JP7121471B2 - game machine - Google Patents
game machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7121471B2 JP7121471B2 JP2017105328A JP2017105328A JP7121471B2 JP 7121471 B2 JP7121471 B2 JP 7121471B2 JP 2017105328 A JP2017105328 A JP 2017105328A JP 2017105328 A JP2017105328 A JP 2017105328A JP 7121471 B2 JP7121471 B2 JP 7121471B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- display
- command
- variable
- special symbol
- cpu
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Pinball Game Machines (AREA)
- Display Devices Of Pinball Game Machines (AREA)
Description
本発明は、遊技を行うパチンコ機やスロット機等の遊技機に関する。 The present invention relates to gaming machines such as pachinko machines and slot machines for playing games.
遊技機として、遊技媒体である遊技球を発射装置によって遊技領域に発射し、遊技領域に設けられている入賞口などの入賞領域に遊技球が入賞すると、所定個の賞球が遊技者に払い出されるものがある。さらに、識別情報を可変表示(「変動」ともいう。)可能な可変表示装置が設けられ、可変表示装置において識別情報の可変表示の表示結果が特定表示結果となった場合に、遊技状態(遊技機の状態。よって、具体的には、遊技機が制御されている状態。)を変更して、所定の遊技価値を遊技者に与えるように構成されたものがある(いわゆるパチンコ機)。 As a gaming machine, game balls, which are game media, are shot into a game area by a shooting device, and when the game balls enter a prize winning area such as a prize winning opening provided in the game area, a predetermined number of prize balls are paid out to the player. There is something that can be done. Furthermore, a variable display device capable of variably displaying (also referred to as “fluctuation”) identification information is provided, and when the display result of the variable display of the identification information on the variable display device is a specific display result, the game state (game There is a so-called pachinko machine configured to change the state of the machine (ie, more specifically, the state in which the game machine is controlled) to give a predetermined game value to the player.
また、所定の遊技媒体を1ゲームに対して所定数の賭数を設定した後、遊技者がスタートレバーを操作することにより可変表示装置による識別情報の可変表示を開始し、遊技者が各可変表示装置に対応して設けられた停止ボタンを操作することにより、その操作タイミングから予め定められた最大遅延時間の範囲内で識別情報の可変表示を停止し、全ての可変表示装置の可変表示を停止したときに導出された表示結果に従って入賞が発生し、入賞に応じて予め定められた所定の遊技媒体が払い出され、特定入賞が発生した場合に、遊技状態を所定の遊技価値を遊技者に与える状態にするように構成されたものがある(いわゆるスロット機)。 After setting a predetermined number of bets for one game of predetermined game media, the player operates the start lever to start variable display of the identification information by the variable display device, and the player starts each variable display. By operating a stop button provided corresponding to the display device, the variable display of the identification information is stopped within the range of the predetermined maximum delay time from the operation timing, and the variable display of all the variable display devices is stopped. Winning occurs according to the display result derived when the game is stopped, predetermined game media are paid out according to the winning, and when a specific winning occurs, the game state is changed to a predetermined game value by the player. (so-called slot machines).
なお、遊技価値とは、遊技機の遊技領域に設けられた可変入賞球装置に打球が入賞しやすい遊技者にとって有利な状態になることや、遊技者にとって有利な状態になるための権利を発生させたりすることや、賞球払出の条件が成立しやすくなる状態になることである。 The game value is defined as a situation in which a ball is likely to win a prize in a variable winning ball device provided in the game area of the gaming machine, or the generation of the right to become in an advantageous situation for the player. or to make it easier to satisfy the conditions for paying out prize balls.
パチンコ遊技機では、始動入賞口に遊技球が入賞したことにもとづいて可変表示装置において開始される特別図柄(識別情報)の可変表示の表示結果として、あらかじめ定められた特定の表示態様が導出表示された場合に、「大当り」が発生する。なお、導出表示とは、図柄(最終停止図柄)を最終的に停止表示させることである。大当りが発生すると、例えば、大入賞口が所定回数開放して打球が入賞しやすい大当り遊技状態に移行する。そして、各開放期間において、所定個(例えば、10個)の大入賞口への入賞があると大入賞口は閉成する。そして、大入賞口の開放回数は、所定回数(例えば、15ラウンド)に固定されている。なお、各開放について開放時間(例えば、29秒)が決められ、入賞数が所定個に達しなくても開放時間が経過すると大入賞口は閉成する。以下、各々の大入賞口の開放期間をラウンドということがある。また、ラウンドにおける遊技をラウンド遊技ということがある。 In a pachinko game machine, a predetermined specific display mode is derived and displayed as a display result of variable display of special symbols (identification information) that is started on the variable display device based on the winning of a game ball in a starting winning hole. If you do, a "jackpot" will occur. It should be noted that the derivation display means that the symbol (final stop symbol) is finally stopped and displayed. When a big win occurs, for example, the big win opening is opened a predetermined number of times, and the game shifts to a big win game state in which the ball is likely to win. Then, in each open period, when a predetermined number (for example, 10) of the large winning openings are won, the large winning opening is closed. The number of openings of the big winning opening is fixed to a predetermined number (for example, 15 rounds). An opening time (for example, 29 seconds) is determined for each opening, and even if the number of winnings does not reach a predetermined number, the big winning opening is closed after the opening time has elapsed. Hereinafter, the opening period of each big winning slot may be called a round. Moreover, the game in a round may be called a round game.
また、可変表示装置において、最終停止図柄(例えば、左中右図柄のうち中図柄)となる図柄以外の図柄が、所定時間継続して、特定の表示結果と一致している状態で停止、揺動、拡大縮小もしくは変形している状態、または、複数の図柄が同一図柄で同期して変動したり、表示図柄の位置が入れ替わっていたりして、最終結果が表示される前で大当り発生の可能性が継続している状態(以下、これらの状態をリーチ状態という。)において行われる演出をリーチ演出という。また、リーチ状態やその様子をリーチ態様という。さらに、リーチ演出を含む可変表示をリーチ可変表示という。そして、可変表示装置に変動表示される図柄の表示結果が特定の表示結果でない場合には「はずれ」となり、変動表示状態は終了する。遊技者は、大当りをいかにして発生させるかを楽しみつつ遊技を行う。 In addition, in the variable display device, patterns other than the final stop pattern (for example, the middle pattern among the left, middle, and right patterns) continue for a predetermined period of time and are stopped and shaken in a state in which they match a specific display result. Big wins can occur before the final result is displayed due to moving, scaling, or deformation, multiple symbols fluctuating in sync with the same symbol, or the positions of the displayed symbols changing. The production performed in the state where the sexuality is continuing (hereinafter, these states are referred to as the reach state) is called the reach production. In addition, the reach state and its state are referred to as a reach state. Further, the variable display including the reach effect is called the reach variable display. Then, if the display result of the pattern variably displayed on the variable display device is not a specific display result, it becomes "missing" and the variable display state ends. A player plays a game while enjoying how to generate a big hit.
そのような遊技機において、引用文献1には、所定表示(例えば、宝箱が閉じた態様の保留表示)を特定表示(例えば、宝箱からキャラクタが出現する態様の保留表示)に変化させる予知報知を行うことが記載されている。
In such a gaming machine,
しかし、特許文献1に記載された発明では、特定表示に変化する前の所定表示の態様によって期待度が決まるため、期待度が低い態様の所定表示が表示された時点で遊技者の期待感が失われ、興趣が低下してしまうおそれがある。
However, in the invention described in
そこで、本発明は、遊技者の期待感を維持することができ、興趣の低下を防止することができる遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION Accordingly, it is an object of the present invention to provide a gaming machine capable of maintaining a player's sense of expectation and preventing a decline in interest.
(A)本発明による遊技機は、遊技を行う遊技機であって、所定表示(例えば、特殊態様により表示される保留表示およびアクティブ表示)を表示可能な表示手段を備え、表示手段は、所定表示を特定表示(例えば、特別態様により表示される保留表示およびアクティブ表示)に変化させて表示することが可能であり(例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ560がステップS8005やS8107を実行する部分)、少なくとも第1所定態様(例えば、第1特殊態様)および該第1所定態様よりも遊技者にとって有利な有利状態に制御される期待度が高い第2所定態様(例えば、第2特殊態様)により所定表示を表示可能であり(図38,図39参照)、所定表示を第1所定態様にて表示した後に、該所定表示を第2所定態様に変化させて表示可能であり、少なくとも第1特定態様(例えば、第1特別態様)および該第1特定態様よりも有利状態に制御される期待度が高い第2特定態様(例えば、第2特別態様)により特定表示を表示可能であり(図38,図39参照)、有利状態に制御される場合に、第1所定態様よりも高い割合で第2所定態様にて所定表示を表示し、第1特定態様よりも高い割合で第2特定態様にて特定表示を表示し、第1所定態様の所定表示が第2特定態様の特定表示に変化する第1変化パターン(例えば、図39(D)に示す最終表示態様が第2特別態様であるときの第2変化パターン)は、第2所定態様の所定表示が第1特定態様の特定表示に変化する第2変化パターン(例えば、図39(C)に示す最終表示態様が第1特別態様であるときの第3変化パターン)よりも有利状態に制御される期待度が高く、有利状態に制御される場合に、第2変化パターンよりも高い割合で第1変化パターンにて所定表示が特定表示に変化し、特定表示の表示形状は、所定表示の表示形状とは異なり、所定表示の表示態様に応じて、特定表示に変化する割合が異なり、変化後の特定表示の態様に応じて、複数のタイミングのいずれにおいて所定表示が該特定表示に変化するかの割合が異なる(例えば、最終表示態様に応じて、変化タイミングの決定割合が異なる。図40(A)~(D)参照)ことを特徴とする。
そのような構成によれば、第1所定態様の所定表示が表示されても、遊技者の期待感を維持することができ、興趣の低下を防止することができる。
(1)他の遊技機は、遊技を行う遊技機であって、所定表示(例えば、特殊態様により表示される保留表示およびアクティブ表示)を表示可能な表示手段を備え、表示手段は、所定表示を特定表示(例えば、特別態様により表示される保留表示およびアクティブ表示)に変化させて表示することが可能であり(例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ560がステップS8005やS8107を実行する部分)、少なくとも第1所定態様(例えば、第1特殊態様)および該第1所定態様よりも期待度が高い第2所定態様(例えば、第2特殊態様)により所定表示を表示可能であり(図38,図39参照)、少なくとも第1特定態様(例えば、第1特別態様)および該第1特定態様よりも期待度が高い第2特定態様(例えば、第2特別態様)により特定表示を表示可能であり(図38,図39参照)、第1所定態様の所定表示が第2特定態様の特定表示に変化する第1変化パターン(例えば、図39(D)に示す最終表示態様が第2特別態様であるときの第2変化パターン)は、第2所定態様の所定表示が第1特定態様の特定表示に変化する第2変化パターン(例えば、図39(C)に示す最終表示態様が第1特別態様であるときの第3変化パターン)よりも期待度が高いことを特徴とする。
そのような構成によれば、第1所定態様の所定表示が表示されても、遊技者の期待感を維持することができ、興趣の低下を防止することができる。
(A) A gaming machine according to the present invention is a gaming machine for playing a game, and includes display means capable of displaying a predetermined display (for example, a suspended display and an active display displayed in a special mode), wherein the display means It is possible to display by changing the display to a specific display (for example, pending display and active display displayed by a special mode) (for example, the part where the
According to such a configuration, even if the predetermined display of the first predetermined mode is displayed, it is possible to maintain the player's sense of expectation and prevent the player from losing interest.
(1) The other gaming machine is a gaming machine for playing a game, and has display means capable of displaying a predetermined display (for example, a suspended display and an active display displayed in a special mode), and the display means is a predetermined display. can be changed to a specific display (for example, a pending display and an active display displayed by a special mode) and displayed (for example, the portion where the
According to such a configuration, even if the predetermined display of the first predetermined mode is displayed, it is possible to maintain the player's sense of expectation and prevent the player from losing interest.
(2)上記(1)の遊技機において、表示手段は、所定表示を経ずに特定表示を表示可能である(例えば、図39(A)の第1変化パターンに決定されたときに実現される。また、アクティブ表示において通常態様から特別態様への変化が行われる変化パターンを設けることにより実現される。)ようにしてもよい。
そのような構成によれば、所定表示が表示されていないときにも、特定表示が表示されることに期待を持たせることができる。
(2) In the gaming machine of (1) above, the display means can display a specific display without going through a predetermined display (for example, when the first change pattern in FIG. 39(A) is determined, Also, it can be realized by providing a change pattern in which the active display changes from the normal mode to the special mode.).
According to such a configuration, even when the predetermined display is not displayed, it is possible to make the user expect that the specific display will be displayed.
(3)上記(1)または(2)の遊技機において、所定表示を経て表示された特定表示と所定表示を経ずに表示された特定表示とで期待度が異なる(例えば、第1変化パターンよりも第2~第4変化パターンの方が、期待度(大当り信頼度やリーチ信頼度)が高い。図39(B)~(F)参照)ようにしてもよい。
そのような構成によれば、特定表示が表示される経緯に注目させることができ、興趣を向上させることができる。
(3) In the gaming machine of (1) or (2) above, the degree of expectation differs between the specific display displayed after the predetermined display and the specific display displayed without the predetermined display (for example, the first change pattern Expectations (big hit reliability and reach reliability) are higher for the second to fourth variation patterns than (see FIGS. 39B to 39F)).
According to such a configuration, it is possible to make the viewer pay attention to the circumstances in which the specific display is displayed, thereby improving interest.
(4)上記(1)~(3)のいずれかの遊技機において、所定表示が特定表示に変化するときに変化演出(例えば、示唆演出および変化演出)を実行可能な変化演出実行手段(例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ560がステップS8107を実行する部分)を備え、変化演出実行手段は、所定表示の態様に応じて、複数の演出態様のいずれかにより変化演出を実行可能である(例えば、アクティブ表示の表示態様に応じた演出態様の示唆演出および変化演出を実行する)ようにしてもよい。
そのような構成によれば、所定表示の態様(すなわち期待度)に応じて、好適な演出態様の変化演出を実行することができ、興趣を向上させることができる。
(4) In the gaming machine according to any one of (1) to (3) above, a change effect execution means (for example, , a portion where the
According to such a configuration, it is possible to execute a change effect of a suitable effect mode according to the predetermined display mode (that is, the degree of expectation), thereby improving interest.
(5)上記(1)~(4)のいずれかの遊技機において、所定表示の態様に応じて、複数のタイミングのいずれにおいて該所定表示が特定表示に変化するかの割合が異なる(例えば、最終表示態様直前の態様に応じて、変化タイミングの決定割合が異なる。図40(A)~(D)参照)ようにしてもよい。
そのような構成によれば、期待感を効果的に持続させることができる。
(5) In the gaming machine according to any one of (1) to (4) above, depending on the mode of the predetermined display, the ratio at which of the plurality of timings the predetermined display changes to the specific display differs (for example, Depending on the mode immediately before the final display mode, the change timing determination ratio may be different (see FIGS. 40A to 40D).
According to such a configuration, it is possible to effectively maintain the sense of expectation.
(6)上記(1)~(5)のいずれかの遊技機において、予告演出を実行可能な予告演出実行手段(例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ560がステップS8013やS8105を実行する部分)を備え、予告演出実行手段は、所定表示の変化パターンに応じて(例えば、第2、第3特殊態様により表示される第3変化パターンまたは第4変化パターンであるか否かに応じて)、予告演出の実行割合が異なるように予告演出を実行可能である(例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ560がステップS8008やS8013、S8105を実行する部分。図44参照)ようにしてもよい。
そのような構成によれば、バランス良く演出を行うことができ、各演出の演出効果を高めることができる。
(6) The gaming machine according to any one of (1) to (5) above includes a notice effect executing means capable of executing a notice effect (for example, a portion where the
According to such a configuration, it is possible to perform a well-balanced presentation, and to enhance the presentation effect of each presentation.
(7)上記(1)~(6)のいずれかの遊技機において、変化後の特定表示の態様に応じて、複数のタイミングのいずれにおいて所定表示が該特定表示に変化するかの割合が異なる(例えば、最終表示態様に応じて、変化タイミングの決定割合が異なる。図40(A)~(D)参照)ようにしてもよい。
そのような構成によれば、所定表示が特定表示に変化するタイミングに注目させることができ、興趣を向上させることができる。
(7) In the gaming machine of any one of (1) to (6) above, the ratio of which of the plurality of timings the predetermined display changes to the specific display differs depending on the mode of the specific display after the change. (For example, the determination ratio of change timing differs depending on the final display mode. See FIGS. 40A to 40D).
According to such a configuration, it is possible to make the viewer pay attention to the timing at which the predetermined display changes to the specific display, thereby improving interest.
実施の形態1.
以下、本発明の第1の実施の形態を、図面を参照して説明する。まず、遊技機の一例であるパチンコ遊技機1の全体の構成について説明する。図1はパチンコ遊技機1を正面からみた正面図である。
A first embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. First, the overall configuration of a
パチンコ遊技機1は、縦長の方形状に形成された外枠(図示せず)と、外枠の内側に開閉可能に取り付けられた遊技枠とで構成される。また、パチンコ遊技機1は、遊技枠に開閉可能に設けられている額縁状に形成されたガラス扉枠2を有する。遊技枠は、外枠に対して開閉自在に設置される前面枠(図示せず)と、機構部品等が取り付けられる機構板(図示せず)と、それらに取り付けられる種々の部品(後述する遊技盤6を除く)とを含む構造体である。
The
ガラス扉枠2の下部表面には打球供給皿(上皿)3がある。打球供給皿3の下部には、打球供給皿3に収容しきれない遊技球を貯留する余剰球受皿4や、打球を発射する打球操作ハンドル(操作ノブ)5が設けられている。また、ガラス扉枠2の背面には、遊技盤6が着脱可能に取り付けられている。なお、遊技盤6は、それを構成する板状体と、その板状体に取り付けられた種々の部品とを含む構造体である。また、遊技盤6の前面には、打ち込まれた遊技球が流下可能な遊技領域7が形成されている。
A batted ball supply tray (upper tray) 3 is provided on the lower surface of the
余剰球受皿(下皿)4を形成する部材には、例えば下皿本体の上面における手前側の所定位置(例えば下皿の中央部分)などに、スティック形状(棒形状)に構成され、遊技者が把持して複数方向(前後左右)に傾倒操作が可能なスティックコントローラ122が取り付けられている。なお、スティックコントローラ122には、遊技者がスティックコントローラ122の操作桿を操作手(例えば左手など)で把持した状態において、所定の操作指(例えば人差し指など)で押引操作することなどにより所定の指示操作が可能なトリガボタン121(図3を参照)が設けられ、スティックコントローラ122の操作桿の内部には、トリガボタン121に対する押引操作などによる所定の指示操作を検知するトリガセンサ125(図3を参照)が内蔵されている。また、スティックコントローラ122の下部における下皿の本体内部などには、操作桿に対する傾倒操作を検知する傾倒方向センサユニット123(図3を参照)が設けられている。また、スティックコントローラ122には、スティックコントローラ122を振動動作させるためのバイブレータ用モータ126(図3を参照)が内蔵されている。 The member forming the surplus ball receiving tray (lower tray) 4 is configured in a stick shape (rod shape), for example, at a predetermined position on the front side of the upper surface of the lower tray body (for example, the central portion of the lower tray). A stick controller 122 that can be gripped and tilted in a plurality of directions (front, back, left, and right) is attached. It should be noted that the stick controller 122 has a predetermined operating finger (for example, the index finger) that is pushed and pulled by the player while holding the operation rod of the stick controller 122 with the operator's hand (for example, the left hand). A trigger button 121 (see FIG. 3) capable of instructing operation is provided, and inside the operation rod of the stick controller 122 is a trigger sensor 125 (see FIG. 3) is built in. A tilting direction sensor unit 123 (see FIG. 3) for detecting a tilting operation with respect to the operation rod is provided inside the main body of the bottom plate of the stick controller 122 or the like. The stick controller 122 also incorporates a vibrator motor 126 (see FIG. 3) for vibrating the stick controller 122 .
打球供給皿(上皿)3を形成する部材には、例えば上皿本体の上面における手前側の所定位置(例えばスティックコントローラ122の上方)などに、遊技者が押下操作などにより所定の指示操作を可能なプッシュボタン120が設けられている。プッシュボタン120は、遊技者からの押下操作などによる所定の指示操作を、機械的、電気的、あるいは、電磁的に、検出できるように構成されていればよい。プッシュボタン120の設置位置における上皿の本体内部などには、プッシュボタン120に対してなされた遊技者の操作行為を検知するプッシュセンサ124(図3を参照)が設けられていればよい。図1に示す構成例では、プッシュボタン120とスティックコントローラ122の取付位置が、上皿及び下皿の中央部分において上下の位置関係にある。これに対して、上下の位置関係を保ったまま、プッシュボタン120及びスティックコントローラ122の取付位置を、上皿及び下皿において左右のいずれかに寄せた位置としてもよい。あるいは、プッシュボタン120とスティックコントローラ122の取付位置が上下の位置関係にはなく、例えば左右の位置関係にあるものとしてもよい。
A member that forms the batted ball supply tray (upper tray) 3 is, for example, at a predetermined position (for example, above the stick controller 122) on the front side of the upper surface of the upper tray main body, and the player presses down to perform a predetermined instruction operation. A
遊技領域7の中央付近には、液晶表示装置(LCD)で構成された演出表示装置9が設けられている。演出表示装置9の表示画面には、第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄の可変表示に同期した演出図柄の可変表示を行う演出図柄表示領域がある。よって、演出表示装置9は、演出図柄の可変表示を行う可変表示装置に相当する。演出図柄表示領域には、例えば「左」、「中」、「右」の3つの装飾用(演出用)の演出図柄を可変表示する図柄表示エリアがある。図柄表示エリアには「左」、「中」、「右」の各図柄表示エリアがあるが、図柄表示エリアの位置は、演出表示装置9の表示画面において固定的でなくてもよいし、図柄表示エリアの3つ領域が離れてもよい。演出表示装置9は、演出制御基板に搭載されている演出制御用マイクロコンピュータによって制御される。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータが、第1特別図柄表示器8aで第1特別図柄の可変表示が実行されているときに、その可変表示に伴って演出表示装置9で演出表示を実行させ、第2特別図柄表示器8bで第2特別図柄の可変表示が実行されているときに、その可変表示に伴って演出表示装置9で演出表示を実行させるので、遊技の進行状況を把握しやすくすることができる。
In the vicinity of the center of the
また、演出表示装置9において、最終停止図柄(例えば左右中図柄のうち中図柄)となる図柄以外の図柄が、所定時間継続して、大当り図柄(例えば左中右の図柄が同じ図柄で揃った図柄の組み合わせ)と一致している状態で停止、揺動、拡大縮小もしくは変形している状態、または、複数の図柄が同一図柄で同期して変動したり、表示図柄の位置が入れ替わっていたりして、最終結果が表示される前で大当り発生の可能性が継続している状態(以下、これらの状態をリーチ状態という。)において行われる演出をリーチ演出という。また、リーチ状態やその様子をリーチ態様という。さらに、リーチ演出を含む可変表示をリーチ可変表示という。そして、演出表示装置9に変動表示される図柄の表示結果が大当り図柄でない場合には「はずれ」となり、変動表示状態は終了する。遊技者は、大当りをいかにして発生させるかを楽しみつつ遊技を行う。
Also, in the
演出表示装置9の表示画面の右上方部には、演出図柄と後述する特別図柄および普通図柄とに次ぐ第4図柄を表示する第4図柄表示領域9c,9dが設けられている。この実施の形態では、後述する第1特別図柄の変動表示に同期して第1特別図柄用の第4図柄の変動表示が行われる第1特別図柄用の第4図柄表示領域9cと、第2特別図柄の変動表示に同期して第2特別図柄用の第4図柄の変動表示が行われる第2特別図柄用の第4図柄表示領域9dとが設けられている。
In the upper right part of the display screen of the
なお、第1特別図柄用の第4図柄と第2特別図柄用の第4図柄とを、第4図柄と総称することがあり、第1特別図柄用の第4図柄表示領域9cと第2特別図柄用の第4図柄表示領域9dを、第4図柄表示領域と総称することがある。 The fourth symbol for the first special symbol and the fourth symbol for the second special symbol may be collectively referred to as the fourth symbol, and the fourth symbol display area 9c for the first special symbol and the second special symbol The fourth design display area 9d for design may be collectively referred to as a fourth design display area.
第4図柄の変動(可変表示)は、第4図柄表示領域9c,9dを所定の表示色(例えば、青色)で一定の時間間隔で点灯と消灯とを繰り返す状態を継続することによって実現される。第1特別図柄表示器8aにおける第1特別図柄の可変表示と、第1特別図柄用の第4図柄表示領域9cにおける第1特別図柄用の第4図柄の可変表示とは同期している。第2特別図柄表示器8bにおける第2特別図柄の可変表示と、第2特別図柄用の第4図柄表示領域9dにおける第2特別図柄用の第4図柄の可変表示とは同期している。同期とは、可変表示の開始時点および終了時点が同じであって、可変表示の期間が同じであることをいう。
Variation (variable display) of the fourth pattern is realized by continuing a state in which the fourth pattern display areas 9c and 9d are repeatedly turned on and off in a predetermined display color (for example, blue) at regular time intervals. . The variable display of the first special symbol on the first
演出表示装置9の右方には、識別情報としての第1特別図柄を可変表示する第1特別図柄表示器(第1可変表示部)8aが設けられている。この実施の形態では、第1特別図柄表示器8aは、0~9の数字を可変表示可能な簡易で小型の表示器(例えば7セグメントLED)で実現されている。すなわち、第1特別図柄表示器8aは、0~9の数字(または、記号)を可変表示するように構成されている。また、演出表示装置9の右方(第1特別図柄表示器8aの右隣)には、識別情報としての第2特別図柄を可変表示する第2特別図柄表示器(第2可変表示部)8bも設けられている。第2特別図柄表示器8bは、0~9の数字を可変表示可能な簡易で小型の表示器(例えば7セグメントLED)で実現されている。すなわち、第2特別図柄表示器8bは、0~9の数字(または、記号)を可変表示するように構成されている。
On the right side of the
小型の表示器は、例えば方形状に形成されている。また、この実施の形態では、第1特別図柄の種類と第2特別図柄の種類とは同じ(例えば、ともに0~9の数字)であるが、種類が異なっていてもよい。また、第1特別図柄表示器8aおよび第2特別図柄表示器8bは、それぞれ、例えば、00~99の数字(または、2桁の記号)を可変表示するように構成されていてもよい。
A small display is formed in a rectangular shape, for example. Also, in this embodiment, the type of the first special design and the type of the second special design are the same (for example, both numbers are 0 to 9), but the types may be different. Also, the first special
以下、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄とを特別図柄と総称することがあり、第1特別図柄表示器8aと第2特別図柄表示器8bとを特別図柄表示器(可変表示部)と総称することがある。
Hereinafter, the first special symbol and the second special symbol may be collectively referred to as special symbols, and the first special
なお、この実施の形態では、2つの特別図柄表示器8a,8bを備える場合を示しているが、遊技機は、特別図柄表示器を1つのみ備えるものであってもよい。
In this embodiment, two
第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄の可変表示は、可変表示の実行条件である第1始動条件または第2始動条件が成立(例えば、遊技球が第1始動入賞口13または第2始動入賞口14を通過(入賞を含む)したこと)した後、可変表示の開始条件(例えば、保留記憶数が0でない場合であって、第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄の可変表示が実行されていない状態であり、かつ、大当り遊技が実行されていない状態)が成立したことにもとづいて開始され、可変表示時間(変動時間)が経過すると表示結果(停止図柄)を導出表示する。なお、遊技球が通過するとは、入賞口やゲートなどのあらかじめ入賞領域として定められている領域を遊技球が通過したことであり、入賞口に遊技球が入った(入賞した)ことを含む概念である。また、表示結果を導出表示するとは、図柄(識別情報の例)を最終的に停止表示させることである。
In the variable display of the first special symbol or the second special symbol, the first starting condition or the second starting condition, which is the execution condition of the variable display, is satisfied (for example, the game ball is the first
演出表示装置9の下方には、第1始動入賞口13を有する入賞装置が設けられている。第1始動入賞口13に入賞した遊技球は、遊技盤6の背面に導かれ、第1始動口スイッチ13aによって検出される。
Below the
また、第1始動入賞口(第1始動口)13を有する入賞装置の下方には、遊技球が入賞可能な第2始動入賞口14を有する可変入賞球装置15が設けられている。第2始動入賞口(第2始動口)14に入賞した遊技球は、遊技盤6の背面に導かれ、第2始動口スイッチ14aによって検出される。可変入賞球装置15は、ソレノイド16によって開状態とされる。可変入賞球装置15が開状態になることによって、遊技球が第2始動入賞口14に入賞可能になり(始動入賞し易くなり)、遊技者にとって有利な状態になる。可変入賞球装置15が開状態になっている状態では、第1始動入賞口13よりも、第2始動入賞口14に遊技球が入賞しやすい。また、可変入賞球装置15が閉状態になっている状態では、遊技球は第2始動入賞口14に入賞しない。従って、可変入賞球装置15が閉状態になっている状態では、第2始動入賞口14よりも、第1始動入賞口13に遊技球が入賞しやすい。なお、可変入賞球装置15が閉状態になっている状態において、入賞はしづらいものの、入賞することは可能である(すなわち、遊技球が入賞しにくい)ように構成されていてもよい。
In addition, below the winning device having the first starting winning opening (first starting opening) 13, a variable winning
以下、第1始動入賞口13と第2始動入賞口14とを総称して始動入賞口または始動口ということがある。
Hereinafter, the first start prize-winning
可変入賞球装置15が開放状態に制御されているときには可変入賞球装置15に向かう遊技球は第2始動入賞口14に極めて入賞しやすい。そして、第1始動入賞口13は演出表示装置9の直下に設けられているが、演出表示装置9の下端と第1始動入賞口13との間の間隔をさらに狭めたり、第1始動入賞口13の周辺で釘を密に配置したり、第1始動入賞口13の周辺での釘配列を遊技球を第1始動入賞口13に導きづらくして、第2始動入賞口14の入賞率の方を第1始動入賞口13の入賞率よりもより高くするようにしてもよい。
When the variable winning
第2特別図柄表示器8bの上方には、第2始動入賞口14に入った有効入賞球数すなわち第2保留記憶数を表示する4つの表示器からなる第2特別図柄保留記憶表示器18bが設けられている。第2特別図柄保留記憶表示器18bは、有効始動入賞がある毎に、点灯する表示器の数を1増やす。そして、第2特別図柄表示器8bでの可変表示が開始される毎に、点灯する表示器の数を1減らす。
Above the second
また、第2特別図柄保留記憶表示器18bのさらに上方には、第1始動入賞口13に入った有効入賞球数すなわち第1保留記憶数(保留記憶を、始動記憶または始動入賞記憶ともいう。)を表示する4つの表示器からなる第1特別図柄保留記憶表示器18aが設けられている。第1特別図柄保留記憶表示器18aは、有効始動入賞がある毎に、点灯する表示器の数を1増やす。そして、第1特別図柄表示器8aでの可変表示が開始される毎に、点灯する表示器の数を1減らす。
Further above the second special symbol reserved
また、演出表示装置9の表示画面には、第1保留記憶数を表示する第1保留記憶表示部9aと、第2保留記憶数を表示する第2保留記憶表示部9bとが設けられている。なお、この実施の形態で示した態様にかぎらず、例えば、第1保留記憶表示部9aと第2保留記憶表示部9bとに代えて、第1保留記憶数と第2保留記憶数との合計である合計数(合算保留記憶数)を表示する領域(合算保留記憶表示部)が設けられるように構成してもよい。
Further, the display screen of the
また、演出表示装置9の表示画面の下部の第1保留記憶表示部9aと第2保留記憶表示部9bとの間には、保留表示の表示態様を引き継いだ表示態様により現在実行中の変動表示に対応したアクティブ表示が表示されるアクティブ表示領域9Fが設けられている。この実施の形態では、アクティブ表示は、原則的に、第1保留記憶表示部9aおよび第2保留記憶表示部9bに表示される保留表示と同様の態様により表示されるが、演出により態様が変化する場合もある。なお、現在実行中の変動表示に対応した表示であることが認識できるものであれば、必ずしも保留表示と同様の態様の表示である必要はなく、他の図形やキャラクタなどを表示してもよい。
In addition, between the first pending
なお、この実施の形態において、「可変表示に対応する表示」は、例えば、アクティブ表示領域9Fに表示されるアクティブ表示と、第1保留記憶表示部9aおよび第2保留記憶表示部9bに表示される保留表示とに該当する。なお、「可変表示に対応する表示」は、この実施の形態で示したものにかぎらず、少なくとも保留表示を含み、何らかの形式で可変表示に対応した表示であればよい。また、この実施の形態では、アクティブ表示領域9Fにおいてアクティブ表示を表示可能に構成する場合を示しているが、必ずしもアクティブ表示の表示を行う必要はなく、アクティブ表示領域9Fを設けなくてもよい。
In this embodiment, the "display corresponding to the variable display" is, for example, the active display displayed in the
演出表示装置9は、第1特別図柄表示器8aによる第1特別図柄の可変表示時間中、および第2特別図柄表示器8bによる第2特別図柄の可変表示時間中に、装飾用(演出用)の図柄としての演出図柄の可変表示を行う。第1特別図柄表示器8aにおける第1特別図柄の可変表示と、演出表示装置9における演出図柄の可変表示とは同期している。また、第2特別図柄表示器8bにおける第2特別図柄の可変表示と、演出表示装置9における演出図柄の可変表示とは同期している。また、第1特別図柄表示器8aにおいて大当り図柄が停止表示されるときと、第2特別図柄表示器8bにおいて大当り図柄が停止表示されるときには、演出表示装置9において大当りを想起させるような演出図柄の組み合わせが停止表示される。
The
また、図1に示すように、可変入賞球装置15の下方には、大入賞口を形成する特別可変入賞球装置20が設けられている。特別可変入賞球装置20は開閉板を備え、第1特別図柄表示器8aに特定表示結果(大当り図柄)が導出表示されたときと、第2特別図柄表示器8bに特定表示結果(大当り図柄)が導出表示されたときに生起する特定遊技状態(大当り遊技状態)においてソレノイド21によって開閉板が開放状態に制御されることによって、入賞領域となる大入賞口が開放状態になる。大入賞口に入賞した遊技球はカウントスイッチ23で検出される。
Further, as shown in FIG. 1, below the variable winning
演出表示装置9の左方には、普通図柄を可変表示する普通図柄表示器10が設けられている。この実施の形態では、普通図柄表示器10は、0~9の数字を可変表示可能な簡易で小型の表示器(例えば7セグメントLED)で実現されている。すなわち、普通図柄表示器10は、0~9の数字(または、記号)を可変表示するように構成されている。また、小型の表示器は、例えば方形状に形成されている。なお、普通図柄表示器10は、例えば、00~99の数字(または、2桁の記号)を可変表示するように構成されていてもよい。また、普通図柄表示器10は、7セグメントLEDなどにかぎらず、例えば、所定の記号表示を点灯表示可能な表示器(例えば、「○」や「×」を交互に点灯表示可能な装飾ランプ)で構成されていてもよい。
On the left side of the
遊技球がゲート32を通過しゲートスイッチ32aで検出されると、普通図柄表示器10の表示の可変表示が開始される。そして、普通図柄表示器10における停止図柄が所定の図柄(当り図柄。例えば、図柄「7」。)である場合に、可変入賞球装置15が所定回数、所定時間だけ開状態になる。すなわち、可変入賞球装置15の状態は、普通図柄の停止図柄が当り図柄である場合に、遊技者にとって不利な状態から有利な状態(第2始動入賞口14に遊技球が入賞可能な状態)に変化する。普通図柄表示器10の近傍には、ゲート32を通過した入賞球数を表示する4つのLEDによる表示部を有する普通図柄保留記憶表示器41が設けられている。ゲート32への遊技球の通過がある毎に、すなわちゲートスイッチ32aによって遊技球が検出される毎に、普通図柄保留記憶表示器41は点灯するLEDを1増やす。そして、普通図柄表示器10の可変表示が開始される毎に、点灯するLEDを1減らす。さらに、通常状態に比べて大当りとすることに決定される確率が高い状態である確変状態(通常状態と比較して、特別図柄の変動表示結果として大当りと判定される確率が高められた状態)では、普通図柄表示器10における停止図柄が当り図柄になる確率が高められるとともに、可変入賞球装置15の開放時間と開放回数が高められる。また、確変状態ではないが図柄の変動時間が短縮されている時短状態(特別図柄の可変表示時間が短縮される遊技状態)でも、可変入賞球装置15の開放時間と開放回数が高められる。
When the game ball passes through the
遊技盤6の下部には、入賞しなかった打球が取り込まれるアウト口26がある。また、遊技領域7の外側の左右上部および左右下部には、所定の音声出力として効果音や音声を発声する4つのスピーカ27が設けられている。遊技領域7の外周には、前面枠に設けられた枠LED28が設けられている。
At the bottom of the
遊技機には、遊技者が打球操作ハンドル5を操作することに応じて駆動モータを駆動し、駆動モータの回転力を利用して遊技球を遊技領域7に発射する打球発射装置(図示せず)が設けられている。打球発射装置から発射された遊技球は、遊技領域7を囲むように円形状に形成された打球レールを通って遊技領域7に入り、その後、遊技領域7を下りてくる。遊技球が第1始動入賞口13に入り第1始動口スイッチ13aで検出されると、第1特別図柄の可変表示を開始できる状態であれば(例えば、特別図柄の可変表示が終了し、第1の開始条件が成立したこと)、第1特別図柄表示器8aにおいて第1特別図柄の可変表示(変動)が開始されるとともに、演出表示装置9において演出図柄の可変表示が開始される。すなわち、第1特別図柄および演出図柄の可変表示は、第1始動入賞口13への入賞に対応する。第1特別図柄の可変表示を開始できる状態でなければ、第1保留記憶数が上限値に達していないことを条件として、第1保留記憶数を1増やす。
The game machine includes a ball shooting device (not shown) that drives a drive motor in response to the player's operation of the
遊技球が第2始動入賞口14に入り第2始動口スイッチ14aで検出されると、第2特別図柄の可変表示を開始できる状態であれば(例えば、特別図柄の可変表示が終了し、第2の開始条件が成立したこと)、第2特別図柄表示器8bにおいて第2特別図柄の可変表示(変動)が開始されるとともに、演出表示装置9において演出図柄の可変表示が開始される。すなわち、第2特別図柄および演出図柄の可変表示は、第2始動入賞口14への入賞に対応する。第2特別図柄の可変表示を開始できる状態でなければ、第2保留記憶数が上限値に達していないことを条件として、第2保留記憶数を1増やす。
When the game ball enters the second
この実施の形態では、確変大当りとなった場合には、遊技状態を高確率状態(確変状態)に移行するとともに、遊技球が始動入賞しやすくなる(すなわち、特別図柄表示器8a,8bや演出表示装置9における可変表示の実行条件が成立しやすくなる)ように制御された遊技状態である高ベース状態に移行(この実施の形態では、時短状態に移行)する。また、遊技状態が時短状態に移行されたときも、高ベース状態に移行する。高ベース状態である場合には、例えば、高ベース状態でない場合と比較して、可変入賞球装置15が開状態となる頻度が高められたり、可変入賞球装置15が開状態となる時間が延長されたりして、始動入賞しやすくなる。
In this embodiment, when a variable probability big hit occurs, the game state is shifted to a high probability state (variable probability state), and the game ball becomes easier to start winning (that is,
なお、可変入賞球装置15が開状態となる時間を延長する(開放延長状態ともいう)のでなく、普通図柄表示器10における停止図柄が当り図柄になる確率が高められる普通図柄確変状態に移行することによって、高ベース状態に移行してもよい。普通図柄表示器10における停止図柄が所定の図柄(当り図柄)となると、可変入賞球装置15が所定回数、所定時間だけ開状態になる。この場合、普通図柄確変状態に移行制御することによって、普通図柄表示器10における停止図柄が当り図柄になる確率が高められ、可変入賞球装置15が開状態となる頻度が高まる。従って、普通図柄確変状態に移行すれば、可変入賞球装置15の開放時間と開放回数が高められ、始動入賞しやすい状態(高ベース状態)となる。すなわち、可変入賞球装置15の開放時間と開放回数は、普通図柄の停止図柄が当り図柄であったり、特別図柄の停止図柄が確変図柄である場合等に高められ、遊技者にとって不利な状態から有利な状態(始動入賞しやすい状態)に変化する。なお、開放回数が高められることは、閉状態から開状態になることも含む概念である。
In addition, instead of extending the time in which the variable winning
また、普通図柄表示器10における普通図柄の変動時間(可変表示期間)が短縮される普通図柄時短状態に移行することによって、高ベース状態に移行してもよい。普通図柄時短状態では、普通図柄の変動時間が短縮されるので、普通図柄の変動が開始される頻度が高くなり、結果として普通図柄が当りとなる頻度が高くなる。従って、普通図柄が当たりとなる頻度が高くなることによって、可変入賞球装置15が開状態となる頻度が高くなり、始動入賞しやすい状態(高ベース状態)となる。
Further, the normal symbol fluctuation time (variable display period) in the normal
また、特別図柄や演出図柄の変動時間(可変表示期間)が短縮される時短状態に移行することによって、特別図柄や演出図柄の変動時間が短縮されるので、特別図柄や演出図柄の変動が開始される頻度が高くなり(換言すれば、保留記憶の消化が速くなる。)、無効な始動入賞が生じてしまう事態を低減することができる。従って、有効な始動入賞が発生しやすくなり、結果として、大当り遊技が行われる可能性が高まる。 In addition, by shifting to a time-saving state in which the fluctuation time (variable display period) of special patterns and production patterns is shortened, the fluctuation time of special patterns and production patterns is shortened, so the fluctuation of special patterns and production patterns starts. (In other words, the reserved memory is consumed more quickly.), and the occurrence of invalid starting winnings can be reduced. Therefore, effective starting winnings are more likely to occur, and as a result, the possibility of playing a big winning game increases.
さらに、上記に示した全ての状態(開放延長状態、普通図柄確変状態、普通図柄時短状態および特別図柄時短状態)に移行させることによって、始動入賞しやすくなる(高ベース状態に移行する)ようにしてもよい。また、上記に示した各状態(開放延長状態、普通図柄確変状態、普通図柄時短状態および特別図柄時短状態)のうちのいずれか複数の状態に移行させることによって、始動入賞しやすくなる(高ベース状態に移行する)ようにしてもよい。また、上記に示した各状態(開放延長状態、普通図柄確変状態、普通図柄時短状態および特別図柄時短状態)のうちのいずれか1つの状態にのみ移行させることによって、始動入賞しやすくなる(高ベース状態に移行する)ようにしてもよい。 In addition, by shifting to all the states shown above (open extension state, normal pattern variable state, normal pattern time saving state and special pattern time saving state), it is easier to start winning (shift to high base state) may In addition, each state shown above (open extension state, normal pattern variable state, normal pattern time saving state and special pattern time saving state) By shifting to any one of the states, it becomes easier to start winning (high base state). In addition, by shifting only to one of the above-described states (open extension state, normal symbol probability variable state, normal symbol time saving state and special symbol time saving state), it becomes easier to start winning (high transition to the base state).
図2は、主基板(遊技制御基板)31における回路構成の一例を示すブロック図である。なお、図2は、払出制御基板37および演出制御基板80等も示されている。主基板31には、プログラムに従ってパチンコ遊技機1を制御する遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ(遊技制御手段に相当)560が搭載されている。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ゲーム制御(遊技進行制御)用のプログラム等を記憶するROM54、ワークメモリとして使用される記憶手段としてのRAM55、プログラムに従って制御動作を行うCPU56およびI/Oポート部57を含む。この実施の形態では、ROM54およびRAM55は遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に内蔵されている。すなわち、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、1チップマイクロコンピュータである。1チップマイクロコンピュータには、少なくともCPU56のほかRAM55が内蔵されていればよく、ROM54は外付けであっても内蔵されていてもよい。また、I/Oポート部57は、外付けであってもよい。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560には、さらに、ハードウェア乱数(ハードウェア回路が発生する乱数)を発生する乱数回路503が内蔵されている。
FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing an example of the circuit configuration of the main board (game control board) 31. As shown in FIG. Note that FIG. 2 also shows the
また、RAM55は、その一部または全部が電源基板において作成されるバックアップ電源によってバックアップされている不揮発性記憶手段としてのバックアップRAMである。すなわち、遊技機に対する電力供給が停止しても、所定のバックアップ期間(バックアップ電源としてのコンデンサが放電してバックアップ電源が電力供給不能になるまで)は、RAM55の一部または全部の内容は保存される。特に、少なくとも、遊技状態すなわち遊技制御手段の制御状態に応じたデータ(特別図柄プロセスフラグや、確変フラグなど)と未払出賞球数を示すデータは、バックアップRAMに保存される。遊技制御手段の制御状態に応じたデータとは、停電等が生じた後に復旧した場合に、そのデータにもとづいて、制御状態を停電等の発生前に復旧させるために必要なデータである。また、制御状態に応じたデータと未払出賞球数を示すデータとを遊技の進行状態を示すデータと定義する。なお、この実施の形態では、RAM55の全部が、電源バックアップされているとする。
Also, the
なお、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560においてCPU56がROM54に格納されているプログラムに従って制御を実行するので、以下、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560(またはCPU56)が実行する(または、処理を行う)ということは、具体的には、CPU56がプログラムに従って制御を実行することである。このことは、主基板31以外の他の基板に搭載されているマイクロコンピュータについても同様である。
In addition, since the
乱数回路503は、特別図柄の可変表示の表示結果により大当りとするか否か判定するための判定用の乱数を発生するために用いられるハードウェア回路である。乱数回路503は、初期値(例えば、0)と上限値(例えば、65535)とが設定された数値範囲内で、数値データを、設定された更新規則に従って更新し、ランダムなタイミングで発生する始動入賞時が数値データの読出(抽出)時であることにもとづいて、読出される数値データが乱数値となる乱数発生機能を有する。 The random number circuit 503 is a hardware circuit used to generate a judgment random number for judging whether or not a big hit is achieved based on the display result of variable display of special symbols. The random number circuit 503 updates the numerical data according to the set update rule within the numerical range in which the initial value (for example, 0) and the upper limit value (for example, 65535) are set, and the start-up occurs at random timing. Based on the fact that the time of winning is the time of reading (extracting) the numerical data, it has a random number generating function in which the numerical data to be read becomes a random number.
また、ゲートスイッチ32a、第1始動口スイッチ13a、第2始動口スイッチ14a、カウントスイッチ23からの検出信号を遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に与える入力ドライバ回路58も主基板31に搭載されている。また、可変入賞球装置15を開閉するソレノイド16、および大入賞口を形成する特別可変入賞球装置20を開閉するソレノイド21を遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560からの指令に従って駆動する出力回路59も主基板31に搭載されている。
Also mounted on the
また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、特別図柄を可変表示する第1特別図柄表示器8a、第2特別図柄表示器8b、普通図柄を可変表示する普通図柄表示器10、第1特別図柄保留記憶表示器18a、第2特別図柄保留記憶表示器18bおよび普通図柄保留記憶表示器41の表示制御を行う。
In addition, the
なお、大当り遊技状態の発生を示す大当り情報等の情報出力信号を、ターミナル基板160を介して、ホールコンピュータ等の外部装置に対して出力する情報出力回路64も主基板31に搭載されている。
Also mounted on the
この実施の形態では、演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御手段(演出制御用マイクロコンピュータで構成される。)が、中継基板77を介して遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から演出内容を指示する演出制御コマンドを受信し、演出図柄を可変表示する演出表示装置9の表示制御を行う。
In this embodiment, the effect control means (comprised of the effect control microcomputer) mounted on the
また、演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御手段が、ランプドライバ基板35を介して、枠側に設けられている枠LED28の表示制御を行うとともに、音声出力基板70を介してスピーカ27からの音出力の制御を行う。
In addition, the effect control means mounted on the
なお、演出制御手段には、後述するように、スティックコントローラ122が備えるトリガセンサ125や傾倒方向センサユニット123、バイブレータ用モータ126、およびプッシュボタン120が備えるプッシュセンサ124にも接続されているのであるが(図3参照)、図2では図示を省略している。
The effect control means is also connected to a
図3は、中継基板77、演出制御基板80、ランプドライバ基板35および音声出力基板70の回路構成例を示すブロック図である。なお、図3に示す例では、ランプドライバ基板35および音声出力基板70には、マイクロコンピュータは搭載されていないが、マイクロコンピュータを搭載してもよい。また、ランプドライバ基板35および音声出力基板70を設けずに、演出制御に関して演出制御基板80のみを設けてもよい。
FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing a circuit configuration example of the
演出制御基板80は、演出制御用CPU101、および演出図柄プロセスフラグ等の演出に関する情報を記憶するRAMを含む演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100を搭載している。なお、RAMは外付けであってもよい。この実施の形態では、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100におけるRAMは電源バックアップされていない。演出制御基板80において、演出制御用CPU101は、内蔵または外付けのROM(図示せず)に格納されたプログラムに従って動作し、中継基板77を介して入力される主基板31からの取込信号(演出制御INT信号)に応じて、入力ドライバ102および入力ポート103を介して演出制御コマンドを受信する。また、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御コマンドにもとづいて、VDP(ビデオディスプレイプロセッサ)109に演出表示装置9の表示制御を行わせる。
The
この実施の形態では、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100と共動して演出表示装置9の表示制御を行うVDP109が演出制御基板80に搭載されている。VDP109は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100とは独立したアドレス空間を有し、そこにVRAMをマッピングする。VRAMは、画像データを展開するためのバッファメモリである。そして、VDP109は、VRAM内の画像データをフレームメモリを介して演出表示装置9に出力する。
In this embodiment, the
演出制御用CPU101は、受信した演出制御コマンドに従ってCGROM(図示せず)から必要なデータを読み出すための指令をVDP109に出力する。CGROMは、演出表示装置9に表示されるキャラクタ画像データや動画像データ、具体的には、人物、文字、図形や記号等(演出図柄を含む)、および背景画像のデータをあらかじめ格納しておくためのROMである。VDP109は、演出制御用CPU101の指令に応じて、CGROMから画像データを読み出す。そして、VDP109は、読み出した画像データにもとづいて表示制御を実行する。
The
演出制御コマンドおよび演出制御INT信号は、演出制御基板80において、まず、入力ドライバ102に入力する。入力ドライバ102は、中継基板77から入力された信号を演出制御基板80の内部に向かう方向にしか通過させない(演出制御基板80の内部から中継基板77への方向には信号を通過させない)信号方向規制手段としての単方向性回路でもある。
The effect control command and the effect control INT signal are first input to the
中継基板77には、主基板31から入力された信号を演出制御基板80に向かう方向にしか通過させない(演出制御基板80から中継基板77への方向には信号を通過させない)信号方向規制手段としての単方向性回路74が搭載されている。単方向性回路として、例えばダイオードやトランジスタが使用される。図3には、ダイオードが例示されている。また、単方向性回路は、信号毎に設けられる。さらに、単方向性回路である出力ポート571を介して主基板31から演出制御コマンドおよび演出制御INT信号が出力されるので、中継基板77から主基板31の内部に向かう信号が規制される。すなわち、中継基板77からの信号は主基板31の内部(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560側)に入り込まない。なお、出力ポート571は、図2に示されたI/Oポート部57の一部である。また、出力ポート571の外側(中継基板77側)に、さらに、単方向性回路である信号ドライバ回路が設けられていてもよい。
The
また、演出制御用CPU101は、スティックコントローラ122のトリガボタン121に対する遊技者の操作行為を検出したことを示す情報信号としての操作検出信号を、トリガセンサ125から、入力ポート106を介して入力する。また、演出制御用CPU101は、プッシュボタン120に対する遊技者の操作行為を検出したことを示す情報信号としての操作検出信号を、プッシュセンサ124から、入力ポート106を介して入力する。また、演出制御用CPU101は、スティックコントローラ122の操作桿に対する遊技者の操作行為を検出したことを示す情報信号としての操作検出信号を、傾倒方向センサユニット123から、入力ポート106を介して入力する。また、演出制御用CPU101は、出力ポート105を介してバイブレータ用モータ126に駆動信号を出力することにより、スティックコントローラ122を振動動作させる。
In addition, the
さらに、演出制御用CPU101は、出力ポート105を介してランプドライバ基板35に対してLEDを駆動する信号を出力する。また、演出制御用CPU101は、出力ポート104を介して音声出力基板70に対して音番号データを出力する。
Furthermore, the
ランプドライバ基板35において、LEDを駆動する信号は、入力ドライバ351を介してLEDドライバ352に入力される。LEDドライバ352は、LEDを駆動する信号にもとづいて枠LED28などの発光体に電流を供給する。
In the
音声出力基板70において、音番号データは、入力ドライバ702を介して音声合成用IC703に入力される。音声合成用IC703は、音番号データに応じた音声や効果音を発生し増幅回路705に出力する。増幅回路705は、音声合成用IC703の出力レベルを、ボリューム706で設定されている音量に応じたレベルに増幅した音声信号をスピーカ27に出力する。音声データROM704には、音番号データに応じた制御データが格納されている。音番号データに応じた制御データは、所定の演出期間(例えば演出図柄の変動期間)における効果音または音声の出力態様を時系列的に示すデータの集まりである。
In the
次に、遊技機の動作について説明する。図4は、主基板31における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が実行するメイン処理を示すフローチャートである。遊技機に対して電源が投入され電力供給が開始されると、リセット信号が入力されるリセット端子の入力レベルがハイレベルになり、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560(具体的には、CPU56)は、プログラムの内容が正当か否か確認するための処理であるセキュリティチェック処理を実行した後、ステップS1以降のメイン処理を開始する。メイン処理において、CPU56は、まず、必要な初期設定を行う。
Next, the operation of the gaming machine will be explained. FIG. 4 is a flow chart showing the main process executed by the
初期設定処理において、CPU56は、まず、割込禁止に設定する(ステップS1)。次に、割込モードを割込モード2に設定し(ステップS2)、スタックポインタにスタックポインタ指定アドレスを設定する(ステップS3)。そして、内蔵デバイスの初期化(内蔵デバイス(内蔵周辺回路)であるCTC(カウンタ/タイマ)およびPIO(パラレル入出力ポート)の初期化など)を行った後(ステップS4)、RAMをアクセス可能状態に設定する(ステップS5)。なお、割込モード2は、CPU56が内蔵する特定レジスタ(Iレジスタ)の値(1バイト)と内蔵デバイスが出力する割込ベクタ(1バイト:最下位ビット0)とから合成されるアドレスが、割込番地を示すモードである。
In the initial setting process, the
次いで、CPU56は、入力ポートを介して入力されるクリアスイッチ(例えば、電源基板に搭載されている。)の出力信号(クリア信号)の状態を確認する(ステップS6)。その確認においてオンを検出した場合には、CPU56は、通常の初期化処理(ステップS10~S15)を実行する。
Next, the
クリアスイッチがオンの状態でない場合には、遊技機への電力供給が停止したときにバックアップRAM領域のデータ保護処理(例えばパリティデータの付加等の電力供給停止時処理)が行われたか否か確認する(ステップS7)。そのような保護処理が行われていないことを確認したら、CPU56は初期化処理を実行する。バックアップRAM領域にバックアップデータがあるか否かは、例えば、電力供給停止時処理においてバックアップRAM領域に設定されるバックアップフラグの状態によって確認される。
If the clear switch is not in the on state, confirm whether or not the data protection processing of the backup RAM area (for example, the processing when the power supply is stopped such as addition of parity data) was performed when the power supply to the game machine was stopped. (step S7). After confirming that such protection processing is not performed, the
電力供給停止時処理が行われたことを確認したら、CPU56は、バックアップRAM領域のデータチェックを行う(ステップS8)。この実施の形態では、データチェックとしてパリティチェックを行う。よって、ステップS8では、算出したチェックサムと、電力供給停止時処理で同一の処理によって算出され保存されているチェックサムとを比較する。不測の停電等の電力供給停止が生じた後に復旧した場合には、バックアップRAM領域のデータは保存されているはずであるから、チェック結果(比較結果)は正常(一致)になる。チェック結果が正常でないということは、バックアップRAM領域のデータが、電力供給停止時のデータとは異なっていることを意味する。そのような場合には、内部状態を電力供給停止時の状態に戻すことができないので、電力供給の停止からの復旧時でない電源投入時に実行される初期化処理を実行する。
After confirming that the power supply stop processing has been performed, the
チェック結果が正常であれば、CPU56は、遊技制御手段の内部状態と演出制御手段等の電気部品制御手段の制御状態を電力供給停止時の状態に戻すための遊技状態復旧処理(ステップS41~S43の処理)を行う。具体的には、ROM54に格納されているバックアップ時設定テーブルの先頭アドレスをポインタに設定し(ステップS41)、バックアップ時設定テーブルの内容を順次作業領域(RAM55内の領域)に設定する(ステップS42)。作業領域はバックアップ電源によって電源バックアップされている。バックアップ時設定テーブルには、作業領域のうち初期化してもよい領域についての初期化データが設定されている。ステップS41およびS42の処理によって、作業領域のうち初期化してはならない部分については、保存されていた内容がそのまま残る。初期化してはならない部分とは、例えば、電力供給停止前の遊技状態を示すデータ(特別図柄プロセスフラグ、確変フラグ、時短フラグなど)、出力ポートの出力状態が保存されている領域(出力ポートバッファ)、未払出賞球数を示すデータが設定されている部分などである。
If the check result is normal, the
また、CPU56は、電力供給復旧時の初期化コマンドとしての停電復旧指定コマンドを送信する(ステップS43)。また、CPU56は、バックアップRAMに保存されている表示結果(通常大当り、確変大当り、突然確変大当り、小当り、またははずれ)を指定した表示結果指定コマンドを演出制御基板80に対して送信する(ステップS44)。そして、ステップS14に移行する。なお、ステップS44において、CPU56は、例えば、後述する特別図柄ポインタの値もバックアップRAMに保存している場合には、第1図柄変動指定コマンドや第2図柄変動指定コマンド(図13参照)も送信するようにしてもよい。この場合、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、第1図柄変動指定コマンドや第2図柄変動指定コマンドを受信したことにもとづいて、第4図柄の変動表示を再開するようにしてもよい。
Further, the
なお、この実施の形態では、バックアップRAM領域には、後述する変動時間タイマの値も保存される。従って、停電復旧した場合には、ステップS44で表示結果指定コマンドが送信された後、保存していた変動時間タイマの値の計測を再開して特別図柄の変動表示が再開されるとともに、保存していた変動時間タイマの値がタイムアウトしたときに、さらに後述する図柄確定指定コマンドが送信される。また、この実施の形態では、バックアップRAM領域には、後述する特別図柄プロセスフラグの値も保存される。従って、停電復旧した場合には、保存されている特別図柄プロセスフラグの値に応じたプロセスから特別図柄プロセス処理が再開される。 In this embodiment, the backup RAM area also stores the value of a variable time timer, which will be described later. Therefore, when the power is restored, after the display result designation command is transmitted in step S44, the measurement of the value of the variable time timer that has been saved is resumed, and the variable display of the special symbols is resumed and saved. When the value of the variable time timer has timed out, a pattern confirmation designation command, which will be described later, is transmitted. In addition, in this embodiment, the backup RAM area also stores the value of a special symbol process flag, which will be described later. Therefore, when the power is restored, the special symbol process is restarted from the process corresponding to the value of the saved special symbol process flag.
なお、停電復旧時に必ず表示結果指定コマンドを送信するのではなく、CPU56は、まず、バックアップRAM領域に保存している変動時間タイマの値が0であるか否かを確認するようにしてもよい。そして、変動時間タイマの値が0でなければ、変動中に停電した場合であると判断して、表示結果指定コマンドを送信するようにし、変動時間タイマが0であれば、停電時に変動中の状態ではなかったと判断して、表示結果指定コマンドを送信しないようにしてもよい。
Instead of always transmitting the display result designation command when power is restored, the
また、CPU56は、まず、バックアップRAM領域に保存している特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が3であるか否かを確認するようにしてもよい。そして、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が3であれば、変動中に停電した場合であると判断して、表示結果指定コマンドを送信するようにし、特別図柄プロセスフラグが3でなければ、停電時に変動中ではなかったと判断して、表示結果指定コマンドを送信しないようにしてもよい。
Also, the
なお、この実施の形態では、バックアップフラグとチェックデータとの双方を用いてバックアップRAM領域のデータが保存されているか否か確認しているが、いずれか一方のみを用いてもよい。すなわち、バックアップフラグとチェックデータとのいずれかを、遊技状態復旧処理を実行するための契機としてもよい。 In this embodiment, both the backup flag and the check data are used to confirm whether or not the data in the backup RAM area is saved, but only one of them may be used. That is, either the backup flag or the check data may be used as a trigger for executing the game state recovery process.
初期化処理では、CPU56は、まず、RAMクリア処理を行う(ステップS10)。なお、RAMクリア処理によって、所定のデータ(例えば、普通図柄当り判定用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値のデータ)は0に初期化されるが、任意の値またはあらかじめ決められている値に初期化するようにしてもよい。また、RAM55の全領域を初期化せず、所定のデータ(例えば、普通図柄当り判定用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値のデータ)をそのままにしてもよい。また、ROM54に格納されている初期化時設定テーブルの先頭アドレスをポインタに設定し(ステップS11)、初期化時設定テーブルの内容を順次作業領域に設定する(ステップS12)。
In the initialization process, the
ステップS11およびS12の処理によって、例えば、普通図柄当り判定用乱数カウンタ、特別図柄バッファ、総賞球数格納バッファ、特別図柄プロセスフラグなど制御状態に応じて選択的に処理を行うためのフラグに初期値が設定される。 By the processing of steps S11 and S12, for example, a random number counter for determining a normal symbol, a special symbol buffer, a buffer for storing the total number of winning balls, a special symbol process flag, etc., are initialized to a flag for selectively performing processing according to the control state. Value is set.
また、CPU56は、サブ基板(主基板31以外のマイクロコンピュータが搭載された基板。)を初期化するための初期化指定コマンド(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が初期化処理を実行したことを示すコマンドでもある。)をサブ基板に送信する(ステップS13)。例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、初期化指定コマンドを受信すると、演出表示装置9において、遊技機の制御の初期化がなされたことを報知するための画面表示、すなわち初期化報知を行う。
In addition, the
また、CPU56は、乱数回路503を初期設定する乱数回路設定処理を実行する(ステップS14)。CPU56は、例えば、乱数回路設定プログラムに従って処理を実行することによって、乱数回路503にランダムRの値を更新させるための設定を行う。
The
そして、ステップS15において、CPU56は、所定時間(例えば4ms)毎に定期的にタイマ割込がかかるように遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に内蔵されているCTCのレジスタの設定を行なう。すなわち、初期値として例えば4msに相当する値が所定のレジスタ(時間定数レジスタ)に設定される。この実施の形態では、4ms毎に定期的にタイマ割込がかかるとする。
Then, in step S15, the
初期化処理の実行(ステップS10~S15)が完了すると、CPU56は、メイン処理で、表示用乱数更新処理(ステップS17)および初期値用乱数更新処理(ステップS18)を繰り返し実行する。表示用乱数更新処理および初期値用乱数更新処理を実行するときには割込禁止状態に設定し(ステップS16)、表示用乱数更新処理および初期値用乱数更新処理の実行が終了すると割込許可状態に設定する(ステップS19)。この実施の形態では、表示用乱数とは、大当りとしない場合の特別図柄の停止図柄を決定するための乱数や大当りとしない場合にリーチとするか否かを決定するための乱数であり、表示用乱数更新処理とは、表示用乱数を発生するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する処理である。また、初期値用乱数更新処理とは、初期値用乱数を発生するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する処理である。この実施の形態では、初期値用乱数とは、普通図柄に関して当りとするか否か決定するための乱数を発生するためのカウンタ(普通図柄当り判定用乱数発生カウンタ)のカウント値の初期値を決定するための乱数である。後述する遊技の進行を制御する遊技制御処理(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が、遊技機に設けられている演出表示装置、可変入賞球装置、球払出装置等の遊技用の装置を、自身で制御する処理、または他のマイクロコンピュータに制御させるために指令信号を送信する処理、遊技装置制御処理ともいう)において、普通図柄当り判定用乱数のカウント値が1周(普通図柄当り判定用乱数の取りうる値の最小値から最大値までの間の数値の個数分歩進したこと)すると、そのカウンタに初期値が設定される。
When the execution of the initialization process (steps S10 to S15) is completed, the
タイマ割込が発生すると、CPU56は、図5に示すステップS20~S34のタイマ割込処理を実行する。タイマ割込処理において、まず、電源断信号が出力されたか否か(オン状態になったか否か)を検出する電源断検出処理を実行する(ステップS20)。電源断信号は、例えば電源基板に搭載されている電源監視回路が、遊技機に供給される電源の電圧の低下を検出した場合に出力する。そして、電源断検出処理において、CPU56は、電源断信号が出力されたことを検出したら、必要なデータをバックアップRAM領域に保存するための電力供給停止時処理を実行する。次いで、入力ドライバ回路58を介して、ゲートスイッチ32a、第1始動口スイッチ13a、第2始動口スイッチ14aおよびカウントスイッチ23の検出信号を入力し、それらの状態判定を行う(スイッチ処理:ステップS21)。
When a timer interrupt occurs, the
次に、CPU56は、第1特別図柄表示器8a、第2特別図柄表示器8b、普通図柄表示器10、第1特別図柄保留記憶表示器18a、第2特別図柄保留記憶表示器18b、普通図柄保留記憶表示器41の表示制御を行う表示制御処理を実行する(ステップS22)。第1特別図柄表示器8a、第2特別図柄表示器8bおよび普通図柄表示器10については、ステップS32,S33で設定される出力バッファの内容に応じて各表示器に対して駆動信号を出力する制御を実行する。
Next, the
また、遊技制御に用いられる普通図柄当り判定用乱数等の各判定用乱数を生成するための各カウンタのカウント値を更新する処理を行う(判定用乱数更新処理:ステップS23)。CPU56は、さらに、初期値用乱数および表示用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する処理を行う(初期値用乱数更新処理,表示用乱数更新処理:ステップS24,S25)。
In addition, processing is performed to update the count value of each counter for generating each judgment random number such as a normal per symbol judgment random number used for game control (judgment random number update processing: step S23). The
さらに、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセス処理を行う(ステップS26)。特別図柄プロセス処理では、第1特別図柄表示器8a、第2特別図柄表示器8bおよび大入賞口を所定の順序で制御するための特別図柄プロセスフラグに従って該当する処理を実行する。CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を、遊技状態に応じて更新する。
Furthermore, the
次いで、普通図柄プロセス処理を行う(ステップS27)。普通図柄プロセス処理では、CPU56は、普通図柄表示器10の表示状態を所定の順序で制御するための普通図柄プロセスフラグに従って該当する処理を実行する。CPU56は、普通図柄プロセスフラグの値を、遊技状態に応じて更新する。
Then, normal design process processing is performed (step S27). In the normal symbol process process, the
また、CPU56は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に演出制御コマンドを送出する処理を行う(演出制御コマンド制御処理:ステップS28)。
Further, the
さらに、CPU56は、例えばホール管理用コンピュータに供給される大当り情報、始動情報、確率変動情報などのデータを出力する情報出力処理を行う(ステップS29)。
Further, the
また、CPU56は、第1始動口スイッチ13a、第2始動口スイッチ14aおよびカウントスイッチ23の検出信号にもとづく賞球個数の設定などを行う賞球処理を実行する(ステップS30)。具体的には、第1始動口スイッチ13a、第2始動口スイッチ14aおよびカウントスイッチ23のいずれかがオンしたことにもとづく入賞検出に応じて、払出制御基板37に搭載されている払出制御用マイクロコンピュータに賞球個数を示す払出制御コマンド(賞球個数信号)を出力する。払出制御用マイクロコンピュータは、賞球個数を示す払出制御コマンドに応じて球払出装置97を駆動する。
Further, the
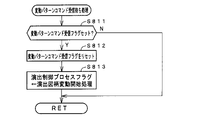
この実施の形態では、出力ポートの出力状態に対応したRAM領域(出力ポートバッファ)が設けられているのであるが、CPU56は、出力ポートの出力状態に対応したRAM領域におけるソレノイドのオン/オフに関する内容を出力ポートに出力する(ステップS31:出力処理)。 In this embodiment, a RAM area (output port buffer) corresponding to the output state of the output port is provided. The content is output to the output port (step S31: output processing).
また、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値に応じて特別図柄の演出表示を行うための特別図柄表示制御データを特別図柄表示制御データ設定用の出力バッファに設定する特別図柄表示制御処理を行う(ステップS32)。
In addition, the
さらに、CPU56は、普通図柄プロセスフラグの値に応じて普通図柄の演出表示を行うための普通図柄表示制御データを普通図柄表示制御データ設定用の出力バッファに設定する普通図柄表示制御処理を行う(ステップS33)。CPU56は、例えば、普通図柄の変動に関する開始フラグがセットされると終了フラグがセットされるまで、普通図柄の変動速度が0.2秒ごとに表示状態(「○」および「×」)を切り替えるような速度であれば、0.2秒が経過する毎に、出力バッファに設定される表示制御データの値(例えば、「○」を示す1と「×」を示す0)を切り替える。また、CPU56は、出力バッファに設定された表示制御データに応じて、ステップS22において駆動信号を出力することによって、普通図柄表示器10における普通図柄の演出表示を実行する。
Furthermore, the
その後、割込許可状態に設定し(ステップS34)、処理を終了する。 After that, the interrupt enabled state is set (step S34), and the process ends.
以上の制御によって、この実施の形態では、遊技制御処理は4ms毎に起動されることになる。なお、遊技制御処理は、タイマ割込処理におけるステップS21~S33(ステップS29を除く。)の処理に相当する。また、この実施の形態では、タイマ割込処理で遊技制御処理が実行されているが、タイマ割込処理では例えば割込が発生したことを示すフラグのセットのみがなされ、遊技制御処理はメイン処理において実行されるようにしてもよい。 By the above control, in this embodiment, the game control process is started every 4 ms. Incidentally, the game control process corresponds to the process of steps S21 to S33 (excluding step S29) in the timer interrupt process. Also, in this embodiment, the game control process is executed in the timer interrupt process, but in the timer interrupt process, for example, only a flag indicating that an interrupt has occurred is set, and the game control process is the main process. may be executed in
図6は、あらかじめ用意された演出図柄の変動パターンを示す説明図である。図6に示すように、この実施の形態では、可変表示結果が「はずれ」であり演出図柄の可変表示態様が「非リーチ」である場合に対応した変動パターンとして、非リーチPA1-1~非リーチPA1-2の変動パターンが用意されている。このうち、非リーチPA1-1は、リーチを伴わず且つ擬似連や滑り演出も伴わない変動パターンであって、短縮変動でない通常変動用の変動パターン(本例では、変動時間12.50秒)である。また、非リーチPA1-2は、リーチを伴わず且つ擬似連や滑り演出も伴わない変動パターンであって、通常変動よりも変動時間が短い短縮変動用の変動パターン(本例では、変動時間2.00秒)である。 FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram showing variation patterns of performance symbols prepared in advance. As shown in FIG. 6, in this embodiment, non-reach PA1-1 to non-reach PA1-1 to non-reach PA1-1 to non-reach PA1-1 to non-reach PA1-1 to non-reach PA1-1 to non-reach PA1-1 to non-reach PA1-1. Variation patterns of reach PA1-2 are prepared. Among these, the non-reach PA1-1 is a variation pattern that does not involve a reach and does not accompany a pseudo-continuation or slip effect, and is a variation pattern for normal variation that is not a shortened variation (in this example, the variation time is 12.50 seconds). is. In addition, the non-reach PA1-2 is a variation pattern that does not involve a reach and does not accompany a pseudo-run or slip effect, and is a variation pattern for shortened variation with a shorter variation time than normal variation (in this example, the variation time is 2 .00 seconds).
なお、この実施の形態では、図6に示すように、非リーチはずれとなる場合には擬似連や滑り演出を伴う変動パターンが含まれない場合を示しているが、非リーチはずれとなる場合にも擬似連や滑り演出を伴う変動パターンを設けるように構成してもよい。 In addition, in this embodiment, as shown in FIG. Also, it may be configured so as to provide a variation pattern accompanied by a pseudo run or a slip performance.
また、可変表示結果が「はずれ」であり演出図柄の可変表示態様が「リーチ」である場合に対応した変動パターンとして、ノーマルPA2-1~ノーマルPA2-2、ノーマルPB2-1~ノーマルPB2-2、スーパーPA3-1~スーパーPA3-2、スーパーPB3-1~スーパーPB3-2の変動パターンが用意されている。なお、図6に示すように、リーチする場合に使用され擬似連の演出を伴う変動パターンのうち、ノーマルPB2-1を用いる場合には、再変動が1回行われる。また、リーチする場合に使用され擬似連の演出を伴う変動パターンのうち、ノーマルPB2-2を用いる場合には、再変動が2回行われる。さらに、リーチする場合に使用され擬似連の演出を伴う変動パターンのうち、スーパーPA3-1~スーパーPA3-2を用いる場合には、再変動が3回行われる。なお、再変動とは、演出図柄の可変表示が開始されてから表示結果が導出表示されるまでに一旦はずれとなる演出図柄を仮停止させた後に演出図柄の可変表示を再度実行することである。 In addition, normal PA2-1 to normal PA2-2, normal PB2-1 to normal PB2-2 are the variation patterns corresponding to the case where the variable display result is "lost" and the variable display mode of the production pattern is "reach". , super PA3-1 to super PA3-2, and super PB3-1 to super PB3-2 are prepared. Incidentally, as shown in FIG. 6, among the variation patterns that are used in the case of reach and are accompanied by pseudo-run effects, when the normal PB2-1 is used, re-variation is performed once. In addition, when normal PB2-2 is used among the variation patterns that are used in the case of reach and are accompanied by pseudo-continue effects, re-variation is performed twice. Furthermore, when super PA3-1 to super PA3-2 are used among the variation patterns that are used in the case of reach and are accompanied by pseudo-continuation effects, re-variation is performed three times. It should be noted that the re-variation is to execute the variable display of the production design again after temporarily stopping the production design that is once lost from the start of the variable display of the production design until the display result is derived and displayed. .
また、図6に示すように、この実施の形態では、特別図柄の可変表示結果が大当り図柄または小当り図柄になる場合に対応した変動パターンとして、ノーマルPA2-3~ノーマルPA2-4、ノーマルPB2-3~ノーマルPB2-4、スーパーPA3-3~スーパーPA3-4、スーパーPB3-3~スーパーPB3-4、特殊PG1-1~特殊PG1-3、特殊PG2-1~特殊PG2-2の変動パターンが用意されている。なお、図6において、特殊PG1-1~特殊PG1-3、特殊PG2-1~特殊PG2-2の変動パターンは、突然確変大当りまたは小当りとなる場合に使用される変動パターンである。また、図6に示すように、突然確変大当りまたは小当りでない場合に使用され擬似連の演出を伴う変動パターンのうち、ノーマルPB2-3を用いる場合には、再変動が1回行われる。また、リーチする場合に使用され擬似連の演出を伴う変動パターンのうち、ノーマルPB2-4を用いる場合には、再変動が2回行われる。さらに、リーチする場合に使用され擬似連の演出を伴う変動パターンのうち、スーパーPA3-3~スーパーPA3-4を用いる場合には、再変動が3回行われる。また、突然確変大当りまたは小当りの場合に使用され擬似連の演出を伴う特殊PG1-3の変動パターンについては、再変動が1回行われる。 In addition, as shown in FIG. 6, in this embodiment, normal PA2-3 to normal PA2-4 and normal PB2 are used as variation patterns corresponding to the case where the variable display result of the special symbols is a big hit symbol or a small winning symbol. -3 to normal PB2-4, super PA3-3 to super PA3-4, super PB3-3 to super PB3-4, special PG1-1 to special PG1-3, special PG2-1 to special PG2-2 fluctuation patterns are provided. In FIG. 6, the variation patterns of special PG1-1 to special PG1-3 and special PG2-1 to special PG2-2 are variation patterns used in the event of a sudden variable probability big win or small win. In addition, as shown in FIG. 6, among the variation patterns accompanied by a simulated run effect which are used when there is no sudden variable probability big win or small win, when normal PB2-3 is used, re-variation is performed once. Further, when normal PB2-4 is used among the variation patterns that are used in the case of reach and are accompanied by pseudo-run effects, re-variation is performed twice. Furthermore, when super PA3-3 to super PA3-4 are used among the variation patterns that are used in the case of reach and are accompanied by pseudo-run effects, re-variation is performed three times. In addition, the variation patterns of the special PG1-3, which are used in the event of a sudden variable probability big hit or a small hit and are accompanied by a pseudo-run effect, are re-varied once.
図7は、各乱数を示す説明図である。各乱数は、以下のように使用される。
(1)ランダム1(MR1):大当りの種類(後述する通常大当り、確変大当り、突然確変大当り)を決定する(大当り種別判定用)
(2)ランダム2(MR2):変動パターンの種類(種別)を決定する(変動パターン種別判定用)
(3)ランダム3(MR3):変動パターン(変動時間)を決定する(変動パターン判定用)
(4)ランダム4(MR4):普通図柄にもとづく当りを発生させるか否か決定する(普通図柄当り判定用)
(5)ランダム5(MR5):ランダム4の初期値を決定する(ランダム4初期値決定用)
FIG. 7 is an explanatory diagram showing each random number. Each random number is used as follows.
(1) Random 1 (MR1): Determines the type of jackpot (normal jackpot, probability variable jackpot, sudden probability jackpot, which will be described later) (for jackpot type determination)
(2) Random 2 (MR2): Determine the type (type) of the fluctuation pattern (for fluctuation pattern type determination)
(3) Random 3 (MR3): Determine the variation pattern (variation time) (for variation pattern determination)
(4) Random 4 (MR4): Determines whether or not to generate a hit based on the normal design (for normal design hit determination)
(5) Random 5 (MR5): Determines the initial value of random 4 (for random 4 initial value determination)
図5に示された遊技制御処理におけるステップS23では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、(1)の大当り種別判定用乱数、および(4)の普通図柄当り判定用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウントアップ(1加算)を行う。すなわち、それらが判定用乱数であり、それら以外の乱数が表示用乱数(ランダム2、ランダム3)または初期値用乱数(ランダム5)である。なお、遊技効果を高めるために、上記の乱数以外の乱数も用いてもよい。また、この実施の形態では、大当り判定用乱数として、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に内蔵されたハードウェア(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560の外部のハードウェアでもよい。)が生成する乱数を用いる。なお、大当り判定用乱数として、ハードウェア乱数ではなく、ソフトウェア乱数を用いてもよい。
At step S23 in the game control process shown in FIG. 5, the
図8(A)は、大当り判定テーブルを示す説明図である。大当り判定テーブルとは、ROM54に記憶されているデータの集まりであって、ランダムRと比較される大当り判定値が設定されているテーブルである。大当り判定テーブルには、通常状態や時短状態(すなわち、確変状態でない遊技状態)において用いられる通常時大当り判定テーブルと、確変状態において用いられる確変時大当り判定テーブルとがある。通常時大当り判定テーブルには、図8(A)の左欄に記載されている各数値が設定され、確変時大当り判定テーブルには、図8(A)の右欄に記載されている各数値が設定されている。図8(A)に記載されている数値が大当り判定値である。
FIG. 8A is an explanatory diagram showing a big hit determination table. The jackpot determination table is a collection of data stored in the
図8(B),(C)は、小当り判定テーブルを示す説明図である。小当り判定テーブルとは、ROM54に記憶されているデータの集まりであって、ランダムRと比較される小当り判定値が設定されているテーブルである。小当り判定テーブルには、第1特別図柄の変動表示を行うときに用いられる小当り判定テーブル(第1特別図柄用)と、第2特別図柄の変動表示を行うときに用いられる小当り判定テーブル(第2特別図柄用)とがある。小当り判定テーブル(第1特別図柄用)には、図8(B)に記載されている各数値が設定され、小当り判定テーブル(第2特別図柄用)には、図8(C)に記載されている各数値が設定されている。また、図8(B),(C)に記載されている数値が小当り判定値である。
FIGS. 8B and 8C are explanatory diagrams showing small hit determination tables. The small hit determination table is a collection of data stored in the
CPU56は、所定の時期に、乱数回路503のカウント値を抽出して抽出値を大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)の値とするのであるが、大当り判定用乱数値が図8(A)に示すいずれかの大当り判定値に一致すると、特別図柄に関して大当り(後述する通常大当り、確変大当り、突然確変大当り)にすることに決定する。また、大当り判定用乱数値が図8(B),(C)に示すいずれかの小当り判定値に一致すると、特別図柄に関して小当りにすることに決定する。なお、図8(A)に示す「確率」は、大当りになる確率(割合)を示す。また、図8(B),(C)に示す「確率」は、小当りになる確率(割合)を示す。また、大当りにするか否か決定するということは、大当り遊技状態に移行させるか否か決定するということであるが、第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bにおける停止図柄を大当り図柄にするか否か決定するということでもある。また、小当りにするか否か決定するということは、小当り遊技状態に移行させるか否か決定するということであるが、第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bにおける停止図柄を小当り図柄にするか否か決定するということでもある。
The
なお、この実施の形態では、図8(B),(C)に示すように、小当り判定テーブル(第1特別図柄用)を用いる場合には300分の1の割合で小当りと決定されるのに対して、小当り判定テーブル(第2特別図柄)を用いる場合には3000分の1の割合で小当りと決定される場合を説明する。従って、この実施の形態では、第1始動入賞口13に始動入賞して第1特別図柄の変動表示が実行される場合には、第2始動入賞口14に始動入賞して第2特別図柄の変動表示が実行される場合と比較して、「小当り」と決定される割合が高い。
In this embodiment, as shown in FIGS. 8B and 8C, when using the small hit determination table (for the first special symbol), the small hit is determined at a rate of 1/300. On the other hand, when using the small hit determination table (second special symbol), the case where the small hit is determined at a rate of 1/3000 will be explained. Therefore, in this embodiment, when the first
図8(D),(E)は、ROM54に記憶されている大当り種別判定テーブル131a,131bを示す説明図である。このうち、図8(D)は、遊技球が第1始動入賞口13に入賞したことにもとづく保留記憶を用いて(すなわち、第1特別図柄の変動表示が行われるとき)大当り種別を決定する場合の大当り種別判定テーブル(第1特別図柄用)131aである。また、図8(E)は、遊技球が第2始動入賞口14に入賞したことにもとづく保留記憶を用いて(すなわち、第2特別図柄の変動表示が行われるとき)大当り種別を決定する場合の大当り種別判定テーブル(第2特別図柄用)131bである。
8(D) and (E) are explanatory diagrams showing the jackpot type determination tables 131a and 131b stored in the
大当り種別判定テーブル131a,131bは、可変表示結果を大当り図柄にする旨の判定がなされたときに、大当り種別判定用の乱数(ランダム1)にもとづいて、大当りの種別を「通常大当り」、「確変大当り」、「突然確変大当り」のうちのいずれかに決定するために参照されるテーブルである。なお、この実施の形態では、図8(D),(E)に示すように、大当り種別判定テーブル131aには「突然確変大当り」に対して5個の判定値が割り当てられている(40分の5の割合で突然確変大当りと決定される)のに対して、大当り種別判定テーブル131bには「突然確変大当り」に対して1個の判定値が割り当てられている(40分の1の割合で突然確変大当りと決定される)場合を説明する。従って、この実施の形態では、第1始動入賞口13に始動入賞して第1特別図柄の変動表示が実行される場合には、第2始動入賞口14に始動入賞して第2特別図柄の変動表示が実行される場合と比較して、「突然確変大当り」と決定される割合が高い。なお、第1特別図柄用の大当り種別判定テーブル131aにのみ「突然確変大当り」を振り分けるようにし、第2特別図柄用の大当り種別判定テーブル131bには「突然確変大当り」の振り分けを行わない(すなわち、第1特別図柄の変動表示を行う場合にのみ、「突然確変大当り」と決定される場合がある)ようにしてもよい。
The jackpot type determination tables 131a and 131b determine the jackpot type as "normal jackpot", " This is a table referred to for determining either the probability variable jackpot” or the “sudden probability variable jackpot”. In addition, in this embodiment, as shown in FIGS. 8(D) and (E), the jackpot type determination table 131a is assigned with five determination values for the "sudden probability variable jackpot" (40 minutes is determined as a sudden variable probability big hit at a rate of 5), one determination value is assigned to the "suddenly variable probability big hit" in the jackpot type determination table 131b (a ratio of 1/40 A case where it is suddenly determined as a probability variable jackpot) will be explained. Therefore, in this embodiment, when the first
この実施の形態では、図8(D),(E)に示すように、大当り種別として、「通常大当り」、「確変大当り」および「突然確変大当り」がある。なお、この実施の形態では、大当り遊技において実行されるラウンド数が15ラウンドおよび2ラウンドの2種類である場合を示しているが、大当り遊技において実行されるラウンド数は、この実施の形態で示したものに限られない。例えば、10ラウンドの大当り遊技に制御する10R確変大当りや、7ラウンドの大当り遊技に制御する7R確変大当り、5ラウンドの大当り遊技に制御する5R確変大当りが設けられていてもよい。また、この実施の形態では、大当り種別が「通常大当り」、「確変大当り」および「突然確変大当り」の3種類である場合を示しているが、3種類にかぎらず、例えば、4種類以上の大当り種別を設けるようにしてもよい。また、逆に、大当り種別が3種類よりも少なくてもよく、例えば、大当り種別として2種類のみ設けられていてもよい。 In this embodiment, as shown in FIGS. 8(D) and (E), the types of jackpots include "normal jackpot", "variable probability jackpot" and "sudden variable probability jackpot". In addition, in this embodiment, the number of rounds executed in the jackpot game is 15 rounds and 2 rounds, but the number of rounds executed in the jackpot game is shown in this embodiment. It is not limited to For example, there may be provided a 10R variable variable jackpot controlled to a 10 round jackpot game, a 7R variable variable jackpot controlled to a 7 round jackpot game, and a 5R variable variable jackpot controlled to a 5 round jackpot game. In addition, in this embodiment, there are three types of jackpot types: "normal jackpot", "probability variable jackpot" and "sudden probability variable jackpot". You may make it provide a jackpot classification. Conversely, the number of jackpot types may be less than three, and for example, only two jackpot types may be provided.
「通常大当り」とは、15ラウンドの大当り遊技状態に制御し、その大当り遊技状態の終了後に時短状態のみに移行させる大当りである(後述するステップS167参照)。そして、時短状態に移行した後、変動表示を所定回数(この実施の形態では100回)終了すると時短状態が終了する(ステップS168,S137~S140参照)。なお、変動表示を所定回数終了する前であっても、次の大当りが発生した場合にも、時短状態を終了する(ステップS132参照)。 "Normal jackpot" is a jackpot controlled to a jackpot game state of 15 rounds and shifted only to a time-saving state after the jackpot game state is completed (see step S167 to be described later). After shifting to the time-saving state, the time-saving state ends when the variable display is completed a predetermined number of times (100 times in this embodiment) (see steps S168, S137 to S140). Even before the variable display is completed a predetermined number of times, the time saving state is terminated even when the next big hit occurs (see step S132).
「確変大当り」とは、15ラウンドの大当り遊技状態に制御し、その大当り遊技状態の終了後に確変状態に移行させる大当りである(この実施の形態では、確変状態に移行されるとともに時短状態にも移行される。後述するステップS169,S170参照)。そして、次の大当りが発生するまで、確変状態および時短状態が継続する(ステップS132参照)。 "Variable probability big hit" is a big hit that is controlled to a 15-round jackpot game state and is shifted to a variable probability state after the end of the jackpot game state (in this embodiment, it is shifted to a variable probability state and also to a time saving state (see steps S169 and S170 to be described later). Then, the variable probability state and the time saving state continue until the next big hit occurs (see step S132).
また、「突然確変大当り」とは、「通常大当り」や「確変大当り」と比較して大入賞口の開放回数が少ない回数(この実施の形態では0.1秒間の開放を2回)まで許容される大当りである。すなわち、「突然確変大当り」となった場合には、2ラウンドの大当り遊技状態に制御される。また、「通常大当り」や「確変大当り」では、1ラウンドあたりの大入賞口の開放時間が29秒と長いのに対して、「突然確変大当り」では1ラウンドあたりの大入賞口の開放時間が0.1秒と極めて短く、大当り遊技中に大入賞口に遊技球が入賞することは殆ど期待できない。そして、この実施の形態では、その突然確変大当り遊技状態の終了後に確変状態に移行される(この実施の形態では、確変状態に移行されるとともに時短状態にも移行される。後述するステップS169,S170参照)。そして、次の大当りが発生するまで、確変状態および時短状態が継続する(ステップS132参照)。 In addition, the "suddenly variable probability big hit" means that the number of openings of the big winning opening is smaller than that of the "normal jackpot" or the "variable probability big hit" (in this embodiment, two openings of 0.1 seconds are allowed). It is a big hit. In other words, when the "sudden probability variation big hit" occurs, the game state is controlled to a 2-round big hit game state. In addition, in the "normal jackpot" and "probable variable jackpot", the opening time of the big prize hole per round is as long as 29 seconds. It is extremely short as 0.1 second, and it is almost impossible to expect the game ball to enter the big winning opening during the big winning game. Then, in this embodiment, after the sudden probability variation big hit game state is completed, the probability variation state is shifted (in this embodiment, the probability variation state is shifted and the time saving state is also shifted. Steps S169, which will be described later, S170). Then, the variable probability state and the time saving state continue until the next big hit occurs (see step S132).
なお、突然確変大当りの態様は、この実施の形態で示したものにかぎられない。例えば、大入賞口の開放回数は通常大当りや突然確変大当りと同じ15回(15ラウンド)とし、大入賞口の開放時間のみ0.1秒と極めて短くするようにしてもよい。 Incidentally, the aspect of the sudden variable probability jackpot is not limited to that shown in this embodiment. For example, the number of openings of the big winning opening may be set to 15 times (15 rounds), which is the same as the normal jackpot and the sudden variable probability jackpot, and only the opening time of the big winning prize gate may be extremely short, 0.1 second.
なお、この実施の形態では、「小当り」となった場合にも、大入賞口の開放が0.1秒間ずつ2回行われ、「突然確変大当り」による大当り遊技状態と同様の制御が行われる。そして、「小当り」となった場合には、大入賞口の2回の開放が終了した後、遊技状態は変化せず、「小当り」となる前の遊技状態が維持される。そのようにすることによって、「突然確変大当り」であるか「小当り」であるかを認識できないようにし、遊技の興趣を向上させている。なお、大当り種別が全て確変大当りであるように構成する場合、小当りを設けなくてもよい。また、大当り種別が全て確変大当りである場合に小当りを設けるように構成する場合には、確変状態(高確率状態)に移行されるのみで時短状態(高ベース状態)を伴わない突然確変大当りを設けるようにすること(大入賞口の開放パターンも突然確変大当りと小当りの場合とで同じにすること)が好ましい。 In this embodiment, even when a "small win" is achieved, the big winning opening is opened twice for 0.1 seconds each, and the same control as the "suddenly variable probability big win" big win game state is performed. will be In the case of a "small win", the game state does not change after the large winning opening is opened twice, and the game state before the "small win" is maintained. By doing so, it is made impossible to recognize whether it is a ``suddenly variable probability big hit'' or a ``small hit'', and the amusement of the game is improved. In addition, when all the big hit types are configured to be variable probability big hits, it is not necessary to provide a small hit. In addition, when all the jackpot types are variable probability big hits, when a small hit is provided, the sudden variable probability big hit is only shifted to the variable probability state (high probability state) and is not accompanied by the time saving state (high base state). (The opening pattern of the big winning opening should be the same for the sudden variable probability big win and the small win).
大当り種別判定テーブル131a,131bには、ランダム1の値と比較される数値であって、「通常大当り」、「確変大当り」、「突然確変大当り」のそれぞれに対応した判定値(大当り種別判定値)が設定されている。CPU56は、ランダム1の値が大当り種別判定値のいずれかに一致した場合に、大当りの種別を、一致した大当り種別判定値に対応する種別に決定する。
In the jackpot type determination tables 131a and 131b, numerical values to be compared with the value of random 1, which are the determination values (jackpot type determination values ) is set. When the value of random 1 matches any of the jackpot type determination values, the
図9(A)~(C)は、大当り用変動パターン種別判定テーブル132A~132Cを示す説明図である。大当り用変動パターン種別判定テーブル132A~132Cは、可変表示結果を大当り図柄にする旨の判定がなされたときに、大当り種別の判定結果に応じて、変動パターン種別を、変動パターン種別判定用の乱数(ランダム2)にもとづいて複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定するために参照されるテーブルである。 FIGS. 9A to 9C are explanatory diagrams showing big hit variation pattern type determination tables 132A to 132C. The big hit variation pattern type determination tables 132A to 132C set the variation pattern type to a random number for determining the variation pattern type according to the determination result of the big win type when it is determined that the variable display result is a big win pattern. It is a table referred to for determining one of a plurality of types based on (random 2).
各大当り用変動パターン種別判定テーブル132A~132Cには、変動パターン種別判定用の乱数(ランダム2)の値と比較される数値(判定値)であって、ノーマルCA3-1~ノーマルCA3-2、スーパーCA3-3、特殊CA4-1、特殊CA4-2の変動パターン種別のいずれかに対応する判定値が設定されている。 Each big hit variation pattern type determination table 132A to 132C contains a numerical value (determination value) to be compared with the value of the random number (random 2) for determining the variation pattern type, normal CA3-1 to normal CA3-2, A determination value corresponding to one of the variation pattern types of super CA3-3, special CA4-1, and special CA4-2 is set.
例えば、大当り種別が「通常大当り」である場合に用いられる図9(A)に示す大当り用変動パターン種別判定テーブル132Aと、大当り種別が「確変大当り」である場合に用いられる図9(B)に示す大当り用変動パターン種別判定テーブル132Bとで、ノーマルCA3-1~ノーマルCA3-2、スーパーCA3-3の変動パターン種別に対する判定値の割り当てが異なっている。 For example, a jackpot variation pattern type determination table 132A shown in FIG. 9A used when the jackpot type is "normal jackpot" and FIG. 9B used when the jackpot type is "probability variable jackpot" 2. Assignment of determination values to the variation pattern types of normal CA3-1 to normal CA3-2 and super CA3-3 is different from the big hit variation pattern type determination table 132B shown in FIG.
このように、大当り種別に応じて選択される大当り用変動パターン種別判定テーブル132A~132Cを比較すると、大当り種別に応じて各変動パターン種別に対する判定値の割り当てが異なっている。また、大当り種別に応じて異なる変動パターン種別に対して判定値が割り当てられている。よって、大当り種別を複数種類のうちのいずれにするかの決定結果に応じて、異なる変動パターン種別に決定することができ、同一の変動パターン種別に決定される割合を異ならせることができる。 In this way, when comparing the big-hit variation pattern type determination tables 132A to 132C selected according to the big-hit type, allocation of the determination value to each variation pattern type differs according to the big-hit type. In addition, determination values are assigned to different variation pattern types according to the jackpot types. Therefore, different variation pattern types can be determined according to the result of determining which one of a plurality of types the jackpot type should be, and the rate of determining the same variation pattern type can be varied.
なお、図9(A),(B)に示すように、この実施の形態では、「通常大当り」または「確変大当り」である場合には、変動パターン種別判定用の乱数(ランダム2)の値が150~251であれば、少なくともスーパーリーチ(スーパーリーチA、スーパーリーチB)を伴う変動表示が実行されることがわかる。 In addition, as shown in FIGS. 9A and 9B, in this embodiment, in the case of "normal jackpot" or "probability variable jackpot", the value of the random number (random 2) for determining the variation pattern type is 150 to 251, variable display with at least super reach (super reach A, super reach B) is executed.
また、スーパーリーチ大当りについて、擬似連を伴う変動パターン種別(スーパーPA3-3、スーパーPA3-4の変動パターンを含む変動パターン種別)と、擬似連を伴わない変動パターン種別(スーパーPB3-3、スーパーPB3-4の変動パターンを含む変動パターン種別)とに分けてもよい。この場合、通常大当り用の大当り用変動パターン種別判定テーブル132Aおよび確変大当り用の大当り用変動パターン種別判定テーブル132Bの両方において、スーパーリーチかつ擬似連を伴う変動パターン種別と、スーパーリーチかつ擬似連を伴わない変動パターン種別とが割り当てられることになる。 In addition, regarding the super reach jackpot, variation pattern types with pseudo-runs (variation pattern types including super PA3-3 and super PA3-4 variation patterns) and variation pattern types without pseudo-runs (super PB3-3, super Variation pattern type including variation pattern of PB3-4) may be divided into. In this case, in both the jackpot variation pattern type determination table 132A for the normal jackpot and the jackpot variation pattern type determination table 132B for the probability variable jackpot, the variation pattern type accompanied by super reach and pseudo-run and the super reach and pseudo-run A variation pattern type that does not accompany is assigned.
また、大当り種別が「突然確変大当り」である場合に用いられる大当り用変動パターン種別判定テーブル132Cでは、例えば、特殊CA4-1、特殊CA4-2といった大当り種別が「突然確変大当り」以外である場合には判定値が割り当てられない変動パターン種別に対して、判定値が割り当てられている。よって、可変表示結果が「大当り」となり大当り種別が「突然確変大当り」となることに応じて突然確変大当り状態に制御する場合には、通常大当りや確変大当りによる大当り状態に制御する場合とは異なる変動パターン種別に決定することができる。 In addition, in the jackpot variation pattern type determination table 132C used when the jackpot type is "suddenly variable probability big hit", for example, when the jackpot type such as special CA4-1, special CA4-2 is other than "suddenly variable probability big hit" A judgment value is assigned to a variation pattern type to which no judgment value is assigned. Therefore, when the variable display result is "big hit" and the big hit type is "suddenly variable probability big hit", when suddenly controlling to the variable probability big hit state, it is different from the case of controlling to the big hit state by the normal big hit or the variable probability big hit. It can be determined by the variation pattern type.
また、図9(D)は、小当り用変動パターン種別判定テーブル132Dを示す説明図である。小当り用変動パターン種別判定テーブル132Dは、可変表示結果を小当り図柄にする旨の判定がなされたときに、変動パターン種別を、変動パターン種別判定用の乱数(ランダム2)にもとづいて複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定するために参照されるテーブルである。なお、この実施の形態では、図9(D)に示すように、小当りとすることに決定されている場合には、変動パターン種別として特殊CA4-1が決定される場合が示されている。 Further, FIG. 9(D) is an explanatory diagram showing the small winning variation pattern type determination table 132D. Small winning variation pattern type determination table 132D, when it is determined that the variable display result is to be a small winning pattern, a plurality of types of variation pattern types based on the random number (random 2) for determining the variation pattern type. It is a table referred to in order to determine one of In addition, in this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 9(D), when it is determined to be a small hit, the case where special CA4-1 is determined as the variation pattern type is shown. .
図10(A)~(C)は、はずれ用変動パターン種別判定テーブル135A~135Cを示す説明図である。このうち、図10(A)は、遊技状態が通常状態であるとともに合算保留記憶数が3未満である場合に用いられるはずれ用変動パターン種別判定テーブル135Aを示している。また、図10(B)は、遊技状態が通常状態であるとともに合算保留記憶数が3以上である場合に用いられるはずれ用変動パターン種別判定テーブル135Bを示している。また、図10(C)は、遊技状態が確変状態や時短状態である場合に用いられるはずれ用変動パターン種別判定テーブル135Cを示している。はずれ用変動パターン種別判定テーブル135A~135Cは、可変表示結果をはずれ図柄にする旨の判定がなされたときに、変動パターン種別を、変動パターン種別判定用の乱数(ランダム2)にもとづいて複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定するために参照されるテーブルである。 FIGS. 10A to 10C are explanatory diagrams showing the deviation pattern type determination tables 135A to 135C. Among them, FIG. 10A shows the losing variation pattern type determination table 135A used when the game state is the normal state and the total pending storage number is less than three. Also, FIG. 10B shows the losing variation pattern type determination table 135B used when the gaming state is the normal state and the total pending storage number is 3 or more. In addition, FIG. 10C shows the variation pattern type determination table 135C for loss used when the game state is the variable probability state or the time saving state. Loss variation pattern type determination tables 135A to 135C select a plurality of types of variation pattern types based on random numbers (random 2) for determining the variation pattern type when it is determined that the variable display result is to be a lost pattern. It is a table referred to in order to determine one of
各はずれ用変動パターン種別判定テーブル135A~135Bには、変動パターン種別判定用の乱数(ランダム2)の値と比較される数値(判定値)であって、非リーチCA2-1~非リーチCA2-2、ノーマルCA2-3~ノーマルCA2-4、スーパーCA2-5の変動パターン種別のいずれかに対応する判定値が設定されている。 Each outlier variation pattern type determination table 135A-135B contains a numerical value (determination value) to be compared with the value of the random number (random 2) for determining the variation pattern type, non-reach CA2-1 to non-reach CA2- 2. A determination value corresponding to one of the variation pattern types of normal CA2-3 to normal CA2-4 and super CA2-5 is set.
なお、図10(A),(B)に示すように、この実施の形態では、はずれであるとともに遊技状態が通常状態である場合には、変動パターン種別判定用の乱数(ランダム2)の値が230~251であれば、合算保留記憶数にかかわらず、少なくともスーパーリーチ(スーパーリーチA、スーパーリーチB)を伴う変動表示が実行されることがわかる。 Incidentally, as shown in FIGS. 10 (A) and (B), in this embodiment, when the game state is normal state while being out, the value of the random number (random 2) for determining the variation pattern type is 230 to 251, variable display with at least super reach (super reach A, super reach B) is executed regardless of the total pending storage number.
また、図10(A)、(B)に示すように、この実施の形態では、はずれであるとともに遊技状態が通常状態である場合には、変動パターン種別判定用の乱数(ランダム2)の値が1~89であれば、合算保留記憶数にかかわらず、少なくともリーチを伴わない(擬似連や滑り演出などの演出も伴わない)通常変動の変動表示が実行されること(非リーチCA2-1の変動パターン種別となることから、後述する図12に示すように非リーチ通常変動の非リーチPA1-1の変動パターンとなること)がわかる。そのようなテーブル構成により、この実施の形態では、判定テーブル(はずれ用変動パターン種別判定テーブル135A,135B)は、リーチ用可変表示パターン(リーチを伴う変動パターン)以外の可変表示パターンのうちの少なくとも一部に対して、保留記憶手段(第1保留記憶バッファや第2保留記憶バッファ)が記憶する権利の数(第1保留記憶数や第2保留記憶数、合算保留記憶数)にかかわらず、共通の判定値(図10(A),(B)に示す例では1~89)が割り当てられるように構成されている。なお、「リーチ用可変表示パターン以外の可変表示パターン」とは、この実施の形態で示したように、例えば、リーチを伴わず、擬似連や滑り演出などの演出も伴わず、可変表示結果が大当りとならない場合に用いられる可変表示パターン(変動パターン)のことである。 Further, as shown in FIGS. 10(A) and (B), in this embodiment, when the game state is a normal state with a loss, the value of the random number (random 2) for determining the variation pattern type is 1 to 89, regardless of the number of total pending memories, at least the variable display of normal variation without reach (without performance such as pseudo run or slip performance) is executed (non-reach CA2-1 , it can be seen that the fluctuation pattern of non-reach PA1-1 of non-reach normal fluctuation as shown in FIG. 12 described later). With such a table configuration, in this embodiment, the determination tables (loss variation pattern type determination tables 135A and 135B) include at least Regardless of the number of rights stored by the reserved storage means (first reserved storage buffer or second reserved storage buffer) (first reserved storage number, second reserved storage number, total reserved storage number), Common judgment values (1 to 89 in the examples shown in FIGS. 10A and 10B) are assigned. It should be noted that the "variable display pattern other than the variable display pattern for reach" means that, as shown in this embodiment, for example, the variable display result is not accompanied by a reach, pseudo run or slide effect. It is a variable display pattern (fluctuation pattern) that is used when there is no big hit.
図11(A),(B)は、ROM54に記憶されている当り変動パターン判定テーブル137A~137Bを示す説明図である。当り変動パターン判定テーブル137A~137Bは、可変表示結果を「大当り」や「小当り」にする旨の判定がなされたときに、大当り種別や変動パターン種別の決定結果などに応じて、変動パターン判定用の乱数(ランダム3)にもとづいて、変動パターンを複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定するために参照されるテーブルである。各当り変動パターン判定テーブル137A~137Bは、変動パターン種別の決定結果に応じて、使用テーブルとして選択される。すなわち、変動パターン種別をノーマルCA3-1~ノーマルCA3-2、スーパーCA3-3のいずれかにする旨の決定結果に応じて当り変動パターン判定テーブル137Aが使用テーブルとして選択され、変動パターン種別を特殊CA4-1、特殊CA4-2のいずれかにする旨の決定結果に応じて当り変動パターン判定テーブル137Bが使用テーブルとして選択される。各当り変動パターン判定テーブル137A~137Bは、変動パターン種別に応じて、変動パターン判定用の乱数(ランダム3)の値と比較される数値(判定値)であって、演出図柄の可変表示結果が「大当り」である場合に対応した複数種類の変動パターンのいずれかに対応するデータ(判定値)を含む。
FIGS. 11A and 11B are explanatory diagrams showing hit variation pattern determination tables 137A to 137B stored in the
図12は、ROM54に記憶されているはずれ変動パターン判定テーブル138Aを示す説明図である。はずれ変動パターン判定テーブル138Aは、可変表示結果を「はずれ」にする旨の判定がなされたときに、変動パターン種別の決定結果に応じて、変動パターン判定用の乱数(ランダム3)にもとづいて、変動パターンを複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定するために参照されるテーブルである。はずれ変動パターン判定テーブル138Aは、変動パターン種別の決定結果に応じて、使用テーブルとして選択される。
FIG. 12 is an explanatory diagram showing the deviation variation pattern determination table 138A stored in the
図13および図14は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が送信する演出制御コマンドの内容の一例を示す説明図である。図13および図14に示す例において、コマンド80XX(H)は、特別図柄の可変表示に対応して演出表示装置9において可変表示される演出図柄の変動パターンを指定する演出制御コマンド(変動パターンコマンド)である(それぞれ変動パターンXXに対応)。つまり、図6に示された使用されうる変動パターンのそれぞれに対して一意な番号を付した場合に、その番号で特定される変動パターンのそれぞれに対応する変動パターンコマンドがある。なお、「(H)」は16進数であることを示す。また、変動パターンを指定する演出制御コマンドは、変動開始を指定するためのコマンドでもある。従って、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、コマンド80XX(H)を受信すると、演出表示装置9において演出図柄の可変表示を開始するように制御する。
13 and 14 are explanatory diagrams showing an example of the content of the effect control command transmitted by the
コマンド8C01(H)~8C05(H)は、大当りとするか否か、小当りとするか否か、および大当り種別を示す演出制御コマンドである。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、コマンド8C01(H)~8C05(H)の受信に応じて演出図柄の表示結果を決定するので、コマンド8C01(H)~8C05(H)を表示結果指定コマンドという。
Commands 8C01(H) to 8C05(H) are effect control commands indicating whether or not to make a big hit, whether or not to make a small hit, and the type of big hit. Since the
コマンド8D01(H)は、第1特別図柄の可変表示(変動)を開始することを示す演出制御コマンド(第1図柄変動指定コマンド)である。コマンド8D02(H)は、第2特別図柄の可変表示(変動)を開始することを示す演出制御コマンド(第2図柄変動指定コマンド)である。第1図柄変動指定コマンドと第2図柄変動指定コマンドとを特別図柄特定コマンド(または図柄変動指定コマンド)と総称することがある。なお、第1特別図柄の可変表示を開始するのか第2特別図柄の可変表示を開始するのかを示す情報を、変動パターンコマンドに含めるようにしてもよい。 The command 8D01 (H) is an effect control command (first symbol variation designation command) indicating to start variable display (variation) of the first special symbol. The command 8D02 (H) is an effect control command (second symbol variation designation command) indicating to start variable display (variation) of the second special symbol. The first symbol variation specification command and the second symbol variation specification command may be collectively called a special symbol specific command (or symbol variation specification command). The variation pattern command may include information indicating whether to start the variable display of the first special symbol or to start the variable display of the second special symbol.
コマンド8F00(H)は、第4図柄の可変表示(変動)を終了して表示結果(停止図柄)を導出表示することを示す演出制御コマンド(図柄確定指定コマンド)である。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、図柄確定指定コマンドを受信すると、第4図柄の可変表示(変動)を終了して表示結果を導出表示する。
Command 8F00(H) is an effect control command (symbol determination designation command) indicating that the variable display (fluctuation) of the fourth symbol is terminated and the display result (stop symbol) is derived and displayed. When the
コマンド9000(H)は、遊技機に対する電力供給が開始されたときに送信される演出制御コマンド(初期化指定コマンド:電源投入指定コマンド)である。コマンド9200(H)は、遊技機に対する電力供給が再開されたときに送信される演出制御コマンド(停電復旧指定コマンド)である。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、遊技機に対する電力供給が開始されたときに、バックアップRAMにデータが保存されている場合には、停電復旧指定コマンドを送信し、そうでない場合には、初期化指定コマンドを送信する。
Command 9000 (H) is an effect control command (initialization designation command: power-on designation command) transmitted when power supply to the gaming machine is started. Command 9200 (H) is an effect control command (power failure recovery designation command) transmitted when the power supply to the gaming machine is restarted. The
コマンド9F00(H)は、客待ちデモンストレーションを指定する演出制御コマンド(客待ちデモ指定コマンド)である。 Command 9F00(H) is an effect control command (customer waiting demonstration designation command) that designates a customer waiting demonstration.
コマンドA001,A002(H)は、ファンファーレ画面を表示すること、すなわち大当り遊技の開始を指定する演出制御コマンド(大当り開始指定コマンド:ファンファーレ指定コマンド)である。この実施の形態では、大当りの種類に応じて、大当り開始指定コマンドまたは小当り/突然確変大当り開始指定コマンドが用いられる。具体的には、「通常大当り」や「確変大当り」である場合には大当り開始指定コマンド(A001(H))が用いられ、「突然確変大当り」や「小当り」である場合には小当り/突然確変大当り開始指定コマンド(A002(H))が用いられる。なお、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、突然大当りである場合に突然確変大当り開始指定用のファンファーレ指定コマンドを送信するものの、小当りである場合にはファンファーレ指定コマンドを送信しないように構成してもよい。
Commands A001 and A002 (H) are effect control commands (big hit start designation command: fanfare designation command) for designating the start of a big hit game, that is, to display a fanfare screen. In this embodiment, a jackpot start designation command or a small hit/sudden probability variable jackpot start designation command is used according to the type of jackpot. Specifically, in the case of "normal big hit" or "probability variable big hit", a big hit start designation command (A001 (H)) is used, and in the case of "sudden probability variable big hit" or "small hit", a small hit / A sudden variable probability jackpot start designation command (A002 (H)) is used. Incidentally, the
コマンドA1XX(H)は、XXで示す回数目(ラウンド)の大入賞口開放中の表示を示す演出制御コマンド(大入賞口開放中指定コマンド)である。また、A2XX(H)は、XXで示す回数目(ラウンド)の大入賞口閉鎖を示す演出制御コマンド(大入賞口開放後指定コマンド)である。 The command A1XX(H) is an effect control command (command for specifying during the opening of the big winning opening) that indicates the display during the opening of the big winning opening in the number of times (round) indicated by XX. A2XX(H) is an effect control command (designated command after opening the big winning opening) indicating closing of the big winning opening of the number of times (round) indicated by XX.
コマンドA301(H)は、大当り終了画面を表示すること、すなわち大当り遊技の終了を指定する演出制御コマンド(大当り終了指定コマンド:エンディング1指定コマンド)である。なお、大当り終了指定コマンド(A301(H))は、「通常大当り」や「確変大当り」による大当り遊技を終了する場合に用いられる。コマンドA302(H)は、小当りの遊技の終了または突然確変大当りの遊技の終了を指定する演出制御コマンド(小当り/突然確変大当り終了指定コマンド:エンディング2指定コマンド)である。なお、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、突然確変大当りである場合に突然確変大当り終了指定用のエンディング指定コマンドを送信するものの、小当りである場合にはエンディング指定コマンドを送信しないように構成してもよい。
The command A301 (H) is an effect control command (jackpot end designation command: ending 1 designation command) for designating the end of the jackpot game, that is, to display the jackpot end screen. Incidentally, the jackpot end designation command (A301 (H)) is used to end a jackpot game based on the "normal jackpot" or "probability variable jackpot". The command A302 (H) is an effect control command (small hit/suddenly variable probability big hit end designation command: Ending 2 designation command) that designates the end of the game of the small hit or the end of the game of the sudden variable probability big hit. In addition, the
コマンドB000(H)は、遊技状態が通常状態であるときの背景表示を指定する演出制御コマンド(通常状態背景指定コマンド)である。コマンドB001(H)は、遊技状態が確変状態であるときの背景表示を指定する演出制御コマンド(確変状態背景指定コマンド)である。コマンドB002(H)は、遊技状態が時短状態であるときの背景表示を指定する演出制御コマンド(時短状態背景指定コマンド)である。 The command B000 (H) is an effect control command (normal state background designation command) for designating the background display when the game state is the normal state. Command B001 (H) is an effect control command (variable probability state background designation command) for designating the background display when the game state is the variable probability state. Command B002 (H) is an effect control command (time saving state background designation command) that designates the background display when the game state is the time saving state.
コマンドC000(H)は、第1保留記憶数が1増加したことを指定する演出制御コマンド(第1保留記憶数加算指定コマンド)である。コマンドC100(H)は、第2保留記憶数が1増加したことを指定する演出制御コマンド(第2保留記憶数加算指定コマンド)である。コマンドC200(H)は、第1保留記憶数が1減少したことを指定する演出制御コマンド(第1保留記憶数減算指定コマンド)である。コマンドC300(H)は、第2保留記憶数が1減少したことを指定する演出制御コマンド(第2保留記憶数減算指定コマンド)である。 Command C000 (H) is an effect control command (first reserved memory number addition designation command) that designates that the first reserved memory number is increased by one. Command C100 (H) is an effect control command (second reserved memory number addition designation command) that designates that the second reserved memory number is increased by one. Command C200 (H) is an effect control command (first reserved memory number subtraction designation command) that designates that the first reserved memory number has decreased by one. Command C300 (H) is an effect control command (second reserved memory number subtraction designation command) that designates that the second reserved memory number has decreased by one.
なお、この実施の形態では、保留記憶情報として、第1保留記憶数と第2保留記憶数とについて、それぞれ保留記憶数が増加または減少したことを示す演出制御コマンド(第1保留記憶数加算指定コマンド、第2保留記憶数加算指定コマンド、第1保留記憶数減算指定コマンド、第2保留記憶数減算指定コマンド)を送信する場合を示しているが、保留記憶情報の形態は、この実施の形態で示したものにかぎらず、例えば、以下のような態様の保留記憶情報を送信するようにしてもよい。 In addition, in this embodiment, as the reserved memory information, for the first reserved memory number and the second reserved memory number, an effect control command (designated to add the first reserved memory number) indicating that the reserved memory number has increased or decreased command, second reserved memory number addition designation command, first reserved memory number subtraction designation command, second reserved memory number subtraction designation command), but the form of the reserved memory information is the same as in this embodiment. In addition to the information shown in , for example, the following forms of pending storage information may be transmitted.
(1)保留記憶情報として、1つのコマンドのみを送信し、その1つのコマンドにおいて、第1保留記憶と第2保留記憶とのいずれが増加したかを指定するとともに、増加した方の保留記憶数(第1保留記憶数または第2保留記憶数)をEXTデータとして設定して送信するようにしてもよい。 (1) Only one command is transmitted as the reserved memory information, and in that one command, which of the first reserved memory and the second reserved memory is increased is specified, and the number of the increased reserved memory is specified. (First reserved storage number or second reserved storage number) may be set as EXT data and transmitted.
(2)保留記憶情報として、1つのコマンドのみを送信し、その1つのコマンドにおいて、第1保留記憶と第2保留記憶とのいずれが増加したかを指定するとともに、合算保留記憶数をEXTデータとして設定して送信するようにしてもよい。 (2) Send only one command as the reserved memory information, specify which of the first reserved memory and the second reserved memory has increased in the one command, and specify the total number of reserved memories as EXT data. may be set as and transmitted.
(3)保留記憶情報として、第1始動入賞口13と第2始動入賞口14とのいずれに始動入賞したか(第1保留記憶と第2保留記憶とのいずれが増加したか)を指定する演出制御コマンド(第1始動入賞指定コマンド、第2始動入賞指定コマンド)を送信するとともに、それとは別に保留記憶数を指定する保留記憶数指定コマンドを送信するようにし、その保留記憶数指定コマンドにおいて合算保留記憶数をEXTデータとして設定して送信するようにしてもよい。
(3) Designate which of the first start
(4)保留記憶情報として、第1始動入賞口13と第2始動入賞口14とのいずれに始動入賞したか(第1保留記憶と第2保留記憶とのいずれが増加したか)を指定する演出制御コマンド(第1始動入賞指定コマンド、第2始動入賞指定コマンド)を送信するとともに、それとは別に保留記憶数を指定する保留記憶数指定コマンドを送信するようにし、その保留記憶数指定コマンドにおいて増加した方の保留記憶数(第1保留記憶数または第2保留記憶数)をEXTデータとして設定して送信するようにしてもよい。
(4) Designate which of the first start
コマンドC4XX(H)およびコマンドC6XX(H)は、入賞時判定結果の内容を示す演出制御コマンド(入賞時判定結果指定コマンド)である。このうち、コマンドC4XX(H)は、入賞時判定結果のうち、大当りとなるか否かや、小当りとなるか否か、大当りの種別の判定結果を示す演出制御コマンド(図柄指定コマンド)である。また、コマンドC6XX(H)は、入賞時判定結果のうち、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値がいずれの判定値の範囲となるかの判定結果(変動パターン種別の判定結果)を示す演出制御コマンド(変動カテゴリコマンド)である。 The command C4XX(H) and the command C6XX(H) are effect control commands (winning determination result specification commands) indicating the content of the winning determination result. Of these commands, the command C4XX (H) is an effect control command (symbol designation command) indicating whether or not a big hit will be made, whether or not a small win will be made, and the judgment result of the type of big win among the judgment results at the time of winning. be. In addition, the command C6XX (H) is a production control command indicating the determination result (variation pattern type determination result) of which range of determination values the value of the random number for determining the variation pattern type is included in the winning determination result. (variation category command).
この実施の形態では、後述する入賞時演出処理(図22参照)において、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、始動入賞時に、大当りとなるか否かや、小当りとなるか否か、大当りの種別、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値がいずれの判定値の範囲にとなるかを判定する。そして、図柄指定コマンドのEXTデータに、大当りや小当りとなることを指定する値や、大当りの種別を指定する値を設定し、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して送信する制御を行う。また、変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータに判定結果としての判定値の範囲を指定する値を設定し、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して送信する制御を行う。なお、この実施の形態では、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、図柄指定コマンドに設定されている値にもとづいて、表示結果が大当りや小当りとなるか否か、大当りの種別を認識できるとともに、変動カテゴリコマンドにもとづいて、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が所定の判定値となる場合には変動パターン種別を認識できる。
In this embodiment, in the winning performance process (see FIG. 22), which will be described later, the
図15は、図柄指定コマンドの内容の一例を示す説明図である。図15に示すように、この実施の形態では、大当りや小当りとなるか否かと、大当りの種別とに応じて、EXTデータが設定され、図柄指定コマンドが送信される。 FIG. 15 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of the content of the design designation command. As shown in FIG. 15, in this embodiment, EXT data is set according to whether it will be a big win or a small win and the type of the big win, and a symbol designation command is transmitted.
例えば、後述する入賞時演出処理において、「はずれ」となると判定された場合には、CPU56は、EXTデータに「00(H)」を設定した図柄指定コマンド(図柄1指定コマンド)を送信する。また、例えば、「通常大当り」となると判定された場合には、CPU56は、EXTデータに「01(H)」を設定した図柄指定コマンド(図柄2指定コマンド)を送信する。また、例えば、「確変大当り」となると判定された場合には、CPU56は、EXTデータに「02(H)」を設定した図柄指定コマンド(図柄3指定コマンド)を送信する。また、例えば、「突然確変大当り」となると判定された場合には、CPU56は、EXTデータに「03(H)」を設定した図柄指定コマンド(図柄4指定コマンド)を送信する。また、例えば、「小当り」となると判定された場合には、CPU56は、EXTデータに「04(H)」を設定した図柄指定コマンド(図柄5指定コマンド)を送信する。なお、図柄指定コマンドに設定されるEXTデータと、表示結果指定コマンドに設定されるEXTデータとを共通化してもよい。そのように構成すれば、図柄指定コマンドを設定する際と表示結果指定コマンドを設定する際とで、読み出すデータを共通化することができる。
For example, when it is determined to be "lost" in the winning effect process described later, the
図16および図17は、変動カテゴリコマンドの内容の一例を示す説明図である。図16および図17に示すように、この実施の形態では、いずれの遊技状態であるかと、特別図柄や演出図柄の表示結果がいずれの表示結果となるかと、始動入賞時に変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値がいずれの判定値の範囲になると判定したとかとに応じて、EXTデータに値が設定され、変動カテゴリコマンドが送信される。 16 and 17 are explanatory diagrams showing an example of the content of the variable category command. As shown in FIGS. 16 and 17, in this embodiment, the game state, the display result of the special symbol and the effect symbol, and the random number for determining the variation pattern type at the time of starting winning A value is set in the EXT data and a variation category command is transmitted according to which judgment value range the value of is judged to fall within.
例えば、始動入賞時に、遊技状態が通常状態且つはずれとなると判定した場合、後述する入賞時演出処理のステップS232において、CPU56は、まず、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が1~89となるか否かを判定する。変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が1~89となる場合には、CPU56は、EXTデータに「00(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ1コマンドを送信する。なお、この実施の形態では、遊技状態が通常状態である場合には、合算保留記憶数にかかわらず、判定値1~89の範囲には非リーチCA2-1の変動パターン種別が共通に割り当てられているのであるから、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、変動カテゴリ1コマンドを受信したことにもとづいて、少なくとも変動パターン種別が非リーチCA2-1となることを認識することができる。次いで、CPU56は、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が90~99となる場合には、EXTデータに「01(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ2コマンドを送信する。次いで、CPU56は、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が100~169となる場合には、EXTデータに「02(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ3コマンドを送信する。次いで、CPU56は、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が170~199となる場合には、EXTデータに「03(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ4コマンドを送信する。次いで、CPU56は、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が200~214となる場合には、EXTデータに「04(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ5コマンドを送信する。次いで、CPU56は、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が215~229となる場合には、EXTデータに「05(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ6コマンドを送信する。次いで、CPU56は、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が230~251となる場合には、EXTデータに「06(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ7コマンドを送信する。なお、この実施の形態では、遊技状態が通常状態である場合には、合算保留記憶数にかかわらず、判定値230~251の範囲にはスーパーCA2-5の変動パターン種別が共通に割り当てられているのであるから、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、変動カテゴリ7コマンドを受信したことにもとづいて、少なくとも変動パターン種別がスーパーCA2-5となることを認識することができる。
For example, when it is determined that the game state is the normal state and is out of the game at the time of starting winning, in step S232 of the winning effect processing described later, the
なお、上記のいずれの変動カテゴリに属するかを判定するために用いられる閾値89、99、169、199、214および229は、具体的には、図10(A),(B)に示すはずれ用変動パターン種別判定テーブルにおける各変動パターン種別に割り当てられた判定値の範囲の境界となりうる値をピックアップして導き出されたものである。このことは、以降の変動カテゴリ8~9,21~29についても同様であり、図9(A)~(D)や図10(C)に示す変動パターン種別判定テーブルにおける各変動パターン種別に割り当てられた判定値の範囲の境界となりうる値をピックアップしてカテゴリ判定のために用いられる閾値が導き出される。
Note that the
また、例えば、始動入賞時に、遊技状態が確変状態または時短状態且つはずれとなると判定した場合、後述する入賞時演出処理のステップS232において、CPU56は、まず、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が1~219となるか否かを判定する。変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が1~219となる場合(すなわち、非リーチCA2-2の変動パターン種別となる場合)には、CPU56は、EXTデータに「07(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ8コマンドを送信する。次いで、CPU56は、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が220~251となる場合(すなわち、スーパーCA2-5の変動パターン種別となる場合)には、EXTデータに「08(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ9コマンドを送信する。
Also, for example, when it is determined that the game state is a probability variable state or a time saving state and a loss at the time of starting winning, in step S232 of the winning effect processing described later, the
なお、遊技状態が確変状態や時短状態である場合にも、判定値230~251の範囲にスーパーCA2-5の変動パターン種別を割り当てるようにしてもよい。そのようにすれば、遊技状態にかかわらず、スーパーCA2-5の変動パターン種別に対して共通の判定値が割り当てられるようにすることができる。そのため、後述する入賞時演出の処理のステップS232の処理を実行する際に、はずれであれば、遊技状態にかかわらず共通の判定処理を行えばよくなり、プログラム容量をより低減することができる。また、この場合、ステップS226の遊技状態の判定処理も不要とすることができる。 In addition, even when the gaming state is the probability variable state or the time saving state, the variation pattern type of super CA2-5 may be assigned to the range of the determination value 230-251. By doing so, it is possible to assign a common determination value to the variation pattern types of super CA2-5 regardless of the gaming state. Therefore, when executing the process of step S232 of the process of winning effects described later, if the game is lost, the common determination process can be performed regardless of the game state, and the program capacity can be further reduced. Also, in this case, the gaming state determination process in step S226 can be omitted.
また、例えば、始動入賞時に、「通常大当り」となると判定した場合、後述する入賞時演出処理のステップS232において、CPU56は、まず、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が1~74となるか否かを判定する。変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が1~74となる場合(すなわち、ノーマルCA3-1の変動パターン種別となる場合)には、CPU56は、EXTデータに「10(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ21コマンドを送信する。次いで、CPU56は、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が75~149となる場合(すなわち、ノーマルCA3-2の変動パターン種別となる場合)には、EXTデータに「11(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ22コマンドを送信する。次いで、CPU56は、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が150~251となる場合(すなわち、スーパーCA3-3の変動パターン種別となる場合)には、EXTデータに「12(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ23コマンドを送信する。
Also, for example, when it is determined that the "normal jackpot" will be achieved at the time of starting winning, in step S232 of the winning effect processing described later, the
また、例えば、始動入賞時に、「確変大当り」となると判定した場合、後述する入賞時演出処理のステップS232において、CPU56は、まず、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が1~38となるか否かを判定する。変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が1~38となる場合(すなわち、ノーマルCA3-1の変動パターン種別となる場合)には、CPU56は、EXTデータに「13(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ24コマンドを送信する。次いで、CPU56は、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が39~79となる場合(すなわち、ノーマルCA3-2の変動パターン種別となる場合)には、EXTデータに「14(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ25コマンドを送信する。次いで、CPU56は、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が80~251となる場合(すなわち、スーパーCA3-3の変動パターン種別となる場合)には、EXTデータに「15(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ26コマンドを送信する。
Also, for example, when it is determined that a "variable probability big hit" will be achieved at the time of starting winning, in step S232 of the winning effect processing described later, the
また、例えば、始動入賞時に、突然確変大当りとなると判定した場合、後述する入賞時演出処理のステップS232において、CPU56は、まず、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が1~100となるか否かを判定する。変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が1~100となる場合(すなわち、特殊CA4-1の変動パターン種別となる場合)には、CPU56は、EXTデータに「16(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ27コマンドを送信する。次いで、CPU56は、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が101~251場合(すなわち、特殊CA4-2の変動パターン種別となる場合)には、EXTデータに「17(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ28コマンドを送信する。
Also, for example, when it is determined that a variable probability big hit will suddenly occur at the time of starting winning, in step S232 of the winning effect processing described later, the
また、例えば、始動入賞時に、小当りとなると判定した場合、CPU56は、EXTデータに「18(H)」を設定した変動カテゴリ29コマンドを送信する。
Further, for example, when it is determined that a small hit will be made at the time of starting winning, the
なお、始動入賞時に入賞時判定を行ったときと実際に変動表示を開始するときとでは必ずしも合算保留記憶数が同じであるとは限らないのであるから、入賞時判定結果指定コマンドで示される変動パターン種別が実際に変動表示で用いられる変動パターン種別と一致しない場合も生じうる。しかし、この実施の形態では、少なくとも非リーチCA2-1、スーパーCA2-5およびスーパーCA3-3の変動パターン種別については、合算保留記憶数にかかわらず共通の判定値が割り当てられているのであるから(図9、図10参照)、入賞時判定結果と実際に実行される変動表示の変動パターン種別とで不整合が生じない。そのため、この実施の形態では、非リーチCA2-1、スーパーCA2-5またはスーパーCA3-3の変動パターン種別になるとの入賞時判定結果にもとづいて先読み予告演出の一種である保留予告演出が実行される。なお、非リーチCA2-1、スーパーCA2-5およびスーパーCA3-3の変動パターン種別となると判定した場合にのみ、図16および図17に示す変動カテゴリコマンド(具体的には、変動カテゴリ1コマンド、変動カテゴリ7コマンド、変動カテゴリ23コマンド、変動カテゴリ26コマンドのみ)を送信し、それ以外の変動パターン種別の入賞時判定結果の場合には変動カテゴリコマンドを送信しないようにしてもよい。また、非リーチCA2-1、スーパーCA2-5およびスーパーCA3-3以外となると入賞時判定された場合には、変動パターン種別を特定不能であることを示す変動カテゴリコマンドを送信するようにしてもよい。
It should be noted that the total pending memory number is not always the same between when the winning determination is performed at the start of winning and when the variable display is actually started. There may be cases where the pattern type does not match the variation pattern type actually used in the variation display. However, in this embodiment, at least for the fluctuation pattern types of non-reach CA2-1, super CA2-5 and super CA3-3, a common judgment value is assigned regardless of the total pending storage number. (See FIGS. 9 and 10), and there is no inconsistency between the winning determination result and the variation pattern type of the variation display that is actually executed. Therefore, in this embodiment, a suspension notice effect, which is a type of foreseeing notice effect, is executed based on the result of determination at the time of winning that the variation pattern type of non-reach CA2-1, super CA2-5 or super CA3-3 will be obtained. be. In addition, only when it is determined that the variation pattern type is non-reach CA2-1, super CA2-5 and super CA3-3, the variation category commands shown in FIGS. 16 and 17 (specifically,
なお、「先読み予告演出」とは、予告演出の対象となる変動表示が開始されるよりも前に実行される予告演出のことである。この実施の形態では、後述するように、始動入賞が発生したときに先読み予告演出の一種である保留予告演出の実行を決定すると、保留表示(または保留表示の表示態様を引き継いで表示されるアクティブ表示)を通常態様(本例では、白色の球形表示)とは異なる特別態様(本例では、青色や緑色、赤色、虹色の球形表示)に最終的に変化させる保留予告演出を実行する。なお、この実施の形態では、保留予告演出を実行する場合、保留表示が通常態様から特別態様に直接変化するのではなく、保留シフトのタイミングで保留表示が特殊態様(本例では、青色や緑色、赤色の箱形表示)に一旦変化し、その後、保留表示の表示態様を引き継いだアクティブ表示がいずれかの特別態様に変化する演出が実行される場合がある。 It should be noted that the “forecast effect” is an effect that is executed before the start of the variable display that is the target of the effect. In this embodiment, as will be described later, when it is decided to execute a pending notice effect, which is a type of predictive notice effect, when a starting prize is generated, a pending display (or an active display that takes over the display mode of the pending display) display) is finally changed to a special mode (in this example, blue, green, red, and iridescent spherical display) different from the normal mode (in this example, white spherical display). In this embodiment, when the suspension notice effect is executed, the suspension display does not change directly from the normal mode to the special mode, but the suspension display changes to the special mode (in this example, blue or green , red box-shaped display), and then the active display that takes over the display mode of the suspended display changes to any special mode.
なお、先読み予告演出の演出態様は、この実施の形態で示したものにかぎらず、保留予告演出に加えて、例えば、先読み予告演出として、複数変動にわたって連続してチャンス目図柄などの特殊表示結果を停止表示させる演出を実行したり、複数変動にわたってカウントダウンするような態様の演出を実行したり、背景画面が変化するような態様で演出モードを変更する演出を実行したりするなど、様々な態様が考えられる。 It should be noted that the effect mode of the pre-reading notice effect is not limited to that shown in this embodiment. Various aspects such as executing a production that stops displaying, executing a production that counts down over multiple fluctuations, or executing a production that changes the production mode in a manner that changes the background screen. can be considered.
演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100(具体的には、演出制御用CPU101)は、主基板31に搭載されている遊技制御用マイクロコンピータ560から上述した演出制御コマンドを受信すると、図13および図14に示された内容に応じて演出表示装置9の表示状態を変更したり、ランプの表示状態を変更したり、音声出力基板70に対して音番号データを出力したりする。
The effect control microcomputer 100 (specifically, the effect control CPU 101) mounted on the
図18および図19は、主基板31に搭載される遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560(具体的には、CPU56)が実行する特別図柄プロセス処理(ステップS26)のプログラムの一例を示すフローチャートである。上述したように、特別図柄プロセス処理では第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bおよび大入賞口を制御するための処理が実行される。特別図柄プロセス処理において、CPU56は、第1始動入賞口13に遊技球が入賞したことを検出するための第1始動口スイッチ13aがオンしていたら、すなわち、第1始動入賞口13への始動入賞が発生していたら、第1始動口スイッチ通過処理を実行する(ステップS311,S312)。また、CPU56は、第2始動入賞口14に遊技球が入賞したことを検出するための第2始動口スイッチ14aがオンしていたら、すなわち第2始動入賞口14への始動入賞が発生していたら、第2始動口スイッチ通過処理を実行する(ステップS313,S314)。そして、ステップS300~S310のうちのいずれかの処理を行う。第1始動入賞口スイッチ13aまたは第2始動口スイッチ14aがオンしていなければ、内部状態に応じて、ステップS300~S310のうちのいずれかの処理を行う。
18 and 19 are flowcharts showing an example of a program of special symbol process processing (step S26) executed by the game control microcomputer 560 (specifically, the CPU 56) mounted on the
ステップS300~S310の処理は、以下のような処理である。 The processing of steps S300 to S310 is as follows.
特別図柄通常処理(ステップS300):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が0であるときに実行される。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、特別図柄の可変表示が開始できる状態になると、保留記憶バッファに記憶される数値データの記憶数(合算保留記憶数)を確認する。保留記憶バッファに記憶される数値データの記憶数は合算保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値により確認できる。また、合算保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値が0でなければ、第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄の可変表示の表示結果を大当りとするか否かを決定する。大当りとする場合には大当りフラグをセットする。そして、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS301に応じた値(この例では1)に更新する。なお、大当りフラグは、大当り遊技が終了するときにリセットされる。
Special symbol normal processing (step S300): Executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is zero. When the
変動パターン設定処理(ステップS301):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が1であるときに実行される。また、変動パターンを決定し、その変動パターンにおける変動時間(可変表示時間:可変表示を開始してから表示結果を導出表示(停止表示)するまでの時間)を特別図柄の可変表示の変動時間とすることに決定する。また、決定した変動パターンに応じた変動パターンコマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行い、特別図柄の変動時間を計測する変動時間タイマをスタートさせる。そして、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS302に対応した値(この例では2)に更新する。
Variation pattern setting process (step S301): Executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 1. In addition, a variation pattern is determined, and the variation time in the variation pattern (variable display time: the time from the start of variable display to the derivation display (stop display) of the display result) is the variable display of special symbols. decide to do. Further, control is performed to transmit a variation pattern command corresponding to the determined variation pattern to the
表示結果指定コマンド送信処理(ステップS302):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が2であるときに実行される。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に、表示結果指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う。そして、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS303に対応した値(この例では3)に更新する。
Display result specification command transmission process (step S302): Executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 2. Control is performed to transmit a display result designation command to the
特別図柄変動中処理(ステップS303):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が3であるときに実行される。変動パターン設定処理で選択された変動パターンの変動時間が経過(ステップS301でセットされる変動時間タイマがタイムアウトすなわち変動時間タイマの値が0になる)すると、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に、図柄確定指定コマンドを送信する制御を行い、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS304に対応した値(この例では4)に更新する。なお、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が送信する図柄確定指定コマンドを受信すると演出表示装置9において第4図柄が停止されるように制御する。
Special symbol fluctuation process (step S303): Executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 3. When the variation time of the variation pattern selected in the variation pattern setting process elapses (the variation time timer set in step S301 times out, i.e., the value of the variation time timer becomes 0), the
特別図柄停止処理(ステップS304):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が4であるときに実行される。大当りフラグがセットされている場合に、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS305に対応した値(この例では5)に更新する。また、小当りフラグがセットされている場合には、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS308に対応した値(この例では8)に更新する。大当りフラグおよび小当りフラグのいずれもセットされていない場合には、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS300に対応した値(この例では0)に更新する。なお、この実施の形態では、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が4となったことにもとづいて、後述するように、特別図柄表示制御処理において特別図柄の停止図柄を停止表示するための特別図柄表示制御データが特別図柄表示制御データ設定用の出力バッファに設定され(図30参照)、ステップS22の表示制御処理において出力バッファの設定内容に応じて実際に特別図柄の停止図柄が停止表示される。 Special symbol stop processing (step S304): Executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 4. When the jackpot flag is set, the internal state (special symbol process flag) is updated to a value (5 in this example) corresponding to step S305. Also, when the small hit flag is set, the internal state (special symbol process flag) is updated to a value (8 in this example) corresponding to step S308. When neither the big hit flag nor the small hit flag is set, the internal state (special symbol process flag) is updated to a value (0 in this example) corresponding to step S300. In addition, in this embodiment, as will be described later, special symbol display control for stop-displaying the stop symbol of the special symbol in the special symbol display control process is based on the fact that the value of the special symbol process flag has become 4. Data is set in the output buffer for setting the special symbol display control data (see FIG. 30), and the stop symbol of the special symbol is actually stop-displayed according to the setting contents of the output buffer in the display control process of step S22.
大入賞口開放前処理(ステップS305):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が5であるときに実行される。大入賞口開放前処理では、大入賞口を開放する制御を行う。具体的には、カウンタ(例えば、大入賞口に入った遊技球数をカウントするカウンタ)などを初期化するとともに、ソレノイド21を駆動して大入賞口を開放状態にする。また、大入賞口開放中指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行うとともに、タイマによって大入賞口開放中処理の実行時間を設定し、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS306に対応した値(この例では6)に更新する。なお、大入賞口開放前処理はラウンド毎に実行されるが、第1ラウンドを開始する場合には、大入賞口開放前処理は大当り遊技を開始する処理でもある。また、大入賞口開放中指定コマンドはラウンドごとにそのラウンドを指定する値がEXTデータに設定されて送信されるので、ラウンドごとに異なる大入賞口開放中指定コマンドが送信される。例えば、大当り遊技中の第1ラウンドを実行する際には、ラウンド1を指定する大入賞口開放中指定コマンド(A101(H))が送信され、大当り遊技中の第10ラウンドを実行する際には、ラウンド10を指定する大入賞口開放中指定コマンド(A10A(H))が送信される。
Big winning opening pre-processing (step S305): Executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 5. In the large winning opening pre-opening process, control is performed to open the large winning opening. Specifically, a counter (for example, a counter that counts the number of game balls that have entered the large winning opening) or the like is initialized, and the
大入賞口開放中処理(ステップS306):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が6であるときに実行される。大入賞口開放中処理では、大入賞口の閉成条件の成立を確認する処理等を行う。大入賞口の閉成条件が成立し、かつ、まだ残りラウンドがある場合には、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS305に対応した値(この例では5)に更新する。また、大当り中開放後指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行うとともに、全てのラウンドを終えた場合には、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS307に対応した値(この例では7)に更新する。
Large winning opening opening process (step S306): Executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 6. In the processing during the opening of the big winning opening, processing for confirming whether the condition for closing the big winning opening is established, or the like is performed. If the conditions for closing the big winning opening are met and there are still rounds remaining, the internal state (special symbol process flag) is updated to a value (5 in this example) corresponding to step S305. In addition, while performing control to transmit the specified command after opening the big hit to the
大当り終了処理(ステップS307):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が7であるときに実行される。大当り遊技状態が終了したことを遊技者に報知する表示制御を演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に行わせるための制御を行う。また、遊技状態を示すフラグ(例えば、確変フラグや時短フラグ)をセットする処理を行う。そして、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS300に対応した値(この例では0)に更新する。
Jackpot end processing (step S307): Executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 7. Control is performed to cause the
小当り開放前処理(ステップS308):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が8であるときに実行される。小当り開放前処理では、大入賞口を開放する制御を行う。具体的には、カウンタ(例えば、大入賞口に入った遊技球数をカウントするカウンタ)などを初期化するとともに、ソレノイド21を駆動して大入賞口を開放状態にする。また、タイマによって大入賞口開放中処理の実行時間を設定し、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS309に対応した値(この例では9)に更新する。なお、小当り開放前処理は小当り遊技中の大入賞口の開放毎に実行されるが、小当り遊技中の最初の開放を開始する場合には、小当り開放前処理は小当り遊技を開始する処理でもある。
Small hit opening preprocessing (step S308): It is executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 8. In the small hit opening preprocessing, control is performed to open the big winning opening. Specifically, a counter (for example, a counter that counts the number of game balls that have entered the large winning opening) or the like is initialized, and the
小当り開放中処理(ステップS309):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が9であるときに実行される。大入賞口の閉成条件の成立を確認する処理等を行う。大入賞口の閉成条件が成立し、かつ、まだ大入賞口の開放回数が残っている場合には、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS308に対応した値(この例では8)に更新する。また、全ての開放を終えた場合には、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS310に対応した値(この例では10)に更新する。 Processing during small hit opening (step S309): Executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 9. A process for confirming whether or not the condition for closing the big prize opening is satisfied is performed. If the condition for closing the big winning opening is met and the number of openings of the big winning opening still remains, the internal state (special symbol process flag) is set to a value (8 in this example) corresponding to step S308. Update. Moreover, when all openings are completed, the internal state (special symbol process flag) is updated to a value (10 in this example) corresponding to step S310.
小当り終了処理(ステップS310):特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が10であるときに実行される。小当り遊技状態が終了したことを遊技者に報知する表示制御を演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に行わせるための制御を行う。そして、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS300に対応した値(この例では0)に更新する。
Small hit end process (step S310): Executed when the value of the special symbol process flag is 10. Control is performed to cause the
図20は、ステップS312,S314の始動口スイッチ通過処理を示すフローチャートである。このうち、図20(A)は、ステップS312の第1始動口スイッチ通過処理を示すフローチャートである。また、図20(B)は、ステップS314の第2始動口スイッチ通過処理を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 20 is a flow chart showing the starting port switch passage processing in steps S312 and S314. Among them, FIG. 20A is a flow chart showing the first start opening switch passage processing in step S312. FIG. 20(B) is a flow chart showing the second start opening switch passing process in step S314.
まず、図20(A)を参照して第1始動口スイッチ通過処理について説明する。第1始動口スイッチ13aがオン状態の場合に実行される第1始動口スイッチ通過処理において、CPU56は、まず、第1保留記憶数が上限値に達しているか否か(具体的には、第1保留記憶数をカウントするための第1保留記憶数カウンタの値が4であるか否か)を確認する(ステップS1211A)。第1保留記憶数が上限値に達していれば、そのまま処理を終了する。
First, with reference to FIG. 20(A), the first start opening switch passage processing will be described. In the first starter switch passing process executed when the
第1保留記憶数が上限値に達していなければ、CPU56は、第1保留記憶数カウンタの値を1増やす(ステップS1212A)とともに、合算保留記憶数をカウントするための合算保留記憶数カウンタの値を1増やす(ステップS1213A)。次いで、CPU56は、乱数回路503やソフトウェア乱数を生成するためのカウンタから値を抽出し、それらを、第1保留記憶バッファ(図21参照)における保存領域に格納する処理を実行する(ステップS1214A)。なお、ステップS1214Aの処理では、ハードウェア乱数であるランダムR(大当り判定用乱数)や、ソフトウェア乱数である大当り種別判定用乱数(ランダム1)、変動パターン種別判定用乱数(ランダム2)および変動パターン判定用乱数(ランダム3)が抽出され、保存領域に格納される。なお、変動パターン判定用乱数(ランダム3)を第1始動口スイッチ通過処理(始動入賞時)において抽出して保存領域にあらかじめ格納しておくのではなく、第1特別図柄の変動開始時に抽出するようにしてもよい。例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、後述する変動パターン設定処理において、変動パターン判定用乱数(ランダム3)を生成するための変動パターン判定用乱数カウンタから値を直接抽出するようにしてもよい。
If the first reserved memory number has not reached the upper limit, the
図21は、保留記憶に対応する乱数等を保存する領域(保留記憶バッファ)の構成例を示す説明図である。図21に示すように、第1保留記憶バッファには、第1保留記憶数の上限値(この例では4)に対応した保存領域が確保されている。また、第2保留記憶バッファには、第2保留記憶数の上限値(この例では4)に対応した保存領域が確保されている。この実施の形態では、第1保留記憶バッファおよび第2保留記憶バッファには、ハードウェア乱数であるランダムR(大当り判定用乱数)や、ソフトウェア乱数である大当り種別判定用乱数(ランダム1)、変動パターン種別判定用乱数(ランダム2)および変動パターン判定用乱数(ランダム3)が記憶される。なお、第1保留記憶バッファおよび第2保留記憶バッファは、RAM55に形成されている。
FIG. 21 is an explanatory diagram showing a configuration example of an area (reserved memory buffer) for storing random numbers and the like corresponding to reserved memory. As shown in FIG. 21, a storage area corresponding to the upper limit value (4 in this example) of the first reserved storage number is reserved in the first reserved storage buffer. In the second reserved storage buffer, a storage area corresponding to the upper limit value of the second reserved storage number (4 in this example) is secured. In this embodiment, in the first reservation storage buffer and the second reservation storage buffer, random R (random number for judging the jackpot) that is a hardware random number, random number for judging the jackpot type that is a software random number (random 1), fluctuation A pattern type determination random number (random 2) and a fluctuation pattern determination random number (random 3) are stored. Note that the first reserved storage buffer and the second reserved storage buffer are formed in the
次いで、CPU56は、遊技状態が時短状態であることを示す時短フラグがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS1215A)。セットされていれば、そのままステップS1220Aに移行する。時短フラグがセットされていなければ、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が5以上であるか否かを確認する(ステップS1216A)。特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が5以上であれば(すなわち、大当り遊技状態または小当り遊技状態であれば)、CPU56は、そのままステップS1220Aに移行する。
Next, the
特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が5未満であれば、検出した始動入賞にもとづく変動がその後実行されたときの変動表示結果や変動パターン種別を始動入賞時にあらかじめ判定する入賞時演出処理を実行する(ステップS1217A)。そして、CPU56は、入賞時演出処理の判定結果にもとづいて図柄指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS1218A)とともに、変動カテゴリコマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS1219A)。また、CPU56は、第1保留記憶数加算指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS1220A)。
If the value of the special pattern process flag is less than 5, a prize-winning performance process is executed for determining in advance the fluctuation display result and the fluctuation pattern type when the fluctuation based on the detected starting prize is executed thereafter (step S1217A). Then, the
なお、ステップS1218A,S1219Aの処理を実行することによって、この実施の形態では、CPU56は、第1始動入賞口13に始動入賞してステップS1217Aの入賞時演出処理を実行するごとに、必ず図柄指定コマンドおよび変動カテゴリコマンドの両方を演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して送信する。
By executing the processes of steps S1218A and S1219A, in this embodiment, the
また、この実施の形態では、ステップS1218A~S1220Aの処理が実行されることによって、第1始動入賞口13への始動入賞が発生してステップS1217Aの入賞時演出処理を実行したときに、図柄指定コマンド、変動カテゴリコマンド、および第1保留記憶数加算指定コマンドの3つのコマンドのセットが1タイマ割込内に一括して送信される。
Further, in this embodiment, by executing the processing of steps S1218A to S1220A, when the start winning to the first
ただし、ステップS1215AまたはステップS1216AでYと判定したことによりステップS1217Aの入賞時演出処理を実行しなかった場合には、CPU56は、ステップS1220Aにおいて、第1保留記憶数加算指定コマンドのみを送信する制御を行い、入賞時判定結果指定コマンド(図柄指定コマンド、変動カテゴリコマンド)を送信する制御は行わない。なお、ステップS1217Aの入賞時演出処理を実行しなかった場合に、入賞判定結果を特定不能であることを示す値(例えば、「FF(H)」)をEXTデータとして設定した入賞時判定結果指定コマンド(図柄指定コマンド、変動カテゴリコマンド)を送信するようにしてもよい。
However, if it is determined to be Y in step S1215A or step S1216A and thus the prize-winning effect process of step S1217A is not executed, the
また、この実施の形態では、ステップS1215Aの処理が実行されることによって、第1始動入賞口13への始動入賞があった場合には、遊技状態が通常状態である場合にのみステップS1217Aの入賞時演出処理が実行される。また、この実施の形態では、ステップS1216Aの処理が実行されることによって、第1始動入賞口13への始動入賞があった場合には、大当り遊技状態や小当り遊技状態でない場合にのみステップS1217Aの入賞時演出処理が実行される。なお、大当り遊技状態である場合にのみステップS1217Aに移行しないようにし、小当り遊技状態である場合にはステップS1217Aに移行して入賞時演出処理が実行されるようにしてもよい。
Further, in this embodiment, by executing the process of step S1215A, when there is a start winning to the first
また、この実施の形態において、大当り遊技状態(特定遊技状態)とは、大当りを開始することが報知されてから、所定数のラウンド(例えば、15ラウンド)にわたって大入賞口が開放する制御が行われ、最終ラウンドの大入賞口の開放を終了して大当りを終了することが報知されるまでの状態である。具体的には、特別図柄プロセス処理における大入賞口開放前処理(ステップS305参照)から大当り終了処理(ステップS307参照)までの処理が実行されている状態である。 In addition, in this embodiment, the jackpot game state (specific game state) means that the jackpot is controlled to open over a predetermined number of rounds (for example, 15 rounds) after notification of the start of the jackpot. This is the state until the end of the big winning opening of the final round is ended and the end of the big win is announced. Specifically, it is a state in which the processing from the big winning opening pre-opening process (see step S305) to the big hit end process (see step S307) in the special symbol process process is being executed.
次に、図20(B)を参照して第2始動口スイッチ通過処理について説明する。第2始動口スイッチ14aがオン状態の場合に実行される第2始動口スイッチ通過処理において、CPU56は、第2保留記憶数が上限値に達しているか否か(具体的には、第2保留記憶数をカウントするための第2保留記憶数カウンタの値が4でるか否か)を確認する(ステップS1211B)。第2保留記憶数が上限値に達していれば、そのまま処理を終了する。
Next, with reference to FIG. 20(B), the second start opening switch passage processing will be described. In the second starter switch passing process executed when the second starter switch 14a is in the ON state, the
第2保留記憶数が上限値に達していなければ、CPU56は、第2保留記憶数カウンタの値を1増やす(ステップS1212B)とともに、合算保留記憶数をカウントするための合算保留記憶数カウンタの値を1増やす(ステップS1213B)。次いで、CPU56は、乱数回路503やソフトウェア乱数を生成するためのカウンタから値を抽出し、それらを、第2保留記憶バッファ(図21参照)における保存領域に格納する処理を実行する(ステップS1214B)。なお、ステップS1214Bの処理では、ハードウェア乱数であるランダムR(大当り判定用乱数)や、ソフトウェア乱数である大当り種別判定用乱数(ランダム1)、変動パターン種別判定用乱数(ランダム2)および変動パターン判定用乱数(ランダム3)が抽出され、保存領域に格納される。なお、変動パターン判定用乱数(ランダム3)を第2始動口スイッチ通過処理(始動入賞時)において抽出して保存領域にあらかじめ格納しておくのではなく、第2特別図柄の変動開始時に抽出するようにしてもよい。例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、後述する変動パターン設定処理において、変動パターン判定用乱数(ランダム3)を生成するための変動パターン判定用乱数カウンタから値を直接抽出するようにしてもよい。
If the second reserved memory number has not reached the upper limit, the
次いで、CPU56は、入賞時演出処理を実行する(ステップS1217B)。そして、CPU56は、入賞時演出処理の判定結果にもとづいて図柄指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS1218B)とともに、変動カテゴリコマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS1219B)。また、CPU56は、第2保留記憶数加算指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS1220B)。
Next, the
なお、ステップS1218B,S1219Bの処理を実行することによって、この実施の形態では、CPU56は、第2始動入賞口14に始動入賞してステップS1217Bの入賞時演出処理を実行するごとに、必ず図柄指定コマンドおよび変動カテゴリコマンドの両方を演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して送信する。
By executing the processes of steps S1218B and S1219B, in this embodiment, the
また、この実施の形態では、ステップS1218B~S1220Bの処理が実行されることによって、第2始動入賞口14への始動入賞が発生してステップS1217Bの入賞時演出処理を実行したときに、図柄指定コマンド、変動カテゴリコマンド、および第2保留記憶数加算指定コマンドの3つのコマンドのセットが1タイマ割込内に一括して送信される。
In addition, in this embodiment, by executing the processing of steps S1218B to S1220B, when the starting winning to the second
なお、第2始動口スイッチ通過処理においても、ステップS1215Aと同様の処理を行い、時短状態(確変状態とともに時短状態に制御されている場合も含む)であればステップS1217Bの入賞時演出処理を実行しないようにしてもよい。すなわち、通常状態である場合にのみステップS1217Bの入賞時演出処理を実行して、図柄指定コマンドおよび変動カテゴリコマンドを送信するようにしてもよい。なお、この実施の形態では、後述するように、時短状態であるときには第2保留記憶に対してのみ先読み予告演出を実行するのであるから、逆に時短状態である場合にのみステップS1217Bの入賞時演出処理を実行して図柄指定コマンドおよび変動カテゴリコマンドを送信するようにし、通常状態である場合にはステップS1217Bの入賞時演出処理を実行せず図柄指定コマンドおよび変動カテゴリコマンドを送信しないようにしてもよい。 In addition, even in the second start opening switch passage processing, the same processing as in step S1215A is performed, and if the time saving state (including the case where it is controlled to the time saving state together with the variable probability state), the winning effect processing of step S1217B is executed. You can choose not to. That is, only in the normal state, the prize-winning effect processing of step S1217B may be executed to transmit the symbol designation command and the variable category command. In addition, in this embodiment, as will be described later, when it is in the time saving state, the pre-reading notice effect is executed only for the second reservation storage, so conversely only when it is in the time saving state At the time of winning in step S1217B The design designation command and the variation category command are transmitted by executing the performance processing, and in the normal state, the performance processing at the time of winning in step S1217B is not executed and the design designation command and the variation category command are not transmitted. good too.
また、第2始動口スイッチ通過処理においても、ステップS1216Aと同様の処理を行い、大当り遊技中であればステップS1217Bの入賞時演出処理を実行しないようにしてもよい。また、第2始動口スイッチ通過処理において、ステップS1217Bの入賞時演出処理を実行しないようにしてもよい(すなわち、第2特別図柄に対しては入賞時判定処理を実行しないようにしてもよい)。そのように構成すれば、先読み予告演出がある程度の期間実行される場合に、変動時間が短くて先読み予告演出が途中で途切れてしまうことを確実に防止することができる。 Also, in the second starting port switch passing process, the same process as in step S1216A may be performed, and if the jackpot game is in progress, the winning effect process of step S1217B may not be performed. In addition, in the second starting port switch passage processing, the winning effect processing of step S1217B may not be executed (that is, the winning determination processing may not be executed for the second special symbol). . With such a configuration, when the look-ahead foretelling effect is executed for a certain period of time, it is possible to reliably prevent interruption of the look-ahead foretelling effect due to a short fluctuation time.
図22は、ステップS1217A,S1217Bの入賞時演出処理を示すフローチャートである。入賞時演出処理では、CPU56は、まず、ステップS1214A,S1214Bで抽出した大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)と図8(A)の左欄に示す通常時の大当り判定値とを比較し、それらが一致するか否かを確認する(ステップS220)。この実施の形態では、特別図柄および演出図柄の変動を開始するタイミングで、後述する特別図柄通常処理において大当りや小当りとするか否か、大当り種別を決定したり、変動パターン設定処理において変動パターンを決定したりするのであるが、それとは別に、遊技球が第1始動入賞口13や第2始動入賞口14に始動入賞したタイミングで、その始動入賞にもとづく変動表示が開始される前に、入賞時演出処理を実行することによって、あらかじめ大当りや小当りとなるか否かや、大当りの種別、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値がいずれの判定値の範囲にとなるかを確認する。そのようにすることによって、演出図柄の変動表示が実行されるより前にあらかじめ変動表示結果や変動パターン種別を予測し、後述するように、入賞時の判定結果にもとづいて、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100によって演出図柄の変動表示中に大当りやスーパーリーチとなることを予告する保留予告演出を実行する。
FIG. 22 is a flow chart showing the effect processing at the time of winning in steps S1217A and S1217B. In the prize-winning effect process, the
大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)が通常時の大当り判定値と一致しなければ(ステップS220のN)、CPU56は、遊技状態が高確率状態(確変状態)であることを示す確変フラグがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS221)。確変フラグがセットされていれば、CPU56は、ステップS1214A,S1214Bで抽出した大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)と図8(A)の右欄に示す確変時の大当り判定値とを比較し、それらが一致するか否かを確認する(ステップS222)。なお、始動入賞時にステップS221で確変状態であるか否かを確認してから、実際にその始動入賞にもとづく変動表示が開始されるまでの間には、複数の変動表示が実行される可能性がある。そのため、始動入賞時にステップS221で確変状態であるか否かを確認してから、実際にその始動入賞にもとづく変動表示が開始されるまでの間に遊技状態が変化している(例えば、変動開始前に確変大当りや突然確変大当りが発生した場合には通常状態から確変状態に変化している。)場合がある。そのため、始動入賞時にステップS221で判定する遊技状態と変動開始時に判定する遊技状態(後述するステップS61参照)とは、必ずしも一致するとは限らない。なお、そのような不一致を防止するため、現在記憶している保留記憶内の遊技状態の変更を伴うものを特定して、変更後の遊技状態にもとづいて始動入賞時の判定を行うようにしてもよい。
If the random number for judging a big hit (random R) does not match the judging value of a big hit at normal time (N in step S220), the
大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)が確変時の大当り判定値とも一致しなければ(ステップS222のN)、CPU56は、ステップS1214A,S1214Bで抽出した大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)と図8(B),(C)に示す小当り判定値とを比較し、それらが一致するか否かを確認する(ステップS223)。この場合、CPU56は、第1始動入賞口13への始動入賞があった場合(ステップS1217Aの入賞時演出処理を実行する場合)には、図8(B)に示す小当り判定テーブル(第1特別図柄用)に設定されている小当り判定値と一致するか否かを判定する。また、第2始動入賞口14への始動入賞があった場合(ステップS1217Bの入賞時演出処理を実行する場合)には、図8(C)に示す小当り判定テーブル(第2特別図柄用)に設定されている小当り判定値と一致するか否かを判定する。
If the random number for judging a big hit (random R) does not match the judgment value for judging a big hit at the time of probability variation (N in step S222), the
大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)が小当り判定値とも一致しなければ(ステップS223のN)、CPU56は、「はずれ」となることを示すEXTデータ「00(H)」を図柄指定コマンドに設定する処理を行う(ステップS224)。
If the random number for judging a big hit (random R) does not match the judging value for a small hit (N in step S223), the
次いで、CPU56は、現在の遊技状態を判定する処理を行う(ステップS225)。この実施の形態では、CPU56は、ステップS225において、遊技状態が確変状態であるか否かおよび時短状態であるか否か(具体的には、確変フラグおよび時短フラグがセットされているか否か)を判定する。なお、始動入賞時にステップS225で確変状態であるか否かおよび時短状態であるか否かを確認してから、実際にその始動入賞にもとづく変動表示が開始されるまでの間には、複数の変動表示が実行される可能性がある。そのため、始動入賞時にステップS225で確変状態であるか否かおよび時短状態であるか否かを確認してから、実際にその始動入賞にもとづく変動表示が開始されるまでの間に遊技状態が変化している(例えば、変動開始前に確変大当りや突然確変大当りが発生した場合には通常状態から確変状態に変化している。)場合がある。そのため、始動入賞時にステップS225で判定する遊技状態と変動開始時に判定する遊技状態(後述するステップS61参照)とは、必ずしも一致するとは限らない。なお、そのような不一致を防止するため、現在記憶している保留記憶内の遊技状態の変更を伴うものを特定して、変更後の遊技状態にもとづいて始動入賞時の判定を行うようにしてもよい。
Next, the
そして、CPU56は、ステップS225の判定結果に応じて、はずれ用の各閾値を設定する(ステップS226)。この実施の形態では、あらかじめ閾値判定を行う閾値判定プログラムが組み込まれており、閾値より大きいか否かを判定することにより、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値がいずれの判定値の範囲にとなるかが判定され、図16および図17に示す変動カテゴリコマンドに設定するEXTデータの値が決定される。
Then, the
例えば、CPU56は、遊技状態が確変状態または時短状態であると判定した場合には閾値219を設定する。この場合、CPU56は、後述するステップS232において、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が閾値219以下であるか否かを判定し、閾値219以下である場合(すなわち、1~219である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「07(H)」を設定すると判定する(図16参照)。また、閾値219以下でない場合(すなわち、220~251である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「08(H)」を設定すると判定する(図16参照)。
For example, the
また、例えば、CPU56は、遊技状態が通常状態であると判定した場合には、合算保留記憶数にかかわらず、閾値89、99、169、199、214および229を設定する。この場合、CPU56は、後述するステップS232において、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が閾値89以下であるか否かを判定し、閾値89以下である場合(すなわち、1~89である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「00(H)」を設定すると判定する(図16参照)。また、閾値99以下である場合(すなわち、90~99である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「01(H)」を設定すると判定する(図16参照)。また、閾値169以下である場合(すなわち、100~169である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「02(H)」を設定すると判定する(図16参照)。また、閾値199以下である場合(すなわち、170~199である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「03(H)」を設定すると判定する(図16参照)。また、閾値214以下である場合(すなわち、200~214である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「04(H)」を設定すると判定する(図16参照)。また、閾値229以下である場合(すなわち、215~229である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「05(H)」を設定すると判定する(図16参照)。また、閾値229以下でない場合(すなわち、230~251である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「06(H)」を設定すると判定する(図16参照)。
Further, for example, when the
なお、上記に示す閾値判定の例では、閾値の値が小さい方から順に89、99、169、199、214および229と判定していくので、後の順番の閾値で判定されたものが前の順番の閾値以下の範囲内となることはない。すなわち、閾値89以下であるか否かを判定した後に、閾値99以下であるか否かを判定するときには、前の順番の閾値以下の1~89の範囲内となることはなく、90~99の範囲であるか否かを判定することになる。また、この実施の形態では、閾値の値が小さい方から順に89、99、169、199、214および229と判定していく場合を示したが、逆に大きい方から順に229、214、199、169、99および89と判定していってもよい。このことは、以下に示す他の閾値を用いた判定を行う場合も同様である。 In the example of threshold determination shown above, since the threshold values are determined to be 89, 99, 169, 199, 214, and 229 in ascending order, the values determined by the later order of the threshold are the earlier ones. It is never within the range below the order threshold. That is, when determining whether or not the threshold value is 99 or less after determining whether or not the threshold value is 89 or less, the range of 1 to 89, which is less than or equal to the threshold value in the previous order, does not fall within the range of 90 to 99. It is determined whether or not it is within the range of Also, in this embodiment, the cases where the threshold values are determined to be 89, 99, 169, 199, 214, and 229 in descending order of the threshold value were shown, but conversely, in descending order of the threshold values, 229, 214, 199, 229, 214, 199, 169, 99 and 89 may be determined. This also applies to the determination using other thresholds described below.
なお、ステップS225の遊技状態の判定を行うことなく、常に通常状態における閾値を設定するようにしてもよい。そのように構成しても、少なくとも「非リーチはずれ」となる変動パターン種別と「スーパーリーチはずれ」となる変動パターン種別とに関しては判定値の範囲が共通化されているのであるから、「非リーチはずれ」や「スーパーリーチはずれ」となるか否かについては判定することができる。 It should be noted that the threshold value for the normal state may be set at all times without determining the game state in step S225. Even with such a configuration, at least the range of judgment values is shared for the variation pattern type that is "non-reach out" and the variation pattern type that is "super reach out", so "non-reach It is possible to determine whether or not it will be a "loss" or a "super reach failure".
大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)が小当り判定値と一致した場合には(ステップS223のY)、CPU56は、「小当り」となることを示すEXTデータ「04(H)」を図柄指定コマンドに設定する処理を行う(ステップS227)。
When the random number for judging a big hit (random R) matches the judging value for a small hit (Y in step S223), the
次いで、CPU56は、小当り用の閾値を設定する(ステップS228)。なお、この実施の形態では、CPU56は、閾値251を設定するものとし、後述するステップS232において、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が閾値251以下である(1~251である)と判定して、変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「18(H)」を設定すると判定するものとする(図17参照)。なお、小当りである場合には、閾値判定を行うことなく、そのままEXTデータ「18(H)」を設定すると判定するようにしてもよい。
Next, the
ステップS220またはステップS222で大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)が大当り判定値と一致した場合には、CPU56は、ステップS1214A,S1214Bで抽出した大当り種別判定用乱数(ランダム1)にもとづいて大当りの種別を判定する(ステップS229)。この場合、CPU56は、第1始動入賞口13への始動入賞があった場合(ステップS1217Aの入賞時演出処理を実行する場合)には、図8(D)に示す大当り種別判定テーブル(第1特別図柄用)131aを用いて大当り種別が「通常大当り」、「確変大当り」または「突然確変大当り」のいずれとなるかを判定する。また、第2始動入賞口14への始動入賞があった場合(ステップS1217Bの入賞時演出処理を実行する場合)には、図8(E)に示す大当り種別判定テーブル(第2特別図柄用)131bを用いて大当り種別が「通常大当り」、「確変大当り」または「突然確変大当り」のいずれとなるかを判定する。
When the random number for judging the big hit (random R) matches the judgment value for the big hit in step S220 or step S222, the
次いで、CPU56は、大当り種別の判定結果に応じたEXTデータを図柄指定コマンドに設定する処理を行う(ステップS230)。この場合、「通常大当り」となると判定した場合には、CPU56は、「通常大当り」となることを示すEXTデータ「01(H)」を図柄指定コマンドに設定する処理を行う。また、「確変大当り」となると判定した場合には、CPU56は、「確変大当り」となることを示すEXTデータ「02(H)」を図柄指定コマンドに設定する処理を行う。また、「突然確変大当り」となると判定した場合には、CPU56は、「突然確変大当り」となることを示すEXTデータ「03(H)」を図柄指定コマンドに設定する処理を行う。
Next, the
そして、CPU56は、ステップS229で判定した大当り種別に応じて、大当り用の各閾値を設定する(ステップS231)。 And CPU56 sets each threshold value for big hits according to the big-hit classification determined by step S229 (step S231).
例えば、CPU56は、「通常大当り」と判定した場合には、閾値74および149を設定する。この場合、CPU56は、後述するステップS232において、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が閾値74以下であるか否かを判定し、閾値74以下である場合(すなわち、1~74である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「10(H)」を設定すると判定する(図17参照)。また、閾値149以下である場合(すなわち、75~149である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「11(H)」を設定すると判定する(図17参照)。また、閾値149以下でない場合(すなわち、150~251である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「12(H)」を設定すると判定する(図17参照)。
For example, the
また、例えば、CPU56は、「確変大当り」と判定した場合には、閾値38および79を設定する。この場合、CPU56は、後述するステップS232において、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が閾値38以下であるか否かを判定し、閾値38以下である場合(すなわち、1~38である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「13(H)」を設定すると判定する(図17参照)。また、閾値79以下である場合(すなわち、39~79である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「14(H)」を設定すると判定する(図17参照)。また、閾値79以下でない場合(すなわち、80~251である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「15(H)」を設定すると判定する(図17参照)。
Further, for example, the
また、例えば、CPU56は、「突然確変大当り」と判定した場合には、閾値100を設定する。この場合、CPU56は、後述するステップS232において、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値が閾値100以下であるか否かを判定し、閾値100以下である場合(すなわち、1~100である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「16(H)」を設定すると判定する(図17参照)。また、閾値100以下でない場合(すなわち、101~251である場合)には変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータとして「17(H)」を設定すると判定する(図17参照)。
Further, for example, the
次いで、CPU56は、ステップS226,S228,S231で設定した閾値と、ステップS1214A,S1214Bで抽出した変動パターン種別判定用乱数(ランダム2)とを用いて、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値がいずれの判定値の範囲となるかを判定する(ステップS232)。
Next, the
なお、ステップS226,S228,S231において、あらかじめ定められた閾値を設定するのではなく、変動パターン種別判定テーブル(図9、図10参照)を設定するようにし、ステップS232において、設定した変動パターン種別判定テーブルを用いて、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値の範囲やいずれの変動パターン種別となるかを判定するようにしてもよい。 In steps S226, S228, and S231, instead of setting a predetermined threshold value, a fluctuation pattern type determination table (see FIGS. 9 and 10) is set, and in step S232, the set fluctuation pattern type A determination table may be used to determine the range of the value of the random number for determining the variation pattern type and the variation pattern type.
