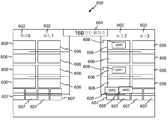
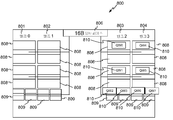
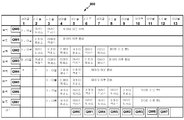
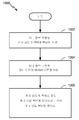
KR20150132360A - 혼합 메모리 타입 하이브리드 캐시 - Google Patents
혼합 메모리 타입 하이브리드 캐시 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20150132360A KR20150132360A KR1020157029023A KR20157029023A KR20150132360A KR 20150132360 A KR20150132360 A KR 20150132360A KR 1020157029023 A KR1020157029023 A KR 1020157029023A KR 20157029023 A KR20157029023 A KR 20157029023A KR 20150132360 A KR20150132360 A KR 20150132360A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- memory
- cache
- type
- accessing
- sram
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F12/00—Accessing, addressing or allocating within memory systems or architectures
- G06F12/02—Addressing or allocation; Relocation
- G06F12/08—Addressing or allocation; Relocation in hierarchically structured memory systems, e.g. virtual memory systems
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F12/00—Accessing, addressing or allocating within memory systems or architectures
- G06F12/02—Addressing or allocation; Relocation
- G06F12/08—Addressing or allocation; Relocation in hierarchically structured memory systems, e.g. virtual memory systems
- G06F12/0802—Addressing of a memory level in which the access to the desired data or data block requires associative addressing means, e.g. caches
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F12/00—Accessing, addressing or allocating within memory systems or architectures
- G06F12/02—Addressing or allocation; Relocation
- G06F12/08—Addressing or allocation; Relocation in hierarchically structured memory systems, e.g. virtual memory systems
- G06F12/0802—Addressing of a memory level in which the access to the desired data or data block requires associative addressing means, e.g. caches
- G06F12/0844—Multiple simultaneous or quasi-simultaneous cache accessing
- G06F12/0846—Cache with multiple tag or data arrays being simultaneously accessible
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F12/00—Accessing, addressing or allocating within memory systems or architectures
- G06F12/02—Addressing or allocation; Relocation
- G06F12/08—Addressing or allocation; Relocation in hierarchically structured memory systems, e.g. virtual memory systems
- G06F12/0802—Addressing of a memory level in which the access to the desired data or data block requires associative addressing means, e.g. caches
- G06F12/0844—Multiple simultaneous or quasi-simultaneous cache accessing
- G06F12/0846—Cache with multiple tag or data arrays being simultaneously accessible
- G06F12/0851—Cache with interleaved addressing
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F12/00—Accessing, addressing or allocating within memory systems or architectures
- G06F12/02—Addressing or allocation; Relocation
- G06F12/08—Addressing or allocation; Relocation in hierarchically structured memory systems, e.g. virtual memory systems
- G06F12/0802—Addressing of a memory level in which the access to the desired data or data block requires associative addressing means, e.g. caches
- G06F12/0893—Caches characterised by their organisation or structure
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F12/00—Accessing, addressing or allocating within memory systems or architectures
- G06F12/02—Addressing or allocation; Relocation
- G06F12/08—Addressing or allocation; Relocation in hierarchically structured memory systems, e.g. virtual memory systems
- G06F12/10—Address translation
- G06F12/1027—Address translation using associative or pseudo-associative address translation means, e.g. translation look-aside buffer [TLB]
- G06F12/1045—Address translation using associative or pseudo-associative address translation means, e.g. translation look-aside buffer [TLB] associated with a data cache
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C11/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor
- G11C11/005—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor comprising combined but independently operative RAM-ROM, RAM-PROM, RAM-EPROM cells
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C11/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor
- G11C11/02—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using magnetic elements
- G11C11/16—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using magnetic elements using elements in which the storage effect is based on magnetic spin effect
- G11C11/165—Auxiliary circuits
- G11C11/1659—Cell access
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C13/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of storage elements not covered by groups G11C11/00, G11C23/00, or G11C25/00
- G11C13/0002—Digital stores characterised by the use of storage elements not covered by groups G11C11/00, G11C23/00, or G11C25/00 using resistive RAM [RRAM] elements
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C13/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of storage elements not covered by groups G11C11/00, G11C23/00, or G11C25/00
- G11C13/0002—Digital stores characterised by the use of storage elements not covered by groups G11C11/00, G11C23/00, or G11C25/00 using resistive RAM [RRAM] elements
- G11C13/0021—Auxiliary circuits
- G11C13/004—Reading or sensing circuits or methods
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C13/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of storage elements not covered by groups G11C11/00, G11C23/00, or G11C25/00
- G11C13/0002—Digital stores characterised by the use of storage elements not covered by groups G11C11/00, G11C23/00, or G11C25/00 using resistive RAM [RRAM] elements
- G11C13/0021—Auxiliary circuits
- G11C13/0069—Writing or programming circuits or methods
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C14/00—Digital stores characterised by arrangements of cells having volatile and non-volatile storage properties for back-up when the power is down
- G11C14/0054—Digital stores characterised by arrangements of cells having volatile and non-volatile storage properties for back-up when the power is down in which the volatile element is a SRAM cell
- G11C14/0081—Digital stores characterised by arrangements of cells having volatile and non-volatile storage properties for back-up when the power is down in which the volatile element is a SRAM cell and the nonvolatile element is a magnetic RAM [MRAM] element or ferromagnetic cell
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F2212/00—Indexing scheme relating to accessing, addressing or allocation within memory systems or architectures
- G06F2212/10—Providing a specific technical effect
- G06F2212/1028—Power efficiency
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F2212/00—Indexing scheme relating to accessing, addressing or allocation within memory systems or architectures
- G06F2212/20—Employing a main memory using a specific memory technology
- G06F2212/202—Non-volatile memory
- G06F2212/2024—Rewritable memory not requiring erasing, e.g. resistive or ferroelectric RAM
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F2212/00—Indexing scheme relating to accessing, addressing or allocation within memory systems or architectures
- G06F2212/20—Employing a main memory using a specific memory technology
- G06F2212/205—Hybrid memory, e.g. using both volatile and non-volatile memory
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F2212/00—Indexing scheme relating to accessing, addressing or allocation within memory systems or architectures
- G06F2212/22—Employing cache memory using specific memory technology
- G06F2212/225—Hybrid cache memory, e.g. having both volatile and non-volatile portions
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C2207/00—Indexing scheme relating to arrangements for writing information into, or reading information out from, a digital store
- G11C2207/22—Control and timing of internal memory operations
- G11C2207/2245—Memory devices with an internal cache buffer
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D10/00—Energy efficient computing, e.g. low power processors, power management or thermal management
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Hall/Mr Elements (AREA)
- Mram Or Spin Memory Techniques (AREA)
- Memory System Of A Hierarchy Structure (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/843,190 US9304913B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2013-03-15 | Mixed memory type hybrid cache |
| US13/843,190 | 2013-03-15 | ||
| PCT/US2014/025971 WO2014151548A1 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-13 | Mixed memory type hybrid cache |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20150132360A true KR20150132360A (ko) | 2015-11-25 |
Family
ID=50628954
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020157029023A Ceased KR20150132360A (ko) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-13 | 혼합 메모리 타입 하이브리드 캐시 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9304913B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP2972892B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6154060B2 (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR20150132360A (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN105009095B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2014151548A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20180051326A (ko) * | 2016-11-07 | 2018-05-16 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 데이터 처리 방법 및 디바이스 |
Families Citing this family (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5520747B2 (ja) * | 2010-08-25 | 2014-06-11 | 株式会社日立製作所 | キャッシュを搭載した情報装置及びコンピュータ読み取り可能な記憶媒体 |
| CN107533459B (zh) | 2016-03-31 | 2020-11-20 | 慧与发展有限责任合伙企业 | 使用电阻存储器阵列的数据处理方法和单元 |
| US10474557B2 (en) | 2016-07-19 | 2019-11-12 | Sap Se | Source code profiling for line-level latency and energy consumption estimation |
| US10437798B2 (en) | 2016-07-19 | 2019-10-08 | Sap Se | Full system simulator and memory-aware splay tree for in-memory databases in hybrid memory systems |
| US10783146B2 (en) | 2016-07-19 | 2020-09-22 | Sap Se | Join operations in hybrid main memory systems |
| US10387127B2 (en) * | 2016-07-19 | 2019-08-20 | Sap Se | Detecting sequential access data and random access data for placement on hybrid main memory for in-memory databases |
| US10452539B2 (en) | 2016-07-19 | 2019-10-22 | Sap Se | Simulator for enterprise-scale simulations on hybrid main memory systems |
| US10540098B2 (en) | 2016-07-19 | 2020-01-21 | Sap Se | Workload-aware page management for in-memory databases in hybrid main memory systems |
| US11977484B2 (en) | 2016-07-19 | 2024-05-07 | Sap Se | Adapting in-memory database in hybrid memory systems and operating system interface |
| US10698732B2 (en) | 2016-07-19 | 2020-06-30 | Sap Se | Page ranking in operating system virtual pages in hybrid memory systems |
| US10235299B2 (en) | 2016-11-07 | 2019-03-19 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method and device for processing data |
| US20180374893A1 (en) * | 2017-06-22 | 2018-12-27 | Globalfoundries Singapore Pte. Ltd. | Differential sensing cell design for stt mram |
| US11010379B2 (en) | 2017-08-15 | 2021-05-18 | Sap Se | Increasing performance of in-memory databases using re-ordered query execution plans |
| WO2019212466A1 (en) * | 2018-04-30 | 2019-11-07 | Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development Lp | Resistive and digital processing cores |
| US10896707B2 (en) * | 2018-12-17 | 2021-01-19 | Arm Limited | Selective clock adjustment during read and/or write memory operations |
| CN118732924B (zh) * | 2023-03-28 | 2025-11-11 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种数据访存方法及片上系统 |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH08328949A (ja) * | 1995-06-06 | 1996-12-13 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 記憶装置 |
| JP3092557B2 (ja) * | 1997-09-16 | 2000-09-25 | 日本電気株式会社 | 半導体記憶装置 |
| JP3604296B2 (ja) * | 1998-01-22 | 2004-12-22 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | 半導体メモリおよびメモリシステム |
| JP2000339954A (ja) | 1999-05-31 | 2000-12-08 | Fujitsu Ltd | 半導体記憶装置 |
| JP2002351741A (ja) * | 2001-05-30 | 2002-12-06 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 半導体集積回路装置 |
| US7293141B1 (en) * | 2005-02-01 | 2007-11-06 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | Cache word of interest latency organization |
| JP4437489B2 (ja) | 2006-10-25 | 2010-03-24 | 株式会社日立製作所 | 揮発性キャッシュメモリと不揮発性メモリとを備えたストレージシステム |
| US7584335B2 (en) * | 2006-11-02 | 2009-09-01 | International Business Machines Corporation | Methods and arrangements for hybrid data storage |
| US7568068B2 (en) | 2006-11-13 | 2009-07-28 | Hitachi Global Storage Technologies Netherlands B. V. | Disk drive with cache having volatile and nonvolatile memory |
| US7962695B2 (en) * | 2007-12-04 | 2011-06-14 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method and system for integrating SRAM and DRAM architecture in set associative cache |
| WO2010148359A1 (en) * | 2009-06-18 | 2010-12-23 | Cypress Semiconductor Corporation | Memory devices and systems including multi-speed access of memory modules |
| US8914568B2 (en) | 2009-12-23 | 2014-12-16 | Intel Corporation | Hybrid memory architectures |
| JP2012190359A (ja) * | 2011-03-11 | 2012-10-04 | Toshiba Corp | キャッシュシステムおよび処理装置 |
| JP5627521B2 (ja) | 2011-03-24 | 2014-11-19 | 株式会社東芝 | キャッシュシステムおよび処理装置 |
-
2013
- 2013-03-15 US US13/843,190 patent/US9304913B2/en active Active
-
2014
- 2014-03-13 EP EP14720791.4A patent/EP2972892B1/en active Active
- 2014-03-13 KR KR1020157029023A patent/KR20150132360A/ko not_active Ceased
- 2014-03-13 WO PCT/US2014/025971 patent/WO2014151548A1/en not_active Ceased
- 2014-03-13 CN CN201480013145.3A patent/CN105009095B/zh active Active
- 2014-03-13 JP JP2016502013A patent/JP6154060B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20180051326A (ko) * | 2016-11-07 | 2018-05-16 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 데이터 처리 방법 및 디바이스 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2014151548A1 (en) | 2014-09-25 |
| US20140281184A1 (en) | 2014-09-18 |
| US9304913B2 (en) | 2016-04-05 |
| EP2972892B1 (en) | 2021-04-14 |
| JP6154060B2 (ja) | 2017-06-28 |
| CN105009095B (zh) | 2017-12-05 |
| EP2972892A1 (en) | 2016-01-20 |
| JP2016515274A (ja) | 2016-05-26 |
| CN105009095A (zh) | 2015-10-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9304913B2 (en) | Mixed memory type hybrid cache | |
| US9165631B2 (en) | OTP scheme with multiple magnetic tunnel junction devices in a cell | |
| US9679663B2 (en) | OTP cell with reversed MTJ connection | |
| US9147457B2 (en) | Reference cell repair scheme | |
| US9165630B2 (en) | Offset canceling dual stage sensing circuit | |
| US8929167B2 (en) | MRAM self-repair with BIST logic | |
| US20140071739A1 (en) | Reference level adjustment scheme | |
| KR20170133072A (ko) | 저항성 메모리 장치 및 이를 포함하는 집적 회로 | |
| US8570797B2 (en) | Magnetic random access memory (MRAM) read with reduced disturb failure | |
| JP6082112B2 (ja) | モノリシックマルチチャネル適合可能stt−mram | |
| US8593173B2 (en) | Programmable logic sensing in magnetic random access memory |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0105 | International application |
Patent event date: 20151013 Patent event code: PA01051R01D Comment text: International Patent Application |
|
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | ||
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| A302 | Request for accelerated examination | ||
| PA0201 | Request for examination |
Patent event code: PA02012R01D Patent event date: 20160525 Comment text: Request for Examination of Application |
|
| PA0302 | Request for accelerated examination |
Patent event date: 20160525 Patent event code: PA03022R01D Comment text: Request for Accelerated Examination |
|
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection |
Comment text: Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date: 20160718 Patent event code: PE09021S01D |
|
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection |
Comment text: Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date: 20161226 Patent event code: PE09021S01D |
|
| E601 | Decision to refuse application | ||
| PE0601 | Decision on rejection of patent |
Patent event date: 20170329 Comment text: Decision to Refuse Application Patent event code: PE06012S01D Patent event date: 20161226 Comment text: Notification of reason for refusal Patent event code: PE06011S01I Patent event date: 20160718 Comment text: Notification of reason for refusal Patent event code: PE06011S01I |