KR20130116632A - Composite insulation board comprising opacifier and method for producing it - Google Patents
Composite insulation board comprising opacifier and method for producing it Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20130116632A KR20130116632A KR20120039202A KR20120039202A KR20130116632A KR 20130116632 A KR20130116632 A KR 20130116632A KR 20120039202 A KR20120039202 A KR 20120039202A KR 20120039202 A KR20120039202 A KR 20120039202A KR 20130116632 A KR20130116632 A KR 20130116632A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- insulation board
- composite
- composite insulation
- fumed silica
- opaque
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C04—CEMENTS; CONCRETE; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES
- C04B—LIME, MAGNESIA; SLAG; CEMENTS; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF, e.g. MORTARS, CONCRETE OR LIKE BUILDING MATERIALS; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES; TREATMENT OF NATURAL STONE
- C04B14/00—Use of inorganic materials as fillers, e.g. pigments, for mortars, concrete or artificial stone; Treatment of inorganic materials specially adapted to enhance their filling properties in mortars, concrete or artificial stone
- C04B14/02—Granular materials, e.g. microballoons
- C04B14/04—Silica-rich materials; Silicates
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C04—CEMENTS; CONCRETE; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES
- C04B—LIME, MAGNESIA; SLAG; CEMENTS; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF, e.g. MORTARS, CONCRETE OR LIKE BUILDING MATERIALS; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES; TREATMENT OF NATURAL STONE
- C04B14/00—Use of inorganic materials as fillers, e.g. pigments, for mortars, concrete or artificial stone; Treatment of inorganic materials specially adapted to enhance their filling properties in mortars, concrete or artificial stone
- C04B14/38—Fibrous materials; Whiskers
- C04B14/42—Glass
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C04—CEMENTS; CONCRETE; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES
- C04B—LIME, MAGNESIA; SLAG; CEMENTS; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF, e.g. MORTARS, CONCRETE OR LIKE BUILDING MATERIALS; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES; TREATMENT OF NATURAL STONE
- C04B18/00—Use of agglomerated or waste materials or refuse as fillers for mortars, concrete or artificial stone; Treatment of agglomerated or waste materials or refuse, specially adapted to enhance their filling properties in mortars, concrete or artificial stone
- C04B18/04—Waste materials; Refuse
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B28—WORKING CEMENT, CLAY, OR STONE
- B28B—SHAPING CLAY OR OTHER CERAMIC COMPOSITIONS; SHAPING SLAG; SHAPING MIXTURES CONTAINING CEMENTITIOUS MATERIAL, e.g. PLASTER
- B28B3/00—Producing shaped articles from the material by using presses; Presses specially adapted therefor
- B28B3/02—Producing shaped articles from the material by using presses; Presses specially adapted therefor wherein a ram exerts pressure on the material in a moulding space; Ram heads of special form
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C04—CEMENTS; CONCRETE; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES
- C04B—LIME, MAGNESIA; SLAG; CEMENTS; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF, e.g. MORTARS, CONCRETE OR LIKE BUILDING MATERIALS; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES; TREATMENT OF NATURAL STONE
- C04B14/00—Use of inorganic materials as fillers, e.g. pigments, for mortars, concrete or artificial stone; Treatment of inorganic materials specially adapted to enhance their filling properties in mortars, concrete or artificial stone
- C04B14/38—Fibrous materials; Whiskers
- C04B14/46—Rock wool ; Ceramic or silicate fibres
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C04—CEMENTS; CONCRETE; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES
- C04B—LIME, MAGNESIA; SLAG; CEMENTS; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF, e.g. MORTARS, CONCRETE OR LIKE BUILDING MATERIALS; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES; TREATMENT OF NATURAL STONE
- C04B22/00—Use of inorganic materials as active ingredients for mortars, concrete or artificial stone, e.g. accelerators, shrinkage compensating agents
- C04B22/06—Oxides, Hydroxides
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04C—STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS; BUILDING MATERIALS
- E04C2/00—Building elements of relatively thin form for the construction of parts of buildings, e.g. sheet materials, slabs, or panels
- E04C2/02—Building elements of relatively thin form for the construction of parts of buildings, e.g. sheet materials, slabs, or panels characterised by specified materials
- E04C2/26—Building elements of relatively thin form for the construction of parts of buildings, e.g. sheet materials, slabs, or panels characterised by specified materials composed of materials covered by two or more of groups E04C2/04, E04C2/08, E04C2/10 or of materials covered by one of these groups with a material not specified in one of the groups
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02W—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO WASTEWATER TREATMENT OR WASTE MANAGEMENT
- Y02W30/00—Technologies for solid waste management
- Y02W30/50—Reuse, recycling or recovery technologies
- Y02W30/91—Use of waste materials as fillers for mortars or concrete
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Civil Engineering (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Thermal Insulation (AREA)
Abstract
Description
본 발명은 흄드 실리카(Fumed Silica)와, 플라이 애쉬(Fly Ash), 실리콘 및 수산화알루미늄 중에서 선택된 1종 이상의 불투명화재를 포함하는 복합 단열 보드 및 이의 제조방법에 관한 것이다.
The present invention relates to a composite insulating board comprising a fumed silica (Fumed Silica), at least one opaque material selected from fly ash, silicon and aluminum hydroxide and a method of manufacturing the same.
일반적으로 진공단열재에 사용되는 심재는 열전도율이 작고, 가스 발생이 적은 무기 화합물이 적합하고, 유리섬유(Glass fiber), 또는 흄드 실리카(Fumed silica)와 유리섬유 복합재 등이 적용되고 있다. In general, the core material used in the vacuum insulation material is a low thermal conductivity, low gas generation inorganic compound is suitable, glass fiber (Flass fiber), or fumed silica (glass) and glass fiber composite materials are applied.
특히 나노크기의 실리카 분말의 한 종류인 흄드 실리카는 실리카(SiO4) 사면체 구조가 비규칙적으로 연결된 그물망 구조를 형성하여 나노 수준의 기공크기를 가지고 있어서, 이러한 소재로 만든 단열재는 공기의 열전도도보다 더 낮은 열전도도를 가질 수 있다.In particular, fumed silica, a kind of nano-sized silica powder, has a nano-scale pore size by forming a network structure in which silica (SiO 4 ) tetrahedral structures are irregularly connected, and the insulation made of these materials has a higher thermal conductivity than air. It may have a lower thermal conductivity.
또한 실리카의 비흡수계수 (specific absorption coefficient)는 8 μm 이하의 파장에서는 매우 작기 때문에 순수한 실리카의 복사열 전도는 온도가 증가됨에 따라 증가한다고 알려져 있다. 따라서 고온에서 복사열전도를 방지하기 위하여 흄드 실리카를 주성분으로 하는 단열재에 고온에서 복사에 의한 열전도를 감소시킬 수 있는 불투명화재가 사용되어 왔다. In addition, since the specific absorption coefficient of silica is very small at a wavelength of 8 μm or less, it is known that the radiant heat conduction of pure silica increases with increasing temperature. Therefore, in order to prevent radiant heat conduction at high temperature, an opaque fire material which can reduce thermal conduction by radiation at high temperature has been used in the heat insulating material mainly composed of fumed silica.
불투명화재로 블랙카본과 철, 티타늄 옥사이드(예를 들어 티탄철석 또는 루콕신), 지르코니움 실리케이드(지르콘), 지르코니움 옥사이드(지르코니아), 산화철(예를 들어 적철광) 및 이의 혼합물, 탄화규소, 티타니아와 같은 산화물이 공지되어 있다. Opaque fires include black carbon and iron, titanium oxide (e.g. titanium or leucoxin), zirconium silicate (zircon), zirconium oxide (zirconia), iron oxide (e.g. hematite) and mixtures thereof, silicon carbide Oxides such as titania are known.
한편, 한국특허공개공보 제2010-0063984호에서는 적외선 불투명화재는 티타니아(TiO2) 또는 탄화규소(SiC)를 적외선 불투명화재로 사용하는 구성이 개시되어 있다. 그러나 상기 탄화규소와 같은 재료의 원가가 비싸 이를 이용하여 단열재를 제조하는 경우 제조 원가가 매우 높아진다. On the other hand, Korean Patent Laid-Open No. 2010-0063984 discloses a configuration in which an infrared opaque fire material uses titania (TiO 2 ) or silicon carbide (SiC) as an infrared opaque fire material. However, when the cost of the material such as silicon carbide is expensive to manufacture the heat insulating material using it, the manufacturing cost is very high.
또한 상기 오븐, 쿡탑과 같은 전자 제품에 적용하기 위하여 고온 단열 성능은 물론 고온에 견디는 자재를 사용하여야 하는데, 일반적인 단열재 내 포함되는 단열 보드의 경우 보강재로서 유기 섬유를 사용하기 때문에 고온에서는 사용하기 어려운 문제가 있다. In addition, in order to apply to electronic products such as ovens and cooktops, materials having high temperature insulation as well as high temperature resistance should be used. In the case of insulation boards included in general insulation materials, it is difficult to use them at high temperatures because organic fibers are used as reinforcement materials. There is.
따라서 보다 경제적으로 제조할 수 있으면서도 고온에서 우수한 단열 성능을 나타낼 수 있는 단열재의 개발이 지속적으로 요구되는 실정이다.
Therefore, the development of a heat insulating material that can be produced more economically, but can exhibit excellent heat insulating performance at a high temperature is constantly required.
이에 본 발명자들은 경제적인 단열재를 개발하고자 연구, 노력한 결과, 흄드 실리카와 함께 불투명화재로서 플라이 애쉬(Fly Ash), 실리콘 또는 수산화알루미늄을 사용하면 원가를 낮추면서도 높은 단열 효과를 얻을 수 있음을 확인함으로써 본 발명을 완성하게 되었다. Therefore, the present inventors researched and tried to develop an economical insulating material, and confirmed that the use of fly ash, silicon, or aluminum hydroxide as an opaque material together with fumed silica can obtain a high thermal insulation effect while reducing the cost. The present invention has been completed.
따라서 본 발명의 목적은 종래 단열 보드에 사용되는 불투명화재로서 저가의 재료를 사용하여 고온에서도 우수한 단열 효과를 나타낼 수 있는 복합 단열 보드를 제공하는 것이다.
Accordingly, an object of the present invention is to provide a composite thermal insulation board that can exhibit an excellent thermal insulation effect even at high temperature by using a low-cost material as an opaque fire material used in the conventional thermal insulation board.
상기 목적을 달성하기 위하여, 흄드 실리카(Fumed Silica); 및 플라이 애쉬(Fly Ash), 실리콘 및 수산화알루미늄 중에서 선택된 1종 이상의 불투명화재를 포함하는 복합 단열 보드를 제공한다. In order to achieve the above object, Fumed Silica; And one or more opaque materials selected from fly ash, silicon, and aluminum hydroxide.
또한 본 발명은 상기 불투명화재, 흄드 실리카 및 무기 섬유의 혼합물을 몰드에 넣고 건식 프레스 성형하여 보드로 제조하는 단계를 포함하는 복합 단열 보드의 제조방법을 제공한다.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a method for producing a composite insulation board comprising the step of putting the mixture of the opaque material, fumed silica and inorganic fibers into a mold and dry press molding.
본 발명의 복합 단열 보드는 플라이 애쉬, 실리콘 또는 수산화 알루미늄을 불투명화재로 사용하는 바, 상기 불투명화재는 종래 사용되는 탄화 규소에 비하여 가격이 매우 싼 장점이 있다. 따라서 제조 원가를 크게 낮출 수 있어 가격 경쟁력이 우수하며, 상온에서의 단열 효과 역시 탄화 규소를 사용한 경우와 대등한 효과를 낼 수 있다. The composite insulation board of the present invention uses fly ash, silicon, or aluminum hydroxide as an opaque fire material, and the opaque fire material has an advantage of being very inexpensive compared to conventional silicon carbide. Therefore, the manufacturing cost can be significantly lowered, so it is excellent in price competitiveness, and the thermal insulation effect at room temperature may also be comparable to that of using silicon carbide.
특히, 본 발명의 복합 단열 보드는 전기오븐의 캐비티(cavity)를 둘러싸고 있는 유리섬유매트 또는 세라믹섬유매트와 같은 단열재를 대체할 수 있고, 보드의 두께를 줄임으로써, 캐비티의 크기를 늘릴 수 있다. 그리고 가스쿡탑, 전기자동차의 단열재로서도 널리 적용될 수 있다. In particular, the composite insulation board of the present invention can replace the heat insulating material such as glass fiber mat or ceramic fiber mat surrounding the cavity of the electric oven (cavity), and by reducing the thickness of the board, it is possible to increase the size of the cavity. In addition, it can be widely applied as a heat insulating material for gas cooktops and electric vehicles.
또한 상기 복합 단열 보드를 진공 단열재의 심재로 사용하는 경우, 불투명화재가 포함되지 않은 흄드 실리카 진공 단열재 보다 단열성능은 우수하면서도 낮은 단가로 제조가 가능하므로 건축용 단열재 등으로도 널리 사용될 가능성이 있다.
In addition, when the composite insulation board is used as the core material of the vacuum insulation material, since the insulation performance is superior to the fumed silica vacuum insulation material that does not include an opaque fire material, it is possible to manufacture at low cost, and thus may be widely used as a building insulation material.
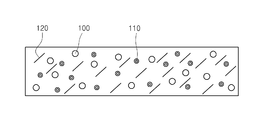
도 1은 본 발명의 복합 단열 보드의 단면을 모식화한 것이다.
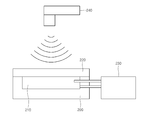
도 2는 실시예 및 비교예의 복합 단열 보드의 고온 단열 성능을 평가하기 위한 장치를 나타낸 것이다. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The cross section of the composite insulation board of this invention is modeled.
2 shows an apparatus for evaluating high-temperature insulation performance of the composite insulation board of the Examples and Comparative Examples.
본 발명의 이점 및 특징, 그리고 그것들을 달성하는 방법은 상세하게 후술되어 있는 실시예들을 참조하면 명확해질 것이다. 그러나, 본 발명은 이하에서 개시되는 실시예들에 한정되는 것이 아니라 서로 다른 다양한 형태로 구현될 것이며, 단지 본 실시예들은 본 발명의 개시가 완전하도록 하며, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 발명의 범주를 완전하게 알려주기 위해 제공되는 것이며, 본 발명은 청구항의 범주에 의해 정의될 뿐이다. Advantages and features of the present invention and methods of achieving them will become apparent with reference to the embodiments described in detail below. It should be understood, however, that the invention is not limited to the disclosed embodiments, but is capable of many different forms and should not be construed as limited to the embodiments set forth herein. Rather, these embodiments are provided so that this disclosure will be thorough and complete, To fully disclose the scope of the invention to those skilled in the art, and the invention is only defined by the scope of the claims.
이하 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 복합 단열 보드 및 이의 제조방법에 관하여 상세히 설명하기로 한다.
Hereinafter, a composite insulating board and a method of manufacturing the same according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail.
복합 단열 보드Composite insulation board
본 발명은 흄드 실리카(Fumed Silica); 및 플라이 애쉬(Fly Ash), 실리콘 및 수산화알루미늄 중에서 선택된 1종 이상의 불투명화재를 포함하는 복합 단열 보드를 특징으로 한다. The present invention is a fumed silica (Fumed Silica); And at least one opaque material selected from fly ash, silicon, and aluminum hydroxide.
상기 흄드 실리카는 염화 실란 화합물의 기상 열분해에 따른 기상 합성법에 의하여 제조될 수 있으며, 바람직하게는 직경이 1 ~ 100 nm 이고, 비표면적이 10 ~ 1000 m2/g 인 것이 유리하며, 더욱 바람직하게는 직경이 10 ~ 50 nm이고, 비표면적이 100 ~ 500 m2/g 인 것이 좋다. The fumed silica may be prepared by a gas phase synthesis method according to the gas phase pyrolysis of a silane chloride compound, preferably, the diameter is 1 ~ 100 nm, it is advantageous that the specific surface area is 10 ~ 1000 m 2 / g, more preferably It is preferable that the diameter is 10 to 50 nm and the specific surface area is 100 to 500 m 2 / g.
상기 불투명화재는 고온에서 복사에 의한 열전도를 감소시키기 위하여 사용되며, 플라이 애쉬(Fly Ash), 실리콘 및 수산화알루미늄 중에서 선택된 1종 이상을 사용한다. The opaque fire is used to reduce the thermal conduction by radiation at high temperatures, and uses at least one selected from fly ash, silicon, and aluminum hydroxide.
플라이 애쉬란 화력발전소등에서 미분탄을 로(爐) 내의 뜨거운 기류속에 고속으로 주입하여 고온에서 부유 상태로 순간적으로 연소시키고 남은 미분체 부산물로서 집진기에 포집되는 재를 말한다. 플라이 애쉬의 발생 비율은 원탄의 약 15~45%정도로서, 연소, 온도, 탄종, 분쇄도, 로(爐)내의 고온부에서의 체류시간 등에 따라 여러 가지 화학적 물리적 성질의 변화가 있을 수 있다. 원탄의 연소 시 유기물은 연료로서 연소되는 반면 무기물은 재로 남아 있게되며 보일러 내에 분산되는 도중에 무거운 입자는 하부에 떨어지고 가벼운 입자는 흩어져 날아다니다가 집진기에 의해서 포집된다. 입자가 무거워서 하부에 낙하되는 재를 바텀애쉬(bottom ash)라고 부르며 분산되어 날아다니다가 집진기에 의해서 포집되는 재를 플라이 애쉬라 한다. Fly ash refers to ash that is collected in dust collector as fine powder by-products are injected at high speed into a hot air stream in a furnace at a high temperature, and then burned instantly at a high temperature in a suspended state. The rate of fly ash is about 15-45% of the raw coal, and there may be various chemical and physical properties changes depending on combustion, temperature, coal type, degree of crushing, and residence time at high temperature in the furnace. In the burning of raw coal, organic matter is burned as fuel, while inorganic matter remains as ash, and while dispersed in the boiler, heavy particles fall to the bottom, light particles are scattered, and are collected by the dust collector. Ash that falls on the bottom because the particles are heavy is called bottom ash, and the ash that is collected by the dust collector is called fly ash.
본 발명에서는 상기 플라이 애쉬 이외에 실리콘 또는 수산화 알루미늄이 불투명화재로 사용될 수 있으며, 상기 플라이 애쉬, 실리콘 및 수산화 알루미늄 중에서 1종 이상이 사용될 수 있다. In the present invention, in addition to the fly ash, silicon or aluminum hydroxide may be used as an opaque material, and at least one of the fly ash, silicon, and aluminum hydroxide may be used.
상기 불투명화재는 평균 입자 크기가 0.1 ~ 1000 ㎛ 범위의 분말 상태로서 사용하는 것이 바람직하며, 보다 바람직하게는 1 ~ 100 ㎛ 의 분말을 사용하는 것이 유리하다. The opaque material is preferably used as a powder state with an average particle size in the range of 0.1 to 1000 μm, more preferably 1 to 100 μm of powder.
또한 상기 불투명화재는 흄드 실리카 100 중량부에 대하여 5 ~ 100 중량부가 사용되는 것이 바람직하며, 보다 바람직하게는 10 ~ 50 중량부를 사용하는 것이 좋다. 상기 불투명화재가 상기 범위 미만으로 사용되면 복사열 차폐 효과가 낮아지므로 열전도도가 높아지는 문제가 있으며, 상기 범위를 초과하여 사용되면 단열재 심재의 기계적 강도가 낮아져 제조 공정 상에서 불리한 문제가 있다. In addition, the opaque material is preferably used 5 to 100 parts by weight, more preferably 10 to 50 parts by weight based on 100 parts by weight of the fumed silica. If the opaque fire material is used in less than the above range because the radiation shielding effect is lowered, there is a problem that the thermal conductivity is increased, if used beyond the above range, the mechanical strength of the insulation core material is lowered there is a disadvantage in the manufacturing process.
그리고, 상기 불투명화재는 산화티타늄(TiO2), 지르콘실리케이트(ZrSiO4) 및 탄화규소(SiC) 중에서 선택된 1종 이상을 더 포함할 수 있는 데, 상기 화합물은 종래 불투명화재로 사용되어 온 것으로 단열 효과의 개선을 위하여 적절하게 첨가될 수 있으며, 바람직하게는 흄드 실리카 100 중량부에 대하여 5 ~ 50 중량부가 포함되는 것이 좋다. The opaque material may further include at least one selected from titanium oxide (TiO 2 ), zirconium silicate (ZrSiO 4 ), and silicon carbide (SiC), wherein the compound has been used as an opaque material. It may be appropriately added to improve the effect, preferably 5 to 50 parts by weight based on 100 parts by weight of the fumed silica.
한편 본 발명의 복합 단열 보드는 고온에서 단열재로서 적용되기 위하여, 보강재로서 무기 섬유를 더 포함하는 것이 바람직하다. 유기 섬유를 사용하는 경우 고온의 열에 의하여 변성되는 문제가 있는 바, 고성능 단열재에 적용될 수 있는 무기 섬유를 포함하며, 상기 무기 섬유로는 유리 섬유, 알루미노실리케이트 섬유 및 암면 섬유 중에서 선택된 1종 이상이 사용될 수 있으나, 그 종류는 제한되지 아니한다. 상기 무기 섬유는 직경이 1 ~ 20 ㎛, 길이는 1 ~ 20 mm 범위로 절단하여 사용하는 것이 바람직하다. On the other hand, the composite insulation board of the present invention, in order to be applied as a heat insulating material at a high temperature, it is preferable to further include an inorganic fiber as a reinforcing material. When using an organic fiber, there is a problem of being denatured by high temperature heat, and includes an inorganic fiber that can be applied to a high-performance heat insulating material, wherein the inorganic fiber includes at least one selected from glass fiber, aluminosilicate fiber, and rock wool fiber. It may be used, but the kind is not limited. The inorganic fiber is preferably used to cut the diameter of 1 to 20 ㎛, length in the range of 1 to 20 mm.
상기와 같은 성분을 포함하는 복합 단열 보드는 450℃의 고온에서 열 전도율이 15 ~ 30 mW/mK 범위에 있으므로, 고온에서 우수한 단열 효과를 나타내어 전기 오븐, 가스 쿡탑, 전기 자동차 등의 단열재로서 사용될 수 있다. Since the composite insulation board including the above components has a thermal conductivity in the range of 15 to 30 mW / mK at a high temperature of 450 ° C., it exhibits excellent thermal insulation effect at high temperatures, and thus can be used as a heat insulating material for electric ovens, gas cooktops, and electric vehicles. have.
또한 상기 복합 단열 보드는 부직포, 유기 필름재 등으로 밀봉되어 진공 단열재로 적용될 수 있으며, 상기 진공 단열재의 열전도율은 상온(25 ℃)에서 3 ~ 5 mW/mK 범위로 나타난다.
In addition, the composite insulation board may be sealed with a nonwoven fabric, an organic film material, or the like, and may be applied as a vacuum insulation material. The thermal conductivity of the vacuum insulation material may be in a range of 3 to 5 mW / mK at room temperature (25 ° C.).
복합 단열 보드의 제조방법Manufacturing method of composite insulation board
본 발명의 복합 단열 보드의 제조방법은, The manufacturing method of the composite heat insulation board of this invention,
플라이 애쉬(Fly Ash), 실리콘 및 수산화알루미늄 중에서 선택된 1종 이상의 불투명화재; 흄드 실리카(Fumed Silica) 및 무기 섬유를 건조시킨 후 혼합하여 혼합물을 얻는 단계; 및One or more opaque fires selected from fly ash, silicon and aluminum hydroxide; Drying the fumed silica and the inorganic fiber and then mixing to obtain a mixture; And
상기 혼합물을 몰드에 넣고 건식 프레스 성형하여 보드로 제조하는 단계를 포함한다. And putting the mixture into a mold to dry press molding it into a board.
불투명화재, 흄드 실리카 및 무기 섬유는 100 ~ 300 ℃ 에서 10 ~ 30 시간 동안 건조한 분말 상태로 혼합하되, 믹서(mixer)로 균일하게 혼련한다. The opaque fire material, the fumed silica and the inorganic fiber are mixed in a dry powder state at 100 to 300 ° C. for 10 to 30 hours, and uniformly kneaded with a mixer.
상기 혼련된 혼합물은 건식 성형법에 의하여 몰드에서 건식 프레스 성형하여 판상의 복합 단열 보드로서 제조된다. 이 때, 혼합물의 조성, 프레스 압력 등을 조절하여 밀도를 변화시킬 수 있으며, 상기 프레스 압력은 100 ~ 500 kgf/cm2 범위로 조절하는 것이 바람직하다.
The kneaded mixture is dry press-molded in a mold by a dry forming method to produce a composite composite board in the form of a plate. At this time, the density of the mixture may be adjusted by adjusting the composition, the press pressure, and the like, and the press pressure is preferably adjusted in the range of 100 to 500 kgf / cm 2 .
진공 단열재의 제조방법Manufacturing method of vacuum insulation
상기 진공 단열 보드를 포함하는 진공 단열재는 상기 복합 단열 보드를 부직포로 1차 밀봉하고, 유기 필름재로 2차 밀봉하는 과정을 통하여 제조된다. The vacuum insulation board including the vacuum insulation board is manufactured through a process of primary sealing the composite insulation board with a nonwoven fabric and secondary sealing with an organic film material.
이 때, 상기 유기 필름재로는 폴리프로필렌, 이축연신 폴리프로필렌(OPP), 저밀도 폴리에틸렌, 고밀도 폴리에틸렌, 폴리스티렌, 폴리메틸메타아크릴레이트, 폴리아미드-6(나일론), 폴리에틸렌테레프탈레이트(PET), 폴리-4-메틸-1-펜텐, 폴리부틸렌, 폴리펜타디엔, 폴리염화비닐, 폴리카보네이트, 폴리부틸렌테레프탈레이트, 에틸렌-프로필렌 공중합체 그리고 에틸렌-부텐-프로필렌터폴리머 등을 포함할 수 있으나, 이에 제한되는 것은 아니다.
In this case, as the organic film material, polypropylene, biaxially oriented polypropylene (OPP), low density polyethylene, high density polyethylene, polystyrene, polymethyl methacrylate, polyamide-6 (nylon), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), poly 4-methyl-1-pentene, polybutylene, polypentadiene, polyvinyl chloride, polycarbonate, polybutylene terephthalate, ethylene-propylene copolymer, ethylene-butene-propylene terpolymer, and the like, It is not limited to this.
이하, 본 발명의 바람직한 실시예 및 비교예를 통하여 본 발명의 복합 단열 보드에 관하여 상세히 설명하기로 한다.Hereinafter, the composite insulating board of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to preferred embodiments and comparative examples of the present invention.
이하의 실시예 및 비교예는 본 발명을 예시하기 위한 것일 뿐, 본 발명의 범위가 하기 실시예에 한정되는 것은 아니다.
The following examples and comparative examples are for illustrative purposes only and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
실시예Example 1 One
흄드 실리카(OCI, KONASIL) 1 kg, 플라이 애쉬 분말(평균 입자 크기 50 ㎛) 0.3 kg, 유리 섬유(직경 15 ㎛, 평균 길이 20cm) 0.1 kg 를 각각 150℃ 에서 12시간 동안 가열하여 건조시켰다. 1 kg of fumed silica (OCI, KONASIL), 0.3 kg of fly ash powder (average particle size 50 µm) and 0.1 kg of glass fiber (15 µm diameter, 20 cm average length) were dried by heating at 150 ° C. for 12 hours.
다음 이를 planatary 믹서를 사용하여 균일하게 혼련한 후, 300 X 300 X 15 mm 의 크기의 몰드에 넣었다. 그리고, 300 kgf/cm2 의 압력으로 프레스하여 프레스 건식 성형을 진행함으로써 판상의 복합 단열 보드를 제조하였다. It was then kneaded uniformly using a planatary mixer and placed in a mold of 300 × 300 × 15 mm. And a plate-shaped composite heat insulation board was manufactured by pressing at the pressure of 300 kgf / cm <2> and carrying out press dry molding.
상기 복합 단열 보드의 단면을 도식화하여 도 1에 나타내었다. The cross section of the said composite insulation board is shown in FIG.
실시예Example 2 2
플라이 애쉬 분말 대신 실리콘 분말(평균 입자 크기 50 ㎛)을 사용하는 것을 제외하고는 실시예 1과 동일하게 복합 단열 보드를 제조하였다.
A composite insulation board was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, except that silicon powder (average particle size 50 µm) was used instead of the fly ash powder.
실시예Example 3 3
플라이 애쉬 분말 대신 수산화 알루미늄(평균 입자 크기 50 ㎛)을 사용하는 것을 제외하고는 실시예 1과 동일하게 복합 단열 보드를 제조하였다.
A composite insulating board was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 except that aluminum hydroxide (average particle size 50 μm) was used instead of the fly ash powder.
비교예Comparative Example 1 One
플라이 애쉬 분말을 사용하지 않는 것을 제외하고는 실시예 1과 동일하게 복합 단열 보드를 제조하였다.
A composite insulating board was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the fly ash powder was not used.
비교예Comparative Example 2 2
플라이 애쉬 분말 대신 종래 불투명화재로 사용되어 온 고가의 탄화규소(SiC)를 사용하는 것을 제외하고는 실시예 1과 동일하게 복합 단열 보드를 제조하였다.
A composite insulation board was manufactured in the same manner as in Example 1 except for using expensive silicon carbide (SiC), which has been used as an opaque fire material instead of the fly ash powder.
평가evaluation
1. 고온에서의 단열 성능 평가 1. Evaluation of insulation performance at high temperature
도 2와 같이 형성된 고온 단열 성능 평가 장치에서, Block heater(210)의 온도를 450℃로 셋팅하고, 상기 실시예 및 비교예의 복합 단열 보드(220)를 상기 Block heater 위에 접촉시켜 덮었다. 다음 30분 간 열을 가한 후, 적외선 온도계(240)를 사용하여 복합 단열 보드의 표면 온도를 측정하였으며, 상기 온도 값으로 단열 성능을 비교하였다. In the high temperature heat insulation performance evaluation apparatus formed as shown in FIG. 2, the temperature of the
상기 측정된 온도 값을 하기 표 1에 나타내었다. The measured temperature values are shown in Table 1 below.
상기 표 1에서 보는 바와 같이 실시예 1 ~ 3의 복합 단열 보드는 불투명화재가 사용되지 아니한 비교예 1에 비하여 고온에서 우수한 단열 성능을 나타내는 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 특히 단위 중량당 가격이 10 ~ 100 배 비싼 탄화 규소(SiC)를 동일 중량으로 사용한 비교예 2와 비교하여도 우수한 단열 효과를 나타내는 것을 확인하였다.
As shown in Table 1, it was confirmed that the composite insulation boards of Examples 1 to 3 exhibited excellent thermal insulation performance at a high temperature compared to Comparative Example 1 in which the opaque fire was not used. In particular, it was confirmed that an excellent heat insulation effect was obtained even when compared to Comparative Example 2 using silicon carbide (SiC), which is 10 to 100 times more expensive per unit weight, in the same weight.
2. 상온에서의 열전도율 측정2. Measurement of thermal conductivity at room temperature
상기 실시예 및 비교예에서 제조된 복합 단열 보드를 심재로 포함하는 진공 단열재로 제조한 후, 상기 진공 단열재의 열 전도율을 Thermal conductivity Test 장치(EKO 사)를 이용하여 측정하였으며, 그 결과를 표 2에 나타내었다. After the composite insulation boards prepared in Examples and Comparative Examples were manufactured with a vacuum insulation material including a core material, the thermal conductivity of the vacuum insulation material was measured using a thermal conductivity test device (EKO), and the results are shown in Table 2 below. Shown in
상기 표 2에서 보는 바와 같이 실시예 1 ~ 3의 복합 단열 보드는 상온에서도 비교예 1 및 2에 비하여 동등하거나 보다 우수한 단열 효과를 나타내는 것을 확인한 바, 본 발명의 복합 단열 보드가 경제적이면서도 우수한 단열 효과를 이끌어낼 수 있음을 알 수 있었다.
As shown in Table 2, it was confirmed that the composite insulation boards of Examples 1 to 3 exhibited the same or better insulation effect than the Comparative Examples 1 and 2 even at room temperature. I was able to draw.
이상 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예 및 비교예들을 설명하였으나, 본 발명은 상기 실시예 및 비교예들에 한정되는 것이 아니라 서로 다른 다양한 형태로 제조될 수 있으며, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자는 본 발명의 기술적 사상이나 필수적인 특징을 변경하지 않고서 다른 구체적인 형태로 실시될 수 있다는 것을 이해할 수 있을 것이다. 그러므로 이상에서 기술한 실시예 및 비교예들은 모든 면에서 예시적인 것이며 한정적이 아닌 것으로 이해해야만 한다.
Although the embodiments and comparative examples of the present invention have been described above with reference to the accompanying drawings, the present invention is not limited to the above examples and comparative examples, but may be manufactured in various forms, and the present invention belongs to the present invention. Those skilled in the art will appreciate that it can be implemented in other specific forms without changing the technical spirit or essential features of the present invention. Therefore, it should be understood that the examples and comparative examples described above are exemplary in all respects and not limiting.
100 : 흄드 실리카 110 : 불투명화재
120 : 무기 섬유 200 : 실리콘 기반 단열재
210 : Block heater 220 : 복합 단열 보드 시편
230 : 파워 유닛(온도 조절기) 240 : 적외선 온도계100: fumed silica 110: opaque fire
120: inorganic fiber 200: silicon-based insulation
210: Block heater 220: composite insulation board specimen
230: power unit (temperature controller) 240: infrared thermometer
Claims (12)
플라이 애쉬(Fly Ash), 실리콘 및 수산화알루미늄 중에서 선택된 1종 이상의 불투명화재를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 복합 단열 보드.
Fumed Silica; And
Composite insulation board, characterized in that it comprises at least one opaque material selected from fly ash, silicon and aluminum hydroxide.
상기 불투명화재는 평균 입자 크기가 0.1 ~ 100 ㎛ 범위의 분말인 것을 특징으로 하는 복합 단열 보드.
The method of claim 1,
The opaque firewood composite composite board, characterized in that the average particle size of the powder in the range of 0.1 ~ 100 ㎛.
상기 불투명화재는 흄드 실리카 100 중량부에 대하여 5 ~ 100 중량부를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 복합 단열 보드.
The method of claim 1,
The opaque material is a composite insulation board, characterized in that it comprises 5 to 100 parts by weight based on 100 parts by weight of fumed silica.
상기 흄드 실리카는 직경이 1 ~ 100 nm 이고, 비표면적이 10 ~ 1000 m2/g 인 것을 특징으로 하는 복합 단열 보드.
The method of claim 1,
The fumed silica has a diameter of 1 to 100 nm, a composite insulation board, characterized in that the specific surface area of 10 ~ 1000 m 2 / g.
무기 섬유를 보강재로서 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 복합 단열 보드.
The method of claim 1,
Composite insulation board further comprising an inorganic fiber as a reinforcing material.
상기 무기 섬유는 유리 섬유, 알루미노실리케이트 섬유 및 암면 섬유 중에서 선택된 1종 이상으로 이루어진 것을 특징으로 하는 복합 단열 보드.
6. The method of claim 5,
The inorganic fiber is a composite insulation board, characterized in that consisting of one or more selected from glass fibers, aluminosilicate fibers and rock wool fibers.
상기 불투명화재는 산화티타늄(TiO2), 지르콘실리케이트(ZrSiO4) 및 탄화규소(SiC) 중에서 선택된 1종 이상을 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 복합 단열 보드.
The method of claim 1,
The opaque firewood further comprises at least one selected from titanium oxide (TiO 2 ), zirconium silicate (ZrSiO 4 ) and silicon carbide (SiC).
상기 복합 단열 보드는 450℃에서 열 전도율이 15 ~ 25 mW/mK 범위에 있는 것을 특징으로 하는 복합 단열 보드.
The method of claim 1,
The composite insulation board is a composite insulation board, characterized in that the thermal conductivity in the range of 15 ~ 25 mW / mK at 450 ℃.
A vacuum insulator, characterized in that it comprises a composite insulation board of any one of claims 1 to 8.
25℃에서 열 전도율이 3 ~ 5 mW/mK 범위에 있는 것을 특징으로 하는 진공 단열재.
The method of claim 9,
Vacuum insulation, characterized in that the thermal conductivity in the range of 3 to 5 mW / mK at 25 ℃.
상기 혼합물을 몰드에 넣고 건식 프레스 성형하여 보드로 제조하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 복합 단열 보드의 제조방법.
One or more opaque fires selected from fly ash, silicon and aluminum hydroxide; Fumed Silica; Drying and drying the inorganic fibers to obtain a mixture; And
The method of manufacturing a composite insulation board comprising the step of putting the mixture into a mold to dry press molding into a board.
상기 밀봉된 복합 단열 보드를 유기 필름재로 2차 밀봉하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 진공 단열재의 제조방법.
Primary sealing the composite insulation board manufactured by the manufacturing method of claim 11 with a nonwoven fabric; And
And secondary sealing the sealed composite thermal insulation board with an organic film material.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020120039202A KR101513777B1 (en) | 2012-04-16 | 2012-04-16 | Composite insulation board comprising opacifier and method for producing it |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020120039202A KR101513777B1 (en) | 2012-04-16 | 2012-04-16 | Composite insulation board comprising opacifier and method for producing it |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20130116632A true KR20130116632A (en) | 2013-10-24 |
| KR101513777B1 KR101513777B1 (en) | 2015-04-23 |
Family
ID=49635660
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020120039202A KR101513777B1 (en) | 2012-04-16 | 2012-04-16 | Composite insulation board comprising opacifier and method for producing it |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101513777B1 (en) |
Cited By (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20160025807A (en) * | 2014-08-28 | 2016-03-09 | 에어로썸 주식회사 | Nano porous silica insulator with anchor structure and manufacturing method thereof |
| WO2016043387A1 (en) * | 2014-09-17 | 2016-03-24 | 한국생산기술연구원 | Method for manufacturing base paper for corrugated board, having improved electromagnetic shielding effect, rodent repellent effect, and strength, and corrugated board and corrugated board box using base paper |
| CN105598130A (en) * | 2015-12-31 | 2016-05-25 | 南京侨兴环保设备有限公司 | Method for treating solid wastes of power plant |
| CN105643771A (en) * | 2015-12-31 | 2016-06-08 | 卓达新材料科技集团有限公司 | Manufacturing method of cold-pressed insulation board |
| WO2017043721A1 (en) * | 2015-09-10 | 2017-03-16 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | Blanket comprising silica aerogel and manufacturing method therefor |
| CN108503267A (en) * | 2018-05-31 | 2018-09-07 | 兰军亚 | A kind of composite material for building and its preparation process |
| CN109650844A (en) * | 2019-02-25 | 2019-04-19 | 南通中保节能科技有限公司 | A kind of dry preparation process of micropore heat-insulating shield |
| US10501326B2 (en) | 2015-09-10 | 2019-12-10 | Lg Chem, Ltd. | Silica aerogel-including blanket and method for preparing the same |
| KR20200025664A (en) * | 2018-08-31 | 2020-03-10 | (주) 에이티 | Core block for fireproof door |
| WO2020074700A1 (en) * | 2018-10-11 | 2020-04-16 | Microtherm Nv | Thermally insulating fabric |
| KR20200055882A (en) * | 2018-11-14 | 2020-05-22 | (주) 에이티 | Composition for nonflammable heat insulator |
| KR20200055883A (en) * | 2018-11-14 | 2020-05-22 | (주) 에이티 | Composition for nonflammable heat insulator |
| WO2024174731A1 (en) * | 2023-02-20 | 2024-08-29 | 巩义市泛锐熠辉复合材料有限公司 | Heat insulation material, preparation method therefor, heat insulation member, heat insulation product, battery and electrical apparatus |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10110731A1 (en) | 2001-02-28 | 2002-10-24 | Ego Elektro Geraetebau Gmbh | Thermal insulation molding |
| JP2005106312A (en) | 2003-09-29 | 2005-04-21 | Hitachi Home & Life Solutions Inc | Refrigerator, vacuum heat insulating panel and its manufacturing method |
-
2012
- 2012-04-16 KR KR1020120039202A patent/KR101513777B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Cited By (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20160025807A (en) * | 2014-08-28 | 2016-03-09 | 에어로썸 주식회사 | Nano porous silica insulator with anchor structure and manufacturing method thereof |
| WO2016043387A1 (en) * | 2014-09-17 | 2016-03-24 | 한국생산기술연구원 | Method for manufacturing base paper for corrugated board, having improved electromagnetic shielding effect, rodent repellent effect, and strength, and corrugated board and corrugated board box using base paper |
| CN107075811B (en) * | 2014-09-17 | 2019-06-28 | 韩国生产技术研究院 | The preparation method that enhances the corrugated paper body paper of effectiveness, rodent repellent effect and intensity, corrugated paper and corrugated case using the body paper |
| CN107075811A (en) * | 2014-09-17 | 2017-08-18 | 韩国生产技术研究院 | Enhance the preparation method of the corrugated paper body paper of effectiveness, rodent repellent effect and intensity, corrugated paper and corrugated case using the body paper |
| WO2017043721A1 (en) * | 2015-09-10 | 2017-03-16 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | Blanket comprising silica aerogel and manufacturing method therefor |
| US10501326B2 (en) | 2015-09-10 | 2019-12-10 | Lg Chem, Ltd. | Silica aerogel-including blanket and method for preparing the same |
| US10836643B2 (en) | 2015-09-10 | 2020-11-17 | Lg Chem, Ltd. | Silica aerogel-including blanket and method for preparing the same |
| CN105643771A (en) * | 2015-12-31 | 2016-06-08 | 卓达新材料科技集团有限公司 | Manufacturing method of cold-pressed insulation board |
| CN105598130A (en) * | 2015-12-31 | 2016-05-25 | 南京侨兴环保设备有限公司 | Method for treating solid wastes of power plant |
| CN108503267A (en) * | 2018-05-31 | 2018-09-07 | 兰军亚 | A kind of composite material for building and its preparation process |
| CN108503267B (en) * | 2018-05-31 | 2021-05-21 | 山东创伟外墙保温材料集团有限公司 | Composite material for building and preparation process thereof |
| KR20200025664A (en) * | 2018-08-31 | 2020-03-10 | (주) 에이티 | Core block for fireproof door |
| WO2020074700A1 (en) * | 2018-10-11 | 2020-04-16 | Microtherm Nv | Thermally insulating fabric |
| KR20200055882A (en) * | 2018-11-14 | 2020-05-22 | (주) 에이티 | Composition for nonflammable heat insulator |
| KR20200055883A (en) * | 2018-11-14 | 2020-05-22 | (주) 에이티 | Composition for nonflammable heat insulator |
| CN109650844A (en) * | 2019-02-25 | 2019-04-19 | 南通中保节能科技有限公司 | A kind of dry preparation process of micropore heat-insulating shield |
| WO2024174731A1 (en) * | 2023-02-20 | 2024-08-29 | 巩义市泛锐熠辉复合材料有限公司 | Heat insulation material, preparation method therefor, heat insulation member, heat insulation product, battery and electrical apparatus |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR101513777B1 (en) | 2015-04-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101513777B1 (en) | Composite insulation board comprising opacifier and method for producing it | |
| Hanu et al. | Development of polymer–ceramic composites for improved fire resistance | |
| Gonçalves et al. | Thermal insulators made with rice husk ashes: Production and correlation between properties and microstructure | |
| CN103896621B (en) | Gas phase nano SiO 2-Al 2o 3composite mesopore lagging material and preparation method thereof | |
| CN104341156B (en) | A kind of carborundum based material microwave-absorbing heat-generating body composition and method of making the same | |
| KR101575989B1 (en) | Lightweight, Sound absorbing And Thermal Insulating Panel with Expaned Graphite And Manufacturing Method of The Same | |
| WO2015192300A1 (en) | Method for preparing porous ceramics, porous ceramics, and electronic cigarette | |
| CN101788096A (en) | Nano heat insulating blanket and production method thereof | |
| JP6109734B2 (en) | Furnace | |
| CN110194649A (en) | Aluminium oxide nano heat-barrier material and preparation method thereof | |
| US10253917B2 (en) | Insulation material and method of manufacturing same | |
| PL192902B1 (en) | Microporous heat insulating body | |
| CN105517212B (en) | A kind of embedded heating panel and preparation method thereof | |
| CN104098936B (en) | A kind of preparation method of high emission infrared energy-conserving radiation coating | |
| CN106966684B (en) | A kind of low-temperature expansion type liner and its manufacturing method | |
| Hu et al. | Preparation of needled nonwoven enhanced silica aerogel for thermal insulation | |
| JP2007161561A (en) | Lightweight heat insulating molded body and method for producing the same | |
| KR950701301A (en) | Ceramic water and its manufacturing method | |
| CN2893603Y (en) | Industrial furnace body structure | |
| ES2218495T3 (en) | MICROPOROUS CONFORMED BODY OF THERMAL INSULATION CONTAINING ELECTRIC ARC SILICONE ACID. | |
| KR20130067712A (en) | Flame retardant insulation material comprising recycled resource having microporous structure and method for preparing the same | |
| CN106517996B (en) | The heat-insulating material and preparation method thereof of ultralow thermal conductivity low-shrinkage | |
| CN114436584A (en) | Inorganic modified graphite polystyrene non-combustible insulation board and preparation method thereof | |
| CN106673669A (en) | Magnesia-alumina spinel-silicon nitride-based honeycomb ceramic heat-absorbing body and preparation method thereof | |
| JPH11339933A (en) | Expansion graphite flat heating element and its manufacture |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| LAPS | Lapse due to unpaid annual fee |