そして、CPU56は、判定結果に応じたEXTデータを変動カテゴリコマンドに設定する処理を行う(ステップS233)。具体的には、CPU56は、ステップS232でいずれの変動パターン種別になると判定したかに応じて、図16および図17に示すような「00(H)」~「08(H)」、「10(H)」~「18(H)」のいずれかの値を変動カテゴリコマンドのEXTデータに設定する処理を行う。
Then, the
なお、この実施の形態では、入賞時判定において大当りや小当りとなると判定した場合であっても一律に変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値がいずれの範囲となるかを判定する場合を示したが、大当りや小当りとなると判定した場合には、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値の範囲の判定を行わないようにしてもよい。そして、大当りまたは小当りとなると入賞時判定したことを示す図柄指定コマンドを送信するとともに、大当りまたは小当りの変動パターン種別となることを包括的に示す変動カテゴリコマンドを送信するようにしてもよい。そして、例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、具体的にいずれの変動パターン種別となるかまでは示されていないものの、包括的にいずれかの大当りの変動パターン種別となることが示された変動カテゴリコマンドを受信したことにもとづいて、後述する保留予告演出を実行するようにしてもよい。
In addition, in this embodiment, even if it is determined to be a big hit or a small hit in the winning determination, it is uniformly determined in which range the value of the random number for determining the variation pattern type is determined. When it is determined that the game will be a big hit or a small hit, the value range of the variation pattern type determination random number may not be determined. Then, when a big win or a small win is achieved, a pattern specifying command indicating that the judgment has been made at the time of winning may be transmitted, and a variation category command comprehensively indicating that the variation pattern type of the big win or minor win may be transmitted. . Then, for example, the
図23および図24は、特別図柄プロセス処理における特別図柄通常処理(ステップS300)を示すフローチャートである。特別図柄通常処理において、CPU56は、合算保留記憶数の値を確認する(ステップS51)。具体的には、合算保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値を確認する。合算保留記憶数が0であれば、まだ客待ちデモ指定コマンドを送信していなければ、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して客待ちデモ指定コマンドを送信する制御を行い(ステップS51A)、処理を終了する。なお、例えば、CPU56は、ステップS51Aで客待ちデモ指定コマンドを送信すると、客待ちデモ指定コマンドを送信したことを示す客待ちデモ指定コマンド送信済フラグをセットする。そして、客待ちデモ指定コマンドを送信した後に次回のタイマ割込以降の特別図柄通常処理を実行する場合には、客待ちデモ指定コマンド送信済フラグがセットされていることにもとづいて重ねて客待ちデモ指定コマンドを送信しないように制御すればよい。また、この場合、客待ちデモ指定コマンド送信済フラグは、次回の特別図柄の変動表示が開始されるときにリセットされるようにすればよい。
23 and 24 are flowcharts showing special symbol normal processing (step S300) in special symbol process processing. In the special symbol normal process, the
合算保留記憶数が0でなければ、CPU56は、第2保留記憶数が0であるか否かを確認する(ステップS52)。具体的には、第2保留記憶数カウンタの値が0であるか否かを確認する。第2保留記憶数が0でなければ、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタ(第1特別図柄について特別図柄プロセス処理を行っているのか第2特別図柄について特別図柄プロセス処理を行っているのかを示すフラグ)に「第2」を示すデータを設定する(ステップS53)。第2保留記憶数が0であれば(すなわち、第1保留記憶数のみが溜まっている場合)には、CPU66は、特別図柄ポインタに「第1」を示すデータを設定する(ステップS54)。
If the combined reserved storage number is not 0, the
この実施の形態では、ステップS52~S54の処理が実行されることによって、第1特別図柄の変動表示に対して、第2特別図柄の変動表示が優先して実行される。言い換えれば、第2特別図柄の変動表示を開始させるための第2の開始条件が第1特別図柄の変動表示を開始させるための第1の開始条件に優先して成立するように制御される。なお、この実施の形態で示した態様にかぎらず、例えば、第1始動入賞口13と第2始動入賞口14への入賞順に第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄の変動表示を実行するように構成してもよい。
In this embodiment, by executing the processes of steps S52 to S54, the variable display of the second special symbol is preferentially executed with respect to the variable display of the first special symbol. In other words, the second start condition for starting the variable display of the second special symbol is controlled to take precedence over the first start condition for starting the variable display of the first special symbol. In addition, not limited to the aspect shown in this embodiment, for example, the variable display of the first special symbol and the second special symbol is executed in order of winning to the first
なお、この実施の形態で示したように第2特別図柄の変動表示を優先して実行するように構成する場合、図22に示した入賞時演出処理において、大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)の値を、低確率状態における大当り判定値と比較する処理のみを実行するようにし、確変状態における大当り判定値とは比較しないようにしてもよい(具体的には、ステップS220の処理のみを実行し、ステップS221,S222の処理は行わないようにしてもよい)。そのように構成すれば、第2特別図柄の変動表示を優先して実行するように構成する場合に、入賞時判定における大当りの判定結果と実際の変動開始時における大当りの決定結果との間にズレが生じることを防止することができる。 It should be noted that, as shown in this embodiment, in the case of configuration so as to preferentially execute the variable display of the second special symbol, in the winning effect processing shown in FIG. value, only the process of comparing with the jackpot determination value in the low probability state may be performed, and may not be compared with the jackpot determination value in the variable probability state (specifically, only the process of step S220 is performed. , Steps S221 and S222 may not be performed). With such a configuration, when the variable display of the second special symbol is preferentially executed, there is a difference between the judgment result of the big win in the judgment at the time of winning and the determination result of the big win at the time of actual fluctuation start. It is possible to prevent deviation from occurring.
次いで、CPU56は、RAM55において、特別図柄ポインタが示す方の保留記憶数=1に対応する保存領域に格納されている各乱数値を読み出してRAM55の乱数バッファ領域に格納する(ステップS55)。具体的には、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが「第1」を示している場合には、第1保留記憶バッファにおける第1保留記憶数=1に対応する保存領域に格納されている各乱数値を読み出してRAM55の乱数バッファ領域に格納する。また、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが「第2」を示している場合には、第2保留記憶バッファにおける第2保留記憶数=1に対応する保存領域に格納されている各乱数値を読み出してRAM55の乱数バッファ領域に格納する。
Next, in the
そして、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが示す方の保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値を1減算し、かつ、各保存領域の内容をシフトする(ステップS56)。具体的には、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが「第1」を示している場合には、第1保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値を1減算し、かつ、第1保留記憶バッファにおける各保存領域の内容をシフトする。また、特別図柄ポインタが「第2」を示している場合に、第2保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値を1減算し、かつ、第2保留記憶バッファにおける各保存領域の内容をシフトする。
Then, the
すなわち、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが「第1」を示している場合に、RAM55の第1保留記憶バッファにおいて第1保留記憶数=n(n=2,3,4)に対応する保存領域に格納されている各乱数値を、第1保留記憶数=n-1に対応する保存領域に格納する。また、特別図柄ポインタが「第2」を示す場合に、RAM55の第2保留記憶バッファにおいて第2保留記憶数=n(n=2,3,4)に対応する保存領域に格納されている各乱数値を、第2保留記憶数=n-1に対応する保存領域に格納する。よって、各第1保留記憶数(または、各第2保留記憶数)に対応するそれぞれの保存領域に格納されている各乱数値が抽出された順番は、常に、第1保留記憶数(または、第2保留記憶数)=1,2,3,4の順番と一致するようになっている。 That is, when the special symbol pointer indicates the "first", the CPU56, in the first reserved storage buffer of the RAM55, in the storage area corresponding to the first reserved storage number = n (n = 2, 3, 4) Each stored random value is stored in a storage area corresponding to the first reserved storage number=n−1. Also, when the special symbol pointer indicates "second", each stored in the storage area corresponding to the second reservation storage number = n (n = 2, 3, 4) in the second reservation storage buffer of RAM55 Store the random value in the storage area corresponding to the second reserved storage number=n-1. Therefore, the order in which each random value stored in each storage area corresponding to each first reserved memory number (or each second reserved memory number) is extracted is always the first reserved memory number (or 2nd reserved storage number)=1, 2, 3, 4.
そして、CPU56は、合算保留記憶数の値を1減らす。すなわち、合算保留記憶数カウンタのカウント値を1減算する(ステップS58)。なお、CPU56は、カウント値が1減算される前の合算保留記憶数カウンタの値をRAM55の所定の領域に保存する。
Then, the
また、CPU56は、現在の遊技状態に応じて背景指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS60)。この場合、CPU56は、確変状態であることを示す確変フラグがセットされている場合には、確変状態背景指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う。また、CPU56は、時短状態であることを示す時短フラグのみがセットされ、確変フラグがセットされていない場合には、時短状態背景指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う。また、CPU56は、確変フラグも時短フラグもセットされていなければ、通常状態背景指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う。
Further, the
なお、具体的には、CPU56は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に演出制御コマンドを送信する際に、演出制御コマンドに応じたコマンド送信テーブル(あらかじめROMにコマンド毎に設定されている)のアドレスをポインタにセットする。そして、演出制御コマンドに応じたコマンド送信テーブルのアドレスをポインタにセットして、演出制御コマンド制御処理(ステップS28)において演出制御コマンドを送信する。なお、この実施の形態では、特別図柄の変動を開始するときに、タイマ割込ごとに、背景指定コマンド、変動パターンコマンド、表示結果指定コマンド、保留記憶数減算指定コマンド(第1保留記憶数減算指定コマンドまたは第2保留記憶数減算指定コマンド)の順に演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信されることになる。具体的には、特別図柄の変動を開始するときに、まず、背景指定コマンドが送信され、4ms経過後に変動パターンコマンドが送信され、さらに4ms経過後に表示結果指定コマンドが送信され、さらに4ms経過後に保留記憶数減算指定コマンド(第1保留記憶数減算指定コマンドまたは第2保留記憶数減算指定コマンド)が送信される。なお、特別図柄の変動を開始するときにはさらに図柄変動指定コマンド(第1図柄変動指定コマンド、第2図柄変動指定コマンド)も送信されるが、図柄変動指定コマンドは、変動パターンコマンドと同じタイマ割込において演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して送信される。
Specifically, when the
特別図柄通常処理では、最初に、第1始動入賞口13を対象として処理を実行することを示す「第1」を示すデータすなわち第1特別図柄を対象として処理を実行することを示す「第1」を示すデータ、または第2始動入賞口14を対象として処理を実行することを示す「第2」を示すデータすなわち第2特別図柄を対象として処理を実行することを示す「第2」を示すデータが、特別図柄ポインタに設定される。そして、特別図柄プロセス処理における以降の処理では、特別図柄ポインタに設定されているデータに応じた処理が実行される。よって、ステップS300~S310の処理を、第1特別図柄を対象とする場合と第2特別図柄を対象とする場合とで共通化することができる。
In the special symbol normal process, first, data indicating "first" indicating that the process is performed for the first
次いで、CPU56は、乱数バッファ領域からランダムR(大当り判定用乱数)を読み出し、大当り判定モジュールを実行する。なお、この場合、CPU56は、第1始動口スイッチ通過処理のステップS1214Aや第2始動口スイッチ通過処理のステップS1214Bで抽出し第1保留記憶バッファや第2保留記憶バッファにあらかじめ格納した大当り判定用乱数を読み出し、大当り判定を行う。大当り判定モジュールは、あらかじめ決められている大当り判定値や小当り判定値(図8参照)と大当り判定用乱数とを比較し、それらが一致したら大当りや小当りとすることに決定する処理を実行するプログラムである。すなわち、大当り判定や小当り判定の処理を実行するプログラムである。
Next, the
大当り判定の処理では、遊技状態が確変状態の場合には、遊技状態が非確変状態(通常状態や時短状態)の場合よりも、大当りとなる確率が高くなるように構成されている。具体的には、あらかじめ大当り判定値の数が多く設定されている確変時大当り判定テーブル(ROM54における図8(A)の右側の数値が設定されているテーブル)と、大当り判定値の数が確変時大当り判定テーブルよりも少なく設定されている通常時大当り判定テーブル(ROM54における図8(A)の左側の数値が設定されているテーブル)とが設けられている。そして、CPU56は、遊技状態が確変状態であるか否かを確認し、遊技状態が確変状態であるときは、確変時大当り判定テーブルを使用して大当りの判定の処理を行い、遊技状態が通常状態であるときは、通常時大当り判定テーブルを使用して大当りの判定の処理を行う。すなわち、CPU56は、大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)の値が図8(A)に示すいずれかの大当り判定値に一致すると、特別図柄に関して大当りとすることに決定する。大当りとすることに決定した場合には(ステップS61)、ステップS71に移行する。なお、大当りとするか否か決定するということは、大当り遊技状態に移行させるか否か決定するということであるが、特別図柄表示器における停止図柄を大当り図柄とするか否か決定するということでもある。
In the process of judging a big win, when the game state is a variable probability state, the probability of winning a big win is higher than when the game state is a non-variable probability state (normal state or time saving state). Specifically, the probability variable jackpot determination table in which a large number of jackpot determination values are set in advance (a table in which the numbers on the right side of FIG. 8 (A) in the
なお、現在の遊技状態が確変状態であるか否かの確認は、確変フラグがセットされているか否かにより行われる。確変フラグは、遊技状態を確変状態に移行するときにセットされ、確変状態を終了するときにリセットされる。具体的には、「確変大当り」または「突然確変大当り」とすることに決定され、大当り遊技を終了する処理においてセットされる。そして、大当り遊技終了後、次の大当りが発生したときにリセットされる。 It should be noted that confirmation of whether or not the current gaming state is the variable probability state is performed by whether or not the variable probability flag is set. The variable probability flag is set when the game state is shifted to the variable probability state, and is reset when ending the variable probability state. Specifically, it is determined to be "variable probability big hit" or "suddenly variable probability big win", and is set in the process of ending the big win game. After the end of the big win game, it is reset when the next big win occurs.
大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)の値がいずれの大当り判定値にも一致しなければ(ステップS61のN)、CPU56は、小当り判定テーブル(図8(B),(C)参照)を使用して小当りの判定の処理を行う。すなわち、CPU56は、大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)の値が図8(B),(C)に示すいずれかの小当り判定値に一致すると、特別図柄に関して小当りとすることに決定する。この場合、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが示すデータを確認し、特別図柄ポインタが示すデータが「第1」である場合には、図8(B)に示す小当り判定テーブル(第1特別図柄用)を用いて小当りとするか否かを決定する。また、特別図柄ポインタが示すデータが「第2」である場合には、図8(C)に示す小当り判定テーブル(第2特別図柄用)を用いて小当りとするか否かを決定する。そして、小当りとすることに決定した場合には(ステップS62)、CPU56は、小当りであることを示す小当りフラグをセットし(ステップS63)、ステップS75に移行する。
If the value of the big hit determination random number (random R) does not match any of the big hit determination values (N in step S61), the
なお、ランダムRの値が大当り判定値および小当り判定値のいずれにも一致しない場合には(ステップS62のN)、すなわち、はずれである場合には、そのままステップS75に移行する。 If the value of random R does not coincide with either the big hit determination value or the small hit determination value (N in step S62), that is, if it is a loss, the process proceeds directly to step S75.
ステップS71では、CPU56は、大当りであることを示す大当りフラグをセットする。そして、大当り種別を複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定するために使用するテーブルとして、特別図柄ポインタが示す方の大当り種別判定テーブルを選択する(ステップS72)。具体的には、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが「第1」を示している場合には、図8(D)に示す第1特別図柄用の大当り種別判定用テーブル131aを選択する。また、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが「第2」を示している場合には、図8(E)に示す第2特別図柄用の大当り種別判定用テーブル131bを選択する。
In step S71, the
次いで、CPU56は、選択した大当り種別判定テーブルを用いて、乱数バッファ領域に格納された大当り種別判定用の乱数(ランダム1)の値と一致する値に対応した種別(「通常大当り」、「確変大当り」または「突然確変大当り」)を大当りの種別に決定する(ステップS73)。なお、この場合、CPU56は、第1始動口スイッチ通過処理のステップS1214Aや第2始動口スイッチ通過処理のステップS1214Bで抽出し第1保留記憶バッファや第2保留記憶バッファにあらかじめ格納した大当り種別判定用乱数を読み出し、大当り種別の決定を行う。また、この場合に、図8(D),(E)に示すように、第1特別図柄の変動表示が実行される場合には、第2特別図柄の変動表示が実行される場合と比較して、突然確変大当りが選択される割合が高い。
Next, using the selected jackpot type determination table, the
また、CPU56は、決定した大当りの種別を示すデータをRAM55における大当り種別バッファに設定する(ステップS74)。例えば、大当り種別が「通常大当り」の場合には大当り種別を示すデータとして「01」が設定され、大当り種別が「確変大当り」の場合には大当り種別を示すデータとして「02」が設定され、大当り種別が「突然確変大当り」の場合には大当り種別を示すデータとして「03」が設定される。
Further, the
次いで、CPU56は、特別図柄の停止図柄を決定する(ステップS75)。具体的には、大当りフラグおよび小当りフラグのいずれもセットされていない場合には、はずれ図柄となる「-」を特別図柄の停止図柄に決定する。大当りフラグがセットされている場合には、大当り種別の決定結果に応じて、大当り図柄となる「1」、「3」、「7」のいずれかを特別図柄の停止図柄に決定する。すなわち、大当り種別を「突然確変大当り」に決定した場合には「1」を特別図柄の停止図柄に決定し、「通常大当り」に決定した場合には「3」を特別図柄の停止図柄に決定し、「確変大当り」に決定した場合には「7」を特別図柄の停止図柄に決定する。また、小当りフラグがセットされている場合には、小当り図柄となる「5」を特別図柄の停止図柄に決定する。
Next, the
なお、この実施の形態では、まず大当り種別を決定し、決定した大当り種別に対応する特別図柄の停止図柄を決定する場合を示したが、大当り種別および特別図柄の停止図柄の決定方法は、この実施の形態で示したものにかぎられない。例えば、あらかじめ特別図柄の停止図柄と大当り種別とを対応付けたテーブルを用意しておき、大当り種別決定用乱数にもとづいてまず特別図柄の停止図柄を決定すると、その決定結果にもとづいて対応する大当り種別も決定されるように構成してもよい。 In this embodiment, first, the jackpot type is determined, and the stop pattern of the special pattern corresponding to the determined jackpot type is determined. It is not limited to those shown in the embodiment. For example, a table in which stop symbols of special symbols are associated with jackpot types is prepared in advance, and when the stop symbols of special symbols are first determined based on the random numbers for determining the jackpot types, the corresponding jackpots are based on the result of the determination. The type may also be determined.
そして、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を変動パターン設定処理(ステップS301)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS76)。 Then, the value of the special symbol process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the variation pattern setting process (step S301) (step S76).
図25は、特別図柄プロセス処理における変動パターン設定処理(ステップS301)を示すフローチャートである。変動パターン設定処理において、CPU56は、大当りフラグがセットされているか否か確認する(ステップS91)。大当りフラグがセットされている場合には、CPU56は、変動パターン種別を複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定するために使用するテーブルとして、大当り用変動パターン種別判定テーブル132A~132C(図9(A)~(C)参照)のいずれかを選択する(ステップS92)。そして、ステップS100に移行する。
FIG. 25 is a flow chart showing the variation pattern setting process (step S301) in the special symbol process process. In the variation pattern setting process, the
大当りフラグがセットされていない場合には、CPU56は、小当りフラグがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS93)。小当りフラグがセットされている場合には、CPU56は、変動パターン種別を複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定するために使用するテーブルとして、小当り用変動パターン種別判定テーブル132D(図9(D)参照)を選択する(ステップS94)。そして、ステップS100に移行する。
When the big hit flag is not set, the
小当りフラグもセットされていない場合には、CPU56は、時短状態であることを示す時短フラグがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS95)。なお、時短フラグは、遊技状態を確変状態や時短状態に移行するときにセットされ、時短状態を終了するときにリセットされる。具体的には、「通常大当り」とすることに決定された場合には、大当り遊技を終了する処理において時短フラグがセットされる。また、大当り遊技終了後、所定回数(この実施の形態では100回)の変動表示を終了したときにリセットされる。なお、所定回数の変動表示を終了する前であっても、次の大当りが発生した場合にも、時短フラグがリセットされる。また、「確変大当り」または「突然確変大当り」とすることに決定された場合には、大当り遊技を終了する処理において確変フラグがセットされるとともに時短フラグがセットされる。そして、次の大当りが発生した場合に、確変フラグとともに時短フラグがリセットされる。
When the small hit flag is not set, the
時短フラグがセットされていなければ(ステップS95のN)、CPU56は、合算保留記憶数が3以上であるか否かを確認する(ステップS96)。合算保留記憶数が3未満であれば(ステップS96のN)、CPU56は、変動パターン種別を複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定するために使用するテーブルとして、はずれ用変動パターン種別判定テーブル135A(図10(A)参照)を選択する(ステップS97)。そして、ステップS100に移行する。
If the time saving flag is not set (N of step S95), the
合算保留記憶数が3以上である場合(ステップS96のY)には、CPU56は、変動パターン種別を複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定するために使用するテーブルとして、はずれ用変動パターン種別判定テーブル135B(図10(B)参照)を選択する(ステップS98)。そして、ステップS100に移行する。
If the total pending storage number is 3 or more (Y in step S96), the
時短フラグがセットされている場合(ステップS95のY)には、すなわち、遊技状態が確変状態または時短状態であれば(この実施の形態では、確変状態に移行される場合には必ず時短状態にも移行されるので(ステップS169,S170参照)、ステップS95でYと判定された場合には、確変状態の場合と時短状態のみに制御されている場合とがある)、CPU56は、変動パターン種別を複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定するために使用するテーブルとして、はずれ用変動パターン種別判定テーブル135C(図10(C)参照)を選択する(ステップS99)。そして、ステップS100に移行する。
If the time saving flag is set (Y in step S95), that is, if the game state is a probability variable state or a time saving state (in this embodiment, when it is shifted to a probability changing state, it is always in a time saving state (See steps S169 and S170), so if it is determined to be Y in step S95, there are cases where it is controlled only in the variable probability state and in the time saving state), the
この実施の形態では、ステップS95~S99の処理が実行されることによって、遊技状態が通常状態であって合算保留記憶数が3以上である場合には、図10(B)に示すはずれ用変動パターン種別判定テーブル135Bが選択される。また、遊技状態が確変状態または時短状態である場合には、図10(C)に示すはずれ用変動パターン種別判定テーブル135Cが選択される。この場合、後述するステップS100の処理で変動パターン種別として非リーチCA2-2が決定される場合があり、非リーチCA2-2の変動パターン種別が決定された場合には、ステップS102の処理で変動パターンとして短縮変動の非リーチPA1-2が決定される(図12参照)。従って、この実施の形態では、遊技状態が確変状態や時短状態である場合または合算保留記憶数が3以上である場合には、短縮変動の変動表示が行われる場合がある。なお、この実施の形態では、確変状態や時短状態で用いる短縮変動用の変動パターン種別判定テーブル(図10(C)参照)と、保留記憶数にもとづく短縮変動用の変動パターン種別判定テーブル(図10(B)参照)とが異なるテーブルである場合を示したが、短縮変動用の変動パターン種別判定テーブルとして共通のテーブルを用いるようにしてもよい。 In this embodiment, by executing the processing of steps S95 to S99, when the game state is the normal state and the total number of reserved storages is 3 or more, the losing variation shown in FIG. The pattern type determination table 135B is selected. Further, when the game state is the variable probability state or the time saving state, the variation pattern type determination table 135C for loss shown in FIG. 10(C) is selected. In this case, non-reach CA2-2 may be determined as the variation pattern type in the process of step S100 described later, and when the variation pattern type of non-reach CA2-2 is determined, the process of step S102 varies A non-reach PA1-2 of shortened variation is determined as a pattern (see FIG. 12). Therefore, in this embodiment, when the game state is the probability variable state or the time saving state, or when the total number of pending memories is 3 or more, the variable display of the shortened variation may be performed. In addition, in this embodiment, the variation pattern type determination table for shortened variation used in the probability variation state and the time saving state (see FIG. 10 (C)) and the variation pattern type determination table for shortened variation based on the number of retained memories (Fig. 10 (B)), but a common table may be used as the variation pattern type determination table for shortened variation.
次いで、CPU56は、乱数バッファ領域(第1保留記憶バッファまたは第2保留記憶バッファ)からランダム2(変動パターン種別判定用乱数)を読み出し、ステップS92、S94、S97、S98またはS99の処理で選択したテーブルを参照することによって、変動パターン種別を複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定する(ステップS100)。
Next, the
次いで、CPU56は、ステップS100の変動パターン種別の決定結果にもとづいて、変動パターンを複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定するために使用するテーブルとして、当り変動パターン判定テーブル137A、137B(図11参照)、はずれ変動パターン判定テーブル138A(図12参照)のうちのいずれかを選択する(ステップS101)。また、乱数バッファ領域(第1保留記憶バッファまたは第2保留記憶バッファ)からランダム3(変動パターン判定用乱数)を読み出し、ステップS101の処理で選択した変動パターン判定テーブルを参照することによって、変動パターンを複数種類のうちのいずれかに決定する(ステップS102)。なお、始動入賞のタイミングでランダム3(変動パターン判定用乱数)を抽出しないように構成する場合には、CPU56は、変動パターン判定用乱数(ランダム3)を生成するための変動パターン判定用乱数カウンタから値を直接抽出し、抽出した乱数値にもとづいて変動パターンを決定するようにしてもよい。
Next, the
次いで、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが示す方の図柄変動指定コマンドを、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS103)。具体的には、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが「第1」を示している場合には、第1図柄変動指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う。また、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが「第2」を示している場合には、第2図柄変動指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う。また、CPU56は、決定した変動パターンに対応する演出制御コマンド(変動パターンコマンド)を、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS104)。
Next, the
次に、CPU56は、RAM55に形成されている変動時間タイマに、選択された変動パターンに対応した変動時間に応じた値を設定する(ステップS105)。そして、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を表示結果指定コマンド送信処理(ステップS302)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS106)。
Next, the
図26は、表示結果指定コマンド送信処理(ステップS302)を示すフローチャートである。表示結果指定コマンド送信処理において、CPU56は、決定されている大当りの種類、小当り、はずれに応じて、表示結果1指定~表示結果5指定のいずれかの演出制御コマンド(図13参照)を送信する制御を行う。具体的には、CPU56は、まず、大当りフラグがセットされているか否か確認する(ステップS110)。セットされていない場合には、ステップS116に移行する。大当りフラグがセットされている場合、大当りの種別が「通常大当り」であるときには、表示結果2指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う(ステップS111,S112)。なお、「通常大当り」であるか否かは、具体的には、特別図柄通常処理のステップS74で大当り種別バッファに設定されたデータが「01」であるか否かを確認することによって判定できる。また、CPU56は、大当りの種別が「確変大当り」であるときには、表示結果3指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う(ステップS113,S114)。なお、「確変大当り」であるか否かは、具体的には、特別図柄通常処理のステップS74で大当り種別バッファに設定されたデータが「02」であるか否かを確認することによって判定できる。そして、「通常大当り」および「確変大当り」のいずれでもないときには(すなわち、「突然確変大当り」であるときには)、CPU56は、表示結果4指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う(ステップS115)。
FIG. 26 is a flow chart showing the display result specification command transmission process (step S302). In the display result designation command transmission process, the
一方、CPU56は、大当りフラグがセットされていないときには(ステップS110のN)、小当りフラグがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS116)。小当りフラグがセットされていれば、CPU56は、表示結果5指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う(ステップS117)。小当りフラグもセットされていないときは(ステップS116のN)、すなわち、はずれである場合には、CPU56は、表示結果1指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う(ステップS118)。
On the other hand, when the big hit flag is not set (N of step S110), the
そして、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を特別図柄変動中処理(ステップS303)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS119)。
Then, the
図27は、特別図柄プロセス処理における特別図柄変動中処理(ステップS303)を示すフローチャートである。特別図柄変動中処理において、CPU56は、まず、保留記憶数減算指定コマンド(第1保留記憶数減算指定コマンドまたは第2保留記憶数減算指定コマンド)を既に送信済みであるか否かを確認する(ステップS1121)。なお、保留記憶数減算指定コマンドを既に送信済みであるか否かは、例えば、後述するステップS1122で保留記憶数減算指定コマンドを送信する際に保留記憶数減算指定コマンドを送信したことを示す保留記憶数減算指定コマンド送信済フラグをセットするようにし、ステップS1121では、その保留記憶数減算指定コマンド送信済フラグがセットされているか否かを確認するようにすればよい。また、この場合、セットした保留記憶数減算指定コマンド送信済フラグは、特別図柄の変動表示を終了する際や大当りを終了する際に後述する特別図柄停止処理や大当り終了処理でリセットするようにすればよい。
FIG. 27 is a flow chart showing the special symbol changing process (step S303) in the special symbol process process. In the special symbol fluctuation processing, the
次いで、保留記憶数減算指定コマンドを送信済みでなければ、CPU56は、保留記憶数減算指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS1122)。この場合、特別図柄ポインタに「第1」を示す値が設定されている場合には、CPU56は、第1保留記憶数減算指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う。また、特別図柄ポインタに「第2」を示す値が設定されている場合には、CPU56は、第2保留記憶数減算指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う。
Next, if the reservation storage number subtraction designation command has not been transmitted, the
次いで、CPU56は、変動時間タイマを1減算し(ステップS1125)、変動時間タイマがタイムアウトしたら(ステップS1126)、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に図柄確定指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う(ステップS1127)。そして、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を特別図柄停止処理(ステップS304)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS1128)。変動時間タイマがタイムアウトしていない場合には、そのまま処理を終了する。
Next, the
図28は、特別図柄プロセス処理における特別図柄停止処理(ステップS304)を示すフローチャートである。特別図柄停止処理において、CPU56は、大当りフラグがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS131)。大当りフラグがセットされている場合には、CPU56は、セットされていれば、確変状態であることを示す確変フラグ、時短状態であることを示す時短フラグ、および時短状態における特別図柄の変動可能回数を示す時短回数カウンタをリセットし(ステップS132)、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に大当り開始指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う(ステップS133)。具体的には、大当りの種別が「通常大当り」または「確変大当り」である場合には大当り開始指定コマンド(コマンドA001(H))を送信する。また、大当りの種別が突然確変大当りである場合には小当り/突然確変大当り開始指定コマンド(コマンドA002(H))を送信する。なお、大当りの種別が「通常大当り」、「確変大当り」または「突然確変大当り」のいずれであるかは、RAM55に記憶されている大当り種別を示すデータ(大当り種別バッファに記憶されているデータ)にもとづいて判定される。
FIG. 28 is a flow chart showing special symbol stop processing (step S304) in special symbol process processing. In the special symbol stop processing, the
また、大当り表示時間タイマに大当り表示時間(大当りが発生したことを、例えば、演出表示装置9において報知する時間)に相当する値を設定する(ステップS134)。また、大入賞口開放回数カウンタに開放回数(例えば、「通常大当り」や「確変大当り」の場合には15回。「突然確変大当り」の場合には2回。)をセットする(ステップS135)。また、大当り遊技における1ラウンドあたりのラウンド時間もセットされる。具体的には、突然確変大当りの場合には、ラウンド時間として0.1秒がセットされ、通常大当りや確変大当りの場合には、ラウンド時間として29秒がセットされる。そして、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を大入賞口開放前処理(ステップS305)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS136)。
Also, a value corresponding to the big win display time (time for notifying the occurrence of the big win by the
また、ステップS131で大当りフラグがセットされていなければ、CPU56は、時短状態における特別図柄の変動可能回数を示す時短回数カウンタの値が0となっているか否かを確認する(ステップS137)。時短回数カウンタの値が0でなければ、CPU56は、時短回数カウンタの値を-1する(ステップS138)。そして、CPU56は、減算後の時短回数カウンタの値が0になった場合には(ステップS139)、時短フラグをリセットする(ステップS140)。
Further, if the big hit flag is not set in step S131, the
次いで、CPU56は、小当りフラグがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS141)。小当りフラグがセットされていれば、CPU56は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に小当り/突然確変大当り開始指定コマンド(コマンドA002(H))を送信する(ステップS142)。また、小当り表示時間タイマに小当り表示時間(小当りが発生したことを、例えば、演出表示装置9において報知する時間)に相当する値を設定する(ステップS143)。また、大入賞口開放回数カウンタに開放回数(例えば2回)をセットする(ステップS144)。また、小当り遊技における大入賞口の1回あたりの開放時間もセットされる。具体的には、突然確変大当りのラウンド時間と同じ0.1秒が、小当り遊技における大入賞口の1回あたりの開放時間としてセットされる。そして、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を小当り開始前処理(ステップS308)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS145)。
Next, the
小当りフラグもセットされていなければ(ステップS141のN)、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を特別図柄通常処理(ステップS300)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS146)。
If the small hit flag is not set (N of step S141), the
図29は、特別図柄プロセス処理における大当り終了処理(ステップS307)を示すフローチャートである。大当り終了処理において、CPU56は、大当り終了表示タイマが設定されているか否か確認し(ステップS160)、大当り終了表示タイマが設定されている場合には、ステップS164に移行する。大当り終了表示タイマが設定されていない場合には、大当りフラグをリセットし(ステップS161)、大当り終了指定コマンドを送信する制御を行う(ステップS162)。ここで、「通常大当り」または「確変大当り」であった場合には大当り終了指定コマンド(コマンドA301(H))を送信し、「突然確変大当り」であった場合には小当り/突然確変大当り終了指定コマンド(コマンドA302(H))を送信する。そして、大当り終了表示タイマに、演出表示装置9において大当り終了表示が行われている時間(大当り終了表示時間)に対応する表示時間に相当する値を設定し(ステップS163)、処理を終了する。
FIG. 29 is a flow chart showing the jackpot ending process (step S307) in the special symbol process process. In the jackpot end processing, the
ステップS164では、大当り終了表示タイマの値を1減算する(ステップS164)。そして、CPU56は、大当り終了表示タイマの値が0になっているか否か、すなわち大当り終了表示時間が経過したか否か確認する(ステップS165)。経過していなければ処理を終了する。
In step S164, 1 is subtracted from the value of the big hit end display timer (step S164). Then, the
大当り終了表示時間を経過していれば(ステップS165のY)、CPU56は、今回終了する大当りが通常大当りであるか否かを確認する(ステップS166)。なお、「通常大当り」であるか否かは、具体的には、特別図柄通常処理のステップS74で大当り種別バッファに設定されたデータが「01」であるか否かを確認することによって判定できる。通常大当りであれば、CPU56は、時短フラグをセットして時短状態に移行させる(ステップS167)。また、CPU56は、時短回数カウンタに所定回数(例えば100回)をセットする(ステップS168)。
If the jackpot end display time has elapsed (Y in step S165), the
通常大当りでなければ(すなわち、確変大当りまたは突然確変大当りであれば)、CPU56は、確変フラグをセットして確変状態に移行させる(ステップS169)とともに、時短フラグをセットして時短状態に移行させる(ステップS170)。
If it is not a normal jackpot (that is, if it is a probability variable jackpot or a sudden probability variable jackpot), the
そして、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を特別図柄通常処理(ステップS300)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS171)。
Then, the
図30は、主基板31に搭載される遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560(具体的には、CPU56)が実行する特別図柄表示制御処理(ステップS32)のプログラムの一例を示すフローチャートである。特別図柄表示制御処理では、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が3であるか否かを確認する(ステップS3201)。特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が3であれば(すなわち、特別図柄変動中処理の実行中であれば)、CPU56は、特別図柄変動表示用の特別図柄表示制御データを特別図柄表示制御データ設定用の出力バッファに設定または更新する処理を行う(ステップS3202)。この場合、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが示す方の特別図柄(第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄)の変動表示を行うための特別図柄表示制御データを設定または更新する。例えば、変動速度が1コマ/0.2秒であれば、0.2秒が経過する毎に、出力バッファに設定される特別図柄表示制御データの値を+1する。そして、その後、表示制御処理(ステップS22参照)が実行され、特別図柄表示制御データ設定用の出力バッファの内容に応じて特別図柄表示器8a,8bに対して駆動信号が出力されることによって、特別図柄表示器8a,8bにおける特別図柄の変動表示が実行される。
FIG. 30 is a flowchart showing an example of a program for special symbol display control processing (step S32) executed by the game control microcomputer 560 (specifically, the CPU 56) mounted on the
特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が3でなければ、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が4であるか否かを確認する(ステップS3203)。特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が4であれば(すなわち、特別図柄停止処理に移行した場合には)、CPU56は、特別図柄通常処理で設定された特別図柄の停止図柄を停止表示するための特別図柄表示制御データを特別図柄表示制御データ設定用の出力バッファに設定する処理を行う(ステップS3204)。この場合、CPU56は、特別図柄ポインタが示す方の特別図柄(第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄)の停止図柄を停止表示するための特別図柄表示制御データを設定する。そして、その後、表示制御処理(ステップS22参照)が実行され、特別図柄表示制御データ設定用の出力バッファの内容に応じて特別図柄表示器8a,8bに対して駆動信号が出力されることによって、特別図柄表示器8a,8bにおいて特別図柄の停止図柄が停止表示される。
If the value of the special symbol process flag is not 3, the
次に、演出制御手段の動作を説明する。図31は、演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御手段としての演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100(具体的には、演出制御用CPU101)が実行するメイン処理を示すフローチャートである。演出制御用CPU101は、電源が投入されると、メイン処理の実行を開始する。メイン処理では、まず、RAM領域のクリアや各種初期値の設定、また演出制御の起動間隔(例えば、4ms)を決めるためのタイマの初期設定等を行うための初期化処理を行う(ステップS701)。その後、演出制御用CPU101は、タイマ割込フラグの監視(ステップS702)を行うループ処理に移行する。タイマ割込が発生すると、演出制御用CPU101は、タイマ割込処理においてタイマ割込フラグをセットする。メイン処理において、タイマ割込フラグがセットされていたら、演出制御用CPU101は、そのフラグをクリアし(ステップS703)、以下の演出制御処理を実行する。
Next, the operation of the production control means will be described. FIG. 31 is a flow chart showing main processing executed by the effect control microcomputer 100 (specifically, the effect control CPU 101) as effect control means mounted on the
演出制御処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、まず、受信した演出制御コマンドを解析し、受信した演出制御コマンドに応じたフラグをセットする処理等を行う(コマンド解析処理:ステップS704)。
In the effect control process, the
次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御プロセス処理を行う(ステップS705)。演出制御プロセス処理では、制御状態に応じた各プロセスのうち、現在の制御状態(演出制御プロセスフラグ)に対応した処理を選択して演出表示装置9の表示制御を実行する。
Next, the
次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、第4図柄プロセス処理を行う(ステップS706)。第4図柄プロセス処理では、制御状態に応じた各プロセスのうち、現在の制御状態(第4図柄プロセスフラグ)に対応した処理を選択して演出表示装置9の第4図柄表示領域9c,9dにおいて第4図柄の表示制御を実行する。
Next, the
次いで、大当り図柄決定用乱数などの乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する乱数更新処理を実行する(ステップS707)。その後、ステップS702に移行する。 Next, random number update processing is executed to update the count value of the counter for generating random numbers such as the random number for determining the jackpot symbol (step S707). After that, the process moves to step S702.
図32は、主基板31の遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から受信した演出制御コマンドを格納するためのコマンド受信バッファの一構成例を示す説明図である。この例では、2バイト構成の演出制御コマンドを6個格納可能なリングバッファ形式のコマンド受信バッファが用いられる。従って、コマンド受信バッファは、受信コマンドバッファ1~12の12バイトの領域で構成される。そして、受信したコマンドをどの領域に格納するのかを示すコマンド受信個数カウンタが用いられる。コマンド受信個数カウンタは、0~11の値をとる。なお、必ずしもリングバッファ形式でなくてもよい。
FIG. 32 is an explanatory diagram showing one configuration example of a command receiving buffer for storing effect control commands received from the
図33~図35は、コマンド解析処理(ステップS704)の具体例を示すフローチャートである。主基板31から受信された演出制御コマンドは受信コマンドバッファに格納されるが、コマンド解析処理では、演出制御用CPU101は、コマンド受信バッファに格納されているコマンドの内容を確認する。
33 to 35 are flowcharts showing specific examples of the command analysis process (step S704). The production control command received from the
コマンド解析処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、まず、コマンド受信バッファに受信コマンドが格納されているか否か確認する(ステップS611)。格納されているか否かは、コマンド受信個数カウンタの値と読出ポインタとを比較することによって判定される。両者が一致している場合が、受信コマンドが格納されていない場合である。コマンド受信バッファに受信コマンドが格納されている場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、コマンド受信バッファから受信コマンドを読み出す(ステップS612)。なお、読み出したら読出ポインタの値を+2しておく(ステップS613)。+2するのは2バイト(1コマンド)ずつ読み出すからである。
In the command analysis process, the
受信した演出制御コマンドが変動パターンコマンドであれば(ステップS614)、演出制御用CPU101は、受信した変動パターンコマンドを、RAMに形成されている変動パターンコマンド格納領域に格納する(ステップS615)。そして、変動パターンコマンド受信フラグをセットする(ステップS616)。
If the received effect control command is a variation pattern command (step S614), the
受信した演出制御コマンドが表示結果指定コマンドであれば(ステップS617)、演出制御用CPU101は、受信した表示結果指定コマンド(表示結果1指定コマンド~表示結果5指定コマンド)を、RAMに形成されている表示結果指定コマンド格納領域に格納する(ステップS618)。
If the received production control command is a display result designation command (step S617), the
受信した演出制御コマンドが図柄確定指定コマンドであれば(ステップS619)、演出制御用CPU101は、確定コマンド受信フラグをセットする(ステップS620)。
If the received effect control command is a pattern confirmation designation command (step S619), the
受信した演出制御コマンドがいずれかの図柄指定コマンドであれば(ステップS621)、演出制御用CPU101は、受信した図柄指定コマンドを、RAMに形成されている始動入賞時コマンド格納領域の空いている最初の格納領域に格納する(ステップS622)。
If the received effect control command is one of the symbol designation commands (step S621), the
受信した演出制御コマンドがいずれかの変動カテゴリコマンドであれば(ステップS623)、演出制御用CPU101は、受信した変動カテゴリコマンドを、RAMに形成されている始動入賞時コマンド格納領域の各格納領域のうち最新の図柄指定コマンドが格納されている格納領域に格納する(ステップS624)。
If the received effect control command is one of the variable category commands (step S623), the
受信した演出制御コマンドが第1保留記憶数加算指定コマンドであれば(ステップS625)、演出制御用CPU101は、受信した第1保留記憶数加算指定コマンドを、RAMに形成されている始動入賞時コマンド格納領域の各格納領域のうち最新の図柄指定コマンドおよび変動カテゴリコマンドが格納されている格納領域に格納する(ステップS626)。ただし、遊技状態が確変状態や時短状態、大当り遊技状態、小当り遊技状態中である場合には、図柄指定コマンドおよび変動カテゴリコマンドが送信されず、第1保留記憶数加算指定コマンドのみが送信される場合もある(ステップS1215A~S1219A参照)ので、その場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、受信した第1保留記憶数加算指定コマンドを、RAMに形成されている始動入賞時コマンド格納領域の空いている最初の格納領域に格納する。
If the received production control command is the first reserved storage number addition designation command (step S625), the
また、演出制御用CPU101は、第1保留記憶表示部9aにおいて通常態様(本例では、白色の球形表示)により保留表示を1つ増加させて、第1保留記憶表示部9aにおける第1保留記憶数表示を更新する(ステップS627)。また、演出制御用CPU101は、RAMに形成されている第1保留記憶数保存領域に格納する第1保留記憶数の値を1加算する(ステップS628)。
In addition, the
受信した演出制御コマンドが第2保留記憶数加算指定コマンドであれば(ステップS629)、演出制御用CPU101は、受信した第2保留記憶数加算指定コマンドを、RAMに形成されている始動入賞時コマンド格納領域の各格納領域のうち最新の図柄指定コマンドおよび変動カテゴリコマンドが格納されている格納領域に格納する(ステップS630)。
If the received effect control command is the second reserved memory number addition designation command (step S629), the
また、演出制御用CPU101は、第2保留記憶表示部9bにおいて通常態様(本例では、白色の球形表示)により保留表示を1つ増加させて、第2保留記憶表示部9bにおける第2保留記憶数表示を更新する(ステップS631)。また、演出制御用CPU101は、RAMに形成されている第2保留記憶数保存領域に格納する第2保留記憶数の値を1加算する(ステップS632)。
In addition, the
受信した演出制御コマンドが第1保留記憶数減算指定コマンドであれば(ステップS633)、演出制御用CPU101は、第1保留記憶表示部9aにおける保留表示を1つ消去し、残りの保留表示を1つずつシフトして、第1保留記憶表示部9aにおける第1保留記憶数表示を更新する(ステップS634)。また、演出制御用CPU101は、RAMに形成されている第1保留記憶数保存領域に格納する第1保留記憶数の値を1減算する(ステップS635)。
If the received production control command is the first reserved storage number subtraction designation command (step S633), the
受信した演出制御コマンドが第2保留記憶数減算指定コマンドであれば(ステップS636)、演出制御用CPU101は、第2保留記憶表示部9bにおける保留表示を1つ消去し、残りの保留表示を1つずつシフトして、第2保留記憶表示部9bにおける第2保留記憶数表示を更新する(ステップS637)。また、演出制御用CPU101は、RAMに形成されている第2保留記憶数保存領域に格納する第2保留記憶数の値を1減算する(ステップS638)。
If the received effect control command is the second reserved memory number subtraction designation command (step S636), the
受信した演出制御コマンドが通常状態背景指定コマンドであれば(ステップS639)、演出制御用CPU101は、演出表示装置9に表示する背景画面を通常状態に応じた背景画面(例えば、青色の表示色の背景画面)に変更する(ステップS640)。また、演出制御用CPU101は、セットされていれば、遊技状態が時短状態であることを示す時短状態フラグをリセットする(ステップS641)。
If the received effect control command is a normal state background designation command (step S639), the
受信した演出制御コマンドが時短状態背景指定コマンドであれば(ステップS642)、演出制御用CPU101は、演出表示装置9に表示する背景画面を時短状態に応じた背景画面(例えば、緑色の表示色の背景画面)に変更する(ステップS643)。また、演出制御用CPU101は、時短状態フラグをセットする(ステップS644)。また、演出制御用CPU101は、セットされていれば、遊技状態が確変状態であることを示す確変状態フラグをリセットする(ステップS645)。
If the received production control command is a time saving state background designation command (step S642), the
受信した演出制御コマンドが確変状態背景指定コマンドであれば(ステップS646)、演出制御用CPU101は、演出表示装置9に表示する背景画面を確変状態に応じた背景画面(例えば、赤色の表示色の背景画面)に変更する(ステップS647)。また、演出制御用CPU101は、確変状態フラグをセットする(ステップS648)。
If the received effect control command is a probability changing state background designation command (step S646), the
受信した演出制御コマンドが第1図柄変動指定コマンドであれば(ステップS649)、演出制御用CPU101は、第1図柄変動指定コマンド受信フラグをセットする(ステップS650)。受信した演出制御コマンドが第2図柄変動指定コマンドであれば(ステップS651)、演出制御用CPU101は、第2図柄変動指定コマンド受信フラグをセットする(ステップS652)。
If the received effect control command is the first symbol variation designation command (step S649), the
受信した演出制御コマンドがその他のコマンドであれば、演出制御用CPU101は、受信した演出制御コマンドに応じたフラグをセットする(ステップS653)。例えば、受信した演出制御コマンドが大当り開始指定コマンドであれば大当り開始指定コマンド受信フラグをセットし、受信した演出制御コマンドが大当り終了指定コマンドであれば大当り終了指定コマンド受信フラグをセットする。そして、ステップS611に移行する。
If the received production control command is another command, the
図36は、図31に示されたメイン処理における演出制御プロセス処理(ステップS705)を示すフローチャートである。演出制御プロセス処理では、演出制御用CPU101は、まず、保留予告演出の有無や変化パターン、変化タイミングを設定する保留予告演出設定処理を実行する(ステップS800A)。
FIG. 36 is a flow chart showing the effect control process (step S705) in the main process shown in FIG. In the effect control process, the
次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御プロセスフラグの値に応じてステップS800~S807のうちのいずれかの処理を行う。各処理において、以下のような処理を実行する。なお、演出制御プロセス処理では、演出表示装置9の表示状態が制御され、演出図柄の可変表示が実現されるが、第1特別図柄の変動に同期した演出図柄の可変表示に関する制御も、第2特別図柄の変動に同期した演出図柄の可変表示に関する制御も、一つの演出制御プロセス処理において実行される。
Next, the
変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(ステップS800):遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から変動パターンコマンドを受信しているか否か確認する。具体的には、コマンド解析処理でセットされる変動パターンコマンド受信フラグがセットされているか否か確認する。変動パターンコマンドを受信していれば、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動開始処理(ステップS801)に対応した値に変更する。
Variation pattern command reception waiting process (step S800): It is confirmed whether or not a variation pattern command is received from the
演出図柄変動開始処理(ステップS801):演出図柄の変動が開始されるように制御する。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動中処理(ステップS802)に対応した値に更新する。 Effect symbol variation start processing (step S801): Control is performed so that the effect symbol variation is started. Then, the value of the production control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the production design changing process (step S802).
演出図柄変動中処理(ステップS802):変動パターンを構成する各変動状態(変動速度)の切替タイミング等を制御するとともに、変動時間の終了を監視する。そして、変動時間が終了したら、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動停止処理(ステップS803)に対応した値に更新する。 Effect symbol change process (step S802): Controls the switching timing of each change state (change speed) that constitutes the change pattern, and monitors the end of the change time. Then, when the fluctuation time ends, the value of the production control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the production symbol fluctuation stop processing (step S803).
演出図柄変動停止処理(ステップS803):演出図柄の変動を停止し表示結果(停止図柄)を導出表示する制御を行う。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を大当り表示処理(ステップS804)または変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(ステップS800)に対応した値に更新する。 Effect symbol variation stop processing (step S803): Control is performed to stop the variation of the effect symbol and derive and display the display result (stop symbol). Then, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the big hit display process (step S804) or the variation pattern command reception waiting process (step S800).
大当り表示処理(ステップS804):変動時間の終了後、演出表示装置9に大当りの発生を報知するための画面を表示する制御を行う。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値をラウンド中処理(ステップS805)に対応した値に更新する。
Big hit display processing (step S804): After the fluctuation time is over, control is performed to display a screen for notifying the occurrence of a big hit on the
ラウンド中処理(ステップS805):ラウンド中の表示制御を行う。そして、ラウンド終了条件が成立したら、最終ラウンドが終了していなければ、演出制御プロセスフラグの値をラウンド後処理(ステップS806)に対応した値に更新する。最終ラウンドが終了していれば、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を大当り終了処理(ステップS807)に対応した値に更新する。 In-round processing (step S805): Perform display control during the round. Then, when the round end condition is met, if the final round has not ended, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the post-round processing (step S806). If the final round has ended, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the jackpot end processing (step S807).
ラウンド後処理(ステップS806):ラウンド間の表示制御を行う。そして、ラウンド開始条件が成立したら、演出制御プロセスフラグの値をラウンド中処理(ステップS805)に対応した値に更新する。 Post-round processing (step S806): Perform display control between rounds. Then, when the round start condition is established, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the round process (step S805).
大当り終了演出処理(ステップS807):演出表示装置9において、大当り遊技状態が終了したことを遊技者に報知する表示制御を行う。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(ステップS800)に対応した値に更新する。
Big hit end effect processing (step S807): The
図37は、保留予告演出設定処理(ステップS800A)を示すフローチャートである。保留予告演出設定処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、まず、1セットの始動入賞時のコマンド(すなわち、図柄指定コマンド、変動カテゴリコマンド、および保留記憶数加算指定コマンド(第1保留記憶数加算指定コマンドまたは第2保留記憶数加算指定コマンド)のセット)を新たに受信したか否かを確認する(ステップS6001)。具体的には、始動入賞時コマンド格納領域に1セットの図柄指定コマンド、変動カテゴリコマンド、および保留記憶数加算指定コマンド(第1保留記憶数加算指定コマンドまたは第2保留記憶数加算指定コマンド)が新たに格納されているか否かを判定することによって確認できる。1セットの始動入賞時のコマンドを新たに受信していなければ、そのまま処理を終了する。
FIG. 37 is a flowchart showing the pending notice effect setting process (step S800A). In the pending notice effect setting process, the
1セットの始動入賞時のコマンドを新たに受信していれば、演出制御用CPU101は、時短状態フラグがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS6002)。時短状態フラグがセットされていれば(すなわち、時短状態であれば)、そのまま処理を終了する。
If the command at the time of starting winning of one set is newly received, the
時短状態フラグがセットされていなければ(すなわち、非時短状態であれば)、演出制御用CPU101は、新たに受信した保留記憶数加算指定コマンド(始動入賞時コマンド格納領域に新たに格納された保留記憶数加算指定コマンド)が第1保留記憶数加算指定コマンドであるか否かを確認する(ステップS6003)。第1保留記憶数加算指定コマンドを新たに受信した場合でなければ(すなわち、第2保留記憶数加算指定コマンドを新たに受信した場合であれば)、そのまま処理を終了する。
If the time saving state flag is not set (that is, if it is a non-working time saving state), the
ステップS6002,S6003の処理が実行されることによって、この実施の形態では、遊技状態が非時短状態に制御されているときに第1始動入賞口13への始動入賞が新たに発生した場合にのみ、ステップS6004以降の処理が実行され、保留予告演出を実行することが可能に構成されている。時短状態に制御されているときに保留予告演出を実行しないのは、保留予告演出を効果的に実行する期間を確保することが難しい場合があるからである。特に、この実施の形態では、特殊態様により表示された後に特別態様に変化する保留予告演出が実行されるが、時短状態に制御されているときには可変表示期間が短いため、特殊態様により表示される期間も短く、早々に特別態様に変化させるようになってしまい、面白味がなくなってしまうおそれがあるからである。
By executing the processing of steps S6002 and S6003, in this embodiment, only when the starting winning to the first
この実施の形態では、第2特別図柄の変動表示は第1特別図柄の変動表示よりも優先されるため、第1始動入賞口13への始動入賞にもとづいて保留予告演出が実行されているとき(例えば、特殊態様により保留表示が表示されているとき)に、第2始動入賞口14への始動入賞が発生すると、保留予告演出の予告対象の第1特別図柄の変動表示よりも先に、第2特別図柄の変動表示が実行される。この場合、優先して実行される第2特別図柄の変動表示が終了するまでは、予告対象の保留表示の表示態様は、特殊態様から特別態様に変化しない(すなわち待機状態となる)。
In this embodiment, since the variable display of the second special symbol has priority over the variable display of the first special symbol, when the suspension notice effect is executed based on the start winning to the first start winning port 13 (For example, when the suspension display is displayed in a special mode), when the start winning to the second
なお、この実施の形態で示した態様にかぎらず、例えば、時短状態に制御されているときに第2始動入賞口14への始動入賞が発生した場合にも保留予告演出を実行可能に構成してもよい。
In addition, not only the mode shown in this embodiment, for example, even when the start winning to the second
また、例えば、第1始動入賞口13と第2始動入賞口14への入賞順に第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄の変動表示を実行するように構成する場合には、遊技状態が時短状態であるか否かに関係なく、また第1始動入賞口13と第2始動入賞口14とのいずれに対しての始動入賞であるかに関係なく、保留予告演出を実行可能に構成してもよい。
Further, for example, in the case of performing the variable display of the first special symbol and the second special symbol in the order of winning to the first start
次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、第1保留記憶数が2以上であるか否かを確認する(ステップS6004)。なお、第1保留記憶数が2以上であるか否かは、例えば、第1保留記憶数保存領域(ステップS628,S635参照)に格納されている第1保留記憶数を確認することにより判定できる。第1保留記憶数が2以上でなければ(すなわち、第1保留記憶数が1であれば)、そのまま処理を終了する。
Next, the
始動入賞のタイミングで第1保留記憶数が1しかないときには、その後、第1保留記憶の保留シフトが行われた場合に直ちにその保留を消化して変動表示が行われるのであるから、保留表示を表示する期間が短く、保留予告演出を実行する期間を十分に確保できないおそれがある。そこで、この実施の形態では、ステップS6004で第1保留記憶数が2以上でなければ、保留予告演出を実行できないと判断して、そのまま処理を終了するように構成している。 When the number of the first reserved memories is only 1 at the timing of starting winning, when the reserved shift of the first reserved memory is performed after that, the reservation is immediately consumed and the variable display is performed, so the reserved display is performed. The display period is short, and there is a possibility that a sufficient period for executing the suspension notice effect cannot be secured. Therefore, in this embodiment, if the first reserved memory number is not equal to or greater than 2 in step S6004, it is determined that the reserved advance notice effect cannot be executed, and the processing is terminated as it is.
なお、この実施の形態で示した態様にかぎらず、第1保留記憶数が1であってもステップS6005以降の処理に移行して保留予告演出を実行可能に構成してもよい。この場合には、例えば、保留表示を引き継いで表示されるアクティブ表示の表示態様を通常態様から特殊態様や特別態様に変化させる保留予告演出を実行可能としてもよい。 It should be noted that, regardless of the mode shown in this embodiment, even if the number of first pending memories is 1, the processing after step S6005 may be shifted to execute the pending notice effect. In this case, for example, it may be possible to execute a suspension notice effect that changes the display mode of the active display that is displayed after taking over the suspension display from the normal mode to the special mode or the special mode.
第1保留記憶数が2以上であれば、演出制御用CPU101は、受信した最新の変動カテゴリコマンドにもとづいて、最新の保留表示の最終表示態様を決定する(ステップS6005)。ステップS6005では、演出制御用CPU101は、最新の変動カテゴリコマンドにもとづいて、最終表示態様決定テーブルを用いて、乱数にもとづく抽選処理を行い、最新の保留表示の最終表示態様を決定する。なお、この実施の形態では、保留表示の表示態様を引き継いでアクティブ表示が表示され、当該アクティブ表示の表示態様が変化する場合もあるため、「最終表示態様」とは、厳密には保留表示を引き継いで表示されるアクティブ表示の最終表示態様を意味する。
If the first pending memory number is 2 or more, the
図38は、最終表示態様決定テーブルの具体例を示す説明図である。図38に示すように、この実施の形態では、最終表示態様決定テーブルにおいて、保留表示およびアクティブ表示の最終表示態様として、通常態様(白色の球形表示)、第1特殊態様(青色の箱形表示)、第2特殊態様(緑色の箱形表示)、第3特殊態様(赤色の箱形表示)、第1特別態様(青色の球形表示)、第2特別態様(緑色の球形表示)、第3特別態様(赤色の球形表示)および第4特別態様(虹色の球形表示)に対して、それぞれ判定値が割り当てられている。以下、第1~第3特殊態様を特殊態様と総称することがある。また、第1~第4特別態様を特別態様と総称することがある。 FIG. 38 is an explanatory diagram showing a specific example of the final display mode determination table. As shown in FIG. 38, in this embodiment, in the final display mode determination table, the final display modes of the pending display and the active display are the normal mode (white spherical display), the first special mode (blue box display), and the final display mode. ), 2nd special mode (green box representation), 3rd special mode (red box representation), 1st special mode (blue sphere representation), 2nd special mode (green sphere representation), 3rd A judgment value is assigned to each of the special mode (red spherical display) and the fourth special mode (rainbow spherical display). Hereinafter, the first to third special modes may be collectively referred to as special modes. Also, the first to fourth special modes may be collectively referred to as special modes.
図38に示すように、この実施の形態では、変動カテゴリコマンドで示される変動カテゴリが非リーチはずれ、スーパーリーチはずれまたはスーパーリーチ大当りである場合に、保留予告演出を実行可能に構成されており、変動カテゴリコマンドで示される変動カテゴリがそれ以外の変動カテゴリである場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、そのまま保留表示の最終表示態様を通常態様(白球)に決定し、保留予告演出を実行しないことに決定する。
As shown in FIG. 38, in this embodiment, when the variable category indicated by the variable category command is non-reach loss, super reach loss, or super reach jackpot, the suspension notice effect can be executed, When the variable category indicated by the variable category command is another variable category, the
また、図38に示すように、この実施の形態では、スーパーリーチはずれやスーパーリーチ大当りとなる場合には、非リーチはずれとなる場合と比較して、最終的に通常態様よりも特別態様に変化する割合が高くなっている。従って、この実施の形態では、保留表示およびアクティブ表示が最終的に特別態様に変化する場合には、最終的に通常態様である場合と比較して、スーパーリーチに対する期待度(リーチ信頼度)が高くなっている。 Also, as shown in FIG. 38, in this embodiment, in the case of a super reach loss or a super reach jackpot, compared with the case of a non-reach loss, the final mode changes from the normal mode to the special mode. are more likely to do so. Therefore, in this embodiment, when the pending display and the active display finally change to the special mode, the degree of expectation (reach reliability) for super reach increases compared to the case of the final normal mode. getting higher.
また、図38に示すように、この実施の形態では、スーパーリーチ大当りとなる場合には、非リーチはずれやスーパーリーチはずれとなる場合と比較して、最終的に通常態様よりも特別態様に変化する割合が高くなっている。また、図38に示すように、この実施の形態では、スーパーリーチ大当りとなる場合には、非リーチはずれやスーパーリーチはずれとなる場合と比較して、最終的に第1特別態様(青球)よりも第2特別態様(緑球)に、第2特別態様(緑球)よりも第3特別態様(赤球)に変化する割合が高くなっている。また、スーパーリーチ大当りとなる場合にのみ第4特別態様(虹球)に変化するようになっている。従って、この実施の形態では、予告対象の保留表示およびアクティブ表示が、最終的に第4特別態様(虹球)に変化すると大当り確定となり、次いで、第3特別態様(赤球)>第2特別態様(緑球)>第1特別態様(青球)の順に大当りに対する期待度(大当り信頼度)が高くなっている。 Also, as shown in FIG. 38, in this embodiment, in the case of a super reach jackpot, compared with the case of non-reach loss and super reach loss, the final mode changes from the normal mode to the special mode. are more likely to do so. In addition, as shown in FIG. 38, in this embodiment, when the super reach jackpot is achieved, the final first special mode (blue ball) is compared with the non-reach loss and the super reach loss. The rate of change to the second special mode (green ball) is higher than that of the second special mode (green ball), and the rate of change to the third special mode (red ball) is higher than that of the second special mode (green ball). In addition, it is changed to the fourth special mode (rainbow ball) only when a super reach jackpot is achieved. Therefore, in this embodiment, when the pending display and active display of the announcement target finally change to the fourth special mode (rainbow ball), the big hit is confirmed, and then the third special mode (red ball) > second special mode. The degree of expectation (reliability of big win) for the big win increases in the order of mode (green ball)>first special mode (blue ball).
この実施の形態では、後述するように、保留予告演出の変化パターンとして、予告対象の保留表示(またはアクティブ表示)が特殊態様により一旦表示された後に、特別態様に変化する変化パターンが設けられている。そのため、特殊態様は、特別態様に変化することを示唆する態様であるともいえる。そのような構成において、この実施の形態では、図38に示すように、非リーチはずれとなる場合に、第1特殊態様(青箱)に対して、判定値が割り当てられている。すなわち、予告対象の保留表示(またはアクティブ表示)が第1特殊態様(青箱)により表示されたものの、特別態様に変化しない場合には、非リーチはずれとなる。このような構成により、特殊態様が特別態様に変化するか否かに着目させることができる。また、第1~第3特殊態様のいずれであるかに応じて、特別態様に変化する割合が異なるため、特殊態様の種類にも着目させることができる。なお、この実施の形態では、第1特殊態様(青箱)よりも期待度(期待度の詳細については後述する)が高い第2特殊態様(緑箱)や第3特殊態様(赤箱)の場合には、必ず特別態様に変化するように構成されているが、変化しない場合があるようにしてもよい。この場合には、例えば、第3特殊態様(赤箱)>第2特殊態様(緑箱)>第1特殊態様(青箱)の順に、特別態様に変化する割合が高くなるようにしてもよい。 In this embodiment, as will be described later, as a change pattern of the pending notice effect, a change pattern is provided in which the pending display (or active display) of the notice target is temporarily displayed in a special mode and then changed to a special mode. there is Therefore, it can also be said that the special mode is a mode that suggests changing to a special mode. In such a configuration, in this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 38, a judgment value is assigned to the first special mode (blue box) in the case of non-reach loss. That is, if the pending display (or active display) of the notice target is displayed in the first special mode (blue box) but does not change to the special mode, the non-reach is lost. With such a configuration, it is possible to focus attention on whether or not the special mode changes to the special mode. Moreover, since the rate of change to the special mode differs depending on which one of the first to third special modes, attention can also be paid to the type of the special mode. In addition, in this embodiment, the second special mode (green box) and the third special mode (red box) whose degree of expectation (details of the degree of expectation will be described later) are higher than the first special mode (blue box) In some cases, it is configured to always change to a special mode, but it may not change in some cases. In this case, for example, the rate of change to the special mode may increase in the order of third special mode (red box)>second special mode (green box)>first special mode (blue box). .
この実施の形態では、図38に示すように、入賞時判定結果が非リーチはずれ、スーパーリーチはずれ、およびスーパーリーチ大当りとなる場合に保留予告演出を実行可能に構成する場合を示しているが、そのような態様にかぎられない。例えば、ノーマルリーチとなることが特定可能な変動カテゴリがある場合に、入賞時判定結果がノーマルリーチはずれやノーマルリーチ大当りとなることにもとづいて保留予告演出を実行可能に構成してもよい。 In this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 38, when the judgment result at the time of winning is non-reach, super reach, and super reach jackpot, the suspension notice effect can be executed. It is not limited to such aspects. For example, when there is a variable category that can be specified as normal reach, the suspension notice performance may be executed based on the result of determination at the time of winning as a loss of normal reach or a big win in normal reach.
保留予告演出を実行しないことに決定した場合(ステップS6006のN)、すなわち、最終表示態様として通常態様に決定した場合や、変動カテゴリが非リーチはずれやスーパーリーチはずれ、スーパーリーチ大当りを示すものでなかった場合には、そのまま処理を終了する。保留予告演出を実行することに決定した場合(ステップS6006のY)、演出制御用CPU101は、受信した最新の変動カテゴリコマンドおよび最終表示態様にもとづいて、予告対象の保留表示およびアクティブ表示の変化パターンを決定する(ステップS6007a)。ステップS6007aでは、演出制御用CPU101は、最新の変動カテゴリコマンドおよび最終表示態様にもとづいて、予告対象の保留表示およびアクティブ表示の変化パターンを決定するための変化パターン決定テーブルを選択する。そして、演出制御用CPU101は、選択した変化パターン決定テーブルを用いて、乱数にもとづく抽選処理を行い、予告対象の保留表示およびアクティブ表示の変化パターンを決定する。
When it is determined not to execute the pending notice effect (N of step S6006), that is, when the normal mode is determined as the final display mode, or when the variation category is non-reach loss, super reach loss, or super reach jackpot. If not, the process ends. When it is decided to execute the pending notice effect (Y in step S6006), the
図39(A)は、変化パターンの具体例を示す説明図である。また、図39(B)~(F)は、変化パターン決定テーブルの具体例を示す説明図である。 FIG. 39A is an explanatory diagram showing a specific example of change patterns. Also, FIGS. 39B to 39F are explanatory diagrams showing specific examples of the change pattern determination table.
図39(A)に示されるように、第1変化パターンでは、予告対象の保留表示が、通常態様で表示された後に、通常態様から最終表示態様に変化する。また、第2変化パターンでは、予告対象の保留表示が、通常態様で表示された後に、通常態様から第1特殊態様に変化し、その後、予告対象の保留表示を引き継いだアクティブ表示が、第1特殊態様から最終表示態様に変化する。また、第3変化パターンでは、予告対象の保留表示が、通常態様で表示された後に、通常態様から第1特殊態様に変化し、さらに第1特殊態様から第2特殊態様に変化し、その後、予告対象の保留表示を引き継いだアクティブ表示が、第2特殊態様から最終表示態様に変化する。また、第4変化パターンでは、予告対象の保留表示が、通常態様で表示された後に、通常態様から第1特殊態様に変化し、次いで第1特殊態様から第2特殊態様に変化し、さらに第2特殊態様から第3特殊態様に変化し、その後、予告対象の保留表示を引き継いだアクティブ表示が、第3特殊態様から最終表示態様に変化する。 As shown in FIG. 39A, in the first change pattern, the pending display of the announcement target is displayed in the normal mode, and then changed from the normal mode to the final display mode. Further, in the second change pattern, after the pending display of the notice target is displayed in the normal mode, it changes from the normal mode to the first special mode, and then the active display taking over the pending display of the notice target is displayed in the first mode. It changes from the special mode to the final display mode. Further, in the third change pattern, after the pending display of the notice target is displayed in the normal mode, it changes from the normal mode to the first special mode, further changes from the first special mode to the second special mode, and then, The active display taking over the pending display of the notice target changes from the second special mode to the final display mode. In addition, in the fourth change pattern, after the pending display of the announcement target is displayed in the normal mode, it changes from the normal mode to the first special mode, then changes from the first special mode to the second special mode, and then changes to the second special mode. The second special mode changes to the third special mode, and then the active display that takes over the pending display of the announcement target changes from the third special mode to the final display mode.
図39(A)に示されるように、この実施の形態では、特殊態様から最終表示態様(すなわち特別態様)への変化は、予告対象の保留表示を引き継いだアクティブ表示においてなされる。そのため、特殊態様は、保留表示を引き継いだアクティブ表示が特別態様に変化することを示唆する態様であるともいえる。なお、このような構成に限らず、例えば、保留表示において特殊態様から最終表示態様(すなわち特別態様)への変化が行われる変化パターンを設けるようにしてもよいし、アクティブ表示において通常態様から特殊態様への変化や、特殊態様間の変化(例えば、第1特殊態様から第2特殊態様への変化)、通常態様から特別態様への変化が行われる変化パターンを設けるようにしてもよい。また、この実施の形態では、第3特殊態様により表示される場合には、必ず第1特殊態様および第2特殊態様を経て表示されるが、このような構成に限らず、通常態様や第1特殊態様から第3特殊態様に変化する変化パターンを設けるようにしてもよい。第2特殊態様についても同様に、通常態様から第2特殊態様に変化する変化パターンを設けるようにしてもよい。また、例えば、特殊態様から特別態様への変化の後に、さらに特別態様間の変化(例えば、第1特別態様から第2特別態様に変化)が行われる変化パターンを設けるようにしてもよい。 As shown in FIG. 39(A), in this embodiment, the change from the special mode to the final display mode (that is, the special mode) is made in the active display that takes over the pending display of the announcement target. Therefore, it can be said that the special mode is a mode that suggests that the active display taking over the hold display changes to the special mode. It should be noted that the present invention is not limited to such a configuration, and for example, a change pattern in which the special mode is changed to the final display mode (that is, the special mode) in the pending display may be provided, or the normal mode may be changed to the special mode in the active display. A change pattern may be provided in which a change to a mode, a change between special modes (for example, a change from a first special mode to a second special mode), or a change from a normal mode to a special mode is performed. Further, in this embodiment, when the display is performed in the third special mode, the display is always performed through the first special mode and the second special mode. You may make it provide the change pattern which changes from a special mode to a 3rd special mode. Similarly, for the second special mode, a change pattern that changes from the normal mode to the second special mode may be provided. Further, for example, a change pattern may be provided in which a change between special modes (for example, a change from a first special mode to a second special mode) is performed after a change from one special mode to another.
また、この実施の形態では、保留表示は通常態様により表示された後に、保留予告演出により特殊態様や特別態様に変化するように構成されているが、このような構成に限らず、始動入賞時に保留予告演出を実行すると決定したときに、最初から保留表示を特殊態様や特別態様で表示するようにしてもよい。 In addition, in this embodiment, after the suspension display is displayed in the normal mode, it is configured to change to a special mode or a special mode by the suspension notice effect, but not limited to such a configuration, at the time of starting winning When it is decided to execute the suspension notice effect, the suspension display may be displayed in a special mode or a special mode from the beginning.
ステップS6007aでは、ステップS6005において決定した最終表示態様が第1特殊態様(青箱)であるときには、図39(B)に示す第1変化パターン決定テーブルを選択し、第1特別態様(青球)であるときには、図39(C)に示す第2変化パターン決定テーブルを選択し、第2特別態様(緑球)であるときには、図39(D)に示す第3変化パターン決定テーブルを選択し、第3特別態様(赤球)であるときには、図39(E)に示す第4変化パターン決定テーブルを選択し、第4特別態様(虹球)であるときには、図39(F)に示す第5変化パターン決定テーブルを選択する。そして、選択した変化パターン決定テーブルを用いて、最新の変動カテゴリコマンドにもとづいて、乱数にもとづく抽選処理を行い、変化パターンを決定する。 In step S6007a, when the final display mode determined in step S6005 is the first special mode (blue box), the first change pattern determination table shown in FIG. When it is, select the second change pattern determination table shown in FIG. 39 (C), when it is the second special mode (green ball), select the third change pattern determination table shown in FIG. When the third special mode (red ball) is selected, the fourth change pattern determination table shown in FIG. 39(E) is selected. Select the change pattern determination table. Then, using the selected change pattern determination table, lottery processing based on random numbers is performed based on the latest variation category command, and the change pattern is determined.
図39(B)に示すように、第1変化パターン決定テーブルには、第1変化パターンが100%の確率で決定されるように判定値が割り当てられている。そのため、最終表示態様が第1特殊態様の場合には、保留表示が通常態様から第1特殊態様に変化する(特別態様には変化しない)第1変化パターンに決定される。 As shown in FIG. 39(B), the determination values are assigned to the first variation pattern determination table so that the first variation pattern is determined with a probability of 100%. Therefore, when the final display mode is the first special mode, the first change pattern in which the pending display changes from the normal mode to the first special mode (does not change to the special mode) is determined.
図39(B)~(F)に示す第1~第5変化パターン決定テーブルには、原則的に、非リーチはずれよりもスーパーリーチはずれの方が、スーパーリーチはずれよりもスーパーリーチ大当りの方が、第2~第4変化パターンに決定される割合が高くなるように判定値が割り当てられている。また、スーパーリーチ大当りよりもスーパーリーチはずれの方が、スーパーリーチはずれよりも非リーチの方が、第1変化パターンに決定される割合が高くなるように判定値が割り当てられている。このような構成により、第4変化パターン>第3変化パターン>第2変化パターン>第1変化パターンの順に、スーパーリーチに対する期待度(リーチ信頼度)や大当りに対する期待度(大当り信頼度)が高くなっている。 In principle, in the first to fifth change pattern determination tables shown in FIGS. 39B to 39F, super reach is better than non reach, and super reach big hit is better than super reach. , the determination values are assigned so that the ratio of determination to the second to fourth change patterns increases. In addition, determination values are assigned so that the ratio of determination to the first change pattern is higher for super ready-to-win losses than for super ready-to-win jackpots, and for non-ready-to-win wins than for super ready-to-win big wins. With such a configuration, expectations for super reach (reach reliability) and expectations for big hits (big hit reliability) are high in the order of fourth change pattern> third change pattern> second change pattern> first change pattern. It's becoming
すなわち、通常態様から特殊態様を経ずに特別態様に変化するときよりも、通常態様から特殊態様を経て特別態様に変化するときの方が、期待度(リーチ信頼度や大当り信頼緯度)が高くなる。また、第1特殊態様のみを経て特別態様に変化するときよりも、第2特殊態様を経て特別態様に変化するときの方が、さらに第3特殊態様を経て特別態様に変化するときの方が、期待度(リーチ信頼度や大当り信頼緯度)が高くなる。このような構成により、どのような経緯で保留表示およびアクティブ表示が変化したかに注目させることができる。 That is, when changing from the normal mode to the special mode through the special mode than when changing from the normal mode to the special mode without going through the special mode, the expectation (reach reliability and jackpot reliability latitude) is higher. Become. In addition, when changing to the special mode via the second special mode, and when changing to the special mode via the third special mode, more than when changing to the special mode via only the first special mode, , the degree of expectation (reach reliability and jackpot reliability latitude) increases. With such a configuration, it is possible to draw attention to how the pending display and the active display are changed.
なお、図39(C)に示す第2変化パターンテーブルには、例外的に、スーパーリーチ大当りよりもスーパーリーチはずれの方が、第3変化パターンに決定される割合が高くなるように判定値が割り当てられている。最終表示態様が第1特別態様であるときに、第3変化パターンに決定されると、保留表示およびアクティブ表示は、通常態様から第1特殊態様に変化し、さらに第1特殊態様から第2特殊態様に変化するが、最終的に第2特殊態様から第1特別態様に変化することになる。この実施の形態では、特殊態様のうち第2特殊態様は第1特殊態様よりも期待度が高く、特別態様のうち第1特別態様は最も期待度が低い。そのため、遊技者にとっては期待度が低下したように感じられる。そこで、図39(C)のように判定値を割り当て、期待度を設定することで、遊技者の感覚と期待度が乖離しないようにすることができる。 In addition, in the second change pattern table shown in FIG. 39(C), exceptionally, the determination value is set so that the rate of determination of the third change pattern is higher for the super reach jackpot than for the super reach jackpot. assigned. When the final display mode is the first special mode, if the third change pattern is determined, the pending display and the active display change from the normal mode to the first special mode, and further from the first special mode to the second special mode. Although it changes to a mode, it will eventually change from the second special mode to the first special mode. In this embodiment, the second special mode among the special modes has a higher degree of expectation than the first special mode, and the first special mode has the lowest degree of expectation among the special modes. Therefore, the player feels that the degree of expectation has decreased. Therefore, by assigning determination values and setting expectations as shown in FIG.
また、図39(D)に示す第3変化パターンテーブルには、スーパーリーチはずれよりもスーパーリーチ大当りの方が、第2変化パターンに決定される割合が高くなるように判定値が割り当てられている。このような構成により、最終表示態様が第1特別態様であり、変化パターンが第3変化パターンであるときよりも、最終表示態様が第2特別態様であり、変化パターンが第2変化パターンであるときの方が、期待度(リーチ信頼度や大当り信頼緯度)が高くなる。具体的には、保留表示およびアクティブ表示が、通常態様から第1特殊態様に変化し、さらに第1特殊態様から第2特殊態様に変化するが、最終的に第2特殊態様から第1特別態様に変化するときよりも、通常態様から第1特殊態様に変化し、第1特殊態様から第2特殊態様には変化しないが、最終的に第1特殊態様から第2特別態様に変化するときの方が、期待度(リーチ信頼度や大当り信頼緯度)が高くなる。そのため、期待度が低い第1特殊態様が表示された時点で直ちに遊技者の期待感が失われてしまうようなことを防ぐことができ、遊技者の期待感を維持することができる。 Also, in the third change pattern table shown in FIG. 39(D), judgment values are assigned so that the ratio of determination of the second change pattern is higher for super reach jackpots than for super reach misses. . With such a configuration, the final display mode is the second special mode and the change pattern is the second change pattern, rather than when the final display mode is the first special mode and the change pattern is the third change pattern. Expectations (reach reliability and jackpot reliability latitude) are higher at times. Specifically, the pending display and the active display change from the normal mode to the first special mode, and further change from the first special mode to the second special mode, but finally change from the second special mode to the first special mode. When changing from the normal mode to the first special mode, not changing from the first special mode to the second special mode, but finally changing from the first special mode to the second special mode The degree of expectation (reach reliability and jackpot reliability latitude) is higher. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the player's sense of expectation from being lost immediately when the first special mode with a low degree of expectation is displayed, and it is possible to maintain the player's sense of expectation.
また、図39(B)~(F)に示す第1~第5変化パターンテーブルでは、最終表示態様が第3特別態様または第4特別態様であるときのみ、第4変化パターンに決定されるように判定値が割り当てられている。さらに、最終表示態様が第4特別態様であるときには、必ず第4変化パターンに決定されるように判定値が割り当てられている。このような構成により、第4変化パターンにより第3特殊態様に変化した場合にのみ、第4特別態様に変化する可能性が発生することになるため、第3特殊態様に変化したときの期待感を高めることができる。 Further, in the first to fifth change pattern tables shown in FIGS. 39B to 39F, the fourth change pattern is determined only when the final display mode is the third special mode or the fourth special mode. is assigned a judgment value. Further, the determination value is assigned such that when the final display mode is the fourth special mode, the fourth change pattern is always determined. With such a configuration, the possibility of changing to the fourth special mode occurs only when the fourth change pattern changes to the third special mode, so the expectation when changing to the third special mode occurs. can increase
また、図39(B)~(F)に示す第1~第5変化パターンテーブルでは、最終表示態様が第1~第2特別態様のときには第4変化パターンに決定されないように判定値が割り当てられている。すなわち、第3特殊態様から第2特別態様や第1特別態様には変化しないように構成されている。このような構成により、期待度が高い特殊態様から、期待度が低い特別態様に変化して、却って興趣を低下させてしまうことを防止することができる。 Also, in the first to fifth change pattern tables shown in FIGS. 39(B) to (F), when the final display mode is the first to second special modes, the judgment values are assigned so that the fourth change pattern is not determined. ing. That is, it is configured so as not to change from the third special mode to the second special mode or the first special mode. With such a configuration, it is possible to prevent a change from a special mode with a high degree of expectation to a special mode with a low degree of expectation, which in turn reduces interest.
なお、この実施の形態では、保留シフトのタイミングで、保留表示が通常態様から特殊態様または最終表示態様に変化するように構成されている。具体的には、第1変化パターンでは、始動入賞発生時に保留表示が通常態様により表示され、保留シフトのタイミングで、保留表示が通常態様から最終表示態様(すなわち特別態様)に変化する。また、第2変化パターンでは、始動入賞発生時に保留表示が通常態様により表示され、保留シフトのタイミングで、保留表示が通常態様から第1特殊態様に変化する。そして、保留表示を引き継いでアクティブ表示が表示された後に、アクティブ表示が、第1特殊態様から最終表示態様(すなわち特別態様)に変化する。また、第3変化パターンでは、始動入賞発生時に保留表示が通常態様により表示され、保留シフトのタイミングで、保留表示が通常態様から第1特殊態様に変化し、さらに所定期間経過後に第1特殊態様から第2特殊態様に変化する。そして、保留表示を引き継いでアクティブ表示が表示された後に、アクティブ表示が、第2特殊態様から最終表示態様に変化する。また、第4変化パターンでは、始動入賞発生時に保留表示が通常態様により表示され、保留シフトのタイミングで、保留表示が通常態様から第1特殊態様に変化し、所定期間経過後に第1特殊態様から第2特殊態様に変化し、さらに所定期間経過後に第2特殊態様から第3特殊態様に変化する。そして、保留表示を引き継いでアクティブ表示が表示された後に、アクティブ表示が、第3特殊態様から最終表示態様に変化する。 Note that this embodiment is configured such that the hold display changes from the normal mode to the special mode or the final display mode at the timing of the hold shift. Specifically, in the first change pattern, the suspension display is displayed in the normal mode when the start winning occurs, and the suspension display changes from the normal mode to the final display mode (that is, the special mode) at the timing of the suspension shift. Further, in the second change pattern, the suspension display is displayed in the normal mode when the starting winning is generated, and the suspension display changes from the normal mode to the first special mode at the timing of the suspension shift. Then, after the pending display is taken over and the active display is displayed, the active display changes from the first special mode to the final display mode (that is, the special mode). In addition, in the third change pattern, the suspension display is displayed in the normal mode when the starting prize is generated, the suspension display changes from the normal mode to the first special mode at the timing of the suspension shift, and furthermore, after a predetermined period of time has passed, the first special mode is displayed. to the second special mode. Then, after the pending display is taken over and the active display is displayed, the active display changes from the second special mode to the final display mode. In addition, in the fourth change pattern, the suspension display is displayed in the normal mode when the start winning is generated, and at the timing of the suspension shift, the suspension display changes from the normal mode to the first special mode, and after the elapse of a predetermined period, the suspension display changes from the first special mode. It changes to a 2nd special mode, and also changes from a 2nd special mode to a 3rd special mode after progress of a predetermined period. Then, after the pending display is taken over and the active display is displayed, the active display changes from the third special mode to the final display mode.
このように、この実施の形態では、第2~第4変化パターンのときには、始動入賞が発生し、保留シフトのタイミングで、保留表示が通常態様から特殊態様に変化する。このとき、例えば、第3変化パターンであれば、1回の保留シフトのタイミングで通常態様→第1特殊態様→第2特殊態様と順次変化し、第4変化パターンであれば、1回の保留シフトのタイミングで通常態様→第1特殊態様→第2特殊態様→第3特殊態様と順次変化する。なお、このような構成に限らず、複数の保留シフトに亘って変化するようにしてもよい。具体的には、第3変化パターンに決定されているときに、1回目の保留シフトのタイミングで、保留表示が通常態様から第1特殊態様に変化し、2回目の保留シフトのタイミングで、保留表示が第1特殊態様から第2特殊態様に変化するようにしてもよい。例えば、複数の保留シフトに亘って変化する変化パターンを設け、第1保留記憶数(すなわち予告対象の変動表示が開始されるまでに行われる保留シフトの回数)に応じて、それらの変化パターンを選択可能とすることにより実現できる。 As described above, in this embodiment, when the second to fourth change patterns are applied, the starting prize is generated, and the hold display changes from the normal mode to the special mode at the timing of the hold shift. At this time, for example, if it is the 3rd change pattern, it changes sequentially from the normal mode → the first special mode → the 2nd special mode at the timing of one hold shift, and if it is the fourth change pattern, one hold is performed. At the timing of the shift, the normal mode→first special mode→second special mode→third special mode sequentially. It should be noted that the configuration is not limited to such a configuration, and may vary over a plurality of hold shifts. Specifically, when the third change pattern is determined, at the timing of the first hold shift, the hold display changes from the normal mode to the first special mode, and at the timing of the second hold shift, the hold The display may change from the first special mode to the second special mode. For example, a change pattern that changes over a plurality of hold shifts is provided, and those change patterns are changed according to the first hold storage number (that is, the number of hold shifts performed until the variable display of the notice target is started). It can be realized by making it selectable.
次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、最終表示態様および変化パターンにもとづいて、アクティブ表示が最終表示態様に変化する変化タイミングを決定する(ステップS6007b)。なお、アクティブ表示が表示される前に最終表示態様に変化している場合、すなわち、変化パターンが第1変化パターンに決定されている場合には、ステップS6007bの処理を省略してもよい。ステップS6007bでは、演出制御用CPU101は、最終表示態様にもとづいて、アクティブ表示が最終表示態様に変化する変化タイミングを決定するための変化タイミング決定テーブルを選択する。そして、演出制御用CPU101は、選択した変化タイミング決定テーブルを用いて、変化パターンにもとづいて、乱数にもとづく抽選処理を行い、アクティブ表示が最終表示態様に変化する変化タイミングを決定する。
Next, the
ステップS6007aでは、ステップS6005において決定した最終表示態様が第1特別態様(青球)であるときには、図40(A)に示す第1変化タイミング決定テーブルを選択し、第2特別態様(緑球)であるときには、図40(B)に示す第2変化タイミング決定テーブルを選択し、第3特別態様(赤球)であるときには、図40(C)に示す第3変化タイミング決定テーブルを選択し、第4特別態様(虹球)であるときには、図40(D)に示す第4変化タイミング決定テーブルを選択する。そして、選択した変化タイミング決定テーブルを用いて、変化パターンにもとづいて、乱数にもとづく抽選処理を行い、変化タイミングを決定する。 In step S6007a, when the final display mode determined in step S6005 is the first special mode (blue ball), the first change timing determination table shown in FIG. 40A is selected, and the second special mode (green ball) is selected. , selecting the second change timing determination table shown in FIG. 40B, and selecting the third change timing determination table shown in FIG. 40C when the third special mode (red ball), In the case of the fourth special mode (rainbow ball), the fourth change timing determination table shown in FIG. 40(D) is selected. Then, using the selected change timing determination table, lottery processing based on random numbers is performed based on the change pattern to determine the change timing.
図40は、変化タイミング決定テーブルの具体例を示す説明図である。図40に示すように、この実施の形態では、第1~第4変化タイミング決定テーブルにおいて、アクティブ表示が最終表示態様に変化する変化タイミングとして、当該変動開始タイミング、リーチ開始タイミングおよびスーパーリーチ開始タイミングに対して、それぞれ判定値が割り当てられている。なお、この実施の形態では、予告対象の変動表示において、当該変動開始タイミング、リーチ開始タイミング、スーパーリーチ開始タイミングの順に訪れる。 FIG. 40 is an explanatory diagram showing a specific example of the change timing determination table. As shown in FIG. 40, in this embodiment, in the first to fourth change timing determination tables, the variation start timing, the reach start timing, and the super reach start timing are set as change timings at which the active display changes to the final display mode. A judgment value is assigned to each. In this embodiment, in the variable display of the notice target, the variable start timing, ready-to-reach start timing, and super ready-to-reach start timing are visited in this order.
図40に示す第1~第4変化タイミング決定テーブルにおける最終表示態様直前の態様は、変化パターンと同義である。具体的には、最終表示態様直前の態様が第1特殊態様であるときとは、第2変化パターンにより変化するときであり、最終表示態様直前の態様が第2特殊態様であるときとは、第3変化パターンにより変化するときであり、最終表示態様直前の態様が第3特殊態様であるときとは、第4変化パターンにより変化するときである。 The mode immediately before the final display mode in the first to fourth change timing determination tables shown in FIG. 40 is synonymous with the change pattern. Specifically, when the mode immediately before the final display mode is the first special mode, it means when it changes according to the second change pattern, and when the mode immediately before the final display mode is the second special mode, When it changes according to the third change pattern, and when the mode immediately before the final display mode is the third special mode, it means when it changes according to the fourth change pattern.
図40(A)~(D)に示す第1~第4変化タイミング決定テーブルには、最終表示態様が第1特別態様よりも第2特別態様の方が、第2特別態様よりも第3特別態様の方が、第3特別態様よりも第4特別態様の方が、遅いタイミングに決定される割合が高くなるように判定値が割り当てられている。このような構成により、いずれの特別態様に変化するかに応じて、複数のタイミングのいずれにおいてアクティブ表示が特殊態様から特別態様に変化するかの割合が異なるようになっている。より具体的には、変化後の特別態様の期待度が高い程、遅いタイミングにおいてアクティブ表示が特殊態様から特別態様に変化する割合が高くなっている。このような構成により、特殊態様から特別態様に変化するタイミングに着目させることができる。 In the first to fourth change timing determination tables shown in FIGS. 40A to 40D, the final display mode is higher in the second special mode than in the first special mode, and in the third special mode than in the second special mode. Judgment values are assigned so that the fourth special mode is more likely to be determined later than the third special mode. With such a configuration, the ratio at which of the plurality of timings the active display changes from the special mode to the special mode differs depending on which special mode it changes to. More specifically, the higher the degree of expectation for the post-change special mode, the higher the rate at which the active display changes from the special mode to the special mode at a later timing. With such a configuration, it is possible to focus attention on the timing at which the special mode changes to the special mode.
なお、図40に示す例では、遅いタイミングで変化する程、期待度が高い特別態様に変化する割合が高くなるように構成されているが、このような構成に限らず、早いタイミングで変化する程、期待度が高い特別態様に変化する割合が高くなるようにしてもよいし、タイミングの早い遅いとは別に、特定のタイミングで変化すると期待度が高い特別態様に変化する割合が高くなるようにしてもよい。 In the example shown in FIG. 40, it is configured such that the later the timing is changed, the higher the rate of change to the special mode with a high degree of expectation. The higher the degree, the higher the rate of change to the special mode with a high degree of expectation. can be
また、図40(A)~(D)に示す第1~第4変化タイミング決定テーブルには、最終表示態様直前の態様が第1特殊態様よりも第2特殊態様の方が、第2特殊態様よりも第3特殊態様の方が、遅いタイミングに決定される割合が高くなるように判定値が割り当てられている。このような構成により、いずれの特殊態様であるかに応じて、複数のタイミングのいずれにおいて特別態様に変化するかの割合が異なるようになっている。より具体的には、最終表示態様直前の特殊態様の期待度が高い程、遅いタイミングにおいてアクティブ表示が特殊態様から特別態様に変化する割合が高くなっている。このような構成により、期待度が高い特殊態様で表示されたときの期待感を効果的に持続させることができる。 Further, in the first to fourth change timing determination tables shown in FIGS. 40A to 40D, the mode immediately before the final display mode is the second special mode more than the first special mode. Judgment values are assigned so that the third special mode is more likely to be determined later than the third special mode. With such a configuration, the ratio of which of the plurality of timings changes to the special mode differs depending on which special mode it is. More specifically, the higher the degree of expectation for the special mode immediately before the final display mode, the higher the rate at which the active display changes from the special mode to the special mode at later timing. With such a configuration, it is possible to effectively sustain the sense of anticipation when the content is displayed in a highly anticipated special mode.
なお、図40に示す例では、最終表示態様直前の特殊態様の期待度が高い程、遅いタイミングで特別態様に変化する割合が高くなるように構成されているが、このような構成に限らず、最終表示態様直前の特殊態様の期待度が高い程、早いタイミングで変化する割合が高くなるようにしてもよい。 In the example shown in FIG. 40, the higher the degree of expectation of the special mode immediately before the final display mode, the higher the rate of changing to the special mode at later timing. Alternatively, the higher the degree of expectation of the special mode immediately before the final display mode, the higher the rate of change at an earlier timing.
そして、演出制御用CPU101は、ステップS6005,S6007a,S6007bで決定した最終表示態様、変化パターンおよび変化タイミングを、予告対象の保留記憶に対応付けて、RAMに設けられた保留予告演出設定情報格納領域に記憶させる(ステップS6008)。なお、この実施の形態では、第1保留記憶表示部9aに表示されている複数の保留表示に対して並行して保留予告演出を実行可能であり、第1保留記憶表示部9aには最大で4つの保留表示を表示可能であることから、保留予告演出設定情報格納領域には4つの格納領域が設けられており、それぞれの保留記憶に対応付けて、最終表示態様、変化パターンおよび変化タイミングが格納される。
Then, the
図41は、図36に示された演出制御プロセス処理における変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(ステップS800)を示すフローチャートである。変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、変動パターンコマンド受信フラグがセットされているか否か確認する(ステップS811)。変動パターンコマンド受信フラグがセットされていれば、変動パターンコマンド受信フラグをリセットする(ステップS812)。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動開始処理(ステップS801)に対応した値に更新する(ステップS813)。
FIG. 41 is a flow chart showing a variation pattern command reception waiting process (step S800) in the effect control process shown in FIG. In the variation pattern command reception waiting process, the
図42は、図36に示された演出制御プロセス処理における演出図柄変動開始処理(ステップS801)を示すフローチャートである。演出図柄変動開始処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、まず、変動パターンコマンド格納領域から変動パターンコマンドを読み出す(ステップS8000)。次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、ステップS8000で読み出した変動パターンコマンド、および表示結果指定コマンド格納領域に格納されているデータ(すなわち、受信した表示結果指定コマンド)に応じて演出図柄の表示結果(停止図柄)を決定する(ステップS8001)。なお、変動パターンコマンドで擬似連が指定されている場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、ステップS8001において、擬似連中の仮停止図柄としてチャンス目図柄(例えば、「223」や「445」のように、リーチとならないものの大当り図柄と1つ図柄がずれている図柄の組み合わせ)も決定する。なお、演出制御用CPU101は、決定した演出図柄の停止図柄を示すデータを演出図柄表示結果格納領域に格納する。
FIG. 42 is a flow chart showing the effect symbol variation start process (step S801) in the effect control process shown in FIG. In the effect symbol variation start process,
図43は、演出表示装置9における演出図柄の停止図柄の一例を示す説明図である。図43に示す例では、受信した表示結果指定コマンドが「通常大当り」を示している場合には(受信した表示結果指定コマンドが表示結果2指定コマンドである場合)、演出制御用CPU101は、停止図柄として3図柄が同じ偶数図柄で揃った演出図柄の組合せを決定する。また、受信した表示結果指定コマンドが「確変大当り」を示している場合には(受信した表示結果指定コマンドが表示結果3指定コマンドである場合)、演出制御用CPU101は、停止図柄として3図柄が同じ奇数図柄で揃った演出図柄の組合せを決定する。
FIG. 43 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of a stop pattern of the effect symbols in the
また、受信した表示結果指定コマンドが「突然確変大当り」や「小当り」を示している場合には(受信した表示結果指定コマンドが表示結果4指定コマンドまたは表示結果5指定コマンドである場合)、演出制御用CPU101は、停止図柄として「135」などの演出図柄の組合せを決定する。そして、「はずれ」の場合には(受信した表示結果指定コマンドが表示結果1指定コマンドである場合)、上記以外の演出図柄の組み合わせを決定する。ただし、リーチ演出を伴う場合には、左右の2図柄が揃った演出図柄の組み合わせを決定する。また、演出表示装置9に導出表示される3図柄の組合せが演出図柄の「停止図柄」である。
Also, if the received display result designation command indicates "suddenly variable probability big hit" or "small hit" (if the received display result designation command is a
演出制御用CPU101は、例えば、停止図柄を決定するための乱数を抽出し、演出図柄の組合せを示すデータと数値とが対応付けられている停止図柄決定テーブルを用いて、演出図柄の停止図柄を決定する。すなわち、抽出した乱数に一致する数値に対応する演出図柄の組合せを示すデータを選択することによって停止図柄を決定する。
For example, the
なお、演出図柄についても、大当りを想起させるような停止図柄(左中右が全て同じ図柄で揃った図柄の組み合わせ)を大当り図柄という。また、はずれを想起させるような停止図柄をはずれ図柄という。また、確変状態となることを想起させる図柄(この実施の形態では、奇数図柄)を確変図柄ともいい、確変状態とならないことを想起させる図柄(この実施の形態では、偶数図柄)を非確変図柄ともいう。 Incidentally, as for the production pattern, a stop pattern (combination of patterns in which the left, middle and right are all the same pattern) that reminds us of a big hit is called a big hit pattern. Also, a stop symbol that reminds us of a loss is called a lost symbol. In addition, the pattern (in this embodiment, the odd number pattern) that reminds me of the probability variation state is also called the probability variation pattern, and the pattern that reminds me that it does not become the probability variation state (the even number pattern in this embodiment) is the non-probability variation pattern. Also called
次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、時短状態フラグがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS8002)。時短状態フラグがセットされていなければ(すなわち、非時短状態であれば)、演出制御用CPU101は、第1図柄変動指定コマンド受信フラグがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS8003)。第1図柄変動指定コマンド受信フラグがセットされていれば(すなわち、第1特別図柄の変動表示を開始する場合であれば)、ステップS8004に移行する。すなわち、この実施の形態では、既に説明したように、遊技状態が非時短状態である場合に第1保留記憶を対象として保留予告演出が実行されるのであるから、ステップS8002,S8003の処理を実行することによって、遊技状態が非時短状態である場合に第1特別図柄の変動表示を実行する場合にのみ、ステップS8004~S8005の処理を実行して、予告対象の保留表示の態様を変化させるように構成している。
Next, the
一方、時短状態フラグがセットされていた場合(ステップS8002のY)および第1図柄変動指定コマンド受信フラグがセットされていなかった場合(ステップS8003のN)には、ステップS8008に移行する。 On the other hand, when the time saving state flag is set (Y of step S8002) and when the first symbol variation designation command reception flag is not set (N of step S8003), the process proceeds to step S8008.
次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、第1保留記憶の中に保留表示の態様を変化するタイミングとなっているものがあるか否かを確認する(ステップS8004)。なお、保留表示の態様を変化するタイミングとなっているものがあるか否かは、例えば、保留予告演出設定情報格納領域(ステップS6008参照)に格納されている変化パターンを確認し、今回の変動開始(保留シフト)のタイミングで通常態様から最終表示態様または特殊態様に変化させるものがあるか否かを確認することにより判定できる。保留表示の態様を変化するタイミングとなっているものがあれば、演出制御用CPU101は、第1保留記憶表示部9aにおいて、変化パターンに従って、予告対象の保留表示の態様を変更する(ステップS8005)。その後、ステップS8008に移行する。
Next, the
ステップS8005では、変化パターンが第1変化パターンに決定されているときには、予告対象の保留表示を通常態様から最終表示態様に変更し、第2変化パターンに決定されているときには、予告対象の保留表示を通常態様から第1特殊態様に変更する。また、第3変化パターンに決定されているときには、予告対象の保留表示を通常態様から第1特殊態様に変更した後に、さらに第1特殊態様から第2特殊態様に変更する。また、第4変化パターンに決定されているときには、予告対象の保留表示を通常態様から第1特殊態様に変更した後に、第1特殊態様から第2特殊態様に変更し、さらに第2特殊態様から第3特殊態様に変更する。 In step S8005, when the change pattern is determined to be the first change pattern, the hold display of the notice target is changed from the normal mode to the final display mode, and when the change pattern is decided to be the second change pattern, the hold display of the notice target is changed. is changed from the normal mode to the first special mode. Further, when the third change pattern is determined, the holding display of the notice object is changed from the normal mode to the first special mode, and then changed from the first special mode to the second special mode. Further, when the fourth change pattern is determined, the pending display of the notice target is changed from the normal mode to the first special mode, then changed from the first special mode to the second special mode, and further from the second special mode. Change to the third special mode.
例えば、後述するアクティブ表示に対する示唆演出と同様に、保留表示の表示態様が変化することを示唆する演出を実行した後に、表示態様を変化させる(または変化させない)ようにしてもよい。具体的には、キャラクタが登場して保留表示に向かってボールを投げ、この投げたボールが保留表示に命中すると保留表示の表示態様が変化し、命中しなければ変化しない態様の演出を実行するようにしてもよい。この場合、第2変化パターンに決定されているときには、キャラクタが登場して保留表示に向かってボールを投げ、このボールが保留表示に命中して通常態様から第1特殊態様に変化する態様の演出が実行される。その後、さらにボールを投げるが、保留表示に命中せず、演出を終了する。また、第3変化パターンに決定されているときには、キャラクタが登場して保留表示に向かってボールを投げ、このボールが保留表示に命中して通常態様から第1特殊態様に変化する態様の演出が実行される。そして、さらにキャラクタがボールを投げ、このボールが保留表示に命中して第1特殊態様から第2特殊態様に変化する態様の演出が実行される。その後、ボールが命中しない演出(またはキャラクタが退場する演出)の後に演出を終了する。なお、この実施の形態では、1回の保留シフト時に保留表示の表示態様が複数回変化するように構成されているが、複数回の保留シフトに亘って変化するように構成する場合には、保留シフト毎に保留表示の表示態様が変化することを示唆する演出を実行する(または抽選により実行する)ようにしてもよい。また、保留表示の表示態様を変化させるタイミングは、変動開始時に限らず、後述する示唆演出の実行タイミングを含む任意のタイミングであってもよい。 For example, the display mode may be changed (or not changed) after execution of an effect suggesting a change in the display mode of the pending display, similar to the suggestive effect for the active display, which will be described later. Specifically, a character appears and throws a ball toward the holding display, and if the thrown ball hits the holding display, the display mode of the holding display changes, and if it does not hit, the display mode does not change. You may do so. In this case, when the second change pattern is determined, the character appears, throws the ball toward the hold display, and the ball hits the hold display to produce a mode of changing from the normal mode to the first special mode. is executed. After that, the ball is thrown again, but it does not hit the pending display, and the presentation ends. Further, when the third change pattern is determined, the character appears, throws the ball toward the hold display, and the ball hits the hold display to change from the normal mode to the first special mode. executed. Then, the character throws the ball, and the ball hits the reserved display, and the effect is executed in which the first special mode changes to the second special mode. After that, the effect ends after the effect that the ball does not hit (or the effect that the character leaves the stage). In this embodiment, the display mode of the hold display is configured to change multiple times during one hold shift. You may make it perform the production|presentation which suggests that the display mode of a pending|holding display changes for every pending|holding shift (or is performed by lottery). Further, the timing of changing the display mode of the pending display is not limited to the start of fluctuation, and may be any timing including the execution timing of the suggestive effect, which will be described later.
次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、予告演出の有無および種類を決定する(ステップS8008)。ステップS8008では、保留表示の表示状況に応じて予告演出決定テーブルを選択し、選択した予告演出決定テーブルを用いて、変動パターンにもとづいて、乱数にもとづく抽選処理を行い、予告演出の有無および種類を決定する
Next, the
図44は、予告演出決定テーブルを示す説明図である。図44(A)に示す第1予告演出決定テーブルは、第2特殊態様または第3特殊態様により表示されている保留表示がないときに選択され、図44(B)に示す第2予告演出決定テーブルは、第2特殊態様または第3特殊態様により表示されている保留表示があるときに選択される。 FIG. 44 is an explanatory diagram showing an advance notice effect determination table. The first notice effect determination table shown in FIG. 44(A) is selected when there is no pending display displayed by the second special mode or the third special mode, and the second notice effect determination table shown in FIG. 44(B) is selected. A table is selected when there is a pending indication being displayed according to the second special aspect or the third special aspect.
図44に示す予告演出決定テーブルでは、「実行なし」、「予告演出A」および「予告演出B」に対して判定値がそれぞれ割り当てられている。予告演出Aは、予告演出Bよりも印象が強い演出である。例えば、予告演出Aは、予告演出Bよりも、演出期間が長かったり、演出より出力される演出音が大きかったり、演出により表示される演出画像のサイズが大きかったりする。 In the announcement effect determination table shown in FIG. 44, determination values are assigned to "no execution", "notice effect A" and "notice effect B". The announcement effect A is an effect with a stronger impression than the announcement effect B. For example, the notice effect A has a longer effect period than the notice effect B, the output sound is louder than the effect, or the size of the effect image displayed by the effect is larger.
図44に示すように、第2特殊態様または第3特殊態様により表示されている保留表示があるときには、第2特殊態様または第3特殊態様により表示されている保留表示がないときに比べて、予告演出の実行なしと決定する割合が高くなるように構成されている。第2特殊態様または第3特殊態様により表示されている保留表示があるときには、遊技者の関心は予告対象となる変動表示に向いているため、現在の変動表示に対する予告演出が却って煩わしく感じさせてしまうおそれがあるが、このような構成により、バランス良く演出を行うことができ、各演出の演出効果を高めることができる。 As shown in FIG. 44, when there is a pending display displayed according to the second special mode or the third special mode, compared to when there is no pending display displayed according to the second special mode or the third special mode, It is configured so that the ratio of determining that the advance notice effect is not executed is high. When there is a hold display displayed by the second special mode or the third special mode, the player's interest is directed toward the variable display to be the subject of the prior notice, so the prior notice effect for the current variable display rather makes the player feel annoyed. Although there is a risk that the display will be overwhelmed, such a configuration enables well-balanced effects to be performed, and the effect of each effect can be enhanced.
また、図44に示すように、第2特殊態様または第3特殊態様により表示されている保留表示があるときには、第2特殊態様または第3特殊態様により表示されている保留表示がないときに比べて、予告演出Aよりも印象が弱い予告演出Bを実行すると決定する割合が高く、第2特殊態様または第3特殊態様により表示されている保留表示がないときには、第2特殊態様または第3特殊態様により表示されている保留表示があるときに比べて、予告演出Bよりも印象が強い予告演出Aを実行すると決定する割合が高くなるように構成されている。このような構成により、バランス良く演出を行うことができ、各演出の演出効果を高めることができる。 In addition, as shown in FIG. 44, when there is a hold display displayed by the second special mode or the third special mode, compared to when there is no hold display displayed by the second special mode or the third special mode Therefore, when the ratio of deciding to execute the announcement effect B which gives a weaker impression than the announcement effect A is high and there is no pending display displayed by the second special mode or the third special mode, the second special mode or the third special mode Compared to when there is a pending display displayed according to the mode, it is configured such that the ratio of deciding to execute the notice performance A with a stronger impression than the notice performance B is higher. With such a configuration, it is possible to perform a well-balanced presentation, and to enhance the presentation effect of each presentation.
なお、図44に示す例に限らず、第2特殊態様または第3特殊態様により表示されている保留表示があるか否かと、変動パターン(非リーチはずれ、ノーマルリーチおよびスーパーリーチ)とに加えて、予告演出の予告対象が大当りであるか否かにより、予告演出の有無や種類の決定割合が異なるようにしてもよい。例えば、予告演出の予告対象が大当りであるときには、そうでないときに比べて、予告演出が実行される割合や予告演出Aが実行される割合が高くなるようにしてもよい。また、保留予告演出設定処理において、先に記憶されている保留記憶にもとづく変動表示(例えば、先に実行される変動表示)の表示結果が大当りであるときや、期待度が高い変動パターンであるときには、保留予告演出を実行しないようにしてもよい。このようにすることにより、実行中の変動表示に対する予告演出と、次回以降に実行される変動表示に対する保留予告演出とのいずれかに注目を集めることができる。 In addition to the example shown in FIG. 44, whether or not there is a hold display displayed by the second special mode or the third special mode, and the fluctuation pattern (non-reach, normal reach and super reach), Depending on whether or not the announcement target of the announcement effect is a big hit, the determination ratio of the presence or absence of the announcement effect and the type may be changed. For example, when the notice object of the notice effect is a big hit, the ratio of executing the notice effect and the ratio of executing the notice effect A may be higher than when it is not. Also, in the pending notice effect setting process, when the display result of the variable display based on the previously stored pending memory (for example, the previously executed variable display) is a big hit, or when the expected variation pattern is high. Sometimes, the suspension notice effect may not be executed. By doing so, it is possible to draw attention to either the advance notice effect for the variable display being executed or the pending notice effect for the variable display to be executed after the next time.
次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、変動パターンおよびステップS8008で決定した予告演出の有無および種類に応じたプロセステーブルを選択する(ステップS8010)。
Next, the
そして、演出制御用CPU101は、ステップS8010で選択したプロセステーブルのプロセスデータ1におけるプロセスタイマをスタートさせる(ステップS8012)。
Then, the
図45は、プロセステーブルの構成例を示す説明図である。プロセステーブルとは、演出制御用CPU101が演出装置の制御を実行する際に参照するプロセスデータが設定されたテーブルである。すなわち、演出制御用CPU101は、プロセステーブルに設定されているプロセスデータに従って演出表示装置9等の演出装置(演出用部品)の制御を行う。プロセステーブルは、プロセスタイマ設定値と表示制御実行データ、ランプ制御実行データおよび音番号データの組み合わせが複数集まったデータで構成されている。表示制御実行データには、演出図柄の可変表示の可変表示時間(変動時間)中の変動態様を構成する各変動の態様を示すデータ等が記載されている。具体的には、演出表示装置9の表示画面の変更に関わるデータが記載されている。また、プロセスタイマ設定値には、その変動の態様での変動時間が設定されている。演出制御用CPU101は、プロセステーブルを参照し、プロセスタイマ設定値に設定されている時間だけ表示制御実行データに設定されている変動の態様で演出図柄を表示させる制御を行う。
FIG. 45 is an explanatory diagram of a configuration example of a process table. The process table is a table in which process data referred to when the
図45に示すプロセステーブルは、演出制御基板80におけるROMに格納されている。また、プロセステーブルは、各変動パターンに応じて用意されている。
The process table shown in FIG. 45 is stored in the ROM of the
なお、リーチ演出を伴う変動パターンについて演出制御を実行する場合に用いられるプロセステーブルには、変動開始から所定時間が経過したときに左図柄を停止表示させ、さらに所定時間が経過すると右図柄を停止表示させることを示すプロセスデータが設定されている。なお、停止表示させる図柄をプロセステーブルに設定するのではなく、決定された停止図柄、擬似連や滑り演出における仮停止図柄に応じて、図柄を表示するための画像を合成して生成するようにしてもよい。 In addition, in the process table used when performing the effect control for the variation pattern involving the ready-to-win effect, the left symbol is stopped when a predetermined time has passed since the start of the variation, and the right symbol is stopped when a predetermined time has passed. Process data indicating to display is set. In addition, instead of setting the symbols to be stopped and displayed in the process table, an image for displaying the symbols is synthesized and generated according to the determined stop symbols, the temporary stop symbols in the simulated run and the sliding effect. may
また、演出制御用CPU101は、プロセスデータ1の内容(表示制御実行データ1、ランプ制御実行データ1、音番号データ1)に従って演出装置(演出用部品としての演出表示装置9、演出用部品としての各種ランプおよび演出用部品としてのスピーカ27)の制御を実行する(ステップS8013)。例えば、演出表示装置9において変動パターンに応じた画像を表示させるために、VDP109に指令を出力する。また、各種ランプを点灯/消灯制御を行わせるために、ランプドライバ基板35に対して制御信号(ランプ制御実行データ)を出力する。また、スピーカ27からの音声出力を行わせるために、音声出力基板70に対して制御信号(音番号データ)を出力する。
In addition, the
なお、この実施の形態では、演出制御用CPU101は、変動パターンコマンドに1対1に対応する変動パターンによる演出図柄の可変表示が行われるように制御するが、演出制御用CPU101は、変動パターンコマンドに対応する複数種類の変動パターンから、使用する変動パターンを選択するようにしてもよい。 In addition, in this embodiment, the effect control CPU101 controls to perform the variable display of the effect pattern by the variation pattern corresponding to the variation pattern command one-to-one, but the effect control CPU101 is the variation pattern command A variation pattern to be used may be selected from a plurality of types of variation patterns corresponding to .
次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、変動時間タイマに、変動パターンコマンドで特定される変動時間に相当する値を設定する(ステップS8014)。
Next, the
次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、アクティブ表示領域9Fにアクティブ表示を表示する(ステップS8015)。ステップS8015では、保留表示時の表示態様を引き継いだ表示態様によりアクティブ表示を表示する。
Next, the
なお、この実施の形態では、アクティブ表示の表示態様が変化するか否かは、始動入賞時に決定されるが、さらに演出図柄変動開始処理においても決定可能としてもよい。例えば、始動入賞時にアクティブ表示の表示態様を変化させると決定されていない場合、演出図柄変動開始処理において、変動パターンにもとづいて、第1~第4特別態様のいずれかに変化させるか否かと、変化させる場合にいずれの変化タイミングで変化させるかとを決定可能とし、決定内容に従って処理を実行することにより、アクティブ表示の表示態様を変化させるようにしてもよい。例えば、アクティブ表示の表示態様が通常態様であるときに、変動パターンの期待度が高い程、特別態様に変化する割合が高い、または期待度が高い特別態様に変化する割合が高いようにしてもよい。 Incidentally, in this embodiment, whether or not the display mode of the active display is changed is determined at the time of start winning, but it may also be determined in the effect symbol variation start process. For example, if it is not decided to change the display mode of the active display at the time of starting winning, in the production pattern variation start process, whether to change to any of the first to fourth special modes based on the variation pattern, It is also possible to change the display mode of the active display by making it possible to decide at which change timing when changing, and executing processing according to the content of the decision. For example, when the display mode of the active display is the normal mode, the higher the expectation of the variation pattern, the higher the rate of change to the special mode, or the higher the rate of change to the special mode with high expectation. good.
次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、始動入賞時コマンド格納領域の格納領域に格納されている始動入賞時のコマンド(図柄指定コマンド、変動カテゴリコマンド、および保留記憶数加算指定コマンド(第1保留記憶数加算指定コマンドまたは第2保留記憶数加算指定コマンド))のうち、1つ目の格納領域に格納されている始動入賞時のコマンドを1つ削除し、始動入賞時コマンド格納領域の内容をシフトする(ステップS8017)。
Next, the
そして、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動中処理(ステップS802)に対応した値にする(ステップS8018)。
Then, the
図46は、演出制御プロセス処理における演出図柄変動中処理(ステップS802)を示すフローチャートである。演出図柄変動中処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、まず、プロセスタイマの値を1減算するとともに(ステップS8101)、変動時間タイマの値を1減算する(ステップS8102)。プロセスタイマがタイムアウトしたら(ステップS8103)、プロセスデータの切替を行う。すなわち、プロセステーブルにおける次に設定されているプロセスタイマ設定値をプロセスタイマに設定する(ステップS8104)。また、その次に設定されている表示制御実行データ、ランプ制御実行データおよび音番号データにもとづいて演出装置に対する制御状態を変更する(ステップS8105)。
FIG. 46 is a flow chart showing the effect symbol changing process (step S802) in the effect control process process. In the effect symbol fluctuation process, the
次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、アクティブ表示の変化タイミングとなっているか否かを確認する(ステップS8106)。なお、アクティブ表示の変化タイミングタイミングとなっているか否かは、この実施の形態では、図40に示す各変化タイミングが変動パターンごとに予め定められているため、ステップS8014でセットされた変動時間タイマの値を確認することにより、変動開始時から変化タイミングまでの期間が経過したか否かを確認することができる。
Next, the
アクティブ表示の変化タイミングとなっていれば、演出制御用CPU101は、アクティブ表示の表示態様が変化することを示唆する示唆演出を、現在のアクティブ表示の表示態様に応じた演出態様により実行するとともに、アクティブ表示の表示態様を最終表示態様に変化させる変化演出を実行する(ステップS8107)。例えば、実行する示唆演出および変化演出に対応するプロセステーブルに切り替えて処理を実行することにより、実現される。
When it is time to change the active display, the
例えば、演出表示装置9の表示画面において、キャラクタが登場し、そのキャラクタがアクティブ表示に向かってボールを投げるような態様の示唆演出が実行される。そして、ボールがアクティブ表示に命中すると、アクティブ表示の表示態様を最終表示態様に変化させる変化演出が実行される。また、例えば、アクティブ表示の表示態様が第1特殊態様(青箱)である場合には、青色のキャラクタAが登場し、そのキャラクタAがアクティブ表示に向かってボールを投げるような態様の示唆演出が実行され、第2特殊態様(緑箱)である場合には、緑色のキャラクタBが登場し、そのキャラクタBがアクティブ表示に向かってボールを投げるような態様の示唆演出が実行され、第3特殊態様(赤箱)である場合には、赤色のキャラクタCが登場し、そのキャラクタCがアクティブ表示に向かってボールを投げるような態様の示唆演出が実行される。
For example, a character appears on the display screen of the
この実施の形態では、アクティブ表示の表示態様が変化することを示唆し、結果的に変化する示唆演出に加えて、アクティブ表示の表示態様が変化することを示唆するものの、結果的に変化しない示唆演出も実行可能であるため、これらを区別するときには、前者を示唆演出(成功)といい、後者を示唆演出(失敗)という。また、示唆演出(成功)と示唆演出(失敗)とを示唆演出と総称することもある。 In this embodiment, in addition to suggesting that the display mode of the active display will change, in addition to suggesting that the display mode of the active display will change, the suggestion that the display mode of the active display will change but will not change as a result. Since the production can also be executed, when distinguishing between them, the former is called a suggestive production (success), and the latter is called a suggestive production (failure). Also, suggestive effects (success) and suggestive effects (failure) may be collectively referred to as suggestive effects.
なお、この実施の形態の構成に限らず、例えば、アクティブ表示の表示態様に関わらず、抽選により複数種類の演出態様のいずれかにより示唆演出が実行されるようにしてもよいし、アクティブ表示の表示態様に応じて、異なる割合により複数種類の演出態様のいずれかにより示唆演出が実行されるようにしてもよい。また、この場合、いずれの演出態様により示唆演出が実行されるかによって、変化後のアクティブ表示の表示態様が異なる割合となるようにしてもよい。例えば、青色のキャラクタAが登場し、そのキャラクタAがアクティブ表示に向かってボールを投げるような態様の示唆演出が実行されると、第1特別態様(青色)に変化する割合が高く(すなわち期待度が高い特別態様に変化する割合が低く)、赤色のキャラクタCが登場し、そのキャラクタCがアクティブ表示に向かってボールを投げるような態様の示唆演出が実行されると、第3特別態様(赤色)に変化する割合が高く(すなわち期待度が高い特別態様に変化する割合が高く)なるようにしてもよい。例えば、アクティブ表示の現在の表示態様と変化後の表示態様とにもとづいて、異なる割合により複数種類の演出態様のいずれかにより示唆演出を実行するかを決定し、実行することで実現できる。 It should be noted that, without being limited to the configuration of this embodiment, for example, regardless of the display mode of the active display, the suggestive effect may be executed in one of a plurality of types of effect modes by lottery, or the active display may be performed. The suggestive effect may be executed in one of a plurality of types of effect modes at different ratios according to the display mode. Further, in this case, the proportion of the display mode of the active display after the change may differ depending on which presentation mode the suggestive effect is executed. For example, when a blue character A appears and a suggestive effect is executed in which the character A throws a ball toward the active display, the rate of change to the first special mode (blue) is high (that is, expected When a red character C appears and a suggestive effect is executed in which the character C throws a ball toward the active display, the third special mode ( red) (that is, the rate of change to a highly anticipated special mode) may be increased. For example, based on the current display mode of the active display and the display mode after the change, it can be realized by determining whether to execute the suggestive effect in one of a plurality of types of effect modes at different ratios, and executing it.
そして、変化後のアクティブ表示の表示態様が第4特別態様である場合(ステップS8108)、演出制御用CPU101は、アクティブ表示の表示態様が第4特別態様に変化したこと(すなわち大当り確定となったこと)を報知する報知演出を実行する(ステップS8109)。報知演出として、例えば、所定の演出音を出力したり、発光体を発光させたり、演出表示装置9において演出画像を表示させたりする。なお、この実施の形態では、第4特別態様に変化したときのみ報知演出が実行されるが、他の特別態様に変化したときにも報知演出が実行されるようにしてもよい。このとき、いずれの特別態様に変化したかに応じて、異なる態様の報知演出が実行されるようにしてもよい。
Then, when the display mode of the active display after the change is the fourth special mode (step S8108), the
アクティブ表示の変化タイミングとなっていなければ、演出制御用CPU101は、アクティブ表示の表示態様が変化することを示唆するものの、結果的に変化しない示唆演出(失敗)を実行するか否かを抽選により決定する(ステップS8110a)。ステップS8110aの処理については、アクティブ表示が第1特殊態様により表示されているときや、アクティブ表示が変化可能なタイミング(すなわち、図40に示す当該変動開始タイミング、リーチ開始タイミングおよびスーパーリーチ開始タイミング)であるときのみ実行するようにしてもよい(すなわちそのような状況においてのみ示唆演出(失敗)が実行されるようにしてもよい)。また、変動パターンやアクティブ表示の表示態様に応じて、示唆演出(失敗)を実行すると決定する割合が異なるようにしてもよい。
If the change timing of the active display has not come, the
例えば、演出表示装置9の表示画面において、キャラクタが登場し、そのキャラクタがアクティブ表示に向かってボールを投げるが、アクティブ表示に命中しないような態様の示唆演出(失敗)が実行される。この実施の形態では、アクティブ表示の表示態様に応じた態様により示唆演出(失敗)が実行される。例えば、アクティブ表示の表示態様が第1特殊態様(青箱)である場合には、青色のキャラクタAが登場し、そのキャラクタAがアクティブ表示に向かってボールを投げるが、アクティブ表示に命中しないような態様の示唆演出(失敗)が実行され、第2特殊態様(緑箱)である場合には、緑色のキャラクタBが登場し、そのキャラクタBがアクティブ表示に向かってボールを投げるが、アクティブ表示に命中しないような態様の示唆演出(失敗)が実行され、第3特殊態様(赤箱)である場合には、赤色のキャラクタCが登場し、そのキャラクタCがアクティブ表示に向かってボールを投げるが、アクティブ表示に命中しないような態様の示唆演出(失敗)が実行される。
For example, a character appears on the display screen of the
なお、この実施の形態の構成に限らず、例えば、アクティブ表示の表示態様に関わらず、抽選により複数種類の演出態様のいずれかにより示唆演出(失敗)が実行されるようにしてもよいし、アクティブ表示の表示態様に応じて、異なる割合により複数種類の演出態様のいずれかにより示唆演出(失敗)が実行されるようにしてもよい。また、この場合、いずれの演出態様により示唆演出が実行されるかによって、アクティブ表示の表示態様が変化する割合が異なるようにしてもよい。例えば、青色のキャラクタAが登場する態様の示唆演出が実行されると、変化しない割合が高く(すなわち示唆演出(失敗)である割合が高く)、赤色のキャラクタCが登場する態様の示唆演出が実行されると、変化する割合が高く(すなわち示唆演出(成功)である割合が高く)なるようにしてもよい。また、例えば、アクティブ表示が特殊態様により表示されているときには、そうでないときに比べて、示唆演出(失敗)を実行すると決定する割合が高くなるように構成してもよい。このように構成することにより、アクティブ表示が特殊態様により表示されているときには示唆演出が実行される頻度が高くなるため、アクティブ表示が特殊態様により表示されているときの期待感を高めることができる。 It should be noted that, without being limited to the configuration of this embodiment, for example, regardless of the display mode of the active display, a suggestive effect (failure) may be executed in one of a plurality of types of effect modes by lottery, The suggestive effect (failure) may be executed in one of a plurality of types of effect modes at different ratios according to the display mode of the active display. Further, in this case, the rate at which the display mode of the active display changes may differ depending on which presentation mode the suggestive effect is executed. For example, when the suggestive effect in which the blue character A appears is executed, the rate of no change is high (that is, the rate of the suggestive effect (failure) is high), and the suggestive effect in which the red character C appears is executed. When executed, the rate of change may be high (that is, the rate of suggestive effects (success) is high). Further, for example, when the active display is displayed in a special mode, the percentage of decisions to execute the suggestive effect (failure) may be higher than when it is not. With this configuration, when the active display is displayed in the special mode, the suggestive effect is executed more frequently, so that the expectation when the active display is displayed in the special mode can be enhanced. .
また、この実施の形態では、示唆演出は、アクティブ表示の表示態様が変化することを示唆するものであるが、保留表示の表示態様が変化することを示唆するものであってもよい。すなわち、示唆演出が実行されることにより、アクティブ表示および保留表示のいずれか(または両方であってもよい)の表示態様が変化することが示唆されるようにしてもよい。例えば、示唆演出が開始されると、キャラクタが登場し、このキャラクタが投げたボールがアクティブ表示に命中するとアクティブ表示の表示態様が変化し、保留表示に命中すると命中した保留表示の表示態様が変化し、いずれにも命中しなければ失敗となるようにしてもよい。この場合にも、アクティブ表示および保留表示のいずれかが特殊態様により表示されているときには、そうでないときに比べて、示唆演出(失敗)を実行すると決定する割合が高くなるように構成してもよい。 Further, in this embodiment, the suggestive effect suggests that the display mode of the active display will change, but it may also suggest that the display mode of the pending display will change. That is, execution of the suggestive effect may suggest that the display mode of either the active display or the hold display (or both of them) will change. For example, when the suggestion effect is started, a character appears, and when the ball thrown by this character hits the active display, the display mode of the active display changes, and when the ball hits the hold display, the display mode of the hit hold display changes. However, if you do not hit any of them, you may fail. In this case also, when either the active display or the pending display is displayed in a special manner, the percentage of decisions to execute the suggestive effect (failure) may be higher than when it is not. good.
ステップS8110aで示唆演出(失敗)を実行すると決定すると(ステップS8110b)、演出制御用CPU101は、アクティブ表示の表示態様に応じた演出態様により、示唆演出(失敗)を実行する(ステップS8110c)。例えば、実行する示唆演出(失敗)の演出態様に対応するプロセステーブルに切り替えて処理を実行することにより、実現される。
When it is determined to execute the suggestive effect (failure) in step S8110a (step S8110b), the
次いで、リーチ演出の開始タイミングとなっていれば(ステップS8111のY)、演出制御用CPU101は、アクティブ表示の表示態様に応じて、リーチ演出を実行する(ステップS8112)。例えば、実行するリーチ演出に対応するプロセステーブルに切り替えて処理を実行することにより、実現される。リーチ演出の開始タイミングであるか否かは、ステップS8014でセットされた変動時間タイマの値を確認することにより判定できる。
Next, if it is time to start the ready-to-win effect (Y in step S8111), the
ステップS8112の処理により、例えば、リーチが成立したときに、発光体を発光させたり、演出表示装置9において演出画像を表示させたりするリーチ演出が、アクティブ表示の表示態様が第1特殊態様(青箱)または第1特別態様である場合には、青色基調により実行され、第2特殊態様(緑箱)または第2特別態様(緑球)である場合には、緑色基調により実行され、第3特殊態様(赤箱)または第3特別態様(赤球)である場合には、赤色基調により実行される。なお、この実施の形態の構成に限らず、例えば、アクティブ表示が特殊態様のときと特別態様のときとで、異なる態様によりリーチ演出を実行するようにしてもよい。また、リーチ演出開始後にアクティブ表示の表示態様が変化したときには、変化後の表示態様に応じた演出態様に切り替えてリーチ演出を実行するようにしてもよい。また、抽選により、複数の演出態様(例えば、演出態様ごとに大当り信頼度が異なる)のいずれかでリーチ演出を実行するようにしてもよい。この場合、アクティブ表示の表示態様に応じて、いずれの演出態様によりリーチ演出が実行されるかの割合が異なるようにしてもよい。例えば、アクティブ表示の表示態様が、期待度が低い第1特別態様の場合には、期待度が高い演出態様によりリーチ演出が実行される割合が低く、期待度が高い第3特別態様の場合には、期待度が高い演出態様によりリーチ演出が実行される割合が高くなるようにしてもよい。
Through the processing in step S8112, for example, when the ready-to-win state is established, the ready-to-win effect is changed such that the light emitting body is caused to emit light or the effect image is displayed on the
そして、演出制御用CPU101は、変動時間タイマがタイムアウトしていれば(ステップS8115)、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動停止処理(ステップS803)に応じた値に更新する(ステップS8116)。
Then, if the variable time timer has timed out (step S8115), the
図47は、演出制御プロセス処理における演出図柄変動停止処理(ステップS803)を示すフローチャートである。演出図柄変動停止処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、まず、演出図柄の停止図柄を表示していることを示す停止図柄表示フラグがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS8301)。停止図柄表示フラグがセットされていれば、ステップS8305に移行する。この実施の形態では、演出図柄の停止図柄として大当り図柄を表示した場合には、ステップS8304で停止図柄表示フラグがセットされる。そして、ファンファーレ演出を実行するときに停止図柄表示フラグがリセットされる。従って、停止図柄表示フラグがセットされているということは、大当り図柄を停止表示したがファンファーレ演出をまだ実行していない段階であるので、ステップS8302の演出図柄の停止図柄を表示する処理を実行することなく、ステップS8305に移行する。
FIG. 47 is a flow chart showing the effect symbol variation stop process (step S803) in the effect control process process. In the effect symbol variation stop process, the
停止図柄表示フラグがセットされていない場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、決定されている停止図柄(はずれ図柄、大当り図柄)を停止表示させる制御を行う(ステップS8302)。また、演出制御用CPU101は、アクティブ表示を消去する制御を行う(ステップS8302a)
When the stop symbol display flag is not set, the
次いで、ステップS8302の処理で大当り図柄および小当り図柄のいずれも表示しなかった場合(すなわち、はずれ図柄を表示した場合)には(ステップS8303のN)、演出制御用CPU101は、ステップS8311に移行する。
Next, when neither the big hit pattern nor the small hit pattern is displayed in the process of step S8302 (that is, when the losing pattern is displayed) (N in step S8303), the
ステップS8302の処理で大当り図柄または小当り図柄を停止表示した場合には(ステップS8303のY)、演出制御用CPU101は、停止図柄表示フラグをセットする(ステップS8304)。
When the big hit design or the small hit design is stopped and displayed in the process of step S8302 (Y in step S8303), the
次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、いずれかの大当り開始指定コマンドを受信したか否かを確認する(ステップS8305)。なお、いずれかの大当り開始指定コマンドを受信したか否かは、具体的には、コマンド解析処理においてセットされる大当り開始指定コマンドを受信したことを示すフラグ(大当り開始指定コマンド受信フラグ)や、小当り/突然確変大当り開始指定コマンドを受信したことを示すフラグ(小当り/突然確変大当り開始指定コマンド受信フラグ)がセットされているか否か確認することにより判定できる。いずれかの大当り開始指定コマンドを受信していれば、演出制御用CPU101は、停止図柄表示フラグをリセットし(ステップS8306)、ファンファーレ演出に応じたプロセステーブルを選択する(ステップS8307)。なお、演出制御用CPU101は、大当り開始指定コマンド受信フラグまたは小当り/突然確変大当り開始指定コマンド受信フラグがセットされていた場合には、セットされていたフラグをリセットする。
Next, the
そして、演出制御用CPU101は、プロセスタイマ設定値をプロセスタイマに設定することによってプロセスタイマをスタートさせ(ステップS8308)、プロセスデータ1の内容(表示制御実行データ1、ランプ制御実行データ1、音番号データ1、可動部材制御データ1)に従って演出装置(演出用部品としての演出表示装置9、演出用部品としての各種ランプ、および演出用部品としてのスピーカ27)の制御を実行する(ステップS8309)。その後、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を大当り表示処理(ステップS804)に応じた値に更新する(ステップS8310)。
Then, the effect control CPU101 starts the process timer by setting the process timer setting value to the process timer (step S8308), the contents of the process data 1 (display
大当りおよび小当りのいずれともしないことに決定されている場合には(ステップS8303のN)、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(ステップS800)に応じた値に更新する(ステップS8311)。
If it is determined that neither the big hit nor the small hit (N of step S8303), the
次に、保留予告演出の演出態様の具体例について説明する。図48は、保留予告演出の演出態様の一例を示す説明図である。このうち、図48は、予告対象の保留表示が第1特殊態様(青箱)に変化し、保留表示の表示態様を引き継いだアクティブ表示が最終的に第2特別態様(緑球)に変化する場合の保留予告演出の演出態様を示している。なお、図48において、(1)(2)(3)の順に演出画面の態様が遷移する。 Next, a specific example of an effect mode of the pending advance notice effect will be described. FIG. 48 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of an effect mode of the pending notice effect. Of these, FIG. 48 shows that the pending display of the notice target changes to the first special mode (blue box), and the active display that takes over the display mode of the pending display finally changes to the second special mode (green ball). 10 shows the effect mode of the pending notice effect in the case. In addition, in FIG. 48, the mode of the effect screen changes in the order of (1), (2), and (3).
図48(1)に示すように、演出表示装置9において左中右の演出図柄の変動表示を実行しているときに新たに第1始動入賞口13への始動入賞が発生したものとする。本例では、第1保留記憶数が2である状態で新たに始動入賞が発生して第1保留記憶数が3に増加したものとし、第1保留記憶表示部9aにおいて通常保留を1つ増加させたものとする。また、本例では、新たな保留表示およびアクティブ表示の最終表示態様を第2特別態様(緑球)に決定したものとし、変化パターンを第2変化パターンに決定したものとする。そして、変動表示時間が終了したことにもとづいて、図48(2)に示すように、演出表示装置9において演出図柄の変動表示を終了する。
As shown in FIG. 48(1), it is assumed that a new start winning to the first
次いで、保留記憶を1つ消化し保留表示を1つずつシフト表示して、図48(3)に示すように、演出表示装置9において次の変動表示を開始する。図48(3)に示す例では、変動表示を開始するときに、第2変化パターンにもとづいて、その予告対象の保留表示を通常態様から第1特殊態様(青箱)に変化させる(ステップS8005参照)。そして、変動表示時間が終了したことにもとづいて、図48(4)に示すように、演出表示装置9において演出図柄の変動表示を終了する。
Then, one reserved memory is consumed and the reserved display is shifted one by one, and the next variable display is started on the
次いで、保留記憶を1つ消化し保留表示を1つずつシフト表示して、図48(5)に示すように、アクティブ表示領域9Fにおいて、アクティブ表示が、保留表示の表示態様を引き継いだ第1特殊態様(青箱)により表示される。なお、この実施の形態では、図48に示すように、アクティブ表示領域9Fにおいてアクティブ表示の下部に台座が表示されており、この台座は、アクティブ表示の表示態様に関わらず、同じ態様により表示されるが、アクティブ表示の表示態様に応じた態様により表示されるようにしてもよい。例えば、アクティブ表示が通常態様(白球)により表示されるときには、台座は白色の態様により表示され、アクティブ表示が第1特殊態様(青箱)により表示されるときには、台座は青色の態様により表示されるようにしてもよい。また、例えば、アクティブ表示が通常態様(または特別態様)により表示されるときには、台座は通常の態様により表示され、アクティブ表示が特殊態様により表示されるときには、台座は特殊態様に応じた態様(例えば、点滅する態様やエフェクト表示が付加された態様等、注目を集めやすい態様)により表示されるようにしてもよい。
Next, one reserved memory is digested and one reserved display is shifted and displayed one by one, and as shown in FIG. It is indicated by a special mode (blue box). In this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 48, a pedestal is displayed below the active display in the
次いで、当該変動開始タイミングにおいて、図48(6)に示すように、アクティブ表示の表示態様が変化することを示唆する示唆演出が実行される。図48(6)に示す例では、現在のアクティブ表示の表示態様に応じて、キャラクタA200が登場し、そのキャラクタA200がアクティブ表示に向かってボールを投げるような態様の示唆演出が実行されている。 Next, at the fluctuation start timing, as shown in FIG. 48(6), a suggestion effect is executed to suggest that the display mode of the active display will change. In the example shown in FIG. 48(6), the character A200 appears according to the display mode of the current active display, and the suggestion effect is executed in which the character A200 throws a ball toward the active display. .
次いで、図48(7)に示すように、示唆演出の終了後に、アクティブ表示の表示態様が第2特別態様(緑球)に変化する変化演出が実行される。ここでは、キャラクタA200が投げたボールがアクティブ表示に命中する示唆演出(成功)が行われた後に、アクティブ表示の表示態様が第2特別態様(緑球)に変化する変化演出が実行される。 Next, as shown in FIG. 48(7), after the suggestion effect is completed, a change effect is executed in which the display mode of the active display changes to the second special mode (green ball). Here, after the suggestive effect (success) that the ball thrown by the character A200 hits the active display, the change effect is executed to change the display mode of the active display to the second special mode (green ball).
なお、図48に示す例に限らず、例えば、示唆演出によりキャラクタが登場させるともに、遊技者の動作(例えば、プッシュボタン120の押圧操作)を促し、遊技者の動作が検出されたことにもとづいて、アクティブ表示の表示態様を変化させる変化演出(または示唆演出(失敗)後にアクティブ表示の表示態様が変化しないことを報知する演出)を実行するようにしてもよい。 It is not limited to the example shown in FIG. 48. For example, a character is made to appear by suggestive effect, and the player's action (for example, pressing the push button 120) is prompted, and the player's action is detected. Then, a change effect of changing the display mode of the active display (or an effect of notifying that the display mode of the active display does not change after the suggestion effect (failure)) may be executed.
また、例えば、示唆演出と並行して他の演出を実行可能とし、他の演出の有無や演出態様により示唆演出の演出結果(すなわち成功であるか失敗であるか)の割合が異なるようにしてもよい。例えば、示唆演出によりキャラクタが登場するタイミングで、背景画像を一時的に変化させる他の演出を実行可能とする。このような構成おいて、示唆演出開始時に他の演出が実行されるかに応じて、または複数種類の背景画像のうちのいずれに変化させる他の演出が実行されるかに応じて、同じキャラクタが登場する示唆演出であっても、演出結果(すなわち成功であるか失敗であるか)の割合が異なるようにしてもよい。なお、このような構成は、例えば、ステップS8107とS8110aとにおいて、示唆演出の演出結果に応じて、他の演出の有無や演出態様を異なる割合により決定し、決定結果に従って処理を実行することにより実現することができる。 Also, for example, other effects can be executed in parallel with the suggestive effect, and the ratio of the effect result of the suggestive effect (that is, success or failure) varies depending on the presence or absence of other effects and the effect mode. good too. For example, at the timing when a character appears in a suggestive effect, another effect that temporarily changes the background image can be executed. In such a configuration, depending on whether another effect is executed at the start of the suggestive effect, or depending on which of the plurality of types of background images is executed, the same character Even in the suggestive effect in which . In addition, for example, in steps S8107 and S8110a, depending on the effect result of the suggestive effect, the presence or absence of another effect and the effect mode are determined at different ratios, and the process is executed according to the determination result. can be realized.
また、この実施の形態では、保留表示またはアクティブ表示が第4特別態様により表示されたときにその旨を報知する演出が実行されるように構成されているが、このような構成に加えて、または代えて、第4特別態様に限らず、保留表示またはアクティブ表示が通常態様以外の表示態様により表示されていることを報知する演出を実行可能としてもよい。例えば、保留表示またはアクティブ表示が通常態様以外の表示態様により表示されているときには、遊技機に設けられたLEDやランプ等の発光体を表示態様に応じた態様(例えば、第1特殊態様のときには青色、第2特殊態様のときには緑色、第3特殊態様のときには赤色等)で発光させる演出や、表示態様に応じた報知音等の演出音(例えば、第1特殊態様のときには小音量、第2特殊態様のときには中音量、第3特殊態様のときには大音量の報知音等の演出音)を出力する演出を実行するようにしてもよい。また、例えば、保留表示またはアクティブ表示が特殊態様から特別態様に変化したときには、遊技機に設けられたLEDやランプ等の発光体を変化後の特別態様に応じた態様により発光させる演出(例えば、第1特殊態様から第2特別態様に変化したときには、青色から緑色に変化させて発光させる演出)や、変化後の特別態様に応じた報知音等の演出音を出力する演出(例えば、第1特殊態様から第2特別態様に変化したときには、小音量から中音量に変化させて報知音等の演出音を出力する演出)を実行するようにしてもよい。また、このように構成する場合には、保留表示またはアクティブ表示が通常態様以外の表示態様により表示されていることを報知するために用いられるLEDやランプ等の発光体は、役物等が動作することにより視認困難となることがない位置に設けられていることが望ましい。このような位置に設けることにより、役物の動作状況や他の演出の実行状況等に関わらず、保留表示またはアクティブ表示が通常態様以外の表示態様により表示されていることを遊技者に認識させることができる。 Further, in this embodiment, when the suspension display or the active display is displayed in the fourth special mode, an effect is executed to notify that effect. In addition to such a configuration, Alternatively, it may be possible to execute an effect for notifying that the pending display or the active display is being displayed in a display mode other than the normal mode, not limited to the fourth special mode. For example, when the pending display or the active display is displayed in a display mode other than the normal mode, the light emitters such as LEDs and lamps provided in the game machine are displayed in a mode corresponding to the display mode (for example, in the first special mode, blue, green in the second special mode, red in the third special mode, etc.), and effect sounds such as notification sounds according to the display mode (for example, low volume in the first special mode, second It is also possible to execute an effect of outputting an effect sound such as a middle volume in the special mode and a high volume in the third special mode. Further, for example, when the hold display or the active display changes from a special mode to a special mode, an effect (for example, When changing from the first special mode to the second special mode, an effect of changing from blue to green and emitting light), and an effect of outputting a production sound such as a notification sound according to the special mode after the change (for example, the first When the special mode is changed to the second special mode, an effect of changing the volume from a small volume to a medium volume and outputting an effect sound such as an information sound may be executed. In addition, in the case of such a configuration, the luminous body such as an LED or a lamp used for notifying that the pending display or the active display is displayed in a display mode other than the normal mode is operated by a character or the like. It is desirable that it is provided at a position where it will not become difficult to see. By providing it at such a position, the player is made aware that the pending display or the active display is displayed in a display mode other than the normal mode regardless of the operation status of the role or the execution status of other effects. be able to.
以上に説明したように、この実施の形態では、所定表示(例えば、特殊態様により表示される保留表示およびアクティブ表示)を表示可能な表示手段を備え、表示手段は、所定表示を特定表示(例えば、特別態様により表示される保留表示およびアクティブ表示)に変化させて表示することが可能であり、少なくとも第1所定態様(例えば、第1特殊態様)および該第1所定態様よりも期待度が高い第2所定態様(例えば、第2特殊態様)により所定表示を表示可能であり(図38,図39参照)、少なくとも第1特定態様(例えば、第1特別態様)および該第1特定態様よりも期待度が高い第2特定態様(例えば、第2特別態様)により特定表示を表示可能であり(図38,図39参照)、第1所定態様の所定表示が第2特定態様の特定表示に変化する第1変化パターン(例えば、図39(D)に示す最終表示態様が第2特別態様であるときの第2変化パターン)は、第2所定態様の所定表示が第1特定態様の特定表示に変化する第2変化パターン(例えば、図39(C)に示す最終表示態様が第1特別態様であるときの第3変化パターン)よりも期待度が高い。特定表示に変化する前の所定表示の態様によって期待度が決まってしまうと、期待度が低い態様の所定表示が表示された時点で遊技者の期待感が失われてしまうが、このような構成により、第1所定態様の所定表示が表示されても、遊技者の期待感を維持することができ、興趣の低下を防止することができる。 As described above, in this embodiment, a display means capable of displaying a predetermined display (for example, a hold display and an active display displayed in a special mode) is provided, and the display means provides a specific display (for example, , pending display and active display displayed by the special mode), and at least the first predetermined mode (for example, the first special mode) and the degree of expectation higher than the first predetermined mode A predetermined display can be displayed by a second predetermined mode (for example, a second special mode) (see FIGS. 38 and 39), and at least a first specific mode (for example, a first special mode) and more than the first specific mode A specific display can be displayed in a second specific mode (for example, a second special mode) with a high degree of expectation (see FIGS. 38 and 39), and the predetermined display in the first predetermined mode changes to the specific display in the second specific mode. The first change pattern (for example, the second change pattern when the final display mode shown in FIG. 39(D) is the second special mode) is that the predetermined display of the second predetermined mode is the specific display of the first specific mode. Expectations are higher than the changing second change pattern (for example, the third change pattern when the final display mode shown in FIG. 39(C) is the first special mode). If the degree of expectation is determined by the mode of the predetermined display before changing to the specific display, the player's sense of expectation is lost when the predetermined display of the mode with the low expectation is displayed. Therefore, even if the predetermined display of the first predetermined mode is displayed, the player's expectation can be maintained, and the loss of interest can be prevented.
なお、この実施の形態では、所定表示として、特殊態様により表示される保留表示およびアクティブ表示が用いられ、特定表示として、特別態様により表示される保留表示およびアクティブ表示が用いられているが、これに限らず、所定表示および特定表示は、特定の演出により表示される画像表示(例えば、演出表示装置9の表示領域における背景画像や、表示領域の一部に表示されるキャラクタ画像やアイテム画像、メッセージ画像等の演出画像)等であってもよい。
It should be noted that, in this embodiment, as the predetermined display, the reserved display and the active display that are displayed in a special mode are used, and as the specific display, the reserved display and the active display that are displayed in the special mode are used. However, the predetermined display and the specific display are image displays displayed by a specific effect (for example, a background image in the display area of the
また、この実施の形態では、表示手段は、所定表示を経ずに特定表示を表示可能である(例えば、図39(A)の第1変化パターンに決定されたときに実現される。また、アクティブ表示において通常態様から特別態様への変化が行われる変化パターンを設けることにより実現される。)。そのため、所定表示が表示されていないときにも、特定表示が表示されることに期待を持たせることができる。 Further, in this embodiment, the display means can display the specific display without going through the predetermined display (for example, it is realized when the first change pattern in FIG. 39(A) is determined. It is realized by providing a change pattern in which the active display changes from the normal mode to the special mode.). Therefore, even when the predetermined display is not displayed, it is possible to make the user expect that the specific display will be displayed.
また、この実施の形態では、所定表示を経て表示された特定表示と所定表示を経ずに表示された特定表示とで期待度が異なる(例えば、第1変化パターンよりも第2~第4変化パターンの方が、期待度(大当り信頼度やリーチ信頼度)が高い。図39(B)~(F)参照)。そのため、特定表示が表示される経緯に注目させることができ、興趣を向上させることができる。 Further, in this embodiment, the degree of expectation differs between the specific display that is displayed after the predetermined display and the specific display that is displayed without the predetermined display (for example, the second to fourth changes are more likely than the first change pattern). The pattern has a higher degree of expectation (reliability of big win and reliability of reach) (see FIGS. 39B to 39F). Therefore, it is possible to make the viewer pay attention to how the specific display is displayed, thereby improving interest.
また、この実施の形態では、所定表示が特定表示に変化するときに変化演出(例えば、示唆演出および変化演出)を実行可能な変化演出実行手段を備え、変化演出実行手段は、所定表示の態様に応じて、複数の演出態様のいずれかにより変化演出を実行可能である(例えば、アクティブ表示の表示態様に応じた演出態様の示唆演出および変化演出を実行する)。そのため、所定表示の態様(すなわち期待度)に応じて、好適な演出態様の変化演出を実行することができ、興趣を向上させることができる。 Further, in this embodiment, there is provided a change effect execution means capable of executing a change effect (for example, a suggestive effect and a change effect) when the predetermined display changes to the specific display, and the change effect execution means performs the predetermined display mode. Depending on this, it is possible to execute a change effect in one of a plurality of effect modes (for example, a suggesting effect and a change effect of the effect mode according to the display mode of the active display are executed). Therefore, it is possible to execute a change effect of a suitable effect mode according to the predetermined display mode (that is, the degree of expectation), thereby improving the interest.
また、この実施の形態では、所定表示の態様に応じて、複数のタイミングのいずれにおいて該所定表示が特定表示に変化するかの割合が異なる(例えば、最終表示態様直前の態様に応じて、変化タイミングの決定割合が異なる。図40(A)~(D)参照)。そのため、期待感を効果的に持続させることができる。 In addition, in this embodiment, the rate at which of the plurality of timings the predetermined display changes to the specific display differs depending on the mode of the predetermined display (for example, the rate of change varies depending on the mode immediately before the final display mode). The timing determination ratio is different (see FIGS. 40A to 40D). Therefore, expectations can be maintained effectively.
また、この実施の形態では、予告演出を実行可能な予告演出実行手段を備え、予告演出実行手段は、所定表示の変化パターンに応じて(例えば、第2、第3特殊態様により表示される第3変化パターンまたは第4変化パターンであるか否かに応じて)、予告演出の実行割合が異なるように予告演出を実行可能である(図44参照)。そのため、バランス良く演出を行うことができ、各演出の演出効果を高めることができる。 Further, in this embodiment, there is provided an advance notice effect executing means capable of executing an advance notice effect, and the notice effect executing means is adapted to execute the notice effect according to the change pattern of the predetermined display (for example, the second and third special modes displayed in the second and third special modes). Depending on whether it is the 3rd change pattern or the 4th change pattern, the notice effect can be executed so that the execution ratio of the notice effect is different (see FIG. 44). Therefore, the production can be performed in a well-balanced manner, and the production effect of each production can be enhanced.
また、この実施の形態では、変化後の特定表示の態様に応じて、複数のタイミングのいずれにおいて所定表示が該特定表示に変化するかの割合が異なる(例えば、最終表示態様に応じて、変化タイミングの決定割合が異なる。図40(A)~(D)参照)。そのため、所定表示が特定表示に変化するタイミングに注目させることができ、興趣を向上させることができる。 In addition, in this embodiment, the ratio at which of the plurality of timings the predetermined display changes to the specific display differs depending on the mode of the specific display after the change (for example, depending on the final display mode, the change The timing determination ratio is different (see FIGS. 40A to 40D). Therefore, it is possible to make the user pay attention to the timing when the predetermined display changes to the specific display, thereby improving interest.
また、この実施の形態では、期待度が異なる複数の態様により所定表示を表示可能(例えば、第1~第3特殊態様により保留表示およびアクティブ表示を表示可能)な表示手段を備え、表示手段は、所定表示を特定表示に変化させて表示することが可能であるとともに(例えば、最終表示態様が特別態様であって、変化パターンが第2~第4変化パターンであるときに実現される)、所定表示を特定表示に変化させることなく消去することが可能であり(例えば、最終表示態様が第1特殊態様であって、変化パターンが第1変化パターンであるときに実現される)、所定表示の態様を段階的に変化させることが可能であり(例えば、期待度が異なる第1特殊態様、第2特殊態様、第3特殊態様に段階的に変化可能である。図39(A)参照)、所定表示の態様に応じて、該所定表示が特定表示に変化する割合が異なる(例えば、第1特殊態様のときよりも、第2特殊態様および第3特殊態様のときの方が、特別態様に変化する割合が高い。図38,図39参照)。一旦表示された所定表示の態様が変化しない構成では、期待度が低い態様の所定表示が表示された時点で遊技者の期待感が失われてしまうが、このような構成によれば、所定表示の態様に注目させることができるとともに、期待度が低い態様の所定表示が表示されても、遊技者の期待感を維持することができ、興趣を向上させることができる。 Further, in this embodiment, display means is provided that can display predetermined displays in a plurality of modes with different expectations (for example, display means that can display pending displays and active displays in the first to third special modes), and the display means is , It is possible to change the predetermined display to a specific display and display it (for example, when the final display mode is a special mode and the change pattern is the second to fourth change patterns), It is possible to erase the predetermined display without changing it to the specific display (for example, it is realized when the final display mode is the first special mode and the change pattern is the first change pattern), and the predetermined display (For example, it is possible to change stepwise to a first special mode, a second special mode, and a third special mode with different expectations. See FIG. 39 (A)) , depending on the mode of the predetermined display, the rate at which the predetermined display changes to the specific display differs (for example, the second special mode and the third special mode are different than the first special mode). (see FIGS. 38 and 39). In a configuration in which the form of the predetermined display once displayed does not change, the player's sense of anticipation is lost at the time when the predetermined display in a mode with a low degree of expectation is displayed. In addition, it is possible to maintain the player's sense of expectation even when the predetermined display of the mode with a low degree of expectation is displayed, thereby improving the interest of the player.
また、この実施の形態では、所定表示の態様に応じて、該所定表示がいずれの態様の特定表示に変化するかの割合が異なる(例えば、最終表示態様に応じて、異なる割合により変化パターンが決定されることにより実現される。図39参照)。そのため、所定表示の態様に注目させることができ、興趣を向上させることができる。 Further, in this embodiment, the ratio of the specific display to which the predetermined display is changed differs depending on the mode of the predetermined display (for example, the change pattern varies depending on the final display mode. It is realized by being determined (see FIG. 39). Therefore, it is possible to make the user pay attention to the predetermined display mode, thereby improving interest.
また、この実施の形態では、所定表示が特定態様(例えば、第4特別態様)に変化したときに報知演出を実行する報知演出実行手段を備えている。そのため、特定態様に変化した所定表示に注目させることができ、興趣を向上させることができる。 Further, in this embodiment, there is provided a notification effect executing means for executing a notification effect when the predetermined display changes to a specific mode (for example, a fourth special mode). Therefore, it is possible to make the user pay attention to the predetermined display that has changed to the specific mode, and to improve interest.
また、この実施の形態では、所定表示の態様が変化することを示唆する示唆演出(例えば、示唆演出(成功)や示唆演出(失敗))を実行可能な示唆演出実行手段を備えている。そのため、所定表示の態様が変化するか否かに注目させることができ、興趣を向上させることができる。 Further, in this embodiment, there is provided a suggestive effect executing means capable of executing a suggestive effect (for example, a suggestive effect (success) or a suggestive effect (failure)) suggesting that the predetermined display mode will change. Therefore, it is possible to make the user pay attention to whether or not the mode of the predetermined display changes, thereby improving interest.
また、この実施の形態では、実行条件が成立した後、開始条件が成立したことにもとづいて可変表示を行う遊技機において、表示手段は、可変表示の実行条件が成立したときから開始条件が成立するときまで所定表示を表示可能である(例えば、始動入賞の発生にもとづいて保留表示が特殊態様により表示され、アクティブ表示として表示されるとき(すなわち当該変動開始タイミング)に特殊態様から特別態様に変化する)ようにしてもよい。そのため、実行条件が成立したときから所定表示に注目させることができる。 Further, in this embodiment, in a gaming machine that performs a variable display based on the satisfaction of the start condition after the execution condition is satisfied, the display means is configured to display the variable display when the start condition is satisfied. (For example, when the suspension display is displayed in a special mode based on the occurrence of the start winning, and is displayed as an active display (that is, the variable start timing), the special mode changes from the special mode to the special mode. change). Therefore, it is possible to draw attention to the predetermined display from when the execution condition is satisfied.
また、この実施の形態では、実行条件が成立した後、開始条件が成立したことにもとづいて可変表示を行う遊技機において、表示手段は、開始条件が成立したときに所定表示を特定表示に変化させて表示することが可能である(例えば、保留表示の表示態様を引き継いで特殊態様で表示されるアクティブ表示が、当該変動開始タイミングで特殊態様から特別態様に変化する)。そのため、開始条件が成立するまで期待感を持続させることができる。 Further, in this embodiment, in the gaming machine that performs variable display based on the establishment of the start condition after the execution condition is established, the display means changes the predetermined display to the specific display when the start condition is established. (For example, the active display that takes over the display mode of the pending display and is displayed in the special mode changes from the special mode to the special mode at the fluctuation start timing). Therefore, the expectation can be maintained until the start condition is satisfied.
また、この実施の形態では、期待度が異なる複数の態様により所定表示および特定表示を表示可能(例えば、第1~第3特殊態様および第1~第3特別態様により保留表示およびアクティブ表示を表示可能。図38,図39参照)な表示手段を備え、表示手段は、所定表示を特定表示に変化させて表示することが可能であり、所定期待度以上の態様により表示される所定表示が特定表示に変化するときには、特定期待度以上の態様により表示される特定表示に変化する(例えば、最終表示態様が第1~第2特別態様のときには第4変化パターンに決定されない。すなわち、第3特殊態様から第2特別態様や第1特別態様には変化しない。図39参照)。期待度が高い態様の所定表示が、期待度が低い態様の特定表示に変化すると、却って興趣を低下させてしまうおそれがあるが、このような構成によれば、興趣の低下を防止することができる。 Further, in this embodiment, it is possible to display the predetermined display and the specific display in a plurality of modes with different expectations (for example, the first to third special modes and the first to third special modes display the pending display and the active display). (see FIGS. 38 and 39), the display means is capable of displaying a predetermined display by changing it to a specific display, and the predetermined display that is displayed in a manner exceeding a predetermined degree of expectation is specified. When changing to display, it changes to a specific display that is displayed in a mode higher than the specific expectation level (for example, when the final display mode is the first to second special modes, the fourth change pattern is not determined. That is, the third special There is no change from the mode to the second special mode or the first special mode (see FIG. 39). If the predetermined display in the form of high expectation changes to the specific display in the form of low expectation, there is a risk that interest will be reduced, but according to such a configuration, it is possible to prevent the deterioration of interest. can.
また、この実施の形態では、表示手段は、特殊態様により所定表示および特定表示を表示可能であり、特殊態様の特定表示(例えば、第4特別態様の保留表示およびアクティブ表示)は、特殊態様の所定表示(例えば、第3特殊態様の保留表示およびアクティブ表示)を経て表示される。そのため、特殊態様の所定表示が表示されたときの期待感を高めることができ、興趣を向上させることができる。 Further, in this embodiment, the display means can display the predetermined display and the specific display according to the special mode, and the specific display of the special mode (for example, the hold display and the active display of the fourth special mode) It is displayed through a predetermined display (for example, a hold display and an active display of the third special mode). Therefore, it is possible to increase the sense of anticipation when the predetermined display of the special mode is displayed, and it is possible to improve interest.
また、この実施の形態では、特定表示の態様に応じて、複数種類のリーチ演出のいずれが実行されるかの割合が異なるようにしてもよい。そのような構成によれば、特定表示の態様に注目させることができ、興趣を向上させることができる。 Further, in this embodiment, the ratio of which of the plurality of types of ready-to-win effects is executed may differ according to the mode of the specific display. According to such a configuration, it is possible to make the user pay attention to the aspect of the specific display, and to improve interest.
また、この実施の形態では、遊技者の動作を検出可能な検出手段(例えば、プッシュボタン120)を備え、検出手段により遊技者の動作が検出されたことにもとづいて、所定表示が特定表示に変化するようにしてもよい。そのような構成によれば、遊技者の参加意欲を高めることができ、興趣を向上させることができる。なお、検出手段は、プッシュボタン120に限らず、スティックコントローラ122や回動操作が可能なジョグダイアル、接触操作や押圧操作が可能なタッチパネルのように、遊技者の動作を直接的に検出する構成により実現されてもよいし、赤外線センサ、超音波センサ、CCDセンサ、CMOSセンサのように、遊技者の動作を間接的(遠隔的)に検出する構成により実現されてもよい。また、所定のカメラを用いて遊技者の手などの被写体を撮影した結果を解析(ビデオ式モーションキャプチャ)して、任意の動作を検出できる構成により実現されてもよい。すなわち、任意対象物の動作を、機械的、電気的、あるいは、電磁的に、検出できる任意の構成により実現されてもよい。
Further, in this embodiment, a detecting means (for example, push button 120) capable of detecting the action of the player is provided, and when the action of the player is detected by the detecting means, the predetermined display becomes the specific display. You may make it change. According to such a configuration, it is possible to increase the player's willingness to participate, and to improve interest. Note that the detection means is not limited to the
なお、上記の各実施の形態では、変動時間およびリーチ演出の種類や擬似連(1回の可変表示中に1回以上の図柄の仮停止と再変動とが実行される演出)の有無等の変動態様を示す変動パターンを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に通知するために、変動を開始するときに1つの変動パターンコマンドを送信する例が示されたが、2つ以上のコマンドで変動パターンを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に通知するようにしてもよい。具体的には、2つのコマンドで通知する場合、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、1つ目のコマンドとして擬似連の有無、滑り演出の有無等、リーチになる前(リーチにならない場合にはいわゆる第2停止の前)の変動時間や変動態様を示すコマンドを送信し、2つ目のコマンドとしてリーチの種類や再抽選演出の有無等、リーチになったとき以降(リーチにならない場合にはいわゆる第2停止以後)の変動時間や変動態様を示すコマンドを送信するようにしてもよい。その場合、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、2つのコマンドの組合せから導かれる変動時間にもとづいて変動表示(可変表示)における演出制御を行うようにすればよい。なお、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、2つのコマンドのそれぞれで変動時間を通知し、それぞれのタイミングで実行される具体的な変動態様については演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100で選択するようにしてもよい。2つのコマンドを送信する場合、同一のタイマ割込内で2つのコマンドを送信するようにしてもよく、1つ目のコマンドを送信した後、所定の期間が経過してから(例えば、次のタイマ割込において)2つ目のコマンドを送信するようにしてもよい。なお、それぞれのコマンドで示される変動態様はそのような例に限定されず、送信する順序についても適宜変更可能である。このように2つ以上のコマンドで変動パターンを通知するようにすることによって、変動パターンコマンドとして記憶しておかなければならないデータ量を削減することができる。
In each of the above-described embodiments, the variable time, the type of reach effect, and the presence or absence of a pseudo-continuation (a effect in which the symbol is temporarily stopped and re-flushed one or more times during one variable display), etc. In order to notify the variation pattern indicating the variation mode to the
また、上記の各実施の形態において、「割合が異なる」とは、A:B=70%:30%やA:B=30%:70%のような関係で割合が異なるものだけにかぎらず、A:B=100%:0%のような関係で割合が異なるもの(すなわち、一方が100%の割り振りで他方が0%の割り振りとなるようなもの)も含む概念である。 Further, in each of the above embodiments, "different proportions" means not only different proportions such as A:B = 70%: 30% or A:B = 30%: 70%. , A:B=100%:0% (ie, 100% allocation to one side and 0% allocation to the other).
また、上記の各実施の形態では、例えば「1」~「9」の複数種類の特別図柄や演出図柄、普通図柄を可変表示し表示結果を導出表示する場合を示したが、可変表示は、そのような態様にかぎられない。例えば、可変表示される図柄と導出表示される図柄とが必ずしも同じである必要ななく、可変表示された図柄とは異なる図柄が導出表示されるものであってもよい。また、必ずしも複数種類の図柄を可変表示する必要はなく、1種類の図柄のみを用いて可変表示を実行するものであってもよい。この場合、例えば、その1種類の図柄表示を交互に点灯および点滅を繰り返すことによって、可変表示を実行するものであってもよい。そして、この場合であっても、その可変表示に用いられる1種類の図柄が最後に導出表示されるものであってもよいし、その1種類の図柄とは異なる図柄が最後に導出表示されるものであってもよい。 Further, in each of the above-described embodiments, for example, a case of variably displaying a plurality of types of special symbols, effect symbols, and normal symbols from "1" to "9" and deriving and displaying the display result was shown. It is not limited to such aspects. For example, the symbol to be variably displayed and the symbol to be derived and displayed do not necessarily have to be the same, and a symbol different from the symbol to be variably displayed may be derived and displayed. Also, it is not always necessary to variably display a plurality of types of symbols, and variably displaying may be performed using only one type of symbol. In this case, for example, the variable display may be performed by alternately repeating lighting and blinking of the one type of pattern display. Even in this case, one type of pattern used for the variable display may be derived and displayed last, or a pattern different from the one type of pattern may be derived and displayed last. can be anything.
また、上記の各実施の形態では、遊技機としてパチンコ機を例にしたが、本発明を、メダルが投入されて所定の賭け数が設定され、遊技者による操作レバーの操作に応じて複数種類の図柄を回転させ、遊技者によるストップボタンの操作に応じて図柄を停止させたときに停止図柄の組合せが特定の図柄の組み合わせになると、所定数のメダルが遊技者に払い出されるスロット機に適用することも可能である。 In each of the above embodiments, a pachinko machine was used as the gaming machine. symbols are rotated and the symbols are stopped in response to the operation of the stop button by the player. It is also possible to
また、本発明による遊技機は、所定数の景品としての遊技媒体を払い出す遊技機に限定されず、遊技球等の遊技媒体を封入し景品の付与条件が成立した場合に得点を付与する封入式の遊技機に適用することもできる。 Further, the gaming machine according to the present invention is not limited to a gaming machine that pays out game media as a predetermined number of prizes. It can also be applied to a game machine of the type.
また、上記の各実施の形態では、大当り種別として確変大当りや通常大当りがあり、大当り種別として確変大当りと決定されたことにもとづいて、大当り遊技終了後に確変状態に制御される遊技機を示したが、そのような遊技機に限定されない。例えば、内部に所定の確変領域が設けられた特別可変入賞球装置(1つだけ設けられた特別可変入賞球装置内に確変領域が設けられていてもよいし、複数設けられた特別可変入賞球装置のうちの一部に確変領域が設けられていてもよい)を備え、大当り遊技中に特別可変入賞球装置内における確変領域を遊技球が通過したことにもとづいて確変が確定し、大当り遊技終了後に確変状態に制御される遊技機に上記の各実施の形態で示した構成を適用することもできる。 Further, in each of the above-described embodiments, the jackpot type includes the variable probability big hit and the normal jackpot, and based on the fact that the variable probability big hit is determined as the jackpot type, the gaming machine is controlled to the variable probability state after the end of the big win game. However, it is not limited to such gaming machines. For example, a special variable winning ball device provided with a predetermined variable probability area inside (the variable probability area may be provided in a special variable winning ball device provided with only one, or a plurality of special variable winning balls provided A variable probability region may be provided in a part of the device), and the variable probability is determined based on the game ball passing through the variable probability region in the special variable winning ball device during the jackpot game, and the jackpot game is played. The configuration shown in each of the above-described embodiments can also be applied to a gaming machine that is controlled to the variable probability state after the end.
また、上記の各実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560側で大当りとなるか否かや変動パターン種別の入賞時判定(先読み判定)を行い、その入賞時判定結果を示すコマンド(図柄指定コマンド、変動カテゴリコマンド)を送信し、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100側で、その入賞時判定結果を示すコマンドにもとづいて保留予告演出を実行する場合を示したが、そのような態様にかぎらず、例えば、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100側で入賞時判定(先読み判定)を行うように構成してもよい。この場合、例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、始動入賞の発生時に抽出した大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)や変動パターン種別判定用乱数(ランダム2)の値のみを指定するコマンドを送信するようにし、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100側で、それらのコマンドで指定される乱数の値にもとづいて入賞時判定(先読み判定)を行うように構成してもよい。
In addition, in each of the above-described embodiments, whether or not the
本発明は、遊技者が所定の遊技を行うことが可能なパチンコ遊技機等の遊技機に好適に適用される。 INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY The present invention is suitably applied to a game machine such as a pachinko game machine in which a player can play a predetermined game.
1 パチンコ遊技機
8a 第1特別図柄表示器
8b 第2特別図柄表示器
9 演出表示装置(メイン表示装置)
9a 第1保留記憶表示部
9b 第2保留記憶表示部
13 第1始動入賞口
14 第2始動入賞口
20 特別可変入賞球装置
31 遊技制御基板(主基板)
56 CPU
560 遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ
80 演出制御基板
100 演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ
101 演出制御用CPU
109 VDP
1
9a 1st reservation
56 CPUs
560
109 VDP
Claims (1)
所定表示を表示可能な表示手段を備え、
前記表示手段は、
所定表示を特定表示に変化させて表示することが可能であり、
少なくとも第1所定態様および該第1所定態様よりも遊技者にとって有利な有利状態に制御される期待度が高い第2所定態様により所定表示を表示可能であり、
所定表示を第1所定態様にて表示した後に、該所定表示を第2所定態様に変化させて表示可能であり、
少なくとも第1特定態様および該第1特定態様よりも有利状態に制御される期待度が高い第2特定態様により特定表示を表示可能であり、
有利状態に制御される場合に、
第1所定態様よりも高い割合で第2所定態様にて所定表示を表示し、
第1特定態様よりも高い割合で第2特定態様にて特定表示を表示し、
第1所定態様の所定表示が第2特定態様の特定表示に変化する第1変化パターンは、第2所定態様の所定表示が第1特定態様の特定表示に変化する第2変化パターンよりも有利状態に制御される期待度が高く、
有利状態に制御される場合に、第2変化パターンよりも高い割合で第1変化パターンにて所定表示が特定表示に変化し、
特定表示の表示形状は、所定表示の表示形状とは異なり、
所定表示の表示態様に応じて、特定表示に変化する割合が異なり、
変化後の特定表示の態様に応じて、複数のタイミングのいずれにおいて所定表示が該特定表示に変化するかの割合が異なる、
ことを特徴とする遊技機。 A gaming machine for playing games,
Equipped with display means capable of displaying a predetermined display,
The display means is
It is possible to display by changing the predetermined display to a specific display,
The predetermined display can be displayed in at least a first predetermined mode and a second predetermined mode in which the player is expected to be controlled to an advantageous state more advantageous than the first predetermined mode, and
After the predetermined display is displayed in the first predetermined mode, the predetermined display can be changed to the second predetermined mode and displayed,
A specific display can be displayed by at least a first specific mode and a second specific mode that is more likely to be controlled in an advantageous state than the first specific mode, and
When controlled in an advantageous state,
displaying the predetermined display in the second predetermined mode at a higher rate than in the first predetermined mode;
displaying the specific display in the second specific mode at a higher rate than in the first specific mode;
The first change pattern in which the predetermined display of the first predetermined mode changes to the specific display in the second specific mode is more advantageous than the second change pattern in which the predetermined display of the second predetermined mode changes to the specific display of the first specific mode. There is a high expectation that it will be controlled by
When controlled to an advantageous state, the predetermined display changes to the specific display in the first change pattern at a higher rate than in the second change pattern,
The display shape of the specific display is different from the display shape of the predetermined display,
Depending on the display mode of the predetermined display, the rate of change to the specific display is different,
Depending on the aspect of the specific display after the change, the ratio at which of the plurality of timings the predetermined display changes to the specific display differs,
A gaming machine characterized by:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017105328A JP7121471B2 (en) | 2017-05-29 | 2017-05-29 | game machine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017105328A JP7121471B2 (en) | 2017-05-29 | 2017-05-29 | game machine |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2018198830A JP2018198830A (en) | 2018-12-20 |
| JP2018198830A5 JP2018198830A5 (en) | 2020-11-12 |
| JP7121471B2 true JP7121471B2 (en) | 2022-08-18 |
Family
ID=64667546
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017105328A Active JP7121471B2 (en) | 2017-05-29 | 2017-05-29 | game machine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7121471B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021171416A (en) * | 2020-04-27 | 2021-11-01 | 株式会社サンセイアールアンドディ | Game machine |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004329226A (en) | 2003-04-30 | 2004-11-25 | Sankyo Kk | Game machine |
| JP2012249717A (en) | 2011-05-31 | 2012-12-20 | Daito Giken:Kk | Game machine |
| JP2013013576A (en) | 2011-07-04 | 2013-01-24 | Newgin Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP2016034424A (en) | 2014-08-04 | 2016-03-17 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP2016198237A (en) | 2015-04-09 | 2016-12-01 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP6115798B1 (en) | 2016-02-29 | 2017-04-19 | 株式会社大都技研 | Amusement stand |
| JP2017080204A (en) | 2015-10-29 | 2017-05-18 | サミー株式会社 | Pachinko game machine |
-
2017
- 2017-05-29 JP JP2017105328A patent/JP7121471B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004329226A (en) | 2003-04-30 | 2004-11-25 | Sankyo Kk | Game machine |
| JP2012249717A (en) | 2011-05-31 | 2012-12-20 | Daito Giken:Kk | Game machine |
| JP2013013576A (en) | 2011-07-04 | 2013-01-24 | Newgin Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP2016034424A (en) | 2014-08-04 | 2016-03-17 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP2016198237A (en) | 2015-04-09 | 2016-12-01 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP2017080204A (en) | 2015-10-29 | 2017-05-18 | サミー株式会社 | Pachinko game machine |
| JP6115798B1 (en) | 2016-02-29 | 2017-04-19 | 株式会社大都技研 | Amusement stand |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2018198830A (en) | 2018-12-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6898896B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP6886348B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP6810069B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2016097105A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6674412B2 (en) | Gaming machine | |
| JP7143387B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP6564359B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP7121471B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP7121472B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP6996870B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP6734224B2 (en) | Amusement machine | |
| JP2018110787A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6793537B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP7143386B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP7143385B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP2019072156A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6682479B2 (en) | Amusement machine | |
| JP2019013395A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6886372B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP6793538B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6754292B2 (en) | Amusement machine | |
| JP6754293B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6793539B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6793540B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2018191837A (en) | Game machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20200420 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200918 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20210430 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20210511 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20210709 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20211124 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20220121 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20220329 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20220624 |
|
| C60 | Trial request (containing other claim documents, opposition documents) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: C60 Effective date: 20220624 |
|
| A911 | Transfer to examiner for re-examination before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20220704 |
|
| C21 | Notice of transfer of a case for reconsideration by examiners before appeal proceedings |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: C21 Effective date: 20220705 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20220802 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20220805 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7121471 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |