A61L2300/402—Anaestetics, analgesics, e.g. lidocaine
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L2300/00—Biologically active materials used in bandages, wound dressings, absorbent pads or medical devices
- A61L2300/40—Biologically active materials used in bandages, wound dressings, absorbent pads or medical devices characterised by a specific therapeutic activity or mode of action
- A61L2300/428—Vitamins, e.g. tocopherol, riboflavin
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L2400/00—Materials characterised by their function or physical properties
- A61L2400/06—Flowable or injectable implant compositions
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L2430/00—Materials or treatment for tissue regeneration
- A61L2430/34—Materials or treatment for tissue regeneration for soft tissue reconstruction
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J2305/00—Characterised by the use of polysaccharides or of their derivatives not provided for in groups C08J2301/00 or C08J2303/00
- C08J2305/08—Chitin; Chondroitin sulfate; Hyaluronic acid; Derivatives thereof
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J3/00—Processes of treating or compounding macromolecular substances
- C08J3/02—Making solutions, dispersions, lattices or gels by other methods than by solution, emulsion or suspension polymerisation techniques
- C08J3/03—Making solutions, dispersions, lattices or gels by other methods than by solution, emulsion or suspension polymerisation techniques in aqueous media
- C08J3/075—Macromolecular gels
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Dermatology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Birds (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- Transplantation (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Gerontology & Geriatric Medicine (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Materials For Medical Uses (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Medicinal Preparation (AREA)
- Acyclic And Carbocyclic Compounds In Medicinal Compositions (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Material From Animals Or Micro-Organisms (AREA)
Abstract
본 발명은 얼굴의 잔주름의 보정에 특히 유리한 고도로 주사용이고, 장기간 지속적인 하이알루론산계 하이드로겔 진피 필러 조성물을 제공한다.The present invention provides a highly injectable, long-lasting hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel dermal filler composition that is particularly advantageous for correcting fine wrinkles on the face.
Description
관련 출원Related application
본 출원은 2011년 9월 14일 출원된 미국 가특허 출원 제61/534,780호의 우선권 및 이익을 주장하며, 이는 2012년 6월 1일 출원된 미국 특허 출원 제13/486,754호의 부분계속출원이며, 2011년 6월 3일 출원된 미국 가특허출원 제61/493,309호의 우선권 및 이익을 주장하는, 2012년 8월 23일 출원된 미국 특허 출원 제13/593,313호의 부분계속출원이고, 이들 기초출원 각각의 전문의 개시내용은 그것의 전문이 이 구체적 참조로서 본 명세서에 포함된다.This application claims the priority and benefit of U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 61/534,780 filed on September 14, 2011, which is a partial continuation application of U.S. Patent Application No. 13/486,754 filed on June 1, 2012, 2011 It is a partial continuing application of U.S. Patent Application No. 13/593,313 filed on August 23, 2012, claiming the priority and interests of U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 61/493,309 filed on June 3, 2012, and the full text of each The disclosures of are incorporated herein by reference in their entirety by this specific reference.
본 발명의 기술분야Technical field of the present invention
본 발명은 일반적으로 진피 필러 조성물, 및 더 구체적으로는 피부 내 잔주름의 치료에 효과적인 주사용 진피 필러 조성물에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates generally to a dermal filler composition, and more specifically to an injection dermal filler composition effective for the treatment of fine wrinkles in the skin.
피부 노화는 진행형인 현상이며, 시간에 걸쳐 일어나고, 알코올 소비, 담배 및 태양광 노출과 같은 생활방식 인자에 의해 영향받을 수 있다. 얼굴 피부의 노화는 위축, 늘어짐 및 비후를 특징으로 할 수 있다. 위축은 피부 조직 두께의 거대한 감소에 대응된다. 피하 조직의 늘어짐은 과량의 피부 및 눈꺼풀 처짐을 야기하며, 볼 및 눈꺼풀의 처짐을 야기한다. 비후는 얼굴 하부 및 목의 팽창에 의한 과도한 체중 증가를 지칭한다. 이들 변화는 전형적으로 건조, 탄력 상실 및 거친 질감과 관련된다.Skin aging is an ongoing phenomenon, occurs over time, and can be influenced by lifestyle factors such as alcohol consumption, tobacco and sun exposure. Aging of the facial skin can be characterized by atrophy, sagging and thickening. Atrophy corresponds to a huge decrease in skin tissue thickness. Sagging of the subcutaneous tissue causes excessive skin and eyelid sagging, and causes sagging of the cheeks and eyelids. Thickening refers to excessive weight gain due to swelling of the lower face and neck. These changes are typically associated with dryness, loss of elasticity and rough texture.
하이알루로난으로도 알려진 하이알루론산(hyaluronic acid: HA)은 관절, 상피, 및 신경 조직에서 인간 신체 전체적으로 넓게 분포되는 비황산화 글라이코사미노글라이칸이다. 하이알루론산은, 예를 들어 양호한 수화를 보장하고, 세포외 기질의 조직화를 도우며, 필러 물질로서 작용하고; 조직 손상 메커니즘에 참여하는 것과 같은 다양한 작용을 갖는 경우, 상이한 층의 피부 내에서 흔하다. 그러나, 연령에 따라, 피부 내 존재하는 하이알루론산, 콜라겐, 엘라스틴 및 다른 기질 중합체의 양은 감소된다. 예를 들어, 태양광과 같은 자외선에 반복된 노출은 진피 세포가 하이알루로난의 생성을 감소시키게 할 뿐만 아니라 그것의 분해 속도를 증가시키도록 야기한다. 물질의 이런 손실은, 예를 들어 주름, 푹 꺼짐(hollowness), 수분 손실 및 노화의 외관에 기여하는 다른 원치않는 병태와 같은 다양한 피부 병태를 초래한다.Hyaluronic acid (HA), also known as hyaluronan, is a non-sulfated glycosaminoglycan widely distributed throughout the human body in joints, epithelium, and nervous tissue. Hyaluronic acid, for example, ensures good hydration, aids in the organization of the extracellular matrix and acts as a filler substance; It is common within different layers of skin when it has a variety of actions, such as participating in tissue damage mechanisms. However, with age, the amount of hyaluronic acid, collagen, elastin and other matrix polymers present in the skin decreases. For example, repeated exposure to ultraviolet light, such as sunlight, causes dermal cells not only to reduce the production of hyaluronan, but also to increase the rate of its degradation. This loss of material leads to a variety of skin conditions, such as, for example, wrinkles, hollowness, moisture loss and other unwanted conditions that contribute to the appearance of aging.
주사용 진피 필러는 노화된 피부를 치료하는데 성공적으로 사용되었다. 이런 피부 병태를 치료하기 위해 필러는 상실된 내인성 기질 중합체를 대체할 수 있거나, 또는 존재하는 기질 중합체의 기능을 향상시키고/촉진시킨다. 하이알루론산-계 진피 필러는 점점 더 인기가 있게 되었는데, 하이알루론산은 인체 전체에서 자연적으로 발견되는 물질이기 때문이다. 이들 필러는 일반적으로 잘 용인되며, 비영구이고, 매우 다양한 피부 병태에 대해 상당히 저위험인 치료이다.Injectable dermal fillers have been used successfully to treat aged skin. To treat such skin conditions, the filler can replace the missing endogenous matrix polymer, or enhance/promote the function of the existing matrix polymer. Hyaluronic acid-based dermal fillers have become more and more popular because hyaluronic acid is a substance found naturally throughout the human body. These fillers are generally well tolerated, non-persistent, and are a fairly low risk treatment for a wide variety of skin conditions.
틴들 효과(Tyndall effect)는 하이알루론산(HA)계 진피 필러가 투여된 일부 환자에서 생기는 부작용이다. 틴들 효과는 진피 필러가 주사된 피부 부위에서 푸른 변색의 출현을 특징으로 하는데, 이는 반투명 표피를 통해 보이는 가시적인 하이알루론산을 나타낸다. 임상적 보고는 필러 투여 기법 및 피부 특성이 이 부작용의 징후에 영향을 미칠 수 있다는 것을 시사한다. 높은 경직 및 탄성을 지니는 필러는 얼굴 변색의 어떤 두려움 없이 팔자주름, 볼, 및 턱과 같은 얼굴 상의 정확한 영역에 성공적으로 사용되는데, 이 물질은 중간 및 깊은 진피 영역에 주사되기 때문이다. 그러나, 이들 필러 물질이, 예를 들어 눈물고랑, 미간주름 눈가주름, 웃음 주름 또는 이마에서 깊지 않은 잔주름 주름살(wrinkle)을 고치기 위해 사용되거나, 또는 실수로 진피의 상부 영역에서 너무 깊지 않게 적용될 때, 피부의 푸르스름한 변색이 종종 관찰된다. 틴들 효과의 결과로 생각되는 이 현상은 적용 부위의 반영구적 변색을 남기며, 때때로 필러 물질을 분해시키기 위한 하이알루로니다제의 투여 후에만 사라진다. 결과적으로, 틴들 효과는 깊지 않은 잔주름에 대해 치료되는 환자에서 더 흔하다. 전형적으로 7개월 동안만큼 겔이 피부에서 지속되는 틴들 효과의 장기적인 징후는 환자에서 주된 걱정의 원인이다.The Tyndall effect is a side effect that occurs in some patients receiving hyaluronic acid (HA)-based dermal fillers. The Tyndle effect is characterized by the appearance of a blue discoloration at the skin site injected with the dermal filler, indicating visible hyaluronic acid seen through the translucent epidermis. Clinical reports suggest that filler administration techniques and skin characteristics may influence the signs of this side effect. Fillers with high stiffness and elasticity are successfully used in precise areas on the face such as nasolabial folds, cheeks, and chin without any fear of facial discoloration, as this material is injected into the middle and deep dermal areas. However, when these filler substances are used, for example, to fix tear furrows, glabellar wrinkles, laugh wrinkles or small wrinkles in the forehead, or when accidentally applied not too deep in the upper area of the dermis, A bluish discoloration of the skin is often observed. This phenomenon, thought to be a result of the Tindle effect, leaves a semi-permanent discoloration of the application site, and sometimes disappears only after administration of hyaluronidase to break down the filler substance. As a result, the Tindle effect is more common in patients treated for minor fine lines. Long-term signs of the Tindle effect, which the gel lasts in the skin as typically as long as 7 months, are a major cause of concern in patients.
HA-계 진피 필러 겔은 눈물고랑, 이마, 눈가주름, 미간주름 등 주위에서 발견되는 "잔주름" 주름살을 치료하기 위해 특별하게 제형화되었다. 상업적으로 입수가능한 HA "잔주름" 겔은 쥬비덤 리파인(Juvederm Refine)(G' ~67 Pa; G"/G' ~0.59, HA 농도 18㎎/㎖), 벨로테로 소프트(Belotero Soft)(G' ~28 Pa; G"/G' ~1.1, HA 농도 20㎎/㎖), 에머벨 터치(Emervel Touch)(G' ~56 Pa; G"/G' ~0.64, HA 농도 20㎎/㎖), 스타일에이지 에스(Stylage S)(G' ~192 Pa; G"/G' ~0.20, HA 농도 16㎎/㎖), 테오시알 퍼스트 라인(Teosyal First Lines)(G' 59 Pa; G"/G' ~0.53, HA 농도 20㎎/㎖), 레스틸렌 터치(Restylane Touch)(G' ~489 Pa; G"/G' ~0.24, HA 농도 18㎎/㎖)를 포함한다. 이들 겔은, 예를 들어 소량의 가교제와 선형 HA 쇄를 가볍게 가교시킴으로써 및/또는 이들 겔의 최종 HA 농도를 감소시킴으로써 낮은 탄성률을 갖도록 제형화되지만, 대부분의 상업적으로 입수가능한 "잔주름" 겔은, 특히 깊지 않게, 예를 들어 약 1㎜ 미만의 깊이에서 주사될 때 여전히 일부 환자에서 틴들 효과를 나타낸다.The HA-based dermal filler gel is specially formulated to treat "fine wrinkles" wrinkles found around the tear sulcus, forehead, crow's feet, glabellar lines and the like. Commercially available HA "fine wrinkles" gels include Juvederm Refine (G' ̃67 Pa; G"/G' ̃0.59, HA concentration 18 mg/mL), Belotero Soft (G' ~28 Pa; G"/G' ~1.1,
콜라겐계겔은 깊지 않은 주름살의 치료에 사용될 수 있으며, 틴들효과를 야기하는 것으로 나타나지 않았다. 콜라겐계 겔은 그것이 피부에서 상대적으로 불량한 지속기간을 가지며, 개체에서 사전시험을 필요로 하기 때문에 고도로 선호되지 않는다. 래디어스(Radiesse)(등록상표)(칼슘 하이드록시아파타이트)는 피하에 주사가능한 이식물이며, 이것의 원칙적 성분은 하이알루론산이 아닌 합성 칼슘 하이드록시아파타이트이다. 하이알루론산계 진피 필러와 달리, 칼슘 하이드록시아파타이트는 투명하지 않으며, 따라서 틴들효과의 문제를 회피한다. 그러나, 너무 깊지 않게 놓인다면, 이 필러는 피부 바로 밑에서 백색 물질로서 보일 수 있다. 더 나아가, 하이알루론산계 필러에 비해, 래디어스(Radiesse)(등록상표)는 주사를 위해 더 큰 바늘을 필요로 하며, 전형적으로 눈 영역에서 사용에 대해 권고되지 않는다.Collagen-based gels can be used in the treatment of shallow wrinkles and have not been shown to cause the tindel effect. Collagen-based gels are not highly preferred because they have a relatively poor duration in the skin and require prior testing in the subject. Radiesse® (calcium hydroxyapatite) is a subcutaneous injectable implant, its principal component is synthetic calcium hydroxyapatite, not hyaluronic acid. Unlike hyaluronic acid-based dermal fillers, calcium hydroxyapatite is not transparent, thus avoiding the problem of the tindle effect. However, if placed not too deep, this filler can appear as a white substance just under the skin. Furthermore, compared to hyaluronic acid-based fillers, Radiesse® requires a larger needle for injection and is typically not recommended for use in the ocular area.
깊지 않게 주사될 때조차 틴들 효과에 기인하는 푸르스름한 변색을 나타내지 않는 주사용 하이알루론산계 진피 필러를 제공하는 것이 바람직하다.It is desirable to provide a hyaluronic acid-based dermal filler for injection that does not exhibit a bluish discoloration due to the tindle effect even when injected not deeply.
미국특허출원공개 제2011/0171286호 (2011.07.14)US Patent Application Publication No. 2011/0171286 (2011.07.14)
미국특허출원공개 제2011/0171311호 (2011.07.14)US Patent Application Publication No. 2011/0171311 (2011.07.14)
Park, D.J. et al. 2010, Orthopaedic Proceedings, Vol. 92-B, No. SUPP IPark, D.J. et al. 2010, Orthopaedic Proceedings, Vol. 92-B, No. SUPP I
본 발명은 피부의 어떤 푸르스름한 변색 또는 적어도 유의하거나 또는 주목할 만한 푸르스름한 변색을 생성하는 일 없이 상부 진피에 투여될 수 있는 HA계 진피 필러를 제조하기 위한 조성물 및 제형화 방법을 기재한다. 추가로, 본 발명의 현재 기재된 필러 겔 중 다수는 현재 상업적으로 입수가능한 겔 보다 생체내에서 유의하게 더 오래 지속되는 것으로 발견되었다. 본 발명의 일부 양태에서, 피부의 외관을 향상시키는데 유용한 광학적으로 투명한 진피 필러가 제공되는데, 이는 볼륨과 풍만함을 더하며, "틴들링" 없이 일정한 잔주름 주름살의 외관을 감소시킨다. 본 조성물은 다수의 통상적인 광학적으로 투명한 진피 필러와 관련된 부정적인 푸른 변색을 야기하는 일 없이 피부 내 잔주름에, 심지어 얇은 피부 영역에서도, 오히려 깊지 않게, 도입될 수 있다.The present invention describes compositions and formulation methods for preparing HA-based dermal fillers that can be administered to the upper dermis without producing any bluish discoloration of the skin or at least significant or noticeable bluish discoloration. Additionally, many of the currently described filler gels of the present invention have been found to last significantly longer in vivo than currently commercially available gels. In some aspects of the present invention, an optically clear dermal filler useful for improving the appearance of the skin is provided, which adds volume and plumpness, and reduces the appearance of certain fine wrinkles without "tindling". The composition can be introduced into fine lines in the skin, even in thin areas of skin, rather not deeply, without causing the negative blue discoloration associated with many conventional optically clear dermal fillers.
더 구체적으로는, 본 발명의 일 양태에서, 일반적으로 생체에 적합한 중합체, 예를 들어, 가교된 하이알루론산 성분 및 하이알루론산 성분과 조합된 첨가제를 포함하는, 장시간 지속되는 치료적 진피 필러 조성물이 제공된다. More specifically, in one aspect of the invention, there is provided a long lasting therapeutic dermal filler composition comprising a generally biocompatible polymer such as a crosslinked hyaluronic acid component and an additive in combination with the hyaluronic acid component.
일 실시형태에서, 중합체는 다당류, 예를 들어, 하이알루론산이다. 하이알루론산은 가교 성분을 포함하고, 추가로 비가교 성분을 포함할 수 있다. 첨가제는 비타민, 예를 들어, 비타민 C, 예를 들어, 비타민 C의 안정화된 형태 또는 비타민 C 유도체, 예를 들어, L-아스콜브산 2-글루코사이드(AA2G), 아스코빌 3-아미노프로필 포스페이트(비타겐(Vitagen)) 또는 나트륨 아스코빌 포스페이트(AA2P)를 포함할 수 있다.In one embodiment, the polymer is a polysaccharide, such as hyaluronic acid. Hyaluronic acid includes a crosslinking component and may further include a non-crosslinking component. Additives include vitamins, e.g. vitamin C, e.g. stabilized forms of vitamin C or vitamin C derivatives, e.g. L-ascorbic acid 2-glucoside (AA2G), ascorbyl 3-aminopropyl phosphate ( Vitagen) or sodium ascorbyl phosphate (AA2P).
본 발명의 일 양태에서, 첨가제는 적합한 반응 과정, 예를 들어 에터화, 아미드화 또는 에스터화에 의해 중합체에 공유적으로 컨쥬게이트된 비타민 유도체이다.In one aspect of the present invention, the additive is a vitamin derivative covalently conjugated to the polymer by a suitable reaction process, for example etherification, amidation or esterification.
본 발명의 넓은 양태에서, 진피 필러 조성물이 제공되되, 해당 조성물은 가교 성분과 가교된 하이알루론산 성분, 및 가교 성분 이외의 첨가제를 포함한다. 하이알루론산 성분은 첨가제에 화학적으로 컨쥬게이트될 수 있다. 추가로, 조성물은 첨가제가 없는 것을 제외하고 실질적으로 동일한 조성물에 대해, 환자의 진피 영역에 투여될 때 감소된 틴들 효과를 나타낸다. 조성물은 다른 첨가제, 예를 들어 리도카인과 같은 마취제를 추가로 포함할 수 있다. 일 실시형태에서, 첨가제는 비타민 C 유도체, 예를 들어, AA2G이다. 다른 실시형태에서, 첨가제는 비타겐(Vitagen)이다.In a broad aspect of the present invention, a dermal filler composition is provided, the composition comprising a crosslinking component and a crosslinked hyaluronic acid component, and an additive other than the crosslinking component. The hyaluronic acid component can be chemically conjugated to the additive. Additionally, the composition exhibits a reduced Tindle effect when administered to the dermal area of a patient for substantially the same composition except for the absence of additives. The composition may further contain other additives, for example an anesthetic such as lidocaine. In one embodiment, the additive is a vitamin C derivative, such as AA2G. In another embodiment, the additive is Vitagen.
일 실시형태에서, 하이알루론산 성분은 약 3㏖% 내지 약 40㏖, 예를 들어, 약 3㏖% 내지 약 10㏖%의 컨쥬게이션 정도를 지니는 첨가제에 화학적으로 컨쥬게이트된다.In one embodiment, the hyaluronic acid component is chemically conjugated to an additive having a degree of conjugation of about 3 mol% to about 40 mol, for example, about 3 mol% to about 10 mol%.
조성물을 실질적으로 광학적으로 투명할 수 있다. 조성물을 일반적으로 약 40㎩ 내지 약 100㎩, 예를 들어, 약 100㎩ 이하 및, 예를 들어, 약 40㎩ 이상의 G' 값을 가진다.The composition may be substantially optically transparent. The composition generally has a G'value from about 40 Pa to about 100 Pa, for example less than or equal to about 100 Pa, and, for example, greater than or equal to about 40 Pa.
본 발명의 다른 양태에서, 환자의 피부에서 잔주름을 치료하는 방법이 제공된다. 일 실시형태에서, 해당 방법은 환자의 피부 내로 하이알루론산 성분, 하이알루론산을 가교시키는 가교 성분 및 가교 성분 이외의 첨가제를 포함하는 조성물을 도입하는 단계를 포함하며, 조성물을 실질적으로 광학적으로 투명하되, 조성물은 첨가제가 없는 것을 제외하고 실질적으로 동일한 조성물에 대해, 환자의 진피 영역에 투여될 때 감소된 틴들 효과를 나타낸다.In another aspect of the present invention, a method of treating fine wrinkles in the skin of a patient is provided. In one embodiment, the method comprises introducing into the skin of a patient a composition comprising a hyaluronic acid component, a crosslinking component that crosslinks the hyaluronic acid, and an additive other than the crosslinking component, wherein the composition is substantially optically transparent, wherein the composition is For substantially the same composition except for the absence of additives, it exhibits a reduced Tindle effect when administered to the dermal area of a patient.
본 발명의 다른 양태에서, 얼굴의외관을 개선시키는 방법이 제공되며, 해당 방법은 일반적으로 환자의 진피 영역에 틴들 효과를 나타내지 않거나 또는 유의하지 않게 나타내는 실질적으로 광학적으로 투명한 진피 필러를 투여하는 단계를 포함한다. 조성물은 하이알루론산을 제공하는 단계, 가교제를 비타민 C 유도체와 반응시키는 단계, 반응된 가교제 및 비타민 C 유도체를 하이알루론산에 첨가하여 공유적으로 컨쥬게이트된 비타민 C를 포함하는 가교된 하이알루론산 조성물을 형성하는 단계; 및 가교된 하이알루론산 조성물을 균질화하고, 중화시켜, 주사용 진피 필러 조성물을 얻는 단계로 구성될 수 있다. 일부 실시형태에서, 비타민 C 유도체는 AA2G이다. 다른 실시형태에서, 비타민 C 유도체는 비타겐이다.In another aspect of the present invention, a method of improving the appearance of the face is provided, the method comprising administering a substantially optically transparent dermal filler that does not or does not significantly exhibit a Tindle effect to a dermal area of a patient. Include. The composition comprises the steps of providing hyaluronic acid, reacting a crosslinking agent with a vitamin C derivative, adding the reacted crosslinking agent and vitamin C derivative to hyaluronic acid to form a crosslinked hyaluronic acid composition comprising covalently conjugated vitamin C; And homogenizing and neutralizing the crosslinked hyaluronic acid composition to obtain a dermal filler composition for injection. In some embodiments, the vitamin C derivative is AA2G. In another embodiment, the vitamin C derivative is Vitagen.
본 발명의 또 다른 양태에서, 환자의 얇은 피부 영역에서 잔주름의 외관을 감소시키는 방법이 제공되되, 해당 방법은 일반적으로 진피 필러 조성물, 즉, 비타민 C 또는 비타민 C 유도체를 포함하는 실질적으로 광학적으로 투명한 하이알루론산계 진피 필러 조성물을 약 1㎜ 이하의 깊이에서 환자에게 투여하는 단계를 포함한다. 일부 실시형태에서, 조성물은 약 0.8㎜ 이하, 약 0.6㎜ 이하 또는 약 0.4㎜ 이하 깊이에서 주사된다.In another aspect of the present invention, a method of reducing the appearance of fine lines in a thin skin area of a patient is provided, wherein the method is generally a dermal filler composition, i.e., a substantially optically transparent composition comprising vitamin C or a vitamin C derivative. And administering the hyaluronic acid-based dermal filler composition to the patient at a depth of about 1 mm or less. In some embodiments, the composition is injected at a depth of about 0.8 mm or less, about 0.6 mm or less, or about 0.4 mm or less.
본 발명의 또 다른 양태에서, 실질적으로 광학적으로 투명하고, 일반적으로 가교 성분과 가교된 하이알루론산 성분 및 하이알루론산 성분과 공유적으로 컨쥬게이트된 비타민 C 유도체를 포함하는 진피 필러 조성물이 제공된다. 예시적인 실시형태에서, 조성물은 약 40㎩ 내지 약 100㎩의 G'값을 가진다. 추가로, 조성물은 약 18㎎/g 내지 약 30㎎/g의 하이알루론산 농도를 가질 수 있다. 이들 조성물은 피부에서, 예를 들어 매우 얇은 피부, 예를 들어 약 1㎜ 이하 두께를 갖는 피부에서조차 잔주름 또는 깊지 않은 주름선(crease)을 치료하는데 특히 유용하고, 효과적일 수 있다. 일부 실시형태에서, 본 발명의 조성물은 피부에 도입된 후 적어도 3개월, 적어도 6개월 또는 1년까지 지속된다.In another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a dermal filler composition comprising a substantially optically transparent, generally crosslinked hyaluronic acid component and a vitamin C derivative covalently conjugated with the hyaluronic acid component. In an exemplary embodiment, the composition has a G'value of about 40 Pa to about 100 Pa. Additionally, the composition may have a hyaluronic acid concentration of about 18 mg/g to about 30 mg/g. These compositions can be particularly useful and effective in treating fine lines or non-deep creases in the skin, for example even in very thin skin, for example with a thickness of about 1 mm or less. In some embodiments, the compositions of the present invention last at least 3 months, at least 6 months or up to 1 year after being introduced into the skin.
본 발명의 이들 및 다른 양태는 다음의 도면 및 상세한 설명을 참조로 하여 더 용이하게 이해되고, 인식될 수 있다.These and other aspects of the invention may be more easily understood and recognized with reference to the following drawings and detailed description.
도 1은 L-아스콜브산 2-글루코사이드(AA2G)의 구조를 도시한 도면;
도 2는 아스코빌 3-아미노프로필 포스페이트(비타겐)의 구조를 도시한 도면;
도 3은 나트륨 아스코빌 포스페이트(AA2P)의 구조를 도시한 도면;
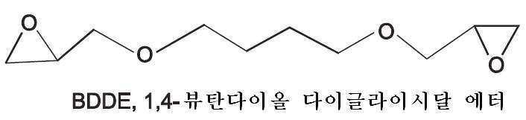
도 4는 1,4-뷰탄다이올 다이글라이시딜 에터(BDDE)의 구조를 도시한 도면;
도 5는 펜타에리트리톨 글라이시달 에터(스타-PEG 에폭사이드)의 구조를 도시한 도면;
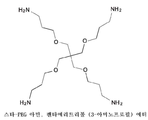
도 6은 펜타에리트리톨 (3-아미노프로필) 에터(스타-PEG 아민)의 구조를 도시한 도면;
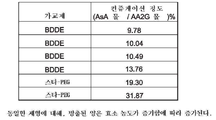
도 7은 본 발명에 따른 다양한 진피 필러 조성물에 대한 컨쥬게이션 정도 및 G' 값을 나타내는 표를 도시한 도면;
도 8은 본 발명에 따른 HA-AA2G(BDDE) 진피 필러 조성물에 대한 컨쥬게이션 정도, HA 농도 및 G' 값을 나타내는 표를 도시한 도면;
도 9는 4가지 상이한 α-글루코시다제 농도에 대해 시간(분)에 대한 PBS 중의 AA2G의 용액으로부터 AsA의 관찰된 방출 백분율의 그래프 표현을 도시한 도면;
도 10은 본 발명에 따른 컨쥬게이트된 진피 필러로부터 유리 AsA의 방출 프로파일(지속방출)의 표현(㏖% 대 반응시간에서 AA2G 전환)을 도시한 도면;
도 11a 및 도 11b는 본 발명에 따른 다양한 진피 필러에 대한 추가적인 방출 데이터를 도시한 도면;
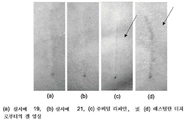
도 12는 잔주름 적용을 위한 본 발명의 HA계 진피 필러 겔 및 일부 상업적으로 입수가능한 겔의 깊지 않은 주사 후 피부의 영상을 도시한 도면;
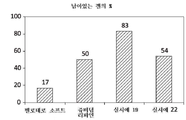
도 13은 잔주름 적용을 위한 본 발명의 HA계 진피 필러 겔 및 특정 상업적으로 입수가능한 겔의 시각적 틴들 스코어를 도시한 도면;
도 14는 잔주름 적용을 위한 본 발명의 HA계 진피 필러 겔 및 일부 상업적으로 입수가능한 겔의 피부로부터 방출된 청색광의 %를 도시한 도면;
도 15는 잔주름 적용을 위한 본 발명의 HA계 진피 필러 겔 및 일부 상업적으로 입수가능한 겔의 이식 1주 후 남아있는 겔의 전반적인 %를 도시한 도면;
도 16은 잔주름 적용을 위한 본 발명의 이식된 HA계 진피 필러 겔 및 일부 상업적으로 입수가능한 겔의 제0주, 제12주, 제24주 및 제40주에 남아있는 겔의 전반적인 %를 도시한 도면.1 is a diagram showing the structure of L-ascorbic acid 2-glucoside (AA2G);
2 is a diagram showing the structure of ascorbyl 3-aminopropyl phosphate (vitagen);
3 is a diagram showing the structure of sodium ascorbyl phosphate (AA2P);
Figure 4 is a diagram showing the structure of 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether (BDDE);
5 is a diagram showing the structure of pentaerythritol glycidal ether (Star-PEG epoxide);
Figure 6 is a diagram showing the structure of pentaerythritol (3-aminopropyl) ether (star-PEG amine);
7 is a view showing a table showing the degree of conjugation and G'value for various dermal filler compositions according to the present invention;
8 is a diagram showing a table showing the degree of conjugation, HA concentration, and G'value for the HA-AA2G (BDDE) dermal filler composition according to the present invention;
Figure 9 shows a graphical representation of the observed percent release of AsA from a solution of AA2G in PBS versus time (minutes) for four different α-glucosidase concentrations;
Figure 10 shows a representation of the release profile (sustained release) of free AsA from conjugated dermal fillers according to the present invention (mol% vs. AA2G conversion in reaction time);
11A and 11B show additional release data for various dermal fillers according to the present invention;
FIG. 12 shows an image of the skin after sub-deep injection of the HA-based dermal filler gel of the present invention and some commercially available gels for fine line application;
FIG. 13 depicts the visual Tindle score of the HA-based dermal filler gel of the present invention and certain commercially available gels for fine line application;
14 shows the% of blue light emitted from the skin of the HA-based dermal filler gel of the present invention and some commercially available gels for fine line application;
FIG. 15 shows the overall percentage of gel remaining after 1 week implantation of the HA-based dermal filler gel of the present invention and some commercially available gels for fine line application;
Figure 16 shows the overall percent of the gel remaining at
본 발명의 일 양태에서, 진피 필러 조성물이 제공되되, 조성물은 일반적으로 생체에 적합한 중합체, 예를 들어, 다당류, 예컨대 가교된 하이알루론산, 및 중합체에 공유적으로 컨쥬게이트된 비타민 C 유도체를 포함한다. 조성물은 피부 자가콜라겐형성(neocollagenesis)뿐만 아니라 다른 치료적 또는 미용적 이점을 위한 비타민 C의 지속 방출을 제공한다. 피부에, 예를 들어 진피 내로 도입되었을 때, 조성물은 신체 내 내인성 효소와 반응하고, 시간에 따라, 생활성 비타민 C가 효소적 절단을 통해 생체내에서 만들어진다. 비타민 C는 몇 주 또는 몇 개월의 기간에 걸쳐 조성물로부터 방출되기 때문에, 그것의 수반되는 이점은 신체에 대해 이용가능하게 만들어진다.In one aspect of the invention, a dermal filler composition is provided, wherein the composition generally comprises a biocompatible polymer, such as a polysaccharide such as crosslinked hyaluronic acid, and a vitamin C derivative covalently conjugated to the polymer. The composition provides a sustained release of vitamin C for skin autocollagenesis as well as other therapeutic or cosmetic benefits. When introduced into the skin, for example into the dermis, the composition reacts with endogenous enzymes in the body, and over time, bioactive vitamin C is made in vivo through enzymatic cleavage. Because vitamin C is released from the composition over a period of weeks or months, its concomitant benefits are made available to the body.
중합체는 단백질, 펩타이드 및 폴리펩타이드, 폴리리신, 콜라겐, 프로-콜라겐, 엘라스틴 및 라미닌으로 이루어진 중합체의 군으로부터 선택될 수 있다.The polymer may be selected from the group of polymers consisting of proteins, peptides and polypeptides, polylysine, collagen, pro-collagen, elastin and laminin.
중합체는 하이드록실, 아민, 및 카복실 작용기를 지니는 합성 중합체: 폴리(비닐 알코올), 폴리에틸렌 글라이콜, 폴리비닐일 아민, 폴리알릴아민, 데아세틸화된 폴리아크릴아마이드, 폴리아크릴산 및 폴리메타크릴산으로 이루어진 중합체의 군으로부터 선택될 수 있다. 중합체는 수지상 폴리올 및 수지상 폴리아민을 포함하는 수지상 또는 분지형 중합체로 이루어진 중합체의 군으로부터 선택될 수 있다. 중합체는 하이드록실, 아민 및 카복실 작용기를 지니는 고체 표면으로 이루어진 중합체의 군으로부터 선택될 수 있다.Polymers are synthetic polymers with hydroxyl, amine, and carboxyl functional groups: poly(vinyl alcohol), polyethylene glycol, polyvinylylamine, polyallylamine, deacetylated polyacrylamide, polyacrylic acid and polymethacrylic acid. It may be selected from the group of polymers consisting of. The polymer may be selected from the group of polymers consisting of dendritic or branched polymers including dendritic polyols and dendritic polyamines. The polymer may be selected from the group of polymers consisting of a solid surface with hydroxyl, amine and carboxyl functional groups.
중합체는, 예를 들어 전분 및 그것의 유도체; 덱스트란 및 그것의 유도체, 셀룰로스 및 그것의 유도체; 키틴 및 키토산 및 알기네이트 및 그것의 유도체의 군으로부터 선택된 다당류일 수 있다.Polymers include, for example, starch and derivatives thereof; Dextran and derivatives thereof, cellulose and derivatives thereof; It may be a polysaccharide selected from the group of chitin and chitosan and alginates and derivatives thereof.
본 발명의 예시적인 실시형태에서, 중합체는 글라이코사미노글라이칸이다. 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 2 이상의 상이한 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체를 추가로 포함할 수 있다. 본 명세서에 사용된 바와 같은 용어 "글라이코사미노글라이칸"은 "GAG" 및 "점액성 다당류"와 동의어이며, 반복적인 이당류 단위로 이루어진 긴 미분지 다당류를 지칭한다. 반복 단위는 헥소사민(질소를 함유하는 6탄당)에 연결된, 헥소스(6탄당) 또는 헥수론산 및 이들의 약제학적으로 허용가능한 염으로 이루어진다. GAG 패밀리의 구성원은 그것들이 함유하는 헥소사민, 헥소스 또는 헥수론산 단위의 유형, 예를 들어 글루쿠론산, 이두론산, 갈락토스, 갈락토사민, 글루코사민)에서 다르며, 또한 글라이코사이드 결합의 기하학에서 다를 수 있다. 임의의 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체는 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물에서 유용하며, 단, 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체는 피부 병태를 개선시킨다. 글라이코사미노글라이칸의 비제한적 예는 콘드로이틴 황산, 더마탄 황산, 케라탄 황산, 하이알루로난을 포함한다. 글라이코사미노글라이칸의 허용가능한 염의 비제한적 예는 나트륨 염, 칼륨 염, 마그네슘 염, 칼슘 염 및 이들의 조합을 포함한다. 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물 및 방법에 유용한 글라이코사미노글라이칸 및 그것의 얻어진 중합체는, 예를 들어 Piron 및 Tholin의 미국 특허 공개 제2003/0148995호(발명의 명칭: Polysaccharide Crosslinking, Hydrogel Preparation, Resulting Polysaccharides(s) and Hydrogel(s), uses Thereof); Lebreton(발명의 명칭: Cross-Linking of Low and High Molecular Weight Polysaccharides Preparation of Injectable Monophase Hydrogels); Lebreton의 미국 특허 공개 제2008/0089918호(발명의 명칭: Viscoelastic Solutions Containing Sodium Hyaluronate and Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose, Preparation and Uses); Lebreton 등의 미국 특허 공개 제2010/0028438호(발명의 명칭: Hyaluronic Acid-Based Gels Including Lidocaine); 및 미국 특허 공개 제2006/0194758호(발명의 명칭: Polysaccharides and Hydrogels thus Obtained); 및 Di Napoli의 국제 특허 공개 WO 2004/073759호(발명의 명칭: Composition and Method for Intradermal Soft Tissue Augmentation)에 기재되어 있고, 이들 각각은 그것의 전문이 본 명세서에 참조로서 포함된다. 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물 및 방법에서 유용한 GAG는, 예를 들어, 하이알루로난계 진피 필러 쥬비덤(JUVEDERM)(등록상표), 쥬비덤(JUVEDERM)(등록상표) 30, 쥬비덤(JUVEDERM)(등록상표) 울트라, 쥬비덤(JUVEDERM)(등록상표) 울트라 플러스, 쥬비덤(JUVEDERM)(등록상표) 울트라 XC, 및 쥬비덤(JUVEDERM)(등록상표) 울트라 플러스 XC(캘리포니아주 얼바인에 소재한 앨러간 인코포레이티드(Allergan Inc))와 같이 상업적으로 입수가능하다. 표 1은 대표적인 GAG를 열거한다.In an exemplary embodiment of the invention, the polymer is a glycosaminoglycan. The hydrogel compositions disclosed herein may further comprise two or more different glycosaminoglycan polymers. The term “glycosaminoglycan” as used herein is synonymous with “GAG” and “mucopolysaccharide” and refers to a long unbranched polysaccharide made up of repetitive disaccharide units. The repeating unit consists of hexose (hexasaccharide) or hexuronic acid and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof linked to hexosamine (hexasaccharide containing nitrogen). Members of the GAG family differ in the type of hexosamine, hexose or hexuronic acid units they contain, e.g. glucuronic acid, iduronic acid, galactose, galactosamine, glucosamine), and also the geometry of glycoside bonds. Can be different from Any glycosaminoglycan polymer is useful in the hydrogel compositions disclosed herein, provided that the glycosaminoglycan polymer improves skin conditions. Non-limiting examples of glycosaminoglycans include chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, keratan sulfate, and hyaluronan. Non-limiting examples of acceptable salts of glycosaminoglycans include sodium salts, potassium salts, magnesium salts, calcium salts and combinations thereof. Glycosaminoglycans and their resulting polymers useful in the hydrogel compositions and methods disclosed herein are, for example, Piron and Tholin, US Patent Publication No. 2003/0148995 (name of the invention: Polysaccharide Crosslinking, Hydrogel Preparation, Resulting Polysaccharides(s) and Hydrogel(s), uses Thereof); Lebreton (name of invention: Cross-Linking of Low and High Molecular Weight Polysaccharides Preparation of Injectable Monophase Hydrogels); US Patent Publication No. 2008/0089918 to Lebreton (name of the invention: Viscoelastic Solutions Containing Sodium Hyaluronate and Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose, Preparation and Uses); US Patent Publication No. 2010/0028438 to Lebreton et al. (name of the invention: Hyaluronic Acid-Based Gels Including Lidocaine); And US Patent Publication No. 2006/0194758 (name of the invention: Polysaccharides and Hydrogels thus Obtained); And Di Napoli's International Patent Publication WO 2004/073759 (name of the invention: Composition and Method for Intradermal Soft Tissue Augmentation), each of which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety. GAGs useful in the hydrogel compositions and methods disclosed herein are, for example, hyaluronan-based dermal filler Juvidum (JUVEDERM) (registered trademark), JUVEDERM (registered trademark) 30, Juvidum (JUVEDERM) (Registered trademark) Ultra, JUVEDERM (registered trademark) Ultra Plus, JUVEDERM (registered trademark) Ultra XC, and JUVEDERM (registered trademark) Ultra Plus XC (AL, located in Irvine, Calif.) It is commercially available such as Allergan Inc. Table 1 lists representative GAGs.
본 발명의 양태는 부분적으로 콘드로이틴 황산 중합체를 포함하는 하이드로겔 조성물을 제공한다. 본 명세서에 사용되는 바와 같은 용어 "콘드로이틴 황산 중합체"는 D-글루쿠론산(GlcA) 및 N-아세틸-D-갈락토사민(GalNAc)의 두 대안의 단당류의 이당류 및 이의 약제학적으로 허용가능한 염을 포함하는 미분지, 황산화된 중합체를 지칭한다. 콘드로이틴 황산 중합체는 L-이두론산(IdoA)으로 에피머화된 D-글루쿠론산 잔기를 포함할 수 있으며, 이 경우에 얻어진 이당류는 더마탄 황산으로서 지칭된다. 콘드로이틴 황산 중합체는 100개 이상의 개개의 당의 쇄를 가질 수 있는데, 이들 각각은 변할 수 있는 위치 및 양에서 황산화될 수 있다. 콘드로이틴 황산 중합체는 중요한 연골의 구조적 성분이며, 압박에 대한 그것의 큰 저항성을 제공한다. 임의의 콘드로이틴 황산 중합체는 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물에서 유용한데, 단, 콘드로이틴 황산 중합체는 피부 병태를 개선시킨다. 콘드로이틴 황산의 약제학적으로 허용가능한 염의 비제한적 예는 콘드로이틴 황산 나트륨, 콘드로이틴 황산 칼륨, 콘드로이틴 황산 마그네슘, 콘드로이틴 황산 칼슘 및 이들의 조합을 포함한다.An aspect of the present invention provides a hydrogel composition, in part, comprising a chondroitin sulfate polymer. The term "chondroitin sulfate polymer" as used herein refers to the disaccharides of two alternative monosaccharides and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof: D-glucuronic acid (GlcA) and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine (GalNAc). Refers to an unbranched, sulfated polymer comprising. The chondroitin sulfate polymer may comprise a D-glucuronic acid residue epimerized with L-iduronic acid (IdoA), and the disaccharide obtained in this case is referred to as dermatan sulfate. Chondroitin sulfate polymers can have a chain of 100 or more individual sugars, each of which can be sulfated in varying positions and amounts. Chondroitin sulfate polymer is an important structural component of cartilage and provides its great resistance to compression. Any chondroitin sulfate polymer is useful in the compositions disclosed herein, provided that the chondroitin sulfate polymer improves skin conditions. Non-limiting examples of pharmaceutically acceptable salts of chondroitin sulfate include sodium chondroitin sulfate, potassium chondroitin sulfate, magnesium chondroitin sulfate, calcium chondroitin sulfate, and combinations thereof.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 케라탄 황산 중합체를 포함하는 하이드로겔 조성물을 제공한다. 본 명세서에서 사용되는 바와 같은 용어 "케라탄 황산 중합체"는 이당류 단위를 포함하는 가변 길이의 중합체를 지칭하며, 그 자체는 β-D-갈락토스 및 N-아세틸-D-갈락토사민(GalNAc) 및 이의 약제학적으로 허용가능한 염을 포함한다. 케라탄 황산의 반복 영역 내에서 이당류는 푸코실화될 수 있으며, N-아세틸뉴라민산은 쇄의 말단을 캡핑한다. 임의의 케라탄 황산 중합체는 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물에서 유용한데, 단, 케라탄 황산 중합체는 피부 병태를 개선시킨다. 케라탄 황산의 약제학적으로 허용가능한 염의 비제한적 예는 케라탄 황산 나트륨, 케라탄 황산 칼륨, 케라탄 황산 마그네슘, 케라탄 황산 칼슘 및 이들의 조합을 포함한다.Aspects of the present specification provide a hydrogel composition comprising, in part, a keratan sulfate polymer. The term "keratan sulfate polymer" as used herein refers to a polymer of variable length comprising disaccharide units, itself β-D-galactose and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine (GalNAc) and And pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. Disaccharides can be fucosylated within the repeating region of keratan sulfuric acid, and N-acetylneuraminic acid caps the end of the chain. Any keratan sulfate polymer is useful in the compositions disclosed herein, provided that the keratan sulfate polymer improves skin conditions. Non-limiting examples of pharmaceutically acceptable salts of keratan sulfate include sodium keratan sulfate, potassium keratan sulfate, magnesium keratan sulfate, calcium keratan sulfate, and combinations thereof.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 하이알루로난 중합체를 포함하는 하이드로겔 조성물을 제공한다. 본 명세서에서 사용되는 바와 같은 용어 "하이알루론산 중합체"는 "HA 중합체", "하이알루론산 중합체"와 동의어이며, "하이알루로네이트 중합체"는 이당류 단위를 포함하는 음이온성 비황산화된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체를 지칭하며, 그 자체는 대안의 β-1,4 및 β-1,3 글라이코사이드 결합을 통해 함께 연결된 D-글루쿠론산 및 D-N-아세틸글루코사민 단량체 및 이의 약제학적으로 허용가능한 염을 포함한다. 하이알루로난 중합체는 동물 및 비동물 공급원으로부터 정제될 수 있다. 하이알루로난의 중합체는 약 5,000Da 내지 약 20,000,000Da 크기의 범위에 있을 수 있다. 임의의 하이알루로난 중합체는 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물에서 유용한데, 단, 하이알루로난 중합체는 피부 병태를 개선시킨다. 하이알루로난의 약제학적으로 허용가능한 염의 비제한적 예는 하이알루로난 나트륨, 하이알루로난 칼륨, 하이알루로난 마그네슘, 하이알루로난 칼슘 및 이들의 조합을 포함한다.Aspects of the present specification provide a hydrogel composition partially comprising a hyaluronan polymer. The term "hyaluronic acid polymer" as used herein is synonymous with "HA polymer", "hyaluronic acid polymer", and "hyaluronate polymer" is an anionic non-sulfurated glycosaminoglycan comprising disaccharide units. Refers to a polymer, which itself includes D-glucuronic acid and DN-acetylglucosamine monomers and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof linked together via alternative β-1,4 and β-1,3 glycoside bonds. do. Hyaluronan polymers can be purified from animal and non-animal sources. Polymers of hyaluronan may range in size from about 5,000 Da to about 20,000,000 Da. Any hyaluronan polymer is useful in the compositions disclosed herein, provided that the hyaluronan polymer improves skin conditions. Non-limiting examples of pharmaceutically acceptable salts of hyaluronan include sodium hyaluronan, potassium hyaluronan, magnesium hyaluronan, calcium hyaluronan, and combinations thereof.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체를 포함하는 하이드로겔 조성물을 제공한다. 본 명세서에서 사용되는 바와 같은 용어 "가교된"은 개개의 중합체 분자 또는 단량체 쇄가 겔과 같은 더 안정한 구조에 결합되는 분자간 결합을 지칭한다. 이와 같이, 가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체는 적어도 하나의 개개 중합체 분자가 서로 결합되는 분자간 결합을 가진다. 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체의 가교는 전형적으로 하이드로겔의 형성을 초래한다. 이러한 하이드로겔은 높은 점도를 가지며, 미세한 바늘을 통해 압출되기 위해 상당한 힘을 필요로 한다. 본 명세서에 개시된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체는 다작용성 PEG계 가교제, 다이비닐 설폰, 다이글라이시딜 에터 및 비스-에폭사이드, 비스카보다이이미드를 포함하지만, 이들로 제한되지 않는 다이알데하이드 및 다이설파이드 가교제를 사용하여 가교될 수 있다. 하이알루로난 가교제의 비제한적 예는 다작용성 PEG계 가교제 유사 펜타에리트리톨 테트라글라이시딜 에터(PETGE), 다이비닐 설폰(DVS), 1,4-뷰탄다이올 다이글라이시딜 에터(BDDE), 1,2-비스(2,3-에폭시프로폭시)에틸렌 (EGDGE), 1,2,7,8-다이에폭시옥탄(DEO), (페닐렌비스-(에틸)-카보다이이미드 및 1,6 헥사메틸렌비스(에틸카보다이이미드), 아디프 다이하이드라자이드(ADH), 비스(설포숙신이미딜)수베레이트(BS), 헥사메틸렌다이아민(HMDA), 1-(2,3-에폭시프로필)-2,3-에폭시사이클로헥산, 리신, 리신 메틸에스터, 또는 이들의 조합을 포함한다. 다른 유용한 가교제는 Stroumpoulis 및 Tezel의 2010년 10월 22일 출원된 미국특허 출원 제12/910,466호(발명의 명칭: Tunably Crosslinked Polysaccharide Compositions)에 개시되어 있으며, 이는 그것의 전문이 참조로서 포함된다. 임의의 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체는 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물에서 유용하며, 단, 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체는 피부 병태를 개선시킨다. 글라이코사미노글라이칸의 비제한적 예는 콘드로이틴 황산, 더마탄 황산, 케라탄 황산, 하이알루로난을 포함한다. 글라이코사미노글라이칸의 허용가능한 염의 비제한적 예는 나트륨 염, 칼륨 염, 마그네슘 염, 칼슘 염 및 이들의 조합을 포함한다. 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물 및 방법에 유용한 글라이코사미노글라이칸 및 그것의 얻어진 중합체는, 예를 들어 Piron 및 Tholin의 미국 특허 공개 제2003/0148995호(발명의 명칭: Polysaccharide Crosslinking, Hydrogel Preparation, Resulting Polysaccharides(s) and Hydrogel(s), uses Thereof); Lebreton(발명의 명칭: Cross-Linking of Low and High Molecular Weight Polysaccharides Preparation of Injectable Monophase Hydrogels); Lebreton의 미국 특허 공개 제2008/0089918호(발명의 명칭: Viscoelastic Solutions Containing Sodium Hyaluronate and Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose, Preparation and Uses); Lebreton 등의 미국 특허 공개 제2010/0028438호(발명의 명칭: Hyaluronic Acid-Based Gels Including Lidocaine); 및 미국 특허 공개 제2006/0194758호(발명의 명칭: Polysaccharides and Hydrogels thus Obtained); 및 Di Napoli의 국제 특허 공개 WO 2004/073759호(발명의 명칭: Composition and Method for Intradermal Soft Tissue Augmentation)에 기재되어 있고, 이들 각각은 그것의 전문이 본 명세서에 참조로서 포함된다.Aspects of the present specification provide a hydrogel composition comprising a partially crosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer. The term “crosslinked” as used herein refers to an intermolecular bond in which individual polymer molecules or monomer chains are bonded to a more stable structure such as a gel. Thus, the crosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer has an intermolecular bond in which at least one individual polymer molecule is bonded to each other. Crosslinking of the glycosaminoglycan polymer typically results in the formation of a hydrogel. These hydrogels have a high viscosity and require considerable force to be extruded through a fine needle. The glycosaminoglycan polymers disclosed herein include, but are not limited to, polyfunctional PEG-based crosslinking agents, divinyl sulfone, diglycidyl ether and bis-epoxides, biscarbodiimides, and dialdehydes and It can be crosslinked using a disulfide crosslinking agent. Non-limiting examples of hyaluronan crosslinking agents include multifunctional PEG-based crosslinkers-like pentaerythritol tetraglycidyl ether (PETGE), divinyl sulfone (DVS), 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether (BDDE). , 1,2-bis(2,3-epoxypropoxy)ethylene (EGDGE), 1,2,7,8-diepoxyoctane (DEO), (phenylenebis-(ethyl)-carbodiimide and 1, 6 Hexamethylenebis(ethylcarbodiimide), adip dihydrazide(ADH), bis(sulfosuccinimidyl)suberate(BS), hexamethylenediamine(HMDA), 1-(2,3-epoxy Propyl)-2,3-epoxycyclohexane, lysine, lysine methylester, or combinations thereof Other useful crosslinking agents are US Patent Application No. 12/910,466 filed October 22, 2010 by Stroumpoulis and Tezel ( Title of the Invention: Tunably Crosslinked Polysaccharide Compositions), which is incorporated by reference in its entirety. Any glycosaminoglycan polymer is useful in the hydrogel compositions disclosed herein, provided that glycosa Minoglycan polymers improve skin conditions Non-limiting examples of glycosaminoglycans include chondroitin sulfuric acid, dermatan sulfuric acid, keratan sulfuric acid, hyaluronan Acceptable glycosaminoglycans Non-limiting examples of salts include sodium salts, potassium salts, magnesium salts, calcium salts, and combinations thereof Glycosaminoglycans useful in the hydrogel compositions and methods disclosed herein and the resulting polymers thereof include, for example, For example, US Patent Publication No. 2003/0148995 of Piron and Tholin (name of invention: Polysaccharide Crosslinking, Hydrogel Preparation, Resulting Polysaccharides(s) and Hydrogel(s), uses Thereof); Lebreton (name of invention: Cross-Linking of Low) and High Molecular Weight Poly saccharides Preparation of Injectable Monophase Hydrogels); US Patent Publication No. 2008/0089918 to Lebreton (name of the invention: Viscoelastic Solutions Containing Sodium Hyaluronate and Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose, Preparation and Uses); US Patent Publication No. 2010/0028438 to Lebreton et al. (name of the invention: Hyaluronic Acid-Based Gels Including Lidocaine); And US Patent Publication No. 2006/0194758 (name of the invention: Polysaccharides and Hydrogels thus Obtained); And Di Napoli's International Patent Publication WO 2004/073759 (name of the invention: Composition and Method for Intradermal Soft Tissue Augmentation), each of which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 가교 정도를 갖는 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체를 포함하는 하이드로겔 조성물을 제공한다. 본 명세서에서 사용되는 용어 "가교 정도"는, 예를 들어 가교제에 결합된 하이알루로난의 이당류 단량체 단위와 같은 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체 단량체 단위의 백분율을 지칭한다. 가교 정도는 가교제 대 글라이코사미노글라이칸의 중량 백분율 비로서 표현된다. 본 발명의 특정 유리한 실시형태에서 가교 정도는 약 3% 내지 약 12%, 예를 들어, 약 5% 내지 약 10%이다.An aspect of the present specification provides a hydrogel composition comprising a glycosaminoglycan polymer having a degree of crosslinking in part. The term "degree of crosslinking" as used herein refers to the percentage of glycosaminoglycan polymer monomer units, such as, for example, the disaccharide monomer units of hyaluronan bound to a crosslinking agent. The degree of crosslinking is expressed as the ratio by weight of crosslinking agent to glycosaminoglycans. In certain advantageous embodiments of the invention the degree of crosslinking is from about 3% to about 12%, for example from about 5% to about 10%.
실시형태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은 가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체, 예를 들어, 가교된 하이알루론산을 포함하되, 가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체는, 예를 들어, 약 18㎎/g 내지 약 30㎎/g의 농도에서 조성물 중에 존재한다. 일부 실시형태에서, 조성물은 약 24㎎/g 또는 약 25㎎/g의 전체 하이알루론산 농도를 가진다.In an embodiment, the hydrogel composition comprises a crosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer, e.g., a crosslinked hyaluronic acid, wherein the crosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer, e.g., from about 18 mg/g to It is present in the composition at a concentration of about 30 mg/g. In some embodiments, the composition has a total hyaluronic acid concentration of about 24 mg/g or about 25 mg/g.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 저분자량의 하이알루로난 중합체, 고분자량의 하이알루로난 중합체 또는 저분자량과 고분자량 둘 다의 하이알루로난 중합체를 포함하는 하이드로겔 조성물을 제공한다. 본 명세서에서 사용되는 용어 "고분자량"은 "하이알루로난"을 지칭할 때, 1,000,000Da 이상의 평균 분자량을 갖는 하이알루로난 중합체를 지칭한다. 고분자량 하이알루로난 중합체의 비제한적 예는 약 1,500,000Da, 약 2,000,000Da, 약 2,500,000Da, 약 3,000,000Da, 약 3,500,000Da, 약 4,000,000Da, 약 4,500,000Da 내지 약 5,000,000Da의 하이알루로난 중합체를 포함한다. 본 명세서에서 사용되는 용어 "저분자량"은 "하이알루로난"을 지칭할 때, 1,000,000Da 미만의 평균 분자량을 갖는 하이알루로난 중합체를 지칭한다. 저분자량 하이알루로난 중합체 의 비제한적 예는 약 200,000Da, 약 300,000Da, 약 400,000Da, 약 500,000Da, 약 600,000Da, 약 700,000Da, 약 800,000Da, 내지 약 900,000Da의 하이알루로난 중합체를 포함한다.Aspects of the present specification provide, in part, a hydrogel composition comprising a low molecular weight hyaluronan polymer, a high molecular weight hyaluronan polymer, or both a low molecular weight and high molecular weight hyaluronan polymer. The term “high molecular weight” as used herein refers to a hyaluronan polymer having an average molecular weight of 1,000,000 Da or more when referring to “hyaluronan”. Non-limiting examples of high molecular weight hyaluronan polymers include hyaluronan polymers of about 1,500,000 Da, about 2,000,000 Da, about 2,500,000 Da, about 3,000,000 Da, about 3,500,000 Da, about 4,000,000 Da, about 4,500,000 Da to about 5,000,000 Da. Include. The term “low molecular weight” as used herein refers to a hyaluronan polymer having an average molecular weight of less than 1,000,000 Da when referring to “hyaluronan”. Non-limiting examples of low molecular weight hyaluronan polymers are hyaluronan polymers of about 200,000 Da, about 300,000 Da, about 400,000 Da, about 500,000 Da, about 600,000 Da, about 700,000 Da, about 800,000 Da, and about 900,000 Da Includes.
실시형태에서, 조성물은 저분자량의 가교된 하이알루로난 중합체를 포함한다. 이 실시형태의 양태에서, 조성물은, 예를 들어, 약 100,000Da, 약 200,000Da, 약 300,000Da, 약 400,000Da, 약 500,000Da, 약 600,000Da, 약 700,000Da, 약 800,000Da, 또는 약 900,000Da의 평균 분자량을 갖는 가교된 하이알루로난 중합체를 포함한다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 조성물은, 예를 들어, 최대 100,000Da, 최대 200,000Da, 최대 300,000Da, 최대 400,000Da, 최대 500,000Da, 최대 600,000Da, 최대 700,000Da, 최대 800,000Da, 최대 900,000Da 또는 최대 950,000Da의 평균 분자량을 갖는 가교된 하이알루로난 중합체를 포함한다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 조성물은, 예를 들어, 약 100,000Da 내지 약 500,000Da, 약 200,000Da 내지 약 500,000Da, 약 300,000 Da 내지 약 500,000Da, 약 400,000Da 내지 약 500,000Da, 약 500,000Da 내지 약 950,000Da, 약 600,000Da 내지 약 950,000Da, 약 700,000Da 내지 약 950,000Da, 약 800,000Da 내지 약 950,000Da, 약 300,000Da 내지 약 600,000Da, 약 300,000Da 내지 약 700,000Da, 약 300,000 Da 내지 약 800,000Da, 또는 약 400,000Da 내지 약 700,000Da의 평균 분자량을 갖는 가교된 하이알루로난 중합체를 포함한다.In an embodiment, the composition comprises a low molecular weight crosslinked hyaluronan polymer. In an aspect of this embodiment, the composition is, for example, about 100,000 Da, about 200,000 Da, about 300,000 Da, about 400,000 Da, about 500,000 Da, about 600,000 Da, about 700,000 Da, about 800,000 Da, or about 900,000 Da And a crosslinked hyaluronan polymer having an average molecular weight of. In another aspect of this embodiment, the composition is, for example, at most 100,000 Da, at most 200,000 Da, at most 300,000 Da, at most 400,000 Da, at most 500,000 Da, at most 600,000 Da, at most 700,000 Da, at most 800,000 Da, at most 900,000. Da or crosslinked hyaluronan polymers with an average molecular weight of up to 950,000 Da. In another aspect of this embodiment, the composition is, for example, about 100,000 Da to about 500,000 Da, about 200,000 Da to about 500,000 Da, about 300,000 Da to about 500,000 Da, about 400,000 Da to about 500,000 Da, about 500,000 Da to about 950,000 Da, about 600,000 Da to about 950,000 Da, about 700,000 Da to about 950,000 Da, about 800,000 Da to about 950,000 Da, about 300,000 Da to about 600,000 Da, about 300,000 Da to about 700,000 Da, about 300,000 Da to Crosslinked hyaluronan polymers having an average molecular weight of about 800,000 Da, or about 400,000 Da to about 700,000 Da.
다른 실시형태에서, 조성물은 고분자량의 가교된 하이알루로난 중합체를 포함한다. 이 실시형태의 양태에서, 조성물은, 예를 들어 약 1,000,000Da, 약 1,500,000Da, 약 2,000,000Da, 약 2,500,000Da, 약 3,000,000Da, 약 3,500,000Da, 약 4,000,000Da, 약 4,500,000Da, 또는 약 5,000,000Da의 평균 분자량을 갖는 가교된 하이알루로난 중합체를 포함한다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 조성물은, 예를 들어, 적어도 1,000,000Da, 적어도 1,500,000Da, 적어도 2,000,000Da, 적어도 2,500,000Da, 적어도 3,000,000Da, 적어도 3,500,000Da, 적어도 4,000,000Da, 적어도 4,500,000Da 또는 적어도 5,000,000Da의 평균 분자량을 갖는 가교된 하이알루로난 중합체를 포함한다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 조성물은, 예를 들어 약 1,000,000Da 내지 약 5,000,000Da, 약 1,500,000Da 내지 약 5,000,000Da, 약 2,000,000Da 내지 약 5,000,000Da, 약 2,500,000Da 내지 약 5,000,000Da, 약 2,000,000Da 내지 약 3,000,000Da, 약 2,500,000Da 내지 약 3,000,000Da의 평균 분자량을 갖는 가교된 하이알루로난 중합체를 포함한다.In another embodiment, the composition comprises a high molecular weight crosslinked hyaluronan polymer. In aspects of this embodiment, the composition is, for example, about 1,000,000 Da, about 1,500,000 Da, about 2,000,000 Da, about 2,500,000 Da, about 3,000,000 Da, about 3,500,000 Da, about 4,000,000 Da, about 4,500,000 Da, or about 5,000,000 Da. Crosslinked hyaluronan polymers having an average molecular weight. In another aspect of this embodiment, the composition is, for example, at least 1,000,000 Da, at least 1,500,000 Da, at least 2,000,000 Da, at least 2,500,000 Da, at least 3,000,000 Da, at least 3,500,000 Da, at least 4,000,000 Da, at least 4,500,000 Da or at least 5,000,000 Crosslinked hyaluronan polymers having an average molecular weight of Da. In another aspect of this embodiment, the composition is, for example, about 1,000,000 Da to about 5,000,000 Da, about 1,500,000 Da to about 5,000,000 Da, about 2,000,000 Da to about 5,000,000 Da, about 2,500,000 Da to about 5,000,000 Da, about 2,000,000 Da And crosslinked hyaluronan polymers having an average molecular weight of from about 3,000,000 Da to about 2,500,000 Da to about 3,000,000 Da.
또 다른 실시형태에서, 조성물은 가교된 하이알루로난 중합체를 포함하며, 여기서 가교된 하이알루로난 중합체는 다양한 비에서 고분자량 하이알루로난 중합체와 저분자량 하이알루로난 중합체의 조합을 포함한다. 또 다른 실시형태에서, 조성물은 가교된 하이알루로난 중합체를 포함하며, 여기서 가교된 하이알루로난 중합체는 약 20:1, 약 15:1, 약 10:1, 약 5:1, 약 1:1, 약 1:5 약 1:10, 약 1:15, 또는 약 1:20의 비에서 고분자량 하이알루로난 중합체 와 저분자량 하이알루로난 중합체의 조합을 포함한다.In yet another embodiment, the composition comprises a crosslinked hyaluronan polymer, wherein the crosslinked hyaluronan polymer comprises a combination of a high molecular weight hyaluronan polymer and a low molecular weight hyaluronan polymer at various ratios. do. In yet another embodiment, the composition comprises a crosslinked hyaluronan polymer, wherein the crosslinked hyaluronan polymer is about 20:1, about 15:1, about 10:1, about 5:1, about 1 And a combination of a high molecular weight hyaluronan polymer and a low molecular weight hyaluronan polymer at a ratio of :1, about 1:5, about 1:10, about 1:15, or about 1:20.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체를 포함하는 하이드로겔 조성물을 제공한다. 본 명세서에서 사용되는 바와 같은 용어 "미가교된"은 개개의 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체 분자 또는 단량체 쇄를 결합하는 분자간 결합의 결여 지칭한다. 이와 같이, 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체는 분자간 결합에 의해 임의의 다른 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체에 연결되지 않는다. 이 실시형태의 양태에서, 조성물은 미가교된 콘드로이틴 황산 중합체, 미가교된 더마탄 황산 중합체, 미가교된 케라탄 황산 중합체, 미가교된 헤파란 중합체, 미가교된 헤파란 황산 중합체, 또는 미가교된 하이알루로난 중합체를 포함한다. 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체는 수용성이며, 일반적으로 자연에서 유체로 남아있다. 이와 같이, 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체는 종종 윤활제로서 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체계 하이드로겔 조성물과 혼합되어 미세한 바늘을 통한 조성물의 압출 과정을 수월하게 한다.Aspects of the present specification provide a hydrogel composition comprising a partially uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer. The term “uncrosslinked” as used herein refers to the lack of intermolecular bonds that bind individual glycosaminoglycan polymer molecules or monomer chains. As such, the uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer is not linked to any other glycosaminoglycan polymer by intermolecular bonds. In an aspect of this embodiment, the composition is an uncrosslinked chondroitin sulfate polymer, an uncrosslinked dermatan sulfate polymer, an uncrosslinked keratan sulfate polymer, an uncrosslinked heparan polymer, an uncrosslinked heparan sulfate polymer, or an uncrosslinked Hyaluronan polymer. Uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymers are water soluble and generally remain fluid in nature. As such, the uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer is often mixed with a glycosaminoglycan polymer-based hydrogel composition as a lubricant to facilitate the extrusion process of the composition through a fine needle.
실시형태에서, 조성물은 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체를 포함하며, 여기서 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체는, 예를 들어 약 2㎎/g, 약 3㎎/g, 약 4㎎/g, 약 5㎎/g, 약 6㎎/g, 약 7㎎/g, 약 8㎎/g, 약 9㎎/g, 약 10㎎/g, 약 11㎎/g, 약 12㎎/g, 약 13㎎/g, 약 13.5㎎/g, 약 14㎎/g, 약 15㎎/g, 약 16㎎/g, 약 17㎎/g, 약 18㎎/g, 약 19㎎/g, 약 20㎎/g, 약 40㎎/g, 또는 약 60㎎/g의 농도에서 존재한다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 조성물은 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸을 제공하며, 여기서 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸은, 예를 들어, 적어도 1㎎/g, 적어도 2㎎/g, 적어도 3㎎/g, 적어도 4㎎/g, 적어도 5㎎/g, 적어도 10㎎/g, 적어도 15㎎/g, 적어도 20㎎/g, 적어도 25㎎/g 적어도 35㎎/g 또는 적어도 40㎎/g의 농도에서 존재한다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 조성물은 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸을 포함하며, 여기서 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸은, 예를 들어, 최대 1㎎/g, 최대 2㎎/g, 최대 3㎎/g, 최대 4㎎/g, 최대 5㎎/g, 최대 10㎎/g, 최대 15㎎/g, 최대 20㎎/g, 또는 최대 25㎎/g의 농도에서 존재한다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 조성물은 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸을 포함하며, 여기서 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸은, 예를 들어, 약 1㎎/g 내지 약 60㎎/g, 약 10㎎/g 내지 약 40㎎/g, 약 7.5㎎/g 내지 약 19.5㎎/g, 약 8.5㎎/g 내지 약 18.5㎎/g, 약 9.5㎎/g 내지 약 17.5㎎/g, 약 10.5㎎/g 내지 약 16.5㎎/g, 약 11.5㎎/g 내지 약 15.5㎎/g, 또는 약 12.5㎎/g 내지 약 14.5㎎/g의 농도에서 존재한다. In an embodiment, the composition comprises an uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer, wherein the uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer is, for example, about 2 mg/g, about 3 mg/g, about 4 Mg/g, about 5 mg/g, about 6 mg/g, about 7 mg/g, about 8 mg/g, about 9 mg/g, about 10 mg/g, about 11 mg/g, about 12 mg/ g, about 13 mg/g, about 13.5 mg/g, about 14 mg/g, about 15 mg/g, about 16 mg/g, about 17 mg/g, about 18 mg/g, about 19 mg/g, It is present at a concentration of about 20 mg/g, about 40 mg/g, or about 60 mg/g. In another aspect of this embodiment, the composition provides an uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan, wherein the uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan is, for example, at least 1 mg/g, at least 2 mg/g , At least 3 mg/g, at least 4 mg/g, at least 5 mg/g, at least 10 mg/g, at least 15 mg/g, at least 20 mg/g, at least 25 mg/g at least 35 mg/g or at least 40 It is present at a concentration of mg/g. In another aspect of this embodiment, the composition comprises an uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan, wherein the uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan is, for example, at most 1 mg/g, at most 2 mg/g. g, up to 3 mg/g, up to 4 mg/g, up to 5 mg/g, up to 10 mg/g, up to 15 mg/g, up to 20 mg/g, or up to 25 mg/g. In another aspect of this embodiment, the composition comprises an uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan, wherein the uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan is, for example, from about 1 mg/g to about 60 mg/g. g, about 10 mg/g to about 40 mg/g, about 7.5 mg/g to about 19.5 mg/g, about 8.5 mg/g to about 18.5 mg/g, about 9.5 mg/g to about 17.5 mg/g, It is present at a concentration of about 10.5 mg/g to about 16.5 mg/g, about 11.5 mg/g to about 15.5 mg/g, or about 12.5 mg/g to about 14.5 mg/g.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체가 본질적으로 없는 하이드로겔 조성물을 제공한다. 본 명세서에 사용된 바와 같은 용어 "본질적으로 없는"(또는 "본질적으로 이루어진")은 단지 미량의 가교된 기질 중합체가 검출될 수 있는 조성물을 지칭한다. 이 실시형태의 양태에서, 조성물은 가교된 콘드로이틴 황산 중합체가 본질적으로 없는 콘드로이틴 황산, 가교된 더마탄 황산 중합체가 본질적으로 없는 더마탄 황산, 가교된 케라탄 황산 중합체가 본질적으로 없는 케라탄 황산, 가교된 헤파란 중합체가 본질적으로 없는 헤파란, 가교된 헤파란 황산 중합체가 본질적으로 없는 헤파란 황산, 또는 가교된 하이알루로난 중합체가 본질적으로 없는 하이알루로난 황산을 포함한다.Aspects of the present specification provide a hydrogel composition essentially free of partially crosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymers. The term “essentially free” (or “consisting essentially of”) as used herein refers to a composition in which only traces of the crosslinked matrix polymer can be detected. In an aspect of this embodiment, the composition comprises chondroitin sulfuric acid essentially free of crosslinked chondroitin sulfate polymer, dermatan sulfuric acid essentially free of crosslinked dermatan sulfate polymer, keratan sulfuric acid essentially free of crosslinked keratan sulfate polymer Heparan sulfuric acid essentially free of the resulting heparan polymer, heparan sulfuric acid essentially free of the crosslinked heparan sulfate polymer, or hyaluronan sulfuric acid essentially free of the crosslinked hyaluronan polymer.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체가 완전히 없는 하이드로겔 조성물을 제공한다. 본 명세서에 사용된 바와 같은 용어 "완전히 없는"은 사용된 기기 또는 과정의 검출 범위 내의 조성물을 지칭하며, 가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체는 검출될 수 없거나 또는 그것의 존재는 확인될 수 없다. 이 실시형태의 양태에서, 조성물은 가교된 콘드로이틴 황산 중합체가 완전히 없는 콘드로이틴 황산, 가교된 더마탄 황산 중합체가 완전히 없는 더마탄 황산, 가교된 케라탄 황산 중합체가 완전히 없는 케라탄 황산, 가교된 헤파란 중합체가 완전히 없는 헤파란, 가교된 헤파란 황산 중합체가 완전히 없는 헤파란 황산, 또는 가교된 하이알루로난 중합체가 완전히 없는 하이알루로난 황산을 포함한다.Aspects of the present specification provide a hydrogel composition completely free of partially crosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymers. The term "completely free" as used herein refers to a composition within the detection range of the instrument or process used, and the crosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer cannot be detected or its presence cannot be ascertained. . In an aspect of this embodiment, the composition comprises chondroitin sulfuric acid completely free of crosslinked chondroitin sulfate polymer, dermatan sulfate completely free of crosslinked dermatan sulfate polymer, keratan sulfate completely free of crosslinked keratan sulfate polymer, crosslinked heparan Heparan completely free of polymer, heparan sulfate completely free of crosslinked heparan sulfate polymer, or hyaluronan sulfate completely free of crosslinked hyaluronan polymer.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체와 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체의 비를 포함하는 하이드로겔 조성물을 제공한다. 가교 및 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체의 이런 비는 겔:유체 비로서 알려져 있다. 임의의 겔:유체 비는 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물의 제조에서 유용하며, 단, 이러한 비는 본 명세서에 개시된 피부 병태를 개선시키는 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물을 생성한다. 본 발명의 조성물 내 겔:유체 비의 비제한적 예는 100:0, 98:2, 90:10, 75:25, 70:30, 60:40, 50:50, 40:60, 30:70, 25:75, 10:90; 2:98, 및 0:100을 포함한다.Aspects of the present specification provide a hydrogel composition comprising a ratio of a partially crosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer and an uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer. This ratio of crosslinked and uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymers is known as the gel:fluid ratio. Any gel:fluid ratio is useful in the preparation of the compositions disclosed herein, provided that such ratio results in a composition disclosed herein that ameliorates the skin conditions disclosed herein. Non-limiting examples of gel:fluid ratios in the compositions of the present invention are 100:0, 98:2, 90:10, 75:25, 70:30, 60:40, 50:50, 40:60, 30:70, 25:75, 10:90; 2:98, and 0:100.
이 실시형태의 양태에서, 조성물은 가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체 및 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체를 포함하며, 여기서 겔:유체 비는, 예를 들어, 약 0:100, 약 1:99, 약 2:98, 약 3:97, 약 4:96, 약 5:95, 약 6:94, 약 7:93, 약 8:92, 약 9:91, 또는 약 10:90이다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 조성물은 가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체 및 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체를 포함하며, 여기서 겔:유체 비는, 예를 들어, 최대 1:99, 최대 2:98, 최대 3:97, 최대 4:96, 최대 5:95, 최대 6:94, 최대 7:93, 최대 8:92, 최대 9:91 또는 최대 10:90이다. 이 실시형태의 양태에서, 조성물은 가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체 및 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체를 포함하며, 여기서 겔:유체 비는, 예를 들어, 약 0:100 내지 약 3:97, 약 0:100 내지 약 5:95, 또는 약 0:100 내지 약 10:90이다.In an aspect of this embodiment, the composition comprises a crosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer and an uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer, wherein the gel:fluid ratio is, for example, about 0:100, about 1:99, about 2:98, about 3:97, about 4:96, about 5:95, about 6:94, about 7:93, about 8:92, about 9:91, or about 10:90 . In another aspect of this embodiment, the composition comprises a crosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer and an uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer, wherein the gel:fluid ratio is, for example, at most 1:99, Maximum 2:98, maximum 3:97, maximum 4:96, maximum 5:95, maximum 6:94, maximum 7:93, maximum 8:92, maximum 9:91, maximum 10:90. In aspects of this embodiment, the composition comprises a crosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer and an uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer, wherein the gel:fluid ratio is, for example, from about 0:100 to about 3:97, about 0:100 to about 5:95, or about 0:100 to about 10:90.
이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 조성물은 가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체 및 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체를 포함하며, 겔:유체 비는, 예를 들어, 약 15:85, 약 20:80, 약 25:75, 약 30:70, 약 35:65, 약 40:60, 약 45:55, 약 50:50, 약 55:45, 약 60:40, 약 65:35, 약 70:30, 약 75:25, 약 80:20, 약 85:15, 약 90:10, 약 95:5, 약 98:2, 또는 약 100:0이다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 조성물은 가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체 및 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체를 포함하며, 겔:유체 비는, 예를 들어, 최대 15:85, 최대 20:80, 최대 25:75, 최대 30:70, 최대 35:65, 최대 40:60, 최대 45:55, 최대 50:50, 최대 55:45, 최대 60:40, 최대 65:35, 최대 70:30, 최대 75:25, 최대 80:20, 최대 85:15, 최대 90:10, 최대 95:5, 최대 98:2 또는 최대 100:0이다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 조성물은 가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체 및 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체를 포함하며, 겔:유체 비는, 예를 들어, 약 10:90 내지 약 70:30, 약 15:85 내지 약 70:30, 약 10:90 내지 약 55:45, 약 80:20 내지 약 95:5, 약 90:10 내지 약 100:0, 약 75:25 내지 약 100:0, 또는 약 60:40 내지 약 100:0이다.In another aspect of this embodiment, the composition comprises a crosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer and an uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer, wherein the gel:fluid ratio is, for example, about 15:85, about 20:80, about 25:75, about 30:70, about 35:65, about 40:60, about 45:55, about 50:50, about 55:45, about 60:40, about 65:35, about 70:30, about 75:25, about 80:20, about 85:15, about 90:10, about 95:5, about 98:2, or about 100:0. In another aspect of this embodiment, the composition comprises a crosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer and an uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer, wherein the gel:fluid ratio is, for example, at most 15:85, Max 20:80, Max 25:75, Max 30:70, Max 35:65, Max 40:60, Max 45:55, Max 50:50, Max 55:45, Max 60:40, Max 65:35, Up to 70:30, up to 75:25, up to 80:20, up to 85:15, up to 90:10, up to 95:5, up to 98:2 or up to 100:0. In another aspect of this embodiment, the composition comprises a crosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer and an uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer, wherein the gel:fluid ratio is, for example, from about 10:90 to About 70:30, about 15:85 to about 70:30, about 10:90 to about 55:45, about 80:20 to about 95:5, about 90:10 to about 100:0, about 75:25 to About 100:0, or about 60:40 to about 100:0.
본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은, 조성물이 개체에 투여될 때 유리한 효과를 제공하는 다른 작용제 또는 작용제의 조합을 추가로 포함할 수 있다. 이러한 유리한 작용제는 항산화제, 가려움 방지제, 셀룰라이트 방지제, 흉터 방지제, 항염증제, 마취제, 자극방지제, 혈관수축제, 혈관확장제, 출혈방지제 유사 지혈제 또는 항섬유소 용해제, 박리제, 팽창제, 여드름 방지제, 색소침착 작용제, 색소침착 방지제 또는 보습제를 포함하지만, 이들로 제한되지 않는다. The hydrogel compositions disclosed herein may further include other agents or combinations of agents that provide beneficial effects when the composition is administered to a subject. Such advantageous agents are antioxidants, anti-itch agents, anti-cellulite agents, anti-scar agents, anti-inflammatory agents, anesthetics, anti-irritants, vasoconstrictors, vasodilators, anti-bleeding agents-like hemostatic agents or anti-fibrin dissolving agents, exfoliating agents, swelling agents, anti-acne agents, pigmentation agents. , Anti-pigmentation agents or moisturizing agents.
본 명세서의 목적을 위해, 달리 언급되지 않는다면, 제형에서 "%"는 중량/중량(즉,w/w) 백분율로서 정의된다. For the purposes of this specification, unless stated otherwise, "%" in the formulation is defined as a weight/weight (ie, w/w) percentage.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 마취제를 선택적으로 포함할 수 있는 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 제공한다. 마취제는 바람직하게는 국소 마취제, 즉, 가역적 국소 마취 및 침해수용의 상실을 야기하는 마취제, 예를 들어, 아미노아마이드 국소 마취제 및 아미노에스터 국소 마취제이다. 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물에 포함된 마취제의 양은 조성물의 투여 시 개체에 의해 경험되는 통증을 완화시키는데 효과적인 양이다. 이와 같이, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물에 포함된 마취제의 양은전체 조성물의 중량으로 약 0.1중량% 내지 약 5중량%이다. 마취제의 비제한적 예는 리도카인, 암부카인, 아몰라논, 아밀로카인, 베녹시네이트, 벤조카인, 베톡시카인, 비펜아민, 부피바카인, 부타카인, 부탐벤, 부타닐리카인, 부테타민, 부톡시카인, 카르티카인, 클로로프로카인, 코코에틸렌, 코카인, 사이클로메티카인, 디부카인, 디메티소퀸, 디메소카인, 디페로돈, 다이사이클로나인, 유프로신, 페날코민, 포모카인, 헥실카인, 하이드록시테트라카인, 아이소뷰틸 p-아미노벤조에이트, 류시노카인 메실레이트, 레복사드롤, 리도카인, 메피바카인, 메프릴카인, 메타뷰톡시카인, 염화메틸, 미르테카인, 나에파인, 옥타카인, 오쏘카인, 옥세타자인, 파르에톡시카인, 페나카인, 페놀, 피페로카인, 피리도카인, 폴리도카놀, 프라목신, 프릴로카인, 프로카인, 프로파노카인, 프로파라카인, 프로피포카인, 프로폭시카인, 슈도코카인, 피로카인, 로피바카인, 살리실 알코올, 테트라카인, 톨리카인, 트리메카인, 졸라민, 이들의 조합 및 이들의 염을 포함한다. 아미노에스터 국소 마취제의 비제한적 예는 프로카인, 클로로프로카인, 코카인, 사이클로메티카인, 시메토카인(라로카인), 프로폭시카인, 프로카인(노보카인), 프로파라카인, 테트라카인(아메토카인)을 포함한다. 아미노아마이드 국소 마취제의 비제한적 예는 아르티카인, 부피바카인, 신쵸카인(다이부카인), 에티도카인, 레보부피바카인, 리도카인(리그노카인), 메피바카인, 피페로카인, 프릴로카인, 로피바카인 및 트라이메카인을 포함한다. 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 단일 마취제 또는 다수의 마취제를 포함할 수 있다. 국소 마취제의 비제한적 예는 리도카인/프릴로카인(EMLA)이다.Aspects of the present specification provide a hydrogel composition disclosed herein that may optionally include an anesthetic agent in part. The anesthetic agent is preferably a local anesthetic, i.e., an anesthetic that causes a loss of reversible local anesthesia and nociception, for example aminoamide local anesthetics and aminoester local anesthetics. The amount of anesthetic agent included in the composition disclosed herein is an amount effective to relieve pain experienced by an individual upon administration of the composition. As such, the amount of anesthetic agent contained in the composition disclosed herein is from about 0.1% to about 5% by weight of the total composition. Non-limiting examples of anesthetics include lidocaine, ambucaine, amolaone, amilocaine, benoxynate, benzocaine, bethoxycaine, biphenamine, bupivacaine, butacaine, butamben, butanilicaine, butetamine, Butoxycaine, Carticaine, Chloroprocaine, Cocoethylene, Cocaine, Cyclomethicine, Dibucaine, Dimethisoquine, Dimethocaine, Diperodone, Dicyclonaine, Euprosine, Phenalcomine, Formokine, Hexyl Caine, hydroxytetracaine, isobutyl p-aminobenzoate, leucinocaine mesylate, reboxadrol, lidocaine, mepivacaine, meprilcaine, metabutoxycaine, methyl chloride, mirtecaine, naepine , Octacaine, orthocaine, oxetazine, parethoxycaine, phenakaine, phenol, piperocaine, pyridocaine, polydocanol, pramoxine, prilocaine, procaine, propanocaine, proparacaine, Propiocaine, propoxycaine, pseudococaine, pyrocaine, ropivacaine, salicyl alcohol, tetracaine, tolicaine, trimecaine, zolamin, combinations thereof, and salts thereof. Non-limiting examples of aminoester local anesthetics include procaine, chloroprocaine, cocaine, cyclomethicine, cytokine (larocaine), propoxycaine, procaine (novocaine), proparacaine, tetracaine (ame. Tocaine). Non-limiting examples of aminoamide local anesthetics include articaine, bupivacaine, synchocaine (dibucaine), etidocaine, levobupivacaine, lidocaine (lignocaine), mepivacaine, piperocaine, prill. Locaine, ropivacaine and trimecaine. The compositions disclosed herein may include a single anesthetic agent or multiple anesthetic agents. A non-limiting example of a local anesthetic is lidocaine/prilocaine (EMLA).
따라서 실시형태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 마취제 및 이의 염을 포함한다. 이 실시형태의 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 아미노아마이드 국소 마취제 및 이의 염 또는 아미노에스터 국소 마취제 및 이의 염을 포함한다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 프로카인, 클로로프로카인, 코카인, 사이클로메티카인, 시메토카인, 프로폭시카인, 프로카인, 프로파라카인, 테트라카인, 또는 이들의 염 또는 이들의 임의의 조합을 포함한다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 아티카인, 부피바카인, 신쵸카인, 에티도카인, 레보부피바카인, 리도카인, 메피바카인, 피페로카인, 프릴로카인, 로피바카인, 트라이메카인, 또는 이들의 염 또는 이들의 임의의 조합을 포함한다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 리도카인/프릴로카인 조합을 포함한다.Thus, in an embodiment, a composition disclosed herein comprises an anesthetic agent and salts thereof. In an aspect of this embodiment, the compositions disclosed herein comprise an aminoamide local anesthetic and salts thereof or an aminoester local anesthetic and salts thereof. In another aspect of this embodiment, the composition disclosed herein is procaine, chloroprocaine, cocaine, cyclomethicine, cytokine, propoxycaine, procaine, proparacaine, tetracaine, or salts thereof, or And any combination of these. In another aspect of this embodiment, the compositions disclosed herein are Articaine, Bupivacaine, Synchocaine, Etidocaine, Levobupivacaine, Lidocaine, Mepivacaine, Piperocaine, Prilocaine, Ropivaca Phosphorus, trimecaine, or salts thereof or any combination thereof. In another aspect of this embodiment, the composition disclosed herein comprises a lidocaine/prilocaine combination.
이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 전체 조성물의, 예를 들어, 약 0.1중량%, 약 0.2중량%, 약 0.3중량%, 약 0.4중량%, 약 0.5중량%, 약 0.6중량%, 약 0.7중량%, 약 0.8중량%, 약 0.9중량%, 약 1.0중량%, 약 2.0중량%, 약 3.0중량%, 약 4.0중량%, 약 5.0중량%, 약 6.0중량%, 약 7.0중량%, 약 8.0중량%, 약 9.0중량%, 또는 약 10중량%의 양으로 마취제를 포함한다. 또 다른 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 전체 조성물의, 예를 들어 적어도 0.1중량%, 적어도 0.2중량%, 적어도 0.3중량%, 적어도 0.4중량%, 적어도 0.5중량%, 적어도 0.6중량%, 적어도 0.7중량%, 적어도 0.8중량% 적어도 0.9중량%, 적어도 1.0중량%, 적어도 2.0중량%, 적어도 3.0중량%, 적어도 4.0중량%, 적어도 5.0중량%, 적어도 6.0중량%, 적어도 7.0중량%, 적어도 8.0중량%, 적어도 9.0중량% 또는 적어도 10중량%의 양으로 마취제를 포함한다. 또 다른 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 전체 조성물의, 예를 들어 최대 0.1중량%, 최대 0.2중량%, 최대 0.3중량%, 최대 0.4중량%, 최대 0.5중량%, 최대 0.6중량%, 최대 0.7중량%, 최대 0.8중량% 최대 0.9중량%, 최대 1.0중량%, 최대 2.0중량%, 최대 3.0중량%, 최대 4.0중량%, 최대 5.0중량%, 최대 6.0중량%, 최대 7.0중량%, 최대 8.0중량%, 최대 9.0중량%, 또는 최대 10중량%의 양으로 마취제를 포함한다. 추가 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 전체 조성물의, 예를 들어, 약 0.1중량% 내지 약 0.5중량%, 약 0.1중량% 내지 약 1.0중량%, 약 0.1중량% 내지 약 2.0중량%, 약 0.1중량% 내지 약 3.0중량%, 약 0.1중량% 내지 약 4.0중량%, 약 0.1중량% 내지 약 5.0중량%, 약 0.2중량% 내지 약 0.9중량%, 약 0.2중량% 내지 약 1.0중량%, 약 0.2중량% 내지 약 2.0중량%, 약 0.5중량% 내지 약 1.0중량%, 또는 약 0.5중량% 내지 약 2.0중량%의 양으로 마취제를 포함한다.In another aspect of this embodiment, the composition disclosed herein comprises, for example, about 0.1%, about 0.2%, about 0.3%, about 0.4%, about 0.5%, about 0.6% by weight of the total composition. %, about 0.7%, about 0.8%, about 0.9%, about 1.0%, about 2.0%, about 3.0%, about 4.0%, about 5.0%, about 6.0%, about 7.0% %, about 8.0%, about 9.0%, or about 10% by weight of an anesthetic agent. In another aspect, the composition disclosed herein comprises, for example, at least 0.1%, at least 0.2%, at least 0.3%, at least 0.4%, at least 0.5%, at least 0.6%, at least 0.7% by weight of the total composition. Wt%, at least 0.8 wt%, at least 0.9 wt%, at least 1.0 wt%, at least 2.0 wt%, at least 3.0 wt%, at least 4.0 wt%, at least 5.0 wt%, at least 6.0 wt%, at least 7.0 wt%, at least 8.0 wt% %, at least 9.0% or at least 10% by weight of an anesthetic agent. In another embodiment, the composition disclosed herein comprises a total composition of, for example, at most 0.1%, at most 0.2%, at most 0.3%, at most 0.4%, at most 0.5%, at most 0.6%, at most 0.7 Wt%, max 0.8 wt% max 0.9 wt%, max 1.0 wt%, max 2.0 wt%, max 3.0 wt%, max 4.0 wt%, max 5.0 wt%, max 6.0 wt%, max 7.0 wt%, max 8.0 wt %, up to 9.0% by weight, or up to 10% by weight of an anesthetic agent. In a further aspect, the composition disclosed herein comprises, for example, about 0.1% to about 0.5%, about 0.1% to about 1.0%, about 0.1% to about 2.0%, about 0.1% by weight of the total composition. Wt% to about 3.0 wt%, about 0.1 wt% to about 4.0 wt%, about 0.1 wt% to about 5.0 wt%, about 0.2 wt% to about 0.9 wt%, about 0.2 wt% to about 1.0 wt%, about 0.2 An anesthetic agent in an amount of from about 0.5% to about 1.0%, or from about 0.5% to about 2.0% by weight.
다른 실시형태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 마취제를 포함하지 않는다.In other embodiments, the compositions disclosed herein do not include an anesthetic agent.
본 발명의 일 양태에서, 중합체, 예를 들어, 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체, 예를 들어 하이알루론산 중합체, 예를 들어, 적어도 일부가 가교된 하이알루론산, 및 중합체와 조합된 첨가제 또는 유리한 작용제를 포함하는 주사용 진피 필러가 제공된다.In one aspect of the invention, a polymer, e.g., a glycosaminoglycan polymer, e.g. a hyaluronic acid polymer, e.g., hyaluronic acid at least partially crosslinked, and an additive or advantageous agent in combination with the polymer. Dermal fillers for injection are provided.
중합체와 조합된 유리한 작용제는 비타민, 예를 들어, 비타민 C를 포함할 수 있다. 비타민 C의 적합한 형태의 비제한적 예는 아스콜브산 및 아스콜브산의 나트륨, 칼륨 및 칼슘 염, 아스콜브산과 장쇄 지방산의 지용성 에스터(아스코빌 팔미테이트 또는 아스코빌 스테아레이트), 마그네슘 아스코빌 포스페이트(MAP), 나트륨 아스코빌 포스페이트(SAP), 및 아스콜브산 2-글루코사이드(AA2G(상표명)), 나트륨 아스코빌 포스페이트(AA2P), 2나트륨 아스코빌 설페이트, 및 아스코빌 3-아미노프로필 포스페이트(비타겐)를 포함한다. Advantageous agents in combination with the polymer may include vitamins such as vitamin C. Non-limiting examples of suitable forms of vitamin C include ascorbic acid and sodium, potassium and calcium salts of ascorbic acid, fat-soluble esters of ascorbic acid and long-chain fatty acids (ascorbyl palmitate or ascorbyl stearate), magnesium ascorbyl phosphate ( MAP), sodium ascorbyl phosphate (SAP), and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside (AA2G (trade name)), sodium ascorbyl phosphate (AA2P), disodium ascorbyl sulfate, and ascorbyl 3-aminopropyl phosphate (vitagen ).
특히 유리한 실시형태에서, 유리한 작용제는 중합체에 공유적으로 컨쥬게이트된다. 예를 들어, 유리한 작용제는 비타민 C, 또는 비타민 C 유도체일 수 있는데, 이는 중합체에 공유적으로 컨쥬게이트되고, 전체 조성물의 약 0.04중량% 내지 약 5.0중량%, 예를 들어 전체 조성물의 약 0.1중량% 내지 약 4.0중량%, 예를 들어 전체 조성물의 약 0.2중량% 내지 약 2.0중량%의 양으로 조성물 중에 존재한다. 일 실시형태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물 중에 포함된 비타민 C의 양은 전체 조성물의 약 0.3중량% 내지 약 1.2중량%이다.In a particularly advantageous embodiment, the advantageous agent is covalently conjugated to the polymer. For example, the beneficial agent may be vitamin C, or a vitamin C derivative, which is covalently conjugated to the polymer and is from about 0.04% to about 5.0% by weight of the total composition, for example about 0.1% by weight of the total composition. % To about 4.0% by weight, for example from about 0.2% to about 2.0% by weight of the total composition. In one embodiment, the amount of vitamin C included in a composition disclosed herein is from about 0.3% to about 1.2% by weight of the total composition.
바람직하게는, 중합체에 공유적으로 컨쥬게이트된 비타민 C는 아스콜브산, L-아스콜브산, L-아스콜브산 2-설페이트(AA-2S) 및 L-아스콜브산 2-포스페이트(AA-2P), 아스콜브산 2-O-글루코사이드 (AA-2G), 6-O-아실-2-O-알파-D-글루코피라노실-L-아스콜브산(6-Acyl-AA-2G), (아스코빌 3-아미노프로필 포스페이트, 아스코빌 팔미테이트), 유도체 및 이들의 유도체 중 적어도 하나를 포함한다. 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 단일 비타민 C 작용제 또는 다수의 비타민 C 작용제를 포함할 수 있다.Preferably, vitamin C covalently conjugated to the polymer is ascorbic acid, L-ascorbic acid, L-ascorbic acid 2-sulfate (AA-2S) and L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (AA- 2P), ascorbic acid 2-O-glucoside (AA-2G), 6-O-acyl-2-O-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-L-ascorbic acid (6-Acyl-AA-2G), (Ascorbyl 3-aminopropyl phosphate, ascorbyl palmitate), derivatives, and at least one of derivatives thereof. The compositions disclosed herein may include a single vitamin C agent or multiple vitamin C agents.
본 발명의 다른 실시형태에서, 진피 필러가 제공되되, 하이알루론산은 BDDE와 가교된다. 이 실시형태에서, 컨쥬게이션 정도는 약 3㏖% 내지 약 10㏖, 내지 약 15㏖% 내지 약 40㏖%일 수 있다.In another embodiment of the present invention, a dermal filler is provided, wherein the hyaluronic acid is crosslinked with BDDE. In this embodiment, the degree of conjugation may be from about 3 mol% to about 10 mol%, and from about 15 mol% to about 40 mol%.
일부 실시형태에서, 진피 필러는 지속된 생체이용가능성을 가진다. 예를 들어, 인간의 피부에 도입될 때, 적어도 약 1개월 내지 약 20개월 이상까지 동안 아스콜브산 또는 다른 비타민이 인간에 방출되는데 효과적인 진피 필러가 제공된다.In some embodiments, the dermal filler has sustained bioavailability. For example, when introduced into human skin, dermal fillers are provided that are effective for the release of ascorbic acid or other vitamins to humans for at least about 1 month to about 20 months or more.
본 발명의 양태는, 부분적으로 복소 탄성률(complex modulus), 탄성률(elastic modulus), 점성률(viscous modulus) 및/또는 tan δ를 나타내는 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 제공한다. 본 명세서에 개시된 바와 같은 조성물은 점탄성이며, 즉, 조성물은 힘이 적용될 때(응력, 변형) 탄성 성분(고체 유사, 예를 들어 가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체) 및 점성 성분(액체 유사, 예를 들어 미가교된 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체 또는 담체상)을 가진다. 이 특성을 설명하는 유동학적 속성은 복소 탄성률(G*)인데, 이는 변형에 대한 조성물의 전체 저항을 정의한다. 복소 탄성률은 실제 및 가상적 부분을 지니는 복소수이다: G*=G'+iG". G*의 절대값은 Abs(G*) = Sqrt(G'2+G"2)이다. 복소 탄성률은 탄성률(G')과 점성률(G")의 합으로서 정의될 수 있다. 문헌[Falcone, et al., Temporary Polysaccharide Dermal Fillers: A Model for Persistence Based on Physical Properties, Dermatol Surg. 35(8): 1238-1243 (2009); Tezel, 상기 참조, 2008; Kablik, 상기 참조, 2009; Beasley, 상기 참조, 2009]; 이들 각각은 전문이 본 명세서에 참조로서 포함된다.Aspects of the present invention provide a hydrogel composition disclosed herein that partially exhibits a complex modulus, an elastic modulus, a viscous modulus, and/or tan δ. The composition as disclosed herein is viscoelastic, i.e. the composition is an elastic component (solid-like, e.g. crosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer) and a viscous component (liquid-like, strain) when a force is applied For example uncrosslinked glycosaminoglycan polymer or carrier phase). The rheological property that explains this property is the complex modulus (G*), which defines the overall resistance of the composition to deformation. The complex modulus of elasticity is a complex number with real and imaginary parts: G*=G'+iG". The absolute value of G* is Abs(G*) = Sqrt(G' 2 +G" 2 ). The complex modulus can be defined as the sum of the modulus of elasticity (G') and the modulus of viscosity (G"). Falcone, et al., Temporary Polysaccharide Dermal Fillers: A Model for Persistence Based on Physical Properties , Dermatol Surg. 35 ( 8): 1238-1243 (2009); Tezel, supra, 2008; Kablik, supra, 2009; Beasley, supra, 2009]; each of which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.
탄성률 또는 탄성 계수는 힘이 물체에 적용될 때, 변형 또는 반대로 비영구적으로 변형되는 물체의 경향에 저항하는 하이드로겔 물질의 능력을 지칭한다. 탄성률은 조성물의 굳기를 특징으로 하며, 또한 저장 탄성률(storage modulus)로서 알려져 있는데, 그것이 조성물의 이동으로부터 에너지의 저장을 설명하기 때문이다. 탄성률은 탄성과 강도 사이의 상호작용(G' = 응력/변형)을 설명하며, 이와 같이, 조성물의 경도 또는 연화의 정량적 측정을 제공한다. 물체의 탄성률은 탄성 변형 영역에서 그것의 응력-변형 곡선의 기울기로서 정의된다: λ = 응력/변형, 여기서 λ는 탄성률(파스칼)이며; 응력은 힘이 적용되는 영역으로 나눈 변형을 야기하는 힘이고; 변형은 응력에 의해 야기되는 변화 대 물체의 본래 상태의 비이다. 힘이 적용되는 속도에 의존함에도 불구하고, 더 강성인 조성물은 더 높은 탄성률을 가질 것이며, 예를 들어 주사와 같이 제공된 거리로 물질을 변형시키는데 더 큰 힘을 취할 것이다. 방향을 포함하여 응력이 측정되는 방법을 구체화하는 것은 다수 유형의 탄성률이 정의되게 한다. 3가지의 주된 탄성률은 인장탄성률, 전단탄성률 및 체적탄성률이다.The modulus or modulus of elasticity refers to the ability of a hydrogel material to resist the tendency of an object to deform or, conversely, non-permanently deform when a force is applied to the object. The modulus of elasticity is characterized by the stiffness of the composition, and is also known as the storage modulus, as it accounts for the storage of energy from movement of the composition. The modulus of elasticity describes the interaction between elasticity and strength (G' = stress/strain) and, as such, provides a quantitative measure of the hardness or softening of the composition. The modulus of elasticity of an object is defined as the slope of its stress-strain curve in the elastically deformed region: λ = stress/strain, where λ is the modulus of elasticity (Pascal); Stress is the force that causes the deformation divided by the area to which the force is applied; Deformation is the ratio of the change caused by stress to the original state of an object. Despite the dependence of the speed at which the force is applied, a stiffer composition will have a higher modulus of elasticity and will take a greater force to deform the material over a given distance, for example by injection. Specifying how the stress, including direction, is measured allows many types of modulus to be defined. The three main modulus are tensile modulus, shear modulus and volume modulus.
점성률은 또한 손실률로서 알려져 있는데, 이는 점성 소멸로서 상실된 에너지를 설명하기 때문이다. Tan δ는 점성률과 탄성률의 비이다, tan δ = G"/G'. 문헌[Falcone, 상기 참조, 2009]. 본 명세서에 개시된 tan δ 값에 대해, tan δ는 1Hz의 주파수에서 동적 탄성률에서 얻어진다. 더 낮은 tan δ는 더 강성, 더 경질 또는 더 탄성인 조성물에 대응된다. The viscous modulus is also known as the loss rate, as it accounts for the energy lost as viscous dissipation. Tan δ is the ratio of the viscous modulus and the elastic modulus, tan δ = G"/G'. Falcone, supra, 2009. For the tan δ values disclosed herein, tan δ is the dynamic modulus at a frequency of 1 Hz. A lower tan δ corresponds to a stiffer, harder or more elastic composition.
다른 실시형태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 탄성률을 나타내지 않는다. 이 실시형태의 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 약 25㎩, 약 50㎩, 약 75㎩, 약 100㎩, 약 125㎩, 약 150㎩, 약 175㎩, 약 200㎩, 약 250㎩, 약 300㎩, 약 350㎩, 약 400㎩, 약 450㎩, 약 500㎩, 약 550㎩, 약 600㎩, 약 650㎩, 약 700㎩, 약 750㎩, 약 800㎩, 약 850㎩, 약 900㎩, 약 950㎩, 약 1,000㎩, 약 1,200㎩, 약 1,300㎩, 약 1,400㎩, 약 1,500㎩, 약 1,600㎩, 약 1700㎩, 약 1800㎩, 약 1900㎩, 약 2,000㎩, 약 2,100㎩, 약 2,200㎩, 약 2,300㎩, 약 2,400 Pa, 또는 약 2,500㎩의 탄성률을 나타낸다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어 적어도 25㎩, 적어도 50㎩, 적어도 75㎩, 적어도 100㎩, 적어도 125㎩, 적어도 150㎩, 적어도 175㎩, 적어도 200㎩, 적어도 250㎩, 적어도 300㎩, 적어도 350㎩, 적어도 400㎩, 적어도 450㎩, 적어도 500㎩, 적어도 550㎩, 적어도 600㎩, 적어도 650㎩, 적어도 700㎩, 적어도 750㎩, 적어도 800㎩, 적어도 850㎩, 적어도 900㎩, 적어도 950㎩, 적어도 1,000㎩, 적어도 1,200㎩, 적어도 1,300㎩, 적어도 1,400㎩, 적어도 1,500㎩, 적어도 1,600㎩, 적어도 1700㎩, 적어도 1800㎩, 적어도 1900㎩, 적어도 2,000㎩, 적어도 2,100㎩, 적어도 2,200㎩, 적어도 2,300㎩, 적어도 2,400㎩ 또는 적어도 2,500㎩의 탄성률을 나타낸다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 최대 25㎩, 최대 50㎩, 최대 75㎩, 최대 100㎩, 최대 125㎩, 최대 150㎩, 최대 175㎩, 최대 200㎩, 최대 250㎩, 최대 300㎩, 최대 350㎩, 최대 400㎩, 최대 450㎩, 최대 500㎩, 최대 550㎩, 최대 600㎩, 최대 650㎩, 최대 700㎩, 최대 750㎩, 최대 800㎩, 최대 850㎩, 최대 900㎩, 최대 950㎩, 최대 1,000㎩, 최대 1,200㎩, 최대 1,300㎩, 최대 1,400㎩, 최대 1,500㎩, 또는 최대 1,600㎩의 탄성률을 나타낸다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 약 25㎩ 내지 약 150㎩, 약 25㎩ 내지 약 300㎩, 약 25㎩ 내지 약 500㎩, 약 25㎩ 내지 약 800㎩, 약 125㎩ 내지 약 300㎩, 약 125㎩ 내지 약 500㎩, 약 125㎩ 내지 약 800㎩, 약 500㎩ 내지 약 1,600㎩, 약 600㎩ 내지 약 1,600㎩, 약 700㎩ 내지 약 1,600㎩, 약 800㎩ 내지 약 1,600㎩, 약 900㎩ 내지 약 1,600㎩, 약 1,000㎩ 내지 약 1,600㎩, 약 1,100㎩ 내지 약 1,600㎩, 약 1,200㎩ 내지 약 1,600㎩, 약 500㎩ 내지 약 2,500㎩, 약 1,000㎩ 내지 약 2,500㎩, 약 1,500㎩ 내지 약 2,500㎩, 약 2,000㎩ 내지 약 2,500㎩, 약 1,300㎩ 내지 약 1,600㎩, 약 1,400㎩ 내지 약 1,700㎩, 약 1,500㎩ 내지 약 1,800㎩, 약 1,600㎩ 내지 약 1,900㎩, 약 1,700㎩ 내지 약 2,000㎩, 약 1,800㎩ 내지 약 2,100㎩, 약 1,900㎩ 내지 약 2,200㎩, 약 2,000㎩ 내지 약 2,300㎩, 약 2,100㎩ 내지 약 2,400㎩, 또는 약 2,200㎩ 내지 약 2,500㎩의 탄성률을 나타낸다.In other embodiments, the compositions disclosed herein do not exhibit an elastic modulus. In aspects of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, about 25 Pa, about 50 Pa, about 75 Pa, about 100 Pa, about 125 Pa, about 150 Pa, about 175 Pa, about 200 Pa, about 250 Pa, about 300 Pa, about 350 Pa, about 400 Pa, about 450 Pa, about 500 Pa, about 550 Pa, about 600 Pa, about 650 Pa, about 700 Pa, about 750 Pa, about 800 Pa, about 850 Pa, About 900 Pa, about 950 Pa, about 1,000 Pa, about 1,200 Pa, about 1,300 Pa, about 1,400 Pa, about 1,500 Pa, about 1,600 Pa, about 1700 Pa, about 1800 Pa, about 1900 Pa, about 2,000 Pa, about 2,100 It exhibits an elastic modulus of Pa, about 2,200 Pa, about 2,300 Pa, about 2,400 Pa, or about 2,500 Pa. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, at least 25 Pa, at least 50 Pa, at least 75 Pa, at least 100 Pa, at least 125 Pa, at least 150 Pa, at least 175 Pa, at least 200 Pa, at least 250 Pa, at least 300 Pa, at least 350 Pa, at least 400 Pa, at least 450 Pa, at least 500 Pa, at least 550 Pa, at least 600 Pa, at least 650 Pa, at least 700 Pa, at least 750 Pa, at least 800 Pa, at least 850 Pa, At least 900 Pa, at least 950 Pa, at least 1,000 Pa, at least 1,200 Pa, at least 1,300 Pa, at least 1,400 Pa, at least 1,500 Pa, at least 1,600 Pa, at least 1700 Pa, at least 1800 Pa, at least 1900 Pa, at least 2,000 Pa, at least 2,100 It exhibits an elastic modulus of Pa, at least 2,200 Pa, at least 2,300 Pa, at least 2,400 Pa, or at least 2,500 Pa. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, at most 25 Pa, at most 50 Pa, at most 75 Pa, at most 100 Pa, at most 125 Pa, at most 150 Pa, at most 175 Pa, at most 200 Pa, Max 250Pa, Max 300Pa, Max 350Pa, Max 400Pa, Max 450Pa, Max 500Pa, Max 550Pa, Max 600Pa, Max 650Pa, Max 700Pa, Max 750Pa, Max 800Pa, Max 850 It represents an elastic modulus of Pa, maximum 900 Pa, maximum 950 Pa, maximum 1,000 Pa, maximum 1,200 Pa, maximum 1,300 Pa, maximum 1,400 Pa, maximum 1,500 Pa, or maximum 1,600 Pa. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, from about 25 Pa to about 150 Pa, from about 25 Pa to about 300 Pa, from about 25 Pa to about 500 Pa, from about 25 Pa to about 800 Pa, About 125 Pa to about 300 Pa, about 125 Pa to about 500 Pa, about 125 Pa to about 800 Pa, about 500 Pa to about 1,600 Pa, about 600 Pa to about 1,600 Pa, about 700 Pa to about 1,600 Pa, about 800 Pa to about 1,600 Pa, from about 900 Pa to about 1,600 Pa, from about 1,000 Pa to about 1,600 Pa, from about 1,100 Pa to about 1,600 Pa, from about 1,200 Pa to about 1,600 Pa, from about 500 Pa to about 2,500 Pa, from about 1,000 Pa to about 1,000 Pa About 2,500 Pa, about 1,500 Pa to about 2,500 Pa, about 2,000 Pa to about 2,500 Pa, about 1,300 Pa to about 1,600 Pa, about 1,400 Pa to about 1,700 Pa, about 1,500 Pa to about 1,800 Pa, about 1,600 Pa to about 1,900 Pa, about 1,700 Pa to about 2,000 Pa, about 1,800 Pa to about 2,100 Pa, about 1,900 Pa to about 2,200 Pa, about 2,000 Pa to about 2,300 Pa, about 2,100 Pa to about 2,400 Pa, or about 2,200 Pa to about 2,500 Pa Represents the modulus of elasticity.
다른 실시형태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 점성률을 나타내지 않는다. 이 실시형태의 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 약 10㎩, 약 20㎩, 약 30㎩, 약 40㎩, 약 50㎩, 약 60㎩, 약 70㎩, 약 80㎩, 약 90㎩, 약 100㎩, 약 150㎩, 약 200㎩, 약 250㎩, 약 300㎩, 약 350㎩, 약 400㎩, 약 450㎩, 약 500㎩, 약 550㎩, 약 600㎩, 약 650㎩, 또는 약 700㎩의 점성률을 나타낸다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 최대 10㎩, 최대 20㎩, 최대 30㎩, 최대 40㎩, 최대 50㎩, 최대 60㎩, 최대 70㎩, 최대 80㎩, 최대 90㎩, 최대 100㎩, 최대 150㎩, 최대 200㎩, 최대 250㎩, 최대 300㎩, 최대 350㎩, 최대 400㎩, 최대 450㎩, 최대 500㎩, 최대 550㎩, 최대 600㎩, 최대 650㎩ 또는 최대 700㎩의 점성률을 나타낸다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 약 10㎩ 내지 약 30㎩, 약 10㎩ 내지 약 50㎩, 약 10㎩ 내지 약 100㎩, 약 10㎩ 내지 약 150㎩, 약 70㎩ 내지 약 100㎩, 약 50㎩ 내지 약 350㎩, 약 150㎩ 내지 약 450㎩, 약 250㎩ 내지 약 550㎩, 약 350㎩ 내지 약 700㎩, 약 50㎩ 내지 약 150㎩, 약 100㎩ 내지 약 200㎩, 약 150㎩ 내지 약 250㎩, 약 200㎩ 내지 약 300㎩, 약 250㎩ 내지 약 350㎩, 약 300㎩ 내지 약 400㎩, 약 350㎩ 내지 약 450㎩, 약 400㎩ 내지 약 500㎩, 약 450㎩ 내지 약 550㎩, 약 500㎩ 내지 약 600㎩, 약 550㎩ 내지 약 650㎩, 또는 약 600㎩ 내지 약 700㎩의 점성률을 나타낸다.In other embodiments, the compositions disclosed herein do not exhibit a viscosity modulus. In aspects of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, about 10 Pa, about 20 Pa, about 30 Pa, about 40 Pa, about 50 Pa, about 60 Pa, about 70 Pa, about 80 Pa, about 90 Pa, about 100 Pa, about 150 Pa, about 200 Pa, about 250 Pa, about 300 Pa, about 350 Pa, about 400 Pa, about 450 Pa, about 500 Pa, about 550 Pa, about 600 Pa, about 650 Pa, Or it shows a viscosity of about 700 Pa. In other aspects of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, at most 10 Pa, at most 20 Pa, at most 30 Pa, at most 40 Pa, at most 50 Pa, at most 60 Pa, at most 70 Pa, at most 80 Pa, at most. 90Pa, Max 100Pa, Max 150Pa, Max 200Pa, Max 250Pa, Max 300Pa, Max 350Pa, Max 400Pa, Max 450Pa, Max 500Pa, Max 550Pa, Max 600Pa, Max 650Pa Or, it shows a viscosity modulus of up to 700 Pa. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, about 10 Pa to about 30 Pa, about 10 Pa to about 50 Pa, about 10 Pa to about 100 Pa, about 10 Pa to about 150 Pa, About 70 Pa to about 100 Pa, about 50 Pa to about 350 Pa, about 150 Pa to about 450 Pa, about 250 Pa to about 550 Pa, about 350 Pa to about 700 Pa, about 50 Pa to about 150 Pa, about 100 Pa to about 200 Pa, about 150 Pa to about 250 Pa, about 200 Pa to about 300 Pa, about 250 Pa to about 350 Pa, about 300 Pa to about 400 Pa, about 350 Pa to about 450 Pa, about 400 Pa It exhibits a viscosity modulus of about 500 Pa, about 450 Pa to about 550 Pa, about 500 Pa to about 600 Pa, about 550 Pa to about 650 Pa, or about 600 Pa to about 700 Pa.
다른 실시형태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 tan δ를 나타낸다. 이 실시형태의 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 약 0.1, 약 0.2, 약 0.3, 약 0.4, 약 0.5, 약 0.6, 약 0.7, 약 0.8, 약 0.9, 약 1.0, 약 1.1, 약 1.2, 약 1.3, 약 1.4, 약 1.5, 약 1.6, 약 1.7, 약 1.8, 약 1.9, 약 2.0, 약 2.1, 약 2.2, 약 2.3, 약 2.4, 또는 약 2.5의 tan δ를 나타낸다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 최대 0.1, 최대 0.2, 최대 0.3, 최대 0.4, 최대 0.5, 최대 0.6, 최대 0.7, 최대 0.8, 최대 0.9, 최대 1.0, 최대 1.1, 최대 1.2, 최대 1.3, 최대 1.4, 최대 1.5, 최대 1.6, 최대 1.7, 최대 1.8, 최대 1.9, 최대 2.0, 최대 2.1, 최대 2.2, 최대 2.3, 최대 2.4 또는 최대 2.5의 tan δ를 나타낸다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 약 0.1 내지 약 0.3, 약 0.3 내지 약 0.5, 약 0.5 내지 약 0.8, 약 1.1 내지 약 1.4, 약 1.4 내지 약 1.7, 약 0.3 내지 약 0.6, 약 0.1 내지 약 0.5, 약 0.5 내지 약 0.9, 약 0.1 내지 약 0.6, 약 0.1 내지 약 1.0, 약 0.5 내지 약 1.5, 약 1.0 내지 약 2.0, 또는 약 1.5 내지 약 2.5의 tan δ를 나타낸다. In another embodiment, a hydrogel composition disclosed herein exhibits tan δ. In aspects of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, about 0.1, about 0.2, about 0.3, about 0.4, about 0.5, about 0.6, about 0.7, about 0.8, about 0.9, about 1.0, about 1.1, about 1.2, about 1.3, about 1.4, about 1.5, about 1.6, about 1.7, about 1.8, about 1.9, about 2.0, about 2.1, about 2.2, about 2.3, about 2.4, or about 2.5. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, at most 0.1, at most 0.2, at most 0.3, at most 0.4, at most 0.5, at most 0.6, at most 0.7, at most 0.8, at most 0.9, at most 1.0, at most 1.1, A tan δ of 1.2 max, 1.3 max, 1.4 max, 1.5 max, 1.6 max, 1.7 max, 1.8 max, 1.9 max, 2.0 max, 2.1 max, 2.2 max, 2.3 max, 2.4 max or 2.5 max. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, about 0.1 to about 0.3, about 0.3 to about 0.5, about 0.5 to about 0.8, about 1.1 to about 1.4, about 1.4 to about 1.7, about 0.3 To about 0.6, about 0.1 to about 0.5, about 0.5 to about 0.9, about 0.1 to about 0.6, about 0.1 to about 1.0, about 0.5 to about 1.5, about 1.0 to about 2.0, or about 1.5 to about 2.5 Show.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 투명도 및/또는 반투명도를 갖는 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 제공한다. 광학적 투명도는 가시광선이 물질을 통과할 수 있게 하는 물리적 특성인 반면, 반투명도(또한 반투명 또는 반투명성으로 불림)는 단지 빛이 분산되어 통과하게 한다. 반대의 특성은 불투명이다. 투명한 재료는 맑은 반면 백색의 반투명한 재료는 깨끗하게 볼 수 없다. 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔은 바람직하게는 광학적으로 투명하거나 또는 적어도 반투명이다. Aspects of the present specification provide a hydrogel composition disclosed herein having partially transparency and/or translucency. Optical transparency is a physical property that allows visible light to pass through a material, whereas translucency (also called translucency or translucency) only allows light to diffuse through. The opposite characteristic is opaque. Transparent materials are clear, while white translucent materials cannot be seen clearly. The hydrogels disclosed herein are preferably optically transparent or at least translucent.
실시형태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 광학적으로 반투명이다. 이 실시형태의 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 약 75%의 빛, 약 80%의 빛, 약 85%의 빛, 약 90%의 빛, 약 95%의 빛, 또는 약 100%의 빛을 분산되게 전달한다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 적어도 75%의 빛, 적어도 80%의 빛, 적어도 85%의 빛, 적어도 90%의 빛, 또는 적어도 95%의 빛을 분산되게 전달한다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 약 75% 내지 약 100%의 빛, 약 80% 내지 약 100%의 빛, 약 85% 내지 약 100%의 빛, 약 90% 내지 약 100%의 빛, 또는 약 95% 내지 약 100%의 빛을 분산되게 전달한다. 실시형태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 광학적으로 투명하고, 100%의 가시광선을 전달한다. In an embodiment, the hydrogel composition disclosed herein is optically translucent. In aspects of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, about 75% light, about 80% light, about 85% light, about 90% light, about 95% light, or about 100% Transmits the light of In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is configured to disperse, for example, at least 75% light, at least 80% light, at least 85% light, at least 90% light, or at least 95% light. Deliver. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition comprises, for example, about 75% to about 100% light, about 80% to about 100% light, about 85% to about 100% light, about 90 % To about 100% of light, or about 95% to about 100% of light is transmitted in a diffuse manner In an embodiment, the hydrogel composition disclosed herein is optically transparent and transmits 100% visible light.
본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 추가로 하이드로겔을 입자로 분쇄시킴으로써 처리될 수 있고, 선택적으로, 예를 들어 물 또는 식염수와 같은 담체상과 혼합되어 주사용 또는 국소 물질 유사 용액, 오일, 로션, 겔, 연고, 크림, 슬러리, 고약 또는 페이스트를 형성한다. 이와 같이, 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 단상 또는 다상 조성물일 수 있다. 하이드로겔은 직경이 약 10㎛ 내지 약 1000㎛, 예컨대 약 15㎛ 내지 약 30㎛, 약 50㎛ 내지 약 75㎛, 약 100㎛ 내지 약 150㎛, 약 200㎛ 내지 약 300㎛, 약 450㎛ 내지 약 550㎛, 약 600㎛ 내지 약 700㎛, 약 750㎛ 내지 약 850㎛, 또는 약 900㎛ 내지 약 1,000㎛의 입자 크기로 밀링될 수 있다.The hydrogel composition disclosed herein can be further treated by grinding the hydrogel into particles, and optionally, mixed with a carrier phase such as water or saline, for injection or topical substance-like solutions, oils, lotions, Forms gels, ointments, creams, slurries, plasters or pastes. As such, the disclosed hydrogel composition may be a single phase or a multiphase composition. The hydrogel has a diameter of about 10 μm to about 1000 μm, such as about 15 μm to about 30 μm, about 50 μm to about 75 μm, about 100 μm to about 150 μm, about 200 μm to about 300 μm, about 450 μm to It may be milled to a particle size of about 550 μm, about 600 μm to about 700 μm, about 750 μm to about 850 μm, or about 900 μm to about 1,000 μm.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물이 주사용이라는 것을 제공한다. 본 명세서에 사용된 바와 같은 용어 "주사용"은 미세한 바늘을 지니는 주사 장치를 사용하여 개체의 피부 영역에 조성물을 투여한 필요가 있는 특성을 갖는 물질을 지칭한다. 본 명세서에 사용된 바와 같은 용어 "미세한 바늘"은 27 게이지 이하의 바늘을 지칭한다. 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물의 주사 능력은 상기 논의한 바와 같은 하이드로겔 입자를 크기 조절함으로써 수행될 수 있다.Aspects of the present specification provide, in part, that the compositions disclosed herein are for injection. The term “injectable” as used herein refers to a substance having the properties that require administration of the composition to an area of the subject's skin using an injection device with a fine needle. The term “fine needle” as used herein refers to a needle of 27 gauge or less. The injection ability of the compositions disclosed herein can be accomplished by sizing the hydrogel particles as discussed above.
이 실시형태의 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 미세한 바늘을 통해 주사될 수 있다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 약 27 게이지, 약 30 게이지, 또는 약 32 게이지의 바늘을 통해 주사가능하다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 22 게이지 이하, 27 게이지 이하, 30 게이지 이하, 또는 32 게이지 이하의 바늘을 통해 주사가능하다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어 약 22 게이지 내지 약 35 게이지, 22 게이지 내지 약 34 게이지, 22 게이지 내지 약 33 게이지, 22 게이지 내지 약 32 게이지, 약 22 게이지 내지 약 27 게이지, 또는 약 27 게이지 내지 약 32 게이지의 바늘을 통해 주사가능하다.In an aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition disclosed herein can be injected through a fine needle. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition disclosed herein is injectable through a needle of, for example, about 27 gauge, about 30 gauge, or about 32 gauge. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition disclosed herein is injectable through a needle of, for example, 22 gauge or less, 27 gauge or less, 30 gauge or less, or 32 gauge or less. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition disclosed herein may be, for example, from about 22 gauge to about 35 gauge, from 22 gauge to about 34 gauge, from 22 gauge to about 33 gauge, from 22 gauge to about 32 gauge, It is injectable through a needle of about 22 gauge to about 27 gauge, or about 27 gauge to about 32 gauge.
이 실시형태의 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 100㎜/분의 속도에서 약 60N, 약 55N, 약 50N, 약 45N, 약 40N, 약 35N, 약 30N, 약 25N, 약 20 N, 또는 약 15N의 압출력으로 주사될 수 있다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 약 60N 이하, 약 55N 이하, 약 50N 이하, 약 45N 이하, 약 40N 이하, 약 35N 이하, 약 30N 이하, 약 25N 이하, 약 20N 이하, 약 15N 이하, 약 10N 이하, 또는 약 5N 이하의 압출력을 지니는 27 게이지 바늘을 통해 주사될 수 있다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 약 60N 이하, 약 55N 이하, 약 50N 이하, 약 45N 이하, 약 40N 이하, 약 35N 이하, 약 30N 이하, 약 25N 이하, 약 20N 이하, 약 15N 이하, 약 10N 이하, 또는 약 5N 이하의 압출력을 지니는 30 게이지 바늘을 통해 주사될 수 있다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 약 60N 이하, 약 55N 이하, 약 50N 이하, 약 45N 이하, 약 40N 이하, 약 35N 이하, 약 30N 이하, 약 25N 이하, 약 20N 이하, 약 15N 이하, 약 10N 이하, 또는 약 5N 이하의 압출력을 지니는 32 게이지 바늘을 통해 주사될 수 있다.In an aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition disclosed herein is about 60N, about 55N, about 50N, about 45N, about 40N, about 35N, about 30N, about 25N, about 20N, at a rate of 100 mm/min. Or it can be injected with an extrusion force of about 15 N. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition disclosed herein is about 60N or less, about 55N or less, about 50N or less, about 45N or less, about 40N or less, about 35N or less, about 30N or less, about 25N or less, about 20N or less. It can be injected through a 27 gauge needle with an extrusion force of about 15N or less, about 10N or less, or about 5N or less. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition disclosed herein is about 60N or less, about 55N or less, about 50N or less, about 45N or less, about 40N or less, about 35N or less, about 30N or less, about 25N or less, about It can be injected through a 30 gauge needle with an extrusion force of 20N or less, about 15N or less, about 10N or less, or about 5N or less. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition disclosed herein is about 60N or less, about 55N or less, about 50N or less, about 45N or less, about 40N or less, about 35N or less, about 30N or less, about 25N or less, about It can be injected through a 32 gauge needle with an extrusion force of 20N or less, about 15N or less, about 10N or less, or about 5N or less.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 접착성을 나타내는 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 제공한다. 결합적 응집 인력, 응집력 또는 압축력으로서도 지칭되는 접착성은 재료의 물리적 특성이며, 분자를 통합시키도록 작용하는 물질 내에서 유사 분자 간의 분자간 인력에 의해 야기된다. 접착성은 그램-힘(gmf)에 대해 표현된다. 응집력은, 특히 초기 유리 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체의 분자량비, 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체, 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체의 가교 정도, 가교 후 잔여 유리 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체의 양, 및 하이드로겔 조성물의 pH에 의해 영향받는다. 조성물은 투여 부위에 국소화된 채로 남아 있는 것과 같이 충분하게 응집력이 있어야 한다. 추가적으로, 특정 적용에서, 충분한 응집력은 기계적 부하 주기의 사건에서 조성물에 대해 그것의 형상 및 그에 따른 기능성을 보유하는데 중요하다. 이와 같이, 일 실시형태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 물과 동등한 응집력을 나타낸다. 또 다른 실시형태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 투여 부위에 국소화된 채로 남아있는 충분한 접착성을 나타낸다. 또 다른 실시형태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 그것의 형상을 보유하는데 충분한 접착성을 나타낸다. 추가 실시형태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 그것의 형상 및 기능성을 보유하는데 충분한 접착성을 나타낸다.Aspects of the present specification provide a hydrogel composition disclosed herein that partially exhibits adhesiveness. Adhesion, also referred to as cohesive, cohesive or compressive force, is a physical property of a material, and is caused by the intermolecular attraction between like molecules within a material that acts to unite the molecules. Adhesion is expressed in terms of gram-force (gmf). Cohesive strength, in particular, the molecular weight ratio of the initial free glycosaminoglycan polymer, the degree of crosslinking of the glycosaminoglycan polymer, the glycosaminoglycan polymer, the amount of the remaining free glycosaminoglycan polymer after crosslinking, And the pH of the hydrogel composition. The composition should be sufficiently cohesive, such as remaining localized at the site of administration. Additionally, in certain applications, sufficient cohesive force is important for retaining its shape and hence functionality for the composition in the event of a mechanical loading cycle. As such, in one embodiment, the compositions disclosed herein exhibit a cohesive force equivalent to water. In another embodiment, a hydrogel composition disclosed herein exhibits sufficient adhesion that remains localized at the site of administration. In another embodiment, the hydrogel composition disclosed herein exhibits sufficient adhesion to retain its shape. In a further embodiment, the hydrogel composition disclosed herein exhibits sufficient adhesion to retain its shape and functionality.
본 명세서의 양태는 부분적으로 생리학적으로 허용가능한 오스몰농도를 나타내는 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 제공한다. 본 명세서에 나타내는 바와 같은 용어 "오스몰농도"는 용액 중에서 삼투적으로 활성인 용질의 농도를 지칭한다. 본 명세서에 나타내는 바와 같은 용어 "생리적으로 허용가능한 오스몰농도"는 살아있는 유기체의 정상 기능의 특징 또는 이에 따른 오스몰농도를 지칭한다. 이와 같이, 본 명세서에 개시된 바와 같은 하이드로겔 조성물의 투여는 포유류에 투여될 때 영구적인 유해한 또는 실질적으로 장기간이 아닌 효과를 갖는 오스몰농도를 나타낸다. 오스몰농도는 용매의 리터 당 삼투적으로 활성인 용질의 오스몰에 대해 표현된다(Os㏖/ℓ 또는 Osm/ℓ). 오스몰농도는 몰농도와 별개인데, 그것이 용질의 몰보다 삼투적으로 활성인 용질 입자의 몰을 측정하기 때문이다. 일부 화합물은 용액 중에서 해리될 수 있는 반면, 다른 것들은 그렇지 못할 수 있기 때문에 차이가 생긴다. 용액의 오스몰농도는 다음의 표현으로부터 계산될 수 있다: Os㏖/ℓ = ∑ φi ηi Ci 여기서 φ는 용액의 비이상 정도를 계산하는 삼투계수이며; η는 분자가 해리되는 입자(예를 들어, 이온)의 수이고; C는 용질의 몰 농도이며; i는 특정 용질의 정체를 나타내는 지수이다. 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 오스몰농도는 용액을 처리하는 통상적인 방법을 사용하여 측정될 수 있다.Aspects of the present specification provide, in part, a hydrogel composition disclosed herein that exhibits a physiologically acceptable osmolarity. The term "osmolarity" as used herein refers to the concentration of osmoticly active solute in a solution. The term "physiologically acceptable osmolarity" as referred to herein refers to a characteristic of the normal function of a living organism or the osmolarity accordingly. As such, administration of a hydrogel composition as disclosed herein exhibits an osmolar concentration that has a permanent deleterious or substantially non-long-term effect when administered to a mammal. Osmolarity is expressed in terms of the osmolality of the osmoly active solute per liter of solvent (Osmol/L or Osm/L). Osmolarity is independent of molarity because it measures the moles of solute particles that are osmolytically active rather than the moles of solute. The difference is because some compounds can dissociate in solution, while others may not. The osmolality of a solution can be calculated from the following expression: Osmol/L = ∑ φ i η i C i where φ is the osmotic coefficient that calculates the degree of abnormality of the solution; η is the number of particles (eg, ions) from which the molecule dissociates; C is the molar concentration of the solute; i is an index indicating the identity of a specific solute. The osmolarity of the hydrogel composition disclosed herein can be measured using a conventional method of treating a solution.
실시형태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 생리적으로 허용가능한 오스몰농도를 나타낸다. 본 명세서에 나타내는 바와 같은 용어 "삼투질 농도"는 신체 내 용매의 킬로 당 삼투적으로 활성인 용질의 농도를 지칭한다. 본 명세서에 나타내는 바와 같은 용어 "생리적으로 허용가능한 삼투질 농도"는 살아있는 유기체의 특징 또는 정상 기능에 따른 삼투질 농도를 지칭한다. 이와 같이, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 투여는 포유류에 대해 투여될 때 영구적인 유해한 또는 실질적으로 장기간이 아닌 효과를 갖는 삼투질 농도를 나타낸다. 삼투질 농도는 용매의 킬르그램 당 삼투적으로 활성인 용질의 오스몰에 대해 표현되며(os㏖/㎏ 또는 Osm/㎏), 해당 용액 내 존재하는 모든 용질의 몰랄농도의 합과 동일하다. 용액의 삼투질 농도는 삼투압계를 사용하여 측정될 수 있다. 현대 실험실에서 가장 흔히 사용되는 기기는 빙점 강하 삼투압측정기이다. 이 기기는 삼투질 농도를 증가시킴에 따라 일어나는 빙점의 변화(빙점 강하 삼투압측정기) 또는 삼투질 농도를 증가시킴에 따라 용액 중에서 생기는 수증기압의 변화(수증기압 강하 삼투압측정기)를 측정한다.In an embodiment, a hydrogel composition disclosed herein exhibits a physiologically acceptable osmolarity. The term "osmolar concentration" as used herein refers to the concentration of osmoly active solute per kilo of solvent in the body. The term "physiologically acceptable osmolality" as referred to herein refers to the osmolyte concentration according to the characteristic or normal function of a living organism. As such, administration of the hydrogel composition disclosed herein exhibits an osmotic concentration that has a permanent deleterious or substantially non-long term effect when administered to a mammal. The osmolality is expressed in terms of the osmolality of the osmoly active solute per kilogram of solvent (osmol/kg or Osm/kg), and is equal to the sum of the molar concentrations of all solutes in the solution. The osmolality of the solution can be measured using an osmometer. The most commonly used instrument in modern laboratories is the freezing point drop osmometer. This instrument measures the change in the freezing point that occurs as the osmotic concentration increases (the freezing point drop osmometer) or the change in the water vapor pressure in the solution as the osmotic concentration increases (the water vapor pressure drop osmometer).
이 실시형태의 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 약 100 mOsm/ℓ, 약 150 mOsm/ℓ, 약 200 mOsm/ℓ, 약 250 mOsm/ℓ, 약 300 mOsm/ℓ, 약 350 mOsm/ℓ, 약 400 mOsm/ℓ, 약 450 mOsm/ℓ, 또는 약 500 mOsm/ℓ의 오스몰농도를 나타낸다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 적어도 100 mOsm/ℓ, 적어도 150 mOsm/ℓ, 적어도 200 mOsm/ℓ, 적어도 250 mOsm/ℓ, 적어도 300 mOsm/ℓ, 적어도 350 mOsm/ℓ, 적어도 400 mOsm/ℓ, 적어도 450 mOsm/ℓ 또는 적어도 500 mOsm/ℓ의 오스몰농도를 나타낸다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어 최대 100 mOsm/ℓ, 최대 150 mOsm/ℓ, 최대 200 mOsm/ℓ, 최대 250 mOsm/ℓ, 최대 300 mOsm/ℓ, 최대 350 mOsm/ℓ, 최대 400 mOsm/ℓ, 최대 450 mOsm/ℓ 또는 최대 500 mOsm/ℓ의 오스몰농도를 나타낸다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어 약 100 mOsm/ℓ 내지 약 500 mOsm/ℓ, 약 200 mOsm/ℓ 내지 약 500 mOsm/ℓ, 약 200 mOsm/ℓ 내지 약 400 mOsm/ℓ, 약 300 mOsm/ℓ 내지 약 400 mOsm/ℓ, 약 270 mOsm/ℓ 내지 약 390 mOsm/ℓ, 약 225 mOsm/ℓ 내지 약 350 mOsm/ℓ, 약 250 mOsm/ℓ 내지 약 325 mOsm/ℓ, 약 275 mOsm/ℓ 내지 약 300 mOsm/ℓ, 또는 약 285 mOsm/ℓ 내지 약 290 mOsm/ℓ의 오스몰농도를 나타낸다.In aspects of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, about 100 mOsm/L, about 150 mOsm/L, about 200 mOsm/L, about 250 mOsm/L, about 300 mOsm/L, about 350 mOsm/L. It represents an osmolar concentration of ℓ, about 400 mOsm/ℓ, about 450 mOsm/ℓ, or about 500 mOsm/ℓ. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, at least 100 mOsm/L, at least 150 mOsm/L, at least 200 mOsm/L, at least 250 mOsm/L, at least 300 mOsm/L, at least 350 mOsm /l, at least 400 mOsm/l, at least 450 mOsm/l, or at least 500 mOsm/l. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, up to 100 mOsm/L, up to 150 mOsm/L, up to 200 mOsm/L, up to 250 mOsm/L, up to 300 mOsm/L, up to 350 mOsm /ℓ, maximum 400 mOsm/ℓ, maximum 450 mOsm/ℓ, or maximum 500 mOsm/ℓ osmolar concentration. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, from about 100 mOsm/L to about 500 mOsm/L, from about 200 mOsm/L to about 500 mOsm/L, from about 200 mOsm/L to about 400 mOsm. /L, from about 300 mOsm/L to about 400 mOsm/L, from about 270 mOsm/L to about 390 mOsm/L, from about 225 mOsm/L to about 350 mOsm/L, from about 250 mOsm/L to about 325 mOsm/L , About 275 mOsm/L to about 300 mOsm/L, or about 285 mOsm/L to about 290 mOsm/L.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 실질적인 안정성을 나타내는 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 제공한다. 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 지칭할 때, 본 명세서에 나타내는 바와 같은 용어 "안정성" 또는 "안정한"은 개체에 투여 전 보관되는 동안 임의의 실질적인 또는 유의한 정도가 강등되거나, 분해되거나 또는 파괴되기 쉽지 않은 조성물을 지칭한다. 본 명세서에 나타내는 바와 같은 용어 "실질적인 열 안정성", "실질적으로 열 안정성", "오토클레이브 안정성" 또는 "스팀 멸균 안정성"은 본 명세서에 개시되는 바와 같은 열 처리가 적용될 때, 실질적으로 안정한 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 지칭한다.Aspects of the present specification provide, in part, a hydrogel composition disclosed herein that exhibits substantial stability. When referring to a hydrogel composition disclosed herein, the term “stable” or “stable” as indicated herein means that any substantial or significant degree is degraded, degraded or destroyed during storage prior to administration to a subject. It refers to a composition that is not easy. The terms "substantial thermal stability", "substantially thermal stability", "autoclave stability" or "steam sterilization stability" as referred to herein refer to the present specification that is substantially stable when a heat treatment as disclosed herein is applied. It refers to the hydrogel composition disclosed in.
본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 안정성은, 예를 들어 정상 압력에서 또는 감압하에(예를 들어, 오토클레이빙) 스팀 멸균과 같은 열 처리를 하이드로겔 조성물에 실시함으로써 결정될 수 있다. 바람직하게는, 열 처리는 약 1분 내지 약 10분 동안 적어도 약 100℃의 온도에서 수행된다. 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 실질적인 안정성은 1) 멸균 후 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 압출력(ΔF)의 변화를 결정함으로써(여기서 2N 미만의 압출력에서 변화는 (구체화된 첨가제를 지니는 하이드로겔 조성물의 압출력) - (첨가된 첨가제가 없는 하이드로겔 조성물의 압출력)에 의해 측정되는 바와 같은 실질적으로 안정한 하이드로겔 조성물을 표시함); 및/또는 2) 멸균 후 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 유동학적 특성에서 변화를 결정함으로써(여기서, 0.1 미만의 tan δ 1Hz에서 변화는 (첨가제에 의한 겔 제형의 tan δ 1 Hz) - (첨가제가 없는 겔 제형의 tan δ 1 Hz)에 의해 측정되는 바와 같은 실질적으로 안정한 하이드로겔 조성물을 표시함) 평가될 수 있다. 이와 같이, 본 명세서에 개시된 실질적으로 안정한 하이드로겔 조성물은 멸균 후 다음의 특징 중 하나 이상을 보유한다: 동종, 압출력, 응집력, 하이알루로난 농도, 작용제(들) 농도, 오스몰농도, pH, 또는 열 처리 전 하이드로 겔에 의해 요망되는 다른 유동학적 특징.The stability of the hydrogel composition disclosed herein can be determined by subjecting the hydrogel composition to a heat treatment such as steam sterilization, for example at normal pressure or under reduced pressure (eg, autoclaving). Preferably, the heat treatment is performed at a temperature of at least about 100° C. for about 1 minute to about 10 minutes. The substantial stability of the hydrogel composition disclosed herein is 1) by determining the change in the extrusion force (ΔF) of the hydrogel composition disclosed herein after sterilization (where the change in the extrusion force less than 2N is (hydrogel with specified additives The extrusion force of the gel composition)-(indicating a substantially stable hydrogel composition as measured by (extrusion force of the hydrogel composition without added additives)); And/or 2) by determining the change in the rheological properties of the hydrogel composition disclosed herein after sterilization (wherein the change at
실시형태에서, 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체 및 본 명세서에 개시된 적어도 하나의 작용제를 포함하는 하이드로겔 조성물은 본 명세서에 개시된 요망되는 하이드로겔 특성을 유지하는 열 처리를 사용하여 처리된다. 이 실시형태의 양태에서, 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체 및 본 명세서에 개시된 적어도 하나의 작용제를 포함하는 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 약 100℃, 약 105℃, 약 110℃, 약 115℃, 약 120℃, 약 125℃, 또는 약 130℃의 열 처리를 사용하여 처리된다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체 및 본 명세서에 개시된 적어도 하나의 작용제를 포함하는 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 적어도 100℃, 적어도 105℃, 적어도 110℃, 적어도 115℃, 적어도 120℃, 적어도 125℃ 또는 적어도 130℃의 열 처리를 사용하여 처리된다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 글라이코사미노글라이칸 중합체 및 본 명세서에 개시된 적어도 하나의 작용제를 포함하는 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어 약 100℃ 내지 약 120℃, 약 100℃ 내지 약 125℃, 약 100℃ 내지 약 130℃, 약 100℃ 내지 약 135℃, 약 110℃ 내지 약 120℃, 약 110℃ 내지 약 125℃, 약 110℃ 내지 약 130℃, 약 110℃ 내지 약 135℃, 약 120℃ 내지 약 125℃, 약 120℃ 내지 약 130℃, 약 120℃ 내지 약 135℃, 약 125℃ 내지 약 130℃, 또는 약 125℃ 내지 약 135℃의 열 처리를 사용하여 처리된다.In an embodiment, a hydrogel composition comprising a glycosaminoglycan polymer and at least one agent disclosed herein is treated using a heat treatment that maintains the desired hydrogel properties disclosed herein. In aspects of this embodiment, a hydrogel composition comprising a glycosaminoglycan polymer and at least one agent disclosed herein is, for example, about 100° C., about 105° C., about 110° C., about 115° C. , About 120°C, about 125°C, or about 130°C. In another aspect of this embodiment, a hydrogel composition comprising a glycosaminoglycan polymer and at least one agent disclosed herein is, for example, at least 100°C, at least 105°C, at least 110°C, at least 115°C. It is treated using a heat treatment of at least 120C, at least 125C or at least 130C. In another aspect of this embodiment, a hydrogel composition comprising a glycosaminoglycan polymer and at least one agent disclosed herein is, for example, about 100° C. to about 120° C., about 100° C. to about 125° C. ℃, about 100 ℃ to about 130 ℃, about 100 ℃ to about 135 ℃, about 110 ℃ to about 120 ℃, about 110 ℃ to about 125 ℃, about 110 ℃ to about 130 ℃, about 110 ℃ to about 135 ℃, It is treated using a heat treatment of about 120°C to about 125°C, about 120°C to about 130°C, about 120°C to about 135°C, about 125°C to about 130°C, or about 125°C to about 135°C.
본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 안정성은, 예를 들어 정상 압력에서 또는 감압하에(예를 들어, 오토클레이빙) 스팀 멸균과 같은 열 처리를 하이드로겔 조성물에 실시함으로써 결정될 수 있다. 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 장기간 안정성은, 예를 들어 약 60일 동안 약 45℃ 환경에서 저장과 같은 열처리를 하이드로겔 조성물에 실시함으로써 결정될 수 있다. 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 장기간 안정성은 1) 45℃ 열처리 후 하이드로겔 조성물의 선명도 및 색을 평가함으로써(맑고, 무색인 하이드로겔 조성물은 실질적으로 안정한 하이드로겔 조성물을 표시함); 2) 45℃ 열처리 후 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 압출력(ΔF)에서 변화를 결정함으로써(2N 미만의 압출력에서 변화는 (45℃ 열처리 전 구체화된 첨가제를 지니는 하이드로겔 조성물의 압출력) - (45℃ 열처리 후 구체화된 첨가제를 지니는 하이드로겔 조성물의 압출력)에 의해 측정되는 바와 같은 실질적으로 안정한 하이드로겔 조성물을 표시함); 및/또는 3) 멸균 후 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 유동학적 특성에서 변화를 결정함으로써(여기서, 0.1 미만의 tan δ 1Hz에서 변화는 (45℃ 열처리 전 구체화된 첨가제를 지니는 겔 제형의 tan δ 1 Hz) - (45℃ 열처리 후 구체화된 첨가제를 지니는 겔 제형의 tan δ 1 Hz)에 의해 측정되는 바와 같은 실질적으로 안정한 하이드로겔 조성물을 표시함) 평가될 수 있다. 이와 같이, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 장기간 안정성은 45℃ 열처리 후 다음의 특징 중 하나 이상의 보유에 의해 평가된다: 선명도(투명도 및 반투명도), 균질함 및 응집력.The stability of the hydrogel composition disclosed herein can be determined by subjecting the hydrogel composition to a heat treatment such as steam sterilization, for example at normal pressure or under reduced pressure (eg, autoclaving). The long-term stability of the hydrogel composition disclosed herein can be determined by subjecting the hydrogel composition to a heat treatment such as storage in an environment of about 45° C. for about 60 days. The long-term stability of the hydrogel composition disclosed herein is 1) by evaluating the clarity and color of the hydrogel composition after heat treatment at 45° C. (clear, colorless hydrogel composition indicates a substantially stable hydrogel composition); 2) By determining the change in the extrusion force (ΔF) of the hydrogel composition disclosed in the present specification after heat treatment at 45°C (change in the extrusion force less than 2N is (extrusion force of the hydrogel composition having the specified additives before heat treatment at 45°C) -(Represents a substantially stable hydrogel composition as measured by the extrusion force of the hydrogel composition with the specified additive after heat treatment at 45° C.); And/or 3) by determining the change in the rheological properties of the hydrogel composition disclosed herein after sterilization (wherein, the change at
이 실시형태의 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어 약 3개월, 약 6개월, 약 9개월, 약 12개월, 약 15개월, 약 18개월, 약 21개월, 약 24개월, 약 27개월, 약 30개월, 약 33개월, 또는 약 36개월에 대해 실온에서 실질적으로 안정하다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 적어도 3개월, 적어도 6개월, 적어도 9개월, 적어도 12개월, 적어도 15개월, 적어도 18개월, 적어도 21개월, 적어도 24개월, 적어도 27개월, 적어도 30개월, 적어도 33개월 또는 적어도 36개월 동안 실온에서 실질적으로 안정하다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 약 3개월 내지 약 12개월, 약 3개월 내지 약 18개월, 약 3개월 내지 약 24개월, 약 3개월 내지 약 30개월, 약 3개월 내지 약 36개월, 약 6개월 내지 약 12개월, 약 6개월 내지 약 18개월, 약 6개월 내지 약 24개월, 약 6개월 내지 약 30개월, 약 6개월 내지 약 36개월, 약 9개월 내지 약 12개월, 약 9개월 내지 약 18개월, 약 9개월 내지 약 24개월, 약 9개월 내지 약 30개월, 약 9개월 내지 약 36개월, 약 12개월 내지 약 18개월, 약 12개월 내지 약 24개월, 약 12개월 내지 약 30개월, 약 12개월 내지 약 36개월, 약 18개월 내지 약 24개월, 약 18개월 내지 약 30개월, 또는 약 18개월 내지 약 36개월 동안 실온에서 실질적으로 안정하다.In an aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, about 3 months, about 6 months, about 9 months, about 12 months, about 15 months, about 18 months, about 21 months, about 24 months, about 27 months. , Is substantially stable at room temperature for about 30 months, about 33 months, or about 36 months. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, at least 3 months, at least 6 months, at least 9 months, at least 12 months, at least 15 months, at least 18 months, at least 21 months, at least 24 months, at least It is substantially stable at room temperature for 27 months, at least 30 months, at least 33 months or at least 36 months. In another aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition is, for example, about 3 months to about 12 months, about 3 months to about 18 months, about 3 months to about 24 months, about 3 months to about 30 months, about 3 months to about 36 months, about 6 months to about 12 months, about 6 months to about 18 months, about 6 months to about 24 months, about 6 months to about 30 months, about 6 months to about 36 months, about 9 months To about 12 months, about 9 months to about 18 months, about 9 months to about 24 months, about 9 months to about 30 months, about 9 months to about 36 months, about 12 months to about 18 months, about 12 months to about Is substantially stable at room temperature for 24 months, about 12 months to about 30 months, about 12 months to about 36 months, about 18 months to about 24 months, about 18 months to about 30 months, or about 18 months to about 36 months .
본 조성물은 선택적으로 완충제, 보존제, 등장 조절제, 염, 항산화제, 삼투질 농도 조절제, 유화제, 습윤제 등을 포함하지만 이들로 제한되지 않는 다른 약제학적으로 허용가능한 성분을 포함할 수 있지만, 이것으로 제한되지 않는다.The composition may optionally contain other pharmaceutically acceptable ingredients including, but not limited to, buffers, preservatives, tonicity modifiers, salts, antioxidants, osmolality modifiers, emulsifiers, wetting agents, etc. It doesn't work.
약제학적으로 허용가능한 완충제는 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 제조하기 위해 사용될 수 있는 완충제이며, 단, 얻어진 제제는 약제학적으로 허용가능하다. 약제학적으로 허용가능한 완충제의 비제한적 예는 아세테이트 완충제, 보레이트 완충제, 시트레이트 완충제, 중성 완충 식염수, 포스페이트 완충제 및 포스페이트 완충 식염수를 포함한다. 약제학적으로 허용가능한 완충제의 임의의 농도는 본 명세서에 개시된 약제학적 조성물을 제형화하는데 유용할 수 있으며, 단, 활성 성분의 치료적 유효량은 완충제의 이런 유효한 농도를 사용하여 회수된다. 생리적으로 허용가능한 완충제 농도의 비제한적 예는 약 0.1mM 내지 약 900mM의 범위에서 생긴다. 약제학적으로 허용가능한 완충제의 pH는 조절될 수 있으며, 단 얻어진 제제는 약제학적으로 허용가능하다. 필요하다면 산 또는 염기가 약제학적 조성물의 pH를 조절하는데 사용될 수 있다는 것이 이해된다. 임의의 완충된 pH 수준은 약제학적 조성물을 제형화하는데 유용할 수 있으며, 단, 기질 중합체 활성 성분의 치료적 유효량은 이런 효과적인 pH 수준을 사용하여 회복된다. 생리적으로 허용가능한 pH의 비제한적 예는 약 pH 5.0 내지 약 pH 8.5의 범위에서 생긴다. 예를 들어, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 pH는 약 5.0 내지 약 8.0, 또는 약 6.5 내지 약 7.5, 약 7.0 내지 약 7.4, 또는 약 7.1 내지 약 7.3일 수 있다.Pharmaceutically acceptable buffers are buffers that can be used to prepare the hydrogel compositions disclosed herein, provided that the obtained preparation is pharmaceutically acceptable. Non-limiting examples of pharmaceutically acceptable buffers include acetate buffer, borate buffer, citrate buffer, neutral buffered saline, phosphate buffer and phosphate buffered saline. Any concentration of pharmaceutically acceptable buffer may be useful in formulating the pharmaceutical compositions disclosed herein, provided that a therapeutically effective amount of the active ingredient is recovered using such effective concentration of the buffer. Non-limiting examples of physiologically acceptable buffer concentrations occur in the range of about 0.1 mM to about 900 mM. The pH of the pharmaceutically acceptable buffer can be adjusted, provided that the resulting formulation is pharmaceutically acceptable. It is understood that an acid or base can be used to adjust the pH of the pharmaceutical composition if necessary. Any buffered pH level may be useful in formulating a pharmaceutical composition, provided that a therapeutically effective amount of the matrix polymeric active ingredient is restored using this effective pH level. Non-limiting examples of physiologically acceptable pH occur in the range of about pH 5.0 to about pH 8.5. For example, the pH of the hydrogel composition disclosed herein may be about 5.0 to about 8.0, or about 6.5 to about 7.5, about 7.0 to about 7.4, or about 7.1 to about 7.3.
약제학적으로 허용가능한 보존제는 나트륨 메타바이설파이트, 나트륨 티오설페이트, 아세틸시스테인, 뷰틸화된 하이드록시아니솔 및 뷰틸화된 하이드록시톨루엔을 포함한다. 약제학적으로 허용가능한 보존제는 벤즈알코늄 클로라이드, 클로로뷰탄올, 티메로살, 페닐수은 아세테이트, 페닐수은 나이트레이트, 안정화된 옥시클로로 조성물, 예를 들어, 퓨라이트(PURITE)(등록상표)(캘리포니아주 얼바인에 소재한 앨러건 인코포레이티드) 및 킬레이트제, 예를 들어, DTPA 또는 DTPA-비스아마이드, 칼슘 DTPA, 및 CaNaDTPA-비스아마이드를 포함한다.Pharmaceutically acceptable preservatives include sodium metabisulfite, sodium thiosulfate, acetylcysteine, butylated hydroxyanisole and butylated hydroxytoluene. Pharmaceutically acceptable preservatives are benzalkonium chloride, chlorobutanol, thimerosal, phenylmercury acetate, phenylmercury nitrate, stabilized oxychloro compositions, such as PURITE® (California). Allergan, Inc.) and chelating agents such as DTPA or DTPA-bisamide, calcium DTPA, and CaNaDTPA-bisamide.
본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물에 유용한 약제학적으로 허용가능한 등장 조절제는, 예를 들어 염화나트륨 및 염화칼륨; 및 글라이세린과 같은 염을 포함하지만, 이들로 제한되지 않는다. 조성물은 염으로서 제공될 수 있으며, 염산, 황산, 아세트산, 락트산, 타르타르산, 말산, 숙신산 등을 포함하지만, 이들로 제한되지 않는 다수의 산에 의해 형성될 수 있다. 염은 대응되는 유리 염기 형태보다 수성 또는 다른 양성자성 용매 중에서 더 가용성인 경향이 있다. 이들 및 약학계에 공지된 다른 물질은 본 명세서에 개시된 약제학적 조성물에 포함될 수 있는 것으로 이해된다. 약리학적으로 허용가능한 성분의 다른 비제한적 예는, 예를 들어 Ansel, 상기 참조, (1999); Gennaro, 상기 참조, (2000); Hardman, 상기 참조, (2001); 및 Rowe, 상기 참조, (2003)에서 찾을 수 있으며, 이들 각각은 전문이 본 명세서에 참조로서 포함된다.Pharmaceutically acceptable tonicity modifiers useful in the hydrogel compositions disclosed herein include, for example, sodium chloride and potassium chloride; And salts such as glycerin, but are not limited thereto. The composition may be provided as a salt and may be formed with a number of acids including, but not limited to, hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, acetic acid, lactic acid, tartaric acid, malic acid, succinic acid, and the like. Salts tend to be more soluble in aqueous or other protic solvents than the corresponding free base form. It is understood that these and other substances known in the pharmaceutical world may be included in the pharmaceutical compositions disclosed herein. Other non-limiting examples of pharmacologically acceptable ingredients are, for example, Ansel, supra, (1999); Gennaro, supra, (2000); Hardman, supra, (2001); And Rowe, supra, (2003), each of which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 투여함으로써 개체의 연조직 병태를 치료하는 방법을 제공한다. 본 명세서에 나타내는 바와 같은 용어 "치료하는"은 연조직 불완전, 결함, 질병 및/또는 장애를 특징으로 하는 연조직 병태의 미용적 또는 임상적 증상을 개체에서 감소시키거나 또는 제거하는 것; 또는 연조직 불완전, 결함, 질병 및/또는 장애를 특징으로 하는 병태의 미용적 또는 임상적 증상의 개시를 개체에서 지연시키거나 또는 방지하는 것을 지칭한다. 예를 들어, 용어 "치료하는"은, 예를 들어, 적어도 20%, 적어도 30%, 적어도 40%, 적어도 50%, 적어도 60%, 적어도 70%, 적어도 80%, 적어도 90% 또는 적어도 100%에 의해 연조직 결함, 질병 및/또는 장애를 특징으로 하는 병태의 증상을 감소시키는 것을 의미할 수 있다. 연조직 불완전, 결함, 질병 및/또는 장애를 특징으로 하는 병태를 치료하는데 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 유효성은 하나 이상의 미용적, 임상적 증상 및/또는 병태와 관련된 생리학적 지표를 관찰함으로써 결정될 수 있다. 연조직 불완전, 결함, 질병 및/또는 장애에서 개선은 또한 병행 치료에 대한 감소된 필요에 의해 표시될 수 있다. 당업자는 구체적 연조직 결함, 질병 및/또는 장애와 관련된 적절한 증상 또는 지표를 알 것이고, 개체가 본 명세서에 개시된 화합물 또는 조성물에 의한 치료를 위한 후보인지 여부를 결정하는 방법을 알 것이다.Aspects of the present specification provide a method of treating a soft tissue condition in a subject, in part, by administering a hydrogel composition disclosed herein. The term “treating” as referred to herein refers to reducing or eliminating in a subject the cosmetic or clinical symptoms of a soft tissue condition characterized by soft tissue imperfections, defects, diseases and/or disorders; Or to delay or prevent the onset of cosmetic or clinical symptoms of a condition characterized by soft tissue imperfections, defects, diseases and/or disorders in a subject. For example, the term “treating” means, for example, at least 20%, at least 30%, at least 40%, at least 50%, at least 60%, at least 70%, at least 80%, at least 90% or at least 100% By may mean reducing the symptoms of a condition characterized by a soft tissue defect, disease and/or disorder. The effectiveness of a hydrogel composition disclosed herein in treating a condition characterized by soft tissue imperfections, defects, diseases and/or disorders can be determined by observing one or more cosmetic, clinical symptoms and/or physiological indicators associated with the condition. have. Improvements in soft tissue imperfections, defects, diseases and/or disorders may also be indicated by a reduced need for concurrent treatment. One of skill in the art will know the appropriate symptoms or indicators associated with a specific soft tissue defect, disease and/or disorder, and will know how to determine whether an individual is a candidate for treatment with a compound or composition disclosed herein.
본 발명에 따른 하이드로겔 조성물은 개체에게 투여된다. 개체는 전형적으로 어떤 연령, 성별 또는 인종의 인간이다. 전형적으로 연조직 질환을 치료하기 위한 통상적인 절차에 대한 후보인 임의의 개체는 본 명세서에 개시된 방법을 위한 후보이다. 노화된 피부의 징후를 경험한 피험체가 성인이라고 하더라도, 치료에 적합한 조기 노화 또는 다른 피부 병태(예를 들어, 흉터)를 경험한 피험체가 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물로 치료될 수 있다. 추가로, 현재 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물 및 방법은 작은/중간 확대, 신체 부분 또는 영역의 형상 변화 또는 윤곽 변경을 추구하는 개체에게 적용될 수 있는데, 이는 기존의 연조직 이식물 기법에 의해 기술적으로 가능하지 않거나 또는 미적으로 허용가능하지 않을 수도 있다. 시술 전 평가는 전형적으로 절차의 모든 관련있는 위험 및 이점을 개시하는 사전동의에 추가로 일상적인 이력 및 생리적 시험을 포함한다.The hydrogel composition according to the present invention is administered to a subject. The individual is typically a human of any age, sex or race. Any individual that is typically a candidate for conventional procedures for treating soft tissue diseases is a candidate for the methods disclosed herein. Even if a subject experiencing signs of aging skin is an adult, a subject experiencing premature aging or other skin conditions (eg, scars) suitable for treatment can be treated with the hydrogel composition disclosed herein. In addition, the currently disclosed hydrogel compositions and methods can be applied to individuals seeking small/medium magnification, shape change or contour change of a body part or area, which is not technically possible by existing soft tissue implantation techniques, or It may not be aesthetically acceptable. Pre-procedure evaluation typically includes routine history and physiological examination in addition to informed consent to disclose all relevant risks and benefits of the procedure.
본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물 및 방법은 연조직 병태를 치료하는데 유용하다. 연조직 병태는 연조직 불완전, 결함, 질병 및/또는 장애를 포함하지만, 이들로 제한되지 않는다. 연조직 병태의 비제한적 예는 유방 불완전, 결함, 질병 및/또는 장애, 예를 들어 유방 불완전, 결함, 질병 및/또는 장애, 예를 들어, 유방 확대, 유방 재건, 유방 고정술, 소유방증, 흉광 저형성증, 폴란드 증후군, 캡슐 수축 및/또는 파열과 같은 이식 합병증에 기인하는 결함; 안면 불완전, 결함, 질병 및/또는 장애, 예를 들어, 안면 확대, 안면 재건, 메소세라피, 패리-롬버그 증후군, 심홍반성 루푸스, 진피 디보트(dermal divot), 흉터, 썬큰 체크(sunken check), 얇은 입술, 비강 불완전 또는 결합, 안와 뒤 불완전 또는 결함, 미간주름과 같은 안면 접힘(fold), 주름 및/또는 주름살, 비순선, 윗입술 주름, 및/또는 입꼬리 주름 및/또는 다른 윤곽 기형 또는 안면의 불완전; 목 불완전, 결함, 질병 및/또는 장애; 피부 불완전, 결함, 질병 및/또는 장애; 다른 연조직 불완전, 결함, 질병 및/또는 장애, 예를 들어, 상부 팔, 하부 팔, 손, 어깨, 등, 복부를 포함하는 몸통, 궁둥이, 상부 다리, 종아리를 포함하는 하부 다리, 발바닥을 포함하는 발, 눈, 생식기 또는 다른 신체 부분, 영역 또는 면적의 확대 또는 재구성, 또는 이들 신체 부분, 영역 또는 면적에 영향을 미치는 질병 또는 장애; 요실금, 변실금, 다른 형태의 실금; 및 위식도 역류 질병(gastroesophageal reflux disease: GERD)을 포함한다. 본 명세서에 나타내는 바와 같은 용어 "메소테라피"는 표피, 진피-표피 접합 및/또는 진피 내로 작은 다수의 방울로서 투여되는 작용제의 표피내, 진피내 및/또는 피하 주사를 수반하는 피부의 비수술적 미용적 치료 기법을 지칭한다.The hydrogel compositions and methods disclosed herein are useful for treating soft tissue conditions. Soft tissue conditions include, but are not limited to, soft tissue imperfections, defects, diseases and/or disorders. Non-limiting examples of soft tissue conditions include breast imperfections, defects, diseases and/or disorders, such as breast imperfections, defects, diseases and/or disorders, such as breast augmentation, breast reconstruction, breast fixation, porosity, pleural hypoplasia. Defects due to transplant complications such as dystrophy, Poland syndrome, capsule contraction and/or rupture; Facial imperfections, defects, diseases and/or disorders, such as facial enlargement, facial reconstruction, mesotherapy, Parry-Romberg syndrome, lupus erythematosus, dermal divot, scars, sunken checks , Thin lips, nasal imperfections or consolidation, posterior orbital imperfections or defects, facial folds such as glabellar lines, wrinkles and/or wrinkles, nasolabial lines, upper lip wrinkles, and/or tail wrinkles and/or other contour anomalies or facial Incomplete; Neck imperfections, defects, diseases and/or disorders; Skin imperfections, defects, diseases and/or disorders; Other soft tissue imperfections, defects, diseases and/or disorders, e.g., upper arms, lower arms, hands, shoulders, back, torso including abdomen, buttocks, upper legs, lower legs including calves, including soles of feet Enlargement or reconstruction of the feet, eyes, genitals, or other body parts, areas or areas, or diseases or disorders affecting those body parts, areas or areas; Urinary incontinence, fecal incontinence, and other forms of incontinence; And gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The term “mesotherapy” as referred to herein refers to the non-surgical beauty of the skin involving intradermal, intradermal and/or subcutaneous injection of an agent administered as a plurality of small droplets into the epidermis, dermal-epidermal junction and/or into the dermis. Refers to a therapeutic technique.
본 명세서에 개시된 방법 중 어떤 것에 의해 사용되는 하이드로겔 조성물의 양은 전형적으로 요망되는 변경 및/또는 개선, 요망되는 연조직 질환 증상의 감소 및/또는 제거, 개체 및/또는 의사에 의해 요망되는 임상적 및/또는 미용적 효과 및 치료되는 신체 부분 또는 영역에 기반하여 결정될 것이다. 조성물 투여의 유효성은 다음의 임상적 및/또는 미용적 측정 중 하나 이상에 의해 나타낼 수 있다: 변경되고/되거나 개선된 연조직 형상, 변경되고/되거나 개선된 연조직 크기, 변경되고/되거나 개선된 연조직 윤곽, 변경되고/되거나 개선된 조직 기능, 조직 내부성장물 및/또는 새로운 콜라겐 침착, 조성물의 지속된 생착, 개선된 환자 만족 및/또는 삶의 질, 및 이식가능한 외래 물질의 감소된 사용.The amount of hydrogel composition used by any of the methods disclosed herein is typically the desired alteration and/or amelioration, reduction and/or elimination of desired soft tissue disease symptoms, clinical and/or clinical and/or desired by the individual and/or physician /Or will be determined based on the cosmetic effect and the body part or area being treated. The effectiveness of administration of the composition may be indicated by one or more of the following clinical and/or cosmetic measurements: altered and/or improved soft tissue shape, altered and/or improved soft tissue size, altered and/or improved soft tissue contour. , Altered and/or improved tissue function, tissue ingrowth and/or new collagen deposition, sustained engraftment of the composition, improved patient satisfaction and/or quality of life, and reduced use of implantable foreign materials.
안면 연조직을 치료하는데 조성물 및 방법의 유효성은 다음의 임상적 및/또는 미용적 측정 중 하나 이상에 의해 나타낼 수 있다: 입술, 볼 또는 눈 영역의 증가된 크기, 형상 및/또는 윤곽과 같은 안면 특징의 증가된 크기, 형상 및/또는 윤곽; 입술, 볼 또는 눈 영역 형상의 변경된 크기, 형상 및/또는 윤곽과 같은 안면 특징의 변경된 크기, 형상 및/또는 윤곽; 피부에서 주름살, 접힘 또는 주름의 감소 또는 제거; 피부에서 주름살, 접힘 또는 주름에 대한 저항; 피부의 재수화; 피부에 대해 증가된 탄성; 피부 거칠기의 감소 또는 제거; 증가되고/되거나 개선된 피부 긴장; 튼살 또는 자국의 감소 또는 제거; 증가되고/되거나 개선된 피부톤, 반짝임, 밝기 및/또는 광채; 증가되고/되거나 개선된 피부색, 피부 창백함의 감소 또는 제거; 조성물의 지속; 감소된 부작용; 개선된 환자 만족도 및/또는 삶의 질.The effectiveness of the compositions and methods in treating facial soft tissue can be indicated by one or more of the following clinical and/or cosmetic measurements: facial features such as increased size, shape and/or contour of the lips, cheeks, or eye area. Increased size, shape and/or contour of the; Altered size, shape and/or contour of facial features such as altered size, shape and/or contour of the shape of the lips, cheek or eye area; Reduction or elimination of wrinkles, folds or wrinkles in the skin; Resistance to wrinkles, folds or wrinkles in the skin; Rehydration of the skin; Increased elasticity to the skin; Reduction or elimination of skin roughness; Increased and/or improved skin tension; Reduction or removal of stretch marks or marks; Increased and/or improved skin tone, shine, brightness and/or radiance; Increased and/or improved skin color, reduction or elimination of skin paleness; Duration of the composition; Reduced side effects; Improved patient satisfaction and/or quality of life.
또 다른 예로서, 요실금 과정에 대해, 괄약근 지지를 위한 조성물 및 방법의 유효성은 다음의 임상적 측정 중 하나 이상에 의해 나타낼 수 있다: 감소된 실금 주기, 지속된 생착, 개선된 환자 만족도 및/또는 삶의 질 및 이식가능한 외래 필러의 감소된 사용.As another example, for the course of urinary incontinence, the effectiveness of compositions and methods for sphincter support may be indicated by one or more of the following clinical measures: reduced incontinence cycle, sustained engraftment, improved patient satisfaction, and/or Quality of life and reduced use of implantable ambulatory fillers.
이 실시형태의 양태에서, 투여된 하이드로겔 조성물의 양은, 예를 들어, 약 0.01g, 약 0.05g, 약 0.1g, 약 0.5g, 약 1g, 약 5g, 약 10g, 약 20g, 약 30g, 약 40g, 약 50g, 약 60g, 약 70g, 약 80g, 약 90g, 약 100g, 약 150g 또는 약 200g이다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 투여된 하이드로겔 조성물의 양은, 예를 들어 약 0.01g 내지 약 0.1g, 약 0.1g 내지 약 1g, 약 1g 내지 약 10g, 약 10g 내지 약 100g, 또는 약 50g 내지 약 200g이다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 투여된 하이드로겔 조성물의 양은, 예를 들어 약 0.01㎖, 약 0.05㎖, 약 0.1㎖, 약 0.5㎖, 약 1㎖, 약 5㎖, 약 10㎖, 약 20㎖, 약 30㎖, 약 40㎖, 약 50㎖, 약 60㎖, 약 70g, 약 80㎖, 약 90㎖, 약 100㎖, 약 150㎖, 또는 약 200㎖이다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 투여된 하이드로겔 조성물의 양은, 예를 들어 약 0.01㎖ 내지 약 0.1㎖, 약 0.1㎖ 내지 약 1㎖, 약 1㎖ 내지 약 10㎖, 약 10㎖ 내지 약 100㎖, 또는 약 50㎖ 내지 약 200㎖이다.In aspects of this embodiment, the amount of hydrogel composition administered is, for example, about 0.01 g, about 0.05 g, about 0.1 g, about 0.5 g, about 1 g, about 5 g, about 10 g, about 20 g, about 30 g, About 40g, about 50g, about 60g, about 70g, about 80g, about 90g, about 100g, about 150g or about 200g. In another aspect of this embodiment, the amount of the hydrogel composition administered is, for example, about 0.01 g to about 0.1 g, about 0.1 g to about 1 g, about 1 g to about 10 g, about 10 g to about 100 g, or about 50 g to It is about 200g. In another aspect of this embodiment, the amount of hydrogel composition administered is, for example, about 0.01 ml, about 0.05 ml, about 0.1 ml, about 0.5 ml, about 1 ml, about 5 ml, about 10 ml, about 20 Ml, about 30 ml, about 40 ml, about 50 ml, about 60 ml, about 70 g, about 80 ml, about 90 ml, about 100 ml, about 150 ml, or about 200 ml. In another aspect of this embodiment, the amount of the hydrogel composition administered is, for example, about 0.01 mL to about 0.1 mL, about 0.1 mL to about 1 mL, about 1 mL to about 10 mL, about 10 mL to about 100 mL. , Or from about 50 ml to about 200 ml.
치료의 지속기간은 전형적으로 개체 및/또는 의사에 의해 요망되는 미용적 및/또는 임상적 효과 및 치료되는 신체 부분 또는 영역에 기반하여 결정될 것이다. 이 실시형태의 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 투여는, 예를 들어, 약 6개월, 약 7개월, 약 8개월, 약 9개월, 약 10개월, 약 11개월, 약 12개월, 약 13개월, 약 14개월, 약 15개월, 약 18개월, 또는 약 24개월 동안 연조직 병태를 치료할 수 있다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 투여는, 예를 들어 적어도 6개월, 적어도 7개월, 적어도 8개월, 적어도 9개월, 적어도 10개월, 적어도 11개월, 적어도 12개월, 적어도 13개월, 적어도 14개월, 적어도 15개월, 적어도 18개월, 또는 적어도 24개월 동안 연조직 병태를 치료할 수 있다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 투여는, 예를 들어, 약 6개월 내지 약 12개월, 약 6개월 내지 약 15개월, 약 6개월 내지 약 18개월, 약 6개월 내지 약 21개월, 약 6개월 내지 약 24개월, 약 9개월 내지 약 12개월, 약 9개월 내지 약 15개월, 약 9개월 내지 약 18개월, 약 9개월 내지 약 21개월, 약 6개월 내지 약 24개월, 약 12개월 내지 약 15개월, 약 12개월 내지 약 18개월, 약 12개월 내지 약 21개월, 약 12개월 내지 약 24개월, 약 15개월 내지 약 18개월, 약 15개월 내지 약 21개월, 약 15개월 내지 약 24개월, 약 18개월 내지 약 21개월, 약 18개월 내지 약 24개월, 또는 약 21개월 내지 약 24개월 동안 연조직 병태를 치료할 수 있다.The duration of treatment will typically be determined by the individual and/or physician based on the desired cosmetic and/or clinical effect and the body part or area being treated. In aspects of this embodiment, administration of the hydrogel composition disclosed herein is, for example, about 6 months, about 7 months, about 8 months, about 9 months, about 10 months, about 11 months, about 12 months, Soft tissue conditions can be treated for about 13 months, about 14 months, about 15 months, about 18 months, or about 24 months. In another aspect of this embodiment, the administration of the hydrogel composition disclosed herein is, for example, at least 6 months, at least 7 months, at least 8 months, at least 9 months, at least 10 months, at least 11 months, at least 12 months, The soft tissue condition can be treated for at least 13 months, at least 14 months, at least 15 months, at least 18 months, or at least 24 months. In another aspect of this embodiment, administration of the hydrogel composition disclosed herein is, for example, about 6 months to about 12 months, about 6 months to about 15 months, about 6 months to about 18 months, about 6 months. To about 21 months, about 6 months to about 24 months, about 9 months to about 12 months, about 9 months to about 15 months, about 9 months to about 18 months, about 9 months to about 21 months, about 6 months to about 24 months, about 12 months to about 15 months, about 12 months to about 18 months, about 12 months to about 21 months, about 12 months to about 24 months, about 15 months to about 18 months, about 15 months to about 21 months , From about 15 months to about 24 months, from about 18 months to about 21 months, from about 18 months to about 24 months, or from about 21 months to about 24 months.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 투여하는 단계를 제공한다. 본 명세서에 나타내는 바와 같은 용어 "투여하는"은 임상적으로, 치료적으로 또는 실험적으로 유리한 결과를 잠재적으로 초래하는 개체에 대해 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물을 제공하는 어떤 전달 메커니즘을 의미한다. 개체에 조성물을 투여하기 위해 사용되는 실제 전달 메커니즘은 피부 병태의 유형, 피부 병태의 위치, 피부 병태의 원인, 피부 병태의 중증도, 요망되는 경감 정도, 사용되는 특정 조성물, 사용되는 특정 조성물의 배설 속도, 사용되는 특정 조성물의 약동학, 사용되는 특정 조성물에 포함된 다른 화합물의 특성, 특정 투여 경로, 특정 특징, 개체의 이력 및 위험 인자, 예를 들어 연령, 체중, 일반적 건강상태 등 또는 이들의 임의의 조합을 포함하지만, 이들로 제한되지 않는 인자를 고려함으로써 당업자에 의해 결정될 수 있다. 이 실시형태의 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 주사에 의해 개체의 피부 영역에 투여된다.Aspects of the present specification provide, in part, a step of administering a hydrogel composition disclosed herein. The term “administering” as indicated herein refers to any delivery mechanism that provides a composition disclosed herein to an individual that potentially results in clinically, therapeutically or experimentally beneficial results. The actual delivery mechanism used to administer the composition to an individual is the type of skin condition, the location of the skin condition, the cause of the skin condition, the severity of the skin condition, the degree of relief desired, the particular composition used, the rate of excretion of the particular composition used. , The pharmacokinetics of the particular composition used, the properties of other compounds included in the particular composition used, the particular route of administration, particular characteristics, the history and risk factors of the individual, such as age, weight, general health, etc. It can be determined by one of ordinary skill in the art by considering factors including, but not limited to, combinations. In an aspect of this embodiment, the composition disclosed herein is administered to an area of the subject's skin by injection.
개개 환자에 대한 하이드로겔 조성물의 투여 경로는 전형적으로 개체 및/또는 의사에 의해 요망되는 미용적 및/또는 임상적 효과 및 치료되는 신체 부분 또는 영역에 기반하여 결정될 것이다. 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 국소적으로 또는 직접적 외과적 이식에 의해 바늘이 있는 주사기, 피스톨(예를 들어, 수공-압축 피스톨), 카테터를 포함하지만, 이들로 제한되지 않는 당업자에게 공지된 임의의 수단에 의해 투여될 수 있다. 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어, 진피 영역 또는 피하 영역과 같은 피부 영역 내로 투여될 수 있다. 예를 들어 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 약 0.26㎜ 내지 약 0.4㎜의 직경 및 약 4㎜ 내지 약 14㎜ 범위의 길이를 지니는 바늘을 이용하여 주사될 수 있다. 대안적으로, 바늘은 21G 내지 32G일 수 있고, 약 4㎜ 내지 약 70㎜의 길이를 가질 수 있다. 바람직하게는, 바늘은 1회용 바늘이다. 바늘은 주사기, 카테터 및/또는 피스톨과 조합될 수 있다.The route of administration of the hydrogel composition to an individual patient will typically be determined by the individual and/or physician based on the desired cosmetic and/or clinical effect and the part or area of the body being treated. The compositions disclosed herein include, but are not limited to, needled syringes, pistols (e.g., hand-compressed pistols), catheters, either locally or by direct surgical implantation, any means known to those skilled in the art. Can be administered by The hydrogel composition disclosed herein can be administered into a skin area such as, for example, a dermal area or a subcutaneous area. For example, a hydrogel composition disclosed herein can be injected using a needle having a diameter of about 0.26 mm to about 0.4 mm and a length in the range of about 4 mm to about 14 mm. Alternatively, the needle can be between 21G and 32G and have a length of between about 4 mm and about 70 mm. Preferably, the needle is a disposable needle. The needle can be combined with a syringe, catheter and/or pistol.
추가로, 본 명세서에 개시된 조성물은 1회 또는 다회에 걸쳐 투여될 수 있다. 궁극적으로, 사용된 시간은 품질 관리 표준을 따를 것이다. 예를 들어, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 며칠 또는 몇 주 떨어진 작업 시간으로 1회 이상의 몇 회의 작업 시간에 투여될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 개체는 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 또는 7일마다 또는 1, 2, 3 또는 4주마다 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물이 투여될 수 있다. 개체에 대한 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물의 투여는 매달 또는 2개월 기준으로 또는 3, 6, 9 또는 12개월마다 투여될 수 있다.Additionally, the compositions disclosed herein may be administered once or multiple times. Ultimately, the time spent will follow quality control standards. For example, the hydrogel compositions disclosed herein may be administered at one or more times several working times, with working times a few days or weeks away. For example, a subject may be administered a hydrogel composition disclosed herein every 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 or 7 days or every 1, 2, 3 or 4 weeks. Administration of the hydrogel compositions disclosed herein to a subject may be administered on a monthly or two-month basis or every 3, 6, 9 or 12 months.
본 명세서의 양태는, 부분적으로 진피 영역을 제공한다. 본 명세서에 나타내는 바와 같은 용어 "진피 영역"은 표피-진피 접합부 및 깊지 않은 진피(유두 영역) 및 깊은 진피(망상 영역)를 포함하는 진피를 포함하는 피부의 영역을 지칭한다. 피부는 3가지의 주된 층으로 구성된다: 방수를 제공하고, 감염에 대한 장벽으로서 작용하는 표피; 피부의 외지에 대한 장소로서 작용하는 진피; 및 하피(피하 지방층). 표피는 혈관을 함유하지 않으며, 진피로부터 확산에 의해 영양분이 공급된다. 표피를 구성하는 세포의 주된 유형은 케라틴세포, 멜라닌 세포, 랑게르한스 세포 및 메르켈 세포이다.Aspects of the present specification provide, in part, a dermal region. The term “dermal region” as referred to herein refers to a region of the skin including the epidermal-dermal junction and the dermis including the non-deep dermis (papillary region) and the deep dermis (reticular region). The skin is made up of three main layers: the epidermis, which provides water resistance and acts as a barrier against infection; The dermis acting as a place for the external part of the skin; And the lower skin (subcutaneous fat layer). The epidermis does not contain blood vessels and is supplied with nutrients by diffusion from the dermis. The main types of cells that make up the epidermis are keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans cells and Merkel cells.
진피는 결합 조직으로 이루어지고, 응력 및 변형으로부터 신체의 충격을 완화하는 표피 밑 피부층이다. 진피는 최하부 막에 의해 표피에 단단하게 결합된다. 또한 접촉 및 열의 감각을 제공하는 다수의 기계적 수용체/신경 말단을 은닉한다. 이는 모공, 땀샘, 피지샘, 아포크린샘, 림프관 및 혈관을 함유한다. 진피 내 혈관은 그 자체의 세포로부터 뿐만 아닐 표피의 기저층으로부터 영양분 및 노폐물 제거를 제공한다. 진피는 구조적으로 2개의 영역으로 나뉜다: 유두 영역으로 불리는 표피에 인접한 초임계 영역 및 망상 영역으로 알려진 더 깊고 두꺼운 영역.The dermis is a layer of skin under the epidermis that is made of connective tissue and relieves the body's impact from stress and deformation. The dermis is tightly bound to the epidermis by the lowermost membrane. It also hides a number of mechanical receptors/nerve endings that provide a sense of touch and heat. It contains pores, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, apocrine glands, lymphatic vessels and blood vessels. The blood vessels in the dermis provide the removal of nutrients and waste products from their own cells as well as from the basal layer of the epidermis. The dermis is structurally divided into two areas: a supercritical area adjacent to the epidermis called the papillary area and a deeper, thicker area known as the reticular area.
유두 영역은 헐거운 세망(areolar) 조직 결합 조직으로 구성된다. 이는 표피 쪽으로 연장된 유두로 불리는 손가락형 돌출부로 명명된다. 유두는 표피와 서로 맞물리는 "울퉁불퉁한" 표면을 지니고, 피부의 두 층 사이의 결합을 강화하는 진피를 제공한다. 망상 영역은 유두 영역보다 깊은 곳에 놓이며, 보통 훨씬 두껍다. 이는 밀집한 불규칙적 결합 조직으로 구성되며, 그것 전체적으로 엮이는 콜라겐성, 탄성 및 망상 섬유의 밀집한 집중으로부터 그것의 명칭을 얻는다. 이들 단백질 섬유는 그것의 강도, 신장성 및 탄성의 특성을 진피에 제공한다. 또한 망상 영역 내에 모근, 피지선, 땀샘, 수용체, 손발톱 및 혈관이 위치된다. 문신 잉크는 진피에 보유된다. 또한 임신으로부터의 튼살은 진피에 위치된다.The papillary area consists of loose areolar tissue connective tissue. It is termed a finger-like protrusion called a nipple extending toward the epidermis. The nipples have a "bumpy" surface that interlocks with the epidermis, providing the dermis that strengthens the bond between the two layers of the skin. The reticular area lies deeper than the nipple area and is usually much thicker. It consists of dense irregular connective tissue, and gets its name from the dense concentration of collagenous, elastic and reticulated fibers that are woven throughout it. These protein fibers give the dermis its strength, extensibility and elasticity properties. In addition, hair roots, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, receptors, nails, and blood vessels are located in the reticulated region. Tattoo ink is retained in the dermis. Also, stretch marks from pregnancy are located in the dermis.
하피는 진피 밑에 놓인다. 그것의 목적은 기저 뼈 및 근육의 진피 영역을 붙일 뿐만 아니라 혈관 및 신경을 그것에 공급하는 것이다. 이는 헐거운 결합 조직 및 엘라스틴으로 이루어진다. 주된 세포 유형은 섬유아세포, 대식세포 및 지방세포이다(하피는 체지방의 50%를 함유한다). 지방은 신체에 대한 패드 및 절연체로서 작용한다.The lower skin is placed under the dermis. Its purpose is to attach the dermal regions of the basal bone and muscles as well as supply blood vessels and nerves to it. It consists of loose connective tissue and elastin. The main cell types are fibroblasts, macrophages and adipocytes (the hypodermis contains 50% of body fat). Fat acts as a pad and insulator for the body.
이 실시형태의 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은 진피 영역 또는 피하조직 영역 내로 주사에 의해 개체의 피부 영역에 투여된다. 이 실시형태의 양태에서, 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물은, 예를 들어 표피-진피 접합 영역, 유두 영역, 망상 영역, 또는 이들의 임의의 조합 내로 주사에 의해 생체의 진피 영역에 투여된다. In an aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition disclosed herein is administered to a skin area of a subject by injection into a dermal area or subcutaneous tissue area. In an aspect of this embodiment, the hydrogel composition disclosed herein is administered to a dermal region of a living body by injection into, for example, an epidermal-dermal junction region, a papillary region, a reticulant region, or any combination thereof.
유리하게는, 본 조성물의 일부는, 예를 들어 환자의 얇은 피부 영역에서 잔주름을 감소시키는데 특히 유용하고 효과적이다. 예를 들어, 본 명세서의 다른 곳에서 기재되는 바와 같은 진피 필러 조성물을 약 1㎜ 이하 깊이에서 환자에게 투여하는 단계를 포함하는 잔주름 치료를 위한 방법이 제공된다.Advantageously, some of the compositions are particularly useful and effective in reducing fine lines, for example in thin skin areas of patients. For example, a method for treating fine wrinkles is provided comprising administering to a patient a dermal filler composition as described elsewhere herein at a depth of about 1 mm or less.
본 명세서의 다른 양태는 부분적으로 피부 질환을 겪고 있는 개체에 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 투여하는 단계를 포함하되, 조성물의 투여는 피부 질환을 개선시키고, 이에 의해 피부 질환을 치료한다. 이 실시형태의 양태에서, 피부 질환은 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 피부 탈수를 겪고 있는 개체에 투여하는 단계를 포함하되, 조성물의 투여는 피부를 재수화시키고, 이에 의해 피부 탈수를 치료한다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 피부 탄성의 결여를 치료하는 방법은 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물 피부 탄성 결여를 겪고 있는 개체에 투여하는 단계를 포함하되, 조성물의 투여는 피부 탄성을 증가시키고, 이에 의해 피부 탄성의 결여를 치료한다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 피부 거칠기를 치료하는 방법은 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 피부 거칠기를 겪고 있는 개체에 투여하는 단계를 포함하되, 조성물의 투여는 피부 거칠기를 감소시키고, 이에 의해 피부 거칠기를 치료한다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 피부 거칠기의 결여를 치료하는 방법은 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 피부 긴장의 결여를 겪고 있는 개체에 투여하는 단계를 포함하되, 조성물의 투여는 피부 긴장을 만들고, 이에 의해 피부 긴장의 결여를 치료한다.Another aspect of the present specification includes the step of administering a hydrogel composition disclosed herein to a subject partially suffering from a skin disease, wherein the administration of the composition improves the skin disease, thereby treating the skin disease. In an aspect of this embodiment, the skin condition comprises administering a hydrogel composition disclosed herein to an individual suffering from skin dehydration, wherein administration of the composition rehydrates the skin, thereby treating skin dehydration. In another aspect of this embodiment, a method of treating a lack of skin elasticity comprises administering to an individual suffering from a lack of skin elasticity a hydrogel composition disclosed herein, wherein administration of the composition increases skin elasticity, thereby By treating the lack of elasticity of the skin. In another aspect of this embodiment, a method of treating skin roughness comprises administering a hydrogel composition disclosed herein to an individual suffering from skin roughness, wherein administration of the composition reduces skin roughness, thereby Treats skin roughness. In another aspect of this embodiment, a method of treating the lack of skin roughness comprises administering a hydrogel composition disclosed herein to an individual suffering from the lack of skin tension, wherein the administration of the composition creates skin tension and , Thereby treating the lack of skin tension.
이 실시형태의 추가 양태에서, 피부 튼살 또는 자국을 치료하는 방법은 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 피부 튼살 또는 자국을 겪고 있는 개체에 투여하는 단계를 포함하되, 조성물의 투여는 피부 튼살 또는 자국을 감소시키거나 또는 제거하고, 이에 의해 피부 튼살 또는 자국을 치료한다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 피부의 창백함을 치료하는 방법은 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 피부의 창백함을 겪고 있는 개체에 투여하는 단계를 포함하되, 조성물의 투여는 피부톤 또는 빛을 증가시키고, 이에 의해 피부의 창백함을 치료한다. 이 실시형태의 다른 양태에서, 피부 주름살을 치료하는 방법은 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 피부 주름살을 겪고 있는 개체에게 투여하는 단계를 포함하되, 조성물의 투여는 피부 주름살을 감소시키거나 또는 제거하고, 이에 의해 피부 주름살을 치료한다. 이 실시형태의 또 다른 양태에서, 피부 주름살을 치료하는 방법은 본 명세서에 개시된 하이드로겔 조성물을 개체에 투여하는 단계를 포함하되, 조성물의 투여는 피부 주름살에 대한 피부 저항성을 만들고, 이에 의해 피부 주름살을 치료한다.In a further aspect of this embodiment, a method of treating a skin stretch mark or mark comprises administering a hydrogel composition disclosed herein to an individual suffering from the skin stretch mark or mark, wherein the administration of the composition Reduce or eliminate, thereby treating skin stretch marks or marks. In another aspect of this embodiment, a method of treating skin paleness comprises administering a hydrogel composition disclosed herein to an individual suffering from skin paleness, wherein administration of the composition increases skin tone or light, This cures the paleness of the skin. In another aspect of this embodiment, a method of treating skin wrinkles comprises administering a hydrogel composition disclosed herein to an individual suffering from skin wrinkles, wherein administration of the composition reduces or eliminates skin wrinkles and , Thereby treating wrinkles on the skin. In another aspect of this embodiment, a method of treating skin wrinkles comprises administering to a subject a hydrogel composition disclosed herein, wherein the administration of the composition creates skin resistance to skin wrinkles, thereby Cure.
일부 실시형태에서, 진피 필러는 지속된 생체이용가능성을 가진다. 예를 들어, 인간의 피부내로 도입될 때(예를 들어, 얼굴 공간의 연조직 결함을 고치기 위해 인간에게 진피내로 또는 피하로), 적어도 약 1개월 내지 약 20개월 이상 인간에게 아스콜브산(또는 다른 비타민)을 방출하는 진피 필러가 제공된다.In some embodiments, the dermal filler has sustained bioavailability. For example, when introduced into the skin of a human (e.g., intradermally or subcutaneously to a human to repair soft tissue defects in the facial space), ascorbic acid (or other A dermal filler that releases vitamins) is provided.
예를 들어, 필러 지속과 함께 지속된 비타민 C 효능을 예측하기 위해, 컨쥬게이트된 정도에 대한 평가가 만들어진다. 이 평가는 에터화를 통한 HA에 대한 AA2G 컨쥬게이션의 제형화에 기반하였다. 제형은 생리적 조건 하에 안정하지만, 세포막에 부착된 α-글루코시다제에 의해 아스콜브산(AsA)의 방출시키는 것을 시작한다.α-글루코시다제가 세포막에 부착된다는 사실에 기인하여 필러/세포 경계면에서 AsA의 방출이 일어난다. HA-AA2G로부터 AsA의 추가적인 방출은 섬유아세포에 이용가능한 AA2G를 만들기 위해 HA 분해를 수반할 것이다. 따라서 AsA의 방출은 AA2G 컨쥬게이션 정도 및 HA의 지속기간에 의존한다. 대략 5㏖%의 컨쥬게이션 정도를 지니는 겔은 적어도 1개월, 예를 들어 3 내지 5개월의 기간에 활성 비타민 C를 방출할 수 있었고; 10㏖% 컨쥬게이션 정도를 지니는 겔은 6 내지 8개월까지의 기간에 활성 비타민 C를 방출시킬 수 있었으며; 15㏖% 컨쥬게이션 정도를 지니는 겔은 10~ 개월까지의 기간에 활성 비타민 C를 방출시킬 수 있고; 30㏖%는 1년 반까지 방출시킬 수 있다.For example, to predict sustained vitamin C efficacy with filler persistence, an assessment of the degree of conjugation is made. This evaluation was based on the formulation of AA2G conjugation to HA via etherification. The formulation is stable under physiological conditions, but begins to release ascorbic acid (AsA) by α-glucosidase attached to the cell membrane, due to the fact that α-glucosidase adheres to the cell membrane at the filler/cell interface. The release of AsA occurs. Further release of AsA from HA-AA2G will entail HA degradation to make AA2G available to fibroblasts. Thus, the release of AsA depends on the degree of AA2G conjugation and the duration of HA. Gels with a degree of conjugation of approximately 5 mol% were capable of releasing active vitamin C in a period of at least 1 month, eg 3 to 5 months; Gels with a degree of 10 mol% conjugation were able to release active vitamin C in a period of up to 6 to 8 months; Gels with a degree of 15 mol% conjugation can release active vitamin C in a period of up to 10 months; 30㏖% can be released up to one and a half years.
본 발명의 실시형태에서, 스타-PEG 에폭사이드와 가교된 하이알루론산을 포함하고 약 3㏖% 내지 약 40㏖%의 컨쥬게이션 정도로 하이알루론산에 컨쥬게이트된 비타민 C 유도체(예를 들어, AA2G (아스콜브산 2-글루코사이드), 비타겐(3-아미노프로필-L-아스코빌 포스페이트) 및 SAP(나트륨 아스코빌 포스페이트) 중 하나)를 포함하는 진피 필러가 제공된다.In an embodiment of the invention, a vitamin C derivative (e.g., AA2G (ascorbic acid 2-glucoside), vitagen (3-aminopropyl-L-ascorbyl phosphate) and SAP (one of sodium ascorbyl phosphate)).
이 진피 필러의 제조방법은 4-암 에폭사이드(AA2G-4 암 에폭사이드), 미반응 4-암 에폭사이드 및 유리 AA2G에 의해 AA2G를 함유하는 조성물을 달성하기에 적합한 반응 온도 및 반응시간의 비에서 펜타에리트리톨 글라이시달 에터(Star-PEG 에폭사이드)를 아스콜브산 2-글루코사이드(AA2G)와 반응시키는 단계를 포함한다. 4 암(arm) 에폭사이드 캡핑된 AA2G(AA2G-4 암 에폭사이드)는 에폭실기를 통해 하이알루론산에 컨쥬게이트된다. 미반응 4 암 에폭사이드는 하이알루론산을 가교하기 위한 가교제로서 그리고 추가로 AA2G를 컨쥬게이트하기 위한 컨쥬게이션 작용제로서 작용한다.The preparation method of this dermal filler is a ratio of reaction temperature and reaction time suitable to achieve a composition containing AA2G by 4-arm epoxide (AA2G-4 arm epoxide), unreacted 4-arm epoxide and free AA2G. In a step of reacting pentaerythritol glycidal ether (Star-PEG epoxide) with ascorbic acid 2-glucoside (AA2G). 4 Arm Epoxide Capped AA2G (AA2G-4 arm epoxide) is conjugated to hyaluronic acid through an epoxy group. The unreacted 4 arm epoxide acts as a crosslinking agent to crosslink hyaluronic acid and as a conjugation agent to further conjugate AA2G.
본 발명의 다른 실시형태에서, BDDE와 가교된 하이알루론산을 포함하고, 3㏖% 내지 약 10㏖%의 컨쥬게이션 정도로 하이알루론산에 컨쥬게이트된 비타민 C 유도체(예를 들어, AA2G (아스콜브산 2-글루코사이드), 비타겐(3-아미노프로필-L-아스코빌 포스페이트) 및 SAP(아스코빌 인산나트륨) 중 하나를 갖는 진피 필러가 제공된다.In another embodiment of the present invention, a vitamin C derivative (e.g., AA2G (ascorbic acid 2-glucoside ), Vitagen (3-aminopropyl-L-ascorbyl phosphate) and SAP (ascorbyl sodium phosphate).
이 진피 필러의 제조방법은 BDDE(AA2G-BDDE), 미반응 BDDE 및 유리 AA2G에 의해 캡핑된 AA2G를 함유하는 조성물을 달성하기에 적합한 반응 온도 및 반응 시간의 비에서 BDDE를 아스콜브산 2-글루코사이드(AA2G)와 반응시키는 단계를 포함한다. BDDE 캡핑 AA2G(AA2G-BDDE)는 에폭실 기를 통해 하이알루론산에 컨쥬게이트된다. 미반응 BDDE는 하이알루론산을 가교하기 위한 가교제로서, 그리고 AA2G를 추가로 컨쥬게이트하기 위한 컨쥬게이션 작용제로서 작용한다.The preparation method of this dermal filler comprises BDDE ascorbic acid 2-glucoside at a ratio of reaction temperature and reaction time suitable to achieve a composition containing AA2G capped by BDDE (AA2G-BDDE), unreacted BDDE and free AA2G. It includes reacting with (AA2G). BDDE capping AA2G (AA2G-BDDE) is conjugated to hyaluronic acid through an epoxy group. Unreacted BDDE acts as a crosslinking agent to crosslink hyaluronic acid and as a conjugation agent to further conjugate AA2G.
도 9는 AA2G-PBS 용액으로부터 AsA 방출에 대한 α-글루코시다제 농도의 효과를 나타내는 표이다. AA2G의 AsA로 전환은 α-글라이코시다제의 농도에 의존한다. α-글라이코시다제 농도가 겔의 그램 당 6.3 단위일 때, 15분 후 거의 완전하게 AA2G는 AsA로 전환된다. α-글라이코시다제 농도가 겔의 그램 당 4.7 단위일 때, AA2G는 AsA로 완전하게 전환되는 데 30분이 걸린다. 추가로 감소된 α-글라이코시다제 농도는 AA2G의 AsA로 느린 전환을 야기하였다.9 is a table showing the effect of α-glucosidase concentration on AsA release from AA2G-PBS solution. Conversion of AA2G to AsA depends on the concentration of α-glycosidase. When the α-glycosidase concentration is 6.3 units per gram of gel, AA2G is converted to AsA almost completely after 15 minutes. When the α-glycosidase concentration is 4.7 units per gram of gel, AA2G takes 30 minutes to completely convert to AsA. Further reduced α-glycosidase concentration resulted in a slow conversion of AA2G to AsA.
도 10은 본 발명에 따른 컨쥬게이트된 진피 필러로부터 유리 AsA의 방출 프로파일(지속방출)의 표현(㏖% 대 반응시간에서 AA2G 전환)을 도시한 도면; AA2G는 40분에 AA2G/HA 혼합에서 AsA로 완전히 전환된다. AA2H/HA 컨쥬게이트는 AsA로 AA2G 전환의 시간 의존도를 나타내었다.10 shows a representation of the release profile (sustained release) of free AsA from conjugated dermal fillers according to the present invention (mol% versus AA2G conversion in reaction time); AA2G is completely converted to AsA in the AA2G/HA blend in 40 minutes. The AA2H/HA conjugate showed the time dependence of AA2G conversion to AsA.
도 11a 및 도 11b는 본 발명에 따른 다양한 진피 필러에 대한 추가적인 방출 데이터를 나타낸다. 더 구체적으로는, HA-AA2G 겔에서 AA2G의 AsA로 전환은 α-글라이코시다제 농도에 의존한다. 높은 α-글라이코시다제 농도는 AA2G의 AsA로 빠른 전환을 야기하였다. 주어진 α-글라이코시다제 농도에 대해, 상이한 제형은 AsA에 대한 AA2G의 상이한 프로파일을 나타내었다.11A and 11B show additional release data for various dermal fillers according to the present invention. More specifically, the conversion of AA2G to AsA in the HA-AA2G gel is dependent on the α-glycosidase concentration. The high α-glycosidase concentration caused rapid conversion of AA2G to AsA. For a given α-glycosidase concentration, different formulations showed different profiles of AA2G against AsA.
본 발명의 일 양태에서, 잔주름의 외관, 예를 들어 피부에서 상대적으로 깊지 않은 주름선, 예를 들어 이하에 제한되는 것은 아니지만, 눈가 잔주름, 눈물고랑 영역, 이마, 눈주위, 미간주름 등을 치료하고, 제거하는데 특히 유효한 진피 필러가 제공된다.In one aspect of the present invention, the appearance of fine wrinkles, for example, wrinkles that are not relatively deep in the skin, for example, but is not limited to the following, fine wrinkles around the eyes, lacrimal furrow area, forehead, eye circumference, glabellar wrinkles, etc. And a dermal filler that is particularly effective in removing is provided.
진피 필러가 주사된 피부 부위에서 청색 변색의 외관인, (틴들 효과)는 일부 진피 필러 환자에 의해 경험되는 중요한 부작용이다. 틴들 효과는 깊지 않은 잔주름 주름살에 대해 치료되는 환자에서 더 흔하다. 틴들효과로부터 어떤 청색 변색을 초래하는 일 없이 상대적으로 얇은 피부의 영역에서조차 잔주름 및 주름살을 치료하기 위해 깊지 않게 주사될 수 있는 장기 지속되는 반투명 필러를 제공하는 본 발명의 실시형태가 개발되었다. 잔주름 또는 깊지 않은 주름살은 일반적으로 피부가 가장 얇은, 즉, 피부가 1㎜ 미만의 진피 두께를 갖는 얼굴 영역에서 전형적으로 발견되는 피부(이마, 측면 안각, 홍순 경계/윗입술 주름)에서 해당 주름살 또는 주름선이 되는 것으로 이해된다. 이마 상에서, 평균 진피 두께는 정상 피부에 대해 약 0.95㎜ 및 주름살 피부에 대해 약 0.81㎜이다. 측면 안각 주위의 진피는 심지어 더 얇다(예를 들어, 정상 피부에 대해 약 0.61㎜, 주름살 피부에 대해 약 0.41㎜). 30 또는 32 게이지 니들의 평균 외부 직경(잔주름 겔 적용을 위해 전형적으로 사용되는 니들)은 약 0.30 내지 약 0.24㎜이다.(Tindle effect), the appearance of a blue discoloration at the skin site where the dermal filler was injected, is an important side effect experienced by some dermal filler patients. The Tindle effect is more common in patients being treated for fine lines that are not deep. Embodiments of the present invention have been developed that provide long lasting translucent fillers that can be injected not deeply to treat fine lines and wrinkles even in areas of relatively thin skin without causing any blue discoloration from the Tindle effect. Fine lines or wrinkles are usually the thinnest, that is, those wrinkles or wrinkles in the skin (forehead, lateral canthal, red lip border/upper lip wrinkles) typically found in areas of the face where the skin has a dermal thickness less than 1 mm It is understood to be good. On the forehead, the average dermal thickness is about 0.95 mm for normal skin and about 0.81 mm for wrinkled skin. The dermis around the lateral canal is even thinner (eg, about 0.61 mm for normal skin and about 0.41 mm for wrinkled skin). The average outer diameter of a 30 or 32 gauge needle (needles typically used for fine wrinkle gel applications) is from about 0.30 to about 0.24 mm.
본 발명은 틴들 효과를 야기하지 않는 본 명세서의 다른 곳에서 기재된 바와 같은 진피 필러 조성물을 제공한다. 예를 들어, 본 발명의 조성물은 가교 성분과 가교된 하이알루론산 성분, 가교 성분 이외의 첨가제를 포함하되; 상기 조성물은 상기 첨가제가 없는 것을 제외하고 실질적으로 동일한 조성물에 대해 환자의 진피 영역 내로 투여될 때 감소된 틴들 효과를 나타내는 것인, 진피 필러 조성물. 조성물을 실질적으로 광학적으로 투명할 수 있다.The present invention provides a dermal filler composition as described elsewhere herein that does not cause the Tindle effect. For example, the composition of the present invention comprises a crosslinking component, a crosslinked hyaluronic acid component, and an additive other than the crosslinking component; The dermal filler composition, wherein the composition exhibits a reduced tindle effect when administered into the dermal area of a patient for substantially the same composition except for the absence of the additive. The composition may be substantially optically transparent.
일 실시형태에서, 첨가제는 비타민 C 유도체, 예를 들어 본 명세서의 다른 곳에 기재된 바와 같은 하이알루론산에 화학적으로 컨쥬게이트될 수 있는 AA2G이다.In one embodiment, the additive is AA2G, which can be chemically conjugated to a vitamin C derivative, for example hyaluronic acid as described elsewhere herein.
일부 실시형태에서, 가교 성분은 BDDE이고, 컨쥬게이션 정도는 약 3㏖% 내지 약 10㏖%, 또는 15㏖%까지 또는 초과이다. 일부 실시형태에서, 조성물은 환자에 주사시 편안함을 제공하는데 적합한 양으로 마취제, 예를 들어, 리도카인을 추가로 포함한다.In some embodiments, the crosslinking component is BDDE and the degree of conjugation is from about 3 mol% to about 10 mol%, or up to or greater than 15 mol%. In some embodiments, the composition further comprises an anesthetic such as lidocaine in an amount suitable to provide comfort upon injection to the patient.
환자의 피부에서 잔주름을 치료하는 방법이 또한 제공된다. 해당 방법은 일반적으로 환자의 피부에 본 명세서에 기재된 바와 같은 조성물을 도입하는 단계를 포함한다. 예를 들어, 조성물은 하이알루론산 성분, 하이알루론산을 가교하는 가교 성분 및 가교 성분 이외의 첨가제의 혼합물을 포함하며, 조성물은 실질적으로 광학적으로 투명하되; 진피 필러 조성물은 첨가제가 없는 것을 제외하고 실질적으로 동일한 조성물에 대해 감소된 틴들 효과를 나타낸다.Also provided is a method of treating fine lines in the skin of a patient. That method is usually Introducing a composition as described herein into the patient's skin. For example, the composition comprises a mixture of a hyaluronic acid component, a crosslinking component for crosslinking hyaluronic acid, and an additive other than the crosslinking component, wherein the composition is substantially optically transparent; The dermal filler composition exhibits a reduced tindle effect for substantially the same composition except for the absence of additives.
본 발명의 일부 실시형태에서, 조성물은 EDC 화학을 사용하여 다이 또는 멀다아민 가교제와 가교된 하이알루론산 성분을 포함한다. 예를 들어, 가교제는 HMDA일 수 있다.In some embodiments of the present invention, the composition comprises a hyaluronic acid component crosslinked with a di or muldaamine crosslinker using EDC chemistry. For example, the crosslinking agent can be HMDA.
본 발명의 특정 실시형태에서, 가교제는 HMDA이되, 조성물은 약 70㎩까지의 G', 약 0.65 내지 약 0.75의 G"/G', 약 24N 이하의 압출력 및 약 24㎎/g 내지 약 25㎎/g의 최종 HA 농도를 가진다.In certain embodiments of the invention, the crosslinking agent is HMDA, wherein the composition has a G'of up to about 70 Pa, a G"/G' of about 0.65 to about 0.75, an extrusion force of about 24 N or less, and an extrusion force of about 24 mg/g to about 25 It has a final HA concentration of mg/g.
본 발명의 특정 실시형태에서, 첨가제가 HA-AA2G 컨쥬게이트 또는 HA-비타겐 컨쥬게이트이되, 컨쥬게이션 정도는 약 3㏖% 내지 약 10㏖%, 또는 약 15㏖%까지, 또는 약 40㏖%까지이다. 이들 조성물은 적어도 약 30㎩, 더 바람직하게는 적어도 약 40㎩, 내지 약 100㎩의 G', 약 0.30 내지 약 0.50의 G"/G', 약 27N 이하의 압출력 및 약 24㎎/g 내지 약 25㎎/g의 최종 HA 농도를 가질 수 있다.In certain embodiments of the invention, the additive is a HA-AA2G conjugate or HA-vitagen conjugate, but the degree of conjugation is from about 3 mol% to about 10 mol%, or up to about 15 mol%, or about 40 mol%. Until. These compositions comprise at least about 30 Pa, more preferably at least about 40 Pa, to about 100 Pa of G', about 0.30 to about 0.50 G"/G', about 27 N or less extrusion force, and about 24 mg/g to It may have a final HA concentration of about 25 mg/g.
본 개시내용의 목적을 위해, 본 명세서에 사용되는 바와 같은 "컨쥬게이션 정도"는 하이알루론산의 반복 단위(예를 들어, HA 다이머)에 대한 컨쥬게이트제, 예를 들어 AA2G의 몰 백분율로서 정의된다. 따라서, 10㏖% 컨쥬게이션 정도는 모든 100HA 반복 단위가 10개의 컨쥬게이트된 AA2G를 함유한다는 것을 의미한다. 컨쥬게이션 정도는 이하의 실시예 2에서 예시되는 방법 또는 당업자에게 공지된 다른 방법을 사용하여 계산될 수 있다.For the purposes of this disclosure, "degree of conjugation" as used herein is defined as the molar percentage of the conjugate agent, eg AA2G, to repeat units of hyaluronic acid (eg, HA dimer). Thus, a degree of 10 mol% conjugation means that every 100HA repeat unit contains 10 conjugated AA2G. The degree of conjugation can be calculated using the method illustrated in Example 2 below or other methods known to those skilled in the art.
실시예Example
실시예 1: 가교제로서 BDDE를 사용하는 HA 겔에 가교된 AA2G 컨쥬게이션Example 1: AA2G conjugation crosslinked to HA gel using BDDE as crosslinking agent
400.6㎎의 저분자량 하이알루론산(LMW HA)을 ~30분 동안 주사기에서 1802㎎의 1 wt% NaOH 중에서 수화시켰다. 800.7㎎의 AA2G를 바이알에 넣은 후, 713.7㎎의 BDDE 및 1416.8㎎의 10% NaOH를 넣었다. 상기 용액(pH >12)을 ~20분 동안 50℃ 수욕에서 반응시킨 후, 수화된 HA를 첨가하였다. 첨가 후, 혼합물을 2개의 주사기 사이에 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 ~20회 혼합하였다. 혼합한 페이스트를 바이알 및 50℃ 수욕에 ~2.5 시간 동안 넣었다. 223.5㎎의 12M HCl을 9.05g PBS, pH7.4에 첨가하였다. ~2.5 시간 후, HA-AA2G 겔이 형성되었다. 겔을 조각으로 절단하였고, HCl-PBS 용액을 그것에 첨가하였다. 겔을 중화시켰고, 오비탈쉐이커 상에서 밤새 팽창시켰다. 겔을 ~60㎛ 스크린을 통해 크기를 바꾸었고, 2개 주사기 사이에 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 ~20회 혼합하였다. 겔을 15,000 MWCO RC 투석 백 내에 넣었고, PBS, pH7.4 완충제 중에서 투석하였다. PBS 완충제의 빈번한 변화와 함께 ~185시간 동안 투석을 진행하였다. 투석 후, 겔을 주사기에 넣었고, 4℃ 냉장고에 저장하였다.400.6 mg of low molecular weight hyaluronic acid (LMW HA) was hydrated in 1802 mg of 1 wt% NaOH in a syringe for -30 minutes. After 800.7 mg of AA2G was put into the vial, 713.7 mg of BDDE and 1416.8 mg of 10% NaOH were added. The solution (pH >12) was reacted in a 50° C. water bath for -20 minutes, and then hydrated HA was added. After addition, the mixture was mixed -20 times by passing it back and forth between two syringes. The mixed paste was placed in a vial and a 50° C. water bath for -2.5 hours. 223.5 mg of 12M HCl was added to 9.05 g PBS, pH 7.4. After ˜2.5 hours, an HA-AA2G gel was formed. The gel was cut into pieces and HCl-PBS solution was added to it. The gel was neutralized and swollen overnight on an orbital shaker. The gel was resized through a -60 μm screen and mixed -20 times by passing back and forth between two syringes. The gel was placed in a 15,000 MWCO RC dialysis bag and dialyzed in PBS, pH 7.4 buffer. Dialysis was performed for ~185 hours with frequent changes in PBS buffer. After dialysis, the gel was put into a syringe and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C.
실시예 2: AA2G 컨쥬게이션의 결정Example 2: Determination of AA2G conjugation
실시예 1에 기재한 바와 같은 겔의 중량을 투석 직전, 및 투석 후 기록하였다. 투석 후 겔은 ~1g/㎖인 것으로 추정하였다. > 8시간 당 1ℓ의 PBS에서 주목할 만한 AA2G가 생성되지 않는 지점에서 투석을 중단하였다. UV/Vis 분광광도계(Nanodrop 2000C, 써모사이언티픽(ThermoScientific))을 사용하여 260㎚에서 AA2G를 측정하였다. 2% HA 중의 AA2G의 상이한 농도를 사용하여 AA2G의 교정 곡선을 계산하였다(A@260㎚ = 1.4838 [AA2G(mM)])The weight of the gel as described in Example 1 was recorded immediately before and after dialysis. After dialysis, the gel was estimated to be -1 g/ml. > Dialysis was stopped at the point where no noticeable AA2G was produced in 1 liter of PBS per 8 hours. AA2G was measured at 260 nm using a UV/Vis spectrophotometer (Nanodrop 2000C, ThermoScientific). The calibration curve of AA2G was calculated using different concentrations of AA2G in 2% HA (A@260nm = 1.4838 [AA2G(mM)])
투석 후 HA의 중량: HA의 시작 중량 x (투석 전 실제 중량/이론적 중량)Weight of HA after dialysis: starting weight of HA x (actual/theoretical weight before dialysis)
투석 후 AA2G의 m㏖: 식(A@260㎚ = 1.4838 [AA2G(mM)])에서 투석 후 260㎚에서 흡광도를 놓음.The mmol of AA2G after dialysis: Put the absorbance at 260nm after dialysis in the formula (A@260nm = 1.4838 [AA2G(mM)]).
AA2G에서 컨쥬게이션: (AA2G의 m㏖/HA의 m㏖)x100%Conjugation in AA2G: (mmol of AA2G/mmol of HA)x100%
실시예 1에 기재되는 바와 같이 겔에서 AA2G 컨쥬게이션 정도는 14.7㏖%이다.As described in Example 1, the degree of AA2G conjugation in the gel is 14.7 mol%.
실시예 3: 겔 유동학적 특성의 결정Example 3: Determination of gel rheological properties
진동 평행판 유동계(안톤 파르(Anton Paar), 피시카(Physica) MCR 301)를 사용하여 실시예 1에서 얻은 겔의 특성을 측정하였다. 사용한 플레이트의 직경은 25㎜였다. 플레이트 사이의 갭을 1㎜에서 설정하였다. 각 측정을 위해, 일정 변형률에서 주파수 스윕을 우선 실행한 후 고정된 주파수에서 변형 스윕을 실행하였다. G'(저장 탄성률)를 1% 변형에서 변형 스윕 곡선으로부터 얻었다. 값은 겔에 대해 1450㎩였다.The properties of the gel obtained in Example 1 were measured using a vibrating parallel plate rheometer (Anton Paar, Physica MCR 301). The diameter of the plate used was 25 mm. The gap between the plates was set at 1 mm. For each measurement, a frequency sweep was first performed at a constant strain and then a strain sweep was performed at a fixed frequency. G'(storage modulus) was obtained from the strain sweep curve at 1% strain. The value was 1450 Pa for the gel.
실시예 4: 가변 컨쥬게이션 정도 및 겔 유동학적 특성을 지니는 가교제로서 BDDE를 사용하는 가교된 HA 겔에 대한 AA2G 컨쥬게이션Example 4: AA2G conjugation to crosslinked HA gel using BDDE as a crosslinking agent with variable degree of conjugation and gel rheological properties
절차는 실시예 1에서 기재한 것과 유사하였다. 컨쥬게이션 정도는 가교제 대 HA 및 AA2G ㏖ 비를 조절함으로써 변형시킨다. 겔 특성을 실시예 3에서 기재한 바와 같이 측정하였다. 세부사항은 다음과 같다:The procedure was similar to that described in Example 1. The degree of conjugation is modified by controlling the ratio of crosslinker to HA and AA2G moles. Gel properties were measured as described in Example 3. Details are as follows:
400.8㎎의 LMW HA를 ~30분 동안 주사기 내 1752.1㎎의 1% NaOH 중에서 수화시켰다. 800.3㎎의 AA2G를 바이알 내에 넣은 후 354.1㎎의 BDDE 및 1402.0㎎의 10% NaOH를 넣었다. 상기 용액(pH >12)을 ~20분 동안 50℃ 수욕에서 반응시킨 후, 수화된 HA를 첨가하였다. 첨가 후, 혼합물을 2개의 주사기 사이에 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 ~20회 혼합하였다. 혼합한 페이스트를 바이알 및 50℃ 수욕에 ~2.5 시간 동안 넣었다. 140.9㎎의 12M HCl을 9.0053g PBS, pH7.4에 첨가하였다. ~2.5 시간 후, HA-AA2G 겔이 형성되었다. 겔을 조각으로 절단하였고, HCl-PBS 용액을 그것에 첨가하였다. 겔을 중화시켰고, 오비탈쉐이커 상에서 밤새 팽창시켰다. 겔을 ~60㎛ 스크린을 통해 크기를 바꾸었고, 2개 주사기 사이에 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 ~20회 혼합하였다. 겔을 15,000 MWCO RC 투석 백 내에 넣었고, PBS, pH7.4 완충제 중에서 투석하였다. PBS 완충제의 빈번한 변화와 함께 ~164.5시간 동안 투석을 진행하였다. 투석 후, 겔을 주사기에 넣었고, 4℃ 냉장고에 저장하였다. 컨쥬게이션 정도는 13%이다. 겔 저장 탄성률(G')은 803㎩이다.400.8 mg of LMW HA was hydrated in 1752.1 mg of 1% NaOH in a syringe for -30 minutes. 800.3 mg of AA2G was put into the vial, followed by 354.1 mg of BDDE and 1402.0 mg of 10% NaOH. The solution (pH >12) was reacted in a 50° C. water bath for -20 minutes, and then hydrated HA was added. After addition, the mixture was mixed -20 times by passing it back and forth between two syringes. The mixed paste was placed in a vial and a 50° C. water bath for -2.5 hours. 140.9 mg of 12M HCl was added to 9.0053 g PBS, pH 7.4. After ˜2.5 hours, an HA-AA2G gel was formed. The gel was cut into pieces and HCl-PBS solution was added to it. The gel was neutralized and swollen overnight on an orbital shaker. The gel was resized through a -60 μm screen and mixed -20 times by passing back and forth between two syringes. The gel was placed in a 15,000 MWCO RC dialysis bag and dialyzed in PBS, pH 7.4 buffer. Dialysis was performed for ~164.5 hours with frequent changes in PBS buffer. After dialysis, the gel was put into a syringe and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C. The degree of conjugation is 13%. The gel storage modulus (G') is 803 Pa.
실시예 5: 가교제로서 BDDE를 사용하는 가교된 HA 겔에 AA2G 컨쥬게이션, 컨쥬게이션 정도는 5.3%이고, G'는 ~ 300㎩이다.Example 5: AA2G conjugation to a crosslinked HA gel using BDDE as a crosslinking agent, the degree of conjugation is 5.3%, and G'is -300 Pa.
400.3㎎의 LMW HA를 ~30분 동안 주사기 내 3002.0㎎의 1% NaOH 중에서 수화시켰다. 800.5㎎의 AA2G를 바이알 내에 넣은 후 264.3㎎의 BDDE 및 1100.0㎎의 10% NaOH를 넣었다. 상기 용액(pH >12)을 ~20분 동안 50℃ 수욕에서 반응시킨 후, 수화된 HA를 첨가하였다. 첨가 후, 혼합물을 2개의 주사기 사이에 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 ~20회 혼합하였다. 혼합한 페이스트를 바이알 및 50℃ 수욕에 ~2.5 시간 동안 넣었다. 104.2㎎의 12M HCl을 8.5128g PBS, pH7.4에 첨가하였다. ~2.5시간 후, HA-AA2G 겔이 형성되었고, HCl-PBS 용액을 그것에 첨가하였다. 겔을 중화시키고, 오비탈쉐이커 상에서 주말(~55시간)에 걸쳐 팽창시켰다. 겔을 ~60㎛ 스크린을 통해 크기를 바꾸었고, 2개 주사기 사이에 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 ~20회 혼합하였다. 겔을 15,000 MWCO RC 투석 백 내에 넣었고, PBS, pH7.4 완충제 중에서 투석하였다. PBS 완충제의 빈번한 변화와 함께 ~114시간 동안 투석을 진행하였다. 투석 후, 겔을 주사기에 넣었고, 4℃ 냉장고에 저장하였다. 컨쥬게이션 정도 및 겔 유동학적 특성을 실시예 2 및 3에 기재한 바와 같은 절차에서 측정한다. 컨쥬게이션 정도는 5.3%이다. 겔 저장률(G')은 ~300㎩이다.400.3 mg of LMW HA was hydrated in 3002.0 mg of 1% NaOH in a syringe for -30 minutes. After 800.5 mg of AA2G was put into the vial, 264.3 mg of BDDE and 1100.0 mg of 10% NaOH were added. The solution (pH >12) was reacted in a 50° C. water bath for -20 minutes, and then hydrated HA was added. After addition, the mixture was mixed -20 times by passing it back and forth between two syringes. The mixed paste was placed in a vial and a 50° C. water bath for -2.5 hours. 104.2 mg of 12M HCl was added to 8.5128g PBS, pH 7.4. After ˜2.5 hours, a HA-AA2G gel was formed, and a HCl-PBS solution was added to it. The gel was neutralized and swollen over the weekend (-55 hours) on an orbital shaker. The gel was resized through a -60 μm screen and mixed -20 times by passing back and forth between two syringes. The gel was placed in a 15,000 MWCO RC dialysis bag and dialyzed in PBS, pH 7.4 buffer. Dialysis was performed for ~114 hours with frequent changes in PBS buffer. After dialysis, the gel was put into a syringe and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C. The degree of conjugation and the gel rheological properties are measured in the procedure as described in Examples 2 and 3. The degree of conjugation is 5.3%. The gel storage rate (G') is -300 Pa.
실시예 6: 가교제로서 스타-PEG 에폭사이드를 사용하는 가교된 HA 겔에 대한 AA2G 컨쥬게이션, 컨쥬게이션 정도는 29.4%이고, G'는 ~ 235㎩이다.Example 6: AA2G conjugation to a crosslinked HA gel using star-PEG epoxide as a crosslinking agent, the degree of conjugation is 29.4%, and G'is -235Pa.
200.4㎎의 LMW HA를 ~30분 동안 주사기 내 2000㎎의 1% NaOH 중에서 수화시켰다. 400㎎의 AA2G를 바이알 내에 넣은 후 312.7㎎의 스타-PEG 에폭사이드 및 1026.5㎎㎎의 10% NaOH를 넣었다. 상기 용액을 ~20분 동안 50℃ 수욕에서 반응시킨 후, 수화된 HA에 첨가하였다. 첨가 후, 혼합물을 2개의 주사기 사이에 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 ~20회 혼합하였다. 혼합한 페이스트를 바이알 및 50℃ 수욕에 ~2.5 시간 동안 넣었다. 187.4㎎의 12M HCl을 3.034g PBS, pH7.4에 첨가하였다. ~2.5시간 후, HA-AA2G 겔이 형성되었고, HCl-PBS 용액을 그것에 첨가하였다. 겔을 중화시키고, 오비탈쉐이커 상에서 주말(~68시간)에 걸쳐 팽창시켰다. 겔을 ~60㎛ 스크린을 통해 크기를 바꾸었고, 2개 주사기 사이에 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 ~20회 혼합하였다. 겔을 15,000 MWCO RC 투석 백 내에 넣었고, PBS, pH7.4 완충제 중에서 투석하였다. PBS 완충제의 빈번한 변화와 함께 ~95시간 동안 투석을 진행하였다. 투석 후, 겔을 주사기에 넣었고, 4℃ 냉장고에 저장하였다. 컨쥬게이션 정도 및 겔 유동학적 특성을 실시예 2 및 3에 기재한 바와 같은 절차에서 측정한다. 컨쥬게이션 정도는 29.4%이다. 겔 저장 탄성률(G')은 ~235㎩이다.200.4 mg of LMW HA was hydrated in 2000 mg of 1% NaOH in a syringe for -30 minutes. After 400 mg of AA2G was put into the vial, 312.7 mg of star-PEG epoxide and 1026.5 mg of 10% NaOH were added. The solution was reacted in a 50° C. water bath for ˜20 minutes, and then added to the hydrated HA. After addition, the mixture was mixed -20 times by passing it back and forth between two syringes. The mixed paste was placed in a vial and a 50° C. water bath for -2.5 hours. 187.4 mg of 12M HCl was added to 3.034 g PBS, pH 7.4. After ˜2.5 hours, a HA-AA2G gel was formed, and a HCl-PBS solution was added to it. The gel was neutralized and swollen over the weekend (-68 hours) on an orbital shaker. The gel was resized through a -60 μm screen and mixed -20 times by passing back and forth between two syringes. The gel was placed in a 15,000 MWCO RC dialysis bag and dialyzed in PBS, pH 7.4 buffer. Dialysis was performed for ~95 hours with frequent changes in PBS buffer. After dialysis, the gel was put into a syringe and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C. The degree of conjugation and the gel rheological properties are measured in the procedure as described in Examples 2 and 3. The degree of conjugation is 29.4%. The gel storage modulus (G') is -235 Pa.
실시예 7: 가교제로서 스타-PEG 에폭사이드를 사용하는 가교된 HA 겔에 대한 AA2G 컨쥬게이션, 컨쥬게이션 정도는 27.8%이고, G'는 ~ 363㎩이다.Example 7: AA2G conjugation to a crosslinked HA gel using star-PEG epoxide as a crosslinking agent, the degree of conjugation is 27.8%, and G'is -363 Pa.
200.3㎎의 LMW HA를 ~30분 동안 주사기 내 2000㎎의 1% NaOH 중에서 수화시켰다. 400.2㎎의 AA2G를 바이알 내에 넣은 후 313.4㎎의 스타-PEG 에폭사이드 및 1022.6㎎㎎의 10% NaOH를 넣었다. 상기 용액을 수화된 HA에 첨가하였다. 첨가 후, 혼합물을 2개의 주사기 사이에 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 ~20회 혼합하였다. 혼합한 페이스트를 바이알 및 50℃ 수욕에 ~2.5 시간 동안 넣었다. 196.5㎎의 12M HCl을 3.016g PBS, pH7.4에 첨가하였다. ~2.5시간 후, HA-AA2G 겔이 형성되었고, HCl-PBS 용액을 그것에 첨가하였다. 겔을 중화시켰고, 오비탈쉐이커 상에서 밤새(~24시간) 팽창시켰다. 겔을 ~60㎛ 스크린을 통해 크기를 바꾸었고, 2개 주사기 사이에 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 ~20회 혼합하였다. 겔을 15,000 MWCO RC 투석 백 내에 넣었고, PBS, pH7.4 완충제 중에서 투석하였다. PBS 완충제의 빈번한 변화와 함께 ~98.5시간 동안 투석을 진행하였다. 투석 후, 겔을 주사기에 넣었고, 4℃ 냉장고에 저장하였다. 컨쥬게이션 정도 및 겔 유동학적 특성을 실시예 2 및 3에 기재한 바와 같은 절차에서 측정한다. 컨쥬게이션 정도는 27.8%이다. 겔 저장 탄성률(G')은 ~363㎩이다.200.3 mg of LMW HA was hydrated in 2000 mg of 1% NaOH in a syringe for -30 minutes. After 400.2 mg of AA2G was put into the vial, 313.4 mg of star-PEG epoxide and 1022.6 mg of 10% NaOH were added. This solution was added to the hydrated HA. After addition, the mixture was mixed -20 times by passing it back and forth between two syringes. The mixed paste was placed in a vial and a 50° C. water bath for -2.5 hours. 196.5 mg of 12M HCl was added to 3.016 g PBS, pH 7.4. After ˜2.5 hours, a HA-AA2G gel was formed, and a HCl-PBS solution was added to it. The gel was neutralized and swollen overnight (-24 hours) on an orbital shaker. The gel was resized through a -60 μm screen and mixed -20 times by passing back and forth between two syringes. The gel was placed in a 15,000 MWCO RC dialysis bag and dialyzed in PBS, pH 7.4 buffer. Dialysis was performed for -98.5 hours with frequent changes in PBS buffer. After dialysis, the gel was put into a syringe and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C. The degree of conjugation and the gel rheological properties are measured in the procedure as described in Examples 2 and 3. The degree of conjugation is 27.8%. The gel storage modulus (G') is -363 Pa.
실시예 8: 가교제로서 BDDE를 사용하는 가교된 HMW HA 겔에 AA2G 컨쥬게이션, 컨쥬게이션 정도는 10㏖%이고, G'는 ~ 240㎩이다.Example 8: AA2G conjugation to a crosslinked HMW HA gel using BDDE as a crosslinking agent, the degree of conjugation is 10 mol%, and G'is -240 Pa.
400.3㎎의 LMW HA를 ~30분 동안 주사기 내 2501.3㎎의 4% NaOH 중에서 수화시켰다. 1200㎎의 AA2G를 바이알 내에 넣은 후 304.7㎎의 BDDE 및 1178.6㎎의 16% NaOH를 넣었다. 상기 용액(pH >12)을 ~20분 동안 50℃ 수욕에서 반응시키고, 20cc 주사기에 옮긴 후, 수화된 HA를 첨가하였다. 첨가 후, 혼합물을 2개의 주사기 사이에 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 ~20회 혼합하였다. 혼합한 페이스트를 20cc 바이알에 및 50℃ 수욕에 ~2.5 시간 동안 넣었다. ~2.5시간 후, HA-AA2G 겔이 형성되었다. 그 다음에, 226.6㎎의 12M HCl을 8492.2㎎ 10X PBS, pH7.4에 첨가하여 HCl-PBS 용액을 얻었고, HCl-PBS 용액을 첨가하여 중화시켰고, 겔을 팽창시켰다. 겔을 중화시켰고, 오비탈쉐이커 상에서 48시간에 걸쳐 팽창시켰다. 겔을 ~60㎛ 스크린을 통해 크기를 바꾸었고, 2개 주사기 사이에 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 ~20회 혼합하였다. 겔을 20,000 MWCO CE 투석 백 내에 넣었고, PBS, pH7.4 완충제 중에서 투석하였다. PBS 완충제의 빈번한 변화와 함께 ~114시간 동안 투석을 진행하였다. 투석 후, 겔을 주사기에 넣었고, 4℃ 냉장고에 저장하였다. 컨쥬게이션 정도 및 겔 유동학적 특성을 실시예 2 및 3에 기재한 바와 같은 절차에서 측정한다. 컨쥬게이션 정도는 10㏖%이다. 겔 저장 탄성률(G')은 ~240㎩이다.400.3 mg of LMW HA was hydrated in 2501.3 mg of 4% NaOH in a syringe for -30 minutes. 1200 mg AA2G was placed in the vial, followed by 304.7 mg of BDDE and 1178.6 mg of 16% NaOH. The solution (pH >12) was reacted in a 50° C. water bath for ~20 minutes, transferred to a 20cc syringe, and hydrated HA was added. After addition, the mixture was mixed -20 times by passing it back and forth between two syringes. The mixed paste was placed in a 20 cc vial and in a 50° C. water bath for -2.5 hours. After ~2.5 hours, a HA-AA2G gel was formed. Then, 226.6 mg of 12M HCl was added to 8492.2 mg 10X PBS, pH 7.4 to obtain a HCl-PBS solution, which was neutralized by adding HCl-PBS solution, and the gel was swollen. The gel was neutralized and swollen over 48 hours on an orbital shaker. The gel was resized through a -60 μm screen and mixed -20 times by passing back and forth between two syringes. The gel was placed in a 20,000 MWCO CE dialysis bag and dialyzed in PBS, pH 7.4 buffer. Dialysis was performed for ~114 hours with frequent changes in PBS buffer. After dialysis, the gel was put into a syringe and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C. The degree of conjugation and the gel rheological properties are measured in the procedure as described in Examples 2 and 3. The degree of conjugation is 10 mol%. The gel storage modulus (G') is -240 Pa.
실시예 9: 가교제로서 BDDE를 사용하는 가교된 HMW HA 겔에 비타겐 컨쥬게이션, 컨쥬게이션 정도는 15㏖%이고, G'는 ~ 365㎩이다.Example 9: Vitagen conjugation to a crosslinked HMW HA gel using BDDE as a crosslinking agent, the degree of conjugation is 15 mol%, and G'is-365 Pa.
398.2㎎의 LMW HA를 ~40분 동안 주사기 내 1753.24㎎의 1 wt% NaOH 중에서 수화시켰다. BDDE(311.7㎎)를 첨가하여 HA를 팽창시켰고, 다른 80분 동안 HA를 팽창시켰다. 팽창된 HA/BDDE 혼합물을 50℃에서 20분 동안 사전반응시켰다.398.2 mg of LMW HA was hydrated in 1753.24 mg of 1 wt% NaOH in a syringe for -40 minutes. The HA was swollen by the addition of BDDE (311.7 mg), and the HA was swollen for another 80 minutes. The expanded HA/BDDE mixture was pre-reacted at 50° C. for 20 minutes.
801.9㎎의 비타겐을 1459.7㎎의 10중량% NaOH 중에서 분리하여 용해시켰고, BDDE와 사전 반응시킨 HA와 혼합하였다. 혼합물을 다른 2.5시간 동안 50℃에서 반응을 계속하였다. ~2.5시간 후, HA-비타겐 겔이 형성되었다. 그 다음에, 195㎎의 12M HCl을 9004.0㎎ 10X PBS, pH7.4에 첨가하여 HCl-PBS 용액을 얻었고, HCl-PBS 용액을 첨가하여 중화시켰고, 겔을 팽창시켰다. 겔을 중화시켰고, 오비탈쉐이커 상에서 48시간에 걸쳐 팽창시켰다. 겔을 ~60㎛ 스크린을 통해 크기를 바꾸었고, 2개 주사기 사이에 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 ~20회 혼합하였다. 겔을 20,000 MWCO CE 투석 백 내에 넣었고, PBS, pH7.4 완충제 중에서 투석하였다. PBS 완충제의 빈번한 변화와 함께 ~120시간 동안 투석을 진행하였다. 투석 후, 겔을 주사기에 넣었고, 4℃ 냉장고에 저장하였다. 겔 유동학적 특성을 실시예 3에 기재한 바와 같은 절차에서 측정한다. 컨쥬게이션 정도는 실시예 2에 기재된 바와 같은 AA2G 결정과 유사한 방법을 사용하여 약 15㏖%가 되는 것으로 결정하였다. 겔 저장 탄성률(G')은 ~365㎩이다.801.9 mg of Vitagen was separated and dissolved in 1459.7 mg of 10 wt% NaOH, and mixed with the HA pre-reacted with BDDE. The mixture was continued to react at 50° C. for another 2.5 hours. After -2.5 hours, an HA-vitagen gel was formed. Then, 195 mg of 12M HCl was added to 9004.0 mg 10X PBS, pH 7.4 to obtain a HCl-PBS solution, which was neutralized by adding HCl-PBS solution, and the gel was swollen. The gel was neutralized and swollen over 48 hours on an orbital shaker. The gel was resized through a -60 μm screen and mixed -20 times by passing back and forth between two syringes. The gel was placed in a 20,000 MWCO CE dialysis bag and dialyzed in PBS, pH 7.4 buffer. Dialysis was performed for ~120 hours with frequent changes in PBS buffer. After dialysis, the gel was put into a syringe and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C. Gel rheological properties are measured in the procedure as described in Example 3. The degree of conjugation was determined to be about 15 mol% using a method similar to AA2G determination as described in Example 2. The gel storage modulus (G') is -365 Pa.
실시예 10: 아미드화 화학을 통한 선형 HA에 비타겐 컨쥬게이션Example 10: Vitagen conjugation to linear HA via amidation chemistry
200.3㎎의 HMW HA를 60cc 주사기 내 10㎖의 수중에서 수화시켰다. 500㎎의 비타겐을 0.5㎖의 수중에서 용해시켰고, 용액을 pH 4.8로 중화시켰다. 197.7㎎의 EDC 및 149㎎의 NHS를 6㎖의 수중에 개별적으로 용해시켰다. 상기 용액(용개 및 EDC/NHS 용액)을 23.5㎖의 물을 함유하는 다른 60cc 주사기에 첨가한다. 2개의 주사기 사이에 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 두 주사기를 ~20회 혼합한다. 혼합물을 하나의 주사기에 저장하였고, 37℃ 욕에서 4시간 동안 침지시켰다. 뚜렷한 비타겐이 관찰되지 않을 때까지 PBS pH7.4 완충제에 대해 용액을 최종적으로 투석하였다. 컨쥬게이션 정도를 실시예 3에 기재한 바와 유사한 방법에 의해 결정하였다. 컨쥬게이션 정도는 약 10㏖%이다.200.3 mg of HMW HA was hydrated in 10 ml of water in a 60 cc syringe. 500 mg of Vitagen was dissolved in 0.5 ml of water and the solution was neutralized to pH 4.8. 197.7 mg of EDC and 149 mg of NHS were individually dissolved in 6 ml of water. This solution (Yunggae and EDC/NHS solution) is added to another 60cc syringe containing 23.5 ml of water. Mix the two syringes -20 times by passing it back and forth between the two syringes. The mixture was stored in one syringe and immersed in a 37° C. bath for 4 hours. The solution was finally dialyzed against PBS pH7.4 buffer until no apparent vitagen was observed. The degree of conjugation was determined by a method similar to that described in Example 3. The degree of conjugation is about 10 mol%.
실시예 11: HA 겔에 가교된 AA2PG 컨쥬게이션Example 11: AA2PG conjugation crosslinked to HA gel
200.4㎎의 LMW HA를 ~30분 동안 주사기 내 1000㎎의 MES 5.2 완충제 중에서 수화시켰다. 292㎎의 AA2P를 바이알 내에 넣은 후 300㎎의 스타-PEG 아민을 첨가하였다. 상기 용액을 실온에서 밤새 반응시켰다. 겔을 PBS 완충제로 수화시켰고, PBS 완충제에 대해 투석시켜 미반응 AA2P를 제거하였다. 최종적으로 겔을 실시예 2 및 3에서 기재한 바와 같이 특성규명하여 컨쥬게이션 정도 및 겔 유동학적 특성을 결정하였다. 컨쥬게이션 정도는 약 20㏖%이다. 겔 저장 탄성률(G')은 약 500㎩이다.200.4 mg of LMW HA was hydrated in 1000 mg of MES 5.2 buffer in a syringe for -30 minutes. After 292 mg of AA2P was placed in the vial, 300 mg of star-PEG amine was added. The solution was reacted at room temperature overnight. The gel was hydrated with PBS buffer and dialyzed against PBS buffer to remove unreacted AA2P. Finally, the gel was characterized as described in Examples 2 and 3 to determine the degree of conjugation and gel rheological properties. The degree of conjugation is about 20 mol%. The gel storage modulus (G') is about 500 Pa.
실시예 12Example 12
잔주름의 외관을 감소시키기 위한 AA2G를 지니는 HA/BDDE 진피 필러의 제형화 Formulation of HA/BDDE dermal filler with AA2G to reduce the appearance of fine lines
투석 후 상기 실시예에서 기재한 겔 중 어떤 것에 대해, 적합한 양의 유리 HA 겔을 겔 응집도 및/또는 주사능력을 개선 또는 변형시키기 위한 겔에 첨가하였다. 예를 들어, 유리 HA 섬유를 인산염 완충 용액 중에서 팽창시켜 균일한 점탄성 겔("유리" HA 겔)을 얻었다. 투석 단계 전 이 가교된 겔을 실시예 1에서 얻은 HA/BDDE 가교 겔에 1 첨가한다(예를 들어, 약 1% 내지 약 5% w/w 유리 HA를 갖는 조성물을 얻기 위함). 그 다음에 얻어진 겔을 바로 채울 수 있는 멸균 주사기에 채우고, 적어도 약 1분 동안 멸균화를 위해 충분한 온도 및 압력에서 오토클레이브한다. 오토클레이빙 후, 최종 HA/AA2G 생성물을 포장하고, 안와 또는 다른 얼굴 영역에서 잔주름의 외관을 개선시키기 위해 깊지 않은 주사를 위한 진피 필러로서 사용을 위해 의사에게 유통시킨다. For any of the gels described in the above examples after dialysis, a suitable amount of free HA gel was added to the gel to improve or modify the degree of gel cohesion and/or injectability. For example, free HA fibers were swollen in a phosphate buffer solution to obtain a homogeneous viscoelastic gel ("free" HA gel). Prior to the dialysis step, this crosslinked gel is added 1 to the HA/BDDE crosslinked gel obtained in Example 1 (eg, to obtain a composition having from about 1% to about 5% w/w free HA). The resulting gel is then filled into a ready-to-fill sterile syringe and autoclaved at a temperature and pressure sufficient for sterilization for at least about 1 minute. After autoclaving, the final HA/AA2G product is packaged and distributed to a physician for use as a dermal filler for non-deep injection to improve the appearance of fine lines in the orbit or other facial areas.
실시예 13Example 13
리도카인을 포함하는HA-AA2G 진피 필러의 제형화Formulation of HA-AA2G Dermal Filler Containing Lidocaine
실시예 12의 절차에 따르지만, 투석 단계 후 및 유리 HA 겔의 첨가 전, 리도카인 염소수화물(리도카인 HCl)을 혼합물에 첨가한다. 분말 형태에서 (리도카인 HCl)을 WFI 중에서 우선 가용화시킬 수 있고, 0.2㎛ 필터를 통해 여과시킬 수 있다. 약간 염기성인 PH에 도달되도록(예를 들어, 약 7.5 내지 약 8의 pH) 묽은 NaOH 용액을 응집성 HA/AA2G 겔에 첨가한다. 그 다음에 리도카인 HCl 용액을 약간 염기성인 겔에 첨가하여, 최종 원하는 농도, 예를 들어 약 0.3% (w/w)의 농도에 도달된다. 그 다음에 HA/AA2G/리도카인 혼합물의 얻어진 pH는 약 7이고, HA 농도는 약 24 mg/g이다. 기계적 혼합을 수행하여 적절한 배합 기계를 구비한 표준 반응기에서 적절한 균일성을 얻는다.Following the procedure of Example 12, but after the dialysis step and before the addition of the free HA gel, lidocaine chlorine hydrate (lidocaine HCl) is added to the mixture. In powder form (lidocaine HCl) can be first solubilized in WFI and filtered through a 0.2 μm filter. Dilute NaOH solution is added to the cohesive HA/AA2G gel so that a slightly basic pH is reached (eg, a pH of about 7.5 to about 8). The lidocaine HCl solution is then added to the slightly basic gel to reach the final desired concentration, for example about 0.3% (w/w). Then the obtained pH of the HA/AA2G/lidocaine mixture is about 7 and the HA concentration is about 24 mg/g. Mechanical mixing is carried out to obtain adequate uniformity in a standard reactor equipped with an appropriate blending machine.
실시예 14Example 14
HA 하이드로겔에 대해 카복실 작용기를 함유하는 첨가제의 컨쥬게이션Conjugation of additives containing carboxyl functional groups to HA hydrogels
레티논산(AKA, 트레티노인), 외관 및 알파-리포산과 같은 첨가제는 카복실 작용기(-COOH)를 함유한다. 이들 첨가제는 EDC 화학을 사용하는 에스터화를 통해 HA 가수분해에 컨쥬게이션된다. 본 발명에 따른 컨쥬게이션을 위한 예는 다음과 같이 기재한다:Additives such as retinoic acid (AKA, tretinoin), appearance and alpha-lipoic acid contain carboxyl functional groups (-COOH). These additives are conjugated to HA hydrolysis through esterification using EDC chemistry. Examples for conjugation according to the invention are described as follows:
200㎎의 HMW HA를 60cc 주사기 내 10㎖의 pH 4.8 MES 완충제 중에서 수화시켰다. 다른 주사기에서, 200㎎의 레티노산을 5㎖의 물-아세톤 혼합물(물/아세톤 용적 비 1:3) 중에서 용해시킨다. 상기 두 주사기를 약 20회 동안 주사기 커넥터를 통해 혼합한다. 그 다음에 197.7㎎의 EDC 및 149㎎의 NHS를 6㎖의 수중에 개별적으로 용해시켰다. EDC 및 NHS를 함유하는 주사기를 HA 및 레티노산을 함유하는 주사기에 연결하여 2개의 주사기를 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 적어도 20회 동안 반응물을 혼합시킨다. 혼합물을 하나의 주사기에 저장하였고, 37℃ 욕에서 4시간 동안 침지시켰다. 겔을 아이소프로판올에 대해 투석시켜 미컨쥬게이트된 레티노산을 제거한 다음, 공비 조건 하에 PBS 완충제에 대해 투석한다. 겔을 멸균 주사기 내로 포장하고, 4℃에서 저장한다.200 mg of HMW HA was hydrated in 10 ml of pH 4.8 MES buffer in a 60 cc syringe. In another syringe, 200 mg of retinoic acid is dissolved in 5 ml of a water-acetone mixture (water/acetone volume ratio 1:3). The two syringes are mixed through the syringe connector for about 20 times. Then 197.7 mg of EDC and 149 mg of NHS were individually dissolved in 6 ml of water. The reaction is mixed for at least 20 times by connecting the syringe containing EDC and NHS to the syringe containing HA and retinoic acid and passing two syringes back and forth. The mixture was stored in one syringe and immersed in a 37° C. bath for 4 hours. The gel is dialyzed against isopropanol to remove unconjugated retinoic acid and then dialyzed against PBS buffer under azeotropic conditions. The gel is packaged into a sterile syringe and stored at 4°C.
실시예 15Example 15
HA 하이드로겔에 하이드록실 작용기를 함유하는 첨가제의 컨쥬게이션.Conjugation of an additive containing a hydroxyl functional group to an HA hydrogel.
레티놀(AKA, 트레티노인), 카탈라제, 다이메틸아미노에탄올 및 g-토코페롤과 같은 첨가제는 하이드록실 작용기(-OH)를 함유한다. 이들 첨가제는 EDC 화학을 사용하는 에스터화를 통해 HA 가수분해에 컨쥬게이션된다. 컨쥬게이션을 위한 전형적인 예를 다음과 같이 기재한다:Additives such as retinol (AKA, tretinoin), catalase, dimethylaminoethanol and g-tocopherol contain hydroxyl functional groups (-OH). These additives are conjugated to HA hydrolysis through esterification using EDC chemistry. A typical example for conjugation is described as follows:
200㎎의 HMW HA를 60cc 주사기 내 10㎖의 pH 4.8 2-(N-모폴리노) 에탄설폰산(MES) 완충제 중에서 수화시킨다. 다른 주사기에서, 200㎎의 레티놀산을 5㎖의 물-아세톤 혼합물(물/아세톤 용적 비 1:3) 중에서 용해시킨다. 상기 두 주사기를 약 20회 동안 주사기 커넥터를 통해 혼합한다. 그 다음에 197.7㎎의 EDC 및 149㎎의 NHS를 6㎖의 수중에 개별적으로 용해시켰다. EDC 및 NHS를 함유하는 주사기를 HA 및 레티놀을 함유하는 주사기에 연결하여 2개의 주사기를 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 적어도 20회 동안 반응물을 혼합시킨다. 혼합물을 하나의 주사기에 저장하였고, 37℃ 욕에서 4시간 동안 침지시켰다. 겔을 아이소프로판올에 대해 투석시켜 미컨쥬게이트된 레티놀을 제거한 다음, 공비 조건 하에 PBS 완충제에 대해 투석한다. 겔을 멸균 주사기 내로 포장하고, 4℃에서 저장한다.200 mg of HMW HA is hydrated in 10 ml of pH 4.8 2-(N-morpholino) ethanesulfonic acid (MES) buffer in a 60 cc syringe. In another syringe, 200 mg of retinoleic acid is dissolved in 5 ml of a water-acetone mixture (water/acetone volume ratio 1:3). The two syringes are mixed through the syringe connector for about 20 times. Then 197.7 mg of EDC and 149 mg of NHS were individually dissolved in 6 ml of water. The reaction is mixed for at least 20 times by connecting the syringe containing EDC and NHS to the syringe containing HA and retinol and passing the two syringes back and forth. The mixture was stored in one syringe and immersed in a 37° C. bath for 4 hours. The gel is dialyzed against isopropanol to remove unconjugated retinol and then dialyzed against PBS buffer under azeotropic conditions. The gel is packaged into a sterile syringe and stored at 4°C.
실시예 16Example 16
개질 후 HA 하이드로겔에 하이드록실 작용기를 함유하는 첨가제의 컨쥬게이션.Conjugation of additives containing hydroxyl functional groups to HA hydrogel after modification.
이는 2단계 과정이다.This is a two-step process.
단계 1: 가교된 HA 겔, 예를 들어 상업적 HA계 진피 필러, 예를 들어 쥬비덤(JUVEDERM)(등록상표), 캘리포니아주 얼바인에 소재한 앨러건 또는 레스틸란(Restylane)(등록상표), 메디시스 에스테틱스 인코포레이티드(Medicis Aesthetics, Inc.)를 EDC/NHS로 처리하여 HA의 카복실기를 활성화시킨다.Step 1: Cross-linked HA gel, such as a commercial HA-based dermal filler, such as JUVEDERM®, Allergan or Restylane®, Irvine, CA, Medisys Aesthetic Treated with EDC/NHS (Medicis Aesthetics, Inc.) to activate the carboxyl group of HA.
단계 2: 활성화된 HA 하이드로겔을 하이드록실기를 함유하는 첨가제로 처리한다. 하이드록실기를 함유하는 첨가제는 레티놀, 카탈라제, 다이메틸아미노에탄올 및 g-토코페롤 하이드록실 작용기(-OH)이다.Step 2: The activated HA hydrogel is treated with an additive containing a hydroxyl group. Additives containing hydroxyl groups are retinol, catalase, dimethylaminoethanol and g-tocopherol hydroxyl functional groups (-OH).
가교된 HA 겔에 첨가제의 컨쥬게이션을 위한 전형적인 예는 다음과 같다:Typical examples for conjugation of additives to crosslinked HA gels are:
2gm의 쥬비덤 겔을 200gm의 EDC 및 150㎎의 NHS와 실온에서 혼합한다. 그 다음에 3㎖의 아세톤-물 혼합물 중의 200㎎의 레티놀을 첨가한다. 상기 혼합물을 37℃에서 4시간 동안 반응시킨다. 겔을 아이소프로판올에 대해 투석시켜 미컨쥬게이트된 레티놀을 제거한 다음, 공비 조건 하에 PBS 완충제에 대해 투석한다. 겔을 멸균 주사기 내로 포장하고, 4℃에서 저장한다.2 gm of Juvidum gel is mixed with 200 gm of EDC and 150 mg of NHS at room temperature. Then 200 mg of retinol in 3 ml of acetone-water mixture are added. The mixture was reacted at 37° C. for 4 hours. The gel is dialyzed against isopropanol to remove unconjugated retinol and then dialyzed against PBS buffer under azeotropic conditions. The gel is packaged into a sterile syringe and stored at 4°C.
실시예 17Example 17
HA 하이드로겔에 성장 인자, 펩타이드 또는 엘라스틴의 컨쥬게이션Conjugation of growth factor, peptide or elastin to HA hydrogel
표피 성장 인자(EGF), 형질전환 성장 인자(TGF) 및 펩타이드와 같은 첨가제는 작용성 아민 기를 함유하고, HA에 컨쥬게이트되어 유리한 진피 필러를 형성한다. 이들 첨가제는 아미드화 화학을 통해 HA에 컨쥬게이션된다. 컨쥬게이션을 위한 전형적인 예를 다음과 같이 기재한다:Additives such as epidermal growth factor (EGF), transforming growth factor (TGF) and peptides contain functional amine groups and are conjugated to HA to form beneficial dermal fillers. These additives are conjugated to HA through amidation chemistry. A typical example for conjugation is described as follows:
200.3㎎의 HMW HA를 10㎖의 MES pH 5.4 완충수 중에서 수화시킨다. 100㎎의 MES 용액 중에 20㎎의 EGF를 첨가한다. 상기 혼합물에, 197.7㎎의 EDC 및 149㎎을 첨가한다. 얻어진 반응 혼합물을 37℃에서 4시간 동안 반응시킨다. 반응이 완료된 후, 겔을 아이소프로판올에 대해 투석시킨 다음, 공비 조건 하에 PBS 완충제에 대해 투석한다. 겔을 멸균 주사기 내로 포장하고, 4℃에서 저장한다.200.3 mg of HMW HA is hydrated in 10 ml of MES pH 5.4 buffer. In 100 mg of MES solution, 20 mg of EGF is added. To the mixture, 197.7 mg of EDC and 149 mg are added. The obtained reaction mixture was reacted at 37° C. for 4 hours. After the reaction is complete, the gel is dialyzed against isopropanol and then against PBS buffer under azeotropic conditions. The gel is packaged into a sterile syringe and stored at 4°C.
본 발명은 이식된 지방 조직의 생존능력을 향상시키는 방법을 제공한다. 해당 방법은 일반적으로 이식된 지방 조직에 인접한 환자의 피부 내로 조성물을 도입하는 단계를 포함하되, 해당 조성물은 본 명세서의 다른 곳에 기재된 바와 같은 조성물이다. 예를 들어, 조성물은 하이알루론산 및 하이알루론산에 공유적으로 컨쥬게이트된 비타민 C 유도체를 포함할 수 있되, 컨쥬게이션 정도는 약 3㏖% 내지 약 40㏖%이다. 본 발명의 다른 양태에서, 피부를 치료하기 위한 방법은 피부에 지방 조직, 하이알루론산 및 하이알루론산에 컨쥬게이트된 비타민 C를 포함하는 조성물을 도입하는 단계를 포함한다.The present invention provides a method of improving the viability of transplanted adipose tissue. The method generally includes introducing the composition into the skin of a patient adjacent to the implanted adipose tissue, the composition being a composition as described elsewhere herein. For example, the composition may include hyaluronic acid and a vitamin C derivative covalently conjugated to hyaluronic acid, but the degree of conjugation is from about 3 mol% to about 40 mol%. In another aspect of the invention, a method for treating skin comprises introducing to the skin a composition comprising adipose tissue, hyaluronic acid and vitamin C conjugated to hyaluronic acid.
실시예 18Example 18
HA 하이드로겔에 성장 인자, 펩타이드 또는 엘라스틴의 컨쥬게이션Conjugation of growth factor, peptide or elastin to HA hydrogel
인간 지방 조직 유래 줄기세포(human adipose tissue derived stem cell: hASC)에 대한 비타민 C 및 그것의 유도체의 미토겐 효과를 평가하기 위해, 유리형태에서 비타민 C(아스콜브산) 또는 그것의 유도체(비타겐 또는 AA2G)로 보충하거나 또는 이들이 없는 hASC를 완전한 MesenPro 배지에서 4일 동안 조직 배양물 플라스틱 상에서 배양시켰다. 제조업자(버지니아주 매너서스에 소재한 ATCC)에 의해 기재된 바와 밭은 MTT 분석에 의해 증식을 평가하였다. 4일 후, 아스콜브산, 0.25, 0.5 및 1mM의 농도는 각각 60%, 80% 및 96%만큼 아스콜브산을 결여하는 상기 대조군의 증식을 향상시키는 것으로 발견되었다(탈수소효소에 의해 옐로 테트라졸륨 MTT의 퍼플 포마잔(퍼플 포마잔은 세정제에 의해 가용화됨)으로 전환되는 양을 측정함). 동일한 농도의 AA2G를 사용하여 상기 대조군의 각각 70%, 60% 및 50%의 증식을 수득하였다. 유사한 결과를 비타겐에 의해 얻었고, 이는 대조군에 걸쳐 각각 70%, 60% 및 30% 증가를 나타내었다. 요약하면, 매질을 함유하는 성장 인자의 존재에서 비타민 C 및 그것의 유도체, AA2G 및 비타겐은 세포 배양물에서 hASC 증식을 향상시킨다.To evaluate the mitogen effect of vitamin C and its derivatives on human adipose tissue derived stem cells (hASC), vitamin C (ascorbic acid) or its derivatives (vitagen) in free form Or AA2G) supplemented with or without them were cultured on tissue culture plastics for 4 days in complete MesenPro medium. The fields as described by the manufacturer (ATCC, Manassas, VA) were assessed for proliferation by MTT assay. After 4 days, concentrations of ascorbic acid, 0.25, 0.5 and 1 mM were found to enhance the proliferation of the control group lacking ascorbic acid by 60%, 80% and 96%, respectively (yellow tetrazolium by dehydrogenase. Measures the amount of MTT converted to purple formazan (purple formazan is solubilized by a detergent). Using the same concentration of AA2G, proliferation of 70%, 60% and 50% of the control group was obtained, respectively. Similar results were obtained with Vitagen, which showed 70%, 60% and 30% increases over the control, respectively. In summary, vitamin C and its derivatives, AA2G and Vitagen, in the presence of medium-containing growth factors, enhance hASC proliferation in cell culture.
컨쥬게이트된 비타민 C를 지니는 가교된 HA 겔Crosslinked HA gel with conjugated vitamin C
틴들 효과 및 다른 이점을 나타내는 본 발명의 특정 실시형태에 따라, 가교제로서 1,4-뷰탄다이올 다이글라이시딜에터(BDDE)를 사용하는 컨쥬게이트된 비타민 C를 지니는 가교된 HA계 겔의 제조를 이하의 실시예 19 및 20에 기재한다. 실시예 19에서, 비타민 C 유도체는 아스콜브산 2-글루코사이드(AA2G)이고, 실시예 20에서, 비타민 C 유도체는 아스코빌 3-아미노프로필 포스페이트(비타겐)이다. 이들 겔은 최적의 유동학적 특성, 우수한 주사능력 및 높은 HA 농도(25㎎/g)를 가진다. 어떤 구체적 이론의 조작으로 구속되지 않지만, 본 발명자에 의해 AA2G 또는 비타겐의 존재에서 BDDE와 HA를 가교하는 것은 겔의 특성을 크게 변화시킨다는 것을 발견하였으며, 겔은 BDDE와 가교된 상업적 HA 겔에 대해 높은 가교 밀도, 높은 HA 농도, 저점성 및 저압출력을 가진다. AA2G 또는 비타겐은 가교 동안 존재하기 때문에, 형성된 겔은 현수기로서 및 HA 쇄를 브릿징하는 가교제로서, 단독으로 또는 BDDE를 통해 결합된 이들 아스콜브산 유도체를 가진다. 겔의 현미경 구조는 크게 변화되며, 이는 30게이지 만큼 미세한 바늘을 통하더라도 매우 낮은 압출력을 갖는 겔을 야기한다. 게다가, 겔은 HA에 컨쥬게이트된 비타민 C의 약 3㏖% 내지 약 10㏖%, 또는 약 15㏖%까지를 가진다. 겔이 주사될 때, 그것들은 섬유아세포 또는 포스포타제로부터 α-글루코시다제와 같은 내인성 효소에 의해 활성 비타민 C를 방출한다. 활성 비타민 C는 피부 콜라겐화를 촉발할 수 있고, 겔 분해를 저해하기 위한 라디칼 스캐빈저로서 작용할 수 있다.According to a specific embodiment of the present invention showing the Tyndle effect and other benefits, of a crosslinked HA-based gel with conjugated vitamin C using 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether (BDDE) as a crosslinking agent. The preparation is described in Examples 19 and 20 below. In Example 19, the vitamin C derivative is ascorbic acid 2-glucoside (AA2G), and in Example 20, the vitamin C derivative is ascorbyl 3-aminopropyl phosphate (vitagen). These gels have optimal rheological properties, good injectability and high HA concentration (25 mg/g). Without being bound by the manipulation of any specific theory, it has been found by the inventors that crosslinking BDDE and HA in the presence of AA2G or Vitagen greatly changes the properties of the gel, and the gel compared to commercial HA gels crosslinked with BDDE. It has high crosslinking density, high HA concentration, low viscosity and low pressure output. Since AA2G or Vitagen is present during crosslinking, the gel formed has these ascorbic acid derivatives bound either alone or via BDDE as a suspension group and as a crosslinking agent bridging the HA chain. The microscopic structure of the gel changes greatly, which results in a gel with very low extrusion force even through a needle as fine as 30 gauge. In addition, the gel has from about 3 mol% to about 10 mol%, or up to about 15 mol%, of vitamin C conjugated to HA. When the gels are injected, they release active vitamin C from fibroblasts or phosphorases by endogenous enzymes such as α-glucosidase. Active vitamin C can trigger skin collagenization and act as a radical scavenger to inhibit gel breakdown.
실시예 19Example 19
감소된 틴들 효과를 지니는 HA/AA2G 겔의 제형화Formulation of HA/AA2G gel with reduced tindle effect
1764.0㎎의 5중량% NaOH 용액을 첨가한 후 60분 동안 주사기 내 400.1㎎의 LMW HA 및 402.3㎎ AA2G 혼합물을 수화시켰다. 별개의 바이알에서 800.8㎎의 AA2G를 첨가한 후 1401.1㎎의 9.1중량% NaOH 용액 및 252.6㎎의 BDDE을 첨가하였다. 얻어진 용액(pH >12)을 ~20분 동안 50℃ 수욕에서 반응시킨 후, 수화된 HA에 옮겼다. 첨가 후, 혼합물을 2개의 주사기 사이에 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 ~20회 혼합하였다. 그 다음에 페이스트를 바이알에 옮긴 후 ~2.5 시간 동안 50℃ 수욕에 넣었다. 가교 후, 197.0㎎의 12 M HCl 및 9.18g 10X PBS, pH 7.4를 함유하는 용액을 첨가하여 염기를 중화시켰고, 오비탈쉐이커 상에서 72시간 동안 겔을 팽창시켰다. ~60㎛ 기공 크기 메쉬를 통해 겔에 힘을 가함으로써 크기를 변경하였다. 두 주사기를 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 크기를 변경한 겔을 ~20회 혼합한 후, 셀룰로스 에스터 투석 백, MWCO ~ 20kDa에 옮겼고, PBS, pH 7.4 완충제에 대해 5일 동안 투석하였으며, 1일 2회 완충제를 변경하였다. 투석 후, 겔을 1㎖ COC 주사기 내로 제공하였고, 5000RPM에서 5분 동안 원심분리시켜 공기 방울을 제거하였고, 수분 스팀으로 멸균시켰다. 겔은 25㎎/g의 최종 HA 농도, 약 10㏖%의 실시예 2에서 기재한 바와 같이 계산한 AA2G㏖% 및 약 80㎩의 G'를 가졌다. 다른 겔을 유사한 방식으로 만들었고, 이는 약 60㎩ 내지 약 80㎩의 G' 값을 지녔다.A mixture of 400.1 mg LMW HA and 402.3 mg AA2G in a syringe was hydrated for 60 minutes after the addition of 1764.0 mg of 5 wt% NaOH solution. In a separate vial 800.8 mg of AA2G was added followed by 1401.1 mg of 9.1 wt% NaOH solution and 252.6 mg of BDDE. The resulting solution (pH >12) was reacted in a 50° C. water bath for -20 minutes, and then transferred to hydrated HA. After addition, the mixture was mixed -20 times by passing it back and forth between two syringes. Then, the paste was transferred to the vial and placed in a 50° C. water bath for -2.5 hours. After crosslinking, a solution containing 197.0 mg of 12 M HCl and 9.18 g 10X PBS, pH 7.4 was added to neutralize the base, and the gel was swollen for 72 hours on an orbital shaker. The size was changed by applying force to the gel through a ˜60 μm pore size mesh. After mixing the gel whose size was changed by passing two syringes back and forth ~20 times, it was transferred to a cellulose ester dialysis bag, MWCO ~ 20kDa, and dialyzed against PBS, pH 7.4 buffer for 5 days, and the buffer was changed twice a day. I did. After dialysis, the gel was supplied into a 1 ml COC syringe, centrifuged at 5000 RPM for 5 minutes to remove air bubbles, and sterilized with water steam. The gel had a final HA concentration of 25 mg/g, an AA2Gmol% calculated as described in Example 2 of about 10 mol%, and a G'of about 80 Pa. Another gel was made in a similar manner, which had a G'value of about 60 Pa to about 80 Pa.
실시예 19AExample 19A
감소된 틴들 효과를 지니는 리도카인 겔에 의한 HA/AA2G의 제형화Formulation of HA/AA2G by lidocaine gel with reduced Tyndle effect
실시예 19의 겔에, 리도카인의 양을 첨가하여 0.3% ww 리도카인을 갖는 리도카인 겔에 의해 HA/AA2G를 생성하였다. PBS 완충제 pH ~7.4 중의 리도카인 HCl을 용해시킴으로써 리도카인 용액을 제조하였다. 리도카인 용액의 알리쿼트를 투석 후 그러나 멸균 전 실시예 19에서 겔에 첨가하였다. 그 다음에 겔을 철저하게 혼합하여 0.3% 리도카인 농도를 지니는 균질화된 혼합물을 얻었다.To the gel of Example 19, the amount of lidocaine was added to produce HA/AA2G by lidocaine gel with 0.3% ww lidocaine. Lidocaine solution was prepared by dissolving lidocaine HCl in PBS buffer pH -7.4. Aliquots of lidocaine solution were added to the gel in Example 19 after dialysis but before sterilization. The gel was then thoroughly mixed to obtain a homogenized mixture with a concentration of 0.3% lidocaine.
실시예 20Example 20
감소된 틴들 효과를 지니는 HA/비타겐 겔의 제형화Formulation of HA/Vitagen Gel with Reduced Tindle Effect
401.0㎎의 LMW HA를 ~45분 동안 주사기 내 2355.0㎎의 1중량% NaOH 용액 중에서 수화시켰다. 303.8㎎ BDDE를 수화 HA에 첨가하였고, 주사기 대 주사기 혼합에 의해 10회 혼합하였다. 15분 동안 50℃ 수욕에서 혼합물을 사전반응시켰다. 800.1㎎의 비타겐을 950.6㎎의 15 wt% NaOH 중에서 그 다음에 510.1 Milli-Q 수 중에서 개별적으로 용해시켰다. 비타겐 용액을 주사기 대 주사기 혼합물 사용하여 사전 가열한 수화 HA/BDDE 혼합물과 30회 앞뒤로 혼합하였다. 혼합물을 50℃ 수욕에 다시 넣었고, 반응을 다른 2시간 동안 진행시킨 후, 148.1㎎의 12M HCl 및 8523.1㎎의 10X PBS, pH7.4를 함유하는 용액을 가교제에 첨가하였다. HCl-PBS 용액을 첨가하여 중화시켰고, 겔을 팽창시켰다. 겔을 중화시켰고, 오비탈쉐이커 상에서 48시간에 걸쳐 팽창시켰다. 겔을 ~60㎛ 스크린을 통해 크기를 바꾸었고, 2개 주사기 사이에 앞뒤로 통과시킴으로써 ~20회 혼합하였다. 겔을 20,000 MWCO CE 투석 백 내에 넣었고, PBS, pH7.4 완충제 중에서 투석하였다. PBS 완충제의 빈번한 변화와 함께 ~197시간 동안 투석을 진행하였다. 투석 후, 겔을 1㎖ COC 주사기 내로 옮겼고, 5000RPM에서 5분 동안 원심분리시켰으며, 수분 스팀으로 멸균시켰다. 겔의 최종 HA 농도는 24㎎/g였다.401.0 mg of LMW HA was hydrated in a solution of 2355.0 mg of 1% NaOH by weight in a syringe for ˜45 minutes. 303.8 mg BDDE was added to hydrated HA and mixed 10 times by syringe to syringe mixing. The mixture was pre-reacted in a 50° C. water bath for 15 minutes. 800.1 mg of Vitagen was individually dissolved in 950.6 mg of 15 wt% NaOH, then in 510.1 Milli-Q water. The Vitagen solution was mixed back and forth 30 times with the preheated hydrated HA/BDDE mixture using a syringe to syringe mixture. The mixture was put back into a 50° C. water bath, and after the reaction was allowed to proceed for another 2 hours, a solution containing 148.1 mg of 12M HCl and 8523.1 mg of 10X PBS, pH 7.4 was added to the crosslinking agent. HCl-PBS solution was added to neutralize and the gel was swollen. The gel was neutralized and swollen over 48 hours on an orbital shaker. The gel was resized through a -60 μm screen and mixed -20 times by passing back and forth between two syringes. The gel was placed in a 20,000 MWCO CE dialysis bag and dialyzed in PBS, pH 7.4 buffer. Dialysis was performed for ~197 hours with frequent changes in PBS buffer. After dialysis, the gel was transferred into a 1 ml COC syringe, centrifuged at 5000 RPM for 5 minutes, and sterilized with water steam. The final HA concentration of the gel was 24 mg/g.
1-에틸-3-[3-다이메틸아미노프로필]카보다이이미드를 통해 가교된 HA 겔 HA gel crosslinked via 1-ethyl-3-[3-dimethylaminopropyl]carbodiimide
하이드로클로라이드(EDC) 화학Hydrochloride (EDC) Chemistry
틴들 효과 및 다른 이점을 나타내는 본 발명의 특정 실시형태에 따라, 가교된 HA계 겔의 제조를 이하의 실시예 21 및 22에 기재한다. 실시예 21에서, 가교제를 사용하는 EDC 화학을 통해 만들어지는 겔은 헥사메틸렌 다이아민(HMDA)이고, 실시예 20에서, 3-[3-(3-아미노프로폭시)-2,2-비스(3-아미노-프로폭시메틸)-프로폭시]-프로필아민(4 암 아민-4 AA)이다. 가교제를 온화한 조건하에, 예를 들어 실온 및, 예를 들어 pH 5.4에서 수행한다. 반응 조건은 고도로 망상인 겔을 제조하도록 조절될 수 있고, 최적의 유동학적 특성, 우수한 주사능력 및 높은 HA 농도(24㎎/g)를 가진다. 매우 낮은 수화 또는 반응 농도에서 HA를 가교하며, 결합제인 1-에틸-3-(3-다이메틸아미노프로필) 카보다이이미드 하이드로클로라이드(EDC) 및 N-하이드록시숙신이미드(NHS) 또는 설포닐-NHS(설포-NHS)와 함께 HMDA 또는 4 AA의 보통의 양을 지니는 것이 유리할 수 있다는 것이 본 발명자들에 의해 발견되었다. 겔은 서로로부터 떨어져 있는 가교점을 가질 것이며, 따라서 고도로 가교된 물질은 높은 감쇠력을 가진다. 대조적으로, 이러한 낮은 수화 또는 반응 농도에서 BDDE와 HA의 가교는 가교제의 상대적 비효율성 때문에 실행불가능할 수 있다.According to a specific embodiment of the present invention showing the Tindle effect and other advantages, the preparation of a crosslinked HA-based gel is described in Examples 21 and 22 below. In Example 21, the gel made through EDC chemistry using a crosslinking agent is hexamethylene diamine (HMDA), and in Example 20, 3-[3-(3-aminopropoxy)-2,2-bis( 3-amino-propoxymethyl)-propoxy]-propylamine (4-arm amine-4 AA). The crosslinking agent is carried out under mild conditions, eg at room temperature and eg at pH 5.4. Reaction conditions can be adjusted to produce highly reticulated gels and have optimal rheological properties, good injection capacity and high HA concentration (24 mg/g). Crosslinks HA at very low hydration or reaction concentrations, and the binders 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) or sulfonyl It has been discovered by the inventors that it may be advantageous to have a moderate amount of HMDA or 4 AA with -NHS (sulfo-NHS). Gels will have crosslinking points that are separated from each other, so highly crosslinked materials have high damping power. In contrast, crosslinking of BDDE and HA at such low hydration or reaction concentrations may be impractical due to the relative inefficiency of the crosslinking agent.
실시예 21Example 21
감소된 틴들 효과를 지니는 HA/HMDA 겔의 제형화Formulation of HA/HMDA gel with reduced tindle effect
20.0g의 100mM MES 완충제 pH 5.2를 1000.0㎎의 LMW HA를 함유하는 주사기에 첨가하였다. 2010.5㎎의 100mM MES 완충제 pH 5.2 중에 260.9㎎ HMDA.HCl을 용해시키고, pH 5.2가 되도록 2㎕의 1M NaOH를 첨가함으로써 HMDA 용액을 제조하였다. EDC 용액을 1188.4㎎ 100mM MES 완충제 pH 5.2 중에서 254.2㎎의 EDC를 용해시킴으로써 제조하였고, 별개의 바이알에서, 44.3㎎의 NHS를 1341.8㎎의 100mM MES 완충제 pH 5.2 중에 용해시켰다. HA의 전체 수화 시, ~1시간 동안, 790㎕의 HMDA 용액을 수화시킨 HA에 첨가하였다. 혼합물을 10회 주사기 대 주사기 혼합에 의해 균질화시켰다. 그 다음에 490㎕ EDC 및 490㎕ NHS 용액을 균질화된 페이스트에 첨가하였고, 다시 주사기 대 주사기 혼합에 의해 10회 혼합하였다. 그 다음에 혼합물을 바이알에 옮겼고, 실온에서 5시간 동안 가교시킨 후, 17.9㎖의 1X PBS 완충제 pH 7.4를 첨가하였다. 겔을 롤러 상에서 3일 동안 팽창시킨 후, 60㎛ 기공 크기 메쉬를 통해 힘을 가하였다. 크기를 바꾼 겔을 MWCO 20 KDa을 튜빙하는 셀룰로스 에스터막에 넣었고, 1일 2회 완충제를 변화시키면서 4일 동안 1X PBS에 대해 투석시켰다. 겔을 1㎖ COC 주사기 내에서 조제하였고, 5000 RPM에서 5분 동안 원심분리시켰고, 수분 스팀으로 멸균시켰다. 겔의 최종 HA 농도는 25㎎/g였다.20.0 g of 100 mM MES buffer pH 5.2 was added to a syringe containing 1000.0 mg of LMW HA. HMDA solution was prepared by dissolving 260.9 mg HMDA.HCl in 2010.5 mg of 100 mM MES buffer pH 5.2, and adding 2 μl of 1M NaOH to a pH of 5.2. EDC solutions were prepared by dissolving 254.2 mg of EDC in 1188.4
실시예 22 Example 22
감소된 틴들 효과를 지니는 HA/4 AA 겔의 제형화Formulation of HA/4 AA gel with reduced tindle effect
32.55의 100mM MES 완충제 pH 5.2를 1000.4㎎의 LMW HA를 함유하는 주사기에 첨가하였다. 1039.8㎎의 100mM MES 완충제 pH 5.2 중에 256.3㎎ 4 AA를 용해시키고, pH 5.2가 되도록 380㎕의 6M HCl을 첨가함으로써 4 AA 용액을 제조하였다. EDC 용액을 1013.8㎎ 100mM MES 완충제 pH 5.2 중에서 251.2㎎의 EDC를 용해시킴으로써 제조하였고, 별개의 바이알에서, 74.7㎎의 NHS를 2020.0㎎의 100mM MES 완충제 pH 5.2 중에 용해시켰다. HA의 전체 수화 시, ~1시간 동안, 260㎕의 4 AA 용액을 수화시킨 HA에 첨가하였다. 혼합물을 10회 주사기 대 주사기 혼합에 의해 균질화시켰다. 그 다음에 277㎕ EDC 및 273㎕ NHS 용액을 균질화된 페이스트에 첨가하였고, 다시 주사기 대 주사기 혼합에 의해 10회 혼합하였다. 그 다음에 혼합물을 바이알에 옮겼고, 실온에서 5시간 동안 가교시킨 후, 6.4㎖의 10X PBS 완충제 pH 7.4를 첨가하였다. 겔을 롤러 상에서 3일 동안 팽창시킨 후, 60㎛ 기공 크기 메쉬를 통해 힘을 가하였다. 크기를 바꾼 겔을 MWCO 20 KDa을 튜빙하는 셀룰로스 에스터막에 넣었고, 1일 2회 완충제를 변화시키면서 4일 동안 1X PBS에 대해 투석시켰다. 겔을 1㎖ COC 주사기 내에서 조제하였고, 5000 RPM에서 5분 동안 원심분리시켰고, 수분 스팀으로 멸균시켰다. 겔은 23㎎/g의 최종 HA 농도를 가졌다.32.55 of 100 mM MES buffer pH 5.2 was added to a syringe containing 1000.4 mg of LMW HA. A 4 AA solution was prepared by dissolving 256.3
실시예 23 Example 23
실시예 19 내지 22의 겔의 유동학적 특성의 결정.Determination of the rheological properties of the gels of Examples 19-22.
진동 평행판 유동계인 안톤 파르 피시카(Anton Paar Physica) MCR 301을 사용하여 겔의 유동학적 특성을 측정하였다. 25㎜의 플레이트 직경을 사용하여 1㎜의 갭 높이에서 사용하였다. 각각의 측정은 25℃의 일정한 온도에서 측정을 행하였다. 2%의 일정 변형률에서 1Hz 내지 10Hz의 주파수 스윕 및 주파수의 대수적 증가 후 변형률에서 대수적 증가에 의한 5Hz의 일정한 주파수에서 1% 내지 300%의 변형 스윕으로 이루어졌다. 저장 탄성률(G') 및 점성률(G")을 1% 변형에서 변형 스윕으로부터 얻었다.The rheological properties of the gel were measured using an oscillating parallel plate rheometer, Anton Paar Physica MCR 301. A plate diameter of 25 mm was used with a gap height of 1 mm. Each measurement was performed at a constant temperature of 25°C. It consisted of a frequency sweep of 1 Hz to 10 Hz at a constant strain of 2% and a strain sweep of 1 to 300% at a constant frequency of 5 Hz due to a logarithmic increase in the strain after a logarithmic increase of the frequency. The storage modulus (G') and viscous modulus (G") were obtained from the strain sweep at 1% strain.
실시예 24 Example 24
실시예 19 내지 22의 겔의 압출력 측정Measurement of the extrusion force of the gels of Examples 19 to 22
30게이지 니들을 통해 겔을 압출하는데 필요한 힘을 인스트론(Instron) 5564 및 블루힐(Bluehill) 2 소프트웨어를 사용하여 측정하였다. 겔을 30G½ TSK 바늘을 통해 1㎖ COC 주사기로부터 압출시켰다. 플런저를 11.35㎜에 대해 100㎜/분의 속도로 밀었고, 압출력을 기록하였다.The force required to extrude the gel through a 30 gauge needle was measured using Instron 5564 and
실시예 25Example 25
실시예 19 내지 22의 겔의 생체이용가능성 시험Bioavailability test of gels of Examples 19-22
겔의 50㎕ 볼루스 주사를 스프래그 돌리 래트의 배면에 진피내로 이식하였다. 이식물을 1주에 제거하였고, 헤마톡실린 및 에오신(H&E) 염색, 단핵 염증 세포에 대한 마커인 CD68 염색에 의해 조직적으로 분석하였다. CD68의 3개의 20X 영상을 염색 정도를 기반으로 0 내지 4로 스코어링하였다. 그 다음에 이들 값을 평균화하여 샘플 스코어를 제공하였다. 4개의 샘플을 각 겔로부터 분석하였다.A 50 μl bolus injection of the gel was implanted intradermally on the back of Sprague Dolly rats. Implants were removed at 1 week, and analyzed systematically by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, and CD68 staining, a marker for mononuclear inflammatory cells. Three 20X images of CD68 were scored from 0 to 4 based on the degree of staining. These values were then averaged to provide a sample score. Four samples were analyzed from each gel.
실시예 26Example 26
실시예 19 내지 22의 세포독성 시험, ISO 10993-5.Cytotoxicity test of Examples 19-22, ISO 10993-5.
겔의 시험관내 세포독성 시험을 문헌[Agarose Overlay Method of ISO 10993-5: biological Evaluation of Medical Devices - Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity]에 따라 NAMSA에 의해 수행하였다. 삼중 웰에 여과시킨 원판 상에 놓은 0.1㎖의 시험 물품뿐만 아니라 0.9% NaCl 용액, 음성 대조군으로서 1cm 길이의 고밀도 폴리에틸렌, 및 양성 대조군으로서 라텍스의 1 x 1㎠ 부분을 투여하였다. 각각을 L929 마우스 섬유아세포의 단일층에 직접 가로놓인 아가로스 표면 상에 놓았다. 37℃에서 5% CO2 중에서 24시간 동안 인큐베이션시킨 후, 배양물을 임의의 비정상 세포 형태 및 세포 용해에 대해 거시적으로 및 미시적으로 시험하였다. 시험 물품을 샘플의 근접한 용해 구역에 기반하여 0 내지 4로 스코어링하였다. 시험 물품으로서 0으로 스코어링된 실시예 1, 3 및 4로부터의 시험 재료는 임의의 세포 용해 또는 독성을 야기하는 증거를 나타내지 않았다.The in vitro cytotoxicity test of the gel was performed by NAMSA according to the literature [Agarose Overlay Method of ISO 10993-5: biological Evaluation of Medical Devices-Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity]. In addition to 0.1 ml of test article placed on a filtered disc in triplicate wells, 0.9% NaCl solution, 1 cm long high density polyethylene as a negative control, and a 1×1
틴들 효과의 정량적 분석Quantitative analysis of tindle effect
추가로 시각적 관찰을 뒷받침하고, HA 필러의 비교 수행 분석을 수행하기 위해, 틴들 효과의 정량적 분석을 하는 것이 필요한 것으로 여겼다. 진피 필러에 특이적인 틴들 효과에 대해 어떤 정량적 기법은 문헌에서 존재하지 않는다. 그러나, 피부와 빛 산란 및 빛의 상호작용에 대한 기존의 과학적 이해를 기반으로, (a) 비색법 및 (b) 분광학에 기반한 2가지 별개의 접근을 사용하여 피부에서 틴들 효과를 정량화하였다. 이들 기법에 기반하여, 생체내 틴들 효과를 측정하기 위해 3가지 별개의 정량적 변수(이하에 약술)를 정하였다.In order to further support visual observation and perform comparative performance analysis of the HA filler, it was considered necessary to perform a quantitative analysis of the Tindle effect. No quantitative technique exists in the literature for the specific Tyndle effect on dermal fillers. However, based on the existing scientific understanding of light scattering and light interactions with skin, we quantified the Tyndle effect in skin using two distinct approaches based on (a) colorimetric and (b) spectroscopy. Based on these techniques, three distinct quantitative variables (abbreviated below) were established to measure the effect of Tyndle in vivo.
a) 틴들 효과 시각적 스코어 : 스케일은 0.5의 증분으로 1내지 5의 범위를 가진다. 정상 피부톤을 지니며 청색 변색이 없는 주사 부위에 스코어 1이 주어진다. 두껍고, 확연한 청색 변색(전형적으로, 레스틸렌(Restylane) 또는 쥬비덤 울트라 플러스와 관련됨)에 대해 최대 스코어 5가 주어진다. 시험 샘플을 스코어링하기 위해 맹검 전 스케일에 대해 3명의 독립적 관찰자를 훈련시켰다.a) Tindle effect visual score : The scale ranges from 1 to 5 in increments of 0.5. A score of 1 is given to the injection site with normal skin tone and no blue discoloration. Thick, pronounced blue discoloration (typically Restylane or Juvidum Ultra Plus Associated with) a maximum score of 5 is given. Three independent observers were trained on the pre-blind scale to score the test samples.
b) 피부 색의 청색 성분 - "b" : 색도계(CM2600D, 뉴저지주에 소재한 코니카 미놀타)를 사용하여 다양한 필러로 주사한 피부 부위로부터 보내진 광의 청색 성분을 정량화하였다. L-a-b 색상 규모의 "b" 성분을 사용함으로써 이를 달성하였다.b) Blue component of skin color-"b" : The blue component of light sent from the skin area injected with various fillers was quantified using a colorimeter (CM2600D, Konica Minolta, NJ). This was achieved by using the "b" component of the Lab color scale.
c) 피부로부터 방출된 "청색광%" : 휴대용 분광 광도계(CM2600D, 뉴저지주에 소재한 코니카 미놀타)를 사용하여 전체 가시광선 범위에서 피부로부터 방출된 청색광%을 정량화하였다. 이를 400㎚ 내지 490㎚ 하의 영역을 통합하고, 스펙트럼 하의(400㎚ 내지 700㎚) 전체 영역에 의해 정규화함으로써 달성하였다. c) "% of blue light" emitted from the skin : A handheld spectrophotometer (CM2600D, Konica Minolta, NJ) was used to quantify the percent of blue light emitted from the skin in the entire visible range. This was achieved by integrating the area under 400 nm to 490 nm and normalizing by the entire area under the spectrum (400 nm to 700 nm).
실시예 27Example 27
겔의 틴들 평가Gel tindle evaluation
2개월령의 털이 없는 래트의 대퇴부 내로 선형 스레딩 기법을 사용하여 27G½ TSK 니들을 통해 겔을 진피내로 주사하였다. 임상적 잔주름 절차를 모방하기 위해 겔을 깊지 않게 이식하였다. 겔 이식 후 48시간에 틴들에 대한 시험을 수행하였다. 틴들 시험을 수행하기 전, 헤모글로빈의 결여에 기인하는 틴들 효과의 콘트라스트를 개선시키기 위해 동물을 안락사시켰다.The gel was injected intradermally through a 27G½ TSK needle using a linear threading technique into the femur of a 2-month-old hairless rat. The gel was implanted not deep to mimic the clinical fine wrinkle procedure. 48 hours after gel implantation, a test for tindle was performed. Before performing the Tindle test, animals were euthanized to improve the contrast of the Tindle effect due to the lack of hemoglobin.
이식 2일 후 실시예 19 내지 21로부터의 겔의 영상을 도 12에 나타낸다. 상업적 쥬비덤 리파인 및 레스틸란 터치(Restylane Touch)에 대한 영상을 비교를 위해 나타낸다. 푸르스름한 선(틴들 효과)은 상업적 겔 쥬비덤 리파인 및 레스틸란 터치의 영상에서 분명하게 볼 수 있다. 실시예 19, 19A(도시하지 않음) 및 21로부터의 겔은 틴들 효과를 나타내지 않았다Images of the gels from Examples 19 to 21 2 days after implantation are shown in FIG. 12. Images for commercial Juvidum Refine and Restylane Touch are shown for comparison. A bluish line (Tindle effect) can be clearly seen in the images of commercial gels Juvidum Refine and Restilan Touch. Gels from Examples 19, 19A (not shown) and 21 did not show the Tindle effect
0.5의 증분으로 1 내지 5의 시각적 스코어를 사용하여 주사 부위를 스코어링하였다. 스코어 1을 지니는 주사 부위는 피부 변색을 나타내지 않은 반면, 스코어 5를 지니는 주사 부위는 중증의 피부 청색 변색을 나타내었다. 색채 측정기(CM2600D, 뉴저지주에 소재한 코니카 미놀타)의 도움으로 주사 부위 상에서 분광학적 분석을 수행하였다. 피부색 "b"의 청색 성분 및 피부(400㎚ 내지 700㎚)으로부터 방출된 청색광의%를 독립적으로 측정하였다. 도 13 및 도14는 시각적 틴들 스코어 및 방출된 청색광의 %를 나타낸다. 실시예 19 및 21로부터의 겔은 틴들 효과를 나타내지 않았고, 더 낮은 시각적 틴들 스코어 및 청색광 방출 값의 %를 가졌다. 틴들 스코어 및 방출된 청색광 값의 %는 쥬비덤 리파인 및 레스틸란 터치에 대해 더 높았다. 벨로테로 소프트(Belotero Soft)는 임의의 틴들을 나타내지 않았고, 값은 실시예 19 및 21의 값과 유사하였다. 도 13 및 도 14를 참조한다.The injection site was scored using a visual score of 1-5 in increments of 0.5. The injection site with
실시예 28Example 28
이력에 의한 겔의 생체내 지속 평가In vivo persistence evaluation of gels by history
본 발명의 겔 및 상업적 겔의 50㎕ 볼루스 주사를 스프래그 돌리 래트의 배면에 진피내로 이식하였다. 이식물을 1주에 제거하였고, 헤마톡실린 및 에오신(H&E) 염색에 의해 조직적으로 분석하였다. 주사 부위에서 정확하게 절편을 취하였다. 두 절편을 각 조직 샘플로부터 절단하였고, H&E 염색 절편을 스티칭 스코프를 사용하여 스티칭하였다. 그 다음에 샘플을 그룹화하였고, 다음과 같이 스코어링하였다: 남아있는 물질의 양에 따라서 없음(0%), 낮은(25%), 중간(50%) 및 높음(100%). 도 15를 참조한다.50 μl bolus injections of the gels of the present invention and commercial gels were implanted intradermally on the back of Sprague Dolly rats. Implants were removed at 1 week and analyzed systematically by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Sections were accurately taken at the injection site. Two sections were cut from each tissue sample, and H&E stained sections were stitched using a stitching scope. The samples were then grouped and scored as follows: none (0%), low (25%), medium (50%) and high (100%) depending on the amount of material remaining. See Figure 15.
실시예 28AExample 28A
MRI에 의한 겔의 생체내 지속 평가In vivo persistence evaluation of gels by MRI
암컷 스프래그 돌리 래트에서 진피내 주사 후, 자기공명영상화(Magnetic Resonance Imaging: MRI)를 사용하여 40주의 기간에 걸쳐 본 발명의 겔 및 상업적 겔의 시간에 따른 용적 및 표면적 변화를 평가하였다. 겔을 이식물 당 150㎕의 표적 용적에서 주사하였다. 이식물을 어깨에 대해 약간 꼬리 쪽으로 2개의 정반대 부위, 무릎으로부터 약간 두측으로 2개의 정반대 부위 및 머리와 꼬리 사이의 중간지점에서 2개의 정반대 부위에 위치시켰다. 7 테슬라(Tesla) 70/30 브루커 바이오스펙(Bruker Biospec) MRI 스캐너 상에서 MRI 스캔을 수행하였다. 이식 당일(제0주) 및 이식 후 제12주, 제24주, 제40주에 영상을 수집하였다. 겔 대 시간의 절대 용적의 플롯을 이하의 도 16에 나타낸다. 고지속성 겔은 40주 이식에서 높은 절대 용적을 가진다.After intradermal injection in female Sprague Dawley rats, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was used to evaluate the volume and surface area changes over time of the gels of the present invention and commercial gels over a period of 40 weeks. The gel was injected at a target volume of 150 μl per implant. The implants were placed in two diametrically opposite sites slightly to the tail with respect to the shoulder, two diametrically opposite sites slightly cranial to the knee, and at the midpoint between the head and tail. MRI scans were performed on a 7 Tesla 70/30 Bruker Biospec MRI scanner. Images were collected on the day of transplantation (week 0) and at
실시예 29Example 29
안와주위 주름의 치료에서 사용되는 바와 같은 본 발명의 조성물Composition of the present invention as used in the treatment of periorbital wrinkles
40세의 마른 여성은 안와주위 영역에서 미세한 주름살이 존재하며, 진피 필러 치료를 요청한다. 30게이지 바늘을 사용하여, 의사는 0.6㎖의 본 발명에 따른 HA계 겔(실시예 19에서 기재된 것과 같음)을 그녀의 눈 밑 잔주름 내로 그리고 눈물고랑 영역에서 선형 스레딩 기법을 사용하여 깊지 않게 도입한다. 겔은 깊지 않게 도입되지만, 청색 변색은 관찰되지 않았고, 환자는 결과에 만족한다. A 40-year-old skinny woman has fine wrinkles in the area around the orbit and requires dermal filler treatment. Using a 30 gauge needle, the doctor introduces 0.6 ml of the HA-based gel according to the invention (as described in Example 19) into the fine lines under her eyes and in the lacrimal sulcus area not deeply using a linear threading technique. . The gel was introduced not deeply, but no blue discoloration was observed, and the patient was satisfied with the result.
나타낸 바와 같이, 본 발명의 조성물, 예를 들어 실시예 19 및 21의 조성물은 감소된 또는 유의하지 않은 틴들 효과를 가졌고, 특정 HA계 상업적 겔, 예를 들어, 쥬비덤 리파인/서지덤(Surgiderm) 18 및 벨로테로 소프트에 대해 신체 내에서 실질적으로 더 긴 지속기간을 가진다. 예를 들어, "잔주름" 제형 벨로테로 소프트에 대해, 본 발명의 실시예 19는 이 상업적 겔에 적어도 유리한 틴들 효과를 가질 뿐만 아니라 유리하게는 생체내 지속기간이 실질적으로 더 길었다.As shown, the compositions of the present invention, e.g. the compositions of Examples 19 and 21, had a reduced or insignificant Tindle effect, and certain HA based commercial gels, such as Juvidum Refine/Surgiderm It has a substantially longer duration in the body for 18 and Velotero Soft. For example, for the “fine wrinkles” formulation Velotero Soft, Example 19 of the present invention not only had at least an advantageous Tindle effect on this commercial gel, but advantageously had a substantially longer duration in vivo.
실시예 30 Example 30
잔주름의 외관을 개선시키기 위한 본 발명의 주사용 조성물Injectable composition of the present invention for improving the appearance of fine wrinkles
비타민 A, 비타민 B, 비타민 C, 비타민 D, 비타민 E 및 이의 유도체와 같은 첨가제는 단독으로 및 조합으로 다양한 실질적으로 투명한, 주사용 HA계 겔을 생성하기 위한 방식으로 가교된 하이알루론산 겔에 컨쥬게이션된다. HA 성분은 적어도 90중량%이며, 예를 들어 본 명세서의 다른 곳에서 정의되는 바와 같이 완전히 저분자량 HA, 또는 약 100% 저분자량 HA이다. 이들 첨가제는 임의의 적합한 수단을 사용하여 HA 하이드로겔에 컨쥬게이션된다. 적어도 약 20㎎/g, 예를 들어, 약 23㎎/g, 약 24㎎/g, 약 25㎎/g, 약 30㎎/g까지의 HA 농도를 갖고, 미세한 게이지 바늘을 통한 주사에 적합한, 주사용 pH 중성, 응집성 조성물을 생성하기 위해 컨쥬게이션된 겔은 크기가 바뀌고, 처리된다. 겔은 적어도 약 50㎩, 약 60㎩, 약 70㎩, 약 80㎩까지 및 약 100㎩ 이하의 G' 값을 가진다. 겔은 오토클레이브, UV 광 또는 다른 적합한 수단을 사용하여 포장되고, 멸균된다.Additives such as vitamin A, vitamin B, vitamin C, vitamin D, vitamin E and derivatives thereof, alone and in combination, are conjugated to crosslinked hyaluronic acid gels in a manner to produce various substantially transparent, injectable HA based gels. . The HA component is at least 90% by weight, for example completely low molecular weight HA, or about 100% low molecular weight HA as defined elsewhere herein. These additives are conjugated to the HA hydrogel using any suitable means. Having HA concentrations up to at least about 20 mg/g, e.g., about 23 mg/g, about 24 mg/g, about 25 mg/g, about 30 mg/g, and suitable for injection through a fine gauge needle, The conjugated gel is sized and processed to produce a pH neutral, cohesive composition for injection. The gel has a G'value of at least about 50 Pa, about 60 Pa, about 70 Pa, up to about 80 Pa, and less than about 100 Pa. Gels are packaged and sterilized using autoclave, UV light or other suitable means.
각각의 겔은 환자의 주름살, 예를 들어 안와주위 영역, 팔자주름 영역, 눈물고랑 영역, 목 영역 또는 진피 필링이 유리한 임의의 다른 얼굴 영역에서 깊지 않은 주사, 예를 들어 약 1.0㎜ 이하의 깊이에서 피부 내로 주사에 대해 유용하다. 겔의 깊지 않은 도입에도 불구하고, 틴들 효과에 기인하는 변색은 관찰되지 않았으며, 환자는 결과에 만족한다.Each gel is injected into the patient's wrinkles, e.g., at a depth of about 1.0 mm or less in the periorbital area, nasolabial fold area, lacrimal furrow area, neck area or any other facial area where dermal peeling is advantageous. Useful for injection into the skin. Despite the shallow introduction of the gel, no discoloration due to the Tindle effect was observed, and the patient was satisfied with the results.
마지막으로, 본 명세서의 양태는 다양한 실시형태를 참조로 하여 기재되었지만, 당업자는 구체적인 개시된 실시형태가 본 명세서에 개시된 대상 원칙을 단지 예시한다는 것을 용이하게 인식하는 것으로 이해되어야 한다. 따라서, 본 명세서에 개시된 대상은 특정 방법, 프로토콜 및/또는 시약 등을 어떤 방법으로 제한하지 않는다. 이와 같이, 당업자는 수많은 및 다양한 변형 또는 변화를 만들 수 있거나, 또는 개시된 대상의 대안적 구성이 본 명세서의 정신으로부터 벗어나는 일 없이 본 명세서의 교시에 따라 만들어질 수 있다. 상세한 설명에서의 변화는 첨부되는 특허청부범위에서 정해지는 바와 같은 본 발명의 정신으로부터 벗어나는 일 없이 만들어질 수 있다. 최종적으로, 본 명세서에 사용된 용어는 단지 특정 실시형태를 설명하는 목적을 위한 것이며, 단지 특허청구범위에 의해서만 정해지는 본 발명의 범주를 제한하는 것으로 의도되지 않는다. 추가로, 상기 설명에 함유되거나 또는 수반되는 도면에 나타낸 모든 대상은 단지 예시적이며, 제한하지 않는 것으로 해석되는 것이 의도된다. 따라서, 본 발명은 나타내고, 기재된 바와 같이 명확하게 제한되지 않는다.Finally, while aspects of the present specification have been described with reference to various embodiments, it should be understood that those skilled in the art will readily appreciate that the specific disclosed embodiments merely illustrate the subject principles disclosed herein. Accordingly, the subject matter disclosed herein is not limited in any way to a particular method, protocol and/or reagent, etc. As such, one of ordinary skill in the art can make numerous and various modifications or variations, or alternative configurations of the disclosed subject matter can be made in accordance with the teachings herein without departing from the spirit of the present specification. Changes in the detailed description can be made without departing from the spirit of the present invention as defined in the appended claims. Finally, the terms used herein are for the purpose of describing specific embodiments only, and are not intended to limit the scope of the invention as defined only by the claims. Additionally, all objects contained in the above description or shown in the accompanying drawings are intended to be interpreted as illustrative only and not limiting. Accordingly, the present invention is not expressly limited as shown and described.
본 발명의 특정 실시형태는 본 발명을 수행하기 위해 본 발명자에게 공지된 최상의 방식을 포함하여 본 명세서에 기재된다. 물론, 이들 기재된 실시형태에 대한 변형은 앞서 언급한 설명을 읽을 때 당업자에게 명백할 것이다. 본 발명자는 적절하다면 당업자가 이러한 변형을 사용하는 것을 예상하며, 본 발명자는 본 명세서에 구체적으로 기재된 것 이외에 본 발명이 실행되는 것을 의도한다. 따라서, 본 발명은 적용가능한 법에 의해 허용된다면, 본 명세서에 첨부된 특허청구범위에서 인용된 대상의 모든 변형 및 동등물을 포함한다. 게다가, 이들의 모든 가능한 변형에서 상기 기재한 구성요소의 어떤 조합은 본 명세서에 달리 표시되지 않거나 또는 문맥에 의해 달리 명확하게 모순되지 않는다면, 본 발명에 의해 포함된다.Certain embodiments of the invention are described herein, including the best way known to the inventors for carrying out the invention. Of course, variations on these described embodiments will be apparent to those skilled in the art upon reading the foregoing description. The inventors expect those skilled in the art to use such variations as appropriate, and the inventors intend for the invention to be practiced in addition to those specifically described herein. Accordingly, the present invention includes all modifications and equivalents of the subject matter recited in the claims appended hereto, if permitted by applicable law. Furthermore, any combination of the above-described elements in all possible variations thereof is encompassed by the present invention unless otherwise indicated herein or otherwise clearly contradicted by context.
본 명세서에 개시된 본 발명의 대안의 구성요소 또는 실시형태의 그룹은 제한으로서 해석되어서는 안 된다. 각 그룹 구성원은 개별적으로 또는 본 명세서에서 발견되는 그룹 또는 다른 구성요소의 다른 구성원과 임의의 조합에 의해 지칭되고, 특허청구될 수 있다. 그룹의 하나 이상의 구성원은 편리함 및/또는 특허가능성의 이유를 위해 그룹 내에 포함되거나 또는 그룹으로부터 삭제될 수 있다. 임의의 이러한 포함 또는 삭제가 일어날 때, 본 명세서는 변형되는 그룹을 함유하는 것으로 여겨지며, 따라서 첨부되는 특허청구범위에서 사용되는 모든 마쿠쉬 그룹의 기재된 설명을 충족한다.A group of alternative elements or embodiments of the invention disclosed herein should not be construed as a limitation. Each group member may be referred to and claimed individually or by any combination with other members of the group or other elements found herein. One or more members of the group may be included in or deleted from the group for convenience and/or patentability reasons. When any such inclusion or deletion occurs, the present specification is deemed to contain the group to be modified, and thus meets the described description of all Markush groups used in the appended claims.
달리 표시되지 않는다면, 본 명세서 및 특허청구범위에서 사용되는 성분의 양, 분자량과 같은 특성, 반응 조건 등을 표현하는 모든 숫자는 용어 "약"에 의해 모든 예에서 변형되는 것으로 이해되어야 한다. 본 명세서에 나타내는 바와 같은 용어 "약"은 이렇게 정량화된 항목, 변수 또는 용어가 언급된 항목, 변수 또는 용어의 값 초과 및 미만의 플러스 또는 마이너스 10%의 범위를 포함하는 것을 의미한다. 달리 표시되지 않는다면, 본 명세서 및 특허청구범위에서 사용되는 성분의 양, 분자량과 같은 특성, 반응 조건 등을 표현하는 모든 숫자는 용어 "약"에 의해 모든 예에서 변형되는 것으로 이해되어야 한다. 본 명세서에 나타내는 바와 같은 용어 "약"은 이렇게 정량화된 항목, 변수 또는 용어가 언급된 항목, 변수 또는 용어의 값 초과 및 미만의 플러스 또는 마이너스 10%의 범위를 포함하는 것을 의미한다. 따라서, 달리 모순되지 않는다면, 본 명세서 및 첨부되는 특허청구범위에 제시된 수치적 변수는 본 발명에 의해 얻어지는 것으로 추구되는 원하는 특성에 따라 다를 수 있는 근삿값이다. 적어도, 특허청구범위의 범주와 동등한 원칙의 적용을 제한하기 위한 시도로서가 아니라, 각각의 수치적 변수는 적어도 보고된 유의한 숫자의 수에 비추어, 그리고 보통의 반올림 기법을 적용함으로써 해석되어야 한다. 본 발명의 넓은 범주를 제시하는 수치적 범위 및 변수는 근삿값이지만, 구체적 실시예에 제시된 수치적 값은 가능한 간결하게 보고한다. 그러나, 임의의 수치적 값은 본질적으로 그것의 각각의 시험 측정에서 발견되는 표준 편차로부터 필수적으로 초래되는 특정 오류를 함유한다.Unless otherwise indicated, all numbers expressing amounts of ingredients, properties such as molecular weight, reaction conditions, and the like used in the specification and claims are to be understood as being modified in all instances by the term “about”. The term “about” as indicated herein means that the item, variable or term so quantified includes a range of plus or minus 10% above and below the value of the stated item, variable or term. Unless otherwise indicated, all numbers expressing amounts of ingredients, properties such as molecular weight, reaction conditions, and the like used in the specification and claims are to be understood as being modified in all instances by the term “about”. The term “about” as indicated herein means that the item, variable or term so quantified includes a range of plus or minus 10% above and below the value of the stated item, variable or term. Thus, unless contradicted otherwise, the numerical variables set forth in this specification and the appended claims are approximations that may vary depending on the desired properties sought to be obtained by the present invention. At the very least, and not as an attempt to limit the application of the principles of equality to the scope of the claims, each numerical variable should be interpreted at least in light of the number of significant figures reported, and by applying ordinary rounding techniques. The numerical ranges and variables presenting the broad scope of the present invention are approximate values, but the numerical values presented in specific examples are reported as concisely as possible. However, any numerical value essentially contains certain errors resulting from the standard deviation found in its respective test measurement.
본 발명을 설명하는 문맥에서 사용되는 단수의 용어 및 유사한 언급(특히 다음의 특허청구범위의 문맥에서)은, 본 명세서에서 달리 표시되지 않거나 또는 문맥에 의해 명확하게 모순되지 않는다면, 단수와 복수를 둘 다 다루는 것으로 해석되어야 한다. 본 명세서의 범위의 인용은 단지 범위 내에 속하는 각각의 별개의 값을 개별적으로 지칭하는 단축된 방법으로서 작용하는 것으로 의도된다. 본 명세서에서 달리 표시되지 않는다면, 각각의 개개의 값은 본 명세서에서 마치 개별적으로 인용되는 것과 같이 명세서에 포함된다. 본 명세서에 기재된 모든 방법은 달리 본 명세서에 표시되지 않거나 또 다르게는 문맥에 의해 명확하게 모순되지 않는다면 임의의 적합한 순서로 수행될 수 있다. 본 명세서에서 제공되는 임의의 및 모든 실시예 또는 예시적인 언어(예를 들어, "예컨대")의 사용은 단지 본 발명을 더 양호하게 설명하기 위한 의도이며, 달리 청구되는 본 발명의 범위의 제한을 제기하지는 않는다. 본 명세서의 어떤 언어도 본 발명의 실행에 필수적인 어떤 청구되지 않는 구성요소를 표시하는 것으로 해석되어서는 안 된다.Singular terms and similar references (especially in the context of the following claims) used in the context of describing the present invention, unless otherwise indicated in the specification or clearly contradicted by the context, may be used as the singular and the plural. It should be interpreted as covering everything. Recitation of ranges in this specification is only intended to serve as a shortened way of referring individually to each distinct value falling within the range. Unless otherwise indicated herein, each individual value is incorporated into the specification as if it were individually recited herein. All methods described herein can be performed in any suitable order unless otherwise indicated herein or otherwise clearly contradicted by context. The use of any and all embodiments or illustrative language (eg, “such as”) provided herein is only intended to better describe the invention, and to limit the scope of the invention otherwise claimed. I do not raise it. No language in this specification is to be construed as representing any unclaimed element essential to the practice of the invention.
본 명세서에 개시된 구체적 실시형태는 이루어지거나 또는 본질적으로 이루어진 언어를 사용하여 특허청구범위에서 추가로 제한될 수 있다. 특허청구범위에서 사용될 때, 보정서가 제출되든 또는 첨가되든, 전개 용어 "이루어진"은 특허청구범위에서 구체화되지 않은 어떤 구성요소, 단계 또는 성분을 제외한다. 전개 용어 "본질적으로 이루어진"은 구체화된 물질 또는 단계 및 기본적 및 신규한 특징(들)에 실질적으로 영향을 미치지 않는 것에 대한 특허청구범위의 범주를 제한한다. 이렇게 청구된 본 발명의 실시형태는 본 명세서에서 본질적으로 또는 명확하게 기재되고, 가능하게 된다.The specific embodiments disclosed herein may be further limited in the claims using language that is made or made essentially of. When used in the claims, whether an amendment is submitted or added, the developing term “consisting of” excludes any element, step or ingredient not specified in the claims. The developing term “consisting essentially of” limits the scope of the claims to those that do not materially affect the material or steps specified and the basic and novel feature(s). Embodiments of the present invention so claimed are essentially or explicitly described and made possible herein.
본 명세서에서 언급되고, 확인된 모든 특허, 특허 공개 및 다른 간행물은, 예를 들어 본 발명과 관련하여 사용되는 이러한 간행물에 기재된 조성물 및 방법을 기재하고, 개시하는 목적을 위해 본 명세서에 전문이 개별적이고, 명확하게 포함된다. 이들 간행물은 단지 본 발명의 출원일 이전에 그것의 개시내용에 대해 제공된다. 이에 대해 어떤 것도 본 발명자들이 본 발명 때문에 또는 어떤 다른 이유로 이러한 개시내용보다 선행하는 것으로 자격을 부여하는 용인으로서 해석되어서는 안 된다. 이들 문헌의 내용에 대한 일자 또는 표현에 관한 모든 언급은 출원인에 대해 이용가능한 정보에 기반하며, 이들 문헌의 날짜 또는 내용의 정확함에 대한 어떤 용인을 구성하지는 않는다.All patents, patent publications and other publications referenced and identified herein describe the compositions and methods described in such publications, e.g., used in connection with the present invention, and are incorporated herein in their entirety for purposes of disclosure. And clearly included. These publications are provided for their disclosure only prior to the filing date of the present invention. Nothing in this regard is to be construed as an admission that the inventors qualify as an precedent for this disclosure because of the invention or for any other reason. All references to dates or representations of the contents of these documents are based on information available to the applicant and do not constitute any admission as to the accuracy of the dates or contents of these documents.
Claims (20)
15. The method of claim 14, wherein the vitamin C derivative is AA2P.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020217032224A KR20210125119A (en) | 2011-09-14 | 2012-09-13 | Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment |
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201161534780P | 2011-09-14 | 2011-09-14 | |
| US61/534,780 | 2011-09-14 | ||
| PCT/US2012/052125 WO2013028904A2 (en) | 2011-08-25 | 2012-08-23 | Dermal filler compositions including antioxidants |
| USPCT/US2012/052125 | 2012-08-23 | ||
| PCT/US2012/055211 WO2013040242A2 (en) | 2011-09-14 | 2012-09-13 | Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020147009782A Division KR102161861B1 (en) | 2011-09-14 | 2012-09-13 | Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020217032224A Division KR20210125119A (en) | 2011-09-14 | 2012-09-13 | Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20200116168A true KR20200116168A (en) | 2020-10-08 |
Family
ID=47883970
Family Applications (4)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020227001920A KR20220013588A (en) | 2011-09-14 | 2012-09-13 | Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment |
| KR1020207027527A KR20200116168A (en) | 2011-09-14 | 2012-09-13 | Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment |
| KR1020147009782A KR102161861B1 (en) | 2011-09-14 | 2012-09-13 | Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment |
| KR1020217032224A KR20210125119A (en) | 2011-09-14 | 2012-09-13 | Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment |
Family Applications Before (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020227001920A KR20220013588A (en) | 2011-09-14 | 2012-09-13 | Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment |
Family Applications After (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020147009782A KR102161861B1 (en) | 2011-09-14 | 2012-09-13 | Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment |
| KR1020217032224A KR20210125119A (en) | 2011-09-14 | 2012-09-13 | Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2755630A2 (en) |
| JP (4) | JP6125509B2 (en) |
| KR (4) | KR20220013588A (en) |
| CN (2) | CN108379112A (en) |
| AU (1) | AU2012308503B2 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2848833C (en) |
| HK (1) | HK1198124A1 (en) |
| RU (1) | RU2626513C2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2013040242A2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (30)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2861734B1 (en) | 2003-04-10 | 2006-04-14 | Corneal Ind | CROSSLINKING OF LOW AND HIGH MOLECULAR MASS POLYSACCHARIDES; PREPARATION OF INJECTABLE SINGLE PHASE HYDROGELS; POLYSACCHARIDES AND HYDROGELS OBTAINED |
| EP2484387A1 (en) | 2011-02-03 | 2012-08-08 | Q-Med AB | Hyaluronic acid composition |
| KR102015676B1 (en) | 2011-06-03 | 2019-10-21 | 알러간, 인코포레이티드 | Dermal filler compositions including antioxidants |
| US20130096081A1 (en) | 2011-06-03 | 2013-04-18 | Allergan, Inc. | Dermal filler compositions |
| US9408797B2 (en) | 2011-06-03 | 2016-08-09 | Allergan, Inc. | Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment |
| US9393263B2 (en) | 2011-06-03 | 2016-07-19 | Allergan, Inc. | Dermal filler compositions including antioxidants |
| CA2848833C (en) * | 2011-09-14 | 2017-04-04 | Gabriel N. NJIKANG | Ascorbate modified crosslinked hyaluronic acid dermal filler compositions that exhibit reduced tyndall effect |
| DK3175840T3 (en) * | 2011-12-08 | 2020-09-28 | Allergan Ind Sas | DERMAL FILLER COMPOSITIONS |
| US20140315828A1 (en) * | 2013-04-22 | 2014-10-23 | Allergan, Inc. | Cross-linked silk-hyaluronic acid compositions |
| EP2988755A4 (en) * | 2013-04-25 | 2016-11-30 | Aluron Biopharma Inc | Crosslinked hyaluronic acid compositions |
| WO2016128783A1 (en) * | 2015-02-09 | 2016-08-18 | Allergan Industrie Sas | Compositions and methods for improving skin appearance |
| RU2715234C2 (en) * | 2015-02-13 | 2020-02-26 | Аллерган Эндюстри, Сас | Implants for sculpting, augmenting or correcting facial features such as chin |
| WO2017220622A1 (en) | 2016-06-23 | 2017-12-28 | Galderma S.A. | Cyclodextrin-grafted cross-linked hyaluronic acid complexed with active drug substances and uses thereof |
| US10300169B2 (en) | 2016-08-24 | 2019-05-28 | Allergan, Inc. | Co-crosslinked hyaluronic acid-silk fibroin hydrogels for improving tissue graft viability and for soft tissue augmentation |
| US11389563B2 (en) | 2017-06-12 | 2022-07-19 | Advanced Aesthetic Technologies, Inc. | Dermal filler |
| CN111263646A (en) * | 2017-06-26 | 2020-06-09 | 自然进化公司 | Silk-hyaluronic acid based tissue fillers and methods of use thereof |
| US20230190997A1 (en) | 2017-06-26 | 2023-06-22 | Evolved By Nature, Inc. | Silk-hyaluronic acid based tissue filers and methods of using the same |
| CA3069968A1 (en) * | 2017-07-19 | 2019-01-24 | Dentsply Sirona Inc. | Water-soluble hydrogel-based dental composition and methods of making and using same |
| WO2019130358A1 (en) * | 2017-12-29 | 2019-07-04 | Matex Lab S.P.A. | Method to prepare a filler with a hyaluronic acid base |
| KR101967153B1 (en) | 2018-04-04 | 2019-04-09 | 윤성준 | The material composition of the filler improving wrinkles, atrophic scars and other skin deficits |
| CN116650519A (en) * | 2018-06-15 | 2023-08-29 | 克罗马药品有限责任公司 | Stabilized Hyaluronic Acid |
| IT201900006929A1 (en) * | 2019-05-16 | 2020-11-16 | Giuliani Spa | KIT FOR AESTHETIC SKIN TREATMENT |
| CN110467689A (en) * | 2019-09-09 | 2019-11-19 | 山东众山生物科技有限公司 | A kind of derivatives of hyaluronic acids and preparation method thereof |
| CN110907370A (en) * | 2019-12-04 | 2020-03-24 | 桂林理工大学 | Universal ultra-sensitive chemical and biological colorimetric sensing method |
| US20230040919A1 (en) * | 2019-12-26 | 2023-02-09 | Allergan, Inc. | Crosslinked ha-collagen hydrogels as dermal fillers |
| CN111249172A (en) * | 2020-01-15 | 2020-06-09 | 陈勇 | Beauty injection gel and preparation method thereof |
| AR128245A1 (en) | 2022-01-11 | 2024-04-10 | Gpq S R L | NEW HYALURONIC ACID DERIVATIVES AS INNOVATIVE FILLERS |
| WO2024055132A1 (en) * | 2022-09-12 | 2024-03-21 | Universidad De Talca | Method for the synthesis of a branched copolymer of hyaluronic acid and poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid |
| KR20240096331A (en) | 2022-12-19 | 2024-06-26 | 주식회사 코루파마 | A preparing method for hydrogel combining hyaluronic acid and agar or agarose, a hydrogel comprising hyaluronic acid and agar or agarose prepared therefrom, and a filler composition comprising the same |
| EP4450062A1 (en) * | 2023-04-20 | 2024-10-23 | Abiogen Pharma S.p.A. | Composition for the treatment of osteoarthrosis |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20110171311A1 (en) | 2010-01-13 | 2011-07-14 | Allergan Industrie, Sas | Stable hydrogel compositions including additives |
| US20110171286A1 (en) | 2010-01-13 | 2011-07-14 | Allergan, Inc. | Hyaluronic acid compositions for dermatological use |
Family Cites Families (30)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6174999B1 (en) * | 1987-09-18 | 2001-01-16 | Genzyme Corporation | Water insoluble derivatives of polyanionic polysaccharides |
| KR100721752B1 (en) * | 2000-01-24 | 2007-05-25 | 쿠라레 메디카루 가부시키가이샤 | Water-swellable polymer gel and process for preparing the same |
| IT1317091B1 (en) * | 2000-02-08 | 2003-05-26 | S F I R Societa Fondaria Ind R | CROSS-LINKED HYALURONIC ACID GEL WITH B-FUNCTIONAL L-AMINO ACIDS. |
| FR2811996B1 (en) | 2000-07-19 | 2003-08-08 | Corneal Ind | CROSS-LINKING OF POLYSACCHARIDE (S), PREPARATION OF HYDROGEL (S); POLYSACCHARIDE (S) AND HYDROGEL (S) OBTAINED, THEIR USES |
| WO2004067575A1 (en) * | 2003-01-31 | 2004-08-12 | Biosphere S.P.A. | Water soluble and biocompatible gels of hyaluronic acid cross-linked with bi-functional l-aminoacids or l-aminoesters |
| AU2003206922A1 (en) | 2003-02-19 | 2004-09-09 | Aventis Pharmaceuticals Holdings Inc. | Composition and method for intradermal soft tissue augmentation |
| FR2861734B1 (en) | 2003-04-10 | 2006-04-14 | Corneal Ind | CROSSLINKING OF LOW AND HIGH MOLECULAR MASS POLYSACCHARIDES; PREPARATION OF INJECTABLE SINGLE PHASE HYDROGELS; POLYSACCHARIDES AND HYDROGELS OBTAINED |
| US8124120B2 (en) * | 2003-12-22 | 2012-02-28 | Anika Therapeutics, Inc. | Crosslinked hyaluronic acid compositions for tissue augmentation |
| WO2005066215A1 (en) * | 2003-12-30 | 2005-07-21 | Genzyme Corporation | Cohesive gels form cross-linked hyaluronan and/or hylan, their preparation and use |
| FR2865737B1 (en) * | 2004-02-03 | 2006-03-31 | Anteis Sa | BIOCOMPATIBLE RETICLE GEL |
| WO2005112888A2 (en) * | 2004-05-20 | 2005-12-01 | Mentor Corporation | Methods for making injectable polymer hydrogels |
| FR2873379B1 (en) * | 2004-07-23 | 2008-05-16 | Jerome Asius | PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF RETICULATED HYALURONIC ACID, RETICULATED HYALURONIC ACID WHICH CAN BE OBTAINED BY THIS METHOD, IMPLANT CONTAINING THE RETICULATED HYALURONIC ACID, AND USE THEREOF |
| FR2878444B1 (en) | 2004-11-30 | 2008-04-25 | Corneal Ind Soc Par Actions Si | VISCOELASTIC SOLUTIONS COMPRISING SODIUM HYALURONATE AND HYDROXYPROPYLMETHYLCELLULOSE, PREPARATION AND USES |
| US20090220607A1 (en) * | 2005-09-15 | 2009-09-03 | Kiser Patrick F | Polymeric compositions and methods of making and using thereof |
| WO2007101243A1 (en) * | 2006-02-28 | 2007-09-07 | Novozymes Biopolymer A/S | Derivatives of hyaluronic acids |
| CN1837265A (en) * | 2006-04-25 | 2006-09-27 | 江南大学 | Process for composite modification of hyaluronic acid and carboxymethyl cellulose |
| CN100417666C (en) * | 2006-09-07 | 2008-09-10 | 重庆大学 | Lysine-chitosan resin and preparation method thereof |
| FR2908415B1 (en) * | 2006-11-10 | 2009-01-23 | Abr Dev Sarl | RETICULATED HYALURONIC ACID AND PROCESS FOR PREPARING THE SAME |
| FR2909560B1 (en) * | 2006-12-06 | 2012-12-28 | Fabre Pierre Dermo Cosmetique | HYALURONIC ACID GEL FOR INTRADERMAL INJECTION |
| FR2918377B1 (en) * | 2007-07-05 | 2010-10-08 | Estelle Piron | CO-RETICLE GEL OF POLYSACCHARIDES |
| US8394782B2 (en) * | 2007-11-30 | 2013-03-12 | Allergan, Inc. | Polysaccharide gel formulation having increased longevity |
| EP2219679A1 (en) * | 2007-12-21 | 2010-08-25 | Encecor AB | Cross-linked hydrogel containing an active substance |
| KR20090110090A (en) * | 2008-04-17 | 2009-10-21 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Synthesis method for indium selenide nanoparticles by ultrasonic waves and a compound semiconductor solar cell comprising the said |
| US8450475B2 (en) | 2008-08-04 | 2013-05-28 | Allergan, Inc. | Hyaluronic acid-based gels including lidocaine |
| CN101961344A (en) * | 2009-07-23 | 2011-02-02 | 山东省生物药物研究院 | Drug composite and application thereof |
| IT1395392B1 (en) * | 2009-08-27 | 2012-09-14 | Fidia Farmaceutici | VISCOELASTIC FROSTS LIKE NEW FILLERS |
| WO2011063394A2 (en) * | 2009-11-23 | 2011-05-26 | Olmstead Stephen F | Compositions and methods comprising serratia peptidase for inhibition and treatment of biofilms related to certain conditions |
| US20110172180A1 (en) * | 2010-01-13 | 2011-07-14 | Allergan Industrie. Sas | Heat stable hyaluronic acid compositions for dermatological use |
| KR102015676B1 (en) * | 2011-06-03 | 2019-10-21 | 알러간, 인코포레이티드 | Dermal filler compositions including antioxidants |
| CA2848833C (en) * | 2011-09-14 | 2017-04-04 | Gabriel N. NJIKANG | Ascorbate modified crosslinked hyaluronic acid dermal filler compositions that exhibit reduced tyndall effect |
-
2012
- 2012-09-13 CA CA2848833A patent/CA2848833C/en active Active
- 2012-09-13 KR KR1020227001920A patent/KR20220013588A/en active Application Filing
- 2012-09-13 RU RU2014113663A patent/RU2626513C2/en active
- 2012-09-13 CN CN201810249654.6A patent/CN108379112A/en active Pending
- 2012-09-13 KR KR1020207027527A patent/KR20200116168A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2012-09-13 EP EP12769798.5A patent/EP2755630A2/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2012-09-13 KR KR1020147009782A patent/KR102161861B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2012-09-13 WO PCT/US2012/055211 patent/WO2013040242A2/en unknown
- 2012-09-13 JP JP2014530798A patent/JP6125509B2/en active Active
- 2012-09-13 AU AU2012308503A patent/AU2012308503B2/en active Active
- 2012-09-13 KR KR1020217032224A patent/KR20210125119A/en active IP Right Grant
- 2012-09-13 CN CN201280055657.7A patent/CN104105474B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2014
- 2014-11-17 HK HK14111615.6A patent/HK1198124A1/en unknown
-
2017
- 2017-04-05 JP JP2017075224A patent/JP2017140433A/en not_active Withdrawn
-
2018
- 2018-11-22 JP JP2018219395A patent/JP2019058692A/en not_active Withdrawn
-
2021
- 2021-03-23 JP JP2021048584A patent/JP2021100603A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20110171311A1 (en) | 2010-01-13 | 2011-07-14 | Allergan Industrie, Sas | Stable hydrogel compositions including additives |
| US20110171286A1 (en) | 2010-01-13 | 2011-07-14 | Allergan, Inc. | Hyaluronic acid compositions for dermatological use |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| Park, D.J. et al. 2010, Orthopaedic Proceedings, Vol. 92-B, No. SUPP I |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR102161861B1 (en) | 2020-10-26 |
| JP2014526342A (en) | 2014-10-06 |
| CA2848833C (en) | 2017-04-04 |
| RU2626513C2 (en) | 2017-07-28 |
| JP2019058692A (en) | 2019-04-18 |
| WO2013040242A2 (en) | 2013-03-21 |
| KR20140096028A (en) | 2014-08-04 |
| EP2755630A2 (en) | 2014-07-23 |
| KR20210125119A (en) | 2021-10-15 |
| CN108379112A (en) | 2018-08-10 |
| AU2012308503B2 (en) | 2015-08-13 |
| AU2012308503A1 (en) | 2014-04-03 |
| JP2021100603A (en) | 2021-07-08 |
| CN104105474B (en) | 2018-04-06 |
| JP2017140433A (en) | 2017-08-17 |
| WO2013040242A3 (en) | 2014-03-13 |
| JP6125509B2 (en) | 2017-05-10 |
| CN104105474A (en) | 2014-10-15 |
| CA2848833A1 (en) | 2013-03-21 |
| HK1198124A1 (en) | 2015-03-13 |
| RU2014113663A (en) | 2015-10-20 |
| KR20220013588A (en) | 2022-02-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102161861B1 (en) | Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment | |
| US20200353124A1 (en) | Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment | |
| KR102238406B1 (en) | Dermal filler compositions including antioxidants | |
| KR102168028B1 (en) | Dermal filler compositions | |
| AU2021200516B2 (en) | Dermal filler compositions for fine line treatment |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A107 | Divisional application of patent | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E90F | Notification of reason for final refusal | ||
| A107 | Divisional application of patent | ||
| E601 | Decision to refuse application |