JP7284735B2 - ELEVATOR DIAGNOSTIC DEVICE AND ELEVATOR DIAGNOSTIC METHOD - Google Patents
ELEVATOR DIAGNOSTIC DEVICE AND ELEVATOR DIAGNOSTIC METHOD Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7284735B2 JP7284735B2 JP2020090324A JP2020090324A JP7284735B2 JP 7284735 B2 JP7284735 B2 JP 7284735B2 JP 2020090324 A JP2020090324 A JP 2020090324A JP 2020090324 A JP2020090324 A JP 2020090324A JP 7284735 B2 JP7284735 B2 JP 7284735B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- door
- floor
- open
- button
- elevator
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B1/00—Control systems of elevators in general
- B66B1/02—Control systems without regulation, i.e. without retroactive action
- B66B1/06—Control systems without regulation, i.e. without retroactive action electric
- B66B1/14—Control systems without regulation, i.e. without retroactive action electric with devices, e.g. push-buttons, for indirect control of movements
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B1/00—Control systems of elevators in general
- B66B1/34—Details, e.g. call counting devices, data transmission from car to control system, devices giving information to the control system
- B66B1/3407—Setting or modification of parameters of the control system
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B1/00—Control systems of elevators in general
- B66B1/34—Details, e.g. call counting devices, data transmission from car to control system, devices giving information to the control system
- B66B1/3415—Control system configuration and the data transmission or communication within the control system
- B66B1/3423—Control system configuration, i.e. lay-out
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B1/00—Control systems of elevators in general
- B66B1/34—Details, e.g. call counting devices, data transmission from car to control system, devices giving information to the control system
- B66B1/3415—Control system configuration and the data transmission or communication within the control system
- B66B1/3446—Data transmission or communication within the control system
- B66B1/3461—Data transmission or communication within the control system between the elevator control system and remote or mobile stations
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B1/00—Control systems of elevators in general
- B66B1/34—Details, e.g. call counting devices, data transmission from car to control system, devices giving information to the control system
- B66B1/3492—Position or motion detectors or driving means for the detector
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B13/00—Doors, gates, or other apparatus controlling access to, or exit from, cages or lift well landings
- B66B13/02—Door or gate operation
- B66B13/14—Control systems or devices
- B66B13/16—Door or gate locking devices controlled or primarily controlled by condition of cage, e.g. movement or position
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B5/00—Applications of checking, fault-correcting, or safety devices in elevators
- B66B5/0006—Monitoring devices or performance analysers
- B66B5/0012—Devices monitoring the users of the elevator system
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B5/00—Applications of checking, fault-correcting, or safety devices in elevators
- B66B5/0006—Monitoring devices or performance analysers
- B66B5/0018—Devices monitoring the operating condition of the elevator system
- B66B5/0025—Devices monitoring the operating condition of the elevator system for maintenance or repair
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B5/00—Applications of checking, fault-correcting, or safety devices in elevators
- B66B5/0006—Monitoring devices or performance analysers
- B66B5/0037—Performance analysers
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B5/00—Applications of checking, fault-correcting, or safety devices in elevators
- B66B5/0087—Devices facilitating maintenance, repair or inspection tasks
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B2201/00—Aspects of control systems of elevators
- B66B2201/40—Details of the change of control mode
- B66B2201/403—Details of the change of control mode by real-time traffic data
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Elevator Door Apparatuses (AREA)
- Maintenance And Inspection Apparatuses For Elevators (AREA)
- Indicating And Signalling Devices For Elevators (AREA)
Description
本発明は、磁気センサを用いた、エレベータ診断装置、および、エレベータ診断方法に関するものである。 TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention relates to an elevator diagnostic apparatus and an elevator diagnostic method using magnetic sensors.
エレベータのドア動作を診断する従来の方法として、特許文献1に記載のエレベータ診断システムが知られている。
As a conventional method for diagnosing elevator door operation, an elevator diagnosis system described in
例えば、同文献の「発明が解決しようとする課題」欄には、「特許文献1では、着床位置の計測にエレベータシステムの制御信号の利用が必要であるため、そもそも制御信号が存在しないリレー式エレベータや、制御信号の意味が不明な他社製のエレベータなど、有意な制御信号を取得できないエレベータシステムを診断対象とする場合には、着床位置の計測や、着床誤差を診断できないという課題があった。」、「そこで、本発明は、有意な制御信号を取得できないエレベータシステムを診断対象とする場合であっても、着床誤差が経年劣化等により拡大したときに、その異常を検出することができるエレベータ診断システムを提供することを目的とする。」と記載されている。
For example, in the "Problems to be Solved by the Invention" column of the same document, "In
そして、この課題を解決する発明の一態様として、同文献の請求項6には「複数の乗り場間を昇降する乗りかごを備えたエレベータシステムを診断するエレベータ診断システムであって、前記乗りかごのかごドアに設置された加速度センサと、前記かごドアに設置された磁気センサと、前記加速度センサの出力信号に基づき、前記乗りかごの走行状態を検出する走行状態検出部と、前記加速度センサの出力信号に基づき、前記乗りかごの移動量を計測するかご移動量計測部と、前記加速度センサと前記磁気センサの出力信号に基づき、前記乗りかごの現在位置を検出するかご位置検出部と、前記加速度センサまたは前記磁気センサの出力信号に基づき、前記かごドアの開閉状態を検出するかごドア開閉検出部と、前記走行状態検出部、前記かご移動量計測部、前記かご位置検出部、前記かごドア開閉検出部の出力信号に基づき、前記乗りかごの着床誤差を計測し、該着床誤差が所定の閾値を超過した場合に、着床異常と診断する異常診断部と、を備えたことを特徴とするエレベータ診断システム。」と記載されている。 As one aspect of the invention for solving this problem, claim 6 of the same document states, "An elevator diagnostic system for diagnosing an elevator system having a car that ascends and descends between a plurality of landings, comprising: An acceleration sensor installed on the car door, a magnetic sensor installed on the car door, a running state detection unit for detecting the running state of the car based on the output signal of the acceleration sensor, and the output of the acceleration sensor A car movement amount measuring unit that measures the movement amount of the car based on the signal, a car position detection unit that detects the current position of the car based on the output signals of the acceleration sensor and the magnetic sensor, and the acceleration A car door open/close detector that detects the open/closed state of the car door based on the output signal of the sensor or the magnetic sensor, the running state detector, the car movement amount measuring unit, the car position detector, and the car door open/close. an abnormality diagnosing unit that measures the landing error of the car based on the output signal of the detecting unit, and diagnoses that the landing is abnormal when the landing error exceeds a predetermined threshold value. and an elevator diagnostic system."
このように、特許文献1では、かごドアに設置した磁気センサの出力信号に基づき、かごドアの開閉状態を検出する方法が提案されている。
Thus,
上記したように、特許文献1の診断システムでは、制御信号が存在しないリレー式エレベータや、制御信号の意味が不明な他社製のエレベータなど、有意な制御信号を取得できないエレベータシステムを診断対象とする場合であっても、事後的にかごドアに設置した磁気センサの出力信号から、かごドアの開閉状態を検出したり、着床位置の異常判定を行ったりしている。
As described above, the diagnostic system of
ここで、エレベータのドア開閉時間は、利用者の乗降りに最適な時間に設定する必要がある。そのため、一般的に、エレベータ毎に任意のドア開閉時間を設定できるようになっているが、ドア開閉の最適時間は利用者毎に異なるため、保守員等がエレベータ毎に、更には、階床毎に、利用者の使い勝手を把握したうえで、最適なドア開閉時間に設定することは困難であった。 Here, it is necessary to set the elevator door opening/closing time to an optimal time for passengers to get on and off. Therefore, in general, the door opening/closing time can be set arbitrarily for each elevator, but the optimum door opening/closing time differs for each user. It was difficult to set the optimal door opening/closing time based on the user's usability.
ドア開閉時間に関する利用者の使い勝手を把握する方法として、ドアの開閉釦の操作を監視する方法が考えられる。例えば、開閉時間が短いと感じている利用者は、乗降り時に開釦によりドアを長く開く傾向がある。このように、利用者の使い勝手は開閉釦の操作から推測できるため、ドア開閉釦の操作信号を直接取得できないエレベータシステムを診断対象とする場合、事後的に設置した磁気センサの出力信号に基づいて、ドアの開閉状態と開閉釦の押下状態を監視できれば、エレベータ毎の最適なドア開閉時間を推測するために非常に有効である。 As a method for grasping the usability of the user regarding the door opening/closing time, a method of monitoring the operation of the door opening/closing button is conceivable. For example, a user who feels that the opening and closing time is short tends to open the door longer by pressing the open button when getting in and out of the vehicle. In this way, the usability of the user can be inferred from the operation of the door open/close button. If it is possible to monitor the opening/closing state of the door and the pressing state of the opening/closing button, it is very effective for estimating the optimum door opening/closing time for each elevator.
しかしながら、特許文献1の診断システムでは、事後的に設置した磁気センサの出力信号に基づいて、ドア開閉釦の操作状態を監視することは考慮されていなかった。
However, in the diagnostic system of
そこで、本発明は、事後的に設置した磁気センサの出力信号に基づいて、ドア開閉釦の押下検出を行い、押下回数により点検指示や調整指示を行うことができるエレベータ診断装置、および、エレベータ診断方法を提供することにある。 Therefore, the present invention provides an elevator diagnosis apparatus capable of detecting the depression of a door opening/closing button based on the output signal of a magnetic sensor installed after the fact, and issuing an inspection instruction or an adjustment instruction based on the number of times the door opening/closing button is depressed, and an elevator diagnosis. It is to provide a method.
上記の課題を解決するため、本発明のエレベータ診断装置は、かごの乗場側に設置した磁気センサの計測値に基づいて診断を実施するものであって、前記計測値に基づいて、かご停止階を判定する階床判定部と、前記計測値に基づいて、開釦と閉釦の操作を判定する開閉釦操作判定部と、前記開釦と前記閉釦の階毎の操作を記録する利用状況記録部と、を備えたものとした。 In order to solve the above problems, the elevator diagnostic apparatus of the present invention performs diagnosis based on the measured values of a magnetic sensor installed on the landing side of the car, and based on the measured values, determines the car stop floor. an open/close button operation determination unit that determines the operation of the open button and the close button based on the measured value; and a usage situation that records the operation of the open button and the close button for each floor. and a recording unit.
本発明のエレベータ診断装置、または、エレベータ診断方法によると、事後的に設置した磁気センサを用いて、ドア開閉釦の操作を検出することができ、利用状況を把握することで、ドア開閉時間の調整を迅速に行うことができる。 According to the elevator diagnostic device or elevator diagnostic method of the present invention, it is possible to detect the operation of the door open/close button using the magnetic sensor installed after the fact, and by grasping the usage situation, the door open/close time can be determined. Adjustments can be made quickly.
以下、図面を参照しながら、本発明の一実施例に係るエレベータの診断装置1を説明する。
Hereinafter, an
まず、図1を用いて、本実施例の診断装置1と、診断対象であるエレベータの概略を説明する。
First, using FIG. 1, the outline of the
ここに例示するエレベータは、7階床以上の建屋に据え付けられたものであり、昇降路20内を昇降するかご21と、各階の乗場ドア22を備えている。かご21の上面の前側(乗場側)には、乗場側の磁束密度を計測する磁気センサ2が設置されており、磁気センサ2が計測した磁束密度(以下、「磁気計測値M」と称する)は、無線通信により診断装置1に送信される。かご21の内部には、ドアを開閉するための開釦21aと閉釦21bが設けられており、乗場ドア22の近傍には、その乗場にかご21を呼ぶための乗場釦22aが設けられている。なお、開釦21a、閉釦21b、乗場釦22aの操作は、図示しないテールコード等を介して図示しないエレベータ制御装置に入力され、かご21の昇降制御や、ドアの開閉制御に反映されるが、診断装置1には入力されないものとする。
The elevator illustrated here is installed in a building with seven or more floors, and includes a
診断装置1は、センサ受信部1a、階床判定部1b、開閉釦操作判定部1c、利用状況記録部1d、機器故障判定部1e、報知部1fを備えている。センサ受信部1aは、磁気センサ2から磁気計測値Mを受信し、階床判定部1b、開閉釦操作判定部1c、機器故障判定部1eへ伝送する。階床判定部1bは、センサ受信部1aからの磁気計測値Mを基にかご停止階を判定する。開閉釦操作判定部1cは、センサ受信部1aからの磁気計測値Mを基に開釦21aや閉釦21bの操作を判定する。利用状況記録部1dは、階床判定部1bと開閉釦操作判定部1cからの情報を基に、階毎の開閉釦の操作回数を記録する。機器故障判定部1eは、センサ受信部1aと階床判定部1bからの情報を基に、ドア周囲機器の故障の有無を判定する。報知部1fは、利用状況記録部1dから受信した利用状況を管制センター3へ送信する。また、機器故障判定部1eで故障と判定された場合には、報知部1fは、故障情報を管制センター3へ送信する。管制センター3は、報知部1fから受信した通知内容を基に、利用状況を確認し、現場の保守員へ連絡することにより、点検指示や調整指示を行う。診断装置1の各部の詳細は後述する。
The
なお、診断装置1は、具体的には、CPU等の演算装置、半導体メモリ等の主記憶装置、補助記憶装置、および、通信装置などのハードウェアを備えたコンピュータである。そして、補助記憶装置から主記憶装置にロードされたプログラムを演算装置が実行することで、上記の各機能を実現するが、以下では、このようなコンピュータでの周知技術を適宜省略しながら説明する。
Specifically, the
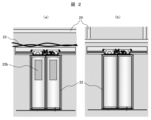
<乗場ドア周囲の金属配置と、磁気センサの計測値Mの関係>
次に、図2と図3を用いて、各階の乗場ドア22の周囲の金属配置と、金属配置の違いによる磁気センサ2の計測値Mの変化について説明する。
<Relationship between the metal arrangement around the landing door and the measured value M of the magnetic sensor>
Next, referring to FIGS. 2 and 3, the arrangement of metal around the
図2は、図1の乗場ドア22を、昇降路20から見た状態を示す図である。(a)は、例えば1階の乗場ドア22であり、(b)は、例えば2階の乗場ドア22である。これらに示すように、乗場ドア22のビジョンガラス22bの有無、昇降路内の配線23の有無により、階毎に金属部品の敷設状況は異なる。また、階床の高さや建屋の構造により、ドア上部の鉄柱24等の配置状況も異なる。従って、乗場ドア22の周囲の金属配置による磁気センサ2への影響度合いが階毎に異なっている。
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing the
図3は、かご21が、1階から7階の各階に停止しながら上昇した時に磁気センサ2が計測した、磁気計測値Mを例示するタイムチャートである。なお、各階の停止中に、乗場ドア22を開閉したため、ドア開閉と連動して、磁気計測値Mが大きく変動している。
FIG. 3 is a time chart exemplifying magnetic measurement values M measured by the magnetic sensor 2 when the
かご21が1階で停止し、1階の乗場ドア22が閉じているとき、磁気センサ2が計測した磁気計測値MをM1とする。これに倣い、かご21がn階で停止し、n階の乗場ドア22が閉じているときに計測された磁気計測値MをMnと定義する。
When the
上記したように、乗場ドア22の周囲の金属配置は階毎に異なるため、各階で計測される磁気計測値M1~M7は各々異なっている。従って、かご21の停止時に計測した磁気計測値Mの大きさに基づいて、かご21の停止階を判定することができる。なお、各階の磁気計測値Mに酷似するものが存在する場合は、何れかの乗場ドア22の周囲に適当な金属を追加することで、各階の磁気計測値Mを積極的に異ならせることも可能である。
As described above, since the metal arrangement around the
<診断装置の全体処理>
図4は、診断装置1の全体処理を示すフローである。ここに示すように、診断装置1は、エレベータにおける一般的なイニシャル処理(S1)を実施した後、本発明特有の処理である、階床検出用の初期値登録処理(S2)、開閉釦操作検出用の初期値登録処理(S3)、階床検出処理(S4)、開閉釦操作検出処理(S5)を実施する。以下、各処理の詳細を、図面を用いて説明する。
<Overall processing of diagnostic device>
FIG. 4 is a flow showing the overall processing of the
<S2 階床検出用の初期値登録処理>
図5は、階床検出用の初期値登録処理を示すフローである。この処理は、かご21が停止している階床の判定に用いる各階の磁気計測値Mの初期値を、階床判定部1bに登録する処理であり、保守員が診断装置1と磁気センサ2を設置する際に実施する。
<S2 Initial value registration process for floor detection>
FIG. 5 is a flow showing initial value registration processing for floor detection. This process is a process of registering the initial value of the magnetic measurement value M of each floor used to determine the floor on which the
まず、S21にて、保守員は、階床登録用変数nの初期値を1に設定する。なお、n=1は、最下階であることを示すものであり、仮に最下階が地下2階であれば、地下2階がn=1に相当する階床となる。ただし、以下では簡単のため、図1や図3のように、地上1階が最下階であるものとする。 First, in S21, the maintenance staff sets the initial value of the floor registration variable n to 1. Note that n=1 indicates the lowest floor, and if the lowest floor is the second basement floor, the second basement floor corresponds to n=1. However, for the sake of simplicity, it is assumed that the first floor above ground is the lowest floor, as shown in FIGS. 1 and 3 .
次に、S22にて、保守員は、かご21を最下階(1階)に移動させる。そして、S23にて、階床判定部1bは、最下階(1階)の磁気計測値M1を取得する。その後、S24にて、階床判定部1bは、最下階(1階)の初期値として、S23にて取得した磁気計測値M1を登録する。
Next, in S22, the maintenance worker moves the
次に、S25にて、保守員は、かご21の停止階が最上階かを確認し、最上階でない場合(S25でNo)、S26にて、保守員は、かご21を1階床上に移動させ、さらに、S27にて、階床登録用変数nに1を加算して、再度、S23からの処理を実施する。
Next, in S25, the maintenance personnel confirms whether or not the stop floor of the
これを繰り返すことで、階床判定部1bに、最下階から最上階の初期値を登録する。そして、最上階の初期値登録が完了した場合(S25でYes)、S2の処理を終了する。
By repeating this, the initial values of the lowest floor to the highest floor are registered in the
<S3 階床検出処理>
図6は、エレベータの稼働中に階床判定部1bが継続的に実施する、階床検出処理の詳細を示すフローである。
<S3 Floor detection processing>
FIG. 6 is a flow showing the details of floor detection processing continuously performed by the
まず、S31にて、階床判定部1bは、磁気センサ2が計測した磁気計測値Mを取得する。
First, in S<b>31 , the
次に、S32にて、階床判定部1bは、磁気計測値Mの前回値が保存済かを確認し、保存されていない場合(S32でNo)、S33に進み、階床判定部1bは、S31で取得した磁気計測値Mの今回値を、次回処理用の前回値として保存した後、S3の処理を終了する。
Next, in S32, the
一方、前回値が保存済の場合(S32でYes)、階床判定部1bは、かご21が停止しているかを確認する。具体的には、まず、S34にて、磁気計測値Mの前回値と今回値の差分を算出する。次に、S35にて、差分が閾値以下であるかを判断する。そして、差分が閾値以下の場合(S35でYes)、かご21は停止している可能性があると判断する。なお、閾値は、磁気センサ2の検出誤差を考慮し、停止時の変動量から決定する。
On the other hand, if the previous value has been saved (Yes in S32), the
また、階床判定部1bは、停止状態であることを確実に判定するため、差分が閾値以下の状態のまま所定時間が経過したかを判断する。具体的には、まず、S36にて、停止検出タイマのカウントアップを開始する。次に、S37にて、停止検出タイマが所定時間に到達したかを判断する。ここでは、例えば、差分が閾値以下の状態が1秒間継続したことを確認する。なお、S35にて、差分が閾値より大きい場合(S35でNo)、かご21は階床間を移動していると判断し、S3cにて、停止検出タイマをリセットする。
Further, the
一方、S37にて、所定時間経過していない場合(S37でNo)は、S33を実施した後、S3の処理を終了する。 On the other hand, if the predetermined time has not elapsed in S37 (No in S37), the process of S3 is terminated after performing S33.
停止検出タイマが所定の時限を超過した場合(S37でYes)、階床判定部1bは、かご21は停止していると判定し、停止階床を特定するための処理を行う。具体的には、まず、S38にて、階床nとして、まず1を選択する。次に、S39にて、1階の初期値である磁気計測値M1と、S31にて取得した磁気計測値Mの今回値を比較する。そして、両者の差分が閾値以下の場合(S39でYes)、かご停止階を1階と判定する(S3a)。
When the stop detection timer exceeds the predetermined time limit (Yes in S37), the
一方、S39にて、差分が閾値より大きい場合(S39でNo)、かご停止階は1階ではないと判断し、S3bにて、階床n=1に1を加算して、S39にて、2階の初期値である磁気計測値M2と、S31にて取得した磁気計測値Mの今回値を比較する。このように、S39とS3bの処理を繰り返すことで、かご停止階を判定することができる。なお、S39にて、磁気計測値の今回値が全ての階床の初期値と一致しない場合は、異常と判定して管制センター3に通知してもよい。
On the other hand, if the difference is greater than the threshold value in S39 (No in S39), it is determined that the car stop floor is not the 1st floor, and 1 is added to the floor n=1 in S3b. The magnetic measurement value M2 , which is the initial value of the second floor, is compared with the current value of the magnetic measurement value M acquired in S31. By repeating the processes of S39 and S3b in this manner, the car stopping floor can be determined. In S39, if the current value of the magnetic measurement value does not match the initial value of all the floors, it may be determined as abnormal and the
<ドアの開閉状態と磁気計測値Mの関係>
ここで、開閉釦操作判定部1cによる、開釦21aや閉釦21bの操作検出処理を説明する前に、図7のタイムチャートを用いて、乗場ドア22の開閉状態と磁気計測値Mの関係を、釦操作と関連付けて説明する。
<Relationship between door open/close state and magnetic measurement value M>
Here, before explaining the operation detection processing of the
一般的に、乗場ドア22は、かご21がその乗場に到着したときに開き、その後、一定の時限経過で閉まるように制御される。開動作の開始から閉動作の完了までの時限は任意に設定でき、利用者の要望により保守員等が変更することも可能である。
Generally, the
図7(a1)(a2)は、開釦21a(または乗場釦22)や閉釦21bを操作しない場合の、ドア開閉状態と磁気計測値Mの関係を示すタイムチャートである。かご21が乗場に停止した直後は、乗場ドア22は閉状態である。このとき、磁気計測値MもS2で登録した階毎の初期値Mnの計測誤差の範囲内で略一定である。その後、乗場ドア22が開状態になると、磁気計測値Mもドアの開動作に伴い低下し、開状態の継続中は、磁気計測値Mも略一定となる。さらにその後、設定された時限が経過すると乗場ドア22が閉じ、磁気計測値Mもドアの閉動作に伴い上昇する。利用者が開釦21a(または乗場釦22)や閉釦21bを操作しない場合、乗場ドア22の開動作開始から閉動作完了までに要する標準時間tsは、常に一定である。
FIGS. 7(a1) and (a2) are time charts showing the relationship between the door opening/closing state and the magnetic measurement value M when the
図7(b1)~(b3)は、ドア開中に利用者が閉釦21bを押下して乗場ドア22を閉じた場合の、ドア開閉状態と磁気計測値Mを示すタイムチャートである。利用者が、(b3)の点線で示すタイミングで閉釦21bを押下すると、乗場ドア22の閉動作が開始されるため、乗場ドア22の開動作開始から閉動作完了までに要する時間tcは、標準時間tsより短くなる。この状態が頻発する場合、利用者にとって標準時間tsが長いと推測できるため、保守員は標準時間tsをより短く設定しても良い。
7(b1) to (b3) are time charts showing the door opening/closing state and the magnetic measurement value M when the user presses the
図7(c1)~(c3)は、ドア開中に利用者が開釦21a(または乗場釦22)を押下して乗場ドア22の開状態を延長させた場合の、ドア開閉状態と磁気計測値Mを示すタイムチャートである。利用者が、(c3)の実線で示すタイミングで開釦21a(または乗場釦22)を押下すると、乗場ドア22の開状態が延長されるため、乗場ドア22の開動作開始から閉動作完了までに要する時間toは、標準時間tsより長くなる。この状態が頻発する場合、利用者にとって標準時間tsが短いと推測できるため、保守員は標準時間tsをより長く設定しても良い。
7(c1) to (c3) show the door opening/closing state and magnetic measurement when the user presses the
図7(d1)~(d3)は、ドア閉動作中に利用者が開釦21a(または乗場釦22)を押下して乗場ドア22を再度開いた場合の、ドア開閉状態と磁気計測値Mを示すタイムチャートである。利用者が、(d3)の実線で示す閉動作中のタイミングで開釦21a(または乗場釦22)を押下すると、閉動作中の乗場ドア22が開動作に切り替わるため、(d2)に示すように、パルス状の磁気計測値Mが計測される。従って、このパルス状の磁気計測値Mに基づいて、ドアの反転を検出することができる。ドアの反転が頻発する場合も、利用者にとって標準時間tsが短いと推測できるため、保守員は標準時間tsをより長く設定しても良い。なお、閉動作中のドアに利用者が接触した結果、ドアが開動作に切り替わった場合も、開釦21a(または乗場釦22)が押下されたものとして扱っても良い。
7(d1) to (d3) show the door opening/closing state and the magnetic measurement value M when the user presses the
このように、乗場ドア22の開閉時間の長さや、磁気検出値Mの挙動から、開釦21a(または乗場釦22)、閉釦21bの操作有無や操作タイミングを判定できる。これを利用し、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、以下の方法で釦操作を判定する。
In this way, it is possible to determine whether or not the
<S4 開閉釦操作検出用の初期値登録処理>
図8は、開閉釦操作検出用の初期値登録処理を示すフローである。この処理は、開釦21a(または乗場釦22)や閉釦21bの操作を検出する際に用いる、ドア開動作、ドア閉動作、ドア開時間の各初期値を、開閉釦操作判定部1cに登録する処理であり、保守員が診断装置1と磁気センサ2を設置する際に実施する。
<S4 Initial value registration process for detecting open/close button operation>
FIG. 8 is a flow showing initial value registration processing for detecting open/close button operation. In this process, each initial value of the door opening operation, the door closing operation, and the door opening time used when detecting the operation of the
まず、S4aにて、保守員は、かご21を何れかの乗場に停止させる。その後、S4bのドア開動作初期値登録処理、S4cのドア閉動作初期値登録処理、S4dのドア開時間初期値登録処理を順次実施する。以下、S4b~S4dを、図9~図11を用いて詳細に説明する。
First, in S4a, the maintenance staff stops the
<S4b ドア開動作初期値登録処理>
図9は、ドア開動作初期値登録処理の詳細を示すフローである。まず、S4b1にて、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、ドア閉状態時の磁気計測値Miを取得する。次に、S4b2にて、保守員がドア開動作を行う。その後、S4b3にて、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、ドア開状態時の磁気計測値Mi’を取得する。
<S4b Door opening operation initial value registration process>
FIG. 9 is a flow showing the details of the door opening operation initial value registration process. First, in S4b1, the open/close button operation determination unit 1c acquires the magnetic measurement value Mi when the door is closed. Next, in S4b2, the maintenance person opens the door. After that, in S4b3, the open/close button operation determination unit 1c acquires the magnetic measurement value Mi' when the door is open.
次に、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、S4b4にて、磁気計測値Mi、Mi’を比較し、閾値以上の変化がある場合(S4b4でYes)、S4b5にて、磁気の変化方向を記憶する。具体的には、式1に示すように、変化量が閾値を超過している場合は、ドア開動作に伴う磁気の変化と判断し、式2にて正または負の変化方向を記憶する。
Next, the open/close button operation determination unit 1c compares the magnetic measurement values Mi and Mi' in S4b4, and if there is a change equal to or greater than the threshold value (Yes in S4b4), stores the magnetic change direction in S4b5. . Specifically, as shown in
最後に、S4b6にて、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、S4b5で記憶した磁気変化方向をドア開動作初期値として記録する。 Finally, at S4b6, the open/close button operation determination unit 1c records the magnetism change direction stored at S4b5 as the door opening operation initial value.
<S4c ドア閉動作初期値登録処理>
図10は、ドア閉動作初期値登録処理の詳細を示すフローである。まず、S4c1にて、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、ドア開状態時の磁気計測値Mjを取得する。次に、S4c2にて、保守員がドア閉動作を行う。その後、S4c3にて、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、ドア閉状態時の磁気計測値Mj’を取得する。
<S4c door closing operation initial value registration processing>
FIG. 10 is a flow showing the details of the door closing operation initial value registration process. First, in S4c1, the open/close button operation determination unit 1c acquires the magnetic measurement value Mj when the door is open. Next, in S4c2, the maintenance person closes the door. After that, in S4c3, the open/close button operation determination unit 1c acquires the magnetic measurement value Mj' when the door is closed.
次に、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、S4c4にて、磁気計測値Mj、Mj’を比較し、閾値以上の変化がある場合(S4c4でYes)、S4c5にて、磁気の変化方向を記憶する。具体的には、式3に示すように、変化量が閾値を超過している場合は、ドア閉動作に伴う磁気の変化と判断し、式4にて正または負の変化方向を記憶する。
Next, the open/close button operation determination unit 1c compares the magnetic measurement values Mj and Mj' in S4c4, and if there is a change equal to or greater than the threshold value (Yes in S4c4), stores the magnetic change direction in S4c5. . Specifically, as shown in
最後に、S4c6にて、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、S4c5で記憶した磁気変化方向をドア閉動作初期値として記録する。 Finally, in S4c6, the open/close button operation determination unit 1c records the magnetism change direction stored in S4c5 as the door closing operation initial value.
<S4d ドア開時間初期値登録処理>
図11は、ドア開時間初期値登録処理の詳細を示すフローである。まず、S4d1にて、保守員がドア開動作を行う。次に、S4d2にて、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、磁気計測値Mtを取得する。ドア開動作に伴い、ドア開動作初期値として登録した磁気変化がある場合(S4d3でYes)、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、S4d4にて、ドア開時間タイマのカウントアップを開始する。一方、ドア開動作初期値として登録した磁気変化がない場合(S4d3でNo)、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、S4d2を繰り返す。
<S4d door open time initial value registration process>
FIG. 11 is a flow showing the details of the door open time initial value registration process. First, in S4d1, a maintenance worker performs a door opening operation. Next, in S4d2, the open/close button operation determination unit 1c acquires the magnetic measurement value Mt. When there is a magnetic change registered as the door opening operation initial value with the door opening operation (Yes in S4d3), the open/close button operation determination unit 1c starts counting up the door opening time timer in S4d4. On the other hand, if there is no magnetic change registered as the door opening operation initial value (No in S4d3), the open/close button operation determination section 1c repeats S4d2.
カウントアップの開始後、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、S4d5にて、磁気計測値Mt’を取得し、S4d6にて、乗場ドア22が自動で閉じるまで待つ。つまり、ドア閉動作初期値として登録したドア閉動作時の磁気変化があるまで待ち、磁気変化がない場合(S4d7でNo)、S4d4のカウントアップを継続する。
After starting the count-up, the opening/closing button operation determination unit 1c acquires the magnetic measurement value Mt' in S4d5, and waits until the
そして、ドア閉動作時の磁気変化を検出した場合(S4d6でYes)、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、S4d7にて、現在のカウント時間を、ドア開時間の初期値tdとして記録する。なお、ここで登録されたドア開時間の初期値tdは、図7(a1)の標準時間tsに相当する。 Then, if a magnetic change during the door closing operation is detected (Yes in S4d6), the open/close button operation determination unit 1c records the current count time as the initial value td of the door open time in S4d7. The initial value td of the door open time registered here corresponds to the standard time ts in FIG. 7(a1).
<S5 開閉釦操作検出処理>
図12は、エレベータの稼働中に、階床判定部1b、開閉釦操作判定部1c、利用状況記録部1dが継続的に実施する、開閉釦操作検出処理の詳細を示すフローである。
<S5 Open/close button operation detection process>
FIG. 12 is a flow showing the details of open/close button operation detection processing continuously performed by the
まず、S51にて、階床判定部1bは、かご21が現在停止している階床が確定しているかを判断する。現在階床が確定している場合(S51でYes)、S52に進む。階床が確定していない場合(S51でNo)、かご21が走行中の可能性があるため、開閉釦操作検出は行わずにS5の処理を終了する。
First, in S51, the
次に、S52にて、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、ドア開動作時の磁気変化があるかを判断する。ドア開動作時の磁気変化がある場合(S52でYes)、S53にて、ドア開時間タイマのカウントアップを開始する。その後、S54にて、ドア閉動作時の磁気変化があるかを判断する。ドア閉動作時の磁気変化がある場合(S53でYes)、S55にて、ドア開時間タイマのカウントを停止する。なお、このときのタイマの計測値td’は、顧客利用中の実際のドア開閉時間である。 Next, in S52, the opening/closing button operation determination section 1c determines whether or not there is a magnetic change during the door opening operation. If there is a magnetism change during the door opening operation (Yes in S52), in S53, the door opening time timer starts counting up. After that, in S54, it is determined whether or not there is a change in magnetism when the door is closed. If there is a magnetism change during the door closing operation (Yes at S53), at S55, the door opening time timer stops counting. Note that the measured value td' of the timer at this time is the actual door open/close time during customer use.
次に、S56にて、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、S4dで登録した初期値tdと、S55で取得した計測値td’を比較する。計測値td’が初期値tdよりも小さい場合(S56でYes)、自動で閉じるよりも早くドアが閉じたため、利用者が閉釦21bを操作したと判断できる(図7(b)参照)。よって、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、S57にて、閉釦21bの操作ありと判定する。
Next, in S56, the open/close button operation determination unit 1c compares the initial value td registered in S4d with the measured value td' acquired in S55. If the measured value td' is smaller than the initial value td (Yes in S56), it can be determined that the user has operated the
一方、計測値td’が初期値td以上であり(S56でNo)、さらに、計測値td’が初期値tdよりも大きい場合(S5bでYes)、自動で閉じるよりも長くドアが開いていたため、利用者が開釦21aを操作したと判断できる(図7(c)、(d)参照)。よって、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、S5cにて、ドア開釦の操作ありと判定する。
On the other hand, if the measured value td' is equal to or greater than the initial value td (No in S56) and if the measured value td' is greater than the initial value td (Yes in S5b), the door was open longer than it automatically closed. , it can be determined that the user has operated the
また、計測値td’が初期値td以上であり(S56でNo)、計測時間td’が初期値tdと同等の場合(S5bでNo)、自動の開閉と判断できる(図7(a)参照)。よって、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、S5fにて、開閉釦の操作なしと判定する。 Further, when the measured value td' is equal to or greater than the initial value td (No in S56) and the measured time td' is equal to the initial value td (No in S5b), it can be determined that the opening/closing is automatic (see FIG. 7A). ). Therefore, the open/close button operation determination unit 1c determines in S5f that the open/close button is not operated.
エレベータの稼働中には、例えば、ドア閉動作中に乗り込む人がいた場合に、かご内の利用者が開釦21aを操作してドアを開くことがある(図7(d)参照)。このとき、ドアは閉動作中に開動作する。つまり、反転動作となる。
During operation of the elevator, for example, when a person enters the elevator while the door is being closed, a user in the car may operate the
S54にて閉動作検出後、S58にて、再度ドア開動作時の磁気変化を検出した場合(S58でYes)、ドア閉動作中に開釦21aが操作されてドアが反転したと判断できる。よって、開閉釦操作判定部1cは、S59にて開釦操作ありと判定し、S5gにてドアの反転動作ありと判定する。
After the closing operation is detected in S54, when the magnetism change during the door opening operation is detected again in S58 (Yes in S58), it can be determined that the
なお、ドアが完全に閉じた後で開いた場合、例えば、かごが走行後に待機状態となった後に、利用者が待機階から乗込む場合と区別するために、S54の閉動作検出からS58の開動作検出までの時間をカウントし、所定の時間未満であれば反転とし、所定の時間以上であれば反転を伴わない開閉動作としても良い。 In addition, in order to distinguish the case where the door is opened after being completely closed, for example, the case where the user enters from the waiting floor after the car is in the waiting state after running, the closing operation detection in S54 is followed by the closing operation in S58. The time until the opening operation is detected may be counted, and if the time is less than the predetermined time, the opening and closing operation may be reversed, and if the predetermined time is longer than the predetermined time, the opening and closing operation may be performed without reversing.
また、S58後に再度S53以降の処理を実施し、反転後の開閉釦操作および再度反転の有無を判定する処理としても良い。 Alternatively, after S58, the processing from S53 onward may be performed again to determine whether or not the opening/closing button is operated after reversal and whether or not reversal is to be performed again.
そして、S5aにて、利用状況記録部1dは、S51で判定した階毎に、開閉釦操作判定部1cが判定した開閉釦の操作および反転回数を記録する。
Then, in S5a, the
また、S54にて、ドア開後閉動作を検出しない場合(S54でNo)、つまりドアが開き続けている状態のときは、S5dにてドア開時間が所定の時間、例えばS5bで想定しているドア開時間を大幅に超過した時間(例えば、10分)を超過した場合(S5dでYes)、S5eにてドア異常と判断する。一方、所定の時間以内の場合(S5dでNo)、S53に戻りドア開時間タイマのカウントを継続する。 In addition, when the closing operation after opening the door is not detected in S54 (No in S54), that is, when the door continues to open, the door opening time is assumed to be a predetermined time in S5d, for example, in S5b. If the time (for example, 10 minutes) that greatly exceeds the current door opening time is exceeded (Yes in S5d), it is determined that the door is abnormal in S5e. On the other hand, if it is within the predetermined time (No in S5d), the process returns to S53 to continue counting the door open time timer.
また、S52にて、ドア開動作を検出しない場合(S52でNo)、ドア開動作が行われるまでは、S5hにてドア開時間タイマをクリアする。 If the door opening operation is not detected in S52 (No in S52), the door opening time timer is cleared in S5h until the door opening operation is performed.
以上の開閉釦操作検出処理により、計測したドアの開閉釦操作回数や反転回数を報知部1fより管制センター3に伝送することで、保守員が利用状況を把握することができる。
By transmitting the counted number of times the opening/closing button is operated and the number of reversals of the door through the above-described opening/closing button operation detection processing, the maintenance personnel can grasp the usage status by transmitting the number of times the opening/closing button is operated and the number of reversals from the
そして、閉釦21bの操作回数が多い場合は、利用者がドアの開閉時間が長いと感じている可能性が高いため、ドア開閉時間の設定を短くする提案を行う、また、開釦21aの操作回数が多い場合は、利用者がドアの開閉時間が短いと感じている可能性が高いため、ドア開閉時間の設定を長くする提案が可能となる。
If the number of times the
また、反転が多い場合はドアの点検を行うことで、故障前に改善することが可能となる。更に、階床情報を利用することで、特定の階床でのみ反転している場合に、特定階の乗場ドア22の異常を早急に対応することが可能となる。
In addition, if there are many reversals, it is possible to improve before failure by inspecting the door. Further, by using the floor information, it is possible to quickly deal with the abnormality of the
また、S5eにてドア異常と判断された場合に、報知部1fより管制センター3に通知することで、保守員に連絡し、現場の対応を早急に行うことが可能となる。
Further, when it is determined that the door is abnormal in S5e, the
<機器故障判定部1eによる破損検出方法>
次に、機器故障判定部1eによる、ドア周辺機器の破損の検出方法、および、かご上機器の破損の検出方法について説明する。
<Damage detection method by the device
Next, a method for detecting damage to door peripheral equipment and a method for detecting damage to on-car equipment by the equipment
図3にて説明したように、各階停止時の磁気計測値Mnは夫々異なるが、一般的に昇降路内では、ケーブルやブラケットは固定されており、金属の位置は変化しない。ただし、経年劣化や走行時の接触により破損または、位置がずれることが考えられる。そのまま放置されると、走行中に接触してエレベータが非常停止する可能性がある。そのため、走行に影響ない状態であっても、昇降路内の機器の状況を把握する必要がある。 As explained with reference to FIG. 3, the magnetic measurement value Mn at each floor stop is different, but generally cables and brackets are fixed in the hoistway and the position of the metal does not change. However, it is conceivable that it may be damaged or displaced due to aged deterioration or contact during running. If left as it is, the elevator may come to an emergency stop due to contact during travel. Therefore, it is necessary to grasp the condition of equipment in the hoistway even if it does not affect running.
図13は、2階のドア周辺機器破損時の各階停止した際の磁気センサ2の計測値を示すタイムチャートである。2階部分における点線が初期の磁気計測値M、実線がドア周辺機器破損後の磁気計測値Mである。例えば、2階のドア上部のブラケットが欠落した場合、金属の配置が変わることにより磁気計測値Mも変化する。S3の階床検出処理にて、2階以外の停止時には磁気計測値Mに該当する初期値があり、2階停止時のみ磁気計測値Mに該当する初期値がない場合、機器故障判定部1eは、2階のドア周辺機器が破損した可能性があると判定して、報知部1fを介して管制センター3に通知することで、故障に至る前に保守員による対応が可能となる。なお、かご21の停止階が2階であることを特定するためには、直前の階床が何階であったかを参照したり、図示しない加速度センサや気圧センサなどの情報を利用したりすることができる。
FIG. 13 is a time chart showing the measured values of the magnetic sensor 2 when stopping at each floor when the door peripheral equipment on the second floor is damaged. The dotted line in the second floor portion is the initial magnetic measurement value M, and the solid line is the magnetic measurement value M after the door peripheral device is damaged. For example, if the bracket on the upper part of the door on the second floor is missing, the magnetic measurement value M will also change due to the change in the placement of the metal. In the floor detection process of S3, if there is an initial value corresponding to the magnetic measurement value M when stopping on floors other than the 2nd floor, and there is no initial value corresponding to the magnetic measurement value M only when stopping on the 2nd floor, the equipment
また、図14は、かご上機器破損時の各階停止した際の磁気センサ2の計測値を示すタイムチャートである。点線が初期設定時の磁気計測値M、実線がかご上機器破損後の磁気計測値Mである。例えば、かご上のドア制御箱のカバーが外れた場合、磁気センサ2の周辺の金属の配置が変わることにより、磁気計測値Mも変化する。S3の階床検出処理にて、全ての階で、初期値から同じように乖離がある場合、かご上の機器が破損した可能性があるとして、報知部1fより管制センター3に通知することで、故障に至る前に保守員による対応が可能となる。
FIG. 14 is a time chart showing the measured values of the magnetic sensor 2 when stopping at each floor when equipment on the car is damaged. The dotted line is the magnetic measurement value M at the time of initial setting, and the solid line is the magnetic measurement value M after the equipment on the car is damaged. For example, when the cover of the door control box on the car comes off, the magnetic measurement value M also changes due to the change in the arrangement of the metal around the magnetic sensor 2 . In the floor detection process of S3, if there is a similar deviation from the initial value on all floors, the equipment on the car may be damaged, and the
以上で説明したように、本実施例の診断装置、または、診断方法によれば、事後的に設置した磁気センサの出力信号に基づいて、利用者によるドア開閉釦の操作状況や、乗場ドアの周辺機器や、かご上機器の異常を検出することができる。 As described above, according to the diagnostic device or the diagnostic method of the present embodiment, based on the output signal of the magnetic sensor installed after the fact, the operation status of the door open/close button by the user and the operation status of the hall door. It is possible to detect abnormalities in peripheral equipment and equipment on the car.
1 診断装置
1a センサ受信部
1b 階床判定部
1c 開閉釦操作判定部
1d 利用状況記録部
1e 機器故障判定部
1f 報知部
2 磁気センサ
3 管制センター
20 昇降路
21 かご
21a 開釦
21b 閉釦
22 乗場ドア
22a 乗場釦
22b ビジョンガラス
23 配線
24 鉄柱
1
Claims (7)
前記計測値に基づいて、かご停止階を判定する階床判定部と、
前記計測値に基づいて、開釦と閉釦の操作を判定する開閉釦操作判定部と、
前記開釦と前記閉釦の階毎の操作を記録する利用状況記録部と、
を備えたことを特徴とするエレベータ診断装置。 An elevator diagnosis device that performs diagnosis based on the measurement values of a magnetic sensor installed on the landing side of the car,
a floor determination unit that determines a car stop floor based on the measured value;
an open/close button operation determination unit that determines operation of the open button and the close button based on the measured value;
a usage recording unit that records the operation of the open button and the close button for each floor;
An elevator diagnostic device comprising:
前記開閉釦操作判定部は、前記計測値の変化方向に基づいて、ドアの開動作または閉動作を検出するものであり、前記ドアの開動作開始から閉動作完了までに要した時間が、所定の標準時間よりも短い場合に、前記閉釦が操作されたと判定することを特徴とするエレベータ診断装置。 The elevator diagnostic apparatus according to claim 1,
The open/close button operation determination unit detects an opening operation or closing operation of the door based on the change direction of the measured value, and the time required from the start of the opening operation to the completion of the closing operation of the door is determined by a predetermined amount of time. and determining that the close button has been operated when the standard time is shorter than the standard time.
前記開閉釦操作判定部は、前記計測値の変化方向に基づいて、ドアの開動作または閉動作を検出するものであり、前記ドアの開動作開始から閉動作完了までに要した時間が、所定の標準時間よりも長い場合に、前記開釦が操作されたと判定することを特徴とするエレベータ診断装置。 The elevator diagnostic apparatus according to claim 1,
The open/close button operation determination unit detects an opening operation or closing operation of the door based on the change direction of the measured value, and the time required from the start of the opening operation to the completion of the closing operation of the door is determined by a predetermined amount of time. is longer than the standard time, it is determined that the opening button has been operated.
前記開閉釦操作判定部は、前記計測値の変化方向に基づいて、ドアの開動作または閉動作を検出するものであり、前記ドアの閉動作完了前に前記計測値の変化方向が切り替わった場合に、前記ドアが反転したと判定することを特徴とするエレベータ診断装置。 The elevator diagnostic apparatus according to claim 1,
The opening/closing button operation determination unit detects whether the door is opened or closed based on the direction of change in the measured value. (2) an elevator diagnostic apparatus, which determines that the door is reversed;
前記階床判定部には、ドア閉時の前記計測値の初期値を階毎に記憶しており、現在の前記計測値と各階の前記初期値を比較することで、現在のかご停止階を判定することを特徴とするエレベータ診断装置。 The elevator diagnostic apparatus according to claim 1,
The floor determination unit stores the initial values of the measured values when the doors are closed for each floor, and compares the current measured values with the initial values of each floor to determine the current car stop floor. An elevator diagnosis device characterized by determining:
さらに、前記利用状況記録部に記録された利用状況を外部の管制センターに送信する報知部を備えたことを特徴とするエレベータ診断装置。 The elevator diagnostic apparatus according to claim 1,
Further, the elevator diagnostic apparatus further comprises a reporting section for transmitting the usage status recorded in the usage status recording section to an external control center.
前記計測値に基づいて、前記かごの停止階を判定するステップと、
前記計測値に基づいて、開釦と閉釦の操作を判定するステップと、
前記開釦と前記閉釦の階毎の操作を、管制センターに送信するステップと、
を備えたことを特徴とするエレベータ診断方法。 An elevator diagnosis method for performing diagnosis based on the measurement values of a magnetic sensor installed on the landing side of a car,
determining a stop floor of the car based on the measured value;
a step of determining the operation of the open button and the close button based on the measured value;
a step of transmitting the operation of the open button and the close button for each floor to a control center;
A method for diagnosing an elevator, comprising:
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020090324A JP7284735B2 (en) | 2020-05-25 | 2020-05-25 | ELEVATOR DIAGNOSTIC DEVICE AND ELEVATOR DIAGNOSTIC METHOD |
| SG10202104556TA SG10202104556TA (en) | 2020-05-25 | 2021-05-03 | Elevator diagnosis apparatus and elevator diagnosis method |
| CN202110530236.6A CN113716406B (en) | 2020-05-25 | 2021-05-14 | Elevator diagnosis device and elevator diagnosis method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020090324A JP7284735B2 (en) | 2020-05-25 | 2020-05-25 | ELEVATOR DIAGNOSTIC DEVICE AND ELEVATOR DIAGNOSTIC METHOD |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2021185107A JP2021185107A (en) | 2021-12-09 |
| JP2021185107A5 JP2021185107A5 (en) | 2022-07-22 |
| JP7284735B2 true JP7284735B2 (en) | 2023-05-31 |
Family
ID=78672683
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020090324A Active JP7284735B2 (en) | 2020-05-25 | 2020-05-25 | ELEVATOR DIAGNOSTIC DEVICE AND ELEVATOR DIAGNOSTIC METHOD |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7284735B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN113716406B (en) |
| SG (1) | SG10202104556TA (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023157106A (en) | 2022-04-14 | 2023-10-26 | 株式会社日立ビルシステム | Anomaly diagnostic device for elevator, elevator system, anomaly diagnostic method for elevator, and anomaly diagnostic program for elevator |
| CN115043291A (en) * | 2022-07-20 | 2022-09-13 | 成都鹏业软件股份有限公司 | Method and device for detecting abnormality of elevator door |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014055038A (en) | 2012-09-11 | 2014-03-27 | Hitachi Building Systems Co Ltd | Failure diagnostic device of elevator |
| JP2019189445A (en) | 2018-04-27 | 2019-10-31 | 株式会社日立ビルシステム | Operation monitoring system of elevator |
| JP2019199347A (en) | 2018-05-18 | 2019-11-21 | 株式会社日立ビルシステム | Elevator car position identifying device and identifying method thereof |
| WO2020031284A1 (en) | 2018-08-08 | 2020-02-13 | 株式会社日立ビルシステム | Elevator diagnosis system |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07291562A (en) * | 1994-04-26 | 1995-11-07 | Hitachi Ltd | Elevator door opening time controller |
| JPH09240951A (en) * | 1996-03-07 | 1997-09-16 | Hitachi Building Syst Co Ltd | Call device of elevator |
| US6543583B1 (en) * | 2001-07-02 | 2003-04-08 | Otis Elevator Company | Elevator auditing with recommended action, reason and severity in maintenance messages |
| JP5263725B2 (en) * | 2007-10-04 | 2013-08-14 | 東芝エレベータ株式会社 | Control device for double deck elevator |
| JP2009149413A (en) * | 2007-12-20 | 2009-07-09 | Hitachi Ltd | Elevator control system in abnormality and failure |
| SG186731A1 (en) * | 2010-06-18 | 2013-02-28 | Hitachi Ltd | Elevator system |
| JP2013180862A (en) * | 2012-03-01 | 2013-09-12 | Hitachi Ltd | Elevator system |
| JP2016016976A (en) * | 2014-07-11 | 2016-02-01 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Elevator system |
| JP2017193418A (en) * | 2016-04-21 | 2017-10-26 | 株式会社日立ビルシステム | Elevator control system |
| JP6510600B2 (en) * | 2017-08-24 | 2019-05-08 | 東芝エレベータ株式会社 | Remote diagnostic operation method of elevator, elevator control device, and remote diagnostic operation program of elevator |
| CN108861906B (en) * | 2018-06-26 | 2021-01-05 | 潍坊学院 | Intelligent elevator control system and method |
| JP6611874B1 (en) * | 2018-07-18 | 2019-11-27 | 東芝エレベータ株式会社 | Elevator door diagnostic apparatus and door diagnostic method |
-
2020
- 2020-05-25 JP JP2020090324A patent/JP7284735B2/en active Active
-
2021
- 2021-05-03 SG SG10202104556TA patent/SG10202104556TA/en unknown
- 2021-05-14 CN CN202110530236.6A patent/CN113716406B/en active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014055038A (en) | 2012-09-11 | 2014-03-27 | Hitachi Building Systems Co Ltd | Failure diagnostic device of elevator |
| JP2019189445A (en) | 2018-04-27 | 2019-10-31 | 株式会社日立ビルシステム | Operation monitoring system of elevator |
| JP2019199347A (en) | 2018-05-18 | 2019-11-21 | 株式会社日立ビルシステム | Elevator car position identifying device and identifying method thereof |
| WO2020031284A1 (en) | 2018-08-08 | 2020-02-13 | 株式会社日立ビルシステム | Elevator diagnosis system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2021185107A (en) | 2021-12-09 |
| CN113716406B (en) | 2023-07-07 |
| CN113716406A (en) | 2021-11-30 |
| SG10202104556TA (en) | 2021-12-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| RU2321533C2 (en) | Method of and device for remote control of lift | |
| JP7284735B2 (en) | ELEVATOR DIAGNOSTIC DEVICE AND ELEVATOR DIAGNOSTIC METHOD | |
| CN110267900A (en) | Improve the mechanism of elevator device safety | |
| CN108569604B (en) | Elevator, and diagnosis system and diagnosis method for abnormality detection device in elevator car | |
| JP6479949B1 (en) | Elevator door abnormality diagnosis system and abnormality diagnosis method | |
| JP6987255B2 (en) | Elevator diagnostic system | |
| JP6997680B2 (en) | Elevator abnormality monitoring system and elevator abnormality monitoring method | |
| US20090314587A1 (en) | Elevator control system | |
| JP5090650B2 (en) | Elevator door opening / closing abnormality monitoring device | |
| JP2007070102A (en) | Diagnostic device for elevator door | |
| JP2020026327A (en) | Elevator control device | |
| JP2019085247A (en) | Abnormality detection device for elevator operation button | |
| JP7112511B2 (en) | People Information Acquisition System, People Information Acquisition Method, and Elevator | |
| JP6673737B2 (en) | System device abnormality diagnosis device, elevator abnormality diagnosis device, and elevator abnormality diagnosis method | |
| CN112672969B (en) | Method and monitoring device for inferring the state of health of a call device in an elevator installation | |
| JP4804777B2 (en) | Elevator equipment | |
| CN110678410B (en) | Elevator device | |
| JP2005126176A (en) | Door opening/closing diagnostic device for elevator | |
| JP7047972B2 (en) | Elevator slip detection system | |
| JP2003238040A (en) | Remote monitoring device for elevator | |
| CN111479767A (en) | Control panel for elevator and elevator system for preventing omission of operation diagnosis resetting | |
| JP6828130B1 (en) | Rope inspection methods, rope inspection systems, and programs | |
| JP7322204B2 (en) | Elevator diagnostic system and diagnostic method | |
| JP7003977B2 (en) | Elevator diagnostic system | |
| JPH09272682A (en) | Elevator door inspection device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20220713 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20220713 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20230209 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20230221 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20230228 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20230516 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20230519 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7284735 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |