JP6319151B2 - Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of semiconductor device - Google Patents
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of semiconductor device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6319151B2 JP6319151B2 JP2015059436A JP2015059436A JP6319151B2 JP 6319151 B2 JP6319151 B2 JP 6319151B2 JP 2015059436 A JP2015059436 A JP 2015059436A JP 2015059436 A JP2015059436 A JP 2015059436A JP 6319151 B2 JP6319151 B2 JP 6319151B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- semiconductor layer
- nitride semiconductor
- semiconductor device
- nitride
- electrode
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims description 462
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 34
- 150000004767 nitrides Chemical class 0.000 claims description 178
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 43
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 41
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 claims description 22
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 claims description 17
- JMASRVWKEDWRBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Gallium nitride Chemical compound [Ga]#N JMASRVWKEDWRBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 14
- 229910002601 GaN Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- GYHNNYVSQQEPJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Gallium Chemical compound [Ga] GYHNNYVSQQEPJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 229910052733 gallium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000000149 penetrating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 52
- 239000013067 intermediate product Substances 0.000 description 19
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 17
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Palladium Chemical compound [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 12
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 11
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 11
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 10
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 10
- 238000001312 dry etching Methods 0.000 description 9
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 8
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 8
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 description 7
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- CSDREXVUYHZDNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N alumanylidynesilicon Chemical compound [Al].[Si] CSDREXVUYHZDNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N platinum Chemical compound [Pt] BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- XCZXGTMEAKBVPV-UHFFFAOYSA-N trimethylgallium Chemical compound C[Ga](C)C XCZXGTMEAKBVPV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229910052763 palladium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorane Chemical compound F KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium nitride Chemical compound [Ti]#N NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- -1 aluminum silicon copper Chemical compound 0.000 description 3
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010304 firing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005468 ion implantation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000002427 irreversible effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 3
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonia Chemical compound N QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BLRPTPMANUNPDV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silane Chemical compound [SiH4] BLRPTPMANUNPDV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- USZGMDQWECZTIQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N [Mg](C1C=CC=C1)C1C=CC=C1 Chemical compound [Mg](C1C=CC=C1)C1C=CC=C1 USZGMDQWECZTIQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- INQLNSVYIFCUML-QZTLEVGFSA-N [[(2r,3s,4r,5r)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl] [(2r,3s,4r,5r)-5-(4-carbamoyl-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl hydrogen phosphate Chemical compound NC(=O)C1=CSC([C@H]2[C@@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H](COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@@H]3[C@H]([C@@H](O)[C@@H](O3)N3C4=NC=NC(N)=C4N=C3)O)O2)O)=N1 INQLNSVYIFCUML-QZTLEVGFSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005229 chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052732 germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N germanium atom Chemical compound [Ge] GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910000077 silane Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910018072 Al 2 O 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910021529 ammonia Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000012159 carrier gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910017052 cobalt Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010941 cobalt Substances 0.000 description 1
- GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N cobalt atom Chemical compound [Co] GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005669 field effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910021478 group 5 element Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical class [H]* 0.000 description 1
- 238000009616 inductively coupled plasma Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001459 lithography Methods 0.000 description 1
- TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Al]O[Al]=O TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BPUBBGLMJRNUCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxygen(2-);tantalum(5+) Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Ta+5].[Ta+5] BPUBBGLMJRNUCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RVTZCBVAJQQJTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxygen(2-);zirconium(4+) Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[Zr+4] RVTZCBVAJQQJTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005268 plasma chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910001936 tantalum oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- JBQYATWDVHIOAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N tellanylidenegermanium Chemical compound [Te]=[Ge] JBQYATWDVHIOAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000001039 wet etching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910001928 zirconium oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0684—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape, relative sizes or dispositions of the semiconductor regions or junctions between the regions
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/02—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers
- H01L27/0203—Particular design considerations for integrated circuits
- H01L27/0248—Particular design considerations for integrated circuits for electrical or thermal protection, e.g. electrostatic discharge [ESD] protection
- H01L27/0251—Particular design considerations for integrated circuits for electrical or thermal protection, e.g. electrostatic discharge [ESD] protection for MOS devices
- H01L27/0255—Particular design considerations for integrated circuits for electrical or thermal protection, e.g. electrostatic discharge [ESD] protection for MOS devices using diodes as protective elements
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02436—Intermediate layers between substrates and deposited layers
- H01L21/02439—Materials
- H01L21/02455—Group 13/15 materials
- H01L21/02458—Nitrides
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02518—Deposited layers
- H01L21/02521—Materials
- H01L21/02538—Group 13/15 materials
- H01L21/0254—Nitrides
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02518—Deposited layers
- H01L21/0257—Doping during depositing
- H01L21/02573—Conductivity type
- H01L21/02576—N-type
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02518—Deposited layers
- H01L21/0257—Doping during depositing
- H01L21/02573—Conductivity type
- H01L21/02579—P-type
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02612—Formation types
- H01L21/02617—Deposition types
- H01L21/0262—Reduction or decomposition of gaseous compounds, e.g. CVD
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0657—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape of the body
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0684—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape, relative sizes or dispositions of the semiconductor regions or junctions between the regions
- H01L29/0688—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape, relative sizes or dispositions of the semiconductor regions or junctions between the regions characterised by the particular shape of a junction between semiconductor regions
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/12—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed
- H01L29/20—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed including, apart from doping materials or other impurities, only AIIIBV compounds
- H01L29/2003—Nitride compounds
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/41—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions
- H01L29/423—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions not carrying the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/42312—Gate electrodes for field effect devices
- H01L29/42316—Gate electrodes for field effect devices for field-effect transistors
- H01L29/4232—Gate electrodes for field effect devices for field-effect transistors with insulated gate
- H01L29/42356—Disposition, e.g. buried gate electrode
- H01L29/4236—Disposition, e.g. buried gate electrode within a trench, e.g. trench gate electrode, groove gate electrode
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66007—Multistep manufacturing processes
- H01L29/66075—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials
- H01L29/66083—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials the devices being controllable only by variation of the electric current supplied or the electric potential applied, to one or more of the electrodes carrying the current to be rectified, amplified, oscillated or switched, e.g. two-terminal devices
- H01L29/6609—Diodes
- H01L29/66136—PN junction diodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/86—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable only by variation of the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to one or more of the electrodes carrying the current to be rectified, amplified, oscillated or switched
- H01L29/861—Diodes
- H01L29/8613—Mesa PN junction diodes
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
- Semiconductor Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Metal-Oxide And Bipolar Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
Description
本発明は、半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing the semiconductor device.
半導体装置の耐圧性向上を目的として、縦型MOSFETに保護素子としてのPN接合ダイオードを併設する技術が知られている。この場合、PN接合ダイオードを保護素子として機能させるため、縦型MOSFETのN−ドリフト層よりも薄いN−層を有するPN接合ダイオードを形成することが好ましい。特許文献1には、保護ダイオードを形成する電極間に挟まれたN−層を薄くするため、N−層の一部を除去した後、除去した部分にP型層を再成長により形成する技術が開示されている。 For the purpose of improving the breakdown voltage of a semiconductor device, a technique is known in which a vertical MOSFET is provided with a PN junction diode as a protection element. In this case, in order for the PN junction diode to function as a protection element, it is preferable to form a PN junction diode having an N − layer thinner than the N − drift layer of the vertical MOSFET. In Patent Document 1, in order to thin the N − layer sandwiched between the electrodes forming the protection diode, after removing a part of the N − layer, a P-type layer is formed by regrowth in the removed portion. Is disclosed.
しかし、半導体として窒化物半導体を用いる場合、特許文献1に記載の技術においては、再成長界面に意図しないN型キャリアが発生することにより、PN接合ダイオードの耐圧が低下するという課題を発明者らが見出した。そのほか、従来の半導体装置においては、その小型化や、省資源化、製造の容易化、製造の精確さ、作業性の向上等が望まれていた。 However, when a nitride semiconductor is used as a semiconductor, the technique disclosed in Patent Document 1 has a problem that the withstand voltage of the PN junction diode is reduced due to the generation of unintended N-type carriers at the regrowth interface. Found. In addition, the conventional semiconductor device has been desired to be downsized, save resources, facilitate manufacturing, improve manufacturing accuracy, and improve workability.
本発明は、上記の課題の少なくとも一部を解決するためになされたものであり、以下の形態として実現することができる。
本発明の第1の形態は、
第1導電型の第1窒化物半導体層と、前記第1導電型の第2窒化物半導体層と、第2導電型の第3窒化物半導体層と、前記第1導電型の第4窒化物半導体層と、がこの順に積層された積層体と、
前記第1窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記第2窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面と接する第1の電極と、を有し、
前記第3窒化物半導体層と、前記第4窒化物半導体層とを貫通し、前記第2窒化物半導体層に達するトレンチが形成され、
前記トレンチに絶縁膜を介して設けられたゲート電極を備える、
縦型MOSトランジスタと、
前記第1の電極と、
前記第3窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記第2窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面と接する前記第2導電型のオーミック電極と、を有する、
保護素子と、を備える、半導体装置であって、
前記第1導電型の不純物濃度は、前記第1窒化物半導体層に比べて前記第2窒化物半導体層のほうが低く、
前記第1窒化物半導体層は、前記第2窒化物半導体層へ突出する凸部を備え、
前記積層体の積層方向から見たときに、前記凸部の上面は、前記第2導電型のオーミック電極と少なくとも一部が重なる位置に配されており、
前記トレンチの底面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みは、前記凸部の上面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みよりも大きい、半導体装置である。
本発明の第2の形態は、
半導体装置の製造方法であって、
第1導電型の第1窒化物半導体層の面に突出する凸部を形成する工程と、
前記第1窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記凸部を備える面に、前記第1窒化物半導体層よりも不純物濃度が小さい前記第1導電型の第2窒化物半導体層と、第2導電型の第3窒化物半導体層と、をこの順に積層する工程と、
前記第3窒化物半導体層を貫通し、前記第2窒化物半導体層に達するトレンチを形成する工程と、
前記第1窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記第2窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面に、第1の電極を形成する工程と、
積層方向において、前記凸部の上面と少なくとも一部が重なる位置であって、前記第3窒化物半導体層の面であり、前記第2窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面に、前記第2導電型のオーミック電極を形成する工程と、
前記トレンチに絶縁膜を介してゲート電極を形成する工程と、
前記第3窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記第2窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面に、前記第1導電型の第4窒化物半導体層を形成する工程と、
前記第4窒化物半導体層にソース電極を形成する工程と、
を有し、
前記第4窒化物半導体層は、前記積層方向において、前記凸部の上面と重ならない位置に配されており、
前記トレンチの底面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みは、前記凸部の上面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みよりも大きい、
前記第1窒化物半導体層から前記第4窒化物半導体層までの窒化物半導体層と前記ゲート電極と前記第1の電極と前記ソース電極とから形成される縦型MOSトランジスタと、前記第1窒化物半導体層から前記第3窒化物半導体層までの窒化物半導体層と前記第1電極と前記第2導電型のオーミック電極から形成されるPN接合ダイオードである保護素子と、を備える半導体装置の製造方法である。また、本発明は以下の形態として実現することもできる。
SUMMARY An advantage of some aspects of the invention is to solve at least a part of the problems described above, and the invention can be implemented as the following forms.
The first aspect of the present invention is:
The first conductivity type first nitride semiconductor layer, the first conductivity type second nitride semiconductor layer, the second conductivity type third nitride semiconductor layer, and the first conductivity type fourth nitride. A stacked body in which semiconductor layers are stacked in this order;
A first electrode in contact with a surface of the first nitride semiconductor layer opposite to a surface in contact with the second nitride semiconductor layer;
A trench penetrating the third nitride semiconductor layer and the fourth nitride semiconductor layer and reaching the second nitride semiconductor layer is formed;
A gate electrode provided in the trench via an insulating film;
A vertical MOS transistor;
The first electrode;
An ohmic electrode of the second conductivity type that is in contact with the surface of the third nitride semiconductor layer that is opposite to the surface in contact with the second nitride semiconductor layer;
A semiconductor device comprising a protection element,
The impurity concentration of the first conductivity type is lower in the second nitride semiconductor layer than in the first nitride semiconductor layer,
The first nitride semiconductor layer includes a protrusion protruding to the second nitride semiconductor layer,
When viewed from the stacking direction of the stacked body, the top surface of the convex portion is disposed at a position at least partially overlapping the second conductivity type ohmic electrode,
In the semiconductor device, the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer in a portion where the bottom surface of the trench is in contact is larger than the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer in a portion where the top surface of the convex portion is in contact.
The second aspect of the present invention is:
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device, comprising:
Forming a protrusion protruding on the surface of the first conductivity type first nitride semiconductor layer;
A second nitride semiconductor layer of the first conductivity type having a lower impurity concentration than the first nitride semiconductor layer on a surface of the first nitride semiconductor layer, the surface having the convex portion; Laminating a conductive third nitride semiconductor layer in this order;
Forming a trench penetrating the third nitride semiconductor layer and reaching the second nitride semiconductor layer;
Forming a first electrode on a surface of the first nitride semiconductor layer opposite to a surface in contact with the second nitride semiconductor layer;
In the stacking direction, at least a part of the upper surface of the convex portion overlaps the surface of the third nitride semiconductor layer, on the surface opposite to the surface in contact with the second nitride semiconductor layer, Forming the second conductivity type ohmic electrode;
Forming a gate electrode in the trench via an insulating film;
Forming the first conductivity type fourth nitride semiconductor layer on the surface of the third nitride semiconductor layer opposite to the surface in contact with the second nitride semiconductor layer;
Forming a source electrode on the fourth nitride semiconductor layer;
Have
The fourth nitride semiconductor layer is arranged in a position not overlapping the upper surface of the convex portion in the stacking direction;
The thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer in the portion where the bottom surface of the trench is in contact is greater than the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer in the portion where the top surface of the convex portion is in contact,
A vertical MOS transistor formed of a nitride semiconductor layer from the first nitride semiconductor layer to the fourth nitride semiconductor layer, the gate electrode, the first electrode, and the source electrode; and the first nitride A semiconductor device comprising: a nitride semiconductor layer from a nitride semiconductor layer to the third nitride semiconductor layer; a protective element that is a PN junction diode formed from the first electrode and the second conductivity type ohmic electrode; Is the method. The present invention can also be realized as the following forms.
(1)本発明の一形態によれば、半導体装置が提供される。この半導体装置は、第1導電型の第1窒化物半導体層と、前記第1導電型の第2窒化物半導体層と、第2導電型の第3窒化物半導体層と、前記第1導電型の第4窒化物半導体層と、がこの順に積層された積層体と、前記第1窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記第2窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面と接する第1の電極と、を有し、前記第3窒化物半導体層と、前記第4窒化物半導体層とを貫通し、前記第2窒化物半導体層に達するトレンチが形成された、縦型MOSトランジスタと、前記第1の電極と、前記第3窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記第2窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面と接する前記第2導電型のオーミック電極と、を有する、保護素子と、を備える、半導体装置であって;前記第1導電型の不純物濃度は、前記第1窒化物半導体層に比べて前記第2窒化物半導体層のほうが低く、前記第1窒化物半導体層は、前記第2窒化物半導体層へ突出する凸部を備え、前記積層体の積層方向から見たときに、前記凸部の上面は、前記第2導電型のオーミック電極と少なくとも一部が重なる位置に配されており、前記トレンチの底面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みは、前記凸部の上面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みよりも大きい。この形態の半導体装置によれば、第1窒化物半導体層は、前記第2窒化物半導体層へ突出する凸部を備え、トレンチの底面における第2窒化物半導体層の厚みは、凸部の上面における第2窒化物半導体層の厚みよりも大きいため、保護素子の耐圧の低下を抑制できる。 (1) According to one aspect of the present invention, a semiconductor device is provided. The semiconductor device includes a first conductivity type first nitride semiconductor layer, the first conductivity type second nitride semiconductor layer, a second conductivity type third nitride semiconductor layer, and the first conductivity type. The fourth nitride semiconductor layer are stacked in this order, and the surface of the first nitride semiconductor layer is in contact with the surface opposite to the surface in contact with the second nitride semiconductor layer. A vertical MOS transistor having a first electrode and having a trench penetrating the third nitride semiconductor layer and the fourth nitride semiconductor layer and reaching the second nitride semiconductor layer And the first electrode, and the second conductivity type ohmic electrode in contact with the surface of the third nitride semiconductor layer opposite to the surface in contact with the second nitride semiconductor layer, A semiconductor device comprising: a protection element; wherein the impurity concentration of the first conductivity type is: The second nitride semiconductor layer is lower than the first nitride semiconductor layer, and the first nitride semiconductor layer includes a protrusion protruding to the second nitride semiconductor layer, When viewed from the direction, the top surface of the convex portion is disposed at a position at least partially overlapping the second conductivity type ohmic electrode, and the second nitride semiconductor layer in a portion where the bottom surface of the trench contacts Is thicker than the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer at the portion where the upper surface of the convex portion is in contact. According to the semiconductor device of this aspect, the first nitride semiconductor layer includes the convex portion protruding to the second nitride semiconductor layer, and the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer on the bottom surface of the trench is the upper surface of the convex portion. Since the thickness is larger than the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer in FIG.
(2)上記形態の半導体装置において、前記積層方向から見たときに、前記第4窒化物半導体層は、前記凸部の上面と重ならない位置に配されていてもよい。この形態の半導体装置によれば、第4窒化物半導体層から凸部へ電流が流れる前に、保護素子に電流が流れることにより、保護素子の耐圧の低下を抑制できる。 (2) In the semiconductor device of the above aspect, the fourth nitride semiconductor layer may be arranged at a position that does not overlap the upper surface of the convex portion when viewed from the stacking direction. According to the semiconductor device of this aspect, the current flows through the protection element before the current flows from the fourth nitride semiconductor layer to the convex portion, so that a reduction in the breakdown voltage of the protection element can be suppressed.
(3)上記形態の半導体装置において、さらに、前記積層方向から見たときに、前記凸部に対して、前記トレンチが配されている側とは反対側に、前記第3窒化物半導体層を貫通し、前記第2窒化物半導体層に達する段差部が形成されており、前記凸部の上面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みは、前記段差部の底面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚み以下としてもよい。この形態の半導体装置によれば、段差部と第1の電極との間に電流が流れる前に、保護素子に電流が流れることにより、半導体装置の耐圧破壊を抑制できる。 (3) In the semiconductor device of the above aspect, the third nitride semiconductor layer may be disposed on a side opposite to the side where the trench is disposed with respect to the convex portion when viewed from the stacking direction. A step portion that penetrates and reaches the second nitride semiconductor layer is formed, and the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer in a portion that is in contact with the upper surface of the convex portion is the thickness in the portion that is in contact with the bottom surface of the step portion. It may be less than or equal to the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer. According to the semiconductor device of this aspect, the breakdown voltage of the semiconductor device can be suppressed by causing the current to flow through the protective element before the current flows between the stepped portion and the first electrode.
(4)上記形態の半導体装置において、前記段差部の底面と前記凸部との距離は、前記段差部の底面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みよりも大きくてもよい。この形態の半導体装置によれば、第1の電極から凸部を介して段差部に電流が流れる前に、保護素子に電流が流れることにより、半導体装置の耐圧破壊を抑制できる。 (4) In the semiconductor device of the above aspect, the distance between the bottom surface of the stepped portion and the convex portion may be larger than the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer at a portion where the bottom surface of the stepped portion is in contact. According to the semiconductor device of this aspect, the breakdown voltage of the semiconductor device can be suppressed by causing the current to flow through the protective element before the current flows from the first electrode to the stepped portion via the convex portion.
(5)上記形態の半導体装置において、さらに、前記第4窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記第3窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面と接する前記第1導電型のオーミック電極を備えてもよい。この形態の半導体装置によれば、第1導電型のオーミック電極が形成されているため、縦型MOSトランジスタのオン抵抗を下げることができる。 (5) In the semiconductor device of the above aspect, the first conductivity type ohmic contact is further made on the surface of the fourth nitride semiconductor layer, which is in contact with the surface opposite to the surface in contact with the third nitride semiconductor layer. An electrode may be provided. According to the semiconductor device of this aspect, since the first conductivity type ohmic electrode is formed, the on-resistance of the vertical MOS transistor can be lowered.
(6)上記形態の半導体装置において、さらに、前記第1導電型のオーミック電極と前記第2導電型のオーミック電極とを電気的に接続する第1配線を備え、前記第1配線は、絶縁膜を介して前記段差部の側面を覆っていてもよい。この形態の半導体装置によれば、第1配線を備えることにより、段差部側面で電界が集中することを抑制でき、その結果、半導体装置の耐圧破壊を抑制できる。 (6) In the semiconductor device of the above aspect, the semiconductor device further includes a first wiring that electrically connects the first conductivity type ohmic electrode and the second conductivity type ohmic electrode, and the first wiring includes an insulating film You may cover the side surface of the said level | step-difference part via. According to the semiconductor device of this aspect, by providing the first wiring, it is possible to suppress the concentration of the electric field on the side surface of the step portion, and as a result, it is possible to suppress the breakdown voltage breakdown of the semiconductor device.
(7)上記形態の半導体装置において、前記第1窒化物半導体層から前記第4窒化物半導体層は、ガリウムを含む窒化物半導体により形成されていてもよい。この形態の半導体装置によれば、保護素子の耐圧の低下を抑制できる。 (7) In the semiconductor device of the above aspect, the first nitride semiconductor layer to the fourth nitride semiconductor layer may be formed of a nitride semiconductor containing gallium. According to this form of the semiconductor device, it is possible to suppress a decrease in the breakdown voltage of the protection element.
(8)上記形態の半導体装置において、前記第1窒化物半導体層は、窒化ガリウムにより形成されていてもよい。この形態の半導体装置によれば、保護素子の耐圧の低下を抑制できる。 (8) In the semiconductor device of the above aspect, the first nitride semiconductor layer may be formed of gallium nitride. According to this form of the semiconductor device, it is possible to suppress a decrease in the breakdown voltage of the protection element.
(9)上記形態の半導体装置において、前記第1窒化物半導体層は、窒化ガリウム基板であってもよい。この形態の半導体装置によれば、保護素子の耐圧の低下を抑制できる。 (9) In the semiconductor device of the above aspect, the first nitride semiconductor layer may be a gallium nitride substrate. According to this form of the semiconductor device, it is possible to suppress a decrease in the breakdown voltage of the protection element.
(10)上記形態の半導体装置において、前記凸部の側面は、前記凸部の上面に対して傾斜していてもよい。この形態の半導体装置によれば、保護素子の耐圧の低下を抑制できる。 (10) In the semiconductor device of the above aspect, the side surface of the convex portion may be inclined with respect to the upper surface of the convex portion. According to this form of the semiconductor device, it is possible to suppress a decrease in the breakdown voltage of the protection element.
(11)上記形態の半導体装置において、前記凸部の側面は、a面またはm面で構成され、前記凸部の上面は、c面で構成されていてもよい。この形態の半導体装置によれば、保護素子の耐圧の低下を抑制できる。 (11) In the semiconductor device according to the above aspect, the side surface of the convex portion may be an a-plane or an m-plane, and the upper surface of the convex portion may be a c-plane. According to this form of the semiconductor device, it is possible to suppress a decrease in the breakdown voltage of the protection element.
(12)本発明の一形態によれば、半導体装置の製造方法が提供される。この半導体装置の製造方法は、第1導電型の第1窒化物半導体層の面に突出する凸部を形成する工程と、前記第1窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記凸部を備える面に、前記第1窒化物半導体層よりも不純物濃度が小さい前記第1導電型の第2窒化物半導体層と、第2導電型の第3窒化物半導体層と、をこの順に積層する工程と、前記第3窒化物半導体層を貫通し、前記第2窒化物半導体層に達するトレンチを形成する工程と、前記第1窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記第2窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面に、第1の電極を形成する工程と、積層方向において、前記凸部の上面と少なくとも一部が重なる位置であって、前記第3窒化物半導体層の面であり、前記第2窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面に、前記第2導電型のオーミック電極を形成する工程と、を有し;前記トレンチの底面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みは、前記凸部の上面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みよりも大きい。この形態の半導体装置の製造方法によれば、第1電極と第2導電型のオーミック電極から形成される保護素子の耐圧の低下を抑制できる。 (12) According to an aspect of the present invention, a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device is provided. The method for manufacturing a semiconductor device includes a step of forming a protrusion protruding on a surface of a first conductivity type first nitride semiconductor layer, and the surface of the first nitride semiconductor layer, the protrusion being provided. Laminating the first conductivity type second nitride semiconductor layer having a lower impurity concentration than the first nitride semiconductor layer and a second conductivity type third nitride semiconductor layer in this order on the surface; A step of forming a trench penetrating the third nitride semiconductor layer and reaching the second nitride semiconductor layer; and a surface of the first nitride semiconductor layer in contact with the second nitride semiconductor layer A step of forming the first electrode on a surface opposite to the surface, and a position at least partially overlapping the upper surface of the convex portion in the stacking direction, the surface of the third nitride semiconductor layer The second conductivity type on the surface opposite to the surface in contact with the second nitride semiconductor layer. Forming an ohmic electrode; and the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer in the portion where the bottom surface of the trench contacts is greater than the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer in the portion where the top surface of the convex portion contacts Is also big. According to the method for manufacturing a semiconductor device of this aspect, it is possible to suppress a decrease in breakdown voltage of the protective element formed from the first electrode and the second conductivity type ohmic electrode.
(13)上記形態の半導体装置の製造方法において、さらに、前記凸部の上面と前記トレンチの底面との距離が、前記トレンチの底面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みよりも大きくてもよい。この形態の半導体装置の製造方法によれば、縦型MOSトランジスタのドレイン電流は、トレンチ側方とトレンチ下方の第1窒化物半導体層との間を流れるので、縦型MOSトランジスタの耐圧は、凸部により低下することはない。これにより、保護素子よりも縦型MOSトランジスタの耐圧が下がることは無いので、縦型MOSトランジスタが耐圧破壊することを抑制できる。 (13) In the method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to the above aspect, the distance between the top surface of the convex portion and the bottom surface of the trench is larger than the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer at a portion where the bottom surface of the trench contacts. May be. According to the method of manufacturing a semiconductor device of this aspect, the drain current of the vertical MOS transistor flows between the side of the trench and the first nitride semiconductor layer below the trench. It does not decrease depending on the part. As a result, the breakdown voltage of the vertical MOS transistor does not drop more than that of the protective element, so that the breakdown of the vertical MOS transistor can be suppressed.
(14)上記形態の半導体装置の製造方法において、前記第3窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記第2窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面に、前記第1導電型の第4窒化物半導体層を形成する工程を、備え、前記第4窒化物半導体層は、前記積層方向において、前記凸部の上面と重ならない位置に配されていてもよい。この形態の半導体装置の製造方法によれば、縦型MOSトランジスタのドレイン電流は、第4窒化物半導体層と、トレンチ下方の第1窒化物半導体層との間を流れるので、縦型MOSトランジスタの耐圧が凸部により低下することはない。保護素子よりも縦型MOSトランジスタの耐圧が下がることは無いので、縦型MOSトランジスタが耐圧破壊することを抑制できる。 (14) In the method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to the above aspect, the surface of the third nitride semiconductor layer, the surface of the first conductivity type on the surface opposite to the surface in contact with the second nitride semiconductor layer. A step of forming a fourth nitride semiconductor layer, wherein the fourth nitride semiconductor layer may be arranged at a position that does not overlap with an upper surface of the convex portion in the stacking direction. According to the method for manufacturing a semiconductor device of this aspect, the drain current of the vertical MOS transistor flows between the fourth nitride semiconductor layer and the first nitride semiconductor layer below the trench. The breakdown voltage is not lowered by the convex portion. Since the breakdown voltage of the vertical MOS transistor does not drop more than the protection element, it is possible to suppress the breakdown of the vertical MOS transistor.
(15)上記形態の半導体装置の製造方法において、前記第1窒化物半導体層から前記第4窒化物半導体層は、ガリウムを含む窒化物半導体により形成されていてもよい。この形態の半導体装置の製造方法によれば、第1電極と第2導電型のオーミック電極から形成される保護素子の耐圧の低下を抑制できる。 (15) In the method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to the above aspect, the first nitride semiconductor layer to the fourth nitride semiconductor layer may be formed of a nitride semiconductor containing gallium. According to the method for manufacturing a semiconductor device of this aspect, it is possible to suppress a decrease in breakdown voltage of the protective element formed from the first electrode and the second conductivity type ohmic electrode.
(16)上記形態の半導体装置の製造方法において、前記第1窒化物半導体層は、窒化ガリウム基板であってもよい。この形態の半導体装置の製造方法によれば、第1電極と第2導電型のオーミック電極から形成される保護素子の耐圧の低下を抑制できる。 (16) In the method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to the above aspect, the first nitride semiconductor layer may be a gallium nitride substrate. According to the method for manufacturing a semiconductor device of this aspect, it is possible to suppress a decrease in breakdown voltage of the protective element formed from the first electrode and the second conductivity type ohmic electrode.
上述した本発明の各形態の有する複数の構成要素はすべてが必須のものではなく、上述の課題の一部又は全部を解決するため、あるいは、本明細書に記載された効果の一部又は全部を達成するために、適宜、前記複数の構成要素の一部の構成要素について、その変更、削除、新たな他の構成要素との差し替え、限定内容の一部削除を行うことが可能である。また、上述の課題の一部又は全部を解決するため、あるいは、本明細書に記載された効果の一部又は全部を達成するために、上述した本発明の一形態に含まれる技術的特徴の一部又は全部を上述した本発明の他の形態に含まれる技術的特徴の一部又は全部と組み合わせて、本発明の独立した一形態とすることも可能である。 A plurality of constituent elements of each aspect of the present invention described above are not indispensable, and some or all of the effects described in the present specification are to be solved to solve part or all of the above-described problems. In order to achieve the above, it is possible to appropriately change, delete, replace with another new component, and partially delete the limited contents of some of the plurality of components. In order to solve part or all of the above-described problems or to achieve part or all of the effects described in this specification, technical features included in one embodiment of the present invention described above. A part or all of the technical features included in the other aspects of the present invention described above may be combined to form an independent form of the present invention.
本発明は、半導体装置およびその製造方法以外の種々の形態で実現することも可能である。例えば、本願発明は、上記形態の半導体装置が組み込まれた電気機器、上記形態の半導体装置を製造する製造装置などの形態で実現することができる。 The present invention can be realized in various forms other than the semiconductor device and the manufacturing method thereof. For example, the present invention can be realized in the form of an electrical apparatus in which the semiconductor device of the above form is incorporated, a manufacturing apparatus for manufacturing the semiconductor device of the above form, and the like.
この形態の半導体装置によれば、第1窒化物半導体層は、前記第2窒化物半導体層へ突出する凸部を備え、トレンチの底面における第2窒化物半導体層の厚みは、凸部の上面における第2窒化物半導体層の厚みよりも大きいため、保護素子の耐圧の低下を抑制できる。また、この形態の半導体装置の製造方法によれば、第1電極と第2導電型のオーミック電極から形成される保護素子の耐圧の低下を抑制できる。 According to the semiconductor device of this aspect, the first nitride semiconductor layer includes the convex portion protruding to the second nitride semiconductor layer, and the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer on the bottom surface of the trench is the upper surface of the convex portion. Since the thickness is larger than the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer in FIG. In addition, according to the method for manufacturing a semiconductor device of this embodiment, it is possible to suppress a decrease in breakdown voltage of the protective element formed from the first electrode and the second conductivity type ohmic electrode.
A.第1実施形態:
A1.半導体装置10の構成:
図1は、第1実施形態における半導体装置10の構成を模式的に示す断面図である。半導体装置10は、縦型MOS(Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor)トランジスタ300と保護素子200とを備える。縦型MOSトランジスタ300は、窒化物半導体を用いて形成されたGaN系の半導体装置である。本実施形態では、縦型MOSトランジスタ300は、トレンチゲート型MOSFET(Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor)であり、例えば、電力制御に用いられ、パワーデバイスとも呼ばれる。保護素子200は、PN接合ダイオードである。本実施形態においては、窒化物半導体として窒化ガリウム(GaN)を用いる。
A. First embodiment:
A1. Configuration of the semiconductor device 10:
FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view schematically showing the configuration of the
半導体装置10は、基板110と、N型半導体層120と、P型半導体層130と、N型半導体層140と、電極210,230,240,250と、配線270と、絶縁膜340とを備える。半導体装置10は、NPN型の半導体装置であり、N型半導体層120とP型半導体層130とN型半導体層140とが順に積層された構造を有する。
The
なお、「基板110」は、「半導体層110」や「第1導電型の第1窒化物半導体層110」とも呼び、「N型半導体層120」は、「第1導電型の第2窒化物半導体層120」とも呼び、「P型半導体層130」は、「第2導電型の第3窒化物半導体層130」とも呼び、「N型半導体層140」は、「第1導電型の第4窒化物半導体層140」とも呼ぶ。また、「半導体基板110と、N型半導体層120と、P型半導体層130と、N型半導体層140と、がこの順に積層された構造体」を、「積層体100」とも呼ぶ。
The “
半導体装置10のN型半導体層120、P型半導体層130、およびN型半導体層140は、有機金属気相成長法(MOCVD:Metal Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition)による結晶成長によって形成された半導体層である。
The N-
図1には、相互に直交するXYZ軸が図示されている。図1のXYZ軸のうち、X軸は、基板110に対してN型半導体層120が積層する積層方向に沿った軸である。X軸に沿ったX軸方向のうち、+X軸方向は、基板110からN型半導体層120に向かう方向であり、−X軸方向は、+X軸方向に対向する方向である。図1のXYZ軸のうち、Y軸およびZ軸は、X軸に直交すると共に相互に直交する軸である。Y軸に沿ったY軸方向のうち、+Y軸方向は、図1の紙面左から紙面右に向かう方向であり、−Y軸方向は、+Y軸方向に対向する方向である。Z軸に沿ったZ軸方向のうち、+Z軸方向は、図1の紙面手前から紙面奥に向かう方向であり、−Z軸方向は、+Z軸方向に対向する方向である。
FIG. 1 shows XYZ axes orthogonal to each other. Of the XYZ axes in FIG. 1, the X axis is an axis along the stacking direction in which the N-
半導体装置10の基板110は、Y軸およびZ軸によって規定される面方向に沿って広がるN型の半導体層であり、本実施形態においては、N+型の半導体層である。基板110は、主に、ガリウム(Ga)を含む窒化物半導体により形成されている。本実施形態において、基板110は、窒化ガリウム(GaN)から主に形成される。基板110は、ゲルマニウム(Ge)、酸素(O)、ケイ素(Si)などのN型不純物をドナーとして含有する。N型の不純物濃度は、基板110に比べてN型半導体層120のほうが低い。なお、窒化ガリウム(GaN)から主に形成されるとは、モル分率において、窒化ガリウム(GaN)を90%以上含有することを示す。
The
基板110は、N型半導体層120へ突出する凸部115を備える。凸部115の側面(Y軸方向側の面)は、a面またはm面で構成され、凸部115の上面(+X軸方向側の面)はc面で構成されている。凸部115を備えることにより得られる効果は、後に詳述する。なお、基板110の代わりに、N+型半導体層を設け、電極210とN+型半導体層との間に基板を設けてもよい。
The
半導体装置10のN型半導体層120は、基板110の+X軸方向側に積層され、Y軸およびZ軸によって規定される面方向に沿って広がる半導体層である。N型半導体層120は、主に、ガリウム(Ga)を含む窒化物半導体により形成されている。本実施形態において、N型半導体層120は、主に、窒化ガリウム(GaN)から形成されている。N型半導体層120は、ケイ素(Si)をドナーとして含有する。N型半導体層120は、「n-−GaN」とも呼ばれる。
The N-
半導体装置10のP型半導体層130は、N型半導体層120の+X軸方向側に積層され、Y軸およびZ軸によって規定される面方向に沿って広がる半導体層である。P型半導体層130は、主に、ガリウム(Ga)を含む窒化物半導体により形成されている。本実施形態において、P型半導体層130は、主に、窒化ガリウム(GaN)から形成されている。P型半導体層130は、マグネシウム(Mg)をP型不純物として含有する。P型半導体層130の不純物濃度は、N型半導体層120の不純物濃度よりも高い。P型半導体層130は、「p−GaN」とも呼ばれる。
The P-
半導体装置10のN型半導体層140は、P型半導体層130の+X軸方向側に積層され、Y軸およびZ軸によって規定される面方向に沿って広がる半導体層である。N型半導体層140は、窒化ガリウム(GaN)から主に形成されている。N型半導体層140は、ケイ素(Si)をN型不純物として含有する。N型半導体層140の不純物濃度は、N型半導体層120の不純物濃度よりも高い。N型半導体層140は、「n+−GaN」とも呼ばれる。基板110、N型半導体層120、P型半導体層130、N型半導体層140は、ガリウムを含む窒化物半導体により形成されている。
The N-
半導体装置10の凹部182は、+X軸方向側からP型半導体層130が露出した部位である。凹部182は、リセス(recess)とも呼ばれる。
The
半導体装置10のトレンチ184は、ドライエッチングによって形成されている。トレンチ184は、N型半導体層140の+X軸方向側から、P型半導体層130と、N型半導体層140とを貫通し、N型半導体層120まで達する部位である。本実施形態では、トレンチ184は、凹部182の+Y軸方向側に位置する。
The
トレンチ184の表面には、積層体100の+X軸方向側に至るまで、絶縁膜340が形成されている。本実施形態では、絶縁膜340は、二酸化ケイ素(SiO2)から形成されている。なお、二酸化ケイ素(SiO2)に代えて、酸化アルミニウム(Al2O3)、酸化ジルコニウム(ZrO2)、酸化タンタル(Ta2O3)を用いてもよい。
An insulating
半導体装置10の段差部186は、ドライエッチングによって形成されている。段差部186は、P型半導体層130を貫通し、N型半導体層120に達する部位である。段差部186は、半導体素子を分離するために設けられた素子分離領域である。積層体100の積層方向(X軸方向)から見たときに、凸部115に対してトレンチ184が配されている側とは反対側に形成されている。つまり、段差部186は、トレンチ184の−Y軸方向側に位置する。
The
半導体装置10の電極210は、基板110の面であって、N型半導体層120と接する面とは反対側の面と接するドレイン電極である。つまり、電極210は、基板110の−X軸方向側に形成されている。電極210は、N型オーミック電極である。本実施形態では、電極210は、チタン(Ti)から形成される層にアルミニウム(Al)から形成される層を積層した後に焼成することによって形成される。なお、「電極210」は、「第1の電極210」とも呼ぶ。
The
半導体装置10の電極230は、凹部182の内側に露出されたP型半導体層130に形成されたボディ電極である。電極230は、P型半導体層130の面であって、N型半導体層120と接する面とは反対側の面と接するP型オーミック電極である。「電極230」は、「第2導電型のオーミック電極230」とも呼ぶ。本実施形態では、電極230は、パラジウム(Pd)から形成される層を積層した後に焼成することによって形成される。
The
半導体装置10の電極240は、凹部182とトレンチ184との間におけるN型半導体層140の上(+X軸方向側)に形成されたソース電極である。つまり、電極240は、N型半導体層140の面であって、P型半導体層130と接する面とは反対側の面と接するN型オーミック電極である。本実施形態では、電極240は、チタン(Ti)から形成される層にアルミニウム(Al)から形成される層を積層した後に焼成することによって形成される。電極240は、オーミック電極であるため、縦型MOSトランジスタ300のON抵抗を下げることができる。
The
半導体装置10の電極250は、トレンチ184における絶縁膜340上に形成されたゲート電極である。本実施形態では、電極250は、アルミニウム(Al)から形成される。なお、アルミニウム(Al)に代えて、アルミニウムシリコン(AlSi)、アルミニウムシリコン銅(AlSiCu)を用いてもよい。
The
半導体装置10の配線270は、電極230と電極240とを電気的に接続する配線である。「配線270」は、「第1配線270」とも呼び、アルミニウム(Al)から形成される。なお、アルミニウム(Al)に代えて、アルミニウムシリコン(AlSi)、アルミニウムシリコン銅(AlSiCu)を用いてもよい。配線270は、絶縁膜340を介して段差部186の側面(Y軸方向側の面)を覆っている。配線270により、段差部186の側面において電界が集中することを抑制でき、その結果、半導体装置10の耐圧破壊を抑制できる。
The
縦型MOSトランジスタ300は、積層体100と、ドレイン電極である電極210と、ゲート電極である電極250と、ソース電極である電極240と、により形成されている。保護素子200は、積層体100と、電極230と、電極210とにより形成されている。保護素子200は、縦型MOSトランジスタ300が耐圧破壊することから保護するために設けられたPN接合ダイオードである。ここで、「耐圧破壊」とは、一度耐圧以上の電圧が印加されると縦型MOSトランジスタ内部が破壊され、元の電流・電圧特性が得られなくなる状態を示す。
The
図2は、半導体装置10を+X軸方向から見た外観図である。図2におけるA−A断面が、図1におけるA−A断面に相当する。半導体装置10は、−Y軸方向側から順に、(i)半導体素子を分離するために用いる素子分離領域と、(ii)保護素子200が形成された領域であるPN接合保護ダイオード形成領域と、(iii)縦型MOSトランジスタ300が形成されたトランジスタ形成領域とを備える。
FIG. 2 is an external view of the
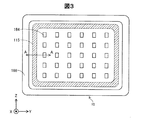
図3は、N型半導体層120とP型半導体層130との界面を+X軸方向から見た概略図である。図2と同様に、図3におけるA−A断面が、図1におけるA−A断面に相当する。凸部115は、段差部186の内周に位置していることがわかる。また、凸部115の内周には、複数のトレンチ184が配されていることが分かる。
FIG. 3 is a schematic view of the interface between the N-
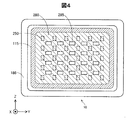
図4は、半導体装置10に備えられた複数の電極250同士を、配線280により電気的に接続した状態において、半導体装置10を+X軸方向から見た外観図である。なお、図4では、理解を容易とするため、凸部115の位置を斜線および破線で示している。配線280は、隣接する電極250同士を直線で結ぶように配されている。配線280の下に電極250が形成されているが、配線280により電極250の表面が覆われているため、図4では、電極250の位置を破線で示している。配線280の一部は、開口部285が形成されている。開口部285は、電極240に接続された配線(不図示)を引き出すための領域である。本実施形態において、配線280は、アルミニウム(Al)により形成されている。なお、アルミニウム(Al)に代えて、アルミニウムシリコン(AlSi)、アルミニウムシリコン銅(AlSiCu)を用いてもよい。
FIG. 4 is an external view of the
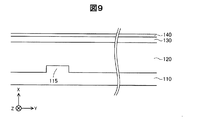
図1に示すように、凸部115の上面は、積層体100の積層方向(X軸方向)から見たときに、電極230の少なくとも一部が重なる位置に配されている。また、トレンチ184の底面(−X軸方向側の面)が接する部分におけるN型半導体層120の厚みd2は、凸部115の上面(+X軸方向側の面)が接する部分におけるN型半導体層120の厚みd5よりも大きい。このため、縦型MOSトランジスタ300に保護素子200の耐圧よりも高いドレイン電圧が印加された場合、電流は、電極250から電極210へ流れるよりも、電極230から電極210へ多く流れる。そして、保護素子200により、電極230と電極210との間の電圧が、保護素子200の耐圧値となる。その結果、電極240と電極210との電圧についても、保護素子200の耐圧値となり、縦型MOSトランジスタ300が耐圧破壊することを防ぐことができる。このようにすることにより、保護素子200は、縦型MOSトランジスタ300を保護することができる。
As shown in FIG. 1, the upper surface of the
次に、本実施形態の作用効果について説明する。保護素子200は縦型MOSトランジスタ300よりも耐圧を低く、かつ、耐圧破壊しないように設計する必要がある。このため、保護素子200の厚みd5を、縦型MOSトランジスタ300の厚みd2よりも小さくする必要がある。厚みd5を厚みd2よりも小さくする方法として、N型半導体層120の+X軸方向側の一部を除去した後、除去した部分にP型半導体層を再成長する方法が考えられる。しかし、この方法を用いた場合、再成長界面に意図しないN型キャリアが発生することにより、PN接合ダイオードの耐圧が低下することが発明者らの検討の結果、明らかとなった。一方、本実施形態の半導体装置10によれば、凸部115を形成することにより厚みd5を厚みd2よりも小さくしている。凸部115を備える基板110上にN型半導体層120が形成されているため、基板110とN型半導体層120との界面に意図しないN型キャリアが発生したとしても、N型層(110,120)の間にN型キャリアが形成されるため、保護素子200の耐圧の低下を抑制できる。なお、厚みd5を厚みd2よりも小さくする方法として、P型のイオン注入を用いる方法も考えられる。しかし、半導体として窒化物半導体を用いる場合、P型のイオン注入を行うことは困難である。これに対して、本実施形態では、凸部115を形成するため、P型のイオン注入を行うことなく厚みd5を厚みd2よりも小さくすることができる。
Next, the effect of this embodiment is demonstrated. The
また、積層方向(X軸方向)から見たときに、N型半導体層140は、凸部115の上面と重ならない位置に配されている。このため、縦型MOSトランジスタのドレイン電流は、N型半導体層140と、トレンチ下方の基板110との間を流れるので、縦型MOSトランジスタ300の耐圧が凸部115により低下することはない。保護素子200よりも縦型MOSトランジスタ300の耐圧が下がることは無いので、縦型MOSトランジスタ300の耐圧破壊を抑制することができる。
Further, when viewed from the stacking direction (X-axis direction), the N-
凸部115の上面が接する部分におけるN型半導体層120の厚みd5は、段差部186の底面(−X軸方向側の面)が接する部分における厚みd4以下である。このため、段差部186と電極210との間に電流が流れる前に、保護素子200に電流が流れる。この結果、半導体装置10の耐圧破壊を抑制できる。
The thickness d5 of the N-
段差部186の底面と凸部115との距離d3は、段差部186の底面(−X軸方向側の面)が接する部分における厚みd4より大きい。このため、段差部186と電極210との間に段差部186を介して電流が流れる前に、保護素子200に電流が流れる。この結果、半導体装置10の耐圧破壊を抑制できる。
The distance d3 between the bottom surface of the stepped
凸部115の上面とトレンチ184の底面との距離d1は、トレンチ184の底面が接する部分におけるN型半導体層120の厚みd2よりも大きい。このため、保護素子200の耐圧以上の電圧が電極210と配線270との間に印加された場合、電極210から凸部115を介してトレンチ184へ電流が流れる前に、保護素子200に電流が流れる。この結果、半導体装置10の耐圧破壊を抑制できる。
A distance d1 between the top surface of the
図5は、本実施形態の半導体装置10から得られる効果を説明する図である。図5(A)は、本実施形態の等価回路を示す。本実施形態において、保護素子200と縦型MOSトランジスタ300と素子分離領域とが、並列に接続されている。縦型MOSトランジスタ300のドレイン電極(電極210)・ソース電極(電極240)間電圧を電圧Vdsとし、ゲート電極(電極250)・ソース電極(電極240)間電圧を電圧Vgsとし、ドレイン電流を電流Idとする。
FIG. 5 is a diagram for explaining the effects obtained from the
図5(B)は、電流・電圧特性を示す。一点鎖線l2は、保護素子200や素子分離領域を備えず、縦型MOSトランジスタ300のみの場合において、ドレイン電極・ソース電極間に電圧Vdsを印加したときの電流Idを示す。ゲート電極・ソース電極間電圧Vgsは0Vである。縦型MOSトランジスタ300のみの場合、一点鎖線l2におけるXで示す点において、半導体装置の耐圧破壊が起こる。耐圧破壊は、不可逆反応であり、一度起こってしまうと、リーク電流が大幅に増加し、元の素子特性には戻らず、素子特性は劣化する。
FIG. 5B shows current / voltage characteristics. An alternate long and short dash line l2 indicates the current Id when the voltage Vds is applied between the drain electrode and the source electrode in the case where only the
実線l1は、素子分離領域のみの場合に、電圧Vdsを印加したときの電流Idを示す。実線l1におけるXで示す点において、半導体装置の耐圧破壊が起こる。
A
二点鎖線l3は、保護素子200のみの場合に、電圧Vdsを印加したときの電流Idを示す。二点鎖線l3におけるOで示す点において、アバランシェ崩壊により電流が急増するため、これ以上の電圧が印加されることが抑制される。つまり、二点鎖線l3で示す結果から、保護素子200が、定電圧ダイオードとして機能することが分かる。ここで、保護素子200のPN接合界面は、均一で平坦な面により形成されるため、PN接合界面に均等な電界が印加される。この結果、アバランシェ崩壊によるPN接合界面へのダメージが入りにくく、半導体装置の耐圧破壊が起きない。つまり、保護素子200の場合、二点鎖線l3におけるOで示す点における電圧Vdsが印加されたとしても、不可逆反応は起きない。なお、Oで示す点における電圧Vdsよりも低い電圧を印加する場合、二点鎖線l3に沿った値の電流が流れ、リーク電流は重畳されない。なお、本実施形態の保護素子200の接合は、ショットキー接合ではなく、PN接合である。この理由としては、ショットキー接合に高電圧が印加された場合に金属と半導体との界面が破壊される結果、リーク電流が増加するという不可逆反応が起こる虞があることを挙げることができる。
An alternate long and two
図5(C)は、本実施形態の半導体装置10全体に電圧Vdsを印加したときの電流Idを示す。なお、図5(A)に示すとおり、保護素子200と縦型MOSトランジスタ300と素子分離領域とは並列に接続されている。
FIG. 5C shows the current Id when the voltage Vds is applied to the
図5(C)における破線l4で示されるとおり、半導体装置10は保護素子200を備えるため、電圧Vdsは、保護素子200の特性によって決定される電圧以上になることはない。つまり、素子分離領域に係る電圧及び縦型MOSトランジスタ300のドレイン電極・ソース電極間電圧は、素子分離領域や縦型MOSトランジスタ300の耐圧破壊が起きる電圧よりも小さい電圧が印加されるのみである。例えば、本実施形態の半導体装置10の外部から半導体装置10へ、素子分離領域や縦型MOSトランジスタ300の耐圧破壊が起きるほどの高い電圧が印加されたとする。このような場合においても、半導体装置10は保護素子200を備えるため、素子分離領域や縦型MOSトランジスタ300に係る電圧は、保護素子200がアバランシェ崩壊する電圧まで抑制される。このため、半導体装置10の耐圧破壊を抑制できる。
As indicated by a broken line l4 in FIG. 5C, the
図6は、TCAD(Technology CAD)シミュレータにより計算した半導体装置10の電流密度分布を示す図である。図面右上方には、ゲートトレンチの左半分が表示されている。図6の電流密度分布は、ドレイン電極(電極210)・ソース電極(電極240)間電圧Vdsを1200Vとし、ゲート電極(電極250)・ソース電極(電極240)間電圧Vgsを0Vとしたときの分布を示す。凸部115の積層方向(X軸方向)の厚みは2μmとし、凸部115の幅方向(Y軸方向)の厚みは5μmとした。凸部115を除くN型半導体層120の厚みd6(図1参照)は6μmとした。段差部186の底面が接する部分における厚みd4は5μmとした。
FIG. 6 is a diagram showing a current density distribution of the
図6に示されるとおり、電圧Vdsを1200Vとした場合、凸部115の上面から上方(+X軸方向)に向かってインパクトイオン化により電流が流れることが分かる(色の濃い部分)。また、図6に示されるとおり、縦型MOSトランジスタ300および素子分離領域において電流密度が低く、インパクトイオン化による電流が流れていないことが分かる(色の薄い部分)。この結果から、半導体装置10の耐圧破壊が抑制されていることが分かる。
As shown in FIG. 6, when the voltage Vds is 1200 V, it can be seen that a current flows by impact ionization from the upper surface of the
A2.半導体装置10の製造方法:
図7は、半導体装置10の製造方法を示す工程図である。まず、工程P105において、基板110の面に突出する凸部115を形成する。
A2. Manufacturing method of the semiconductor device 10:
FIG. 7 is a process diagram illustrating a method for manufacturing the
図8は、工程P105における半導体装置10の中間製品を示す断面図である。本実施形態において、工程P105では、まず、製造者は、基板110の上にプラズマCVD(Chemical Vapor Deposition)装置により二酸化ケイ素(SiO2)の絶縁膜を形成する。次に、製造者は、リソグラフィ法によりパターニングしたレジストをマスクとしてバッファードフッ酸(BHF:Buffered Hydrogen Fluoride)に浸漬することにより、絶縁膜をエッチングする。その後、製造者は、半導体装置10の中間製品を剥離液に浸漬することによりレジストパターンを除去する。図8(A)は、基板110の上に絶縁膜510が形成された半導体装置10の中間製品を示す。
FIG. 8 is a cross-sectional view showing an intermediate product of the
次に、製造者は、誘導結合方式(ICP:Inductively Coupled Plasma)を採用したドライエッチング装置により、基板110を約2μmドライエッチングする。図8(B)は、ドライエッチングを行った後の半導体装置10の中間製品を示す。最後に、製造者は、絶縁膜をバッファードフッ酸に浸漬することにより、絶縁膜を除去する。このようにすることにより、基板110の面に突出する凸部115が形成される。
Next, the manufacturer performs dry etching of the
次に、工程P110(図7)において、基板110の上に、N型半導体層120と、P型半導体層130と、N型半導体層140と、をこの順に積層する。本実施形態では、製造者は、基板110をMOCVD炉内に導入し、N型半導体層120の成長する温度(例えば、1050℃)まで加熱する。MOCVD炉内は、キャリアガスとしての水素(H)及びV族元素としてのアンモニア(NH3)雰囲気とする。その後、製造者は、III族原料としてトリメチルガリウム(TMGa)とN型不純物としてシラン(SiH4)を炉内に導入し、ドナー濃度1×1016cm−3程度のN型半導体層120を約6μm成長させる。ドナー濃度は、1×1015cm−3から1×1016cm−3が好ましく、N型半導体層120の厚みは、5μmから20μmが好ましい。
Next, in step P110 (FIG. 7), the N-
次に、製造者は、III族原料としてトリメチルガリウム(TMGa)とP型不純物としてビス(シクロペンタジエニル)マグネシウム(Cp2Mg:bis (cyclopentadienyl) magnesium)を炉内に導入し、マグネシウム(Mg)濃度4×1018cm−3程度のP型半導体層130を約0.7μm成長させる。マグネシウム(Mg)濃度は、1×1018cm−3以上が好ましく、P型半導体層130の厚みは、0.5μmから2μmが好ましい。
Next, the manufacturer introduces trimethylgallium (TMGa) as a Group III raw material and bis (cyclopentadienyl) magnesium (Cp2Mg: bis (cyclopentadienyl) magnesium) as a P-type impurity into the furnace, and the magnesium (Mg) concentration A P-
次に、本実施形態では、製造者は、III族原料としてトリメチルガリウム(TMGa)とN型不純物としてシラン(SiH4)を炉内に導入し、ドナー濃度1×1018cm−3程度のN型半導体層140を約0.2μm成長させる。
Next, in the present embodiment, the manufacturer introduces trimethylgallium (TMGa) as a group III material and silane (SiH 4 ) as an N-type impurity into the furnace, and N having a donor concentration of about 1 × 10 18 cm −3. The
図9は、上記工程P110により、基板110上に半導体層(120,130,140)を形成させた半導体装置10の中間製品を示す断面図である。ここで、再成長界面は、基板110とN型半導体層120との界面となる。N型半導体層120とP型半導体層130との界面(PN接合界面)が再成長界面とする場合、保護素子200の耐圧が低下する虞があるが、半導体装置10の再成長界面はN型の基板110とN型半導体層120との界面(N/N界面)であるため、保護素子200の耐圧の低下を抑制できる。
FIG. 9 is a cross-sectional view showing an intermediate product of the
工程P110の後、工程P215(図7)において、半導体装置10の中間製品にトレンチ184と段差部186とを形成する。製造者は、まずマスクとなる絶縁膜を積層した後、フォトレジストにてパターニングを行なう。その後、エッチングを行なうことにより、製造者は、トレンチ184と段差部186とを形成する。
After step P110, in step P215 (FIG. 7), a
図10は、トレンチ184と段差部186とを形成させた半導体装置10の中間製品を示す断面図である。本実施形態において、エッチングとして、ドライエッチングを採用する。なお、ドライエッチングの後に、エッチングによるダメージ層を除去するため、ウェットエッチングを行なってもよい。
FIG. 10 is a cross-sectional view illustrating an intermediate product of the
次に、工程P220(図7)において、絶縁膜340を形成する。製造者は、まずマスクとなる絶縁膜を積層した後、フォトレジストにてパターニングを行なう。
Next, in the process P220 (FIG. 7), the insulating
図11は、絶縁膜340を形成させた半導体装置10の中間製品を示す断面図である。工程P220によって、絶縁膜340が形成後、パターニングしたレジストをマスクとしてドライエッチングにより一部の絶縁膜340が除去されることにより、凹部182についても形成される。
FIG. 11 is a cross-sectional view showing an intermediate product of the
工程P240(図7)において、製造者は、リフトオフ法を用いて電極230、240、250を形成する。
In the process P240 (FIG. 7), the manufacturer forms the
図12は、電極230、240、250を形成させた半導体装置10の中間製品を示す断面図である。
FIG. 12 is a cross-sectional view showing an intermediate product of the
その後、工程P250(図7)において、製造者は、電極230と電極240とを電気的に接続する配線270を形成する。最後に、製造者は、半導体装置10の中間製品の−X側に電極210を形成する(工程P255)。これらの工程を経て、図1に示す半導体装置10が完成する。
Thereafter, in the process P250 (FIG. 7), the manufacturer forms the
B.第2実施形態:
図13は、第2実施形態における半導体装置10Aの構成を模式的に示す図である。半導体装置10Aは、半導体装置10と比較して、凸部の形状が異なるが、それ以外は同じである。半導体装置10Aの凸部115Aの側面(Y軸方向側の面)は、凸部115Aの上面(+X軸方向側の面)に対して傾斜している。本実施形態において、半導体装置10Aの凸部115Aの側面(Y軸方向側の面)は、テーパー形状である。半導体装置10Aの製造方法は、半導体装置10の製造方法と比較して、凸部115Aを形成する工程(工程P105)において異なるが、それ以外は同じである。
B. Second embodiment:
FIG. 13 is a diagram schematically showing the configuration of the
図14は、凸部115Aを形成する工程を説明する図である。まず、製造者は、上面に対して側面が傾斜している形状の絶縁膜510Aを形成する。図14(A)は、基板110の上に絶縁膜510Aが形成された半導体装置10Aの中間製品を示す。その後、製造者は、異方性ドライエッチング法によって半導体基板110をエッチングすることにより、凸部115Aを形成する。図14(B)は、凸部115Aが形成された半導体装置10Aの中間製品を示す。凸部の側面を凸部の上面に対して傾斜された形状としても、保護素子の耐圧の低下を抑制する効果が得られる。
FIG. 14 is a diagram illustrating a process of forming the
C.変形例:
この発明は上記の実施形態に限られるものではなく、その要旨を逸脱しない範囲において種々の形態において実施することが可能であり、例えば次のような変形も可能である。
C. Variations:
The present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and can be implemented in various forms without departing from the gist thereof. For example, the following modifications are possible.
C1.変形例1:
本実施形態において、凸部115はエッチングにより形成したが、本発明はこれに限られない。凸部115の形成方法を、再成長を用いる方法としてもよい。
C1. Modification 1:
In the present embodiment, the
図15は、再成長により凸部115Bを形成する工程を説明する図である。まず、製造者は、凸部115Bを形成する部分の基板110が露出するように絶縁膜510Bを形成する。図15(A)は、絶縁膜510Bを形成させた半導体装置の中間製品を示す断面図である。次に、製造者は、MOCVD法によって半導体層110を再成長させる。図15(B)は、半導体層110を再成長させた半導体装置の中間製品を示す断面図である。最後に、製造者は、絶縁膜510Bを除去することにより、凸部115Bが形成される。
FIG. 15 is a diagram illustrating a process of forming the
C2.変形例2:
本実施形態において、積層体100の積層方向(X軸方向)において、N型半導体層140は、凸部115の上面と重ならない位置に配されている。しかし、本発明はこれに限らない。
C2. Modification 2:
In the present embodiment, in the stacking direction (X-axis direction) of the
図16は、積層方向(X軸方向)において、N型半導体層140Cは、凸部115の上面の一部と重なる位置に配されている半導体装置10Cの構成を模式的に示す断面図である。N型半導体層140Cは、凸部115の上面の少なくとも一部と重なる位置に配されていてもよい。
FIG. 16 is a cross-sectional view schematically showing the configuration of the
C3.変形例3:
本実施形態において、凸部115Dは、段差部186の下方(−X軸方向側)には配置されていない。しかし、本発明はこれに限らない。
C3. Modification 3:
In the present embodiment, the
図17は、凸部115Dが段差部186の下方においても配置されている半導体装置の構成を模式的に示す断面図である。凸部115Dは、段差部186の下方に配置されていてもよい。この形態によれば、本実施形態の製造方法と比較して、凸部115Dの形成が容易となる。
FIG. 17 is a cross-sectional view schematically showing the configuration of the semiconductor device in which the
C4.変形例4:
本実施形態において、基板とN型半導体層との少なくとも一方に含まれるドナーとして、ケイ素(Si)を用いているが、本発明はこれに限られない。ドナーとして、ゲルマニウム(Ge)や、酸素(O)を用いてもよい。
C4. Modification 4:
In this embodiment, silicon (Si) is used as a donor contained in at least one of the substrate and the N-type semiconductor layer, but the present invention is not limited to this. As the donor, germanium (Ge) or oxygen (O) may be used.
C5.変形例5:
本実施形態において、P型半導体層に含まれるアクセプタとして、マグネシウム(Mg)を用いているが、本発明はこれに限られない。アクセプタとして、亜鉛(Zn)や、炭素(C)を用いてもよい。
C5. Modification 5:
In this embodiment, magnesium (Mg) is used as an acceptor included in the P-type semiconductor layer, but the present invention is not limited to this. As the acceptor, zinc (Zn) or carbon (C) may be used.
C6.変形例6:
本実施形態において、電極230は、パラジウム(Pd)から形成される。しかし、本発明はこれに限られない。電極230は、他の材料により形成されていてもよく、複数層の構成であってもよい。例えば、電極230は、ニッケル(Ni)、白金(Pt)、コバルト(Co)等の導電性材料の少なくとも1つを含む電極であってもよく、ニッケル(Ni)/パラジウム(Pd)構成や、白金(Pt)/パラジウム(Pd)構成(パラジウムが半導体基板側)のような2層構成であってもよい。
C6. Modification 6:
In this embodiment, the
C7.変形例7:
本実施形態において、ゲート電極である電極250は、アルミニウム(Al)から形成される。しかし、本発明はこれに限られない。電極250は、ポリシリコンを用いてもよい。また、電極250は、他の材料により形成されていてもよく、複数層の構成であってもよい。例えば、電極250は、金(Au)/ニッケル(Ni)構成や、アルミニウム(Al)/チタン(Ti)構成、アルミニウム(Al)/窒化チタン(TiN)構成(それぞれ、ニッケル、チタン、窒化チタンがゲート絶縁膜側)のような2層構成であってもよいし、窒化チタン(TiN)/アルミニウム(Al)/窒化チタン(TiN)構成のような3層構成であってもよい。
C7. Modification 7:
In this embodiment, the
本発明は、上述の実施形態や変形例に限られるものではなく、その趣旨を逸脱しない範囲において種々の構成で実現することができる。例えば、発明の概要の欄に記載した各形態中の技術的特徴に対応する実施形態、変形例中の技術的特徴は、上述の課題の一部又は全部を解決するために、あるいは、上述の効果の一部又は全部を達成するために、適宜、差し替えや、組み合わせを行うことが可能である。また、その技術的特徴が本明細書中に必須なものとして説明されていなければ、適宜、削除することが可能である。 The present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiments and modifications, and can be realized with various configurations without departing from the spirit thereof. For example, the technical features in the embodiments and the modifications corresponding to the technical features in each embodiment described in the summary section of the invention are to solve some or all of the above-described problems, or In order to achieve part or all of the effects, replacement or combination can be performed as appropriate. Further, if the technical feature is not described as essential in the present specification, it can be deleted as appropriate.
10…半導体装置
10A…半導体装置
10C…半導体装置
100…積層体
110…基板
115…凸部
115A…凸部
115B…凸部
115D…凸部
120…N型半導体層
130…P型半導体層
140…N型半導体層
140C…N型半導体層
182…凹部
184…トレンチ
186…段差部
200…保護素子
210…電極
230…電極
240…電極
250…電極
270…配線
280…配線
285…開口部
300…縦型MOSトランジスタ
340…絶縁膜
510…絶縁膜
510A…絶縁膜
510B…絶縁膜
Id…電流
Vds…電圧
Vgs…電圧
d1…距離
d3…距離
l1…実線
l2…一点鎖線
l3…二点鎖線
l4…破線
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (15)
前記第1窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記第2窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面と接する第1の電極と、を有し、
前記第3窒化物半導体層と、前記第4窒化物半導体層とを貫通し、前記第2窒化物半導体層に達するトレンチが形成され、
前記トレンチに絶縁膜を介して設けられたゲート電極を備える、
縦型MOSトランジスタと、
前記第1の電極と、
前記第3窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記第2窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面と接する前記第2導電型のオーミック電極と、を有する、
保護素子と、を備える、半導体装置であって、
前記第1導電型の不純物濃度は、前記第1窒化物半導体層に比べて前記第2窒化物半導体層のほうが低く、
前記第1窒化物半導体層は、前記第2窒化物半導体層へ突出する凸部を備え、
前記積層体の積層方向から見たときに、前記凸部の上面は、前記第2導電型のオーミック電極と少なくとも一部が重なる位置に配されており、
前記トレンチの底面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みは、前記凸部の上面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みよりも大きい、半導体装置。 The first conductivity type first nitride semiconductor layer, the first conductivity type second nitride semiconductor layer, the second conductivity type third nitride semiconductor layer, and the first conductivity type fourth nitride. A stacked body in which semiconductor layers are stacked in this order;
A first electrode in contact with a surface of the first nitride semiconductor layer opposite to a surface in contact with the second nitride semiconductor layer;
A trench penetrating the third nitride semiconductor layer and the fourth nitride semiconductor layer and reaching the second nitride semiconductor layer is formed;
A gate electrode provided in the trench via an insulating film;
A vertical MOS transistor;
The first electrode;
An ohmic electrode of the second conductivity type that is in contact with the surface of the third nitride semiconductor layer that is opposite to the surface in contact with the second nitride semiconductor layer;
A semiconductor device comprising a protection element,
The impurity concentration of the first conductivity type is lower in the second nitride semiconductor layer than in the first nitride semiconductor layer,
The first nitride semiconductor layer includes a protrusion protruding to the second nitride semiconductor layer,
When viewed from the stacking direction of the stacked body, the top surface of the convex portion is disposed at a position at least partially overlapping the second conductivity type ohmic electrode,
The semiconductor device, wherein a thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer at a portion where the bottom surface of the trench is in contact is larger than a thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer at a portion where the top surface of the convex portion is in contact.
前記積層方向から見たときに、前記第4窒化物半導体層は、前記凸部の上面と重ならない位置に配されている、半導体装置。 The semiconductor device according to claim 1,
The semiconductor device, wherein when viewed from the stacking direction, the fourth nitride semiconductor layer is disposed at a position that does not overlap an upper surface of the convex portion.
前記積層方向から見たときに、前記凸部に対して、前記トレンチが配されている側とは反対側に、前記第3窒化物半導体層を貫通し、前記第2窒化物半導体層に達する段差部が形成されており、
前記凸部の上面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みは、前記段差部の底面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚み以下である、半導体装置。 The semiconductor device according to claim 1, further comprising:
When viewed from the stacking direction, it penetrates the third nitride semiconductor layer on the side opposite to the side where the trench is disposed with respect to the convex portion, and reaches the second nitride semiconductor layer. A step is formed,
The thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer in a portion where the upper surface of the convex portion is in contact is equal to or less than the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer in a portion where the bottom surface of the step portion is in contact.
前記段差部の底面と前記凸部との距離は、前記段差部の底面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みよりも大きい、半導体装置。 The semiconductor device according to claim 3,
The distance between the bottom surface of the step portion and the convex portion is a semiconductor device that is larger than the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer at a portion where the bottom surface of the step portion is in contact.
前記第4窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記第3窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面と接する前記第1導電型のオーミック電極を備える、半導体装置。 The semiconductor device according to any one of claims 1 to 4, further comprising:
A semiconductor device comprising the first conductivity type ohmic electrode in contact with a surface of the fourth nitride semiconductor layer opposite to a surface in contact with the third nitride semiconductor layer.
前記第1導電型のオーミック電極と前記第2導電型のオーミック電極とを電気的に接続する第1配線を備え、
前記第1配線は、絶縁膜を介して前記段差部の側面を覆っている、半導体装置。 A semiconductor device according to claim 5 that is dependent on claim 3 or claim 4, further comprising:
A first wiring electrically connecting the first conductivity type ohmic electrode and the second conductivity type ohmic electrode;
The semiconductor device, wherein the first wiring covers a side surface of the stepped portion via an insulating film.
前記第1窒化物半導体層から前記第4窒化物半導体層は、ガリウムを含む窒化物半導体により形成されている、半導体装置。 A semiconductor device according to any one of claims 1 to 6,
The semiconductor device, wherein the first nitride semiconductor layer to the fourth nitride semiconductor layer are formed of a nitride semiconductor containing gallium.
前記第1窒化物半導体層は、窒化ガリウムにより形成されている、半導体装置。 A semiconductor device according to any one of claims 1 to 7,
The semiconductor device, wherein the first nitride semiconductor layer is made of gallium nitride.
前記第1窒化物半導体層は、窒化ガリウム基板である、半導体装置。 The semiconductor device according to claim 8,
The semiconductor device, wherein the first nitride semiconductor layer is a gallium nitride substrate.
前記凸部の側面は、前記凸部の上面に対して傾斜している、半導体装置。 The semiconductor device according to claim 9,
The semiconductor device, wherein a side surface of the convex portion is inclined with respect to an upper surface of the convex portion.
前記凸部の側面は、a面またはm面で構成され、前記凸部の上面は、c面で構成されている、半導体装置。 A semiconductor device according to any one of claims 1 to 9,
A semiconductor device, wherein a side surface of the convex portion is formed of an a-plane or an m-plane, and an upper surface of the convex portion is formed of a c-plane.
第1導電型の第1窒化物半導体層の面に突出する凸部を形成する工程と、
前記第1窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記凸部を備える面に、前記第1窒化物半導体層よりも不純物濃度が小さい前記第1導電型の第2窒化物半導体層と、第2導電型の第3窒化物半導体層と、をこの順に積層する工程と、
前記第3窒化物半導体層を貫通し、前記第2窒化物半導体層に達するトレンチを形成する工程と、
前記第1窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記第2窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面に、第1の電極を形成する工程と、
積層方向において、前記凸部の上面と少なくとも一部が重なる位置であって、前記第3窒化物半導体層の面であり、前記第2窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面に、前記第2導電型のオーミック電極を形成する工程と、
前記トレンチに絶縁膜を介してゲート電極を形成する工程と、
前記第3窒化物半導体層の面であって、前記第2窒化物半導体層と接する面とは反対側の面に、前記第1導電型の第4窒化物半導体層を形成する工程と、
前記第4窒化物半導体層にソース電極を形成する工程と、
を有し、
前記第4窒化物半導体層は、前記積層方向において、前記凸部の上面と重ならない位置に配されており、
前記トレンチの底面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みは、前記凸部の上面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みよりも大きい、
前記第1窒化物半導体層から前記第4窒化物半導体層までの窒化物半導体層と前記ゲート電極と前記第1の電極と前記ソース電極とから形成される縦型MOSトランジスタと、前記第1窒化物半導体層から前記第3窒化物半導体層までの窒化物半導体層と前記第1電極と前記第2導電型のオーミック電極から形成されるPN接合ダイオードである保護素子と、を備える半導体装置の製造方法。 A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device, comprising:
Forming a protrusion protruding on the surface of the first conductivity type first nitride semiconductor layer;
A second nitride semiconductor layer of the first conductivity type having a lower impurity concentration than the first nitride semiconductor layer on a surface of the first nitride semiconductor layer, the surface having the convex portion; Laminating a conductive third nitride semiconductor layer in this order;
Forming a trench penetrating the third nitride semiconductor layer and reaching the second nitride semiconductor layer;
Forming a first electrode on a surface of the first nitride semiconductor layer opposite to a surface in contact with the second nitride semiconductor layer;
In the stacking direction, at least a part of the upper surface of the convex portion overlaps the surface of the third nitride semiconductor layer, on the surface opposite to the surface in contact with the second nitride semiconductor layer, Forming the second conductivity type ohmic electrode;
Forming a gate electrode in the trench via an insulating film;
Forming the first conductivity type fourth nitride semiconductor layer on the surface of the third nitride semiconductor layer opposite to the surface in contact with the second nitride semiconductor layer;
Forming a source electrode on the fourth nitride semiconductor layer;
Have
The fourth nitride semiconductor layer is arranged in a position not overlapping the upper surface of the convex portion in the stacking direction;
The thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer in the portion where the bottom surface of the trench is in contact is greater than the thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer in the portion where the top surface of the convex portion is in contact,
A vertical MOS transistor formed of a nitride semiconductor layer from the first nitride semiconductor layer to the fourth nitride semiconductor layer, the gate electrode, the first electrode, and the source electrode; and the first nitride A semiconductor device comprising: a nitride semiconductor layer from a nitride semiconductor layer to the third nitride semiconductor layer; a protective element that is a PN junction diode formed from the first electrode and the second conductivity type ohmic electrode; Method.
前記凸部の上面と前記トレンチの底面との距離が、前記トレンチの底面が接する部分における前記第2窒化物半導体層の厚みよりも大きい、半導体装置の製造方法。 The method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to claim 12, further comprising:
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device, wherein a distance between an upper surface of the convex portion and a bottom surface of the trench is larger than a thickness of the second nitride semiconductor layer in a portion where the bottom surface of the trench is in contact.
前記第1窒化物半導体層から前記第4窒化物半導体層は、ガリウムを含む窒化物半導体により形成されている、半導体装置の製造方法。 A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to claim 12 or claim 13 ,
The method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, wherein the first nitride semiconductor layer to the fourth nitride semiconductor layer are formed of a nitride semiconductor containing gallium.
前記第1窒化物半導体層は、窒化ガリウム基板である、半導体装置の製造方法。 A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to any one of claims 12 to claims 1 to 4,
The method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, wherein the first nitride semiconductor layer is a gallium nitride substrate.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015059436A JP6319151B2 (en) | 2015-03-23 | 2015-03-23 | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of semiconductor device |
| US15/065,708 US9704952B2 (en) | 2015-03-23 | 2016-03-09 | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015059436A JP6319151B2 (en) | 2015-03-23 | 2015-03-23 | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of semiconductor device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2016181534A JP2016181534A (en) | 2016-10-13 |
| JP2016181534A5 JP2016181534A5 (en) | 2017-07-27 |
| JP6319151B2 true JP6319151B2 (en) | 2018-05-09 |
Family
ID=56975895
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015059436A Active JP6319151B2 (en) | 2015-03-23 | 2015-03-23 | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of semiconductor device |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9704952B2 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP6319151B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6685278B2 (en) * | 2015-03-11 | 2020-04-22 | パナソニック株式会社 | Nitride semiconductor device |
| JP6581614B2 (en) * | 2017-03-14 | 2019-09-25 | 株式会社サイオクス | Semiconductor structure manufacturing method, inspection method, and program |
| TWI791871B (en) * | 2019-07-19 | 2023-02-11 | 力晶積成電子製造股份有限公司 | Channel all around semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same |
| TWI707438B (en) * | 2019-07-19 | 2020-10-11 | 力晶積成電子製造股份有限公司 | Circuit structure |
| JP7337739B2 (en) * | 2020-03-19 | 2023-09-04 | 株式会社東芝 | semiconductor equipment |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH025482A (en) * | 1988-06-24 | 1990-01-10 | Hitachi Ltd | Vertical mosfet |
| JP4167313B2 (en) * | 1997-03-18 | 2008-10-15 | 株式会社東芝 | High voltage power semiconductor device |
| US6767783B2 (en) | 2001-07-12 | 2004-07-27 | Mississippi State University-Research And Technology Corporation (Rtc) | Self-aligned transistor and diode topologies in silicon carbide through the use of selective epitaxy or selective implantation |
| GB0312512D0 (en) * | 2003-05-31 | 2003-07-09 | Koninkl Philips Electronics Nv | Termination structures for semiconductor devices and the manufacture thereof |
| JP4561247B2 (en) | 2004-08-31 | 2010-10-13 | 株式会社デンソー | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| DE102006025958B3 (en) | 2006-06-02 | 2007-10-11 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Semiconductor component e.g. crystal diode, for use in semiconductor power electronics, has three sets of semiconductor zones, where one set of zones is arranged at distance from each other |
| JP2010114248A (en) * | 2008-11-06 | 2010-05-20 | Toyota Central R&D Labs Inc | Semiconductor device |
| JP5582102B2 (en) | 2010-07-01 | 2014-09-03 | 株式会社デンソー | Semiconductor device |
| DE112012006039B4 (en) * | 2012-03-16 | 2021-07-01 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp. | METHOD OF MANUFACTURING A SEMICONDUCTOR COMPONENT |
| JP6092680B2 (en) * | 2013-03-26 | 2017-03-08 | 新電元工業株式会社 | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of semiconductor device |
| JP6107597B2 (en) * | 2013-03-26 | 2017-04-05 | 豊田合成株式会社 | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
-
2015
- 2015-03-23 JP JP2015059436A patent/JP6319151B2/en active Active
-
2016
- 2016-03-09 US US15/065,708 patent/US9704952B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2016181534A (en) | 2016-10-13 |
| US9704952B2 (en) | 2017-07-11 |
| US20160284843A1 (en) | 2016-09-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TWI770134B (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of semiconductor device | |
| TWI663698B (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP5564791B2 (en) | Compound semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP6319151B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of semiconductor device | |
| US8963203B2 (en) | Nitride semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same | |
| US8530937B2 (en) | Compound semiconductor device having insulation film with different film thicknesses beneath electrodes | |
| JP7065370B2 (en) | Semiconductor devices and their manufacturing methods | |
| JP6631950B2 (en) | Nitride semiconductor device and method of manufacturing nitride semiconductor device | |
| CN103715253B (en) | Compound semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP7082508B2 (en) | Nitride semiconductor equipment | |
| JP2010103425A (en) | Nitride semiconductor device | |
| KR20150093117A (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| CN103545362B (en) | Compound semiconductor device and manufacture method thereof | |
| US20150311331A1 (en) | Nitride semiconductor device and method for manufacturing nitride semiconductor device | |
| CN105826252A (en) | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| JP6627441B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP2015099903A (en) | Nitride semiconductor device and manufacturing method of the same | |
| CN112531025A (en) | High electron mobility transistor | |
| CN112750700B (en) | High electron mobility transistor and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2018157100A (en) | Nitride semiconductor device | |
| CN104465655B (en) | Semiconductor device and its manufacture method | |
| JP2020061414A (en) | Nitride semiconductor device and manufacturing method of nitride semiconductor device | |
| CN112652659B (en) | High electron mobility transistor and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP6406080B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of semiconductor device | |
| CN112928161A (en) | High electron mobility transistor and manufacturing method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20170419 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20170615 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20171130 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20171226 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20180221 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20180306 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20180319 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6319151 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |