以下、本発明の一実施形態を図面を参照して説明する。
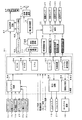
まず、遊技機の一例であるパチンコ遊技機の全体の構成について説明する。図1はパチンコ遊技機を正面からみた正面図、図2は遊技盤の前面を示す正面図である。なお、以下の実施の形態では、パチンコ遊技機を例に説明を行うが、本発明による遊技機はパチンコ遊技機に限られず、スロット機などの他の遊技機に適用することもできる。
Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
First, the entire configuration of a pachinko gaming machine, which is an example of a gaming machine, will be described. FIG. 1 is a front view of the pachinko gaming machine as viewed from the front, and FIG. 2 is a front view showing the front of the game board. In the following embodiments, a pachinko gaming machine is described as an example, but the gaming machine according to the present invention is not limited to a pachinko gaming machine, and can be applied to other gaming machines such as slot machines.
パチンコ遊技機1は、縦長の方形状に形成された外枠(図示せず)と、外枠の内側に開閉可能に取り付けられた遊技枠とで構成される。また、パチンコ遊技機1は、遊技枠に開閉可能に設けられている額縁状に形成されたガラス扉枠2を有する。遊技枠は、外枠に対して開閉自在に設置される前面枠(図示せず)を備え、前面枠には機構部品等が取り付けられる機構板が取り付けられる。また、前面枠にも、種々の部品が取り付けられる。
The pachinko gaming machine 1 is configured of an outer frame (not shown) formed in a vertically-long rectangular shape and a game frame attached to the inside of the outer frame so as to be openable and closable. In addition, the pachinko gaming machine 1 has a glass door frame 2 formed in a frame shape provided so as to be openable and closable in the game frame. The play space has a front frame (not shown) installed so as to be openable and closable with respect to the outer frame, and a mechanical plate to which mechanical parts and the like are attached is attached to the front frame. Also, various parts can be attached to the front frame.
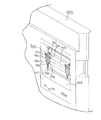
図1に示すように、パチンコ遊技機1は、額縁状に形成されたガラス扉枠2を有する。ガラス扉枠2の下部表面には打球供給皿(上皿)3がある。打球供給皿3の下部には、打球供給皿3に収容しきれない遊技球を貯留する余剰球受皿4と遊技球を発射する打球操作ハンドル(操作ノブ)5が設けられている。ガラス扉枠2の背面には、遊技盤6が着脱可能に取り付けられている。なお、遊技盤6は、それを構成する板状体と、その板状体に取り付けられた種々の部品とを含む構造体である。また、遊技盤6の前面には遊技領域7が形成されている。
As shown in FIG. 1, the pachinko gaming machine 1 has a glass door frame 2 formed in a frame shape. On the lower surface of the glass door frame 2, there is a hitting ball supply plate (upper plate) 3. At the lower part of the hit ball supply tray 3, there are provided a surplus ball receiver 4 for storing game balls which can not be accommodated in the hit ball supply tray 3 and a hit ball operation handle (operation knob) 5 for firing the game balls. A game board 6 is removably attached to the back of the glass door frame 2. The game board 6 is a structure including a plate-like body that constitutes the game board and various components attached to the plate-like body. In addition, a game area 7 is formed on the front of the game board 6.
遊技領域7の中央付近には、それぞれが演出用の飾り図柄(演出図柄)を可変表示する複数の可変表示部を含む演出表示装置(飾り図柄表示装置)9が設けられている。演出表示装置9には、例えば「左」、「中」、「右」の3つの可変表示部(図柄表示エリア)がある。演出表示装置9は、特別図柄表示器8による特別図柄の可変表示期間中に、装飾用(演出用)の図柄としての演出図柄の可変表示を行う。演出図柄の可変表示を行う演出表示装置9は、演出制御基板に搭載されている演出制御用マイクロコンピュータによって制御される。
In the vicinity of the center of the game area 7, there is provided an effect display device (decorative symbol display device) 9 including a plurality of variable display portions each of which variably displays a decorative symbol (rendering symbol) for effect. The effect display device 9 has, for example, three variable display portions (symbol display areas) of “left”, “middle” and “right”. During the variable display period of the special symbol by the special symbol display 8, the effect display device 9 performs the variable display of the effect symbol as a symbol for decoration (for effect). The effect display device 9 that performs variable display of the effect pattern is controlled by the effect control microcomputer mounted on the effect control board.
演出表示装置9の下部には、始動入賞口14に入った有効入賞球数すなわち保留記憶(始動記憶または始動入賞記憶ともいう。)数を表示する4つの特別図柄保留記憶表示器18が設けられている。特別図柄保留記憶表示器18は、保留記憶数を入賞順に4個まで表示する。特別図柄保留記憶表示器18は、始動入賞口14に始動入賞があるごとに、点灯状態のLEDの数を1増やす。そして、特別図柄保留記憶表示器18は、特別図柄表示器8で可変表示が開始されるごとに、点灯状態のLEDの数を1減らす(すなわち1つのLEDを消灯する)。具体的には、特別図柄保留記憶表示器18は、特別図柄表示器8で可変表示が開始されるごとに、点灯状態をシフトする。なお、この例では、始動入賞口14への入賞による始動記憶数に上限数(4個まで)が設けられているが、上限数を4個以上にしてもよい。
At the lower part of the effect display device 9, four special symbol hold storage indicators 18 are provided to display the number of activated winning balls that have entered the start winning opening 14, that is, the number of retention memories (also referred to as start memories or start prize memories). ing. The special symbol holding storage indicator 18 displays the number of holding storages up to four in the winning order. The special symbol holding memory indicator 18 increases the number of lighted LEDs by one each time the start winning opening 14 has a start winning. And each time the variable display is started by the special symbol display 8, the special symbol hold storage indicator 18 reduces the number of lighted LEDs by one (that is, turns off one LED). Specifically, the special symbol hold storage indicator 18 shifts the lighting state each time variable display is started by the special symbol indicator 8. In this example, although the upper limit number (up to four) is provided in the start memory number by the winning of the start winning opening 14, the upper limit number may be four or more.
演出表示装置9の上部には、識別情報としての特別図柄を可変表示する特別図柄表示器(特別図柄表示装置)8が設けられている。この実施の形態では、特別図柄表示器8は、例えば0〜9の数字を可変表示可能な簡易で小型の表示器(例えば7セグメントLED)で実現されている。特別図柄表示器8は、遊技者に特定の停止図柄を把握しづらくさせるために、0〜99など、より多種類の数字を可変表示するように構成されていてもよい。また、演出表示装置9は、特別図柄表示器8による特別図柄の可変表示期間中に、装飾用(演出用)の図柄としての演出図柄の可変表示を行う。
At the upper part of the effect display device 9, a special symbol display (special symbol display device) 8 for variably displaying a special symbol as identification information is provided. In this embodiment, the special symbol display 8 is realized by a simple and small display (for example, a 7-segment LED) capable of variably displaying the numbers 0 to 9, for example. The special symbol display 8 may be configured to variably display more types of numbers, such as 0 to 99, in order to make it difficult for the player to grasp a specific stop symbol. Further, the effect display device 9 performs variable display of the effect pattern as a symbol for decoration (for effect) during a variable display period of the special symbol by the special symbol display 8.
演出表示装置9の下方には、始動入賞口14を形成する可変入賞球装置15が設けられている。可変入賞球装置15は、羽根を開閉可能に構成され、羽根が開放しているときに遊技球が入賞し易い状態(開状態)となり、羽根が開放していないとき(閉じているとき)に遊技球が入賞し難い状態(閉状態)となる。始動入賞口14に入った入賞球は、遊技盤6の背面に導かれ、始動口スイッチ14a(例えば、近接スイッチ)によって検出されるとともに、入賞確認スイッチ14b(例えば、フォトセンサ)によって検出される。なお、この実施の形態では、後述するように、始動口スイッチ14aによって遊技球が検出されたことにもとづいて、特別図柄の変動表示が開始され、賞球払出が実行される。また、後述するように、始動口スイッチ14aによる検出結果に加えて入賞確認スイッチ14bの検出結果にもとづいて異常入賞の発生の有無が判定され、異常入賞の発生を検出したことにもとづいてセキュリティ信号が外部出力される。また、可変入賞球装置15は、ソレノイド16によって開状態にされる。
Below the effect display device 9, a variable winning ball device 15 that forms the start winning hole 14 is provided. The variable winning ball device 15 is configured to be able to open and close the wings, and when the wings are open, the gaming ball is in a state (open state) where it is easy to win, and when the wings are not open (when closed). It becomes a state (closed state) where it is difficult for the game ball to win. The winning balls that have entered the starting winning opening 14 are guided to the back of the game board 6, detected by the starting opening switch 14a (for example, proximity switch), and detected by the winning confirmation switch 14b (for example, photosensor) . In this embodiment, as described later, based on the fact that the game ball has been detected by the starting opening switch 14a, the variable display of the special symbol is started, and the award ball payout is executed. Further, as described later, in addition to the detection result by the starting opening switch 14a, the presence or absence of the occurrence of the abnormal prize is determined based on the detection result of the prize confirmation switch 14b, and the security signal is Is output to the outside. Also, the variable winning ball device 15 is opened by the solenoid 16.
なお、可変入賞球装置15の真上に第1始動入賞口を設け、可変入賞球装置15を第2始動入賞口としてもよい。この場合、第1始動入賞口および第2始動入賞口のそれぞれについて、始動口スイッチ(例えば、近接スイッチ)を設けるとともに入賞確認スイッチ(例えば、フォトセンサ)を設けるようにしてもよい。そして、第1始動入賞口および第2始動入賞口のそれぞれについて、この実施の形態と同様に、始動口スイッチによって遊技球が検出されたことにもとづいて、特別図柄の変動表示が開始され、賞球払出が実行されるようにしてもよい。また、第1始動入賞口および第2始動入賞口のそれぞれについて、この実施の形態と同様に、始動口スイッチによる検出結果に加えて入賞確認スイッチの検出結果にもとづいて異常入賞の発生の有無が判定され、異常入賞の発生を検出したことにもとづいてセキュリティ信号が外部出力されるようにしてもよい。
The first starting winning opening may be provided immediately above the variable winning ball device 15, and the variable winning ball device 15 may be used as a second starting winning opening. In this case, for each of the first starting winning opening and the second starting winning opening, a starting opening switch (for example, a proximity switch) may be provided and a winning confirmation switch (for example, a photo sensor) may be provided. Then, for each of the first starting winning opening and the second starting winning opening, the variation display of the special symbol is started based on the detection of the gaming ball by the starting opening switch as in this embodiment, and the prize Ball dispensing may be performed. Further, for each of the first starting winning opening and the second starting winning opening, in the same manner as in this embodiment, the presence or absence of occurrence of abnormal winning based on the detection result of the winning confirmation switch in addition to the detection result by the starting opening switch The security signal may be externally output based on the determination and the detection of the occurrence of the abnormal winning.
可変入賞球装置15の下部には、特定遊技状態(大当り状態)においてソレノイド21によって開状態に制御される開閉板を用いた特別可変入賞球装置20が設けられている。特別可変入賞球装置20は大入賞口を開閉する手段である。特別可変入賞球装置20に入賞し遊技盤6の背面に導かれた入賞球は、カウントスイッチ23で検出される。
At the lower part of the variable winning ball device 15, a special variable winning ball device 20 using an open / close plate controlled to an open state by the solenoid 21 in the specific gaming state (big hit state) is provided. The special variable winning prize ball device 20 is means for opening and closing the big prize winning opening. The winning ball that has won the special variable winning ball device 20 and is led to the back of the gaming board 6 is detected by the count switch 23.
なお、この実施の形態では、始動入賞口14にのみ、始動口スイッチ14aに加えて入賞確認スイッチ14bを設ける場合を示しているが、大入賞口にも、カウントスイッチ23に加えて入賞確認スイッチを備えるようにしてもよい。この場合、例えば、始動入賞口14と同様に、カウントスイッチ13を近接スイッチを用いて構成し、入賞確認スイッチをフォトセンサを用いて構成するようにすればよい(なお、逆に、カウントスイッチ13をフォトセンサを用いて構成し、入賞確認スイッチを近接スイッチを用いて構成してもよいし、近接スイッチやフォトセンサに代えてマイクロスイッチなどの機械式のスイッチを用いてもよい)。また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータは、大入賞口への遊技球の入賞にもとづく賞球払出処理については、カウントスイッチ23の検出結果にのみもとづいて賞球の払い出しを行うようにすればよい(ステップS32参照)。一方で、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータは、大入賞口への異常入賞を行う場合には、カウントスイッチ23の検出結果と入賞確認スイッチの検出結果との両方に基づいて判定を行うようにすればよい。この場合、例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータは、後述するスイッチ正常/異常チェック処理と同様の処理に従って、カウントスイッチ23の検出数と入賞確認スイッチの検出数との差が所定値(例えば、10)以上となったことにもとづいて、大入賞口への異常入賞が発生したと判定するようにすればよい(ステップS121〜S126参照)。
In this embodiment, only the start winning opening 14 is provided with the winning confirmation switch 14b in addition to the starting opening switch 14a. However, the winning confirmation switch is added to the count switch 23 also in the special winning opening. May be provided. In this case, for example, similarly to the start winning hole 14, the count switch 13 may be configured using a proximity switch, and the winning confirmation switch may be configured using a photo sensor (conversely, the count switch 13). May be configured using a photo sensor, and the winning confirmation switch may be configured using a proximity switch, or a mechanical switch such as a micro switch may be used instead of the proximity switch or the photo sensor). In addition, the game control microcomputer may pay out the winning balls based only on the detection result of the count switch 23 for the winning ball payout processing based on the winning of the gaming ball to the big winning opening (Step See S32). On the other hand, the microcomputer for game control may make a determination based on both of the detection result of the count switch 23 and the detection result of the prize confirmation switch when performing an abnormal prize to the special prize port. . In this case, for example, in the game control microcomputer, the difference between the number of detections of the count switch 23 and the number of detections of the winning confirmation switches is a predetermined value (for example, 10) according to the same processing as the switch normal / abnormality check processing described later Based on the above, it may be determined that an abnormal winning to the special winning opening has occurred (see steps S121 to S126).
遊技球がゲート32を通過しゲートスイッチ32aで検出されると、普通図柄表示器10の表示の可変表示が開始される。この実施の形態では、左右のランプ(点灯時に図柄が視認可能になる)が交互に点灯することによって可変表示が行われ、例えば、可変表示の終了時に左側のランプが点灯すれば当たりになる。そして、普通図柄表示器10における停止図柄が所定の図柄(当り図柄)である場合に、可変入賞球装置15が所定回数、所定時間だけ開状態になる。普通図柄表示器10の近傍には、ゲート32を通過した入賞球数を表示する4つのLEDによる表示部を有する普通図柄始動記憶表示器41が設けられている。ゲート32への遊技球の通過があるごとに、普通図柄始動記憶表示器41は点灯するLEDを1増やす。そして、普通図柄表示器10の可変表示が開始されるごとに、点灯するLEDを1減らす。
When the game ball passes through the gate 32 and is detected by the gate switch 32a, the variable display of the display of the normal symbol display 10 is started. In this embodiment, the variable display is performed by alternately turning on the left and right lamps (the symbols become visible when lit). For example, if the left lamp is turned on at the end of the variable display, it is a hit. Then, when the stop symbol in the normal symbol display 10 is a predetermined symbol (hit symbol), the variable winning ball device 15 is opened for a predetermined number of times and for a predetermined time. In the vicinity of the normal symbol display 10, a normal symbol start memory indicator 41 having a display unit with four LEDs for displaying the number of winning balls having passed through the gate 32 is provided. Each time there is a passage of the game ball to the gate 32, the normal symbol start memory indicator 41 increases the number of LEDs to be lit by one. Then, every time variable display of the normal symbol display 10 is started, the number of LEDs to be lit is reduced by one.
遊技盤6には、複数の入賞口29,30が設けられ、遊技球の入賞口29,30への入賞は、それぞれ入賞口スイッチ29a,30aによって検出される。各入賞口29,30は、遊技媒体を受け入れて入賞を許容する領域として遊技盤6に設けられる入賞領域を構成している。なお、始動入賞口14や大入賞口も、遊技媒体を受け入れて入賞を許容する入賞領域を構成する。なお、各入賞口29,30に入賞した遊技球を入賞スイッチで検出する構成に代えて、遊技球が所定領域(例えばゲート)を通過したことを検出スイッチで検出する構成としてもよい。遊技領域7の左右周辺には、遊技中に点滅表示される装飾ランプ25が設けられ、下部には、入賞しなかった遊技球を吸収するアウト口26がある。また、遊技領域7の外側の左右上部には、効果音を発する2つのスピーカ27が設けられている。遊技領域7の外周には、天枠ランプ28a、左枠ランプ28bおよび右枠ランプ28cが設けられている。さらに、遊技領域7における各構造物(大入賞口等)の周囲には装飾LEDが設置されている。天枠ランプ28a、左枠ランプ28bおよび右枠ランプ28cおよび装飾用LEDは、遊技機に設けられている装飾発光体の一例である。なお、この実施の形態では、遊技機に設けられている発光体をランプやLEDを用いて構成する場合を示しているが、この実施の形態で示した態様にかぎらず、例えば、遊技機に設けられている発光体を全てLEDを用いて構成するようにしてもよい。
A plurality of winning openings 29, 30 are provided on the game board 6, and the winnings on the winning openings 29, 30 of the gaming balls are detected by the winning opening switches 29a, 30a, respectively. The respective winning openings 29, 30 constitute a winning area provided on the game board 6 as an area for accepting gaming media and allowing winning. The start winning opening 14 and the big winning opening also constitute a winning area for accepting gaming media and allowing winning. It should be noted that instead of the configuration in which the game balls that have won in each of the winning openings 29 and 30 are detected by the prize switch, the detection switch may detect that the game ball has passed a predetermined area (for example, a gate). On the left and right peripheries of the game area 7, a decoration lamp 25 which blinks during the game is provided, and at the lower part, there is an out port 26 for absorbing the game ball which has not won. In addition, two speakers 27 that emit sound effects are provided on the upper left and right of the game area 7. On the outer periphery of the game area 7, a sky lamp 28a, a left frame lamp 28b and a right frame lamp 28c are provided. Furthermore, decoration LED is installed around each structure (big winning opening etc) in the game area 7. The sky lamp 28a, the left frame lamp 28b, the right frame lamp 28c, and the decorative LED are examples of a decorative light-emitting body provided in a game machine. Although this embodiment shows the case where the light-emitting body provided in the gaming machine is configured using a lamp or an LED, the invention is not limited to the mode shown in this embodiment, and, for example, All of the provided light emitters may be configured using LEDs.
なお、図1および図2では、図示を省略しているが、左枠ランプ28bの近傍に、賞球払出中に点灯する賞球ランプが設けられ、天枠ランプ28aの近傍に、補給球が切れたときに点灯する球切れランプが設けられている。なお、賞球ランプおよび球切れランプは、賞球の払出中である場合や球切れが検出された場合に、演出制御基板に搭載された演出制御用マイクロコンピュータによって点灯制御される。さらに、プリペイドカードが挿入されることによって球貸しを可能にするプリペイドカードユニット(以下、「カードユニット」という。)50が、パチンコ遊技機1に隣接して設置されている。
In addition, although illustration is abbreviate | omitted in FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, the prize ball lamp lighted during award ball payout is provided in the vicinity of the left frame lamp 28b, and the replenishment ball is provided in the vicinity of the sky lamp 28a. There is a bulb break lamp that lights up when it runs out. The prize ball lamp and the ball out lamp are controlled to be lighted by the effect control microcomputer mounted on the effect control board when the prize ball is being dispensed or when the ball out is detected. Further, a prepaid card unit (hereinafter referred to as a "card unit") 50 that enables a ball rental by inserting a prepaid card is installed adjacent to the pachinko gaming machine 1.
カードユニット50には、例えば、使用可能状態であるか否かを示す使用可表示ランプ、カードユニットがいずれの側のパチンコ遊技機1に対応しているのかを示す連結台方向表示器、カードユニット内にカードが投入されていることを示すカード投入表示ランプ、記録媒体としてのカードが挿入されるカード挿入口、およびカード挿入口の裏面に設けられているカードリーダライタの機構を点検する場合にカードユニットを解放するためのカードユニット錠が設けられている。
The card unit 50 has, for example, an available display lamp indicating whether or not it is usable, a coupling table direction indicator indicating on which side the pachinko gaming machine 1 corresponds to the card unit, and the card unit When checking the mechanism of the card insertion indicator lamp indicating that the card is inserted inside, the card insertion slot in which the card as the recording medium is inserted, and the back of the card insertion slot A card unit lock is provided to release the card unit.
遊技者の操作により打球発射装置から発射された遊技球は、打球レールを通って遊技領域7に入り、その後、遊技領域7を下りてくる。遊技球が始動入賞口14に入り始動口スイッチ14aで検出されると、図柄の可変表示を開始できる状態であれば、特別図柄表示器8において特別図柄が可変表示(変動)を始める。図柄の可変表示を開始できる状態でなければ、保留記憶数を1増やす。
The game balls fired from the hit ball launcher by the operation of the player enter the game area 7 through the hit rails, and then go down the game area 7. When the game ball enters the start winning opening 14 and is detected by the start opening switch 14a, the special symbol starts variable display (variation) in the special symbol display 8 if it can start variable display of the symbol. If it is not in a state where variable display of symbols can be started, the number of pending storages is increased by one.
特別図柄表示器8における特別図柄の可変表示は、一定時間が経過したときに停止する。停止時の特別図柄(停止図柄)が大当り図柄(特定表示結果)であると、大当り遊技状態に移行する。すなわち、特別可変入賞球装置20が、一定時間経過するまで、または、所定個数(例えば10個)の遊技球が入賞するまで開放する。そして、特別可変入賞球装置20の開放は、決定されたラウンド数の最後のラウンドまで(例えば、15ラウンドまで)許容される。
The variable display of the special symbol in the special symbol display 8 stops when a predetermined time has elapsed. When the special symbol (stop symbol) at the time of stop is the big hit symbol (specific display result), it shifts to the big hit game state. That is, the special variable winning prize ball device 20 is opened until a predetermined time passes or until a predetermined number (for example, 10) of gaming balls win. And, the release of the special variable winning prize ball device 20 is permitted until the last round of the determined number of rounds (for example, up to 15 rounds).
停止時の特別図柄表示器8における特別図柄が確率変動を伴う大当り図柄(確変図柄)である場合には、次に大当りになる確率が高くなる。すなわち、確変状態という遊技者にとってさらに有利な状態になる。
When the special symbol in the special symbol display 8 at the time of stop is the big hit symbol (probable variation symbol) with probability fluctuation, the probability of the next big hit becomes high. That is, it is more advantageous for the player of the probability change state.
遊技球がゲート32を通過すると、普通図柄表示器10において普通図柄が可変表示される状態になる。また、普通図柄表示器10における停止図柄が所定の図柄(当り図柄)である場合に、可変入賞球装置15が所定時間だけ開状態になる。
When the gaming ball passes through the gate 32, the normal symbol is variably displayed on the normal symbol display 10. Also, when the stop symbol in the normal symbol display 10 is a predetermined symbol (hit symbol), the variable winning ball device 15 is in an open state for a predetermined time.
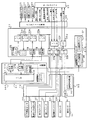
次に、パチンコ遊技機1の裏面の構造について図3を参照して説明する。図3は、遊技機を裏面から見た背面図である。図3に示すように、パチンコ遊技機1裏面側では、演出表示装置9を制御する演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が搭載された演出制御基板80を含む変動表示制御ユニット、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ等が搭載された遊技制御基板(主基板)31、音声出力基板70、ランプドライバ基板35、および球払出制御を行なう払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ等が搭載された払出制御基板37等の各種基板が設置されている。なお、遊技制御基板31は基板収納ケース200に収納されている。
Next, the structure of the back surface of the pachinko gaming machine 1 will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 3 is a rear view of the gaming machine as viewed from the rear. As shown in FIG. 3, on the back side of the pachinko gaming machine 1, a variable display control unit including a presentation control board 80 on which the presentation control microcomputer 100 for controlling the presentation display device 9 is mounted, a game control microcomputer, etc. Various boards such as a game control board (main board) 31 mounted, a voice output board 70, a lamp driver board 35, a payout control board 37 on which a payout control microcomputer for performing ball payout control, etc. are mounted are installed There is. The game control board 31 is stored in the board storage case 200.
さらに、パチンコ遊技機1裏面側には、DC30V、DC21V、DC12VおよびDC5V等の各種電源電圧を作成する電源回路が搭載された電源基板910やタッチセンサ基板91が設けられている。電源基板910には、パチンコ遊技機1における遊技制御基板31および各電気部品制御基板(演出制御基板80および払出制御基板37)やパチンコ遊技機1に設けられている各電気部品(電力が供給されることによって動作する部品)への電力供給を実行あるいは遮断するための電力供給許可手段としての電源スイッチ、遊技制御基板31の遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のRAM55をクリアするためのクリアスイッチが設けられている。さらに、電源スイッチの内側(基板内部側)には、交換可能なヒューズが設けられている。
Further, on the back side of the pachinko gaming machine 1, there are provided a power supply substrate 910 and a touch sensor substrate 91 on which power supply circuits for generating various power supply voltages such as DC30V, DC21V, DC12V and DC5V are mounted. The power supply substrate 910 is supplied with the game control substrate 31 and the respective electric component control substrates (the effect control substrate 80 and the payout control substrate 37) in the pachinko gaming machine 1 and the respective electric components (power) provided in the pachinko gaming machine 1 A power switch as a power supply permission unit for executing or cutting off the power supply to the component (operating by), and a clear switch for clearing the RAM 55 of the game control microcomputer 560 of the game control board 31 ing. Furthermore, a replaceable fuse is provided inside the power switch (inside of the substrate).
なお、この実施の形態では、主基板31は遊技盤側に設けられ、払出制御基板37は遊技枠側に設けられている。このような構成であっても、後述するように、主基板31と払出制御基板37との間の通信をシリアル通信で行うことによって、遊技盤を交換する際の配線の取り回しを容易にしている。
In this embodiment, the main substrate 31 is provided on the game board side, and the payout control board 37 is provided on the game frame side. Even with such a configuration, as will be described later, the communication between the main board 31 and the payout control board 37 is performed by serial communication, thereby facilitating the arrangement of wiring when replacing the game board .
なお、各制御基板には、制御用マイクロコンピュータを含む制御手段が搭載されている。制御手段は、遊技制御手段等からのコマンドとしての指令信号(制御信号)に従って遊技機に設けられている電気部品(遊技用装置:球払出装置97、演出表示装置9、ランプやLEDなどの発光体、スピーカ27等)を制御する。以下、主基板31を制御基板に含めて説明を行うことがある。その場合には、制御基板に搭載される制御手段は、遊技制御手段と、遊技制御手段等からの指令信号に従って遊技機に設けられている電気部品を制御する手段とのそれぞれを指す。また、主基板31以外のマイクロコンピュータが搭載された基板をサブ基板ということがある。なお、球払出装置97は、遊技球を誘導する通路とステッピングモータ等により駆動されるスプロケット等によって誘導された遊技球を上皿や下皿に払い出すための装置であって、払い出された賞球や貸し球をカウントする払出個数カウントスイッチ等もユニットの一部として構成されている。なお、この実施の形態では、払出検出手段は、払出個数カウントスイッチ301によって実現され、球払出装置97から実際に賞球や貸し球が払い出されたことを検出する機能を備える。この場合、払出個数カウントスイッチ301は、賞球や貸し球の払い出しを1球検出するごとに検出信号を出力する。
Control means including a control microcomputer is mounted on each control board. The control means is an electric component provided in the gaming machine according to a command signal (control signal) as a command from the game control means or the like (gaming device: light emitting device such as ball payout device 97, effect display device 9, lamp or LED) Control the body, speaker 27 etc.). Hereinafter, the main substrate 31 may be included in the control substrate to be described. In that case, the control means mounted on the control board refers to each of the game control means and the means for controlling the electric components provided in the game machine according to the command signal from the game control means or the like. Moreover, the board | substrate with which microcomputers other than the main board | substrate 31 were mounted may be called a sub board | substrate. The ball payout device 97 is a device for paying out, to the upper plate or the lower plate, the gaming ball induced by the passage for guiding the gaming ball and the sprocket driven by the stepping motor or the like. A prize ball, a payout number counting switch for counting the lent balls, and the like are also configured as part of the unit. In this embodiment, the payout detecting means is realized by the payout number counting switch 301, and has a function of detecting that the winning balls and the rental balls are actually paid out from the ball payout device 97. In this case, the payout number counting switch 301 outputs a detection signal each time one payout of a winning ball or a rental ball is detected.
パチンコ遊技機1裏面において、上方には、各種情報をパチンコ遊技機1の外部に出力するための各端子を備えたターミナル基板160が設置されている。ターミナル基板160には、例えば、大当り遊技状態の発生を示す大当り情報等の情報出力信号(図60に示す始動口信号、図柄確定回数1信号、大当り1信号、大当り2信号、大当り3信号、時短信号、セキュリティ信号、賞球信号1、遊技機エラー状態信号)を外部出力するための情報出力端子が設けられている。
A terminal board 160 provided with terminals for outputting various information to the outside of the pachinko gaming machine 1 is installed on the upper side of the back of the pachinko gaming machine 1. Terminal board 160, for example, information output signal such as big hit information indicating occurrence of big hit gaming state (start opening signal shown in FIG. 60, symbol determination number 1 signal, big hit 1 signal, big hit 2 signal, big hit 3 signal, hour An information output terminal is provided to externally output a short signal, a security signal, a prize ball signal 1, and a gaming machine error state signal).
貯留タンク38に貯留された遊技球は誘導レール(図示せず)を通り、カーブ樋を経て払出ケース40Aで覆われた球払出装置97に至る。球払出装置97の上方には、遊技媒体切れ検出手段としての球切れスイッチ187が設けられている。球切れスイッチ187が球切れを検出すると、球払出装置97の払出動作が停止する。球切れスイッチ187は遊技球通路内の遊技球の有無を検出するスイッチであるが、貯留タンク38内の補給球の不足を検出する球切れ検出スイッチ167も誘導レールにおける上流部分(貯留タンク38に近接する部分)に設けられている。球切れ検出スイッチ167が遊技球の不足を検知すると、遊技機設置島に設けられている補給機構からパチンコ遊技機1に対して遊技球の補給が行なわれる。
The game balls stored in the storage tank 38 pass through a guiding rail (not shown), pass through a curved weir, and reach the ball dispensing device 97 covered by the dispensing case 40A. Above the ball payout device 97, a ball out switch 187 is provided as a game medium out detection means. When the ball breakage switch 187 detects the ball breakage, the dispensing operation of the ball dispensing device 97 is stopped. The out-of-ball switch 187 is a switch for detecting the presence or absence of a game ball in the game ball passage, but the out-of-ball detection switch 167 for detecting a shortage of supply balls in the storage tank 38 is also an upstream portion of the guide rail It is provided in the adjacent part). When the out-of-ball detection switch 167 detects a shortage of gaming balls, the gaming mechanism is replenished to the pachinko gaming machine 1 from the replenishment mechanism provided on the gaming machine installation island.
入賞にもとづく景品としての遊技球や球貸し要求にもとづく遊技球が多数払出されて打球供給皿3が満杯になると、遊技球は、余剰球誘導通路を経て余剰球受皿4に導かれる。さらに遊技球が払出されると、感知レバー(図示せず)が貯留状態検出手段としての満タンスイッチを押圧して、貯留状態検出手段としての満タンスイッチがオンする。その状態では、球払出装置内の払出モータの回転が停止して球払出装置の動作が停止するとともに打球発射装置の駆動も停止する。
When a large number of gaming balls as prizes based on the prize and a gaming ball based on a ball lending request are paid out and the hitting ball supply tray 3 becomes full, the gaming balls are guided to the surplus ball tray 4 through the surplus ball guiding passage. Further, when the gaming ball is paid out, the sensing lever (not shown) presses the full tank switch as the storage state detection means, and the full tank switch as the storage state detection means is turned on. In that state, the rotation of the dispensing motor in the ball dispensing device is stopped, the operation of the ball dispensing device is stopped, and the driving of the ball striking device is also stopped.
また、図3に示すように、前面枠の上方には、扉体(この例では、ガラス扉枠2)の状態(遊技領域7を覆う閉鎖状態または遊技領域7を外部から接触可能な状態にする開放状態)を検出(具体的には、前面に遊技領域7が形成されている遊技盤6が取り付けられた前面枠に対してガラス扉枠2が開放されたか否かを検出)するためのドア開放センサ155が取り付けられている。
In addition, as shown in FIG. 3, the state of the door (in this example, the glass door frame 2) above the front frame (the closed state covering the game area 7 or the game area 7 can be contacted from the outside) To detect an open state) (specifically, it is detected whether the glass door frame 2 is opened with respect to the front frame to which the game board 6 having the game area 7 formed on the front surface is attached) A door open sensor 155 is attached.
図4は、始動入賞口14内の断面構造の具体例を示す説明図である。図4に示すように、始動入賞口14内には、始動入賞口内に入賞した遊技球を検出可能な2つのスイッチ(始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14b)が設けられている。この実施の形態では、図4に示すように、始動入賞口14内で、始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14bとが上下に配置されている(本例では、始動口スイッチ14aが上側に配置され、入賞確認スイッチ14bが下側に配置されている)。従って、この実施の形態では、始動入賞口14内に入賞した遊技球は、遊技盤6の背面に導かれ、まず始動口スイッチ14aで検出され、次いで入賞確認スイッチ14bで検出される。
FIG. 4 is an explanatory view showing a specific example of the sectional structure in the start winning hole 14. As shown in FIG. 4, in the start winning opening 14, two switches (a starting opening switch 14a and a winning confirmation switch 14b) capable of detecting the game ball having won in the start winning opening are provided. In this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 4, the starting opening switch 14a and the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b are arranged vertically in the starting winning opening 14 (in this example, the starting opening switch 14a is arranged on the upper side) And the prize confirmation switch 14b is disposed on the lower side). Therefore, in this embodiment, the gaming ball having won a prize in the start winning opening 14 is guided to the back of the gaming board 6, first detected by the starting opening switch 14a, and then detected by the winning confirmation switch 14b.
また、始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14bとして、それぞれ異なる検出方式のスイッチが用いられる。この実施の形態では、始動口スイッチ14aとして近接スイッチを用い、入賞確認スイッチ14bとしてフォトセンサを用いる場合を示している。
Further, switches of different detection methods are used as the starting opening switch 14a and the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b. In this embodiment, a proximity switch is used as the starting opening switch 14a, and a photo sensor is used as the winning confirmation switch 14b.
また、この実施の形態では、後述するように、始動口スイッチ14aによって遊技球が検出されたことにもとづいて、特別図柄の変動表示が開始され、賞球払出が実行される。また、後述するように、始動口スイッチ14aによる検出結果に加えて入賞確認スイッチ14bの検出結果にもとづいて異常入賞の発生の有無が判定され、異常入賞の発生を検出したことにもとづいてセキュリティ信号が外部出力される。従って、この実施の形態では、入賞確認スイッチ14bは、異常入賞の判定のみに用いられる。なお、遊技球が始動口スイッチ14aによって検出されても、特別図柄の変動表示が開始されるが、景品払出を生じさせないように構成されていてもよい。その場合には始動口は、景品払出を伴う入賞領域ではなく、遊技球が進入する領域である進入領域(そこを通過しても景品払出を伴わない。)である。また、入賞領域および進入領域を特定領域または通過領域とする。
Further, in this embodiment, as described later, based on the fact that the game ball has been detected by the starting opening switch 14a, the variable display of the special symbol is started, and the award ball payout is executed. Further, as described later, in addition to the detection result by the starting opening switch 14a, the presence or absence of the occurrence of the abnormal prize is determined based on the detection result of the prize confirmation switch 14b, and the security signal is Is output to the outside. Therefore, in this embodiment, the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b is used only for the determination of the abnormal winning. In addition, although the game ball is detected by the starting opening switch 14a, the variable display of the special symbol is started, but it may be configured so as not to generate a prize payout. In that case, the starting opening is not a winning area accompanied by a prize payout but an entry area where the gaming ball enters (even if there is no prize payout even if passing there). In addition, the winning area and the entry area are designated as a specific area or a passing area.
また、始動口スイッチ14aおよび入賞確認スイッチ14bの検出方式は、この実施の形態で示したものにかぎらず、例えば、始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14bとで異なる検出方式であれば、逆に始動口スイッチ14aとしてフォトセンサを用い、入賞確認スイッチ14bとして近接スイッチを用いてもよい。この場合、フォトセンサである始動口スイッチ14aの検出結果にもとづいて特別図柄の変動表示や賞球払出処理が実行され、近接スイッチである入賞確認スイッチ14bの検出結果は、始動入賞口14の異常入賞の判定のみに用いられることになる。また、例えば、電磁式のスイッチである近接スイッチや光学式のフォトセンサに代えて、始動口スイッチ14aまたは入賞確認スイッチ14bとして、機械式のスイッチ(マイクロスイッチなど)を用いてもよい。
Further, the detection method of the starting opening switch 14a and the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b is not limited to that shown in this embodiment, for example, if it is a detection method different between the starting opening switch 14a and the winning affirmation confirmation switch 14b, reversely. A photosensor may be used as the starting opening switch 14a, and a proximity switch may be used as the winning confirmation switch 14b. In this case, the variation display of the special symbol and the prize ball payout processing are executed based on the detection result of the start opening switch 14a which is a photo sensor, and the detection result of the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b which is a proximity switch is an abnormality of the start winning opening 14 It will be used only for winning determination. For example, instead of the proximity switch or the optical photosensor which is an electromagnetic switch, a mechanical switch (micro switch or the like) may be used as the starting opening switch 14a or the prize confirmation switch 14b.
図5は、遊技球を検出可能な検出手段の方式を説明するための回路図である。図5(A)には、始動口スイッチ14a(近接スイッチ)が示されている。始動口スイッチ14aの一方の端子には、電源基板910から+12V電源電圧が供給されている。始動口スイッチ14aの他方の端子の電圧レベルである検出信号は、主基板31に入力される。主基板31において、検出信号は、入力ドライバ回路から遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータの入力ポートに入力される。また、始動口スイッチ14aの出力側には、一端が接地されている抵抗RとコンデンサCが接続されている。
FIG. 5 is a circuit diagram for explaining a method of detecting means capable of detecting a game ball. The starting opening switch 14a (proximity switch) is shown by FIG. 5 (A). The +12 V power supply voltage is supplied from the power supply substrate 910 to one terminal of the start port switch 14a. A detection signal which is a voltage level of the other terminal of the start port switch 14 a is input to the main substrate 31. In the main board 31, the detection signal is inputted from the input driver circuit to the input port of the game control microcomputer. Further, a resistor R and a capacitor C, one end of which is grounded, are connected to the output side of the start port switch 14a.
近接スイッチである始動口スイッチ14aに設けられている穴を金属の遊技球が通過するとコイルLに逆起電力が生じ、コイルLの等価的な抵抗値が極めて大きくなる。従って、始動口スイッチ14aの出力は、0Vに近いローレベルになる。すなわち、検出信号は、ローレベルである。始動口スイッチ14aに設けられている穴を金属の遊技球が通過していない場合には、始動口スイッチ14aの出力は、+12VがコイルLと抵抗Rの抵抗値で分圧された値であり、ハイレベルであるとみなされるしきい値レベルを越える。すなわち、検出信号は、ハイレベルである。従って、この実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータは、始動口スイッチ14aからの出力がハイレベルであれば始動口スイッチ14aがオフ状態であると判断することができ、始動口スイッチ14aからの出力がローレベルであれば始動口スイッチ14aがオン状態であると判断することができる(すなわち、始動口スイッチ14aの出力は負論理となっている)。なお、検出信号のレベルを入力ドライバ回路で論理反転してから遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に入力するように構成してもよい。
When a metal game ball passes through a hole provided in the starting opening switch 14a which is a proximity switch, a back electromotive force is generated in the coil L, and the equivalent resistance value of the coil L becomes extremely large. Therefore, the output of the start port switch 14a becomes low level close to 0V. That is, the detection signal is at the low level. When the metal game ball does not pass through the hole provided in the starting opening switch 14a, the output of the starting opening switch 14a is a value obtained by dividing +12 V by the resistance value of the coil L and the resistance R and , A threshold level considered to be high level is exceeded. That is, the detection signal is at high level. Therefore, in this embodiment, the microcomputer for game control can judge that the start opening switch 14a is in the off state if the output from the start opening switch 14a is at high level, and the microcomputer from the start opening switch 14a If the output is low, it can be determined that the start port switch 14a is in the on state (ie, the output of the start port switch 14a has a negative logic). The level of the detection signal may be logically inverted by the input driver circuit and then input to the game control microcomputer 560.
図5(B)には、入賞確認スイッチ14b(フォトセンサ)が示されている。図5(B)に示すフォトセンサは、発光する発光ダイオード(LED)341と、受光して電流を出力するフォトトランジスタ342とで構成されている。発光ダイオード341およびフォトトランジスタ342の近傍を遊技球が通過すると、遊技球が反射した発光ダイオード341からの光をフォトトランジスタ342が受光して出力側に電流を流す。なお、この場合、フォトトランジスタ342のコレクタ端子からエミッタ端子の向きに電流が流れることにより、フォトセンサの検出信号は、近接スイッチと同様に負論理である。フォトセンサの出力側は主基板31に接続され、主基板31において、フォトセンサの検出信号は、入力ドライバ回路から遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータの入力ポートに入力される。フォトセンサの出力側(具体的には、フォトトランジスタ342の出力側)に電流が流れると、入力ドライバ回路は、ハイレベルの検出信号を遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータに出力する。なお、近接スイッチと同様に、検出信号のレベルを入力ドライバ回路で論理反転してから遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に入力するように構成してもよい。
The winning a prize confirmation switch 14b (photo sensor) is shown by FIG. 5 (B). The photosensor illustrated in FIG. 5B includes a light emitting diode (LED) 341 that emits light, and a phototransistor 342 that receives light and outputs a current. When the gaming ball passes near the light emitting diode 341 and the photo transistor 342, the photo transistor 342 receives the light from the light emitting diode 341 reflected by the gaming ball and causes a current to flow on the output side. In this case, the current flows from the collector terminal of the phototransistor 342 in the direction of the emitter terminal, and the detection signal of the photo sensor has a negative logic as in the proximity switch. The output side of the photo sensor is connected to the main board 31, and on the main board 31, the detection signal of the photo sensor is inputted from the input driver circuit to the input port of the game control microcomputer. When a current flows to the output side of the photosensor (specifically, the output side of the phototransistor 342), the input driver circuit outputs a high level detection signal to the game control microcomputer. As in the proximity switch, the level of the detection signal may be logically inverted by the input driver circuit and then input to the game control microcomputer 560.
遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータは、入力ドライバ回路からの検出信号がローレベルである場合に、遊技球がフォトセンサを通過したと判定することができる。
The game control microcomputer can determine that the game ball has passed the photo sensor when the detection signal from the input driver circuit is at a low level.
なお、この実施の形態では、フォトセンサとして反射型のフォトセンサが用いられるが、図5(C)における上段に示すように、発光素子(LED341)と受光素子(フォトトランジスタ342)とを入賞球経路を挟むように対向させて設置し、遊技球が発光素子からの光を遮ることによって受光素子が光を検出しなくなることによって、発光素子と受光素子との間を通過した遊技球を検出する透過型のフォトセンサを用いてもよい。透過型のフォトセンサを用いる場合に、図5(C)における下段に示すように、発光素子の光軸(図5(C)において黒丸で例示されている。)が、遊技球経路(入賞球経路)を通過する遊技球の中央部からずれるように、発光素子および受光素子を設置することが好ましい。光軸が遊技球の中央部に相当するように設置する場合に比べて、連続して通過する2つの遊技球の間隔が相対的に広い部分(図5(C)における「空隙」の部分)において遊技球を検知することができ、2つの遊技球を別個に検出しやすいからである。同様の理由で、図5(B)に例示する反射型のフォトセンサを用いる場合にも、発光素子からの光の反射点が遊技球の中央部からずれるように、発光素子および受光素子を設置することが好ましい。
In this embodiment, a reflection type photosensor is used as the photosensor, but as shown in the upper part of FIG. 5C, the light emitting element (LED 341) and the light receiving element (phototransistor 342) are winning balls. The game balls are placed facing each other so as to sandwich the path, and the game ball intercepts the light from the light emitting element so that the light receiving element does not detect the light, thereby detecting the game ball passed between the light emitting element and the light receiving element A transmissive photosensor may be used. When a transmission type photo sensor is used, as shown in the lower part of FIG. 5C, the optical axis of the light emitting element (exemplified by black circles in FIG. 5C) is a game ball path (winning ball) Preferably, the light emitting element and the light receiving element are provided so as to be offset from the central portion of the gaming ball passing through the path). Compared with the case where the optical axis corresponds to the central portion of the gaming ball, a portion where the distance between two gaming balls passing continuously is relatively wide (portion of “void” in FIG. 5 (C)) The game ball can be detected in and it is easy to detect two game balls separately. For the same reason, even in the case of using the reflection type photo sensor illustrated in FIG. 5B, the light emitting element and the light receiving element are installed such that the reflection point of the light from the light emitting element deviates from the central portion of the game ball It is preferable to do.
図6は、主基板(遊技制御基板)31における回路構成の一例を示すブロック図である。なお、図6には、払出制御基板37および演出制御基板80等も示されている。主基板31には、プログラムに従ってパチンコ遊技機1を制御する遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ(遊技制御手段に相当)560が搭載されている。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ゲーム制御(遊技進行制御)用のプログラム等を記憶するROM54、ワークメモリとして使用される記憶手段としてのRAM55、プログラムに従って制御動作を行うCPU56およびI/Oポート部57を含む。この実施の形態では、ROM54およびRAM55は遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に内蔵されている。すなわち、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、1チップマイクロコンピュータである。1チップマイクロコンピュータには、少なくともRAM55が内蔵されていればよく、ROM54は外付けであっても内蔵されていてもよい。また、I/Oポート部57は、外付けであってもよい。
FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing an example of the circuit configuration of the main board (game control board) 31. As shown in FIG. In FIG. 6, the payout control board 37, the effect control board 80 and the like are also shown. The main substrate 31 is mounted with a game control microcomputer (corresponding to game control means) 560 for controlling the pachinko gaming machine 1 according to a program. The game control microcomputer 560 has a ROM 54 for storing a program for game control (game progression control) and the like, a RAM 55 as storage means used as a work memory, a CPU 56 for performing control operations according to the program, and an I / O port unit 57 including. In this embodiment, the ROM 54 and the RAM 55 are incorporated in the game control microcomputer 560. That is, the game control microcomputer 560 is a one-chip microcomputer. The one-chip microcomputer only needs to have at least the RAM 55 built-in, and the ROM 54 may be external or built-in. Also, the I / O port unit 57 may be externally attached.
なお、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560においてCPU56がROM54に格納されているプログラムに従って制御を実行するので、以下、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560(またはCPU56)が実行する(または、処理を行う)ということは、具体的には、CPU56がプログラムに従って制御を実行することである。このことは、主基板31以外の他の基板に搭載されているマイクロコンピュータについても同様である。
In the game control microcomputer 560, the CPU 56 executes control in accordance with the program stored in the ROM 54, so that the game control microcomputer 560 (or the CPU 56) executes (or performs processing) hereinafter. Specifically, the CPU 56 executes control in accordance with a program. The same applies to a microcomputer mounted on another substrate other than the main substrate 31.
また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560には、乱数回路503が内蔵されている。乱数回路503は、特別図柄の可変表示の表示結果により大当りとするか否か判定するための判定用の乱数を発生するために用いられるハードウェア回路である。乱数回路503は、初期値(例えば、0)と上限値(例えば、65535)とが設定された数値範囲内で、数値データを、設定された更新規則に従って更新し、ランダムなタイミングで発生する始動入賞時が数値データの読出(抽出)時であることにもとづいて、読出される数値データが乱数値となる乱数発生機能を有する。
Further, the game control microcomputer 560 incorporates a random number circuit 503. The random number circuit 503 is a hardware circuit used to generate a random number for determination to determine whether or not to make a big hit according to the display result of the variable display of the special symbol. The random number circuit 503 updates numerical data in accordance with a set update rule within a numerical range in which an initial value (for example, 0) and an upper limit value (for example, 65535) are set, and start occurs at random timing. Based on the fact that the winning is at the time of reading out (extraction) of numerical data, it has a random number generation function in which the numerical data to be read out is a random number.
乱数回路503は、数値データの更新範囲の選択設定機能(初期値の選択設定機能、および、上限値の選択設定機能)、数値データの更新規則の選択設定機能、および数値データの更新規則の選択切換え機能等の各種の機能を有する。このような機能によって、生成する乱数のランダム性を向上させることができる。
The random number circuit 503 has a selection setting function of updating range of numerical data (setting selection function of initial value and selection setting function of upper limit value), a selection setting function of updating rule of numerical data, and selection of update rule of numerical data It has various functions such as switching function. Such a function can improve the randomness of the generated random number.
また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、乱数回路503が更新する数値データの初期値を設定する機能を有している。例えば、ROM54等の所定の記憶領域に記憶された遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のIDナンバ(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560の各製品ごとに異なる数値で付与されたIDナンバ)を用いて所定の演算を行なって得られた数値データを、乱数回路503が更新する数値データの初期値として設定する。そのような処理を行うことによって、乱数回路503が発生する乱数のランダム性をより向上させることができる。
Further, the game control microcomputer 560 has a function of setting an initial value of numerical data to be updated by the random number circuit 503. For example, using the ID number of the game control microcomputer 560 stored in a predetermined storage area such as the ROM 54 (ID number assigned with a different numerical value for each product of the game control microcomputer 560) The numerical data obtained by the execution is set as the initial value of the numerical data to be updated by the random number circuit 503. By performing such processing, the randomness of the random number generated by the random number circuit 503 can be further improved.
遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、始動口スイッチ14aへの始動入賞が生じたときに乱数回路503から数値データをランダムRとして読み出し、特別図柄および演出図柄の変動開始時にランダムRにもとづいて特定の表示結果としての大当り表示結果にするか否か、すなわち、大当りとするか否かを決定する。そして、大当りとすると決定したときに、遊技状態を遊技者にとって有利な特定遊技状態としての大当り遊技状態に移行させる。
The game control microcomputer 560 reads out the numerical data from the random number circuit 503 as random R when the start winning on the start opening switch 14a occurs, and a specific display based on the random R at the start of the fluctuation of the special symbol and the effect symbol. It is determined whether or not to make the resulting big hit display result, that is, whether to make it a big hit. Then, when it is determined to be a big hit, the gaming state is shifted to the big hit gaming state as a specific gaming state that is advantageous for the player.
また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560には、払出制御基板37(の払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370)や演出制御基板80(の演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ)とシリアル通信で信号を入出力(送受信)するためのシリアル通信回路505が内蔵されている。なお、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370や演出制御用マイクロコンピュータにも、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560とシリアル通信で信号を入出力するためのシリアル通信回路が内蔵されている(払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に内蔵されたシリアル通信回路については、図7参照)。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、2チャネルのシリアル通信回路505を内蔵しており、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370とシリアル通信を行うことが可能であるとともに、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100ともシリアル通信を行うことが可能である。ただし、この実施の形態では、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100との間のシリアル通信に関しては、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から演出制御用マイクロコンピュータに対してのみ信号が出力され、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータから遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に対しては信号が出力されない。なお、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と演出制御用マイクロコンピュータとの間の通信については、シリアル通信で行う構成に限られるわけではなく、パラレル通信で行うように構成してもよい。
In addition, in order to input / output (transmit / receive) signals to / from the game control microcomputer 560 by serial communication with the payout control board 37 (the payout control microcomputer 370) or the effect control board 80 (the effect control microcomputer). Serial communication circuit 505 is incorporated. The payout control microcomputer 370 and the effect control microcomputer also include a serial communication circuit for inputting and outputting signals in serial communication with the game control microcomputer 560 (in the payout control microcomputer 370). See Figure 7 for the built-in serial communication circuit. The game control microcomputer 560 incorporates a two-channel serial communication circuit 505 and can perform serial communication with the payout control microcomputer 370 and also performs serial communication with the effect control microcomputer 100. It is possible. However, in this embodiment, regarding serial communication with the effect control microcomputer 100, a signal is outputted only from the game control microcomputer 560 to the effect control microcomputer and from the effect control microcomputer No signal is output to the gaming control microcomputer 560. Communication between the game control microcomputer 560 and the effect control microcomputer is not limited to serial communication, and may be parallel communication.
また、RAM55は、その一部または全部が電源基板において作成されるバックアップ電源によってバックアップされている不揮発性記憶手段としてのバックアップRAMである。すなわち、遊技機に対する電力供給が停止しても、所定期間(バックアップ電源としてのコンデンサが放電してバックアップ電源が電力供給不能になるまで)は、RAM55の一部または全部の内容は保存される。特に、少なくとも、遊技状態すなわち遊技制御手段の制御状態に応じたデータ(特別図柄プロセスフラグや保留記憶数カウンタの値など)と未払出賞球数を示すデータ(具体的には、後述する賞球コマンド出力カウンタの値)は、バックアップRAMに保存される。遊技制御手段の制御状態に応じたデータとは、停電等が生じた後に復旧した場合に、そのデータにもとづいて、制御状態を停電等の発生前に復旧させるために必要なデータである。また、制御状態に応じたデータと未払出賞球数を示すデータとを遊技の進行状態を示すデータと定義する。なお、この実施の形態では、RAM55の全部が、電源バックアップされているとする。
In addition, the RAM 55 is a backup RAM as a non-volatile storage means backed up by a backup power source, part or all of which is created on the power supply substrate. That is, even if the power supply to the gaming machine is stopped, the content of part or all of the RAM 55 is saved for a predetermined period (until the capacitor as the backup power supply is discharged and the power supply of the backup power supply becomes impossible). In particular, data indicating at least the gaming state, that is, the control state of the gaming control means (such as the value of the special symbol process flag or the value of the pending storage number counter) and data indicating the number of unpaid award balls (specifically, the award balls described later) The value of the command output counter) is stored in the backup RAM. The data corresponding to the control state of the game control means is data necessary to restore the control state before the occurrence of a power failure or the like on the basis of the data when the power failure or the like is restored after the occurrence of a power failure or the like. Further, data corresponding to the control state and data indicating the number of unpaid prize balls are defined as data indicating the progress of the game. In this embodiment, it is assumed that all of the RAM 55 is backed up by the power supply.
遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のリセット端子には、電源基板からのリセット信号が入力される。電源基板には、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560等に供給されるリセット信号を生成するリセット回路が搭載されている。なお、リセット信号がハイレベルになると遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560等は動作可能状態になり、リセット信号がローレベルになると遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560等は動作停止状態になる。従って、リセット信号がハイレベルである期間は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560等の動作を許容する許容信号が出力されていることになり、リセット信号がローレベルである期間は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560等の動作を停止させる動作停止信号が出力されていることになる。なお、リセット回路をそれぞれの電気部品制御基板(電気部品を制御するためのマイクロコンピュータが搭載されている基板)に搭載してもよい。
A reset signal from the power supply substrate is input to the reset terminal of the game control microcomputer 560. The power supply substrate is provided with a reset circuit that generates a reset signal supplied to the game control microcomputer 560 or the like. When the reset signal goes high, the gaming control microcomputer 560 becomes operable, and when the resetting signal goes low, the gaming control microcomputer 560 goes into a stopped state. Therefore, while the reset signal is at the high level, an allowance signal for permitting the operation of the gaming control microcomputer 560 or the like is output, and the period when the reset signal is at the low level is the gaming control microcomputer. An operation stop signal for stopping the operation of 560 and the like is output. The reset circuit may be mounted on each of the electric component control boards (a board on which a microcomputer for controlling the electric parts is mounted).
さらに、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560の入力ポートには、電源基板からの電源電圧が所定値以下に低下したことを示す電源断信号が入力される。すなわち、電源基板には、遊技機において使用される所定電圧(例えば、DC30VやDC5Vなど)の電圧値を監視して、電圧値があらかじめ定められた所定値にまで低下すると(電源電圧の低下を検出すると)、その旨を示す電源断信号を出力する電源監視回路が搭載されている。なお、電源監視回路を電源基板に搭載するのではなく、バックアップ電源によって電源バックアップされる基板(例えば、主基板31)に搭載するようにしてもよい。また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560の入力ポートには、RAMの内容をクリアすることを指示するためのクリアスイッチが操作されたことを示すクリア信号(図示せず)が入力される。
Further, to the input port of the game control microcomputer 560, a power-off signal indicating that the power supply voltage from the power supply board has dropped to a predetermined value or less is input. That is, the power supply substrate monitors the voltage value of a predetermined voltage (for example, DC 30 V, DC 5 V, etc.) used in the game machine, and when the voltage value decreases to a predetermined value determined in advance A power supply monitoring circuit is mounted which outputs a power-off signal indicating that when it detects it). The power supply monitoring circuit may not be mounted on the power supply substrate, but may be mounted on a substrate (for example, the main substrate 31) which is backed up by the backup power supply. A clear signal (not shown) indicating that the clear switch for instructing to clear the contents of the RAM is operated is input to the input port of the game control microcomputer 560.
また、ゲートスイッチ32a、始動口スイッチ14a、入賞確認スイッチ14b、カウントスイッチ23、および各入賞口スイッチ29a,30aからの検出信号を基本回路53に与える入力ドライバ回路58も主基板31に搭載され、可変入賞球装置15を開閉するソレノイド16、および特別可変入賞球装置を開閉するソレノイド21を基本回路53からの指令に従って駆動する出力回路59も主基板31に搭載され、電源投入時に遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560をリセットするためのシステムリセット回路(図示せず)や、大当り遊技状態の発生を示す大当り情報等の情報出力信号を、ターミナル基板160を介して、ホールコンピュータ等の外部装置に対して出力する情報出力回路64も主基板31に搭載されている。
Further, an input driver circuit 58 for supplying a detection signal from the gate switch 32a, the start opening switch 14a, the winning confirmation switch 14b, the count switch 23, and each winning opening switch 29a, 30a to the basic circuit 53 is also mounted on the main board 31. A solenoid 16 for opening and closing the variable winning ball device 15 and an output circuit 59 for driving the solenoid 21 for opening and closing the special variable winning ball device in accordance with a command from the basic circuit 53 are also mounted on the main board 31. An information output signal such as a system reset circuit (not shown) for resetting the computer 560 or a big hit information indicating the occurrence of a big hit gaming state is output to an external device such as a hall computer via the terminal board 160. The information output circuit 64 is also mounted on the main board 31.
この実施の形態では、演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御手段(演出制御用マイクロコンピュータで構成される。)が、中継基板77を介して遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560からの演出制御コマンドを受信し、演出図柄を可変表示する演出表示装置9の表示制御を行う。
In this embodiment, the effect control means (composed of the effect control microcomputer) mounted on the effect control board 80 performs the effect control command from the game control microcomputer 560 via the relay board 77. Display control of the effect display device 9 which receives and displays the effect pattern variably is performed.
図7は、払出制御基板37および球払出装置97などの払出に関連する構成要素を示すブロック図である。図7に示すように、払出制御基板37には、払出制御用CPU371を含む払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370が搭載されている。この実施の形態では、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、1チップマイクロコンピュータであり、少なくともRAMが内蔵されている。払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370、RAM(図示せず)、払出制御用プログラムを格納したROM(図示せず)およびI/Oポート等は、払出制御手段を構成する。すなわち、払出制御手段は、払出制御用CPU371、RAMおよびROMを有する払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370と、I/Oポートとで実現される。また、I/Oポートは、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に内蔵されていてもよい。なお、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と異なり、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370が内蔵するRAMは、バックアップ電源による電源バックアップを受けていない。そのため、遊技機に対する電力供給が停止してしまうと、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370が内蔵するRAMの記憶内容は失われることになる。
FIG. 7 is a block diagram showing the components related to the dispensing, such as the dispensing control board 37 and the ball dispensing device 97. As shown in FIG. As shown in FIG. 7, a payout control microcomputer 370 including a payout control CPU 371 is mounted on the payout control board 37. In this embodiment, the payout control microcomputer 370 is a one-chip microcomputer and incorporates at least a RAM. The payout control microcomputer 370, a RAM (not shown), a ROM (not shown) storing a payout control program, an I / O port and the like constitute a payout control means. That is, the payout control means is realized by a payout control microcomputer 370 having a payout control CPU 371, a RAM and a ROM, and an I / O port. Further, the I / O port may be built in the payout control microcomputer 370. Note that, unlike the gaming control microcomputer 560, the RAM built in the payout control microcomputer 370 has not received power supply backup by the backup power supply. Therefore, when the power supply to the gaming machine is stopped, the stored contents of the RAM built in the payout control microcomputer 370 will be lost.
なお、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、所定の払出条件が成立したことにもとづいて遊技球を払い出す制御を行う。なお、所定の払出条件は、遊技領域に設けられた入賞領域(普通入賞口29,30、大入賞口、始動入賞口14)に遊技球が入賞したことや、貸し球要求がなされたことによって成立する。また、例えば、パロット機やスロットマシンなどの遊技機に適用する場合には、所定の払出条件は、遊技球やメダルの返却要求がなされたことによっても成立する。さらに、例えば、パロット機やスロットマシンなどの遊技機に適用する場合には、所定の払出条件は、図柄の停止図柄が所定の入賞図柄となったことによっても成立する。
The payout control microcomputer 370 controls the payout of the game balls based on the satisfaction of the predetermined payout condition. In addition, the predetermined payout condition is that the game ball has won in the winning area (normal winning opening 29, 30, big winning opening, starting winning opening 14) provided in the game area, or that the rental ball request is made. To establish. Further, for example, in the case of applying to a gaming machine such as a parrot machine or a slot machine, the predetermined payout condition is also satisfied by the return request of the gaming ball or the medal. Furthermore, for example, when applied to a gaming machine such as a parrot machine or a slot machine, the predetermined payout condition is also satisfied by the fact that the stop symbol of the symbol becomes a predetermined winning symbol.
球切れスイッチ187、満タンスイッチ48および払出個数カウントスイッチ301からの検出信号は、中継基板72を介して払出制御基板37のI/Oポート372fに入力される。なお、この実施の形態では、払出個数カウントスイッチ301からの検出信号は、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に入力されたあと、I/Oポート372aおよび出力回路373Bを介して主基板31に出力される。
Detection signals from the out-of-ball switch 187, the full tank switch 48, and the payout number counting switch 301 are input to the I / O port 372 f of the payout control substrate 37 via the relay substrate 72. In this embodiment, the detection signal from the payout number counting switch 301 is input to the payout control microcomputer 370 and then output to the main substrate 31 via the I / O port 372a and the output circuit 373B. .
また、払出モータ位置センサ295からの検出信号は、中継基板72を介して払出制御基板37のI/Oポート372eに入力される。払出モータ位置センサ295は、払出モータ289の回転位置を検出するための発光素子(LED)と受光素子とによるセンサであり、遊技球が詰まったこと、すなわちいわゆる球噛みを検出するために用いられる。払出制御基板37に搭載されている払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、球切れスイッチ187からの検出信号が球切れ状態を示していたり、満タンスイッチ48からの検出信号が満タン状態を示していると、球払出処理を停止する。
A detection signal from the payout motor position sensor 295 is input to the I / O port 372 e of the payout control substrate 37 via the relay substrate 72. The payout motor position sensor 295 is a sensor based on a light emitting element (LED) and a light receiving element for detecting the rotational position of the payout motor 289, and is used to detect that the gaming ball is clogged, ie . The payout control microcomputer 370 mounted on the payout control board 37 indicates that the detection signal from the out-of-ball switch 187 indicates the out-of-sphere state, and the detection signal from the full-tank switch 48 indicates the full-tank state. And stop the ball payout process.
さらに、満タンスイッチ48からの検出信号が満タン状態を示していると、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、打球発射装置からの球発射を停止させるために、発射基板90に対してローレベルの満タン信号を出力する。発射基板90のAND回路91が出力する発射モータ94への発射モータ信号は、発射基板90から発射モータ94に伝えられる。払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370からの満タン信号は、発射基板90に搭載されたAND回路91の入力側の一方に入力され、駆動信号生成回路92からの駆動信号(発射モータ94を駆動するための信号であって、電源基板からの電源を供給する役割を果たす信号である。)は、AND回路91の入力側の他方に入力される。そして、AND回路91の発射モータ信号が発射モータ94に入力される。すなわち、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370が満タン信号を出力している間は、発射モータ94への発射モータ信号の出力が停止される。払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370が満タン信号を出力している間であっても、発射モータ94への発射モータ信号の出力を停止せず、打球発射装置からの球発射を停止させないように構成してもよい。
Furthermore, when the detection signal from the full tank switch 48 indicates the full tank condition, the payout control microcomputer 370 sets the low level to the firing base plate 90 to stop the ball firing from the ball striking launcher. Output a full signal. The launch motor signal to the launch motor 94 output from the AND circuit 91 of the launch substrate 90 is transmitted from the launch substrate 90 to the launch motor 94. The full signal from the payout control microcomputer 370 is input to one of the input sides of the AND circuit 91 mounted on the launch substrate 90, and the drive signal from the drive signal generation circuit 92 (for driving the launch motor 94 The signal, which serves to supply power from the power supply substrate, is input to the other of the input sides of the AND circuit 91. Then, the firing motor signal of the AND circuit 91 is input to the firing motor 94. That is, while the payout control microcomputer 370 outputs the full signal, the output of the firing motor signal to the firing motor 94 is stopped. Even while the dispensing control microcomputer 370 outputs a full signal, the output of the firing motor signal to the firing motor 94 is not stopped, and the ball firing from the ball striking device is not stopped. May be
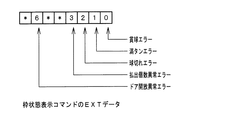
払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370には、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560とシリアル通信で信号を入出力(送受信)するためのシリアル通信回路380が内蔵されている。この実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370とは、シリアル通信回路505,380を介して、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との間の接続確認を行うために、一定の間隔(例えば1秒)で払出制御コマンド(接続確認コマンド、接続OKコマンド)をやり取り(送受信)している。例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、シリアル通信回路505を介して、一定の間隔で接続確認を行うための接続確認コマンドを送信し、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560からの接続確認コマンドを受信した場合、その旨を通知する接続OKコマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。また、例えば、入賞が発生した場合には、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、払い出すべき賞球個数を示すデータを賞球個数コマンドの下位4ビットに設定し、当該設定がなされた賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。そして、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球個数を受け付けたことを示す賞球個数受付コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。さらに、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球払出動作が終了すると、賞球終了を示賞球終了コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。なお、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球払出動作を終了するまでの間、一定の間隔で賞球準備中コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。また、所定のエラー(球貸し、満タン、球切れなどのエラー)が発生した場合には、エラーの内容を示すデータを、接続OKコマンドや賞球準備中コマンドの下位4ビットを異ならせることにより設定し、当該設定がなされた接続OKコマンドや賞球準備中コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。なお、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370におけるシリアル通信による具体的な信号のやり取りについては、図30〜図37において詳述する。
The payout control microcomputer 370 incorporates a serial communication circuit 380 for inputting / outputting (transmitting / receiving) signals in serial communication with the game control microcomputer 560. In this embodiment, the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 are connected between the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 via the serial communication circuits 505 and 380. In order to confirm, a delivery control command (connection confirmation command, connection OK command) is exchanged (transmitted / received) at a fixed interval (for example, one second). For example, the gaming control microcomputer 560 transmits a connection confirmation command for performing connection confirmation at regular intervals via the serial communication circuit 505, and the payout control microcomputer 370 receives the connection from the gaming control microcomputer 560. When the connection confirmation command of is received, a connection OK command notifying that effect is transmitted to the game control microcomputer 560. Also, for example, when a winning occurs, the gaming control microcomputer 560 sets data indicating the number of prize balls to be paid out to the lower 4 bits of the prize ball number command, and the number of prize balls for which the setting is made. The command is sent to the dispensing control microcomputer 370. Then, the payout control microcomputer 370 transmits a winning ball number reception command indicating that the number of winning balls has been received to the game control microcomputer 560. Further, the payout control microcomputer 370 transmits an award ball end command indicating the end of the award ball to the game control microcomputer 560 when the award ball payout operation is completed. The payout control microcomputer 370 transmits a prize ball preparing command to the game control microcomputer 560 at fixed intervals until the prize ball payout operation is completed. In addition, when a predetermined error (error such as ball rental, full tank, ball breakage, etc.) occurs, the data indicating the content of the error should be made different in the lower 4 bits of the connection OK command or the prize ball preparing command. Setting, and the connection OK command and the prize ball preparing command in which the setting has been made are transmitted to the game control microcomputer 560. Specific signal exchange by serial communication in microcomputer 560 for game control and microcomputer 370 for payout control will be described in detail with reference to FIGS.
また、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、出力ポート372cを介して、7セグメントLEDによるエラー表示用LED374にエラー信号を出力する。なお、払出制御基板37の入力ポート372fには、エラー状態を解除するためのエラー解除スイッチ375からの検出信号が入力される。エラー解除スイッチ375は、ソフトウェアリセットによってエラー状態を解除するために用いられる。
Further, the payout control microcomputer 370 outputs an error signal to the error display LED 374 by the 7-segment LED through the output port 372 c. A detection signal from an error release switch 375 for releasing an error state is input to the input port 372f of the payout control board 37. The error release switch 375 is used to release an error state by software reset.
さらに、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370からの払出モータ289への駆動信号は、出力ポート372aおよび中継基板72を介して球払出装置97の払出機構部分における払出モータ289に伝えられる。なお、出力ポート372aの外側に、ドライバ回路(モータ駆動回路)が設置されているが、図7では記載省略されている。
Further, a drive signal to the dispensing motor 289 from the dispensing control microcomputer 370 is transmitted to the dispensing motor 289 in the dispensing mechanism portion of the ball dispensing device 97 through the output port 372 a and the relay board 72. Although a driver circuit (motor drive circuit) is installed outside the output port 372a, it is omitted in FIG.
遊技機に隣接して設置されているカードユニット50には、カードユニット制御用マイクロコンピュータが搭載されている。また、カードユニット50には、使用可表示ランプ、連結台方向表示器、カード投入表示ランプおよびカード挿入口が設けられている。インタフェース基板(中継基板)66には、打球供給皿3の近傍に設けられている度数表示LED60、球貸し可LED61、球貸しスイッチ62および返却スイッチ63が接続される。
A card unit control microcomputer is mounted on the card unit 50 installed adjacent to the gaming machine. In addition, the card unit 50 is provided with an availability indicator lamp, a connecting base direction indicator, a card insertion indicator lamp and a card slot. Connected to the interface board (relay board) 66 are a frequency display LED 60 provided near the ball hitting supply tray 3, a ball lendable LED 61, a ball lend switch 62 and a return switch 63.
インタフェース基板66からカードユニット50には、遊技者の操作に応じて、球貸しスイッチ62が操作されたことを示す球貸しスイッチ信号および返却スイッチ63が操作されたことを示す返却スイッチ信号が与えられる。また、カードユニット50からインタフェース基板66には、プリペイドカードの残高を示すカード残高表示信号および球貸し可表示信号が与えられる。カードユニット50と払出制御基板37の間では、接続信号(VL信号)、ユニット操作信号(BRDY信号)、球貸し要求信号(BRQ信号)、球貸し完了信号(EXS信号)およびパチンコ機動作信号(PRDY信号)が入力ポート372fおよび出力ポート372dを介して送受信される。カードユニット50と払出制御基板37の間には、インタフェース基板66が介在している。よって、接続信号(VL信号)等の信号は、図7に示すように、インタフェース基板66を介してカードユニット50と払出制御基板37の間で送受信されることになる。
From interface board 66 to card unit 50, a ball lending switch signal indicating that ball lending switch 62 is operated and a return switch signal indicating that return switch 63 is operated are given in response to the player's operation. . In addition, a card balance display signal indicating a balance of the prepaid card and a sphere lendable display signal are provided from the card unit 50 to the interface board 66. Between the card unit 50 and the payout control board 37, connection signal (VL signal), unit operation signal (BRDY signal), ball lending request signal (BRQ signal), ball lending completion signal (EXS signal) and pachinko machine operation signal ( The PRDY signal is transmitted and received through the input port 372 f and the output port 372 d. An interface board 66 is interposed between the card unit 50 and the payout control board 37. Therefore, signals such as connection signals (VL signals) are transmitted and received between the card unit 50 and the payout control board 37 through the interface board 66 as shown in FIG.
パチンコ遊技機1の電源が投入されると、払出制御基板37に搭載されている払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、カードユニット50にPRDY信号を出力する。また、カードユニット制御用マイクロコンピュータは、電源が投入されると、VL信号を出力する。払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、VL信号の入力状態によってカードユニット50の接続状態/未接続状態を判定する。カードユニット50においてカードが受け付けられ、球貸しスイッチが操作され球貸しスイッチ信号が入力されると、カードユニット制御用マイクロコンピュータは、払出制御基板37にBRDY信号を出力する。この時点から所定の遅延時間が経過すると、カードユニット制御用マイクロコンピュータは、払出制御基板37にBRQ信号を出力する。
When the pachinko gaming machine 1 is powered on, the payout control microcomputer 370 mounted on the payout control board 37 outputs a PRDY signal to the card unit 50. In addition, the card unit control microcomputer outputs a VL signal when the power is turned on. The payout control microcomputer 370 determines the connection state / non-connection state of the card unit 50 based on the input state of the VL signal. When a card is accepted in the card unit 50, the ball lending switch is operated, and the ball lending switch signal is input, the card unit control microcomputer outputs the BRDY signal to the payout control board 37. When a predetermined delay time has elapsed from this time point, the card unit control microcomputer outputs a BRQ signal to the payout control board 37.
そして、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、カードユニット50に対するEXS信号を立ち上げ、カードユニット50からのBRQ信号の立ち下がりを検出すると、払出モータ289を駆動し、所定個の貸し球を遊技者に払い出す。そして、払出が完了したら、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、カードユニット50に対するEXS信号を立ち下げる。その後、カードユニット50からのBRDY信号がオン状態でないことを条件に、遊技制御手段から払出指令信号を受けると賞球払出制御を実行する。
Then, the payout control microcomputer 370 raises the EXS signal to the card unit 50, and when detecting the fall of the BRQ signal from the card unit 50, drives the payout motor 289 to make the predetermined number of rental balls for the player. Pay out. Then, when the payout is completed, the payout control microcomputer 370 lowers the EXS signal to the card unit 50. Thereafter, on the condition that the BRDY signal from the card unit 50 is not in the on state, when the payout command signal is received from the game control means, the prize ball payout control is executed.
カードユニット50で用いられる電源電圧AC24Vは払出制御基板37から供給される。すなわち、カードユニット50に対する電源基板910からの電力供給は、払出制御基板37およびインタフェース基板66を介して行われる。この例では、インタフェース基板66内に配されているカードユニット50に対するAC24Vの電源供給ラインに、カードユニット50を保護するためのヒューズが設けられ、カードユニット50に所定電圧以上の電圧が供給されることが防止される。
The power supply voltage AC 24 V used in the card unit 50 is supplied from the payout control board 37. That is, power supply from the power supply substrate 910 to the card unit 50 is performed via the payout control substrate 37 and the interface substrate 66. In this example, a fuse for protecting the card unit 50 is provided on the AC 24 V power supply line for the card unit 50 disposed in the interface board 66, and a voltage higher than a predetermined voltage is supplied to the card unit 50. Is prevented.
また、この実施の形態では、カードユニット50が遊技機とは別体として遊技機に隣接して設置されている場合を例にするが、カードユニット50は遊技機と一体化されていてもよい。また、コイン投入に応じてその金額に応じた遊技球が貸し出されるような場合でも本発明を適用できる。
Also, in this embodiment, the case where the card unit 50 is installed adjacent to the gaming machine as a separate body from the gaming machine is exemplified, but the card unit 50 may be integrated with the gaming machine . Further, the present invention can be applied to the case where a gaming ball according to the amount is lent out in response to coin insertion.
また、ガラス扉枠2の状態を検出するドア開放センサ155(図3参照)の検出信号が、払出制御基板37に入力される。払出制御基板37において、ドア開放センサ155の検出信号は、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370には入力されず、払出制御基板37上を分岐して主基板31に出力される。なお、払出制御基板37上で分岐した後、出力回路373Bを介して主基板31に出力されるようにしてもよい。また、ドア開放センサ155の検出信号を払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に入力するようにし、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370を介してドア開放信号を主基板31に出力するようにしてもよい。
Further, a detection signal of a door opening sensor 155 (see FIG. 3) for detecting the state of the glass door frame 2 is input to the payout control substrate 37. In the payout control substrate 37, the detection signal of the door opening sensor 155 is not input to the payout control microcomputer 370, but is branched on the payout control substrate 37 and output to the main substrate 31. Alternatively, after being branched on the payout control substrate 37, the signal may be output to the main substrate 31 via the output circuit 373B. Alternatively, the detection signal of the door opening sensor 155 may be input to the payout control microcomputer 370, and the door opening signal may be output to the main substrate 31 via the payout control microcomputer 370.
図8は、中継基板77、演出制御基板80、ランプドライバ基板35および音声出力基板70の回路構成例を示すブロック図である。なお、図8に示す例では、ランプドライバ基板35および音声出力基板70には、マイクロコンピュータは搭載されていないが、マイクロコンピュータを搭載してもよい。また、ランプドライバ基板35および音声出力基板70を設けずに、演出制御に関して演出制御基板80のみを設けてもよい。
FIG. 8 is a block diagram showing an example of the circuit configuration of the relay board 77, the effect control board 80, the lamp driver board 35, and the sound output board 70. As shown in FIG. Although the microcomputer is not mounted on the lamp driver substrate 35 and the audio output substrate 70 in the example shown in FIG. 8, a microcomputer may be mounted. Further, only the effect control substrate 80 may be provided for effect control without providing the lamp driver substrate 35 and the sound output substrate 70.
演出制御基板80は、演出制御用CPU101a、および演出図柄プロセスフラグ等の演出に関する情報を記憶するRAMを含む演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100を搭載している。なお、RAMは外付けであってもよい。この実施の形態では、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100におけるRAMは電源バックアップされていない。演出制御基板80において、演出制御用CPU101aは、内蔵または外付けのROM(図示せず)に格納されたプログラムに従って動作する。また、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560とシリアル通信で信号を入出力(送受信)するシリアル通信回路101bを内蔵している。また、演出制御用CPU101aは、演出制御コマンドにもとづいて、VDP(ビデオディスプレイプロセッサ)109に演出表示装置9の表示制御を行わせる。
The effect control board 80 is mounted with an effect control microcomputer 100 including a effect control CPU 101a and a RAM for storing information on effects such as an effect pattern process flag and the like. The RAM may be externally attached. In this embodiment, the RAM in the effect control microcomputer 100 is not backed up by a power supply. In the effect control board 80, the effect control CPU 101a operates in accordance with a program stored in a built-in or external ROM (not shown). Further, the effect control microcomputer 100 incorporates a serial communication circuit 101b that inputs / outputs (transmits / receives) signals to / from the game control microcomputer 560 in serial communication. Further, the effect control CPU 101a causes the VDP (video display processor) 109 to perform display control of the effect display device 9 based on the effect control command.
この実施の形態では、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100と共動して演出表示装置9の表示制御を行うVDP109が演出制御基板80に搭載されている。VDP109は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100とは独立したアドレス空間を有し、そこにVRAMをマッピングする。VRAMは、画像データを展開するためのバッファメモリである。そして、VDP109は、VRAM内の画像データをフレームメモリを介して演出表示装置9に出力する。
In this embodiment, a VDP 109 for controlling display of the effect display device 9 in cooperation with the effect control microcomputer 100 is mounted on the effect control board 80. The VDP 109 has an address space independent of the effect control microcomputer 100, and maps a VRAM there. VRAM is a buffer memory for expanding image data. Then, the VDP 109 outputs the image data in the VRAM to the effect display device 9 via the frame memory.
演出制御用CPU101aは、受信した演出制御コマンドに従ってCGROM(図示せず)から必要なデータを読み出すための指令をVDP109に出力する。CGROMは、演出表示装置9に表示されるキャラクタ画像データや動画像データ、具体的には、人物、文字、図形や記号等(演出図柄を含む)、および背景画像のデータをあらかじめ格納しておくためのROMである。VDP109は、演出制御用CPU101aの指令に応じて、CGROMから画像データを読み出す。そして、VDP109は、読み出した画像データにもとづいて表示制御を実行する。
The effect control CPU 101a outputs, to the VDP 109, an instruction for reading out necessary data from a CGROM (not shown) in accordance with the received effect control command. The CGROM stores in advance character image data and moving image data displayed on the effect display device 9, specifically, data of a person, characters, figures, symbols, etc. (including effect patterns), and background image data. It is a ROM for. The VDP 109 reads image data from the CGROM in accordance with an instruction from the effect control CPU 101a. Then, the VDP 109 executes display control based on the read image data.
さらに、演出制御用CPU101aは、出力ポート105を介してランプドライバ基板35に対してLEDを駆動する信号を出力する。また、演出制御用CPU101aは、出力ポート104を介して音声出力基板70に対して音番号データを出力する。
Further, the effect control CPU 101 a outputs a signal for driving the LED to the lamp driver board 35 via the output port 105. Further, the effect control CPU 101 a outputs sound number data to the audio output board 70 via the output port 104.
ランプドライバ基板35において、LEDを駆動する信号は、入力ドライバ351を介してLEDドライバ352に入力される。LEDドライバ352は、LEDを駆動する信号にもとづいて枠LED28などの枠側に設けられている発光体に電流を供給する。また、遊技盤側に設けられている装飾LED25に電流を供給する。
In the lamp driver substrate 35, a signal for driving the LED is input to the LED driver 352 via the input driver 351. The LED driver 352 supplies current to a light emitter provided on the frame side such as the frame LED 28 based on a signal for driving the LED. In addition, current is supplied to the decoration LED 25 provided on the game board side.
音声出力基板70において、音番号データは、入力ドライバ702を介して音声合成用IC703に入力される。音声合成用IC703は、音番号データに応じた音声や効果音を発生し増幅回路705に出力する。増幅回路705は、音声合成用IC703の出力レベルを、ボリューム706で設定されている音量に応じたレベルに増幅した音声信号をスピーカ27に出力する。音声データROM704には、音番号データに応じた制御データが格納されている。音番号データに応じた制御データは、所定期間(例えば演出図柄の変動期間)における効果音または音声の出力態様を時系列的に示すデータの集まりである。
In the voice output board 70, the sound number data is input to the voice synthesis IC 703 via the input driver 702. The speech synthesis IC 703 generates speech and sound effects according to the sound number data and outputs the speech and the sound effects to the amplification circuit 705. The amplifier circuit 705 outputs to the speaker 27 an audio signal obtained by amplifying the output level of the voice synthesis IC 703 to a level according to the volume set by the volume 706. The voice data ROM 704 stores control data corresponding to the sound number data. The control data corresponding to the sound number data is a collection of data indicating in time series the output mode of the sound effect or the sound in a predetermined period (for example, a fluctuation period of the effect pattern).
図9は、主基板31における回路構成および主基板31から演出制御基板80に送信される演出制御コマンドの信号線を示すブロック図である。図9に示すように、この実施の形態では、主基板31が搭載する遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、演出制御信号送信用の1本の信号線を用いて、演出制御コマンド(演出制御信号)を演出制御基板80に送信する。
FIG. 9 is a block diagram showing the circuit configuration of the main board 31 and signal lines of the effect control command transmitted from the main board 31 to the effect control board 80. As shown in FIG. As shown in FIG. 9, in this embodiment, the game control microcomputer 560 mounted on the main substrate 31 uses a single signal line for effect control signal transmission to produce an effect control command (effect control signal). Is transmitted to the effect control board 80.
主基板31には、図9に示すように、始動口スイッチ14aや入賞確認スイッチ14bからの配線が接続されている。また、主基板31には、大入賞口である特別可変入賞球装置20や、その他の入賞口への遊技球の入賞等を検出するための各種スイッチ29a,30aからの配線も接続されている。さらに、主基板31には、可変入賞球装置15を開閉するソレノイド16、および特別可変入賞球装置20を開閉するソレノイド21への配線が接続されている。
As shown in FIG. 9, the main board 31 is connected to the wiring from the starting opening switch 14a and the prize confirmation switch 14b. In addition, the main substrate 31 is also connected with wiring from the special variable winning ball device 20 which is a big winning opening, and various switches 29a and 30a for detecting the winning of the game ball to the other winning openings, etc. . Furthermore, the main substrate 31 is connected to the solenoid 16 for opening and closing the variable winning ball device 15 and the wiring for the solenoid 21 for opening and closing the special variable winning ball device 20.
主基板31は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560、入力ドライバ回路58および出力回路59を搭載する。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、クロック回路501、システムリセット手段として機能するリセットコントローラ502、乱数回路503a,503b、ゲーム制御用のプログラム等を記憶するROM54、ワークメモリとして使用されるRAM55、プログラムに従って動作するCPU56、CPU56に割込要求信号(タイマ割込による割込要求信号)を送出するCTC504、払出制御基板37や演出制御基板80が備えるマイクロコンピュータと非同期シリアル通信を行うシリアル通信回路505およびI/Oポート部57を内蔵する。
The main board 31 mounts a game control microcomputer 560, an input driver circuit 58 and an output circuit 59. The game control microcomputer 560 operates according to a clock circuit 501, a reset controller 502 functioning as a system reset means, random number circuits 503a and 503b, a ROM 54 for storing a program for game control, etc., a RAM 55 used as a work memory, CPU 56, CTC 504 for sending an interrupt request signal (interrupt request signal due to timer interrupt) to CPU 56, serial communication circuit 505 for performing asynchronous serial communication with a microcomputer provided in payout control board 37 and effect control board 80, and I / I. An O port unit 57 is incorporated.
なお、この実施の形態では、シリアル通信回路505を内蔵するマイクロコンピュータを搭載した基板(例えば、主基板31)とは異なる基板(例えば、払出制御基板37や演出制御基板80)のマイクロコンピュータとの通信にシリアル通信回路505を用いる場合を説明するが、シリアル通信回路505は、シリアル通信回路505を内蔵するマイクロコンピュータを搭載した基板が備える別のマイクロコンピュータとシリアル通信を行ってもよい。例えば、同じ構成の2つのマイクロコンピュータが同じ基板に搭載されている場合に、各マイクロコンピュータが内蔵するシリアル通信回路が相互にシリアル通信を行ってもよい。
In this embodiment, the microcomputer of a board (for example, the payout control board 37 or the effect control board 80) different from the board (for example, the main board 31) on which the microcomputer incorporating the serial communication circuit 505 is mounted. Although the case of using the serial communication circuit 505 for communication will be described, the serial communication circuit 505 may perform serial communication with another microcomputer provided on a substrate on which a microcomputer incorporating the serial communication circuit 505 is mounted. For example, when two microcomputers having the same configuration are mounted on the same substrate, serial communication circuits built in each microcomputer may perform serial communication with each other.
クロック回路501は、システムクロック信号を27(=128)分周して生成した所定の周期の基準クロック信号CLKを、各乱数回路503a,503bに出力する。リセットコントローラ502は、ローレベルの信号が一定期間入力されたとき、CPU56および各乱数回路503a,503bに所定の初期化信号を出力して、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560をシステムリセットする。
The clock circuit 501 outputs a reference clock signal CLK of a predetermined cycle generated by dividing the system clock signal by 2 7 (= 128) to the random number circuits 503 a and 503 b. The reset controller 502 outputs a predetermined initialization signal to the CPU 56 and the random number circuits 503a and 503b when the low level signal is input for a certain period, and resets the game control microcomputer 560 as a system.
また、この実施の形態では、図9に示すように、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、発生可能な乱数の値の範囲が異なる2つの乱数回路503a,503bを搭載する。乱数回路503aは、12ビットの疑似乱数を発生する乱数回路(以下、12ビット乱数回路ともいう)である。12ビット乱数回路503aは、12ビットで発生できる範囲(すなわち、0から4095までの範囲)の値の乱数を発生する機能を備える。また、乱数回路503bは、16ビットの疑似乱数を発生する乱数回路(以下、16ビット乱数回路ともいう)である。16ビット乱数回路503bは、16ビットで発生できる範囲(すなわち、0から65535までの範囲)の値の乱数を発生する機能を備える。なお、この実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が2つの乱数回路を内蔵する場合を説明するが、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、3以上の乱数回路を内蔵してもよい。また、この実施の形態では、12ビット乱数回路503aおよび16ビット乱数回路503bを包括的に表現する場合、または、12ビット乱数回路503aと16ビット乱数回路503bとのうちいずれかを指す場合に、乱数回路503という。
Further, in this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 9, the game control microcomputer 560 is mounted with two random number circuits 503a and 503b having different ranges of possible random numbers. The random number circuit 503a is a random number circuit (hereinafter also referred to as a 12-bit random number circuit) that generates a 12-bit pseudo random number. The 12-bit random number circuit 503a has a function of generating random numbers in a range that can be generated by 12 bits (that is, in the range of 0 to 4095). The random number circuit 503b is a random number circuit (hereinafter also referred to as a 16-bit random number circuit) that generates a 16-bit pseudo random number. The 16-bit random number circuit 503 b has a function of generating random numbers in a range that can be generated by 16 bits (that is, in the range of 0 to 65535). In this embodiment, although the case where the game control microcomputer 560 incorporates two random number circuits is described, the game control microcomputer 560 may incorporate three or more random number circuits. Further, in this embodiment, when expressing the 12-bit random number circuit 503a and the 16-bit random number circuit 503b comprehensively, or when referring to either of the 12-bit random number circuit 503a and the 16-bit random number circuit 503b, It is called a random number circuit 503.
次に、シリアル通信回路505の構成について説明する。シリアル通信回路505は、全二重方式、非同期方式および標準NRZ(ノンリターンゼロ)符号化を用いたデータフォーマットで、各制御基板(例えば、払出制御基板37や演出制御基板80)のマイクロコンピュータとシリアル通信を行う。シリアル通信回路505は、各制御基板のマイクロコンピュータに各種データ(例えば、賞球個数コマンドや演出制御コマンド)を送信する送信部と、各制御基板のマイクロコンピュータからの各種データ(例えば、賞球ACKコマンド)を受信する受信部とを含む。
Next, the configuration of the serial communication circuit 505 will be described. The serial communication circuit 505 is a data format using a full duplex system, an asynchronous system and standard NRZ (non-return zero) encoding, and with a microcomputer of each control board (for example, the payout control board 37 and the effect control board 80) Perform serial communication. The serial communication circuit 505 is a transmission unit that transmits various data (for example, award ball number command and effect control command) to the microcomputer of each control board, and various data from the microcomputer of each control board (for example, the award ball ACK) And a receiver for receiving the command.
図10は、シリアル通信回路505の送信部の構成例を示すブロック図である。また、図11は、シリアル通信回路505の受信部の構成例を示すブロック図である。シリアル通信回路505は、ボーレートレジスタ702、ボーレート生成回路703、2つのステータスレジスタ705,706、3つの制御レジスタ707,708,709、送信データレジスタ710、受信データレジスタ711、送信用シフトレジスタ712、受信用シフトレジスタ713、割り込み制御回路714、送信フォーマット/パリティ生成回路715および受信フォーマット/パリティチェック回路716を含む。また、図10に示すように、シリアル通信回路505の送信部は、これらの構成要素のうち、ボーレートレジスタ702、ボーレート生成回路703、ステータスレジスタA705、制御レジスタ707,708,709、送信データレジスタ710、送信用シフトレジスタ712、割り込み制御回路714および送信フォーマット/パリティ生成回路715によって構成される。また、図11に示すように、シリアル通信回路505の受信部は、これらの構成要素のうち、ボーレートレジスタ702、ボーレート生成回路703、ステータスレジスタ705,706、制御レジスタ707,708,709、受信データレジスタ711、受信用シフトレジスタ713、割り込み制御回路714および受信フォーマット/パリティチェック回路716によって構成される。
FIG. 10 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of the transmission unit of the serial communication circuit 505. FIG. 11 is a block diagram showing an example of the configuration of the reception unit of the serial communication circuit 505. The serial communication circuit 505 includes a baud rate register 702, a baud rate generation circuit 703, two status registers 705 and 706, three control registers 707, 708 and 709, a transmission data register 710, a reception data register 711, a transmission shift register 712, and reception. , Shift control circuit 714, transmission format / parity generation circuit 715, and reception format / parity check circuit 716. Further, as shown in FIG. 10, the transmission unit of the serial communication circuit 505 includes the baud rate register 702, the baud rate generation circuit 703, the status register A 705, the control registers 707, 708, and 709, and the transmission data register 710 among these components. , A transmission shift register 712, an interrupt control circuit 714, and a transmission format / parity generation circuit 715. Further, as shown in FIG. 11, the reception unit of the serial communication circuit 505 includes, among these components, the baud rate register 702, the baud rate generation circuit 703, the status registers 705 and 706, the control registers 707, 708 and 709, and received data. A register 711, a reception shift register 713, an interrupt control circuit 714, and a reception format / parity check circuit 716 are provided.
なお、シリアル通信回路505において、送信部と受信部とは、実際には、共通の回路を用いて構成される。そして、シリアル通信回路505は、上記に示したように、シリアル通信回路505の各構成要素を使い分けて用いることによって、送信回路又は受信回路として機能する。
In the serial communication circuit 505, the transmitting unit and the receiving unit are actually configured using a common circuit. The serial communication circuit 505 functions as a transmitting circuit or a receiving circuit by selectively using each component of the serial communication circuit 505 as described above.
まず、シリアル通信回路505が各制御基板が搭載するマイクロコンピュータと送受信するデータのデータフォーマットを説明する。図12は、シリアル通信回路505が各制御基板に搭載されるマイクロコンピュータと送受信するデータのデータフォーマットの例を示す説明図である。図12に示すように、シリアル通信回路505が送受信するデータのデータフォーマットは、スタートビット、データおよびストップビットを1フレームとして構成される。また、シリアル通信回路505が送受信するデータのデータ長は、後述するシリアル通信回路設定処理において初期設定を行えば、8ビットまたは9ビットのいずれかに設定できる。図12(a)は、データ長を8ビットに設定した場合のデータフォーマットの例である。また、図12(b)は、データ長を9ビットに設定した場合のデータフォーマットの例である。
First, a data format of data transmitted / received by the serial communication circuit 505 to / from a microcomputer mounted on each control board will be described. FIG. 12 is an explanatory view showing an example of a data format of data transmitted / received to / from a microcomputer mounted on each control board by the serial communication circuit 505. As shown in FIG. As shown in FIG. 12, the data format of data transmitted and received by the serial communication circuit 505 is configured such that the start bit, the data and the stop bit are one frame. Further, the data length of the data transmitted and received by the serial communication circuit 505 can be set to either 8 bits or 9 bits if the initial setting is performed in the serial communication circuit setting process described later. FIG. 12A shows an example of the data format when the data length is set to 8 bits. Further, FIG. 12 (b) is an example of a data format in the case where the data length is set to 9 bits.
図12に示すように、シリアル通信回路505が送受信するデータのデータフォーマットは、ハイレベル(論理「1」)のアイドルラインのあとに、1フレームの始まりであることを示すスタートビット(論理「0」)を含む。また、データフォーマットは、スタートビットのあとに、8ビットまたは9ビットの送受信データを含む。そして、データフォーマットは、送受信データのあとに、1フレームの終わりであることを示すストップビット(論理「1」)を含む。
As shown in FIG. 12, the data format of data transmitted / received by the serial communication circuit 505 is a start bit (logic "0" indicating that it is the start of one frame after an idle line at high level (logic "1"). ")including. The data format also includes 8-bit or 9-bit transmit / receive data after the start bit. Then, the data format includes, after the transmission / reception data, a stop bit (logic "1") indicating that the end of one frame is reached.
シリアル通信回路505は、図12に示すデータフォーマットに従って、送受信データの最下位ビット(ビット0)から先にデータを送受信する。また、後述するシリアル通信回路設定処理において初期設定を行えば、送受信データにパリティビットを付加するように設定することもできる。パリティビットを付加するように設定した場合、送受信データの最上位ビットがパリティビット(奇数パリティまたは偶数パリティ)として用いられる。例えば、データ長を8ビットに設定した場合、送受信データのビット7がパリティビットとして用いられる。また、例えば、データ長を9ビットに設定した場合、送受信データのビット8がパリティビットとして用いられる。
The serial communication circuit 505 transmits and receives data first from the least significant bit (bit 0) of transmission / reception data in accordance with the data format shown in FIG. In addition, if initialization is performed in serial communication circuit setting processing described later, parity bits can be set to be added to transmission / reception data. When the parity bit is set to be added, the most significant bit of transmission / reception data is used as a parity bit (odd parity or even parity). For example, when the data length is set to 8 bits, bit 7 of transmission / reception data is used as a parity bit. Also, for example, when the data length is set to 9 bits, bit 8 of transmission / reception data is used as a parity bit.
ボーレート生成回路703は、クロック回路501が出力するクロック信号およびボーレートレジスタ702に設定されている設定値(ボーレート設定値ともいう)にもとづいて、シリアル通信回路505が用いるボーレートを生成する。この場合、ボーレート生成回路703は、クロック信号およびボーレート設定値にもとづいて、所定の計算式を用いてボーレートを求める。例えば、ボーレート生成回路703は、式(1)を用いて、シリアル通信回路505が用いるボーレートを求める。
The baud rate generation circuit 703 generates a baud rate used by the serial communication circuit 505 based on the clock signal output from the clock circuit 501 and the setting value (also referred to as a baud rate setting value) set in the baud rate register 702. In this case, the baud rate generation circuit 703 obtains the baud rate using a predetermined calculation formula based on the clock signal and the baud rate setting value. For example, the baud rate generation circuit 703 obtains the baud rate used by the serial communication circuit 505 by using the equation (1).
ボーレート=クロック周波数/(ボーレート設定値×16) 式(1)
Baud rate = Clock frequency / (Baud rate setting value x 16) Equation (1)
図13は、ボーレートレジスタ702の例を示す説明図である。ボーレートレジスタ702は、ボーレート生成回路703が生成するボーレートの値を指定するための所定の設定値を設定するレジスタである。例えば、ボーレートレジスタ702が式(1)を用いてボーレートを求めるものとし、クロック周波数が3MHzであるとする。この場合、所望の目標ボーレートが1200bpsであるとすると、ボーレートレジスタ702に設定値「156」を設定する。すると、ボーレート生成回路703は、クロック周波数「3MHz」およびボーレート設定値「156」にもとづいて、式(1)を用いて、ボーレート「1201.92bps」を生成する。ボーレートレジスタ702は、16ビットレジスタであり、初期値が「0(=00h)」に設定されている。また、ボーレートレジスタ702は、ビット0〜ビット12が書込および読出ともに可能な状態に構成されている。また、ボーレートレジスタ702は、ビット13〜ビット15が書込および読出ともに不可能な状態に構成されている。したがって、ボーレートレジスタ702のビット13〜ビット15に値を書き込む制御を行っても無効とされ、ビット13〜ビット15から読み出す値は全て「0(=000b)」である。
FIG. 13 is an explanatory view showing an example of the baud rate register 702. As shown in FIG. The baud rate register 702 is a register for setting a predetermined setting value for specifying a baud rate value generated by the baud rate generation circuit 703. For example, assume that the baud rate register 702 obtains the baud rate using equation (1), and the clock frequency is 3 MHz. In this case, assuming that the desired target baud rate is 1200 bps, the set value "156" is set in the baud rate register 702. Then, the baud rate generation circuit 703 generates the baud rate "1201.92 bps" using the equation (1) based on the clock frequency "3 MHz" and the baud rate setting value "156". The baud rate register 702 is a 16-bit register, and its initial value is set to “0 (= 00 h)”. Further, the baud rate register 702 is configured in a state where bit 0 to bit 12 can be written and read. Also, the baud rate register 702 is configured such that bits 13 to 15 can not be written or read. Therefore, even if control is performed to write a value to bits 13 to 15 of the baud rate register 702, it is invalidated, and all values read from bits 13 to 15 are "0 (= 000b)".
図14(A)は、制御レジスタA707の例を示す説明図である。制御レジスタA707は、シリアル通信回路505の通信フォーマットを設定するレジスタである。この実施の形態では、制御レジスタA707の各ビットの値が設定されることによって、シリアル通信回路505の通信フォーマットが設定される。制御レジスタA707には、送受信データのデータ形式や各種通信方式等の通信フォーマットを設定するための通信フォーマット設定データが設定される。図14(A)に示すように、制御レジスタA707は、8ビットレジスタであり、初期値が「0(=00h)」に設定されている。また、制御レジスタA707は、ビット0〜ビット4が書込および読出ともに可能な状態に構成されている。また、制御レジスタA707は、ビット5〜ビット7が書込および読出ともに不可能な状態に構成されている。したがって、制御レジスタA707のビット5〜ビット7に値を書き込む制御を行っても無効とされ、ビット5〜ビット7から読み出す値は全て「0(=000b)」である。
FIG. 14A is an explanatory view showing an example of the control register A 707. The control register A 707 is a register for setting the communication format of the serial communication circuit 505. In this embodiment, the communication format of the serial communication circuit 505 is set by setting the value of each bit of the control register A 707. In the control register A 707, communication format setting data for setting communication formats such as the data format of transmission / reception data and various communication methods are set. As shown in FIG. 14A, the control register A 707 is an 8-bit register, and its initial value is set to “0 (= 00 h)”. Further, control register A 707 is configured such that bits 0 to 4 can be written and read. Further, control register A 707 is configured such that bits 5 to 7 can not be written or read. Therefore, even if control is performed to write a value to bit 5 to bit 7 of the control register A 707, it is invalidated, and all values read from bit 5 to bit 7 are “0 (= 000 b)”.
図14(B)は、制御レジスタA707に設定される通信フォーマット設定データの一例の説明図である。図14(B)に示すように、制御レジスタA707のビット4(ビット名「M」)には、送受信するデータのデータ長を設定するための設定データが設定される。図14(B)に示すように、ビット4を「0」に設定することによって、送受信データのデータ長が8ビットに設定される。また、ビット4を「1」に設定することによって、送受信データのデータ長が9ビットに設定される。
FIG. 14B is an explanatory diagram of an example of communication format setting data set in the control register A 707. As shown in FIG. 14B, in bit 4 (bit name "M") of the control register A 707, setting data for setting the data length of the data to be transmitted and received is set. As shown in FIG. 14B, by setting bit 4 to "0", the data length of transmission / reception data is set to 8 bits. Further, by setting bit 4 to "1", the data length of transmission / reception data is set to 9 bits.
制御レジスタA707のビット3(ビット名「WAKE」)には、スタンバイ状態の受信回路(シリアル通信回路505の受信部)をウエイクアップする(オンライン状態にさせる)ウエイクアップ方式を設定するための設定データが設定される。図14(B)に示すように、ビット3を「0」に設定することによって、アイドルラインを認識したときにウエイクアップするアイドルラインウエイクアップ方式が設定される。また、ビット3を「1」に設定することによって、所定のアドレスマークを認識することによってウエイクアップするアドレスマークウエイクアップ方式が設定される。
Setting data for setting a wake-up method for waking up the reception circuit in the standby state (the reception unit of the serial communication circuit 505) to bit 3 (bit name "WAKE") of the control register A 707 Is set. As shown in FIG. 14B, by setting the bit 3 to “0”, an idle line wake-up method for waking up when an idle line is recognized is set. Also, by setting bit 3 to “1”, an address mark wake-up method is set up to wake up by recognizing a predetermined address mark.
制御レジスタA707のビット2(ビット名「ILT」)には、受信データのアイドルラインの検出方式を選択するための設定データが設定される。図14(B)に示すように、ビット2を「0」に設定することによって、受信データに含まれるスタートビットの後からアイドルラインを検出する検出方式が設定される。また、ビット2を「1」に設定することによって、受信データに含まれるストップビットの後からアイドルラインを検出する検出方式が設定される。
In bit 2 (bit name "ILT") of the control register A 707, setting data for selecting an idle line detection method for received data is set. As shown in FIG. 14B, setting bit 2 to “0” sets a detection method for detecting an idle line after the start bit included in the received data. Also, by setting bit 2 to “1”, a detection method for detecting an idle line after the stop bit included in the received data is set.
制御レジスタA707のビット1(ビット名「PE」)には、パリティ機能を使用するか否かを設定するための設定データが設定される。図14(B)に示すように、ビット1を「0」に設定することによって、パリティ機能を使用しないように設定される。また、ビット1を「1」に設定することによって、パリティ機能を使用するように設定される。
Setting data for setting whether or not to use the parity function is set in bit 1 (bit name “PE”) of the control register A 707. As shown in FIG. 14B, setting the bit 1 to “0” sets the parity function not to be used. Also, by setting bit 1 to "1", it is set to use the parity function.
制御レジスタA707のビット0(ビット名「PT」)には、パリティ機能を使用すると設定した場合のパリティの種類を設定するための設定データが設定される。図14(B)に示すように、ビット0を「0」に設定することによって、パリティの種類として偶数パリティが設定される。また、ビット0を「1」に設定することによって、パリティの種類として奇数パリティが設定される。
In bit 0 (bit name “PT”) of the control register A 707, setting data for setting the type of parity when setting to use the parity function is set. As shown in FIG. 14 (B), even parity is set as the type of parity by setting bit 0 to “0”. Also, by setting bit 0 to “1”, odd parity is set as the type of parity.
図15(A)は、制御レジスタB708の例を示す説明図である。制御レジスタB708は、シリアル通信回路505の割り込み要求を許可するか否かを設定するレジスタである。この実施の形態では、制御レジスタB708の各ビットの値が設定されることによって、シリアル通信回路505からの割り込み要求を許可するか禁止するかが設定される。制御レジスタB708には、各種割り込み要求を許可するか否かを示す割り込み要求設定データが主として設定される。なお、制御レジスタB708には、割り込み要求設定データ以外に、シリアル通信回路505の各種設定を行うための設定データも設定される。図15(A)に示すように、制御レジスタB708は、8ビットレジスタであり、初期値が「0(=00h)」に設定されている。また、制御レジスタB708は、ビット0〜ビット7が書込および読出ともに可能な状態に構成されている。
FIG. 15A is an explanatory view showing an example of the control register B 708. The control register B 708 is a register that sets whether to permit an interrupt request of the serial communication circuit 505. In this embodiment, by setting the value of each bit of the control register B 708, it is set whether the interrupt request from the serial communication circuit 505 is permitted or prohibited. In the control register B 708, interrupt request setting data indicating whether to permit various interrupt requests is mainly set. In addition to the interrupt request setting data, setting data for performing various settings of the serial communication circuit 505 is also set in the control register B 708. As shown in FIG. 15A, the control register B 708 is an 8-bit register, and its initial value is set to “0 (= 00 h)”. Further, control register B 708 is configured such that bit 0 to bit 7 can be written and read.
図15(B)は、制御レジスタB708に設定される割り込み要求設定データの一例を示す説明図である。図15(B)に示すように、制御レジスタB708のビット7(ビット名「TIE」)には、データの送信時に行う割り込み要求である送信割り込み要求を許可するか否かを示す設定データが設定される。図15(B)に示すように、ビット7を「0」に設定することによって、送信割り込み要求を禁止するように設定される。また、ビット7を「1」に設定することによって、送信割り込み要求を許可するように設定される。
FIG. 15B is an explanatory view showing an example of interrupt request setting data set in the control register B 708. As shown in FIG. As shown in FIG. 15B, in bit 7 (bit name "TIE") of control register B 708, setting data indicating whether to permit a transmission interrupt request which is an interrupt request to be issued at the time of data transmission is set. Be done. As shown in FIG. 15B, by setting the bit 7 to “0”, the transmission interrupt request is set to be inhibited. Also, by setting bit 7 to "1", it is set to permit the transmission interrupt request.
制御レジスタB708のビット6(ビット名「TCIE」)には、データの送信完了時に行う割り込み要求である送信完了割り込み要求を許可するか否かを示す設定データが設定される。図15(B)に示すように、ビット6を「0」に設定することによって、送信完了割り込み要求を禁止するように設定される。また、ビット6を「1」に設定することによって、送信完了割り込み要求を許可するように設定される。
In bit 6 (bit name "TCIE") of the control register B 708, setting data indicating whether or not to permit a transmission completion interrupt request, which is an interrupt request to be issued when data transmission is completed, is set. As shown in FIG. 15B, by setting bit 6 to “0”, the transmission completion interrupt request is set to be prohibited. Also, by setting bit 6 to "1", it is set to permit a transmission completion interrupt request.
制御レジスタB708のビット5(ビット名「RIE」)には、データの受信時に行う割り込み要求である受信割り込み要求を許可するか否かを示す設定データが設定される。図15(B)に示すように、ビット5を「0」に設定することによって、受信割り込み要求を禁止するように設定される。また、ビット5を「1」に設定することによって、受信割り込み要求を許可するように設定される。
In bit 5 (bit name "RIE") of the control register B 708, setting data indicating whether to permit a reception interrupt request, which is an interrupt request to be issued at the time of data reception, is set. As shown in FIG. 15 (B), setting bit 5 to “0” enables the reception interrupt request to be inhibited. Also, by setting bit 5 to "1", the reception interrupt request is set to be permitted.
制御レジスタB708のビット4(ビット名「ILIE」)には、受信データのアイドルラインを検出したときに行う割り込み要求であるアイドルライン割り込み要求を許可するか否かを示す設定データが設定される。図15(B)に示すように、ビット4を「0」に設定することによって、アイドルライン割り込み要求を禁止するように設定される。また、ビット4を「1」に設定することによって、アイドルライン割り込み要求を許可するように設定される。
In bit 4 (bit name "ILIE") of the control register B 708, setting data indicating whether to permit an idle line interrupt request, which is an interrupt request to be issued when an idle line of received data is detected, is set. As shown in FIG. 15B, by setting bit 4 to "0", an idle line interrupt request is set to be prohibited. It is also set to allow idle line interrupt requests by setting bit 4 to "1".
制御レジスタB708のビット3(ビット名「TE」)には、送信回路(シリアル通信回路505の送信部)を使用するか否かを示す設定データが設定される。図15(B)に示すように、ビット3を「0」に設定することによって、送信回路を使用しないように設定される。また、ビット3を「1」に設定することによって、送信回路を使用するように設定される。なお、この実施の形態では、ビット3を「1」に設定することによって、送信回路を使用する設定が行われる。このような設定は、メイン処理の初期設定(例えばステップS15a)において行われる。
In bit 3 (bit name “TE”) of the control register B 708, setting data indicating whether to use a transmission circuit (transmission unit of the serial communication circuit 505) is set. As shown in FIG. 15 (B), by setting bit 3 to “0”, the transmission circuit is set not to be used. Also, by setting bit 3 to "1", the transmission circuit is set to be used. In this embodiment, setting to use the transmission circuit is performed by setting bit 3 to "1". Such setting is performed in initial setting of the main processing (for example, step S15a).
制御レジスタB708のビット2(ビット名「RE」)には、受信回路を使用するか否かを示す設定データが設定される。図15(B)に示すように、ビット2を「0」に設定することによって、受信回路を使用しないように設定される。また、ビット2を「1」に設定することによって、受信回路を使用するように設定される。なお、この実施の形態では、ビット2を「1」に設定することによって、受信回路を使用する設定が行われる。このような設定は、メイン処理の初期設定(例えばステップS15a)において行われる。
In bit 2 (bit name “RE”) of the control register B 708, setting data indicating whether or not to use the receiving circuit is set. As shown in FIG. 15B, by setting bit 2 to “0”, the receiver circuit is set not to be used. Also, by setting bit 2 to "1", it is set to use the receiving circuit. In this embodiment, setting of the reception circuit is performed by setting bit 2 to "1". Such setting is performed in initial setting of the main processing (for example, step S15a).
制御レジスタB708のビット1(ビット名「RWU」)には、受信回路のウエイクアップ機能を使用するか否かを示す設定データが設定される。図15(B)に示すように、ビット1を「0」に設定することによって、ウエイクアップ機能を使用しないように設定される。また、ビット1を「1」に設定することによって、ウエイクアップ機能を使用するように設定される。
In bit 1 (bit name "RWU") of the control register B 708, setting data indicating whether or not to use the wakeup function of the receiving circuit is set. As shown in FIG. 15B, setting the bit 1 to “0” sets the wakeup function not to be used. Also, by setting bit 1 to "1", the wakeup function is set to be used.
制御レジスタB708のビット0(ビット名「SBK」)には、所定のブレークコード送信機能を使用するか否かを示す設定データが設定される。図15(B)に示すように、ビット1を「0」に設定することによって、ブレークコード送信機能を使用しないように設定される。また、ビット1を「1」に設定することによって、ブレークコード送信機能を使用するように設定される。ビット1を「1」に設定すると、シリアル通信回路505は、ブレークコード(例えば、「0」を連続して含む信号)を制御基板(払出制御基板37や演出制御基板80)が搭載するマイクロコンピュータに送信する。
In bit 0 (bit name “SBK”) of the control register B 708, setting data indicating whether or not to use a predetermined break code transmission function is set. As shown in FIG. 15B, setting the bit 1 to “0” makes it possible not to use the break code transmission function. Also, by setting bit 1 to "1", it is set to use the break code transmission function. When bit 1 is set to “1”, the serial communication circuit 505 is a microcomputer on which a control board (the payout control board 37 or the effect control board 80) mounts a break code (for example, a signal continuously including “0”). Send to
図16(A)は、ステータスレジスタA705の例を示す説明図である。ステータスレジスタA705は、シリアル通信回路505の各種ステータスを確認するためのレジスタである。この実施の形態では、ステータスレジスタA705の各ビットの値を確認することによって、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505の各種ステータスを確認することができる。図16(A)に示すように、ステータスレジスタA705は、8ビットレジスタであり、初期値が「0(=00h)」に設定されている。また、ステータスレジスタA705は、ビット0〜ビット7が読出のみ可能な状態に構成されている。したがって、ステータスレジスタA705のビット0〜ビット7に値を書き込む制御を行っても無効とされる。
FIG. 16A is an explanatory view showing an example of the status register A 705. The status register A 705 is a register for confirming various statuses of the serial communication circuit 505. In this embodiment, the CPU 56 can confirm various statuses of the serial communication circuit 505 by confirming the value of each bit of the status register A 705. As shown in FIG. 16A, the status register A 705 is an 8-bit register, and its initial value is set to “0 (= 00 h)”. Further, status register A 705 is configured such that bit 0 to bit 7 can be read only. Therefore, control to write values to bit 0 to bit 7 of status register A 705 is invalidated.
本実施の形態では、後述するように、送信データレジスタ710に送信データが入っていない状態(送信データエンプティ)となったり、送信用シフトレジスタ712が格納する送信データの送信を完了すると、割り込み制御回路714によって、ステータスレジスタA705の対応するビットがセットされる。そして、CPU56は、ステータスレジスタA705にセットされた各ビットの値を読み出す。
In the present embodiment, as described later, interrupt control is performed when transmission data is not in the transmission data register 710 (transmission data empty) or transmission of transmission data stored in the transmission shift register 712 is completed. Circuit 714 sets the corresponding bit of status register A 705. Then, the CPU 56 reads the value of each bit set in the status register A 705.
図16(B)は、ステータスレジスタA705に格納されるステータス確認データの一例を示す図である。図16(B)に示すように、ステータスレジスタA705のビット7(ビット名「TDRE」)には、送信データレジスタ710に送信データが入っていない状態であること(送信データエンプティ)を示す送信データエンプティフラグが格納される。図16(B)に示すように、ビット7に「0」が格納されている場合、送信データレジスタ710から送信用シフトレジスタ712に送信データが未だに転送されておらず、送信データレジスタ710に送信データが格納されたままの状態であることを示す。また、ビット7に「0」が格納されている状態では、送信データレジスタにデータが書き込まれない。例えば、ステップS5211,S52305ではビット7に「0」が格納されていないことを条件に送信データを設定する。また、ビット7に「1」が格納されている場合、送信データレジスタ710から送信用シフトレジスタ712に送信データが転送されており、送信データレジスタ710に送信データが入っていない状態(送信データエンプティ)であることを示す。
FIG. 16B shows an example of status confirmation data stored in status register A 705. Referring to FIG. As shown in FIG. 16B, transmission data indicating that transmission data is not included in transmission data register 710 in bit 7 (bit name “TDRE”) of status register A 705 (transmission data empty). The empty flag is stored. As shown in FIG. 16B, when "0" is stored in bit 7, transmission data has not yet been transferred from the transmission data register 710 to the transmission shift register 712, and transmission is performed to the transmission data register 710. Indicates that data is stored as it is. Also, when "0" is stored in the bit 7, data is not written to the transmission data register. For example, in steps S5211 and S52305, transmission data is set on the condition that "0" is not stored in bit 7. Also, when “1” is stored in bit 7, transmission data is transferred from transmission data register 710 to transmission shift register 712, and transmission data is not contained in transmission data register 710 (transmission data empty). Indicates that).
ステータスレジスタA705のビット6(ビット名「TC」)には、シリアル通信回路505からの送信データの送信を完了した旨を示す送信完了フラグが格納される。図16(B)に示すように、ビット6に「0」が格納されている場合、送信用シフトレジスタ712が格納する送信データの送信中の状態であり、シリアル通信回路505からの送信データの送信が完了していない状態であることを示す。また、ビット6に「1」が格納されている場合、送信用シフトレジスタ712が格納する送信データの転送を完了した状態であり、シリアル通信回路505からの送信データの送信が完了した状態であることを示す。コマンド格納領域がリングバッファ形式の場合には、ビット6に「1」が格納された状態となれば、コマンドの読出ポインタを更新する。
A transmission completion flag indicating that transmission of transmission data from the serial communication circuit 505 has been completed is stored in bit 6 (bit name "TC") of the status register A 705. As shown in FIG. 16B, when “0” is stored in bit 6, the transmission shift register 712 is in the state of transmitting transmission data, and it is in the state of transmission data from the serial communication circuit 505. Indicates that transmission is not complete. In addition, when “1” is stored in bit 6, the transfer of transmission data stored in the transmission shift register 712 is completed, and the transmission of transmission data from the serial communication circuit 505 is completed. Indicates that. When the command storage area is in the ring buffer format, if "1" is stored in bit 6, the read pointer of the command is updated.
なお、送信データの送信を完了した状態となり、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、送信先のマイクロコンピュータからの受信確認信号の待ち状態となる。この実施の形態では、後述する送信時割込の設定が行われると、シリアル通信回路505は、送信データの送信完了を検出すると、ステータスレジスタA705のビット6を「1」にするとともに、受信確認信号の待ち状態になったものとしてCPU56に割り込み要求(送信時割り込み要求という)を行う。
When the transmission of transmission data is completed, the game control microcomputer 560 waits for a reception confirmation signal from the transmission destination microcomputer. In this embodiment, when transmission interrupt setting described later is performed, serial communication circuit 505 sets bit 6 of status register A 705 to “1” upon detection of transmission data transmission completion, and acknowledges reception. An interrupt request (referred to as a transmission interrupt request) is issued to the CPU 56 as a signal waiting state.
ステータスレジスタA705のビット5(ビット名「RDRF」)には、受信データレジスタ711に受信データが格納された状態であること(受信データフル)を示す受信データフルフラグが格納される。図16(B)に示すように、ビット5に「0」が格納されている場合、受信データレジスタ711に受信データが入っていない状態であることを示す。また、ビット5に「1」が格納されている場合、受信用シフトレジスタ713の値が受信データレジスタ711に転送され、受信データレジスタ711に受信データが格納されている状態であること(受信データフル)を示す。払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370からのコマンドを受信したかどうかは、ビット5に「1」が格納された状態となっているかどうかによって確認される。例えば、ステップS5221,S52401,S52501ではビット5に「0」が格納されていないことを条件にコマンドを受信していると判定する。なお、この実施の形態では、ステータスレジスタA705のビット5(RDRF)は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560によって受信データレジスタ711から受信データが読み出されるとクリアされる。なお、受信データが読み出されたときにステータスレジスタA705のビット5(RDRF)が自動的にクリアされるように構成されていない場合には、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、受信データレジスタ711から受信データを読み出すごとに、ステータスレジスタA705のビット5(RDRF)をクリアする処理を行う必要がある。
A bit 5 (bit name “RDRF”) of the status register A 705 stores a reception data full flag indicating that reception data is stored in the reception data register 711 (reception data is full). As shown in FIG. 16B, when “0” is stored in bit 5, it indicates that the reception data register 711 does not contain reception data. Also, when “1” is stored in bit 5, the value of the reception shift register 713 is transferred to the reception data register 711 and the reception data is stored in the reception data register 711 (reception data (reception data) Show full) Whether or not the command from the payout control microcomputer 370 has been received is confirmed depending on whether or not "1" is stored in bit 5. For example, in steps S5221, S52401, and S52501, it is determined that a command is received on the condition that "0" is not stored in bit 5. In this embodiment, bit 5 (RDRF) of status register A 705 is cleared when the microcomputer 560 for gaming control reads out received data from the received data register 711. When the reception data is read out and bit 5 (RDRF) of status register A 705 is not cleared automatically, microcomputer 560 for gaming control receives from reception data register 711 Every time the reception data is read, it is necessary to clear bit 5 (RDRF) of the status register A 705.
なお、受信データレジスタ711に受信データが格納された状態となると、CPU56は、受信データを受信データレジスタ711から読み込んで受信処理を行える状態となる。この実施の形態では、受信時割込の設定が行われると、シリアル通信回路505は、受信データフルを検出すると、ステータスレジスタA705のビット5を「1」にするとともに、受信処理が可能になったものとしてCPU56に割り込み要求(受信時割り込み要求という)を行う。
When the reception data is stored in the reception data register 711, the CPU 56 can read the reception data from the reception data register 711 and can perform the reception process. In this embodiment, when reception interrupt setting is performed, serial communication circuit 505 sets bit 5 of status register A 705 to “1” when reception data full is detected, and enables reception processing. The CPU 56 issues an interrupt request (referred to as a reception interrupt request) to the CPU 56.
ステータスレジスタA705のビット4(ビット名「IDLE」)には、受信回路がアイドルラインを検出したことを示すアイドルライン検出フラグが格納される。図16(B)に示すように、ビット4に「0」が格納されている場合、シリアル通信回路505の受信部がアイドルラインを検出していない状態であることを示す。また、ビット4に「1」が格納されている場合、シリアル通信回路505の受信部がアイドルラインを検出した状態であることを示す。
An idle line detection flag indicating that the receiving circuit has detected an idle line is stored in bit 4 (bit name "IDLE") of the status register A 705. As shown in FIG. 16B, when “0” is stored in the bit 4, it indicates that the reception unit of the serial communication circuit 505 is not detecting an idle line. Also, when “1” is stored in bit 4, it indicates that the reception unit of the serial communication circuit 505 has detected an idle line.
ステータスレジスタA705のビット3(ビット名「OR」)には、CPU56が受信データレジスタ711が格納する受信データを読み込む前に、受信用シフトレジスタ713が次のデータを受信してしまったこと(オーバーラン)を示すオーバーランフラグが格納される。図16(B)に示すように、ビット3に「0」が格納されている場合、受信回路がオーバーランを検出していない状態であることを示す。また、ビット3に「1」が格納されている場合、受信回路がオーバーランを検出した状態であることを示す。
The reception shift register 713 has received the next data before the CPU 56 reads the reception data stored in the reception data register 711 in bit 3 (bit name “OR”) of the status register A 705 (over An overrun flag indicating a run is stored. As shown in FIG. 16B, when "0" is stored in bit 3, it indicates that the receiving circuit has not detected an overrun. When "1" is stored in bit 3, it indicates that the receiving circuit has detected an overrun.
なお、オーバーランが発生すると、受信データレジスタ711内の受信データが読み込まれる前に受信用シフトレジスタ713に次の受信データが格納されてしまうので、受信データが上書きされてしまいCPU56が受信データを正しく読み込めなくなってしまう。そのため、各制御基板が搭載するマイクロコンピュータと正しく通信を行えなくなり、CPU56が誤動作をする原因となる。この実施の形態では、シリアル通信回路505は、オーバーランを検出すると、ステータスレジスタA705のビット3を「1」にするとともに、通信時にエラーが発生したものとしてCPU56に割り込み要求を行う。
If an overrun occurs, the next reception data is stored in the reception shift register 713 before the reception data in the reception data register 711 is read, so the reception data is overwritten and the CPU 56 receives the reception data. It can not be read correctly. Therefore, communication can not be properly performed with the microcomputer mounted on each control board, which causes the CPU 56 to malfunction. In this embodiment, when the serial communication circuit 505 detects an overrun, it sets bit 3 of the status register A 705 to “1” and issues an interrupt request to the CPU 56 as an error has occurred during communication.
ステータスレジスタA705のビット2(ビット名「NF」)には、受信データにノイズを検出したことを示すノイズエラーフラグが格納される。図16(B)に示すように、ビット2に「0」が格納されている場合、受信回路が受信データにノイズを検出していない状態であることを示す。また、ビット2に「1」が格納されている場合、受信回路が受信データにノイズを検出した状態であることを示す。
A bit 2 (bit name “NF”) of the status register A 705 stores a noise error flag indicating that noise is detected in the received data. As shown in FIG. 16B, when “0” is stored in bit 2, it indicates that the receiving circuit is not detecting noise in the received data. When "1" is stored in bit 2, it indicates that the receiving circuit has detected noise in the received data.
例えば、シリアル通信回路505は、受信データの各ビットを検出する際に、ボーレート生成回路703が生成したボーレートを用いて、所定ビット長の「1」または「0」を検出する。この場合、検出した「1」または「0」の長さが所定ビット長に満たない場合、シリアル通信回路505は、受信データにノイズが発生したものとしてノイズエラーを検出する。ノイズエラーが発生すると、ノイズによって正しい受信データを受信できない可能性が高く、CPU56が誤動作をする原因となる。この実施の形態では、シリアル通信回路505は、ノイズエラーを検出すると、ステータスレジスタA705のビット2を「1」にするとともに、通信時にエラーが発生したものとしてCPU56に割り込み要求を行う。
For example, when detecting each bit of the received data, the serial communication circuit 505 detects "1" or "0" of a predetermined bit length using the baud rate generated by the baud rate generation circuit 703. In this case, when the length of the detected “1” or “0” is less than the predetermined bit length, the serial communication circuit 505 detects a noise error as noise occurring in the received data. When a noise error occurs, there is a high possibility that the received data can not be received correctly due to the noise, which causes the CPU 56 to malfunction. In this embodiment, when detecting a noise error, the serial communication circuit 505 sets bit 2 of the status register A 705 to “1” and issues an interrupt request to the CPU 56 as an error has occurred during communication.
ステータスレジスタA705のビット1(ビット名「FE」)には、受信データのストップビットの位置が「0」(本来、ストップビットは「1」)であることを検出したこと(フレーミングエラー)を示すフレーミングエラーフラグが格納される。図16(B)に示すように、ビット1に「0」が格納されている場合、受信回路が受信データにフレーミングエラーを検出していない状態であることを示す。また、ビット1に「1」が格納されている場合、受信回路がフレーミングエラーを検出した状態であることを示す。
The bit 1 (bit name "FE") of the status register A 705 indicates that the position of the stop bit of the received data is "0" (essentially, the stop bit is "1") (framing error) A framing error flag is stored. As shown in FIG. 16 (B), when "0" is stored in bit 1, it indicates that the receiving circuit has not detected a framing error in the received data. Also, when "1" is stored in bit 1, it indicates that the receiving circuit has detected a framing error.
フレーミングエラーが発生すると、受信データのストップビットを正しく受信できなかった状態であるので、正しい受信データを受信できない可能性が高く、CPU56が誤動作をする原因となる。この実施の形態では、シリアル通信回路505は、フレーミングエラーを検出すると、ステータスレジスタA705のビット1を「1」にするとともに、通信時にエラーが発生したものとしてCPU56に割り込み要求を行う。
If a framing error occurs, the stop bit of received data can not be received correctly. Therefore, there is a high possibility that correct received data can not be received, which causes the CPU 56 to malfunction. In this embodiment, when the serial communication circuit 505 detects a framing error, it sets bit 1 of the status register A 705 to “1” and issues an interrupt request to the CPU 56 as an error has occurred during communication.
ステータスレジスタA705のビット0(ビット名「PF」)には、受信データから求めたパリティの値と、受信データに含まれるパリティの値とが一致しなかったこと(パリティエラー)を示すパリティエラーフラグが格納される。図16(B)に示すように、ビット0に「0」が格納されている場合、受信回路が受信データにパリティエラーを検出していない状態であることを示す。また、ビット0に「1」が格納されている場合、受信回路がパリティエラーを検出した状態であることを示す。
A parity error flag indicating that the parity value obtained from the received data and the parity value included in the received data do not match (parity error) in bit 0 (bit name “PF”) of the status register A 705 Is stored. As shown in FIG. 16B, when “0” is stored in bit 0, it indicates that the reception circuit has not detected a parity error in the reception data. In addition, when “1” is stored in bit 0, it indicates that the reception circuit has detected a parity error.
パリティエラーが発生すると、受信データの各データビットまたはパリティビットを正しく受信できなかった状態であるので、正しい受信データを受信できない可能性が高く、CPU56が誤動作をする原因となる。この実施の形態では、シリアル通信回路505は、パリティエラーを検出すると、ステータスレジスタA705のビット0を「1」にするとともに、通信時にエラーが発生したものとしてCPU56に割り込み要求を行う。
When a parity error occurs, since each data bit or parity bit of the received data can not be received correctly, there is a high possibility that the correct received data can not be received, which causes the CPU 56 to malfunction. In this embodiment, when detecting a parity error, the serial communication circuit 505 sets bit 0 of the status register A 705 to “1” and issues an interrupt request to the CPU 56 as an error has occurred during communication.
図17(A)は、ステータスレジスタB706の例を示す説明図である。ステータスレジスタB706は、シリアル通信回路505の受信状態(受信ステータス)を確認するためのレジスタである。この実施の形態では、ステータスレジスタB706のビットの値を確認することによって、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505の受信ステータスを確認することができる。図17(B)に示すように、ステータスレジスタB706は、8ビットレジスタであり、初期値が「0(=00h)」に設定されている。また、ステータスレジスタB706は、ビット0が読出のみ可能な状態に構成されている。したがって、ステータスレジスタA705のビット0に値を書き込む制御を行っても無効とされる。また、ステータスレジスタB706は、ビット1〜ビット7が書込および読出ともに不可能な状態に構成されている。したがって、ステータスレジスタA705のビット1〜ビット7に値を書き込む制御を行っても無効とされ、ビット1〜ビット7から読み出す値は全て「0(=0000b)」である。
FIG. 17A is an explanatory view showing an example of the status register B706. The status register B706 is a register for confirming the reception state (reception status) of the serial communication circuit 505. In this embodiment, the CPU 56 can confirm the reception status of the serial communication circuit 505 by confirming the value of the bit of the status register B706. As shown in FIG. 17B, the status register B 706 is an 8-bit register, and its initial value is set to “0 (= 00 h)”. Further, status register B 706 is configured such that bit 0 can only be read. Therefore, control to write a value to bit 0 of status register A 705 is invalidated. Further, status register B 706 is configured in a state where bit 1 to bit 7 can not be written or read. Therefore, even if control is performed to write a value to bit 1 to bit 7 of status register A 705, it is invalidated, and all values read from bit 1 to bit 7 are “0 (= 0000 b)”.
図17(B)は、ステータスレジスタB706に格納されるステータス確認データの一例を示す図である。図17(B)に示すように、ステータスレジスタB706のビット0(ビット名「RAF」)には、受信回路が受信データを受信中であること(受信アクティブ)を示す受信アクティブフラグが格納される。図17(B)に示すように、ビット0に「0」が格納されている場合、受信回路が受信データを受信中でないことを示す。また、ビット0に「1」が格納されている場合、受信回路が受信データを受信中であることを示す。また、ビット0に「1」が格納されている場合にも、コマンドデータの書き込みを行わない、もしくはコマンドデータを書き込めなくなっている。なお、シリアル通信回路505は、スタートビットを検出すると、受信データの受信が開始されたものとして、ステータスレジスタB706のビット0を「1」にする。
FIG. 17B shows an example of status confirmation data stored in status register B706. As shown in FIG. 17B, the reception active flag indicating that the reception circuit is receiving reception data (reception active) is stored in bit 0 (bit name "RAF") of status register B 706. . As shown in FIG. 17B, when “0” is stored in bit 0, it indicates that the reception circuit is not receiving reception data. In addition, when “1” is stored in bit 0, it indicates that the receiving circuit is receiving received data. Also, even when "1" is stored in bit 0, command data can not be written or command data can not be written. When the serial communication circuit 505 detects the start bit, it sets bit 0 of the status register B 706 to “1”, assuming that reception of reception data has been started.
図18(A)は、制御レジスタC709の例を示す説明図である。制御レジスタC709は、シリアル通信回路505の通信エラー時の割り込み要求を許可するか否かを設定するレジスタである。この実施の形態では、制御レジスタC709の各ビットの値が設定されることによって、シリアル通信回路505からの通信時の割り込み要求を許可するか禁止するかが設定される。制御レジスタC709には、通信エラー時の各種割り込み要求を許可するか否かを示すエラー割り込み要求設定データが主として設定される。なお、制御レジスタC709には、エラー割り込み要求設定データ以外に、データ長を9ビットに設定した場合の9ビット目のデータが格納される。シリアル通信回路505の各種設も設定される。図18(A)に示すように、制御レジスタC709は、8ビットレジスタであり、初期値が「0(=00h)」に設定されている。また、制御レジスタC709は、ビット0〜ビット3およびビット6,7が書込および読出ともに可能な状態に構成されている。また、制御レジスタC709は、ビット4,5が書込および読出ともに不可能な状態に構成されている。したがって、制御レジスタC709のビット4,5に値を書き込む制御を行っても無効とされ、ビット4,5から読み出す値は全て「0(=0000b)」である。
FIG. 18A is an explanatory view showing an example of the control register C709. The control register C 709 is a register for setting whether to permit an interrupt request at the time of a communication error of the serial communication circuit 505. In this embodiment, by setting the value of each bit of the control register C 709, it is set whether to permit or prohibit an interrupt request during communication from the serial communication circuit 505. In the control register C709, error interrupt request setting data indicating whether to enable various interrupt requests at the time of a communication error is mainly set. In addition to the error interrupt request setting data, the control register C 709 stores ninth bit data when the data length is set to 9 bits. Various settings of the serial communication circuit 505 are also set. As shown in FIG. 18A, the control register C 709 is an 8-bit register, and its initial value is set to “0 (= 00 h)”. Further, control register C 709 is configured such that bit 0 to bit 3 and bits 6 and 7 can both write and read. Control register C 709 is configured such that bits 4 and 5 can not be written or read. Therefore, even if control is performed to write a value to bits 4 and 5 of control register C 709, it is invalidated, and all values read from bits 4 and 5 are “0 (= 0000 b)”.
図18(B)は、制御レジスタC709に設定されるエラー割り込み要求設定データの一例を示す説明図である。図18(B)に示すように、制御レジスタC709のビット7(ビット名「R8」)には、データ長を9ビットに設定した場合の受信データの9ビット目のデータが格納される。また、制御レジスタC709のビット6(ビット名「T8」)には、データ長を9ビットに設定した場合の送信データの9ビット目のデータが格納される。
FIG. 18B is an explanatory view showing an example of the error interrupt request setting data set in the control register C709. As shown in FIG. 18B, the bit 7 (bit name “R8”) of the control register C 709 stores the 9th bit data of received data when the data length is set to 9 bits. Also, bit 6 (bit name “T8”) of the control register C 709 stores the ninth bit data of transmission data when the data length is set to 9 bits.
制御レジスタC709のビット3(ビット名「ORIE」)には、オーバーランを検出した場合に行う割り込み要求であるオーバーランフラグ割り込み要求を許可するか否かを示す設定データが設定される。図18(B)に示すように、ビット3を「0」に設定することによって、オーバーランフラグ割り込み要求を禁止するように設定される。また、ビット3を「1」に設定することによって、オーバーランフラグ割り込み要求を許可するように設定される。
In bit 3 (bit name “ORIE”) of the control register C 709, setting data indicating whether to permit an overrun flag interrupt request, which is an interrupt request to be issued when an overrun is detected, is set. As shown in FIG. 18B, by setting bit 3 to “0”, the overrun flag interrupt request is set to be inhibited. Also, by setting bit 3 to "1", the overrun flag interrupt request is set to be permitted.
制御レジスタC709のビット2(ビット名「NEIE」)には、ノイズエラーを検出した場合に行う割り込み要求であるノイズエラーフラグ割り込み要求を許可するか否かを示す設定データが設定される。図18(B)に示すように、ビット2を「0」に設定することによって、ノイズエラーフラグ割り込み要求を禁止するように設定される。また、ビット2を「1」に設定することによって、ノイズエラーフラグ割り込み要求を許可するように設定される。
In bit 2 (bit name “NEIE”) of the control register C 709, setting data indicating whether or not to allow a noise error flag interrupt request, which is an interrupt request performed when a noise error is detected, is set. As shown in FIG. 18B, by setting bit 2 to “0”, the noise error flag interrupt request is set to be inhibited. Also, by setting bit 2 to "1", the noise error flag interrupt request is set to be permitted.
制御レジスタC709のビット1(ビット名「FEIE」)には、フレーミングエラーを検出した場合に行う割り込み要求であるフレーミングエラーフラグ割り込み要求を許可するか否かを示す設定データが設定される。図18(B)に示すように、ビット1を「0」に設定することによって、フレーミングエラーフラグ割り込み要求を禁止するように設定される。また、ビット1を「1」に設定することによって、フレーミングエラーフラグ割り込み要求を許可するように設定される。
In bit 1 (bit name “FEIE”) of the control register C 709, setting data indicating whether or not to permit a framing error flag interrupt request, which is an interrupt request to be issued when a framing error is detected, is set. As shown in FIG. 18B, by setting bit 1 to “0”, the framing error flag interrupt request is set to be inhibited. Also, by setting bit 1 to "1", a framing error flag interrupt request is set to be permitted.
制御レジスタC709のビット0(ビット名「PEIE」)には、パリティエラーを検出した場合に行う割り込み要求であるパリティエラーフラグ割り込み要求を許可するか否かを示す設定データが設定される。図18(B)に示すように、ビット0を「0」に設定することによって、パリティエラーフラグ割り込み要求を禁止するように設定される。また、ビット0を「1」に設定することによって、パリティエラーフラグ割り込み要求を許可するように設定される。
In bit 0 (bit name "PEIE") of the control register C709, setting data indicating whether or not to permit a parity error flag interrupt request, which is an interrupt request to be issued when a parity error is detected, is set. As shown in FIG. 18B, by setting bit 0 to “0”, the parity error flag interrupt request is set to be prohibited. Also, by setting bit 0 to "1", it is set to permit a parity error flag interrupt request.
図19は、シリアル通信回路505が備えるデータレジスタの例を示す説明図である。データレジスタ701は、シリアル通信回路505が送受信するデータを格納するレジスタである。図19に示すように、データレジスタは、8ビットレジスタであり、初期値が「0(=00h)」に設定されている。また、データレジスタ701は、ビット0〜ビット7が書込および読出ともに可能な状態に構成されている。
FIG. 19 is an explanatory view showing an example of a data register provided in the serial communication circuit 505. As shown in FIG. The data register 701 is a register that stores data transmitted and received by the serial communication circuit 505. As shown in FIG. 19, the data register is an 8-bit register, and its initial value is set to "0 (= 00 h)". Data register 701 is configured in a state where bit 0 to bit 7 can be written and read.
この実施の形態では、シリアル通信回路505が送信データを送信する場合、データレジスタは、送信データレジスタ710として用いられる。なお、データ長を9ビットに設定した場合、データレジスタおよび制御レジスタC709のビット6が送信データレジスタ710として用いられる。この場合、データレジスタのビット0〜ビット7が送信データレジスタ710のビット0〜ビット7として用いられ、制御レジスタC709のビット6が送信データレジスタ710のビット8として用いられる。
In this embodiment, when serial communication circuit 505 transmits transmission data, the data register is used as transmission data register 710. When the data length is set to 9 bits, bit 6 of the data register and control register C 709 is used as the transmission data register 710. In this case, bit 0 to bit 7 of the data register are used as bit 0 to bit 7 of the transmission data register 710, and bit 6 of the control register C 709 is used as bit 8 of the transmission data register 710.
また、シリアル通信回路505が受信データを受信する場合、データレジスタは、受信データレジスタ711として用いられる。なお、データ長を9ビットに設定した場合、データレジスタおよび制御レジスタC709のビット7が受信データレジスタ711として用いられる。この場合、データレジスタのビット0〜ビット7が受信データレジスタ711のビット0〜ビット7として用いられ、制御レジスタC709のビット7が受信データレジスタ711のビット8として用いられる。
When the serial communication circuit 505 receives received data, the data register is used as the received data register 711. When the data length is set to 9 bits, bit 7 of the data register and control register C 709 is used as the reception data register 711. In this case, bit 0 to bit 7 of the data register are used as bit 0 to bit 7 of the reception data register 711, and bit 7 of the control register C 709 is used as bit 8 of the reception data register 711.
割り込み制御回路714は、CPU56に各種割り込み要求を行う。この実施の形態では、割り込み制御回路714は、制御レジスタB708のビット6(TCIE)が「1」に設定されている場合、送信データレジスタ710に送信データの送信を完了した状態となると、CPU56に割り込み信号を出力するとともに、ステータスレジスタA705のビット6(TC)に「1」を設定することによって割り込み要求を行う。なお、ステータスレジスタA705のビットの設定値により割込要因を識別可能とするのでなく、割り込み制御回路714は、割込要因毎に異なる割り込み信号をCPU56に出力するようにしてもよい。
The interrupt control circuit 714 issues various interrupt requests to the CPU 56. In this embodiment, when bit 6 (TCIE) of the control register B 708 is set to “1”, the interrupt control circuit 714 sends the transmission data to the transmission data register 710 in a state where transmission of transmission data is completed. While outputting an interrupt signal, an interrupt request is made by setting "1" in bit 6 (TC) of the status register A 705. The interrupt control circuit 714 may output an interrupt signal different for each interrupt factor to the CPU 56, instead of making it possible to identify the interrupt factor by the set value of the bit of the status register A 705.
また、割り込み制御回路714は、制御レジスタB708のビット5(RIE)が「1」に設定されている場合、受信データレジスタ711に受信データが格納されている状態になると(受信データフルを検出すると)、CPU56に割り込み信号を出力するとともに、ステータスレジスタA705のビット5(RDRF)に「1」を設定することによって割り込み要求を行う。
When bit 5 (RIE) of control register B 708 is set to “1”, interrupt control circuit 714 detects that reception data is stored in reception data register 711 (when reception data is full is detected). , And outputs an interrupt signal to the CPU 56, and performs an interrupt request by setting "1" in bit 5 (RDRF) of the status register A 705.
また、割り込み制御回路714は、制御レジスタC709のビット0〜3のいずれかが「1」に設定されている場合、各種通信エラーが発生すると、CPU56に割り込み信号を出力するとともに、通信エラーの種類に応じて、ステータスレジスタA705のビット0〜ビット3に「1」を設定することによって割り込み要求を行う。例えば、制御レジスタC709のビット3(ORIE)が「1」に設定されている場合、オーバーランを検出して割り込み要求を行うときに、ステータスレジスタA705のビット3(OR)に「1」を設定する。また、例えば、制御レジスタC709のビット2(NEIE)が「1」に設定されている場合、ノイズエラーを検出して割り込み要求を行うときに、ステータスレジスタA705のビット2(NF)に「1」を設定する。また、例えば、制御レジスタC709のビット1(FEIE)が「1」に設定されている場合、フレーミングエラーを検出して割り込み要求を行うときに、ステータスレジスタA705のビット1(FE)に「1」を設定する。また、例えば、制御レジスタC709のビット0(PEIE)が「1」に設定されている場合、パリティエラーを検出して割り込み要求を行うときに、ステータスレジスタA705のビット0(PF)に「1」を設定する。なお、複数の通信エラーを検出した場合、割り込み制御回路714は、複数の通信エラーにもとづいて割り込み要求を行うとともに、ステータスレジスタA705の該当するビットをそれぞれ「1」に設定する。
The interrupt control circuit 714 outputs an interrupt signal to the CPU 56 when various communication errors occur when any one of the bits 0 to 3 of the control register C 709 is set to “1”, and the type of communication error is generated. In response to this, an interrupt request is issued by setting "1" to bit 0 to bit 3 of the status register A 705. For example, when bit 3 (ORIE) of control register C 709 is set to "1", bit 3 (OR) of status register A 705 is set to "1" when an overrun is detected and an interrupt request is issued. Do. Also, for example, when bit 2 (NEIE) of control register C 709 is set to “1”, bit 1 (NF) of status register A 705 is set to “1” when a noise error is detected and an interrupt request is made. Set Also, for example, when bit 1 (FEIE) of control register C 709 is set to “1”, “1” is set to bit 1 (FE) of status register A 705 when a framing error is detected and an interrupt request is made. Set Also, for example, when bit 0 (PEIE) of control register C 709 is set to “1”, “1” is set to bit 0 (PF) of status register A 705 when a parity error is detected and an interrupt request is made. Set When a plurality of communication errors are detected, the interrupt control circuit 714 issues an interrupt request based on the plurality of communication errors, and sets the corresponding bit of the status register A 705 to “1”.
送信フォーマット/パリティ生成回路715は、送信データのデータフォーマットを生成する。この実施の形態では、送信フォーマット/パリティ生成回路715は、送信データレジスタ710に格納される送信データにスタートビットおよびストップビットを付加してデータフォーマットを生成し、送信用シフトレジスタ712に転送する。また、制御レジスタA707のビット1(PE)に「1」が設定され、パリティ機能を使用する旨が設定されている場合、送信フォーマット/パリティ生成回路715は、送信データにパリティビットを付加してデータフォーマットを生成する。
The transmission format / parity generation circuit 715 generates a data format of transmission data. In this embodiment, the transmission format / parity generation circuit 715 adds a start bit and a stop bit to transmission data stored in the transmission data register 710 to generate a data format, and transfers the data format to the transmission shift register 712. When bit 1 (PE) of control register A 707 is set to “1” to indicate that the parity function is to be used, transmission format / parity generation circuit 715 adds a parity bit to transmission data. Generate data format.
受信フォーマット/パリティチェック回路716は、受信データのデータフォーマットを検出する。この実施の形態では、受信フォーマット/パリティチェック回路716は、受信用シフトレジスタ713に格納される受信データからスタートビットおよびストップビットを検出し、受信データに含まれるデータ部分を検出して受信データレジスタ711に転送する。また、制御レジスタA707のビット1(PE)に「1」が設定され、パリティ機能を使用する旨が設定されている場合、受信フォーマット/パリティチェック回路716は、受信データのパリティを求め、受信データに含まれるパリティと一致するか否かを検出する。また、求めた値が受信データに含まれるパリティと一致しない場合、受信フォーマット/パリティチェック回路716は、パリティエラーを検出する。なお、後述するシリアル通信回路設定処理において通信エラー時割り込み要求を許可する旨が設定されている場合、割り込み制御回路714は、パリティエラーを検出すると、通信エラーの発生を割込原因としてCPU56に割り込み要求を行う。
The reception format / parity check circuit 716 detects the data format of the received data. In this embodiment, the reception format / parity check circuit 716 detects the start bit and the stop bit from the reception data stored in the reception shift register 713, detects the data portion included in the reception data, and detects the reception data register. Transfer to 711 If bit 1 (PE) of control register A 707 is set to "1" to indicate that the parity function is to be used, reception format / parity check circuit 716 determines the parity of received data, and receives data. It is detected whether or not it matches the parity included in. Also, if the obtained value does not match the parity included in the received data, the reception format / parity check circuit 716 detects a parity error. When it is set in the serial communication circuit setting process to be described later that permission to interrupt request for communication error is set, the interrupt control circuit 714 interrupts the CPU 56 as occurrence of communication error as an interrupt cause when detecting a parity error. Make a request.
大当り判定用テーブルメモリ571は、CPU56が特別図柄表示器8の表示結果を大当り図柄とするか否かを判定するために用いる複数の大当り判定テーブルを記憶する。具体的には、大当り判定用テーブルメモリ571は、図20(A)に示すように、確変状態以外の遊技状態(通常状態という)において用いられる通常時大当り判定テーブル571aを記憶する。また、大当り判定用テーブルメモリ571は、図20(B)に示すように、確変状態において用いられる確変時大当り判定テーブル571bを格納する。なお、図20に示す判定テーブルを用いて大当り判定を行う場合、乱数最大値設定レジスタ535に設定された乱数最大値によって大当りと判定する確率が大きく変化することになる。この場合、例えば、設定される乱数最大値が小さすぎると、通常時大当り判定テーブル571aを用いた場合と、確変時大当り判定テーブル571bを用いた場合とで、大当りと判定する確率の差が小さくなってしまい、遊技者の遊技に対する興味を減退させてしまうことになる。そのため、乱数回路503および乱数最大値に対応づけて、複数の判定テーブル(複数の通常時大当り判定用テーブル571aおよび複数の確変時大当り判定用テーブル571b)を大当り判定用テーブルメモリ571に記憶してもよい。そして、CPU56は、大当り判定用テーブルメモリ571が記憶する判定テーブルのうち、使用する乱数回路503および乱数最大値に対応する判定テーブル571a,571bを用いて、表示結果決定プログラム552に従って、特別図柄表示器8の表示結果を大当り図柄とするか否かを判定するようにしてもよい。そのようにすることによって、使用する乱数回路503の種類や乱数最大値が異なっても、大当りと判定する確率がある程度同じになるように制御することができる。
The jackpot determination table memory 571 stores a plurality of jackpot determination tables used to determine whether the CPU 56 sets the display result of the special symbol display 8 as a jackpot symbol. Specifically, as shown in FIG. 20A, the big hit determination table memory 571 stores a normal time big hit determination table 571 a used in a gaming state other than the definite change state (referred to as a normal state). Further, as shown in FIG. 20B, the jackpot determination table memory 571 stores a probability variation time jackpot determination table 571b used in the probability variation state. In the case of making a big hit determination using the determination table shown in FIG. 20, the probability of determining a big hit changes greatly depending on the random number maximum value set in the random number maximum value setting register 535. In this case, for example, when the set maximum random number is too small, the difference between the probability of determining a big hit and the probability of determining a big hit between the normal big hit determination table 571a and the positive variation big hit determination table 571b are small. As a result, the player's interest in the game is diminished. Therefore, in correspondence with the random number circuit 503 and the random number maximum value, a plurality of determination tables (a plurality of normal time jackpot determination tables 571a and a plurality of probability variation time jackpot determination tables 571b) are stored in the jackpot determination table memory 571 It is also good. Then, the CPU 56 displays the special symbol according to the display result determination program 552 using the random number circuit 503 to be used and the determination tables 571 a and 571 b corresponding to the maximum random number among the determination tables stored in the big hit determination table memory 571. It may be determined whether or not the display result of the container 8 is to be a big hit symbol. By doing so, even if the type of the random number circuit 503 to be used and the maximum random number are different, it is possible to control so that the probability of determining a big hit is the same to some extent.
なお、図20に示す例では、例えば、図20(A)に示す通常時大当り判定テーブルの場合、1020〜1059、13360〜13399、34400〜34439および57700〜57739の4つの範囲に判定値が割り当てられ、図20(B)に示す確変時大当り判定テーブルの場合、1020〜1219、13360〜13559、34400〜34599および57700〜57899の4つの範囲に判定値が割り当てられている場合を示しているが、各大当り判定テーブルにおいて、一連の1つの範囲にまとめて判定値が割り当てられているように構成してもよい。
In the example shown in FIG. 20, for example, in the case of the normal time big hit determination table shown in FIG. 20A, determination values are assigned to four ranges of 1020 to 1059, 13360 to 13399, 34400 to 34439 and 57700 to 57739. In the case of the probability variation big hit determination table shown in FIG. 20 (B), the case where the determination values are assigned to four ranges of 1020 to 1219, 13360 to 13559, 34400 to 34599, and 57700 to 57899 is shown. In each of the jackpot determination tables, it may be configured such that the determination values are assigned together in a series of one range.
図21は、遊技制御手段における出力ポートの割り当ての例を示す説明図である。図21に示すように、出力ポート0からは、払出制御基板37に送信される払出制御信号(本例では、接続信号)が出力される。また、大入賞口を開閉する可変入賞球装置20を開閉するためのソレノイド(大入賞口扉ソレノイド)21、および可変入賞球装置15を開閉するためのソレノイド(普通電動役物ソレノイド)16に対する駆動信号も、出力ポート0から出力される。
FIG. 21 is an explanatory view showing an example of assignment of output ports in the game control means. As shown in FIG. 21, from the output port 0, a payout control signal (a connection signal in this example) transmitted to the payout control board 37 is output. In addition, a solenoid (large winning opening door solenoid) 21 for opening and closing the variable winning ball device 20 for opening and closing the big winning opening, and a drive for the solenoid (normal electric role thing solenoid) 16 for opening and closing the variable winning ball device 15 A signal is also output from output port 0.
なお、図21に示された「論理」(例えば1がオン状態)と逆の論理(例えば0がオン状態)を用いてもよいが、特に、接続信号については、主基板31と払出制御基板37との間の信号線において断線が生じた場合やケーブル外れの場合(ケーブル未接続を含む)等に、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370では必ずオフ状態と検知されるように「論理」が定められる。具体的には、一般に、断線やケーブル外れが生ずると信号の受信側ではハイレベルが検知されるので、主基板31と払出制御基板37との間の信号線でのハイレベルが、遊技制御手段における出力ポートにおいてオフ状態になるように「論理」が定められる。従って、必要であれば、主基板31において出力ポートの外側に、信号を論理反転させる出力バッファ回路が設置される。
In addition, although the logic (for example, 0 is in an ON state) opposite to the “logic” (for example, 1 is in an ON state) shown in FIG. 21 may be used, in particular, for the connection signal, the main substrate 31 and the payout control substrate The “logic” is defined so that the payout control microcomputer 370 always detects an off state when there is a break in the signal line between 37 and when there is a cable disconnection (including cable disconnection). . Specifically, since high level is generally detected on the receiving side of the signal when disconnection or cable disconnection occurs, high level at the signal line between the main board 31 and the payout control board 37 is a game control means. "Logic" is defined to be off at the output port at. Therefore, an output buffer circuit that logically inverts a signal is provided outside the output port on the main substrate 31 if necessary.
そして、出力ポート1から、ターミナル基板160を介して、外部装置(例えば、ホールコンピュータ)に対して、種情報出力用信号すなわち制御に関わる情報(例えば、始動口信号、図柄確定回数1信号、大当り1信号、大当り2信号、大当り3信号、時短信号、セキュリティ信号)の出力データが出力される。なお、この実施の形態では、後述する賞球信号1(賞球払出を1個検出するごとに出力される信号)や、遊技機エラー状態信号(遊技機がエラー状態(本例では、球切れエラー状態または満タンエラー状態)であることを示す信号)も、ターミナル基板160を介して外部装置に出力される。この場合、払出制御基板37側において、賞球払出や遊技機のエラー状態が検出され、賞球信号1や遊技機エラー状態信号が主基板31に入力される。そして、主基板31に入力された賞球信号1や遊技機エラー状態信号は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560を経由することなく、主基板31上をそのまま経由してターミナル基板160を介して外部出力される。なお、主基板31に入力された賞球信号1や遊技機エラー状態信号は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560を一旦経由してから、ターミナル基板160を介して外部出力されるようにしてもよい。
Then, from the output port 1 to the external device (for example, a hall computer) via the terminal substrate 160, a seed information output signal, that is, information related to control (for example, starting opening signal, symbol determination number 1 signal, big hit Output data of 1 signal, 2 signals of big hit, 3 signals of big hit, short time signal, security signal) is output. In this embodiment, a winning ball signal 1 (a signal output each time one winning ball payout is detected) to be described later or a gaming machine error status signal (a gaming machine is in an error status (in this example, the ball is out). The signal (indicating an error state or a full error state) is also output to the external device via the terminal board 160. In this case, on the side of the payout control board 37, a prize ball payout or an error state of the gaming machine is detected, and a winning ball signal 1 or a gaming machine error state signal is input to the main board 31. The prize ball signal 1 and the gaming machine error status signal input to the main substrate 31 are output to the outside via the terminal substrate 160 directly on the main substrate 31 without passing through the game control microcomputer 560. Be done. The prize ball signal 1 and the gaming machine error state signal input to the main substrate 31 may be output to the outside via the terminal substrate 160 after temporarily passing through the gaming control microcomputer 560.
なお、ターミナル基板160を介して外部出力される信号は、この実施の形態で示したものに限られない。例えば、ガラス扉枠2が開放状態であることを示すドア開放信号や、賞球の払出を10個検出するごとに出力される賞球情報も、ターミナル基板160を介して外部装置に出力されるようにしてもよい。この場合、払出制御基板37側において、ガラス扉枠2が開放状態であることや賞球の払出も検出され、ドア開放信号や賞球情報が主基板31に入力される。そして、主基板31に入力されたドア開放信号や賞球情報は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560を経由することなく、主基板31上をそのまま経由してターミナル基板160を介して外部出力される。だたし、ドア開放信号および賞球情報は、主基板31上で分岐され、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560にも入力されるものとする。なお、この場合も、主基板31に入力されたドア開放信号や賞球情報は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560を一旦経由してから、ターミナル基板160を介して外部出力されるようにしてもよい。
The signal externally output through the terminal substrate 160 is not limited to that shown in this embodiment. For example, a door open signal indicating that the glass door frame 2 is in an open state, and prize ball information which is output each time ten prize balls are detected are also output to the external device through the terminal substrate 160. You may do so. In this case, on the payout control substrate 37 side, the open state of the glass door frame 2 and the payout of the winning balls are also detected, and the door opening signal and the winning ball information are input to the main substrate 31. Then, the door open signal and the prize ball information input to the main substrate 31 are externally output via the terminal substrate 160 via the main substrate 31 as it is without passing through the game control microcomputer 560. However, it is assumed that the door open signal and the winning ball information are branched on the main substrate 31 and are also input to the game control microcomputer 560. Also in this case, the door open signal and the winning ball information input to the main substrate 31 may be externally output through the terminal substrate 160 after temporarily passing through the game control microcomputer 560. .
また、例えば、遊技機が第1始動入賞口と第2始動入賞口との2つの始動入賞口を備え、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄との2つの特別図柄を変動表示可能に構成されている場合には、特別図柄の変動回数を通知するための図柄確定回数信号として図柄確定回数1信号に加えて図柄確定回数2信号も、ターミナル基板160を介して外部出力するようにしてもよい。この場合、例えば、第1特別図柄の変動回数のみを通知するための信号として図柄確定回数2信号を外部出力するようにし、第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄の両方の変動回数を通知するための信号として図柄確定回数1信号を外部出力するように構成すればよい。そのように構成すれば、ホールコンピュータなどの外部装置側において、第1特別図柄のみの変動回数に加えて、第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄合計の変動回数や、第2特別図柄のみの変動回数も把握することができる。
Also, for example, the gaming machine is provided with two start winning openings of the first starting winning opening and the second starting winning opening, and can be variably displayed with two special symbols of the first special symbol and the second special symbol. In addition to the symbol determination frequency 1 signal as the symbol determination frequency signal for notifying the special symbol variation frequency, the symbol determination frequency 2 signal may be externally output through the terminal substrate 160, if it is . In this case, for example, the symbol determination frequency 2 signal is externally output as a signal for notifying only the number of changes in the first special symbol, and to notify both the number of changes in the first special symbol and the second special symbol The symbol determination number 1 signal may be externally output as the signal of. If so configured, on the external device side such as a hall computer, in addition to the number of fluctuations of only the first special symbol, the number of fluctuations of the total of the first special symbol and the second special symbol, or the fluctuation of only the second special symbol The number of times can also be grasped.
図22は、遊技制御手段における入力ポートのビット割り当ての例を示す説明図である。図22に示すように、入力ポート0のビット0〜7には、それぞれ、カウントスイッチ23、ゲートスイッチ32a、入賞口スイッチ29a,30a、磁石センサ信号1、磁石センサ信号2、ドア開放信号、賞球情報が入力される。なお、この実施の形態では、磁石を用いた不正行為を検出するための磁石センサ(図示せず)が2個設けられており、それぞれの磁石センサからの検出信号も入力ポート0から入力される。また、入力ポート1のビット0には、始動口スイッチ14aの検出信号が入力される。また、入力ポート1のビット1には、入賞確認スイッチ14bの検出信号が入力される。また、入力ポート1のビット3,4には、それぞれ、電源基板910からの電源断信号およびクリアスイッチの検出信号が入力される。
FIG. 22 is an explanatory view showing an example of bit assignment of the input port in the game control means. As shown in FIG. 22, in the bits 0 to 7 of the input port 0, the count switch 23, the gate switch 32a, the winning opening switch 29a, 30a, the magnet sensor signal 1, the magnet sensor signal 2, the door open signal, and the prize respectively Sphere information is input. In this embodiment, two magnet sensors (not shown) for detecting fraudulent activity using a magnet are provided, and detection signals from the respective magnet sensors are also input from input port 0. . A detection signal of the start port switch 14a is input to bit 0 of the input port 1. Further, a detection signal of the winning a prize confirmation switch 14 b is input to bit 1 of the input port 1. Further, a power-off signal from the power supply substrate 910 and a detection signal of the clear switch are input to the bits 3 and 4 of the input port 1, respectively.
図23は、ターミナル基板160の内部構成を示す回路図である。図23に示すターミナル基板160において、左側上段のコネクタCN−1は、主基板31からの信号を伝達するケーブルを接続するためのコネクタであり、左側下段のコネクタCN1−2は、払出制御基板37からの信号を、主基板31を経由して伝達するケーブルを接続するためのコネクタである。また、右側のコネクタCN1〜CN9は、ホールコンピュータなど外部装置に対して信号を伝達するケーブルを接続するためのコネクタである。また、ターミナル基板160には、ドライバ回路としての半導体リレー(PhotoMOSリレー)PC1〜PC9が搭載されている。
FIG. 23 is a circuit diagram showing an internal configuration of terminal board 160. Referring to FIG. In the terminal board 160 shown in FIG. 23, the connector CN-1 on the upper left side is a connector for connecting a cable for transmitting a signal from the main board 31, and the connector CN1-2 on the lower left side is a payout control board 37. Is a connector for connecting a cable that transmits the signal from the main board 31 via the main board 31. Further, the connectors CN1 to CN9 on the right side are connectors for connecting a cable for transmitting a signal to an external device such as a hall computer. Further, on the terminal substrate 160, semiconductor relays (PhotoMOS relays) PC1 to PC9 as driver circuits are mounted.
主基板31からのケーブルがコネクタCN−1に接続されることにより、主基板31(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560)から各種信号がターミナル基板160に入力される。具体的には、コネクタCN−1の端子「2」に始動口信号が入力され、コネクタCN−1の端子「3」に図柄確定回数1信号が入力され、コネクタCN−1の端子「5」に大当り1信号が入力され、コネクタCN−1の端子「6」に大当り2信号が入力され、コネクタCN−1の端子「7」に大当り3信号が入力され、コネクタCN−1の端子「8」に時短信号が入力され、コネクタCN−1の端子「9」にセキュリティ信号が入力される。
By connecting the cable from the main board 31 to the connector CN-1, various signals are inputted from the main board 31 (microcomputer for game control 560) to the terminal board 160. Specifically, the start opening signal is input to the terminal "2" of the connector CN-1, the symbol determination number 1 signal is input to the terminal "3" of the connector CN-1, and the terminal "5" of the connector CN-1 A big hit 1 signal is input to the terminal, a big hit 2 signal is input to the terminal "6" of the connector CN-1, a big hit 3 signal is input to the terminal "7" of the connector CN-1, and the terminal "8 of the connector CN-1 The short time signal is input to “1”, and the security signal is input to the terminal “9” of the connector CN-1.
また、払出制御基板37からのケーブルが主基板31を経由してコネクタCN−2に接続されることにより、払出制御基板37(払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370)からの各種信号がターミナル基板160に入力される。具体的には、コネクタCN−2の端子「2」に賞球信号1が入力され、コネクタCN−2の端子「3」に遊技機エラー状態信号が入力される。
Further, the cable from the payout control substrate 37 is connected to the connector CN-2 via the main substrate 31 so that various signals from the payout control substrate 37 (the microcomputer 370 for payout control) are input to the terminal substrate 160. Be done. Specifically, the prize ball signal 1 is input to the terminal "2" of the connector CN-2, and the gaming machine error state signal is input to the terminal "3" of the connector CN-2.
図23に示すように、ターミナル基板160では、コネクタCN−1およびコネクタCN−2の端子「1」に基準電位の信号線が接続され、その信号線が分岐して、各々の半導体リレーPC1〜PC9の入力端子「1」に接続されている。また、コネクタCN−1の端子「2」、「3」、「5」〜「9」およびコネクタCN−2のコネクタ「2」、「3」に接続された信号線は、それぞれ、1KΩの抵抗R1〜R9を介して半導体リレーPC1〜PC9の入力端子「2」に接続されている。また、半導体リレーPC1〜PC9の出力端子「4」に接続された信号線は、それぞれ、コネクタCN1〜CN9の端子「1」に接続されている。また、半導体リレーPC1〜PC9の出力端子「3」に接続された信号線は、それぞれ、コネクタCN1〜CN9の端子「2」に接続されている。
As shown in FIG. 23, in the terminal substrate 160, the signal line of the reference potential is connected to the terminal "1" of the connector CN-1 and the connector CN-2, the signal line branches, and each semiconductor relay PC1- It is connected to the input terminal “1” of the PC 9. In addition, the signal lines connected to the terminals “2”, “3”, “5” to “9” of the connector CN-1 and the connectors “2” and “3” of the connector CN-2 respectively have a resistance of 1 KΩ The semiconductor relays PC1 to PC9 are connected to input terminals "2" through R1 to R9. The signal lines connected to the output terminals "4" of the semiconductor relays PC1 to PC9 are connected to the terminals "1" of the connectors CN1 to CN9, respectively. The signal lines connected to the output terminals "3" of the semiconductor relays PC1 to PC9 are connected to the terminals "2" of the connectors CN1 to CN9, respectively.
半導体リレーPC1〜PC9では、入力端子に信号電流が流れると、入力側の発光素子(LED)が発光する。発光された光は、LEDと対向に設けられた光電素子(太陽電池)に透明シリコンを通って照射される。光を受けた光電素子は、光の量に応じて電圧に交換し、この電圧は制御回路を通って出力部のMOSFETゲートを充電する。光電素子より供給されるMOSFETゲート電圧が設定電圧値に達すると、MOSFETが導通状態になり、負荷をオンさせる。入力端子の信号電流が切れると、発光素子(LED)の発光が止まる。LEDの発光が止まると、光電素子の電圧が下がり、光電素子から供給される電圧が下がると制御回路により、MOSFETのゲート負荷を急速に放電させる。この制御回路によりMOSFETが非導通状態になり、負荷をオフさせる。
In the semiconductor relays PC1 to PC9, when the signal current flows to the input terminal, the light emitting element (LED) on the input side emits light. The emitted light is irradiated through transparent silicon to a photoelectric element (solar cell) provided opposite to the LED. The light receiving photoelectric elements exchange voltage according to the amount of light, which charges the MOSFET gate at the output through the control circuit. When the MOSFET gate voltage supplied from the photoelectric element reaches the set voltage value, the MOSFET becomes conductive to turn on the load. When the signal current at the input terminal is cut off, the light emitting element (LED) stops emitting light. When the light emission of the LED stops, the voltage of the photoelectric element decreases, and when the voltage supplied from the photoelectric element decreases, the control circuit rapidly discharges the gate load of the MOSFET. This control circuit causes the MOSFET to become nonconductive and turn off the load.
以上のような半導体リレーPC1〜PC9の動作により、入力側のコネクタCN−1およびコネクタCN−2から入力された信号が出力側のコネクタCN1〜CN9に伝達され、ホールコンピュータなど外部装置に対して出力される。具体的には、コネクタCN1から始動口信号が出力され、コネクタCN2から図柄確定回数1信号が出力され、コネクタCN3から大当り1信号が出力され、コネクタCN4から大当り2信号が出力され、コネクタCN5から大当り3信号が出力され、コネクタCN6から時短信号が出力され、コネクタCN7からセキュリティ信号が出力され、コネクタCN8から賞球信号1が出力され、コネクタCN9から遊技機エラー状態信号が出力される。なお、ターミナル基板160における各外部出力信号に対するコネクタの割り当ては、この実施の形態で示したものにかぎられない。例えば、セキュリティ信号については、ターミナル基板160に設けられた一番端のコネクタ(例えば、コネクタCN9)から出力されるようにしてもよい。
By the operation of the semiconductor relays PC1 to PC9 as described above, the signals inputted from the connector CN-1 and the connector CN-2 on the input side are transmitted to the connectors CN1 to CN9 on the output side, and the external device such as a hall computer It is output. Specifically, a start opening signal is output from the connector CN1, a symbol determination frequency 1 signal is output from the connector CN2, a big hit 1 signal is output from the connector CN3, and a big hit 2 signal is output from the connector CN4, and the connector CN5 A big hit 3 signal is output, a short time signal is output from the connector CN6, a security signal is output from the connector CN7, a prize ball signal 1 is output from the connector CN8, and a gaming machine error state signal is output from the connector CN9. The assignment of connectors to each external output signal in terminal board 160 is not limited to that shown in this embodiment. For example, the security signal may be output from the endmost connector (for example, connector CN9) provided on the terminal substrate 160.
なお、コネクタCN7から出力されるセキュリティ信号は、遊技機のセキュリティ状態を示す信号である。具体的には、後述するように、始動口スイッチ14aの検出結果と入賞確認スイッチ14bの検出結果とにもとづいて、始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したと判定された場合に、セキュリティ信号が所定期間(例えば、4分間)ホールコンピュータなどの外部装置に出力される。そのように構成することによって、電波などを用いて始動入賞口14への入賞数が実際の入賞数よりも多くなるように認識させるような不正行為が行われたことを、ホールコンピュータなどの外部装置側で認識できるようにすることができる。
The security signal output from the connector CN7 is a signal indicating the security state of the gaming machine. Specifically, as described later, when it is determined that the abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14 has occurred based on the detection result of the starting opening switch 14a and the detection result of the winning confirmation switch 14b, the security signal Is output to an external device such as a hall computer for a predetermined period (for example, 4 minutes). By configuring in this way, it is possible that an illegal operation is performed such that the number of winnings to the start winning opening 14 is recognized to be larger than the actual number of winnings using radio waves etc. It can be made recognizable on the device side.
また、この実施の形態では、遊技機への電源投入が行われて初期化処理が実行された場合にも、セキュリティ信号が所定期間(例えば、30秒間)ホールコンピュータなどの外部装置に出力される。そのように構成することによって、不自然なタイミングで(例えば、遊技店の開店時に全ての遊技機の電源リセット作業を終えた後であるにもかかわらず)初期化処理が実行されたことを認識可能とすることによって、不正に遊技機を電源リセットさせて電源リセットのタイミングで大当りを狙うような不正行為が行われた可能性を、ホールコンピュータなどの外部装置側で認識できるようにすることができる。
In this embodiment, the security signal is output to an external device such as a hall computer for a predetermined period (for example, 30 seconds) even when the game machine is powered on and initialization processing is executed. . By configuring as such, it is recognized that the initialization process is executed at an unnatural timing (for example, despite the fact that the power reset operation for all gaming machines has been completed at the time of opening the gaming arcade) By making it possible, an external device such as a hall computer can recognize the possibility that fraudulent activity such as aiming at a big hit at the timing of power reset by making the power of the gaming machine reset improperly can be performed. it can.
なお、この実施の形態では、上記のように、異常入賞が検出された場合と、初期化処理(例えば、遊技機への電源投入時に、クリアスイッチによる操作が行われたことにもとづいてRAM55の記憶内容をクリアするなどの処理)が実行された場合とで、共通のセキュリティ信号をターミナル基板160の共通のコネクタCN7から外部出力している。これは、初期化処理が実行されるのは、通常、遊技店の開店時に遊技機の電源リセット作業を行う場合のみであることから、1日のうち1回程度しか出力されない信号のためにターミナル基板160上に専用のコネクタや半導体リレーを設けることは効率的ではなく無駄が多い。そこで、この実施の形態では、異常入賞が検出された場合と、初期化処理が実行された場合とで、共通のコネクタCN7からセキュリティ信号を出力するように構成することによって、外部出力用の信号線や回路素子の無駄を低減している。すなわち、ホールコンピュータなどの外部装置に情報を出力するための機構の部品数の増加や配線作業の複雑化を防ぐことができる。
In this embodiment, as described above, the abnormal winning is detected as described above, and the initialization process (for example, based on the fact that the operation by the clear switch is performed when the power is turned on to the gaming machine) A common security signal is externally output from the common connector CN7 of the terminal substrate 160 when processing such as clearing stored contents is executed. This is because the initialization process is usually performed only when the game machine power is reset when the game arcade is opened, so the terminal can not be output because it is output only once in a day. Providing a dedicated connector or semiconductor relay on the substrate 160 is not efficient and wasteful. Therefore, in this embodiment, a signal for external output is configured by outputting the security signal from the common connector CN7 when the abnormal winning is detected and when the initialization process is performed. The waste of wires and circuit elements is reduced. That is, it is possible to prevent an increase in the number of parts of a mechanism for outputting information to an external device such as a hall computer and a complication of wiring work.
なお、セキュリティ信号として共通のコネクタから外部出力される信号は、この実施の形態で示したものにかぎられない。例えば、始動入賞口14への異常入賞にかぎらず、大入賞口や普通入賞口29,30への異常入賞を検出して、ターミナル基板160の共通のコネクタCN7からセキュリティ信号として外部出力可能なように構成してもよい。この場合、例えば、大入賞口や普通入賞口29,30についても、始動入賞口14と同様に、遊技球の入賞を検出するためのスイッチとして検出方式の異なる2種類のスイッチ(近接スイッチとフォトセンサ)を設けるようにし、始動入賞口14と同様の判定方法に従って、異常入賞の有無を判定するようにすればよい。
The signal externally output from the common connector as a security signal is not limited to that shown in this embodiment. For example, not only the abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14 but also the abnormal winning on the large winning opening and the normal winning opening 29, 30 can be detected and output from the common connector CN7 of the terminal board 160 as a security signal. You may configure it. In this case, for example, also for the special winning opening and the normal winning openings 29, 30, as in the case of the starting winning opening 14, two types of switches (proximity switch and photo) having different detection methods as switches for detecting winning of gaming balls. A sensor may be provided, and the presence or absence of an abnormal winning may be determined according to the same determination method as the start winning opening 14.
また、例えば、遊技機に設けられた磁石センサで異常磁気を検出した場合や、遊技機に設けられた電波センサで異常電波を検出した場合に、ターミナル基板160の共通のコネクタCN7からセキュリティ信号として外部出力可能なように構成してもよい。また、例えば、遊技機に設けられた各種スイッチの異常を検出した場合(例えば、入力値が閾値を超えたと判定したことにより、短絡などの発生を検出した場合)に、ターミナル基板160の共通のコネクタCN7からセキュリティ信号として外部出力可能なように構成してもよい。
Also, for example, when abnormal magnetism is detected by a magnet sensor provided in a game machine, or when an abnormal radio wave is detected by a radio wave sensor provided in a game machine, as a security signal from the common connector CN7 of the terminal board 160 It may be configured to allow external output. In addition, for example, when an abnormality of various switches provided in a game machine is detected (for example, when occurrence of a short circuit or the like is detected by determining that an input value exceeds a threshold), the terminal board 160 is common. The connector CN7 may be configured to be able to output an external signal as a security signal.
上記のように、大入賞口への異常入賞や異常磁気エラー、異常電波エラーについてもターミナル基板160の共通のコネクタCN7からセキュリティ信号として外部出力可能なように構成すれば、1本の信号線さえ接続すればホールコンピュータなど外部装置でエラー検出を行えるようにすることができ、エラー検出に関する作業負担を軽減することができる。
As described above, even if one signal line is configured as an external output as a security signal from the common connector CN7 of the terminal board 160 for abnormal winnings to the special winning opening, abnormal magnetic errors, and abnormal radio errors as well. If connected, error detection can be performed by an external device such as a hall computer, and the work load for error detection can be reduced.
なお、大入賞口への異常入賞を検出する場合には、カウントスイッチ23による検出数と入賞確認スイッチによる検出数とが所定値(例えば、10)以上となったことにもとづいて判定する場合に加えて、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が大当り遊技中であることを示す値となっていない場合(例えば、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が4以上となっていない場合。図50参照)にカウントスイッチ23により遊技球を検出した場合にも、大入賞口への異常入賞が発生したと判定するようにしてもよい。また、このように、カウントスイッチ23および入賞確認スイッチの検出結果にもとづいて大入賞口への異常入賞が発生したと判定した場合や、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値にもとづいて大入賞口への異常入賞が発生したと判定した場合にも、スイッチ正常/異常チェック処理におけるステップS127と同様に、セキュリティ信号情報タイマに所定時間(例えば、4分)をセットすることにより、セキュリティ信号を外部出力するようにすればよい。
In the case of detecting an abnormal winning to the special winning opening, it is determined based on the fact that the number of detections by the count switch 23 and the number of detections by the winning confirmation switch become equal to or greater than a predetermined value (for example, 10). In addition, when the value of the special symbol process flag is not a value indicating that a big hit is in progress (for example, when the value of the special symbol process flag is not 4 or more. See FIG. 50). It may be determined that an abnormal winning to the big winning opening has occurred even when the game ball is detected by the. In addition, when it is determined that an abnormal winning to the big winning opening has occurred based on the detection results of the count switch 23 and the winning confirmation switch, or to the special winning opening based on the value of the special symbol process flag. Even when it is determined that a winning has occurred, as in step S127 in the switch normality / abnormality check process, the security signal information timer is set to a predetermined time (for example, 4 minutes) to externally output the security signal. You should do it.
また、例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との間の通信エラーを検出した場合にも、ターミナル基板160の共通のコネクタCN7からセキュリティ信号として外部出力可能なように構成してもよい。この場合、例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370から後述する接続OKコマンドや賞球個数受付コマンドを受信できなかったことにもとづいて通信エラーが発生したと判定し、ターミナル基板160の共通のコネクタCN7からセキュリティ信号として外部出力してもよい。また、例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、シリアル通信回路505のステータスレジスタAのビット0〜4のいずれかのエラービットの値がセットされていることにもとづいて通信エラーが発生したと判定し、ターミナル基板160の共通のコネクタCN7からセキュリティ信号として外部出力してもよい。
Also, for example, when a communication error between the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 is detected, the common connector CN7 of the terminal substrate 160 can be externally output as a security signal. May be In this case, for example, the game control microcomputer 560 determines that a communication error has occurred based on the failure to receive a connection OK command or a prize ball number reception command described later from the payout control microcomputer 370, and the terminal It may be externally output as a security signal from the common connector CN7 of the substrate 160. Also, for example, based on the fact that the value of one of the error bits of bits 0 to 4 of status register A of serial communication circuit 505 is set, microcomputer 560 for gaming control determines that a communication error has occurred. , And may be externally output as a security signal from the common connector CN7 of the terminal substrate 160.
なお、セキュリティ信号用の信号線およびコネクタCN7とは別に、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との間の通信エラー専用の信号線およびコネクタをターミナル基板160に設けてもよい。そして、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との間の通信エラーを検出した場合には、セキュリティ信号とは別の信号として、ターミナル基板160を経由してホールコンピュータなどの外部装置に出力するようにしてもよい。
A signal line and a connector dedicated to communication errors between the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 may be provided on the terminal substrate 160 separately from the signal line for the security signal and the connector CN7. Then, when a communication error between the gaming control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 is detected, an external device such as a hall computer or the like via the terminal substrate 160 as a signal different from the security signal. It may be output to
また、セキュリティ信号出力用の信号線とは別に、初期化処理実行の検出や、始動入賞口14への異常入賞の検出、大入賞口への異常入賞の検出、異常磁気エラーの検出、異常電波エラーの検出、通信エラーの検出について、それぞれ別々の信号線を設けるようにし、ターミナル基板160から、セキュリティ信号とともに、それぞれのエラーに対応した外部出力信号も、ホールコンピュータなどの外部装置に出力するようにしてもよい。そのように構成すれば、セキュリティ信号を確認することによって何らかのエラーが発生していることを認識できるとともに、さらにエラーの種類ごとに出力される信号を確認することによって遊技店側でエラーの種類を確認することができる。従って、遊技店側からエラーの種類の確認まで要求されているような場合には、セキュリティ信号とは別にエラー種類ごとの外部出力信号を設けることによって、より遊技店のニーズに応えた外部出力を行えるようにすることができる。一方で、何らかのエラーが発生していることの確認のみを要求しているような遊技店の場合には、外部出力される信号のうち、セキュリティ信号のみをホールコンピュータなどの外部装置に接続して確認するようにすればよい。
Also, apart from the signal line for security signal output, detection of execution of initialization processing, detection of abnormal winning to start winning opening 14, detection of abnormal winning to large winning opening, detection of abnormal magnetic error, abnormal electric wave Separate signal lines are provided for error detection and communication error detection, and the terminal board 160 also outputs the security signal and an external output signal corresponding to each error to an external device such as a hall computer. You may With such a configuration, it is possible to recognize that an error has occurred by confirming the security signal, and to further confirm the type of error on the game store side by confirming the signal output for each type of error. It can be confirmed. Therefore, when it is requested from the game arcade side to confirm the type of error, by providing an external output signal for each type of error separately from the security signal, the external output more responsive to the needs of the game arcade It can be done. On the other hand, in the case of a game arcade requiring only confirmation that an error has occurred, of the externally output signals, only the security signal is connected to an external device such as a hall computer. You should check it.
上記のように、半導体リレーPC1〜PC9をターミナル基板160に設けたことにより、外部から遊技機内部への信号入力を防止することができ、その結果、不正行為を確実に防止することができる。なお、上記の例では、ターミナル基板160に半導体リレーPC1〜PC9を設けていたが、半導体リレーPC1〜PC9ではなく、機械式のリレー等の他のリレー素子であってもよい。
As described above, by providing the semiconductor relays PC1 to PC9 on the terminal substrate 160, it is possible to prevent signal input from the outside into the interior of the gaming machine, and as a result, it is possible to reliably prevent fraud. In the above example, the semiconductor relays PC1 to PC9 are provided on the terminal substrate 160. However, other relay elements such as mechanical relays may be used instead of the semiconductor relays PC1 to PC9.
次に遊技機の動作について説明する。図24は、遊技機に対して電力供給が開始され遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560へのリセット信号がハイレベルになったことに応じて遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のCPU56が実行するメイン処理を示すフローチャートである。リセット信号が入力されるリセット端子の入力レベルがハイレベルになると、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のCPU56は、プログラムの内容が正当か否かを確認するための処理であるセキュリティチェック処理を実行した後、ステップS1以降のメイン処理を開始する。メイン処理において、CPU56は、まず、必要な初期設定を行う。
Next, the operation of the gaming machine will be described. FIG. 24 is a flowchart showing main processing executed by the CPU 56 of the game control microcomputer 560 in response to power supply to the game machine being started and the reset signal to the game control microcomputer 560 becoming high level. It is. When the input level of the reset terminal to which the reset signal is input becomes high level, the CPU 56 of the game control microcomputer 560 executes security check processing, which is processing for confirming whether the content of the program is valid or not. , The main processing after step S1 is started. In the main processing, the CPU 56 first performs necessary initialization.
初期設定処理において、CPU56は、まず、割込禁止に設定する(ステップS1)。次に、マスク可能割込の割込モードを設定し(ステップS2)、スタックポインタにスタックポインタ指定アドレスを設定する(ステップS3)。なお、ステップS2では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560の特定レジスタ(Iレジスタ)の値(1バイト)と内蔵デバイスが出力する割込ベクタ(1バイト:最下位ビット0)から合成されるアドレスが、割込番地を示すモードに設定する。また、マスク可能な割込が発生すると、CPU56は、自動的に割込禁止状態に設定するとともに、プログラムカウンタの内容をスタックにセーブする。
In the initial setting process, the CPU 56 first sets interrupt prohibition (step S1). Next, the interrupt mode of the maskable interrupt is set (step S2), and the stack pointer designation address is set in the stack pointer (step S3). In step S2, an address synthesized from the value (1 byte) of the specific register (I register) of microcomputer 560 for gaming control and the interrupt vector (1 byte: least significant bit 0) output from the built-in device is Set to the mode that indicates the interrupt address. When a maskable interrupt occurs, the CPU 56 automatically sets the interrupt disabled state and saves the contents of the program counter on the stack.
次いで、CPU56は、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に対して、接続信号の出力を開始する(ステップS4)。なお、CPU56は、ステップS4で接続信号の出力を開始すると、遊技機の電源供給が停止したり、何らかの通信エラーが生じて出力不能とならないかぎり、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に対して接続信号を継続して出力する。
Next, the CPU 56 starts outputting a connection signal to the payout control microcomputer 370 (step S4). When the CPU 56 starts outputting the connection signal in step S4, the CPU 56 outputs a connection signal to the payout control microcomputer 370 as long as the power supply of the gaming machine is stopped or any communication error occurs and the output becomes impossible. Continue to output.
次いで、内蔵デバイスレジスタの設定(初期化)を行う(ステップS5)。ステップS5の処理によって、内蔵デバイス(内蔵周辺回路)であるCTC(カウンタ/タイマ)およびPIO(パラレル入出力ポート)の設定(初期化)がなされる。
Next, setting (initialization) of the built-in device register is performed (step S5). By the process of step S5, setting (initialization) of CTC (counter / timer) and PIO (parallel input / output port) as built-in devices (built-in peripheral circuits) is performed.
この実施の形態で用いられる遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、I/Oポート(PIO)およびタイマ/カウンタ回路(CTC)504も内蔵している。
The game control microcomputer 560 used in this embodiment also incorporates an I / O port (PIO) and a timer / counter circuit (CTC) 504.
次いで、CPU56は、RAM55をアクセス可能状態に設定し(ステップS6)、クリア信号のチェック処理に移行する。
Next, the CPU 56 sets the RAM 55 in an accessible state (step S6), and shifts to a clear signal check process.
なお、遊技の進行を制御する遊技装置制御処理(遊技制御処理)の開始タイミングをソフトウェアで遅らせるためのソフトウェア遅延処理を実行するようにしてもよい。そのようなソフトウェア遅延処理によって、ソフトウェア遅延処理を実行しない場合に比べて、遊技制御処理の開始タイミングを遅延させることができる。遅延処理を実行したときには、他の制御基板(例えば、払出制御基板37)に対して、遊技制御基板(主基板31)が送信するコマンドを他の制御基板のマイクロコンピュータが受信できないという状況が発生することを防止できる。
Note that software delay processing may be executed to delay the start timing of the gaming apparatus control processing (game control processing) for controlling the progress of the game by software. Such software delay processing can delay the start timing of the game control processing as compared with the case where the software delay processing is not performed. When delay processing is performed, a situation occurs in which the microcomputer of the other control board can not receive the command transmitted by the game control board (main board 31) to the other control board (for example, the payout control board 37) Can be prevented.
次いで、CPU56は、クリアスイッチがオンされているか否か確認する(ステップS7)。なお、CPU56は、入力ポート0を介して1回だけクリア信号の状態を確認するようにしてもよいが、複数回クリア信号の状態を確認するようにしてもよい。例えば、クリア信号の状態がオフ状態であることを確認したら、所定時間(例えば、0.1秒)の遅延時間をおいた後、クリア信号の状態を再確認する。そのときにクリア信号の状態がオン状態であることを確認したら、クリア信号がオン状態になっていると判定する。また、このときにクリア信号の状態がオフ状態であることを確認したら、所定時間の遅延時間をおいた後、再度、クリア信号の状態を再確認するようにしてもよい。ここで、再確認の回数は、1回または2回に限られず、3回以上であってもよい。また、2回チェックして、チェック結果が一致していなかったときにもう一度確認するようにしてもよい。
Next, the CPU 56 confirms whether the clear switch is turned on (step S7). The CPU 56 may check the state of the clear signal only once via the input port 0, but may check the state of the clear signal multiple times. For example, when it is confirmed that the state of the clear signal is in the off state, the state of the clear signal is reconfirmed after delaying a predetermined time (for example, 0.1 seconds). If it is confirmed that the state of the clear signal is in the on state at that time, it is determined that the clear signal is in the on state. At this time, if it is confirmed that the state of the clear signal is in the off state, the state of the clear signal may be reconfirmed again after setting a delay time of a predetermined time. Here, the number of reconfirmation is not limited to one or two, and may be three or more. Alternatively, the check may be made twice, and when the check results do not match, it may be confirmed again.
ステップS7でクリアスイッチがオンでない場合には、遊技機への電力供給が停止したときにバックアップRAM領域のデータ保護処理(例えばパリティデータの付加等の電力供給停止時処理)が行われたか否か確認する(ステップS8)。この実施の形態では、電力供給の停止が生じた場合には、バックアップRAM領域のデータを保護するための処理が行われている。そのような電力供給停止時処理が行われていたことを確認した場合には、CPU56は、電力供給停止時処理が行われた、すなわち電力供給停止時の制御状態が保存されていると判定する。電力供給停止時処理が行われていないことを確認した場合には、CPU56は初期化処理を実行する。
If the clear switch is not turned on in step S7, whether or not the data protection process (for example, power supply stop process such as addition of parity data) of the backup RAM area is performed when the power supply to the gaming machine is stopped. It confirms (step S8). In this embodiment, processing for protecting data in the backup RAM area is performed when the power supply is stopped. If it is confirmed that the power supply stop processing has been performed, the CPU 56 determines that the power supply stop processing has been performed, that is, the control state at the time of the power supply stop is stored. . When it is confirmed that the power supply stop processing is not performed, the CPU 56 executes the initialization processing.
電力供給停止時処理が行われていたか否かは、電力供給停止時処理においてバックアップRAM領域に保存されるバックアップ監視タイマの値が、電力供給停止時処理を実行したことに応じた値(例えば2)になっているか否かによって確認される。なお、そのような確認の仕方は一例であって、例えば、電力供給停止時処理においてバックアップフラグ領域に電力供給停止時処理を実行したことを示すフラグをセットし、ステップS8において、そのフラグがセットされていることを確認したら電力供給停止時処理が行われたと判定してもよい。
Whether or not the power supply stop processing has been performed is a value corresponding to the execution of the power supply stop processing (for example, 2). It is confirmed by whether it is). Note that such a confirmation method is an example, for example, a flag indicating that the power supply stop processing has been performed is set in the backup flag area in the power supply stop processing, and the flag is set in step S8. If it is confirmed that the power supply is stopped, it may be determined that the power supply stop processing has been performed.
電力供給停止時の制御状態が保存されていると判定したら、CPU56は、バックアップRAM領域のデータチェック(この例ではパリティチェック)を行う(ステップS9)。この実施の形態では、クリアデータ(00)をチェックサムデータエリアにセットし、チェックサム算出開始アドレスをポインタにセットする。また、チェックサムの対象になるデータ数に対応するチェックサム算出回数をセットする。そして、チェックサムデータエリアの内容とポインタが指すRAM領域の内容との排他的論理和を演算する。演算結果をチェックサムデータエリアにストアするとともに、ポインタの値を1増やし、チェックサム算出回数の値を1減算する。以上の処理が、チェックサム算出回数の値が0になるまで繰り返される。チェックサム算出回数の値が0になったら、CPU56は、チェックサムデータエリアの内容の各ビットの値を反転し、反転後のデータをチェックサムにする。
If it is determined that the control state at the time of stopping the power supply is stored, the CPU 56 performs data check (parity check in this example) of the backup RAM area (step S9). In this embodiment, clear data (00) is set in the checksum data area, and the checksum calculation start address is set in the pointer. In addition, the number of times of checksum calculation corresponding to the number of data to be checked is set. Then, an exclusive OR operation is performed on the contents of the checksum data area and the contents of the RAM area pointed to by the pointer. While storing the operation result in the checksum data area, the value of the pointer is increased by 1 and the value of the checksum calculation number is decremented by 1. The above process is repeated until the value of the checksum calculation count becomes zero. When the value of the checksum calculation count becomes 0, the CPU 56 inverts the value of each bit of the contents of the checksum data area, and uses the data after the inversion as a checksum.
電力供給停止時処理において、上記の処理と同様の処理によってチェックサムが算出され、チェックサムはバックアップRAM領域に保存されている。ステップS9では、算出したチェックサムと保存されているチェックサムとを比較する。不測の停電等の電力供給停止が生じた後に復旧した場合には、バックアップRAM領域のデータは保存されているはずであるから、チェック結果(比較結果)は正常(一致)になる。チェック結果が正常でないということは、バックアップRAM領域のデータが、電力供給停止時のデータとは異なっている可能性があることを意味する。そのような場合には、内部状態を電力供給停止時の状態に戻すことができないので、電力供給の停止からの復旧時でない電源投入時に実行される初期化処理(ステップS10〜S14の処理)を実行する。
In the power supply stop processing, the checksum is calculated by the same processing as the above processing, and the checksum is stored in the backup RAM area. In step S9, the calculated checksum is compared with the stored checksum. If recovery is performed after a power supply stop such as an unexpected power failure occurs, the data in the backup RAM area should be saved, so the check result (comparison result) becomes normal (match). If the check result is not normal, it means that the data in the backup RAM area may be different from the data at the time of the power supply interruption. In such a case, since the internal state can not be returned to the state at the time of the power supply stop, the initialization process (steps S10 to S14) to be executed at the time of power on not at the time of recovery from the power supply stop. Run.
チェック結果が正常であれば、CPU56は、遊技制御手段の内部状態と演出制御手段等の電気部品制御手段の制御状態を電力供給停止時の状態に戻すための遊技状態復旧処理を行う。具体的には、ROM54に格納されているバックアップ時設定テーブルの先頭アドレスをポインタに設定し(ステップS91)、バックアップ時設定テーブルの内容を順次作業領域(RAM55内の領域)に設定する(ステップS92)。作業領域はバックアップ電源によって電源バックアップされている。バックアップ時設定テーブルには、作業領域のうち初期化してもよい領域についての初期化データが設定されている。ステップS91およびS92の処理によって、作業領域のうち初期化してはならない部分については、保存されていた内容がそのまま残る。初期化してはならない部分とは、例えば、電力供給停止前の遊技状態を示すデータ(特別図柄プロセスフラグなど)、出力ポートの出力状態が保存されている領域(出力ポートバッファ)、未払出賞球数を示すデータが設定されている部分などである。
If the check result is normal, the CPU 56 performs gaming state recovery processing for returning the internal state of the game control means and the control state of the electric component control means such as the effect control means to the state at the time of the power supply stop. Specifically, the top address of the backup setting table stored in the ROM 54 is set as a pointer (step S91), and the contents of the backup setting table are sequentially set in the work area (the area in the RAM 55) (step S92). ). The work area is backed up by a backup power supply. In the backup setting table, initialization data for an area that may be initialized in the work area is set. With the processing of steps S91 and S92, the saved content remains as it is for the portion of the work area that should not be initialized. The parts that should not be initialized are, for example, data (such as a special symbol process flag) indicating the gaming state before the power supply is stopped, an area in which the output state of the output port is stored (output port buffer) It is a part where data indicating the number is set.
また、CPU56は、ROM54に格納されているバックアップ時コマンド送信テーブルの先頭アドレスをポインタに設定し(ステップS93)、ステップS15に移行する。なお、ステップS93で設定された後、後述するステップS15aのシリアル通信回路設定処理が行われてからバックアップコマンドが送信されることになる。
Further, the CPU 56 sets the top address of the backup command transmission table stored in the ROM 54 as a pointer (step S93), and the process proceeds to step S15. The backup command is transmitted after the serial communication circuit setting process of step S15a described later is performed after the setting in step S93.
初期化処理では、CPU56は、まず、RAMクリア処理を行う(ステップS10)。なお、RAM55の全領域を初期化せず、所定のデータをそのままにしてもよい。また、ROM54に格納されている初期化時設定テーブルの先頭アドレスをポインタに設定し(ステップS11)、初期化時設定テーブルの内容を順次業領域に設定する(ステップS12)。
In the initialization process, the CPU 56 first performs a RAM clear process (step S10). The predetermined data may be left as it is without initializing the entire area of the RAM 55. Further, the start address of the initialization setting table stored in the ROM 54 is set as a pointer (step S11), and the contents of the initialization setting table are sequentially set in the work area (step S12).
ステップS11およびS12の処理によって、例えば、普通図柄判定用乱数カウンタ、普通図柄判定用バッファ、特別図柄バッファ、特別図柄プロセスフラグ、賞球中フラグ、球切れフラグなど制御状態に応じて選択的に処理を行うためのフラグに初期値が設定される。
By the processing of steps S11 and S12, for example, a random symbol counter for normal symbol determination, a buffer for normal symbol determination, a special symbol buffer, a special symbol process flag, a prize symbol flag, an out of ball flag, etc. The initial value is set to the flag for performing.
また、CPU56は、ROM54に格納されている初期化時コマンド送信テーブルの先頭アドレスをポインタに設定し(ステップS13)、その内容に従ってサブ基板を初期化するための初期化コマンドをサブ基板に送信する処理を実行する(ステップS14)。初期化コマンドとして、演出表示装置9に表示される初期図柄を示すコマンドや払出制御基板37への初期化コマンド等を使用することができる。なお、ステップS13で設定された後、後述するステップS15aのシリアル通信回路設定処理が行われてから初期化コマンドが送信されることになる。
The CPU 56 sets the start address of the command transmission table for initialization stored in the ROM 54 as a pointer (step S13), and transmits an initialization command for initializing the sub board according to the contents to the sub board A process is performed (step S14). As the initialization command, a command indicating an initial symbol displayed on the effect display device 9, an initialization command to the payout control board 37, or the like can be used. Note that after being set in step S13, an initialization command is transmitted after serial communication circuit setting processing in step S15a described later is performed.
また、CPU56は、セキュリティ信号情報タイマに所定時間(本例では、30秒)をセットする(ステップS14a)。セキュリティ信号情報タイマは、ターミナル基板160から出力するセキュリティ信号のオン時間を計測するためのタイマである。この実施の形態では、ステップS14aでセキュリティ信号情報タイマに所定時間がセットされたことにもとづいて、後述する情報出力処理(S31参照)が実行されることによって、遊技機の電源投入時に初期化処理が実行されたときに、セキュリティ信号が所定時間(本例では、30秒)外部出力される。
Further, the CPU 56 sets a predetermined time (30 seconds in this example) in the security signal information timer (step S14a). The security signal information timer is a timer for measuring the on time of the security signal output from the terminal board 160. In this embodiment, the information output process (see S31) to be described later is executed based on the predetermined time set in the security signal information timer in step S14a, whereby the initialization process is performed when the gaming machine is powered on. When is executed, the security signal is externally output for a predetermined time (30 seconds in this example).
また、CPU56は、各乱数回路503a,503bを初期設定する乱数回路設定処理を実行する(ステップS15)。この場合、CPU56は、乱数回路設定プログラム551に従って処理を実行することによって、各乱数回路503a,503bにランダムRの値を更新させるための設定を行う。
Further, the CPU 56 executes random number circuit setting processing for initializing each of the random number circuits 503a and 503b (step S15). In this case, the CPU 56 performs processing in accordance with the random number circuit setting program 551 to perform setting for causing the random number circuits 503 a and 503 b to update the value of random R.
また、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505を初期設定するシリアル通信回路設定処理を実行する(ステップS15a)。この場合、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路設定プログラムに従ってROM54の所定領域に格納されているデータをシリアル通信回路505に設定することによって、シリアル通信回路505に払出制御用マイクロコンピュータとシリアル通信させるための設定を行う。
The CPU 56 also executes serial communication circuit setting processing to initialize the serial communication circuit 505 (step S15a). In this case, the CPU 56 sets the data stored in the predetermined area of the ROM 54 in the serial communication circuit 505 according to the serial communication circuit setting program, thereby setting the serial communication circuit 505 to make serial communication with the payout control microcomputer. I do.
シリアル通信回路505を初期設定すると、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505の割り込み要求に応じて実行する割込処理の優先順位を初期設定する(ステップS15b)。この場合、CPU56は、割込優先順位設定プログラム557に従って処理を実行することによって、割込処理の優先順位を初期設定する。
When the serial communication circuit 505 is initialized, the CPU 56 initializes the priority of interrupt processing to be executed in response to the interrupt request of the serial communication circuit 505 (step S15 b). In this case, the CPU 56 initializes the priority of interrupt processing by executing processing according to the interrupt priority setting program 557.
例えば、CPU56は、各割込処理のデフォルトの優先順位を含む所定の割込処理優先順位テーブルに従って、各割込処理の優先順位を初期設定する。この実施の形態では、CPU56は、割込処理優先順位テーブルに従って、シリアル通信回路505において通信エラーが発生したことを割込原因とする割込処理を優先して実行するように初期設定する。この場合、例えば、CPU56は、通信エラーが発生したことを割込原因とする割込処理を優先して実行する旨を示す通信エラー時割込優先実行フラグをセットする。
For example, the CPU 56 initializes the priority of each interrupt process according to a predetermined interrupt process priority table including the default priority of each interrupt process. In this embodiment, in accordance with the interrupt processing priority order table, the CPU 56 performs initialization so that priority is given to interrupt processing which causes the occurrence of a communication error in the serial communication circuit 505 as an interrupt cause. In this case, for example, the CPU 56 sets a communication error interrupt priority execution flag indicating that the interrupt processing with the occurrence of the communication error as the cause of the interrupt is preferentially executed.
なお、この実施の形態では、タイマ割込とシリアル通信回路505からの割り込み要求とが同時に発生した場合、CPU56は、タイマ割込による割込処理を優先して行う。
In this embodiment, when the timer interrupt and the interrupt request from the serial communication circuit 505 occur simultaneously, the CPU 56 prioritizes the interrupt processing by the timer interrupt.
また、ユーザによって各割込処理のデフォルトの優先順位を変更することもできる。例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ユーザ(例えば、遊技機の製作者)によって設定された割込処理を指定する指定情報を、あらかじめROM54の所定の記憶領域に記憶している。そして、CPU56は、ROM54の所定の記憶領域に記憶された指定情報に従って、割込処理の優先順位を設定する。
The user can also change the default priority of each interrupt process. For example, the game control microcomputer 560 stores in advance in a predetermined storage area of the ROM 54 designation information for designating an interruption process set by a user (for example, a maker of a game machine). Then, the CPU 56 sets the priority of the interrupt processing in accordance with the designation information stored in the predetermined storage area of the ROM 54.
なお、ステップS15〜S15bだけでなく、乱数回路503やシリアル通信回路505の設定処理の一部は、ステップS5の処理においても実行される。例えば、ステップS5において、内蔵デバイスレジスタとして、シリアル通信回路505のボーレートレジスタや通信設定レジスタ、割込制御レジスタ、ステータスレジスタに、初期値を設定する処理が実行される。
In addition to the steps S15 to S15b, part of the setting process of the random number circuit 503 and the serial communication circuit 505 is also performed in the process of step S5. For example, in step S5, processing is performed to set initial values in the baud rate register, communication setting register, interrupt control register, and status register of the serial communication circuit 505 as the built-in device register.
例えば、内蔵デバイスレジスタの設定において、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505のボーレートを設定する。この場合、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505のボーレートレジスタ702に、設定するボーレートに対応する設定値を書き込む。例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ユーザ(例えば、遊技機の製作者)によって設定された設定値を指定する指定情報を、あらかじめROM54の所定の記憶領域に記憶している。そして、CPU56は、ROM54の所定の記憶領域に記憶された指定情報に従って、設定値をボーレートレジスタ702に書き込む。例えば、CPU56によってボーレート設定値「156」が設定された場合、ボーレート生成回路703によって、式(1)およびクロック周波数「3MHz」を用いてボーレート「1201.92bps」が生成される。
For example, in the setting of the built-in device register, the CPU 56 sets the baud rate of the serial communication circuit 505. In this case, the CPU 56 writes the setting value corresponding to the baud rate to be set in the baud rate register 702 of the serial communication circuit 505. For example, the gaming control microcomputer 560 prestores designation information for designating a setting value set by a user (for example, a maker of a gaming machine) in a predetermined storage area of the ROM 54 in advance. Then, the CPU 56 writes the setting value into the baud rate register 702 in accordance with the designation information stored in the predetermined storage area of the ROM 54. For example, when the baud rate setting value “156” is set by the CPU 56, the baud rate generation circuit 703 generates a baud rate “1201.92 bps” using the equation (1) and the clock frequency “3 MHz”.
また、例えば、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505が送受信するデータのデータフォーマットを設定する。この場合、CPU56は、制御レジスタA707の各ビットの値を設定することによって、送受信データのデータ長(8ビットまたは9ビット)、パリティ機能の使用の有無を設定する。例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ユーザ(例えば、遊技機の製作者)によって設定された制御レジスタA707の各ビットの値を指定する指定情報を、あらかじめROM54の所定の記憶領域に記憶している。そして、CPU56は、ROM54の所定の記憶領域に記憶された指定情報に従って、制御レジスタA707の各ビットの値を設定する。
Further, for example, the CPU 56 sets a data format of data transmitted and received by the serial communication circuit 505. In this case, the CPU 56 sets the value of each bit of the control register A 707 to set the data length (8 bits or 9 bits) of transmission / reception data and whether to use the parity function. For example, the gaming control microcomputer 560 stores in advance in a predetermined storage area of the ROM 54 designation information for designating the value of each bit of the control register A 707 set by the user (for example, the maker of the gaming machine). There is. Then, the CPU 56 sets the value of each bit of the control register A 707 in accordance with the designation information stored in the predetermined storage area of the ROM 54.
また、例えば、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505が発生する各割込要求を許可するか否かを設定する。この場合、CPU56は、制御レジスタB708のビット5,6,7の値を設定することによって、送信時割り込み要求(データの送信時に行う割り込み要求である送信割り込み要求や、送信完了時に行う送信完了割り込み要求)および受信時割り込み要求を許可するか否かを設定する。なお、CPU56は、送信時割り込み要求と受信時割り込み要求との両方を許可するように設定することも可能であり、送信時割り込み要求と受信時割り込み要求とのいずれか一方のみを許可するように設定することも可能である。また、CPU56は、制御レジスタC709のビット0〜3の値を設定することによって、各通信エラー時割り込み要求を許可するか否かを設定する。例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ユーザ(例えば、遊技機の製作者)によって設定された制御レジスタB708および制御レジスタC709の各ビットの値を指定する指定情報を、あらかじめROM54の所定の記憶領域に記憶している。そして、CPU56は、ROM54の所定の記憶領域に記憶された指定情報に従って、制御レジスタB708および制御レジスタC709の各ビットの値を設定する。
Also, for example, the CPU 56 sets whether to permit each interrupt request generated by the serial communication circuit 505. In this case, the CPU 56 sets the values of bits 5, 6 and 7 of the control register B 708 to make a transmission interrupt request (a transmission interrupt request which is an interrupt request issued at the time of data transmission) and a transmission completion interrupt performed at the transmission completion. Set whether to allow request request and interrupt request at reception. The CPU 56 can also be set to allow both the transmission interrupt request and the reception interrupt request, and allows only one of the transmission interrupt request and the reception interrupt request. It is also possible to set. Further, the CPU 56 sets the values of bits 0 to 3 of the control register C 709 to set whether or not to permit each communication error interrupt request. For example, the microcomputer for game control 560 is a predetermined storage area of the ROM 54 in advance for specifying information for specifying the value of each bit of the control register B 708 and the control register C 709 set by the user (for example, a maker of a game machine). I remember it. Then, the CPU 56 sets the value of each bit of the control register B 708 and the control register C 709 according to the designation information stored in the predetermined storage area of the ROM 54.
また、メイン処理の初期化処理において、後述する賞球不足エラーや賞球過剰エラーを検出するために用いられる賞球個数カウンタに初期値として「250」が設定される処理も実行される。なお、賞球個数カウンタに初期値を設定する処理を、例えば、ステップS92,S12の作業領域に各初期値を順次設定する処理において実行してもよく、ステップS15〜S17の処理に移行するまでの間に実行していればよい。
Further, in the initialization process of the main process, a process is also executed in which "250" is set as an initial value to a prize ball number counter used to detect a prize ball shortage error or prize ball excess error described later. The process of setting the initial value in the prize ball number counter may be performed, for example, in the process of sequentially setting each initial value in the work area in steps S92 and S12, and the process proceeds to step S15 to S17. It should be performed during the
そして、CPU56は、所定時間(例えば4ms)ごとに定期的にタイマ割込がかかるように遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に内蔵されているCTCのレジスタの設定を行なうタイマ割込設定処理を実行する(ステップS16)。すなわち、初期値として例えば4msに相当する値が所定のレジスタ(時間定数レジスタ)に設定される。この実施の形態では、4msごとに定期的にタイマ割込がかかるとする。
Then, the CPU 56 executes a timer interrupt setting process for setting a register of the CTC incorporated in the game control microcomputer 560 so that a timer interrupt is periodically generated every predetermined time (for example, 4 ms) Step S16). That is, a value corresponding to 4 ms, for example, is set as an initial value in a predetermined register (time constant register). In this embodiment, it is assumed that a timer interrupt is periodically performed every 4 ms.
タイマ割込の設定が完了すると、CPU56は、まず、割込禁止状態にして(ステップS17)、初期値用乱数更新処理(ステップS18a)と表示用乱数更新処理(ステップS18b)を実行して、再び割込許可状態にする(ステップS19)。すなわち、CPU56は、初期値用乱数更新処理および表示用乱数更新処理が実行されるときには割込禁止状態にして、初期値用乱数更新処理および表示用乱数更新処理の実行が終了すると割込許可状態にする。
When the setting of the timer interrupt is completed, the CPU 56 first sets the interrupt disable state (step S17), executes the initial value random number updating process (step S18a) and the display random number updating process (step S18b). The interrupt permission state is set again (step S19). That is, when the initial value random number update process and the display random number update process are executed, the CPU 56 is in the interrupt prohibition state, and when the execution of the initial value random number update process and the display random number update process is completed Make it
なお、初期値用乱数更新処理とは、初期値用乱数を発生するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する処理である。初期値用乱数とは、大当りの種類を決定するための判定用乱数(例えば、大当りを発生させる特別図柄を決定するための大当り図柄決定用乱数や、遊技状態を確変状態に移行させるかを決定するための確変決定用乱数、普通図柄にもとづく当りを発生させるか否かを決定するための普通図柄当たり判定用乱数)を発生するためのカウンタ(判定用乱数発生カウンタ)等のカウント値の初期値を決定するための乱数である。後述する遊技制御処理(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータが、遊技機に設けられている演出表示装置9、可変入賞球装置15、球払出装置97等の遊技用の装置を、自身で制御する処理、または他のマイクロコンピュータに制御させるために指令信号を送信する処理、遊技装置制御処理ともいう)において、判定用乱数発生カウンタのカウント値が1周すると、そのカウンタに初期値が設定される。
The initial value random number updating process is a process of updating the count value of the counter for generating the initial value random number. The initial value random number is a random number for determination to determine the type of the big hit (for example, the big hit symbol determination random number for determining the special symbol that generates the big hit, and whether to shift the gaming state to a definite variation state Initial value of count value such as random number for probability variation decision to be used, counter for generating normal pattern hit judgment random number to decide whether to generate hit based on normal pattern etc. It is a random number to determine the value. Game control processing (processing for controlling the gaming devices such as the effect display device 9, the variable winning ball device 15, the ball payout device 97 and the like provided to the gaming machine by the gaming control microcomputer) In the process of transmitting a command signal to control another microcomputer (also referred to as gaming device control process), when the count value of the determination random number generation counter makes one revolution, an initial value is set to the counter.
また、表示用乱数とは、特別図柄表示器8の表示を決定するための乱数である。この実施の形態では、表示用乱数として、特別図柄の変動パターンを決定するための変動パターン決定用乱数や、大当りを発生させない場合にリーチとするか否かを決定するためのリーチ判定用乱数が用いられる。また、表示用乱数更新処理とは、表示用乱数を発生するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する処理である。
Further, the display random number is a random number for determining the display of the special symbol display 8. In this embodiment, as a display random number, a variation pattern determination random number for determining a variation pattern of a special symbol, and a reach determination random number for determining whether or not to reach when a big hit is not generated. Used. The display random number updating process is a process of updating the count value of the counter for generating the display random number.
また、表示用乱数更新処理が実行されるときに割込禁止状態にされるのは、表示用乱数更新処理および初期値用乱数更新処理が後述するタイマ割込処理でも実行される(すなわち、タイマ割込処理のステップS26,S27でも同じ処理が実行される)ことから、タイマ割込処理における処理と競合してしまうのを避けるためである。すなわち、ステップS18a,S18bの処理中にタイマ割込が発生してタイマ割込処理中で初期値用乱数や表示用乱数を発生するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新してしまったのでは、カウント値の連続性が損なわれる場合がある。しかし、ステップS18a,S18bの処理中では割込禁止状態にしておけば、そのような不都合が生ずることはない。
Further, it is also executed in the timer interrupt process that the display random number update process and the initial value random number update process are described later (that is, the timer is in an interrupt-prohibited state when the display random number update process is executed). Since the same process is executed in steps S26 and S27 of the interrupt process, the conflict with the process in the timer interrupt process is avoided. That is, if the timer interruption occurs during the processing of steps S18a and S18b and the count value of the counter for generating the initial value random number and the display random number is updated during the timer interruption processing, the count is counted. The continuity of the values may be lost. However, such an inconvenience does not occur if the interrupt disabled state is set during the processing of steps S18a and S18b.
ステップS19で割込許可状態に設定されると、次にステップS17の処理が実行されて割込禁止状態とされるまで、タイマ割込またはシリアル通信回路505からの割り込み要求を許可する状態となる。そして、割込許可状態に設定されている間に、タイマ割込が発生すると、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のCPU56は、後述するタイマ割込処理を実行する。また、割込許可状態に設定されている間に、シリアル通信回路505から割り込み要求が発生すると、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のCPU56は、後述する各割込処理(通信エラー割込処理や、受信時割込処理、送信完了割込処理)を実行する。また、本実施の形態では、ステップS17からステップS19までのループ処理の前にステップS15bを実行することによって、タイマ割込または割り込み要求を許可する状態に設定される前に、割込処理の優先順位を設定または変更する処理が行われる。
When the interrupt enabled state is set in step S19, the timer interrupt or the interrupt request from the serial communication circuit 505 is allowed until the process of step S17 is executed next and the interrupt disabled state is set. . When the timer interrupt occurs while being set in the interrupt enabled state, the CPU 56 of the game control microcomputer 560 executes a timer interrupt process described later. Also, when an interrupt request is generated from the serial communication circuit 505 while being set in the interrupt enabled state, the CPU 56 of the game control microcomputer 560 performs each interrupt processing (communication error interrupt processing, reception, etc. described later) Execute time interrupt processing and transmission completion interrupt processing). Further, in the present embodiment, by executing step S15b before the loop processing from step S17 to step S19, priority is given to interrupt processing before the timer interrupt or interrupt request is permitted. Processing is performed to set or change the order.
次に、タイマ割込処理について説明する。図25は、タイマ割込処理を示すフローチャートである。メイン処理の実行中に、具体的には、ステップS17〜S19のループ処理の実行中における割込許可になっている期間において、タイマ割込が発生すると、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のCPU56は、タイマ割込の発生に応じて起動されるタイマ割込処理を実行する。タイマ割込処理において、CPU56は、まず、電源断信号が出力されたか否か(オン状態になったか否か)を検出する電源断処理(電源断検出処理)を実行する(ステップS20)。そして、CPU56は、スイッチ回路58を介して、ゲートスイッチ32a、始動口スイッチ14a、入賞確認スイッチ14b、カウントスイッチ23および入賞口スイッチ29a,30a等のスイッチの検出信号を入力し、各スイッチの入力を検出する(スイッチ処理:ステップS21)。具体的には、各スイッチの検出信号を入力する入力ポートの状態がオン状態であれば、各スイッチに対応して設けられているスイッチタイマの値を+1する。
Next, timer interrupt processing will be described. FIG. 25 is a flowchart showing timer interrupt processing. Specifically, during the execution of the main processing, when a timer interrupt occurs during a period in which the interrupt processing is permitted during the execution of the loop processing of steps S17 to S19, the CPU 56 of the game control microcomputer 560 Execute timer interrupt processing which is started in response to the occurrence of timer interrupt. In the timer interrupt process, the CPU 56 first executes a power-off process (power-off detection process) for detecting whether or not the power-off signal is output (is turned on or not) (step S20). Then, the CPU 56 receives detection signals of switches such as the gate switch 32a, the start opening switch 14a, the winning confirmation switch 14b, the count switch 23, and the winning opening switches 29a and 30a via the switch circuit 58, and inputs each switch. Is detected (switching process: step S21). Specifically, if the state of the input port to which the detection signal of each switch is input is the on state, the value of the switch timer provided corresponding to each switch is incremented by one.
次に、CPU56は、特別図柄表示器8、普通図柄表示器10、特別図柄保留記憶表示器18、普通図柄保留記憶表示器41の表示制御を行う表示制御処理を実行する(ステップS22)。特別図柄表示器8および普通図柄表示器10については、ステップS36,S37で設定される出力バッファの内容に応じて各表示器に対して駆動信号を出力する制御を実行する。
Next, the CPU 56 executes display control processing for performing display control of the special symbol display 8, the normal symbol display 10, the special symbol hold storage indicator 18, and the normal symbol hold storage indicator 41 (step S22). With regard to the special symbol display 8 and the normal symbol display 10, control is performed to output a drive signal to each display according to the contents of the output buffer set in steps S36 and S37.
次いで、CPU56は、磁石センサから検出信号を入力したことにもとづいて磁石センサエラー報知を行う磁石センサエラー報知処理を実行する(ステップS24)。
Next, the CPU 56 executes a magnet sensor error notification process of notifying a magnet sensor error based on the detection signal input from the magnet sensor (step S24).
次いで、CPU56は、遊技制御に用いられる普通図柄当り判定用乱数等の各判定用乱数を生成するための各カウンタのカウント値を更新する処理を行う(判定用乱数更新処理:ステップS25)。また、CPU56は、初期値用乱数を発生するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する処理を行う(初期値用乱数更新処理:ステップS26)。さらに、CPU56は、表示用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する処理を行う(表示用乱数更新処理:ステップS27)。
Next, the CPU 56 performs a process of updating the count value of each counter for generating each determination random number such as a normal symbol determination random number used for game control (determination random number update process: step S25). Further, the CPU 56 performs a process of updating the count value of the counter for generating the initial value random number (initial value random number update process: step S26). Further, the CPU 56 performs a process of updating the count value of the counter for generating the display random number (display random number update process: step S27).
次いで、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセス処理を行う(ステップS28)。特別図柄プロセス処理では、遊技状態に応じてパチンコ遊技機1を所定の順序で制御するための特別図柄プロセスフラグに従って該当する処理が選び出されて実行される。そして、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値は、遊技状態に応じて各処理中に更新される。また、普通図柄プロセス処理を行う(ステップS29)。普通図柄プロセス処理では、普通図柄表示器10の表示状態を所定の順序で制御するための普通図柄プロセスフラグに従って該当する処理が選び出されて実行される。そして、普通図柄プロセスフラグの値は、遊技状態に応じて各処理中に更新される。
Next, the CPU 56 performs special symbol process processing (step S28). In the special symbol process processing, the corresponding processing is selected and executed in accordance with the special symbol process flag for controlling the pachinko gaming machine 1 in a predetermined order according to the gaming state. And, the value of the special symbol process flag is updated during each processing according to the gaming state. Also, normal symbol process processing is performed (step S29). In the normal symbol process processing, the corresponding processing is selected and executed according to the normal symbol process flag for controlling the display state of the normal symbol display 10 in a predetermined order. Then, the value of the normal symbol process flag is updated during each process according to the gaming state.
次いで、CPU56は、特別図柄の変動に同期する演出図柄に関する演出制御コマンドをシリアル通信回路505の送信データレジスタに設定して演出制御コマンドを送出する処理を行う(演出図柄コマンド制御処理:ステップS30)。なお、演出図柄の変動が特別図柄の変動に同期するとは、変動時間(可変表示期間)が同じであることを意味する。
Next, the CPU 56 sets the effect control command on the effect symbol synchronized with the variation of the special symbol in the transmission data register of the serial communication circuit 505 and sends the effect control command (effect symbol command control process: step S30). . In addition, that the fluctuation of a production | presentation pattern synchronizes with the fluctuation | variation of a special symbol means that the fluctuation time (variable display period) is the same.
次いで、CPU56は、例えばホール管理用コンピュータに供給される始動口信号、図柄確定回数1信号、大当り1〜3信号、時短信号、セキュリティ信号などのデータを出力する情報出力処理を行う(ステップS31)。
Next, the CPU 56 performs an information output process to output data such as a starting opening signal supplied to the hall management computer, one symbol determination number signal, one to three big hit signals, a short time signal, a security signal, etc. (step S31) ).
次いで、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505を介して、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370と信号を送受信(入出力)する処理を実行するとともに、入賞が発生した場合には入賞口スイッチ29a,30a等の検出信号にもとづく賞球個数の設定などを行う賞球処理を実行する(ステップS32)。なお、この実施の形態では、入賞口スイッチ29a,30a等がオンしたことにもとづく入賞検出に応じて、賞球個数コマンドの下位4ビットを異ならせることにより賞球個数を示すデータを賞球個数コマンドに設定し、当該設定した賞球個数コマンドをシリアル通信回路505を介して払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に出力する。払出制御基板37に搭載されている払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球個数を示すデータが設定された賞球個数コマンドの受信に応じて球払出装置97を駆動する。
Next, the CPU 56 executes processing for transmitting / receiving (input / output) signals to / from the payout control microcomputer 370 via the serial communication circuit 505, and detects a winning opening switch 29a, 30a, etc. when a winning occurs. A winning ball process is performed to set the number of winning balls based on the signal (step S32). In this embodiment, the data indicating the number of prize balls is made different by changing the lower 4 bits of the prize ball number command according to the prize detection based on the prize hole switches 29a, 30a, etc. being turned on. The command is set, and the set prize ball number command is output to the payout control microcomputer 370 via the serial communication circuit 505. The payout control microcomputer 370 mounted on the payout control board 37 drives the ball payout unit 97 in response to the reception of the number-of-balls command in which data indicating the number of balls is set.
また、遊技機の制御状態を遊技機外部で確認できるようにするための試験信号を出力する処理である試験端子処理を実行する(ステップS33)。また、この実施の形態では、出力ポートの出力状態に対応したRAM領域(出力ポートバッファ)が設けられているのであるが、CPU56は、出力ポート0のRAM領域における接続信号に関する内容およびソレノイドに関する内容を出力ポートに出力する(ステップS34:出力処理)。そして、CPU56は、保留記憶数の増減をチェックする記憶処理を実行する(ステップS35)。
In addition, test terminal processing, which is processing of outputting a test signal for enabling the control state of the gaming machine to be confirmed outside the gaming machine, is executed (step S33). Further, in this embodiment, the RAM area (output port buffer) corresponding to the output state of the output port is provided, but the CPU 56 relates to the contents of the connection signal in the RAM area of the output port 0 and the contents of the solenoid. Are output to the output port (step S34: output processing). Then, the CPU 56 executes a storage process of checking whether the number of pending storages increases or decreases (step S35).
また、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値に応じて特別図柄の演出表示を行うための特別図柄表示制御データを特別図柄表示制御データ設定用の出力バッファに設定する特別図柄表示制御処理を行う(ステップS36)。さらに、CPU56は、普通図柄プロセスフラグの値に応じて普通図柄の演出表示を行うための普通図柄表示制御データを普通図柄表示制御データ設定用の出力バッファに設定する普通図柄表示制御処理を行う(ステップS37)。
In addition, the CPU 56 performs special symbol display control processing of setting special symbol display control data for performing special symbol effect display according to the value of the special symbol process flag in the output buffer for setting the special symbol display control data ( Step S36). Furthermore, the CPU 56 performs normal symbol display control processing of setting normal symbol display control data for performing effect display of normal symbols according to the value of the normal symbol process flag in the output buffer for setting normal symbol display control data ( Step S37).
次いで、CPU56は、各状態表示灯の表示を行うための状態表示制御データを状態表示制御データ設定用の出力バッファに設定する状態表示灯表示処理を行う(ステップS38)。この場合、遊技状態が時短状態である場合には、時短状態であることを示す状態表示灯の表示を行うための状態表示制御データを出力バッファに設定する。なお、遊技状態が高確率状態(例えば、確変状態)にも制御される場合には、高確率状態であることを示す状態表示灯の表示を行うための状態表示制御データを出力バッファに設定するようにしてもよい。
Next, the CPU 56 performs a status indicator display process of setting status display control data for displaying each status indicator in an output buffer for setting the status display control data (step S38). In this case, when the gaming state is the time saving state, state display control data for displaying a state indicator light indicating that the time saving state is set is set in the output buffer. If the gaming state is also controlled to a high probability state (for example, a probability change state), state display control data for displaying a state indicator light indicating that the state is a high probability state is set in the output buffer. You may do so.
次いで、CPU56は、遊技機のエラー状態などを表示させるために遊技機のエラー状態などを示す情報が設定された枠状態表示コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して送信する枠状態出力処理を実行する(ステップS39)。
Next, the CPU 56 performs a frame state output process of transmitting to the effect control microcomputer 100 a frame state display command in which information indicating an error state or the like of the gaming machine is set to display an error state or the like of the gaming machine. Execute (step S39).
その後、割込許可状態に設定し(ステップS40)、処理を終了する。
Thereafter, the interrupt enabled state is set (step S40), and the process ends.
次に、メイン処理における賞球処理(ステップS32)を説明する。まず、主基板31と払出制御基板37との間で送受信される払出制御信号(接続信号、賞球情報)および払出制御コマンドについて説明する。
Next, prize ball processing (step S32) in the main processing will be described. First, a payout control signal (connection signal, winning ball information) transmitted and received between the main substrate 31 and the payout control substrate 37 and a payout control command will be described.
図26は、遊技制御手段から払出制御手段に対して出力される制御信号の内容の一例を示す説明図である。この実施の形態では、払出制御等に関する各種の制御を行うために、主基板31と払出制御基板37との間で制御信号として接続信号および賞球情報が送受信される。図26に示すように、接続信号は、主基板31の立ち上がり時(遊技制御手段が遊技制御処理を開始したとき)に出力され、払出制御基板37に対して主基板31が立ち上がったことを通知するための信号(主基板31の接続信号)である。また、接続信号は、賞球払出が可能な状態であることを示す。なお、接続信号は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のI/Oポート57および出力回路67Aを介して出力され、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370の入力回路373AおよびI/Oポート372eを介して払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に入力される。接続信号は、1ビットのデータであり、1本の信号線によって送信される。なお、接続信号は、電源投入時に実行されるステップS4の処理によって出力ポート0の接続信号に対応するビットに初期値が設定されることによって出力可能な状態となる(具体的にはステップS34の処理によって出力されるが、ステップS4のタイミングで出力されるようにしてもよい)。また、賞球情報は、払出制御基板37側において賞球の払出を1個検出するごとに、主基板31に対して、10個の賞球払出を検出したことを通知するための情報である。なお、賞球情報は、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370のI/Oポート372aおよび出力回路373Bを介して出力され、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560の入力回路67BおよびI/Oポート57を介して遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に入力される。賞球情報は、1ビットのデータであり、1本の信号線によって送信される。
FIG. 26 is an explanatory view showing an example of the contents of a control signal output from the game control means to the payout control means. In this embodiment, in order to perform various controls related to the payout control and the like, connection signals and winning sphere information are transmitted and received as control signals between the main substrate 31 and the payout control substrate 37. As shown in FIG. 26, the connection signal is output when the main board 31 rises (when the game control means starts the game control process), and notifies the payout control board 37 that the main board 31 has risen. Signal (connection signal of the main substrate 31). Further, the connection signal indicates that the winning balls can be paid out. The connection signal is output via the I / O port 57 and the output circuit 67A of the game control microcomputer 560, and for payout control via the input circuit 373A and the I / O port 372e of the payout control microcomputer 370. It is input to the microcomputer 370. The connection signal is 1-bit data and is transmitted by one signal line. The connection signal can be output by setting the initial value to the bit corresponding to the connection signal of the output port 0 by the process of step S4 executed when the power is turned on (specifically, step S34). It is output by the process, but may be output at the timing of step S4). The winning ball information is information for notifying the main substrate 31 that 10 winning balls have been paid out, each time the payout control board 37 detects one payout of the winning balls. . The prize ball information is output through the I / O port 372a and the output circuit 373B of the payout control microcomputer 370, and the game control is performed through the input circuit 67B and the I / O port 57 of the game control microcomputer 560. Is input to the microcomputer 560. The prize ball information is 1-bit data and is transmitted by one signal line.
払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と同様に、シリアル通信回路380を内蔵する。また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が内蔵するシリアル通信回路505と、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370が内蔵するシリアル通信回路380との間で、各種払出制御コマンドが送受信される。なお、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370が内蔵するシリアル通信回路380の構成及び機能は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が内蔵するシリアル通信回路505の構成及び機能と同様である。
Similar to the game control microcomputer 560, the payout control microcomputer 370 incorporates a serial communication circuit 380. In addition, various payout control commands are transmitted and received between the serial communication circuit 505 incorporated in the game control microcomputer 560 and the serial communication circuit 380 incorporated in the payout control microcomputer 370. The configuration and function of the serial communication circuit 380 incorporated in the payout control microcomputer 370 are the same as the configuration and function of the serial communication circuit 505 incorporated in the game control microcomputer 560.
図27は、遊技制御手段と払出制御手段との間で送受信される制御コマンドの内容の一例を示す説明図である。この実施の形態では、払出制御等に関する各種の制御を行うために、主基板31と払出制御基板37とのマイクロコンピュータの間で各種払出制御コマンドが送受信される。
FIG. 27 is an explanatory view showing an example of the content of a control command transmitted and received between the game control means and the payout control means. In this embodiment, various payout control commands are transmitted and received between the microcomputers of the main substrate 31 and the payout control substrate 37 in order to perform various controls relating to the payout control and the like.
上述したように、払出制御コマンドは、8ビットのデータ(2進8桁のデータ)によって構成され、設定された8ビットのデータの内容によって所定の内容を示す制御コマンドとして出力される。
As described above, the payout control command is composed of 8-bit data (binary 8-digit data), and is output as a control command indicating predetermined content according to the set 8-bit data content.
接続確認コマンドは、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との間の接続状態が正常であるか否かを確認するために一定間隔(1s)毎に遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から送信される制御コマンドである。接続確認コマンドのデータの内容は「A0(H)」すなわち「10100000」とされている。
The connection confirmation command is used to check whether the connection state between the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 is normal or not from the game control microcomputer 560 at regular intervals (1s). It is a control command to be sent. The content of the data of the connection confirmation command is "A0 (H)", that is, "10100000".
接続OKコマンドは、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との間の接続状態が正常であることを通知するための制御コマンドであって、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370が接続確認コマンドの受信に応じて応答信号として送信する制御コマンドである。接続OKコマンドのデータの内容は「8x(H)」すなわち「1000xxxx」とされている。ここで、接続OKコマンドの2バイト目の「xxxx」については、図28に示すように、賞球エラー(入賞にもとづく賞球払出動作や球貸し要求にもとづく球貸払出動作が正常に行えない状態になった異常状態:具体的には、図85に示す主制御未接続エラーや、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー1、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー2、払出ケースエラー、主制御通信エラー)が発生した場合には、1ビット目(ビット0)の「x」に「1」が設定される。また、満タンエラーが発生した場合には、2ビット目(ビット1)の「x」に「1」が設定される。また、球切れエラーが発生した場合には、3ビット目(ビット2)の「x」に「1」が設定される。また、後述する賞球や貸し球の払出数の個数異常の累積値が所定値(例えば、2000個)に達した場合の払出個数異常エラーが発生した場合には、4ビット目(ビット3)の「x」に「1」が設定される。このようにして、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との間の接続確認を行っている最中に、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370における所定のエラーの発生を遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に通知することができる。なお、図28に示す例では、接続OKコマンドに、制御状態として払い出しに関するエラー(賞球エラーや、満タンエラー、球切れエラー、払出個数異常エラー)を示す値を設定する場合を示したが、エラー以外の制御状態を接続OKコマンドに設定するようにしてもよい。例えば、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球払出動作中である旨や貸し球払出動作中である旨を示す値を制御状態として接続OKコマンドにセットして、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信するようにしてもよい。
The connection OK command is a control command for notifying that the connection state between the gaming control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 is normal, and the payout control microcomputer 370 is a connection confirmation command. Is a control command to be transmitted as a response signal in response to the reception of. The content of data of the connection OK command is "8x (H)", that is, "1000xxxx". Here, for the second byte “xxxx” of the connection OK command, as shown in FIG. 28, a winning ball error (a winning ball paying-out operation based on winning or a ball lending paying-out operation based on a ball lending request can not be performed normally) Abnormal state: Specifically, when the main control disconnection error shown in Fig. 85, or the withdrawal switch abnormality detection error 1, the withdrawal switch abnormality detection error 2, the dispensing case error, the main control communication error) occurs , “1” is set to “x” of the first bit (bit 0). When a full tank error occurs, “1” is set to “x” of the second bit (bit 1). In addition, when a ball breakage error occurs, “1” is set to “x” of the third bit (bit 2). In addition, the fourth bit (bit 3) occurs when a payout number anomaly error occurs when the cumulative value of the number anomalies of the number of payouts of the winning balls and the lending balls described later reaches a predetermined value (for example, 2000). "1" is set to "x" of. In this manner, while checking the connection between the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370, the occurrence of a predetermined error in the payout control microcomputer 370 can be determined by the game control microcomputer 560 can be notified. In the example shown in FIG. 28, the connection OK command is set to a value indicating an error related to payout (control ball error, full tank error, out-of-ball error, payout number error) as the control state. A control state other than an error may be set in the connection OK command. For example, the payout control microcomputer 370 sets a value indicating that it is in a prize ball payout operation or a bonus ball payout operation as a control state in a connection OK command, and transmits it to the game control microcomputer 560 You may do it.
賞球個数コマンドは、払出要求を行う遊技球の個数(0〜15個)を通知するための制御コマンドであって、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が入賞の発生にもとづいて送信する制御コマンドである。賞球個数コマンドのデータの内容は「5x(H)」すなわち「0101xxxx」とされている。この実施の形態では、始動口スイッチ14aで遊技球が検出されると3個の賞球払出を行い、入賞口スイッチ29a,30aのいずれかで遊技球が検出されると10個の賞球払出を行い、カウントスイッチ23で遊技球が検出されると15個の賞球払出を行う。よって、始動口スイッチ14aで遊技球が検出された場合、賞球数3個を通知するための賞球個数コマンド「01010011」が送信され、入賞口スイッチ29a,30aのいずれかで遊技球が検出された場合、賞球数10個を通知するための賞球個数コマンド「01011010」が送信され、カウントスイッチ23で遊技球が検出された場合、賞球数15個を通知するための賞球個数コマンド「01011111」が送信される。
The prize ball number command is a control command for notifying the number (0 to 15) of the game balls to which a payout request is issued, and is a control command transmitted by the game control microcomputer 560 based on the occurrence of a winning. . The content of the data of the award ball count command is "5x (H)", that is, "0101 xxxx". In this embodiment, three winning balls are paid out when the gaming ball is detected by the starting opening switch 14a, and ten winning balls are paid out when the gaming ball is detected by any of the winning opening switches 29a, 30a. When the game ball is detected by the count switch 23, 15 balls are paid out. Therefore, when the game ball is detected by the starting opening switch 14a, the winning ball number command "01010011" for notifying the number of winning balls 3 is transmitted, and the game ball is detected by any of the winning opening switches 29a, 30a If it is determined that the winning ball number command "01011010" for notifying the winning ball number 10 is transmitted and the gaming ball is detected by the count switch 23, the winning ball number for notifying the winning ball number 15 The command "01011111" is transmitted.
賞球個数受付コマンドは、賞球個数コマンドで指定された賞球個数を受け付けたことを通知するための制御コマンドであって、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370が賞球個数コマンドの受信に応じて応答信号として送信する制御コマンドである。賞球個数受付コマンドのデータの内容は「70(H)」すなわち、「01110000」とされている。
The prize ball number reception command is a control command for notifying that the number of prize balls specified by the prize ball number command is accepted, and the payout control microcomputer 370 responds in response to the reception of the prize ball number command. It is a control command to be transmitted as a signal. The content of the data of the winning balls number reception command is "70 (H)", that is, "01110000".
賞球終了コマンドは、賞球動作(賞球払出動作)が終了したことを示す制御コマンドであって、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370が賞球動作の終了にもとづいて送信する制御コマンドである。賞球終了コマンドのデータの内容は「50(H)」すなわち「01010000」とされている。
The award ball end command is a control command indicating that the award ball operation (prize ball payout operation) has ended, and is a control command that the payout control microcomputer 370 transmits based on the end of the award ball operation. The content of the data of the award ball end command is "50 (H)", that is, "01010000".
賞球準備中コマンドは、賞球動作に時間がかかっている場合や、貸し球動作中であったり所定のエラーが発生したりして賞球動作が終了していないことを通知する制御コマンドである。賞球準備中コマンドのデータの内容は「4x(H)」すなわち「0100xxxx」とされている。ここで、賞球準備中コマンドの2バイト目の「xxxx」については、図28に示すように、賞球エラーが発生した場合には、1ビット目(ビット0)の「x」に「1」が設定される。また、満タンエラーが発生した場合には、2ビット目(ビット1)の「x」に「1」が設定される。また、球切れエラーが発生した場合には、3ビット目(ビット2)の「x」に「1」が設定される。また、後述する賞球や貸し球の払出数の個数異常の累積値が所定値(例えば、2000個)に達した場合の払出個数異常エラーが発生した場合には、4ビット目(ビット3)の「x」に「1」が設定される。このようにして、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370から、賞球動作に時間がかかっている場合や、貸し球動作中であったり賞球動作の実行中に所定のエラーが発生したりして賞球動作が終了していないことを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に通知することができるとともに、エラーの内容も遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に通知することができる。賞球準備中コマンドは、接続OKコマンドと同様に、下位4ビットの内容をエラー状態に応じて異ならせる(所定ビットを異ならせる)ことによって所定のエラーが発生したことを通知している。なお、賞球準備中コマンドは、エラーが発生して賞球動作が実行できない状態のみならず、貸し球払出動作中であるために賞球の払出動作を直ちに開始できない状態や、賞球動作の実行中の状態(賞球個数コマンドで指定された賞球個数の払出動作を完了していない状態)においても出力されるコマンド(信号)である。なお、図28に示す例では、賞球準備中コマンドに、制御状態として払い出しに関するエラー(賞球エラーや、満タンエラー、球切れエラー、払出個数異常エラー)を示す値を設定する場合を示したが、エラー以外の制御状態を接続OKコマンドに設定するようにしてもよい。例えば、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球払出動作中である旨や貸し球払出動作中である旨を示す値を制御状態として賞球準備中コマンドにセットして、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信するようにしてもよい。
The prize ball preparation command is a control command to notify that the prize ball operation has not ended when the prize ball operation takes a long time or while the rental ball operation is in progress or a predetermined error occurs. is there. The content of the data of the prize ball preparation command is "4x (H)", that is, "0100xxxx". Here, with respect to the second byte “xxxx” of the award ball preparation command, as shown in FIG. 28, when a prize ball error occurs, “1” is set to “x” of the first bit (bit 0). "Is set. When a full tank error occurs, “1” is set to “x” of the second bit (bit 1). In addition, when a ball breakage error occurs, “1” is set to “x” of the third bit (bit 2). In addition, the fourth bit (bit 3) occurs when a payout number anomaly error occurs when the cumulative value of the number anomalies of the number of payouts of the winning balls and the lending balls described later reaches a predetermined value (for example, 2000). "1" is set to "x" of. In this manner, the prize ball operation takes a long time from the payout control microcomputer 370, or a predetermined error occurs during the rental ball operation or the execution of the prize ball operation, and the prize ball The fact that the operation has not ended can be notified to the gaming control microcomputer 560, and the contents of the error can also be notified to the gaming control microcomputer 560. Similarly to the connection OK command, the award ball preparation command notifies that a predetermined error has occurred by making the contents of the lower 4 bits different according to the error state (different predetermined bits). It should be noted that the command for preparing the winning ball is not only a state in which an error occurs and the winning ball operation can not be executed, but also a state in which the payout operation of the winning ball can not be started immediately because the rental ball is in payout operation. It is a command (signal) which is also output in a running state (a state where the payout operation for the number of winning balls specified by the winning ball number command is not completed). In the example shown in FIG. 28, a case is shown in which a value representing an error related to payout (control ball error, full tank error, out-of-ball error, payout number abnormality error) is set as a control state in the winning ball preparation command. However, a control state other than an error may be set in the connection OK command. For example, the payout control microcomputer 370 sets a value indicating the fact that a prize ball payout operation is in progress or a rental ball payout operation is in progress as a control state in a prize ball preparation command, and the microcomputer 560 for gaming control It may be sent to the
なお、この実施の形態では、接続確認信号は払出制御コマンドのうちの接続確認コマンドによって実現され、応答信号は接続OKコマンドによって実現され、払出数信号は賞球個数コマンドによって実現され、受付信号は賞球個数受付コマンドによって実現され、払出終了信号は賞球終了コマンドによって実現され、払出中信号は賞球準備中コマンドによって実現される。
In this embodiment, the connection confirmation signal is realized by the connection confirmation command in the payout control command, the response signal is realized by the connection OK command, the payout number signal is realized by the prize ball number command, and the acceptance signal is It is realized by the prize ball number reception command, the payout end signal is realized by the prize ball end command, and the payout in-progress signal is realized by the prize ball preparation command.
図29は、図26に示す制御信号および図27に示す制御コマンドの送受信に用いられる信号線等を示すブロック図である。図29に示すように、接続信号は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560によって出力回路67Aを介して出力され、入力回路373Aを介して払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に入力される。また、賞球情報は、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370によって出力回路373Bを介して出力され、入力回路67Bを介して遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に入力される。なお、後述する賞球信号1や遊技機エラー状態信号も、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370によって出力回路373Bを介して出力され、入力回路67Bを介して遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に入力されるようにしてもよい。また、ドア開放信号も、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370によって出力回路373Bを介して出力され、入力回路67Bを介して遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に入力されるようにしてもよい。
FIG. 29 is a block diagram showing signal lines and the like used for transmission and reception of control signals shown in FIG. 26 and control commands shown in FIG. As shown in FIG. 29, the connection signal is output by the game control microcomputer 560 via the output circuit 67A, and is input to the payout control microcomputer 370 via the input circuit 373A. Further, the prize ball information is output by the payout control microcomputer 370 via the output circuit 373B, and is input to the game control microcomputer 560 via the input circuit 67B. The prize ball signal 1 and the gaming machine error state signal, which will be described later, are also outputted by the payout control microcomputer 370 through the output circuit 373B and inputted into the game control microcomputer 560 through the input circuit 67B. May be The door open signal may also be output by the payout control microcomputer 370 via the output circuit 373B and may be input to the game control microcomputer 560 via the input circuit 67B.
また、制御コマンドのうちの接続確認コマンドおよび賞球個数コマンドは、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が内蔵するシリアル回路505から出力され、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370が内蔵するシリアル回路380に入力される。制御コマンドのうちの接続OKコマンド、賞球個数受付コマンド、賞球終了コマンドおよび賞球準備中コマンドは、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370が内蔵するシリアル回路380から出力され、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が内蔵するシリアル回路505に入力される。なお、図29では、シリアル通信を行うための信号線として2本の信号線(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370側にコマンドを送信するための信号線と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370から遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560側にコマンドを送信するための信号線)を示しているが、実際は1本の信号線で払出制御コマンドを送受信する。なお、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370側にコマンドを送信するための信号線と、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370から遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560側にコマンドを送信するための信号線とを、別々の信号線として構成するようにしてもよい。
Further, the connection confirmation command and the prize ball number command among the control commands are output from the serial circuit 505 built in the game control microcomputer 560 and are input to the serial circuit 380 built in the payout control microcomputer 370. Among the control commands, the connection OK command, the prize ball number reception command, the prize ball end command and the prize ball preparation command are outputted from the serial circuit 380 built in the payout control microcomputer 370, and the game control microcomputer 560 It is input to the built-in serial circuit 505. In FIG. 29, two signal lines (signal lines for transmitting a command from microcomputer for gaming control 560 to microcomputer 370 for payout control and a microcomputer for payout control) are used as signal lines for performing serial communication. Although a signal line for transmitting a command from the memory 370 to the game control microcomputer 560 is shown, in actuality, the payout control command is transmitted / received by one signal line. A signal line for transmitting a command from the gaming control microcomputer 560 to the payout control microcomputer 370 and a signal line for transmitting a command from the payout control microcomputer 370 to the gaming control microcomputer 560. And may be configured as separate signal lines.
次に、通常動作時における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータと払出制御用マイクロコンピュータとの払出制御コマンドの送受信について説明する。この実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370には接続確認コマンドと賞球個数コマンドとが送信され、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370から遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560には接続OKコマンドと賞球個数受付コマンドと賞球終了コマンドと賞球準備中コマンドとが送信される。
Next, transmission and reception of a payout control command between the game control microcomputer and the payout control microcomputer in the normal operation will be described. In this embodiment, a connection confirmation command and a prize ball count command are transmitted from the game control microcomputer 560 to the payout control microcomputer 370, and the payout control microcomputer 370 is connected to the game control microcomputer 560. An OK command, a prize ball number reception command, a prize ball end command, and a prize ball preparing command are transmitted.
図30は、通常動作時における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータと払出制御用マイクロコンピュータとの信号の送受信を示すシーケンス図である。図30に示すように、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、シリアル通信回路505を介して、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との間の信号線の接続が切れていないかどうかを確認するために、接続確認コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、接続確認コマンドをシリアル通信回路380を介して受信すると、接続OKコマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、接続OKコマンドを受信すると、受信した時点から1s(1秒)経過後に接続確認コマンドを送信する。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560および払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、接続状態が正常である限り、上記のような接続確認の通信処理を繰り返し実行する。
FIG. 30 is a sequence diagram showing transmission and reception of signals between the gaming control microcomputer and the payout control microcomputer during normal operation. As shown in FIG. 30, the game control microcomputer 560 is connected via the serial communication circuit 505 in order to confirm whether or not the signal line with the payout control microcomputer 370 is disconnected. A confirmation command is sent to the payout control microcomputer 370. When the payout control microcomputer 370 receives the connection confirmation command via the serial communication circuit 380, the payout control microcomputer 370 transmits a connection OK command to the game control microcomputer 560. When receiving the connection OK command, the game control microcomputer 560 transmits a connection confirmation command after 1 s (one second) has elapsed from the time of reception. As long as the connection state is normal, the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 repeatedly execute the communication process of the connection confirmation as described above.
図31および図32は、賞球動作時における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータと払出制御用マイクロコンピュータとの信号の送受信を示すシーケンス図である。図31および図32に示すように、入賞が発生して賞球払出動作を実行するときに、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、シリアル通信回路505を介して、賞球個数を示すデータが設定された賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。なお、この場合、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、前回送信した接続確認コマンドに対して受信した接続OKコマンドの下位4ビットにエラーを示す値が設定されておらず(図28参照)、かつ当該接続OK信号を受信してから1秒が経過するまでの間に始動入賞していることを条件として、賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。
31 and 32 are sequence diagrams showing transmission and reception of signals between the game control microcomputer and the payout control microcomputer at the time of prize ball operation. As shown in FIGS. 31 and 32, when a prize is generated and a prize ball payout operation is performed, the microcomputer 560 for gaming control sets data indicating the number of prize balls via the serial communication circuit 505. The prize ball quantity command is transmitted to the payout control microcomputer 370. In this case, in the gaming control microcomputer 560, a value indicating an error is not set in the lower 4 bits of the connection OK command received in response to the connection confirmation command transmitted previously (see FIG. 28), and A prize ball count command is transmitted to the payout control microcomputer 370 on the condition that the start-up winning is performed until one second elapses after the connection OK signal is received.
次いで、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球個数コマンドを受信すると、直ちに賞球動作の実行が可能であれば(すなわち、貸し球の払出動作中でなくエラーも発生していなければ)、賞球個数を受け付けたことを示す賞球個数受付コマンドをシリアル通信回路380を介して遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。なお、賞球個数受付コマンドを送信した時点から1s(1秒)以内に賞球払出が完了しない場合には、賞球個数受付コマンドを送信した時点から1s(1秒)経過後に賞球準備中コマンドを送信する。そして、以後、賞球払出が完了するまでの間、賞球準備中コマンドを送信した時点から1s(1秒)経過するごとに繰り返し賞球準備中コマンドを送信する。また、賞球個数コマンドで指定された個数の賞球の払出動作を実行し、賞球払出動作が終了すると、賞球払出動作の終了を示す賞球終了コマンドをシリアル通信回路380を介して遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。
Next, when the payout control microcomputer 370 receives the prize ball count command, it is possible to immediately execute the prize ball operation (ie, if the rental ball is not being dispensed and no error is generated), A prize ball number reception command indicating that the ball number has been received is transmitted to the game control microcomputer 560 via the serial communication circuit 380. In addition, when the award ball payout is not completed within 1s (1 second) from the time of sending the award ball number reception command, the prize balls are being prepared after 1s (1 second) elapses from the time of sending the award ball number reception command. Send a command After that, while the balls are being prepared, the balls are prepared and the command being prepared is repeatedly transmitted every 1 s (one second) after the balls are prepared. In addition, the payout operation of the number of prize balls specified by the prize ball number command is executed, and when the prize ball payout operation is completed, the prize ball end command indicating the end of the prize ball payout operation is played through the serial communication circuit 380. It transmits to the control microcomputer 560.
次いで、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、賞球終了コマンドを受信したときに、図31に示すように、次に払い出すべき賞球個数がまだ記憶されていない場合には、賞球終了コマンドを受信した時点から1s(1秒)経過後に新たな接続確認コマンドの送信を再開する。一方、図32に示すように、次に払い出すべき賞球個数が既に記憶されている場合には、1s(1秒)待つことなく、直ちに次の賞球個数を指定する賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。なお、この場合にも、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、前回受信した接続OKコマンドまたは賞球準備中コマンドの下位4ビットにエラーを示す値が設定されておらず(図28参照)、かつ賞球終了コマンドを受信してから1秒が経過するまでの間に始動入賞していることを条件として、賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。以降、同様のシーケンスに従って制御コマンドの送受信が繰り返される。
Next, when the game control microcomputer 560 receives the winning ball end command, as shown in FIG. 31, if the number of winning balls to be paid out next is not stored yet, the winning ball end command is The transmission of a new connection confirmation command is resumed after 1 s (1 second) has elapsed from the time of reception. On the other hand, as shown in FIG. 32, when the number of winning balls to be paid out next is already stored, the winning balls number command for designating the next winning balls number is immediately without waiting for 1 s (1 second). It transmits to the payout control microcomputer 370. Also in this case, in the gaming control microcomputer 560, a value indicating an error is not set in the lower 4 bits of the connection OK command or the prize ball preparation command received previously (see FIG. 28), and the prize A prize ball count command is transmitted to the payout control microcomputer 370 on the condition that the start winning is achieved between the time when the ball end command is received and one second elapses. Thereafter, transmission and reception of control commands are repeated according to the same sequence.
図33は、直ちに賞球動作を実行できない場合における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータと払出制御用マイクロコンピュータとの信号の送受信を示すシーケンス図である。払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球個数コマンドを受信しても、貸し球の払出動作中である場合や、エラー状態である場合には、受信した賞球個数コマンドで指定された賞球個数の賞球払出の動作を開始できない。このような場合には、図33に示すように、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球個数コマンドを受信しても、直ちに賞球個数受付コマンドを送信せず、賞球払出動作が終了していないことを通知する賞球準備中コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。この場合、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、貸し球の払出動作を終了して賞球動作を開始可能な状態となるか、エラーが解除されない限り、一定間隔で(1s毎に)賞球準備中コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。
FIG. 33 is a sequence diagram showing transmission and reception of signals between the game control microcomputer and the payout control microcomputer when the prize ball operation can not be executed immediately. The payout control microcomputer 370 receives the number-of-winning-balls command, but if the lending balls are being dispensed, or if it is in an error state, the number of winning balls specified by the received number-of-balls command Can not start the prize ball payout action. In such a case, as shown in FIG. 33, even when the payout control microcomputer 370 receives the winning balls count command, it does not immediately transmit the winning balls count reception command, and the winning balls payout operation is completed. A prize ball preparing command notifying that the game is not performed is transmitted to the game control microcomputer 560. In this case, the payout control microcomputer 370 ends the payout operation of the rental ball and becomes ready to start the prize ball operation, or the prize ball is being prepared at regular intervals (every 1s) unless the error is canceled. The command is transmitted to the game control microcomputer 560.
次いで、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、貸し球の払出動作を終了して次の賞球動作を開始可能な状態となるか、エラーが解除されると、賞球個数を受け付けたことを示す賞球個数受付コマンドをシリアル通信回路380を介して遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。なお、賞球個数受付コマンドを送信した時点から1s(1秒)以内に賞球払出が完了しない場合には、賞球個数受付コマンドを送信した時点から1s(1秒)経過後に賞球準備中コマンドを送信する。そして、以後、賞球払出が完了するまでの間、賞球準備中コマンドを送信した時点から1s(1秒)経過するごとに繰り返し賞球準備中コマンドを送信する。また、賞球個数コマンドで指定された個数の賞球の払出動作を実行し、賞球払出動作が終了すると、賞球払出動作の終了を示す賞球終了コマンドをシリアル通信回路380を介して遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。
Subsequently, the payout control microcomputer 370 ends the payout operation of the rental ball and becomes ready to start the next winning ball operation, or when the error is canceled, the award indicating that the number of winning balls has been received. A ball number reception command is transmitted to the game control microcomputer 560 via the serial communication circuit 380. In addition, when the award ball payout is not completed within 1s (1 second) from the time of sending the award ball number reception command, the prize balls are being prepared after 1s (1 second) elapses from the time of sending the award ball number reception command. Send a command After that, while the balls are being prepared, the balls are prepared and the command being prepared is repeatedly transmitted every 1 s (one second) after the balls are prepared. In addition, the payout operation of the number of prize balls specified by the prize ball number command is executed, and when the prize ball payout operation is completed, the prize ball end command indicating the end of the prize ball payout operation is played through the serial communication circuit 380. It transmits to the control microcomputer 560.
図34は、通常動作時における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータと払出制御用マイクロコンピュータとの信号の送受信を示すタイミング図である。図34に示すように、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、接続確認コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信すると、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370から送信される接続OKコマンドを受信する。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、接続OKコマンドを受信すると、受信した時点から1s(1秒)経過後に接続確認コマンドを再び送信する。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560および払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、接続状態が正常である限り、上記のような接続確認の通信処理を繰り返し実行する。
FIG. 34 is a timing chart showing transmission and reception of signals between the gaming control microcomputer and the payout control microcomputer during normal operation. As shown in FIG. 34, when the game control microcomputer 560 transmits a connection confirmation command to the payout control microcomputer 370, the game control microcomputer 560 receives a connection OK command transmitted from the payout control microcomputer 370. When receiving the connection OK command, the game control microcomputer 560 transmits a connection confirmation command again after 1 s (one second) has elapsed from the time of reception. As long as the connection state is normal, the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 repeatedly execute the communication process of the connection confirmation as described above.
接続確認の通信処理を実行していないとき(接続OKコマンドを受信してから次の接続確認コマンドを送信するまでの間)に入賞があった場合には、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、接続確認コマンドを繰り返し送信する制御を中断し、賞球個数を示すデータを賞球個数コマンドの下位4ビットに設定し、当該設定した賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球個数コマンドを受信すると、賞球個数受付コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。この場合、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、賞球個数受付コマンドを受信したことにもとづいて、賞球個数記憶を減算する処理を行う(具体的には、後述する賞球コマンド出力カウンタを1減算する処理を行う。ステップS52404参照)。そして、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球個数コマンドで指定された個数の賞球の払い出しを行い、賞球の払い出し(賞球払出動作)が終了すると、賞球終了コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。なお、前述したように、賞球払出動作に時間がかかる場合には、賞球払出動作が完了するまで、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、1s(1秒)経過するごとに賞球準備中コマンドを繰り返し送信する。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、賞球終了コマンドを受信すると、次に払い出すべき賞球個数がまだ記憶されていない場合には、受信した時点から1s(1秒)経過後に接続確認コマンドを送信する。
When there is a prize when the communication process of the connection confirmation is not executed (during the time from the reception of the connection OK command to the transmission of the next connection confirmation command), the game control microcomputer 560 performs the connection, The control for repeatedly transmitting the confirmation command is interrupted, data indicating the number of prize balls is set to the lower 4 bits of the prize ball number command, and the set prize ball number command is transmitted to the payout control microcomputer 370. When receiving the winning balls count command, the payout control microcomputer 370 transmits the winning balls count reception command to the gaming control microcomputer 560. In this case, the game control microcomputer 560 performs processing of subtracting the number-of-winning-ball number storage based on the reception of the winning-ball number reception command (specifically, subtracting one of the winning-ball command output counter described later) (See step S52404). Then, the payout control microcomputer 370 pays out the number of winning balls specified by the winning ball number command, and when the winning balls have been paid out (winning ball paying-out operation), the winning ball ending command is used as a game control micro Send to computer 560. As described above, when it takes time to pay out the winning balls, the payout control microcomputer 370 executes the preparing ball command every 1 s (one second) until the winning balls dispensing operation is completed. Send repeatedly. When the game control microcomputer 560 receives the award ball end command, it transmits a connection confirmation command after 1 s (one second) elapses from the reception time point, when the number of award balls to be paid out next is not stored yet. Do.
接続確認の通信処理の実行中(接続確認コマンドを送信してから接続OKコマンドを受信するまでの間)に入賞があった場合は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との接続状態が確認できていない段階であるので、賞球個数コマンドを直ちに送信せずに、接続OKコマンドの受信を確認できるまで待つ。そして、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370からの接続OKコマンドを受信すると、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、賞球個数を示すデータを賞球個数コマンドの下位4ビットに設定し、当該設定した賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球個数コマンドを受信すると、賞球個数受付コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。そして、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、以下同様の処理を実行し、賞球個数コマンドで指定された個数の賞球の払い出しを行い、賞球の払い出し(賞球払出動作)が終了すると、賞球終了コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。
When there is a prize during the execution of the connection confirmation communication process (between the transmission of the connection confirmation command and the reception of the connection OK command), the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 Since it is in the stage where the connection state of the is not confirmed, it waits until the reception of the connection OK command can be confirmed without immediately transmitting the prize ball number command. Then, when receiving the connection OK command from the payout control microcomputer 370, the gaming control microcomputer 560 sets data indicating the number of prize balls to the lower 4 bits of the prize ball number command, and the set number of prize balls is set. The command is sent to the dispensing control microcomputer 370. When receiving the winning balls count command, the payout control microcomputer 370 transmits the winning balls count reception command to the gaming control microcomputer 560. Then, the payout control microcomputer 370 executes the same processing as described above, pays out the number of winning balls specified by the winning ball number command, and when the winning balls are paid out (winning balls paying out operation), the prize A sphere end command is sent to the game control microcomputer 560.
なお、賞球終了コマンドを受信した後、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、前回受信した接続OKコマンドまたは賞球準備中コマンドの下位4ビットにエラーを示す値が設定されておらず(図28参照)、かつ賞球終了コマンドを受信してから1秒が経過するまでの間に始動入賞している場合にも、賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。すなわち、この実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、エラーを示す値が設定されていない接続OK信号を受信してから1秒が経過するまでの間と、賞球終了コマンドを受信してから1秒を経過するまでの間とに、賞球個数コマンドを送信可能な状態になっている。
In the game control microcomputer 560 after receiving the award ball end command, a value indicating an error is not set in the lower 4 bits of the previously received connection OK command or award ball preparing command (see FIG. 28). Also, even when the start winning combination is made between the reception of the award ball end command and the elapse of one second, the award ball count command is transmitted to the payout control microcomputer 370. That is, in this embodiment, the game control microcomputer 560 receives the award ball end command from the time when 1 second elapses after the connection OK signal whose value indicating the error is not set is received. Between 1 second and 1 second, it is possible to transmit the prize ball number command.
図35は、賞球中にエラーが発生した場合における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータと払出制御用マイクロコンピュータとの信号の送受信を示すタイミング図である。図35に示すように、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、接続確認コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信すると、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370から送信される接続OKコマンドを受信する。接続確認の通信処理を実行していないときに入賞があった場合は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、賞球個数を示すデータを賞球個数コマンドの下位4ビットに設定し、当該設定した賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球個数コマンドを受信すると、賞球個数受付コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。そして、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球個数コマンドで指定された個数の賞球の払い出しを行う。賞球個数コマンドで指定された個数の賞球の払出動作を実行しているときに、所定のエラー(例えば、払出個数異常エラー、球貸し、満タン、球切れのエラー)が発生し、賞球払出動作ができない状態(異常状態、エラー状態)になった場合は、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、エラーが発生し賞球払出動作が終了していないことを通知する賞球準備中コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。この場合、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、発生したエラーが解除されない限り、一定間隔で(1s毎に)賞球準備中コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。所定のエラー状態が解除(解消)されて賞球払出動作が終了すると、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球終了コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。なお、賞球準備中コマンドは、賞球個数受付コマンドを送信した後、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370から遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に1s毎に送信されることになる。また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が賞球準備中コマンドを受信している間には、接続確認コマンドを送信しないように制御される。具体的には、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は賞球払出動作が終了したことにもとづいて賞球終了コマンドを出力するようにし、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は当該賞球終了コマンドを受信したことにもとづいて、所定周期(1S)毎に接続確認コマンドを出力する状態に復帰するように制御する。
FIG. 35 is a timing chart showing transmission and reception of signals between the game control microcomputer and the payout control microcomputer when an error occurs during the winning ball. As shown in FIG. 35, when transmitting the connection confirmation command to the payout control microcomputer 370, the gaming control microcomputer 560 receives the connection OK command transmitted from the payout control microcomputer 370. If there is a winning when the communication processing for connection confirmation is not executed, the gaming control microcomputer 560 sets data indicating the number of winning balls in the lower 4 bits of the winning balls number command, and the set winning The ball count command is sent to the payout control microcomputer 370. When receiving the winning balls count command, the payout control microcomputer 370 transmits the winning balls count reception command to the gaming control microcomputer 560. Then, the payout control microcomputer 370 pays out the number of winning balls specified by the winning ball number command. When the payout operation of the number of prize balls specified by the prize ball quantity command is executed, a predetermined error (for example, an error in the number of dispensed quantities, a ball lend, a full tank, an out-of-ball error) occurs and the prize When the ball dispensing operation can not be performed (abnormal state, error state), the payout control microcomputer 370 generates a prize ball preparing command to notify that an error has occurred and the prize ball dispensing operation has not ended. It transmits to the game control microcomputer 560. In this case, the payout control microcomputer 370 transmits a prize ball in-provision command to the game control microcomputer 560 at regular intervals (every 1 s) unless the generated error is released. When the predetermined error state is canceled (canceled) and the winning balls payout operation is finished, the payout control microcomputer 370 transmits a winning ball end command to the gaming control microcomputer 560. It should be noted that the prize ball preparation command is transmitted from the payout control microcomputer 370 to the game control microcomputer 560 every 1 s after transmitting the prize ball number reception command. Further, while the game control microcomputer 560 receives the in-provision ball preparation command, control is performed so as not to transmit the connection confirmation command. Specifically, the payout control microcomputer 370 outputs a winning ball end command based on the end of the winning ball payout operation, and the gaming control microcomputer 560 receives the winning ball end command. Based on the control, control is performed to return to the state of outputting the connection confirmation command every predetermined period (1S).
図36は、接続確認中の通信エラー時における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータと払出制御用マイクロコンピュータとの信号の送受信を示すタイミング図である。図36に示すように、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、接続確認コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信したが、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370からの接続OKコマンドを受信していない場合、つまり、接続状態の異常(通信エラー)が発生した場合には、接続確認コマンドを送信した時点から10s(10秒)経過後に再度、接続確認コマンドを送信する。すなわち、接続OKコマンドを受信できない場合に接続確認コマンドを1s(1秒)ごとに送信する処理を継続したのでは、通信状態が不安定な状態であるにもかかわらず接続確認コマンドの送信回数が無駄に多くなってしまうので、接続確認コマンドの送信間隔を10s(10秒)に広げて、通信状態が回復するまで必要最低限の送信回数の接続確認コマンドを送信する制御に切り替える。通信エラーが発生しているときに入賞が発生した場合には、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370から接続OKコマンドを受信するまでは、新たな入賞が発生しても、賞球個数コマンドを送信せずに、一定間隔(10s)毎に接続確認コマンドを送信し続ける。通信エラーが解除(解消)され、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370から接続OKコマンドが送信されると、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、賞球個数コマンドを送信する。
FIG. 36 is a timing chart showing transmission and reception of signals between the gaming control microcomputer and the payout control microcomputer at the time of a communication error during connection confirmation. As shown in FIG. 36, when the game control microcomputer 560 transmits the connection confirmation command to the payout control microcomputer 370, but does not receive the connection OK command from the payout control microcomputer 370, that is, When an abnormality in the connection state (communication error) occurs, the connection confirmation command is transmitted again after 10 seconds (10 seconds) has elapsed since the transmission of the connection confirmation command. That is, if the process of transmitting the connection confirmation command every 1 s (1 second) is continued when the connection OK command can not be received, the number of transmissions of the connection confirmation command is in spite of the unstable communication state. Since it will be uselessly increased, the transmission interval of the connection confirmation command is extended to 10 seconds (10 seconds), and control is switched to transmission of the connection confirmation command with the minimum number of transmissions until the communication state is recovered. If a winning occurs while a communication error occurs, the game control microcomputer 560 may receive a new winning until it receives a connection OK command from the payout control microcomputer 370. The connection confirmation command is continued to be transmitted at regular intervals (10 s) without transmitting the award ball number command. When the communication error is canceled (canceled) and the connection control OK command is transmitted from the payout control microcomputer 370, the game control microcomputer 560 transmits a winning ball count command.
図37は、賞球個数通知中の通信エラー時における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータと払出制御用マイクロコンピュータとの信号の送受信を示すタイミング図である。図37に示すように、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、入賞が発生したことにもとづいて賞球個数コマンドを送信したが、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370からの賞球個数受付コマンドを受信していない場合、つまり、接続状態の異常(通信エラー)が発生した場合には、賞球個数コマンドを送信した時点から10s(10秒)経過後に、接続確認コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。そして、通信状態が回復するまで10s(10秒)経過ごとに接続確認コマンドを繰り返し送信する。その後、通信エラーが解除(解消)され、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370から接続OKコマンドを受信した場合には、賞遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、通常(正常時)の動作に戻り、賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に再送信(リトライ)する。なお、具体的には、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、賞球個数コマンドを送信しても賞球個数受付コマンドを受信できなかった場合には、賞球個数記憶を減算しないようにし(後述するステップS52403でNであればステップS52404の賞球コマンド出力カウンタの値を1減算しないようにし)、次に賞球個数コマンドの送信を行うときに賞球コマンド出力カウンタの値がそのまま維持されていることにもとづいて賞球個数コマンドを再送信する(後述するステップS52301〜S52035参照)。
FIG. 37 is a timing chart showing transmission and reception of signals between the gaming control microcomputer and the payout control microcomputer at the time of a communication error during notification of the number of winning balls. As shown in FIG. 37, the game control microcomputer 560 has transmitted a prize ball count command based on the occurrence of a winning, but has not received a prize ball count reception command from the payout control microcomputer 370. In this case, that is, when an abnormality in the connection state (communication error) occurs, a connection confirmation command is transmitted to the payout control microcomputer 370 after 10 seconds (10 seconds) has elapsed since the point number command was transmitted. Then, the connection confirmation command is repeatedly transmitted every 10 seconds (10 seconds) until the communication state is recovered. Thereafter, when the communication error is canceled (canceled) and the connection OK command is received from the payout control microcomputer 370, the prize game control microcomputer 560 returns to the normal (normal) operation and the number of prize balls The command is retransmitted (retry) to the dispensing control microcomputer 370. In addition, specifically, when the game control microcomputer 560 can not receive the award ball count reception command even though it transmits the award ball count command, it does not subtract the award ball count storage (described later) If N in step S52403, the value of the prize ball command output counter in step S52404 is not decremented by 1), and the value of the prize ball command output counter is maintained as it is when transmitting the prize ball number command next. In this case, the winning ball number command is retransmitted based on the above (refer to steps S52301 to S52035 described later).
次に、賞球処理(ステップS32)について説明する。図38は、ステップS32の賞球処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。賞球処理において、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560(具体的には、CPU56)は、賞球コマンド出力カウンタ加算処理(ステップS501)、賞球制御処理(ステップS502)および賞球カウンタ減算処理(ステップS503)を実行する。
Next, the winning ball processing (step S32) will be described. FIG. 38 is a flowchart showing an example of the winning ball processing of step S32. In the prize ball processing, the game control microcomputer 560 (specifically, the CPU 56) performs a prize ball command output counter addition process (step S501), a prize ball control process (step S502), and a prize ball counter subtraction process (step S503). To do).
