JP7052567B2 - Eyeglass lens processing control data acquisition device - Google Patents
Eyeglass lens processing control data acquisition device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7052567B2 JP7052567B2 JP2018104224A JP2018104224A JP7052567B2 JP 7052567 B2 JP7052567 B2 JP 7052567B2 JP 2018104224 A JP2018104224 A JP 2018104224A JP 2018104224 A JP2018104224 A JP 2018104224A JP 7052567 B2 JP7052567 B2 JP 7052567B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- lens
- control data
- facet
- processing
- shape information
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B24—GRINDING; POLISHING
- B24B—MACHINES, DEVICES, OR PROCESSES FOR GRINDING OR POLISHING; DRESSING OR CONDITIONING OF ABRADING SURFACES; FEEDING OF GRINDING, POLISHING, OR LAPPING AGENTS
- B24B9/00—Machines or devices designed for grinding edges or bevels on work or for removing burrs; Accessories therefor
- B24B9/02—Machines or devices designed for grinding edges or bevels on work or for removing burrs; Accessories therefor characterised by a special design with respect to properties of materials specific to articles to be ground
- B24B9/06—Machines or devices designed for grinding edges or bevels on work or for removing burrs; Accessories therefor characterised by a special design with respect to properties of materials specific to articles to be ground of non-metallic inorganic material, e.g. stone, ceramics, porcelain
- B24B9/08—Machines or devices designed for grinding edges or bevels on work or for removing burrs; Accessories therefor characterised by a special design with respect to properties of materials specific to articles to be ground of non-metallic inorganic material, e.g. stone, ceramics, porcelain of glass
- B24B9/14—Machines or devices designed for grinding edges or bevels on work or for removing burrs; Accessories therefor characterised by a special design with respect to properties of materials specific to articles to be ground of non-metallic inorganic material, e.g. stone, ceramics, porcelain of glass of optical work, e.g. lenses, prisms
- B24B9/148—Machines or devices designed for grinding edges or bevels on work or for removing burrs; Accessories therefor characterised by a special design with respect to properties of materials specific to articles to be ground of non-metallic inorganic material, e.g. stone, ceramics, porcelain of glass of optical work, e.g. lenses, prisms electrically, e.g. numerically, controlled
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B24—GRINDING; POLISHING
- B24B—MACHINES, DEVICES, OR PROCESSES FOR GRINDING OR POLISHING; DRESSING OR CONDITIONING OF ABRADING SURFACES; FEEDING OF GRINDING, POLISHING, OR LAPPING AGENTS
- B24B49/00—Measuring or gauging equipment for controlling the feed movement of the grinding tool or work; Arrangements of indicating or measuring equipment, e.g. for indicating the start of the grinding operation
- B24B49/12—Measuring or gauging equipment for controlling the feed movement of the grinding tool or work; Arrangements of indicating or measuring equipment, e.g. for indicating the start of the grinding operation involving optical means
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B24—GRINDING; POLISHING
- B24B—MACHINES, DEVICES, OR PROCESSES FOR GRINDING OR POLISHING; DRESSING OR CONDITIONING OF ABRADING SURFACES; FEEDING OF GRINDING, POLISHING, OR LAPPING AGENTS
- B24B51/00—Arrangements for automatic control of a series of individual steps in grinding a workpiece
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Grinding And Polishing Of Tertiary Curved Surfaces And Surfaces With Complex Shapes (AREA)
- Eyeglasses (AREA)
Description
本開示は、眼鏡レンズを加工するための加工制御データを取得する眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置に関する。 The present disclosure relates to a spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device for acquiring processing control data for processing a spectacle lens.
眼鏡レンズを加工する眼鏡レンズ加工装置が知られている。眼鏡レンズ加工装置では、眼鏡レンズの周縁にヤゲンや溝を形成したり、眼鏡レンズに穴を開けたりするための加工制御データが取得され、これに基づく加工が行われる。眼鏡レンズにデザイン性をもたせるため、眼鏡レンズのレンズ面に平面を形成するファセット加工を施すこともある。例えば、ファセット加工によって、レンズ面に宝石のような多角面を形成することもできる。 A spectacle lens processing device for processing a spectacle lens is known. In the spectacle lens processing apparatus, processing control data for forming a bevel or a groove on the peripheral edge of the spectacle lens or making a hole in the spectacle lens is acquired, and processing is performed based on the data. In order to give the spectacle lens a design, the lens surface of the spectacle lens may be faceted to form a flat surface. For example, facet processing can be used to form a jewel-like polygonal surface on the lens surface.
ところで、ファセット加工は手動で設定されているが、ファセット加工後のレンズの形状は想像しづらく、精度よく設定することが難しかった。このため、ファセット加工後のレンズの出来栄えがよくないことがあった。また、ファセット加工の設定には手間がかかっていた。 By the way, although the facet processing is set manually, it is difficult to imagine the shape of the lens after the facet processing, and it is difficult to set it accurately. For this reason, the quality of the lens after facet processing may not be good. In addition, it took time and effort to set the facet processing.
本開示は、上記従来技術に鑑み、ファセット加工を容易に設定することができる眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置を提供することを技術課題とする。 In view of the above-mentioned prior art, it is a technical subject of the present disclosure to provide a spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device capable of easily setting facet processing.
上記課題を解決するため、本開示は以下の構成を備えることを特徴とする。
(1) 本開示の第1態様に係る眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置は、眼鏡レンズを加工するための加工制御データを取得する眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置であって、眼鏡の玉型形状情報を取得する第1形状情報取得手段と、前記眼鏡用のデモレンズから検出されたファセット形状情報であって、前記デモレンズに施されたファセット形状情報を取得する第2形状情報取得手段と、前記玉型形状情報及び前記ファセット形状情報に基づいて、前記眼鏡レンズのレンズ面に、少なくとも1つの平面を形成するためのファセット加工制御データを取得する加工制御データ取得手段と、を備えることを特徴とする。
(2) 本開示の第2態様に係る眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得プログラムは、眼鏡レンズを加工するための加工制御データを取得する眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置において用いられる眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得プログラムであって、前記眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置のプロセッサに実行されることで、眼鏡の玉型形状情報を取得する第1形状情報取得ステップと、前記眼鏡用のデモレンズから検出されたファセット形状情報であって、前記デモレンズに施されたファセット形状情報を取得する第2形状情報取得ステップと、前記玉型形状情報及び前記ファセット形状情報に基づいて、前記眼鏡レンズのレンズ面に、少なくとも1つの平面を形成するためのファセット加工制御データを取得する加工制御データ取得ステップと、を前記眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置に実行させることを特徴とする。
In order to solve the above problems, the present disclosure is characterized by having the following configurations.
(1) The spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device according to the first aspect of the present disclosure is a spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device for acquiring processing control data for processing spectacle lenses, and is spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device. The first shape information acquisition means for acquiring the facet shape information, the second shape information acquisition means for acquiring the facet shape information applied to the demo lens, which is the facet shape information detected from the demo lens for the spectacles, and the lens mold. It is characterized by comprising a processing control data acquisition means for acquiring facet processing control data for forming at least one plane on the lens surface of the spectacle lens based on the shape information and the facet shape information.
(2) The spectacle lens processing control data acquisition program according to the second aspect of the present disclosure is a spectacle lens processing control data acquisition program used in the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device for acquiring processing control data for processing the spectacle lens. The first shape information acquisition step for acquiring the eyeball shape information of the spectacles and the facet shape information detected from the demo lens for the spectacles are executed by the processor of the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device. At least one flat surface on the lens surface of the spectacle lens based on the second shape information acquisition step for acquiring the facet shape information applied to the demo lens, the lens shape information, and the facet shape information. It is characterized in that the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device executes the processing control data acquisition step of acquiring the facet processing control data for forming the spectacle lens processing control data.
<概要>
本開示の実施形態に係る眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置の概要について説明する。なお、以下の<>にて分類された項目は、独立または関連して利用されうる。
<Overview>
An outline of the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device according to the embodiment of the present disclosure will be described. The items classified by <> below can be used independently or in relation to each other.
<第1形状情報取得手段>
例えば、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置は、第1形状情報取得手段(例えば、制御部80)を備える。第1形状情報取得手段は、眼鏡の玉型形状情報を取得する。眼鏡の玉型形状情報は、デモレンズまたは型板の外形形状であってもよい。また、眼鏡の玉型形状情報は、眼鏡フレーム(以下、フレーム)のリムの内形形状であってもよい。例えば、フレームのリムが、レンズに形成した溝に嵌め込む凸部を有する場合には、フレームの内形形状として、リムの凸部の内形形状を取得してもよい。例えば、フレームのリムが、レンズに形成したヤゲンを嵌め込む凹部を有する場合には、フレームの内形形状として、リムの凹部の内形形状を取得してもよい。
<First shape information acquisition means>
For example, the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device includes a first shape information acquisition unit (for example, a control unit 80). The first shape information acquisition means acquires the eyeglass shape information. The eyeglass shape information may be the outer shape of the demo lens or the template. Further, the spectacle shape information may be the internal shape of the rim of the spectacle frame (hereinafter, frame). For example, when the rim of the frame has a convex portion to be fitted into the groove formed in the lens, the internal shape of the convex portion of the rim may be acquired as the internal shape of the frame. For example, when the rim of the frame has a recess for fitting the bevel formed in the lens, the internal shape of the concave portion of the rim may be acquired as the internal shape of the frame.
第1形状情報取得手段は、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置とは異なる別の装置が測定した第1形状情報取得手段を取得してもよい。また、第1形状情報取得手段は、測定手段(例えば、眼鏡枠形状測定ユニット20、ブロッカーユニット30)を用いて眼鏡の玉型形状情報を測定することで、眼鏡の玉型形状情報を取得してもよい。測定手段は、フレーム、デモレンズ、及び型板の少なくともいずれかに接触する接触式の構成であってもよい。また、測定手段は、フレーム、デモレンズ、及び型板のいずれにも接触しない非接触式の構成であってもよい。
The first shape information acquisition means may acquire the first shape information acquisition means measured by another device different from the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device. Further, the first shape information acquisition means acquires the spectacle shape information by measuring the spectacle shape information using the measuring means (for example, the spectacle frame
接触式の構成としては、測定子及び測定子軸を備えていてもよい。測定子は、リムの凹部に接触し、リムの凹部に沿って移動されてもよい。測定子軸は、リムの凸部、デモレンズの周縁、型板の周縁、等の少なくともいずれかに接触し、これらに沿って移動されてもよい。第1形状情報取得手段は、測定子または測定子軸の移動位置を検出することで、眼鏡の玉型形状情報を取得することができる。 The contact type configuration may include a stylus and a stylus shaft. The stylus may come into contact with the recess of the rim and be moved along the recess of the rim. The stylus axis may contact and move along at least one of the convex portions of the rim, the periphery of the demo lens, the periphery of the template, and the like. The first shape information acquisition means can acquire the eyeglass shape information by detecting the moving position of the stylus or the stylus axis.
非接触式の構成としては、測定光束を照射する投光光学系と、測定光束が反射された反射光束を受光する受光光学系と、を備えていてもよい。投光光学系は、フレームのリム、デモレンズの周縁、型板の周縁、等の少なくともいずれかに測定光束を照射してもよい。また、受光光学系は、測定光束がフレームのリム、デモレンズの周縁、型板の周縁、等の少なくともいずれかに反射された反射光束を受光してもよい。第1形状情報取得手段は、このような反射光束を解析処理することで、眼鏡の玉型形状情報を取得することができる。 The non-contact type configuration may include a light projecting optical system that irradiates the measured light flux and a light receiving optical system that receives the reflected light beam reflected from the measured light beam. The floodlight optical system may irradiate at least one of the rim of the frame, the peripheral edge of the demo lens, the peripheral edge of the template, and the like with the measured luminous flux. Further, the light receiving optical system may receive the reflected light flux whose measured light flux is reflected on at least one of the rim of the frame, the peripheral edge of the demo lens, the peripheral edge of the template, and the like. The first shape information acquisition means can acquire the eyeglass shape information by analyzing such a reflected luminous flux.
<第2形状情報取得手段>
例えば、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置は、第2形状情報取得手段(例えば、制御部80)を備える。第2形状情報取得手段は、眼鏡用のデモレンズから検出されたファセット形状情報であって、デモレンズに施されたファセット形状情報を取得する。例えば、眼鏡用のデモレンズとは、フレームに嵌め込まれていたデモレンズ、フレームに留められていたデモレンズ、等の少なくともいずれかであってもよい。例えば、ファセット形状情報は、ファセット加工により形成された切子面の形状(言い換えると、ファセット加工により形成された小面の形状)、ファセット加工の加工ライン(すなわち、ファセット加工により形成されたエッジライン)、ファセット加工の加工幅、等の少なくともいずれかを含む情報であってもよい。例えば、デモレンズから検出されたファセット形状情報とは、デモレンズを撮像したレンズ像(デモレンズ像)から検出されたファセット形状情報であってもよい。
<Second shape information acquisition means>
For example, the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device includes a second shape information acquisition unit (for example, a control unit 80). The second shape information acquisition means is facet shape information detected from the demo lens for spectacles, and acquires facet shape information applied to the demo lens. For example, the demo lens for eyeglasses may be at least one of a demo lens fitted in the frame, a demo lens fastened to the frame, and the like. For example, the facet shape information includes the shape of the facet surface formed by facet processing (in other words, the shape of the facet formed by facet processing) and the processing line of facet processing (that is, the edge line formed by facet processing). , Facet processing width, etc. may be information including at least one of them. For example, the facet shape information detected from the demo lens may be facet shape information detected from a lens image (demo lens image) obtained by imaging the demo lens.
第2形状情報取得手段は、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置が備える測定手段(例えば、ブロッカーユニット30)を用いてファセット形状情報を測定することで、デモレンズに施されたファセット形状情報を取得してもよい。この場合、測定手段は、デモレンズのレンズ面を撮像する撮像光学系(例えば、撮像光学系63)を備えていてもよい。第2形状情報取得手段は、撮像光学系により撮像されたデモレンズ像からファセット形状情報を検出することで、ファセット形状情報を取得してもよい。これによって、操作者は、眼鏡レンズに施されたファセット形状情報を容易に取得することができる。また、このような撮像光学系を、眼鏡の玉型形状情報の取得と、ファセット形状情報の取得と、の双方に用いることで、これらの情報を取得する際の操作をより簡単にすることもできる。 The second shape information acquisition means acquires the facet shape information applied to the demo lens by measuring the facet shape information using the measuring means (for example, the blocker unit 30) provided in the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device. May be good. In this case, the measuring means may include an imaging optical system (for example, an imaging optical system 63) that images the lens surface of the demo lens. The second shape information acquisition means may acquire facet shape information by detecting facet shape information from the demo lens image captured by the imaging optical system. As a result, the operator can easily acquire the facet shape information applied to the spectacle lens. Further, by using such an imaging optical system for both acquisition of eyeglass shape information and facet shape information, it is possible to simplify the operation for acquiring such information. can.
また、第2形状情報取得手段は、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置とは異なる別の装置が測定したファセット形状情報を取得してもよい。この場合、第2形状情報取得手段は、別の装置により撮像されたデモレンズ像を受信し、このデモレンズ像からファセット形状情報を検出することで、ファセット形状情報を取得してもよい。また、この場合、第2形状情報取得手段は、別の装置が撮像したデモレンズ像から検出されたファセット形状情報を受信することで、ファセット形状情報を取得してもよい。 Further, the second shape information acquisition means may acquire facet shape information measured by another device different from the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device. In this case, the second shape information acquisition means may acquire facet shape information by receiving a demo lens image captured by another device and detecting facet shape information from the demo lens image. Further, in this case, the second shape information acquisition means may acquire the facet shape information by receiving the facet shape information detected from the demo lens image captured by another device.
なお、例えば、第2形状情報取得手段は、デモレンズ像の各画素位置における輝度の立ち上がりや立ち下がりを検出することでエッジを検出し、ファセット形状情報を取得する構成であってもよい。また、例えば、第2形状情報取得手段は、デモレンズがない基準像と、デモレンズ像と、の差分処理からエッジを検出し、ファセット形状情報を取得する構成であってもよい。差分処理としては、基準像とデモレンズ像の各画素位置から検出した輝度値を除算してもよい。基準像とデモレンズ像の各画素位置から検出した輝度値を減算してもよい。なお、画素位置から検出されるものは彩度や色相等であってもよく、輝度値に限定されない。 For example, the second shape information acquisition means may be configured to detect the edge by detecting the rise and fall of the luminance at each pixel position of the demo lens image and acquire the facet shape information. Further, for example, the second shape information acquisition means may be configured to detect the edge from the difference processing between the reference image without the demo lens and the demo lens image and acquire the facet shape information. As the difference processing, the luminance value detected from each pixel position of the reference image and the demo lens image may be divided. The detected luminance value may be subtracted from each pixel position of the reference image and the demo lens image. It should be noted that what is detected from the pixel position may be saturation, hue, or the like, and is not limited to the luminance value.
<第3形状情報取得手段>
例えば、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置は、第3形状情報取得手段(例えば、制御部80)を備える。第3形状情報取得手段は、眼鏡レンズのレンズ面におけるカーブ情報を取得する。なお、第3形状情報取得手段は、眼鏡レンズのレンズ面における少なくともカーブ情報を取得する構成であればよい。例えば、第3形状情報取得手段は、カーブ情報に加えて、コバ情報を取得するようにしてもよい。コバ情報は、コバ面の厚み、コバ面の位置、等であってもよい。
<Third shape information acquisition means>
For example, the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device includes a third shape information acquisition unit (for example, a control unit 80). The third shape information acquisition means acquires curve information on the lens surface of the spectacle lens. The third shape information acquisition means may be configured to acquire at least curve information on the lens surface of the spectacle lens. For example, the third shape information acquisition means may acquire edge information in addition to curve information. The edge information may be the thickness of the edge surface, the position of the edge surface, and the like.
第3形状情報取得手段は、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置とは異なる別の装置が測定した第3形状情報取得手段を取得してもよい。この場合には、操作者が操作手段(例えば、スイッチ部6)を操作することによって、予め測定した眼鏡レンズカーブ情報を入力する構成であってもよい。また、第3形状情報取得手段は、測定手段(例えば、レンズ面形状測定ユニット400)を用いてカーブ情報を測定することで、眼鏡レンズのレンズ面におけるカーブ情報を取得してもよい。 The third shape information acquisition means may acquire the third shape information acquisition means measured by another device different from the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device. In this case, the operator may operate the operating means (for example, the switch unit 6) to input the pre-measured spectacle lens curve information. Further, the third shape information acquisition means may acquire the curve information on the lens surface of the spectacle lens by measuring the curve information using the measuring means (for example, the lens surface shape measuring unit 400).
例えば、第3形状情報取得手段は、眼鏡レンズにファセット加工を施す側のレンズ面におけるカーブ情報を取得してもよい。すなわち、眼鏡レンズの前面にファセット加工を施す場合には、眼鏡レンズの少なくとも前面におけるカーブ情報が取得される。また、眼鏡レンズの後面にファセット加工を施す場合には、眼鏡レンズの少なくとも後面におけるカーブ情報が取得される。なお、眼鏡レンズの前面及び後面のいずれか一面にのみファセット加工を施す場合には、ファセット加工を施す面と、ファセット加工を施さない面と、の双方のカーブ情報が取得されてもよい。眼鏡レンズの前面と後面にファセット加工を施す場合には、眼鏡レンズの前面と後面におけるカーブ情報がそれぞれ取得される。 For example, the third shape information acquisition means may acquire curve information on the lens surface on the side where the facet processing is applied to the spectacle lens. That is, when faceting is applied to the front surface of the spectacle lens, curve information at least on the front surface of the spectacle lens is acquired. Further, when faceting the rear surface of the spectacle lens, curve information on at least the rear surface of the spectacle lens is acquired. When faceting is applied to only one of the front surface and the rear surface of the spectacle lens, curve information of both the faceted surface and the non-faceted surface may be acquired. When faceting is applied to the front and rear surfaces of the spectacle lens, curve information on the front and rear surfaces of the spectacle lens is acquired, respectively.
<加工制御データ取得手段>
例えば、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置は、加工制御データ取得手段(例えば、制御部80)を備える。加工制御データ取得手段は、玉型形状情報及びファセット形状情報に基づいて、眼鏡レンズのレンズ面に、少なくとも1つの平面を形成するためのファセット加工制御データを取得する。すなわち、加工制御データ取得手段は、玉型形状情報及びファセット形状情報に基づいて、眼鏡レンズの前面及び後面の少なくともいずれかに、少なくとも1つの平面を形成するためのファセット加工制御データを取得する。なお、ファセット加工制御データは、眼鏡レンズの前面に複数の平面を形成するためのファセット加工制御データであってもよい。眼鏡レンズの後面に複数の平面を形成するためのファセット加工制御データであってもよい。眼鏡レンズの前面に複数の平面を形成し、眼鏡レンズの後面に複数の平面を形成するためのファセット加工制御データであってもよい。例えば、ファセット加工制御データは、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置の制御部(例えば、制御部80)により演算されることで取得されてもよい。
<Machining control data acquisition means>
For example, the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device includes processing control data acquisition means (for example, a control unit 80). The processing control data acquisition means acquires facet processing control data for forming at least one plane on the lens surface of the spectacle lens based on the lens shape information and the facet shape information. That is, the processing control data acquisition means acquires facet processing control data for forming at least one plane on at least one of the front surface and the rear surface of the spectacle lens based on the lens shape information and the facet shape information. The facet processing control data may be facet processing control data for forming a plurality of planes on the front surface of the spectacle lens. It may be facet processing control data for forming a plurality of planes on the rear surface of the spectacle lens. It may be facet processing control data for forming a plurality of planes on the front surface of the spectacle lens and forming a plurality of planes on the rear surface of the spectacle lens. For example, the facet processing control data may be acquired by being calculated by a control unit (for example, the control unit 80) of the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device.
例えば、加工制御データ取得手段は、第1形状情報取得手段により取得された玉型形状情報、及び、第2形状情報取得手段により取得されたファセット形状情報、に基づいて、眼鏡レンズのレンズ面に、少なくとも1つの平面を形成するためのファセット加工制御データを取得してもよい。これによって、操作者は、ファセット形状情報を自動的に取得することができるとともに、このようなファセット加工制御データを利用することで、眼鏡レンズに好適なファセット加工を施すことができる。 For example, the processing control data acquisition means is applied to the lens surface of the spectacle lens based on the lens shape information acquired by the first shape information acquisition means and the facet shape information acquired by the second shape information acquisition means. , The facet processing control data for forming at least one plane may be acquired. As a result, the operator can automatically acquire facet shape information, and by using such facet processing control data, it is possible to perform facet processing suitable for the spectacle lens.
また、例えば、加工制御データ取得手段は、玉型形状情報と、ファセット形状情報と、第3形状情報取得手段により取得されたカーブ情報と、に基づいて、ファセット加工制御データを取得してもよい。眼鏡レンズのカーブ情報と、デモレンズのカーブ情報と、は必ずしも一致しないため、眼鏡レンズのカーブ情報を考慮したファセット加工制御データを取得してこれを用いることで、より精度よくファセット加工を実施することができる。 Further, for example, the machining control data acquisition means may acquire facet machining control data based on the lens shape information, the facet shape information, and the curve information acquired by the third shape information acquisition means. .. Since the curve information of the spectacle lens and the curve information of the demo lens do not always match, the facet processing can be performed more accurately by acquiring the facet processing control data considering the curve information of the spectacle lens and using this. Can be done.
なお、本実施例では、第1形状情報取得手段が眼鏡の玉型形状情報を取得し、第2形状情報取得手段がデモレンズの前面に施されたファセット形状情報を取得し、第3形状情報取得手段が眼鏡レンズの前面におけるカーブ情報を取得し、加工制御データ取得手段が眼鏡レンズの前面に少なくとも1つの平面を形成するためのファセット加工制御データを取得する構成であってもよい。 In this embodiment, the first shape information acquisition means acquires the eyeglass shape information, the second shape information acquisition means acquires the facet shape information provided on the front surface of the demo lens, and the third shape information acquisition. The means may be configured to acquire curve information on the front surface of the spectacle lens, and the processing control data acquisition means may acquire facet processing control data for forming at least one plane on the front surface of the spectacle lens.
なお、本実施例において、加工制御データ取得手段は、玉型形状情報及びファセット形状情報に基づく加工制御データを直接取得してもよい。もちろん、加工制御データ取得手段は、玉型形状情報、ファセット形状情報、及びカーブ情報に基づく加工制御データを直接取得してもよい。また、本実施例において、加工制御データ取得手段は、眼鏡レンズに施すファセット加工の加工領域を取得し、この加工領域に対して加工制御データを取得してもよい。 In this embodiment, the machining control data acquisition means may directly acquire the machining control data based on the lens shape information and the facet shape information. Of course, the machining control data acquisition means may directly acquire machining control data based on the lens shape information, facet shape information, and curve information. Further, in the present embodiment, the processing control data acquisition means may acquire a processing region for facet processing applied to the spectacle lens, and may acquire processing control data for this processing region.
<設定手段>
例えば、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置は、設定手段(例えば、制御部80)を備える。設定手段は、眼鏡レンズに施すファセット加工の加工領域を設定する。設定手段は、ファセット加工の加工ラインにおける始点と終点の位置、ファセット加工の加工幅、等の少なくともいずれかを加工領域として設定してもよい。なお、加工領域は、玉型形状情報及びファセット形状情報に基づいて設定される加工領域であってもよい。もちろん、カーブ情報を取得している場合、加工領域は、玉型形状情報、ファセット形状情報、及びカーブ情報に基づいて設定される加工領域であってもよい。このような場合、加工制御データ取得手段は、設定された加工領域に基づくファセット加工制御データを取得してもよい。これによって、操作者は、設定された加工領域を確認し、眼鏡レンズのファセット加工後の形状を想像することができる。また、操作者は、設定された加工領域が適切かどうかを判断することができる。
<Setting means>
For example, the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device includes setting means (for example, a control unit 80). The setting means sets the processing area of the facet processing applied to the spectacle lens. As the setting means, at least one of the positions of the start point and the end point in the facet processing processing line, the processing width of facet processing, and the like may be set as the processing region. The machining area may be a machining area set based on the lens shape information and the facet shape information. Of course, when the curve information is acquired, the machining area may be a machining area set based on the lens shape information, the facet shape information, and the curve information. In such a case, the machining control data acquisition means may acquire faceted machining control data based on the set machining area. As a result, the operator can confirm the set processing area and imagine the shape of the spectacle lens after facet processing. In addition, the operator can determine whether or not the set machining area is appropriate.
なお、設定手段は、表示手段(例えば、モニタ5)に表示された加工領域を調整するための操作手段からの操作信号に基づいて、加工領域を設定する構成であってもよい。この場合、加工制御データ取得手段は、設定手段の設定に基づいて調整されたファセット加工制御データを取得してもよい。これによって、操作者は、眼鏡レンズに施すファセット加工をより好適な状態に修正したファセット加工制御データを取得することができる。 The setting means may be configured to set the machining area based on the operation signal from the operation means for adjusting the machining area displayed on the display means (for example, the monitor 5). In this case, the machining control data acquisition means may acquire faceted machining control data adjusted based on the settings of the setting means. As a result, the operator can acquire facet processing control data in which the facet processing applied to the spectacle lens is modified to a more suitable state.
例えば、本実施例においては、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置が眼鏡レンズを加工するための加工具を有していてもよい。すなわち、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置が、眼鏡レンズにファセット加工を施すための眼鏡レンズ加工装置を兼ねていてもよい。この場合、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置は、加工制御データ取得手段によって取得されたファセット加工制御データに基づいて加工具を制御し、眼鏡レンズにファセット加工を施すようにしてもよい。 For example, in this embodiment, the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device may have a processing tool for processing the spectacle lens. That is, the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device may also serve as a spectacle lens processing device for performing facet processing on the spectacle lens. In this case, the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device may control the processing tool based on the facet processing control data acquired by the processing control data acquisition means to perform facet processing on the spectacle lens.
また、例えば、本実施例においては、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置が備える加工制御データ取得手段により取得されたファセット加工制御データが、眼鏡レンズを加工するための加工具を有する眼鏡レンズ加工装置において用いられてもよい。この場合、眼鏡レンズ加工装置は、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置にて取得されたファセット加工制御データに基づいて、加工具を制御し、眼鏡レンズにファセット加工を施すようにしてもよい。 Further, for example, in the present embodiment, the facet processing control data acquired by the processing control data acquisition means included in the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device is used in the spectacle lens processing apparatus having a processing tool for processing the spectacle lens. It may be used. In this case, the spectacle lens processing device may control the processing tool based on the facet processing control data acquired by the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device to perform facet processing on the spectacle lens.
なお、本開示は、本実施形態に記載する装置に限定されない。例えば、下記実施形態の機能を行う端末制御ソフトウェア(プログラム)を、ネットワークまたは各種記憶媒体等を介してシステムあるいは装置に供給し、システムあるいは装置の制御装置(例えば、CPU等)がプログラムを読み出して実行することも可能である。 The present disclosure is not limited to the apparatus described in the present embodiment. For example, terminal control software (program) that performs the functions of the following embodiments is supplied to the system or device via a network or various storage media, and the control device (for example, CPU or the like) of the system or device reads the program. It is also possible to do it.
<実施例>
眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置1(以下、加工制御データ取得装置1)について、図面を参照して説明する。本実施例では、加工制御データ取得装置1の左右方向(水平方向)をX方向、上下方向(鉛直方向)をY方向、前後方向をZ方向として表す。
<Example>
The spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device 1 (hereinafter, processing control data acquisition device 1) will be described with reference to the drawings. In this embodiment, the left-right direction (horizontal direction) of the machining control
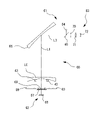
図1は加工制御データ取得装置1の外観図である。加工制御データ取得装置1は、ベース2、筐体3、窓4、モニタ5、レンズ加工機構部10(図2参照)、眼鏡枠形状測定ユニット20、ブロッカーユニット30、等を備える。ベース2には、レンズ加工機構部10、眼鏡枠形状測定ユニット20、ブロッカーユニット30、等が一体的に取り付けられる。窓4は開閉可能であり、レンズLEをレンズ加工機構部10に出し入れするために用いる。
FIG. 1 is an external view of the machining control
モニタ5は、加工制御データ取得装置1に搭載されている。なお、モニタ5は、加工制御データ取得装置1に接続されたモニタであってもよい。この場合には、パーソナルコンピュータのモニタを用いる構成としてもよい。モニタ5は、複数のモニタを併用する構成としてもよい。また、モニタ5は、タッチパネル機能をもつディスプレイである。すなわち、モニタ5が操作部(スイッチ部6)として機能する。なお、モニタ5はタッチパネル式でなくてもよく、モニタ5と操作部とを別に設ける構成であってもよい。この場合には、マウス、ジョイスティック、キーボード、携帯端末、等の少なくともいずれかを操作部として用いてもよい。モニタ5から入力された操作指示に応じた信号は、後述する制御部80に出力される。
The
<レンズ加工機構部>
図2はレンズ加工機構部10の概略図である。レンズ加工機構部10は、筐体3の内部に配置される。例えば、レンズ加工機構部10は、砥石群100、キャリッジ部200、面取りユニット300、レンズ面形状測定ユニット400、穴加工・溝掘りユニット500、等を備える。
<Lens processing mechanism>
FIG. 2 is a schematic view of the lens
<砥石群>
例えば、砥石群100は、プラスチック用の粗砥石100a、ヤゲン加工用及び平加工用の仕上げ砥石100b、鏡面仕上げ用砥石100c、等を備える。砥石群100は、砥石回転軸101に取り付けられている。砥石回転軸101は、モータ102により回転される。後述するレンズチャック軸202に挟持されたレンズLEの周縁は、モータ102の駆動により回転する砥石群100に圧接されることで加工される。
<Grinding stone group>
For example, the
<キャリッジ部>
例えば、キャリッジ部200は、キャリッジ201、レンズチャック軸202、移動支基203、モータ(モータ210及び220)、等を備える。キャリッジ201は、レンズチャック軸(レンズ回転軸)202を保持する。キャリッジ201は、左腕201Lと右腕201Rからなる。レンズチャック軸202は、レンズLEを保持する。レンズチャック軸202は、左チャック軸202L及び右チャック軸202Rからなる。
<Carriage part>
For example, the
キャリッジ201の左腕201Lには、左チャック軸202Lが回転可能かつ同軸に保持される。キャリッジ201の右腕201Rには、右チャック軸202Rが回転可能かつ同軸に保持される。左腕201Lにはモータ220が取り付けられており、モータ220を駆動させると、図示なきギヤ等の回転伝達機構が回転する。左右の左チャック軸202L及び202Rは、この回転伝達機構を介すことで、互いに同期して回転する。右腕201Rにはモータ210が取り付けられており、モータ210を駆動させると、右チャック軸202Rが左チャック軸202L側に移動する。これにより、レンズLEは左右の左チャック軸202L及び102Rに保持される。
The
キャリッジ201は、移動支基203上に搭載される。移動支基203は、レンズチャック軸202と、砥石回転軸101に平行なシャフト(シャフト208及び209)と、に沿ってキャリッジ201を移動させる。移動支基203の後部には、シャフト208と平行に延びる図示なきボールネジが取り付けられている。このボールネジは、モータ230の回転軸に取り付けられている。モータ230が駆動すると、キャリッジ201は移動支基203とともにX軸方向(すなわち、レンズチャック軸202の軸方向)に直線移動する。モータ230の回転軸には、キャリッジ201のX軸方向の移動を検出する図示なきエンコーダが設けられる。また、移動支基203には、Y軸方向(すなわち、左チャック軸202L及び202Rと、砥石回転軸101と、の軸間距離を変動する方向)に延びるシャフト205及び206が固定される。移動支基203にはモータ240が固定され、モータ240の駆動がY軸方向に延びるボールネジ207に伝達される。キャリッジ201は、ボールネジ207の回転によって、Y軸方向に移動する。モータ240の回転軸には、キャリッジ201のY軸方向の移動を検出する図示なきエンコーダが設けられる。
The
<面取りユニット>
図3は面取りユニット300の概略図である。面取りユニット300は、キャリッジ201の前方に設けられる。例えば、面取りユニット300は、支基ブロック301、固定板302、保持部材311、モータ(パルスモータ305及びモータ321)、ギヤ(ギヤ307、アイドラギヤ315、及び大ギヤ313)、アーム回転部材310、砥石回転軸330、砥石部340、等を備える。
<Chamfering unit>
FIG. 3 is a schematic view of the
ベース2には支基ブロック301が固定され、支基ブロック301には固定板302が固定される。固定板302には、保持部材311と、パルスモータ305と、がそれぞれ固定される。保持部材311は、アーム回転部材310を回転可能に保持する。パルスモータ305の回転軸にはギヤ307が取り付けられる。ギヤ307はアイドラギヤ315と噛み合い、アイドラギヤ315は大ギヤ313と噛み合う。大ギヤ313はアーム回転部材310に固定され、アーム回転部材310にはアーム320が固定される。パルスモータ305が駆動すると、ギヤ307の回転がアイドラギヤ315を介して大ギヤ313に伝達され、アーム回転部材310に固定されたアーム320が回転される。これによって、砥石部340が加工位置と退避位置とに移動される。
The
砥石回転用のモータ321は、大ギヤ313に固定され、大ギヤ313とともに回転する。モータ321の回転軸は軸323に連結される。軸323は、アーム回転部材310の内部で回転可能に保持されている。軸323の端には、プーリ324が取り付けられる。アーム320には保持部材331が固定される。保持部材331は砥石回転軸330を回転可能に保持する。砥石回転軸330の端にはプーリ332が取り付けられる。プーリ332とプーリ324は、ベルト335によって繋がれている。モータ321が駆動すると、軸323の回転がプーリ332、プーリ324、及びベルト335によって砥石回転軸330に伝達され、砥石回転軸330が回転する。
The motor 321 for rotating the grindstone is fixed to the
砥石回転軸330には、砥石部340が設けられる。砥石部340は、面取り砥石350と、鏡面面取り砥石360と、を備える。面取り砥石350は、レンズ前面用面取り砥石350aと、レンズ後面用面取り砥石350bと、を有する。鏡面面取り砥石360は、レンズ前面用鏡面面取り砥石360aと、レンズ後面用鏡面面取り砥石360bと、を有する。砥石部340の加工位置は、レンズチャック軸202と砥石回転軸101との間で、レンズチャック軸202の回転軸と、砥石回転軸101の回転軸と、が位置する平面上に、砥石回転軸330が配置される位置である。これによって、砥石群100によるレンズ周縁加工と同様、レンズLEをモータ230によりX軸方向へ移動させ、モータ240によりY軸方向へ移動させることができる。レンズチャック軸202と砥石回転軸330との軸間距離を変動させ、レンズ周縁に面取り加工を施すことができる。
The
なお、レンズLEのレンズ面(すなわち、レンズLEの前面あるいは後面の少なくともいずれか)に、少なくとも1つの平面を形成するファセット加工を施す場合は、加工具として面取り砥石350が使用される。鏡面加工時には、加工具として、さらに鏡面面取り砥石360が使用される。本実施例では、ファセット加工を施す加工具として砥石を用いる例を挙げたが、加工具としてエンドミルを用いてもよい。
When faceting is performed on the lens surface of the lens LE (that is, at least one of the front surface and the rear surface of the lens LE) to form at least one flat surface, a
<レンズ面形状測定ユニット>
図4はレンズ面形状測定ユニット400の概略図である。レンズ面形状測定ユニット400は、レンズLEの前面のコバ位置を測定する測定部400Fと、レンズLEの後面のコバ位置を測定する測定部400Rと、を有するが、図2では測定部400Fを図示する。なお、測定部400Rは測定部400Fと左右対称であるため、測定部400Fの各構成要素に付した符号末尾の「F」を「R」に付け替えて考えることができる。
<Lens surface shape measurement unit>
FIG. 4 is a schematic view of the lens surface shape measuring unit 400. The lens surface shape measuring unit 400 has a measuring
レンズ面形状測定ユニット400は、キャリッジ201の上方に設けられる。例えば、レンズ面形状測定ユニット400は、支基ブロック400a、取付支基401F、測定子アーム404F、ハンド405F、測定子406F、スライドベース410F、モータ416F、ギヤ(ギヤ415F及びアイドルギヤ414F)、等を備える。
The lens surface shape measuring unit 400 is provided above the
ベース2には支基ブロック400aが固定され、支基ブロック400aには取付支基401Fが固定される。取付支基401Fにはレール402Fが固定され、レール402F上にはスライダー403Fが摺動可能に取付けられる。スライダー403Fにはスライドベース410Fが固定され、スライドベース410Fには測定子アーム404Fが固定される。測定子アーム404Fの先端にはL型のハンド405Fが固定され、ハンド405Fの先端には測定子406Fが固定される。測定子406FはレンズLEの前面に接触される。
The support base block 400a is fixed to the
支基ブロック400aには、モータ416Fとエンコーダ413Fとが固定される。モータ416Fの回転軸はギヤ415Fと噛み合い、ギヤ415Fはアイドルギヤ414Fと噛み合う。アイドルギヤ414Fは、エンコーダ413Fのピニオン412Fと噛み合う。スライドベース410Fの下端にはラック411Fが固定され、ラック411Fはピニオン412Fと噛み合う。モータ416Fが駆動すると、モータ416Fの回転は、ギヤ415F、アイドルギヤ414F、及びピニオン412Fを介してラック411Fに伝達される。これにより、スライドベース410FはX軸方向に移動する。
The
なお、レンズ面形状の測定中は、モータ416Fが常に一定の力で測定子406FをレンズLEに押し当てる。エンコーダ413Fは、スライドベース410FのX軸方向の移動位置を検知する。スライドベース410FのX軸方向の移動位置、レンズチャック軸202の回転角度、レンズチャック軸202のY軸方向の移動位置、等の情報により、レンズLEの前面のコバ位置が測定される。
During the measurement of the lens surface shape, the
<穴加工・溝掘りユニット>
穴加工・溝掘りユニット500は、レンズLEに対して穴加工及び溝掘り加工の少なくともいずれかを施す際に用いる。穴加工・溝掘りユニット500には、レンズLEに穴加工を施す加工具としてのエンドミルと、レンズLEに溝掘りを施す加工具としての溝掘りカッターと、が備えられる。なお、穴加工・溝掘りユニットの詳細な構成については、例えば、特開2003-145328号公報を参照されたい。
<Hole processing / grooving unit>
The hole drilling /
<眼鏡枠形状測定ユニット>
眼鏡枠形状測定ユニット20は、フレームの形状をトレースする際に用いる。眼鏡枠形状測定ユニット20によって、フレームのリムの内形形状を取得することができる。すなわち、眼鏡枠形状測定ユニット20によって、眼鏡の玉型形状を取得することができる。なお、眼鏡枠形状測定ユニット20の詳細については、例えば、特開2014-52222号公報を参照されたい。
<Glasses frame shape measurement unit>
The spectacle frame
<ブロッカーユニット>
図5はブロッカーユニット30の概略図である。例えば、ブロッカーユニット30は、レンズ支持機構40と、カップ取付機構50と、レンズ測定機構60(図6参照)と、を備える。レンズ支持機構40には、レンズの前面を上方向にしてレンズを載置する。カップ取付機構50は、レンズLEの前面にカップCUを取り付ける際に用いる。すなわち、カップ取付機構50は、レンズLEの前面にカップCUを固定(軸打ち)する際に用いる。
<Blocker unit>
FIG. 5 is a schematic view of the
<レンズ支持機構>
例えば、レンズ支持機構40は、円筒ベース41、保護カバー42、支持ピン43、等を備える。円筒ベース41上には保護カバー42が設置される。円筒ベース41内には後述する指標板67等が配置されている。保護カバー42上には、カップ取り付けの基準軸(光軸)L1を中心に、3つの支持ピン43が等距離かつ等角度で配置される。支持ピン43は、レンズLEの後面(裏面)に当接することで、レンズLEを保持する。
<Lens support mechanism>
For example, the
<カップ取付機構>
例えば、カップ取付機構50は、移動支基51、支持アーム52、移動アーム53、シャフト54、カップ装着部55、等を備える。円筒ベース41には2本の支柱56が固定され、支柱56はその上端でブロック57を支える。支柱56には、移動アーム53が一体的に設けられた移動支基51が、上下方向に移動可能に取り付けられる。移動支基51の内部には、移動支基51を常時上方向に付勢するための図示なきバネが配置される。移動アーム53は、移動支基51の前方に延びるように、移動支基51に取り付けられる。移動アーム53にはシャフト54が取り付けられる。シャフト54の軸は、光軸L1に対して左右の直交方向に延びる軸L2と同軸である。移動アーム53は支持アーム52を保持し、支持アーム52はカップ装着部55を支持する。支持アーム52は、シャフト54(すなわち、軸L2)を中心として、カップ装着部55が前側(操作者側)を向く方向と、下側に向く方向と、に回転可能となっている。支持アーム52には、操作者が支持アーム52を回転させるためのレバー58が固定される。シャフト54には、カップ装着部55が下方向から前方向を向くように付勢力を与える図示なきコイルバネが設けられる。操作者がレバー58を操作していない状態では、カップ装着部55が常に前方向を向くようになっている。カップ装着部55には、レンズLEをレンズチャック軸202に挟持させるための治具であるカップCUが装着される。
<Cup mounting mechanism>
For example, the
<レンズ測定機構>
図6はレンズ測定機構60の概略構成図である。本実施例におけるレンズ測定機構60は、レンズの光学特性を取得するための測定光学系と、レンズの光学特性とは異なる情報(例えば、レンズの外形形状、レンズに付された印点、レンズに形成された隠しマーク、等)を取得するための測定光学系と、を兼ねている。なお、レンズの光学特性を取得するための測定光学系と、レンズの光学特性とは異なるレンズの情報を取得するための測定光学系と、はそれぞれが別に設けられた構成でもよい。
<Lens measurement mechanism>
FIG. 6 is a schematic configuration diagram of the
例えば、レンズ測定機構60は、照明光学系61、受光光学系62、撮像光学系63、等を備える。例えば、照明光学系61は、光源64、ハーフミラー65、凹面ミラー66、等を備える。光源64は測定光束をレンズに照射する。例えば、光源64はLED(Light Emitting Diode)であってもよい。光源64から出射された測定光束は、光軸L3上に配置されたハーフミラー65に反射されて、光軸L3に一致する。例えば、凹面ミラー66は、測定光束を光軸L1から光軸L3の方向へと反射するとともに、測定光束を光軸L1上に配置されたレンズLEよりも大きな径の平行光束(略平行光束)に整形する。
For example, the
例えば、受光光学系62は、指標板67、撮像素子68、等を備える。例えば、指標板67は、レンズLEの光学中心等を検出するために用いる。指標板67には、多数の開口(光束の通過口)が所定のパターンにて形成される。本実施例では、所定のパターン以外の領域に、再帰性反射部材69を貼り付けることによって、所定のパターン以外が形成される。撮像素子68は、光源64から照射されて、レンズLE及び指標板67を通過した測定光束を撮像する。例えば、撮像素子68は、CCD(Charge Coupled Device)、CMOS(Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor)、等であってもよい。なお、本実施例における受光光学系62は、指標板67と撮像素子68との間にレンズが配置された構成であってもよい。
For example, the light receiving
例えば、撮像光学系63は、凹面ミラー66、絞り70、撮像レンズ71、撮像素子72、等を備える。撮像光学系63の撮像倍率は、撮像素子72によってレンズLEの全体が撮像される倍率となっている。撮像光学系63における凹面ミラー66は、照明光学系61における凹面ミラー66と共用される。絞り70は凹面ミラー66の焦点位置(略焦点位置)に配置される。絞り70は、光源64と共役(略共役)な位置関係である。撮像素子72は、光源64から照射され、再帰性反射部材69により反射された反射光束を撮像する。例えば、撮像素子72は、CCD、CMOS、等であってもよい。撮像素子72のピント位置は、撮像レンズ71及び凹面ミラー66によって、レンズLEの表面付近に合わされている。これにより、レンズの表面に付された印点、レンズに形成された隠しマーク、等をほぼ焦点の合った状態で撮像することができる。
For example, the image pickup
<制御部>
図7は加工制御データ取得装置1の制御系を示す図である。例えば、制御部80には、モニタ5、スイッチ部6、光源64、各エンコーダ、各モータ(モータ102、210、110、230、240、305、321、416F、等)、各撮像素子(撮像素子68、撮像素子72、等)不揮発性メモリ85(以下、メモリ85)、等が電気的に接続されている。メモリ85は、電源の供給が遮断されても記憶内容を保持できる非一過性の記憶媒体であってもよい。例えば、メモリ85としては、ハードディスクドライブ、フラッシュROM、着脱可能なUSBメモリ、等を使用することができる。メモリ85は、眼鏡の玉型形状(第1形状情報)、デモレンズDLのファセット形状情報(第2形状情報)、レンズLEのカーブ情報(第3形状情報)、制御部80が取得した加工制御データ、等を記憶してもよい。
<Control unit>
FIG. 7 is a diagram showing a control system of the machining control
例えば、制御部80は、一般的なCPU(プロセッサ)、RAM、ROM、等で実現される。例えば、CPUは、加工制御データ取得装置1における各部の駆動を制御する。例えば、RAMは、各種の情報を一時的に記憶する。例えば、ROMには、CPUが実行する各種プログラムが記憶されている。なお、制御部80は、複数の制御部(つまり、複数のプロセッサ)によって構成されてもよい。
For example, the
<制御動作>
以下、加工制御データ取得装置1を用いて加工制御データを取得する手順を、図8に示すフローチャートを用いて、加工制御データ取得装置1の制御動作とともに説明する。なお、本実施例では、デモレンズDLの前面にファセット加工が施されており、レンズLEの前面に少なくとも1つの平面を形成するためのファセット加工制御データを取得する場合を例に挙げる。
<Control operation>
Hereinafter, a procedure for acquiring machining control data using the machining control
<第1形状情報の取得(S1)>
まず、制御部80は眼鏡の玉型形状情報を取得する。眼鏡の玉型形状情報は、フレームのリムの内形形状であってもよいし、デモレンズ(または型板)の外形形状であってもよい。例えば、本実施例では、制御部80が、ブロッカーユニット30を用いてデモレンズの全体像を撮影し、デモレンズの外形形状を測定することで、眼鏡の玉型形状情報を取得する場合を例示する。もちろん、制御部80は、別の装置を用いて測定した玉型形状情報を読み込むことで取得してもよい。
<Acquisition of first shape information (S1)>
First, the
操作者は、デモレンズDLを支持ピン43上に載置し、モニタ5に表示されたスイッチ部6から、デモレンズDLの外形形状の測定を開始するための開始ボタンを選択する。制御部80は、開始ボタンからの入力信号に応じて光源64を点灯させ、デモレンズDLに向けて測定光束を照射させる。再帰性反射部材69に反射され、デモレンズDLを後面から照明する測定光束が、撮像素子72により受光される。これによって、デモレンズDLの全体像(デモレンズ像)が撮影される。なお、制御部80は、外形形状や後述するファセットライン等を検出しやすいデモレンズ像を得るため、光源64の光量を増減させた複数のデモレンズ像を撮影するようにしてもよい。
The operator places the demo lens DL on the
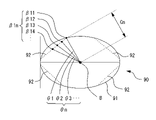
制御部80は、デモレンズ像を画像処理することで、デモレンズDLの外形形状、外形の位置座標、ボクシング中心位置B、等を取得する。例えば、デモレンズDLの外形形状は、デモレンズDLを支持ピン43上に載置していない状態の像(基準像)と、デモレンズ像と、の差分を検出することにより取得される。図9は基準像とデモレンズ像の差分を検出した差分像90である。基準像とデモレンズ像は、どちらも撮像素子72が受光した受光像である。このため、基準像とデモレンズ像の画素数は同一であり、基準像の各画素位置はデモレンズ像の各画素位置に対応する。すなわち、基準像とデモレンズ像はpixel to pixelの関係である。制御部80は、基準像とデモレンズ像の各画素位置から輝度値を検出し、各画素位置について基準像の輝度値からデモレンズ像の輝度値を減算することで、差分像90を得ることができる。制御部80は、差分像90に現れたエッジのうち、エッジに囲まれた図形の面積を最大とするエッジ(図8にて実線で示すエッジ)を検出する。また、制御部80は、このエッジをデモレンズの外形形状91としてメモリ85に記憶する。
The
ボクシング中心位置Bは、外形形状91を囲む四角形において、対向する各辺の中点を結んだ直線の交点として算出される。外形の位置座標は、ボクシング中心位置Bを基準とした2次元座標で表される。例えば、ボクシング中心位置Bから所定の角度毎(例えば、0.36度毎)に、外形形状91上の点の位置座標が求められてもよい。
The boxing center position B is calculated as the intersection of straight lines connecting the midpoints of the opposing sides in the quadrangle surrounding the
<第2形状情報の取得(S2)>
続いて、制御部80は、デモレンズDLに施されたファセット形状情報を取得する。ファセット形状情報は、ファセット加工により形成された切子面の形状(言い換えると、ファセット加工により形成された小面の形状)、ファセット加工の加工ライン(すなわち、ファセット加工により形成されたエッジライン)、ファセット加工の加工幅、等であってもよい。本実施例では、デモレンズDLの前面に施されたファセット加工の加工ラインを取得する場合を例示する。
<Acquisition of second shape information (S2)>
Subsequently, the
例えば、制御部80は、撮像素子72が撮像したデモレンズ像から、ファセット形状情報として、ファセット加工の加工ライン92(以下、ファセットライン92)を検出する。言い換えると、制御部80は、ファセット形状情報として、デモレンズDLのレンズ面に形成されたエッジを検出する。本実施例では、デモレンズ像に基づいて取得された差分像90から、ファセットライン92が検出される。制御部80は、差分像90に現れたエッジのうち、デモレンズDLの外形形状91に接するエッジ(図8にて点線で示すエッジ)を検出する。また、制御部80は、このようなエッジをデモレンズDLのファセットライン92として記憶する。なお、ファセットライン92の検出精度を向上させるため、差分像90からファセットライン92を検出する範囲を予め設定しておいてもよい。この場合、差分像90において、デモレンズDLの外形形状91から5mm内側に対応する画素領域の範囲、等がファセットライン92を検出する範囲として設定されてもよい。
For example, the
例えば、本実施例において、制御部80は、検出されたデモレンズDLのファセットライン92から、ボクシング中心位置Bを中心とした所定の角度毎に(すなわち、動径角θ1、θ2、θ3、・・・、θn毎に)、ファセットライン上の点β11、β12、β13、β14、・・・β1nの位置座標を求める。また、制御部80は、ボクシング中心位置Bと、ファセットライン92上の各点β1nと、を結ぶ線分Cnの長さを求める。
For example, in the present embodiment, the
<第3形状情報の取得(S3)>
続いて、制御部80は、レンズLEのレンズ面におけるカーブ情報を取得する。制御部80は、レンズ前面及び後面の少なくともいずれかにおけるカーブ情報を取得してもよい。また、制御部80は、前述のカーブ情報に加えて、レンズのコバ情報を取得してもよい。例えば、本実施例では、デモレンズDLの前面にファセット加工が施された場合を例示しているため、制御部80によって、レンズLEの前面におけるカーブ情報が取得される。もちろん、制御部80は、レンズLEの前面におけるカーブ情報とともに、レンズLEの後面におけるカーブ情報を取得してもよい。
<Acquisition of third shape information (S3)>
Subsequently, the
例えば、制御部80は、レンズ面形状測定ユニット400を用いてレンズLEの前面を測定することで、そのカーブ情報を取得する。もちろん、制御部80は、別の装置を用いて測定したカーブ情報を読み込むことで取得してもよい。また、制御部80は、操作者がカーブスケール等で予めカーブ情報を測定し、操作者が入力したカーブ情報を取得してもよい。
For example, the
操作者は、ブロッカーユニット30を使用して、レンズLEの表面に加工治具であるカップCUを取り付ける。カップCUの取付位置は、レンズLEの光学中心位置A、ボクシング中心位置B(すなわち、幾何学中心位置B)、等の少なくともいずれかであってもよい。もちろん、カップCUの取付位置は、レンズLEの光学中心位置Aやボクシング中心位置Bとは異なる位置であってもよい。続いて、操作者は、レンズLEの表面に取り付けたカップCUを、レンズチャック軸202が備える図示なきカップホルダに装着する。制御部80は、キャリッジ部200を駆動して右チャック軸202Rを移動させ、レンズLEをレンズチャック軸202に所定の状態で保持させる。
The operator uses the
制御部80は、レンズ面形状測定ユニット400が備える測定子406Fが、レンズLEの前面の2点の測定位置に接触するように、レンズチャック軸202の相対的な移動を制御する。例えば、レンズLEの前面の2点の測定位置は、レンズチャック軸202の軸(すなわち、レンズLEの光学中心位置A、等)を中心とした少なくとも1つの経線方向における2点の測定位置であってもよい。より詳細には、レンズチャック軸202の軸から最も動径長が長い方向上で、眼鏡の玉型形状(本実施例では、デモレンズDLの外形形状)から2mm内側の位置と、3mm内側の位置と、が測定位置に設定されてもよい。これによって、レンズLEの前面における2点のX方向の位置が取得される。制御部80は、2点の測定位置におけるX方向の位置、レンズチャック軸202の軸から2点の測定位置までの距離、及び、レンズLEの前面におけるレンズチャック軸202のX方向の位置(これは、X方向の測定基準として既知である)、に基づいて、レンズLEの前面のカーブ情報を取得する。
The
例えば、制御部80は、レンズLEのカーブ情報を用いて、レンズLEの前面が、光学中心位置Aからどの程度の傾斜角度をもってカーブしているかを推測する。すなわち、制御部80は、レンズLEの前面のカーブ形状を推測する。
For example, the
<加工領域の設定(S4)>
続いて、制御部80は、レンズLEに施すファセット加工の加工領域を設定する。例えば、ファセット加工の加工領域は、デモレンズDLの外形形状91(すなわち、眼鏡の玉型形状)と、デモレンズDLから検出されたファセットライン92(すなわち、ファセット形状情報)と、に基づいて設定されてもよい。本実施例のように、レンズLEのカーブ情報を取得している場合、制御部80は、以下で説明するように、デモレンズDLの外形形状91と、ファセットライン92と、レンズLEのカーブ情報と、に基づいた加工領域を設定してもよい。
<Setting of machining area (S4)>
Subsequently, the
制御部80は、デモレンズDLの外形形状91、デモレンズDLのファセットライン92、及びレンズLEのカーブ情報を取得すると、レンズLEに施すファセット加工の加工領域を、レンズLEの動径角毎に設定する。例えば、本実施例では、ファセットライン92上の点β1n(言い換えると、ファセット加工の前側の加工軌跡92上の点β1n)と、レンズ前面用面取り砥石350aの砥石面の傾斜角度と、に基づくファセット加工の後側の加工軌跡93上の点α2n(図10参照)を動径角θn毎に算出することで、ファセット加工の加工領域が設定される。
When the
図10はファセット加工の後側の加工軌跡93上の点α2nの算出を説明する図である。図10(a)はデモレンズDLの側面をある動径角方向から示す図である。図10(b)はレンズLEの側面をある動径角方向から示す図である。図10(c)はファセット加工を施した状態のレンズLEを示す図である。例えば、ステップS1及びステップS2にて取得したデモレンズDLの外形形状91とファセットライン92を用いて、ファセットライン92上の各点β1nと、ボクシング中心位置Bからファセットライン92上の各点β1nまでを結ぶ線分Cnの長さと、が動径角毎に求められる。デモレンズDLの外形形状91とファセットライン92は2次元形状であるため、これらの点の位置は2次元座標(YZ座標)で表される。しかし、加工を施したいレンズLEはカーブしているため、デモレンズDLにおけるファセットライン92上の各点β1nは、必ずしもレンズLEの前面に位置しない。
FIG. 10 is a diagram illustrating the calculation of the point α2n on the
そこで、制御部80は、ファセットライン92上の点β1nに対応するレンズLE上の点β2nの位置座標を求める。例えば、制御部80は、点β1nをX方向に平行移動させ、レンズLEの前面に接した点β2nの位置を、レンズLEの前面のカーブ形状を用いることで算出する。また、例えば、制御部80は、光学中心位置Aと点β2nを結ぶ辺g1の長さを直線近似により求め、辺g1及び線分Cnを用いた三角関数から、点β1nをX方向に平行移動させた距離である辺g2の長さを算出する。これによって、ファセットライン92上の点β1nにおける位置座標に対して、X方向の座標の変化量が求められ、レンズLE上の点β2nの3次元座標(XYZ座標)が算出される。
Therefore, the
続いて、制御部80は、レンズLE上の点β2nからレンズLEのコバ面に向けて、レンズ前面用面取り砥石350aの砥石面の傾斜角度γで直線を延ばし、この直線がレンズLEのコバ面に接する位置である点α2nの位置座標(xn,yn,zn)(n=1、2、3、・・・、N)を求める。例えば、このような演算処理によって、ファセット加工の後側の加工軌跡93上の点α2nが、動径角毎に求められる。なお、本実施例において、点α2nは3次元の直交座標で表されている。点α2nは、X方向及びY方向の位置を動径角θn及び動径長rnによって2次元の極座標で表すとともに、Z方向の位置をZ座標で表した(rn,zn,θn)(n=1,2,3、・・・、N)に適宜変換して表されてもよい。
Subsequently, the
なお、制御部80によって設定されたファセット加工の加工領域は、操作者が手動で調整することもできる。この場合、制御部80は、デモレンズDLの外形形状91、デモレンズDLのファセットライン92、レンズLEのカーブ情報、等に基づく加工領域をモニタ5に表示する。また、制御部80は、モニタ5上に表示された加工領域を調整するためのスイッチ部6からの操作信号に基づいて、加工領域を設定する。図11はモニタ5の表示画面の一例である。例えば、モニタ5には、レンズLEの断面形状95、外形形状91、ファセットライン92、カーソル96、入力欄97、等が表示される。レンズLEの断面形状95は、外形形状91との対応関係を把握しやすいように、外形形状91と同一のサイズで表示されてもよい。レンズLEの断面形状95は、レンズLEのコバ情報(例えば、レンズLEの前面及び後面のコバ位置、レンズLEのコバ厚、等)と、外形形状91と、に基づいて表示されてもよい。
The facet machining area set by the
例えば、操作者は、カーソル96を操作してレンズLEのコバ面の観察方向を指定し、断面形状95を表示させる。また、例えば、操作者は、外形形状91上の点P1及びP2の2点を指定することで、これらの点を結ぶファセットライン92を設定してもよい。また、例えば、操作者は、入力欄97からファセット加工の加工幅W等を入力してもよい。これによって、レンズLEに施すファセット加工の加工領域を、より最適な状態に修正することができる。
For example, the operator operates the
<加工制御データの取得(S5)>
制御部80は、ファセット加工の加工領域を設定すると、レンズLEのレンズ面(本実施例では、レンズLEの前面)に少なくとも1つの平面を形成するためのファセット加工制御データを取得する。例えば、本実施例では、ステップS4にて設定されたファセット加工の加工領域に基づいて、ファセット加工制御データが取得される。
<Acquisition of machining control data (S5)>
When the facet processing region is set, the
制御部80は、デモレンズDLの外形形状91、デモレンズDLのファセットライン92、及びレンズLEのカーブ情報、を用いて設定されたファセット加工の加工領域に基づいて、キャリッジ部200におけるレンズチャック軸202の回転、レンズチャック軸202の移動、等を制御するファセット加工制御データを演算する。例えば、制御部80は、レンズLEにおけるファセット加工の後側の加工軌跡93を用いて、各点β2nの位置座標(rn,zn,θn)(n=1,2,3、・・・、N)を、キャリッジ201のX軸及びY軸の移動量に変換することで、ファセット加工制御データを取得してもよい。
The
<ファセット加工の実施(S6)>
操作者がモニタ5に表示されたスイッチ部6から、レンズLEの加工を開始するための開始ボタンを選択すると、制御部80はレンズLEの周縁及びレンズ面の加工を実施する。制御部80は、キャリッジ201を移動させ、デモレンズDLの外形形状91に基づいて、レンズチャック軸202に挟持されたレンズLEの周縁を加工する。例えば、制御部80は、レンズLEの周縁を粗砥石100aで粗加工した後、仕上げ砥石100bで平仕上げ加工する。次に、制御部80は、面取りユニット300の砥石回転軸330を加工位置に配置し、ファセット加工制御データに基づいて、レンズLEのレンズ面を加工する。例えば、制御部80は、レンズチャック軸202のX軸方向及びY軸方向の移動を制御し、レンズLEの前面をレンズ前面用面取り砥石350aに接触させることで、レンズLEの前面をファセット加工する。これによって、ファセット加工が好適に施されたレンズLEを得ることができる。
<Implementation of facet processing (S6)>
When the operator selects the start button for starting the processing of the lens LE from the
以上説明したように、例えば、本実施例における眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置は、眼鏡の玉型形状情報と、眼鏡用のデモレンズから検出されたファセット形状情報であって、デモレンズに施されたファセット形状情報と、を取得し、玉型形状情報及びファセット形状情報に基づいて、眼鏡レンズのレンズ面に少なくとも1つの平面を形成するためのファセット加工制御データを取得する。操作者は、ファセット加工を自動的に設定できるとともに、このようなファセット加工制御データを利用することで、眼鏡レンズに好適なファセット加工を施すことができる。 As described above, for example, the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device in the present embodiment is the spectacle lens shape information and the facet shape information detected from the spectacle demo lens, and is the facet applied to the spectacle lens. The shape information and the facet processing control data for forming at least one plane on the lens surface of the spectacle lens are acquired based on the shape information and the facet shape information. The operator can automatically set the facet processing, and by using such facet processing control data, it is possible to perform the facet processing suitable for the spectacle lens.
また、例えば、本実施例における眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置は、眼鏡レンズのレンズ面におけるカーブ情報を取得し、玉型形状情報と、ファセット形状情報と、カーブ情報と、に基づいて、ファセット加工制御データを取得する。眼鏡レンズのカーブ情報と、デモレンズのカーブ情報と、は必ずしも一致しないため、眼鏡レンズのカーブ情報を考慮したファセット加工制御データを取得してこれを用いることで、より精度よくファセット加工を実施することができる。 Further, for example, the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device in the present embodiment acquires curve information on the lens surface of the spectacle lens, and facet processing is performed based on the lens shape information, the facet shape information, and the curve information. Get control data. Since the curve information of the spectacle lens and the curve information of the demo lens do not always match, the facet processing can be performed more accurately by acquiring the facet processing control data considering the curve information of the spectacle lens and using this. Can be done.
また、例えば、本実施例における眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置は、デモレンズのレンズ面を撮像する撮像光学系を備え、撮像光学系により撮像されたデモレンズのレンズ像からファセット形状情報を検出する。これによって、操作者は、眼鏡レンズに施されたファセット形状情報を容易に取得することができる。なお、このような撮像光学系を、眼鏡の玉型形状情報の取得と、ファセット形状情報の取得と、の双方に用いることで、これらの情報を取得する際の操作をより簡単にすることもできる。 Further, for example, the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device in the present embodiment includes an image pickup optical system that images the lens surface of the demo lens, and detects facet shape information from the lens image of the demo lens imaged by the image pickup optical system. As a result, the operator can easily acquire the facet shape information applied to the spectacle lens. By using such an imaging optical system for both acquisition of eyeglass shape information and facet shape information, it is possible to simplify the operation for acquiring such information. can.
また、例えば、本実施例における眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置は、眼鏡レンズに施すファセット加工の加工領域を設定し、設定された加工領域に基づくファセット加工制御データを取得する。操作者は、設定された加工領域を確認することで、眼鏡レンズのファセット加工後の形状を想像しやすくなる。また、操作者は、設定された加工領域が適切かどうかを判断することができる。 Further, for example, the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device in the present embodiment sets a processing area for facet processing applied to the spectacle lens, and acquires facet processing control data based on the set processing area. By checking the set processing area, the operator can easily imagine the shape of the spectacle lens after facet processing. In addition, the operator can determine whether or not the set machining area is appropriate.
また、例えば、本実施例における眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置は、眼鏡レンズに施すファセット加工の加工領域を表示部に表示し、表示部に表示された加工領域を調整するための操作部からの操作信号に基づいて、加工領域を設定するとともに、このような設定に基づいて調整されたファセット加工制御データを取得する。これによって、操作者は、眼鏡レンズに施すファセット加工をより好適な状態に修正したファセット加工制御データを取得することができる。 Further, for example, in the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device in the present embodiment, the processing area of the facet processing applied to the spectacle lens is displayed on the display unit, and the processing area displayed on the display unit is adjusted from the operation unit. The machining area is set based on the operation signal, and the facet machining control data adjusted based on such a setting is acquired. As a result, the operator can acquire facet processing control data in which the facet processing applied to the spectacle lens is modified to a more suitable state.
<変容例>
なお、本実施例では、眼鏡の玉型形状情報として、デモレンズDLの外形形状を取得する構成を例に挙げて説明したがこれに限定されない。例えば、眼鏡の玉型形状情報として、フレームの内形形状が取得されてもよい。例えば、フレームのリムがレンズLEに形成した溝に嵌め込む凸部を有する場合には、フレームの内形形状としてリムの凸部の内形形状を取得してもよい。また、例えば、フレームのリムがレンズLEに形成したヤゲンを嵌め込む凹部を有する場合には、フレームの内形形状としてリムの凹部の内形形状を取得してもよい。なお、このようなフレームの内形形状は、眼鏡枠形状測定ユニット20が備える測定子をフレームに接触させる等の接触式の構成によって取得されてもよい。もちろん、このようなフレームの内形形状は、測定光束を投光する投光光学系と、測定光束が反射された反射光束を受光する受光光学系と、を備える非接触式の構成によって取得されてもよい。
<Example of transformation>
In this embodiment, the configuration for acquiring the outer shape of the demo lens DL as the eyeglass shape information has been described as an example, but the present invention is not limited to this. For example, the internal shape of the frame may be acquired as the ball shape information of the spectacles. For example, when the rim of the frame has a convex portion to be fitted into the groove formed in the lens LE, the internal shape of the convex portion of the rim may be acquired as the internal shape of the frame. Further, for example, when the rim of the frame has a recess for fitting the bevel formed in the lens LE, the internal shape of the concave portion of the rim may be acquired as the internal shape of the frame. The internal shape of such a frame may be acquired by a contact-type configuration such as bringing a stylus included in the spectacle frame
また、本実施例では、ブロッカーユニット30(すなわち、非接触式の構成)を用いてデモレンズDLの外形形状91を取得する構成を例に挙げて説明したがこれに限定されない。もちろん、デモレンズDLの外形形状91は、眼鏡枠形状測定ユニット20が備える測定子をフレームに接触させる等の接触式の構成によって取得されてもよい。例えば、この場合、デモレンズDLの周縁に測定子を接触させた状態で、デモレンズDLの周縁に沿って測定子を移動させ、その移動位置からデモレンズDLの外形形状を取得してもよい。
Further, in this embodiment, a configuration in which the
なお、本実施例では、デモレンズDLを撮像したデモレンズ像を画像処理することで、ファセット形状情報を検出する構成を例に挙げて説明したがこれに限定されない。例えば、ファセット形状情報は、デモレンズDLに多方向から測定光束を照射し、その反射光束を受光した受光面の位置や、反射光束を受光した時間、等の情報に基づいて検出されてもよい。 In this embodiment, a configuration in which facet shape information is detected by image processing a demo lens image obtained by capturing a demo lens DL has been described as an example, but the present invention is not limited to this. For example, the facet shape information may be detected based on information such as the position of the light receiving surface where the measured luminous flux is applied to the demo lens DL from multiple directions and the reflected luminous flux is received, the time when the reflected luminous flux is received, and the like.
なお、本実施例では、加工領域を設定するための表示画面をモニタ5に表示し、表示画面上のファセットライン92等を変更することで、ファセット加工の加工領域を設定する構成を例に挙げて説明したがこれに限定されない。例えば、ブロッカーユニット30により撮像されているデモレンズ像がモニタ5に表示されるとともに、ステップS1及びステップS2で取得されたデモレンズDLの外形形状91やファセットライン92が、デモレンズ像上に重ね合せて表示されてもよい。これによって、デモレンズ像に写るファセットライン92をトレースし、ファセット加工の加工領域を設定することができる。なお、デモレンズDLのファセットライン92に限らず、デモレンズDLの外形形状91をトレースしてもよい。デモレンズDLに穴加工が施されている場合には、穴の位置をトレースしてもよい。
In this embodiment, a configuration in which a display screen for setting a machining area is displayed on the
なお、本実施例では、レンズLEのカーブ情報を取得する構成を例に挙げて説明したがこれに限定されない。前述のように、レンズLEのカーブ情報に加えて、レンズLEのコバ情報が含まれていてもよい。コバ情報は、コバ厚やコバ位置であってもよい。この場合、制御部80は、コバ情報を用いて、ファセット加工を施すことができるか否かを判定してもよい。例えば、レンズLEのカーブ形状によっては、ファセット加工の後側の加工軌跡93上の点α2nがコバ面上に位置しないことがある。この状態でファセット加工制御データを作成し、レンズLEを加工すると、ファセット加工によってコバ面が削れ、玉型形状が小さくなってしまう。そこで、制御部80はレンズLEのコバ情報を利用し、点α2nがコバ面上から外れてしまう場合に、ファセット加工を施すことができないと判定してもよい。なお、制御部80は、このような判定結果を得たときに、デモレンズDLの外形形状91とファセットライン92とが接する2点の位置を自動的に変更し、ファセット加工制御データを再度作成してもよい。
In this embodiment, the configuration for acquiring the curve information of the lens LE has been described as an example, but the present invention is not limited to this. As described above, in addition to the curve information of the lens LE, the edge information of the lens LE may be included. The edge information may be the edge thickness or the edge position. In this case, the
なお、本実施例では、眼鏡の玉型形状情報、デモレンズDLのファセット形状情報、及びレンズLEのカーブ情報に基づいてファセット加工の加工領域を設定し、この加工領域に基づいてファセット加工制御データを取得する構成を例に挙げて説明したがこれに限定されない。例えば、眼鏡の玉型形状情報、デモレンズDLのファセット形状情報、及びレンズLEのカーブ情報に基づいて、ファセット加工制御データを直接取得する構成としてもよい。 In this embodiment, the facet processing processing area is set based on the eyeglass shape information, the facet shape information of the demo lens DL, and the curve information of the lens LE, and the facet processing control data is generated based on this processing area. The configuration to be acquired has been described as an example, but the present invention is not limited to this. For example, the facet processing control data may be directly acquired based on the eyeglass shape information, the facet shape information of the demo lens DL, and the curve information of the lens LE.
なお、本実施例では、レンズLEのカーブ情報とともに、デモレンズDLのカーブ情報を取得する構成であってもよい。この場合には、ファセット加工の加工領域が、デモレンズDLのカーブ情報を考慮して設定されてもよい。また、この場合には、ファセット加工制御データが、デモレンズDLのカーブ情報を考慮して作成されてもよい。 In this embodiment, the curve information of the demo lens DL may be acquired together with the curve information of the lens LE. In this case, the facet processing area may be set in consideration of the curve information of the demo lens DL. Further, in this case, facet processing control data may be created in consideration of the curve information of the demo lens DL.
なお、本実施例では、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置1がレンズLEの周縁及びレンズ面を加工するためのレンズ加工機構部10を備え、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置1によって、レンズLEにファセット加工が施される構成を例に挙げて説明したがこれに限定されない。例えば、眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置1にて取得された加工制御データが別装置に転送され、別装置にてファセット加工が実施されてもよい。
In this embodiment, the spectacle lens processing control
1 眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置
10 レンズ加工機構部
20 眼鏡枠形状測定ユニット
30 ブロッカーユニット
40 レンズ支持機構
50 カップ取付機構
60 レンズ測定機構
80 制御部
85 メモリ
100 砥石群
200 キャリッジ部
300 面取りユニット
400 レンズ面形状測定ユニット
1 Eyeglass lens processing control
Claims (7)
眼鏡の玉型形状情報を取得する第1形状情報取得手段と、
前記眼鏡用のデモレンズから検出されたファセット形状情報であって、前記デモレンズに施されたファセット形状情報を取得する第2形状情報取得手段と、
前記玉型形状情報及び前記ファセット形状情報に基づいて、前記眼鏡レンズのレンズ面に、少なくとも1つの平面を形成するためのファセット加工制御データを取得する加工制御データ取得手段と、
を備えることを特徴とする眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置。 It is a spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device that acquires processing control data for processing spectacle lenses.
The first shape information acquisition means for acquiring the eyeglass shape information and
Second shape information acquisition means for acquiring facet shape information applied to the demo lens, which is facet shape information detected from the demo lens for eyeglasses.
A processing control data acquisition means for acquiring facet processing control data for forming at least one plane on the lens surface of the spectacle lens based on the lens shape information and the facet shape information.
A spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device characterized by being equipped with.
前記眼鏡レンズの前記レンズ面におけるカーブ情報を取得する第3形状情報取得手段を備え、
前記加工制御データ取得手段は、前記玉型形状情報と、前記ファセット形状情報と、前記カーブ情報と、に基づいて、前記ファセット加工制御データを取得することを特徴とする眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置。 In the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device of claim 1,
A third shape information acquisition means for acquiring curve information on the lens surface of the spectacle lens is provided.
The processing control data acquisition unit is a spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device characterized by acquiring the facet processing control data based on the lens shape information, the facet shape information, and the curve information. ..
前記第2形状情報取得手段は、前記デモレンズの前面に施されたファセット形状情報を取得し、
前記第3形状情報取得手段は、前記眼鏡レンズの前面における前記カーブ情報を取得し、
前記加工制御データ取得手段は、前記眼鏡レンズの前面に、少なくとも1つの平面を形成するための前記ファセット加工制御データを取得することを特徴とする眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置。 In the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device of claim 2,
The second shape information acquisition means acquires facet shape information provided on the front surface of the demo lens, and obtains the facet shape information.
The third shape information acquisition means acquires the curve information on the front surface of the spectacle lens, and obtains the curve information.
The processing control data acquisition unit is a spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device, which acquires the facet processing control data for forming at least one plane on the front surface of the spectacle lens.
前記デモレンズのレンズ面を撮像する撮像光学系を備え、
前記第2形状情報取得手段は、前記撮像光学系により撮像された前記デモレンズのレンズ像から、前記ファセット形状情報を検出することで、前記ファセット形状情報を取得することを特徴とする眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置。 In the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device according to any one of claims 1 to 3.
It is equipped with an imaging optical system that captures the lens surface of the demo lens.
The second shape information acquisition means obtains the facet shape information by detecting the facet shape information from the lens image of the demo lens imaged by the image pickup optical system. Data acquisition device.
前記眼鏡レンズに施すファセット加工の加工領域を設定する設定手段を備え、
前記加工制御データ取得手段は、設定された前記加工領域に基づく前記ファセット加工制御データを取得することを特徴とする眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置。 In the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device according to any one of claims 1 to 4.
A setting means for setting a processing area for facet processing applied to the spectacle lens is provided.
The processing control data acquisition means is a spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device characterized by acquiring the facet processing control data based on the set processing area.
請求項1~5のいずれかの眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置にて取得された前記ファセット加工制御データに基づいて、前記加工具を制御し、前記眼鏡レンズにファセット加工を施すことを特徴とする眼鏡レンズ加工装置。It is characterized in that the processing tool is controlled based on the facet processing control data acquired by the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device according to any one of claims 1 to 5, and the spectacle lens is subjected to facet processing. Eyeglass lens processing equipment.
眼鏡の玉型形状情報を取得する第1形状情報取得ステップと、The first shape information acquisition step to acquire the eyeglass shape information and
前記眼鏡用のデモレンズから検出されたファセット形状情報であって、前記デモレンズに施されたファセット形状情報を取得する第2形状情報取得ステップと、The second shape information acquisition step of acquiring the facet shape information applied to the demo lens, which is the facet shape information detected from the demo lens for eyeglasses,
前記玉型形状情報及び前記ファセット形状情報に基づいて、前記眼鏡レンズのレンズ面に、少なくとも1つの平面を形成するためのファセット加工制御データを取得する加工制御データ取得ステップと、A processing control data acquisition step for acquiring facet processing control data for forming at least one plane on the lens surface of the spectacle lens based on the lens shape information and the facet shape information.
を前記眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得装置に実行させることを特徴とする眼鏡レンズ加工制御データ取得プログラム。A spectacle lens processing control data acquisition program, characterized in that the spectacle lens processing control data acquisition device is executed.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018104224A JP7052567B2 (en) | 2018-05-31 | 2018-05-31 | Eyeglass lens processing control data acquisition device |
| EP19176890.2A EP3575033B1 (en) | 2018-05-31 | 2019-05-28 | Processing control data acquiring apparatus, processing control data acquiring method and processing control data acquiring program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018104224A JP7052567B2 (en) | 2018-05-31 | 2018-05-31 | Eyeglass lens processing control data acquisition device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2019209380A JP2019209380A (en) | 2019-12-12 |
| JP2019209380A5 JP2019209380A5 (en) | 2021-07-26 |
| JP7052567B2 true JP7052567B2 (en) | 2022-04-12 |
Family
ID=66668769
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018104224A Active JP7052567B2 (en) | 2018-05-31 | 2018-05-31 | Eyeglass lens processing control data acquisition device |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP3575033B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP7052567B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102544092B1 (en) * | 2022-01-10 | 2023-06-16 | 주식회사 아이니어 | Remote controllable lens edger and bigdata management server |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007296620A (en) | 2006-05-02 | 2007-11-15 | Nidek Co Ltd | Spectacle lens peripheral edge machining device |
| JP2014136287A (en) | 2013-01-17 | 2014-07-28 | Nidek Co Ltd | Spectacle lens machining device and machining control data creation program |
| JP2017164897A (en) | 2017-05-04 | 2017-09-21 | 波田野 義行 | Eyeglass lens processing equipment |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE4200637A1 (en) * | 1992-01-13 | 1993-07-15 | Wernicke & Co Gmbh | DEVICE FOR FACETTING EYE GLASSES |
| DE19702287C2 (en) * | 1997-01-23 | 1999-02-11 | Wernicke & Co Gmbh | Method for determining the course of the facets on the edge of spectacle lenses to be processed and for controlling the processing of shapes in accordance with the determined course of the facets |
| JP3990104B2 (en) | 2000-10-17 | 2007-10-10 | 株式会社ニデック | Lens grinding machine |
| JP3916445B2 (en) | 2001-11-08 | 2007-05-16 | 株式会社ニデック | Eyeglass lens processing equipment |
| JP4562343B2 (en) * | 2002-04-08 | 2010-10-13 | Hoya株式会社 | EX-type multifocal lens bevel locus determination method and EX-type multifocal lens processing apparatus |
| JP6172430B2 (en) | 2012-09-05 | 2017-08-02 | 株式会社ニデック | Eyeglass frame shape measuring device |
-
2018
- 2018-05-31 JP JP2018104224A patent/JP7052567B2/en active Active
-
2019
- 2019-05-28 EP EP19176890.2A patent/EP3575033B1/en active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007296620A (en) | 2006-05-02 | 2007-11-15 | Nidek Co Ltd | Spectacle lens peripheral edge machining device |
| JP2014136287A (en) | 2013-01-17 | 2014-07-28 | Nidek Co Ltd | Spectacle lens machining device and machining control data creation program |
| JP2017164897A (en) | 2017-05-04 | 2017-09-21 | 波田野 義行 | Eyeglass lens processing equipment |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3575033B1 (en) | 2023-07-05 |
| JP2019209380A (en) | 2019-12-12 |
| EP3575033A1 (en) | 2019-12-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN110998225B (en) | Spectacle frame shape measuring device and lens processing device | |
| JP4920284B2 (en) | Cup mounting device | |
| JP2007268700A (en) | Cup mounting device | |
| JP2016040531A (en) | Working tool measuring method and measuring device | |
| JP7052567B2 (en) | Eyeglass lens processing control data acquisition device | |
| EP3798566B1 (en) | Eyeglass frame shape measurement device and lens processing device | |
| JP5328025B2 (en) | Edge detection apparatus, machine tool using the same, and edge detection method | |
| JP4920285B2 (en) | Cup mounting device | |
| JP7196849B2 (en) | Spectacle frame shape measuring device and spectacle frame shape measuring program | |
| JP7243043B2 (en) | Target shape measuring device | |
| JP7087366B2 (en) | Axis setting device, spectacle lens processing system, and spectacle lens processing method | |
| JP7187799B2 (en) | Spectacle lens periphery processing information acquisition device and spectacle lens periphery processing information acquisition program | |
| JP7172029B2 (en) | Alignment device | |
| JP5302936B2 (en) | measuring device | |
| JP7156288B2 (en) | Spectacle frame shape measuring device and spectacle frame shape measuring program | |
| JP7143652B2 (en) | Eyeglass measurement system and eyeglass measurement program | |
| TWM494051U (en) | Measurement equipment of micro drill bit | |
| JP7243706B2 (en) | Lens shape acquisition device | |
| JP7467896B2 (en) | Apparatus for processing periphery of eyeglass lenses, program for processing periphery of eyeglass lenses, and method for processing eyeglass lenses | |
| JP7413697B2 (en) | Eyeglass frame shape measuring device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20220208 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20220301 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20220314 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7052567 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |