KR20190111592A - Food Composition Comprising Polygonum Cuspidatum and Noble Preparation Method thereof - Google Patents
Food Composition Comprising Polygonum Cuspidatum and Noble Preparation Method thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20190111592A KR20190111592A KR1020180033939A KR20180033939A KR20190111592A KR 20190111592 A KR20190111592 A KR 20190111592A KR 1020180033939 A KR1020180033939 A KR 1020180033939A KR 20180033939 A KR20180033939 A KR 20180033939A KR 20190111592 A KR20190111592 A KR 20190111592A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- vinegar
- extract
- producing bacteria
- food composition
- yeast
- Prior art date
Links
- 235000013305 food Nutrition 0.000 title claims abstract description 18
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 16
- 235000018167 Reynoutria japonica Nutrition 0.000 title abstract 9
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 title description 6
- 241001648835 Polygonum cuspidatum Species 0.000 title 1
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 35
- 238000000855 fermentation Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 31
- 230000004151 fermentation Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 31
- 235000021419 vinegar Nutrition 0.000 claims abstract description 29
- 239000000052 vinegar Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 29
- 241000894006 Bacteria Species 0.000 claims abstract description 16
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 15
- 240000004808 Saccharomyces cerevisiae Species 0.000 claims abstract description 13
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- GXCLVBGFBYZDAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-[2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]-N-methylprop-2-en-1-amine Chemical compound CN(CCC1=CNC2=C1C=CC=C2)CC=C GXCLVBGFBYZDAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 210000004209 hair Anatomy 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000013538 functional additive Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 235000000346 sugar Nutrition 0.000 claims description 4
- 240000004670 Glycyrrhiza echinata Species 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000001453 Glycyrrhiza echinata Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000006200 Glycyrrhiza glabra Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000017382 Glycyrrhiza lepidota Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 240000002045 Guettarda speciosa Species 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000001287 Guettarda speciosa Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 240000000599 Lentinula edodes Species 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000008331 Pinus X rigitaeda Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000011613 Pinus brutia Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 241000018646 Pinus brutia Species 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000021329 brown rice Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940010454 licorice Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000001715 Lentinula edodes Nutrition 0.000 claims 1
- 208000002193 Pain Diseases 0.000 abstract description 3
- 208000004880 Polyuria Diseases 0.000 abstract description 3
- 230000035619 diuresis Effects 0.000 abstract description 3
- 230000001093 anti-cancer Effects 0.000 abstract description 2
- 230000003110 anti-inflammatory effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 2
- 230000003579 anti-obesity Effects 0.000 abstract description 2
- 230000003078 antioxidant effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 2
- 150000001720 carbohydrates Chemical class 0.000 abstract description 2
- 238000001784 detoxification Methods 0.000 abstract description 2
- 235000015872 dietary supplement Nutrition 0.000 abstract description 2
- 240000001341 Reynoutria japonica Species 0.000 abstract 8
- 238000012258 culturing Methods 0.000 abstract 2
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 8
- 229960000583 acetic acid Drugs 0.000 description 5
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 description 5
- 241000589220 Acetobacter Species 0.000 description 4
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 4
- 210000003205 muscle Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 244000292697 Polygonum aviculare Species 0.000 description 3
- 235000006386 Polygonum aviculare Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 244000082988 Secale cereale Species 0.000 description 3
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000013399 edible fruits Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 241000196324 Embryophyta Species 0.000 description 2
- 244000068988 Glycine max Species 0.000 description 2
- 235000010469 Glycine max Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 206010031252 Osteomyelitis Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000008280 blood Substances 0.000 description 2
- 210000004369 blood Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 235000013339 cereals Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 235000021107 fermented food Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 235000011194 food seasoning agent Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229940093915 gynecological organic acid Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 239000004615 ingredient Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000007524 organic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 235000005985 organic acids Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000008163 sugars Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 244000283763 Acetobacter aceti Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000007847 Acetobacter aceti Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 241001497697 Acetobacter orleanensis Species 0.000 description 1
- 201000009030 Carcinoma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000034656 Contusions Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010012735 Diarrhoea Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000005171 Dysmenorrhea Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010013935 Dysmenorrhoea Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000218671 Ephedra Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000588724 Escherichia coli Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000589232 Gluconobacter oxydans Species 0.000 description 1
- 206010018612 Gonorrhoea Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 244000158996 Hedysarum boreale Species 0.000 description 1
- 206010023126 Jaundice Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010030113 Oedema Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000001467 acupuncture Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000032683 aging Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000001014 amino acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000001413 amino acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000003963 antioxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019658 bitter taste Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000010411 cooking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000008242 dietary patterns Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000007865 diluting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000035622 drinking Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 208000001848 dysentery Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000004064 dysfunction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003912 environmental pollution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000796 flavoring agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019634 flavors Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000015203 fruit juice Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000011389 fruit/vegetable juice Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000012362 glacial acetic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 1
- 208000001786 gonorrhea Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000003780 hair follicle Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000003779 hair growth Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000013402 health food Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 208000014617 hemorrhoid Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000006454 hepatitis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 231100000283 hepatitis Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 241000411851 herbal medicine Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000008216 herbs Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000968 intestinal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002075 main ingredient Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 244000005700 microbiome Species 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000005445 natural material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000005416 organic matter Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000021422 persimmon vinegar Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000001766 physiological effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005070 ripening Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229930000044 secondary metabolite Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 230000001953 sensory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000014347 soups Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000019614 sour taste Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 241000894007 species Species 0.000 description 1
- 230000008961 swelling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000001519 tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000002137 ultrasound extraction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A23—FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS; TREATMENT THEREOF, NOT COVERED BY OTHER CLASSES
- A23L—FOODS, FOODSTUFFS, OR NON-ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES, NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES A21D OR A23B-A23J; THEIR PREPARATION OR TREATMENT, e.g. COOKING, MODIFICATION OF NUTRITIVE QUALITIES, PHYSICAL TREATMENT; PRESERVATION OF FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS, IN GENERAL
- A23L33/00—Modifying nutritive qualities of foods; Dietetic products; Preparation or treatment thereof
- A23L33/10—Modifying nutritive qualities of foods; Dietetic products; Preparation or treatment thereof using additives
- A23L33/105—Plant extracts, their artificial duplicates or their derivatives
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A23—FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS; TREATMENT THEREOF, NOT COVERED BY OTHER CLASSES
- A23L—FOODS, FOODSTUFFS, OR NON-ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES, NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES A21D OR A23B-A23J; THEIR PREPARATION OR TREATMENT, e.g. COOKING, MODIFICATION OF NUTRITIVE QUALITIES, PHYSICAL TREATMENT; PRESERVATION OF FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS, IN GENERAL
- A23L29/00—Foods or foodstuffs containing additives; Preparation or treatment thereof
- A23L29/06—Enzymes
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A23—FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS; TREATMENT THEREOF, NOT COVERED BY OTHER CLASSES
- A23V—INDEXING SCHEME RELATING TO FOODS, FOODSTUFFS OR NON-ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES AND LACTIC OR PROPIONIC ACID BACTERIA USED IN FOODSTUFFS OR FOOD PREPARATION
- A23V2002/00—Food compositions, function of food ingredients or processes for food or foodstuffs
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Nutrition Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Food Science & Technology (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Botany (AREA)
- Mycology (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Plant Substances (AREA)
- Coloring Foods And Improving Nutritive Qualities (AREA)
Abstract
Description
본 발명은 통경, 이뇨, 진정, 해독, 항암, 항염, 항비만 및 항산화 효능이 있는 호장근의 유효성분을 함유하여 건강보조식품으로서 유용하게 사용될 수 있는 발효 호장근을 함유하는 식품 조성물 및 그의 제조방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention is a food composition containing fermented jangjanggeun that can be usefully used as a dietary supplement containing the active ingredient of pyeonjanggeun of diarrhea, diuresis, soothing, detoxification, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity and antioxidant efficacy and its preparation It is about a method.
최근 경제수준이 향상되고 선진국형 식생활 패턴으로 변화됨에 따라 남녀노소를 불문하고 현대인들의 영양과잉, 환경오염, 운동부족 등으로 인한 생활습관병의 만연이 중요한 사회문제로 대두되고 있다. 또한 평균수명의 연장으로 인하여 노령화 사회로의 진입속도가 빨라지면서 건강증진에 대한 소비자의 관심도 크게 높아지고 있으며, 식품에 대한 소비자의 인식 변화로 몸에 좋은 건강식과 더불어 식품의 맛과 기능성을 더욱 중요시하게 되었다.Recently, as the economic level has improved and changed into a developed country-type dietary pattern, the prevalence of lifestyle-related diseases caused by overnourishment, environmental pollution, and lack of exercise, etc. of both men and women is emerging as an important social problem. In addition, as the speed of entry into an aging society is accelerating due to the extension of the average life span, consumers' interest in health promotion is also greatly increased. It became.
발효식품에는 미생물이 생산한 다양한 유기물들과 2차 대사산물이 포함되어 있어 원래의 식품에는 없는 독특한 풍미를 만들어내므로 저장식품으로서의 목적을 달성함과 동시에, 기호성 식품으로 유용한 효과가 있다. 식초는 동서고금을 막론하고 사용되는 대표적인 발효식품으로 소량의 휘발산 및 비휘발성의 유기산, 당류, 아미노산, ester 등을 함유하여 독특한 방향과 신맛을 가지며, 특유의 강한 산성 때문에 식품 내 유해미생물의 생육을 억제하는 효과가 있다. 현재 국내의 식품의약품안전처고시에 의한 식초의 정의는 "곡류, 과실류, 주류 등을 주원료로 하여 발효시켜 제조하거나 이에 곡물당화액, 과실착즙액 등을 혼합·숙성하여 만든 발효식초와 빙초산 또는 초산을 먹는 물로 희석하여 만든 희석초산"이며, 총산(초산으로서, w/v%)을 4.0 ~ 20.0%(감식초는 2.6 이상) 함유할 것으로 규정하고 있다. Fermented food contains a variety of organic matter and secondary metabolites produced by microorganisms to create a unique flavor not found in the original food, while achieving the purpose as a stored food, and has a useful effect as a favorite food. Vinegar is a representative fermented food used regardless of East-West Gold. It contains a small amount of volatile acids and nonvolatile organic acids, sugars, amino acids, esters, etc., and has a unique aroma and sour taste. It has a suppressing effect. The definition of vinegar by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety at present is defined as "fermented vinegar, glacial acetic acid or acetic acid produced by fermenting grains, fruits, liquor, etc. as main ingredients or by mixing and ripening grain saccharification liquid, fruit juice juice, etc. Dilute acetic acid made by diluting it with water to drink ", and it is specified that it will contain 4.0-20.0% (persimmon vinegar more than 2.6) of total acid (as acetic acid, w / v%).
최근에는 건강식품으로서의 식초에 대한 관심이 증가하면서 과실류를 이용한 발효식초의 수요가 급증함과 동시에 더욱 고급화되고 다양화되려는 경향을 보이고 있다. 이에 등록특허 제10-1568600호(홍국식초 제조방법), 등록특허 제10-1620184호(와송을 이용한 천연양조식초의 제조방법 및 이를 이용한 양조식초), 등록특허 제10-1803370호(쑥식초 및 그 제조방법), 등록특허 제10-1825288호(더덕 식초의 제조 방법), 등록특허 제10-1820027호(무화과 발효식초의 제조방법 및 이의 제조방법에 의해 제조된 무화과 발효식초)와 같이 다양한 소재를 활용한 식초가 개발되고 있다.Recently, as the interest in vinegar as a health food increases, the demand for fermented vinegar using fruits increases rapidly, and there is a tendency to become more advanced and diversified. Thus, Patent No. 10-1568600 (Hongkuk vinegar manufacturing method), Patent No. 10-1620184 (Preparation method of natural brewed vinegar using wasong and brewing vinegar using the same), Patent No. 10-1803370 (Sugly vinegar and Its manufacturing method), Patent No. 10-1825288 (Method of manufacturing deodeok vinegar), Patent No. 10-1820027 (Method of manufacturing fig fermented vinegar and Fig fermented vinegar manufactured by the method) Vinegar utilizing the oil is being developed.
호장근은 우리나라 각처의 산과 들에 야생하는 다년생 초본식물로 이른 봄 또는 늦가을에 뿌리를 채취하여 햇볕에 말려서 약용한다. 데쳐서 나물로 하는 이외에 국거리나 기름으로 볶아먹기도 한다. 약성은 평하고 쓴맛이 있으며, 거풍, 이뇨, 구어혈, 소종의 효능이 있어 어혈을 풀어주고 풍습성 동통, 수종, 임탁, 골수염, 이질, 약장, 암종 등에 이용되고, 적용질환은 풍습으로 인한 팔다리통증, 골수염, 임질, 황달, 간염, 수종, 월경불순, 산후오로불하, 타박상, 종기, 치질에 사용된다. 그러나 호장근은 약용으로서 한방분야에서 사용되는 외에, 일상 생활에서 우수한 관능성으로 용이하게 섭취할 수 있도록 가공한 식품에 대해서는 알려진 바 없다. Ho Jang-geun is a perennial herbaceous plant that is wild in the mountains and fields of Korea, and its roots are harvested in early spring or late autumn, and then medicated by drying in the sun. In addition to boiled herbs, they are fried in soup or oil. The drug has a flat and bitter taste, and it has the effects of feng shui, diuresis, gore blood, and swelling to release the blood and is used for customary pain, species, deposit, osteomyelitis, dysentery, medicine cabinet, and carcinoma. It is used for pain, osteomyelitis, gonorrhea, jaundice, hepatitis, edema, dysmenorrhea, postpartum dysfunction, bruises, boils and hemorrhoids. However, in addition to being used in the field of herbal medicine as medicinal, Kwon Keun-Geun is not known for foods processed to be easily consumed with excellent sensory activity in daily life.
본 발명은 호장근의 유용성분을 함유하면서도, 일상 생활에서 우수한 관능성으로 용이하게 섭취할 수 있는 발효 호장근을 함유하는 식품 조성물 및 그의 제조방법을 제공하는 것을 목적으로 한다. It is an object of the present invention to provide a food composition containing fermented koji muscle which can be easily ingested with excellent organoleptic properties in daily life while containing useful ingredients of kojang muscle.
전술한 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 발명은 (A) 호장근 추출물을 제조하는 호장근 추출물 제조 단계; (B) 상기 호장근 추출물에 효모를 접종하여 배양하는 주모 생성 단계; (C) 상기 호장근 추출물, 상기 주모, 당류 및 맥아를 혼합하여 발효하는 1차 발효 단계; (D) 상기 1차 발효액에 식초생성균을 접종하여 배양하는 식초생성균 배양 단계; 및 (E) 상기 호장근 추출물에 상기 식초생성균을 혼합하여 발효하는 2차 발효 단계;를 포함하여 제조되는 것을 특징으로 하는 발효 호장근을 함유하는 식품 조성물에 관한 것이다. The present invention for achieving the above object is (A) the preparation of the extract Kwon-Geun-Geun extract; (B) jujugi production step of inoculating the yeast root extract with yeast; (C) a primary fermentation step of fermenting by mixing the kojang root extract, the main hair, sugar and malt; (D) vinegar-producing bacteria culture step of inoculating the primary fermentation broth by inoculating vinegar-producing bacteria; And (E) a second fermentation step of mixing and fermenting the vinegar-producing bacteria in the extract of E. coli muscle.
이상과 같이 본 발명의 식품 조성물에 의하면 다양한 생리활성을 갖는 호장근을 발효하여 조미용으로 식품 제조에 사용하거나, 음용이 가능하도록 하여 호장근의 유용성분을 우수한 관능성으로 섭취할 수 있다. As described above, according to the food composition of the present invention, fermented rye roots having various physiological activities can be used for food preparation for seasoning, or drinkable so that useful ingredients of rye roots can be ingested with excellent functional properties.
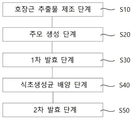
도 1은 본 발명의 발효 호장근의 제조과정을 보여주는 블록도.Figure 1 is a block diagram showing the manufacturing process of the fermented kojang root of the present invention.
이하 첨부된 도면과 실시예를 들어 본 발명을 보다 상세히 설명한다. 그러나 이러한 도면과 실시예는 본 발명의 기술적 사상의 내용과 범위를 쉽게 설명하기 위한 예시일 뿐, 이에 의해 본 발명의 기술적 범위가 한정되거나 변경되는 것은 아니다. 이러한 예시에 기초하여 본 발명의 기술적 사상의 범위 안에서 다양한 변형과 변경이 가능함은 당업자에게는 당연할 것이다.Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail with reference to the accompanying drawings and examples. However, these drawings and embodiments are only examples for easily explaining the contents and scope of the technical idea of the present invention, and thus the technical scope of the present invention is not limited or changed. It will be apparent to those skilled in the art that various modifications and variations are possible within the scope of the present invention based on these examples.
도 1은 본 발명에 의한 발효 호장근의 제조과정을 보여주는 블록도이다.Figure 1 is a block diagram showing the manufacturing process of the fermented kojang root according to the present invention.
먼저 호장근 추출물 제조 단계(S10)에서는 호장근을 세척하고, 추출하여 호장근 추출물을 제조한다. 본 발명에서 호장근은 호장근의 뿌리, 줄기, 잎, 꽃, 열매, 전초 또는 식물 조직의 배양물을 사용할 수 있으며, 호장근의 천연, 잡종 및 변종 식물을 사용할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 상기 호장근은 왕호장근, 호장근 또는 감절대일 수 있다. 본 단계는 호장근 내 유용성분이 발효액으로 효율적으로 용출되어 발효가 이루어질 수 있도록 하기 위한 것으로, 생호장근이나 건조된 호장근을 원료로 사용할 수 있으며, 추출이 효율적으로 이루어질 수 있도록 잘게 자르거나, 분쇄 또는 마쇄하거나 건조된 호장근인 경우 분말화하여 추출하는 것이 바람직하다. 추출을 위한 용매로는 물 또는 C1~C4의 저급 알코올 또는 이들의 혼합물을 사용할 수 있다. 추출 방법은 천연물질의 추출에 사용되는 방법 중 어느 것을 사용하여도 무방하며, 예를 들면, 냉침, 열추출, 초음파추출 등의 방법을 사용할 수 있으나 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다. 또한 추출물을 추가로 분획한 분획물을 사용할 수도 있다. 또한 호장근 추출물은 추출 후 그대로 사용하거나, 혹은 여과 및 농축 공정을 거친 후 사용할 수도 있다. 예를 들어, 호장근을 세척하여 세절한 후 5~10배(v/v)의 물을 넣고 90 ~ 95℃에서 2~4 시간 동안 추출한 다음, 고형물을 제거하고 740 mmHg, 60℃ 조건에서 6시간 감압농축하여 호장근 추출물을 제조할 수 있다. 호장근 추출에 사용되는 용매의 양이나 추출 시간, 추출 횟수 등은 경제성과 추출 효율을 고려하여 적절히 선택할 수 있음은 당연하다. First, in the preparation of the extract of S. roots (S10), the extract is washed and extracted to prepare the extracts. In the present invention, the roots of the roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, outposts or plant tissues of the root may be used, and natural, hybrid and varieties of the root of the roots. For example, the jangjanggeun may be king janggeun, hojanggeun or dead band. This step is to enable the fermentation to be effective by eluting the useful components in the keunjangeun, fermented broth, can be used as raw keunjangeun or dried keunjangeun raw material, finely chopped, crushed or In the case of ground or dried ephedra root, it is preferable to extract it by powdering. As a solvent for extraction, water or a lower alcohol of C1 to C4 or a mixture thereof may be used. The extraction method may be any one of methods used for extraction of natural substances, for example, but may be used, such as cold acupuncture, heat extraction, ultrasonic extraction, but is not limited thereto. It is also possible to use fractions which further fractionate the extract. In addition, the extract may be used as it is after extraction, or after the filtration and concentration process. For example, after washing and cutting the rye roots, add 5-10 times (v / v) of water, extract for 2-4 hours at 90-95 ° C, remove the solids, and remove the solids at 740 mmHg, 60 ° C. Concentrated under reduced pressure for a time may be prepared extracts. Naturally, the amount, extraction time, and extraction frequency of the solvent used for extracting Keun-Geun-Geun can be appropriately selected in consideration of economic efficiency and extraction efficiency.
주모 생성 단계(S20)는 상기 호장근 추출물에 효모를 접종하여 배양하는 것에 의해 주모를 생산하는 단계로 하기 1차 발효를 위하여 다량의 효모를 증식시키기 위한 것이다. 본 발명에서는 주모 생성단계에 호장근 추출물을 사용함으로써 호장근의 유용성분을 더욱 효율적으로 함유할 수 있다. 주모의 생성을 위해서는 상기 호장근 추출물에 효모를 예를 들어, 107~109 cells/㎖의 농도로 접종하여 48~96시간 배양한다. 효모의 배양은 26~32℃를 유지하는 것이 가장 바람직하다. Main hair production step (S20) is to incubate a large amount of yeast for the following primary fermentation by producing a hair seed by inoculating and incubating the yeast root extract with yeast. In the present invention, it is possible to more efficiently contain the useful components of the knotweed root by using the extract of the knotweed in the hair growth stage. For the production of hair follicles, the intestinal root extract is inoculated with yeast, for example, at a concentration of 10 7 to 10 9 cells / ml and incubated for 48 to 96 hours. The culture of yeast is most preferably maintained at 26 ~ 32 ℃.
1차 발효 단계(S30)는 혼합된 재료를 알코올 발효하는 단계이다. 1차 발효를 위하여 상기 단계에서 제조한 주모와, 당류 및 맥아를 혼합하여 1차 발효를 위한 혼합물을 준비한다. 호장근 추출액에 대한 주모와 당류, 맥아의 첨가량은 각각 호장근 추출물의 2~5 wt%, 0.1~3 wt%, 0.05~1.5 wt%일 수 있으나, 상기 범위를 벗어나는 경우에도 1차 발효가 효율적으로 진행될 수 있도록 적절히 조절할 수 있다. Primary fermentation step (S30) is a step of alcohol fermentation of the mixed material. For primary fermentation, a mixture for primary fermentation is prepared by mixing the main hair, sugars and malt prepared in the above step. Addition of the main hair, saccharides and malt to the extract of Kwonjang-geun may be 2 ~ 5 wt%, 0.1 ~ 3 wt%, 0.05 ~ 1.5 wt% of the extract, but even if the primary fermentation is effective It can be adjusted appropriately to proceed.
혼합물은 혼합물 중 알코올의 함량이 5~7%(v/v)가 되도록 발효시키는 것이 바람직하며, 이를 위해서 예를 들어, 초기 1~3일간은 20~24℃를 유지하고, 이후 8~12일간은 16~18℃를 유지하여 발효시킬 수 있다. 발효 후 알코올의 함량이 5%(v/v)보다 낮거나, 7%(v/v)보다 높다면 하기 2차 발효 단계의 효율이 낮아진다. The mixture is preferably fermented so that the content of alcohol in the mixture is 5-7% (v / v). For this purpose, for example, the initial 1 to 3 days are maintained at 20 to 24 ° C, and then 8 to 12 days. Silver can be fermented by maintaining 16 ~ 18 ℃. If the content of alcohol after fermentation is lower than 5% (v / v) or higher than 7% (v / v), the efficiency of the following secondary fermentation step is lowered.
1차 발효가 완료되면, 여과에 의해 다량의 효모와 세포파편과 같은 불순물을 제거한다. 예를 들어, 본 단계의 여과는 분자량 6,000 이상의 물질을 제거할 수 있는 멤브레인(membrane)을 사용하여 여과할 수 있다. Once primary fermentation is complete, filtration removes large amounts of impurities such as yeast and cell debris. For example, the filtration of this step may be filtered using a membrane (membrane) capable of removing a substance having a molecular weight of 6,000 or more.
식초생성균 배양 단계(S40)에서는 상기 1차 여과 단계에서 얻어진 1차 발효액에 상기 주모 생성 단계(S20)에서 제조한 주모와 식초생성균을 접종하여 배양하는 단계이다. 예를 들어, 주모는 1차 발효액에 대하여 2~5 wt%, 식초생성균은 107~109 cells/㎖의 농도로 접종할 수 있다. 식초생성균으로는 아세토박터 속(Acetobacter sp.) 균주로서 Acetobacter schuetzenbachii, Acetobacter ascendans, Acetobacter gengenum, Acetobacter mesoxydans, Acetobacter melanoogenum, Acetobacter suboxydans, Acetobacter aceti를 예로 들 수 있으나, 이에 한정된 것은 아니며 초산 발효에 효과적인 균주로서 인체에 무해한 것이라면 어떠한 것을 사용하여도 무방하며 내산성과 내열성이 있는 것이 더욱 바람직하다. 또한 단일 균주는 물론 둘 이상의 균주를 혼합하여 접종할 수도 있다. 당업자라면 접종되는 균주의 특성을 고려하여 배양온도와 시간을 적절히 조절하는 것은 용이할 것이다. In vinegar-producing bacteria culture step (S40) is a step of inoculating the primary fermentation broth obtained in the primary filtration step and inoculated with the main hair and vinegar-producing bacteria prepared in the main hair production step (S20). For example, the parent may inoculate 2 to 5 wt% of the primary fermentation broth and the vinegar producing bacteria may be inoculated at a concentration of 10 7 to 10 9 cells / ml. Examples of the vinegar-producing bacteria include Acetobacter schuetzenbachii, Acetobacter ascendans, Acetobacter gengenum, Acetobacter mesoxydans, Acetobacter melanoogenum, Acetobacter suboxydans, and Acetobacter aceti, but are not limited thereto. As long as it is harmless to a human body, it can be used any thing, and it is more preferable to have acid resistance and heat resistance. It is also possible to inoculate a mixture of two or more strains as well as a single strain. Those skilled in the art will be able to easily adjust the culture temperature and time in consideration of the characteristics of the strain inoculated.
2차 발효 단계(S50)는 상기 식초생성균 배양 단계(S40)에서 배양한 식초생성균을 상기 호장근 추출물 제조 단계(S10)에서 제조한 호장근 추출물에 접종하여 발효하는 단계이다. 호장근 추출물 100 중량부에 대해 상기 배양된 식초생성균은 3~7 중량부의 비율로 혼합될 수 있으나, 상기 범위 이외에도 호장근 추출물의 농축 정도에 따라 적절히 조절될 수 있음은 당연할 것이다. 2차 발효는 18~22℃에서 15~30일간 정치 발효하는 것이 바람직하다. 본 단계의 2차 발효 단계에서는 발효 중 다양한 유기산이 생성되어 초산의 자극적인 신맛이 부드럽고 상큼한 신맛으로 바뀌고 pH가 안정화된다.The secondary fermentation step (S50) is a step of inoculating the vinegar-producing bacteria cultured in the vinegar-producing bacteria culture step (S40) inoculated into the extract of the kojang root prepared in the production step (S10). The cultured vinegar-producing bacteria may be mixed at a ratio of 3 to 7 parts by weight with respect to 100 parts by weight of the extract of the extract, it will be obvious that it can be appropriately adjusted according to the concentration of the extract of the extract. It is preferable to carry out stationary fermentation for secondary fermentation for 15-30 days at 18-22 degreeC. In the second fermentation step of this step, various organic acids are produced during fermentation, so that the irritating acidity of acetic acid is changed to a soft and fresh acidity, and the pH is stabilized.
본 단계에서는 조성물의 기능성을 향상시키기 위하여 솔잎, 천궁, 당귀, 갈근, 갈화, 감초, 어성초, 표고버섯, 현미 중 선택되는 어느 하나 이상의 기능성 첨가물 또는 첨가물의 추출물을 추가하여 발효시킬 수 있다. 이때 기능성 첨가물은 호장근 100 중량부를 기준으로 2~10 중량부일 수 있다. 기능성 첨가물의 첨가량이 너무 낮은 경우에는 첨가물로 인한 기능성의 향상 효과가 낮으며, 첨가량이 너무 높은 경우에는 호장근의 유효성분의 함량이 상대적으로 감소할 뿐 아니라, 발효에 지장이 있을 수 있어 고품질의 발효물을 얻기 어려울 수 있다. In this step, in order to improve the functionality of the composition may be fermented by adding any one or more functional additives or extracts selected from pine needles, cheonggung, Angelica, brown root, browning, licorice, eochocho, shiitake mushroom, brown rice. At this time, the functional additive may be 2 to 10 parts by weight based on 100 parts by weight of the knotweed. If the addition amount of the functional additive is too low, the effect of improving the functionality due to the additive is low, and if the addition amount is too high, the content of the active ingredient of keunjangeun relatively decreases, it may interfere with the fermentation, Fermentation can be difficult to obtain.
2차 발효가 완료되면 발효물로부터 균주 및 세포파편 등을 제거하기 위해 여과하여 발효 호장근을 함유하는 식품 조성물을 제조한다. 예를 들어, 본 단계의 여과는 분자량 6,000 이상의 물질을 제거할 수 있는 멤브레인(membrane)을 사용하여 여과할 수 있다. When the secondary fermentation is complete, to remove strains and cell debris from the fermentation, and filtered to prepare a food composition containing the fermented splendid muscle. For example, the filtration of this step may be filtered using a membrane (membrane) capable of removing a substance having a molecular weight of 6,000 or more.
상기 단계에 의해 얻어진 호장근 발효물은 식품 조성물로서 음식의 조리 시 조미를 위하여 사용되어 음식물로서 호장근을 우수한 관능성으로 섭취할 수 있다. 혹은 그 자체를 음료 형태로 제조하여 음용할 수도 있다. The fermented soybean root obtained by the above step may be used for seasoning when cooking the food as a food composition, so that the soybean root may be ingested with excellent functionality as food. Or it can be prepared in the form of a drink for drinking.
Claims (2)
(B) 상기 호장근 추출물에 효모를 접종하여 배양하는 주모 생성 단계;
(C) 상기 호장근 추출물, 상기 주모, 당류 및 맥아를 혼합하여 발효하는 1차 발효 단계;
(D) 상기 1차 발효액에 식초생성균을 접종하여 배양하는 식초생성균 배양 단계; 및
(E) 상기 호장근 추출물에 상기 식초생성균을 혼합하여 발효하는 2차 발효 단계;
를 포함하여 제조되는 것을 특징으로 하는 발효 호장근을 함유하는 식품 조성물.
(A) a step of preparing a root extract extract to prepare a root extract;
(B) jujugi production step of inoculating the yeast root extract with yeast;
(C) a primary fermentation step of fermenting by mixing the kojang root extract, the main hair, sugar and malt;
(D) vinegar-producing bacteria culture step of inoculating the primary fermentation broth by inoculating vinegar-producing bacteria; And
(E) a secondary fermentation step of fermenting the vinegar-producing bacteria mixed with the extract of the Kwonjang;
Food composition containing fermented jangjanggeun characterized in that it is prepared.
상기 (E) 단계에서,
솔잎, 천궁, 당귀, 갈근, 갈화, 감초, 어성초, 표고버섯, 현미 중 선택되는 어느 하나 이상의 기능성 첨가물 또는 첨가물의 추출물을 추가하여 발효시키는 것을 특징으로 하는 발효 호장근을 함유하는 식품 조성물.The method of claim 1,
In the step (E),
A food composition containing fermented jangjanggeun, characterized in that the fermentation by adding any one or more functional additives or extracts of the additives selected from pine needles, cheonggung, Angelica, brown root, browning, licorice, eoseongcho, shiitake, brown rice.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180033939A KR20190111592A (en) | 2018-03-23 | 2018-03-23 | Food Composition Comprising Polygonum Cuspidatum and Noble Preparation Method thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180033939A KR20190111592A (en) | 2018-03-23 | 2018-03-23 | Food Composition Comprising Polygonum Cuspidatum and Noble Preparation Method thereof |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20190111592A true KR20190111592A (en) | 2019-10-02 |
Family
ID=68423154
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180033939A KR20190111592A (en) | 2018-03-23 | 2018-03-23 | Food Composition Comprising Polygonum Cuspidatum and Noble Preparation Method thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR20190111592A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20210049029A (en) * | 2019-10-24 | 2021-05-04 | 임우종 | Composition for improving anticancer efficacy of sorafenib containing polygonum cuspidatum extract as an active ingredient |
| KR20210048866A (en) * | 2019-10-24 | 2021-05-04 | 임우종 | Composition for improving anticancer efficacy of sorafenib containing polygonum cuspidatum extract as an active ingredient and extracting method thereof |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101568600B1 (en) | 2014-08-14 | 2015-11-11 | 서정임 | Method for making red yeast rice vinegar |
| KR101620184B1 (en) | 2014-08-18 | 2016-05-11 | 배재영 | A method of manufacturing orostachys japonicus vinegar and orostachys japonicus using it |
| KR101803370B1 (en) | 2016-07-28 | 2017-12-29 | 남해섬애약쑥 영농조합법인 | Mugwort vinegar and the manufacturing method thereof |
| KR101820027B1 (en) | 2016-11-11 | 2018-01-19 | 신유토 토종약초 영농조합법인 | Process for the production of fig fermentation vinegar and the fig fermentation vinegar produced by the process |
| KR101825288B1 (en) | 2016-03-22 | 2018-02-06 | 김연길 | the manufacture method of Deodeok vinegar |
-
2018
- 2018-03-23 KR KR1020180033939A patent/KR20190111592A/en unknown
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101568600B1 (en) | 2014-08-14 | 2015-11-11 | 서정임 | Method for making red yeast rice vinegar |
| KR101620184B1 (en) | 2014-08-18 | 2016-05-11 | 배재영 | A method of manufacturing orostachys japonicus vinegar and orostachys japonicus using it |
| KR101825288B1 (en) | 2016-03-22 | 2018-02-06 | 김연길 | the manufacture method of Deodeok vinegar |
| KR101803370B1 (en) | 2016-07-28 | 2017-12-29 | 남해섬애약쑥 영농조합법인 | Mugwort vinegar and the manufacturing method thereof |
| KR101820027B1 (en) | 2016-11-11 | 2018-01-19 | 신유토 토종약초 영농조합법인 | Process for the production of fig fermentation vinegar and the fig fermentation vinegar produced by the process |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20210049029A (en) * | 2019-10-24 | 2021-05-04 | 임우종 | Composition for improving anticancer efficacy of sorafenib containing polygonum cuspidatum extract as an active ingredient |
| KR20210048866A (en) * | 2019-10-24 | 2021-05-04 | 임우종 | Composition for improving anticancer efficacy of sorafenib containing polygonum cuspidatum extract as an active ingredient and extracting method thereof |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5119343B2 (en) | Wine and its manufacturing method | |
| KR101278657B1 (en) | Polygonum multiflorum for promoting hair to be black and method thereof | |
| KR100549286B1 (en) | Manufacturing method for traditional rice wine flavoring with citrus junos | |
| CN102805169B (en) | Mixed effervescence tea drink | |
| KR101663379B1 (en) | MANUFACTURE OF FERMENTED Allium hookeri FROM YEASTS AND NATURAL ENZYME AND PREPARATION OF COMBINED BEVERAGE FOR QUENCHING THIRST | |
| CN103039647A (en) | Mixed healthcare effervescent beverage | |
| KR20190111592A (en) | Food Composition Comprising Polygonum Cuspidatum and Noble Preparation Method thereof | |
| KR101733549B1 (en) | Wine or vinegar of Orostachys japonicus made from fermented sugar extract of Orostachys japonicus | |
| CN106318788A (en) | Brewing method of fermented wine with selenium-rich purple potatoes | |
| CN109735418A (en) | A kind of tea wine and preparation method thereof | |
| KR20130012447A (en) | A rice ferment using cordyceps militaris body fruits and method for preparing of the same | |
| KR101327810B1 (en) | The method for manufacture of functional vinegar | |
| KR102279890B1 (en) | Manufacturing method of Chicken Broth using Curing agent | |
| KR101037572B1 (en) | Powder manufacturing process using rind and pip of rubus coreanus | |
| KR101752571B1 (en) | Chungkukjang with cultivating, ripening of using Galwha extracts and Gochujang manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR20160075114A (en) | Preparation Metod of Vinegar Containing Coffee Extract | |
| CN108059519A (en) | A kind of preparation method of greenery promotor composition | |
| KR102296716B1 (en) | Method for producing aronia seasoning sauce | |
| KR20020061425A (en) | Health food making method | |
| KR20040087854A (en) | Fermented Wine made from Fruit of Araliaceous Shrubs, and Method for producing Thereof | |
| KR102082820B1 (en) | Fermented vinegar beverage concentrates and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR101203790B1 (en) | Method for manufacturing soybean paste including butterbur and soybean paste thereof | |
| KR20180063427A (en) | A method of preparing beverage comprising fermented acanthopanax fruit extract and beverage prepared therefrom | |
| KR102355029B1 (en) | Manufacturing method of Raw Rice Wine using Cultivated Wild Ginseng | |
| KR102390434B1 (en) | Sikhye using Autumn radish |