賞球コマンド出力カウンタ加算処理では、図39に示す賞球個数テーブルが使用される。賞球個数テーブルは、ROM54に設定されている。賞球個数テーブルの先頭アドレスには処理数(この例では「4」)が設定され、その後に、スイッチオンバッファの下位アドレスと、賞球コマンド出力カウンタと、賞球数を指定する賞球指定データとが、順次設定されている。賞球コマンド出力カウンタとは、入賞口への入賞数をカウントするカウンタであり、例えば、ROM54に設定される。また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、賞球数(0〜15個)毎に、対応する賞球コマンド出力カウンタを備える。この実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、賞球数「15」に対応する賞球コマンド出力カウンタ1と、賞球数「10」に対応する賞球コマンド出力カウンタ2,3(2つの普通入賞口29,30に対応)と、賞球数「3」に対応する賞球コマンド出力カウンタ4とを備える。なお、各賞球コマンド出力カウンタは、後述するように、賞球コマンド出力カウンタ加算処理でカウントアップされる。CPU56は、賞球個数テーブルに設定されている賞球コマンド出力カウンタ1が0でなければ、賞球数(15個)を指定する賞球指定データにもとづいて賞球個数(15個)を示すデータを賞球個数コマンドの下位4ビットに設定し、当該設定された賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。また、CPU56は、賞球個数テーブルに設定されている賞球コマンド出力カウンタ1の値が0であり、賞球コマンド出力カウンタ2,3の値が0でなければ、賞球数(10個)を指定する賞球指定データにもとづいて賞球個数(10個)を示すデータを賞球個数コマンドの下位4ビットに設定し、当該設定された賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。また、CPU56は、賞球個数テーブルに設定されている賞球コマンド出力カウンタ1および賞球コマンド出力カウンタ2,3の値が0であり、賞球コマンド出力カウンタ4の値が0でなければ、賞球数(3個)を指定する賞球指定データにもとづいて賞球個数(3個)を示すデータを賞球個数コマンドの下位4ビットに設定し、当該設定された賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。また、図39において、スイッチオンバッファ1は入力ポート0に対応しており、スイッチオンバッファ2は入力ポート2に対応している。
In the prize ball command output counter addition process, a prize ball number table shown in FIG. 39 is used. The winning ball number table is set in the ROM 54. The processing number ("4" in this example) is set at the top address of the prize ball quantity table, and thereafter, the lower address of the switch on buffer, the prize ball command output counter, and the prize ball designation specifying the number of prize balls Data are set sequentially. The winning ball command output counter is a counter that counts the number of winnings on the winning opening, and is set in, for example, the ROM 54. Further, the gaming control microcomputer 560 is provided with a corresponding winning ball command output counter for each winning ball number (0 to 15). In this embodiment, the microcomputer 560 for game control includes an award ball command output counter 1 corresponding to the award ball number “15” and an award ball command output counter 2, 3 (2 corresponding to the award ball number “10”. Provided with three ordinary winning openings 29, 30) and an award ball command output counter 4 corresponding to the award ball number "3". Each prize ball command output counter is counted up in the prize ball command output counter addition process as described later. If the prize ball command output counter 1 set in the prize ball number table is not 0, the CPU 56 indicates the number of prize balls (15 pieces) based on the prize ball designation data specifying the number of prize balls (15 pieces). The data is set to the lower 4 bits of the award ball count command, and the set award ball count command is transmitted to the payout control microcomputer 370. The CPU 56 also determines the number of winning balls (10) if the value of the winning ball command output counter 1 set in the winning ball number table is 0 and the values of the winning ball command output counters 2 and 3 are not 0. The data indicating the number of prize balls (10 pieces) is set in the lower 4 bits of the prize ball number command based on the prize ball designation data specifying the, and the set prize ball number command is transmitted to the payout control microcomputer 370 Do. Further, the CPU 56 determines that the values of the prize ball command output counter 1 and the prize ball command output counters 2 and 3 set in the prize ball number table are 0 and the value of the prize ball command output counter 4 is not 0, Data indicating the number of prize balls (3 pieces) is set in the lower 4 bits of the prize ball number command based on the prize ball specification data specifying the number of prize balls (3 pieces), and the set prize ball number command is dispensed It transmits to the control microcomputer 370. Further, in FIG. 39, the switch on buffer 1 corresponds to the input port 0, and the switch on buffer 2 corresponds to the input port 2.
図40は、ステップS501の賞球コマンド出力カウンタ加算処理を示すフローチャートである。賞球コマンド出力カウンタ加算処理において、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560(具体的には、CPU56)は、賞球個数テーブルの先頭アドレスをポインタにセットする(ステップS5101)。そして、ポインタが指すアドレスのデータ(この場合には処理数)をロードする(ステップS5102)。
FIG. 40 is a flow chart showing the prize ball command output counter addition process of step S501. In the prize ball command output counter addition process, the gaming control microcomputer 560 (specifically, the CPU 56) sets the top address of the prize ball number table to the pointer (step S5101). Then, the data of the address pointed to by the pointer (in this case, the number of processes) is loaded (step S5102).
次いで、CPU56は、ポインタの値を1増やし(ステップS5103)、ポインタが指すスイッチオンバッファの下位アドレスをポインタバッファの下位バイトにロードし(ステップS5104)、ポインタバッファの指すスイッチオンバッファをレジスタにロードする(ステップS5105)。次いで、CPU56は、ポインタの値を1増やし(ステップS5106)、ポインタが指す賞球コマンド出力カウンタの下位アドレスをポインタバッファの下位バイトにロードする(ステップS5107)。次いで、CPU56は、ポインタの値を1増やし(ステップS5108)、レジスタにロードしたスイッチオンバッファの内容と、ポインタが指す賞球指定データとの論理積をとる(ステップS5109)。
Next, the CPU 56 increments the value of the pointer by 1 (step S5103), loads the lower address of the switch on buffer pointed by the pointer into the lower byte of the pointer buffer (step S5104), and loads the switch on buffer pointed by the pointer buffer into the register (Step S5105). Next, the CPU 56 increments the value of the pointer by 1 (step S5106), and loads the lower address of the award ball command output counter pointed by the pointer into the lower byte of the pointer buffer (step S5107). Next, the CPU 56 increments the value of the pointer by 1 (step S5108), and ANDs the contents of the switch on buffer loaded in the register with the prize ball designation data pointed by the pointer (step S5109).
ステップS5109における演算結果が0であれば(ステップS5110のY)、すなわち、検査対象のスイッチの検出信号がオン状態でなければ、処理数を1減らし(ステップS5114)、処理数が0であれば処理を終了し、処理数が0でなければステップS5103に戻る(ステップS5115)。
If the calculation result in step S5109 is 0 (Y in step S5110), that is, if the detection signal of the switch to be inspected is not in the on state, the number of processes is reduced by 1 (step S5114). The process ends, and if the number of processes is not 0, the process returns to step S5103 (step S5115).
ステップS5109における演算結果が0でなければ(ステップS5110のN)、すなわち、検査対象のスイッチの検出信号がオン状態であれば、CPU56は、ポインタが指す賞球コマンド出力カウンタの値を1加算する(ステップS111)。ただし、CPU56は、加算の結果、賞球コマンド出力カウンタの値に桁上げが発生した場合には、賞球コマンド出力カウンタの値を1減算し元に戻す(ステップS5112,S5113)。そしてステップS5113の処理に移行する。
If the calculation result in step S5109 is not 0 (N in step S5110), that is, if the detection signal of the switch to be inspected is on, the CPU 56 adds 1 to the value of the award ball command output counter pointed by the pointer. (Step S111). However, when a carry occurs in the value of the award ball command output counter as a result of the addition, the CPU 56 subtracts one from the value of the award ball command output counter and returns it to the original value (steps S5112, S5113). Then, the process proceeds to step S5113.
図41は、ステップS502の賞球制御処理を示すフローチャートである。賞球制御処理では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560(具体的には、CPU56)は、賞球プロセスコードの値に応じて、ステップS521〜S525のいずれかの処理を実行する。
FIG. 41 is a flowchart showing the winning ball control process of step S502. In the prize ball control process, the game control microcomputer 560 (specifically, the CPU 56) executes any of the processes in steps S521 to S525 according to the value of the prize ball process code.
図42は、賞球プロセスコードの値が0の場合に実行される賞球送信処理1(ステップS521)を示すフローチャートである。CPU56は、賞球送信処理1において、接続確認コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータに送信する制御を行う(ステップS5211)。具体的には、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505の送信データレジスタに接続確認コマンドを出力する処理を行う。そして、CPU56は、賞球プロセスコードに賞球接続確認処理を示す値「1」をセットし(ステップS5212)、賞球プロセスタイマに接続確認時間2(例えば10秒)をセットする(ステップS5213)。なお、ステップS5213でセットされた接続確認時間2にもとづいて、接続確認コマンドを送信した後、10秒を経過しても接続OKコマンドを受信できなかった場合には、以後、接続確認コマンドを送信する間隔を10秒に広げるように制御される。具体的には、ステップS5213でセットされた賞球プロセスタイマは、後述するステップS5229の処理で計測され、接続OKコマンドを受信することなく10秒が経過してタイムアウトしステップS5227でYと判定されると、賞球送信処理1に戻り次の接続確認コマンドが送信される(ステップS5228,S5211参照)。
FIG. 42 is a flow chart showing a prize ball transmission process 1 (step S521) executed when the value of the prize ball process code is zero. The CPU 56 performs control to transmit a connection confirmation command to the payout control microcomputer in the prize ball transmission process 1 (step S5211). Specifically, the CPU 56 performs a process of outputting a connection confirmation command to the transmission data register of the serial communication circuit 505. Then, the CPU 56 sets the value "1" indicating the winning ball connection confirmation process in the winning ball process code (step S5212), and sets the connection checking time 2 (for example, 10 seconds) in the winning ball process timer (step S5213). . After the connection confirmation command is transmitted based on the connection confirmation time 2 set in step S5213, if the connection OK command can not be received after 10 seconds, the connection confirmation command is transmitted thereafter. Control interval to 10 seconds. Specifically, the prize ball process timer set in step S5213 is measured in the process of step S5229 described later, and is determined to be Y in step S5227 after 10 seconds have elapsed without receiving a connection OK command. Then, the processing returns to the prize ball transmission processing 1, and the next connection confirmation command is transmitted (see steps S5228 and S5211).
なお、賞球プロセスタイマには、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560で実行されるタイマ割込処理における割込周期も考慮した値(例えば、割込周期の整数倍)がセットされる。このことは、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560や、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100で用いられる他のタイマ(例えば、主制御通信制御タイマや、払出制御タイマ、再払出待ちタイマ、賞球情報出力タイマ、賞球信号1出力タイマ)についても同様である。
A value (for example, an integral multiple of the interrupt cycle) in which the interrupt cycle in the timer interrupt processing executed by the game control microcomputer 560 is also set is set in the prize ball process timer. This means that the game control microcomputer 560, the payout control microcomputer 370, and other timers used in the effect control microcomputer 100 (for example, a main control communication control timer, a payout control timer, a repayment wait timer, The same applies to the award ball information output timer and the award ball signal 1 output timer.
図43は、賞球プロセスコードの値が1の場合に実行される賞球接続確認処理(ステップS522)を示すフローチャートである。CPU56は、賞球接続確認処理において、まず、シリアル通信回路505の受信データレジスタにデータがあるか否かを確認する(ステップS5221)。具体的には、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505のステータスレジスタAのビット5の値を確認するようにすればよい(図16参照)。受信データレジスタにデータがなければ(すなわち、コマンドを受信していなければ)、ステップS5227に移行する。
FIG. 43 is a flowchart showing a winning ball connection confirmation process (step S522) executed when the value of the winning ball process code is 1. In the award ball connection confirmation process, the CPU 56 first confirms whether or not there is data in the reception data register of the serial communication circuit 505 (step S5221). Specifically, the CPU 56 may check the value of bit 5 of the status register A of the serial communication circuit 505 (see FIG. 16). If there is no data in the reception data register (ie, if no command has been received), the process moves to step S5227.
受信データレジスタにデータがあれば(すなわち、コマンドを受信していれば)、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505のエラーが発生しているか否かを確認する(ステップS5222)。具体的には、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505のステータスレジスタAのビット0〜4のいずれかのエラービットの値がセットされているか否かを確認するようにすればよい(図16参照)。エラーが発生していれば、ステップS5227に移行する。
If there is data in the reception data register (that is, if a command is received), the CPU 56 checks whether an error has occurred in the serial communication circuit 505 (step S5222). Specifically, the CPU 56 may check whether the value of any error bit of the bits 0 to 4 of the status register A of the serial communication circuit 505 is set (see FIG. 16). If an error has occurred, the process proceeds to step S5227.
シリアル通信回路505のエラーも発生していなければ、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505の受信データレジスタからコマンドを読み出し、受信したコマンドが接続OKコマンドであるか否かを確認する(ステップS5223)。接続OKコマンドでなければ、ステップS5227に移行する。
If no error occurs in the serial communication circuit 505, the CPU 56 reads a command from the reception data register of the serial communication circuit 505, and confirms whether the received command is a connection OK command (step S5223). If it is not the connection OK command, the process proceeds to step S5227.
接続OKコマンドを受信していれば、CPU56は、接続OKコマンドの下位4ビットに設定されているエラー情報(図28参照)を枠状態表示バッファに格納する(ステップS5224)。
If the connection OK command has been received, the CPU 56 stores the error information (see FIG. 28) set in the lower 4 bits of the connection OK command in the frame state display buffer (step S5224).
次いで、CPU56は、賞球プロセスコードに賞球送信処理2を示す値「2」をセットし(ステップS5225)、賞球プロセスタイマに接続確認時間1(例えば1秒)をセットする(ステップS5226)。なお、ステップS5226でセットされた接続確認時間1にもとづいて、接続OKコマンドの受信後に1秒経過するごとに次の接続確認コマンドを繰り返し送信する制御が行われる。具体的には、ステップS5226でセットされた賞球プロセスタイマは、後述するステップS52315の処理で計測され、賞球個数コマンドを送信することなく1秒が経過してタイムアウトしステップS52313でYと判定されると、賞球送信処理1に戻り次の接続確認コマンドが送信される(ステップS52314,S5211参照)。
Next, the CPU 56 sets the value "2" indicating the winning ball transmission processing 2 in the winning ball process code (step S5225), and sets the connection check time 1 (for example, 1 second) in the winning ball process timer (step S5226). . Note that, based on the connection confirmation time 1 set in step S5226, control is performed to repeatedly transmit the next connection confirmation command each time one second elapses after the reception of the connection OK command. Specifically, the prize ball process timer set in step S5226 is measured in the process of step S52315 described later, and one second elapses without transmitting the prize ball quantity command, and it is determined that it is Y in step S52313. Then, the processing returns to the prize ball transmission processing 1, and the next connection confirmation command is transmitted (see steps S52314 and S5211).
ステップS5227では、CPU56は、賞球プロセスタイマがタイムアウトしたか否かを確認する。賞球プロセスタイマがタイムアウトしていれば(すなわち、接続確認コマンドを送信した後、10秒を経過しても接続OKコマンドを受信できなかった場合)、CPU56は、賞球プロセスコードに賞球送信処理1を示す値「0」をセットし(ステップS5228)、処理を終了する。賞球プロセスタイマがタイムアウトしていなければ、CPU56は、賞球プロセスタイマの値を1減算する(ステップS5229)。
In step S5227, the CPU 56 confirms whether or not the winning ball process timer has timed out. If the prize ball process timer has timed out (that is, if the connection OK command can not be received after 10 seconds after sending the connection confirmation command), the CPU 56 transmits the prize ball to the prize ball process code. The value "0" indicating the process 1 is set (step S5228), and the process ends. If the prize ball process timer has not timed out, the CPU 56 subtracts one from the value of the prize ball process timer (step S5229).
図44は、賞球プロセスコードの値が2の場合に実行される賞球送信処理2(ステップS523)を示すフローチャートである。CPU56は、賞球送信処理2において、賞球コマンド出力カウンタ1〜4の中にカウント値が0でないものがあるか否かを確認する(ステップS52301)。カウント値が0でないものがなければ、ステップS52313に移行する。
FIG. 44 is a flowchart showing the prize ball transmitting process 2 (step S523) executed when the value of the prize ball process code is 2. The CPU 56 confirms whether or not there is a winning ball command output counter 1 to 4 having a count value other than 0 in the winning ball transmission processing 2 (step S52301). If the count value is not 0, the process proceeds to step S52313.
賞球コマンド出力カウンタ1〜4の中にカウント値が0でないものがある場合には(すなわち、カウント値が1以上のものがある場合には)、CPU56は、枠状態表示バッファの内容をロードし、枠状態表示バッファの内容が0であるか否かを確認する(ステップS52302)。枠状態表示バッファの内容が0でなければ、そのまま処理を終了する。そのように制御することによって、エラー情報が設定された接続OKコマンドを受信し、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370側で払出停止状態に制御されている場合には、ステップS52303以降の処理に移行しないようし、賞球個数コマンドの送信を保留するように制御する。
If there is a prize ball command output counter 1 to 4 whose count value is not 0 (that is, if the count value is 1 or more), the CPU 56 loads the contents of the frame status display buffer. Then, it is checked whether the content of the frame status display buffer is 0 (step S52302). If the content of the frame status display buffer is not 0, the processing ends. By performing control in such a manner, when the connection OK command in which the error information is set is received and the dispensing control microcomputer 370 side is controlled to the dispensing stop state, the process does not shift to the processing after step S52303 Control to hold transmission of the prize ball number command.
枠状態表示バッファの内容が0であれば(すなわち、払出に関するエラーが発生していなければ)、払出制御用CPU371は、そのカウント値が0でない賞球コマンド出力カウンタに対応する賞球個数を個数バッファにセットする(ステップS52303)。具体的には、ステップS52301において、CPU56は、まず、賞球コマンド出力カウンタ1のカウント値が0であるか否かを確認する。そして、賞球コマンド出力カウンタ1のカウント値が1以上であった場合には、ステップS52303において、CPU56は、個数バッファに賞球個数15個をセットする。また、ステップS52301において、CPU56は、賞球コマンド出力カウンタ1のカウント値が0であった場合には、賞球コマンド出力カウンタ2,3のカウント値が0であるか否かを確認する。そして、賞球コマンド出力カウンタ2,3のカウント値が1以上であった場合には、ステップS52303において、CPU56は、個数バッファに賞球個数10個をセットする。さらに、ステップS52301において、CPU56は、賞球コマンド出力カウンタ2,3のカウント値も0であった場合には、賞球コマンド出力カウンタ4のカウント値が0であるか否かを確認する。そして、賞球コマンド出力カウンタ4のカウント値が1以上であった場合には、ステップS52303において、CPU56は、個数バッファに賞球個数3個をセットする。
If the content of the frame status display buffer is 0 (that is, if an error related to payout has not occurred), the payout control CPU 371 counts the number of prize balls corresponding to the prize ball command output counter whose count value is not 0. It sets to a buffer (step S52303). Specifically, in step S52301, the CPU 56 first confirms whether the count value of the award ball command output counter 1 is zero or not. Then, if the count value of the prize ball command output counter 1 is 1 or more, the CPU 56 sets the number of prize balls 15 in the number buffer in step S52303. In step S52301, when the count value of the award ball command output counter 1 is 0, the CPU 56 confirms whether the count values of the award ball command output counters 2 and 3 are 0 or not. If the count values of the prize ball command output counters 2 and 3 are 1 or more, the CPU 56 sets ten prize balls in the number buffer in step S52303. Further, in step S52301, when the count values of the award ball command output counters 2 and 3 are also 0, the CPU 56 confirms whether the count value of the award ball command output counter 4 is 0 or not. Then, if the count value of the prize ball command output counter 4 is 1 or more, the CPU 56 sets three prize balls in the number buffer in step S52303.
また、CPU56は、そのカウント値が0でない賞球コマンド出力カウンタに対応する賞球個数を賞球個数コマンドにセットする(ステップS52304)とともに、賞球個数をセットした賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する制御を行う(ステップS52305)。具体的には、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505の送信データレジスタに、賞球個数をセットした賞球個数コマンドを出力する処理を行う。
Further, the CPU 56 sets the number of prize balls corresponding to the prize ball command output counter whose count value is not 0 in the number-of-bumps ball command (step S52304), and also for the payout control Control to transmit to the microcomputer 370 is performed (step S52305). Specifically, the CPU 56 performs a process of outputting to the transmission data register of the serial communication circuit 505 the prize ball number command in which the number of prize balls is set.
なお、ステップS52301,S52305の処理が実行されることによって、この実施の形態では、接続確認コマンドの送信タイミングにかかわりなく、賞球コマンド出力カウンタの中にカウント値が0でないものがあれば(すなわち、賞球個数記憶があり、所定の払出条件が成立していれば)、賞球個数コマンドが払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信される。
By executing the processing of steps S52301 and S52305, in this embodiment, regardless of the transmission timing of the connection confirmation command, if there is a prize ball command output counter that has a count value other than 0 (that is, If the predetermined payout condition is satisfied), the winning ball number command is transmitted to the payout control microcomputer 370.
そして、CPU56は、賞球プロセスコードに賞球受領確認処理を示す値「3」をセットし(ステップS52306)、賞球プロセスタイマに接続確認時間2(例えば10秒)をセットする(ステップS52307)。なお、ステップS52307でセットされた接続確認時間2にもとづいて、賞球個数コマンドを送信した後、10秒以内に賞球個数受付コマンドや賞球準備中コマンドを受信したか否かが確認される。具体的には、ステップS52307でセットされた賞球プロセスタイマは、後述するステップS52411の処理で計測され、賞球個数受付コマンドや賞球準備中コマンドを受信することなく10秒が経過してタイムアウトしステップS52409でYと判定されると、賞球送信処理1に戻り次の接続確認コマンドが送信される(ステップS52410,S5211参照)。
Then, the CPU 56 sets the value "3" indicating the winning ball reception confirmation process in the winning ball process code (step S52306), and sets the connection checking time 2 (for example, 10 seconds) in the winning ball process timer (step S52307). . In addition, based on the connection confirmation time 2 set in step S52307, after transmitting the prize ball quantity command, it is confirmed whether or not the prize ball quantity reception command and the prize ball preparation command are received within 10 seconds. . Specifically, the prize ball process timer set in step S52307 is measured in the process of step S52411 described later, and a timeout occurs after 10 seconds without receiving a prize ball number reception command or a prize ball preparation command. If it is determined as Y in step S52409, the processing returns to prize ball transmission processing 1, and the next connection confirmation command is transmitted (see steps S52410 and S5211).
なお、ステップS52306の処理が実行されることによってステップS52305で賞球個数コマンドが送信されると、接続確認コマンドの送信処理を含む賞球送信処理1に戻ることなく、賞球受領確認処理に移行される。従って、この実施の形態では、賞球個数コマンドを送信するまでは所定時間(例えば1秒)ごとに繰り返し接続確認コマンドを送信する処理が実行されているのであるが、賞球個数コマンドを送信したことにもとづいて接続確認コマンドを送信する制御が停止される(より具体的には、賞球個数コマンドを送信した後、後述する賞球個数受付コマンドを受信したことにより賞球終了確認処理に移行する(ステップS52403〜S52405参照)ことによって、または賞球準備中コマンドを受信したことにより賞球受領確認処理を繰り返す(ステップS52406〜S52408参照)ことによって、賞球送信処理1に戻ることなく、接続確認コマンドを送信する制御が停止される。この場合、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370側から何も払出制御コマンドが返信されないという異常状態が発生しない限り、賞球個数コマンドを送信した後、賞球払出動作を終了して賞球終了コマンドを受信するまで、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から接続確認コマンドが送信されることはない。
When the number-of-balls command is transmitted in step S52305 by the execution of the process of step S52306, the process proceeds to the ball reception confirmation process without returning to the ball communication process 1 including the process of transmitting the connection confirmation command. Be done. Therefore, in this embodiment, the process of repeatedly transmitting the connection confirmation command every predetermined time (for example, one second) is performed until the prize ball quantity command is transmitted. However, the prize ball quantity command is transmitted. The control for transmitting the connection confirmation command is stopped based on the above (more specifically, after transmitting the prize ball quantity command, the process proceeds to the prize ball end confirmation processing by receiving the prize ball quantity reception command described later) (Refer to steps S 52403 to S 52405), or by repeating the award ball reception confirmation process (see steps S 52406 to S 52408) by receiving the in-progress ball preparation command (refer to steps S 52406 to S 52408), the connection is not made. In this case, the control for sending the confirmation command is stopped. Nothing is sent from the game control microcomputer 560 until the prize ball payout operation is finished and the prize ball end command is received after sending the prize ball number command unless an abnormal state that no payout control command is returned occurs. Confirmation commands are never sent.
次いで、CPU56は、ステップS52303でセットした個数バッファの値を賞球個数カウンタに加算し(ステップS52308)、加算後のカウント値が所定の賞球不足判定値(例えば501)以上であるか否かを確認する(ステップS52309)。この実施の形態において、賞球個数カウンタは、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560側で未払い出しの賞球数を把握するために用いられるカウンタであり、賞球個数コマンドを送信する際に賞球個数コマンドで指定される賞球個数が加算され、賞球払出を10球検出するごとに払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370から出力される賞球情報にもとづいて10ずつ減算される。また、前述したように、賞球個数カウンタには、メイン処理の初期設定処理において初期値として「250」がセットされている。そして、賞球個数カウンタのカウント値が所定の賞球不足判定値(例えば501)以上に達する場合には、未払い出しの賞球数が異常に多すぎるのであるから、賞球不足の事態が生じていると判定することができる。また、賞球個数カウンタのカウント値が所定の賞球過剰判定値(例えば0)未満となった場合には、本来払い出されるべき数を超えて異常に多くの遊技球が払い出されているのであるから、賞球過剰の事態が生じていると判定することができる。
Next, the CPU 56 adds the value of the number buffer set in step S52303 to the prize ball number counter (step S52308), and whether the count value after addition is equal to or more than a predetermined prize ball shortage determination value (for example, 501). (Step S52309). In this embodiment, the prize ball number counter is a counter used for grasping the number of unpaid prize balls on the game control microcomputer 560 side, and the prize ball number command is transmitted when the prize ball number command is transmitted. The number of winning balls specified in is added, and every 10 balls of winning balls are detected, 10 is subtracted on the basis of the winning ball information outputted from the payout control microcomputer 370. Further, as described above, "250" is set as the initial value in the initial setting process of the main process in the prize ball number counter. Then, when the count value of the prize ball number counter reaches a predetermined prize ball shortage determination value (for example, 501) or more, the number of unpaid prize balls is excessively large, so a situation of prize ball shortage occurs. It can be determined that In addition, when the count value of the prize ball number counter becomes less than a predetermined prize ball excess judgment value (for example, 0), an excessively large number of game balls are paid out exceeding the number originally to be paid out. Since there is a prize ball, it can be determined that an over-whelming event has occurred.
なお、この実施の形態では、賞球個数コマンドを送信(ステップS52305参照)した直後に、賞球個数カウンタの加算処理(ステップS52308参照)する場合を示しているが、賞球個数コマンドが送信されるタイミングで加算するものであれば、例えば、まず賞球個数カウンタの加算処理を実行してから、その直後に賞球個数コマンドを送信するようにしてもよい。
Although this embodiment shows the case of performing the addition processing of the prize ball number counter (see step S52308) immediately after transmitting the prize ball quantity command (see step S52305), the prize ball quantity command is transmitted. For example, the addition processing of the winning balls number counter may be performed first, and then the winning balls number command may be transmitted immediately after that.
また、賞球不足と判定される場合には、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370側に何らかの障害が生じて払出動作を正常に行えない場合の他、賞球情報を出力する信号線が断線している場合も考えられる。また、逆に、賞球過剰と判定される場合には、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370側に何らかの障害が生じて払出動作が必要以上に行われている場合の他、賞球個数コマンドを送信するコマンド線に何らかの不正が施されて不正に賞球個数コマンドが払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に入力されている場合も考えられる。
In addition, when it is determined that the winning balls are insufficient, some failure occurs in the payout control microcomputer 370 side, and the signal line for outputting the winning ball information is broken other than the case where the dispensing operation can not be normally performed. The case is also conceivable. On the contrary, when it is determined that the prize ball is excessive, the prize ball count command is transmitted other than when the payout control is performed more than necessary due to some failure in the payout control microcomputer 370 side. It is also conceivable that a prize ball count command is input to the payout control microcomputer 370 illegally because the command line is subjected to some fraud.
賞球個数カウンタのカウント値が所定の賞球不足判定値(例えば501)以上であった場合には、CPU56は、賞球不足や賞球過剰が発生していることを示す賞球エラーフラグが既にセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS52310)。既に賞球エラーフラグがセットされていれば、そのまま処理を終了する。賞球エラーフラグがセットされていなければ、CPU56は、賞球エラーフラグをセットする(ステップS52311)とともに、賞球不足エラーコマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS52312)。具体的には、CPU56は、賞球不足エラーコマンド送信テーブルのアドレスをポインタにセットする処理を行う。そして、ステップS52312で賞球不足エラーコマンド送信テーブルのアドレスがポインタにセットされたことにもとづいて、その後、ステップS30の演出図柄コマンド制御処理において、演出制御基板80との送受信用チャネルのシリアル通信回路505の送信データレジスタに賞球不足エラーコマンドが出力され、賞球不足エラーコマンドが演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信される。なお、賞球エラーフラグは、一度セットされると、遊技機への電力供給が停止された後、遊技機へ電源が再投入されるまで、クリアされずに維持される。また、この実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100との間の通信に関しては、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対してコマンドが送信されるのみで、その逆はない。そのため、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560には、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100との通信に関しては、送信専用のシリアル通信回路が搭載されていてもよい。
If the count value of the prize ball number counter is equal to or more than a predetermined prize ball shortage determination value (for example, 501), the CPU 56 displays a prize ball error flag indicating that a prize ball deficiency or a prize ball excess has occurred. It is checked whether it is already set (step S52310). If the prize ball error flag has already been set, the processing ends. If the prize ball error flag is not set, the CPU 56 sets a prize ball error flag (step S52311) and performs control to transmit a prize ball shortage error command to the effect control microcomputer 100 (step S52312). Specifically, the CPU 56 performs a process of setting the address of the award ball shortage error command transmission table in the pointer. Then, based on the address of the award ball shortage error command transmission table being set to the pointer in step S52312, the serial communication circuit of the transmission / reception channel with the effect control board 80 in the effect symbol command control process of step S30 thereafter. A prize ball shortage error command is output to the transmission data register 505, and a prize ball shortage error command is transmitted to the effect control microcomputer 100. Once the prize ball error flag is set, it is maintained without being cleared until the game machine is powered on again after the power supply to the game machine is stopped. Further, in this embodiment, regarding communication between the game control microcomputer 560 and the effect control microcomputer 100, a command is transmitted from the game control microcomputer 560 to the effect control microcomputer 100. Only, not the opposite. Therefore, a serial communication circuit dedicated to transmission may be mounted on the game control microcomputer 560 for communication with the effect control microcomputer 100.
なお、この実施の形態では、賞球不足エラーコマンドや、後述する賞球過剰エラーコマンドを受信したことにもとづいて、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100によって賞球不足や賞球過剰のエラー報知が行われるのであるが(ステップS625〜S628参照)、賞球不足や賞球過剰のエラー報知は、報知開始から所定期間を経過したときに復旧するようにしてもよい。また、例えば、賞球個数カウンタの値が所定の賞球不足判定値(例えば501)や所定の賞球過剰判定値(例えば0)の範囲内に復帰したときに、賞球不足や賞球過剰のエラー報知から復旧するようにしてもよい。
In this embodiment, the effect control microcomputer 100 performs an alert notification of an award ball deficiency or an award ball excess based on reception of an award ball deficiency error command or an award ball excess error command described later. However, the error notification of the award ball shortage or the award ball excess may be restored when a predetermined period has elapsed from the start of the notification (see steps S625 to S628). In addition, for example, when the value of the winning ball number counter returns to within a predetermined winning ball shortage determination value (for example, 501) or a predetermined winning ball excess determining value (for example, 0), the winning balls are insufficient or the winning balls are excessive. It may be recovered from the error notification of
なお、この実施の形態では、ステップS52308において、賞球個数コマンドを送信したタイミングで賞球個数カウンタに賞球個数を加算する場合を示したが、賞球個数カウンタのカウントアップの仕方は、この実施の形態で示したものにかぎらず、例えば、逆に賞球個数を減算するようにしてもよい。この場合、例えば、後述するステップS5311の処理において、賞球情報を入力したことにもとづいて賞球個数カウンタの値に逆に10加算するようにすればよい。そして、ステップS52309の処理では賞球個数カウンタの値が0未満であれば賞球不足エラーと判定するようにし、後述するステップS5312の処理では賞球個数カウンタの値が501以上であれば賞球過剰エラーと判定するようにすればよい。
In this embodiment, although the case where the number of balls is added to the number ball counter at the timing of transmitting the number ball command in step S52308 is shown, the method of counting up the number ball of balls is described For example, the number of winning balls may be reduced in addition to the one described in the embodiment. In this case, for example, in the process of step S5311, which will be described later, 10 may be reversely added to the value of the winning ball number counter based on the fact that the winning ball information has been input. Then, in the process of step S52309, if the value of the winning ball number counter is less than 0, it is determined that the winning ball lack error, and if the value of the winning ball number counter is 501 or more in the process of step S5312, described later It may be determined that the error is excessive.
ステップS52313では、CPU56は、賞球プロセスタイマがタイムアウトしたか否かを確認する。賞球プロセスタイマがタイムアウトしていれば(すなわち、接続OKコマンドを受信した後、1秒を経過するまでに、賞球個数の記憶もなく、新たな入賞も発生しなかった場合)、CPU56は、賞球プロセスコードに賞球送信処理1を示す値「0」をセットし(ステップS52314)、処理を終了する。賞球プロセスタイマがタイムアウトしていなければ、CPU56は、賞球プロセスタイマの値を1減算する(ステップS52315)。
In step S52313, the CPU 56 confirms whether or not the winning ball process timer has timed out. If the prize ball process timer has timed out (that is, if there is no memory of the number of prize balls and no new prize has not occurred by one second after the connection OK command is received), the CPU 56 The value “0” indicating the winning ball transmission process 1 is set in the winning ball process code (step S52314), and the process ends. If the prize ball process timer has not timed out, the CPU 56 subtracts one from the value of the prize ball process timer (step S52315).
図45は、賞球プロセスコードの値が3の場合に実行される賞球受領確認処理(ステップS524)を示すフローチャートである。CPU56は、賞球受領確認処理において、まず、シリアル通信回路505の受信データレジスタにデータがあるか否かを確認する(ステップS52401)。具体的には、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505のステータスレジスタAのビット5の値を確認するようにすればよい(図16参照)。受信データレジスタにデータがなければ(すなわち、コマンドを受信していなければ)、ステップS52409に移行する。
FIG. 45 is a flow chart showing a winning ball reception confirmation process (step S524) executed when the value of the winning ball process code is 3. In the prize ball reception confirmation process, the CPU 56 first confirms whether or not there is data in the reception data register of the serial communication circuit 505 (step S52401). Specifically, the CPU 56 may check the value of bit 5 of the status register A of the serial communication circuit 505 (see FIG. 16). If there is no data in the reception data register (ie, if no command has been received), the process proceeds to step S52409.
受信データレジスタにデータがあれば(すなわち、コマンドを受信していれば)、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505のエラーが発生しているか否かを確認する(ステップS52402)。具体的には、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505のステータスレジスタAのビット0〜4のいずれかのエラービットの値がセットされているか否かを確認するようにすればよい(図16参照)。エラーが発生していれば、ステップS52409に移行する。
If there is data in the reception data register (that is, if a command has been received), the CPU 56 checks whether an error has occurred in the serial communication circuit 505 (step S 52402). Specifically, the CPU 56 may check whether the value of any error bit of the bits 0 to 4 of the status register A of the serial communication circuit 505 is set (see FIG. 16). If an error has occurred, the process proceeds to step S52409.
シリアル通信回路505のエラーも発生していなければ、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505の受信データレジスタからコマンドを読み出し、受信したコマンドが賞球個数受付コマンドであるか否かを確認する(ステップS52403)。賞球個数受付コマンドを受信していれば、CPU56は、送信した賞球個数コマンドで設定した賞球個数に対応する賞球コマンド出力カウンタの値を1減算する(ステップS52404)。また、CPU56は、賞球プロセスコードに賞球終了確認処理を示す値「4」をセットし(ステップS52405)、ステップS52408に移行する。
If no error occurs in the serial communication circuit 505, the CPU 56 reads a command from the reception data register of the serial communication circuit 505, and confirms whether the received command is a prize ball reception command (step S52403). . If the prize ball number reception command has been received, the CPU 56 subtracts 1 from the value of the prize ball command output counter corresponding to the number of prize balls set by the transmitted prize ball number command (step S52404). In addition, the CPU 56 sets the value “4” indicating the winning ball end confirmation process in the winning ball process code (step S52405), and the process proceeds to step S52408.
受信したコマンドが賞球個数受付コマンドでなければ、CPU56は、受信したコマンドが賞球準備中コマンドであるか否かを確認する(ステップS52406)。賞球準備中コマンドでもなければ、ステップS52409に移行する。
If the received command is not a winning ball number reception command, the CPU 56 confirms whether the received command is a winning ball preparation command (step S52406). If it is not the winning ball preparation command, the process proceeds to step S52409.
賞球準備中コマンドを受信していれば、CPU56は、賞球準備中コマンドの下位4ビットに設定されているエラー情報(図28参照)を枠状態表示バッファに格納する(ステップS52407)。そして、CPU56は、賞球プロセスタイマに接続確認時間2(例えば10秒)をセットする(ステップS52408)。なお、ステップS52408でセットされた接続確認時間2にもとづいて、賞球準備中コマンドを受信した後、10秒を経過しても賞球個数受付コマンドも次の賞球準備中コマンドも受信できなかった場合には、接続確認コマンドを送信する制御に戻る。具体的には、ステップS52408でセットされた賞球プロセスタイマは、後述するステップS52409,S52411の処理で計測され、賞球個数受付コマンドや次の賞球準備中コマンドを受信することなく10秒が経過してタイムアウトしステップS52409でYと判定されると、賞球送信処理1に戻り次の接続確認コマンドが送信される(ステップS52410,S5211参照)。
If the award ball preparation command is received, the CPU 56 stores the error information (see FIG. 28) set in the lower 4 bits of the award ball preparation command in the frame state display buffer (step S52407). Then, the CPU 56 sets the connection check time 2 (for example, 10 seconds) in the winning ball process timer (step S52408). In addition, based on the connection confirmation time 2 set in step S52408, after receiving the preparation ball preparation command, even if 10 seconds have passed, neither the preparation ball reception command nor the preparation ball preparation command can be received. If yes, the process returns to the control of transmitting a connection confirmation command. Specifically, the prize ball process timer set in step S52408 is measured by the processing of steps S52409 and S52411 described later, and 10 seconds are received without receiving the prize ball number reception command or the next prize ball preparation command. If it has timed out and it is judged as Y in step S52409, it returns to the prize ball transmission processing 1 and the next connection confirmation command is transmitted (see steps S52410 and S5211).
ステップS52409では、CPU56は、賞球プロセスタイマがタイムアウトしたか否かを確認する。賞球プロセスタイマがタイムアウトしていれば(すなわち、賞球個数コマンドを送信した後、10秒を経過しても賞球個数受付コマンドや賞球準備中コマンドを受信できなかった場合)、CPU56は、賞球プロセスコードに賞球送信処理1を示す値「0」をセットし(ステップS52410)、処理を終了する。賞球プロセスタイマがタイムアウトしていなければ、CPU56は、賞球プロセスタイマの値を1減算する(ステップS52411)。
In step S52409, the CPU 56 confirms whether or not the winning ball process timer has timed out. If the prize ball process timer has timed out (that is, if the prize ball quantity reception command or the prize ball preparation command can not be received even after 10 seconds after sending the prize ball quantity command), the CPU 56 The value "0" indicating the winning ball transmission process 1 is set in the winning ball process code (step S52410), and the process is ended. If the prize ball process timer has not timed out, the CPU 56 subtracts one from the value of the prize ball process timer (step S52411).
図46は、賞球プロセスコードの値が4の場合に実行される賞球終了確認処理(ステップS525)を示すフローチャートである。CPU56は、賞球終了確認処理において、まず、シリアル通信回路505の受信データレジスタにデータがあるか否かを確認する(ステップS52501)。具体的には、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505のステータスレジスタAのビット5の値を確認するようにすればよい(図16参照)。受信データレジスタにデータがなければ(すなわち、コマンドを受信していなければ)、ステップS52509に移行する。
FIG. 46 is a flow chart showing a winning ball end confirmation process (step S525) executed when the value of the winning ball process code is 4. In the award ball end confirmation process, the CPU 56 first confirms whether there is data in the reception data register of the serial communication circuit 505 (step S52501). Specifically, the CPU 56 may check the value of bit 5 of the status register A of the serial communication circuit 505 (see FIG. 16). If there is no data in the reception data register (ie, if no command has been received), the process proceeds to step S52509.
受信データレジスタにデータがあれば(すなわち、コマンドを受信していれば)、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505のエラーが発生しているか否かを確認する(ステップS52502)。具体的には、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505のステータスレジスタAのビット0〜4のいずれかのエラービットの値がセットされているか否かを確認するようにすればよい(図16参照)。エラーが発生していれば、ステップS52509に移行する。
If there is data in the reception data register (that is, if a command has been received), the CPU 56 confirms whether an error has occurred in the serial communication circuit 505 (step S 52502). Specifically, the CPU 56 may check whether the value of any error bit of the bits 0 to 4 of the status register A of the serial communication circuit 505 is set (see FIG. 16). If an error has occurred, the process proceeds to step S52509.
シリアル通信回路505のエラーも発生していなければ、CPU56は、シリアル通信回路505の受信データレジスタからコマンドを読み出し、受信したコマンドが賞球終了コマンドであるか否かを確認する(ステップS52503)。賞球終了コマンドを受信していれば、CPU56は、賞球プロセスコードに賞球送信処理2を示す値「2」をセットし(ステップS52504)、賞球プロセスタイマに接続確認時間1(例えば1秒)をセットする(ステップS52505)。なお、ステップS52505でセットされた接続確認時間1にもとづいて、賞球終了コマンドを受信した後、1秒を経過しても始動入賞が発生しなかった場合には、接続確認コマンドを送信する制御に戻る。具体的には、ステップS52505でセットされた賞球プロセスタイマは、ステップS52313,S52315の処理で計測され、新たな始動入賞が発生せず賞球個数コマンドを送信することなく1秒が経過してタイムアウトしステップS52313でYと判定されると、賞球送信処理1に戻り次の接続確認コマンドが送信される(ステップS52314,S5211参照)。
If no error occurs in the serial communication circuit 505, the CPU 56 reads a command from the reception data register of the serial communication circuit 505, and confirms whether the received command is a prize ball end command (step S52503). If the prize ball end command has been received, the CPU 56 sets the value "2" indicating the prize ball transmission processing 2 in the prize ball process code (step S52504), and the connection confirmation time 1 (for example, 1) Second) is set (step S52505). In addition, based on the connection confirmation time 1 set in step S52505, if the start winning combination does not occur even after 1 second after receiving the award ball end command, the control to transmit the connection confirmation command Return to Specifically, the prize ball process timer set in step S52505 is measured in the processes of steps S52313 and S52315, and a new start winning does not occur, and one second elapses without transmitting the prize ball quantity command. When it times out and it is determined as Y in step S52313, the processing returns to prize ball transmission processing 1, and the next connection confirmation command is transmitted (see steps S52314 and S5211).
なお、ステップS52504の処理が実行されることによって、賞球終了コマンドを受信した場合にはまず賞球送信処理2に移行されるので、賞球個数の記憶が溜まっている場合には直ちに次の賞球個数コマンドが送信されるように制御される。一方で、賞球送信処理2に移行された後、賞球個数の記憶もなく、ステップS52505でセットされた接続確認時間1(例えば1秒)が経過するまでの間に新たな入賞も発生しなかった場合には、さらに賞球送信処理1に移行され、接続確認コマンドを繰り返し送信する処理が再開される。
When the award ball end command is received by executing the process of step S52504, the process first proceeds to award ball transmission processing 2, so when the memory of the number of award balls is accumulated, the next process is immediately performed. It is controlled so that the prize ball number command is transmitted. On the other hand, there is no memory of the number of winning balls after shifting to the winning ball transmission processing 2, and new winnings occur while the connection check time 1 (for example, 1 second) set in step S52505 elapses. If not, the process is further shifted to the winning ball transmission process 1, and the process of repeatedly transmitting the connection confirmation command is resumed.
受信したコマンドが賞球終了コマンドでなければ、CPU56は、受信したコマンドが賞球準備中コマンドであるか否かを確認する(ステップS52506)。賞球準備中コマンドでもなければ、ステップS52509に移行する。
If the received command is not a winning ball end command, the CPU 56 confirms whether the received command is a winning ball preparation command (step S52506). If it is not the award ball preparation command, the process proceeds to step S52509.
賞球準備中コマンドを受信していれば、CPU56は、賞球準備中コマンドの下位4ビットに設定されているエラー情報(図28参照)を枠状態表示バッファに格納する(ステップS52507)。そして、CPU56は、賞球プロセスタイマに接続確認時間2(例えば10秒)をセットする(ステップS52508)。なお、ステップS52508でセットされた接続確認時間2にもとづいて、賞球準備中コマンドを受信した後、10秒を経過しても賞球終了コマンドも次の賞球準備中コマンドも受信できなかった場合には、接続確認コマンドを送信する制御に戻る。具体的には、ステップS52508でセットされた賞球プロセスタイマは、後述するステップS52511の処理で計測され、賞球終了コマンドや次の賞球準備中コマンドを受信することなく10秒が経過してタイムアウトしステップS52509でYと判定されると、賞球送信処理1に戻り次の接続確認コマンドが送信される(ステップS52510,S5211参照)。
If the award ball preparation command is received, the CPU 56 stores the error information (see FIG. 28) set in the lower 4 bits of the award ball preparation command in the frame state display buffer (step S52507). Then, the CPU 56 sets the connection check time 2 (for example, 10 seconds) in the winning ball process timer (step S52508). Furthermore, based on the connection confirmation time 2 set in step S52508, after receiving the preparation ball preparation command, even after 10 seconds, neither the prize ball termination command nor the next preparation ball preparation command can be received. If so, control is returned to sending a connection confirmation command. Specifically, the prize ball process timer set in step S52508 is measured in the process of step S52511 described later, and 10 seconds have elapsed without receiving the prize ball end command or the next prize ball preparation command. When it times out and it is determined as Y in step S52509, the processing returns to the prize ball transmission processing 1, and the next connection confirmation command is transmitted (see steps S52510 and S5211).
ステップS52509では、CPU56は、賞球プロセスタイマがタイムアウトしたか否かを確認する。賞球プロセスタイマがタイムアウトしていれば(すなわち、賞球個数受付コマンドや賞球準備中コマンドを受信した後、10秒を経過しても賞球終了コマンドや賞球準備中コマンドを受信できなかった場合)、CPU56は、賞球プロセスコードに賞球送信処理1を示す値「0」をセットし(ステップS52510)、処理を終了する。賞球プロセスタイマがタイムアウトしていなければ、CPU56は、賞球プロセスタイマの値を1減算する(ステップS52511)。
In step S52509, the CPU 56 confirms whether or not the winning ball process timer has timed out. If the prize ball process timer has timed out (that is, after receiving the prize ball number reception command and the prize ball preparation command, even if 10 seconds have passed, the prize ball end command and the prize ball preparation command can not be received In the case of (1), the CPU 56 sets the value “0” indicating the winning ball transmission processing 1 in the winning ball process code (step S52510), and ends the processing. If the prize ball process timer has not timed out, the CPU 56 subtracts one from the value of the prize ball process timer (step S52511).
図47は、ステップS503の賞球カウンタ減算処理を示すフローチャートである。CPU56は、賞球カウンタ減算処理において、まず、賞球情報入力無効タイマがタイムアウトしたか否かを確認する(ステップS5301)。なお、賞球情報入力無効タイマは、賞球情報の入力を確認した後、次の賞球情報の入力を確認するまでの間にインターバル期間を設けるために計測されるタイマである。タイムアウトしていなければ、CPU56は、賞球情報入力無効タイマの値を1減算して(ステップS5302)、処理を終了する。
FIG. 47 is a flow chart showing the winning ball counter subtraction process of step S503. In the prize ball counter subtraction process, the CPU 56 first confirms whether or not the prize ball information input invalidation timer has timed out (step S5301). The prize ball information input invalidation timer is a timer that is measured to provide an interval period from the confirmation of the input of the prize ball information to the confirmation of the input of the next prize ball information. If the time has not timed out, the CPU 56 subtracts one from the value of the award ball information input invalidation timer (step S5302), and ends the processing.
賞球情報入力無効タイマがタイムアウトしていれば、CPU56は、入力ポート0の内容を入力し(ステップS5303)、賞球情報のビットがオン状態であるか否かを確認する(ステップS5304)。賞球情報のビットがオン状態であれば、ステップS5305に移行する。
If the award ball information input invalidation timer has timed out, the CPU 56 inputs the content of the input port 0 (step S5303), and confirms whether or not the bit of the award ball information is on (step S5304). If the bit of the winning ball information is on, the process moves to step S5305.
ステップS5305では、CPU56は、処理数として所定の賞球情報確認回数(例えば8)をセットする(ステップS5305)。そして、CPU56は、賞球情報を入力しているか否かを確認し、賞球情報の入力を確認できれば賞球情報オンカウンタの値を1加算する処理を、処理数(本例では8)を終了するまで繰り返し実行する(ステップS5306〜S5308)。
In step S5305, the CPU 56 sets a predetermined number (for example, 8) of winning ball information confirmation times as the processing number (step S5305). Then, the CPU 56 confirms whether or not the winning ball information is input, and if it is possible to confirm the input of the winning ball information, the processing for adding 1 to the value of the winning ball information on counter is processed number (8 in this example). The process is repeated until the process ends (steps S5306 to S5308).
次いで、CPU56は、賞球情報オンカウンタの値が6以上であるか否かを確認する(ステップS5309)。賞球情報オンカウンタの値が6以上であれば、CPU56は、賞球情報入力無効タイマに所定時間(例えば0.8秒)をセットする(ステップS5310)とともに、賞球個数カウンタの値を10減算する(ステップS5311)。
Next, the CPU 56 confirms whether the value of the winning ball information on counter is 6 or more (step S5309). If the value of the prize ball information on counter is 6 or more, the CPU 56 sets a predetermined time (for example, 0.8 seconds) in the prize ball information input invalidation timer (step S5310) and the value of the prize ball number counter is 10 The subtraction is performed (step S5311).
以上の処理が実行されることによって、この実施の形態では、賞球情報の入力を8回の確認処理中6回以上確認したことを条件として賞球情報を入力したと判定し、10個の賞球払出が行われたものとして賞球個数カウンタの値を10減算している。そのような処理によって、この実施の形態では、誤って賞球情報を入力したと判定する事態を低減し、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560側で未払い出しの賞球数を適切に把握できなくなる事態を防止している。
By executing the above processing, in this embodiment, it is determined that the winning ball information has been input on the condition that the inputting of the winning ball information has been confirmed six times or more during the confirmation processing of eight times. The value of the winning ball number counter is decremented by 10 on the assumption that the winning ball has been paid out. By such processing, in this embodiment, the situation where it is determined that the prize ball information has been input by mistake is reduced, and the situation where the microcomputer 560 for game control can not appropriately grasp the number of unpaid prize balls. It is preventing.
次いで、CPU56は、減算後のカウント値が所定の賞球過剰判定値(例えば0)未満であるか否かを確認する(ステップS5312)。賞球個数カウンタのカウント値が所定の賞球過剰判定値(例えば0)未満であった場合には、CPU56は、賞球エラーフラグが既にセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS5313)。既に賞球エラーフラグがセットされていれば、そのまま処理を終了する。賞球エラーフラグがセットされていなければ、CPU56は、賞球エラーフラグをセットする(ステップS5314)とともに、賞球過剰エラーコマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS5315)。具体的には、CPU56は、賞球過剰エラーコマンド送信テーブルのアドレスをポインタにセットする処理を行う。そして、ステップS5315で賞球過剰エラーコマンド送信テーブルのアドレスがポインタにセットされたことにもとづいて、その後、ステップS30の演出図柄コマンド制御処理において、演出制御基板80との送受信用チャネルのシリアル通信回路505の送信データレジスタに賞球過剰エラーコマンドが出力され、賞球過剰エラーコマンドが演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信される。
Next, the CPU 56 checks whether the count value after subtraction is less than a predetermined winning ball excess judgment value (for example, 0) (step S5312). If the count value of the winning ball number counter is less than a predetermined winning ball excess determination value (for example, 0), the CPU 56 checks whether the winning ball error flag has already been set (step S5313). If the prize ball error flag has already been set, the processing ends. If the prize ball error flag is not set, the CPU 56 sets a prize ball error flag (step S5314) and performs control to transmit a prize ball excess error command to the effect control microcomputer 100 (step S5315). Specifically, the CPU 56 sets the address of the prize ball excess error command transmission table in the pointer. Then, based on the address of the prize ball excess error command transmission table being set to the pointer in step S5315, thereafter, in the effect symbol command control process of step S30, the serial communication circuit of the transmission / reception channel with the effect control board 80 A prize ball excess error command is output to the transmission data register 505, and a prize ball excess error command is sent to the effect control microcomputer 100.
次に、枠状態出力処理(ステップS39)について説明する。図48は、ステップS39の枠状態出力処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。CPU56は、枠状態出力処理において、まず、枠状態表示バッファの内容をロードする(ステップS391)。次いで、CPU56は、入力ポート0の内容を入力する(ステップS392)とともに、入力した入力ポート0の内容を所定のドア開放信号確認用のマスク値(具体的には、01000000)と論理積をとる(ステップS393)。さらに、CPU56は、論理積をとった演算結果と、ステップS391でロードした枠状態表示バッファの内容との論理積をとる(ステップS394)。以上の処理が実行されることによって、枠状態表示バッファの内容にさらにドア開放信号の入力状態が付加された演算結果が得られる。
Next, the frame state output process (step S39) will be described. FIG. 48 is a flowchart showing an example of the frame state output process of step S39. In the frame state output process, the CPU 56 first loads the contents of the frame state display buffer (step S391). Next, the CPU 56 inputs the contents of the input port 0 (step S392), and logically ANDs the contents of the input port 0 with the mask value (specifically, 01000000) for confirmation of the door opening signal. (Step S393). Furthermore, the CPU 56 performs an AND operation on the operation result obtained by the AND operation and the contents of the frame state display buffer loaded in step S391 (step S394). By performing the above-described processing, an operation result can be obtained in which the input state of the door open signal is further added to the contents of the frame state display buffer.
次いで、CPU56は、演算結果と前回枠状態表示バッファの内容とを比較する(ステップS395)。なお、前回枠状態表示バッファには、前回のタイマ割込によって枠状態出力処理が実行されたときに算出されたステップS394の演算結果が格納されている。演算結果が前回枠状態表示バッファの内容と異なる場合には(ステップS396のY)、CPU56は、前回枠状態表示バッファにステップS394で算出した演算結果を格納して前回枠状態表示バッファを更新する(ステップS397)とともに、ステップS394で算出した演算結果をそのまま枠状態表示コマンドのEXTデータとして設定して、枠状態表示コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う(ステップS398)。具体的には、CPU56は、枠状態表示コマンド送信テーブルのアドレスをポインタにセットする処理を行う。そして、ステップS398で枠状態表示コマンド送信テーブルのアドレスがポインタにセットされたことにもとづいて、その後、ステップS30の演出図柄コマンド制御処理において、演出制御基板80との送受信用チャネルのシリアル通信回路505の送信データレジスタに枠状態表示コマンドが出力され、枠状態表示コマンドが演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信される。
Next, the CPU 56 compares the calculation result with the content of the previous frame state display buffer (step S395). The previous frame status display buffer stores the calculation result of step S394 calculated when the frame status output process is executed by the previous timer interruption. If the calculation result is different from the content of the previous frame status display buffer (Y in step S396), the CPU 56 stores the calculation result calculated in step S394 in the previous frame status display buffer and updates the previous frame status display buffer. At the same time as (step S397), control is performed to transmit the frame state display command to the effect control microcomputer 100 by setting the calculation result calculated in step S394 directly as EXT data of the frame state display command (step S398). Specifically, the CPU 56 sets the address of the frame status display command transmission table in the pointer. Then, based on the address of the frame status display command transmission table being set to the pointer in step S 398, the serial communication circuit 505 of the transmission / reception channel with the rendering control board 80 is subsequently performed in the rendering symbol command control process of step S 30. The frame state display command is output to the transmission data register of (1), and the frame state display command is transmitted to the effect control microcomputer 100.
図49は、枠状態表示コマンドに設定されるEXTデータの具体例を示す説明図である。図49に示すように、賞球エラー(入賞にもとづく賞球払出動作や球貸し要求にもとづく球貸払出動作が正常に行えない状態になった異常状態:具体的には、図85に示す主制御未接続エラーや、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー1、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー2、払出ケースエラー、主制御通信エラー)が検出されている場合には、1ビット目(ビット0)の賞球エラービットに「1」が設定される。また、満タンエラーが検出されている場合には、2ビット目(ビット1)の満タンエラービットに「1」が設定される。また、球切れエラーが検出されている場合には、3ビット目(ビット2)の球切れエラービットに「1」が設定される。また、後述する賞球や貸し球の払出数の個数異常の累積値が所定値(例えば、2000個)に達した場合の払出個数異常エラーが検出されている場合には、4ビット目(ビット3)の払出個数異常エラービットに「1」が設定される。また、ガラス扉枠2が開放状態であることが検出されている場合には、7ビット目(ビット6)のドア開放異常エラービットに「1」設定される。
FIG. 49 is an explanatory view showing a specific example of the EXT data set in the frame state display command. As shown in FIG. 49, a prize ball error (abnormal state in which the prize ball dispensing operation based on the winning or the ball loan dispensing operation based on the ball lending request can not be performed normally: specifically, the main state shown in FIG. The prize ball error bit of the 1st bit (bit 0) when the control non-connection error, the delivery switch abnormality detection error 1, the delivery switch abnormality detection error 2, the delivery case error, the main control communication error) is detected Is set to "1". When a full tank error is detected, "1" is set to the full tank error bit of the second bit (bit 1). In addition, when the ball breakage error is detected, “1” is set to the ball breakage error bit of the third bit (bit 2). In addition, the fourth bit (bit) is detected when a payout number anomaly error is detected when the cumulative value of the number anomalies of the number of payouts of the winning balls and the lending balls described later reaches a predetermined value (for example, 2000) “1” is set to the payout amount abnormality error bit of 3). When it is detected that the glass door frame 2 is in the open state, the door open abnormality error bit of the seventh bit (bit 6) is set to "1".
以上の処理が実行されることによって、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から接続OKコマンドや賞球準備中コマンドで設定されたエラー情報(払出個数異常エラーや、球切れエラー、満タンエラー、賞球エラー)の内容やドア開放信号の入力状態が枠状態表示コマンドに設定されて、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信される。
Error information set by the connection control OK command or the in-progress ball preparation command from the payout control microcomputer 560 by executing the above processing (disbursement number error, out-of-ball error, full error, winning ball error) The contents of and the input state of the door open signal are set in the frame state display command and transmitted to the effect control microcomputer 100.
次に、メイン処理における特別図柄プロセス処理(ステップS28)を説明する。図50は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のCPU56が実行する特別図柄プロセス処理のプログラムの一例を示すフローチャートである。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のCPU56は、遊技盤6に設けられている始動入賞口14に遊技球が入賞したことを検出するための始動口スイッチ14aがオンしていたら、すなわち遊技球が始動入賞口14に入賞し、入賞検出信号SSが始動口スイッチ14aから入力されていたら(ステップS311)、始動口スイッチ通過処理(ステップS312)を行った後に、内部状態に応じて、ステップS300〜S306のうちのいずれかの処理を行う。
Next, special symbol process processing (step S28) in the main processing will be described. FIG. 50 is a flow chart showing an example of a special symbol process processing program executed by the CPU 56 of the game control microcomputer 560. The CPU 56 of the game control microcomputer 560 detects that the game ball has won the start winning hole 14 provided on the game board 6 when the start opening switch 14a is turned on, that is, the game ball starts winning. If a winning is made in the mouth 14 and the winning detection signal SS is inputted from the starting opening switch 14a (step S311), the starting opening switch passing process (step S312) is carried out, and then the steps Perform one of the processes.
特別図柄通常処理(ステップS300):特別図柄の可変表示を開始できる状態(例えば、特別図柄表示器8において図柄の変動がなされておらず、特別図柄表示器8における前回の図柄変動が終了してから所定期間が経過しており、かつ、大当り遊技中でもない状態)になるのを待つ。特別図柄の可変表示が開始できる状態になると、特別図柄についての始動入賞記憶数を確認する。始動入賞記憶数が0でなければ、特図保留メモリに記憶されている乱数回路503が発生したランダムRにもとづいて、特別図柄の可変表示の結果を大当りとするか否か決定する。また、大当りとすると決定した場合には、さらに、確変大当りとするか否かなど大当り種別を決定し、決定した表示結果を特定可能な表示結果指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う。そして、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS301に移行するように更新する。
Special symbol normal processing (step S300): A state where variable display of the special symbol can be started (for example, no symbol variation is made in the special symbol indicator 8, and the previous symbol variation in the special symbol indicator 8 is completed) Wait for a predetermined period of time has passed and the player is not in a jackpot game). When the variable display of the special symbol can be started, the start winning memory number for the special symbol is confirmed. If the start winning memory number is not 0, it is determined based on the random R generated by the random number circuit 503 stored in the special view reservation memory, whether or not the result of the variable display of the special symbol is a big hit. Further, when it is determined to be a big hit, further determine the big hit type such as whether or not to be a definite variation big hit, control to transmit a display result designation command capable of specifying the determined display result to the microcomputer 100 for effect control I do. And an internal state (special symbol process flag) is updated so that it may transfer to step S301.
変動時間設定処理(ステップS301):変動パターンを決定し、その変動パターンにおける変動時間(可変表示時間:可変表示を開始してから表示結果が導出表示(停止表示)するまでの時間)を特別図柄の可変表示の変動時間とすることに決定する。また、決定した変動パターンを指定する変動パターンコマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行うとともに、決定した特別図柄の変動時間を計測する変動時間タイマをスタートさせる。そして、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS302に移行するように更新する。
Fluctuation time setting process (step S301): A fluctuation pattern is determined, and fluctuation time in the fluctuation pattern (variable display time: time from start of variable display to derivation display (stop display)) is a special symbol It is decided to make the fluctuation time of the variable display of. Further, control is performed to transmit a variation pattern command specifying the determined variation pattern to the effect control microcomputer 100, and a variation time timer is started to measure the variation time of the determined special symbol. And an internal state (special symbol process flag) is updated so that it may transfer to step S302.
特別図柄変動処理(ステップS302):所定時間(ステップS301の変動時間タイマで示された時間)が経過すると、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS303に移行するように更新する。
Special symbol variation processing (step S302): When a predetermined time (time indicated by the variation time timer in step S301) has elapsed, the internal state (special symbol process flag) is updated to shift to step S303.
特別図柄停止処理(ステップS303):演出制御基板80に対して、演出図柄の停止を指示するための演出図柄停止コマンドを送信する。また、特別図柄表示器8における特別図柄を停止させる。そして、特別図柄の停止図柄が大当り図柄である場合には、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS304に移行するように更新する。そうでない場合には、内部状態をステップS300に移行するように更新する。なお、演出図柄停止コマンドを送信しない構成としてもよい。この場合、演出制御基板80は、主基板31から受信した変動パターンコマンドにもとづいて変動時間タイマに変動時間を設定するとともに、その変動時間タイマを更新していくことで演出図柄の変動時間を独自に監視し、その変動時間が経過したと判定したときに演出図柄を停止する処理を行うようにすればよい。
Special symbol stop processing (step S303): An effect design stop command for instructing stop of the effect design is transmitted to the effect control board 80. Moreover, the special symbol in the special symbol display 8 is stopped. Then, if the stop symbol of the special symbol is a big hit symbol, the internal state (special symbol process flag) is updated to shift to step S304. If not, the internal state is updated to shift to step S300. Note that the effect symbol stop command may not be transmitted. In this case, the effect control board 80 sets the change time to the change time timer based on the change pattern command received from the main board 31, and updates the change time timer to uniquely change the change time of the effect pattern When it is determined that the fluctuation time has elapsed, processing for stopping the effect pattern may be performed.
大入賞口開放前処理(ステップS304):大入賞口を開放する制御を開始する。具体的には、カウンタ(例えば大入賞口に入った遊技球数をカウントするカウンタ)やフラグ(入賞口への入賞を検出する際に用いられるフラグ)を初期化するとともに、ソレノイド21を駆動して大入賞口を開放する。また、プロセスタイマによって大入賞口開放中処理の実行時間を設定し、大当り中フラグをセットする。そして、内部状態(特別図柄プロセスフラグ)をステップS305に移行するように更新する。
Large winning a prize opening opening processing (step S304): Control which opens the special winning a prize opening is started. Specifically, a counter (for example, a counter for counting the number of game balls entering the big winning opening) and a flag (flag used when detecting a winning on the winning opening) are initialized, and the solenoid 21 is driven. Open the big winning opening. In addition, the execution time of the special winning opening open process is set by the process timer, and the big hit flag is set. And an internal state (special symbol process flag) is updated so that it may transfer to step S305.
大入賞口開放中処理(ステップS305):大入賞口ラウンド表示の演出制御コマンドを演出制御基板80に送出する制御や大入賞口の閉成条件(例えば、大入賞口に所定個数(例えば10個)の遊技球が入賞したこと)の成立を確認する処理等を行う。大入賞口の閉成条件が成立したら、まだ残りラウンドがある場合には、内部状態をステップS304に移行するように更新する。また、全てのラウンドを終えた場合には、内部状態をステップS306に移行するように更新する。
Large winning opening open process (step S305): control to send the effect control command of the large winning opening round display to the effect control board 80, closing conditions of the special winning opening (for example, a predetermined number of large winning opening (for example 10 Processing etc. to confirm the establishment of the game ball of. If the closing condition of the special winning opening is satisfied, if there is still a remaining round, the internal state is updated to shift to step S304. When all the rounds are finished, the internal state is updated to shift to step S306.
大当り終了処理(ステップS306):大当り遊技状態が終了したことを遊技者に報知する表示制御を演出制御手段に行わせるための制御を行う。そして、内部状態をステップS300に移行するように更新する。
Big hit end processing (step S306): Control is performed to cause the effect control means to perform display control to notify the player that the big hit gaming state has ended. Then, the internal state is updated to shift to step S300.
図51は、始動口スイッチ通過処理(ステップS312)を示すフローチャートである。始動口スイッチ通過処理において、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のCPU56は、始動入賞記憶カウンタが示す始動入賞記憶数(または特図保留メモリが記憶している始動入賞記憶数)が最大値である4に達しているかどうか確認する(ステップS321)。始動入賞記憶数が4に達していなければ、CPU56は、乱数回路503の乱数値記憶回路から、乱数値として記憶されているランダムRの値を読み出す(ステップS322)。また、CPU56は、読み出したランダムRの値を、始動入賞記憶数の値に対応した保存領域(特別図柄判定用バッファ(特図保留メモリ))に格納する(ステップS323)。なお、この実施の形態では、乱数回路503は、始動口スイッチ14aからの入力信号をラッチ信号として入力する。この場合、乱数回路503は、始動口スイッチ14aから入力信号を入力したタイミングで、乱数回路503が内蔵するカウンタのカウンタ値を乱数値記憶回路(ラッチ回路)にラッチする。そして、CPU56は、ステップS322において、乱数回路503の乱数値記憶回路にラッチされている値をランダムRとして読み出す。
FIG. 51 is a flowchart showing the starting opening switch passing process (step S312). In the starting opening switch passing process, the CPU 56 of the microcomputer 560 for gaming control sets the starting winning memory number indicated by the starting winning memory counter (or the starting winning memory number stored in the special view holding memory) to 4 as the maximum value. It is checked whether it has reached (step S321). If the start winning memory number has not reached 4, the CPU 56 reads the value of random R stored as a random number from the random number storage circuit of the random number circuit 503 (step S322). Further, the CPU 56 stores the read value of the random R in a storage area (special symbol determination buffer (special drawing reserve memory)) corresponding to the value of the start winning storage number (step S323). In this embodiment, the random number circuit 503 inputs an input signal from the start port switch 14a as a latch signal. In this case, the random number circuit 503 latches the counter value of the counter built in the random number circuit 503 in the random number value storage circuit (latch circuit) at the timing when the input signal is inputted from the starting opening switch 14a. Then, in step S322, the CPU 56 reads the value latched in the random number value storage circuit of the random number circuit 503 as random R.
なお、乱数値記憶回路(ラッチ回路)にラッチされたカウント値を読み出さないかぎり、ラッチ信号を出力しても新たなカウント値をラッチ回路にラッチできないように乱数回路503が構成されている場合には、ステップS321で始動入賞記憶数が最大値4に達していると判定されている間は、ラッチ回路からカウント値が読み出されず、新たなカウント値がラッチ回路にラッチされない状態となる。そのため、その後、始動入賞記憶数が4未満となってステップS322が実行されてラッチ回路からカウント値が読み出されても、本来のラッチタイミング以外でラッチされた古いカウント値が読み出され、誤って古いカウント値にもとづく乱数値を用いて大当り判定などの処理が行われてしまうおそれがある。そのため、ラッチ回路にラッチされたカウント値を読み出さないかぎり新しいカウント値をラッチできないように乱数回路503が構成されている場合には、ステップS321でNと判定した場合であっても(始動入賞記憶数が4未満であった場合でも)、ステップS322の処理を実行して、ラッチ回路にラッチされたカウント値を読み出すようにしてもよい(ただし、ステップS323〜S325は実行しない)。そのようにすれば、本来のラッチタイミング以外でラッチされた古いカウント値にもとづく乱数値を用いて大当り判定などの処理を行ってしまう事態を防止することができる。
It should be noted that the random number circuit 503 is configured such that a new count value can not be latched in the latch circuit even if the latch signal is output unless the count value latched in the random number storage circuit (latch circuit) is read. In step S321, while it is determined that the start winning storage number has reached the maximum value 4, the count value is not read from the latch circuit, and the new count value is not latched in the latch circuit. Therefore, even if the start winning memory number becomes less than 4 and step S322 is executed and the count value is read from the latch circuit, the old count value latched at other than the original latch timing is read out, which is incorrect. There is a possibility that processing such as big hit judgment may be performed using a random number value based on the old count value. Therefore, if the random number circuit 503 is configured such that a new count value can not be latched unless the count value latched in the latch circuit is read out, even if it is determined as N in step S 321 (start prize memory Even if the number is less than four, the process of step S322 may be performed to read the count value latched in the latch circuit (however, steps S323 to S325 are not performed). By doing so, it is possible to prevent a situation such as performing a process such as a big hit determination using a random number value based on the old count value latched at other than the original latch timing.
次いで、CPU56は、所定のバッファ領域に格納したランダムRの値を特図保留メモリの空エントリの先頭にセットし(ステップS324)、始動入賞カウンタのカウント数を1加算することで始動入賞記憶数を1増やす(ステップS325)。
Next, the CPU 56 sets the value of the random R stored in the predetermined buffer area at the top of the empty entry of the special view reservation memory (step S324), and adds 1 to the count of the start winning counter, thereby storing the number of starting winnings. Is increased by 1 (step S325).
なお、ステップS321において始動入賞記憶するが最大値である4に達している場合には、そのまま始動口スイッチ通過処理を終了する。
If the start winning game is stored in step S321 but the maximum value of 4 is reached, the start opening switch passing process is ended.
次に、特別図柄プロセス処理における特別図柄通常処理(ステップS300)について説明する。図52は、特別図柄通常処理を示すフローチャートである。特別図柄通常処理において、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のCPU56は、特別図柄の変動を開始することができる状態のとき(例えば特別図柄プロセスフラグの値がステップS300を示す値となっている場合)には(ステップS380)、特図保留メモリから保留番号「1」に対応して格納されているランダムRの値を読み出す(ステップS381)。この場合、CPU56は、始動入賞カウンタのカウント数を1減算することで保留記憶数を1減らし、且つ、特図保留メモリの第2〜第4エントリ(保留番号「2」〜「4」)に格納されたランダムRの値を1エントリずつ上位にシフトする(ステップS382)。
Next, special symbol normal processing (step S300) in the special symbol process processing will be described. FIG. 52 is a flowchart showing the special symbol normal processing. In the special symbol normal processing, when the CPU 56 of the gaming control microcomputer 560 can start the variation of the special symbol (for example, when the value of the special symbol process flag is a value indicating step S300) (Step S380), the value of random R stored corresponding to the hold number "1" is read from the special view hold memory (step S381). In this case, the CPU 56 reduces the number of pending storages by 1 by subtracting 1 from the count of the start winning counter and sets the second to fourth entries (pending numbers "2" to "4") of the special view pending memory. The value of the stored random R is shifted upward by one entry (step S382).
また、CPU56は、確変フラグがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS383)。すなわち、CPU56は、遊技状態が確変状態に制御されているか否かを確認する。確変フラグがセットされていない場合、CPU56は、遊技状態が確変状態以外の通常状態であると判断し、特別図柄表示器8の表示結果を大当り図柄とするか否かを判定するために用いるテーブルとして、通常時大当り判定テーブル571a(図20(A)参照)を設定する(ステップS384)。また、確変フラグがセットされている場合、CPU56は、遊技状態が確変状態であると判断し、特別図柄表示器8の表示結果を大当り図柄とするか否かを判定するために用いるテーブルとして、確変時大当り判定テーブル571b(図20(B)参照)を設定する(ステップS385)。
In addition, the CPU 56 confirms whether the probability change flag is set (step S383). That is, the CPU 56 confirms whether or not the gaming state is controlled to the definite change state. When the definite change flag is not set, the CPU 56 determines that the gaming state is the normal state other than the definite change state, and uses the table used to determine whether the display result of the special symbol display 8 is to be the big hit symbol. As a normal, the jackpot determination table 571a (see FIG. 20A) is set (step S384). In addition, when the definite change flag is set, the CPU 56 determines that the gaming state is the definite change state, and as a table used to determine whether the display result of the special symbol display 8 is to be the big hit symbol, The probability variation big hit determination table 571b (see FIG. 20B) is set (step S385).
CPU56は、始動口スイッチ通過処理において所定のバッファ領域に格納したランダムRの値にもとづいて、特別図柄表示器8の表示結果を大当り図柄とするか否かを判定する(ステップS386)。この場合、CPU56は、ステップS384で設定した通常時大当り判定テーブル571aまたはステップS385で設定した確変時大当り判定テーブル571bを用いて、大当りとするか否かを判定する。
The CPU 56 determines whether or not to make the display result of the special symbol display 8 a big hit symbol based on the value of the random R stored in the predetermined buffer area in the starting opening switch passing process (step S 386). In this case, the CPU 56 determines whether or not to make a big hit, using the normal time big hit determination table 571a set in step S384 or the probability variation time big hit determination table 571 b set in step S385.
特別図柄表示器8の表示結果を大当り図柄とすると決定すると、CPU56は、大当り状態であることを示す大当りフラグをオン状態にする(ステップS387)。また、特別図柄表示器8の表示結果を大当り図柄としないと決定すると、CPU56は、大当りフラグをオフ状態にする(ステップS388)。そして、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を変動時間設定処理に対応した値に更新する(ステップS389)。
When it is determined that the display result of the special symbol display 8 is a big hit symbol, the CPU 56 turns on a big hit flag indicating that it is a big hit state (step S387). In addition, when it is determined that the display result of the special symbol display 8 is not determined to be the big hit symbol, the CPU 56 turns off the big hit flag (step S388). Then, CPU 56 updates the value of the special symbol process flag to a value corresponding to the fluctuation time setting process (step S389).
なお、図52では記載を省略しているが、特別図柄通常処理において、特別図柄表示器8の表示結果を大当り図柄とすること(大当りとすること)に決定した場合には、CPU56は、大当り種別決定用乱数にもとづいて、大当り種別(例えば、確変大当りや通常大当り、突然確変大当り)も決定する。そして、CPU56は、大当り判定の結果や大当り種別の決定結果に応じた値を、RAM55に形成された大当り図柄判定バッファにセットする。例えば、通常大当りである場合には「1」をセットし、確変大当りである場合には「2」をセットし、突然確変大当りである場合には「3」をセットするものとする。また、CPU56は、決定した表示結果を特定可能な表示結果指定コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行う。
In addition, although description is abbreviate | omitted in FIG. 52, in special symbol normal processing, when it determines that the display result of the special symbol indicator 8 is made a big hit (it is considered as a big hit), CPU56 is a big hit. Based on the type determination random number, the type of jackpot (for example, a probability variation big hit or a normal big hit, a sudden probability variation big hit) is also determined. Then, the CPU 56 sets a value corresponding to the result of the big hit determination or the determination result of the big hit type in the big hit symbol determination buffer formed in the RAM 55. For example, "1" is set when the game is a big hit normally, "2" is set when the game is a big hit, and "3" is set when it is a big hit. Further, the CPU 56 performs control to transmit a display result designation command capable of specifying the determined display result to the effect control microcomputer 100.
次に、タイマ割込処理におけるスイッチ処理(ステップS21)を説明する。この実施の形態では、入賞検出またはゲート通過に関わる各スイッチの検出信号のオン状態が所定時間継続すると、確かにスイッチがオンしたと判定されスイッチオンに対応した処理が開始される。図53は、スイッチ処理で使用されるRAM55に形成される各2バイトのバッファを示す説明図である。前回ポートバッファは、前回(例えば4ms前)のスイッチオン/オフの判定結果が格納されるバッファである。ポートバッファは、今回入力したポート0,1の内容が格納されるバッファである。スイッチオンバッファは、スイッチのオンが検出された場合に対応ビットが1に設定され、スイッチのオフが検出された場合に対応ビットが0に設定されるバッファである。なお、図53に示す前回ポートバッファ、ポートバッファ、およびスイッチオンバッファは、入力ポート0,1ごとに用意される。例えば、この実施の形態では、2つのスイッチオンバッファ1,2が用意されており、入力ポート0のスイッチの状態がスイッチオンバッファ1に設定され、入力ポート1のスイッチの状態がスイッチオンバッファ2に設定される。
Next, the switch process (step S21) in the timer interrupt process will be described. In this embodiment, when the on state of the detection signal of each switch involved in winning detection or gate passage continues for a predetermined time, it is determined that the switch has been turned on, and the processing corresponding to the switch on is started. FIG. 53 is an explanatory drawing showing each 2-byte buffer formed in the RAM 55 used in the switch processing. The previous port buffer is a buffer in which the determination result of the previous (for example, 4 ms before) switch on / off is stored. The port buffer is a buffer in which the contents of ports 0 and 1 input this time are stored. The switch on buffer is a buffer in which the corresponding bit is set to 1 when the switch on is detected, and the corresponding bit is set to 0 when the switch off is detected. The previous port buffer, port buffer, and switch on buffer shown in FIG. 53 are prepared for each of the input ports 0 and 1. For example, in this embodiment, two switch on buffers 1 and 2 are prepared, the switch state of the input port 0 is set to the switch on buffer 1, and the switch state of the input port 1 is the switch on buffer 2 Set to
図54は、遊技制御処理におけるステップS21のスイッチ処理の処理例を示すフローチャートである。スイッチ処理において、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、まず、入力ポート0,1(図22参照)に入力されているデータを入力し(ステップS101)、入力したデータをポートバッファにセットする(ステップS102)。
FIG. 54 is a flowchart showing a process example of the switch process of step S21 in the game control process. In the switch processing, the microcomputer 560 for game control first inputs data input to the input ports 0 and 1 (see FIG. 22) (step S101), and sets the input data in the port buffer (step S102). ).
次いで、RAM55に形成されるウェイトカウンタの初期値をセットし(ステップS103)、ウェイトカウンタの値が0になるまで、ウェイトカウンタの値を1ずつ減算する(ステップS104,S105)。
Next, the initial value of the weight counter formed in the RAM 55 is set (step S103), and the value of the weight counter is decremented by 1 until the value of the weight counter becomes 0 (steps S104 and S105).
ウェイトカウンタの値が0になると、再度、入力ポート0,1のデータを入力し(ステップS106)、入力したデータとポートバッファにセットされているデータとの間で、ビット毎に論理積をとる(ステップS107)。そして、論理積の演算結果を、ポートバッファにセットする(ステップS108)。ステップS103〜S108の処理によって、ほぼ[ウェイトカウンタの初期値×(ステップS104,S105の処理時間)]の時間間隔を置いて入力ポート0から入力した2回の入力データのうち、2回とも「1」になっているビットのみが、ポートバッファにおいて「1」になる。つまり、所定期間としての[ウェイトカウンタの初期値×(ステップS104,S105の処理時間)]だけスイッチの検出信号のオン状態が継続すると、ポートバッファにおける対応するビットが「1」になる。
When the value of the weight counter becomes 0, the data of the input ports 0 and 1 are input again (step S106), and the input data and the data set in the port buffer are logically ANDed bit by bit. (Step S107). Then, the operation result of the logical product is set in the port buffer (step S108). By the process of steps S103 to S108, two times out of the two input data inputted from the input port 0 with a time interval of approximately [initial value of weight counter × (processing time of steps S104 and S105)] approximately twice. Only bits that are 1's will be '1' in the port buffer. That is, when the on state of the detection signal of the switch continues for [predetermined value of wait counter × (processing time of steps S104 and S105)] as a predetermined period, the corresponding bit in the port buffer becomes “1”.
さらに、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、前回ポートバッファにセットされているデータとポートバッファにセットされているデータとの間で、ビット毎に排他的論理和をとる(ステップS109)。排他的論理和の演算結果において、前回(例えば4ms前)のスイッチオン/オフの判定結果と、今回オンと判定されたスイッチオン/オフの判定結果とが異なっているスイッチに対応したビットが「1」になる。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、さらに、排他的論理和の演算結果と、ポートバッファにセットされているデータとの間で、ビット毎に論理積をとる(ステップS110)。この結果、前回のスイッチオン/オフの判定結果と今回オンと判定されたスイッチオン/オフの判定結果とが異なっているスイッチに対応したビット(排他的論理和演算結果による)のうち、今回オンと判定されたスイッチに対応したビット(論理積演算による)のみが「1」として残る。
Further, the game control microcomputer 560 exclusively ORs the data set in the previous port buffer and the data set in the port buffer for each bit (step S109). In the exclusive-OR operation result, a bit corresponding to a switch in which the previous determination result (for example, 4 ms before) of the switch on / off determination result and the determination result of the switch on / off determined this time are different is “ It will be 1 ". The game control microcomputer 560 further performs an AND operation bit by bit between the result of the exclusive OR operation and the data set in the port buffer (step S110). As a result, among the bits (according to the exclusive OR operation result) corresponding to the switch in which the previous determination result of the switch on / off and the determination result of the switch on / off determined to be on this time are different, Only the bit (due to the logical AND operation) corresponding to the switch determined to remain as "1".
そして、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ステップS110における論理積の演算結果をスイッチオンバッファにセットし(ステップS111)、ステップS108における演算結果がセットされているポートバッファの内容を前回ポートバッファにセットする(ステップS112)。
Then, the game control microcomputer 560 sets the calculation result of the logical product in step S110 in the switch on buffer (step S111), and sets the content of the port buffer in which the calculation result in step S108 is set in the previous port buffer (Step S112).
以上の処理によって、所定期間継続してオン状態であったスイッチのうち、前回(例えば4ms前)のスイッチオン/オフの判定結果がオフであったスイッチ、すなわち、オフ状態からオン状態に変化したスイッチに対応したビットが、スイッチオンバッファにおいて「1」になっている。
Among the switches that have been in the on state for a predetermined period continuously by the above processing, the switch in which the determination result of the on / off of the previous (for example, 4 ms) was off, ie, changed from the off state to the on state The bit corresponding to the switch is "1" in the switch on buffer.
さらに、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560(具体的には、CPU56)は、スイッチ正常/異常チェック処理を行う(ステップS113)。また、CPU56は、ドア開放時入賞異常チェック処理を行う(ステップS114)。
Further, the game control microcomputer 560 (specifically, the CPU 56) performs switch normal / abnormality check processing (step S113). Further, the CPU 56 performs a prize opening abnormality check process at the time of door opening (step S114).
図55は、スイッチ正常/異常チェック処理を示すフローチャートである。図55に示すスイッチ正常/異常チェック処理において、CPU56は、入力ポート1に対応するスイッチオンバッファの内容を読み出す(ステップS121)。そして、入力ポート1に対応するスイッチオンバッファにおける始動口スイッチ14aに対応するビット0の値が0であるか否か確認する(ステップS122)。すなわち、始動入賞口14内の上部に設けられた始動口スイッチ14a(近接スイッチ)がオン(遊技球を検出)したか否か確認する。
FIG. 55 is a flowchart showing the switch normal / abnormal check process. In the switch normal / abnormal check process shown in FIG. 55, the CPU 56 reads the contents of the switch on buffer corresponding to the input port 1 (step S121). Then, it is checked whether or not the value of bit 0 corresponding to the start port switch 14a in the switch on buffer corresponding to the input port 1 is 0 (step S122). That is, it is checked whether or not the starting opening switch 14a (proximity switch) provided at the upper portion in the starting winning opening 14 has been turned on (detecting the gaming ball).
入力ポート1に対応するスイッチオンバッファにおける始動口スイッチ14aに対応するビット0の値が0である場合(すなわち、始動口スイッチ14aがオン状態である場合)には、RAM55に形成されているスイッチ用カウンタの値を1増やす(ステップS123)。
When the value of bit 0 corresponding to starting opening switch 14a in the switch on buffer corresponding to input port 1 is 0 (ie, when starting opening switch 14a is in the on state), the switch formed in RAM 55 The value of the counter is increased by 1 (step S123).
また、CPU56は、入力ポート1に対応するスイッチオンバッファにおける入賞確認スイッチ14bに対応するビット1の値が0であるか否か確認する(ステップS124)。すなわち、始動入賞口14内の下部に設けられた入賞確認スイッチ14b(フォトセンサ)がオン(遊技球を検出)したか否か確認する。
Further, the CPU 56 confirms whether or not the value of the bit 1 corresponding to the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b in the switch on buffer corresponding to the input port 1 is 0 (step S124). That is, it is confirmed whether or not the prize confirmation switch 14 b (photo sensor) provided at the lower part in the start winning hole 14 is turned on (detects the gaming ball).
入力ポート1に対応するスイッチオンバッファにおける入賞確認スイッチ14bに対応するビット1の値が0である場合(すなわち、入賞確認スイッチ14bがオン状態である場合)には、RAM55に形成されているスイッチ用カウンタの値を1減らす(ステップS125)。
When the value of bit 1 corresponding to the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b in the switch on buffer corresponding to the input port 1 is 0 (ie, when the prize confirmation switch 14b is in an on state), the switch formed in the RAM 55 The value of the counter for is decreased by 1 (step S125).
そして、CPU56は、スイッチ用カウンタの値が所定値以上になっているか否か確認する(ステップステップS126)。スイッチ用カウンタの値が所定値以上になっている場合には、CPU56は、始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したと判定し、セキュリティ信号情報タイマに所定時間(本例では、4分)をセットする(ステップS127)。なお、この実施の形態では、CPU56は、スイッチ用カウンタの値が所定値として10以上となったことにもとづいて、セキュリティ信号情報タイマに所定時間(本例では、4分)をセットするものとする。この実施の形態では、ステップS127でセキュリティ信号情報タイマに所定時間がセットされたことにもとづいて、情報出力処理(S31参照)が実行されることによって、始動入賞口14の異常入賞が検出されたときに、セキュリティ信号が所定時間(本例では、4分)外部出力される。
Then, the CPU 56 checks whether or not the value of the switch counter is equal to or greater than a predetermined value (step S126). If the value of the switch counter is equal to or greater than a predetermined value, the CPU 56 determines that an abnormal winning at the start winning opening 14 has occurred, and the security signal information timer is for a predetermined time (four minutes in this example). Is set (step S127). In this embodiment, the CPU 56 sets the security signal information timer for a predetermined time (four minutes in this example) based on the fact that the value of the switch counter has become 10 or more as the predetermined value. Do. In this embodiment, based on the fact that the security signal information timer has been set to the predetermined time in step S127, the information output process (see S31) is executed, whereby an abnormal winning of the start winning opening 14 is detected. At the same time, the security signal is externally output for a predetermined time (four minutes in this example).
なお、ステップS126の処理において、CPU56は、例えば、スイッチ用カウンタの値が10以上となったことにもとづいて、始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したと判定することに加えて、逆にスイッチ用カウンタの値が−10以下となったことにもとづいても、始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したと判定するようにしてもよい。この場合、スイッチ用カウンタの値がマイナス値となっていることを認識できないように構成されている場合には、例えば、スイッチ用カウンタの値のデフォルト値として10をセットするようにしておき、スイッチ用カウンタの値が0または20以上となったことにもとづいて、始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したと判定するようにしてもよい。
In the process of step S126, the CPU 56 determines that the abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14 has occurred, for example, based on the fact that the value of the switch counter has become 10 or more. Even when the value of the switch counter has become -10 or less, it may be determined that an abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14 has occurred. In this case, when it is configured not to recognize that the value of the switch counter is a negative value, for example, 10 is set as the default value of the value of the switch counter. It may be determined that the abnormal winning to the start winning opening 14 has occurred based on the value of the counter for 0 or 20 or more.
なお、この実施の形態では、既にセキュリティ信号情報タイマに値が設定されセキュリティ信号を外部出力中であっても、新たに異常入賞を検出した場合には、再度ステップS127の処理が実行されて、セキュリティ信号情報タイマに所定時間(本例では、4分)が上書きされる。従って、セキュリティ信号の外部出力中に新たな異常入賞を検出した場合には、実質的にセキュリティ信号の外部出力期間が延長され、その新たに異常入賞を検出した時点から更に所定時間(本例では、4分)セキュリティ信号の出力が継続されることになる。
In this embodiment, even if a value is already set in the security signal information timer and the security signal is being output to the outside, the process of step S127 is executed again when an abnormal winning is newly detected. A predetermined time (4 minutes in this example) is overwritten on the security signal information timer. Therefore, when a new abnormal winning is detected during the external output of the security signal, the external output period of the security signal is substantially extended, and a predetermined time (in this example, from the time when the new abnormal winning is detected). , 4 minutes) Output of security signal will be continued.
なお、この実施の形態では、1つのスイッチ用カウンタのみを用いて始動入賞口14への異常入賞を検出する場合を示したが、始動口スイッチ14aの検出回数と入賞確認スイッチ14bの検出回数とで異なるスイッチ用カウンタを用いてもよい。この場合、例えば、始動口スイッチ14aのオン状態を検出するごとに第1スイッチ用カウンタの値を1加算するようにするとともに、入賞確認スイッチ14bのオン状態を検出するごとに第2スイッチ用カウンタの値を1加算するようにすればよい。そして、ステップS126では、第1スイッチ用カウンタの値と第2スイッチ用カウンタの値との差が所定値(例えば、10)以上であると判定したことにもとづいて、始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したと判定し、ステップS127の処理を実行してセキュリティ信号を外部出力するようにすればよい。
In this embodiment, only one switch counter is used to detect an abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14, but the number of times of detection of the starting opening switch 14a and the number of times of detection of the winning confirmation switch 14b are used. Different switch counters may be used. In this case, for example, the value of the first switch counter is incremented by one each time the on state of the starting opening switch 14a is detected, and the second switch counter is detected each time the on state of the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b is detected. The value of may be added by one. Then, in step S126, based on the determination that the difference between the value of the first switch counter and the value of the second switch counter is greater than or equal to a predetermined value (for example, 10), an abnormality to the start winning opening 14 It may be determined that a winning has occurred, and the process of step S127 may be executed to externally output the security signal.
また、始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したことを検出した場合には、ステップS127の処理を実行してセキュリティ信号を外部出力するとともに、所定のエラー報知コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信するようにして、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100側において演出表示装置9に所定のエラー画面を表示させるなどによりエラー報知を行えるようにすることが望ましい。
When it is detected that an abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14 has been generated, the processing in step S127 is executed to externally output a security signal, and a predetermined error notification command is sent to the microcomputer 100 for effect control. It is preferable that error notification can be performed by transmitting a predetermined error screen on the effect display device 9 on the effect control microcomputer 100 side.
また、例えば、始動入賞口14への異常入賞に加えて、大入賞口への異常入賞や、異常磁気エラー、異常電波エラー、通信エラーを検出した場合にもセキュリティ信号を出力するように構成する場合には、それぞれエラーの種類ごとに異なるエラー報知コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信するようにしてもよい。そして、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100側において、演出表示装置9に、エラーの種類ごとにそれぞれ異なるエラー画面を表示させるなどによりエラー報知を行えるようにしてもよい。
Further, for example, in addition to the abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14, the security signal is configured to be output also when an abnormal winning on the large winning opening, an abnormal magnetic error, an abnormal radio wave error, or a communication error is detected. In this case, different error notification commands may be transmitted to the effect control microcomputer 100 depending on the type of error. Then, on the effect control microcomputer 100 side, error notification may be performed by displaying different error screens on the effect display device 9 for each type of error.
なお、上記のように構成する場合、遊技機への電力供給が停止した後に電力供給が再開したときには、電力供給の停止前にエラー報知中であった場合には、電源供給の再開時に所定のエラー報知コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して再度送信するようにするようにしてもよい。すなわち、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100側ではRAMなどの記憶内容がバックアップ電源によってバックアップされていないので、停電が発生してしまうと、そのままでは、それまで実行していたエラー報知などの演出を実行できないのであるが、停電復旧時に所定のエラー報知コマンドを再度送信するように構成することによって、停電復旧時にエラー報知を再開できるようにすることができる。また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、セキュリティ信号情報タイマの値もバックアップRAMにバックアップしておくようにし、電力供給の停止前にセキュリティ信号の出力中であった場合には、停電復旧時にバックアップされていたセキュリティ信号情報タイマの値にもとづいてセキュリティ信号の出力を再開できるようにしてもよい。それらの構成を備えることによって、故意に遊技機への電源断を発生させることによって、エラー報知を消したりセキュリティ信号の出力を停止させたりするような不正行為を防止することができる。
In the case of configuring as described above, when power supply is resumed after power supply to the gaming machine is stopped, a predetermined error occurs when power supply is resumed if error notification is in progress before power supply is stopped. The error notification command may be transmitted to the effect control microcomputer 100 again. That is, since the storage content such as the RAM is not backed up by the backup power supply on the side of the effect control microcomputer 100, if a power failure occurs, the effect such as an error notification that has been executed can not be executed as it is However, it is possible to resume the error notification at the time of the power failure recovery by configuring to transmit the predetermined error notification command again at the time of the power failure recovery. The game control microcomputer 560 also backs up the value of the security signal information timer in the backup RAM, and when the security signal is being output before stopping the power supply, it is backed up at the time of power failure recovery. The output of the security signal may be resumed based on the value of the security signal information timer. By providing these configurations, it is possible to prevent a fraudulent act such as turning off an error notification or stopping the output of a security signal by intentionally generating a power-off to a gaming machine.
図56は、ドア開放時入賞異常チェック処理を示すフローチャートである。図56に示すドア開放時入賞異常チェック処理において、CPU56は、入力ポート1に対応するスイッチオンバッファの内容を読み出す(ステップS131)。そして、入力ポート1に対応するスイッチオンバッファにおける始動口スイッチ14aに対応するビット0の値が0であるか否か確認する(ステップS132)。すなわち、始動入賞口14内の上部に設けられた始動口スイッチ14a(近接スイッチ)がオン(遊技球を検出)したか否か確認する。
FIG. 56 is a flow chart showing a prize opening abnormality check process when the door is open. In the door opening prize error check process shown in FIG. 56, the CPU 56 reads the content of the switch on buffer corresponding to the input port 1 (step S131). Then, it is checked whether or not the value of bit 0 corresponding to the start port switch 14a in the switch on buffer corresponding to the input port 1 is 0 (step S132). That is, it is checked whether or not the starting opening switch 14a (proximity switch) provided at the upper portion in the starting winning opening 14 has been turned on (detecting the gaming ball).
入力ポート1に対応するスイッチオンバッファにおける始動口スイッチ14aに対応するビット0の値が0である場合(すなわち、始動口スイッチ14aがオン状態である場合)には、ステップS135に移行する。入力ポート1に対応するスイッチオンバッファにおける始動口スイッチ14aに対応するビット0の値が0でなかった場合(すなわち、始動口スイッチ14aがオフ状態である場合)には、CPU56は、入力ポート0に対応するスイッチオンバッファの内容を読み出す(ステップS133)。そして、入力ポート0に対応するスイッチオンバッファにおけるカウントスイッチ23または入賞口スイッチ29a,30aに対応するビット0、ビット2またはビット3の値が1であるか否か確認する(ステップS134)。すなわち、大入賞口内に設けられたカウントスイッチ23や、普通入賞口29,30に設けられた入賞口スイッチ29a,30aがオン(遊技球を検出)したか否か確認する。
If the value of bit 0 corresponding to the start port switch 14a in the switch on buffer corresponding to the input port 1 is 0 (that is, if the start port switch 14a is in the on state), the process proceeds to step S135. If the value of bit 0 corresponding to the start port switch 14 a in the switch on buffer corresponding to the input port 1 is not 0 (that is, if the start port switch 14 a is in the off state), the CPU 56 selects the input port 0. The contents of the switch-on buffer corresponding to are read out (step S133). Then, it is checked whether the value of bit 0, bit 2 or bit 3 corresponding to the count switch 23 or the winning opening switches 29a, 30a in the switch on buffer corresponding to the input port 0 is 1 (step S134). That is, it is checked whether the count switch 23 provided in the special winning opening and the winning opening switches 29a and 30a provided in the normal winning openings 29 and 30 are turned on (detecting the game ball).
入力ポート0に対応するスイッチオンバッファにおけるカウントスイッチ23または入賞口スイッチ29a,30aに対応するビット0、ビット2またはビット3の値が1である場合(すなわち、カウントスイッチ23または入賞口スイッチ29a,30aがオン状態である場合)には、ステップS135に移行する。入力ポート0に対応するスイッチオンバッファにおけるカウントスイッチ23または入賞口スイッチ29a,30に対応するビット0、ビット2またはビット3の値も1でなかった場合(すなわち、カウントスイッチ23および入賞口スイッチ29a,30もオフ状態である場合)には、そのまま処理を終了する。
When the value of bit 0, bit 2 or bit 3 corresponding to the count switch 23 or the winning opening switch 29a, 30a in the switch on buffer corresponding to the input port 0 is 1 (ie, the count switch 23 or the winning opening switch 29a, When 30a is in the on state), the process proceeds to step S135. When the value of bit 0, bit 2 or bit 3 corresponding to the count switch 23 or the winning opening switch 29a, 30 in the switch on buffer corresponding to the input port 0 is also not 1 (ie, the count switch 23 and the winning opening switch 29a , 30 are also in the off state), the processing is ended as it is.
ステップS135では、CPU56は、入力ポート0に対応するスイッチオンバッファにおけるドア開放信号に対応するビット6の値が1であるか否か確認する。すなわち、払出制御基板37を経由して、ドア開放センサ155によってガラス扉枠2が開放状態であることが検出されたことを示すドア開放信号が入力されているか否かを確認する。
In step S135, the CPU 56 checks whether the value of the bit 6 corresponding to the door open signal in the switch on buffer corresponding to the input port 0 is one. That is, it is checked whether a door open signal indicating that the glass door frame 2 is in the open state is detected by the door open sensor 155 is inputted via the payout control board 37.
入力ポート0に対応するスイッチオンバッファにおけるドア開放信号に対応するビット6の値が1である場合(すなわち、ガラス扉枠2の開放状態が検出されている場合)には、CPU56は、ガラス扉枠2の開放状態において異常入賞を検出したことを示すドア開放時入賞異常コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して送信する制御を行う(ステップS136)。
When the value of the bit 6 corresponding to the door open signal in the switch on buffer corresponding to the input port 0 is 1 (that is, when the open state of the glass door frame 2 is detected), the CPU 56 controls the glass door Control is performed to transmit to the effect control microcomputer 100 a door opening prize winning command indicating that an abnormal prize has been detected in the opening state of the frame 2 (step S136).
以上の処理が実行されることによって、この実施の形態では、ガラス扉枠2が開放状態となっている状態においていずれかの入賞口(大入賞口、始動入賞口14、普通入賞口29,30)で遊技球の入賞を検出したことにもとづいて、異常入賞が発生したと判定し、ドア開放時入賞異常コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する。
In this embodiment, any of the winning openings (large winning opening, starting winning opening 14, ordinary winning openings 29, 30) is performed in this embodiment by the above processing being executed. Based on the fact that the winning of the game ball has been detected, it is determined that an abnormal winning has occurred, and the door open winning combination abnormal command is transmitted to the effect control microcomputer 100.
図57および図58は、スイッチ正常/異常チェック処理を説明するための説明図である。このうち、図57は、正常な状態におけるスイッチ正常/異常チェック処理の例を示しており、図58は、異常入賞につながる不正行為が行われているときのスイッチ正常/異常チェック処理の例を示している。
57 and 58 are explanatory diagrams for explaining the switch normal / abnormal check process. Among them, FIG. 57 shows an example of the switch normality / abnormality check process in a normal state, and FIG. 58 shows an example of the switch normality / abnormality check process when an illegal action leading to an abnormal winning is performed. It shows.
図57および図58に示すように、入力ポート1に対応するスイッチオンバッファのビット0は、そのビット0に対応する始動口スイッチ14a(近接スイッチ)によって遊技球が検出されると「0」になる。また、入力ポート1に対応するスイッチオンバッファのビット1は、そのビット1に対応する入賞確認スイッチ14b(フォトセンサ)によって遊技球が検出されると「0」になる。スイッチが正常に動作し、かつ、不正行為(スイッチからの検出信号を不正にオン状態にしたり、オン状態の検出信号を不正にオフ状態にしたりする行為)を受けていない場合には、始動口スイッチ14aが入賞確認スイッチ14bよりも上流側に配置されていることから、まず、始動口スイッチ14a(近接スイッチ)がオンし、次いで、入賞確認スイッチ14b(フォトセンサ)がオンするはずである。従って、まず始動口スイッチ14aがオンしたことにもとづいてスイッチ用カウンタの値が1加算されて1となり(ステップS123参照)、次いで入賞確認スイッチ14bがオンしたことにもとづいてスイッチ用カウンタの値が1減算されて0に戻る(ステップS125参照)。よって、遊技球がスイッチを通過するときに、入力ポート1に対応するスイッチオンバッファのビット0とビット1とがともに「0」となり、正常な動作状態であれば、カウントアップのタイミングにずれ(遊技球の通過タイミングのずれに相当)があるものの、図57に示すように、スイッチ用カウンタの値は0に保たれる筈である。
As shown in FIG. 57 and FIG. 58, bit 0 of the switch on buffer corresponding to input port 1 is set to “0” when the game ball is detected by start opening switch 14 a (proximity switch) corresponding to bit 0 Become. In addition, bit 1 of the switch on buffer corresponding to the input port 1 becomes “0” when the gaming ball is detected by the winning a prize confirmation switch 14 b (photo sensor) corresponding to the bit 1. If the switch operates normally and has not been tampered with (action to turn on the detection signal from the switch illegally or to turn off the detection signal from the switch illegally), the starting opening Since the switch 14a is disposed upstream of the winning confirmation switch 14b, first, the starting opening switch 14a (proximity switch) should be turned on, and then the winning confirmation switch 14b (photosensor) should be turned on. Therefore, first, the value of the switch counter is incremented by 1 based on the fact that the start port switch 14a is turned on (see step S123), and then the value of the switch counter is determined based on the winning confirmation switch 14b being turned on. It is decremented by 1 and returned to 0 (see step S125). Therefore, when the gaming ball passes the switch, both the bit 0 and the bit 1 of the switch on buffer corresponding to the input port 1 become “0”. The value of the switch counter should be maintained at 0 as shown in FIG.
しかし、電波による不正行為が行われた場合には、図58に示すように、始動口スイッチ14aが1回オンする筈の期間に、電波により不正にオフ状態を割り込ませ、恰も始動口スイッチ14aが2回オンしたかのように認識させる不正行為が行われるおそれがある。従って、始動口スイッチ14aが1回だけオンとなったにもかかわらず、始動口スイッチ14aが2回に亘ってオンしたと誤認識させられてスイッチ用カウンタの値が合計で2加算されて2となる(ステップS123が2回実行されることになる)。一方、下流側に配置されている入賞確認スイッチ14bは、電磁式である始動口スイッチ14aとは検出方式が異なり、光学式のフォトセンサが用いられていることから、電波による不正行為の影響を受けない。そのため、図58に示すように、始動口スイッチ14aで遊技球を1球検出した後に、少し遅れて入賞確認スイッチ14b側で遊技球を検出されたときに、正常に入賞確認スイッチ14bのオンを1回だけ検出して、スイッチ用カウンタの値を1減算して1とする(ステップS125参照)。従って、電波による不正行為が行われた場合には、検出方式の異なる始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14bとの間で検出数に差が生じるのであるから、図58に示すように、スイッチ用カウンタの値が0に保たれず、スイッチ用カウンタの値が所定値(本例では10)以上となったことにもとづいて(始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14bとの間の検出誤差の累積値が所定値(本例では10)以上となったことにもとづいて)、始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したことを検出することができる。
However, if fraudulent activity by radio waves is performed, as shown in FIG. 58, the off state is interrupted by radio waves illegally during the period until the start port switch 14a is turned on once, and the spear is also the start port switch 14a. There is a risk of fraudulent action being taken as if it were turned on twice. Therefore, even though the start port switch 14a is turned on only once, it is erroneously recognized that the start port switch 14a is turned on twice, and the value of the switch counter is added by a total of 2 and 2 (Step S123 will be executed twice). On the other hand, since the winning confirmation switch 14b disposed on the downstream side has a detection method different from that of the start port switch 14a which is an electromagnetic type, and an optical photosensor is used, the influence of the fraudulent action by the radio wave is I do not receive it. Therefore, as shown in FIG. 58, when one game ball is detected by the starting opening switch 14a and then the game ball is detected by the prize confirmation switch 14b after a slight delay, the prize confirmation switch 14b is normally turned on. Detection is performed only once, and the value of the switch counter is decremented by 1 to 1 (see step S125). Therefore, when an illegal act is performed by radio waves, a difference occurs in the number of detections between the start port switch 14a and the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b having different detection methods, so as shown in FIG. Based on the fact that the value of the counter is not maintained at 0 and the value of the switch counter has reached a predetermined value (10 in this example) or more (accumulation of detection error between the starting opening switch 14a and the winning affirmation confirmation switch 14b) Based on the fact that the value has become equal to or more than a predetermined value (10 in this example), it is possible to detect that an abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14 has occurred.
なお、不正に光を照射するなどの行為によって同様な不正行為が行われることも考えられる。この場合、入賞確認スイッチ14bが1回オンする筈の期間に、光により不正にオフ状態を割り込ませ、恰も入賞確認スイッチ14bが2回オンしたかのように認識させる不正行為が行われるおそれがある。しかし、この場合、逆に電磁式の始動口スイッチ14a側では光による不正行為の影響をうけず正常に遊技球を検出できるのであるから、同様にスイッチ用カウンタの値が0に保たれず、スイッチ用カウンタの値が所定値(本例では10)以上となったことにもとづいて(始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14bとの間の検出誤差の累積値が所定値(本例では10)以上となったことにもとづいて)、始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したことを検出することができる。
In addition, it is also considered that the same cheating is carried out by the action of irradiating light to the wrong. In this case, there is a risk that an illegal action will be made to cause the light to interrupt the off state with light improperly during a period until the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b is turned on once, and for the spear to be recognized as if the prize confirmation switch 14b has been turned on twice. is there. However, in this case, since the game ball can be detected normally on the side of the electromagnetic start port switch 14a without being affected by the cheating by light, the value of the switch counter is not maintained at 0 as well. Based on the fact that the value of the switch counter has become equal to or greater than a predetermined value (10 in this example) (the accumulated value of the detection error between the start opening switch 14a and the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b is a predetermined value (10 in this example) Based on the above, it is possible to detect that an abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14 has occurred.
なお、この実施の形態では、始動口スイッチ14aおよび入賞確認スイッチ14bの出力が負論理である場合を示しているが、始動口スイッチ14aおよび入賞確認スイッチ14bの出力が正論理となるように構成してもよい。この場合、例えば、始動口スイッチ14aおよび入賞確認スイッチ14bの出力レベルをそれぞれ入力ドライバ回路で論理反転してから遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に入力するように構成すればよい。
In this embodiment, although the case where the outputs of the starting opening switch 14a and the prize confirmation switch 14b are negative logic is shown, the outputs of the starting opening switch 14a and the prize confirmation switch 14b are positive logic. You may In this case, for example, the output levels of the starting opening switch 14a and the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b may be logically inverted by the input driver circuit and then input to the game control microcomputer 560.
また、この実施の形態では、スイッチ用カウンタの値が0に保たれていないこと(始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14bとの間に検出誤差が発生したこと)にもとづいて直ちに異常入賞と判定するのではなく、スイッチ用カウンタの値が所定値(本例では10)以上となったことにもとづいて異常入賞が発生したと判定している。そのように構成することによって、例えば、始動入賞口14内で遊技球が球詰まり状態を起こした場合などを不正行為による異常入賞と判定することを防止している。
Further, in this embodiment, it is immediately determined as an abnormal prize based on the fact that the value of the switch counter is not maintained at 0 (the occurrence of a detection error between the starting opening switch 14a and the prize confirmation switch 14b). Rather, it is determined that an abnormal winning has occurred based on the fact that the value of the switch counter has become equal to or greater than a predetermined value (10 in this example). By configuring as such, for example, it is possible to prevent the case where the game ball is clogged in the start winning opening 14 and the like to be determined as the abnormal prize due to the injustice.
図59は、始動入賞口14内で遊技球が球詰まり状態を起こした場合を示す説明図である。図59に示すように、始動入賞口14内において、始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14bとは、上下に一定の距離をおいて配置されている。そのため、始動入賞口14に入賞した遊技球は、まず始動口スイッチ14aで検出された後、少し時間をおいて下流側の入賞確認スイッチ14bで検出されることになる。図59に示すように、始動入賞口14内において遊技球が球詰まり状態を起こした場合には、始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14bとの物理的な距離差によって、その検出数に差が生じた状態となる。この実施の形態では、図59に示すように、始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14bとの間で最大3個の検出誤差が生じるものとする。そこで、この実施の形態では、スイッチ用カウンタの値が、球詰まり状態における始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14bとの検出誤差3個に対して十分余裕をもたせた所定値(本例では10)以上となったことにもとづいて異常入賞が発生したと判定することによって、始動入賞口14内で遊技球が球詰まり状態を起こした場合などを不正行為による異常入賞と判定することを防止している。
FIG. 59 is an explanatory view showing a case where the gaming ball is jammed in the start winning hole 14. As shown in FIG. 59, in the starting winning opening 14, the starting opening switch 14a and the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b are arranged at a certain distance vertically. Therefore, the gaming ball having won the start winning opening 14 is first detected by the starting opening switch 14a, and then is detected by the winning confirmation switch 14b on the downstream side after a short time. As shown in FIG. 59, when the gaming ball is jammed in the start winning opening 14, a difference in the number of detections is caused by the physical distance difference between the starting opening switch 14a and the winning affirmation confirmation switch 14b. It will be in a state of being generated. In this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 59, it is assumed that a maximum of three detection errors occur between the starting opening switch 14a and the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b. Therefore, in this embodiment, the value of the switch counter is a predetermined value (10 in this example) which is sufficiently large for three detection errors between the start opening switch 14a and the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b in the ball clogging state. By determining that the abnormal prize has occurred based on the above, it is prevented that the game ball is clogged in the start winning hole 14 and the like is not determined as the abnormal prize due to the injustice. There is.
なお、この実施の形態では、球詰まり状態における始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14bとの検出誤差3個に対して十分余裕をもたせた所定値(本例では10)以上となったことにもとづいて異常入賞が発生したと判定する場合を示しているが、異常入賞の判定に用いる所定値は、この実施の形態で示したものにかぎられない。例えば、少なくとも、球詰まり状態における始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14bとの検出誤差3個より多い数であれば、誤って異常入賞と判定してしまうことを防止できるのであるから、スイッチ用カウンタの値が4以上となったことにもとづいて異常入賞が発生したと判定するようにしてもよい。
In this embodiment, it is based on the fact that a sufficient margin is provided for three detection errors between the starting opening switch 14a and the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b in the ball clogging state or more, which is not less than a predetermined value (10 in this example). In the case where it is determined that the abnormal winning has occurred, the predetermined value used for determining the abnormal winning is not limited to that shown in this embodiment. For example, if the number of detection errors between the starting opening switch 14a and the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b at least in the ball clogging state is more than three, it is possible to prevent the erroneous determination of an abnormal prize, so a switch counter It may be determined that the abnormal winning has occurred based on the value of 4 being 4 or more.
また、複数の入賞口における異常入賞を検出可能に構成した場合には、これら全ての入賞口における球詰まり状態における検出誤差を合計した数より多い数を所定値として用いて、異常入賞の判定を行うようにしてもよい。例えば、始動入賞口を2つ備えた遊技機において、2つの始動入賞口に加えて大入賞口の異常入賞を検出可能に構成した場合には、1つ当りの入賞口において球詰まり状態における検出誤差がそれぞれ3個ずつであるとすると、最大3個×3=9個までの検出誤差であれば、電波を用いた不正行為によらなくても、入賞口における球詰まりによって生じる可能性がある。そこで、そのような場合には、スイッチ用カウンタの値が少なくとも10以上となったことにもとづいて異常入賞が発生したと判定すれば、誤って異常入賞を判定することを防止することができる。
In addition, when it is configured to be able to detect abnormal winnings in a plurality of winning openings, determination of abnormal winnings is performed using a number greater than the total number of detection errors in the ball clogging state in all these winning openings as a predetermined value. You may do so. For example, in a gaming machine provided with two start winning openings, when it is configured to be able to detect an abnormal winning of a large winning opening in addition to the two start winning openings, detection in a jammed state at one winning opening per one. Assuming that the errors are respectively three each, detection errors of up to 3 × 3 = 9 may be caused by a ball jam at the winning opening, even if it is not due to a fraudulent action using radio waves . Therefore, in such a case, if it is determined that the abnormal winning has occurred based on the value of the switch counter being at least 10 or more, it is possible to prevent the abnormal winning from being determined by mistake.
図60は、ターミナル基板160に出力される各種信号を示すブロック図である。図60に示すように、この実施の形態では、主基板31に搭載されている遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560からターミナル基板160に対して、始動口信号、図柄確定回数1信号、大当り1信号、大当り2信号、大当り3信号、時短信号、およびセキュリティ信号が、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560側の情報出力処理(ステップS31参照)によって出力される。また、この実施の形態では、払出制御基板37に搭載されている払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370から、主基板31を経由して、ターミナル基板160に対して、賞球信号1および遊技機エラー状態信号が、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370側の情報出力処理(ステップS759参照)によって出力される。
FIG. 60 is a block diagram showing various signals output to the terminal substrate 160. As shown in FIG. As shown in FIG. 60, in this embodiment, the game control microcomputer 560 mounted on the main substrate 31 transmits a start opening signal, a symbol determination number 1 signal, a big hit 1 signal, a big hit to the terminal substrate 160. Two signals, a big hit 3 signal, a short time signal, and a security signal are output by the information output process (see step S31) on the game control microcomputer 560 side. Further, in this embodiment, the payout control microcomputer 370 mounted on the payout control substrate 37 passes the main substrate 31 to the terminal substrate 160 for the winning ball signal 1 and the gaming machine error status signal. Are output by the information output process (see step S759) on the payout control microcomputer 370 side.
始動口信号は、始動入賞口14への入賞個数を通知するための信号である。図柄確定回数1信号は、特別図柄の変動回数を通知するための信号である。大当り1信号は、大当り遊技中(特別可変入賞球装置の動作中)であることを通知するための信号である。大当り2信号は、大当り遊技中(特別可変入賞球装置の動作中)で、または特別図柄の変動時間短縮機能が作動中(時短状態中)であることを通知するための信号である。大当り3信号は、15ラウンドの大当り遊技中であることを通知するための信号である。時短信号は、特別図柄の変動時間短縮機能が作動中(時短状態中)であることを通知するための信号である。
The starting opening signal is a signal for notifying the number of winnings to the starting winning opening 14. The symbol determination number 1 signal is a signal for notifying the variation number of the special symbol. The jackpot 1 signal is a signal for notifying that a jackpot game is in progress (during operation of the special variable winning prize ball device). The jackpot 2 signal is a signal for notifying that a jackpot game is in progress (during operation of the special variable winning prize ball device) or that the special symbol fluctuation time shortening function is in operation (during a short time). The jackpot 3 signal is a signal for notifying that 15 rounds of jackpot games are being played. The short time signal is a signal for notifying that the variation time shortening function of the special symbol is in operation (during the short time condition).
また、セキュリティ信号は、遊技機のセキュリティ状態を示す信号である。具体的には、始動口スイッチ14aの検出結果と入賞確認スイッチ14bの検出結果とにもとづいて、始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したと判定された場合に、セキュリティ信号が所定期間(例えば、4分間)ホールコンピュータなどの外部装置に出力される。また、遊技機への電源投入が行われて初期化処理が実行された場合にも、セキュリティ信号が所定期間(例えば、30秒間)ホールコンピュータなどの外部装置に出力される。
The security signal is a signal indicating the security state of the gaming machine. Specifically, based on the detection result of the starting opening switch 14a and the detection result of the winning confirmation switch 14b, when it is determined that an abnormal winning on the starting winning opening 14 has occurred, the security signal is for a predetermined period (for example, 4 minutes) output to an external device such as a hall computer. Also, when the game machine is powered on and initialization processing is performed, a security signal is output to an external device such as a hall computer for a predetermined period (for example, 30 seconds).
なお、セキュリティ信号として外部出力される信号は、この実施の形態で示したものにかぎられない。例えば、始動入賞口14への異常入賞にかぎらず、大入賞口や普通入賞口29,30への異常入賞を検出して、セキュリティ信号として外部出力可能なように構成してもよい。また、例えば、遊技機に設けられた磁石センサで異常磁気を検出した場合や、遊技機に設けられた電波センサで異常電波を検出した場合に、セキュリティ信号として外部出力可能なように構成してもよい。また、例えば、遊技機に設けられた各種スイッチの異常を検出した場合(例えば、入力値が閾値を超えたと判定したことにより、短絡などの発生を検出した場合)に、セキュリティ信号として外部出力可能なように構成してもよい。そのように、大入賞口への異常入賞や異常磁気エラー、異常電波エラーについてもターミナル基板160の共通のコネクタCN7からセキュリティ信号として外部出力可能なように構成すれば、1本の信号線さえ接続すればホールコンピュータなど外部装置でエラー検出を行えるようにすることができ、エラー検出に関する作業負担を軽減することができる。
Note that the signal externally output as a security signal is not limited to that shown in this embodiment. For example, not only the abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14 but also the abnormal winning on the large winning opening and the normal winning openings 29, 30 may be detected and externally output as a security signal. In addition, for example, when abnormal magnetism is detected by a magnet sensor provided in a game machine, or when an abnormal radio wave is detected by a radio wave sensor provided in the game machine, an external output can be made as a security signal. It is also good. Also, for example, when an abnormality of various switches provided in a game machine is detected (for example, when occurrence of a short circuit or the like is detected by determining that an input value exceeds a threshold), external output is possible. It may be configured as follows. In this way, even a signal line can be connected by configuring the external connector as the security signal from the common connector CN7 of the terminal board 160 also for abnormal winning to the special winning opening, abnormal magnetic error and abnormal radio error. If this is done, error detection can be performed by an external device such as a hall computer, and the work load for error detection can be reduced.
また、例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との間の通信エラーを検出した場合にも、ターミナル基板160の共通のコネクタCN7からセキュリティ信号として外部出力可能なように構成してもよい。この場合、例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370から後述する接続OKコマンドや賞球個数受付コマンドを受信できなかったことにもとづいて通信エラーが発生したと判定し、ターミナル基板160の共通のコネクタCN7からセキュリティ信号として外部出力してもよい。また、例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、シリアル通信回路505のステータスレジスタAのビット0〜4のいずれかのエラービットの値がセットされていることにもとづいて通信エラーが発生したと判定し、ターミナル基板160の共通のコネクタCN7からセキュリティ信号として外部出力してもよい。
Also, for example, when a communication error between the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 is detected, the common connector CN7 of the terminal substrate 160 can be externally output as a security signal. May be In this case, for example, the game control microcomputer 560 determines that a communication error has occurred based on the failure to receive a connection OK command or a prize ball number reception command described later from the payout control microcomputer 370, and the terminal It may be externally output as a security signal from the common connector CN7 of the substrate 160. Also, for example, based on the fact that the value of one of the error bits of bits 0 to 4 of status register A of serial communication circuit 505 is set, microcomputer 560 for gaming control determines that a communication error has occurred. , And may be externally output as a security signal from the common connector CN7 of the terminal substrate 160.
なお、セキュリティ信号用の信号線およびコネクタCN7とは別に、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との間の通信エラー専用の信号線およびコネクタをターミナル基板160に設けてもよい。そして、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との間の通信エラーを検出した場合には、セキュリティ信号とは別の信号として、ターミナル基板160を経由してホールコンピュータなどの外部装置に出力するようにしてもよい。
A signal line and a connector dedicated to communication errors between the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 may be provided on the terminal substrate 160 separately from the signal line for the security signal and the connector CN7. Then, when a communication error between the gaming control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 is detected, an external device such as a hall computer or the like via the terminal substrate 160 as a signal different from the security signal. It may be output to
また、賞球信号1は、賞球払出を1個検出するごとに出力される信号である。また、遊技機エラー状態信号は、遊技機がエラー状態(本例では、球切れエラー状態または満タンエラー状態)であることを示す信号である。なお、賞球払出を1個検出するごとに賞球信号1を外部出力するのではなく、賞球払出を所定個(例えば、10個)検出するごとに何らかの賞球信号を出力するようにしてもよい。
Also, the prize ball signal 1 is a signal that is output each time one prize ball payout is detected. Further, the gaming machine error status signal is a signal indicating that the gaming machine is in an error status (in this example, a ball out error status or a full tank error status). It should be noted that instead of externally outputting the prize ball signal 1 every time one prize ball payout is detected, some kind of prize ball signal is output each time a predetermined number (for example, 10) of prize ball payouts are detected. It is also good.
図61〜図64は、ステップS31の情報出力処理を示すフローチャートである。なお、図61〜図64に示す処理のうち、ステップS1002〜S1030が始動口信号を出力するための処理であり、ステップS1031〜S1036が図柄確定回数1信号を出力するための処理であり、ステップS1050〜S1068が大当り1信号、大当り2信号、大当り3信号および時短信号を出力するための処理である。また、ステップS1069〜S1074がセキュリティ信号を出力するための処理である。
61 to 64 are flowcharts showing the information output process of step S31. Of the processes shown in FIG. 61 to FIG. 64, steps S1002 to S1030 are processes for outputting the starting opening signal, and steps S1031 to S1036 are processes for outputting the symbol determination number 1 signal, step Steps S1050 to S1068 are processes for outputting one big hit signal, two big hit signals, three big hit signals and a short time signal. Steps S1069 to S1074 are processes for outputting a security signal.
情報出力処理において、CPU56は、初期値(00(H))をRAM55に形成されている情報バッファにセットする(ステップS1001)。そして、始動口情報設定テーブルのアドレスをポインタにセットし(ステップS1002)、ポインタの指す処理数をロードする(ステップS1003)。始動口情報設定テーブルには、処理数(=1)と始動口スイッチ入力ビット(始動口スイッチ入力ビット判定値(01(H))が設定されている。ステップS1003では、ポインタが始動口情報設定テーブルの処理数のアドレスを指しているので、始動口情報設定テーブルにおける処理数(=1)のデータがロードされることになる。なお、遊技機が2つの始動入賞口を備えている場合には、始動口情報設定テーブルに、処理数として2が設定されるとともに、2つの始動入賞口に対する始動口スイッチ入力ビットがそれぞれ設定されるようにすればよい。
In the information output process, the CPU 56 sets an initial value (00 (H)) in the information buffer formed in the RAM 55 (step S1001). Then, the address of the starting opening information setting table is set to the pointer (step S1002), and the number of processing indicated by the pointer is loaded (step S1003). In the starting port information setting table, the processing number (= 1) and the starting port switch input bit (starting port switch input bit judgment value (01 (H)) are set. In step S1003, the pointer is for setting the starting port information. Since it indicates the address of the processing number of the table, the data of the processing number (= 1) in the starting opening information setting table will be loaded Note that the gaming machine has two starting winning openings. In the starting opening information setting table, 2 may be set as the number of processes, and the starting opening switch input bits for the two starting winning openings may be set.
次いで、CPU56は、スイッチオンバッファの内容をレジスタにロードし(ステップS1004)、スイッチオンバッファをスイッチ入力データにセットする(ステップS1005)。そして、ポインタを1加算し(ステップS1006)、ポインタの指す始動口スイッチ入力ビットをレジスタにロードし(ステップS1007)、始動口スイッチ入力ビットとスイッチ入力データの論理積をとる(ステップS1008)。スイッチオンバッファの内容が01(H)であったとき、すなわち始動口スイッチ14aがオンしているときは、論理積の演算結果は01(H)になる。始動口スイッチ14aがオンしていないときは、論理積の演算結果は、00(H)になる。
Next, the CPU 56 loads the contents of the switch on buffer into the register (step S1004), and sets the switch on buffer as switch input data (step S1005). Then, the pointer is incremented by 1 (step S1006), the start port switch input bit pointed by the pointer is loaded into the register (step S1007), and the start port switch input bit and switch input data are ANDed (step S1008). When the content of the switch on buffer is 01 (H), that is, when the start port switch 14a is on, the calculation result of the logical product becomes 01 (H). When the start port switch 14a is not turned on, the calculation result of the logical product is 00 (H).
論理積の演算結果が0の場合には(ステップS1009のY)、ステップS1015の処理に移行する。論理積の演算結果が0でない場合には(ステップS1009のN)、始動入賞口14への入賞が生じたと判定し、始動口情報記憶カウンタをレジスタにロードする(ステップS1010)。始動口情報記憶カウンタは、始動口信号の残り出力回数(つまり、始動口信号の未出力の始動入賞の残り入賞個数)をカウントするカウンタである。次いで、CPU56は、始動口情報記憶カウンタを1加算する(ステップS1011)。そして、演算結果(加算した結果)が0でないかどうかを確認する(ステップS1012)。演算結果が0のときは(ステップS1012のN)、演算結果を1減算する(ステップS1013)。そして、演算結果を始動口情報記憶カウンタにストアする(ステップS1014)。
If the operation result of the logical product is 0 (Y in step S1009), the process proceeds to step S1015. If the calculation result of the logical product is not 0 (N in step S1009), it is determined that a winning on the start winning opening 14 has occurred, and the starting opening information storage counter is loaded into the register (step S1010). The starting opening information storage counter is a counter that counts the number of remaining outputs of the starting opening signal (that is, the number of remaining winning combinations of starting winning not yet output). Next, the CPU 56 adds 1 to the starting opening information storage counter (step S1011). Then, it is checked whether the operation result (the result of addition) is not 0 (step S1012). When the operation result is 0 (N in step S1012), 1 is subtracted from the operation result (step S1013). Then, the calculation result is stored in the starting opening information storage counter (step S1014).
次に、CPU56は、処理数を1減算し(ステップS1015)、処理数が0でないかどうかを判定する(ステップS1016)。処理数が0でないときは(ステップS1016のY)、ステップS1004の処理に移行する。なお、この実施の形態では、遊技機は1つの始動入賞口14のみを備えていることから、処理数の初期値として1が設定され、ステップS1016では必ず処理数が0であると判定されることになる。
Next, the CPU 56 subtracts one from the number of processes (step S1015), and determines whether the number of processes is not zero (step S1016). If the number of processes is not 0 (Y in step S1016), the process proceeds to step S1004. In this embodiment, since the gaming machine has only one starting winning opening 14, the initial value of the number of processes is set to 1, and it is determined that the number of processes is always 0 in step S1016. It will be.
ステップS1016で処理数が0であると判定されると(ステップS1016のN)、CPU56は、始動口情報記憶タイマをロードし(ステップS1017)、始動口情報記憶タイマの状態をフラグレジスタに反映させて(ステップS1018)、始動口信号が出力中であるか否かを判定する(ステップS1019)。始動口情報記憶タイマは、始動口信号のオン時間およびオフ時間(例えば、オン時間200msとオフ時間200ms)を計測するためのタイマである。始動口情報記憶タイマの値が0でなければ始動口信号が出力中であると判定され、始動口情報記憶タイマの値が0であれば始動口信号が出力中でないと判定される。
If it is determined in step S1016 that the number of processes is 0 (N in step S1016), the CPU 56 loads the starting opening information storage timer (step S1017) and reflects the state of the starting opening information storage timer in the flag register Then (step S1018), it is determined whether or not the starting opening signal is being output (step S1019). The starting opening information storage timer is a timer for measuring the on time and off time (for example, on time 200 ms and off time 200 ms) of the starting opening signal. If the value of the starting opening information storage timer is not 0, it is determined that the starting opening signal is being output, and if the value of the starting opening information storage timer is 0, it is determined that the starting opening signal is not being output.
始動口信号が出力中であれば(ステップS1019のY)、ステップS1026の処理に移行する。始動口信号が出力中でなければ(ステップS1019のN)、CPU56は、始動口情報記憶カウンタをロードし(ステップS1020)、始動口情報記憶カウンタの状態をフラグレジスタに反映させて(ステップS1021)、始動口信号の出力回数の残数があるかどうかを判定する(ステップS1022)。なお、始動口スイッチ14aがオンしたときは(ステップS1009のN)、始動口情報記憶カウンタが1加算されるので、始動口信号の出力回数の残数があると判定されることになる。
If the starting opening signal is being output (Y in step S1019), the process proceeds to step S1026. If the starting opening signal is not being output (N in step S1019), the CPU 56 loads the starting opening information storage counter (step S1020) and reflects the state of the starting opening information storage counter in the flag register (step S1021) It is determined whether there is a remaining number of times of output of the starting opening signal (step S1022). When the starting opening switch 14a is turned on (N in step S1009), since the starting opening information storage counter is incremented by 1, it is determined that there is the remaining number of times of output of the starting opening signal.
始動口信号の出力回数の残数がなければ(ステップS1022のY)、ステップS1031の処理に移行する。始動口信号の出力回数の残数があれば(ステップS1023のN)、CPU56は、始動口情報記憶カウンタを1減算し(ステップS1023)、演算結果(1減算した結果)を始動口情報記憶カウンタにストアする(ステップS1024)。そして、入賞情報動作時間(100)をレジスタにセットする(ステップS1025)。なお、入賞情報動作時間(100)は、4msのタイマ割込みが100回実行される時間、すなわち、0.400秒(400ms)の時間となっている。
If there is no remaining number of times of output of the starting opening signal (Y in step S1022), the process proceeds to step S1031. If there is the remaining number of output times of the starting opening signal (N in step S1023), the CPU 56 subtracts 1 from the starting opening information storage counter (step S1023), and the calculation result (the result of subtracting 1) is obtained from the starting opening information storage counter (Step S1024). Then, the winning information operation time (100) is set in the register (step S1025). The winning information operation time (100) is a time in which a 4 ms timer interrupt is executed 100 times, that is, a time of 0.400 seconds (400 ms).
次に、CPU56は、ステップS1025で入賞情報動作時間がセットされていなければ始動口情報記憶タイマを1減算し、ステップS1025で入賞情報動作時間がセットされていれば入賞情報動作時間を1減算する(ステップS1026)。そして、演算結果(1減算した結果)を始動口情報記憶タイマにストアする(ステップS1027)。
Next, the CPU 56 subtracts 1 from the starting opening information storage timer if the winning information operation time is not set in step S1025, and subtracts 1 from the winning information operation time if the winning information operation time is set in step S1025. (Step S1026). Then, the operation result (the result of subtracting 1) is stored in the starting opening information storage timer (step S1027).
CPU56は、演算結果と入賞情報オン時間(50)を比較し(ステップS1029)、演算結果が入賞情報オン時間よりも短い時間であるかどうかを判定する(ステップS1030)。なお、入賞情報オン時間(50)は、4msのタイマ割込みが50回実行される時間、すなわち、0.200秒(200ms)の時間となっている。
The CPU 56 compares the calculation result with the winning information on time (50) (step S1029), and determines whether the calculation result is shorter than the winning information on time (step S1030). The winning information on time (50) is a time for which a 4 ms timer interrupt is executed 50 times, that is, a time of 0.200 seconds (200 ms).
演算結果が入賞情報オン時間よりも短い時間でない場合、つまり、演算結果(始動口1情報記憶タイマの残り時間)が入賞情報オン時間(200ms)よりも長い時間である場合は(ステップS1029のN)、CPU56は、情報バッファの始動口出力ビット位置(図21に示す例では出力ポート1のビット0)をセットする(ステップS1030)。情報バッファの始動口出力ビット位置がセットされると、その後のステップS1102で情報バッファを出力値にセットし、ステップS1103で出力値を出力ポート1に出力することによって、始動口信号が出力ポート1から出力されることになる。
If the calculation result is not shorter than the winning information on time, that is, if the calculation result (remaining time of the starting opening 1 information storage timer) is longer than the winning information on time (200 ms) (N in step S1029) The CPU 56 sets the starting opening output bit position of the information buffer (bit 0 of the output port 1 in the example shown in FIG. 21) (step S1030). When the start opening output bit position of the information buffer is set, the information buffer is set to the output value in the subsequent step S1102, and the start opening signal is output port 1 by outputting the output value to the output port 1 in step S1103. Will be output from
以上に示したステップS1001〜S1030の処理によって、始動入賞口14への入賞(始動口スイッチ14aのオン)が発生すると、始動口信号が出力される。すなわち、始動口信号が200ms間オン状態となった後、200ms間オフ状態になる。この始動口信号がホールコンピュータに入力されることによって、始動入賞口14への入賞個数を認識させることができる。
When a winning on the start winning opening 14 (on of the start opening switch 14a) occurs by the processing of steps S1001 to S1030 described above, a start opening signal is output. That is, after the starting opening signal is turned on for 200 ms, it is turned off for 200 ms. By inputting the starting opening signal to the hall computer, it is possible to recognize the number of winnings on the starting winning opening 14.
始動口信号は、200ms間オン状態となった後、200ms間オフ状態になるので、短時間に連続して始動入賞が発生した場合であっても、200ms間のオフ状態の後に次の始動口信号が出力される。すなわち、始動口信号は少なくとも200msの間隔をあけて出力される。
The start opening signal is turned on for 200 ms and then turned off for 200 ms. Therefore, even if the start winning combination occurs continuously for a short time, the next start opening after the off state for 200 ms. A signal is output. That is, the starting opening signal is output at intervals of at least 200 ms.
このように、始動口信号は少なくとも200msの間隔をあけて出力されるので、ホールコンピュータは、全始動入賞数を確実に把握することができる。
As described above, since the starting opening signal is outputted at intervals of at least 200 ms, the hall computer can reliably grasp the total number of starting winnings.
次に、CPU56は、図柄確定回数1情報タイマをレジスタにロードし(ステップS1031)、図柄確定回数1情報タイマの状態をフラグレジスタに反映させて(ステップS1032)、図柄確定回数1情報タイマがタイムアウトしているかどうかを判定する(ステップS1033)。この実施の形態では、特別図柄変動処理(ステップS302参照)において、変動時間がタイムアウトすると、特別図柄の変動を停止するときに、図柄確定回数1情報タイマに図柄確定回数出力時間(本例では0.500秒)がセットされ、その図柄確定回数出力時間が経過していないときは、図柄確定回数1情報タイマがタイムアウトしていないと判定され、図柄確定回数出力時間が経過したとき(図柄確定回数1情報タイマの値が0のとき)に、図柄確定回数1情報タイマがタイムアウトしたと判定される。
Next, the CPU 56 loads the symbol determination frequency 1 information timer into the register (step S1031), reflects the status of the symbol determination frequency 1 information timer in the flag register (step S1032), and the symbol determination frequency 1 information timer times out. It is determined whether or not it is (step S1033). In this embodiment, when the fluctuation time is timed out in the special symbol fluctuation process (see step S302), when the fluctuation of the special symbol is stopped, the symbol fixed frequency 1 information timer outputs the symbol fixed frequency (0 in this example). .500 seconds) is set, and when the symbol determination frequency output time has not elapsed, it is determined that the symbol determination frequency 1 information timer has not timed out and the symbol determination frequency output time has elapsed (symbol determination frequency When the value of (1) information timer is 0), it is determined that the symbol determination number 1 information timer has timed out.
図柄確定回数1情報タイマがタイムアウトしていなければ(ステップS1033のN)、図柄確定回数1情報タイマを1減算し(ステップS1034)、演算結果を図柄確定回数1情報タイマにストアする(ステップS1035)。そして、情報バッファの図柄確定回数1出力ビット位置(図21に示す例では出力ポート1のビット1)をセットする(ステップS1036)。情報バッファの図柄確定回数1出力ビット位置がセットされると、その後のステップS1102で情報バッファを出力値にセットし、ステップS1103で出力値を出力ポート1に出力することによって、図柄確定回数1信号が出力ポート1から出力される(オン状態となる)。なお、図柄確定回数1情報タイマがタイムアウトすれば(ステップS1033のY)、ステップS1036の処理が実行されない結果、図柄確定回数1信号はオフ状態となる。
If the symbol determination frequency 1 information timer has not timed out (N in step S1033), the symbol determination frequency 1 information timer is decremented by 1 (step S1034), and the calculation result is stored in the symbol determination frequency 1 information timer (step S1035) . Then, the symbol determination number 1 output bit position (bit 1 of output port 1 in the example shown in FIG. 21) of the information buffer is set (step S1036). When the symbol fixed number 1 output bit position of the information buffer is set, the information buffer is set as an output value in the subsequent step S 1102, and the output value is output to the output port 1 in step S 1103. Are output from the output port 1 (turned on). When the symbol determination number 1 information timer times out (Y in step S1033), the processing in step S1036 is not executed, so that the symbol determination number 1 signal is turned off.
以上に示したステップS1031〜S1036の処理によって、特別図柄の変動が停止(停止図柄が確定)する度に、図柄確定回数1信号が図柄確定回数出力時間(例えば500ms)オン状態となる。
By the processing of steps S1031 to S1036 described above, whenever the variation of the special symbol is stopped (the stopped symbol is determined), the symbol determination number 1 signal is turned on for the symbol determination number output time (for example, 500 ms).
次に、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグをロードし(ステップS1050)、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値と大入賞口開放前処理指定値(「4」)を比較し(ステップS1051)、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が4未満であるかどうかを判定する(ステップS1052)。特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が4未満であるときは(ステップS1052のY)、ステップS1058の処理に移行する。特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が4以上であるときは(ステップS1052のN)、情報バッファの大当り1出力ビット位置をセットする(ステップS1053)。また、情報バッファの大当り2出力ビット位置をセットする(ステップS1054)。情報バッファの大当り1出力ビット位置および大当り2出力ビット位置がセットされると、その後のステップS1102で情報バッファを出力値にセットし、ステップS1103で出力値を出力ポート1に出力することによって、大当り1信号および大当り2信号が出力ポート1から出力される(オン状態となる)。
Next, the CPU 56 loads the special symbol process flag (step S1050), and compares the value of the special symbol process flag with the special winning opening opening pre-processing designated value ("4") (step S1051), the special symbol process flag It is determined whether the value of is less than 4 (step S1052). If the value of the special symbol process flag is less than 4 (Y in step S1052), the process proceeds to step S1058. If the value of the special symbol process flag is 4 or more (N in step S1052), the jackpot 1 output bit position of the information buffer is set (step S1053). Also, the jackpot 2 output bit position of the information buffer is set (step S1054). When the big hit 1 output bit position and the big hit 2 output bit position of the information buffer are set, the information buffer is set as an output value in the subsequent step S 1102, and the output value is outputted to the output port 1 in step S 1103. One signal and two jackpot signals are output from the output port 1 (turned on).
また、CPU56は、時短状態であるか否かを確認する時短チェック処理を実行し(ステップS1058)、時短状態であるか否かを判定する(ステップS1059)。具体的には、CPU56は、時短状態に移行するときにセットされる時短フラグがセットされているか否かを確認することによって、時短状態であるか否かを判定する。時短状態であるときは(ステップS1059のY)、情報バッファの時短出力ビット位置をセットする(ステップS1060)。時短出力ビット位置がセットされると、その後のステップS1102で情報バッファを出力値にセットし、ステップS1103で出力値を出力ポート1に出力することによって、時短信号が出力ポート1から出力される(オン状態となる)。また、情報バッファの大当り2出力ビット位置をセットする(ステップS1061)。大当り2出力ビット位置がセットされると、その後のステップS1102で情報バッファを出力値にセットし、ステップS1103で出力値を出力ポート1に出力することによって、大当り2信号が出力ポート1から出力される(オン状態となる)。
Further, the CPU 56 executes a time saving check process to check whether or not the time saving state is set (step S1058), and determines whether or not the time saving state is set (step S1059). Specifically, the CPU 56 determines whether or not the time saving state is established by checking whether the time saving flag set when transitioning to the time saving state is set. When the time saving state is set (Y in step S1059), the time saving output bit position of the information buffer is set (step S1060). When the short time output bit position is set, the information buffer is set to the output value in the subsequent step S1102, and the short time signal is output from the output port 1 by outputting the output value to the output port 1 in step S1103. (Turned on). In addition, the jackpot 2 output bit position of the information buffer is set (step S1061). When the big hit 2 output bit position is set, the information buffer is set to the output value in the subsequent step S 1102, and the big hit 2 signal is outputted from the output port 1 by outputting the output value to the output port 1 in step S 1103. Turn on (turns on).
また、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグをロードし(ステップS1062)、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値と大入賞口開放前処理指定値(「4」)を比較し(ステップS1063)、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が4未満であるかどうかを判定する(ステップS1064)。特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が4未満であるときは(ステップS1064のY)、ステップS1069の処理に移行する。特別図柄プロセスフラグの値が4以上であるときは(ステップS1064のN)、大当り図柄判定バッファの内容をロードし(ステップS1065)、15ラウンドの大当りであるか否かを確認する(ステップS1067)。なお、15ラウンドの大当りであるか否かは、例えば、特別図柄通常処理において設定された大当り図柄判定バッファの内容を確認することによって判定できる。例えば、大当り図柄判定バッファには、特別図柄通常処理で決定された大当り種別の内容や大当り判定結果を示す内容が格納されており、例えば、「1」が通常大当り、「2」が確変大当り、「3」が突然確変大当りとされている。そして、大当り図柄判定バッファの内容が「1」または「2」であれば、大当り時のラウンド数が15ラウンドであると判断される。この場合、情報バッファの大当り3出力ビット位置をセットする(ステップS1068)。大当り3出力ビット位置がセットされると、その後のステップS1102で情報バッファを出力値にセットし、ステップS1103で出力値を出力ポート1に出力することによって、大当り3信号が出力ポート1から出力される(オン状態となる)。
Also, the CPU 56 loads the special symbol process flag (step S1062), compares the value of the special symbol process flag with the special winning opening opening pre-processing designated value ("4") (step S1063), and the special symbol process flag It is determined whether the value is less than 4 (step S1064). If the value of the special symbol process flag is less than 4 (Y in step S1064), the process proceeds to step S1069. If the value of the special symbol process flag is 4 or more (N in step S1064), the contents of the big hit symbol determination buffer are loaded (step S1065), and it is confirmed whether it is a big hit of 15 rounds (step S1067) . In addition, it can be determined by checking the content of the big hit symbol determination buffer set in the special symbol normal processing, for example, whether it is a big hit of 15 rounds. For example, the jackpot design determination buffer stores the contents of the jackpot classification determined in the special symbol normal processing and the contents showing the jackpot judgment result, for example, "1" is usually a big hit, "2" is a definite big hit, "3" is suddenly considered to be a big hit. Then, if the content of the jackpot symbol determination buffer is “1” or “2”, it is determined that the number of rounds at the jackpot is 15 rounds. In this case, the jackpot 3 output bit position of the information buffer is set (step S1068). When the big hit 3 output bit position is set, the information buffer is set to the output value in the subsequent step S 1102, and the big hit 3 signal is outputted from the output port 1 by outputting the output value to the output port 1 in step S 1103. Turn on (turns on).
以上に示したステップS1050〜S1068の処理によって、大当りの種別や遊技状態に応じた大当り1信号、大当り2信号、大当り3信号および時短信号が出力される(オン状態になる)。
By the processing of steps S1050 to S1068 described above, one jackpot signal, two jackpot signals, three jackpot signals and time-shortening signals corresponding to the jackpot type and the game state are output (turned on).
次いで、CPU56は、セキュリティ信号情報タイマをロードし(ステップS1069)、セキュリティ信号情報タイマの状態をフラグレジスタに反映させて(ステップS1070)、セキュリティ信号情報タイマがタイムアウトしているかどうかを判定する(ステップS1071)。この実施の形態では、始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14bとの検出差が所定値(本例では10)以上に達したと判定され、始動入賞口への異常入賞が発生したと判定された場合には、セキュリティ信号情報タイマに所定時間(本例では4分)がセットされ(スイッチ正常/異常チェック処理におけるステップS126,S127参照)、その所定時間が経過していないときは、セキュリティ信号情報タイマがタイムアウトしていないと判定され、その所定時間が経過したとき(セキュリティ信号情報タイマの値が0のとき)に、セキュリティ信号情報タイマがタイムアウトしたと判定される。
Next, the CPU 56 loads the security signal information timer (step S1069), reflects the state of the security signal information timer in the flag register (step S1070), and determines whether the security signal information timer has timed out (step S1070) S1071). In this embodiment, it is determined that the detection difference between the starting opening switch 14a and the winning confirmation switch 14b has reached a predetermined value (10 in this example) or more, and it is determined that an abnormal winning on the starting winning opening has occurred. In this case, the security signal information timer is set to a predetermined time (four minutes in this example) (see steps S126 and S127 in the switch normality / abnormality check process), and when the predetermined time has not elapsed, security signal information It is determined that the timer has not timed out, and when the predetermined time has elapsed (when the value of the security signal information timer is 0), it is determined that the security signal information timer has timed out.
また、この実施の形態では、遊技機への電力供給が開始されて初期化処理が実行されたときにも、セキュリティ信号情報タイマに所定時間(本例では30秒)がセットされ(メイン処理におけるステップS14a参照)、その所定時間が経過していないときは、セキュリティ信号情報タイマがタイムアウトしていないと判定され、その所定時間が経過したとき(セキュリティ信号情報タイマの値が0のとき)に、セキュリティ信号情報タイマがタイムアウトしたと判定される。
Also, in this embodiment, even when the power supply to the gaming machine is started and the initialization process is executed, a predetermined time (30 seconds in this example) is set in the security signal information timer (in the main process). When the predetermined time has not elapsed, it is determined that the security signal information timer has not timed out, and when the predetermined time has elapsed (when the value of the security signal information timer is 0), It is determined that the security signal information timer has timed out.
セキュリティ信号情報タイマがタイムアウトしていなければ(ステップS1071のN)、セキュリティ信号情報タイマを1減算し(ステップS1072)、演算結果をセキュリティ信号情報タイマにストアする(ステップS1073)。そして、情報バッファのセキュリティ信号出力ビット位置(図21に示す例では出力ポート1のビット7)をセットする(ステップS1074)。情報バッファのセキュリティ信号出力ビット位置がセットされると、その後のステップS1102で情報バッファを出力値にセットし、ステップS1103で出力値を出力ポート1に出力することによって、セキュリティ信号が出力ポート1から出力される(オン状態となる)。なお、セキュリティ信号情報タイマがタイムアウトすれば(ステップS1071のY)、ステップS1074の処理が実行されない結果、セキュリティ信号はオフ状態となる。
If the security signal information timer has not timed out (N in step S1071), the security signal information timer is decremented by 1 (step S1072), and the operation result is stored in the security signal information timer (step S1073). Then, the security signal output bit position of the information buffer (bit 7 of output port 1 in the example shown in FIG. 21) is set (step S1074). When the security signal output bit position of the information buffer is set, the information buffer is set to the output value in the subsequent step S 1102, and the security signal is output from the output port 1 by outputting the output value to the output port 1 in step S 1103. It is output (turned on). When the security signal information timer times out (Y in step S1071), the processing in step S1074 is not executed, and as a result, the security signal is turned off.
以上に示したステップS1069〜S1074の処理によって、始動入賞口14への異常入賞が検出されてから4分が経過するまで、または遊技機への電力供給開始時に初期化処理が実行されてから30秒が経過するまで、ターミナル基板160の共通のコネクタCN7を用いてセキュリティ信号が出力される。なお、セキュリティ信号の出力中更に新たな異常入賞を検出した場合には、最後に異常入賞を検出してから4分間が経過するまでセキュリティ信号の出力が継続される。
By the processing of steps S1069 to S1074 shown above, until 4 minutes have passed since the abnormal winning to the start winning opening 14 was detected, or 30 minutes after the initialization processing is executed when the power supply to the gaming machine is started. The security signal is output using the common connector CN7 of the terminal board 160 until the second elapses. When a new abnormal prize is detected during the output of the security signal, the output of the security signal is continued until four minutes have elapsed since the final detection of the abnormal prize.
次に、セキュリティ信号の出力タイミングについて説明する。図65は、セキュリティ信号の出力タイミングを示す説明図である。この実施の形態では、遊技機への電力供給開始時に初期化処理が実行されると(ステップS10〜S14参照)、セキュリティ信号情報タイマに所定時間(本例では、30秒)がセットされたことにもとづいて(ステップS14a参照)、情報出力処理(ステップS31参照)でステップS1069〜S1103の処理が実行されて、図65(A)に示すように、ターミナル基板160のコネクタCN7から、ホールコンピュータなどの外部装置に対してセキュリティ信号が出力される。また、遊技機への電源供給が開始された後に、始動口スイッチ14aの検出数と入賞確認スイッチ14bの検出数との検出誤差が所定値(本例では、10)以上となったことにもとづいて、始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したと判定されたときにも(ステップS121〜S126参照)、セキュリティ信号情報タイマに所定時間(本例では、4分)がセットされたことにもとづいて(ステップS127参照)、情報出力処理(ステップS31参照)でステップS1069〜S1103の処理が実行されて、図65(A)に示すように、ターミナル基板160のコネクタCN7から、ホールコンピュータなどの外部装置に対してセキュリティ信号が出力される。このように、この実施の形態では、遊技機への電源供給開始時に初期化処理が実行されたときと、始動入賞口14への異常入賞を検出したときとで、ターミナル基板160の共通のコネクタCN7からセキュリティ信号が外部出力される。
Next, the output timing of the security signal will be described. FIG. 65 is an explanatory view showing the output timing of the security signal. In this embodiment, when initialization processing is executed at the start of power supply to the gaming machine (see steps S10 to S14), the security signal information timer is set to a predetermined time (30 seconds in this example). Based on (refer to step S14a), the processing of steps S1069 to S1103 is executed in the information output processing (refer to step S31), and as shown in FIG. The security signal is output to the external device of Also, based on the detection error between the number of detections of the start opening switch 14a and the number of detections of the prize confirmation switch 14b becoming equal to or more than a predetermined value (10 in this example) after the power supply to the gaming machine is started. Even when it is determined that an abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14 has occurred (see steps S121 to S126), the security signal information timer is set based on the fact that a predetermined time (four minutes in this example) is set. (See step S127), the processing of steps S1069 to S1103 is executed in the information output process (see step S31), and as shown in FIG. A security signal is output to the device. As described above, in this embodiment, the common connector of the terminal board 160 is used when the initialization process is executed at the start of power supply to the gaming machine and when an abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14 is detected. A security signal is externally output from CN7.
また、この実施の形態では、セキュリティ信号の外部出力中である場合に、新たに始動入賞口14への異常入賞を検出した場合には、実質的にセキュリティ信号の出力期間が延長され、最後に始動入賞口14への異常入賞を検出した時点から所定時間(本例では、4分)が経過するまで、セキュリティ信号の出力が継続される。例えば、遊技機への電源供給開始時に初期化処理が実行されたことにもとづいてセキュリティ信号の出力を開始した場合には、図65(A)に示すように、原則として30秒を経過するまでセキュリティ信号の出力が継続される筈である。しかし、図65(B)に示すように、その30秒を経過する前であっても、始動口スイッチ14aの検出数と入賞確認スイッチ14bの検出数との検出誤差が所定値(本例では、10)以上となって始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したと判定される可能性がある。この場合、異常入賞の発生が検出されたことにもとづいてセキュリティ信号情報タイマに所定時間(本例では、4分)が上書きで書き込まれることになり(ステップS127参照)、情報出力処理(ステップS31参照)でステップS1069〜S1103の処理が実行されて、図65(B)に示すように、そのままセキュリティ信号の出力が継続される。ただし、セキュリティ信号情報タイマの値が4分に上書きされたのであるから、この場合、図65(B)に示すように、その始動入賞口14への異常入賞を検出した時点から4分が経過するまでセキュリティ信号の出力が継続されることになり、実質的にセキュリティ信号の出力が延長されることになる。
Further, in this embodiment, when the abnormal winning of the start winning opening 14 is newly detected while the security signal is being externally output, the output period of the security signal is substantially extended, and finally, The output of the security signal is continued until a predetermined time (four minutes in this example) elapses from the time when the abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14 is detected. For example, when the output of the security signal is started based on the execution of the initialization process when the power supply to the gaming machine is started, as shown in FIG. 65A, in principle, 30 seconds have elapsed. The output of the security signal should continue. However, as shown in FIG. 65 (B), even before the lapse of 30 seconds, the detection error between the number of detections of the start port switch 14a and the number of detections of the prize confirmation switch 14b is a predetermined value (in this example) 10) or more and it may be determined that the abnormal winning to the start winning opening 14 has occurred. In this case, a predetermined time (four minutes in this example) is written over in the security signal information timer based on the occurrence of the abnormal winning being detected (see step S127), and the information output process (step S31). The processing of steps S1069 to S1103 is executed in reference), and the output of the security signal is continued as shown in FIG. 65 (B). However, since the value of the security signal information timer is overwritten to 4 minutes, in this case, as shown in FIG. 65 (B), 4 minutes have passed from the point when the abnormal winning combination to the start winning opening 14 is detected. Thus, the output of the security signal will be continued, and the output of the security signal will be substantially extended.
また、例えば、始動入賞口14への異常入賞を検出したことにもとづいてセキュリティ信号の出力を開始した場合には、図65(A)に示すように、原則として4分を経過するまでセキュリティ信号の出力が継続される筈である。しかし、図65(C)に示すように、その4分を経過する前であっても、始動口スイッチ14aの検出数と入賞確認スイッチ14bの検出数との検出誤差が所定値(本例では、10)以上となって、新たに始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したと判定される可能性がある。この場合、新たに異常入賞の発生が検出されたことにもとづいてセキュリティ信号情報タイマに所定時間(本例では、4分)が上書きで書き込まれることになり(ステップS127参照)、情報出力処理(ステップS31参照)でステップS1069〜S1103の処理が実行されて、図65(C)に示すように、そのままセキュリティ信号の出力が継続される。ただし、セキュリティ信号情報タイマの値が4分に上書きされたのであるから、この場合、図65(C)に示すように、その新たに始動入賞口14への異常入賞を検出した時点から4分が経過するまでセキュリティ信号の出力が継続されることになり、実質的にセキュリティ信号の出力が延長されることになる。
Also, for example, when the output of the security signal is started based on the detection of the abnormal winning to the start winning opening 14, as shown in FIG. Output should continue. However, as shown in FIG. 65 (C), even before the lapse of four minutes, the detection error between the number of detections of starting opening switch 14a and the number of detections of winning a prize confirmation switch 14b is a predetermined value 10) or more, it may be determined that an abnormal winning to the start winning opening 14 has newly occurred. In this case, a predetermined time (four minutes in this example) is written over in the security signal information timer based on the new occurrence of the abnormal winning being detected (refer to step S127), and the information output process ((step S127) The processes of steps S1069 to S1103 are executed in step S31), and the output of the security signal is continued as shown in FIG. 65 (C). However, since the value of the security signal information timer is overwritten to four minutes, in this case, as shown in FIG. 65C, four minutes from the time when the abnormal winning combination to the start winning opening 14 is detected. The output of the security signal will be continued until the elapse of, substantially extending the output of the security signal.
なお、既にセキュリティ信号の出力中であるときに始動入賞口14への異常入賞を検出した場合に、出力中のセキュリティ信号の出力を終了してから、改めて次のセキュリティ信号の出力を開始するように構成することも考えられるが、この実施の形態では、図65(B)および図65(C)に示すように、出力中のセキュリティ信号の出力時間をそのまま延長することによって、セキュリティ信号の出力処理にかかる処理負担を軽減するとともに、セキュリティ信号の出力処理用のプログラム容量を低減している。すなわち、出力中のセキュリティ信号の出力を終了してから、改めて次のセキュリティ信号の出力を開始するように構成する場合には、セキュリティ信号の出力を終了した後、次のセキュリティ信号の出力を開始するまでのインターバル時間を計測する処理などが必要となり、処理負担が増加するとともにプログラム容量も増加してしまう。これに対して、この実施の形態では、セキュリティ信号情報タイマの値をそのまま上書きするので、セキュリティ信号情報タイマの値をセットする処理のみを行えば(ステップS14a,S127参照)、セキュリティ信号の出力を行うことができ、処理負担の増加やプログラム容量の増加を防止することができる。
In addition, when the abnormal winning combination to the start winning a prize mouth 14 is detected while the security signal is already being output, after the output of the security signal being output is ended, the output of the next security signal is started anew In this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 65 (B) and FIG. 65 (C), the output of the security signal is extended by simply extending the output time of the security signal being output. In addition to reducing the processing load for processing, the program capacity for output processing of security signals is reduced. That is, when the output of the next security signal is started again after the output of the security signal being output is ended, the output of the next security signal is started after the output of the security signal is ended. It is necessary to have a process of measuring the interval time until the process is performed, and the processing load increases and the program capacity also increases. On the other hand, in this embodiment, since the value of the security signal information timer is overwritten as it is, if only the process of setting the value of the security signal information timer is performed (see steps S14a and S127), the output of the security signal is It is possible to prevent an increase in processing load and an increase in program capacity.
なお、この実施の形態では、遊技機への電力供給開始時に初期化処理が実行された場合には30秒間に亘ってセキュリティ信号を出力し、始動入賞口14への異常入賞を検出した場合には4分間に亘ってセキュリティ信号を出力する場合を示したが、セキュリティ信号の出力時間は、この実施の形態で示したものにかぎられない。すなわち、初期化処理が実行された場合であるか始動入賞口14への異常入賞を検出した場合であるかを認識可能に、初期化処理が実行された場合と始動入賞口14への異常入賞が検出された場合とで異なる出力時間に亘ってセキュリティ信号を出力するものであればよい。
In this embodiment, when the initialization process is executed at the start of power supply to the gaming machine, the security signal is output for 30 seconds, and the abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14 is detected. Although the case where the security signal is output for 4 minutes has been shown, the output time of the security signal is not limited to that shown in this embodiment. That is, it is possible to recognize whether the initialization process is executed or the abnormal prize to the start winning opening 14 is detected, the case where the initialization process is executed and the abnormal prize to the start winning opening 14 It is sufficient if the security signal is output over different output times in the case where is detected.
なお、この実施の形態において、始動入賞口14への異常入賞を検出した場合のセキュリティ信号の出力期間を4分間としたのは、始動入賞口14への異常入賞の場合には、できるかぎり長い時間に亘ってセキュリティ信号を出力すべく、設定可能な略最大時間としたものである。すなわち、この実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、セキュリティ信号情報タイマの値として2バイトの値を設定可能であるので、セキュリティ信号情報タイマには最大値として「FFFF(H)=65535」を設定可能である。そこで、この実施の形態では、セキュリティ信号情報タイマに、ほぼ最大値に近い「60000」をセットするようにし、タイマ割込の周期が4msであることから、4ms×60000=4分間に亘ってセキュリティ信号を出力するようにしたものである。
In this embodiment, the reason that the output period of the security signal when detecting an abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14 is four minutes is as long as possible in the case of an abnormal winning on the starting winning opening 14. In order to output the security signal over time, the maximum time that can be set is set as the maximum time. That is, in this embodiment, since the microcomputer 560 for game control can set a value of 2 bytes as the value of the security signal information timer, the maximum value of the security signal information timer is “FFFF (H) = 65535 Can be set. Therefore, in this embodiment, "60000" close to the maximum value is set to the security signal information timer, and since the timer interrupt cycle is 4 ms, security is maintained for 4 ms × 60000 = 4 minutes. It is intended to output a signal.
次に、払出制御手段(払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370)の動作を説明する。図66は、払出制御手段における出力ポートの割り当ての例を示す説明図である。図66に示すように、出力ポート0からは、ステッピングモータによる払出モータ289に供給される各相の信号が出力される。また、出力ポート0からは、カードユニット50に対してPRDY信号やEXS信号が出力されるとともに、遊技機がエラー状態(本例では、球切れエラー状態または満タンエラー状態)であることを示す遊技機エラー状態信号や、賞球払出を検出したことを示す賞球信号1も出力される。また、出力ポート1からは、7セグメントLEDによるエラー表示LED374の各セグメント出力信号が出力される。また、出力ポート1からは、賞球払出を10球検出したことを示す賞球情報も出力される。
Next, the operation of the payout control means (microcomputer 370 for payout control) will be described. FIG. 66 is an explanatory drawing showing an example of output port assignment in the payout control means. As shown in FIG. 66, the output port 0 outputs signals of respective phases supplied to the dispensing motor 289 by the stepping motor. The output port 0 outputs a PRDY signal or an EXS signal to the card unit 50, and indicates that the gaming machine is in an error state (in this example, a ball out error state or a full error state) A machine error state signal and a winning ball signal 1 indicating that a winning ball payout has been detected are also output. Further, from the output port 1, each segment output signal of the error display LED 374 by the 7-segment LED is output. Further, the output port 1 also outputs winning ball information indicating that 10 winning balls have been detected.
図67は、払出制御手段における入力ポートのビット割り当ての例を示す説明図である。図67に示すように、入力ポート0のビット0〜2には、それぞれ、カードユニット50からのVL信号、BRDY信号、およびBRQ信号が入力される。また、入力ポート0のビット4には、主基板31からの接続信号が入力される。また、入力ポート0のビット5〜7には、それぞれ、満タンスイッチ48の検出信号、球切れスイッチ187の検出信号、および払出モータ位置センサ295の検出信号が入力される。また、入力ポート1のビット0,1には、それぞれ、エラー解除スイッチ375からの操作信号、および払出個数カウントスイッチ301の検出信号が入力される。
FIG. 67 is an explanatory view showing an example of bit assignment of the input port in the payout control means. As shown in FIG. 67, the VL signal, the BRDY signal, and the BRQ signal from the card unit 50 are input to bits 0 to 2 of the input port 0, respectively. Also, a connection signal from the main board 31 is input to bit 4 of the input port 0. The detection signal of the full tank switch 48, the detection signal of the out-of-ball switch 187, and the detection signal of the payout motor position sensor 295 are input to the bits 5 to 7 of the input port 0, respectively. Further, the operation signal from the error release switch 375 and the detection signal of the payout number counting switch 301 are input to the bits 0 and 1 of the input port 1, respectively.
次に、払出制御手段の動作について説明する。図68は、払出制御手段が実行するメイン処理を示すフローチャートである。メイン処理では、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370の払出制御用CPU371は、まず、必要な初期設定を行う。すなわち、払出制御用CPU371は、まず、割込禁止に設定する(ステップS701)。次に、割込モードを割込モード2に設定し(ステップS702)、スタックポインタにスタックポインタ指定アドレスを設定する(ステップS703)。
Next, the operation of the payout control means will be described. FIG. 68 is a flowchart showing the main process performed by the payout control means. In the main processing, the payout control CPU 371 of the payout control microcomputer 370 first performs necessary initialization. That is, the payout control CPU 371 first sets interruption prohibition (step S701). Next, the interrupt mode is set to interrupt mode 2 (step S702), and the stack pointer designation address is set in the stack pointer (step S703).
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、内蔵デバイスレジスタの設定を行う(ステップS704)。ステップS704の内蔵デバイスレジスタの設定の処理では、払出制御用CPU371は、CTCの設定を行う。また、この実施の形態では、内蔵CTCのうちの一つのチャネルがタイマモードで使用される。そのため、払出制御用CPU371は、使用するチャネルをタイマモードに設定するためのレジスタ設定、割込発生を許可するためのレジスタ設定および割込ベクタを設定するためのレジスタ設定を行う。そして、そのチャネルによる割込がタイマ割込として用いられる。タイマ割込を例えば1ms毎に発生させたい場合は、初期値として1msに相当する値が所定のレジスタ(時間定数レジスタ)に設定される。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 sets the built-in device register (step S704). In the process of setting the built-in device register in step S704, the payout control CPU 371 performs setting of CTC. Also, in this embodiment, one channel of the built-in CTC is used in the timer mode. Therefore, the payout control CPU 371 performs register setting for setting the channel to be used in the timer mode, register setting for permitting interrupt generation, and register setting for setting an interrupt vector. Then, the interrupt by that channel is used as a timer interrupt. When it is desired to generate a timer interrupt, for example, every 1 ms, a value corresponding to 1 ms is set in a predetermined register (time constant register) as an initial value.
また、ステップS704において、払出制御用CPU371は、シリアル通信回路380の割り込み要求に応じて実行する割込処理の優先順位を初期設定する。この場合、この場合、払出制御用CPU371は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のCPU56が行う優先順位の初期設定処理(ステップS15b参照)と同様の処理に従って、割込処理の優先順位を初期設定する。
In step S704, the payout control CPU 371 initializes the priority of interrupt processing to be executed in response to the interrupt request of the serial communication circuit 380. In this case, in this case, the payout control CPU 371 initializes the priority of the interrupt processing in accordance with the same processing as the initialization processing of the priority (see step S15 b) performed by the CPU 56 of the game control microcomputer 560.
また、ステップS704において、払出制御用CPU371は、シリアル通信回路380の設定を行う。この場合、払出制御用CPU371は、受信回路のボーレートの設定、受信モード(8ビットまたは9ビットのデータフォーマットのいずれにするか)の設定、パリティ設定(パリティの有無や、偶数パリティまたは奇数パリティの設定)を行う。また、受信回路の各制御レジスタを初期化するとともに、各ステータスレジスタを初期化する。また、払出制御用CPU371は、送信回路のボーレートの設定、送信モード(8ビットまたは9ビットのデータフォーマットのいずれにするか)の設定、パリティ設定(パリティの有無や、偶数パリティまたは奇数パリティの設定)を行う。また、送信回路の各制御レジスタを初期化する。
In step S704, the payout control CPU 371 sets the serial communication circuit 380. In this case, the payout control CPU 371 sets the baud rate of the reception circuit, the reception mode (either 8-bit or 9-bit data format), parity setting (presence or absence of parity, even parity or odd parity). Set). Further, each control register of the receiving circuit is initialized, and each status register is initialized. Further, the payout control CPU 371 sets the baud rate of the transmission circuit, the transmission mode (whether the data format is 8 bits or 9 bits), the parity setting (presence of parity, even parity or odd parity) )I do. In addition, each control register of the transmission circuit is initialized.
なお、タイマモードに設定されたチャネル(この実施の形態ではチャネル3)に設定される割込ベクタは、タイマ割込処理の先頭アドレスに相当するものである。具体的は、Iレジスタに設定された値と割込ベクタとでタイマ割込処理の先頭アドレスが特定される。タイマ割込処理では、払出手段を制御する払出制御処理(少なくとも主基板からの賞球払出に関する指令信号に応じて球払出装置97を駆動する処理を含み、球貸し要求に応じて球払出装置97を駆動する処理が含まれていてもよい。)が実行される。
The interrupt vector set to the channel set to the timer mode (channel 3 in this embodiment) corresponds to the top address of the timer interrupt process. Specifically, the start address of the timer interrupt process is specified by the value set in the I register and the interrupt vector. The timer interrupt process includes a payout control process for controlling the payout means (a process for driving the ball payout device 97 in accordance with at least a command signal related to the winning ball payout from the main substrate), and the ball payout device 97 in response to the ball lending request. Processing may be included).
また、この実施の形態では、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370でも割込モード2が設定される。従って、内蔵CTCのカウントアップにもとづく割込処理を使用することができる。また、CTCが送出した割込ベクタに応じた割込処理開始アドレスを設定することができる。CTCのチャネル3(CH3)のカウントアップにもとづく割込は、CPUの内部クロック(システムクロック)をカウントダウンしてレジスタ値が「0」になったら発生する割込であり、タイマ割込として用いられる。
Further, in this embodiment, interrupt mode 2 is also set by the payout control microcomputer 370. Therefore, it is possible to use interrupt processing based on count-up of built-in CTC. Also, the interrupt processing start address can be set according to the interrupt vector sent out by CTC. The interrupt based on the count up of channel 3 (CH3) of CTC is an interrupt generated when the internal clock (system clock) of the CPU is counted down and the register value becomes “0”, and is used as a timer interrupt .
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、RAMをアクセス可能状態に設定し(ステップS705)、RAMクリア処理を行う(ステップS706)。また、RAM領域のフラグやカウンタなどに初期値を設定する(ステップS707)。なお、ステップS707の処理には、未払出個数カウンタ初期値を未払出個数カウンタにセットする処理が含まれる。また、ステップS707の処理では、払出制御用CPU371は、払出個数異常エラーや満タンエラー、球切れエラーの検出状態を示すエラーフラグをクリアする処理も行う。なお、この実施の形態では、払出個数異常エラーと判定されてエラーフラグの払出個数異常エラー指定ビットがセットされた場合には、電源リセットがされるまで払出個数異常エラー指定ビットがクリアされず払出個数異常エラーから復旧しないのであるが、具体的には、電源投入時にステップS707の処理が実行されることによって、エラーフラグの払出個数異常エラー指定ビットがクリアされ、払出個数異常エラーから復旧する。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 sets the RAM to an accessible state (step S705), and performs a RAM clear process (step S706). Further, an initial value is set to a flag or a counter in the RAM area (step S 707). The process of step S 707 includes the process of setting the initial value of the unpaid-number counter to the unpaid-number counter. Further, in the process of step S 707, the payout control CPU 371 also performs a process of clearing an error flag indicating a detected state of a payout number abnormality error, a full tank error, or a ball out error. In this embodiment, if it is determined that the number-of-disbursements error is made and the number-of-dispenses-number error designation bit of the error flag is set, the number-of-dispenses number error designation bits are not cleared until the power is reset Although the number abnormal error is not recovered, specifically, the process of step S 707 is executed when the power is turned on, whereby the payout number abnormal error designated bit of the error flag is cleared, and the payout number abnormal error is recovered.
また、払出制御用CPU371は、シリアル通信回路380を初期設定するシリアル通信回路設定処理を実行する(ステップS708)。この場合、払出制御用CPU371は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560のCPU56が行うシリアル通信回路設定処理(ステップS15a参照)と同様の処理に従って、シリアル通信回路380に遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560とシリアル通信させるための設定を行う。また、前述したように、シリアル通信回路380の初期設定の一部は、ステップS704の内蔵デバイスレジスタの設定処理において実行される。なお、シリアル通信回路380の全ての設定処理をステップS708のシリアル通信回路設定処理で行うようにしてもよい。
Further, the payout control CPU 371 executes serial communication circuit setting processing for initializing the serial communication circuit 380 (step S 708). In this case, the payout control CPU 371 causes the serial communication circuit 380 to serially communicate with the game control microcomputer 560 according to the same process as the serial communication circuit setting process (see step S15a) performed by the CPU 56 of the game control microcomputer 560. Make settings for In addition, as described above, part of the initial setting of the serial communication circuit 380 is executed in the setting process of the built-in device register in step S704. All setting processing of the serial communication circuit 380 may be performed in the serial communication circuit setting processing of step S 708.
そして、初期設定処理のステップS701において割込禁止とされているので、初期化処理を終える前に割込が許可される(ステップS709)。その後、タイマ割込の発生を監視するループ処理に入る。
Since the interrupt is prohibited in step S701 of the initial setting process, the interrupt is permitted before the initialization process is completed (step S709). Thereafter, loop processing is started to monitor the occurrence of the timer interrupt.
上記のように、この実施の形態では、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370の内蔵CTCが繰り返しタイマ割込を発生するように設定される。そして、タイマ割込が発生すると、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370の払出制御用CPU371は、タイマ割込処理を実行する。
As described above, in this embodiment, the built-in CTC of the payout control microcomputer 370 is set to generate the timer interrupt repeatedly. When a timer interrupt occurs, the payout control CPU 371 of the payout control microcomputer 370 executes timer interrupt processing.
図69は、払出制御手段が実行するタイマ割込処理の例を示すフローチャートである。タイマ割込処理にて、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370の払出制御用CPU371は、以下の処理を実行する。まず、払出制御用CPU371は、スイッチチェック処理を行う(ステップS751)。スイッチチェック処理では、払出制御用CPU371は、入力ポート1の入力にもとづいて、払出個数カウントスイッチ301およびエラー解除スイッチ375のオン/オフ状態を確認する処理を行う。次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、入力判定処理を行う(ステップS752)。入力判定処理は、入力ポート0のビット0〜7(図67参照)の状態を検出して検出結果をRAMの所定の1バイト(センサ入力状態フラグと呼ぶ。)に反映する処理である。なお、払出制御用CPU371は、入力ポート0のビット0〜7の状態にもとづいて制御を行う場合には、直接入力ポートの状態をチェックするのではなく、センサ入力状態フラグの状態をチェックする。
FIG. 69 is a flowchart showing an example of timer interrupt processing executed by the payout control means. In the timer interrupt process, the payout control CPU 371 of the payout control microcomputer 370 executes the following process. First, the payout control CPU 371 performs switch check processing (step S751). In the switch check process, the payout control CPU 371 performs a process of confirming the on / off state of the payout number counting switch 301 and the error release switch 375 based on the input of the input port 1. Next, the payout control CPU 371 performs an input determination process (step S752). The input determination process is a process of detecting the states of bits 0 to 7 (see FIG. 67) of the input port 0 and reflecting the detection result on a predetermined 1 byte of the RAM (referred to as a sensor input state flag). When performing control based on the states of bits 0 to 7 of the input port 0, the payout control CPU 371 does not check the state of the direct input port but checks the state of the sensor input state flag.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、カードユニット50と通信を行うプリペイドカードユニット制御処理を実行する(ステップS753)。次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、主基板31の遊技制御手段と通信を行う主制御通信処理を実行する(ステップS754)。次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、カードユニット50からの球貸し要求に応じて貸し球を払い出す制御を行い、また、主基板31からの賞球個数コマンドが示す個数の賞球を払い出す制御を行う払出制御処理を実行する(ステップS755)。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 executes prepaid card unit control processing to communicate with the card unit 50 (step S753). Next, the payout control CPU 371 executes main control communication processing to communicate with the game control means of the main substrate 31 (step S754). Next, the payout control CPU 371 performs control of paying out the rental balls in response to the ball lending request from the card unit 50, and also performs control of discharging the number of winning balls indicated by the winning ball number command from the main substrate 31. A payout control process to be performed is executed (step S755).
次に、払出制御用CPU371は、払出モータ制御処理を実行する(ステップS756)。払出モータ制御処理では、払出モータ289を駆動すべきときには、払出モータφ1〜φ4のパターンを出力ポート0に出力するための処理を行う。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 executes a payout motor control process (step S756). In the payout motor control process, when the payout motor 289 is to be driven, a process for outputting the pattern of the payout motors φ1 to φ4 to the output port 0 is performed.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、各種のエラーを検出するエラー処理を実行する(ステップS757)。次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、カードユニット50のエラー制御を行うプリペイドカードユニットエラー制御処理を実行する(ステップS758)。次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、主基板31に対して賞球情報を出力したり、賞球信号1や遊技機エラー状態信号を外部出力するための情報出力処理を実行する(ステップS759)。また、エラー処理の結果に応じてエラー表示LED374に所定の表示を行う表示制御処理を実行する(ステップS760)。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 executes error processing to detect various errors (step S757). Next, the payout control CPU 371 executes prepaid card unit error control processing for error control of the card unit 50 (step S758). Next, the payout control CPU 371 executes an information output process for outputting the winning ball information to the main substrate 31, and externally outputting the winning ball signal 1 and the gaming machine error state signal (step S759). Further, display control processing for performing predetermined display on the error display LED 374 in accordance with the result of the error processing is executed (step S760).
本実施の形態では、後述するエラー処理において各種エラー(例えば、払出個数異常エラーや、満タンエラー、球切れエラー、プリペイドカードユニット未接続エラー)が検出されると、検出されたエラーに対応するエラービットがセットされる。そして、ステップS760の表示制御処理において、エラービットがセットされていることにもとづいて、払出制御用CPU371は、エラー表示LED374に所定の表示を行う。
In the present embodiment, when various errors (for example, a number-of-payouts error, a full tank error, an out-of-ball error, a prepaid card unit non-connection error) are detected in error processing described later, an error corresponding to the detected error The bit is set. Then, in the display control process of step S760, the payout control CPU 371 performs a predetermined display on the error display LED 374 based on the fact that the error bit is set.
また、この実施の形態では、出力ポートの出力状態に対応したRAM領域(出力ポート0バッファ、出力ポート1バッファ)が設けられているのであるが、払出制御用CPU371は、出力ポート0バッファおよび出力ポート1バッファの内容を出力ポートに出力する(ステップS761:出力処理)。出力ポート0バッファおよび出力ポート1バッファは、払出モータ制御処理(ステップS756)、プリペイドカード制御処理(ステップS753)、主制御通信処理(ステップS754)、情報出力処理(ステップS759)および表示制御処理(ステップS760)で更新される。
Further, in this embodiment, the RAM area (output port 0 buffer, output port 1 buffer) corresponding to the output state of the output port is provided. However, the payout control CPU 371 has an output port 0 buffer and an output. The contents of the port 1 buffer are output to the output port (step S761: output processing). The output port 0 buffer and the output port 1 buffer are subjected to payout motor control processing (step S 756), prepaid card control processing (step S 753), main control communication processing (step S 754), information output processing (step S 759) and display control processing ( It is updated at step S760).
図70は、ステップS754の主制御通信処理を示すフローチャートである。主制御通信処理では、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370(具体的には、払出制御用CPU371)は、主制御コマンド受信処理(ステップS740)を実行する。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御コードの値に応じて、ステップS741〜S744のいずれかの処理を実行する。
FIG. 70 is a flowchart showing the main control communication process of step S754. In the main control communication process, the payout control microcomputer 370 (specifically, the payout control CPU 371) executes a main control command reception process (step S740). Then, the payout control CPU 371 executes one of the processes in steps S741 to S744 in accordance with the value of the main control communication control code.
図71は、主制御通信処理におけるステップS740の主制御コマンド受信処理を示すフローチャートである。払出制御用CPU371は、主制御コマンド受信処理において、まず、接続信号を入力しているか否かを確認する(ステップS74001)。接続信号を入力していなければ、払出制御用CPU101は、シリアル通信回路380の送信回路および受信回路の初期化を行う(ステップS74002)。このように、接続信号を受信できない場合にシリアル通信回路380の送信回路および受信回路を初期化することによって、主基板31との接続状態が異常な状態下であるにもかかわらずコマンドを送信データレジスタや受信データレジスタに格納してしまう事態を防止することができる。次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御コードの値をロードし(ステップS74003)、主制御通信制御コードの値が主制御接続確認処理を示す値「0」となっているか否かを確認する(ステップS74004)。
FIG. 71 is a flowchart showing the main control command reception process of step S740 in the main control communication process. In the main control command reception process, the payout control CPU 371 first confirms whether a connection signal is input (step S74001). If the connection signal is not input, the payout control CPU 101 initializes the transmission circuit and the reception circuit of the serial communication circuit 380 (step S74002). As described above, when the connection signal can not be received, the transmission circuit and the reception circuit of the serial communication circuit 380 are initialized to transmit the command even though the connection state with the main board 31 is under abnormal state. It is possible to prevent the situation where the data is stored in the register or the reception data register. Next, the payout control CPU 371 loads the value of the main control communication control code (step S74003), and confirms whether or not the value of the main control communication control code is the value "0" indicating the main control connection confirmation process. (Step S74004).
この実施の形態では、主制御通信処理において、遊技機への電源供給が開始されてから遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560からの接続信号の入力が開始され、最初の接続確認コマンドの受信を確認できるまでステップS741の主制御接続確認処理が実行される。そして、接続確認コマンドの受信を確認できると、ステップS742以降の処理に移行し、各種払出制御コマンドの送受信の処理が実行される。また、以降、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560との間の通信状態が正常に維持されていれば、ステップS742〜S744のいずれかの処理が実行され、ステップS741の主制御接続確認処理は原則として遊技機への電源投入時にのみ実行されることになる。ステップS74004において、主制御通信制御コードの値が主制御接続確認処理以外の値を示しているということは、ステップS742以降の処理に移行した後に、何らかの通信エラーが生じて接続信号を入力不能となった場合である。そのため、払出制御用CPU371は、ステップS74004で主制御通信制御コードの値が主制御接続確認処理以外の値を示している場合には、エラーフラグの主制御通信エラー指定ビット(遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560との間の通信状態に異常が生じたことを示すビット)をセットする(ステップS74005)。なお、エラーフラグは、各種賞球エラーがセットされるフラグであり、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370が備えるRAMに形成されている。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御コードに主制御接続確認処理を示す値「0」をセットする(ステップS74006)。なお、ステップS74004で主制御通信制御コードの値が主制御接続確認処理を示す値「0」となっていれば、そのままステップS74006)に移行する。
In this embodiment, in the main control communication process, the input of the connection signal from the game control microcomputer 560 is started after the supply of power to the gaming machine is started, and the reception of the first connection confirmation command can be confirmed. The main control connection confirmation process of step S741 is executed. Then, when the reception of the connection confirmation command can be confirmed, the processing proceeds to step S742 and subsequent steps, and processing of transmitting and receiving various payout control commands is executed. Further, after that, if the communication state with the game control microcomputer 560 is normally maintained, one of the processes of steps S742 to S744 is executed, and the main control connection confirmation process of step S741 is basically a game. It will only be executed when the machine is powered on. The fact that the value of the main control communication control code indicates a value other than the main control connection confirmation processing in step S74004 means that some kind of communication error occurs and the connection signal can not be input after shifting to the processing after step S742. It is the case. Therefore, when the value of the main control communication control code indicates a value other than the main control connection confirmation process in step S74004, the payout control CPU 371 determines that the main control communication error designation bit of the error flag (microcomputer for game control The bit indicating that an abnormality has occurred in the communication state with 560 is set (step S 74005). The error flag is a flag in which various award ball errors are set, and is formed in the RAM provided in the payout control microcomputer 370. Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets the value "0" indicating the main control connection confirmation process in the main control communication control code (step S74006). If it is determined in step S74004 that the value of the main control communication control code is "0" indicating the main control connection confirmation process, the process directly proceeds to step S74006).
なお、ステップS741の主制御確認処理は、遊技機への電源投入時以降であっても例外的に実行される場合がある。具体的には、上記したように、ステップS74001で接続信号を入力していないと判定した後、ステップS74004で主制御接続確認処理の実行中でなければ、遊技機への電源投入後に接続信号が切断されてしまった可能性があると判断して主制御接続確認処理に戻り(ステップS74006参照)、再び遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560との接続状態を確認する(具体的には、接続確認コマンドを受信できることを確認。ステップS7412参照。)。また、後述する主制御通信通常処理において、接続OKコマンドを送信してから所定期間(本例では1050ms)を経過しても、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から接続確認コマンドも賞球個数コマンドも受信していない場合には、何らかの通信異常が生じたものとして主制御接続確認処理に戻り(ステップS74202,S74203参照)、再び遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560との接続状態を確認する(具体的には、接続確認コマンドを受信できることを確認。ステップS7412参照。)。
Note that the main control confirmation process in step S741 may be exceptionally executed even after power-on of the gaming machine. Specifically, as described above, after determining that the connection signal is not input in step S74001, if the main control connection confirmation process is not being performed in step S74004, the connection signal is output after the power is turned on to the gaming machine. It judges that there is a possibility that it has been disconnected, returns to the main control connection confirmation processing (see step S74006), confirms the connection state with the game control microcomputer 560 again (specifically, the connection confirmation command Confirm that it can be received (see step S7412). Also, in the main control communication normal processing described later, even if a predetermined period (in this example, 1050 ms) has passed since the connection OK command was sent, both the connection check command and the prize ball number command are received from the game control microcomputer 560 If not, the process returns to the main control connection confirmation process (see steps S74202 and S74203) on the assumption that some kind of communication abnormality has occurred, and confirms the connection state with the game control microcomputer 560 again (specifically, Confirm that the connection confirmation command can be received (see step S7412).
接続信号を入力していれば、払出制御用CPU371は、シリアル通信回路380のステータスレジスタに受信エラーフラグがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS74007)。例えば、払出制御用CPU371は、シリアル通信回路380のステータスレジスタにパリティエラーや、フレーミングエラー、ノイズエラー、オーバーランエラー、アイドルラインエラーを示すフラグがセットされていれば、シリアル通信回路380の受信エラー状態であると判定する。
If the connection signal is input, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether the reception error flag is set in the status register of the serial communication circuit 380 (step S74007). For example, if the payout control CPU 371 sets flags indicating a parity error, a framing error, a noise error, an overrun error, an idle line error in the status register of the serial communication circuit 380, the reception error of the serial communication circuit 380 It determines that it is a state.
受信エラーフラグがセットされていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、シリアル通信回路380の受信回路を初期化する(ステップS74008)。このように、受信エラー状態である場合にシリアル通信回路380の受信回路を初期化することによって、何らかの受信異常が生じているにもかかわらず受信コマンドを受信データレジスタに格納してしまう事態を防止することができる。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、エラーフラグの主制御通信エラー指定ビットをセットする(ステップS74009)。
If the reception error flag is set, the payout control CPU 371 initializes the reception circuit of the serial communication circuit 380 (step S74008). As described above, by initializing the reception circuit of the serial communication circuit 380 in the reception error state, it is possible to prevent the reception command from being stored in the reception data register despite the occurrence of some reception abnormality. can do. Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets the main control communication error designation bit of the error flag (step S74009).
受信エラーフラグもセットされていなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、受信バッファの内容をロードし(ステップS74010)、接続確認コマンドを受信しているか否かを確認する(ステップS74011)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、ロードした受信バッファの内容が「A0(H)」であるか否か(図27参照)を確認する。接続確認コマンドを受信していれば、払出制御用CPU371は、ステップS74014に移行する。
If the reception error flag is not set either, the payout control CPU 371 loads the contents of the reception buffer (step S74010), and confirms whether a connection confirmation command has been received (step S74011). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether the content of the loaded reception buffer is “A0 (H)” (see FIG. 27). If the connection confirmation command has been received, the payout control CPU 371 proceeds to step S74014.
接続確認コマンドを受信していなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、賞球個数コマンドを受信しているか否かを確認する。この実施の形態では、図27に示すように、接続個数コマンドの内容は、少なくとも「51(H)」以上、「60(H)」未満の値となる筈である。従って、払出制御用CPU371は、まず、ロードした受信バッファの内容が賞球個数コマンド最小値「51(H)」以上であるか否かを確認する(ステップS74012)。次いで、賞球個数コマンド最小判定値「51(H)」以上であれば、払出制御用CPU371は、ロードした受信バッファの内容が賞球個数コマンド最大判定値「60(H)」未満であるか否かを確認する(ステップS74013)。賞球個数コマンド最大判定値「60(H)」未満であれば、払出制御用CPU371は、賞球個数コマンドを受信していると判定し、ステップS74014に移行する。
If the connection confirmation command has not been received, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the winning ball number command has been received. In this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 27, the content of the connection number command should be at least "51 (H)" and less than "60 (H)". Therefore, the payout control CPU 371 first confirms whether or not the content of the loaded reception buffer is equal to or more than the winning ball number command minimum value “51 (H)” (step S74012). Next, if the prize ball count command minimum judgment value is “51 (H)” or more, the payout control CPU 371 determines whether the content of the loaded reception buffer is less than the prize ball count command maximum judgment value “60 (H)” It is confirmed whether or not it is (step S74013). If it is less than the winning balls number command maximum judgment value "60 (H)", the payout control CPU 371 determines that the winning balls number command has been received, and proceeds to step S74014.
そして、ステップS74014では、払出制御用CPU371は、受信バッファの内容(接続確認コマンド、賞球個数コマンド)を主制御通信受信バッファに格納する。なお、主制御通信受信バッファは、1バイトで構成され、1度に1つの受信コマンドのみを格納することができる。このように構成しても、この実施の形態では、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370におけるタイマ割込の周期(本例では1ms)は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560におけるタイマ割込の周期(本例では4ms)より短いので、1回のタイマ割込内で複数の払出制御コマンドが受信される事態が生じることはなく、不都合は生じない。また、万一、遊技機への電源投入後、誤処理などにより、最初の接続確認コマンドを受信する前に賞球個数コマンドを受信してしまった場合であっても、その後、接続確認コマンドを受信すれば主制御通信受信バッファに上書きで格納されるので、後述する主制御接続確認処理(ステップS741)で接続確認コマンドを全く確認できず主制御通信通常処理に移行できなくなる事態が生じることを防止することができる。
Then, in step S74014, the payout control CPU 371 stores the contents of the reception buffer (connection confirmation command, award ball number command) in the main control communication reception buffer. The main control communication reception buffer is formed of one byte and can store only one reception command at a time. Even in this configuration, in this embodiment, the timer interrupt cycle (1 ms in this example) in payout control microcomputer 370 is the timer interrupt cycle (in this example) in game control microcomputer 560. Since it is shorter than 4 ms), there will not occur a case where a plurality of payout control commands are received within one timer interrupt, and no inconvenience occurs. Also, even if it is the case that the prize ball quantity command is received before the first connection confirmation command is received after the power is turned on to the gaming machine due to an erroneous process or the like, the connection confirmation command is then issued. If it is received, it is stored in the main control communication reception buffer as overwritten, so that there is a possibility that the connection confirmation command can not be confirmed at all in the main control connection confirmation process (step S741) described later It can be prevented.
図72は、主制御通信制御コードの値が0の場合に実行される主制御接続確認処理(ステップS741)を示すフローチャートである。主制御接続確認処理において、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信受信バッファの内容をロードし(ステップS7411)、接続確認コマンドを受信しているか否かを確認する(ステップS7412)。接続確認コマンドを受信していれば、払出制御用CPU371は、接続OKコマンドをセットし(ステップS7413)、主制御送信コマンド変換処理を実行する(ステップS7414)。なお、ステップS7414の主制御送信コマンド変換処理では、接続OKコマンドの下位4ビットに制御状態(払出個数異常エラーや、球切れエラー、満タンエラー、賞球エラーなどのエラー状態)をセットする処理が行われる。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、変換後の接続OKコマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する制御を行う(ステップS7415)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、シリアル通信回路380の送信レジスタに接続OKコマンドを出力する処理を行う。
FIG. 72 is a flowchart showing a main control connection confirmation process (step S741) that is executed when the value of the main control communication control code is 0. In the main control connection confirmation process, the payout control CPU 371 loads the contents of the main control communication reception buffer (step S7411), and confirms whether a connection confirmation command has been received (step S7412). If the connection confirmation command has been received, the payout control CPU 371 sets a connection OK command (step S7413), and executes main control transmission command conversion processing (step S7414). In the main control transmission command conversion process of step S7414, the process of setting the control state (error state such as payout number abnormality error, ball out error, full error, award ball error, etc.) in the lower 4 bits of the connection OK command is performed. To be done. Then, the payout control CPU 371 performs control to transmit the converted connection OK command to the game control microcomputer 560 (step S7415). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 performs a process of outputting a connection OK command to the transmission register of the serial communication circuit 380.
なお、払出制御用CPU371は、ステップS7415で接続OKコマンドを送信すると、主制御通信受信バッファをクリアする。そのようにすることによって、その後の処理で受信コマンドを誤って認識して誤った処理を実行してしまう事態を防止することができる。
The payout control CPU 371 clears the main control communication reception buffer when the connection OK command is transmitted in step S7415. By doing so, it is possible to prevent the situation in which the received command is erroneously recognized in the subsequent process and the erroneous process is executed.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御コードに主制御通信通常処理を示す値「1」をセットする(ステップS7416)。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御タイマに所定値(本例では1050ms)をセットする(ステップS7417)。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 sets the value “1” indicating the main control communication normal processing in the main control communication control code (step S7416). Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets a predetermined value (1050 ms in this example) in the main control communication control timer (step S7417).
図73および図74は、主制御通信制御コードの値が1の場合に実行される主制御通信通常処理(ステップS742)を示すフローチャートである。主制御通信通常処理において、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御タイマの値を1減算し(ステップS74201)、主制御通信制御タイマがタイムアウトしたか否かを確認する(ステップS74202)。
73 and 74 are flowcharts showing the main control communication normal processing (step S742) executed when the value of the main control communication control code is "1". In the main control communication normal processing, the payout control CPU 371 subtracts 1 from the value of the main control communication control timer (step S74201), and checks whether the main control communication control timer has timed out (step S74202).
この実施の形態では、前述したように、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370から接続OKコマンドを受信して1秒経過するごとに、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から次の接続確認コマンドが送信される。従って、ステップS74202において主制御通信制御タイマがタイムアウトしたということは、接続OKコマンドの送信後1秒を遙かに超えて1050ms(ステップS7417,S74209参照)を経過しても次の接続確認コマンドを受信できなかった場合である。そのため、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御コードに主制御接続確認処理を示す値「0」をセットして(ステップS74203)、主制御接続確認処理に戻り通信状態の回復を待つように制御する。
In this embodiment, as described above, the next connection confirmation command is transmitted from the game control microcomputer 560 every one second after the connection OK command is received from the payout control microcomputer 370. Therefore, that the main control communication control timer has timed out in step S74202 means that the next connection confirmation command is sent even after 1050 ms (see steps S7417 and S74209) far beyond 1 second after transmission of the connection OK command. It is a case where it could not receive. Therefore, the payout control CPU 371 sets the value "0" indicating the main control connection confirmation process in the main control communication control code (step S74203), returns control to the main control connection confirmation process, and waits for recovery of the communication state. Do.
なお、払出制御用CPU371は、ステップS74202で主制御通信制御タイマがタイムアウトしていれば、主制御通信受信バッファをクリアする。そのようにすることによって、その後の処理で受信コマンドを誤って認識して誤った処理を実行してしまう事態を防止することができる。
When the main control communication control timer has timed out in step S74202, the payout control CPU 371 clears the main control communication reception buffer. By doing so, it is possible to prevent the situation in which the received command is erroneously recognized in the subsequent process and the erroneous process is executed.
主制御通信制御タイマがタイムアウトしていなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信受信バッファに受信コマンドが格納されているか否かを確認する(ステップS74204)。主制御通信受信バッファに受信コマンドが格納されていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、受信したコマンドが接続確認コマンドであるか否かを確認する(ステップS74205)。接続確認コマンドを受信していれば、払出制御用CPU371は、接続OKコマンドをセットし(ステップS74206)、主制御送信コマンド変換処理を実行する(ステップS74207)。なお、ステップS74207の主制御送信コマンド変換処理では、接続OKコマンドの下位4ビットに制御状態(払出個数異常エラーや、球切れエラー、満タンエラー、賞球エラーなどのエラー状態)をセットする処理が行われる。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、変換後の接続OKコマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する制御を行う(ステップS74208)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、シリアル通信回路380の送信レジスタに接続OKコマンドを出力する処理を行う。
If the main control communication control timer has not timed out, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the reception command is stored in the main control communication reception buffer (step S74204). If the reception command is stored in the main control communication reception buffer, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether the received command is a connection confirmation command or not (step S74205). If the connection confirmation command has been received, the payout control CPU 371 sets a connection OK command (step S74206), and executes main control transmission command conversion processing (step S74207). In the main control transmission command conversion process of step S74207, the process of setting the control state (error state such as payout number abnormality error, ball out error, full error, award ball error, etc.) in the lower 4 bits of the connection OK command is performed. To be done. Then, the payout control CPU 371 performs control to transmit the converted connection OK command to the game control microcomputer 560 (step S74208). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 performs a process of outputting a connection OK command to the transmission register of the serial communication circuit 380.
なお、払出制御用CPU371は、ステップS74208で接続OKコマンドを送信すると、主制御通信受信バッファをクリアする。そのようにすることによって、その後の処理で受信コマンドを誤って認識して誤った処理を実行してしまう事態を防止することができる。
The payout control CPU 371 clears the main control communication reception buffer when the connection OK command is transmitted in step S74208. By doing so, it is possible to prevent the situation in which the received command is erroneously recognized in the subsequent process and the erroneous process is executed.
そして、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御タイマに所定値(本例では1050ms)をセットする(ステップS74209)。
Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets a predetermined value (1050 ms in this example) in the main control communication control timer (step S74209).
ステップS74205で受信したコマンドが接続確認コマンドでなければ、賞球個数コマンドを受信していることになる。この場合、払出制御用CPU371は、エラーフラグの値が0であるか否かを確認する(ステップS74210)。エラーフラグの値が0でなければ(すなわち、エラー状態であり、いずれかのエラービットがセットされていれば)、ステップS74219に移行する。エラーフラグの値が0であれば(すなわち、エラー状態となっておらず、いずれのエラービットもセットされていなければ)、払出制御用CPU371は、BRDY信号を入力しているか否かを確認する(ステップS74211)。BRDY信号を入力していれば、ステップS74219に移行する。
If the command received in step S74205 is not a connection confirmation command, it means that the winning balls number command has been received. In this case, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether the value of the error flag is 0 or not (step S74210). If the value of the error flag is not 0 (i.e., an error state and any error bit is set), the process proceeds to step S74219. If the value of the error flag is 0 (that is, the error state is not set and any error bit is not set), the payout control CPU 371 checks whether the BRDY signal is input or not. (Step S74211). If the BRDY signal is input, the process proceeds to step S74219.
BRDY信号も入力していなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態を示す払出制御状態フラグをロードし(ステップS74212)、賞球払出動作中または球貸し払出動作中であるか否かを確認する(ステップS74213)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグに賞球払出動作中指定ビット(賞球払出動作中であることを示すビット)または球貸し払出動作中指定ビット(球貸し払出動作中であることを示すビット)がセットされているか否かを確認する。賞球払出動作中または球貸し払出動作中であれば、ステップS74219に移行する。なお、この実施の形態では、賞球払出動作を終了して賞球終了コマンドを受信してから次の賞球個数コマンドが送信されるので、通信エラーなどの異常が発生していないかぎり、ステップS74213において賞球払出動作中であると判定されることはない。
If the BRDY signal is not input either, the payout control CPU 371 loads the payout control status flag indicating the payout control status (step S74212), and checks whether or not the winning ball payout operation or the ball loan payout operation is in progress. (Step S74213). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 sets a payout control state flag to a designated bit during payout ball payout operation (a bit indicating that a prize ball payout operation is being performed) or a sphere rental payout designation bit (a ball loan payout operation is in progress) Check whether the bit) is set. If a prize ball payout operation or a ball loan payout operation is in progress, the process moves to step S74219. In this embodiment, since the next prize ball number command is transmitted after the prize ball payout operation is finished and the prize ball end command is received, the step is performed unless an error such as a communication error occurs. It is not determined in S74213 that a prize ball dispensing operation is in progress.
賞球払出動作中でも球貸し払出動作中でもなければ、受信した賞球個数コマンドにもとづく賞球払出動作を直ちに開始できる場合である。この場合、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信受信バッファの下位4ビット(すなわち、賞球個数コマンドにセットされた賞球個数)を未払出個数カウンタにセットする(ステップS74214)。なお、未払出個数カウンタは、賞球や貸し球の未払出数をカウントするためのカウンタである。
If there is neither the prize ball dispensing operation nor the ball lending dispensing operation, there is a case where the prize ball dispensing operation based on the received prize ball number command can be immediately started. In this case, the payout control CPU 371 sets the lower 4 bits of the main control communication reception buffer (that is, the number of winning balls set in the winning ball number command) in the unpaid number counter (step S74214). The unpaid number counter is a counter for counting the number of unpaid balls such as winning balls and rental balls.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、賞球個数受付コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する制御を行う(ステップS74215)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、シリアル通信回路380の送信レジスタに賞球個数受付コマンドを出力する処理を行う。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 performs control to transmit a winning ball number reception command to the game control microcomputer 560 (step S74215). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 performs a process of outputting an award ball number reception command to the transmission register of the serial communication circuit 380.
なお、払出制御用CPU371は、ステップS74215で賞球個数受付コマンドを送信すると、主制御通信受信バッファをクリアする。そのようにすることによって、その後の処理で受信コマンドを誤って認識して誤った処理を実行してしまう事態を防止することができる。
Note that the payout control CPU 371 clears the main control communication reception buffer when the award ball number reception command is transmitted in step S74215. By doing so, it is possible to prevent the situation in which the received command is erroneously recognized in the subsequent process and the erroneous process is executed.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御コードに主制御通信終了処理を示す値「3」をセットする(ステップS74216)。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御タイマに所定値(本例では1秒)をセットする(ステップS74218)。なお、ステップS74218でセットされた値にもとづいて、賞球個数受付コマンドを送信した後、1秒経過後に賞球払出動作を完了していなければ賞球準備中コマンドが送信されることになる。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 sets the value "3" indicating the main control communication end processing in the main control communication control code (step S74216). Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets a predetermined value (one second in this example) in the main control communication control timer (step S74218). In addition, based on the value set in step S74218, after the award ball number reception command is transmitted, if the award ball payout operation has not been completed after one second has elapsed, a prize ball preparing command will be transmitted.
ステップS74219では、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信受信バッファの下位4ビット(すなわち、賞球個数コマンドのセットされた賞球個数)を主制御通信賞球個数バッファに格納する。すなわち、この場合、何らかのエラー状態が発生していたり、賞球払出動作中や球貸し払出動作中、球貸し準備中の場合であるので、受信した賞球個数コマンドにもとづく賞球払出動作を直ちに開始することはできない。そのため、払出制御用CPU371は、賞球個数受付コマンドの返信を保留するとともに、賞球個数コマンドにセットされた賞球個数を主制御通信賞球個数バッファに一旦退避する。
In step S74219, the payout control CPU 371 stores the lower 4 bits of the main control communication reception buffer (that is, the number of award balls set with the award ball number command) in the main control communication sphere number buffer. That is, in this case, since there is an error condition, a prize ball dispensing operation, a ball lending dispensing operation, or a ball lending preparation in progress, the prize ball dispensing operation based on the received prize ball number command is immediately You can not start. Therefore, the payout control CPU 371 suspends the reply of the award ball number reception command, and temporarily saves the number of award balls set in the award ball number command into the main control communication ball number buffer.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、賞球準備中コマンドをセットし(ステップS74220)、主制御送信コマンド変換処理を実行する(ステップS74221)。なお、ステップS74221の主制御送信コマンド変換処理では、賞球準備中コマンドの下位4ビットに制御状態(払出個数異常エラーや、球切れエラー、満タンエラー、賞球エラーなどのエラー状態)をセットする処理が行われる。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、変換後の賞球準備中コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する制御を行う(ステップS74222)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、シリアル通信回路380の送信レジスタに賞球準備中コマンドを出力する処理を行う。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 sets a winning ball preparation command (step S74220), and executes main control transmission command conversion processing (step S74221). In the main control transmission command conversion process of step S74221, the control state (error states such as payout number abnormality error, ball out error, full error, prize ball error, etc.) is set in the lower 4 bits of the prize ball preparation command. Processing is performed. Then, the payout control CPU 371 performs control to transmit the converted prize ball preparing command to the game control microcomputer 560 (step S74222). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 performs a process of outputting a prize ball in-provision command to the transmission register of the serial communication circuit 380.
なお、払出制御用CPU371は、ステップS74222で賞球準備中コマンドを送信すると、主制御通信受信バッファをクリアする。そのようにすることによって、その後の処理で受信コマンドを誤って認識して誤った処理を実行してしまう事態を防止することができる。
Note that the payout control CPU 371 clears the main control communication reception buffer when the award ball preparing command is transmitted in step S74222. By doing so, it is possible to prevent the situation in which the received command is erroneously recognized in the subsequent process and the erroneous process is executed.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御コードに主制御通信中処理を示す値「2」をセットする(ステップS74223)。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御タイマに所定値(本例では1秒)をセットする(ステップS74224)。なお、ステップS74224でセットされた値にもとづいて、賞球準備中コマンドを送信した後、1秒経過後にまだ賞球払出動作を開始できる状態になっていなければ次の賞球準備中コマンドが送信されることになる。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 sets the value "2" indicating the main control in-communication process to the main control communication control code (step S74223). Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets a predetermined value (1 second in this example) in the main control communication control timer (step S74224). In addition, based on the value set in step S74224, after transmitting the in-progress ball preparation command, if it is not ready to start the out-delivery ball payout operation after one second, the next in-progress ball preparation command is transmitted. It will be done.
図75および図76は、主制御通信制御コードの値が2の場合に実行される主制御通信中処理(ステップS743)を示すフローチャートである。主制御通信中処理において、払出制御用CPU371は、まず、主制御通信受信バッファに受信コマンドが格納されているか否かを確認する(ステップS74301)。主制御通信受信バッファに受信コマンドが格納されていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、受信したコマンドが接続確認コマンドであるか否かを確認する(ステップS74302)。接続確認コマンドでなければ、ステップS74306に移行する。接続確認コマンドを受信していれば、払出制御用CPU371は、接続OKコマンドをセットし(ステップS74303)、主制御送信コマンド変換処理を実行する(ステップS74304)。なお、ステップS74304の主制御送信コマンド変換処理では、接続OKコマンドの下位4ビットに制御状態(払出個数異常エラーや、球切れエラー、満タンエラー、賞球エラーなどのエラー状態)をセットする処理が行われる。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、変換後の接続OKコマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する制御を行う(ステップS74305)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、シリアル通信回路380の送信レジスタに接続OKコマンドを出力する処理を行う。そして、ステップS74306に移行する。
FIGS. 75 and 76 are flowcharts showing the main control in-communication process (step S743) executed when the value of the main control communication control code is 2. In the main control in-communication process, the payout control CPU 371 first confirms whether or not a reception command is stored in the main control communication reception buffer (step S74301). If the reception command is stored in the main control communication reception buffer, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether the received command is a connection confirmation command (step S74302). If it is not a connection confirmation command, it will transfer to step S74306. If the connection confirmation command has been received, the payout control CPU 371 sets a connection OK command (step S74303), and executes main control transmission command conversion processing (step S74304). In the main control transmission command conversion process of step S74304, a process of setting the control state (error state such as payout number abnormality error, ball out error, full error, award ball error, etc.) in the lower 4 bits of the connection OK command is performed. To be done. Then, the payout control CPU 371 performs control to transmit the converted connection OK command to the game control microcomputer 560 (step S74305). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 performs a process of outputting a connection OK command to the transmission register of the serial communication circuit 380. Then, the process proceeds to step S74306.
ステップS74306では、払出制御用CPU371は、エラーフラグに主制御通信エラー指定ビットをセットする。すなわち、主制御通信中処理は、賞球個数コマンドを受信した後、受信した賞球個数コマンドにもとづく賞球払出動作を開始可能な状態となるまでに実行される処理であり、賞球個数受付コマンドの返信が保留されて、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は賞球個数受付コマンドの受信待ち状態となっているのであるから、この間に遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から新たに払出制御コマンドを受信することはない筈である。それにもかかわらず、新たなコマンドを受信したということは通信状態に何らかの異常が生じたと判断することができるのであるから、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信エラー指定ビットをセットする処理を行う。
In step S74306, the payout control CPU 371 sets a main control communication error designation bit in the error flag. That is, the main control in-communication process is a process that is executed until a state in which a prize ball payout operation based on the received prize ball quantity command can be started can be started after the prize ball quantity command is received. Since the reply of the command is suspended and the game control microcomputer 560 is in a state of waiting for the reception of the award ball number reception command, a payout control command is newly received from the game control microcomputer 560 during this time. There is no nephew. Nevertheless, the fact that a new command has been received means that it is possible to determine that some abnormality has occurred in the communication state, so the payout control CPU 371 performs processing for setting the main control communication error designation bit.
なお、払出制御用CPU371は、ステップS74306で主制御通信エラー指定ビットをセットすると、主制御通信受信バッファをクリアする。そのようにすることによって、その後の処理で受信コマンドを誤って認識して誤った処理を実行してしまう事態を防止することができる。
When the main control communication error designation bit is set in step S74306, the payout control CPU 371 clears the main control communication reception buffer. By doing so, it is possible to prevent the situation in which the received command is erroneously recognized in the subsequent process and the erroneous process is executed.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御コードに主制御通信通常処理を示す値「1」をセットする(ステップS74307)。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御タイマに所定値(本例では1050ms)をセットする(ステップS74308)。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 sets the value “1” indicating the main control communication normal processing in the main control communication control code (step S74307). Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets a predetermined value (1050 ms in this example) in the main control communication control timer (step S74308).
主制御通信受信バッファに受信コマンドがなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御タイマの値を1減算し(ステップS74309)、主制御通信制御タイマがタイムアウトしたか否かを確認する(ステップS74310)。
If there is no reception command in the main control communication reception buffer, the payout control CPU 371 subtracts 1 from the value of the main control communication control timer (step S74309) and confirms whether the main control communication control timer has timed out (step S74310).
主制御通信制御タイマがタイムアウトしていれば(ステップS74310のY)、賞球準備中コマンドを前回送信してから1秒以上経過したことを意味する。この場合、払出制御用CPU371は、次の賞球準備中コマンドを送信するために、賞球準備中コマンドをセットし(ステップS74311)、主制御送信コマンド変換処理を実行する(ステップS74312)。なお、ステップS74312の主制御送信コマンド変換処理では、賞球準備中コマンドの下位4ビットに制御状態(払出個数異常エラーや、球切れエラー、満タンエラー、賞球エラーなどのエラー状態)をセットする処理が行われる。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、変換後の賞球準備中コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する制御を行う(ステップS74313)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、シリアル通信回路380の送信レジスタに賞球準備中コマンドを出力する処理を行う。
If the main control communication control timer has timed out (Y in step S74310), it means that one second or more has elapsed since the award ball preparing command was transmitted last time. In this case, the payout control CPU 371 sets a prize ball preparation command to transmit the next prize ball preparation command (step S74311), and executes main control transmission command conversion processing (step S74312). In the main control transmission command conversion process of step S74312, the control state (error condition such as payout number abnormality error, ball out error, full error, prize ball error, etc.) is set in the lower 4 bits of the prize ball preparation command. Processing is performed. Then, the payout control CPU 371 performs control to transmit the converted award ball preparing command to the game control microcomputer 560 (step S74313). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 performs a process of outputting a prize ball in-provision command to the transmission register of the serial communication circuit 380.
そして、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御タイマに所定値(本例では1秒)をセットする(ステップS74314)。なお、ステップS74314でセットされた値にもとづいて、賞球準備中コマンドを送信した後、さらに1秒経過後にまだ賞球払出動作を開始できる状態になっていなければ次の賞球準備中コマンドが送信されることになる。
Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets a predetermined value (one second in this example) in the main control communication control timer (step S74314). In addition, based on the value set in step S74314, after transmitting the in-progress ball preparation command, if it is not ready to start the out-delivery ball payout operation after one second, the next in-progress ball preparation command is It will be sent.
主制御通信制御タイマがタイムアウトしていなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、エラーフラグの値が0であるか否かを確認する(ステップS74315)。エラーフラグの値が0でなければ(すなわち、エラー状態であり、いずれかのエラービットがセットされていれば)、まだ賞球払出動作を開始できないので、そのまま処理を終了する。エラーフラグの値が0であれば(すなわち、エラー状態となっておらず、いずれのエラービットもセットされていなければ)、払出制御用CPU371は、BRDY信号を入力しているか否かを確認する(ステップS74316)。BRDY信号を入力していれば、まだ賞球払出動作を開始できないので、そのまま処理を終了する。
If the main control communication control timer has not timed out, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether the value of the error flag is 0 or not (step S74315). If the value of the error flag is not 0 (i.e., it is an error state and any error bit is set), the processing is ended because the prize ball payout operation can not be started yet. If the value of the error flag is 0 (that is, the error state is not set and any error bit is not set), the payout control CPU 371 checks whether the BRDY signal is input or not. (Step S74316). If the BRDY signal has been input, it is not possible to start the prize ball dispensing operation yet, so the processing is terminated.
BRDY信号も入力していなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態を示す払出制御状態フラグをロードし(ステップS74317)、賞球払出動作中または球貸し払出動作中であるか否かを確認する(ステップS74318)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグに賞球払出動作中指定ビット(賞球払出動作中であることを示すビット)または球貸し払出動作中指定ビット(球貸し払出動作中であることを示すビット)がセットされているか否かを確認する。賞球払出動作中または球貸し払出動作中であれば、まだ賞球払出動作を開始できないので、そのまま処理を終了する。なお、この実施の形態では、賞球払出動作を終了して賞球終了コマンドを受信してから次の賞球個数コマンドが送信されるので、通信エラーなどの異常が発生していないかぎり、ステップS74318において賞球払出動作中であると判定されることはない。
If the BRDY signal is not input either, the payout control CPU 371 loads the payout control status flag indicating the payout control status (step S74317), and confirms whether or not the winning ball payout operation or the ball loan payout operation is in progress. (Step S74318). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 sets a payout control state flag to a designated bit during payout ball payout operation (a bit indicating that a prize ball payout operation is being performed) or a sphere rental payout designation bit (a ball loan payout operation is in progress) Check whether the bit) is set. If the prize ball payout operation or the ball lending payout operation is in progress, the prize ball payout operation can not be started yet, so the processing is ended as it is. In this embodiment, since the next prize ball number command is transmitted after the prize ball payout operation is finished and the prize ball end command is received, the step is performed unless an error such as a communication error occurs. It is not determined in S74318 that the winning balls are being dispensed.
賞球払出動作中でも球貸し払出動作中でもなければ、受信した賞球個数コマンドにもとづく賞球払出動作を開始可能な状態となったことを意味する。この場合、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信賞球個数バッファの下位4ビット(すなわち、一時退避した賞球個数)を未払出個数カウンタにセットする(ステップS74319)。
If it is not in the prize ball dispensing operation or in the ball lending payout operation, it means that it becomes possible to start the prize ball dispensing operation based on the received prize ball number command. In this case, the payout control CPU 371 sets the lower 4 bits of the main control communication prize ball number buffer (that is, the number of prize balls saved temporarily) in the unpaid quantity counter (step S74319).
なお、この実施の形態では、既に述べたように、賞球個数コマンドを受信したときに直ちに賞球払出動作を開始できない場合に、賞球個数コマンドで特定される賞球個数を直ちに未払出個数カウンタにセットするのではなく、主制御通信賞球個数バッファに一旦退避するのであるが、このように制御するのは、例えば、貸し球払出動作中に未払出個数カウンタに賞球個数が上乗せされて賞球個数を正確に管理できなくなる事態を防止するなど、払出制御に関する処理に不都合が生じないようにするためである。
In this embodiment, as described above, when it is not possible to immediately start the prize ball payout operation when the prize ball quantity command is received, the number of prize balls specified by the prize ball quantity command is immediately output. The main control communication prize ball number buffer is temporarily saved instead of being set in the counter, but such control is performed by, for example, adding the prize ball number to the unpaid quantity counter during the rental ball payout operation. This is to prevent problems in the processing relating to the payout control, such as preventing the situation where the number of winning balls can not be accurately managed.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、賞球個数受付コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する制御を行う(ステップS74320)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、シリアル通信回路380の送信レジスタに賞球個数受付コマンドを出力する処理を行う。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 performs control to transmit a winning ball number reception command to the game control microcomputer 560 (step S74320). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 performs a process of outputting an award ball number reception command to the transmission register of the serial communication circuit 380.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御コードに主制御通信終了処理を示す値「3」をセットする(ステップS74321)。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御タイマに所定値(本例では1秒)をセットする(ステップS74322)。なお、ステップS74322でセットされた値にもとづいて、賞球個数受付コマンドを送信した後、1秒経過後に賞球払出動作を完了していなければ賞球準備中コマンドが送信されることになる。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 sets the value "3" indicating the main control communication end processing in the main control communication control code (step S74321). Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets a predetermined value (one second in this example) in the main control communication control timer (step S74322). In addition, based on the value set in step S74322, after the award ball number reception command is transmitted, if the award ball payout operation has not been completed after one second has passed, the command for preparing the award ball will be transmitted.
図77は、主制御通信制御コードの値が3の場合に実行される主制御通信終了処理(ステップS744)を示すフローチャートである。主制御通信終了処理において、払出制御用CPU371は、まず、主制御通信受信バッファに受信コマンドが格納されているか否かを確認する(ステップS74401)。主制御通信受信バッファに受信コマンドが格納されていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、受信したコマンドが接続確認コマンドであるか否かを確認する(ステップS74402)。接続確認コマンドでなければ、ステップS74406に移行する。接続確認コマンドを受信していれば、払出制御用CPU371は、接続OKコマンドをセットし(ステップS74403)、主制御送信コマンド変換処理を実行する(ステップS74404)。なお、ステップS74404の主制御送信コマンド変換処理では、接続OKコマンドの下位4ビットに制御状態(払出個数異常エラーや、球切れエラー、満タンエラー、賞球エラーなどのエラー状態)をセットする処理が行われる。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、変換後の接続OKコマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する制御を行う(ステップS74405)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、シリアル通信回路380の送信レジスタに接続OKコマンドを出力する処理を行う。そして、ステップS74406に移行する。
FIG. 77 is a flowchart showing a main control communication termination process (step S744) executed when the value of the main control communication control code is 3. In the main control communication termination process, the payout control CPU 371 first confirms whether or not the reception command is stored in the main control communication reception buffer (step S74401). If the reception command is stored in the main control communication reception buffer, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether the received command is a connection confirmation command (step S74402). If it is not a connection confirmation command, it will transfer to step S74406. If the connection confirmation command has been received, the payout control CPU 371 sets a connection OK command (step S74403), and executes main control transmission command conversion processing (step S74404). In the main control transmission command conversion process of step S74404, the process of setting the control state (error state such as payout number abnormality error, ball out error, full error, award ball error, etc.) in the lower 4 bits of the connection OK command is performed. To be done. Then, the payout control CPU 371 performs control to transmit the converted connection OK command to the game control microcomputer 560 (step S74405). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 performs a process of outputting a connection OK command to the transmission register of the serial communication circuit 380. Then, the process proceeds to step S74406.
ステップS74406では、払出制御用CPU371は、エラーフラグに主制御通信エラー指定ビットをセットする。すなわち、主制御通信終了処理は、賞球個数コマンドを受信して賞球払出動作を開始した後、受信した賞球個数コマンドにもとづく賞球払出動作を終了するまで実行する処理であり、技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は賞球終了コマンドの受信待ち状態となっているのであるから、この間に遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から新たに払出制御コマンドを受信することはない筈である。それにもかかわらず、新たなコマンドを受信したということは通信状態に何らかの異常が生じたと判断することができるのであるから、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信エラー指定ビットをセットする処理を行う。
In step S74406, the payout control CPU 371 sets a main control communication error designation bit in the error flag. That is, the main control communication end process is a process that is executed until the award ball payout operation based on the received award ball count command is terminated after the award ball count command is received and the award ball payout operation is started. Since the microcomputer 560 is in a state of waiting for the reception of the award ball end command, it should not receive a new payout control command from the game control microcomputer 560 during this time. Nevertheless, the fact that a new command has been received means that it is possible to determine that some abnormality has occurred in the communication state, so the payout control CPU 371 performs processing for setting the main control communication error designation bit.
なお、払出制御用CPU371は、ステップS74406で主制御通信エラー指定ビットをセットすると、主制御通信受信バッファをクリアする。そのようにすることによって、その後の処理で受信コマンドを誤って認識して誤った処理を実行してしまう事態を防止することができる。
When the main control communication error designation bit is set in step S74406, the payout control CPU 371 clears the main control communication reception buffer. By doing so, it is possible to prevent the situation in which the received command is erroneously recognized in the subsequent process and the erroneous process is executed.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御コードに主制御通信通常処理を示す値「1」をセットする(ステップS74407)。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御タイマに所定値(本例では1050ms)をセットする(ステップS74408)。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 sets the value “1” indicating the main control communication normal processing in the main control communication control code (step S74407). Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets a predetermined value (1050 ms in this example) in the main control communication control timer (step S74408).
主制御通信受信バッファに受信コマンドがなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御タイマの値を1減算し(ステップS74409)、主制御通信制御タイマがタイムアウトしたか否かを確認する(ステップS74410)。
If there is no reception command in the main control communication reception buffer, the payout control CPU 371 subtracts 1 from the value of the main control communication control timer (step S74409), and confirms whether or not the main control communication control timer has timed out (step S74410).
主制御通信制御タイマがタイムアウトしていれば(ステップS74410のY)、賞球個数受付コマンドや賞球準備中コマンドを前回送信してから1秒以上経過したことを意味する。この場合、払出制御用CPU371は、次の賞球準備中コマンドを送信するために、賞球準備中コマンドをセットし(ステップS74411)、主制御送信コマンド変換処理を実行する(ステップS74412)。なお、ステップS74412の主制御送信コマンド変換処理では、賞球準備中コマンドの下位4ビットに制御状態(払出個数異常エラーや、球切れエラー、満タンエラー、賞球エラーなどのエラー状態)をセットする処理が行われる。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、変換後の賞球準備中コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する制御を行う(ステップS74413)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、シリアル通信回路380の送信レジスタに賞球準備中コマンドを出力する処理を行う。
If the main control communication control timer has timed out (Y in step S74410), it means that one second or more has elapsed since the award ball count reception command and the award ball preparation command were transmitted last time. In this case, the payout control CPU 371 sets a prize ball preparation command to transmit the next prize ball preparation command (step S74411), and executes main control transmission command conversion processing (step S74412). In the main control transmission command conversion process of step S74412, the control state (error states such as payout number abnormality error, ball out error, full error, prize ball error, etc.) is set in the lower 4 bits of the prize ball preparation command. Processing is performed. Then, the payout control CPU 371 performs control to transmit the converted award ball preparing command to the game control microcomputer 560 (step S74413). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 performs a process of outputting a prize ball in-provision command to the transmission register of the serial communication circuit 380.
そして、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御タイマに所定値(本例では1秒)をセットする(ステップS74414)。なお、ステップS74414でセットされた値にもとづいて、賞球準備中コマンドを送信した後、さらに1秒経過後にまだ賞球払出動作が終了していなければ次の賞球準備中コマンドが送信されることになる。
Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets a predetermined value (one second in this example) in the main control communication control timer (step S74414). Note that after transmitting the in-progress ball preparation command based on the value set in step S74414, the next in-progress ball preparation command is transmitted if the out-of-prize ball dispensing operation is not yet finished after 1 second It will be.
主制御通信制御タイマがタイムアウトしていなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグをロードし(ステップS74415)、賞球払出動作中であるか否かを確認する(ステップS74416)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグに賞球払出動作中指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する。賞球払出動作中であれば、受信した賞球個数コマンドにもとづく賞球払出動作をまだ終了していないことを意味するので、払出制御用CPU371は、そのまま処理を終了する。賞球払出動作中でなければ、受信した賞球個数コマンドにもとづく賞球払出動作を終了したことを意味する。そのため、払出制御用CPU371は、賞球終了コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する制御を行う(ステップS74417)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、シリアル通信回路380の送信レジスタに賞球終了コマンドを出力する処理を行う。
If the main control communication control timer has not timed out, the payout control CPU 371 loads a payout control status flag (step S74415), and checks whether or not the winning ball payout operation is in progress (step S74416). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the in-progress ball payout operation designated bit is set in the payout control state flag. If the award ball payout operation is being performed, it means that the award ball payout operation based on the received award ball number command has not ended yet, the payout control CPU 371 ends the process as it is. If the prize ball payout operation is not in progress, it means that the prize ball payout operation based on the received prize ball number command is ended. Therefore, the payout control CPU 371 performs control to transmit a winning ball end command to the game control microcomputer 560 (step S74417). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 performs a process of outputting a prize ball end command to the transmission register of the serial communication circuit 380.
なお、払出制御用CPU371は、ステップS74417で賞球終了コマンドを送信すると、主制御通信受信バッファをクリアする。そのようにすることによって、その後の処理で受信コマンドを誤って認識して誤った処理を実行してしまう事態を防止することができる。
When the payout control end command is transmitted in step S74417, the payout control CPU 371 clears the main control communication reception buffer. By doing so, it is possible to prevent the situation in which the received command is erroneously recognized in the subsequent process and the erroneous process is executed.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御コードに主制御通信通常処理を示す値「1」をセットする(ステップS74418)。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、主制御通信制御タイマに所定値(本例では1050ms)をセットする(ステップS74419)。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 sets the value “1” indicating the main control communication normal processing in the main control communication control code (step S74418). Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets a predetermined value (1050 ms in this example) in the main control communication control timer (step S74419).
図78は、ステップS7414,S74207,S74221,S74304,S74312,S74404,S74412で実行される主制御送信コマンド変換処理を示すフローチャートである。主制御送信コマンド変換処理において、払出制御用CPU371は、まず、エラーフラグをロードし、払出個数異常エラー指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS731)。払出個数異常エラー指定ビットがセットされていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、変換バッファの主制御通信用払出個数異常エラー出力ビット(具体的にはビット3)をセットする(ステップS732)。
FIG. 78 is a flowchart showing the main control transmission command conversion process executed in steps S7414, S74207, S74221, S74304, S74312, S74404, and S74412. In the main control transmission command conversion process, the payout control CPU 371 first loads an error flag, and checks whether or not the payout number abnormality error designation bit is set (step S731). If the payout number abnormality error designation bit is set, the payout control CPU 371 sets the payout number abnormality error output bit (specifically, bit 3) for the main control communication of the conversion buffer (step S732).
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、球切れエラー指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS733)。球切れエラー指定ビットがセットされていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、変換バッファの主制御通信用球切れ出力ビット(具体的にはビット2)をセットする(ステップS734)。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the out-of-ball error designation bit is set (step S733). If the out-of-sphere error designation bit is set, the payout control CPU 371 sets an out-of-sphere output bit (specifically, bit 2) for main control communication of the conversion buffer (step S734).
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、満タンエラー指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS735)。満タンエラー指定ビットがセットされていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、変換バッファの主制御通信用満タン出力ビット(具体的にはビット1)をセットする(ステップS736)。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the full tank error designation bit is set (step S735). If the full tank error designating bit is set, the payout control CPU 371 sets the main control communication full tank output bit (specifically, bit 1) of the conversion buffer (step S736).
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、その他の賞球エラー指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS737)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、エラーフラグに、主制御通信エラー指定ビットや、主制御未接続エラー指定ビット、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー1指定ビット、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー2指定ビット、払出ケースエラー指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する。その他の賞球エラー指定ビットがセットされていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、変換バッファの主制御通信用球切れ出力ビット(具体的にはビット0)をセットする(ステップS738)。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the other award ball error designation bit is set (step S737). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 sets an error flag to a main control communication error designation bit, a main control non-connection error designation bit, a payout switch abnormality detection error 1 designation bit, a payout switch abnormality detection error 2 designation bit, a payout Check if the case error specification bit is set. If the other prize ball error designating bit is set, the payout control CPU 371 sets a sphere out output bit (specifically, bit 0) for the main control communication of the conversion buffer (step S738).
そして、払出制御用CPU371は、送信するためにセットされている払出制御コマンド(接続OKコマンドまたは賞球準備中コマンド)に変換バッファの内容をセットする(ステップS739)。
Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets the contents of the conversion buffer in the payout control command (connection OK command or award ball preparing command) set for transmission (step S739).
図79は、ステップS755の払出制御処理を示すフローチャートである。払出制御処理において、払出制御用CPU371は、払出個数カウントスイッチ301の検出信号がオン状態となったことを確認したら(ステップS7501)、未払出個数カウンタの値が0となっているか否かを確認する(ステップS7502)。未払出個数カウンタの値が0となっていた場合には、払出制御用CPU371は、異常な払出の累積数をカウントするための払出個数異常カウンタの値を1加算する(ステップS7503)。すなわち、ステップS7502でYであるということは、未払出個数カウンタに払い出すべき未払い出し数がセットされていないのであるから、遊技球の払い出しが行われない筈であるにもかかわらず、払出動作が行われ払出個数カウントスイッチ301で遊技球の払い出しが検出された場合である。そのため、何らかの不正行為により払出動作が行われた可能性があるので、払出制御用CPU101は、払出個数異常カウンタの値を累積的に1加算する。
FIG. 79 is a flowchart showing the payout control process of step S755. In the payout control process, when the payout control CPU 371 confirms that the detection signal of the payout number counting switch 301 is turned on (step S7501), it checks whether or not the value of the unpaid number counter is 0. (Step S7502). If the value of the unpaid item counter is 0, the payout control CPU 371 adds 1 to the value of the paid item abnormality counter for counting the cumulative number of abnormal payments (step S7503). That is, "Y" in step S7502 means that the number of unpaid money to be paid out is not set in the unpaid number counter, so it is the payout operation even though the game balls should not be paid out. Is performed and the payout number counting switch 301 detects the payout of the game ball. Therefore, since there is a possibility that the payout operation has been performed due to some fraudulent action, the payout control CPU 101 cumulatively adds 1 to the value of the payout amount abnormality counter.
なお、払出個数異常カウンタは、賞球や貸し球の払い出すべき数の未払出の遊技球を超えた払出過多数と払い出すべき数の未払出の遊技球に満たなかった払出不足数とを累積的にカウントするためのカウンタである。後述するように、この実施の形態では、払出個数異常カウンタの値が所定の払出個数異常エラー判定値(本例では2000)以上となると、払出個数異常エラーが発生したと判定して、払出停止状態に制御する処理が行われる。なお、ステップS7503の処理は、払出個数異常カウンタに払出過多数を累積的にカウントする処理に相当する。
The payout amount abnormality counter includes an excessive number of payout balls exceeding the number of unpaid gaming balls to be paid out of the winning balls and the rental balls, and an insufficient number of payouts not satisfying the unpaid gaming balls of the number to be paid out. It is a counter for counting cumulatively. As described later, in this embodiment, when the value of the payout amount abnormality counter is equal to or more than a predetermined payout number abnormal error determination value (2000 in this example), it is determined that a payout number abnormal error has occurred, and the payout is stopped. Processing is performed to control the state. Note that the process of step S7503 corresponds to a process of cumulatively counting the excessive number of payouts in the payout amount abnormality counter.
なお、この実施の形態では、賞球であるか貸し球であるかを区別することなく、払出過多数と払出不足数とを払出個数異常カウンタに累積的にカウントするのであるが、賞球と貸し球のうちのいずれか一方のみを対象として、払出過多数と払出不足数とを払出個数異常カウンタに累積的にカウントするようにしてもよい。また、例えば、賞球と貸し球について、それぞれ別々のカウンタを用いて払出過多数と払出不足数とを累積的にカウントするようにしてもよい。この場合、いずれか一方のカウンタの値が所定の閾値に達したときに払出個数異常エラーと判定するようにしてもよく、両カウンタの合計値が所定の閾値に達したときに払出個数異常エラーと判定するようにしてもよい。
In this embodiment, it is counted cumulatively in the overdelivery counter and the underfunded number in the number-of-dispenses abnormal counter without discriminating whether it is a winning ball or a lending ball. The overdelivery number and the underdelivery number may be counted cumulatively in the number-of-outfalls counter, targeting only one of the lending balls. Further, for example, with regard to winning balls and rental balls, it is also possible to count the overdelivery amount and the underpayment number cumulatively using separate counters. In this case, when the value of one of the counters reaches a predetermined threshold value, it may be determined that the payout amount error has occurred, and when the total value of both counters has reached a predetermined threshold value, the payout number error has occurred. It may be determined that
また、この実施の形態では、ステップS7503において払出過多を検出したときに払出個数異常カウンタの値を1加算する場合を示したが、払出個数異常カウンタの値のカウントアップの仕方は、この実施の形態で示したものにかぎられない。例えば、逆に、払出個数異常カウンタの値から払出過多数を減算するとともに、払出不足数を払出個数異常カウンタの値に加算するようにしてもよい。この場合、払出制御用CPU371は、例えば、電源投入時の初期設定処理において払出個数異常カウンタに初期値として「2000」をセットするとともに、ステップS7503において、払出個数異常カウンタの値を1減算するようにし、後述するステップS75320,S75325,S75335において払出個数異常カウンタの値に払出不足数に相当する値を加算するようにすればよい。そして、例えば、後述するステップS7504,S75321,S7725の処理では、払出個数異常カウンタの値が2000以下となっていることにもとづいて、払出個数異常エラーが発生したと判定するようにしてもよい。
Further, in this embodiment, the case where the value of the payout amount abnormality counter is incremented by one when the excessive amount of payout is detected in step S7503 is shown, but the method of counting up the value of the payout number abnormality counter is described in this embodiment. It is not limited to what is shown in the form. For example, conversely, the excess payout number may be subtracted from the value of the payout amount abnormality counter, and the payout shortage number may be added to the value of the payout number abnormality counter. In this case, the payout control CPU 371 sets, for example, “2000” as an initial value to the payout amount abnormality counter in the initialization processing at power on, and subtracts 1 from the value of the payout number abnormality counter in step S7503. Then, in steps S75320, S75325, and S75335 described later, a value corresponding to the insufficient number of payouts may be added to the value of the payout amount abnormality counter. Then, for example, in the processing of steps S7504, S75321, and S7725 described later, it may be determined that a payout amount abnormality error has occurred, based on the value of the payout amount abnormality counter being 2000 or less.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、加算後の払出個数異常カウンタの値が所定の払出個数異常エラー判定値(例えば2000)以上となったか否かを確認する(ステップS7504)。所定の払出個数異常エラー判定値(例えば2000)以上となっていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、払出個数異常エラーが発生したと判断し、払出個数異常エラーが発生したことを示す払出個数異常エラーフラグをセットする(ステップS7505)。すなわち、この実施の形態では、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370側で異常な払出の検出数を累積的に管理し、その累積値が所定の払出個数異常エラー判定値(例えば2000)以上となれば、何らかの不正行為により払出動作が行われている可能性が極めて高いと判断して、払出個数異常エラー(払い出された遊技球数が異常である旨のエラー)が発生したと判定される。なお、誤動作などにより遊技球が過剰に払い出されたり払出不足が生じたりすることも少なからずあるので、払出数の異常を検出したときに直ちに払出個数異常エラーと判定してしまったのでは、払出個数異常エラーと判定される頻度が必要以上に高くなり却って遊技に支障を生じてしまう。そこで、この実施の形態では、異常な払出の検出数を累積的に管理し、その累積値が所定の払出個数異常エラー判定値(例えば2000)以上となったことを条件として払出個数異常エラーと判定するようにすることによって、必要以上に払出個数異常エラーと判定されることを防止している。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 checks whether or not the value of the payout amount abnormality counter after the addition is equal to or greater than a predetermined payout number abnormality error determination value (for example, 2000) (step S7504). If the payout amount abnormality error determination value (for example, 2000) or more, the payout control CPU 371 determines that a payout amount abnormality error has occurred, and indicates that a payout amount abnormality error has occurred. A flag is set (step S7505). That is, in this embodiment, the number of abnormal payout detections is cumulatively managed on the payout control microcomputer 370 side, and if the cumulative value becomes equal to or greater than a predetermined payout number abnormality error determination value (for example, 2000), It is determined that there is a very high possibility that the payout operation is being performed due to some fraudulent act, and it is determined that a payout number abnormality error (error indicating that the number of game balls paid out is abnormal) has occurred. It should be noted that there are not a few cases in which game balls are excessively paid out or insufficiently paid out due to a malfunction etc. Therefore, if an abnormality in the number of payouts is detected, it is immediately judged as an error in the number of payouts. The frequency with which it is determined that the payout amount abnormality error is higher than necessary, which in turn causes trouble in the game. Therefore, in this embodiment, the detected number of abnormal payouts is cumulatively managed, and the payout number abnormal error is determined on the condition that the accumulated value becomes equal to or more than a predetermined payout number abnormal error judgment value (for example, 2000). By making the determination, it is prevented that it is determined that the payout amount abnormality error is more than necessary.
なお、この実施の形態では、払出個数異常エラーと判定されて払出個数異常エラーフラグが一度セットされると、電源リセットされるまで払出個数異常エラーフラグはクリアされず払出個数異常エラーから復旧しないので、払出個数異常エラーフラグがセットされると、以降、ステップS7504,S7505の処理や後述するS75321,S75322、S7725,S7726の処理は実行しないようにしてもよい。そのようにすれば、払出個数異常エラーと一度判定してしまった後の無駄な処理を防止し処理負担を軽減することができる。
In this embodiment, if it is determined that the payout amount abnormality error and the payout amount abnormality error flag is set once, the payout amount abnormality error flag is not cleared until the power is reset, and the payout number abnormality error is not recovered. After the payout amount abnormality error flag is set, the processes of steps S7504 and S7505 and the processes of S75321, S75322, S7725, and S7726 described later may not be performed. By doing so, it is possible to prevent unnecessary processing after determining once that the error is a dispensing number error, and to reduce the processing load.
また、この実施の形態では、所定の払出個数異常エラー判定値として、一般に、遊技店で用いられる遊技球の収納箱(いわゆるドル箱)に収納可能な遊技球の数に相当する「2000」を用いる場合を示しているが、所定の払出個数異常エラー判定値として他の値(例えば、1000や3000)を用いてもよい。
Further, in this embodiment, "2000", which corresponds to the number of gaming balls that can be stored in a gaming ball storage box (so-called dollar box) generally used in a game arcade, is generally used as the predetermined payout number abnormality error determination value. Although the case where it uses is shown, you may use another value (for example, 1000 or 3000) as a predetermined | prescribed number-of-payouts abnormal error judgment value.
なお、この実施の形態では、図79に示す払出制御処理は、賞球払出動作を実行するときと貸し球払出動作を実行するときとで共通に実行される処理であり、未払出個数カウンタは、賞球による未払出の遊技球数をカウントするときと貸し球による未払出の遊技球数をカウントするときとで共通に用いられるカウンタである。そして、払出個数の異常を検出した場合には、賞球による払出と貸し球による払出とを区別することなく払出個数異常カウンタの値がカウントアップされ、払出個数異常エラーが発生したか否かの判定が行われる。
In this embodiment, the payout control process shown in FIG. 79 is a process commonly executed when executing the winning ball payout operation and when performing the rental ball payout operation, and the unpaid item counter is The counter is used in common when counting the number of unpaid gaming balls by the winning balls and when counting the number of unpaid gaming balls by the rental balls. Then, when an abnormality in the number of dispensed pieces is detected, the value of the number-of-discounted-portions abnormal counter is counted up without distinguishing between the dispensing by the winning balls and the dispensing by the rental balls A determination is made.
未払出個数カウンタの値が0でなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、未払出個数カウンタの値を1減算し(ステップS7506)、払出制御状態のフラグに払出球検知指定ビット(遊技球の払い出しを検出したことを示すビット)をセットする(ステップS7507)。なお、払出球検知指定ビットは、払出個数カウントスイッチ301がオンしたときにセットされるビットであり、払出動作中に払出個数カウントスイッチ301が少なくとも1個の遊技球を検出したことを示すビットである。
If the value of the unpaid item counter is not 0, the payout control CPU 371 subtracts 1 from the value of the unpaid item counter (step S7506), and the payout ball detection designating bit (disbursement of gaming ball is made to the flag of the payout control state A bit indicating that it has been detected is set (step S7507). The payout ball detection designation bit is a bit set when the payout number count switch 301 is turned on, and is a bit indicating that the payout number count switch 301 has detected at least one gaming ball during the payout operation. is there.
その後、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御コードの値に応じてステップS7511〜S7513のいずれかの処理を実行する。
Thereafter, the payout control CPU 371 executes one of the processes in steps S7511 to S7513 in accordance with the value of the payout control code.
図80は、払出制御コードが0の場合に実行される払出開始待ち処理(ステップS7511)を示すフローチャートである。払出開始待ち処理において、払出制御用CPU371は、まず、エラーフラグの値が0であるか否かを確認する(ステップS75101)。そして、エラービット(エラーフラグにおける全てのエラービットのうちの1つ以上)がセットされていたら、払出制御用CPU371は、以降の処理を実行しないように制御する。なお、この実施の形態では、ステップS75101の処理が実行されることによって、払出個数異常エラーと判定されてエラービットの払出個数異常エラー指定ビットがセットされていることにもとづいて、ステップS75102以降の処理に移行しないように制御され、払出停止状態に制御される。
FIG. 80 is a flowchart showing a payout start waiting process (step S7511) that is executed when the payout control code is 0. In the payout start waiting process, the payout control CPU 371 first confirms whether the value of the error flag is 0 or not (step S75101). Then, if the error bit (one or more of all the error bits in the error flag) is set, the payout control CPU 371 controls not to execute the subsequent processing. In this embodiment, the processing in step S75101 is executed to determine that the payout amount abnormality error has occurred, and based on the fact that the payout number abnormality error designating bit for the error bit is set, step S75102 and subsequent steps are performed. It is controlled not to shift to processing, and is controlled to be in the dispensing stop state.
エラーフラグの値が0であれば、払出制御用CPU371は、BRDY信号を入力しているか否かを確認する(ステップS75102)。BRDY信号を入力していれば、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグをロードし(ステップS75103)、球貸し要求中であるか否かを確認する(ステップS75104)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグに球貸し要求中指定ビット(球貸し要求中であることを示すビット)がセットされているか否かを確認する。なお、払出制御用CPU371は、BRQ信号を入力しているか否かを確認することによって、球貸し要求中であるか否かを判定するようにしてもよい。球貸し要求中であれば(すなわち、球貸し払出動作を開始する場合)、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグの球貸し要求中指定ビットをリセットする(ステップS75105)とともに、払出制御状態フラグの球貸し払出動作中指定ビットをセットする(ステップS75106)。次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、未払出個数カウンタに所定の球貸し個数(本例では25)をセットする(ステップS75107)とともに、払出モータ回転回数バッファに所定の球貸し個数(本例では25)をセットする(ステップS75108)。そして、ステップS75113に移行する。
If the value of the error flag is 0, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the BRDY signal is input (step S75102). If the BRDY signal is input, the payout control CPU 371 loads a payout control state flag (step S75103), and confirms whether or not ball lending is requested (step S75104). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 checks whether or not the ball lending request flag (a bit indicating that a ball lending request is in progress) is set in the payout control state flag. Note that the payout control CPU 371 may determine whether or not the ball lending request is being made by confirming whether or not the BRQ signal is input. If the ball lending request is being made (that is, if the ball lending payout operation is started), the payout control CPU 371 resets the ball lending request during designation bit of the payout control status flag (step S75105), and the payout control status flag During the ball lending and dispensing operation, the designated bit is set (step S75106). Next, the payout control CPU 371 sets a predetermined number of ball lends (25 in this example) in the unpaid quantity counter (step S75107) and a predetermined number of ball lends (25 in this example) in the payout motor rotation number buffer. Is set (step S75108). Then, the process proceeds to step S75113.
なお、払出モータ回転回数バッファは、払出モータ制御処理(ステップS756)において参照される。すなわち、払出モータ制御処理では、払出モータ回転回数バッファにセットされた値に対応した回転数分だけ払出モータ289を回転させる制御が実行される。
The payout motor rotation number buffer is referred to in the payout motor control process (step S756). That is, in the payout motor control process, control is performed to rotate the payout motor 289 by the number of rotations corresponding to the value set in the payout motor rotation number buffer.
BRDY信号を入力していなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、未払出個数カウンタの値が0であるか否かを確認する(ステップS75109)。未払出個数カウンタの値が0でなければ(すなわち、賞球払出動作を開始する場合)、払出制御用CPU371は、払出モータ回転回数バッファに未払出個数カウンタの値をセットする(ステップS75110)。すなわち、この場合、未払出個数カウンタには、受信した賞球個数コマンドで指定された賞球個数がセットされている筈であるから(ステップS74214,S74319参照)、賞球払出動作を開始するために、賞球個数を払出モータ回転回数バッファにセットする処理を行う。次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグをロードし(ステップS75111)、払出制御状態フラグに賞球払出動作中指定ビットをセットする(ステップS75112)。そして、ステップS75113に移行する。
If the BRDY signal has not been input, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether the value of the unpaid item counter is 0 or not (step S75109). If the value of the unpaid piece counter is not 0 (that is, when the winning balls payout operation is started), the payout control CPU 371 sets the value of the unpaid piece counter in the payout motor rotation number buffer (step S75110). That is, in this case, since the number of winning balls specified by the received winning balls number command is set in the unpaid number counter (see steps S74214 and S74319), the winning balls paying-out operation is started. And the number of winning balls is set in the payout motor rotation frequency buffer. Next, the payout control CPU 371 loads a payout control state flag (step S75111), and sets a prize ball payout in-operation designation bit to the payout control state flag (step S75112). Then, the process proceeds to step S75113.
ステップS75113では、払出制御用CPU371は、払出モータ制御処理で実行される処理を選択するための払出モータ制御コードに、払出モータ起動処理に応じて値をセットする。これにより、ステップS756の払出モータ制御処理において、払出モータ289を起動する払出モータ起動処理が実行され、貸し球払出動作または賞球払出動作が開始される。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御コードに払出モータ停止待ち処理を示す値「1」をセットし(ステップS75114)、処理を終了する。
In step S75113, the payout control CPU 371 sets a value to the payout motor control code for selecting the process to be executed in the payout motor control process according to the payout motor activation process. Thereby, in the payout motor control process of step S756, a payout motor activation process for starting the payout motor 289 is executed, and a rental ball payout operation or a winning ball payout operation is started. Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets the value “1” indicating the payout motor stop waiting process in the payout control code (step S75114), and ends the process.
図81は、払出制御コードが1の場合に実行される払出モータ停止待ち処理(ステップS7512)を示すフローチャートである。払出モータ停止待ち処理において、払出制御用CPU371は、まず、払出制御状態フラグをロードし(ステップS7521)、払出動作が終了したか否かを確認する(ステップS7522)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグに払出動作終了指定ビット(払出動作を終了したことを示すビット)がセットされているか否かを確認する。なお、払出動作終了指定ビットは、図69に示すステップS756の払出モータ制御処理における払出モータブレーキ処理や払出モータ球噛み解除処理においてセットされる。
FIG. 81 is a flowchart showing a payout motor stop waiting process (step S7512) executed when the payout control code is 1. In the payout motor stop waiting process, the payout control CPU 371 first loads a payout control state flag (step S7521), and checks whether the payout operation has ended (step S7522). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the payout operation end designation bit (a bit indicating that the payout operation has ended) is set in the payout control state flag. The payout operation end designation bit is set in the payout motor brake processing and the payout motor ball biting cancellation processing in the payout motor control processing of step S756 shown in FIG.
なお、払出モータ制御処理では、払出制御用CPU371は、払出モータ制御コードの値に応じて、払出モータ通常処理(ポインタをROMに格納されているテーブルの先頭アドレスにセットする等の処理)、払出モータ起動処理(出力ポート0の出力状態に対応したポート0バッファのビット4〜7に励磁パターンの初期値を設定する等の処理)、払出モータスローアップ処理(払出モータ289を滑らかに回転開始させるために、定速処理の場合よりも長い間隔で、かつ、徐々に定速処理の場合の時間間隔に近づくような時間間隔で、払出モータ励磁パターンテーブルの内容を読み出して出力ポート0の出力状態に対応したポート0バッファのビット4〜7に設定する等の処理)、払出モータ定速処理(定期的に払出モータ励磁パターンテーブルの内容を読み出して出力ポート0の出力状態に対応したポート0バッファのビット4〜7に設定する等の処理)、払出モータブレーキ処理(払出モータ289を滑らかに停止させるために、定速処理の場合よりも長い間隔で、かつ、徐々に定速処理の場合の時間間隔から遠ざかるような時間間隔で、払出モータ励磁パターンテーブルの内容を読み出して出力ポート0の出力状態に対応したポート0バッファのビット4〜7に設定する等の処理)、払出モータ球噛み処理(球噛み状態を検出した場合に、球噛みを解除するために、払出モータ励磁パターンテーブルの内容を読み出して出力ポート0の出力状態に対応したポート0バッファのビット4〜7に設定する処理)、および払出モータ球噛み解除処理(球噛み状態が解除されたときに払出モータ通常処理に移行して通常のモータ制御状態に復帰する処理)のいずれかの処理を実行する。
In the payout motor control process, the payout control CPU 371 executes a payout motor normal process (a process of setting the pointer to the top address of the table stored in the ROM, etc.) according to the value of the payout motor control code, and the payout. Motor start processing (processing to set the initial value of the excitation pattern to bits 4 to 7 of the port 0 buffer corresponding to the output state of output port 0, etc.), and payout motor slow-up processing (smoothly start the payout motor 289 to rotate) Therefore, the content of the payout motor excitation pattern table is read at a longer interval than in the case of constant speed processing and at a time interval gradually approaching the time interval in the case of constant speed processing, and the output state of output port 0 Processing such as setting to bits 4 to 7 of the port 0 buffer corresponding to the above), dispensing motor constant speed processing (periodically dispensing motor excitation pattern Processing such as reading out the contents of the table and setting to bits 4 to 7 of the port 0 buffer corresponding to the output state of the output port 0), dispensing motor brake processing (constant speed processing to smoothly stop the dispensing motor 289) The contents of the payout motor excitation pattern table are read out at a longer interval than in the case of, and at a time interval gradually getting away from the time interval in the case of constant speed processing, and the port 0 buffer corresponding to the output state of the output port 0 Of the bit 4 to 7 of the bit), dispensing motor ball bit processing (when the ball biting state is detected, the content of the dispensing motor excitation pattern table is read out to release the ball biting, and the output port 0 Processing to set to bits 4 to 7 of the port 0 buffer corresponding to the output state, and dispensation motor ball bite cancellation processing (when the ball biting state is cancelled) Either processing shifts to the payout motor normal processing process returns to the normal motor control state) execution.
払出動作を終了していれば、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグの払出動作終了指定ビットをリセットする(ステップS7523)とともに、後述する払出通過監視時間などをセットするために用いる払出モータ停止待ち処理設定テーブル2をセットする(ステップS7524)。
If the dispensing operation has been completed, the dispensing control CPU 371 resets the dispensing operation end designation bit of the dispensing control status flag (step S 7523) and stops the dispensing motor used to set the dispensing passage monitoring time described later, etc. The waiting process setting table 2 is set (step S 7524).
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグに払出球数検査済み指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS7525)。払出球数検査済み指定ビットは、払出モータ289による払出動作終了時(正常動作の終了時)に払出個数カウントスイッチ301による検出の判定を行ったことを示すビットである。払出球数検査済み指定ビットがセットされていれば、ステップS7527に移行する。払出球数検査済み指定ビットがセットされていなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、払出モータ停止待ち処理設定テーブルをセットする(ステップS7526)。すなわち、払出制御用CPU371は、ステップS7524でセットしたテーブルを払出モータ停止待ち処理設定テーブルに差し替える。そして、ステップS7527に移行する。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the payout ball number inspection designated bit is set in the payout control state flag (step S7525). The dispensing ball number inspection designated bit is a bit indicating that the determination of the detection by the dispensing number counting switch 301 is performed at the end of the dispensing operation by the dispensing motor 289 (at the end of the normal operation). If the payout ball number inspection designated bit is set, the process proceeds to step S7527. If the payout ball number inspection designated bit is not set, the payout control CPU 371 sets a payout motor stop waiting process setting table (step S7526). That is, the payout control CPU 371 replaces the table set in step S 7524 with the payout motor stop waiting process setting table. Then, the process proceeds to step S7527.
ステップS7527では、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御コードに払出通過待ち処理を示す値「2」をセットする。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、ステップS7524,S7526でセットしたテーブルにもとづいて、払出制御タイマに払出通過監視時間をセットする(ステップS7527)。払出通過監視時間は、最後の払出球が払出モータ289によって払い出されてから払出個数カウントスイッチ301を通過するまでの時間に、余裕を持たせた時間である。この実施の形態では、ステップS7525で払出球数検査済みビットがセットされていた場合には、ステップS7524でセットした払出モータ停止待ち処理設定テーブル2にもとづいて、払出通過監視時間として1秒をセットする。また、ステップS7525で払出球数検査済みビットがセットされていなかった場合には、ステップS7526で差し替えた払出モータ停止待ち処理設定テーブルにもとづいて、払出通過監視時間として0.6秒をセットする。
In step S7527, the payout control CPU 371 sets the value “2” indicating the payout passage waiting process in the payout control code. Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets the payout passage monitoring time in the payout control timer based on the table set in steps S7524, S7526 (step S7527). The payout passage monitoring time is a time in which the time from the last payout ball being paid out by the payout motor 289 to the time when it passes through the number-of-discounted-pieces count switch 301 has a margin. In this embodiment, if the number-of-dispensed-balls-number-tested bit is set in step S7525, 1 second is set as the dispensing passage monitoring time based on the dispensing motor stop waiting process setting table 2 set in step S7524. Do. If it is determined in step S7525 that the ball-out-inspected bit has not been set yet, 0.6 seconds is set as the payout passage monitoring time based on the payout motor stop waiting process setting table replaced in step S7526.
図82〜図84は、払出制御コードの値が2の場合に実行される払出通過待ち処理(ステップS7513)を示すフローチャートである。払出通過待ち処理において、払出制御用CPU371は、まず、払出制御タイマの値を確認し(ステップS75301)、その値が0になっていれば、ステップS75304に移行する。払出制御タイマの値が0でなければ、払出制御タイマの値を−1する(ステップS75302)。そして、払出制御タイマの値が0になっていなければ(ステップS75303)、すなわち払出制御タイマがタイムアウトしていなければ処理を終了する。
82 to 84 are flowcharts showing a payout passage waiting process (step S7513) that is executed when the value of the payout control code is 2. In the payout passage waiting process, the payout control CPU 371 first confirms the value of the payout control timer (step S75301). If the value is 0, the process shifts to step S75304. If the value of the payout control timer is not 0, the value of the payout control timer is decremented by 1 (step S75302). Then, if the value of the payout control timer is not 0 (step S75303), that is, if the payout control timer has not timed out, the processing ends.
払出制御タイマがタイムアウトしていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、エラーフラグをロードし、払出個数異常エラー指定ビット、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー1指定ビット、または払出スイッチ異常検知エラー2指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS75304)。払出個数異常エラー指定ビット、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー1指定ビット、または払出スイッチ異常検知エラー2指定ビットのいずれかがセットされていれば、払出動作をこれ以上継続できないと判断して、ステップS75306に移行する。払出個数異常エラー指定ビット、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー1指定ビット、および払出スイッチ異常検知エラー2指定ビットのいずれもセットされていなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、未払出個数カウンタの値が0となっているか否かを確認する(ステップS75305)。未払出個数カウンタの値が0となっていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、正常に払出動作が終了したとして、払出制御状態フラグをロードし(ステップS75306)、払出制御状態フラグの球貸し要求中指定ビットおよび払出動作終了指定ビット以外のビットをリセットする(ステップS75307)。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御コードに払出開始待ち処理を示す値「0」をセットし(ステップS75308)、処理を終了する。
If the payout control timer has timed out, the payout control CPU 371 loads an error flag, and the number-of-dispensing error designation bit, the payout switch abnormality detection error 1 designation bit, or the payout switch abnormality detection error 2 designation bit is set. Whether or not it is confirmed (step S75304). If any of the number-of-dispenses abnormality error specification bit, the distribution switch abnormality detection error 1 specification bit, or the distribution switch abnormality detection error 2 specification bit is set, it is determined that the dispensing operation can not be continued any more, and the process proceeds to step S75306. Transition. The payout control CPU 371 determines that the value of the number-of-unpaid-pieces counter is 0 if none of the payout number abnormal error designation bit, the payout switch abnormality detection error 1 designation bit, and the payout switch abnormality detection error 2 designation bit is set. Whether or not it is confirmed (step S75305). If the value of the unpaid item number counter is 0, the payout control CPU 371 assumes that the payout operation has ended normally, loads the payout control status flag (step S75306), and requests a ball lending of the payout control status flag. The bits other than the designated bit and the payout operation end designated bit are reset (step S75307). Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets the value “0” indicating the payout start waiting process in the payout control code (step S75308), and ends the process.
未払出個数カウンタの値が0となっていなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、エラーフラグをロードし、球切れエラー指定ビットまたは満タンエラー指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS75309)。球切れエラー指定ビットまたは満タンエラー指定ビットがセットされていれば、そのまま処理を終了する。球切れエラー指定ビットおよび満タンエラー指定ビットのいずれもセットされていなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、エラーフラグに払出ケースエラー指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS75310)。払出ケースエラー指定ビットがセットされていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグをロードして(ステップS75311)、払出制御状態フラグに払出球数検査済み指定ビットをセットする(ステップS75312)。また、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグの再払出動作中1指定ビット(1回目の再払出動作の実行を示すビット)と再払出動作中2指定ビット(2回目の再払出動作の実行を示すビット)をリセットし(ステップS75313)、処理を終了する。
If the value of the unpaid piece counter is not 0, the payout control CPU 371 loads an error flag, and checks whether the out-of-ball error designation bit or the full-part error designation bit is set (step S75309). . If the ball out error specification bit or the full error specification bit is set, the processing ends. If neither the out-of-ball error designation bit nor the full-tank error designation bit is set, the payout control CPU 371 checks whether the payout case error designation bit is set in the error flag (step S75310). If the payout case error designation bit is set, the payout control CPU 371 loads the payout control status flag (step S75311), and sets the payout ball number checked designated bit in the payout control status flag (step S75312). . Further, the payout control CPU 371 executes 1 designation bit during repayment operation of the payout control status flag (bit indicating execution of the first repayment operation) and 2 designation bit during repayment operation (execution of the second repayment operation) Is reset (step S75313), and the process ends.
なお、払出球数検査済み指定ビットは、払出モータ289による払出動作終了時(正常動作の終了時)に払出個数カウントスイッチ301による検出の判定を行ったことを示すビットである。なお、払出動作を終了したにもかかわらず、未払出個数カウンタの値が2以上残っている場合には、払出個数異常カウンタにその残数が加算される。また、払出動作終了時の払出個数カウントスイッチ301による検出の判定は、払出動作を1回実行するごとに1回のみ実行され、払出モータ球噛み処理や払出モータ球噛み解除処理を実行して球噛み動作を終了するときには実行しない(具体的には、球噛み状態では払出ケースエラー指定ビットがセットされるので、ステップS75312であらかじめ払出球数検査済み指定ビットがセットされることによって、球噛み動作を終了しても払出個数カウントスイッチ301による検出の判定を行わない)ように制御される。なお、払出球数検査済み指定ビットは、払出モータ制御処理内における払出モータ定速処理で満タン状態となったときにもセットされる。
The payout ball number inspection designated bit is a bit indicating that the detection by the payout number counting switch 301 has been performed at the end of the payout operation by the payout motor 289 (at the end of the normal operation). If the value of the unpaid-number counter remains 2 or more despite the fact that the dispensing operation has ended, the remaining number is added to the number-of-dispensed-abnormality counter. In addition, the determination of detection by the dispensing number counting switch 301 at the end of the dispensing operation is performed only once each time the dispensing operation is performed, and the dispensing motor ball bit processing and the dispensing motor ball bit releasing processing are performed to execute the ball processing. The bit is not executed when the bit operation is finished (specifically, since the payout case error designating bit is set in the ball bit state, the ball bit examining operation designated bit is set in advance in step S75312). Control is performed so that the determination of the detection by the payout number counting switch 301 is not performed. The payout ball number inspection designated bit is also set when the dispensing motor control process is full in the dispensing motor constant speed processing.
ステップS75310で払出ケースエラー指定ビットもセットされていなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグをロードし(ステップS75314)、ステップS75315以降の再払出処理を実行するための処理を行う。
If the payout case error designation bit is not set in step S75310, the payout control CPU 371 loads a payout control state flag (step S75314), and performs processing for executing the repayment process from step S75315.
再払出処理を実行するために、払出制御用CPU371は、まず、払出制御状態フラグの再払出動作中2指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS75315)。セットされていなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグの再払出動作中1指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS75316)。再払出動作中1指定ビットもセットされていなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、初回の再払出動作を実行するために、払出制御状態フラグに再払出動作中1指定ビットをセットする(ステップS75317)。
In order to execute the repayment process, the payout control CPU 371 first confirms whether or not the 2 designated bits are set during the repayment operation of the payout control state flag (step S75315). If it is not set, the payout control CPU 371 checks whether or not the 1-designated bit is set during the repayment operation of the payout control state flag (step S75316). During the repayment operation, if the 1 designation bit is not set either, the payout control CPU 371 sets the repayment operation in progress flag to the 1 selection bit in order to execute the first repayment operation (step S75317). .
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグに払出球数検査済み指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS75318)。払出球数検査済み指定ビットがセットされていれば、ステップS75326に移行する。払出球数検査済み指定ビットがセットされていなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、未払出個数カウンタの値が2以上であるか否かを確認する(ステップS75319)。未払出個数カウンタの値が2以上でなければ、ステップS75326に移行する。未払出個数カウンタの値が2以上であれば、払出制御用CPU371は、払出個数異常カウンタに未払個数カウンタの値を加算する(ステップS75320)。なお、ステップS75320の処理は、払出個数異常カウンタに払出不足数を累積的にカウントする処理に相当する。次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、加算後の払出個数異常カウンタの値が所定の払出個数異常エラー判定値(例えば2000)以上となったか否かを確認する(ステップS75321)。所定の払出個数異常エラー判定値(例えば2000)以上となっていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、払出個数異常エラーが発生したと判断し、払出個数異常エラーが発生したことを示す払出個数異常エラーフラグをセットする(ステップS75322)。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the payout ball number inspection designated bit is set in the payout control state flag (step S75318). If the payout ball number inspection designated bit is set, the process proceeds to step S75326. If the payout ball number inspection designated bit is not set, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the value of the unpaid number counter is 2 or more (step S75319). If the value of the unpaid item number counter is not 2 or more, the process proceeds to step S75326. If the value of the unpaid item counter is 2 or more, the payout control CPU 371 adds the value of the unpaid item counter to the paid item abnormality counter (step S75320). Note that the process of step S75320 corresponds to a process of cumulatively counting the insufficient number of payouts in the payout amount abnormality counter. Next, the payout control CPU 371 checks whether or not the value of the payout amount abnormality counter after the addition is equal to or greater than a predetermined payout number abnormality error determination value (for example, 2000) (step S75321). If the payout amount abnormality error determination value (for example, 2000) or more, the payout control CPU 371 determines that a payout amount abnormality error has occurred, and indicates that a payout amount abnormality error has occurred. A flag is set (step S75322).
なお、この実施の形態では、ステップS75319の処理により、払出動作を終了したにもかかわらず、未払出個数カウンタの値が所定基準数(本例では2)以上残っていることを条件として、払出個数異常カウンタに未払出個数カウンタの値を加算する。すなわち、誤動作などにより、払出動作を終了したにもかかわらず、未払出個数カウンタの値がごく少数(本例では1)残った状態となることも少なからずあるので、払出動作を終了したときに未払出個数カウンタの値が1つでも残っているときに直ちに払出個数異常カウンタに累積カウントとしてしまったのでは、払出個数異常エラーと判定される頻度が必要以上に高くなり却って遊技に支障を生じてしまう。そこで、この実施の形態では、少し余裕をもたせて未払出個数カウンタの値が2以上残っていることを条件として、払出個数異常カウンタに累積カウントすることとし、必要以上に払出個数異常エラーと判定されることを防止している。なお、ステップS75319の処理では、払出不足数が所定基準数(本例では2)以上であることを条件に払出個数異常カウンタを累積的にカウントアップする場合を示しているが、払出過多数についても所定基準数(本例では2)以上であることを条件に払出個数異常カウンタを累積的にカウントアップするようにしてもよい。この場合、例えば、図79に示すステップS7502でYと判定した回数が累積して2回以上に達したことを条件にステップS7503で払出過多数分のカウント値を払出個数異常カウンタを累積的にカウントアップするようにすればよい。また、ステップS75319,S75320の処理において、未払出個数カウンタの値が所定基準数(本例では2)以上残っているか否かにかかわらず、必ず払出個数異常カウンタに未払出個数カウンタの値をそのまま加算するようにしてもよい。
In this embodiment, although the payout operation is ended by the process of step S75319, the payout is performed under the condition that the value of the unpaid number counter remains equal to or more than a predetermined reference number (2 in this example). The value of the unpaid item counter is added to the item abnormality counter. That is, even though the dispensing operation is ended due to a malfunction or the like, the value of the unpaid piece counter may be left in a very small number (1 in this example). If the number of unpaid pieces is still counted as an accumulated count immediately when the value of the unpaid pieces counter is left as it is, the frequency determined as the number of paid out defects error becomes higher than necessary, causing trouble in the game. It will Therefore, in this embodiment, it is determined that the payout amount abnormality counter is cumulatively counted on the condition that the value of the undisbursed number counter remains with a slight margin with a slight margin, and the dispensed number abnormality error is determined more than necessary. To prevent being done. Although the process in step S75319 shows the case where the payout amount abnormality counter is counted up cumulatively on condition that the number of underpayments is equal to or more than the predetermined reference number (2 in this example), the number of overdelivery is large. Alternatively, the payout amount abnormality counter may be counted up cumulatively on condition that the predetermined reference number (2 in this example) or more is exceeded. In this case, for example, on the condition that the number of times determined as Y in step S7502 shown in FIG. 79 has accumulated and reached two or more, the count value for the overdelivery amount in step S7503 is accumulated It is sufficient to count up. In the processes of steps S75319 and S75320, the value of the unpaid item counter is always left as it is in the paid-out item abnormality counter regardless of whether the value of the unpaid item counter remains equal to or greater than a predetermined reference number (2 in this example). It may be added.
ステップS75316で再払出動作中1指定ビットがセットされていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグに払出球検知指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS75323)。払出球検知指定ビットがセットされていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、ステップS75326に移行する。払出球検知指定ビットがセットされていなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、2回目の再払出動作を実行するために、払出制御状態フラグに再払出動作中2指定ビットをセットする(ステップS75324)とともに、払出個数異常カウンタの値を1加算する(ステップS75325)。なお、ステップS75325の処理は、払出個数異常カウンタに払出不足数を累積的にカウントする処理に相当する。そして、ステップS75326に移行する。なお、ステップS75325の処理を実行することによって、1回目の再払出動作を実行したにもかかわらず、再払出動作が正常に行われなかった場合に、払出個数異常カウンタの値が1カウントアップされる。また、正常に払出が完了した場合でも、誤カウントなどにより未払出個数カウンタの値が0になっていいないこともある。そこで、ステップS75323の処理が実行されることによって、払出球検知指定ビットがセットされていれば、すなわち払出個数カウントスイッチ301が払出動作中に少なくとも1個の遊技球の払出を検出していれば、正常に払出が完了している可能性があるので、払出個数異常カウンタの累積カウントを行うことなく、そのままステップS75326に移行する。
If it is determined in step S75316 that the 1-designation bit is set during the repayment operation, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the payout ball detection designation bit is set in the payout control state flag (step S75323). If the payout ball detection designation bit is set, the payout control CPU 371 proceeds to step S75326. If the payout ball detection designation bit is not set, the payout control CPU 371 sets the 2 designation bit during repayment operation in the payout control status flag to execute the second repayment operation (step S75324). Then, the value of the payout amount abnormality counter is incremented by 1 (step S75325). Note that the process of step S75325 corresponds to a process of cumulatively counting the number of underpayments in the payout amount abnormality counter. Then, the process proceeds to step S75326. By executing the processing of step S75325, the value of the payout amount abnormality counter is incremented by one when the repayment operation is not normally performed although the first repayment operation is performed. Ru. In addition, even when the payout is normally completed, the value of the unpaid item counter may not be 0 due to an erroneous count or the like. Therefore, if the payout ball detection designation bit is set by executing the process of step S75323, that is, if the payout number counting switch 301 detects the payout of at least one gaming ball during the payout operation. Since there is a possibility that the payout is normally completed, the process directly proceeds to step S75326 without performing the cumulative count of the payout amount abnormality counter.
ステップS75326では、払出制御用CPU371は、初回の再払出動作を実行するために、再払出動作個数として1をセットする。次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、払出モータ回転回数バッファに再払出動作個数(本例では1)をセットする(ステップS75327)。次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグをロードし(ステップS75328)、払出制御状態フラグの払出球検知指定ビットをリセットする(ステップ75329)。
In step S75326, the payout control CPU 371 sets 1 as the number of repayment operations in order to execute the first repayment operation. Next, the payout control CPU 371 sets the number of repayment operations (1 in this example) in the payout motor rotation number buffer (step S75327). Next, the payout control CPU 371 loads the payout control state flag (step S75328), and resets the payout ball detection designation bit of the payout control state flag (step 75329).
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、払出モータ制御処理で実行される処理を選択するための払出モータ制御コードに、払出モータ起動処理に応じて値をセットする(ステップS75330)。これにより、ステップS756の払出モータ制御処理において、払出モータ289を起動する払出モータ起動処理が実行され、再払出動作が開始される。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御コードに払出モータ停止待ち処理を示す値「1」をセットし(ステップS75331)、処理を終了する。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 sets a value to the payout motor control code for selecting the process to be executed in the payout motor control process according to the payout motor activation process (step S75330). As a result, in the payout motor control process of step S756, a payout motor activation process for starting the payout motor 289 is executed, and the repayment operation is started. Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets the value “1” indicating the payout motor stop waiting process in the payout control code (step S75331), and ends the process.
ステップS75315で再払出動作中2指定ビットがセットされていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグの再払出動作中2指定ビットをリセットする(ステップS75332)。次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグの払出球検知指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS75333)。払出球検知指定ビットがセットされていれば、ステップS75326に移行する。払出球検知指定ビットがセットされていなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグの再払出動作中2指定ビットをリセットする(ステップS75334)とともに、払出個数異常カウンタの値を1加算する(ステップS75335)。なお、ステップS75335の処理は、払出個数異常カウンタに払出不足数を累積的にカウントする処理に相当する。また、ステップS75335の処理を実行することによって、2回目の再払出動作を実行しても、再払出動作が正常に行われなかった場合に、払出個数異常カウンタの値が1カウントアップされる。また、正常に払出が完了した場合でも、誤カウントなどにより未払出個数カウンタの値が0になっていいないこともある。そこで、ステップS75333の処理が実行されることによって、払出球検知指定ビットがセットされていれば、すなわち払出個数カウントスイッチ301が払出動作中に少なくとも1個の遊技球の払出を検出していれば、正常に払出が完了している可能性があるので、払出個数異常カウンタの累積カウントを行うことなく、そのままステップS75326に移行する。
If it is determined in step S75315 that the second designation bit during repayment is set, the payout control CPU 371 resets the second designation bit during repayment operation of the payout control state flag (step S75332). Next, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the payout ball detection designation bit of the payout control state flag is set (step S75333). If the payout ball detection designation bit is set, the process proceeds to step S75326. If the payout ball detection designation bit is not set, the payout control CPU 371 resets the 2 designation bit during repayment operation of the payout control state flag (step S75334) and adds 1 to the value of the payout number abnormality counter ((7). Step S75335). Note that the process of step S75335 corresponds to a process of cumulatively counting the number of underpayments in the payout amount abnormality counter. Further, by executing the processing of step S75335, the value of the payout amount abnormality counter is incremented by one when the repayment operation is not properly performed even if the second repayment operation is performed. In addition, even when the payout is normally completed, the value of the unpaid item counter may not be 0 due to an erroneous count or the like. Therefore, if the payout ball detection designation bit is set by executing the process of step S75333, that is, if the payout number counting switch 301 detects the payout of at least one gaming ball during the payout operation. Since there is a possibility that the payout is normally completed, the process directly proceeds to step S75326 without performing the cumulative count of the payout amount abnormality counter.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、エラーフラグをロードして、エラーフラグに払出ケースエラー指定ビットをセットする(ステップS75336)。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、再払出待ちタイマに所定時間(例えば2分)をセットし(ステップS75337)、処理を終了する。なお、ステップS57337でセットされた再払出待ちタイマは、後述するエラー処理で計測され(ステップS7710参照)、再払出タイマがタイムアウトしたことにもとづいて、エラーフラグの払出ケースエラー指定ビットがリセットされる(ステップS7711,S7712参照)。そのような処理が実行されることによって、この実施の形態では、払出ケースエラーが検出された後、2分経過したことにもとづいてエラー状態が自動復旧される。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 loads an error flag, and sets a payout case error designation bit in the error flag (step S75336). Then, the payout control CPU 371 sets a predetermined time (for example, 2 minutes) in the repayment standby timer (step S75337), and ends the process. The repayment withdrawal waiting timer set in step S57337 is measured in an error process to be described later (refer to step S7710), and the payout case error designation bit of the error flag is reset based on the repayment timer having timed out. (See steps S7711 and S7712). By performing such processing, in this embodiment, the error state is automatically recovered based on the passage of 2 minutes after the detection of the dispensing case error.
次に、エラー処理について説明する。図85は、エラーの種類とエラー表示用LED374の表示との関係等を示す説明図である。図85に示すように、エラーが発生していない状態である場合には、エラー表示用LED374には「−」が表示される。また、払出個数異常カウンタの累積カウント値が2000個以上となり、払出個数異常エラーを検出した場合には、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370の払出制御用CPU371は、払出個数異常エラーとして、エラー表示用LED374に「A」を表示する制御を行う。なお、払出個数異常エラーとなった場合には、遊技機の電源がリセットされるまで、エラー状態が継続される。
Next, error processing will be described. FIG. 85 is an explanatory drawing showing the relationship between the type of error and the display of the error display LED 374. As shown in FIG. 85, when no error occurs, “−” is displayed on the error display LED 374. Further, when the accumulated count value of the dispensing number abnormality counter becomes 2000 or more and the dispensing number abnormality error is detected, the payout control CPU 371 of the microcomputer 370 for dispensing control detects the LED 374 for error display as the dispensing number abnormality error. Control to display “A” on. When the payout amount abnormality error occurs, the error state continues until the power supply of the gaming machine is reset.
主基板31からの接続信号がオフ状態になった場合には、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370の払出制御用CPU371は、主基板未接続エラーとして、エラー表示用LED374に「1」を表示する制御を行う。
When the connection signal from the main substrate 31 is turned off, the payout control CPU 371 of the payout control microcomputer 370 performs control to display “1” on the error display LED 374 as a main substrate non-connection error. Do.
払出個数カウントスイッチ301の断線または払出個数カウントスイッチ301の部分において球詰まりが発生した場合には、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー1として、エラー表示用LED374に「2」を表示する制御を行う。なお、払出個数カウントスイッチ301の断線または払出個数カウントスイッチ301の部分において球詰まりが発生したことは、払出個数カウントスイッチ301の検出信号がオフ状態にならなかったことによって判定される。
When a ball clogging occurs in the portion of the disconnection number counting switch 301 or in the portion of the number-of-dispensing state counting switch 301, control is performed to display “2” on the error display LED 374 as a dispensing switch abnormality detection error 1. The occurrence of the ball clogging in the portion of the disconnection number counting switch 301 or the number-of-dispensing number counting switch 301 is determined by the fact that the detection signal of the number-of-delivery counting switch 301 is not turned off.
遊技球の払出動作中でないにも関わらず払出個数カウントスイッチ301の検出信号がオン状態になった場合には、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー2として、エラー表示用LED374に「3」を表示する制御を行う。払出モータ289の回転異常または遊技球が払い出されたにも関わらず払出個数カウントスイッチ301の検出信号がオン状態にならない場合には、払出ケースエラーとして、エラー表示用LED374に「4」を表示する制御を行う。払出個数カウントスイッチ301の検出信号がオン状態にならないことの具体的な検出方法は既に説明したとおりである。
If the detection signal of the number-of-payouts count switch 301 is turned on despite the fact that the game ball is not being dispensed, control is performed to display "3" on the error display LED 374 as a payout switch abnormality detection error 2. Do. If the detection signal of the number-of-payouts count switch 301 does not turn on despite the abnormal rotation of the payout motor 289 or the game balls are paid out, “4” is displayed on the error display LED 374 as a payout case error Control to The specific method of detecting that the detection signal of the payout number counting switch 301 is not turned on is as described above.
また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との間のシリアル通信エラーが検出された場合には、主制御通信エラーとして、エラー表示用LED374に「5」を表示する制御を行う。
Also, when a serial communication error between the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 is detected, control is performed to display "5" on the error display LED 374 as a main control communication error. .
また、下皿満タン状態すなわち満タンスイッチ48がオン状態になった場合には、満タンエラーとして、エラー表示用LED374に「6」を表示する制御を行う。補給球の不足状態すなわち球切れスイッチ187がオン状態になった場合には、球切れエラーとして、エラー表示用LED374に「7」を表示する制御を行う。
Further, when the lower tray full state, ie, the full tank switch 48 is turned on, control is performed to display "6" on the error display LED 374 as a full tank error. When the supply ball shortage state, that is, the ball breakage switch 187 is turned on, control is performed to display “7” on the error display LED 374 as a ball breakage error.
また、カードユニット50からのVL信号がオフ状態になった場合には、プリペイドカードユニット未接続エラーとして、エラー表示用LED374に「8」を表示する制御を行う。不正なタイミングでカードユニット50と通信がなされた場合には、プリペイドカードユニット通信エラーとして、エラー表示用LED374に「9」を表示する制御を行う。なお、プリペイドカードユニット通信エラーは、プリペイドカードユニット制御処理(ステップS758)において検出される。
When the VL signal from the card unit 50 is turned off, control is performed to display “8” on the error display LED 374 as a prepaid card unit non-connection error. When communication with the card unit 50 is made at an incorrect timing, control is performed to display “9” on the error display LED 374 as a prepaid card unit communication error. The prepaid card unit communication error is detected in the prepaid card unit control process (step S758).
以上のエラーのうち、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー2、払出ケースエラー、または主制御通信エラーが発生した後、エラー解除スイッチ375が操作されエラー解除スイッチ375から操作信号が出力されたら(オン状態になったら)、払出制御手段は、エラーが発生する前の状態に復帰する。
If an error release switch 375 is operated and an operation signal is output from the error release switch 375 after the occurrence of a payout switch error detection error 2, a payout case error, or a main control communication error among the above errors, ), The payout control means returns to the state before the error occurred.
なお、払出制御用CPU371は、既に述べたように、具体的には、タイマ割込処理の表示制御処理(ステップS760参照)において、図85に示す関係に従ってエラー表示LED374にエラー表示を行う。例えば、払出制御用CPU371は、後述するエラー処理においてプリペイドカードユニット未接続状態指定ビットをセットしたことにもとづいて(ステップS7729参照)、表示制御処理において、プリペイドカードユニット未接続エラーが発生している旨を示すエラー表示「8」をエラー表示用LED374に表示する制御を行う。また、例えば、エラー処理において満タンエラー指定ビットをセットしたことにもとづいて(ステップS7714参照)、表示制御処理において、満タンエラーが発生している旨を示すエラー表示「6」をエラー表示用LED374に表示する制御を行う。
As described above, specifically, the payout control CPU 371 displays an error on the error display LED 374 according to the relationship shown in FIG. 85 in the display control process (see step S760) of the timer interrupt process. For example, the payout control CPU 371 generates a prepaid card unit non-connection error in the display control process based on setting of the prepaid card unit non-connection state designation bit in an error process to be described later (see step S7729). Control is performed to display an error display "8" indicating that on the error display LED 374. Also, for example, based on the fact that the full tank error designation bit is set in the error processing (see step S7714), an error display “6” indicating that a full tank error has occurred in the display control process is displayed on the error display LED 374. Control to display.
図86および図87は、ステップS757のエラー処理を示すフローチャートである。エラー処理において、払出制御用CPU371は、まず、エラーフラグをロードし、エラーフラグの払出スイッチ異常検知エラー2指定ビット、払出ケースエラー指定ビット、主制御通信エラー指定ビット、および払出個数異常エラー指定ビット以外のエラービットをリセットする(ステップS7701)。次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、エラーフラグの値が0となっているか否かを確認する(ステップS7702)。エラーフラグの値が0となっていれば、ステップS7710に移行する。エラーフラグの値が0でなければ(すなわち、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー2指定ビット、払出ケースエラー指定ビット、主制御通信エラー指定ビット、または払出個数異常エラー指定ビットがセットされていれば)、払出制御用CPU371は、エラー解除スイッチ375から操作信号がオン状態になったか否か確認する(ステップS7703)。操作信号がオン状態になったら、エラー復帰時間をエラー復帰前タイマにセットする(ステップS7709)。エラー復帰時間は、エラー解除スイッチ375が操作されてから、実際にエラー状態から通常状態に復帰するまでの時間である。
FIGS. 86 and 87 are flowcharts showing the error processing of step S757. In the error processing, the payout control CPU 371 first loads an error flag, and the payout switch error detection error 2 designation bit of the error flag, the payout case error designation bit, the main control communication error designation bit, and the delivery quantity abnormality error designation bit The other error bits are reset (step S7701). Next, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether the value of the error flag is 0 (step S7702). If the value of the error flag is 0, the process proceeds to step S7710. If the value of the error flag is not 0 (that is, if the payout switch error detection error 2 designation bit, the payout case error designation bit, the main control communication error designation bit, or the payout number error error designation bit is set), the payout The control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the operation signal from the error release switch 375 is turned on (step S7703). When the operation signal is turned on, the error recovery time is set to the timer before error recovery (step S7709). The error recovery time is the time from when the error release switch 375 is operated to when it actually recovers from the error state to the normal state.
エラー解除スイッチ375から操作信号がオン状態でない場合には、エラー復帰前タイマの値を確認する(ステップS7704)。エラー復帰前タイマの値が0であれば、すなわち、エラー復帰前タイマがセットされていなければ、ステップS7710に移行する。エラー復帰前タイマがセットされていれば、エラー復帰前タイマの値を−1し(ステップS7705)、エラー復帰前タイマの値が0になったら(ステップS7706)、エラーフラグのうちの、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー2指定ビット、払出ケースエラー指定ビット、および主制御通信エラー指定ビットをリセットする(ステップS7707)とともに、セットされていれば再払出待ちタイマをリセットする(ステップS7708)。そして、ステップS7710に移行する。また、エラー復帰前タイマがタイムアウトしていなければ、ステップS7713に移行する。
If the operation signal from the error release switch 375 is not in the on state, the value of the timer before error recovery is confirmed (step S7704). If the value of the timer before error recovery is 0, that is, if the timer before error recovery is not set, the process proceeds to step S7710. If the timer before error recovery is set, the value of the timer before error recovery is decremented by 1 (step S7705), and if the value of the timer before error recovery becomes 0 (step S7706), the payout switch of the error flags The abnormality detection error 2 designation bit, the payout case error designation bit, and the main control communication error designation bit are reset (step S7707), and if set, the repayment wait timer is reset (step S7708). Then, the process proceeds to step S7710. If the timer before error recovery has not timed out, the process proceeds to step S7713.
なお、ステップS7707の処理が実行されるときに、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー2指定ビット、払出ケースエラー指定ビット、および主制御通信エラー指定ビットのうちには、セット状態ではないエラービットがある場合もあるが、セット状態にないエラービットをリセットしても何ら問題はない。以上のように、この実施の形態では、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー2、払出ケースエラー、および主制御通信エラーのビットをセットする原因になったエラー(図85参照)が発生した場合には、エラー解除スイッチ375が押下されることによってエラー解除される。
When the process of step S7707 is executed, an error bit not in the set state is present among the payout switch error detection error 2 designation bit, the payout case error designation bit, and the main control communication error designation bit. There is no problem in resetting an error bit that is not in the set state, though it is. As described above, in this embodiment, if an error (see FIG. 85) that causes setting of the bit for the dispensing switch abnormality detection error 2, the dispensing case error, and the main control communication error occurs, an error occurs. When the release switch 375 is pressed, the error is released.
ステップS7710では、払出制御用CPU371は、セットされていれば、再払出待ちタイマの値を1減算し、減算後の再払出待ちタイマがタイムアウトしているか否かを確認する(ステップS7711)。再払出待ちタイマがタイムアウトしていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、エラーフラグの払出ケースエラー指定ビットをリセットする(ステップS7712)。そして、ステップS7713に移行する。
In step S7710, if it is set, the payout control CPU 371 subtracts 1 from the value of the repayment wait timer, and checks whether or not the repayment wait timer after subtraction has timed out (step S7711). If the repayment request waiting timer has timed out, the payout control CPU 371 resets the payment case error designation bit of the error flag (step S7712). Then, the process proceeds to step S7713.
以上のように、この実施の形態では、ステップS7707,S7712の処理が実行されることによって、払出ケースエラーが検出されて払出検出エラー指定ビットがセットされた場合には、エラー解除スイッチ375が押下されたこと(正確には、さらにエラー復帰前時間を経過したこと)を条件にエラー解除される場合と、払出ケースエラーの検出後に所定時間(本例では2分)を経過したことを条件にエラーが自動解除される場合とがある。なお、この実施の形態では、払出個数異常エラーに関しては、一度検出されると、遊技機への電源供給をリセットしないかぎり解除されない。
As described above, in this embodiment, when the payout case error is detected and the payout detection error designation bit is set by executing the processing of steps S7707 and S7712, the error release switch 375 is pressed. On the condition that the error is canceled (more precisely, the time before error recovery has passed) and the condition that the predetermined time (two minutes in this example) has passed after the detection of the dispensing case error Errors may be cleared automatically. In this embodiment, once the payout amount abnormality error is detected, it is not canceled unless the power supply to the gaming machine is reset.
ステップS7707,S7712の処理が実行されて払出ケースエラー指定ビットがリセットされた場合には、払出制御コードが「2」(図82〜図84に示す払出通過待ち処理の実行に対応)であるときには、遊技球払出のリトライ動作が開始される。つまり、次にステップS755の払出制御処理が実行されるときにステップS7513の払出通過待ち処理が実行されると、再び、再払出処理が行われる。例えば、賞球払出処理が行われていた場合には、未払出個数カウンタの値が0でないときには、ステップS75305からステップS75309,S75310に移行し、ステップS75310において払出ケースエラー指定ビットがリセット状態であることが確認されるので、ステップS75314以降の再払出処理を開始するための処理が再度実行され、再払出処理が実行される。
When the processing in steps S7707 and S7712 is executed and the payout case error designation bit is reset, the payout control code is “2” (corresponding to execution of the payout passage waiting process shown in FIGS. 82 to 84). The retry operation of game ball payout is started. That is, when the payout passage waiting process of step S7513 is executed when the payout control process of step S755 is executed next, the repayment process is performed again. For example, when the award ball payout process is performed, if the value of the unpaid item number counter is not 0, the process proceeds from step S75305 to steps S75309 and S75310, and the payout case error designation bit is reset in step S75310. Since it is confirmed, the processing for starting the repayment processing after step S75314 is executed again, and the repayment processing is executed.
以上のように、払出制御手段は、球払出装置97が遊技球の払い出しを行ったにもかかわらず払出個数カウントスイッチ301が1個も遊技球を検出しなかったときには遊技球を払い出すためのリトライ動作をあらかじめ決められた所定回(例えば2回)を限度として球払出装置97に実行させる補正払出制御を行った後、払出個数カウントスイッチ301が1個も遊技球を検出しなかったことが検出されたときには(図82〜図84のステップS75314以降を参照)、払い出しに関わる制御状態をエラー状態に移行させ、エラー状態においてエラー解除スイッチ375からエラー解除信号が出力されたこと、または払出ケースエラーを検出してから所定時間(本例では2分)を経過したことを条件に再度補正払出制御を行わせる補正払出制御再起動処理を実行する。
As described above, the payout control means is for paying out the game ball when the number-of-payouts count switch 301 detects no game ball even though the ball payout device 97 has paid out the game ball. After performing the correction payout control to make the ball payout device 97 execute the retry operation with a predetermined number of times (for example, twice) as a limit, the number-of-payouts count switch 301 does not detect even one game ball When it is detected (refer to step S75314 or later in FIG. 82 to FIG. 84), the control state related to the payout is shifted to the error state, and in the error state, the error clear signal is outputted from the error clear switch 375; Correction payment to perform correction payment control again on condition that a predetermined time (two minutes in this example) has passed since an error was detected To run the control restart processing.
さらに、エラー状態における再払出処理の実行中(具体的には払出ケースエラーをセットする前の再払出処理中およびエラー解除スイッチ375押下後の再払出処理中)でも、図79に示すステップS7501,S7502,S7506処理は実行されている。すなわち、払い出しに関わるエラーが生じているときでも、遊技球が払出個数カウントスイッチ301を通過すれば、未払出個数カウンタの値が減算される。従って、エラー状態から復帰したときの未払出個数カウンタの値は、実際に払い出された遊技球数を反映した値になっている。すなわち、払い出しに関わるエラーが発生しても、実際に払い出した遊技球数を正確に管理することができる。
Furthermore, even during the execution of the repayment process in the error state (specifically, during the repayment process before setting the payment case error and during the repayment process after pressing the error release switch 375), step S7501 shown in FIG. The processes of S7502 and S7506 are being executed. That is, even when an error related to the payout occurs, if the gaming ball passes the payout number counting switch 301, the value of the unpaid number counter is subtracted. Therefore, the value of the unpaid number counter at the time of recovery from the error state is a value reflecting the number of gaming balls actually paid out. That is, even if an error related to the payout occurs, the number of gaming balls actually paid can be accurately managed.
また、図82〜図84に示された払出通過待ち処理において、再払出処理が実行された結果、遊技球が払い出されたことが確認されたときでも、払出ケースエラーのビットはリセットされない。払出ケースエラーのビットがリセットされるのは、あくまでも、エラー解除スイッチ375が操作されたとき(具体的は、操作後エラー復帰時間が経過したとき)、または払出ケースエラーを検出してから所定時間(本例では2分)を経過したときである(ステップS7707,S7712)。すなわち、払出ケースエラーを検出してから所定時間(本例では2分)を経過するまでは、遊技球が払出個数カウントスイッチ301を通過したこと等にもとづいて自動的に払出ケースエラー(払出不足エラー)の状態が解除されるということはなく、人為的な操作を経ないと払出ケースエラーは解除されない。従って、遊技店員等は、確実に払出不足が発生したことを認識することができる。ただし、この実施の形態では、少なくとも、払出ケースエラーが発生してからある程度長い時間(本例では2分)が経過すれば払出ケースエラーを自動解除するように構成することによって、払出ケースエラーが必要以上に長時間継続することを防止している。
Further, in the payout passage waiting process shown in FIGS. 82 to 84, even if it is confirmed that the gaming balls have been paid out as a result of execution of the repayment processing, the bit of the payout case error is not reset. The bit of the dispensing case error is reset only when the error release switch 375 is operated (specifically, when the error recovery time has elapsed after operation) or a predetermined time after the dispensing case error is detected. It is when (in this example, 2 minutes) has passed (steps S7707 and S7712). That is, based on the fact that the gaming ball has passed the number-of-payouts count switch 301 and the like until the predetermined time (two minutes in this example) elapses from the detection of the payout case error, the payout case error (the payout is insufficient) The error state is not released, and the withdrawal case error can not be released without manual operation. Therefore, the gaming staff can surely recognize that the lack of payout has occurred. However, in this embodiment, the payout case error is generated by automatically canceling the payout case error if at least a long time (two minutes in this example) elapses after the payout case error occurs. It is prevented from continuing for a long time more than necessary.
なお、エラー解除スイッチ375が操作されたことによってハードウェア的にリセット(払出制御用CPU371に対するリセット)がかかるように遊技機を構成する場合もあるが、そのように遊技機を構成した場合には、エラー解除スイッチ375が操作されたことによって例えば未払出個数カウンタの値もクリアされてしまう。しかし、この実施の形態では、払出制御手段が、エラー解除スイッチ375が操作されたことによって再払出動作を再び行うように構成されているので、確実に払出処理が実行され、遊技者に不利益を与えないようにすることができる。
The game machine may be configured to be reset in hardware (reset to the payout control CPU 371) by operating the error release switch 375. However, when the game machine is configured as such, By operating the error release switch 375, for example, the value of the unpaid item counter is also cleared. However, in this embodiment, since the payout control means is configured to perform the repayment operation again by the operation of the error release switch 375, the payout processing is surely executed, which is disadvantageous for the player. It is possible not to give
ステップS7713では、払出制御用CPU371は、満タンスイッチ48の検出信号を確認する。満タンスイッチ48の検出信号が出力されていれば(オン状態であれば)、エラーフラグのうちの満タンエラー指定ビットをセットする(ステップS7714)。
In step S7713, the payout control CPU 371 confirms the detection signal of the full tank switch 48. If the detection signal of the full tank switch 48 is output (if it is in the ON state), the full tank error designation bit of the error flag is set (step S7714).
また、払出制御用CPU371は、球切れスイッチ187の検出信号を確認する(ステップS7715)。球切れスイッチ187の検出信号が出力されていれば(オン状態であれば)、エラーフラグのうちの球切れエラー指定ビットをセットする(ステップS7716)。
Further, the payout control CPU 371 confirms the detection signal of the out-of-ball switch 187 (step S7715). If the detection signal of the out-of-ball switch 187 is output (if it is in the ON state), the out-of-sphere error designation bit in the error flag is set (step S7716).
さらに、払出制御用CPU371は、主基板31からの接続信号の状態を確認し(ステップS7717)、接続信号が出力されていなければ(オフ状態であれば)、主基板未接続エラー指定ビットをセットする(ステップS7718)。
Furthermore, the payout control CPU 371 confirms the state of the connection signal from the main board 31 (step S7717), and if the connection signal is not output (if it is in the off state), the main board disconnection error designating bit is set. (Step S7718).
また、払出制御用CPU371は、各スイッチの検出信号の状態が設定される各スイッチタイマのうち払出個数カウントスイッチ301に対応したスイッチタイマの値を確認し、その値がスイッチオン最大時間(例えば「250」)を越えていたら(ステップS7719)、エラーフラグのうち払出スイッチ異常検知エラー1のビットをセットする(ステップS7720)。なお、各スイッチタイマの値は、ステップS752の入力判定処理において、各スイッチの検出信号を入力する入力ポートの状態がスイッチオン状態であれば+1され、オフ状態であれば0クリアされる。従って、払出個数カウントスイッチ301に対応したスイッチタイマの値がスイッチオン最大時間を越えていたということは、スイッチオン最大時間を越えて払出個数カウントスイッチ301がオン状態になっていることを意味し、払出個数カウントスイッチ301の断線または払出個数カウントスイッチ301の部分で遊技球が詰まっていると判断される。
Further, the payout control CPU 371 checks the value of the switch timer corresponding to the payout number counting switch 301 among the switch timers in which the state of the detection signal of each switch is set, and the value is the switch on maximum time (for example, “ If it exceeds 250 ") (step S7719), the bit of the payout switch abnormality detection error 1 among the error flags is set (step S7720). Note that the value of each switch timer is incremented by 1 if the state of the input port to which the detection signal of each switch is input is the switch on state or is cleared to 0 if the state is the off state in the input determination process of step S752. Therefore, the fact that the value of the switch timer corresponding to the payout number counting switch 301 exceeds the switch on maximum time means that the payout number counting switch 301 is in the on state beyond the switch on maximum time. It is determined that the game ball is clogged by disconnection of the payout number counting switch 301 or the portion of the payout number counting switch 301.
また、払出制御用CPU371は、払出個数カウントスイッチ301に対応したスイッチタイマの値がスイッチオン判定値(例えば「4」)になった場合には(ステップS7721)、払出制御状態フラグをロードし(ステップS7722)、賞球払出動作中または球貸し払出動作中であるか否かを確認する(ステップS7723)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグに賞球払出動作中指定ビットまたは球貸し払出動作中指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する。賞球払出動作中指定ビットおよび球貸し払出動作中指定ビットがともにリセット状態であれば、払出制御用CPU371は、払出動作中でないのに払出個数カウントスイッチ301を遊技球が通過したとして、エラーフラグのうち払出スイッチ異常検知エラー2のビットをセットする(ステップS7724)。
In addition, when the value of the switch timer corresponding to the payout number counting switch 301 becomes the switch-on determination value (for example, “4”) (step S7721), the payout control CPU 371 loads the payout control state flag ( Step S7722) It is checked whether or not a prize ball payout operation or a ball loan payout operation is in progress (step S7723). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the prize ball payout operation designated bit or the ball loan payout designated bit is set in the payout control state flag. If both the prize ball payout operation designated bit and the ball loan payout operation designated bit are reset, the payout control CPU 371 determines that the game ball has passed the payout number count switch 301 even though the payout operation is not in progress, and the error flag Among them, the bit of the payout switch abnormality detection error 2 is set (step S7724).
また、払出制御用CPU371は、払出個数異常カウンタの値が所定の払出個数異常エラー判定値(例えば2000)以上となっているか否かを確認する(ステップS7725)。所定の払出個数異常エラー判定値(例えば2000)以上となっていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、払出個数異常エラーが発生したと判断し、払出個数異常エラーフラグをセットする(ステップS7726)。
Further, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the value of the payout amount abnormality counter is equal to or more than a predetermined payout number abnormality error determination value (for example, 2000) (step S7725). If the payout amount abnormality error determination value (for example, 2000) or more, the payout control CPU 371 determines that a payout number abnormality error has occurred, and sets a payout number abnormality error flag (step S7726).
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、プリペイドカードユニット50のエラー状態を設定するためのプリペイドカードユニット用エラーフラグをリセットする(ステップS7727)。また、払出制御用CPU371は、カードユニット50からのVL信号の入力状態を確認し(ステップS7728)、VL信号が入力されていなければ(オフ状態であれば)、プリペイドカードユニット用エラーフラグのうちプリペイドカードユニット未接続エラー指定ビットをセットする(ステップS7729)。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 resets a prepaid card unit error flag for setting an error state of the prepaid card unit 50 (step S7727). Further, the payout control CPU 371 confirms the input state of the VL signal from the card unit 50 (step S7728), and if the VL signal is not input (if it is in the off state), the error flag for prepaid card unit A prepaid card unit non-connection error designation bit is set (step S7729).
なお、ステップS760の表示制御処理では、エラーフラグおよびプリペイドカードユニット用エラーフラグ中のエラービットに応じた表示(数値表示)による報知をエラー表示用LED374によって行う。従って、通信エラーをエラー表示用LED374によって報知することができる。また、通信エラーは、払出制御手段の側で検出されるので、遊技制御手段の負担を増すことなく通信エラーを検出できる。
In the display control process of step S760, the error display LED 374 performs notification by means of a display (numerical display) according to the error flag and the error bit in the prepaid card unit error flag. Therefore, the communication error can be notified by the error display LED 374. Further, since the communication error is detected on the side of the payout control means, the communication error can be detected without increasing the load on the game control means.
また、この実施の形態では、主基板未接続エラーは接続信号がオン状態になると自動的に解消されるが(ステップS7701,S7717,S7718参照)、さらにエラー解除スイッチ375が操作されたという条件を加えて、エラー状態が解消されるようにしてもよい。
In this embodiment, the main board disconnection error is automatically eliminated when the connection signal is turned on (see steps S7701, S7717 and S7718), but the condition that the error release switch 375 is operated is In addition, error conditions may be eliminated.
また、この実施の形態では、通信エラーが、カードユニット50との間の通信エラー(プリペイドカードユニット未接続エラーおよびプリペイドカードユニット通信エラー)やその他のエラーと区別可能に報知される(図85参照)。従って、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との間の通信エラーが容易に特定される。
Further, in this embodiment, the communication error is notified distinguishably from the communication error with the card unit 50 (the prepaid card unit non-connection error and the prepaid card unit communication error) and other errors (see FIG. 85). ). Therefore, a communication error between the gaming control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 can be easily identified.
また、この実施の形態では、エラー処理において、まず、エラーフラグのうち、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー2指定ビット、払出ケースエラー指定ビット、主制御通信エラー指定ビット、および払出個数異常エラー指定ビット以外のビットを一旦リセット(ステップS7701参照)してから、エラー処理を実行するごとに満タンエラーや球切れエラー、主制御未接続エラーとなっているか否かを確認している。そして、払出スイッチ異常検知エラー2指定ビット、払出ケースエラー指定ビット、および主制御通信エラー指定ビットについては、エラー解除スイッチ375が操作されたことを条件にリセットしている。しかし、払出個数異常エラーについては、一度セットされれば解除されることはない。従って、この実施の形態では、払出個数異常エラーとなった場合には、電源リセットが行われたこと条件として払出個数異常エラーが解除されることになる。
Further, in this embodiment, in the error processing, first, among the error flags, a payout switch abnormality detection error 2 designation bit, a payout case error designation bit, a main control communication error designation bit, and a payout number abnormality error designation bit. Once the bit is reset (see step S7701), it is checked every time error processing is executed whether a full tank error, an out-of-balls error, or a main control non-connection error has occurred. The payout switch error detection error 2 designation bit, the payout case error designation bit, and the main control communication error designation bit are reset on the condition that the error release switch 375 is operated. However, the payout amount error is not canceled once it is set. Therefore, in this embodiment, when a payout amount abnormality error occurs, the payout number abnormality error is canceled as a condition that the power supply has been reset.
図88および図89は、ステップS759の情報出力処理を示すフローチャートである。情報出力処理において、払出制御用CPU371は、まず、払出制御状態フラグをロードし(ステップS7901)、球貸し払出動作中であるか否かを確認する(ステップS7902)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、払出制御状態フラグの球貸し払出動作中指定ビットがセットされているか否かを確認する。球貸し払出動作中であれば、ステップS7909に移行する。球貸し払出動作中でなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、払出個数カウントスイッチ301がオン状態であるか否かを確認する(ステップS7903)。払出個数カウントスイッチ301がオン状態であれば(この場合、賞球による払い出しを検出したことになる)、払出制御用CPU371は、賞球信号1出力回数カウンタの値を1加算する(ステップS7904)とともに、賞球払出個数カウンタの値を1加算する(ステップS7905)。なお、賞球信号1出力回数カウンタは、賞球信号1を出力する条件が成立した回数をカウントするためのカウンタである。また、賞球払出個数カウンタは、賞球払出により払い出された遊技球の数をカウントするためのカウンタである。
88 and 89 are flowcharts showing the information output process of step S759. In the information output process, the payout control CPU 371 first loads a payout control state flag (step S7901), and checks whether or not a ball lending payout operation is in progress (step S7902). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the ball lending payout operation designated bit of the payout control state flag is set. If the ball lending operation is in progress, the process moves to step S7909. If the ball lending payout operation is not in progress, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the payout number counting switch 301 is in the on state (step S7903). If the number-of-payouts count switch 301 is on (in this case, the payout due to the prize ball is detected), the payout control CPU 371 adds 1 to the value of the prize ball signal 1 output frequency counter (step S7904). At the same time, the value of the prize ball payout number counter is incremented by 1 (step S7905). The prize ball signal 1 output number counter is a counter for counting the number of times the conditions for outputting the prize ball signal 1 are satisfied. The prize ball payout number counter is a counter for counting the number of gaming balls paid out by the prize ball payout.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、加算後の賞球払出個数カウンタの値が所定の賞球情報出力判定値(本例では10)以上となっているか否かを確認する(ステップS7906)。所定の賞球情報出力判定値(本例では10)以上となっていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、賞球払出個数カウンタをリセットする(ステップS7907)とともに、賞球情報出力回数カウンタの値を1加算する(ステップS7908)。なお、賞球情報出力回数カウンタは、賞球情報を出力する条件が成立した回数をカウントするためのカウンタである。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 checks whether or not the value of the winning ball payout number counter after the addition is equal to or greater than a predetermined winning ball information output determination value (10 in this example) (step S7906). If the predetermined winning ball information output judgment value (10 in the present example) or more, the payout control CPU 371 resets the winning ball payout number counter (step S7907), the value of the winning ball information output frequency counter One is added (step S7908). The prize ball information output number counter is a counter for counting the number of times the conditions for outputting the prize ball information are satisfied.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、セットされていれば賞球情報出力タイマを1減算し(ステップS7909)、減算後の賞球情報出力タイマがタイムアウトしているか否かを確認する(ステップS7910)。なお、賞球情報出力タイマは、賞球情報の出力継続時間を計測するためのタイマである。タイムアウトしていなければ、ステップS7914に移行する。タイムアウトしていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、賞球情報出力回数カウンタの値が0となっているか否かを確認する(ステップS7911)。賞球情報出力回数カウンタの値が0であれば、ステップS7915に移行する。賞球情報出力回数カウンタの値が0でなければ(すなわち、賞球情報の出力条件の成立数がまだ残っていれば)、払出制御用CPU371は、賞球情報出力回数カウンタの値を1減算する(ステップS7912)。次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、次の賞球情報の出力を開始するために、賞球情報出力タイマをセットする(ステップS7913)。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、賞球情報を遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に出力する制御を行う(ステップS7914)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、出力ポート1の賞球情報出力ビット(ビット7。図66参照。)に出力データをセットする処理を行う。
Next, if it is set, the payout control CPU 371 subtracts 1 from the award ball information output timer (step S7909), and checks whether the award ball information output timer after subtraction times out (step S7910). The winning ball information output timer is a timer for measuring the output duration time of the winning ball information. If it does not time out, it will transfer to step S7914. If it has timed out, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the value of the award ball information output number counter is 0 (step S7911). If the value of the winning ball information output number counter is 0, the process proceeds to step S7915. If the value of the prize ball information output frequency counter is not 0 (that is, the number of satisfaction of the output condition of the prize ball information still remains), the payout control CPU 371 subtracts 1 from the value of the prize ball information output frequency counter. (Step S7912). Next, the payout control CPU 371 sets a winning ball information output timer to start outputting the next winning ball information (step S7913). Then, the payout control CPU 371 performs control to output the winning ball information to the game control microcomputer 560 (step S7914). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 sets output data in the award ball information output bit (bit 7. Refer to FIG. 66) of the output port 1.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、セットされていれば賞球信号1出力タイマを1減算し(ステップS7915)、減算後の賞球信号1出力タイマがタイムアウトしているか否かを確認する(ステップS7916)。なお、賞球信号1出力タイマは、賞球信号1の出力継続時間を計測するためのタイマである。タイムアウトしていなければ、ステップS7920に移行する。タイムアウトしていれば、払出制御用CPU371は、賞球信号1出力回数カウンタの値が0となっているか否かを確認する(ステップS7917)。賞球信号1出力回数カウンタの値が0であれば、ステップS7921に移行する。賞球信号1出力回数カウンタの値が0でなければ(すなわち、賞球信号1の出力条件の成立数がまだ残っていれば)、払出制御用CPU371は、賞球信号1出力回数カウンタの値を1減算する(ステップS7918)。次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、次の賞球信号1の出力を開始するために、賞球信号1出力タイマをセットする(ステップS7919)。そして、払出制御用CPU371は、賞球信号1を外部出力する制御を行う(ステップS7920)。具体的には、払出制御用CPU371は、出力ポート0の賞球信号1出力ビット(ビット0。図66参照。)に出力データをセットする処理を行う。なお、この実施の形態では、賞球信号1は、払出制御基板31から直接ターミナル基板160に入力されて外部出力されるのではなく、主基板31を一旦経由してからターミナル基板160に入力されて外部出力される。
Next, if it is set, the payout control CPU 371 decrements the prize ball signal 1 output timer by 1 (step S7915), and confirms whether the prize ball signal 1 output timer after subtraction times out (step S7916). ). The prize ball signal 1 output timer is a timer for measuring the output duration time of the prize ball signal 1. If it does not time out, it will transfer to step S7920. If it has timed out, the payout control CPU 371 confirms whether or not the value of the prize ball signal 1 output number counter is 0 (step S7917). If the value of the winning ball signal 1 output number counter is 0, the process proceeds to step S7921. If the value of the prize ball signal 1 output frequency counter is not 0 (that is, the number of satisfaction of the output condition of the prize ball signal 1 still remains), the payout control CPU 371 determines the value of the prize ball signal 1 output frequency counter. Is decremented by 1 (step S7918). Next, the payout control CPU 371 sets a winning ball signal 1 output timer to start outputting the next winning ball signal 1 (step S7919). Then, the payout control CPU 371 performs control to externally output the winning ball signal 1 (step S7920). Specifically, the payout control CPU 371 sets the output data to the prize ball signal 1 output bit (bit 0; see FIG. 66) of the output port 0. In this embodiment, the prize ball signal 1 is not directly input from the payout control substrate 31 to the terminal substrate 160 and output to the outside, but is once input to the terminal substrate 160 through the main substrate 31 once. Output to the outside.
次いで、払出制御用CPU371は、出力ポート0の遊技機エラー状態信号出力ビット(ビット1。図66参照。)に出力データをセットする処理を行い(ステップS7921)、エラーフラグをロードする(ステップS7922)。エラーフラグに球切れエラー指定ビットまたは満タンエラー指定ビットのいずれかがセットされていれば(ステップS7923,S7924のY)、出力ポート0の遊技機エラー状態信号出力ビットがセットされたままの状態で処理を終了する。この場合、ステップS7921で出力ポート0の遊技機エラー状態信号出力ビットがセットされたことにもとづいて、遊技機エラー状態信号が外部出力されることになる。なお、この実施の形態では、遊技機エラー状態信号は、払出制御基板31から直接ターミナル基板160に入力されて外部出力されるのではなく、主基板31を一旦経由してからターミナル基板160に入力されて外部出力される。一方、エラーフラグに球切れエラー指定ビットおよび満タンエラー指定ビットのいずれもセットされていなければ、払出制御用CPU371は、出力ポート0の遊技機エラー状態信号出力ビットをクリアし(ステップS7925)、処理を終了する。
Next, the payout control CPU 371 sets the output data in the gaming machine error status signal output bit (bit 1. see FIG. 66) of the output port 0 (step S7921), and loads an error flag (step S7922). ). If either the out-of-ball error designation bit or the full-tank error designation bit is set in the error flag (Y in steps S7923 and S7924), the gaming machine error status signal output bit of output port 0 remains set. End the process. In this case, based on the setting of the gaming machine error status signal output bit of the output port 0 in step S7921, the gaming machine error status signal is externally output. In this embodiment, the gaming machine error status signal is not directly input from the payout control substrate 31 to the terminal substrate 160 and output to the outside, but is once input to the terminal substrate 160 after passing through the main substrate 31. And output to the outside. On the other hand, if neither the out-of-sphere error designation bit nor the full-tank error designation bit is set in the error flag, the payout control CPU 371 clears the gaming machine error status signal output bit of the output port 0 (step S7925). Finish.
以上の処理が実行されることによって、この実施の形態では、払出制御手段側で賞球払出を1球検出するごとに賞球信号1が外部出力される。また、払出制御手段側で賞球払出を10球検出するごとに遊技制御手段側に対して賞球情報が出力される。さらに、払出制御手段側で球切れエラーまたは満タンエラーを検出すると遊技機エラー状態信号が外部出力される。
By executing the above-described process, in this embodiment, the winning ball signal 1 is output to the outside every time one winning ball is detected on the payout control means side. In addition, the winning ball information is outputted to the game control means side every time 10 balls of the winning balls are detected on the payout control means side. Furthermore, when the ball out error or the full tank error is detected on the side of the payout control means, a gaming machine error state signal is output to the outside.
次に、演出制御手段の動作を説明する。図90は、演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御手段としての演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100(具体的には、演出制御用CPU101a)が実行するメイン処理を示すフローチャートである。演出制御用CPU101aは、電源が投入されると、メイン処理の実行を開始する。メイン処理では、まず、RAM領域のクリアや各種初期値の設定、また演出制御の起動間隔(例えば、4ms)を決めるためのタイマの初期設定等を行うための初期化処理を行う(ステップS781)。その後、演出制御用CPU101aは、タイマ割込フラグの監視(ステップS782)を行うループ処理に移行する。タイマ割込が発生すると、演出制御用CPU101aは、タイマ割込処理においてタイマ割込フラグをセットする。メイン処理において、タイマ割込フラグがセットされていたら、演出制御用CPU101aは、そのフラグをクリアし(ステップS783)、以下の演出制御処理を実行する。
Next, the operation of the effect control means will be described. FIG. 90 is a flowchart showing main processing executed by the effect control microcomputer 100 (specifically, effect control CPU 101a) mounted on the effect control board 80 as effect control means. When the power is turned on, the effect control CPU 101a starts executing the main processing. In the main processing, first, initialization processing is performed to clear the RAM area, set various initial values, and initialize the timer for determining the start interval (for example, 4 ms) of effect control (step S 781). . Thereafter, the effect control CPU 101a shifts to loop processing for monitoring the timer interrupt flag (step S782). When a timer interrupt occurs, the effect control CPU 101a sets a timer interrupt flag in the timer interrupt process. In the main processing, when the timer interruption flag is set, the effect control CPU 101a clears the flag (step S783), and executes the following effect control processing.
演出制御処理において、演出制御用CPU101aは、まず、受信した演出制御コマンドを解析し、受信した演出制御コマンドに応じたフラグをセットする処理等を行う(コマンド解析処理:ステップS784)。
In the effect control process, the effect control CPU 101a first analyzes the received effect control command and performs a process of setting a flag according to the received effect control command (command analysis process: step S784).
次いで、演出制御用CPU101aは、演出制御プロセス処理を行う(ステップS785)。演出制御プロセス処理では、制御状態に応じた各プロセスのうち、現在の制御状態(演出制御プロセスフラグ)に対応した処理を選択して演出表示装置9の表示制御を実行する。
Next, the effect control CPU 101a performs an effect control process (step S785). In the effect control process, among the processes corresponding to the control state, the process corresponding to the current control state (effect control process flag) is selected to execute display control of the effect display device 9.
次いで、大当り図柄決定用乱数などの乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する乱数更新処理を実行する(ステップS786)。その後、ステップS782に移行する。
Next, random number update processing is performed to update the count value of the counter for generating a random number such as a jackpot symbol determination random number (step S786). Thereafter, the process proceeds to step S782.
図91は、コマンド解析処理(ステップS784)の具体例を示すフローチャートである。主基板31から受信された演出制御コマンドは受信コマンドバッファに格納されるが、コマンド解析処理では、演出制御用CPU101aは、コマンド受信バッファに格納されているコマンドの内容を確認する。
FIG. 91 is a flowchart of a specific example of the command analysis process (step S784). Although the effect control command received from the main substrate 31 is stored in the reception command buffer, in the command analysis process, the effect control CPU 101a confirms the content of the command stored in the command reception buffer.
なお、図91では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から送信される演出制御コマンドのうち、特に、払出制御に関するエラーを示すコマンドを受信した場合の処理について示しているが、実際には、演出図柄の変動パターンを示す変動パターンコマンドや、大当りとするか否かの表示結果を示す表示結果指定コマンドなど、様々な演出制御コマンドが遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から送信される。
In FIG. 91, among the effect control commands transmitted from the game control microcomputer 560, particularly, the processing in the case of receiving a command indicating an error relating to payout control is shown, but in fact, Various effect control commands are transmitted from the game control microcomputer 560, such as a variation pattern command indicating a variation pattern, and a display result designation command indicating a display result as to whether or not to make a big hit.
コマンド解析処理において、演出制御用CPU101aは、まず、コマンド受信バッファに受信コマンドが格納されているか否か確認する(ステップS611)。格納されているか否かは、コマンド受信個数カウンタの値と読出ポインタとを比較することによって判定される。両者が一致している場合が、受信コマンドが格納されていない場合である。コマンド受信バッファに受信コマンドが格納されている場合には、演出制御用CPU101aは、コマンド受信バッファから受信コマンドを読み出す(ステップS612)。なお、読み出したら読出ポインタの値を+2しておく(ステップS613)。+2するのは2バイト(1コマンド)ずつ読み出すからである。
In the command analysis process, the effect control CPU 101a first confirms whether or not a reception command is stored in the command reception buffer (step S611). Whether or not it is stored is determined by comparing the value of the command reception number counter with the read pointer. The case where the two match each other is the case where the reception command is not stored. When the reception command is stored in the command reception buffer, the effect control CPU 101a reads the reception command from the command reception buffer (step S612). Note that when read out, the value of the read pointer is incremented by 2 (step S613). The reason for +2 is that two bytes (one command) are read at a time.
受信した演出制御コマンドが枠状態表示コマンドであれば(ステップS614)、演出制御用CPU101aは、枠状態表示コマンドのEXTデータのうちの賞球エラービット(ビット0。図49参照。)がセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS615)。セットされていれば、演出制御用CPU101aは、演出表示装置9の表示画面に所定の賞球エラー報知情報を重畳表示する制御を行う(ステップS616)。例えば、演出制御用CPU101aは、演出表示装置9の表示画面に「賞球エラーが発生しました」などの文字列を表示させる制御を行う。
If the received effect control command is a frame state display command (step S614), the effect control CPU 101a sets the award ball error bit (bit 0, see FIG. 49) of the EXT data of the frame state display command. Whether or not it is confirmed (step S615). If set, the effect control CPU 101a performs control to superimpose and display predetermined award ball error notification information on the display screen of the effect display device 9 (step S616). For example, the effect control CPU 101 a performs control to display a character string such as “A prize ball error has occurred” on the display screen of the effect display device 9.
また、演出制御用CPU101aは、枠状態表示コマンドのEXTデータのうちの満タンエラービット(ビット1。図49参照。)がセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS617)。セットされていれば、演出制御用CPU101aは、演出表示装置9の表示画面に所定の満タンエラー報知情報を重畳表示する制御を行う(ステップS618)。例えば、演出制御用CPU101aは、演出表示装置9の表示画面に「満タンエラーが発生しました」などの文字列を表示させる制御を行う。
Further, the effect control CPU 101a checks whether or not the full error bit (bit 1. see FIG. 49) of the EXT data of the frame state display command is set (step S617). If set, the effect control CPU 101a performs control to superimpose and display predetermined full-tank error notification information on the display screen of the effect display device 9 (step S618). For example, the effect control CPU 101 a performs control to display a character string such as “full error has occurred” on the display screen of the effect display device 9.
また、演出制御用CPU101aは、枠状態表示コマンドのEXTデータのうちの球切れエラービット(ビット2。図49参照。)がセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS619)。セットされていれば、演出制御用CPU101aは、演出表示装置9の表示画面に所定の球切れエラー報知情報を重畳表示する制御を行う(ステップS620)。例えば、演出制御用CPU101aは、演出表示装置9の表示画面に「球切れエラーが発生しました」などの文字列を表示させる制御を行う。
Further, the effect control CPU 101a checks whether or not the out-of-sphere error bit (bit 2. see FIG. 49) of the EXT data of the frame state display command is set (step S619). If it is set, the effect control CPU 101a performs control to superimpose and display predetermined out-of-ball error notification information on the display screen of the effect display device 9 (step S620). For example, the effect control CPU 101 a performs control to display a character string such as “ball out error has occurred” on the display screen of the effect display device 9.
また、演出制御用CPU101aは、枠状態表示コマンドのEXTデータのうちの払出個数異常エラービット(ビット3。図49参照。)がセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS621)。セットされていれば、演出制御用CPU101aは、演出表示装置9の表示画面に所定の払出個数異常エラー報知情報を重畳表示する制御を行う(ステップS622)。例えば、演出制御用CPU101aは、演出表示装置9の表示画面に「払出個数異常エラーが発生しました」などの文字列を表示させる制御を行う。
Further, the effect control CPU 101a confirms whether or not the payout amount abnormality error bit (bit 3. see FIG. 49) of the EXT data of the frame state display command is set (step S621). If it is set, the effect control CPU 101a performs control to superimpose and display predetermined payout amount abnormality error notification information on the display screen of the effect display device 9 (step S622). For example, the effect control CPU 101 a performs control to display a character string such as “Payout number abnormality error has occurred” on the display screen of the effect display device 9.
また、演出制御用CPU101aは、枠状態表示コマンドのEXTデータのうちのドア開放異常エラービット(ビット6。図49参照。)がセットされているか否かを確認する(ステップS623)。セットされていれば、演出制御用CPU101aは、ガラス扉枠2の開放状態を検出したことを報知する所定の特殊音1を出力させるための音信号(音番号データ)を音声出力基板70に出力する(ステップS624)。この場合、音声出力基板70において、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100から入力した特殊音1用の音番号データは、入力ドライバ702を介して音声合成用IC703に入力される。そして、音声合成用IC703は、音番号データに応じた特殊音1(例えば、ビープ音などの警告音)を発生し、増幅回路705を介してスピーカ27から出力させる。ただし、この場合、後述するステップS630において、ガラス扉枠2の開放状態において異常入賞を検出した場合に出力される特殊音2とは異なる態様(例えば、音の出力パターンやトーン、音の高低が異なる)の音が出力される。
Further, the effect control CPU 101a confirms whether or not the door open abnormality error bit (bit 6. Refer to FIG. 49) in the EXT data of the frame state display command is set (step S623). If set, the effect control CPU 101a outputs a sound signal (sound number data) for outputting a predetermined special sound 1 notifying that the open state of the glass door frame 2 has been detected to the sound output board 70 (Step S624). In this case, sound number data for special sound 1 input from the effect control microcomputer 100 in the sound output board 70 is input to the speech synthesis IC 703 via the input driver 702. Then, the voice synthesis IC 703 generates a special sound 1 (for example, a warning sound such as a beep sound) corresponding to the sound number data, and causes the speaker 27 to output the special sound 1 via the amplification circuit 705. However, in this case, an aspect different from the special sound 2 output when an abnormal winning is detected in the open state of the glass door frame 2 in step S630 described later (for example, the output pattern or tone of the sound, the height of the sound Different sounds are output.
なお、特殊音1の出力は、例えば、遊技機に対する電力供給がオフするまで、またはガラス扉枠2が閉鎖状態にされるまで継続して出力されるようにしてもよいが、出力開始から所定期間(例えば、10秒)が経過するまで継続して出力されるようにしてもよい。ガラス扉枠2が閉鎖状態にされるまで継続して出力されるようにする場合には、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ガラス扉枠2が開放状態から閉鎖状態に変化したことを検出すると、その旨を示すコマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する。
The output of the special sound 1 may be continuously output, for example, until the power supply to the game machine is turned off, or until the glass door frame 2 is closed, but a predetermined amount of time has passed since the start of the output. The output may be continued until the period (for example, 10 seconds) elapses. When the glass door frame 2 is to be continuously output until it is put in the closed state, the game control microcomputer 560 detects that the glass door frame 2 has changed from the open state to the closed state, A command indicating that is transmitted to the effect control microcomputer 100.
受信した演出制御コマンドが賞球不足エラーコマンドであれば(ステップS625)、演出制御用CPU101aは、演出表示装置9の表示画面に所定の賞球不足エラー報知情報を重畳表示する制御を行う(ステップS626)。例えば、演出制御用CPU101aは、演出表示装置9の表示画面に「賞球不足エラーが発生しました」などの文字列を表示させる制御を行う。
If the received effect control command is an award ball shortage error command (step S625), the effect control CPU 101a performs control to superimpose and display predetermined award ball shortage error notification information on the display screen of the effect display device 9 (step S625) S 626). For example, the effect control CPU 101 a performs control to display a character string such as “A prize ball shortage error has occurred” on the display screen of the effect display device 9.
受信した演出制御コマンドが賞球過剰エラーコマンドであれば(ステップS627)、演出制御用CPU101aは、演出表示装置9の表示画面に所定の賞球過剰エラー報知情報を重畳表示する制御を行う(ステップS628)。例えば、演出制御用CPU101aは、演出表示装置9の表示画面に「賞球過剰エラーが発生しました」などの文字列を表示させる制御を行う。
If the received effect control command is an award ball excess error command (step S627), the effect control CPU 101a performs control to superimpose predetermined award ball excess error notification information on the display screen of the effect display device 9 (step S627) S628). For example, the effect control CPU 101 a performs control to display a character string such as “A prize ball excess error has occurred” on the display screen of the effect display device 9.
なお、各エラー表示を単に重畳表示させるのではなく、不正の重要度の観点から順位付けを行って優先順位が高いエラーを優先して報知するようにしてもよい。例えば、払出個数異常エラーを最も高い優先順位で優先的に報知するようにしてもよく、エラー状態が変化した場合に新たに発生したエラーを優先して報知するようにしてもよい。
The error display may be prioritized from the viewpoint of the degree of importance of fraud instead of simply superimposing each error display, and errors with high priority may be notified with priority. For example, the payout number abnormality error may be preferentially notified at the highest priority, or a newly generated error may be preferentially notified when the error state changes.
受信した演出制御コマンドがドア開放時入賞異常コマンドであれば(ステップS629)、演出制御用CPU101aは、ガラス扉枠2の開放状態において異常入賞を検出したことを報知する所定の特殊音2を出力させるための音信号(音番号データ)を音声出力基板70に出力する(ステップS630)。この場合、音声出力基板70において、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100から入力した特殊音2用の音番号データは、入力ドライバ702を介して音声合成用IC703に入力される。そして、音声合成用IC703は、音番号データに応じた特殊音2(例えば、ビープ音などの警告音)を発生し、増幅回路705を介してスピーカ27から出力させる。ただし、この場合、前述したステップS624において、ガラス扉枠2の開放状態を検出した場合に出力される特殊音1とは異なる態様(例えば、音の出力パターンや、音量や、音の高低が異なる)の音が出力される。
If the received effect control command is a door open winning combination abnormal command (step S629), the effect control CPU 101a outputs a predetermined special sound 2 notifying that an abnormal winning combination has been detected in the open state of the glass door frame 2. A sound signal (sound number data) for causing the sound output is output to the sound output board 70 (step S630). In this case, sound number data for special sound 2 input from the effect control microcomputer 100 in the sound output substrate 70 is input to the speech synthesis IC 703 via the input driver 702. Then, the voice synthesis IC 703 generates a special sound 2 (for example, a warning sound such as a beep sound) corresponding to the sound number data, and causes the speaker 27 to output the special sound 2 via the amplification circuit 705. However, in this case, an aspect different from the special sound 1 output when the open state of the glass door frame 2 is detected in the above-described step S 624 (for example, the output pattern of the sound, the volume, or the height of the sound is different) The sound of) is output.
ステップS630の処理が実行されることによって、この実施の形態では、ガラス扉枠2の開放状態においていずれかの入賞口(大入賞口、始動入賞口14、普通入賞口29,30)で遊技球の入賞を検出したことにもとづいて異常入賞が検出されると、スピーカ27から特殊音が出力されて、不正行為が行われていることを報知する。
By executing the process of step S630, in this embodiment, in the open state of the glass door frame 2, the gaming ball is held at one of the winning openings (large winning opening, starting winning opening 14, ordinary winning openings 29, 30). When an abnormal prize is detected based on the detection of the prize, a special sound is output from the speaker 27 to notify that an illegal act is being performed.
なお、特殊音2の出力は、例えば、遊技機に対する電力供給がオフするまで、またはガラス扉枠2が閉鎖状態にされるまで継続して出力されるようにしてもよいが、出力開始から所定期間(例えば、20秒)が経過するまで継続して出力されるようにしてもよい。出力開始から所定期間が経過するまで継続して出力されるようにする場合には、演出制御用CPU101は、特殊音2の出力開始時にタイマをスタートさせ、そのタイマによって所定期間が経過したことが確認されたら、特殊音2の出力を停止させるための音番号データを音声出力基板70に出力する。ガラス扉枠2が閉鎖状態にされるまで継続して出力されるようにする場合には、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ガラス扉枠2が開放状態から閉鎖状態に変化したことを検出すると、その旨を示すコマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100の演出制御用CPU101は、その旨を示すコマンドを受信すると、特殊音2を出力していた場合には、特殊音2の出力を停止させるための音番号データを音声出力基板70に出力する。また、この実施の形態では、ガラス扉枠2が開放状態であるときに入賞が検出される度に遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560からドア開放時入賞異常コマンドが送信され(図56参照)、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、ドア開放時入賞異常コマンドを受信すると特殊音2の出力を開始するので(ステップS629,S630参照)、ドア開放時入賞異常コマンドが受信される度に最初から特殊音2の出力が開始されることになる(すなわち、出力開始から所定期間が経過すると停止するように構成されている場合には出力期間が実質的に延長される。)が、そのように制御しなくてもよい。例えば、特殊音2が出力されているときに新たにドア開放時入賞異常コマンドを受信した場合には、そのドア開放時入賞異常コマンドを無視するようにしてもよい。よって、出力開始から例えば20秒が経過すると停止するように構成されている場合には、出力期間は必ず20秒である。そして、そのように制御する場合には、特殊音2の出力が終了した後に、新たにドア開放時入賞異常コマンドを受信したときに特殊音2の出力を最初から行う。なお、無視したドア開放時入賞異常コマンドの受信を記憶しておき、特殊音2の出力が終了したときに、記憶されているドア開放時入賞異常コマンドがあれば、それにもとづいて特殊音2の出力を開始するようにしてもよい。
The output of the special sound 2 may be continuously output, for example, until the power supply to the gaming machine is turned off, or until the glass door frame 2 is closed, but a predetermined amount of time has passed from the start of the output. The output may be continued until the period (for example, 20 seconds) elapses. In the case where the output is continued until the predetermined period elapses from the start of the output, the effect control CPU 101 starts the timer at the start of the output of the special sound 2, and the predetermined period has elapsed by the timer. If confirmed, sound number data for stopping the output of the special sound 2 is output to the sound output board 70. When the glass door frame 2 is to be continuously output until it is put in the closed state, the game control microcomputer 560 detects that the glass door frame 2 has changed from the open state to the closed state, A command indicating that is transmitted to the effect control microcomputer 100. If the effect control CPU 101 of the effect control microcomputer 100 receives the command to that effect, it outputs the sound number data for stopping the output of the special sound 2 when the special sound 2 is output. Output to the substrate 70. Further, in this embodiment, when the winning is detected when the glass door frame 2 is in the open state, the game control microcomputer 560 transmits a door opening prize abnormal command (see FIG. 56), and effect control is performed. Since the microcomputer 100 starts outputting the special sound 2 when receiving the door opening prize failure command (see steps S629 and S630), the microcomputer 100 starts receiving the special sound 2 from the beginning every time the door opening prize error command is received. The output will be started (ie, the output period will be substantially extended if it is configured to stop when a predetermined period has elapsed from the start of output), but without such control. It is also good. For example, when the door open winning a prize abnormal command is newly received while the special sound 2 is being outputted, the door open prize winning command may be ignored. Therefore, when it is comprised so that it may stop, for example, 20 seconds after an output start, an output period is always 20 seconds. Then, in the case of such control, the special sound 2 is output from the beginning when the door opening prize failure command is newly received after the output of the special sound 2 is finished. In addition, the reception of the door opening prize failure command ignored is stored, and when the output of the special sound 2 ends, if there is a door opening prize failure command stored, the special sound 2 is The output may be started.
また、この実施の形態では、ガラス扉枠2が開放状態になると特殊音1の出力が開始され、特殊音1の出力が継続しているときに、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100においてドア開放時入賞異常コマンドが受信されたら、特殊音2の出力が開始される。その場合、特殊音1の出力を中止して特殊音2の出力が開始されるようにしてもよいし、特殊音2が、特殊音1に重ねて出力されるようにしてもよい。重ねて出力する場合には、例えば、音声合成用IC703(図8参照)は、特殊音1の出力中に特殊音2の音番号データが入力されたら、特殊音1と特殊音2とを同時に出力するように構成される。また、特殊音1に重ねて特殊音2を出力する場合には、特殊音1の音量に比べて、より音量が高い音を特殊音2として使用することが好ましい。また、特殊音1または特殊音2の出力開始時に、スピーカ27から演出効果音の出力(例えば、演出図柄の変動や大当り遊技に伴う音出力)などの他の音の出力がなされている場合があるが、その場合には、演出効果音などの出力を中止して特殊音2の出力が開始されるようにしてもよいし、特殊音2が、演出効果音などに重ねて出力されるようにしてもよい。演出効果音などに重ねて出力する場合には、演出効果音などの音量に比べて、より音量が高い音を特殊音2として使用する。
Further, in this embodiment, when the glass door frame 2 is in the open state, the output of the special sound 1 is started, and when the output of the special sound 1 is continued, the door control winning in the microcomputer 100 for prize opening When the abnormal command is received, the output of the special sound 2 is started. In that case, the output of the special sound 1 may be stopped and the output of the special sound 2 may be started, or the special sound 2 may be output superimposed on the special sound 1. In the case of overlapping output, for example, when the sound number data of the special sound 2 is input during the output of the special sound 1, for example, the voice synthesis IC 703 (see FIG. 8) simultaneously performs the special sound 1 and the special sound 2 Configured to output. Further, when the special sound 2 is output by being superimposed on the special sound 1, it is preferable to use a sound with a higher volume than the volume of the special sound 1 as the special sound 2. In addition, when output of special sound 1 or special sound 2 is started, other sounds such as output of effect sound (for example, output of fluctuation of effect pattern or sound output associated with a big hit game) from speaker 27 may be output. In this case, however, the output of the special sound 2 may be started by stopping the output of the effect sound, etc., or the special sound 2 may be output superimposed on the effect sound, etc. You may When the sound is superimposed on the effect sound and the like, a sound with a higher volume is used as the special sound 2 than the volume of the effect sound and the like.
また、特殊音2として、例えば、特殊音1と同じ出力パターンの音であるが音量が大きい音を使用したり、特殊音1と同じ出力パターンの音であるがより高い音を使用したりしてもよい。また、特殊音2は、ビープ音(連続音)であってもよいが、断続音であってもよい。一例として、特殊音1をビープ音とし、特殊音2を断続音とする。また、特殊音1も断続音である場合に断続間隔を特殊音1の場合よりも短くするようにしてもよい。さらに、遊技店員等が特殊音2をより認識しやすくなるように、特殊音2として、音声(例えば、「イジョウ」の連呼)を使用してもよい。
Also, as the special sound 2, for example, a sound having the same output pattern as the special sound 1 but having a large volume, or a sound having the same output pattern as the special sound 1 but having a higher sound is used. May be Further, the special sound 2 may be a beep sound (continuous sound), but may be an intermittent sound. As an example, the special sound 1 is a beep sound, and the special sound 2 is an intermittent sound. Further, when the special sound 1 is also the intermittent sound, the intermittent interval may be shorter than that of the special sound 1. Furthermore, voice (for example, continuous call of "Ijo") may be used as the special sound 2 so that a game clerk or the like can more easily recognize the special sound 2.
なお、この実施の形態では、特殊音を出力することによって不正行為が行われていることを報知する場合を示したが、報知の仕方は、この実施の形態で示したものにかぎらず、例えば、演出表示装置9の表示画面に不正行為が行われている旨を重畳表示してもよいし、各ランプ25,28a〜28cを所定の点灯/点滅パターンで点灯または点滅させることによって不正行為が行われていることを報知してもよい。また、例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、不正行為が行われている旨を示す不正検出信号を、ターミナル基板160を介してホールコンピュータなどの外部装置に出力するように構成してもよい。
In this embodiment, a special sound is output to notify that an unauthorized action is being performed. However, the method of notification is not limited to that shown in this embodiment, for example. The effect display may be superimposed on the display screen of the effect display device 9 to indicate that cheating is being performed, or cheating may be achieved by lighting or blinking each lamp 25, 28a to 28c in a predetermined lighting / flashing pattern. It may be informed that it is being performed. Further, for example, the game control microcomputer 560 may be configured to output a fraud detection signal indicating that fraudulent activity is being performed to an external device such as a hall computer via the terminal substrate 160.
受信した演出制御コマンドがその他のコマンドであれば、演出制御用CPU101aは、受信した演出制御コマンドに応じたフラグをセットする(ステップS631)。そして、ステップS611に移行する。なお、例えば、変動パターンコマンドや表示結果指定コマンドを受信した場合には、演出制御用CPU101aは、受信した変動パターンコマンドや表示結果指定コマンドをRAMに形成された所定の格納領域に格納する処理も行う。
If the received effect control command is another command, the effect control CPU 101a sets a flag according to the received effect control command (step S631). Then, the process proceeds to step S611. For example, when receiving a variation pattern command or a display result designation command, the effect control CPU 101a also stores the received variation pattern command or display result designation command in a predetermined storage area formed in the RAM. Do.
図92は、図90に示されたメイン処理における演出制御プロセス処理(ステップS785)を示すフローチャートである。演出制御プロセス処理では、演出制御用CPU101aは、演出制御プロセスフラグの値に応じてステップS800〜S806のうちのいずれかの処理を行う。各処理において、以下のような処理を実行する。なお、演出制御プロセス処理では、演出表示装置9の表示状態が制御され、演出図柄の可変表示が実現されるが、第1特別図柄の変動に同期した演出図柄の可変表示に関する制御も、第2特別図柄の変動に同期した演出図柄の可変表示に関する制御も、一つの演出制御プロセス処理において実行される。なお、第1特別図柄の変動に同期した演出図柄の可変表示と、第2特別図柄の変動に同期した演出図柄の可変表示とを、別の演出制御プロセス処理により実行するように構成してもよい。また、この場合、いずれの演出制御プロセス処理により演出図柄の変動表示が実行されているかによって、いずれの特別図柄の変動表示が実行されているかを判断するようにしてもよい。
FIG. 92 is a flowchart showing an effect control process (step S785) in the main process shown in FIG. In the effect control process, the effect control CPU 101a performs any one of steps S800 to S806 in accordance with the value of the effect control process flag. In each process, the following process is performed. In the effect control process, the display state of the effect display device 9 is controlled, and variable display of the effect symbol is realized. However, control regarding variable display of the effect symbol synchronized with the fluctuation of the first special symbol is also the second Control relating to variable display of the rendering symbol synchronized with the variation of the special symbol is also executed in one rendering control process. In addition, even if it is configured to execute the variable display of the effect symbol synchronized with the change of the first special symbol and the variable display of the effect symbol synchronized with the change of the second special symbol by another effect control process process. Good. Further, in this case, it may be determined which of the special symbols is displayed depending on which of the effect control process processing is executed.
変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(ステップS800):遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から変動パターンコマンドを受信しているか否か確認する。具体的には、コマンド解析処理でセットされる変動パターンコマンド受信フラグがセットされているか否か確認する。変動パターンコマンドを受信していれば、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動開始処理(ステップS801)に対応した値に変更する。
Fluctuation pattern command reception waiting process (step S800): It is confirmed whether or not a fluctuation pattern command is received from the game control microcomputer 560. Specifically, it is checked whether or not the variation pattern command reception flag set in the command analysis process is set. If the fluctuation pattern command is received, the value of the effect control process flag is changed to a value corresponding to the effect symbol fluctuation start process (step S801).
演出図柄変動開始処理(ステップS801):演出図柄の変動が開始されるように制御する。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動中処理(ステップS802)に対応した値に更新する。
Effect pattern fluctuation start processing (step S801): Control is performed so that the change of effect pattern is started. Then, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the effect symbol process (step S802).
演出図柄変動中処理(ステップS802):変動パターンを構成する各変動状態(変動速度)の切替タイミング等を制御するとともに、変動時間の終了を監視する。そして、変動時間が終了したら、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を演出図柄変動停止処理(ステップS803)に対応した値に更新する。
Process during production symbol fluctuation (step S802): While controlling the switching timing and the like of each fluctuation state (variation speed) constituting the fluctuation pattern, the end of fluctuation time is monitored. Then, when the fluctuation time is over, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the effect symbol fluctuation stop process (step S803).
演出図柄変動停止処理(ステップS803):演出図柄の変動を停止し表示結果(停止図柄)を導出表示する制御を行う。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を大当り表示処理(ステップS804)または変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(ステップS800)に対応した値に更新する。
Effect pattern fluctuation stop processing (step S803): The change of the effect pattern is stopped and control is performed to derive and display the display result (stop pattern). Then, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the big hit display process (step S804) or the variation pattern command reception waiting process (step S800).
大当り表示処理(ステップS804):大当りである場合には、変動時間の終了後、演出表示装置9に大当りの発生を報知するための画面を表示する制御を行う。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を大当り遊技中処理(ステップS805)に対応した値に更新する。
Big hit display process (step S804): If it is a big hit, control is performed to display a screen for notifying the occurrence of the big hit on the effect display device 9 after the fluctuation time ends. Then, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the process during the big hit game (step S805).
大当り遊技中処理(ステップS805):大当り遊技中の制御を行う。例えば、大入賞口開放中指定コマンドや大入賞口開放後指定コマンドを受信したら、演出表示装置9におけるラウンド数の表示制御等を行う。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を大当り終了演出処理(ステップS806)に対応した値に更新する。
During the big hit game processing (step S805): Control during the big hit game is performed. For example, when a special winning opening open designation command or a special winning opening open designation command is received, display control of the number of rounds in the effect display device 9 is performed. Then, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the big hit end effect processing (step S806).
大当り終了演出処理(ステップS806):演出表示装置9において、大当り遊技状態が終了したことを遊技者に報知する表示制御を行う。そして、演出制御プロセスフラグの値を変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(ステップS800)に対応した値に更新する。
Big hit end effect processing (step S806): In the effect display device 9, display control is performed to notify the player that the big hit gaming state has ended. Then, the value of the effect control process flag is updated to a value corresponding to the fluctuation pattern command reception waiting process (step S800).
以上に説明したように、この実施の形態によれば、ガラス扉枠2の開放状態を検出するドア開放センサ155と、各入賞口(大入賞口、始動入賞口14、普通入賞口29,30)にて遊技球を検出する各入賞スイッチ(カウントスイッチ23、始動口スイッチ14a、入賞口スイッチ29a,30a)を備える。また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ドア開放センサ155によってガラス扉枠2が開放状態であることが検出されているときに、いずれかの入賞スイッチによって入賞口にて遊技球が検出されたことにもとづいて、異常入賞が発生したと判定する。そして、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560によって異常入賞が発生したと判定されたことにもとづいて、異常入賞を報知するための特殊音を出力する制御を行う。そのため、ガラス扉枠2が開放状態となっているときに、さらにいずれかの入賞口にて遊技球が検出されたことにもとづいて特殊音を出力して異常入賞を報知できるので、ガラス扉枠2が開放状態となっているときに行われる不正行為を確実に検出して報知することによって、不正行為を防止することができる。
As described above, according to this embodiment, the door opening sensor 155 for detecting the open state of the glass door frame 2, and each winning opening (large winning opening, starting winning opening 14, ordinary winning openings 29, 30) And the respective winning switches (count switch 23, starting opening switch 14a, and winning opening switches 29a, 30a). In the game control microcomputer 560, when the door opening sensor 155 detects that the glass door frame 2 is in the open state, the game ball is detected at the winning opening by any one of the winning switches. Based on the above, it is determined that an abnormal winning has occurred. Then, based on the fact that the game control microcomputer 560 determines that the abnormal winning has occurred, the effect control microcomputer 100 performs control to output a special sound for notifying of the abnormal win. Therefore, when the glass door frame 2 is in the open state, a special sound can be output based on the fact that the game ball is detected at any one of the winning openings, and an abnormal winning can be notified, so the glass door frame The fraud can be prevented by reliably detecting and notifying the fraud that is conducted when 2 is in the open state.
例えば、特開平2−280786号公報に記載された遊技機では、単にガラス扉が開放されていることを検出しただけで警報音を発することができるにすぎないので、必ずしも不正行為が行われていることを検出して報知できるとはかぎらない。これに対して、この実施の形態によれば、ガラス扉枠2の開放状態を検出するだけでなく、ガラス扉枠2の開放状態においてさらに入賞を検出したことにもとづいて異常入賞であると判定し報知するので、ガラス扉枠2が開放状態となっているときに行われる不正行為を確実に検出して報知することができる。
For example, in the gaming machine described in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2-280786, it is only possible to emit an alarm sound simply by detecting that the glass door is opened, so that cheating is not always performed. It is not always possible to detect and report on On the other hand, according to this embodiment, not only the open state of the glass door frame 2 is detected, but also it is determined as the abnormal prize based on the fact that the winning is detected in the open state of the glass door frame 2 Since the notification is performed, it is possible to reliably detect and notify the injustice which is performed when the glass door frame 2 is in the open state.
なお、この実施の形態では、ガラス扉枠2が開放状態となっているときの異常入賞の検出の仕方として、スイッチ処理(ステップS21参照)において各入賞スイッチ23,14a,29a,30aのオン状態を検出したときにドア開放信号を入力しているか否かを確認することによって行う場合を示したが(図56参照)、ガラス扉枠2が開放状態となっているときの異常入賞の検出の仕方は、この実施の形態で示したものにかぎられない。例えば、賞球処理(ステップS32参照)において各入賞口(大入賞口、始動入賞口14、普通入賞口29,30)への入賞を判定したタイミングで、ガラス扉枠2が開放状態となっているときの異常入賞であるか否かを判定するようにしてもよい。
In this embodiment, as a method of detecting an abnormal prize when the glass door frame 2 is in the open state, the on state of each prize switch 23, 14a, 29a, 30a in the switch process (see step S21) In the case of detecting an abnormal winning when the glass door frame 2 is in the open state, the case is shown by checking whether or not the door open signal is input when detecting the (see FIG. 56). The manner is not limited to the one shown in this embodiment. For example, the glass door frame 2 is opened at the timing at which it is determined that the winnings on each winning opening (large winning opening, starting winning opening 14, normal winning openings 29, 30) have been made in the winning ball processing (see step S32). It may be determined whether or not it is an abnormal prize when being hit.
図93は、賞球コマンド出力カウンタ加算処理の他の例を示すフローチャートである。図93に示す例では、CPU56は、ステップS5111でポインタが指す賞球コマンド出力カウンタの値を1加算すると、ドア開放センサ155からのドア開放信号がオン状態となっているか否かを確認する(ステップS5115A)。ドア開放信号がオン状態となっていれば、CPU56は、ガラス扉枠2の開放状態において異常入賞を検出したことを示すドア開放時入賞異常コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に対して送信する制御を行う(ステップS5111B)。
FIG. 93 is a flowchart showing another example of the award ball command output counter addition process. In the example shown in FIG. 93, the CPU 56 checks whether the door open signal from the door open sensor 155 is in the on state by adding 1 to the value of the award ball command output counter pointed by the pointer in step S5111 ( Step S5115A). If the door open signal is in the on state, the CPU 56 controls to transmit the door open prize error command to the effect control microcomputer 100, which indicates that the abnormal prize is detected in the open state of the glass door frame 2. (Step S5111B).
図93のように構成しても、ステップS5111A,S5111Bの処理が実行されることによって、ガラス扉枠2が開放状態となっている状態においていずれかの入賞口(大入賞口、始動入賞口14、普通入賞口29,30)で遊技球の入賞を検出することができ、異常入賞が発生したと判定して、ドア開放時入賞異常コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信することができる。
Even in the configuration as shown in FIG. 93, any of the winning openings (big winning opening, start winning opening 14) can be performed in a state where the glass door frame 2 is in the open state by executing the processing of steps S5111A and S5111B. The normal winning opening 29, 30) can detect the winning of the gaming ball, and it is determined that an abnormal winning has occurred, and the door opening winning abnormal command can be transmitted to the effect control microcomputer 100.
また、遊技機では、遊技状態を示す信号や遊技機の異常を示す信号を、遊技機に設けられた外部情報出力端子基板を介してホールコンピュータなどに出力可能に構成することが行われている。例えば、特開2003−024553号公報(段落0006、段落0025、段落0043)には、出力処理回路を介して、ホールコンピュータに対して、大当り回数などの営業情報や、初期化処理が実行されたことを示す信号を出力するように構成することが記載されている。
In addition, in the gaming machine, a signal indicating the gaming state and a signal indicating an abnormality in the gaming machine are configured to be able to be output to a hall computer or the like through an external information output terminal board provided in the gaming machine. . For example, according to Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2003-024553 (paragraph 0006, paragraph 0025, paragraph 0043), business information such as the number of big hits and initialization processing are executed for the hole computer via the output processing circuit. It is described to be configured to output a signal indicating that.
上記特開2003−024553号公報に記載された遊技機では、初期化処理が実行されたことを示す信号を外部出力するように構成することによって、不正に初期化処理(RAMのクリアなど)を行わせて大当りを狙う不正行為が行われている可能性を外部のホールコンピュータなどで認識可能にしている。しかし、遊技機への電源投入時にのみ行われる可能性のある初期化処理のために専用の外部出力用の信号線を設けなければならず、外部出力用の信号線に無駄が生じる。
In the gaming machine described in the above-mentioned Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2003-024553, the initialization process (clearing of the RAM, etc.) is illegally performed by externally outputting a signal indicating that the initialization process has been executed. It is possible to recognize the possibility of fraudulent activity aimed at making a big hit with an external hall computer etc. However, a dedicated signal line for external output must be provided for the initialization process that may be performed only when power is supplied to the gaming machine, and the signal line for external output is wasted.
そこで、不正行為を防止しつつ、外部出力用の信号線の無駄を低減できるようにすることが望まれる。
Therefore, it is desirable to reduce waste of signal lines for external output while preventing fraud.
この実施の形態によれば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、遊技機への電源投入時に初期化処理が実行されたこと、および所定のエラー(本例では、始動入賞口14への異常入賞)が発生していると判定されたことを含む所定の信号出力条件が成立したことにもとづいて、遊技機の外部にセキュリティ信号を出力する。この場合、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、初期化処理が実行されたときと所定のエラーが発生していると判定されたときとで、遊技機に設けられた共通の出力端子(ターミナル基板の共通のコネクタCN7)からセキュリティ信号を出力する。また、セキュリティ信号を出力しているときに新たに所定の信号出力条件が成立(本例では、新たに始動入賞口14への異常入賞を検出)した場合には、セキュリティ信号を出力する出力時間を延長する。そのため、初期化処理が実行されたことにもとづいてセキュリティ信号を出力することによって、遊技機への電源投入時に行われる不正行為を防止することができる。また、初期化処理が実行されたときと所定のエラーが発生していると判定されたときとで共通の出力端子にセキュリティ信号を出力するので、外部出力用の信号線の無駄を低減することができる。従って、遊技機への電源投入時に行われる不正行為を防止しつつ、外部出力用の信号線の無駄を低減することができる。
According to this embodiment, microcomputer 560 for game control executes an initialization process when power is supplied to the gaming machine, and a predetermined error (in this example, an abnormal winning to start winning opening 14). A security signal is output to the outside of the gaming machine on the basis of the satisfaction of a predetermined signal output condition including that it has been determined that an occurrence of. In this case, the microcomputer 560 for gaming control has a common output terminal (terminal board) provided on the gaming machine when the initialization process is executed and when it is determined that a predetermined error has occurred. Output security signal from common connector CN7). In addition, an output time for outputting a security signal when a predetermined signal output condition is newly satisfied (in the present example, when an abnormal winning to the start winning opening 14 is newly detected) while the security signal is being output. To extend Therefore, by outputting the security signal based on the execution of the initialization process, it is possible to prevent the fraudulent acts performed when the gaming machine is powered on. In addition, since the security signal is output to the common output terminal when the initialization processing is performed and when it is determined that the predetermined error occurs, waste of the signal line for external output is reduced. Can. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the waste of the signal line for external output while preventing the fraudulent acts performed at the time of power supply to the gaming machine.
また、この実施の形態によれば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、始動口スイッチ14a(近接スイッチ)から入力した検出信号と入賞確認スイッチ14b(フォトセンサ)から入力した検出信号とにもとづいて、始動口スイッチ14aにて検出された遊技球数と入賞確認スイッチ14bにて検出された遊技球数との差が所定の閾値を超えた(本例では、10以上となった)と判定すると、所定のエラーとして、始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したと判定する。なお、この実施の形態では、始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14bとを互いに異なる検出方式のセンサ(本例では、近接スイッチとフォトセンサ)により構成している。そのため、遊技球を検出するスイッチに対する不正行為をより確実に検知して、確実な不正行為対策を講ずることができる。
Further, according to this embodiment, the microcomputer 560 for gaming control is based on the detection signal inputted from the starting opening switch 14a (proximity switch) and the detection signal inputted from the prize confirmation switch 14b (photo sensor). If it is determined that the difference between the number of gaming balls detected by the starting opening switch 14a and the number of gaming balls detected by the winning confirmation switch 14b exceeds a predetermined threshold (in this example, 10 or more), As a predetermined error, it is determined that an abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14 has occurred. In this embodiment, the starting opening switch 14a and the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b are constituted by sensors of different detection methods (in this example, proximity switches and photosensors). Therefore, it is possible to more reliably detect the cheating against the switch for detecting the gaming ball, and to take certain measures against the cheating.
また、この実施の形態によれば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、始動口スイッチ14aから検出信号を入力したことのみにもとづいて、特別図柄の変動表示を実行するとともに賞球払出処理を実行する。また、入賞確認スイッチ14bから入力した検出信号は、始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したか否かの判定のみに用いられる。そのため、特別図柄の変動表示および賞球払出処理については、一方のスイッチにおける検出結果にもとづいて処理を行うので、不正行為対策の強化に伴う処理負担の増加を防止することができる。
Further, according to this embodiment, the microcomputer 560 for game control executes the variation display of the special symbol and the award ball payout processing only on the basis of the detection signal being inputted from the starting opening switch 14a. . Further, the detection signal input from the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b is used only for determining whether or not an abnormal winning on the start winning a prize opening 14 has occurred. Therefore, since the variation display of special symbols and the prize ball payout processing are performed based on the detection result of one of the switches, it is possible to prevent an increase in the processing load associated with the strengthening of the measures against fraud.
また、この実施の形態によれば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、始動口スイッチ14aにて検出された遊技球数と入賞確認スイッチ14bにて検出された遊技球数との差が、所定の閾値として、始動入賞口14内が球詰まり状態となったときの始動口スイッチ14aにおける遊技球の検出数と入賞確認スイッチ14bにおける遊技球の検出数との差分(例えば、3個)よりも多い値(本例では、10)を超えたか否かを判定する。そのため、始動入賞口14内が球詰まり状態となってしまった場合に、誤って始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したと判定することを防止することができる。従って、不正行為対策の強化に伴う誤判定を防止することができる。
Further, according to this embodiment, in the gaming control microcomputer 560, the difference between the number of gaming balls detected by the starting opening switch 14a and the number of gaming balls detected by the winning confirmation switch 14b is predetermined. As a threshold value, it is greater than the difference (for example, three) between the number of detected gaming balls in the starting opening switch 14a and the number of detected gaming balls in the winning confirmation switch 14b when the inside of the starting winning opening 14 becomes blocked. It is determined whether the value (10 in this example) is exceeded. Therefore, when the inside of the start winning opening 14 is clogged, it is possible to prevent the determination that the abnormal winning to the starting winning opening 14 has occurred by mistake. Therefore, it is possible to prevent an erroneous determination that accompanies strengthening of measures against fraud.
また、この実施の形態によれば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、遊技機への電源投入時に初期化処理が実行されたときと所定のエラー(本例では、始動入賞口14への異常入賞)が発生していると判定されたときとで、異なる時間にわたってセキュリティ信号を出力する。具体的には、この実施の形態では、遊技機への電源投入時に初期化処理が実行された場合には30秒間に亘ってセキュリティ信号が外部出力され、始動入賞口14への異常入賞が検出された場合には4分間にわたってセキュリティ信号が外部出力される。そのため、セキュリティ信号の出力時間を判定することによって、ホールコンピュータなどの外部装置において、初期化処理が行われた場合であるか所定のエラーが発生している場合であるかを判別することが可能となる。
Further, according to this embodiment, microcomputer 560 for gaming control is given a predetermined error when initialization processing is executed at the time of power supply to the gaming machine (in this example, abnormal winning to start winning opening 14) The security signal is output over different times when it is determined that the occurrence of. Specifically, in this embodiment, when the initialization process is executed when the game machine is powered on, the security signal is externally output over 30 seconds, and the abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14 is detected. If this is done, the security signal is output externally for 4 minutes. Therefore, by determining the output time of the security signal, it is possible to determine in the external device such as the hall computer whether the initialization process has been performed or a predetermined error has occurred. It becomes.
また、この実施の形態によれば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370とは、シリアル通信で制御コマンドを送受信する。また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との通信接続状態を確認するための接続確認コマンドを、所定期間(本例では1秒)が経過する毎に払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。また、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、接続確認コマンドを受信したことにもとづいて接続OKコマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。この場合、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が制御状態(本例では、賞球エラー、満タンエラー、球切れエラー、および払出個数異常エラー)を認識可能な態様で接続OKコマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。そのような構成により、シリアル通信方式を用いることにより、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との配線の取り回しの容易化を図ることができる。また、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370が接続確認コマンドの受信にもとづいて定期的に出力する接続OKコマンドに制御状態を乗せることにより、制御状態信号(制御状態が付加された応答信号)を送信することができる。そのため、制御状態信号の出力タイミングを考慮することなく制御状態信号の取りこぼし等の発生を防止することができ、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との間の通信を確実に行うことができる。なお、この実施の形態では、接続確認コマンドを送信する周期(間隔)を1秒としていたが、0.5秒等としてもよい。
Further, according to this embodiment, the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 transmit and receive control commands by serial communication. The game control microcomputer 560 also executes a connection confirmation command for confirming the communication connection state with the payout control microcomputer 370, each time a predetermined period (1 second in this example) elapses. Send to 370 Further, the payout control microcomputer 370 transmits a connection OK command to the game control microcomputer 560 based on the reception of the connection confirmation command. In this case, the payout control microcomputer 370 is connected in a manner that allows the gaming control microcomputer 560 to recognize the control state (in this example, a winning ball error, a full tank error, a out-of-ball error, and a payout number abnormality error). The command is transmitted to the game control microcomputer 560. With such a configuration, by using the serial communication method, the wiring between the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 can be facilitated. In addition, the control state signal is put on the connection OK command periodically output by the payout control microcomputer 370 based on the reception of the connection confirmation command, thereby transmitting the control state signal (the response signal to which the control state is added). Can. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of the drop of the control state signal without considering the output timing of the control state signal, and the communication between the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 is reliably performed. be able to. In this embodiment, the period (interval) for transmitting the connection confirmation command is 1 second, but may be 0.5 seconds or the like.
また、この実施の形態によれば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、払出制御の実行を終了したときに、賞球プロセスタイマに所定期間(本例では1秒)を再設定して賞球プロセスタイマによる計測制御を開始する(ステップS52505参照)。そして、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、賞球個数が記憶されていなければ(具体的には、ステップS52301で賞球コマンド出力カウンタの中にカウント値が1以上のものがなければ)、再設定した賞球プロセスタイマがタイムアウトしたことにもとづいて、新たな接続確認コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。そのため、払出制御の実行の終了後に新たな接続確認コマンドを送信するまでの間にインターバル期間を設けることができ、払出制御の実行の終了時における処理が集中して新たな接続確認コマンドの取りこぼし等が発生することを防止することができる。
Further, according to this embodiment, when the execution of the payout control is finished, the game control microcomputer 560 resets the predetermined period (1 second in this example) to the award ball process timer to execute the award ball process. Measurement control by the timer is started (see step S52505). Then, if the number of winning balls is not stored (specifically, if there is one having a count value of 1 or more in the winning ball command output counter in step S52301), the microcomputer 560 for gaming control is reset. A new connection confirmation command is sent to the payout control microcomputer 370 based on the fact that the winning ball process timer has timed out. Therefore, an interval period can be provided between the end of the execution of the payout control and the transmission of a new connection confirmation command, and the processing at the end of the execution of the payout control is concentrated, and the new connection confirmation command is missed, etc. Can be prevented.
また、この実施の形態によれば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、接続確認コマンドの送信タイミングにかかわらず、入賞を検出したことにもとづいて、賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。また、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球個数コマンドを受信したことにもとづいて賞球個数受付コマンドを送信するとともに、払出制御の実行の実行中に賞球準備中コマンドを、所定の払出中信号出力期間(本例では1秒)毎に遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。この場合、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が制御状態(本例では、賞球エラー、満タンエラー、球切れエラー、および払出個数異常エラー)を認識可能な態様で賞球準備中コマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、賞球個数受付コマンドを受信したことにもとづいて、接続確認コマンドの送信を停止する。そのため、払出制御の実行中は無駄に接続確認コマンドの送信制御を行わないようにすることによって、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560の制御負担を軽減することができる。また、払出制御の実行中であっても、賞球準備中コマンドに制御状態を乗せることにより制御状態信号を出力することができるため、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560側で制御状態を認識することができる。
Further, according to this embodiment, the game control microcomputer 560 transmits the winning ball number command to the payout control microcomputer 370 based on the detection of the winning regardless of the transmission timing of the connection confirmation command. Do. Further, the payout control microcomputer 370 transmits a prize ball count reception command based on the reception of the prize ball count command, and during the execution of the payout control, a predetermined prize ball preparing command is being dispensed. It is transmitted to the game control microcomputer 560 every signal output period (one second in this example). In this case, the payout control microcomputer 370 can recognize the prize ball in a manner that the gaming control microcomputer 560 can recognize the control state (in this example, the prize ball error, the full tank error, the out-of-ball error, and the payout number abnormality error). The command under preparation is transmitted to the game control microcomputer 560. Further, the game control microcomputer 560 stops the transmission of the connection confirmation command based on the reception of the winning balls number reception command. Therefore, by not performing the transmission control of the connection confirmation command in vain while the payout control is being executed, the control burden on the game control microcomputer 560 can be reduced. Further, even during the execution of the payout control, the control state signal can be output by putting the control state on the in-progress ball preparation command, so that the game control microcomputer 560 can recognize the control state. it can.
また、この実施の形態によれば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、賞球終了コマンドを受信した後、賞球個数が記憶されていれば(具体的には、ステップS52301で賞球コマンド出力カウンタの中にカウント値が1以上のものがあれば)、接続確認コマンドの送信にかかわらず、直ちに新たな賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。そのため、払出制御の実行処理の迅速化を図ることができる。
Further, according to this embodiment, after the game control microcomputer 560 receives the award ball end command, if the number of award balls is stored (specifically, at step S52301, the award ball command output counter If there is one having a count value of 1 or more), a new winning ball number command is immediately transmitted to the payout control microcomputer 370 regardless of the transmission of the connection confirmation command. Therefore, it is possible to accelerate the execution process of the payout control.
また、この実施の形態によれば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ60は、受信した接続OKコマンドで示される制御状態にもとづいて、所定のエラー(本例では、賞球エラー、満タンエラー、球切れエラー、および払出個数異常エラー)が発生しているか否かを判定する。そして、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ60は、所定のエラーが発生していないと判定したことを条件として、賞球個数コマンドを払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信する。そのため、エラー状態となっていて正常に払出制御を行えない場合に賞球個数コマンドを送信してしまう不都合を防止することができる。特に、この実施の形態では、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370が備えるRAMはバックアップ電源によりバックアップされていないので、払出制御に異常が生じているときに賞球個数コマンドを送信してしまうと、電源リセットなどにより賞球個数の記憶が消滅し、遊技者に大きな不利益を与えてしまう可能性がある。そこで、この実施の形態では、払出制御に異常が生じている場合には、バックアップ電源でバックアップされている遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560側で賞球個数の記憶を保持したまま賞球個数コマンドの送信を保留するように制御することによって、そのような不利益が生じることを防止することができる。
Further, according to this embodiment, the microcomputer 60 for game control is based on the control state indicated by the received connection OK command, and a predetermined error (in this example, winning ball error, full error, out-of-ball error) , And it is determined whether or not a payout amount abnormality error) has occurred. Then, on the condition that it is determined that the predetermined error has not occurred, the game control microcomputer 60 transmits a prize ball count command to the payout control microcomputer 370. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the inconvenience of transmitting the winning balls number command when the player is in the error state and can not perform the payout control normally. In particular, in this embodiment, the RAM included in the payout control microcomputer 370 is not backed up by the backup power supply, so when a prize ball count command is transmitted when an abnormality occurs in the payout control, the power is reset. As a result, the memory of the number of winning balls disappears, which may cause a great disadvantage to the player. Therefore, in this embodiment, when there is an abnormality in the payout control, the game control microcomputer 560 side backed up by the backup power source transmits the prize ball number command while holding the memory of the number of prize balls. By controlling to hold down, it is possible to prevent such disadvantages from occurring.
また、この実施の形態によれば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、接続確認コマンドを送信した後、接続OKコマンドを受信できなかった場合には、接続確認コマンドを送信する時間間隔を長くし、特定期間(本例では10秒)が経過する毎に接続確認コマンドを送信する制御に切り替える。そのため、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との間の通信状態が不安定な状態では、接続確認コマンドを送信するまでのインターバル期間を長くすることによって、接続確認コマンドの送信処理を無駄に実行する頻度を低減し、無駄な処理負担を軽減することができる。
Further, according to this embodiment, after transmitting the connection confirmation command, if the connection OK command can not be received after transmitting the connection confirmation command, the time interval for transmitting the connection confirmation command is increased. The control is switched to transmission of a connection confirmation command each time a specific period (10 seconds in this example) elapses. Therefore, in a state in which the communication state between the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370 is unstable, the connection confirmation command transmission process is performed by extending the interval period until the connection confirmation command is transmitted. The frequency of wasteful execution can be reduced, and the unnecessary processing burden can be reduced.
また、この実施の形態によれば、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、所定のエラー(本例では、賞球エラー、満タンエラー、球切れエラー、および払出個数異常エラー)が発生したときに、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が所定のエラーを認識可能な情報を、接続OKコマンドの特定ビットを異ならせることにより設定し、当該設定がなされた接続OKコマンドを遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に送信する。また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、受信した接続OKコマンドに設定された所定のエラーを認識可能な情報をそのまま設定した枠状態表示コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する。そして、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、枠状態表示コマンドを受信したことにもとづいて、演出装置(本例では、演出表示装置9)を制御して所定のエラーが発生したことを報知する制御を行う。そのため、演出装置を用いて所定のエラーが発生したことを報知することができるとともに、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560の処理負担を軽減することができる。
Further, according to this embodiment, the payout control microcomputer 370 can play the game when a predetermined error (in this example, the winning ball error, the full tank error, the out-of-ball error, and the payout number abnormality error) occurs. The control microcomputer 560 sets information by which a predetermined error can be recognized, by making the specific bit of the connection OK command different, and transmits the connection OK command in which the setting is made to the game control microcomputer 560. Further, the game control microcomputer 560 transmits, to the effect control microcomputer 100, a frame state display command in which the information capable of recognizing a predetermined error set in the received connection OK command is set as it is. Then, the effect control microcomputer 100 controls the effect device (in this example, the effect display device 9) based on the reception of the frame state display command to notify that a predetermined error has occurred. Do. Therefore, the effect device can be used to notify that a predetermined error has occurred, and the processing load on the game control microcomputer 560 can be reduced.
また、この実施の形態によれば、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、賞球や貸し球の払い出すべき数の未払出の遊技球を超えた払出過多数と払い出すべき数の未払出の遊技球に満たなかった払出不足数とを払出個数異常カウンタを用いて累積的にカウントする。そして、払出個数異常カウンタの値が所定の払出個数異常エラー判定値(本例では2000)以上となると、払出制御の実行を停止させて払出停止状態に制御する。そのため、各々の払出制御について判断するのではなく、累積的にカウントアップされた払出個数異常カウンタの値にもとづいて異常な状況下で実行された払出制御を総合的に判断して払出制御の実行を停止させることができる。従って、不正に遊技球を払い出させる行為をより的確に防止することを可能とすることができる。
Further, according to this embodiment, the payout control microcomputer 370 is configured to receive an excessive number of payouts exceeding the number of unpaid gaming balls to be paid out of the winning balls and the lending balls and a large number of unpaid games to be paid out. The number of underpayments which did not reach the ball is cumulatively counted using a number-of-deliverys abnormality counter. Then, when the value of the payout amount abnormality counter becomes equal to or more than a predetermined payout number abnormality error determination value (2000 in this example), the execution of the payout control is stopped to control to the payout stop state. Therefore, instead of judging each of the payout control, the payout control is comprehensively judged based on the value of the cumulative-counted payout amount abnormality counter to execute the payout control. Can be stopped. Therefore, it is possible to more accurately prevent the act of causing the game balls to be paid out illegally.
また、この実施の形態によれば、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、所定基準数(本例では2)以上の払出不足数が発生したときに払出個数異常カウンタの値をカウントアップする。そのため、必要以上に払出制御の実行を停止させてしまう不都合を防止することができる。すなわち、遊技機の稼働状態ではごく少数(本例では1個)の払出不足数が生じることが少なからずあるのであるから、所定基準数(本例では2)以上の払出不足数が発生したことを条件としてカウントアップを行うことによって、必要以上に払出制御の実行を停止させてしまうことを防止している。
Further, according to this embodiment, the payout control microcomputer 370 counts up the value of the payout amount abnormality counter when the number of payout deficits equal to or more than the predetermined reference number (2 in this example) occurs. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the inconvenience of stopping the execution of the payout control more than necessary. That is, in the operating state of the gaming machine, a very small number (1 in this example) of the insufficient number of payouts may occur. By performing the count-up under the condition, it is possible to prevent the execution of the payout control from being stopped more than necessary.
また、この実施の形態によれば、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370は、払出不足数が発生したときに球払出装置97を駆動制御して遊技球を1つだけ払い出させる再払出制御を実行する。そして、再払出制御を実行しても遊技球の払い出しを検出しなかった場合には払出個数異常カウンタの値をカウントアップする。そのため、払出不足数が少ない場合でも適切に払出個数異常カウンタのカウント値に反映させて払出制御の実行の停止を行うことができ、不正に遊技球を払い出させる行為を防止する不正対策をより強化することができる。
Further, according to this embodiment, the payout control microcomputer 370 executes the repayment control to drive and control the ball payout device 97 to pay out only one game ball when the number of shortage of payout occurs. . If the payout of the game ball is not detected even if the repayment control is executed, the value of the payout amount abnormality counter is counted up. Therefore, even when the number of underpayments is small, it is possible to appropriately stop the execution of the payout control by reflecting the count value of the payout amount abnormality counter properly, and to prevent fraudulent actions to cause the game balls to be dispensed more It can be strengthened.
また、この実施の形態によれば、払出個数異常エラーが検出されて払出停止状態に制御されたときに、遊技機の電源リセットが行われたことを条件として払出停止状態を解除する。そのため、払出停止状態を解除するためには遊技店員が異常状態を確認した上で解除操作を行わなければならないので、不正に払出停止状態を解除されて異常な状態のまま遊技を継続されてしまうことを防止することができる。
Further, according to this embodiment, when the payout amount abnormality error is detected and controlled to the payout stop state, the payout stop state is canceled on the condition that the power supply of the gaming machine is reset. Therefore, since the gaming clerk must confirm the abnormal state and then perform the releasing operation in order to cancel the payout stop state, the payout stop state is unfairly canceled and the game is continued with the abnormal state. Can be prevented.
また、この実施の形態によれば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が備えるRAM55は、遊技機への電力供給が停止してもバックアップ電源により記憶内容を所定期間保持可能である。また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、払出停止状態に制御されているときには、入賞が生じても賞球個数コマンドの送信を禁止する。そのため、不正行為によらない遊技機側に起因する異常により払出停止状態となったにもかかわらずRAM55記憶された賞球個数(具体的には、賞球コマンド出力カウンタの値)がクリアされてしまう事態を防止することができ、遊技者に対して不利益が生じることを防止することができる。
Further, according to this embodiment, the RAM 55 provided in the gaming control microcomputer 560 can hold the stored content for a predetermined period by the backup power supply even if the power supply to the gaming machine is stopped. Further, when being controlled to be in the payout stop state, the game control microcomputer 560 prohibits the transmission of the winning ball number command even if a prize is generated. Therefore, the number of prize balls (specifically, the value of the prize ball command output counter) stored in the RAM 55 is cleared even though the payout is stopped due to an abnormality caused by the gaming machine side which is not caused by a fraudulent act. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the player from being disadvantaged.
また、この実施の形態によれば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、賞球個数コマンドを送信するタイミングで賞球個数カウンタに賞球個数を加算し、賞球情報を受信したことにもとづいて賞球個数カウンタの値を10減算する。そして、賞球個数カウンタの値が所定の賞球不足判定値(本例では501)以上となったことにもとづいて賞球不足エラーと判定し、賞球個数カウンタの値が所定の賞球過剰判定値(本例では0)未満となったことにもとづいて賞球過剰エラーと判定する。そのため、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560と払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との双方で異常状態を検出することができる。従って、不正に遊技球を払い出させる行為を防止する不正対策をより強固なものとすることができる。
Further, according to this embodiment, the game control microcomputer 560 adds the number of prize balls to the number of prize balls counter at the timing of transmitting the number of balls command, and the prize ball information is received based on the reception of the prize ball information. Subtract 10 from the value of the ball number counter. Then, based on the value of the prize ball number counter being equal to or more than the predetermined prize ball shortage determination value (501 in this example), it is determined that the prize ball shortage error, and the value of the prize ball number counter is the predetermined prize ball excess. Based on the fact that it is less than the judgment value (0 in this example), it is judged that the prize ball excess error. Therefore, the abnormal state can be detected by both the game control microcomputer 560 and the payout control microcomputer 370. Therefore, it is possible to make the fraud measures for preventing an act of paying out the gaming balls illegally stronger.
また、この実施の形態によれば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370との通信の接続状態を示す接続信号を出力ポート57を介して払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370に送信するように構成されているので、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータ370側でどのタイミングにおいても通信の接続状態を確認することができるため、通信の接続状態が異常状態であるときに賞球の払い出しが行われることを確実に防止することができる。
Further, according to this embodiment, the game control microcomputer 560 transmits a connection signal indicating a connection state of communication with the payout control microcomputer 370 to the payout control microcomputer 370 via the output port 57. Since the payment control microcomputer 370 can check the communication connection state at any timing because it is configured as described above, the prize ball is paid out when the communication connection state is abnormal. Can be reliably prevented.
なお、上記の実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が、通常時は接続OKコマンドの受信後1秒経過後に接続確認コマンドを送信し、通信エラーが発生しているときは(例えば、接続OKコマンドを受信できないときには)、接続確認コマンドの送信後10秒経過後に接続確認コマンドを送信するように構成し、1秒や10秒の期間をタイマ(ソフトウェアで構成されたカウンタ)で計測するように構成していたが、内部クロックによってハードウェアとして更新されるカウンタが所定値になったとき(1秒や10秒)発生する内部割込で接続確認コマンドを送信するようにしてもよい。その場合、接続OKコマンドの受信によってカウンタをクリアするようにするか、所定値となって内部割込を発生させたらカウンタがクリアされるものであればよい。
In the above embodiment, normally, the game control microcomputer 560 transmits a connection confirmation command one second after the reception of the connection OK command, and when a communication error occurs (for example, connection is made. If it can not receive an OK command), it will be configured to send a connection confirmation command 10 seconds after sending a connection confirmation command, and measure a 1 second or 10 second period with a timer (counter configured by software) The connection confirmation command may be transmitted by an internal interrupt that occurs when the counter updated as hardware by the internal clock reaches a predetermined value (1 second or 10 seconds). In that case, the counter may be cleared by receiving the connection OK command, or the counter may be cleared when an internal interrupt is generated with a predetermined value.
次に、遊技機が搭載するターミナル基板160の物理構成の変形例について説明する。図94および図95は、ターミナル基板160の物理構成の変形例を示す説明図である。遊技機には、例えば、主基板31や演出制御基板80、払出制御基板37などの各基板を覆って保護するためのカバー部材800が設けられているのであるが、図94および図95に示すように、このようなカバー部材800にターミナル基板160を埋め込む形式で構成してもよい。また、カバー部材800のターミナル基板160が取り付けられている部分には、ターミナル基板160を覆って保護するためのターミナル基板用カバー801が取り付けられる。ここで、図94は、カバー部材800にターミナル基板用カバー801が取り付けられている状態を示しており、図95は、カバー部材800からターミナル基板用カバー801が取り外された状態を示している。図95に示すように、ターミナル基板用カバー801の上部には、取り付け用の爪部801aが2つ設けられており、爪部801aを嵌め込み、ビス801bを用いてビス止めすることによって、ターミナル基板用カバー801を取り付けることができる。
Next, a variation of the physical configuration of the terminal substrate 160 mounted on the gaming machine will be described. FIGS. 94 and 95 are explanatory views showing a modification of the physical configuration of the terminal substrate 160. FIG. The gaming machine is provided with a cover member 800 for covering and protecting each substrate such as the main substrate 31, the effect control substrate 80, and the payout control substrate 37, for example, as shown in FIGS. 94 and 95. As such, the terminal substrate 160 may be embedded in such a cover member 800. Further, a terminal substrate cover 801 for covering and protecting the terminal substrate 160 is attached to the portion of the cover member 800 to which the terminal substrate 160 is attached. Here, FIG. 94 shows a state in which the terminal substrate cover 801 is attached to the cover member 800, and FIG. 95 shows a state in which the terminal substrate cover 801 is removed from the cover member 800. As shown in FIG. 95, two attachment claws 801a are provided on the upper portion of the terminal substrate cover 801, and the terminal 801 is fitted by inserting the claws 801a and screwing using a screw 801b. A cover 801 can be attached.
また、図94および図95に示すように、ターミナル基板160上には、ホールコンピュータなど外部装置との間のケーブルを接続するための複数の端子96a,96b,98a,98b・・・が設けられた端子盤900が設けられている。また、端子盤900は、端子96a,96b・・・を含む端子列と、端子98a,98b・・・を含む端子列との上下2段構成となっており、横方向に並ぶ2つの端子によって1セット(信号線とグランド線とのセット)となっている。例えば、図94および図95に示す例では、上段側の端子列において各端子のうち横方向に並ぶ端子96aと端子96bとで1セットであり、下段側の端子列において各端子のうち横方向に並ぶ端子98aと端子98bとで1セットである。また、端子盤900に設けられている各端子96a,96b,98a,98b・・・には、それぞれ摘み部95a,95b,99a,99b・・・が設けられており、摘み部95a,95b,99a,99b・・・を押すなどの操作を行うことにより端子96a,96b,98a,98b・・・が開放されてケーブルを接続可能となる。例えば、上段側の摘み部95aを押すと端子96aにケーブルを接続可能となり、下段側の摘み部99aを押すと端子98aにケーブルを接続可能となる。また、例えば、上段側の摘み部95bを押すと端子96bにケーブルを接続可能となり、下段側の摘み部99bを押すと端子98bにケーブルを接続可能となる。
In addition, as shown in FIGS. 94 and 95, a plurality of terminals 96a, 96b, 98a, 98b,... For connecting cables with an external device such as a hall computer are provided on the terminal substrate 160. A terminal board 900 is provided. The terminal board 900 has upper and lower two stages of terminal rows including the terminals 96a, 96b, ... and terminal rows including the terminals 98a, 98b, ... It is one set (set of signal line and ground line). For example, in the example shown in FIGS. 94 and 95, one set of the terminals 96a and 96b arranged in the lateral direction among the terminals in the terminal row on the upper side is one set, and in the terminal row on the lower side, the lateral direction There are one set of the terminals 98a and the terminals 98b arranged in parallel. Further, knobs 95a, 95b, 99a, 99b,... Are provided on the terminals 96a, 96b, 98a, 98b,... Provided on the terminal board 900, and the knobs 95a, 95b, Terminals 96a, 96b, 98a, 98b,... Are opened by performing an operation such as pressing 99a, 99b,. For example, pressing the upper handle portion 95a enables connection of a cable to the terminal 96a, and pressing the lower handle portion 99a enables connection of a cable to the terminal 98a. Also, for example, pressing the upper handle portion 95b enables connection of a cable to the terminal 96b, and pressing the lower handle portion 99b enables connection of a cable to the terminal 98b.
また、図94および図95に示すように、端子96a,96b,98a,98b・・・ごとに設けられた摘み部95a,95b,99a,99b・・・は、相互に互い違いになるように配置されている。そのように構成することによって、誤って隣の端子用の摘み部を操作してしまうなどの不都合を防止することができ、端子盤900にケーブルを接続する作業を行う際における作業性を向上させることができる。
Further, as shown in FIGS. 94 and 95, the knobs 95a, 95b, 99a, 99b,... Provided for each of the terminals 96a, 96b, 98a, 98b,... Are arranged alternately with each other. It is done. By such a configuration, it is possible to prevent inconveniences such as erroneously operating the knobs for the adjacent terminals, and to improve the workability at the time of connecting the cable to the terminal board 900. be able to.
図96は、カバー部材800のターミナル基板160が取り付けられている部位の断面構造を示す説明図である。図96に示すように、ターミナル基板160は、そのターミナル基板160に設けられている端子盤900が、カバー部材800の表面(図96に示すX面)よりも内側に位置するように、十分にカバー部材800内の奥側に取り付けられる。そのように、ターミナル基板160に設けられている端子盤900が、カバー部材800の表面(図96に示すX面)よりも内側になるように構成されているので、遊技中に誤って遊技球が端子盤900に接触してしまうなどの不都合が生じる事態を防止することができる。
FIG. 96 is an explanatory view showing the cross-sectional structure of a portion of the cover member 800 to which the terminal substrate 160 is attached. As shown in FIG. 96, the terminal board 160 is sufficiently provided that the terminal board 900 provided on the terminal board 160 is positioned inside the surface (X plane shown in FIG. 96) of the cover member 800. It is attached to the back side in the cover member 800. As described above, since the terminal board 900 provided on the terminal substrate 160 is configured to be inside the surface (X surface shown in FIG. 96) of the cover member 800, the game ball is erroneously played during the game It is possible to prevent the occurrence of inconveniences such as contact with the terminal board 900.
また、図96に示すように、ターミナル基板用カバー801は、その側壁部801cが徐々に狭まっていくように傾きがつけられている。そのように側壁部801cに傾きがつけられていることによって、ターミナル基板用カバー801が取り付けられている状態であっても指などが入りやすく、端子盤900にケーブルを接続する作業を行う際における作業性を向上させることができる。
Further, as shown in FIG. 96, the terminal substrate cover 801 is inclined so that the side wall portion 801c is gradually narrowed. Since the side wall portion 801c is inclined as described above, a finger or the like can easily enter even when the terminal substrate cover 801 is attached, and a cable can be connected to the terminal board 900. Workability can be improved.
なお、上記の実施の形態において本発明による遊技機としてパチンコ機を適用した場合について説明したが、本発明による遊技機としてパロット機を適用することも可能である。この場合、上記の実施の形態で示した構成を適用して、パロット機における遊技球の取込数や返却数を累積的にカウンタにカウントアップし、カウンタの値が所定の異常判定値(例えば2000)以上となったら、遊技球の取込数や返却数に異常が生じたと判定して取込動作や返却動作を停止状態に制御するようにしてもよい。また、本発明による遊技機としてスロットマシンを適用することも可能である。この場合、上記の実施の形態で示した構成を適用して、スロットマシンにおけるホッパータンクからのメダルの払出数を累積的にカウンタにカウントアップし、カウンタの値が所定の異常判定値(例えば2000)以上となったら、メダルの払出数に異常が生じたと判定してホッパータンクからのメダルの払出動作を停止状態に制御するようにしてもよい。
Although the case where a pachinko machine is applied as the gaming machine according to the present invention has been described in the above embodiment, it is also possible to apply a parrot machine as the gaming machine according to the present invention. In this case, applying the configuration described in the above embodiment, the number of game balls taken in and returned from the parrot machine is cumulatively counted up to a counter, and the value of the counter is a predetermined abnormality determination value (for example, If it becomes 2000 or more, it may be determined that an abnormality has occurred in the number of taking in and the number of returning of the game balls, and the taking in operation and the returning operation may be controlled to a stop state. In addition, it is also possible to apply a slot machine as a gaming machine according to the present invention. In this case, applying the configuration described in the above embodiment, the number of medals paid out from the hopper tank in the slot machine is cumulatively counted up to a counter, and the value of the counter is a predetermined abnormality judgment value (for example, 2000). If it is the above, it may be determined that an abnormality has occurred in the payout number of medals, and the payout operation of medals from the hopper tank may be controlled to a stop state.
例えば、スロットマシンやパロット機に適用する場合、メダルや遊技球の返却動作が行われた場合に、過剰な返却数や返却の未払出数を累積的にカウントアップするようにしてもよい。また、例えば、スロットマシンのホッパータンクに適用する場合には、メダルの過剰な払出数と払出の未払出数を累積的にカウントアップするようにしてもよい。さらに、例えば、パロット機に適用する場合には、不正としてではなく遊技機の異常動作を検出する目的で、過剰な遊技球の取込数や遊技球の取込不足数を累積的にカウントアップするようにしてもよい。
For example, when the present invention is applied to a slot machine or a parrot machine, the excess return number or the number of unpaid returns may be counted up cumulatively when a medal or game ball return operation is performed. Further, for example, when applied to the hopper tank of a slot machine, the number of excessive payouts of medals and the number of unpaid payouts may be counted up cumulatively. Furthermore, for example, when applied to a parrot machine, the number of game balls taken in excessively and the number of game balls taken in insufficiently are counted up cumulatively for the purpose of detecting an abnormal operation of the gaming machine, not as an unauthorized operation. You may do it.
以下、スロットマシンの実施例について図面(図97および図98)を用いて説明する。本実施例(変形例)のスロットマシン601は、図97に示すように、前面が開口する筐体(図示略)と、この筺体の側端に回動自在に枢支された前面扉と、から構成されている。
Hereinafter, an embodiment of the slot machine will be described with reference to the drawings (FIGS. 97 and 98). As shown in FIG. 97, the slot machine 601 of the present embodiment (modification) has a housing (not shown) with an open front, and a front door pivotally supported by the side end of the housing, It consists of
本実施例のスロットマシン601の筐体内部には、外周に複数種の図柄が配列されたリール602L、602C、602R(以下、左リール、中リール、右リールともいう)が水平方向に並設されており、図97に示すように、これらリール602L、602C、602Rに配列された図柄のうち連続する3つの図柄が前面扉に設けられた透視窓603から見えるように配置されている。
Inside the housing of the slot machine 601 of this embodiment, reels 602L, 602C, 602R (hereinafter, also referred to as left reel, middle reel, and right reel) in which plural kinds of symbols are arranged on the outer periphery are arranged side by side in the horizontal direction. As shown in FIG. 97, three consecutive symbols among the symbols arranged on the reels 602L, 602C and 602R are arranged so as to be seen through the perspective window 603 provided on the front door.
リール602L、602C、602Rの外周部には、例えば、「赤7(図中白抜き7)」、「BAR」、「リプレイ」、「スイカ」、「チェリー」、「ベル」といった互いに識別可能な複数種類の図柄が所定の順序で、それぞれ21個ずつ描かれている。リール602L、602C、602Rの外周部に描かれた図柄は、透視窓603において各々上中下三段に表示される。
In the outer peripheral part of the reels 602L, 602C, 602R, for example, “red 7 (white outline 7)”, “BAR”, “replay”, “watermelon”, “cherry”, “bell” can be distinguished from each other A plurality of kinds of symbols are drawn 21 each in a predetermined order. The symbols drawn on the outer circumferences of the reels 602L, 602C, 602R are displayed in three stages, upper, middle, lower, respectively, in the transparent window 603.
各リール602L、602C、602Rは、各々対応して設けられリールモータ632L、632C、632R(図98参照)によって回転させることで、各リール602L、602C、602Rの図柄が透視窓603に連続的に変化しつつ表示されるとともに、各リール602L、602C、602Rの回転を停止させることで、透視窓603に3つの連続する図柄が表示結果として導出表示されるようになっている。
The respective reels 602L, 602C, 602R are respectively provided corresponding to each other and rotated by the reel motors 632L, 632C, 632R (see FIG. 98) so that the designs of the respective reels 602L, 602C, 602R are continuously transmitted to the see-through window 603. While changing and being displayed, by stopping the rotation of each of the reels 602L, 602C, and 602R, three successive symbols are derived and displayed as a display result on the transparent window 603.
また、前面扉には、メダルを投入可能なメダル投入部604、メダルが払い出されるメダル払出口609、クレジット(遊技者所有の遊技用価値として記憶されているメダル数)を用いてメダル1枚分の賭数を設定する際に操作される1枚BETスイッチ605、クレジットを用いて、その範囲内において遊技状態に応じて定められた規定数の賭数(本実施例では通常遊技状態においては「3」、レギュラーボーナスにおいては「1」)を設定する際に操作されるMAXBETスイッチ606、クレジットとして記憶されているメダル及び賭数の設定に用いたメダルを精算する(クレジット及び賭数の設定に用いた分のメダルを返却させる)際に操作される精算スイッチ610、ゲームを開始する際に操作されるスタートスイッチ607、リール602L、602C、602Rの回転を各々停止する際に操作されるストップスイッチ608L、608C、608Rが設けられている。
Also, on the front door, a medal insertion portion 604 capable of inserting medals, a medal payout opening 609 from which medals are paid out, and one medal using a credit (the number of medals stored as gaming value owned by a player) The number of bets specified in the range according to the game state within that range (in the normal game state in this embodiment, “1” in the normal game state) 3), MAXBET switch 606 operated when setting the regular bonus is "1", the medals stored as credits and the medals used for setting the bet number are settled (setting of the credit and bet number) Settlement switch 610 operated when returning the medals used, start switch 607 operated when starting the game Le 602L, 602C, stop switch 608L is operated to stop each rotation of the 602R, 608C, 608R are provided.
また、前面扉には、クレジットとして記憶されているメダル枚数が表示されるクレジット表示器611、後述するビッグボーナス中のメダルの獲得枚数やエラー発生時にその内容を示すエラーコード等が表示される遊技補助表示器612、入賞の発生により払い出されたメダル枚数が表示されるペイアウト表示器613が設けられている。
In addition, on the front door, there is a credit display 611 on which the number of medals stored as credits is displayed, a game on which the number of medals acquired during a big bonus to be described later and an error code indicating the contents when an error occurs are displayed. The auxiliary display 612 is provided with a payout display 613 for displaying the number of medals paid out due to the occurrence of a winning.
また、前面扉には、賭数が1設定されている旨を点灯により報知する1BETLED614、賭数が2設定されている旨を点灯により報知する2BETLED615、賭数が3設定されている旨を点灯により報知する3BETLED616、メダルの投入が可能な状態を点灯により報知する投入要求LED617、スタートスイッチ607の操作によるゲームのスタート操作が有効である旨を点灯により報知するスタート有効LED618、ウェイト(前回のゲーム開始から一定期間経過していないためにリールの回転開始を待機している状態)中である旨を点灯により報知するウェイト中LED619、後述するリプレイゲーム中である旨を点灯により報知するリプレイ中LED620が設けられている。
In addition, 1 BET LED 614 notifies that the bet number is set by lighting on the front door, 2 BET LED 615 notifies that the bet number is set by 2 lighting, and lights that the bet number is set by 3 3 BET LED 616 notified by, insertion request LED 617 notifying by light that the medal can be inserted, start effective LED 618 notifying by lighting that the start operation of the game by the operation of the start switch 607, weight (previous game The in-wait LED 619 informs by lighting that it is in a standby state for waiting to start the rotation of the reel because a certain period has not elapsed since the start, and during in-replay LED 620 informs that it is in a replay game described later Is provided.
また、MAXBETスイッチ606の内部には、1枚BETスイッチ605及びMAXBETスイッチ606の操作による賭数の設定操作が有効である旨を点灯により報知するBETスイッチ有効LED621(図98参照)が設けられており、ストップスイッチ608L、608C、608Rの内部には、該当するストップスイッチ608L、608C、608Rによるリールの停止操作が有効である旨を点灯により報知する左、中、右停止有効LED622L、622C、622R(図98参照)がそれぞれ設けられている。
In addition, inside the MAX BET switch 606, a BET switch valid LED 621 (see FIG. 98) is provided to notify that the setting operation of the bet number by the operation of the one BET switch 605 and the MAX BET switch 606 is effective. In the inside of the stop switches 608L, 608C, 608R, the left, middle, right stop enable LEDs 622L, 622C, 622R notify by lighting that the stop operation of the reel by the corresponding stop switches 608L, 608C, 608R is effective. (See FIG. 98) are provided respectively.
前面扉の内側上方中央位置には、遊技に関連する演出画像等を表示可能な液晶表示器651が設けられており、その前方に配置された液晶表示窓670を通して表示画面に表示される表示画像を視認できるようになっている。また、該液晶表示器651の左右側には、遊技に関連する演出を行う2つの可動役物675L,675Rがそれぞれ配設されており、左右の可動役物675L,675Rの前方に配置されるように前面扉に設けられた透明パネルからなる演出用透視窓671L,671Rから内部の可動役物675L,675Rを透視できるようになっている。
A liquid crystal display 651 capable of displaying an effect image or the like relating to a game is provided at an inner upper central position of the front door, and a display image displayed on the display screen through a liquid crystal display window 670 disposed in front of it. Is visible. In addition, on the left and right sides of the liquid crystal display 651, two movable actors 675L and 675R that provide effects related to a game are respectively disposed, and are disposed in front of the left and right movable actors 675L and 675R. As described above, the movable movable objects 675L and 675R inside can be seen through the perspective windows 671L and 671R for effect formed of transparent panels provided on the front door.
また、左右の可動役物675L,675Rと演出用透視窓671L,671Rとの間には、左右の可動役物675L,675Rを演出用透視窓671L,671Rから透視不可能に隠蔽する隠蔽状態と、左右の可動役物675L,675Rを演出用透視窓671L,671Rから透視可能とする非隠蔽状態と、に変更可能な2つのシャッタ装置(図示せず)を構成する無端状のシャッタシートが配設されている。
In addition, between the movable role products 675L and 675R on the left and right and the see-through windows 671L and 671R for effect, a concealed state for concealing the moveable objects 675L and 675R on the left and , And an endless shutter sheet forming two shutter devices (not shown) that can be changed to a non-hidden state in which left and right movable roles 675L and 675R can be seen through perspective windows 671L and 671R for effect It is set up.
また、前面扉の内側には、所定のキー操作によりRAM異常エラーを除くエラー状態及び打止状態を解除するためのリセット操作を検出するリセットスイッチ623、設定値の変更中や設定値の確認中にその時点の設定値が表示される設定値表示器624、メダル投入部604から投入されたメダルの流路を、筐体内部に設けられたホッパータンク(図示略)側またはメダル払出口609側のいずれか一方に選択的に切り替えるための流路切替ソレノイド630、メダル投入部604から投入され、ホッパータンク側に流下したメダルを検出する投入メダルセンサ631が設けられている。
In addition, inside the front door, reset switch 623 that detects an error state excluding RAM abnormal error by a predetermined key operation and a reset operation for releasing the suspension state, changing setting values or checking setting values The setting value indicator 624 at which the setting value at that time is displayed, the flow path of the medal inserted from the medal insertion unit 604, the hopper tank (not shown) side provided inside the housing or the medal payout port 609 side A passage switching solenoid 630 for selectively switching to one of the two, and an inserted medal sensor 631 for detecting a medal that has been inserted from the medal insertion unit 604 and flowed down to the hopper tank side is provided.
筐体内部には、前述したリール602L、602C、602R、リールモータ632L、632C、632R、各リール602L、602C、602Rのリール基準位置をそれぞれ検出可能なリールセンサ633からなるリールユニット(図示略)、メダル投入部604から投入されたメダルを貯留するホッパータンク(図示略)、ホッパータンクに貯留されたメダルをメダル払出口609より払い出すためのホッパーモータ634、ホッパーモータ634の駆動により払い出されたメダルを検出する払出センサ635、電源ボックス(図示略)が設けられている。
A reel unit (not shown) including a reel sensor 633 capable of detecting the reel reference positions of the reels 602L, 602C and 602R, the reel motors 632L, 632C and 632R, and the respective reels 602L, 602C and 602R inside the housing Hopper tank (not shown) for storing medals inserted from the medal insertion portion 604, hopper motor 634 for discharging medals stored in the hopper tank from the medal payout port 609, and payout by driving the hopper motor 634 A payout sensor 635 for detecting the medals and a power supply box (not shown) are provided.
電源ボックスの前面には、ビッグボーナス終了時に打止状態(リセット操作がなされるまでゲームの進行が規制される状態)に制御する打止機能の有効/無効を選択するための打止スイッチ636、ビッグボーナス終了時に自動精算処理(クレジットとして記憶されているメダルを遊技者の操作によらず精算(返却)する処理)に制御する自動精算機能の有効/無効を選択するための自動精算スイッチ629、起動時に設定変更モードに切り替えるための設定キースイッチ637、通常時においてはRAM異常エラーを除くエラー状態や打止状態を解除するためのリセットスイッチとして機能し、設定変更モードにおいては内部抽選の当選確率(出玉率)の設定値を変更するための設定スイッチとして機能するリセット/設定スイッチ638、電源をON/OFFする際に操作される電源スイッチ639が設けられている。
On the front of the power supply box, a stop switch 636 for selecting enabling / disabling of the stop function to control to a stop state (a state in which the progress of the game is restricted until a reset operation is performed) at the end of the big bonus Automatic settlement switch 629 for selecting the validity / invalidity of the automatic settlement function to control automatic settlement processing (processing to settle (return) the medal stored as a credit regardless of the operation of the player) at the end of the big bonus, It functions as a setting key switch 637 for switching to the setting change mode at startup, and normally functions as a reset switch for releasing an error state or a halting state except RAM abnormal error, and in the setting change mode, winning probability of internal lottery Resetting / setting switch 638 that functions as a setting switch for changing the setting value of (ball speed) Power switch 639 is operated to ON / OFF the power is provided.
本実施例のスロットマシン601においてゲームを行う場合には、まず、メダルをメダル投入部604から投入するか、あるいはクレジットを使用して賭数を設定する。クレジットを使用するには1枚BETスイッチ605、またはMAXBETスイッチ606を操作すれば良い。遊技状態に応じて定められた規定数の賭数が設定されると、入賞ラインL1〜L5(図97参照)が有効となり、スタートスイッチ607の操作が有効な状態、すなわち、ゲームが開始可能な状態となる。尚、本実施例では、規定数の賭数として通常遊技状態においては3枚が定められており、レギュラーボーナス中においては、1枚が定められている。尚、遊技状態に対応する規定数を超えてメダルが投入された場合には、その分はクレジットに加算される。
When playing a game in the slot machine 601 of this embodiment, first, medals are inserted from the medal insertion unit 604 or credits are used to set the number of bets. In order to use the credit, the single bet switch 605 or the max bet switch 606 may be operated. When a prescribed number of bets determined according to the gaming state is set, the paylines L1 to L5 (see FIG. 97) become effective, and the operation of the start switch 607 is effective, that is, the game can be started. It becomes a state. In the present embodiment, three cards are defined as the specified number of bets in the normal gaming state, and one card is defined in the regular bonus. When a medal is inserted exceeding the specified number corresponding to the gaming state, that amount is added to the credit.
ゲームが開始可能な状態でスタートスイッチ(レバーともいう)607を操作すると、各リール602L、602C、602Rが回転し、各リール602L、602C、602Rの図柄が連続的に変動する。この状態でいずれかのストップスイッチ608L、608C、608Rを操作すると、対応するリール602L、602C、602Rの回転が停止し、透視窓603に表示結果が導出表示される。
When the start switch (also referred to as a lever) 607 is operated in a state where the game can be started, the reels 602L, 602C, and 602R rotate, and the symbols of the reels 602L, 602C, and 602R continuously change. In this state, when any one of the stop switches 608L, 608C, 608R is operated, the rotation of the corresponding reels 602L, 602C, 602R is stopped, and the display result is derived and displayed on the transparent window 603.
そして全てのリール602L、602C、602Rが停止されることで1ゲームが終了し、有効化されたいずれかの入賞ラインL1〜L5上に予め定められた図柄の組み合わせ(以下、役とも呼ぶ)が各リール602L、602C、602Rの表示結果として停止した場合には入賞が発生し、その入賞に応じて定められた枚数のメダルが遊技者に対して付与され、クレジットに加算される。また、クレジットが上限数(本実施例では50)に達した場合には、メダルが直接メダル払出口609(図97参照)から払い出されるようになっている。尚、有効化された複数の入賞ライン上にメダルの払出を伴う図柄の組み合わせが揃った場合には、有効化された入賞ラインに揃った図柄の組み合わせそれぞれに対して定められた払出枚数を合計し、合計した枚数のメダルが遊技者に対して付与されることとなる。ただし、1ゲームで付与されるメダルの払出枚数には、上限(本実施例では、15枚)が定められており、合計した払出枚数が上限を超える場合には、上限枚数のメダルが付与されることとなる。また、有効化されたいずれかの入賞ラインL1〜L5上に、遊技状態の移行を伴う図柄の組み合わせが各リール602L、602C、602Rの表示結果として停止した場合には図柄の組み合わせに応じた遊技状態に移行するようになっている。
And one game is ended by stopping all the reels 602L, 602C, 602R, and a combination of symbols (hereinafter also referred to as a winning combination) predetermined on any activated paylines L1 to L5 is displayed. When the reels 602L, 602C, 602R are stopped as a display result, a winning occurs, and the number of medals determined according to the winning is awarded to the player and added to the credit. Further, when the credit reaches the upper limit number (50 in the present embodiment), the medals are paid out directly from the medal payout opening 609 (see FIG. 97). In addition, when the combination of symbols accompanied by the payout of medals is aligned on a plurality of activated pay lines, the number of payouts determined for each combination of symbols aligned to activated pay lines is totaled The total number of medals will be awarded to the player. However, an upper limit (15 in the present embodiment) is set as the payout number of medals awarded in one game, and when the total payout number exceeds the upper limit, the upper limit number of medals is awarded. The Rukoto. In addition, when the combination of symbols accompanied by the transition of the gaming state is stopped as the display result of each reel 602L, 602C, 602R on any of the activated pay lines L1 to L5, the game according to the combination of symbols It is supposed to move to the state.
図98は、スロットマシン601の構成を示すブロック図である。スロットマシン601には、図98に示すように、遊技制御基板640(図6の遊技制御基板(主基板)31に相当)、演出制御基板690(図6の演出制御基板80に相当)、電源基板600が設けられており、遊技制御基板640によって遊技状態が制御され、演出制御基板690によって遊技状態に応じた演出が制御され、電源基板600によってスロットマシン601を構成する電気部品の駆動電源が生成され、各部に供給される。
FIG. 98 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the slot machine 601. As shown in FIG. In the slot machine 601, as shown in FIG. 98, a game control board 640 (corresponding to the game control board (main board) 31 in FIG. 6), an effect control board 690 (corresponding to the effect control board 80 in FIG. 6) A board 600 is provided, the gaming control board 640 controls the gaming state, the presentation control board 690 controls the effects according to the gaming state, and the power board 600 controls the driving power of the electric components constituting the slot machine 601. It is generated and supplied to each part.
遊技制御基板640には、前述した1枚BETスイッチ605、MAXBETスイッチ606、スタートスイッチ607、ストップスイッチ608L、608C、608R、精算スイッチ610、リセットスイッチ623、投入メダルセンサ631、リールセンサ633が接続されているとともに、電源基板600を介して前述した払出センサ635、打止スイッチ636、自動精算スイッチ629、設定キースイッチ637、リセット/設定スイッチ638が接続されており、これら接続されたスイッチ類の検出信号が入力されるようになっている。
The game control board 640 is connected to the one-piece BET switch 605, the MAX BET switch 606, the start switch 607, the stop switches 608L, 608C, 608R, the settlement switch 610, the reset switch 623, the inserted medal sensor 631, and the reel sensor 633. And the discharge sensor 635, the stop switch 636, the automatic settlement switch 629, the setting key switch 637, and the reset / setting switch 638 are connected via the power supply substrate 600, and these connected switches are detected. A signal is input.
また、遊技制御基板640には、前述したクレジット表示器611、遊技補助表示器612、ペイアウト表示器613、1〜3BETLED614〜616、投入要求LED617、スタート有効LED618、ウェイト中LED619、リプレイ中LED620、BETスイッチ有効LED621、左、中、右停止有効LED622L、622C、622R、設定値表示器624、流路切替ソレノイド630、リールモータ632L、632C、632Rが接続されているとともに、電源基板600を介して前述したホッパーモータ634が接続されており、これら電気部品は、遊技制御基板640に搭載された後述のメイン制御部641(図6の遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に相当)の制御に基づいて駆動されるようになっている。
In addition, the gaming control board 640, the aforementioned credit indicator 611, gaming auxiliary indicator 612, payout indicator 613, 1-3 BET LED 614-616, entry request LED 617, start effective LED 618, during weight LED 619, during replay LED 620, BET The switch enable LED 621, left, middle, right stop enable LEDs 622L, 622C, 622R, the setting value display 624, the flow path switching solenoid 630, the reel motors 632L, 632C, 632R are connected, and the power supply board 600 The hopper motor 634 is connected, and these electric components are driven under the control of a main control unit 641 (corresponding to the game control microcomputer 560 of FIG. 6) described later mounted on the game control board 640. It becomes like That.
遊技制御基板640には、CPU641a、ROM641b、RAM641c、I/Oポート641dを備えたマイクロコンピュータからなり、遊技の制御を行うメイン制御部641、所定範囲(本実施例では0〜16383)の乱数を発生させる乱数発生回路642、乱数発生回路から乱数を取得するサンプリング回路643、遊技制御基板640に直接または電源基板600を介して接続されたセンサやスイッチ等のスイッチ類から入力された検出信号を検出するスイッチ検出回路644、リールモータ632L、632C、632Rの駆動制御を行うモータ駆動回路645、流路切替ソレノイド630の駆動制御を行うソレノイド駆動回路646、遊技制御基板640に接続された各種表示器やLEDの駆動制御を行うLED駆動回路647、スロットマシン601に供給される電源電圧を監視し、電圧低下を検出したときに、その旨を示す電圧低下信号をメイン制御部641に対して出力する電断検出回路648、電源投入時またはCPU641aからの初期化命令が入力されないときにCPU641aにリセット信号を与えるリセット回路649、その他各種デバイス、回路が搭載されている。
The game control board 640 includes a microcomputer having a CPU 641a, a ROM 641b, a RAM 641c, and an I / O port 641d, and a main control unit 641 for controlling the game and random numbers in a predetermined range (0 to 16383 in this embodiment) Random number generation circuit 642 to generate, sampling circuit 643 to obtain random numbers from random number generation circuit, detection signal input from switches such as sensors and switches connected directly to game control board 640 or through power supply board 600 Switch detection circuit 644, a motor drive circuit 645 for controlling the drive of the reel motors 632L, 632C, 632R, a solenoid drive circuit 646 for controlling the drive of the flow path switching solenoid 630, various indicators connected to the game control board 640 LED drive circuit which performs drive control of LED 47, a power failure detection circuit 648 that monitors the power supply voltage supplied to the slot machine 601 and outputs a voltage drop signal indicating that to the main control unit 641 when a voltage drop is detected; A reset circuit 649 for giving a reset signal to the CPU 641a when an initialization instruction from the CPU 641a is not input, and various other devices and circuits are mounted.
CPU641aは、I/Oポート641dを介して演出制御基板690に、各種のコマンドを送信する。遊技制御基板640から演出制御基板690へ送信されるコマンドは一方向のみで送られ、演出制御基板690から遊技制御基板640へ向けてコマンドが送られることはない。遊技制御基板640から演出制御基板690へ送信されるコマンドの伝送ラインは、ストローブ(INT)信号ライン、データ伝送ライン、グラウンドラインから構成されているとともに、演出中継基板680を介して接続されており、遊技制御基板640と演出制御基板690とが直接接続されない構成とされている。
The CPU 641a transmits various commands to the effect control board 690 via the I / O port 641d. The command transmitted from the game control board 640 to the effect control board 690 is sent in one direction only, and the command is not sent from the effect control board 690 toward the game control board 640. The transmission line of the command transmitted from the game control board 640 to the effect control board 690 comprises a strobe (INT) signal line, a data transmission line, and a ground line, and is connected via the effect relay board 680. The game control board 640 and the effect control board 690 are not directly connected.
演出制御基板690には、スロットマシン601の前面扉に配置された液晶表示器651(図97参照)、演出効果LED652、スピーカ653、654、リールLED655及びシャッタモータ810、シャッタセンサ811、可動物用LED881、可動物用モータ805、可動物用センサ829等の電気部品が接続されており、これら電気部品は、演出制御基板690に搭載された後述のサブ制御部691による制御に基づいて駆動されるようになっている。
On the presentation control board 690, a liquid crystal display 651 (see FIG. 97) disposed on the front door of the slot machine 601, presentation effect LEDs 652, speakers 653, 654, a reel LED 655 and a shutter motor 810, a shutter sensor 811, for movable objects Electrical components such as the LED 881, the movable object motor 805, and the movable object sensor 829 are connected, and these electrical components are driven based on control by a sub control unit 691 described later mounted on the effect control board 690. It is supposed to be.
演出制御基板690には、メイン制御部641と同様にCPU691a、ROM691b、RAM691c、I/Oポート691dを備えたマイクロコンピュータにて構成され、演出の制御を行うサブ制御部691、演出制御基板690に接続された液晶表示器651の駆動制御を行う液晶駆動回路692、演出効果LED652、リールLED655、可動物用LED881の駆動制御を行うLED駆動回路693、スピーカ653、654からの音声出力制御を行う音声出力回路694、電源投入時またはCPU691aからの初期化命令が入力されないときにCPU691aにリセット信号を与えるリセット回路695、シャッタセンサ811、可動物用センサ829やスイッチ等のスイッチ類から入力された検出信号を検出するスイッチ検出回路696、シャッタモータ810及び可動物用モータ805の駆動制御を行うモータ駆動回路697やその他の回路等、が搭載されており、CPU691aは、遊技制御基板640から送信されるコマンドを受けて、演出を行うための各種の制御を行うとともに、演出制御基板690に搭載された制御回路の各部を直接的または間接的に制御する。
Similar to the main control unit 641, the effect control substrate 690 includes a microcomputer including a CPU 691 a, a ROM 691 b, a RAM 691 c, and an I / O port 691 d, and a sub control unit 691 for controlling effects and a effect control substrate 690. The liquid crystal drive circuit 692 which controls the drive of the connected liquid crystal display 651, the effect effect LED 652, the reel LED 655, the LED drive circuit 693 which controls the drive of the LED 881 for moving objects, the sound which performs audio output control from the speakers 653 and 654 A detection signal input from an output circuit 694, a reset circuit 695 giving a reset signal to the CPU 691a when power is turned on or when an initialization instruction from the CPU 691a is not input, a shutter sensor 811, a movable object sensor 829 or switches such as switches Sui to detect And a motor drive circuit 697 for controlling the drive of the shutter motor 810 and the movable object motor 805, and other circuits. The CPU 691a receives a command transmitted from the game control board 640. And performing various controls for effecting, and directly or indirectly controlling each part of the control circuit mounted on the effect control board 690.
次に、メイン制御部641により実行される内部抽選の処理について説明する。スタートスイッチ607がオンしたタイミングで、サンプリング回路643が乱数発生回路642によってカウントされている数値(乱数)を取得(抽出)する。サンプリング回路643は、乱数として取得した数値をメイン制御部641におけるCPU641aに出力する。
Next, the process of the internal lottery performed by the main control unit 641 will be described. At the timing when the start switch 607 is turned on, the sampling circuit 643 acquires (extracts) the numerical value (random number) counted by the random number generation circuit 642. The sampling circuit 643 outputs the numerical value acquired as a random number to the CPU 641 a in the main control unit 641.
メイン制御部641におけるCPU641aは、サンプリング回路643から取得した数値を、ROM641bに格納されている内部抽選用のテーブルにおける役(小役・再遊技役・特別役など)毎に設定された判定値と比較することによって、小役・再遊技役・特別役に当選したか否かを判定する。また、内部抽選用のテーブルとして、設定値・遊技状態(通常遊技状態、レギュラーボーナス)に応じてメダルの払出率が変わるように複数のテーブルが設けられている。例えば、内部抽選用のテーブルには、小役(チェリー、ベル)・再遊技役(リプレイ)・特別役(レギュラーボーナス、ビッグボーナス)・はずれのそれぞれに対して複数の判定値が設定される。また、例えば、リセット/設定スイッチ638によって設定可能な設定値として「1」から「6」が設けられている場合に、設定値の数字が大きいほどメダルの払出率が変わるように判定値が割り振られたテーブルが用いられる。また、遊技状態が通常遊技状態の場合には、小役・再遊技役・特別役のいずれも当選可能となるように各々の役およびはずれに判定値が割り振られたテーブルが用いられ、遊技状態がレギュラーボーナスの場合には、小役のみ当選可能となるように小役およびはずれに判定値が割り振られたテーブル(再遊技役・特別役には判定値が割り振られていないテーブル)が用いられる。なお、上記のテーブルの判定値の設定は一例であって、そのような判定値の設定に限られるわけではない。本実施例では、賭数として、通常遊技状態においては「3」、レギュラーボーナスにおいては「1」しか遊技者は設定することができないこととされているが、通常遊技状態・レギュラーボーナスのいずれの遊技状態においても、賭数として、「1」〜「3」のいずれも遊技者が設定可能とすることも可能であり、この場合、同一の設定値であっても賭数に応じて小役・再遊技役・特別役の当選確率の異なる複数の内部抽選用のテーブルを用意し、賭数に対応したテーブルを用いて内部抽選を行うようにしてもよい。
The CPU 641a in the main control unit 641 sets the numerical value obtained from the sampling circuit 643 to a determination value set for each combination (small combination, re-play combination, special combination, etc.) in the internal lottery table stored in the ROM 641b. By comparing, it is determined whether or not the small winning combination, re-playing combination, or special combination is won. Further, as a table for internal lottery, a plurality of tables are provided so that the payout rate of medals changes according to the setting value and the gaming state (normal gaming state, regular bonus). For example, in the table for the internal lottery, a plurality of judgment values are set for each of the small combination (cherry, bell), the re-play combination (replay), the special combination (regular bonus, big bonus), and outliers. Also, for example, when “1” to “6” are provided as setting values that can be set by the reset / setting switch 638, determination values are allocated such that the payout rate of medals changes as the setting number increases. Table is used. In addition, when the gaming state is the normal gaming state, a table is used in which the judgment value is assigned to each combination and cancellation so that any of the small combination, re-play combination and the special combination can be won, the gaming condition If the regular bonus is used, a table in which the judgment value is assigned to the small winning combination and the cancellation so that only the small winning combination can be won (a table to which the judgment value is not assigned to the replay role or special combination) is used. . Note that the setting of the determination values in the above-described table is an example, and the present invention is not limited to the setting of such determination values. In this embodiment, it is assumed that the player can only set "3" in the normal gaming state and "1" in the regular bonus as the number of bets, but any of the normal gaming state and the regular bonus can be set. Even in the gaming state, it is possible for the player to be able to set any of “1” to “3” as the number of bets. In this case, even if the same setting value is used, the small winning combination according to the number of bets It is also possible to prepare a plurality of internal lottery tables having different winning probabilities of replay player and special player, and perform an internal lottery using a table corresponding to the number of bets.
上述したように、本実施例のスロットマシン601は、設定値に応じてメダルの払出率が変わるものであり、内部抽選の当選確率は、設定値に応じて定まるものとなる。
As described above, in the slot machine 601 of this embodiment, the payout rate of medals changes according to the set value, and the winning probability of the internal lottery is determined according to the set value.
本実施例のスロットマシン601は、前述のように遊技状態に応じて設定可能な賭数の規定数が定められており、遊技状態に応じて定められた規定数の賭数が設定されたことを条件にゲームを開始させることが可能となる。本実施例では、遊技状態として、レギュラーボーナス、通常遊技状態があり、このうちレギュラーボーナスに対応する賭数の規定数として1が定められており、通常遊技状態に対応する賭数の規定数として3が定められている。このため、遊技状態がレギュラーボーナスにあるときには、賭数として1が設定されるとゲームを開始させることが可能となり、遊技状態が通常遊技状態にあるときには、賭数として3が設定されるとゲームを開始させることが可能となる。尚、本実施例では、遊技状態に応じた規定数の賭数が設定された時点で、全ての入賞ラインL1〜L5が有効化されるようになっており、遊技状態に応じた規定数が1であれば、賭数として1が設定された時点で全ての入賞ラインL1〜L5が有効化され、遊技状態に応じた規定数が3であれば、賭数として3が設定された時点で全ての入賞ラインL1〜L5が有効化されることとなる。
In the slot machine 601 of the present embodiment, the specified number of bets that can be set according to the game state is determined as described above, and the specified number of bets determined according to the game state is set. It is possible to start the game on condition of. In the present embodiment, there are regular bonus and normal gaming states as the gaming state, and 1 is defined as the prescribed number of bets corresponding to the regular bonus among them, as the prescribed number of bets corresponding to the normal gaming state 3 is defined. Therefore, when the gaming state is in the regular bonus, it is possible to start the game when 1 is set as the bet number, and when the gaming state is in the normal gaming state, when 3 is set as the bet number, the game It is possible to start the In the present embodiment, all pay lines L1 to L5 are activated when the specified number of bets is set according to the game state, and the specified number according to the game state is If it is 1, then all the pay lines L1 to L5 are activated when 1 is set as the bet number, and if the prescribed number according to the gaming state is 3, when 3 is set as the bet number All pay lines L1 to L5 are activated.
本実施例のスロットマシン601は、全てのリール602L、602C、602Rが停止した際に、有効化された入賞ライン(本実施例の場合、常に全ての入賞ラインが有効化されるため、以下では、有効化された入賞ラインを単に入賞ラインと呼ぶ)上に役と呼ばれる図柄の組み合わせが揃うと入賞となる。入賞となる役の種類は、遊技状態に応じて定められているが、大きく分けて、メダルの払い出しを伴う小役と、賭数の設定を必要とせずに次のゲームを開始可能となる再遊技役と、遊技状態の移行を伴う特別役と、がある。以下では、小役と再遊技役をまとめて一般役とも呼ぶ。遊技状態に応じて定められた各役の入賞が発生するためには、内部抽選に当選して、当該役の当選フラグがRAM641cに設定されている必要がある。
In the slot machine 601 of this embodiment, when all the reels 602L, 602C, and 602R stop, activated pay lines (in the case of this embodiment, all pay lines are always activated. When a combination of symbols called a winning combination is aligned on the activated pay line is simply called a pay line), a prize is won. The type of winning combination is determined according to the game state, but can be roughly divided into a small combination with payout of medals and the need to set the number of bets, and the next game can be started again There are a game role and a special role accompanied by a transition of the game state. In the following, the small part and the re-play part are collectively referred to as a general part. In order to generate a winning of each combination determined in accordance with the gaming state, it is necessary to win an internal lottery and to set a winning flag of the combination to the RAM 641c.
尚、これら各役の当選フラグのうち、小役及び再遊技役の当選フラグは、当該フラグが設定されたゲームにおいてのみ有効とされ、次のゲームでは無効となるが、特別役の当選フラグは、当該フラグにより許容された役の組み合わせが揃うまで有効とされ、許容された役の組み合わせが揃ったゲームにおいて無効となる。すなわち特別役の当選フラグが一度当選すると、たとえ、当該フラグにより許容された役の組み合わせを揃えることができなかった場合にも、その当選フラグは無効とされずに、次のゲームへ持ち越されることとなる。このように、本発明によるスロットマシン601において、入賞用事前決定手段により特定入賞の発生を許容する旨が決定され、特定入賞表示結果が入賞用可変表示部に導出されなかったときに、当該特定入賞の発生を許容する旨の決定を次ゲーム以降に持ち越す持越手段を備えている。そのように構成された場合には、特定入賞表示結果が入賞用可変表示部に導出されなかったときであっても、当該特定入賞の発生を許容する旨の決定を次ゲーム以降に持ち越され、遊技者に損失を与えることを防ぐことができる。
Of the winning flags for each of these winning combinations, the winning flags for the small winning combination and the re-playing combination are only valid in the game for which the flag is set and are invalid in the next game, but the special winning combination is The game is valid until the combination of the roles accepted by the flag is complete, and the game is invalidated in the game in which the combination of the accepted roles is complete. That is, once the winning combination of the special part is won, even if the combination of the combinations permitted by the flag can not be aligned, the winning flag is carried over to the next game without being invalidated. It becomes. As described above, in the slot machine 601 according to the present invention, it is determined that the occurrence of the specific winning is permitted by the pre-determination means for winning, and the specific winning display result is not derived to the variable display for winning. A carry-over means is provided for carrying over the decision to allow the occurrence of a winning after the next game. In such a configuration, even if the specific winning display result is not derived to the variable display for winning, the determination to permit the occurrence of the specific winning is carried over to the next game and thereafter. It is possible to prevent giving the player a loss.
このスロットマシン601における役としては、特別役としてビッグボーナス、レギュラーボーナスが、小役としてチェリー、ベルが、再遊技役としてリプレイが定められている。また、スロットマシン601における役の組み合わせとしては、ビッグボーナス+チェリー、レギュラーボーナス+チェリーが定められている。すなわち、役及び役の組み合わせの合計は7となっている。
As a part in the slot machine 601, a big bonus as a special part, a regular bonus, a cherry as a small part, a bell, and a replay as a replay part are defined. Also, as a combination of roles in the slot machine 601, a big bonus + cherries and a regular bonus + cherries are defined. In other words, the combination of role and role combination is seven.
本実施例のスロットマシン601においては、遊技状態が、通常遊技状態であるか、レギュラーボーナスであるか、によって抽選の対象となる役及び役の組み合わせが異なる。更に遊技状態が通常遊技状態である場合には、いずれかの特別役の持ち越し中か否か(特別役の当選フラグにいずれかの特別役が当選した旨が既に設定されているか否か)によっても抽選の対象となる役及び役の組み合わせが異なる。本実施例では、遊技状態に応じた状態番号が割り当てられており、内部抽選を行う際に、現在の遊技状態に応じた状態番号を設定し、この状態番号に応じて抽選対象となる役を特定することが可能となる。具体的には、通常遊技状態においていずれの特別役も持ち越されていない場合には、状態番号として「0」が設定され、通常遊技状態においていずれかの特別役が持ち越されている場合には、状態番号として「1」が設定され、レギュラーボーナスである場合には、状態番号として「2」が設定されるようになっている。
In the slot machine 601 of the present embodiment, the combination of a combination of a combination of a combination to be a target of the lottery differs depending on whether the gaming state is a normal gaming state or a regular bonus. Furthermore, if the gaming state is the normal gaming state, whether or not carrying any special role (whether the special winning combination flag is already set in the special part winning flag is already set) Also, the combination of the role to be drawn and the combination of roles are different. In the present embodiment, a state number corresponding to the gaming state is assigned, and when performing an internal lottery, a state number corresponding to the current gaming state is set, and a role to be drawn for the lottery according to the state number It becomes possible to identify. Specifically, when no special combination is carried over in the normal gaming state, “0” is set as the state number, and when any special combination is carried over in the normal gaming state, “1” is set as the state number, and “2” is set as the state number in the case of the regular bonus.
遊技状態が通常遊技状態であり、いずれの特別役も持ち越されていない状態、すなわち状態番号として「0」が設定されている場合には、ビッグボーナス、レギュラーボーナス、ビッグボーナス+チェリー、レギュラーボーナス+チェリー、リプレイ、チェリー、ベル、すなわち全ての役及び役の組み合わせが内部抽選の対象となる。また、遊技状態が通常遊技状態であり、いずれかの特別役が持ち越されている状態、すなわち状態番号として「1」が設定されている場合には、リプレイ、チェリー、ベルの役及び役の組み合わせが内部抽選の対象となる。また、遊技状態がレギュラーボーナス、すなわち状態番号として「2」が設定されている場合には、チェリー、ベルの役及び役の組み合わせが内部抽選の対象となる。
If the gaming state is the normal gaming state and no special part is carried over, ie, "0" is set as the state number, the big bonus, regular bonus, big bonus + cherry, regular bonus + The combination of cherries, replays, cherries, bells, that is, all roles and combinations is subject to the internal lottery. In addition, when the gaming state is the normal gaming state and one of the special roles is carried over, that is, “1” is set as the state number, a combination of the role of replay, cherries, and the bell Is the subject of the internal lottery. In addition, when the gaming state is a regular bonus, that is, "2" is set as the state number, a combination of a combination of cherries and bells is a target of the internal lottery.
チェリーは、いずれの遊技状態においても左リールについて入賞ラインのいずれかに「チェリー」の図柄が導出されたときに入賞となり、通常遊技状態においては2枚のメダルが払い出され、レギュラーボーナスにおいては15枚のメダルが払い出される。尚、「チェリー」の図柄が左リールの上段または下段に停止した場合には、入賞ラインL2、L4または入賞ラインL3、L5の2本の入賞ラインにチェリーの組み合わせが揃うこととなり、2本の入賞ライン上でチェリーに入賞したこととなるので、通常遊技状態においては4枚のメダルが払い出されることとなるが、レギュラーボーナスでは、2本の入賞ライン上でチェリーに入賞しても、1ゲームにおいて払い出されるメダル枚数の上限が15枚に設定されているため、15枚のみメダルが払い出されることとなる。ベルは、いずれの遊技状態においても入賞ラインのいずれかに「ベル−ベル−ベル」の組み合わせが揃ったときに入賞となり、通常遊技状態においては8枚のメダルが払い出され、レギュラーボーナスにおいては15枚のメダルが払い出される。
Cherry is a prize when the symbol of "Cherry" is derived to any of the pay lines for the left reel in any gaming state, and two medals are paid out in the normal gaming state, and in the regular bonus, 15 medals are paid out. In addition, when the symbol of "Cherry" is stopped at the upper or lower end of the left reel, the combination of cherries will be aligned with the two pay lines of pay lines L2, L4 or pay lines L3, L5. As it is to be cherries on the pay line, 4 medals will be paid out in the normal gaming state, but in the regular bonus, even if cherries are won on two pay lines, 1 game Since the upper limit of the number of medals to be paid out is set at 15, the medals will be paid out only for fifteen. The bell is awarded when the combination of "Bell-Bell-Bell" is aligned with any of the pay lines in any gaming state, and eight medals are paid out in the normal gaming state, and in the regular bonus, 15 medals are paid out.
リプレイは、通常遊技状態において入賞ラインのいずれかに「リプレイ−リプレイ−リプレイ」の組み合わせが揃ったときに入賞となる。リプレイ入賞したときには、メダルの払い出しはないが次のゲームを改めて賭数を設定することなく開始できるので、次のゲームで設定不要となった賭数(レギュラーボーナスではリプレイ入賞しないので必ず3)に対応した3枚のメダルが払い出されるのと実質的には同じこととなる。
Replay is a prize when the combination of "replay-replay-replay" is complete in any of the pay lines in the normal gaming state. When you win the Replay, you can start the next game without setting the number of bets, but you can start the next game without setting the number of bets. This is essentially the same as the corresponding three medals being paid out.
レギュラーボーナスは、通常遊技状態において入賞ラインのいずれかに「赤7−赤7−BAR」の組み合わせが揃ったときに入賞となる。レギュラーボーナス入賞すると、遊技状態が通常遊技状態からレギュラーボーナスに移行する。レギュラーボーナスは、12ゲームを消化したとき、または8ゲーム入賞(役の種類は、いずれでも可)したとき、のいずれか早いほうで終了する。遊技状態がレギュラーボーナスにある間は、レギュラーボーナス中フラグがRAM641cに設定される。
The regular bonus is won when the combination of “red 7-red 7-BAR” is aligned with any of the pay lines in the normal gaming state. When the regular bonus prize is won, the gaming state shifts from the normal gaming state to the regular bonus. The regular bonus ends when the 12 games are completed or when the 8 games are won (any type of winning combination is acceptable), whichever is earlier. While the gaming state is in the regular bonus, the regular bonus in progress flag is set in the RAM 641c.
ビッグボーナスは、通常遊技状態において入賞ラインのいずれかに「赤7−赤7−赤7」の組み合わせが揃ったときに入賞となる。ビッグボーナス入賞すると、遊技状態がビッグボーナスに移行する。ビッグボーナスに移行すると、ビッグボーナスへの移行と同時にレギュラーボーナスに移行し、レギュラーボーナスが終了した際に、ビッグボーナスが終了していなければ、再度レギュラーボーナスに移行し、ビッグボーナスが終了するまで繰り返しレギュラーボーナスに制御される。すなわちビッグボーナス中は、常にレギュラーボーナスに制御されることとなる。そして、ビッグボーナスは、当該ビッグボーナス中において遊技者に払い出したメダルの総数が465枚を超えたときに終了する。この際、レギュラーボーナスの終了条件が成立しているか否かに関わらずレギュラーボーナスも終了する。遊技状態がビッグボーナスにある間は、ビッグボーナス中フラグがRAM641cに設定される。
The big bonus is won when the combination of "red 7-red 7-red 7" is complete in any of the pay lines in the normal gaming state. When the big bonus is won, the gaming state shifts to the big bonus. When transitioning to the big bonus, transition to the regular bonus simultaneously with transition to the big bonus, and when the regular bonus ends, if the big bonus has not ended, transition to the regular bonus again, and repeatedly until the big bonus ends Controlled by regular bonus. That is, during a big bonus, it will always be controlled to a regular bonus. Then, the big bonus ends when the total number of medals paid out to the player during the big bonus exceeds 465. At this time, the regular bonus also ends regardless of whether the regular bonus end condition is satisfied. While the gaming state is in the big bonus, the big bonus in progress flag is set in the RAM 641c.
なお、前述したレギュラーボーナス、ビッグボーナスをまとめて、単に「ボーナス」と呼ぶ場合がある。
The regular bonus and the big bonus described above may be collectively referred to simply as "bonus".
なお、図97におけるリール601L,601C,601Rにおいて、白抜き7の図柄のみ描かれているが、図示を省略しているだけで、実際にはリール601L,601C,601Rにおける点線囲いの部分にも図柄が描かれている。
Note that although only the white outline 7 is drawn on the reels 601L, 601C, and 601R in FIG. 97, in actuality, the dotted line enclosures on the reels 601L, 601C, and 601R are only illustrated. A pattern is drawn.
本実施例のスロットマシン601では、内部抽選で小役、再遊技役または特別役(ボーナス)に当選している可能性があること(内部抽選に当選して小役、再遊技役または特別役の当選フラグがRAM641cに設定されている状態である可能性があること)を示唆する示唆演出が演出部材(液晶表示器651、液晶表示器651の左右側の可動役物675L,675Rなど)を用いて実行される。特に、内部抽選処理により、特別役の発生を許容する旨を決定された(内部抽選に当選して特別役の当選フラグがRAM641cに設定されている状態)ことにもとづいて、CPU691aは、液晶表示器651の表示画面に表示される左・中・右の図柄Z1〜Z3の停止図柄の組み合わせとして特定表示結果(例えば「7・7・7」が揃うこと)となるように示唆演出を実行する。
In the slot machine 601 of this embodiment, there is a possibility that a small winning combination, a re-playing combination or a special combination (bonus) may be won in the internal lottery (a small winning combination, a re-playing combination or a special combination winning the internal lottery). Suggestion effects that suggest that the winning flag of the is likely to be set in the RAM 641c) effect members (such as the liquid crystal display 651 and movable roles 675L and 675R on the left and right sides of the liquid crystal display 651) It is executed using. In particular, the CPU 691a displays a liquid crystal display based on the fact that the occurrence of the special combination has been determined by the internal lottery process (the internal lottery has been won and the special combination winning flag is set in the RAM 641c). Perform the suggestion effect so that the specific display result (for example, "7 · 7 · 7" will be aligned) as the combination of the stop symbols of the left, middle and right symbols Z1 to Z3 displayed on the display screen of the bowl 651 .
なお、遊技者によって有利な遊技状態としては、上記のビッグボーナスやレギュラーボーナスに限らず、例えば、リールの導出条件(例えば停止順や停止タイミング)が満たされることを条件に発生する報知対象入賞の導出条件を満たす操作手順が報知される遊技状態(いわゆるアシストタイム(AT))や、少なくともいずれか1つのリールの引込範囲を制限することで、ストップスイッチ606L、606C、606Rが操作された際に表示されている図柄が停止しやすいように制御し、遊技者が目押しを行うことで入賞図柄の組合せを導出させることが可能となるチャレンジタイム(CT)、特定の入賞(例えばリプレイ入賞やシングルボーナス入賞等)の発生が許容される確率が高まる遊技状態(いわゆるリプレイタイム(RT)や集中状態)等、さらには、これらを組み合わせた遊技状態(例えばアシストタイムとリプレイタイムを組み合わせたART)などを搭載してもよく、示唆演出手段は、これらの遊技状態に移行する移行条件が成立していることにもとづいて特定表示結果となるように示唆演出を行ってもよい。
In addition, the gaming state advantageous by the player is not limited to the above-mentioned big bonus and regular bonus, for example, notification target winning that occurs on the condition that reel derivation conditions (for example, stop order and stop timing) are satisfied. When the stop switches 606L, 606C, and 606R are operated by restricting the game state (so-called assist time (AT)) in which the operation procedure satisfying the derivation condition is notified or the pull-in range of at least one of the reels. It is controlled to make it easy to stop the displayed symbols, and the player can make a combination of the winning symbols by making a look at a challenge time (CT), a specific winning (for example, a replay winning or a single) A game state (so-called replay time (RT) or In addition, a gaming state (for example, ART combining assist time and replay time) may be mounted, etc., and the suggestion effect means establishes transition conditions for transitioning to these gaming states. Suggestive effects may be given based on what is being done so as to result in a specific display result.
また、移行条件が成立している遊技状態の種類に応じて特定表示結果の種類を異なるようにしてもよい。(例えば、内部抽選により特別役としてビッグボーナスが当選したことにもとづいて「7・7・7」または「3・3・3」が揃い、内部抽選により特別役としてレギュラーボーナスが当選したことにもとづいて「3・3・3」が揃い、リプレイタイム(RT)に移行する移行条件が成立していることにもとづいて「1・1・1」が揃う。)
Further, the type of the specific display result may be different according to the type of the gaming state in which the transition condition is established. (For example, based on the fact that "7, 7 or 7" or "3, 3 or 3" are aligned based on the fact that the big bonus is won as the special role by the internal lottery, and the regular bonus is elected as the special role by the internal lottery. “1 · 3 · 3” are aligned, and “1 · 1 · 1” is aligned based on the transition condition for transitioning to the replay time (RT).
なお、図97および図98に示す遊技機の例では、制御用マイクロコンピュータは、遊技制御基板640に搭載されたメイン制御部641によって実現される。また、払出手段は、ホッパーモータ634によって駆動されるホッパーによって実現される。また、遊技制御媒体払出制御手段は、メイン制御部641によってホッパーモータ634を制御する処理が実行されることによって実現れる。また、累積更新手段は、メイン制御部641によって払出過多数や払出不足数をカウンタに累積的に加算する処理が実行されることによって実現される。また、払出停止手段は、メイン制御部641によってホッパーモータ634を動作させないように制御されることによって実現される。なお、図97および図98に示す遊技機の例に示すように、スロットマシンなどでは、遊技制御基板640に搭載されたメイン制御部641によって、遊技の進行を制御する遊技制御処理が実行されるとともに、ホッパーモータ634を制御して払出制御も実行される。従って、図97および図98に示す遊技機の例では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータがメイン制御部641によって実現されるとともに、払出制御用マイクロコンピュータもメイン制御部641によって実現される。
In the example of the gaming machine shown in FIGS. 97 and 98, the control microcomputer is realized by the main control unit 641 mounted on the gaming control board 640. Also, the dispensing means is realized by a hopper driven by a hopper motor 634. Further, the game control medium payout control means is realized by the main control unit 641 executing a process of controlling the hopper motor 634. Further, the cumulative updating means is realized by the main control unit 641 executing a process of cumulatively adding the overdelivery number and the underdelivery number to the counter. Further, the dispensing stop means is realized by the main control unit 641 so as not to operate the hopper motor 634. In the slot machine or the like, as shown in the example of the gaming machine shown in FIGS. 97 and 98, the main control unit 641 mounted on the gaming control board 640 executes the gaming control process for controlling the progression of the game. At the same time, the hopper motor 634 is controlled to execute dispensing control. Therefore, in the example of the gaming machine shown in FIGS. 97 and 98, the game control microcomputer is realized by the main control unit 641, and the payout control microcomputer is also realized by the main control unit 641.
また、図97および図98に示すスロットマシンの場合においても、各種エラーを検出した場合に、ターミナル基板などを介してセキュリティ信号を外部出力するようにしてもよい。この場合、例えば、スロットマシンの起動時にRAM初期化処理や設定変更が行われたことにもとづいてセキュリティ信号を外部出力するようにするとともに、ホッパーエラーを検出した場合(ホッパータンクからの払出数が所定の異常判定値(例えば、2000)以上となったことにもとづいて、メダルの払出数の異常を検出した場合)にも、セキュリティ信号を外部出力するように構成してもよい。また、例えば、これらの場合に加えて、または代えて、例えば、ホッパータンク内にメダルがなくなり払出を行えなくなった場合(メダル切れ)や、メダル詰まりを起こした場合、投入されたメダルを振り分けたり検出したりするセレクターのエラーを検出した場合などの各種エラーを検出した場合にも、セキュリティ信号を外部出力するように構成されていてもよい。
Also, in the case of the slot machines shown in FIGS. 97 and 98, when various errors are detected, the security signal may be externally output through the terminal board or the like. In this case, for example, when a security signal is externally output based on RAM initialization processing or setting change performed at the time of starting the slot machine, and a hopper error is detected (the number of payouts from the hopper tank is The security signal may be output to the outside also when an abnormality in the number of medals is paid out is detected based on the fact that the predetermined abnormality determination value (for example, 2000) or more is reached. Also, for example, in addition to or in these cases, for example, when the hopper tank runs out of medals and can not be dispensed (the medals have run out) or when the medals are clogged, the inserted medals are distributed The security signal may be configured to be output to the outside also when various errors are detected, such as when an error in the selector to be detected is detected.
なお、上記に示した実施の形態では、以下の(1)〜(5)に示すような遊技機の特徴的構成も示されている。
In the embodiment shown above, characteristic configurations of gaming machines as shown in the following (1) to (5) are also shown.
(1)所定の遊技を行うことが可能な遊技機であって、制御を行う際に発生する変動データ(例えば、特別図柄プロセスフラグ、保留記憶数カウンタの値)を記憶する変動データ記憶手段(例えば、RAM55)と、遊技機への電力供給が停止していても変動データ記憶手段の記憶内容を所定期間保持させることが可能な記憶内容保持手段(例えば、バックアップ電源としてのコンデンサ)と、操作に応じて操作信号を出力する初期化操作手段(例えば、クリアスイッチ)と、電力供給が開始されたときに、初期化操作手段からの操作信号が入力されたときに、変動データ記憶手段の記憶内容を初期化する初期化処理を実行する初期化処理実行手段(例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560におけるステップS10〜S14を実行する部分)と、所定のエラーが発生しているか否かを判定するエラー判定手段(例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560におけるステップS121〜S126を実行する部分)と、少なくとも、初期化処理実行手段によって初期化処理が実行されたこと、およびエラー判定手段によって所定のエラーが発生していると判定されたことを含む所定の信号出力条件が成立したこと(例えば、初期化処理が実行されたこと、始動入賞口14への異常入賞を検出したこと)にもとづいて、遊技機の外部に所定の外部出力信号(例えば、セキュリティ信号)を出力する外部出力手段(例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560におけるステップS14a,S127でセキュリティ信号情報タイマをセットした後に、ステップS1069〜S1103を実行して、セキュリティ信号を出力する部分)と、を備え、外部出力手段は、初期化処理実行手段によって初期化処理が実行されたときとエラー判定手段によって所定のエラーが発生していると判定されたときとで、遊技機に設けられた共通の出力端子(例えば、ターミナル基板160に設けられたコネクタCN7)から所定の外部出力信号を出力し(例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ステップS14a,S127,S1069〜S1103を実行することによって、ターミナル基板160のコネクタCN7から共通のセキュリティ信号として外部出力する)、所定の外部出力信号を出力しているときに新たに所定の信号出力条件が成立した場合には、所定の外部出力信号を出力する出力時間を延長する(例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、セキュリティ信号の出力中であるか否かにかかわらず、ステップS121〜S126を実行して始動入賞口14への異常入賞を検出した場合には、ステップS127を実行してセキュリティ信号情報タイマの値を上書きする)ことを特徴とする遊技機。そのような構成により、初期化処理が実行されたことにもとづいて所定の外部出力信号を出力することによって、遊技機への電源投入時に行われる不正行為を防止することができる。また、初期化処理が実行されたときと所定のエラーが発生していると判定されたときとで共通の出力端子に所定の外部出力信号を出力するので、外部出力用の信号線の無駄を低減することができる。従って、遊技機への電源投入時に行われる不正行為を防止しつつ、外部出力用の信号線の無駄を低減することができる。
(1) A gaming machine capable of playing a predetermined game, which is a variation data storage means for storing variation data (for example, special symbol process flag, value of pending storage number counter) generated when performing control For example, the RAM 55), memory content holding means (for example, a capacitor as a backup power supply) capable of holding the memory contents of the variable data storage means for a predetermined period even if the power supply to the gaming machine is stopped. And an initialization operation means (for example, a clear switch) for outputting an operation signal according to the storage of the variation data storage means when the operation signal from the initialization operation means is input when the power supply is started. Initialization processing execution means (for example, steps S10 to S14 in the game control microcomputer 560) for executing the initialization processing for initializing the content Part), an error determination means (for example, a part for executing steps S121 to S126 in the game control microcomputer 560) for determining whether or not a predetermined error has occurred, and at least an initial process by the initialization process execution means That a predetermined signal output condition is satisfied including that the initialization process has been performed and that the error determination means has determined that a predetermined error has occurred (eg, the initialization process has been executed, starting External output means (e.g., the game control microcomputer 560) for outputting a predetermined external output signal (e.g., a security signal) to the outside of the gaming machine based on detection of an abnormal winning on the winning opening 14). , S127 after setting the security signal information timer in steps S1069 to S (103) to output a security signal), and the external output unit has a predetermined error generated by the error determination unit when the initialization processing is performed by the initialization processing execution unit Outputs a predetermined external output signal from a common output terminal (for example, the connector CN7 provided on the terminal substrate 160) provided in the gaming machine (for example, the microcomputer 560 for gaming control , And externally output as a common security signal from the connector CN7 of the terminal substrate 160 by executing steps S14a, S127, and S1069 to S1103), and newly output a predetermined signal when the predetermined external output signal is output. If the condition is satisfied, the output time for outputting a predetermined external output signal is extended (for example, The game control microcomputer 560 executes steps S121 to S126 and executes step S127 when detecting an abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14, regardless of whether the security signal is being output or not. And the value of the security signal information timer is overwritten). With such a configuration, by outputting a predetermined external output signal based on the execution of the initialization process, it is possible to prevent a fraudulent act performed when the gaming machine is powered on. Further, since the predetermined external output signal is output to the common output terminal when the initialization processing is performed and when it is determined that the predetermined error has occurred, the waste of the signal line for external output can be avoided. It can be reduced. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the waste of the signal line for external output while preventing the fraudulent acts performed at the time of power supply to the gaming machine.
(2)遊技機は、遊技領域に設けられている通過領域(例えば、始動入賞口14)を通過する遊技媒体(例えば、遊技球)を検出する第1検出部(例えば、始動口スイッチ(近接スイッチ)14aにおけるコイルL)と、該第1検出部にて遊技媒体を検出したときに第1の検出信号を出力する第1遊技媒体検出手段(例えば、始動口スイッチ(近接スイッチ)14aにおける信号出力部(検出信号を出力する遊技媒体検出手段:電源、コイルL、抵抗RおよびコンデンサCに相当))と、第1検出部より下流に配置され、通過領域を通過する遊技媒体を検出する第2検出部(例えば、入賞確認スイッチ(フォトセンサ)14bにおけるフォトトランジスタ342の入力部)と、該第2検出部にて遊技媒体を検出したときに第2の検出信号を出力する第2遊技媒体検出手段(例えば、入賞確認スイッチ(フォトセンサ)14bにおけるフォトトランジスタ342の出力部)と、を備え、エラー判定手段は、第1遊技媒体検出手段から入力した第1の検出信号と第2遊技媒体検出手段から入力した第2の検出信号とにもとづいて、第1検出部にて検出された遊技媒体数と第2検出部にて検出された遊技媒体数との差が所定の閾値(例えば、10)を超えたと判定すると、所定のエラーとして、通過領域への遊技媒体の通過異常が発生したと判定し(例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ステップS126でYと判定し、始動入賞口14への異常入賞が発生したと判定する)、第1検出部と第2検出部とを互いに異なる検出方式のセンサにより構成(例えば、始動口スイッチ14aは近接スイッチとして構成され、入賞確認スイッチ14bはフォトセンサとして構成される)してもよい。そのような構成によれば、遊技媒体を検出する検出部に対する不正行為をより確実に検知して、確実な不正行為対策を講ずることができる。
(2) The gaming machine is a first detection unit (for example, a starting opening switch (for example, a proximity opening switch) for detecting gaming media (for example, gaming balls) passing through a passing area (for example, starting winning opening 14) provided in the gaming area. A coil L) in the switch 14a, and a first game medium detection unit (for example, a signal in the starting opening switch (proximity switch) 14a that outputs a first detection signal when the game medium is detected by the first detection unit An output unit (gaming medium detection means for outputting a detection signal: corresponding to a power supply, a coil L, a resistor R and a capacitor C) and a first detection unit disposed downstream of the first detection unit for detecting gaming media passing through the passage area 2) A second detection signal is output when a game medium is detected by the second detection unit and the second detection unit (for example, the input unit of the phototransistor 342 in the winning confirmation switch (photosensor) 14b). The second game medium detection unit (for example, the output unit of the phototransistor 342 in the winning confirmation switch (photosensor) 14b), and the error determination unit is a first detection signal input from the first game medium detection unit The difference between the number of game media detected by the first detection unit and the number of game media detected by the second detection unit is predetermined based on the second detection signal input from the second game medium detection unit and the second game medium detection unit If it is determined that the threshold (for example, 10) of the threshold value is exceeded, it is determined that the passage abnormality of the gaming media to the passage area has occurred as a predetermined error (for example, the microcomputer 560 for gaming control is determined as Y in step S126 The first detection part and the second detection part are composed of sensors of different detection methods (for example, the start opening switch). 14a is configured as a proximity switch, the winning confirmation switch 14b may be configured) as a photo sensor. According to such a configuration, it is possible to more reliably detect fraudulent activity on the detection unit that detects gaming media, and to take certain fraudulent activity measures.
(3)遊技機は、第1遊技媒体検出手段から第1の検出信号を入力したこと(例えば、始動口スイッチ14aからの検出信号を入力したこと)のみにもとづいて、該第1の検出信号の入力後、可変表示の開始を許容する開始条件が成立したこと(例えば、特別図柄の可変表示も実行されておらず、かつ大当り遊技状態でもないこと)にもとづいて各々を識別可能な複数種類の識別情報(例えば、特別図柄)の可変表示を実行する可変表示実行手段(例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560におけるステップS300〜S303を実行する部分)と、第1遊技媒体検出手段から第1の検出信号を入力したこと(例えば、始動口スイッチ14aからの検出信号を入力したこと)のみにもとづいて、景品として景品遊技媒体を払い出す制御を行う払出制御実行手段(例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560におけるステップS32を実行する部分)と、を備え、第2遊技媒体検出手段から入力した第2の検出信号は、エラー判定手段による通過領域への遊技媒体の通過異常が発生したか否かの判定のみに用いられる(例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、入賞確認スイッチ14bからの検出信号をステップS124の処理でのみ確認し、ステップS126で始動入賞口14への異常入賞の有無の判定に用いる)ように構成してもよい。そのような構成によれば、識別情報の可変表示および景品遊技媒体の払い出しについては、一方の検出部における検出結果にもとづいて処理を行うので、不正行為対策の強化に伴う処理負担の増加を防止することができる。
(3) The gaming machine only receives the first detection signal from the first gaming medium detection means (for example, having received the detection signal from the starting opening switch 14a), the first detection signal. After input, a plurality of types that can identify each on the basis of the start condition for allowing the start of variable display to be established (for example, that the variable display of the special symbol is not executed nor the big hit gaming state) Variable display execution means (for example, a portion for executing steps S300 to S303 in the game control microcomputer 560) for performing variable display of identification information (for example, special symbol) of the first game medium from the first game medium detection means Control for paying out a premium game medium as a premium only on the basis of the detection signal being input (for example, the detection signal being input from the starting opening switch 14a) And a second detection signal input from the second game medium detection unit to the passage area by the error determination unit. (For example, the microcomputer 560 for game control confirms the detection signal from the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b only in the process of step S124, and in step S126 It may be configured to be used to determine the presence or absence of an abnormal winning on the start winning opening 14). According to such a configuration, the variable display of the identification information and the payout of the premium game medium are processed based on the detection result of one of the detection units, thereby preventing an increase in the processing load associated with the strengthening of the anti-corruption measures. can do.
(4)エラー判定手段は、第1検出部にて検出された遊技媒体数と第2検出部にて検出された遊技媒体数との差が、所定の閾値として、通過領域の第1検出部と第2検出部との間に複数の遊技媒体が滞留した状態となったとき(例えば、始動入賞口14が球詰まり状態となったとき)の第1検出部における遊技媒体の検出数と第2検出部における遊技媒体の検出数との差分(例えば、3個。図59参照。)よりも多い値を超えたか否かを判定する(例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ステップS126において、図59に示す始動口スイッチ14aと入賞確認スイッチ14bとの検出誤差3個に対して十分余裕をもたせた10以上であるか否かを判定する)ように構成してもよい。そのような構成によれば、通過領域に複数の遊技媒体が滞留してしまった場合(球詰まりを生じた場合)に、誤って遊技媒体の通過異常(入賞異常)が発生したと判定することを防止することができる。従って、不正行為対策の強化に伴う誤判定を防止することができる。
(4) The error determination means determines that the difference between the number of gaming media detected by the first detection unit and the number of gaming media detected by the second detection unit is the first detection unit of the passing area as a predetermined threshold. The number of detected game media in the first detection unit and the number of game media detected when a plurality of game media is in a state of stagnation between the second detection unit and the second detection unit (for example, when the start winning opening 14 is clogged) It is determined whether or not the value greater than the difference (for example, three, see FIG. 59) with the number of detections of gaming media in the second detection unit (for example, the microcomputer 560 for gaming control is step S126) It may be configured to determine whether or not it is 10 or more with a sufficient margin with respect to three detection errors of the starting opening switch 14a and the winning a prize confirmation switch 14b shown in FIG. According to such a configuration, when a plurality of game media are stagnant in the passage area (when a ball jam occurs), it is determined that the passage abnormality (winning error) of the game media has occurred by mistake. Can be prevented. Therefore, it is possible to prevent an erroneous determination that accompanies strengthening of measures against fraud.
(5)外部出力手段は、初期化処理実行手段によって初期化処理が実行されたときとエラー判定手段によって所定のエラーが発生していると判定されたときとで、異なる時間にわたって所定の外部出力信号を出力する(例えば、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、初期化処理が実行された場合には、ステップS14aでセキュリティ信号情報タイマに30秒をセットしてステップS1069〜S1103を実行し、始動入賞口14への異常入賞を検出した場合には、ステップS127でセキュリティ信号情報タイマに4分をセットしてステップS1069〜S1103を実行する)ように構成してもよい。そのような構成によれば、所定の外部出力信号の出力時間を判定することによって、外部装置において、初期化処理が行われた場合であるか所定のエラーが発生している場合であるかを判別することが可能となる。
(5) The external output unit performs predetermined external output for different times depending on whether the initialization processing is performed by the initialization processing execution unit and when the error determination unit determines that a predetermined error occurs. A signal is output (for example, when the initialization processing is executed, the game control microcomputer 560 sets 30 seconds in the security signal information timer in step S14a and executes steps S1069 to S1103 to start a winning prize. When an abnormal prize winning on the mouth 14 is detected, four minutes may be set in the security signal information timer in step S127 and steps S1069 to S1103 may be executed. According to such a configuration, by determining the output time of the predetermined external output signal, whether the initialization processing has been performed or the predetermined error has occurred in the external device It becomes possible to distinguish.