JP6270134B2 - Cooling device and image forming apparatus - Google Patents
Cooling device and image forming apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6270134B2 JP6270134B2 JP2014035955A JP2014035955A JP6270134B2 JP 6270134 B2 JP6270134 B2 JP 6270134B2 JP 2014035955 A JP2014035955 A JP 2014035955A JP 2014035955 A JP2014035955 A JP 2014035955A JP 6270134 B2 JP6270134 B2 JP 6270134B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- temperature
- heat
- cooling
- abnormality
- cooling device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Cooling Or The Like Of Electrical Apparatus (AREA)
- Accessory Devices And Overall Control Thereof (AREA)
- Fixing For Electrophotography (AREA)
- Control Or Security For Electrophotography (AREA)
Description
本発明は、冷却対象の熱を直接、又は間接的に受熱する受熱部と、この受熱部との間で循環する冷媒の熱を放熱する放熱部とを備えた冷却装置、及びこの冷却装置を備えた画像形成装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a cooling device including a heat receiving portion that directly or indirectly receives heat to be cooled, and a heat radiating portion that radiates heat of a refrigerant circulating between the heat receiving portion and the cooling device. The present invention relates to an image forming apparatus provided.
従来から、発熱箇所や処理を施したものを冷却対象とする冷却装置を備えた電子機器が知られている。
電子写真方式の画像形成装置では、装置内に複数の発熱箇所を有している。このため、目標とする装置の大きさ、画像形成速度、装置の製造コスト等の条件に応じて、装置内の複数の発熱箇所を冷却対象として、空冷方式や液冷方式の冷却装置を、任意の箇所、又は複数の任意の箇所に設けたものが知られている。
画像形成装置内の冷却対象としては、例えば、トナーに電荷を付与する際のトナーや現像剤の攪拌によって摩擦熱が生じる現像装置の攪拌・搬送部や、表面に転写されたトナー画像が定着された後の記録媒体としてのシート(用紙)等が挙げられる。
2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, there is known an electronic apparatus including a cooling device for cooling a heat generation place or a processed object.
An electrophotographic image forming apparatus has a plurality of heat generation points in the apparatus. For this reason, depending on conditions such as the target device size, image forming speed, device manufacturing cost, etc., an air cooling type or liquid cooling type cooling device can be arbitrarily selected with a plurality of heat generation points in the device as cooling targets. Or those provided at a plurality of arbitrary locations are known.
As an object to be cooled in the image forming apparatus, for example, a stirring / conveying portion of a developing device in which frictional heat is generated by stirring of toner or developer when a charge is applied to the toner, or a toner image transferred to the surface is fixed. And a sheet (paper) as a recording medium after that.
例えば、特許文献1には、定着後のシート(シート状部材)を冷却する、次のような液冷方式の冷却装置を備えた画像形成装置が記載されている。シートを挟持搬送する1対の無端ベルトを備えたベルト搬送機構を設け、各無端ベルトのシートに接触する部分の内周面(裏面)に受熱部としての略平板状の冷却部材を接触させ、シートの熱を無端ベルトを介して間接的に受熱している。冷却部材には冷媒である冷却液が通過する内部流路が設けられ、放熱部に設けた熱交換器(ラジエータ)との間で冷却液が循環する循環路が形成されている。また、放熱部には、熱交換器に当たる空気の流れ(以下、気流という)を強制的に発生させて、熱交換器内を通過する冷却液と気流との熱交換効率を高めて、熱交換器による放熱能力を高める送風手段(ファン)が設けられている。
For example,
しかし、特許文献1の画像形成装置は、送風手段の故障や熱交換器の目詰まりにより熱交換器に当たる気流速度が低下したり、目詰まりにより熱交換効率が低下した熱交換器の面積が増えたりして熱交換効率が低下した放熱部が異常な状態で稼動を続けるおそれがある。
このように放熱部が異常な状態では、冷却装置でシートを冷却する際に、所望の冷却能力が得られない。そして、冷却装置を通過して積載トレイ等に積み重なる、冷却が不十分なシート内にこもった熱でトナーが軟化するとともに、重なったシートの自重で圧力が生じて軟化したトナーによりシート間が貼り付く、所謂、ブロッキングが発生するという問題があった。
However, in the image forming apparatus disclosed in
Thus, when the heat radiating portion is in an abnormal state, a desired cooling capacity cannot be obtained when the sheet is cooled by the cooling device. Then, the toner is softened by the heat accumulated in the sheets that are insufficiently cooled and stacked on the stacking tray through the cooling device, and the sheets are stuck between the sheets by the pressure generated by the weight of the overlapped sheets. There is a problem that so-called blocking occurs.
また、特許文献1の画像形成装置と異なり、装置内の他の発熱箇所を冷却する液冷方式の冷却装置を備えた画像形成装置でも、放熱部が異常な状態、つまり、冷却装置の冷却能力が低下した状態で稼動を続けると様々な問題が生じる。
例えば、現像装置を冷却する冷却装置を備えた画像形成装置では、現像装置内の現像剤温度が上昇して軟化したトナーが凝集して異常画像が発生したり、現像装置内のいずれかの構成部材に固着して現像装置が故障してしまったりするという問題がある。
Further, unlike the image forming apparatus of
For example, in an image forming apparatus provided with a cooling device for cooling the developing device, the developer temperature in the developing device rises and the softened toner aggregates to generate an abnormal image, or any configuration in the developing device. There is a problem that the developing device breaks down due to being fixed to the member.
本発明は以上の問題点に鑑みなされたものであり、その目的は、受熱部との間で循環する冷媒の熱を、放熱する放熱部の異常に起因した、不具合の発生を抑制できる冷却装置を提供することである。 The present invention has been made in view of the above problems, and an object of the present invention is to provide a cooling device that can suppress the occurrence of problems due to an abnormality in the heat dissipating part that radiates the heat of the refrigerant circulating between the heat receiving part and the heat receiving part. Is to provide.
上記目的を達成するために、請求項1に記載の発明は、冷却対象の熱を直接、又は間接的に受熱する受熱部と、該受熱部との間で循環する冷媒の熱を放熱する放熱部とを備えた冷却装置において、前記放熱部で冷媒と熱交換される空気の、熱交換される前の温度を検出する空気温度検出手段と、前記受熱部から前記放熱部に流入する冷媒温度を検出する流入温度検出手段と、前記放熱部から前記受熱部に流出する冷媒温度を検出する流出温度検出手段と、前記放熱部の異常の有無を判断する異常判断手段と、を備え、前記異常判断手段は、前記空気温度検出手段で検出する温度範囲を区分した複数の温度区分と、該複数の温度区分毎の、前記放熱部が正常に動作している状態で、前記放熱部に有した熱交換器に流入する媒体温度と該熱交換器から流出する媒体温度の閾値の経時変化情報と、を予め定めて保持し、前記空気温度検出手段で検出した温度を含む温度区分の前記閾値の経時変化情報と、前記流入温度検出手段及び前記流出温度検出手段の検出結果の差分とに基づいて、前記放熱部の異常の有無を判断することを特徴とするものである。
In order to achieve the above object, the invention according to
本発明は、受熱部との間で循環する冷媒の熱を、放熱する放熱部の異常に起因した、不具合の発生を抑制できる冷却装置を提供できる。 INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY The present invention can provide a cooling device that can suppress the occurrence of problems caused by an abnormality in a heat radiating part that radiates heat of a refrigerant that circulates between the heat receiving part.
以下、本発明を画像形成装置に備えた冷却装置に適用した一実施形態について、図を用いて説明する。まず、各実施例に共通する本実施形態の画像形成装置であるプリンタ300の概略について説明する。
図1は、本実施形態に係るプリンタ300の概略構成図である。
Hereinafter, an embodiment in which the present invention is applied to a cooling device provided in an image forming apparatus will be described with reference to the drawings. First, an outline of a
FIG. 1 is a schematic configuration diagram of a
図1に示すように、本実施形態のプリンタ300は、装置本体200内に、複数のローラ(第一張架ローラ22、第二張架ローラ23、第三張架ローラ24等)によって中間転写体としての中間転写ベルト21を張架している。そして、中間転写ベルト21は、複数のローラのうちの1つが回転駆動することにより図中矢印a方向に回転する構成である。また、プリンタ300は、中間転写ベルト21のまわりに画像形成用のプロセス手段を配置している。ここで、符号の後に付されたY,C,M,Bkという添字は、イエロー,シアン,マゼンタ,ブラック用の仕様であることを示している。
As shown in FIG. 1, the
中間転写ベルト21の回転方向を図中矢印aとするとき、中間転写ベルト21の上方であって第一張架ローラ22と第二張架ローラ23との間には、各色用の画像形成用のプロセス手段として4つの画像ステーション10(Y,C,M,Bk)が配置されている。そして、中間転写ベルト21の表面移動方向の上流側から順に、Y用の画像ステーション10Y、C用の画像ステーション10C、M用の画像ステーション10M、及びBk用の画像ステーション10Bkが配置されている。
When the direction of rotation of the
4つの画像ステーション10(Y,C,M,Bk)は使用するトナーの色が異なる点以外は、略同一の構成となっている。
各画像ステーション10は、ドラム状の感光体1の周囲に帯電装置5、光書き込み装置2、現像装置3、感光体クリーニング装置4が配置されている。さらに、中間転写ベルト21を挟んで感光体1の対向する位置には、中間転写ベルト21へのトナー像の転写手段としての一次転写ローラ11が設けられている。このような、4つの画像ステーション10(Y,C,M,Bk)が互いに所定のピッチ間隔となるように中間転写ベルト21の表面移動方向に沿って配置されている。
このプリンタ300では、光書き込み装置2をLEDを光源とする光学系としているが、半導体レーザーを光源とするレーザー光学系で構成することもでき、各感光体1に対して画像情報に応じた露光を行う。
The four image stations 10 (Y, C, M, Bk) have substantially the same configuration except that the colors of the toners used are different.
In each image station 10, a charging device 5, an
In this
中間転写ベルト21の下方には、記録媒体としてのシートである用紙Pの給紙カセット31及び給紙コロ41、レジストローラ対42が配置されている。また、中間転写ベルト21を張架する第三張架ローラ24に対して中間転写ベルト21を介して対向するように、中間転写ベルト21から用紙Pへのトナー像の転写手段としての二次転写ローラ25が配置されている。さらに、中間転写ベルト21の裏面に接するクリーニング対向ローラ26が中間転写ベルト21に接触する位置で中間転写ベルト21のおもて面に接するように、中間転写ベルト21の表側の面をクリーニングするベルトクリーニング装置27が設けられている。
なお、図1図中、レジストローラ対42の右側には、手差し給紙を行う場合の手差し給紙路35、手差し給紙コロ43、及び手差しトレイ34が配置されている。
Below the
In FIG. 1, on the right side of the registration roller pair 42, a manual
また、給紙カセット31から排紙トレイ33へ至る用紙搬送路32が延びており、用紙搬送路32における二次転写ローラ25の用紙搬送方向下流側(以下、単に下流側という)には、加熱ローラと加圧ローラとを有した定着装置15が配置されている。この定着装置15の加圧ローラ内には加熱部材であるヒータ(不図示)が設けられており、用紙Pを熱定着するときの熱源として機能する。そして、定着装置15の用紙搬送路32における下流側には、用紙Pを冷却する冷却装置100が配置されている。この冷却装置100のさらに下流側の装置本体200の外部には、加熱定着後の用紙Pの排出部である排紙トレイ33が配置されている。また、両面画像形成時に用紙Pの裏面への画像形成を行う際に、冷却装置100を一度通過した用紙Pの表裏を反転させ、再度、レジストローラ対42へ搬送する両面画像形成用の反転用紙搬送路36も備えている。
Further, a
なお、装置本体200内には、CPU(中央演算装置)、RAM(ラム)、ROM(ロム)、及び不揮発性メモリや各部のドライバー等を有した本体制御部210(不図示)が設けられている(図7参照)。そして、ROMや不揮発性メモリに記憶したプログラム等を、RAMにロードして、外部機器からの情報、各センサ等の検出結果、及び表示・操作部220からの入力データに基づいて演算を行い、各部の制御部や各装置と通信して、その制御を行う。また、表示・操作部220は、タッチパネル方式の液晶パネル(以下、タッチパネルという)を有するとともに、操作した際のクリック音や、装置本体200内の各装置に異常が生じた場合に発する警告音等を出力するスピーカーを有している。
そして、異常が生じた場合、本体制御部210は表示・操作部220に警告を表示したり、スピーカーから警告音を鳴らしたり、印刷ジョブ等の信号を送信している利用者のパソコン等に異常が発生していることを通知して、警告メッセージを表示させたりする。すなわち、本体制御部210は、利用者への通知手段として、表示・操作部220のタッチパネルやスピーカー、及び印刷ジョブ等の信号を送信している利用者のパソコン等への通信手段等を有している。
In the apparatus
When an abnormality occurs, the main body control unit 210 displays a warning on the display / operation unit 220, sounds a warning sound from a speaker, or abnormally transmits to a user's personal computer that is transmitting a signal such as a print job. Notify that has occurred and display a warning message. In other words, the main body control unit 210 has, as means for notifying the user, a touch panel, a speaker of the display / operation unit 220, a means for communicating with a user's personal computer or the like transmitting a signal such as a print job, and the like. ing.
次に、本実施形態のプリンタ300の画像の形成プロセスについて説明する。
プリンタ300の画像の形成プロセスは、1つの画像ステーション10について説明すると、一般の静電記録方式に準じていて、暗中にて帯電装置5により一様に帯電された感光体1上に光書き込み装置2により露光して静電潜像を形成する。そして、この静電潜像を現像装置3によりトナー像として可視像化する。そのトナー像は一次転写ローラ11により感光体1上から中間転写ベルト21に転写される。転写後の感光体1の表面は感光体クリーニング装置4によりクリーニングされる。このような画像形成プロセスが4つの画像ステーション10(Y,C,M,Bk)のそれぞれにおいて行われる。
Next, an image forming process of the
The image forming process of the
4つの画像ステーション10(Y,C,M,Bk)における各現像装置3(Y,C,M,Bk)は、それぞれ異なる4色のトナーによる可視像化機能を有している。このため、各画像ステーション10(Y,C,M,Bk)でイエロー、シアン、マゼンタ、ブラックを分担すれば、フルカラーのトナー像を形成することができる。また、各画像ステーション10は、中間転写ベルト21を挟むようにして各感光体1とそれぞれ対向して設けられた一次転写ローラ11を備え、この一次転写ローラ11には転写バイアスが印加され、一次転写部を構成する。
Each of the developing devices 3 (Y, C, M, Bk) in the four image stations 10 (Y, C, M, Bk) has a visible image forming function using different four color toners. For this reason, if each image station 10 (Y, C, M, Bk) shares yellow, cyan, magenta, and black, a full-color toner image can be formed. Further, each image station 10 includes a primary transfer roller 11 provided so as to face each
上記の構成により、中間転写ベルト21の同一画像形成領域が4つの画像ステーション10(Y,C,M,Bk)を順次通過する。この順次通過する間に、一次転写ローラ11に印加された転写バイアスによって、それぞれ1色ずつトナー像を中間転写ベルト21上で重ね合わせるように転写する。これにより、上述した同一画像形成領域が各画像ステーション10(Y,C,M,Bk)の一次転写部を1回通過した時点で、この同一画像領域に、重ね転写によってフルカラーのトナー像を得ることができる。
With the above configuration, the same image forming area of the
このようにして中間転写ベルト21上に形成されてフルカラーのトナー像は、給紙カセット31又は手差しトレイ34から搬送された用紙Pに転写され、転写後の中間転写ベルト21はベルトクリーニング装置27によりクリーニングされる。
ここで、中間転写ベルト21から用紙Pへのフルカラーのトナー像の転写は、次のようにして行われる。転写時において二次転写ローラ25に転写バイアスを印加して、中間転写ベルト21を介して二次転写ローラ25と第三張架ローラ24との間に転写電界を形成し、二次転写ローラ25と中間転写ベルト21とのニップ部に用紙Pを通過させることにより行なわれる。なお、給紙カセット31又は手差しトレイ34から搬送された用紙Pは、転写ニップ部の用紙搬送方向上流側に配置されたレジストローラ対42により、転写ニップ部に搬送される中間転写ベルト21上のトナー像のタイミングに合わせ、転写ニップ部に搬送される。
The full-color toner image formed on the
Here, the transfer of the full-color toner image from the
中間転写ベルト21から用紙Pへのフルカラーのトナー像の転写後、用紙P上に担持されたフルカラーのトナー像を定着装置15で加熱及び加圧することで用紙P上に定着(以下、加熱定着という)し、用紙P上にフルカラーの最終画像が形成される。その後、用紙Pは、この用紙Pを挟持搬送するベルト搬送装置と、ベルト搬送装置の搬送ベルトの内周面に設けられた受熱部材である冷却部材141とを有する冷却装置100により冷却され、排紙トレイ33上に積載される。このため、用紙Pが排紙トレイ33上に積載される時点で、用紙P上のトナーを確実に硬化状態とさせることができ、冷却不足の用紙Pが排紙トレイ33上に積載されることによるブロッキング現象(以下、ブロッキングという)を回避することができる。
なお、本実施形態のプリンタ300は、オプションのスキャナーユニット(不図示)やファックスユニット(不図示)を接続することで、コピー機能やファックス機能を備えた複合機としても機能する。また、装置本体200に備えた給紙カセット31に加え、オプションの複数の給紙カセットを有した給紙部である給紙テーブル(不図示)を装置本体200の下方や手差しトレイ34側に接続することができる。
After the transfer of the full-color toner image from the
Note that the
また、本実施形態では、本発明を加熱定着後の用紙Pを温度が高いまま排紙トレイにスタッキングした場合に生じる、重なり合った用紙Pがくっつくブロッキングを防止するために、加熱定着後の用紙Pを冷却する冷却装置100に適用した例について説明する。しかし、本発明はこのような構成に限定されるものではない。
例えば、現像装置内の攪拌スクリュー等によるトナー等からなる現像剤の摩擦熱による、現像剤の凝集や、攪拌スクリュー等の固着を防止するために、現像装置の発熱部を冷却する冷却装置にも適用可能である。また、上記した現像剤の摩擦熱、各プロセス手段で用いるモータ等の発熱、及び定着装置のヒータ等の発熱により、画像形成装置内の温度が許容温度を超えて上昇するのを防止するために、任意の発熱部を冷却対象とする冷却装置等にも適用可能である。
Further, in this embodiment, in order to prevent the overlapping sheets P from sticking and blocking, which occurs when the sheet P after heat fixing is stacked on the sheet discharge tray while the temperature is high, the sheet P after heat fixing is used. An example applied to the
For example, a cooling device that cools the heat generating part of the developing device in order to prevent the developer from agglomerating due to the frictional heat of the developer and the sticking of the stirring screw due to the frictional heat of the developer in the developing device. Applicable. In order to prevent the temperature in the image forming apparatus from exceeding the allowable temperature due to the frictional heat of the developer, the heat generated by the motor used in each process unit, and the heat generated by the heater of the fixing device. The present invention can also be applied to a cooling device or the like in which an arbitrary heat generating portion is a cooling target.
次に、本発明の特徴である、本実施形態のプリンタ300に備えた冷却装置100の基本的な構成、及びその動作について説明する。
ここで、以下の説明では、特に個別の用語を用いて説明する必要がない限り、定着装置15により加熱定着された用紙Pの、トナーが軟化した状態で付着している側を用紙Pの表側と呼称し、その反対側を用紙Pの裏側と呼称して説明する。また、プリンタ300及び冷却装置100に有した各構成部材の相対的な方向を説明する場合には、図1図中、略水平な用紙搬送路32の用紙搬送方向上流側を右側、用紙搬送方向下流側を左側と呼称して説明する。また、図1の紙面、手前側を前側、紙面奥側を後側と呼称して説明する。
図2は、本実施例に係る冷却装置100の説明図、図3は、図2の冷却装置100に有した冷却部材141についての説明図である。
Next, a basic configuration and operation of the
Here, in the following description, the side to which the toner is adhered in the softened state of the paper P heat-fixed by the fixing
FIG. 2 is an explanatory diagram of the
本実施形態の冷却装置100は、図2に示すように定着装置15で加熱定着された後の用紙Pを挟持搬送する挟持部として、トナーが軟化した状態で付着している用紙Pの表側から挟持する表側挟持部160と、裏側から挟持する裏側挟持部170とを備えている。また、表側挟持部160に設けられた受熱部140には、表側挟持部160に有した表側従動ローラ162を介して、定着後の用紙Pから熱を吸熱する金属製(アルミニウム製)の冷却部材141を有している。また、冷却部材141で、用紙Pから吸熱した熱を、放熱する熱交換器であるラジエータ181を有した放熱部180も有している。そして、冷却部材141で吸熱した熱は、冷媒である冷却液が、冷却部材141の内部流路である液流路部143(図3参照)と、ラジエータ181の内部流路(液冷菅)との間で、循環することで輸送されるように循環路が構成されている。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
表側挟持部160は、主に、図1に示した用紙搬送路32の図中、上方に台形状に配置された4つの表側従動ローラ162、これらの表側従動ローラ162に架け渡された表側搬送ベルト161、及び冷却部材141等を有している。一方、裏側挟持部170は、主に、用紙搬送路32の図中、下方に台形状に配置された3つの裏側従動ローラ172、駆動ローラ173、これらの裏側従動ローラ172及び駆動ローラ173に架け渡された裏側搬送ベルト171等を有している。
The front-
冷却液の循環路は、主に、冷却部材141の液流路部143、ラジエータ181の内部流路、冷却液を搬送する液送ポンプ182、冷却液を貯留する液溜タンク183、及びゴムチューブ184等から構成されている。ゴムチューブ184は、冷却液の搬送方向の上流側の構成部材の流出口と、下流側の構成部材の流入口とを繋いで冷却液を流す外部流路として機能し、上記した循環路を形成する各構成部材を繋ぐ管路である。そして、上記した冷却液の循環路内を循環する冷却液が、表側搬送ベルト161を介して冷却部材141の冷却面142から吸熱した用紙Pの熱を、冷却液が流れる内部流路を有したラジエータ181に伝達する熱伝達手段の役割を果す。
ここで、冷媒である冷却液としては、水を主成分とし、凍結温度を下げるための不凍液として知られるプロピレングリコール溶液を用いている。また、水を主成分とし、凍結温度を下げるためのエチレングリコールや、金属製の部品の錆を防止するための防錆剤(例えば、リン酸塩系物質:リン酸カリ塩、無機カリ塩等)が添加されたもの等も好適に用いることができる。
The coolant circulation path is mainly composed of a fluid
Here, as a coolant that is a refrigerant, a propylene glycol solution that contains water as a main component and is known as an antifreeze for lowering the freezing temperature is used. Also, ethylene glycol for lowering the freezing temperature based on water as the main component, and rust preventives for preventing rusting of metal parts (for example, phosphate substances: potassium phosphate, inorganic potassium, etc. ) And the like can also be suitably used.
ラジエータ181は、図2に示すように、図中略水平方向に並列して設けられた複数の冷媒菅に複数の冷却フィン(不図示)が直交するように設けられたものである。ラジエータ181の流入口から流入する冷却液は、導入路を下方向に流れるときに順次、各冷媒菅に分岐されて、図中右から左に各冷媒菅内を流れ、導出路で順次合流して上部に設けられた流出口から流出する。そして、冷却液は、各冷媒菅、各冷却フィン、及び導入路や導出路を形成する菅材を通過するときに、各部材間の通風部を通過するとともに、各部材の表面に接触(当たる)する外気(空気)と熱交換(放熱)されて低温になる。
なお、本実施形態の冷却装置100では、上記のようなラジエータ181を用いたが、ラジエータの形式は、上記の構成に限定されるものではなく、冷却装置100やプリンタ300の、サイズ、コスト、要求される放熱能力等に応じた形式として良い。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
In the
また、放熱部180には、ラジエータ181に当たる気流を強制的に発生させて、冷却液と外気との熱交換効率を高めて、ラジエータ181による放熱能力を高める送風手段であるファンユニット185も有している。
ファンユニット185は、8つの送風ファン186とファンダクト194を有しており、各送風ファン186を回転駆動して発生させた気流を、ファンダクト194に形成したファンダクト開口194a(図5参照)に対向して設けるラジエータ181に当てる。このように気流を当てることで、ラジエータ181による放熱能力を高め、冷却装置100の冷却能力を高めている。
Further, the
The
また、ファンダクト194には、上記したファンダクト開口194aとは別に、送風ファン186を取り付けるファン取付け開口194bを8つ形成している。そして、送風ファン186により生じさせた気流を通す開口とファンダクト開口194aとを除く部分の隙間をできるだけ無くしている。このように隙間を無くすことで、ラジエータ181、液送ポンプ182等を収容するダクトである内部ダクト191(図4,5参照)の送風開口部に接続し、各送風ファン186の内部ダクト191内への送風能力を高めている。
In addition to the
なお、受熱部140に設けた冷却部材141は、図3に示すように表側搬送ベルト161の用紙幅方向を包括するように設けられ、液流路部143の用紙幅方向に略平行な直線部が折り返す折り返し部を図中右側に2箇所、図中左側に1箇所設けている。そして、液流路部143の用紙搬送方向の上流側及び下流側、図中左側端部に液流路部143の流入口と流出口とが形成され、上記した放熱部180からのゴムチューブ184がそれぞれ接続されている。なお、上記した液流路部143の折り返し部は、本実施例のプリンタ300に通紙する最大用紙幅:Wの用紙Pが搬送されても良好な冷却効果を得るために、最大用紙幅:Wの用紙Pが搬送される領域よりも外側に設けられている。特に、流入口と流出口が設けられない図中右側の2つの折り返し部は、表側搬送ベルト161の図中右側端部よりも外側に設けられている。
The cooling
上記のように構成された冷却装置100では、裏側従動ローラ172を図2図中、反時計回りに回転駆動させることで、裏側搬送ベルト171を反時計回りに無端移動させる。そして、この裏側搬送ベルト171の無端移動により、直接又は用紙Pを介して接触する表側搬送ベルト161を時計回りに無端移動させる。このように無端移動する表側搬送ベルト161及び裏側搬送ベルト171(以下、各搬送ベルトという)で用紙Pを挟持することで、加熱定着後の用紙Pを用紙搬送路32に沿って挟持搬送することができる。
In the
そして、液送ポンプ182を駆動して冷却液を、図3に示す冷却部材141の液流路部143とラジエータ181の間で循環させ、表側搬送ベルト161を介して用紙Pに間接的に接触する冷却部材141の冷却面142で、用紙Pから熱を吸熱して冷却できる。より具体的には、上記のように冷却部材141の内部には冷却液が通過する内部流路である液流路部143が設けられており、冷却部材141の冷却面142に接触する表側搬送ベルト161を介して用紙Pから吸熱した熱(熱量)を冷却液が外部に輸送する。このようにして冷却部材141は低温に保たれる。
ここで、冷却液は、液溜タンク183に貯液されており、液送ポンプ182によって送液された後、冷却液はラジエータ181の内部流路を通過する際に外気への放熱が行われて、その温度が低下する。
Then, the
Here, the cooling liquid is stored in the
上記のようにして低温になった冷却液は冷却部材141の液流路部143を通過する際に、熱伝達によって冷却部材141から熱を吸熱し、高温になった冷却液は液溜タンク183に帰る。そして、冷却液は、液送ポンプ182を駆動している間、冷却部材141の液流路部143とラジエータ181の内部流路との間で循環し、ラジエータ181を通過する際の放熱と、冷却部材141の液流路部143を通過する際の吸熱とを繰り返すことになる。ここで、上記したように本実施例の冷却装置100では、冷却液が循環する経路を、例えば液送ポンプ182を基点とした場合に、上記のように液送ポンプ182、ラジエータ181、冷却部材141、液溜タンク183の順で循環させている。
The cooling liquid having a low temperature as described above absorbs heat from the cooling
このように冷却液を循環させることで、ラジエータ181を通過する際に放熱されて低温になった冷却液が、受熱部140の冷却部材141に送液される経路長を短くできる。したがって、ゴムチューブ184表面から熱を受け冷却液が温度上昇することによる、冷却装置100の冷却性能の低下を防ぐことができる。
上記のように用紙Pを冷却することで、定着装置15で加熱定着されて軟化したトナーの温度を低下させ、用紙P上のトナーを確実に硬化状態とでき、図1に示した排紙トレイ33上に排出・積載されても、所謂、ブロッキングの発生を抑制することができる。
By circulating the coolant in this manner, the length of the path through which the coolant that has been radiated and is cooled when passing through the
By cooling the sheet P as described above, the temperature of the toner heated and fixed by the fixing
なお、この冷却装置100は、本体制御部210と通信を行い、各駆動モータ等を制御する冷却制御部230を、本体制御部210とは別に設けている(図7参照)。この冷却制御部230は、本体制御部210と同様に、中央演算装置、RAM、ROM、及び不揮発性メモリや各部のドライバー等を有している。そして、ROMや不揮発性メモリに記憶したプログラム等を、RAMにロードして、本体制御部210からの情報や制御信号、及び各センサ等の検出結果に基づいて演算を行って、冷却装置100の各部の制御を行っている。
但し、本発明はこのような構成に限定されるものではなく、本体制御部210内に冷却制御部230を設けた構成にも適用可能である。
The
However, the present invention is not limited to such a configuration, and can be applied to a configuration in which the cooling control unit 230 is provided in the main body control unit 210.
次に、本実施形態の冷却装置100に備えた放熱部180の構成を、図を用いてより詳細に説明する。
図4は、本実施例に係るプリンタ300の後側からの斜視説明図である。図5は、本実施例に係る冷却装置100の放熱部180から外部ダクト195を取り外した斜視説明図である。
Next, the structure of the
FIG. 4 is an explanatory perspective view from the rear side of the
図2に示したように、本実施形態の送風手段であるファンユニット185には、送風ファン186を8つ有している。これは、本実施形態の冷却装置100の冷却対象が加熱定着後の用紙Pであるとともに、プリンタ300に用いる用紙Pの紙厚が薄紙から厚紙まで幅広い紙種に対応し、放熱部180で放熱する最大熱量が、現像装置3等を冷却する場合に比べて大きいためである。そして、上記したようにファンユニット185に有した8つの送風ファン186による排気量に見合った吸気量を確保するため、内部ダクト191に、第一通過開口部192a及び第二通過開口部192bの2つの通過開口部を設けている。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
まず、図4を用いて、放熱部180の配置、及び放熱部180と放熱部180に設ける外部ダクト195や、装置本体200に設ける外装パネル等との関係について説明する。
図4に示すように、プリンタ300の装置本体200に設ける外装パネルの、後側及び左側の側面が接する部分の近傍の内部に放熱部180を設けている。このように放熱部180を設けることで、2つの通過開口部である第一通過開口部192a及び第二通過開口部192bから装置本体200外の外気を吸気し、ファンユニット185のファン取付け開口194bから装置本体200外へ排気させることが容易になる。
First, with reference to FIG. 4, the arrangement of the
As shown in FIG. 4, a
具体的には、装置本体200の後方からファンユニット185の部分を突出させ、ファンユニット185の上方に内部ダクト191の第一通過開口部192aを配置し、装置本体200の後方左側に内部ダクト191の第二通過開口部192bを配置している。そして、第一通過開口部192aとファンユニット185の後方には外部ダクト195が接続され、第一通過開口部192aに装置本体200の後方から外気を導き、ファンユニット185から吹き出す熱交換後の空気を装置本体200の後方下方へ導く。また、第二通過開口部192bに対向する装置本体200の後方左側の外装パネルには開口が設けられ、第二通過開口部192bに装置本体200の左側から外気を導く。
Specifically, the
外部ダクト195は、略直方体の外形をしており、上部及び左右の側壁は空気が通過する開口は設けられておらず、後方の側壁には上部に第一外部開口部196aが設けられ、下部には第二外部開口部197aが形成される。そして、外部ダクト仕切り部材195aにより、第一通過開口部192aから吸気する空気を通過させる第一外部ダクト部196と、ファンユニット185から吹き出す空気を通過させる外部ダクトである第二外部ダクト部197とに仕切られている。
The
第一外部ダクト部196の内部ダクト191側には、外部ダクト195の3つの側壁と外部ダクト仕切り部材195aとで、第一通過開口部192aの周囲の内部ダクト191の側壁に4つの壁で接続する第一外部連通開口部196bが形成されている。一方、第一外部開口部196aには、空気を通すとともに、異物等の侵入を抑制するための複数の長孔が形成されている。このように第一外部ダクト部196を構成することで、装置本体200の後方に突出させた外部ダクト195の後方の空間から、第一通過開口部192aを介して内部ダクト191内に吸気する空気(外気)の流路を形成することができる。
On the side of the
第二外部ダクト部197の内部ダクト191側には、外部ダクト195の2つの側壁と外部ダクト仕切り部材195aとで、ファンユニット185の周囲の内部ダクト191の側壁に3つの壁で接続する第二外部連通開口部197bが形成されている。また、この第二外部連通開口部197bは、第二外部ダクト部197の下部の開口である第二外部開口部197aと連通している。なお、本実施例の第二外部開口部197aには、空気を通すとともに、異物等の侵入を抑制するための金網が取り付けられている。このように第二外部ダクト部197を構成することで、装置本体200の後方に突出させた外部ダクト195の下方の空間へ、ファンユニット185により内部ダクト191内から排気する空気(外気)の流路を形成することができる。
On the side of the
また、内部ダクト191の第二通過開口部192bに対向して装置本体200の左側の外装パネルに設けられた開口には、空気を通すとともに、異物等の侵入を抑制するための複数のスリット(不図示)が設けられたスリットパネル199が取り付けられている。このように内部ダクト191の第二通過開口部192bの周辺を構成することで、装置本体200の左側の空間から、第二通過開口部192bを介して内部ダクト191内に吸気する空気(外気)の流路を形成することができる。なお、この第二通過開口部192bに対向して設けるスリットパネル199には、第二通過開口部192bを設けた内部ダクト191の側壁に接続し、他の装置本体200内の空間から空気が流入しないような仕切り部材を設けることが望ましい。
Also, a plurality of slits (which allow air to pass through the opening provided in the left exterior panel of the apparatus
次に放熱部180のファンダクト194、及び内部ダクト191の構成について、さらに詳細に説明する。
プリンタ300内に備えた冷却装置100に係る主な各構成部材のみ示すと図5に示すようになる。すなわち、冷却装置100で冷却する冷却対象である用紙Pを加熱する定着装置15、加熱された用紙Pから熱を吸熱する受熱部140が配置された表側挟持部160、この表側挟持部160に対向配置された裏側挟持部170、及び放熱部180である。
また、放熱部180には、ファンダクト194とで放熱部ケーシング190を形成するとともに、ファンダクト194と8つの送風ファン186により構成されるファンユニット185とで放熱部180を構成する内部ダクト191が設けられている。
Next, the configuration of the
FIG. 5 shows only main components related to the
In addition, the
内部ダクト191は、略直方体の形状をしており、後側の側壁には、ファンユニット185が接続されるとともに、その上方に第一通過開口部192aが形成され、左側の側壁には、第二通過開口部192bが形成されている。また、第一通過開口部192aは、補強用の4つの部材で分けられた5つの開口からなり、第二通過開口部192bは、補強用の3つの部材で分けられた4つの開口からなる。
そして、ファンユニット185は、ファンダクト194の後側の側壁に8つのファン取付け開口194bにそれぞれ送風ファン186が取付けられている。また、ファン取付け開口194bに対向する側には、ファンダクト開口194aが設けられ内部ダクト191の送風開口部に接続される。この内部ダクト191の送風開口部に、熱交換器であるラジエータ181が内側から、その通風部がファンダクト開口194aに対向するように接続されている。
The
In the
次に、本実施形態の冷却装置100の最大の特徴部である、放熱部180の異常を判断する異常判断手段に係る構成、及びその動作について、複数の実施例を挙げて説明する。
なお、各実施例の冷却装置100については、特に区別する必要がない限り、同一の構成部材や同様な機能を有した構成部材については、同一の符号を付して説明する。
Next, the configuration and operation of the abnormality determination unit that determines the abnormality of the
In addition, about the
(実施例1)
まず、本実施形態の冷却装置100に備えた、放熱部180の異常を判断する異常判断手段に係る構成、及びその動作(制御)の実施例1について、図を用いて説明する。
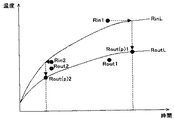
図6は、放熱部180に設けたラジエータ181に当たる気流の気流温度:T0毎の、ラジエータ181に流入する冷却液の流入温度:Rinと、ラジエータ181から流出する冷却液の流出温度:Routの経時変化のグラフである。図7は、本実施例の冷却装置100に設けた冷却制御部230、各センサ、及び各可動部材と、本体制御部210等のブロック図である。
Example 1
First, a configuration relating to an abnormality determination unit that determines an abnormality of the
FIG. 6 shows the time of the airflow temperature of the airflow hitting the
図8は、本実施例の放熱部180の異常を判断する原理の説明図、図9は、本実施例の放熱部180の異常を判断するときの制御フロー図である。図10は、本実施例の放熱部180の異常を判断する原理の説明図の別例、図11は、本実施例の放熱部180の異常を判断するときの制御フロー図の別例である。
FIG. 8 is an explanatory diagram of the principle of determining abnormality of the
一般に、ラジエータ181に当たる空気の流れである気流温度:T0によって、ラジエータ181に流入する冷却液の温度と、ラジエータ181から流出する冷却液の温度が変わる。
例えば、ラジエータ181に当たる気流温度を15℃としたときの環境をL環境とし、ラジエータ181に流入する冷却液の温度をL環境流入温度:RinL、ラジエータ181から流出する冷却液の温度をL環境流出温度:RoutLとする。また、気流温度を24℃としたときの環境をM環境とし、ラジエータ181に流入する冷却液の温度をM環境流入温度:RinM、ラジエータ181から流出する冷却液の温度をM環境流出温度:RoutMとする。そして、気流温度を32℃としたときの環境をH環境とし、ラジエータ181に流入する冷却液の温度をH環境流入温度:RinH、ラジエータ181から流出する冷却液の温度をH環境流出温度:RoutHとする。
In general, the temperature of the coolant flowing into the
For example, the environment when the airflow temperature hitting the
上記のように規定したときの、印刷開始からの時間に対する各温度の関係、つまり、印刷開始からの各環境における流入温度:Rin、及び流出温度:Routの経時変化は、冷却装置100が正常に動作している場合は、図6に示すようになる。
このときのラジエータ181に流入する各環境における冷却液の流入温度:Rinと、流出する冷却液の流出温度:Routの差分は、次の式1の関係となる。
(RinL−RoutL)>(RinM−RoutM)>(RinH−RoutH) ・・・・ (式1)
なお、放熱部180が正常な状態にはるときには、上記した各温度はそれぞれ時間経過とともに、一定の温度に収束する。ここで、以下の説明では、例えば、H環境の冷却液の流出温度である流出温度:RoutHが時間経過とともに収束する温度を、図6に、記号、RoutHeで示す、H環境収束流出温度:RoutHeという。また、H環境の冷却液の流入温度である流出温度:RinHが時間経過とともに収束する温度を、図6に、記号、RinHeで示す、H環境収束流入温度:RinHeという。
The relationship of each temperature with respect to the time from the start of printing when defined as described above, that is, the time-dependent changes in the inflow temperature: Rin and the outflow temperature: Rout in each environment from the start of printing, When it is operating, it is as shown in FIG.
The difference between the coolant inflow temperature Rin and the coolant outflow temperature Rout in each environment flowing into the
(RinL-RoutL)>(RinM-RoutM)> (RinH-RoutH) (Equation 1)
In addition, when the
そこで、本実施例の冷却装置100では、図2に示す、放熱部180に有したラジエータ181に当たって熱交換される前の空気の温度である気流温度:T0を検出する空気温度検出手段である気流温度センサ151を、図5に示す内部ダクト191内に備えた。具体的には、本実施例では、内部ダクト191内に設けたラジエータ181に外気を取り込む気流方向上流の直前に設けたが、第二通過開口部192bに設けても良い。
Therefore, in the
また、ラジエータ181の流入口近傍である、図2に実線の円で囲んだ部分のゴムチューブ184の内部には、ラジエータ181に流入する冷却液の流入温度:Rinを検出する流入温度検出手段である流入温度センサ152を備えた。一方、ラジエータ181の流出口近傍である、図2に破線円で囲んだ部分のゴムチューブ184の内部には、ラジエータ181から流出する冷却液の流出温度:Routを検出する流出温度検出手段である流出温度センサ153を備えた。なお、本実施例では、ゴムチューブ184の内部に流入温度センサ152及び流出温度センサ153を設けたが、次のように設けても良い。ゴムチューブ184の流入口及び流出口の近傍の一部を金属製チューブに替え、金属製チューブの外表面の温度を検出するように、流入温度センサ152及び流出温度センサ153を設け、間接的に内部の冷却液の温度を推定しても良い。
そして、冷却制御部230のROMには、気流温度センサ151、流入温度センサ152、及び流出温度センサ153の検出結果に基づいて、放熱部180の異常の有無を判断する異常判断手段として冷却制御部230を機能させる異常判定プログラムを格納した。
Also, in the vicinity of the inlet of the
The ROM of the cooling control unit 230 includes a cooling control unit as an abnormality determination unit that determines whether there is an abnormality in the
このように、冷却装置100を構成することで、次のような効果を奏することができる。
受熱部140が正常、且つ放熱部180が正常な場合、流入温度:Rinや流出温度:Routは、気流温度:T0毎に、放熱部180による放熱開始からの経過時間に応じて、それぞれ、図6に示すような所定の曲線を描くように変化する。そして、それぞれ、一定の温度に収束する。このため、冷却装置100は、気流温度:T0に応じた放熱能力を発揮して、用紙Pを十分に冷却する冷却能力を維持することができる。
一方、受熱部140が正常でもラジエータ181が目詰まりしたり、ファンユニット185が故障したりした放熱部180が異常な場合、流入温度:Rinや流出温度:Routは、それぞれ上記した所定の曲線とは異なった曲線を描くように変化する。このため、冷却装置100は、気流温度:T0に応じた放熱能力を発揮できず、用紙Pを十分に冷却する冷却能力を維持することができなくなる。
In this way, by configuring the
When the
On the other hand, when the
そこで、冷却制御部230では、流出温度センサ153の検出結果と、図6に示した放熱部180が正常な場合の環境の流入温度:Rin及び流出温度:Routの時間との関係の曲線の値とから冷却液の予測流入温度:Rin(P)を予測する。そして、予測した予測流入温度:Rin(P)と、流入温度センサ152の検出結果とを比較することで、放熱部の異常の有無を適切に判断することが可能となる。
したがって、異常判断手段として機能する冷却制御部230は、プリンタ300が、放熱部180が異常な状態のままで稼動し続けて、ブロッキングが発生する前に、放熱部180の異常の有無を判断できる。
よって、受熱部140との間で循環する冷却液の熱を、放熱する放熱部180の異常に起因した、不具合であるブロッキングの発生を抑制可能な冷却装置100を提供できる。
Therefore, in the cooling control unit 230, the value of the curve of the relationship between the detection result of the
Therefore, the cooling control unit 230 that functions as an abnormality determination unit can determine whether the
Therefore, it is possible to provide the
より具体的には、図7に示すように、冷却制御部230に、各センサの検出値を冷却制御部230内で演算を行える信号に信号化するセンサコントローラを設けた。一方、冷却制御部230の不揮発性メモリには、予め冷却装置100が正常動作している場合の、図6に示す各気流温度毎の放熱部180による放熱開始からの経過時間と流入温度:Rin及び流出温度:Routの関係を数値化したプロファイルの情報を格納した。ここで、放熱部180による放熱開始は、プリンタ300による印刷動作(画像形成動作)が開始され、定着装置15を通過した用紙Pの熱が、冷却部材141の液流路部143を通過する冷却液により、ラジエータ181に輸送され放熱が開始されるときである。
More specifically, as shown in FIG. 7, the cooling controller 230 is provided with a sensor controller that converts the detection value of each sensor into a signal that can be calculated in the cooling controller 230. On the other hand, in the non-volatile memory of the cooling control unit 230, the elapsed time from the start of heat dissipation by the
また、気流温度センサ151で検出する温度範囲を、図6に示した放熱部180が正常な場合の、各環境における入温度:Rin及び流出温度:Routの時間との関係の曲線を経時変化情報であるプロファイル化した閾値として用いる温度区分に区分した。
なお、各プロファイル化した閾値を用いるときの、具体的な各温度区分の範囲とプロファイルは、気流温度:T0がL環境の温度である15℃以下である場合に、L環境のプロファイルを用いる。また、気流温度:T0がL環境の温度である15℃を超え、M環境の温度である24℃以下である場合には、M環境のプロファイルを用いる。そして、気流温度:T0がM環境の温度である24℃を超えた場合には、H環境のプロファイルを用いる。
上記した温度区分と各環境のプロファイルは、予め定めて冷却制御部230の不揮発性メモリに格納して保持するようにした。
Further, the temperature range detected by the
In addition, the range and profile of each specific temperature division when using each profiled threshold value use the profile of the L environment when the airflow temperature: T0 is 15 ° C. or less which is the temperature of the L environment. In addition, when the airflow temperature T0 exceeds 15 ° C. which is the temperature of the L environment and is 24 ° C. or less which is the temperature of the M environment, the profile of the M environment is used. And when airflow temperature: T0 exceeds 24 degreeC which is the temperature of M environment, the profile of H environment is used.
The temperature classification and the profile of each environment described above are determined in advance and stored in the nonvolatile memory of the cooling control unit 230.
そして、放熱部180の異常の有無を判断する際には、冷却制御部230ではRAMに気流温度センサ151の検出結果に応じて、不揮発性メモリから必要なプロファイルをロードし、ROMに格納した異常判定プログラムを用いてCPUで演算して判断する。
このように構成することで、次のような効果を奏することができる。
各温度区分毎の、放熱部180が正常な場合の流出温度:Routの閾値のプロファイルと、流出温度:Routとから予測される冷却液の予測流入温度:Rin(P)を取得して、この予測流入温度:Rin(P)と、検出した流入温度:Rinと比較できる。
そして、検出した流入温度:Rinが予測流入温度:Rin(P)以上の場合には、ラジエータ181は所定の熱量を放熱しており、ラジエータ181の流入温度と流出温度の差分が所定の値以上になっていると考えられる。したがって、放熱部180に異常はないと判断できる。
Then, when determining whether there is an abnormality in the
By configuring in this way, the following effects can be achieved.
For each temperature category, obtain an estimated flow-in temperature: Rin (P) of the coolant that is predicted from the outflow temperature: Rout threshold profile and the outflow temperature: Rout when the
When the detected inflow temperature Rin is equal to or higher than the predicted inflow temperature Rin (P), the
一方、検出した流入温度:Rinが予測流入温度:Rin(P)より小さい場合には、ラジエータ181は所定の熱量を放熱しておらず、ラジエータ181の流入温度と流出温度の差分が所定の値より小さくなっていると考えられる。したがって、放熱部180に異常があると判断することができる。
よって、放熱部180の異常の有無を、異常判定プログラムを用いてCPUで演算する際の演算負荷を低減しつつ、適切に判断できる。
On the other hand, when the detected inflow temperature Rin is smaller than the predicted inflow temperature Rin (P), the
Therefore, the presence or absence of abnormality of the
なお、本実施例では、流入温度:Rin及び流出温度:Routの時間との関係の曲線を経時変化情報であるプロファイル、及び予め定める温度区分を、L環境、M環境、及びH環境の3つのプロファイル、及び3つ温度範囲とした例について説明した。しかし、本発明はこのような構成に限定されるものではなく、所定温度ずつに分割した温度範囲、及び各温度範囲の境界の温度環境のプロファイルを予め定めて保持しても良い。 In this embodiment, the curve of the relationship between the time of the inflow temperature: Rin and the outflow temperature: Rout is a profile that is time-varying information, and the predetermined temperature divisions are the three environments of L environment, M environment, and H environment. The profile and the example with three temperature ranges have been described. However, the present invention is not limited to such a configuration, and a temperature range divided for each predetermined temperature and a profile of the temperature environment at the boundary of each temperature range may be determined and held in advance.
また、液冷方式の冷却装置100では、ラジエータ181に流入した冷却液の流入温度:Rinが、流出するときにどのような流出温度:Routになったかを検知するのが理想的だが、冷却液が流れる各瞬間で大きく温度が変化するものではなくその差異は無視できる。このため、本実施例では、ラジエータ181に流入する冷却液の流入温度:Rinを検出するタイミングで、ラジエータ181を流出する冷却液の流出温度:Routを検出している。
なお、厳密に検出するのであれば、冷却液の流量とラジエータ181の容積から、ラジエータ181に流入してから流出するまでの流出時間:T1を求める。そして、ラジエータ181に流入してから、流出時間:T1経過後にラジエータ181から流出する冷却液の流出温度:Routを検出するように構成すれば良い。
In the liquid cooling
If the detection is strictly performed, an outflow time T1 from inflow to outflow of the
次に、本実施例の冷却制御部230で、異常判定プログラムを用いて、放熱部180の異常の有無を判断するときの原理、及び制御フローを図8、図9を用いて説明する。
まず、プリンタ300の用紙Pへの印刷(画像形成)が開始され、受熱部140で高温となった冷却液の熱の放熱部180での放熱が開始されるタイミングで、冷却制御部230は、流出温度センサ153の検出結果から流出温度:Routを取得する(S101)。そして、流出温度:Routが図6に示すH環境収束流出温度:RoutHeより高い温度になっていないかどうか(流出温度:RoutがH環境収束流出温度:RoutHe以下であるか否か)により、画像形成動作中止の必要性の有無を判断する(S102)。
Next, the principle and control flow when the cooling control unit 230 according to the present embodiment determines whether or not the
First, at the timing when printing (image formation) on the paper P of the
H環境収束流出温度:RoutHeは高温なH環境時の温度であるから、これよりもRoutが高い場合(S102のNo)は、用紙Pを冷却することが難しい状態にあり、画像形成動作を中止する必要があると判断できる。このため、冷却制御部230は、直ちに画像形成(印刷)動作を中止ように、本体制御部210に信号を送信(通信を行い)し、画像形成動作を中止させる(S103)。その後、図7に示す表示・操作部220に、本体制御部210を介して異常が発生していることを表示したり、スピーカーから警告音を鳴らしたり、印刷ジョブ等の信号を送信している利用者のパソコン等に異常が発生していることを通知したりする(S104)。そして、異常判定プログラムを用いた制御フローを終了する。 H environment convergence outflow temperature: Since RoutHe is a temperature in a high temperature H environment, when Rout is higher than this (No in S102), it is difficult to cool the paper P, and the image forming operation is stopped. It can be judged that it is necessary. Therefore, the cooling control unit 230 transmits a signal (communication) to the main body control unit 210 so as to immediately stop the image forming (printing) operation, and stops the image forming operation (S103). After that, the display / operation unit 220 shown in FIG. 7 displays that an abnormality has occurred via the main body control unit 210, sounds a warning sound from a speaker, and transmits a signal such as a print job. The user's personal computer or the like is notified that an abnormality has occurred (S104). Then, the control flow using the abnormality determination program is terminated.
一方、流出温度:RoutがH環境収束流出温度:RoutHe以下である場合(S102のYes)、画像形成動作を中止する必要がないと判断し、気流温度センサ151の検出結果から気流温度:T0を取得する(S105)。そして、冷却制御部230は、取得した気流温度:T0に対応する環境のプロファイルを、図7に示す不揮発性メモリ内から特定して、RAMにロードする。これを図8に示すプロファイルだと仮定する。
On the other hand, when the outflow temperature: Rout is equal to or lower than the H environment convergence outflow temperature: RoutHe (Yes in S102), it is determined that it is not necessary to stop the image forming operation, and the airflow temperature: T0 is determined from the detection result of the
次に、冷却制御部230は、取得した流出温度:Rout(S101)から、RAMにロードしたプロファイル上のRoutに対応するラジエータ181に流入する冷却液温度を予測した予測流入温度:Rin(p)を取得する(S106)。
その後、流入温度センサ152の検出結果から流入温度:Rin(実測値)を取得する(S107)。
Next, the cooling control unit 230 predicts the coolant temperature that flows into the
Thereafter, the inflow temperature: Rin (actually measured value) is acquired from the detection result of the inflow temperature sensor 152 (S107).
そして、流入温度:Rinが予測流入温度:Rin(p)以上であるか否かの判断を行う(S108)。つまり、予測流入温度:Rin(p)と流入温度センサ152の検出結果である流入温度:Rinとを比較する判断を行う。
この判断で、図8のグラフの右寄りに示すように、流出温度:RoutがRout1、予測流入温度:Rin(p)がRin(p)1、流入温度:Rinが予測流入温度:Rin(p)1以上であるRin1であれば(S108のYes)、次のように判断できる。
流入温度:Rin1が予測流入温度:Rin(p)1以上の場合には、ラジエータ181は所定の熱量を放熱しており、ラジエータ181の流入温度と流出温度の差分が所定の値以上になっていると考えられ、放熱部180に異常はないと判断できる。つまり、予測流入温度:Rin(p)1と流出温度:Rout1との差分が、流入温度:Rin1と流出温度:Rout1との差分以下となっており(Rin(p)1−Rout ≦ Rin−Rout)、放熱部180に異常はないと判断できる。
Then, it is determined whether or not the inflow temperature Rin is equal to or higher than the predicted inflow temperature Rin (p) (S108). That is, a determination is made to compare the predicted inflow temperature: Rin (p) with the inflow temperature: Rin that is the detection result of the
In this determination, as shown on the right side of the graph of FIG. 8, the outflow temperature: Rout is Rout1, the predicted inflow temperature: Rin (p) is Rin (p) 1, the inflow temperature: Rin is the predicted inflow temperature: Rin (p). If Rin1 is 1 or more (Yes in S108), it can be determined as follows.
When the inflow temperature Rin1 is equal to or higher than the predicted inflow temperature Rin (p) 1, the
上記のように流入温度:Rinが予測流入温度:Rin(p)以上であると判断した場合には(S108のYes)、本体制御部210と通信を行って、印刷動作が継続しているかどうか、つまり、印刷動作が終了したか否かを判断する(S110)。
そして、印刷動作が終了しておらず、継続していると判断した場合には(S110のNo)、流出温度の取得(S101)に戻り、印刷動作が終了していると判断した場合には(S110のYes)、異常判定プログラムを用いた制御フローを終了する。
As described above, when it is determined that the inflow temperature: Rin is equal to or higher than the predicted inflow temperature: Rin (p) (Yes in S108), communication with the main body control unit 210 is performed to check whether the printing operation is continued. That is, it is determined whether or not the printing operation is completed (S110).
If it is determined that the printing operation has not been completed and is continuing (No in S110), the process returns to the acquisition of the outflow temperature (S101), and if it is determined that the printing operation has been completed. (Yes in S110), the control flow using the abnormality determination program is terminated.
一方、図8のグラフの左寄りに示すように、流出温度:RoutがRout2、予測流入温度:Rin(p)がRin(p)2、流入温度:Rinが予測流入温度:Rin(p)2よりも小さいRin2であれば(S108のNo)、次のように判断できる。
流入温度:Rin2が予測流入温度:Rin(p)2よりも小さい場合、ラジエータ181は所定の熱量を放熱しておらず、ラジエータ181の流入温度と流出温度の差分が所定の値より小さくなっていると考えられ、放熱部180に異常があると判断できる。つまり、予測流入温度:Rin(p)2と流出温度:Rout2との差分が、流入温度:Rin2と流出温度:Rout2との差分よりも大きくなっており(Rin(p)1−Rout > Rin−Rout)、放熱部180に異常があると判断できる。
On the other hand, as shown on the left side of the graph of FIG. 8, the outflow temperature: Rout is Rout2, the predicted inflow temperature: Rin (p) is Rin (p) 2, and the inflow temperature: Rin is from the predicted inflow temperature: Rin (p) 2. Can be determined as follows (No in S108).
When the inflow temperature: Rin2 is smaller than the predicted inflow temperature: Rin (p) 2, the
上記のように流入温度:Rinが予測流入温度:Rin(p)よりも小さいと判断した場合(S108のNo)、つまり、放熱部180が異常であると判断した場合、冷却制御部230では、次のような制御を行う。放熱部180が異常であることを、本体制御部210を介して表示・操作部220のタッチパネルに表示したり、スピーカーから警告音を鳴らして通知したり、利用者のパソコン等に通知して、警告メッセージを表示させたりする(S109)。但し、印刷動作(画像形成動作)を中止(停止)しなければならないほどの放熱部180の放熱能力の低下ではないため、印刷動作は継続する。
その後、本体制御部210と通信を行って、印刷動作が継続しているかどうか、つまり、印刷動作が終了したか否かを判断する(S110)。
そして、印刷動作が終了しておらず、継続していると判断した場合には(S110のNo)、流出温度の取得(S101)に戻り、印刷動作が終了していると判断した場合には(S110のYes)、異常判定プログラムを用いた制御フローを終了する。
As described above, when it is determined that the inflow temperature: Rin is smaller than the predicted inflow temperature: Rin (p) (No in S108), that is, when it is determined that the
Thereafter, communication with the main body control unit 210 is performed to determine whether the printing operation is continued, that is, whether the printing operation is finished (S110).
If it is determined that the printing operation has not been completed and is continuing (No in S110), the process returns to the acquisition of the outflow temperature (S101), and if it is determined that the printing operation has been completed. (Yes in S110), the control flow using the abnormality determination program is terminated.
上記のように、本実施例の冷却装置100では、異常判定プログラムを有した冷却制御部230は、気流温度センサ151で検出する温度範囲を区分したL環境、M環境、及びH環境等の複数の温度区分を予め定めて保持している。また、各温度区分毎の、放熱部180が正常に動作している状態で、ラジエータ181の流入温度:Rinと、流出温度:Routからなる閾値のプロファイルも、予め定めて保持している。そして、気流温度センサ151で検出した気流温度:T0を含む温度区分の閾値のプロファイルと、流入温度センサ152及び流出温度センサ153の検出結果とに基づいて、放熱部180の異常の有無を判断する。
このように判断することで、放熱部の異常の有無を、冷却制御部230のCPUで行う演算負荷を低減しつつ、適切に判断できる。
As described above, in the
By determining in this way, the presence or absence of abnormality of the heat radiating unit can be appropriately determined while reducing the calculation load performed by the CPU of the cooling control unit 230.
また、冷却制御部230は、実質的には上記したように、流入温度センサ152と流出温度センサ153の検出結果の差分に基づいて、放熱部180の異常の有無を判断する。
このように判断することで、流入温度センサ152と流出温度センサ153の検出結果の差分から放熱部180での放熱能力を数値化して、気流温度センサ151の検出結果に応じた、正常な放熱能力を得られているか否かの判断が行える。したがって、放熱部180の異常の有無を適切に判断できる。
In addition, as described above, the cooling control unit 230 determines whether there is an abnormality in the
By determining in this way, the heat dissipation capability in the
また、冷却制御部230は、放熱部180に異常が有ると判断したとき、用紙Pに画像形成を施す(印刷する)、プリンタ300の本体制御部210と通信を行う。そして、プリンタ300の利用者への表示・操作部220等の通知手段を介して、放熱部180の異常、又はその異常に関わるより詳細な情報の通知を行うことができる。
このように通知することができるので、放熱部180の異常を利用者に通知して、放熱部180のメンテナンス(調査)を促がすことができる。したがって、放熱部180の異常を放置した状態でプリンタ300の稼動が続けられて不具合であるブロッキングが発生することを抑制できる。
When the cooling control unit 230 determines that the
Since the notification can be made in this way, the user can be notified of the abnormality of the
また、冷却制御部230は、検出した流出温度:Routが、正常状態時のH環境収束流出温度:RoutHe以下でないとき、プリンタ300の本体制御部210と通信を行い、プリンタ300の用紙Pに関わる各画像形成プロセスを中止させる。
このように各画像形成プロセスを中止させることで、放熱部180の異常を放置した状態で冷却装置100を用いるプリンタ300の稼動が続けられて、不具合であるブロッキングが発生することを確実に抑制できる。
The cooling control unit 230 communicates with the main body control unit 210 of the
By stopping each image forming process in this manner, the operation of the
なお、上記した本実施例では、本発明を熱定着後の用紙Pを冷却する冷却装置100に適用した例について説明したが、本発明はこのような構成に限定されるものではない。
例えば、プリンタ300に有した4つの画像ステーション10に、それぞれ有した現像装置3の攪拌・搬送部に接触させた冷却ジャケットを有する受熱部との間で、循環する冷却液の熱を、ラジエータと冷却ファンとを有する液冷方式の冷却装置にも適用可能である。
In the above-described embodiment, an example in which the present invention is applied to the
For example, the heat of the circulating coolant between the four image stations 10 in the
このような現像装置3の攪拌・搬送部を冷却する冷却装置を設けた場合、ラジエータ及び送風ファンを有した放熱部が異常な状態となると、上記した本実施例の冷却装置100と同様に、様々な不具合が発生してしまうという問題がある。具体的には、現像装置3内の現像剤温度が上昇して軟化したトナーが凝集して異常画像が発生したり、現像装置3内のいずれかの構成部材に固着して現像装置3が故障してしまったりするという不具合が発生してしまうという問題である。
そして、各現像装置3の攪拌・搬送部を冷却する冷却装置に本発明を適用することで、受熱部との間で循環する冷媒の熱を、放熱する放熱部の異常に起因した、不具合の発生を抑制できる冷却装置を提供することができる。
When such a cooling device for cooling the agitating / conveying unit of the developing device 3 is provided, if the heat radiating unit having the radiator and the blower fan is in an abnormal state, similarly to the
Then, by applying the present invention to the cooling device that cools the agitating / conveying unit of each developing device 3, the heat of the refrigerant circulating between the heat receiving unit and the malfunction caused by the abnormality of the heat radiating unit that radiates heat A cooling device capable of suppressing generation can be provided.
また、放熱部180に、送風ファン186を有したファンユニット185を設けた冷却装置100について説明したが、本発明はこのような構成に限定されるものではない。
例えば、送風ファン等の送風手段を有さず、外気がラジエータの通風部を通過するように、下方に設けた外気を取り込む吸気口と、ラジエータを通過して高温となった気流を自然排気する排気口とを設けたダクト内にラジエータを収納した構成にも適用可能である。
Moreover, although the
For example, it does not have a blowing means such as a blower fan, and naturally exhausts the airflow that has passed through the radiator and the intake port that takes in outside air so that the outside air passes through the ventilation section of the radiator The present invention can also be applied to a configuration in which a radiator is housed in a duct provided with an exhaust port.
また、検出した流出温度:Routから予測流入温度:Rin(p)を取得し、予測流入温度:Rin(p)と検出した流入温度:Rinとを比較して、放熱部180に異常があるか否かの判断を行ったが、本発明はこのような構成に限定されるもにではない。
例えば、検出した流入温度:Rinから予測流出温度:Rout(p)を取得し、予測流出温度:Rout(p)と検出した流出温度:Routとを比較して、放熱部180に異常があるか否かの判断を行うこともできる。
以下に、冷却制御部230で、異常判定プログラムを用いて、放熱部180の異常の有無を判断するときの原理、及び制御フローを図10、図11を用いて説明する。なお、上図8、図9を用いて説明した原理、及び制御フローと同様な点については、適宜、省略して説明する。
In addition, the predicted inflow temperature: Rin (p) is acquired from the detected outflow temperature: Rout, and the predicted inflow temperature: Rin (p) is compared with the detected inflow temperature: Rin to determine whether there is an abnormality in the
For example, the predicted outflow temperature: Rout (p) is obtained from the detected inflow temperature: Rin, and the predicted outflow temperature: Rout (p) is compared with the detected outflow temperature: Rout to determine whether there is an abnormality in the
Hereinafter, the principle and control flow when the cooling control unit 230 uses the abnormality determination program to determine whether or not the
まず、プリンタ300の用紙Pへの印刷(画像形成)が開始され、受熱部140で高温となった冷却液の熱の放熱部180での放熱が開始されるタイミングで、冷却制御部230は、流出温度センサ153の検出結果から流入温度:Rinを取得する(S101’)。そして、流入温度:Rinが図6に示すH環境収束流入温度:RinHeより高い温度になっていないかどうか(流入温度:RinがH環境収束流入温度:RinHe以下であるか否か)により、画像形成動作中止の必要性の有無を判断する(S102’)。
First, at the timing when printing (image formation) on the paper P of the
H環境収束流入温度:RinHeは高温なH環境時の温度であるから、これよりもRinが高い場合(S102’のNo)は、用紙Pを冷却することが難しい状態にあり、画像形成動作を中止する必要があると判断できる。このため、冷却制御部230は、直ちに画像形成(印刷)動作を中止ように、本体制御部210に信号を送信(通信を行い)し、画像形成動作を中止させる(S103)。その後、図7に示す表示・操作部220に、本体制御部210を介して異常が発生していることを表示したり、スピーカーから警告音を鳴らしたり、印刷ジョブ等の信号を送信している利用者のパソコン等に異常が発生していることを通知したりする(S104)。そして、異常判定プログラムを用いた制御フローを終了する。 H environment convergence inflow temperature: Since RinHe is a temperature in a high H environment, when Rin is higher than this (No in S102 ′), it is difficult to cool the sheet P, and the image forming operation is performed. It can be judged that it is necessary to cancel. Therefore, the cooling control unit 230 transmits a signal (communication) to the main body control unit 210 so as to immediately stop the image forming (printing) operation, and stops the image forming operation (S103). After that, the display / operation unit 220 shown in FIG. 7 displays that an abnormality has occurred via the main body control unit 210, sounds a warning sound from a speaker, and transmits a signal such as a print job. The user's personal computer or the like is notified that an abnormality has occurred (S104). Then, the control flow using the abnormality determination program is terminated.
一方、流入温度:RinがH環境収束流入温度:RinHe以下である場合(S102’のYes)、画像形成動作を中止する必要がないと判断し、気流温度センサ151の検出結果から気流温度:T0を取得する(S105)。そして、冷却制御部230は、取得した気流温度:T0に対応する環境のプロファイルを、図7に示す不揮発性メモリ内から特定して、RAMにロードする。これを図10に示すプロファイルだと仮定する。
On the other hand, when the inflow temperature Rin is equal to or lower than the H environment convergence inflow temperature RinHe (Yes in S102 ′), it is determined that it is not necessary to stop the image forming operation, and the airflow temperature T0 is determined from the detection result of the
次に、冷却制御部230は、取得した流入温度:Rin(S101’)から、RAMにロードしたプロファイル上のRinに対応するラジエータ181から流出する冷却液温度を予測した予測流出温度:Rout(p)を取得する(S106’)。
その後、流出温度センサ153の検出結果から流出温度:Rout(実測値)を取得する(S107’)。
Next, the cooling control unit 230 predicts the coolant temperature flowing out from the
Thereafter, the outflow temperature: Rout (actually measured value) is acquired from the detection result of the outflow temperature sensor 153 (S107 ′).
そして、流出温度:Routが予測流出温度:Rout(p)以下であるか否かの判断を行う(S108’)。つまり、予測流出温度:Rout(p)と流出温度センサ153の検出結果である流出温度:Routとを比較する判断を行う。
この判断で、図10のグラフの右寄りに示すように、流入温度:RinがRin1、予測流出温度:Rout(p)がRout(p)1であるとする。そして、流出温度:Routが予測流出温度:Rout(p)1以下であるRout1であれば(S108’のYes)、次のように判断できる。
Then, it is determined whether the outflow temperature: Rout is equal to or lower than the predicted outflow temperature: Rout (p) (S108 ′). That is, a determination is made to compare the predicted outflow temperature: Rout (p) with the outflow temperature: Rout, which is the detection result of the
In this determination, it is assumed that the inflow temperature: Rin is Rin1 and the predicted outflow temperature: Rout (p) is Rout (p) 1, as shown on the right side of the graph of FIG. If the outflow temperature: Rout is Rout1 which is equal to or lower than the predicted outflow temperature: Rout (p) 1 (Yes in S108 ′), it can be determined as follows.
流出温度:Rout1が予測流出温度:Rout(p)1以下である場合には、ラジエータ181は所定の熱量を放熱しており、ラジエータ181の流入温度と流出温度の差分が所定の値以上になっていると考えられ、放熱部180に異常はないと判断できる。つまり、流入温度:Rin1と予測流出温度:Rout(p)1との差分が、流入温度:Rin1と流出温度:Rout1との差分以下となっており(Rin−Rout(p)1 ≦ Rin−Rout)、放熱部180に異常はないと判断できる。
When the outflow temperature: Rout1 is equal to or less than the predicted outflow temperature: Rout (p) 1, the
上記のように流出温度:Routが予測流出温度:Rout(p)以下であると判断した場合には(S108’のYes)、本体制御部210と通信を行って、印刷動作が継続しているかどうか、つまり、印刷動作が終了したか否かを判断する(S110)。
そして、印刷動作が終了しておらず、継続していると判断した場合には(S110のNo)、流入温度の取得(S101)に戻り、印刷動作が終了していると判断した場合には(S110のYes)、異常判定プログラムを用いた制御フローを終了する。
As described above, when it is determined that the outflow temperature: Rout is equal to or less than the predicted outflow temperature: Rout (p) (Yes in S108 ′), communication is performed with the main body control unit 210, and the printing operation is continued. It is determined whether or not the printing operation is finished (S110).
If it is determined that the printing operation has not been completed and continues (No in S110), the process returns to the acquisition of the inflow temperature (S101), and if it is determined that the printing operation has been completed. (Yes in S110), the control flow using the abnormality determination program is terminated.
一方、図10のグラフの左寄りに示すように、流入温度:RinがRin2、予測流出温度:Rout(p)がRout(p)2、流出温度:Routが予測流出温度:Rout(p)2よりも大きいRout2であれば(S108’のNo)、次のように判断できる。
流出温度:Rout2が予測流出温度:Rout(p)2よりも大きい場合、ラジエータ181は所定の熱量を放熱しておらず、ラジエータ181の流入温度と流出温度の差分が所定の値より小さくなっていると考えられ、放熱部180に異常があると判断できる。つまり、流入温度:Rin2と予測流出温度:Rout(p)2との差分が、流入温度:Rin2と流出温度:Rout2との差分よりも大きくなっており(Rin2−Rout(p)2 > Rin−Rout)、放熱部180に異常があると判断できる。
On the other hand, as shown on the left side of the graph of FIG. 10, the inflow temperature: Rin is Rin2, the predicted outflow temperature: Rout (p) is Rout (p) 2, and the outflow temperature: Rout is from the predicted outflow temperature: Rout (p) 2. Is larger (No in S108 ′), it can be determined as follows.
When the outflow temperature Rout2 is larger than the predicted outflow temperature Rout (p) 2, the
上記のように流出温度:Routが予測流出温度:Rout(p)よりも大きいと判断した場合(S108’のNo)、つまり、放熱部180が異常であると判断した場合、冷却制御部230では、次のような制御を行う。放熱部180が異常であることを、本体制御部210を介して表示・操作部220のタッチパネルに表示したり、スピーカーから警告音を鳴らして通知したり、利用者のパソコン等に通知して、警告メッセージを表示させたりする(S109)。但し、印刷動作(画像形成動作)を中止(停止)しなければならないほどの放熱部180の放熱能力の低下ではないため、印刷動作は継続する。
その後、本体制御部210と通信を行って、印刷動作が継続しているかどうか、つまり、印刷動作が終了したか否かを判断する(S110)。
そして、印刷動作が終了しておらず、継続していると判断した場合には(S110のNo)、流入温度の取得(S101)に戻り、印刷動作が終了していると判断した場合には(S110のYes)、異常判定プログラムを用いた制御フローを終了する。
As described above, when it is determined that the outflow temperature: Rout is larger than the predicted outflow temperature: Rout (p) (No in S108 ′), that is, when it is determined that the
Thereafter, communication with the main body control unit 210 is performed to determine whether the printing operation is continued, that is, whether the printing operation is finished (S110).
If it is determined that the printing operation has not been completed and continues (No in S110), the process returns to the acquisition of the inflow temperature (S101), and if it is determined that the printing operation has been completed. (Yes in S110), the control flow using the abnormality determination program is terminated.
(実施例2)
本実施形態の冷却装置100に備えた、放熱部180の異常を判断する異常判断手段に係る構成、及びその動作(制御)の実施例2について、図を用いて説明する。
図12は、本実施例の放熱部180の異常を判断するときの制御フロー図である。
本実施例と、上記した実施例1の冷却装置とでは、次のことに係る点のみ異なる。実施例1の冷却装置に備えた、放熱部180の異常を判断する異常判断手段に係る構成では、放熱部180が異常な状態にあるか否かを判断して、異常な状態にある場合に利用者に通知したり、プリンタ300の画像形成動作を中止するものであった。これに対して、本実施例の異常判断手段に係る構成では、放熱部180に有した熱交換器であるラジエータ181と、送風手段であるファンユニット185(送風ファン186)のいづれが、異常な状態にあるかも区別して判断できる点である。
(Example 2)
A configuration relating to an abnormality determination unit that determines an abnormality of the
FIG. 12 is a control flow diagram when determining an abnormality of the
This embodiment differs from the cooling device according to the first embodiment only in the following points. In the configuration relating to the abnormality determining means for determining the abnormality of the
他のことに係る点については、本実施例の冷却装置100に備えた、放熱部180の異常を判断する異常判断手段の構成、及びその作用・効果は、実施例1のものと同様であるので、以下の説明では同様な構成、作用・効果については、適宜、省略して説明する。また、特に区別する必要がない限り、同一の構成部材や同様な機能を果たす構成部材等には、同一の符号、及び呼称を用いて説明する。
About the point which concerns on another thing, the structure of the abnormality determination means with which the
本実施例では、放熱部180の異常の有無を判断することに加え、熱交換機であるラジエータ181と、送風手段であるファンユニット185のいずれが異常な状態にあるか区別して判断するために、次のように冷却装置100及び冷却制御部230を構成した。
本実施例の冷却装置100では、ファンユニット185に有した8つの送風ファン186として、回転パルス信号を出力できるものを使用し、その回転パルス信号から送風ファン186の回転数を取得して、放熱部180の異常の有無の判断に用いることとした。
具体的には、冷却制御部230に、送風ファン186の回転数をファンコンロローラから取得(検知)できるように、各送風ファン186のパルス信号用の端子を接続する端子を設けるとともに、冷却制御部230のファンコンローラ内にパルス検知回路を設けた。
また、パルス検知回路で検知するパルス信号が、冷却制御部230で制御する各送風ファン186の回転数に応じた、許容できる周波数範囲内にあるか否かを判定するサブルーチンを異常判定プログラムに追加した。
In this embodiment, in addition to determining whether there is an abnormality in the
In the
Specifically, the cooling control unit 230 is provided with a terminal for connecting a terminal for a pulse signal of each
In addition, a subroutine for determining whether or not the pulse signal detected by the pulse detection circuit is within an allowable frequency range according to the rotation speed of each
次に、本実施例の冷却制御部230で、異常判定プログラムを用いて、放熱部180の異常の有無を判断するときの制御フローを図12を用いて説明する。
なお、本実施例では、図9を用いて説明した実施例1の流入温度:Rinが予測流入温度:Rin(p)よりも小さいと判断した(S108のNo)後の、放熱部180の異常を表示したり、通知したりしするステップ(S109)に替え、次の各ステップを追加した。
Next, the control flow when the cooling control unit 230 according to the present embodiment determines whether or not the
In the present embodiment, the abnormality of the
図12の制御フロー図に示すように、冷却制御部230は、流入温度:Rinが予測流入温度:Rin(p)よりも小さいと判断した(S108のNo)場合、送風ファン186が正常に回転しているかどうかを確認する(S201)。
そして、送風ファン186が正常に回転していない場合(S201でNo)、放熱部180の異常、つまり、冷却液の熱が正常に放熱されない原因を送風ファン186の異常と判断し送風ファン186が異常であることを表示したり、通知したりする(S202)。
一方、送風ファン186が正常に回転している場合(S201でYes)、ラジエータ181が目詰まりしている(空気抵抗が増ましている)可能性がある。このため、ラジエータ181の異常であることを表示したり、通知したりして、利用者にラジエータ181のメンテナンス、つまり、ラジエータ181の目詰まりの有無の点検を促す(S203)。
As shown in the control flow diagram of FIG. 12, when the cooling control unit 230 determines that the inflow temperature: Rin is smaller than the predicted inflow temperature: Rin (p) (No in S108), the
If the
On the other hand, when the
上記のように構成することで、ラジエータ181の目詰りと、送風手段の故障等の異常とを区別して判断でき、より詳細な点検箇所を特定して、放熱部のメンテナンス時間を短縮できる。したがって、この冷却装置100を用いるプリンタ300のダウンタイムを短縮して稼動率を高めることができる。
なお、本実施例の冷却装置100に備えた、放熱部180の異常を判断する異常判断手段に係る構成、及びその動作(制御)は、実施例1と同様に、他の冷却対象を冷却する液冷方式の冷却装置にも適用可能である。
By configuring as described above, it is possible to distinguish between the clogging of the
In addition, the structure which concerns on the abnormality judgment means which judges the abnormality of the
(実施例3)
本実施形態の冷却装置100に備えた、放熱部180の異常を判断する異常判断手段に係る構成、及びその動作(制御)の実施例3について、図を用いて説明する。
図13は、M環境における、用紙の種類毎の、受熱部140の冷却部材141側からラジエータ181に流入する冷却液の温度と、ラジエータ181から冷却部材141側に流出する冷却液の経時変化のグラフである。図14は、ラジエータ181に当たる気流の気流温度:T0毎の、ラジエータ181に流入する冷却液の流入温度:Rinと、ラジエータ181から流出する冷却液の流出温度:Routの、普通紙、及び厚紙における経時変化のグラフである。
(Example 3)
A configuration relating to an abnormality determination unit that determines an abnormality of the
FIG. 13 shows the temperature change of the coolant flowing into the
図15は、本実施例の放熱部180の異常を判断するときの制御フロー図である。図16は、気流温度:T0毎の、流入温度:Rinと、冷却液の流出温度:Routの、普通紙における経時変化のグラフに、画像形成動作の中止の判断に用いるH環境収束流出温度を追記したグラフ。図17は、本実施例の放熱部180の異常を判断するときの別例の制御フロー図である。
なお、本実施例の特徴である、用紙の種類を取得するステップは、実施例1の図9、及び実施例2の図12のいずれの制御フローにも追加可能であるが、図15、及び図17では、実施例2の図12に用紙の種類を取得するステップを追加したものを記載している。
FIG. 15 is a control flow diagram for determining an abnormality of the
The step of acquiring the sheet type, which is a feature of the present embodiment, can be added to any of the control flows in FIG. 9 of the first embodiment and FIG. 12 of the second embodiment. FIG. 17 shows a case where a step of acquiring the paper type is added to FIG. 12 of the second embodiment.
本実施例と、上記した実施例1、2の冷却装置とでは、次のことに係る点のみ異なる。本実施例では、実施例1、2の放熱部180の異常判断手段に係る構成で、放熱部180が異常な状態にあるか否かを判断するときの条件として、用紙の種類も加えた点である。
他のことに係る点については、本実施例の冷却装置100に備えた、放熱部180の異常を判断する異常判断手段の構成、及びその作用・効果は、実施例1のものと同様であるので、以下の説明では同様な構成、作用・効果については、適宜、省略して説明する。また、特に区別する必要がない限り、同一の構成部材や同様な機能を果たす構成部材等には、同一の符号、及び呼称を用いて説明する。
This embodiment differs from the cooling devices according to the first and second embodiments only in the following points. In the present embodiment, in the configuration relating to the abnormality determining unit of the
About the point which concerns on another thing, the structure of the abnormality determination means with which the
まず、放熱部180が異常な状態にあるか否かを判断するときの条件として、用紙の種類も加えた理由について説明する。
プリンタ300は、複数の種類の用紙Pに画像形成が可能なように構成されている。例えば、紙厚が厚い厚紙、通常頻繁に用いられる紙厚の普通紙、及び紙厚が薄い薄紙等である。これらの種類の用紙Pは、その厚さに応じて坪量が異なり、利用者が印刷指示を行うパソコン等の端末で設定した用紙の種類によって、定着装置15による定着温度が変わる。例えば、普通紙を定着するときの定着温度よりも、坪量が大きい厚紙では定着温度が高く、坪量が小さい薄紙では定着温度が低い。このため、定着装置15で熱定着された後の用紙Pの温度も、その種類によって異なってしまい、冷却部材141で受熱(吸熱)する熱量も異なる。
First, the reason why the type of paper is added as a condition for determining whether or not the
The
上記のように、受熱する熱量が異なると、ラジエータ181に流入する冷却液の流入温度:Rinが異なってしまい、各気流温度:TO毎の、流入温度:Rinやラジエータ181から流出する冷却液の流出温度:Routの経時変化も異なってしまう。
例えば、M環境では、図13に示すように、紙厚が厚くなる程、収束流入温度や収束流出温度が高くなるように各温度の曲線の曲率がきつくなる。また、他の温度環境でも同様な傾向がある。
そして、例えば、各温度環境における流入温度:Rin及び流出温度:Routの経時変化のグラフの温度曲線が、図14(a)に示す普通紙のものよりも、図14(b)に示す厚紙のものの方が高くなるとともに、各温度曲線の収束値も高くなる。
このため、異なる種類の用紙Pを冷却する冷却装置100の、放熱部180の異常の有無を、ある用紙種類のプロファイルだけに基づいて判断すると、誤った判断を行うおそれがある。
As described above, when the amount of heat received is different, the inflow temperature: Rin of the coolant flowing into the
For example, in the M environment, as shown in FIG. 13, as the paper thickness increases, the curvature of each temperature curve becomes tighter so that the convergence inflow temperature and the convergence outflow temperature become higher. In addition, there is a similar tendency in other temperature environments.
For example, the temperature curve of the time-dependent change graph of the inflow temperature: Rin and the outflow temperature: Rout in each temperature environment is higher than that of the plain paper shown in FIG. As the object becomes higher, the convergence value of each temperature curve also becomes higher.
For this reason, if the
そこで、本実施例では、不揮発性メモリに格納するプロファイルを、図6に示す温度区分に応じた3組(H環境、M環境、L環境)のプロファイルではなく、さらに用紙の種類(厚紙、普通紙、薄紙)毎に規定した9組のプロファイルとした。そして、放熱部180の異常の有無を判断する制御フローに、9組のプロファイルから、適宜、必要なプロファイルをRAMにロードするために、本体制御部210から用紙Pの種類の情報を取得するステップ(S311 or S321)を追加した。
本実施例の制御フローでは、用紙の種類の情報を本体制御部210から冷却制御部230が取得する制御を、次のいずれかのタイミングで取得すれば良い。図9や図12の制御フローの流出温度:Routを取得する(S101)前に取得する(S311)か、画像形成動作を中止する必要がないと判断し(S102のYes)、気流温度:T0を取得する(S105)前に取得する(S321)ように構成すれば良い。
Therefore, in this embodiment, the profiles stored in the non-volatile memory are not the profiles of the three sets (H environment, M environment, L environment) corresponding to the temperature classification shown in FIG. Nine sets of profiles defined for each paper and thin paper. Then, in order to load the necessary profile into the RAM as appropriate from the nine sets of profiles in the control flow for determining whether there is an abnormality in the
In the control flow of the present embodiment, the control for acquiring the sheet type information from the main body control unit 210 by the cooling control unit 230 may be acquired at any of the following timings. The flow out temperature: Rout in FIG. 9 and FIG. 12 is acquired before acquiring (S101) (S311), or it is determined that it is not necessary to stop the image forming operation (Yes in S102), and the airflow temperature: T0 (S321) may be obtained before obtaining (S105).
具体的には、図15の制御フロー図に示すように、流出温度:Routを取得する(S101)前に取得する場合、用紙Pへの印刷が開始されると、冷却制御部230は、本体制御部210と通信を行って用紙Pの種類の情報を取得する(S311)。そして、取得した用紙Pの種類に応じた、以降の判断にそれぞれ必要なプロファイルをRAMにロードし、このロードしたプロファイルを用いて行う。
例えば、冷却する用紙Pが普通紙であった場合、画像形成動作の中止の判断(S102)では、図14(a)に対応する普通紙のH環境のプロファイルをRAMにロードし、H環境の収束流出温度:RoutHeを抽出して、取得した流出温度:Routと比較する。また、画像形成動作を中止する必要がないと判断(S102のYes)し、印刷終了の判断を行う(S110)までの間では、取得した用紙Pの種類、及び気流温度:T0に応じたプロファイルを用いて各判断を行う。
すなわち、冷却する用紙Pの種類情報をS101の前で取得する場合、S102以降では紙の種類情報を加味したプロファイルを用いて各判断を行う。
Specifically, as shown in the control flow diagram of FIG. 15, when acquiring the outflow temperature: Rout (S101), when the printing on the paper P is started, the cooling control unit 230 Information on the type of paper P is acquired by communicating with the control unit 210 (S311). Then, the profiles necessary for the subsequent determination according to the type of the acquired paper P are loaded into the RAM, and the loaded profile is used.
For example, if the paper P to be cooled is plain paper, in the determination of stopping the image forming operation (S102), the H environment profile of plain paper corresponding to FIG. Convergent outflow temperature: RoutHe is extracted and compared with the acquired outflow temperature: Rout. Further, until it is determined that it is not necessary to stop the image forming operation (Yes in S102) and the end of printing is determined (S110), the profile corresponding to the type of the acquired paper P and the airflow temperature: T0 Each decision is made using.
That is, when the type information of the paper P to be cooled is acquired before S101, each determination is made using a profile that takes into account the paper type information after S102.
一方、図17の制御フロー図に示すように、画像形成動作を中止する必要がないと判断し(S102のYes)、気流温度:T0を取得する(S105)前に取得する(S321)場合も、本体制御部210と通信を行って用紙Pの種類の情報を取得する(S321)。この場合は、画像形成動作の中止の判断(S102)では、図14(b)に対応する厚紙のH環境のプロファイルをRAMにロードし、H環境の収束流出温度:RoutHeを抽出して、取得した流出温度:Routと比較する。そして、画像形成動作を中止する必要がないと判断(S102のYes)し、印刷終了の判断を行う(S110)までの間では、取得した用紙Pの種類、及び気流温度:T0に応じたプロファイルを用いて各判断を行う。
すなわち、用紙Pの種類情報をS102とS105の間で取得する場合、S102では、最も坪量の大きい厚紙の用紙Pに対応するH環境のプロファイルを用いて判断し、S105以降で用紙Pの種類情報を加味したプロファイルを用いて判断することになる。
On the other hand, as shown in the control flow diagram of FIG. 17, it is determined that it is not necessary to stop the image forming operation (Yes in S102), and the airflow temperature: T0 is acquired (S105) before (S321). Then, communication with the main body control unit 210 is performed to acquire information on the type of the paper P (S321). In this case, in the determination of stopping the image forming operation (S102), the H environment profile of cardboard corresponding to FIG. 14B is loaded into the RAM, and the convergence outflow temperature: RoutHe of the H environment is extracted and acquired. Outflow temperature: Compared with Rout. Then, until it is determined that it is not necessary to stop the image forming operation (Yes in S102) and the end of printing is determined (S110), the profile corresponding to the type of the acquired paper P and the airflow temperature: T0 Each decision is made using.
That is, when the type information of the paper P is acquired between S102 and S105, in S102, the determination is made using the profile of the H environment corresponding to the thick paper P having the largest basis weight. Judgment is made using a profile that takes into account information.
上記したいずれかの制御フローにより、用紙Pの種類(坪量)に応じた、より詳細な判断を行うことができ、誤った判断を行ってしまうことを抑制できる。
ここで、上記した誤った判断とは、用紙Pの坪量が大きいために、坪量を加味しないときの正常な冷却温度の範囲を超えて(Rin(p)−Rout > Rin−Rout)冷却制御部230が、放熱部180の異常を判断してしまうことである。
With any one of the control flows described above, it is possible to make a more detailed determination according to the type (basis weight) of the paper P, and to suppress making an erroneous determination.
Here, the above-mentioned erroneous determination means that the paper P has a large basis weight, and thus exceeds the normal cooling temperature range when the basis weight is not taken into account (Rin (p) −Rout> Rin−Rout). That is, the control unit 230 determines that the
なお、本実施例の冷却装置100に備えた、放熱部180の異常を判断する異常判断手段に係る構成は、及びその動作(制御)は、実施例1、2と同様に、他の冷却対象を冷却する液冷方式の冷却装置にも適用可能である。
例えば、プリンタ300に有した4つの画像ステーション10に、それぞれ有した現像装置3の攪拌・搬送部に接触させた冷却ジャケットを有する受熱部との間で、循環する冷却液の熱を、ラジエータと冷却ファンとを有する液冷方式の冷却装置にも適用可能である。
In addition, the structure which concerns on the abnormality judgment means which judges the abnormality of the
For example, the heat of the circulating coolant between the four image stations 10 in the
このように現像装置3の攪拌・搬送部を冷却する冷却装置を設けたプリンタ300でも、利用者が印刷指示を行うパソコン等の端末で設定した用紙の種類によって、定着装置15による定着温度が変わる。このため、プリンタ300内の環境温度が変化に応じて現像装置3の攪拌・搬送部の温度も変化し、受熱部の冷却ジャケットで受熱する熱量も異なってしまう。このため、放熱部のラジエータに流入する冷却液の流入温度が異なってしまい、各気流温度毎の、流入温度やラジエータから流出する冷却液の流出温度の経時変化も異なってしまい、誤った判断を行ってしまうおそれがある。
そして、各現像装置3の攪拌・搬送部を冷却する冷却装置で、放熱部の異常にお有無を判断する場合に、上記したいずれか制御フローを適用することで、用紙Pの種類に応じた、より詳細な判断を行うことができ、誤った判断を行ってしまうことを抑制できる。
As described above, even in the
Then, in the cooling device that cools the stirring / conveying unit of each developing device 3, when determining the presence / absence of abnormality in the heat radiating unit, any one of the above-described control flows is applied, and according to the type of the paper P More detailed determination can be made, and erroneous determination can be suppressed.
上記した本実施形態では、本発明をカラー対応の画像形成装置であるプリンタ300に適用した例について説明したが、本発明はこのような構成に限定されるものではない。
例えば、モノクロ対応の画送形成装置や、複写機や複合機等にも適用可能である。また、電子写真方式の画像形成装置に限らず、冷却液を用いる液冷方式の冷却装置を備えた電子機器全般に適用可能である。
すなわち、冷媒として冷却液を用い、受熱部と放熱部との間で冷却液を循環させる冷却装置であって、放熱部にラジエータ等の熱交換器を有した電子機器全般に適用可能である。
In the above-described embodiment, an example in which the present invention is applied to the
For example, the present invention can also be applied to a monochrome image feed forming apparatus, a copying machine, a multifunction machine, and the like. Further, the present invention is not limited to an electrophotographic image forming apparatus, and can be applied to all electronic devices including a liquid cooling type cooling device using a cooling liquid.
That is, it is a cooling device that uses a coolant as a coolant and circulates the coolant between the heat receiving portion and the heat radiating portion, and can be applied to all electronic devices having a heat exchanger such as a radiator in the heat radiating portion.
以上に説明したものは一例であり、次の態様毎に特有の効果を奏する。
(態様A)
用紙Pなどの冷却対象の熱を直接、又は表側搬送ベルト161を介するなどして間接的に受熱する受熱部140などの受熱部と、該受熱部との間で循環する冷却液などの冷媒の熱を放熱する放熱部180などの放熱部とを備えた冷却装置100などの冷却装置において、前記放熱部で冷媒と熱交換される外気などの空気の、気流温度:T0などの熱交換される前の温度を検出する気流温度センサ151などの空気温度検出手段と、前記受熱部から前記放熱部に流入する冷媒温度を検出する流入温度センサ152などの流入温度検出手段と、前記放熱部から前記受熱部に流出する冷媒温度を検出する流出温度センサ153などの流出温度検出手段と、前記空気温度検出手段、前記流入温度検出手段、及び前記流出温度検出手段の検出結果に基づいて、前記放熱部の異常の有無を判断する異常判定プログラムを有した冷却制御部230などの異常判断手段と、を備えることを特徴とするものである。
What was demonstrated above is an example, and there exists an effect peculiar for every following aspect.
(Aspect A)
The coolant such as a coolant circulating between the heat receiving portion such as the
これによれば、実施例1(乃至3)に説明したように、次のような効果を奏することができる。
受熱部の受熱量が一定、且つ放熱部が正常な場合、放熱部における冷媒の流入温度や流出温度は、冷媒と熱交換される前の空気の温度毎に、放熱部による放熱開始からの経過時間に応じて、それぞれ所定の曲線を描くように変化して一定の温度に収束する。このため、冷却装置は、放熱部で冷媒と熱交換される前の空気の温度に応じた放熱能力を発揮して、冷却対象を十分に冷却する冷却能力を維持することができる。
一方、受熱部の受熱量が一定でもラジエータ181などの熱交換器が目詰まりしたり、ファンユニット185などの送風手段が故障したりした放熱部が異常な場合、冷媒の流入温度や流出温度は、それぞれ上記した所定の曲線とは異なった曲線を描くように変化する。そして、冷却装置は、放熱部で冷媒と熱交換される前の空気の温度に応じた放熱能力を発揮できず、冷却対象を十分に冷却する冷却能力を維持することができなくなる。
According to this, as described in the first embodiment (to 3), the following effects can be obtained.
When the amount of heat received by the heat receiving unit is constant and the heat radiating unit is normal, the refrigerant inflow and outflow temperatures in the heat radiating unit are the elapsed time from the start of heat radiation by the heat radiating unit for each temperature of the air before heat exchange with the refrigerant. Depending on the time, each changes so as to draw a predetermined curve and converges to a certain temperature. For this reason, the cooling device can maintain the cooling capability of sufficiently cooling the object to be cooled by exhibiting the heat dissipation capability according to the temperature of the air before heat exchange with the refrigerant in the heat dissipation portion.
On the other hand, even if the heat receiving amount of the heat receiving unit is constant, if the heat exchanger such as the
そこで、異常判断手段では、例えば、流出温度検出手段の検出結果と、空気温度検出手段の検出結果に対応した放熱部が正常な場合の冷媒の流入温度や流出温度の所定の曲線とから冷媒の予測流入温度を予測する。そして、予測した予測流入温度と、流入温度検出手段の検出結果とを比較することで、放熱部の異常の有無を適切に判断することが可能となる。
したがって、異常判断手段は、冷却装置を用いるプリンタ300などの装置が、放熱部が異常な状態のままで稼動し続けて、ブロッキングなどの不具合が発生する前に、放熱部の異常の有無を判断できる。
よって、受熱部との間で循環する冷媒の熱を、放熱する放熱部の異常に起因した、不具合の発生を抑制可能な冷却装置を提供できる。
Therefore, in the abnormality determination means, for example, from the detection result of the outflow temperature detection means and a predetermined curve of the refrigerant inflow temperature and outflow temperature when the heat dissipating part corresponding to the detection result of the air temperature detection means is normal, Predict the predicted inflow temperature. Then, by comparing the predicted predicted inflow temperature with the detection result of the inflow temperature detecting means, it is possible to appropriately determine whether there is an abnormality in the heat radiating unit.
Accordingly, the abnormality determination means determines whether or not there is an abnormality in the heat radiating unit before a device such as the
Therefore, the cooling device which can suppress generation | occurrence | production of the malfunction resulting from abnormality of the thermal radiation part which thermally radiates the heat | fever of the refrigerant | coolant which circulates between heat receiving parts can be provided.
(態様B)
(態様A)において、異常判定プログラムを有した冷却制御部230などの前記異常判断手段は、流入温度センサ152などの前記流入温度検出手段と流出温度センサ153などの前記流出温度検出手段の検出結果の差分に基づいて、放熱部180などの前記放熱部の異常の有無を判断することを特徴とするものである。
これによれば、実施例1(乃至3)に説明したように、次のような効果を奏することができる。
流入温度検出手段と流出温度検出手段の検出結果の差分から放熱部での放熱能力を数値化して、空気温度検出手段の検出結果に応じた、正常な放熱能力を得られているか否かの判断が行え、放熱部の異常の有無を適切に判断できる。
(Aspect B)
In (Aspect A), the abnormality determination means such as the cooling control unit 230 having the abnormality determination program is the detection result of the inflow temperature detection means such as the
According to this, as described in the first embodiment (to 3), the following effects can be obtained.
Determining whether normal heat dissipation capability is obtained according to the detection result of the air temperature detection means by quantifying the heat dissipation capacity at the heat dissipation part from the difference between the detection results of the inflow temperature detection means and the outflow temperature detection means It is possible to appropriately determine whether there is an abnormality in the heat radiating section.
(態様C)
(態様B)において、放熱部180などの前記放熱部は、ラジエータ181などの熱交換器と、該熱交換器に当たる外気などの空気の流を強制的に発生させるファンユニット185などの送風手段とを有し、異常判定プログラムを有した冷却制御部230などの前記異常判断手段は、前記差分が所定の条件を満たさないとき、前記送風手段の各送風ファン186の回転数などの動作状態から、前記熱交換器、又は前記送風手段のいずれに異常があるかを判断することを特徴とするものである。
これによれば、実施例2(又は3)に説明したように、熱交換器の目詰りと、送風手段の故障等の異常とを区別して判断でき、より詳細な点検箇所を特定して、放熱部のメンテナンス時間を短縮できる。したがって、この冷却装置100などの冷却装置を用いるプリンタ300などの装置のダウンタイムを短縮して稼動率を高めることができる。
(Aspect C)
In (Aspect B), the heat dissipating part such as the
According to this, as explained in Example 2 (or 3), it is possible to distinguish and judge the clogging of the heat exchanger and the abnormality such as the failure of the air blowing means, and specify a more detailed inspection location, Maintenance time of the heat dissipation part can be shortened. Therefore, the downtime of the apparatus such as the
(態様D)
(態様A)乃至(態様C)のいずれかにおいて、異常判定プログラムを有した冷却制御部230などの前記異常判断手段は、気流温度センサ151などの前記空気温度検出手段で検出する温度範囲を区分したL環境、M環境、及びH環境などの複数の温度区分と、該複数の温度区分毎の、前記放熱部が正常に動作している状態で、前記熱交換器に流入する流入温度:Rinなどの媒体温度と前記熱交換器から流出する媒体温度の閾値のプロファイルなどの経時変化情報と、を予め定めて保持し、前記温度検出手段で検出した温度を含む温度区分の前記閾値の経時変化情報と、流入温度センサ152などの前記流入温度検出手段及び流出温度センサ153などの前記流出温度検出手段の検出結果とに基づいて、放熱部180などの前記放熱部の異常の有無を判断することを特徴とするものである。
(Aspect D)
In any one of (Aspect A) to (Aspect C), the abnormality determination unit such as the cooling control unit 230 having the abnormality determination program classifies the temperature range detected by the air temperature detection unit such as the
これによれば、実施例1(乃至3)に説明したように、次のような効果を奏することができる。
温度区分毎の、放熱部が正常な場合の熱交換器から流出する冷媒温度の閾値の経時変化情報と、流出温度検出手段の検出結果とから予測される冷媒の予測流入温度を取得して、この予測流入温度と、流入温度検出手段の検出結果と比較できる。
そして、流入温度検出手段の検出結果が予測流入温度以上の場合には、熱交換器は所定の熱量を放熱しており、熱交換器の流入温度と流出温度の差分が所定の値以上になっていると考えられ、放熱部に異常はないと判断できる。一方、流入温度検出手段の検出結果が予測流入温度よりも小さい場合には、熱交換器は所定の熱量を放熱しておらず、熱交換器の流入温度と流出温度の差分が所定の値より小さくなっていると考えられ、放熱部に異常があると判断することができる。
よって、放熱部の異常の有無を、異常判断手段で行う演算負荷を低減しつつ、適切に判断できる。
According to this, as described in the first embodiment (to 3), the following effects can be obtained.
For each temperature category, obtain the predicted inflow temperature of the refrigerant predicted from the temporal change information of the threshold value of the refrigerant temperature flowing out from the heat exchanger when the heat radiating unit is normal, and the detection result of the outflow temperature detecting means, This predicted inflow temperature can be compared with the detection result of the inflow temperature detecting means.
When the detection result of the inflow temperature detection means is equal to or higher than the predicted inflow temperature, the heat exchanger dissipates a predetermined amount of heat, and the difference between the inflow temperature and the outflow temperature of the heat exchanger is equal to or greater than a predetermined value. It can be judged that there is no abnormality in the heat dissipation part. On the other hand, when the detection result of the inflow temperature detection means is smaller than the predicted inflow temperature, the heat exchanger does not dissipate the predetermined amount of heat, and the difference between the inflow temperature and the outflow temperature of the heat exchanger is less than the predetermined value. It is thought that it has become small, and it can be judged that there is an abnormality in the heat dissipation part.
Therefore, the presence or absence of abnormality of the heat radiating portion can be appropriately determined while reducing the calculation load performed by the abnormality determination means.
(態様E)
(態様A)乃至(態様D)のいずれかにおいて、異常判定プログラムを有した冷却制御部230などの前記異常判断手段は、放熱部180などの前記放熱部に異常が有ると判断したとき、用紙Pなどの前記冷却対象に画像形成などの処理を施す、又は前記冷却対象を備えるプリンタ300などの装置の本体制御部210などの制御手段と通信を行い、前記装置の利用者への表示・操作部220などの通知手段を介して、前記放熱部の異常、又はその異常に関わるより詳細な点検箇所などの情報の通知を行うことを特徴とするものである。
これによれば、実施例1(乃至3)に説明したように、放熱部の異常を利用者に通知して、放熱部のメンテナンス(調査)を促がすことができる。したがって、放熱部の異常を放置した状態で冷却装置を用いる装置の稼動が続けられてブロッキングなどの不具合が発生することを抑制できる。
(Aspect E)
In any one of (Aspect A) to (Aspect D), when the abnormality determination unit such as the cooling control unit 230 having the abnormality determination program determines that there is an abnormality in the heat dissipation unit such as the
According to this, as described in the first embodiment (to 3), it is possible to notify the user of the abnormality of the heat radiating section and to promote maintenance (investigation) of the heat radiating section. Therefore, it is possible to suppress the occurrence of problems such as blocking by continuing the operation of the apparatus using the cooling device in a state where the abnormality of the heat radiating portion is left unattended.
(態様F)
(態様A)乃至(態様E)のいずれかにおいて、異常判定プログラムを有した冷却制御部230などの前記異常判断手段は、流出温度センサ153などの前記流出温度検出手段の流出温度:Routなどの検出結果が、正常状態時のH環境収束流出温度:RoutHe以下であることなどの所定の条件を満たさないとき、用紙Pなどの前記冷却対象に画像形成などの処理を施す、又は前記冷却対象を備えるプリンタ300などの装置の本体制御部210などの制御手段と通信を行い、前記装置の前記冷却対象に関わる各画像形成プロセスなどの動作を中止させることを特徴とするものである。
これによれば、実施例1(乃至3)に説明したように、放熱部の異常を放置した状態で冷却装置を用いる装置の稼動が続けられてブロッキングなどの不具合が発生することを確実に抑制できる。
(Aspect F)
In any one of (Aspect A) to (Aspect E), the abnormality determination means such as the cooling control unit 230 having an abnormality determination program is an outflow temperature of the outflow temperature detection means such as the outflow temperature sensor 153: Rout When the detection result does not satisfy a predetermined condition such as H environment convergence outflow temperature: RoutHe or less in a normal state, the cooling target such as paper P is subjected to processing such as image formation or the cooling target It communicates with control means such as a main body control unit 210 of an apparatus such as a
According to this, as described in the first embodiment (to 3), it is possible to reliably suppress the occurrence of problems such as blocking by continuing the operation of the apparatus using the cooling device while leaving the abnormality of the heat radiating portion left unattended. it can.
(態様G)
(態様E)乃至(態様F)のいずれかにおいて、前記装置が用紙Pなどのシート上にトナー像を転写し、転写したトナー像を前記シート上に加熱定着するプリンタ300などの画像形成装置であることを特徴とするものである。
これによれば、実施例1(乃至3)に説明したように、放熱部180などの放熱部の異常を放置した状態で冷却装置100などの冷却装置を用いる装置の稼動が続けられてブロッキングなどの不具合が発生することを確実に抑制できる。
(Aspect G)
In any one of (Embodiment E) to (Aspect F), an image forming apparatus such as a
According to this, as described in the first embodiment (to 3), the operation of the apparatus using the cooling device such as the
(態様H)
(態様G)において、異常判定プログラムを有した冷却制御部230などの前記異常判断手段は、用紙Pなどの前記シートの厚紙、普通紙、及び薄紙などの種類に応じて、放熱部180などの前記放熱部の異常の有無を判断するときのプロファイルなどの条件を異ならせることを特徴とするものである。
これによれば、実施例3に説明したように、シートの種類(坪量)に応じた、より詳細な判断を行うことができ、誤った判断を行ってしまうことを抑制できる。
(Aspect H)
In (Aspect G), the abnormality determination unit such as the cooling control unit 230 having the abnormality determination program is configured such that the
According to this, as described in the third embodiment, it is possible to make a more detailed determination according to the type (basis weight) of the sheet, and to suppress making an erroneous determination.
(態様I)
(態様G)又は(態様H)において、前記冷却対象が用紙Pなどの前記シートであることを特徴とするものである。
これによれば、実施例3に説明したように、冷却不足のシートが排紙トレイ33などの積載トレイ上に積み重ねられて、ブロッキングが発生することを確実に抑制できる。
(Aspect I)
In (Aspect G) or (Aspect H), the object to be cooled is the sheet such as paper P.
According to this, as described in the third embodiment, it is possible to reliably suppress the occurrence of blocking due to the sheets that are undercooled being stacked on the stacking tray such as the
(態様J)
用紙Pなどのシート上に画像形成を行い、現像装置3の攪拌・搬送部などの装置内の発熱箇所、又はシートを冷却対象とする冷却装置を備えたプリンタ300などの画像形成装置において、前記冷却装置として、(態様A)乃至(態様I)のいづれの冷却装置100などの冷却装置を備えたことを特徴とするものである。
これによれば、本実施形態に説明したように、(態様A)乃至(態様I)のいづれの冷却装置と同様な効果を奏することができる画像形成装置を提供できる。
(Aspect J)
In an image forming apparatus, such as a
According to this, as described in the present embodiment, it is possible to provide an image forming apparatus that can achieve the same effects as any of the cooling devices of (Aspect A) to (Aspect I).
1 感光体
2 光書き込み装置
3 現像装置
4 感光体クリーニング装置
5 帯電装置
10 画像ステーション
11 一次転写ローラ
15 定着装置
21 中間転写ベルト
22 第一張架ローラ
23 第二張架ローラ
24 第三張架ローラ
25 二次転写ローラ
26 クリーニング対向ローラ
27 ベルトクリーニング装置
31 給紙カセット
32 用紙搬送路
33 排紙トレイ
34 手差しトレイ
35 給紙路
36 反転用紙搬送路
41 給紙コロ(給紙カセット)
42 レジストローラ対
43 手差し給紙コロ
100 冷却装置
140 受熱部
141 冷却部材
142 冷却面
143 液流路部
151 気流温度センサ
152 流入温度センサ
153 流出温度センサ
160 表側挟持部
161 表側搬送ベルト
162 表側従動ローラ
170 裏側挟持部
171 裏側搬送ベルト
172 裏側従動ローラ
173 駆動ローラ
180 放熱部
181 ラジエータ
182 液送ポンプ
183 液溜タンク
184 ゴムチューブ
185 ファンユニット
186 送風ファン
190 放熱部ケーシング
191 内部ダクト
192 通過開口部
192a 第一通過開口部
192b 第二通過開口部
194 ファンダクト
194a ファンダクト開口
194b ファン取付け開口
195 外部ダクト
195a 外部ダクト仕切り部材
196 第一外部ダクト部
196a 第一外部開口部
196b 第一外部連通開口部
197 第二外部ダクト部
197a 第二外部開口部
197b 第二外部連通開口部
199 スリットパネル
200 装置本体
210 本体制御部
220 表示・操作部
230 冷却制御部
300 プリンタ
P 用紙
DESCRIPTION OF
42
Claims (8)
前記放熱部で冷媒と熱交換される空気の、熱交換される前の温度を検出する空気温度検出手段と、
前記受熱部から前記放熱部に流入する冷媒温度を検出する流入温度検出手段と、
前記放熱部から前記受熱部に流出する冷媒温度を検出する流出温度検出手段と、
前記放熱部の異常の有無を判断する異常判断手段と、を備え、
前記異常判断手段は、前記空気温度検出手段で検出する温度範囲を区分した複数の温度区分と、該複数の温度区分毎の、前記放熱部が正常に動作している状態で、前記放熱部に有した熱交換器に流入する媒体温度と該熱交換器から流出する媒体温度の閾値の経時変化情報と、を予め定めて保持し、前記空気温度検出手段で検出した温度を含む温度区分の前記閾値の経時変化情報と、前記流入温度検出手段及び前記流出温度検出手段の検出結果の差分とに基づいて、前記放熱部の異常の有無を判断することを特徴とする冷却装置。 In a cooling device comprising a heat receiving part that directly or indirectly receives heat to be cooled, and a heat radiating part that radiates heat of the refrigerant circulating between the heat receiving part,
Air temperature detecting means for detecting the temperature of the heat exchanged with the refrigerant in the heat radiating section before the heat exchange;
Inflow temperature detecting means for detecting a refrigerant temperature flowing into the heat radiating section from the heat receiving section;
Outflow temperature detection means for detecting the refrigerant temperature flowing out from the heat radiating section to the heat receiving section;
Includes an abnormality determination means for determining presence of an abnormality before Symbol radiating portion,
The abnormality determining means includes a plurality of temperature sections that divide a temperature range detected by the air temperature detecting means, and the heat radiating section is in a state where the heat radiating section is operating normally for each of the plurality of temperature sections. A temperature change information of a medium temperature flowing into the heat exchanger and a threshold value of the medium temperature flowing out from the heat exchanger is previously determined and held, and the temperature section including the temperature detected by the air temperature detecting means and aging information in the threshold, the inlet temperature detecting means and the on the basis of the difference between the outflow temperature detection means of the detection result, the cooling apparatus characterized that you determine the presence or absence of abnormality of the heat radiating portion.
前記放熱部は、熱交換器と、該熱交換器に当たる空気の流を強制的に発生させる送風手段とを有し、
前記異常判断手段は、前記差分が所定の条件を満たさないとき、前記送風手段の動作状態から、前記熱交換器、又は前記送風手段のいずれに異常があるかを判断することを特徴とする冷却装置。 The cooling device according to claim 1 , wherein
The heat dissipating part has a heat exchanger and a blowing means for forcibly generating a flow of air hitting the heat exchanger,
The abnormality determining means determines whether the heat exchanger or the air blowing means is abnormal from the operating state of the air blowing means when the difference does not satisfy a predetermined condition. apparatus.
前記異常判断手段は、前記放熱部に異常が有ると判断したとき、前記冷却対象に加熱処理を施す装置又は前記冷却対象を備える装置の制御手段と通信を行い、前記装置の利用者への通知手段を介して、前記放熱部の異常、又はその異常に関わる情報の通知を行うことを特徴とする冷却装置。 The cooling device according to claim 1 or 2 ,
The abnormality determining means, when it is determined that an abnormality in the heat radiating portion is present, notification to the heating to the cooling target process performed apparatus or communicates with the control means of the apparatus comprising the cooling object, the device user The cooling device characterized by notifying the abnormality of the heat radiating section or information relating to the abnormality through the means.
前記異常判断手段は、前記流出温度検出手段の検出結果が、所定の条件を満たさないとき、前記冷却対象に加熱処理を施す装置又は前記冷却対象を備える装置の制御手段と通信を行い、前記装置の前記冷却対象に関わる動作を中止させることを特徴とする冷却装置。 In the cooling device according to any one of claims 1 to 3 ,
The abnormality determination means, the detection result of the outlet temperature detecting means, when not satisfy the predetermined condition, communicates with the control means of the apparatus including the device or the cooling object subjected to a heat treatment to said cooling target, said device The cooling apparatus characterized by stopping the operation related to the cooling object.
前記装置がシート上にトナー像を転写し、転写したトナー像を前記シート上に加熱定着する画像形成装置であることを特徴とする冷却装置。 The cooling device according to claim 3 or 4 ,
A cooling apparatus, wherein the apparatus is an image forming apparatus that transfers a toner image onto a sheet and heat-fixes the transferred toner image onto the sheet.
前記異常判断手段は、前記シートの種類に応じて、前記放熱部の異常の有無を判断するときの条件を異ならせることを特徴とする冷却装置。 The cooling device according to claim 5 , wherein
The cooling device according to claim 1, wherein the abnormality determination unit changes a condition when determining whether or not there is an abnormality in the heat radiating unit according to the type of the sheet.
前記冷却対象が前記シートであることを特徴とする冷却装置。 The cooling device according to claim 5 or 6 ,
The cooling device, wherein the object to be cooled is the sheet.
前記冷却装置として、請求項1乃至7のいずれか一に記載の冷却装置を備えたことを特徴とする画像形成装置。 In an image forming apparatus provided with a cooling device that performs image formation on a sheet and generates heat in the apparatus or a sheet to be cooled,
Wherein as a cooling device, an image forming apparatus comprising the cooling device according to any one of claims 1 to 7.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014035955A JP6270134B2 (en) | 2014-02-26 | 2014-02-26 | Cooling device and image forming apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014035955A JP6270134B2 (en) | 2014-02-26 | 2014-02-26 | Cooling device and image forming apparatus |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015161746A JP2015161746A (en) | 2015-09-07 |
| JP2015161746A5 JP2015161746A5 (en) | 2017-01-12 |
| JP6270134B2 true JP6270134B2 (en) | 2018-01-31 |
Family
ID=54184888
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014035955A Active JP6270134B2 (en) | 2014-02-26 | 2014-02-26 | Cooling device and image forming apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6270134B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105196698B (en) * | 2015-11-03 | 2018-01-02 | 江苏利特尔绿色包装股份有限公司 | Printing machine chill roll constant temperature control box |
| JP6637812B2 (en) * | 2016-03-30 | 2020-01-29 | 株式会社ケーヒン | Semiconductor device |
| JP7316546B2 (en) * | 2019-08-02 | 2023-07-28 | 株式会社リコー | image forming device |
| JP2023119864A (en) * | 2022-02-17 | 2023-08-29 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | Monitor apparatus |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003130524A (en) * | 2001-10-22 | 2003-05-08 | Advantest Corp | Circulating flow monitor of liquid cooling system |
| JP4564828B2 (en) * | 2004-11-15 | 2010-10-20 | 株式会社リコー | Image forming apparatus |
| JP5182073B2 (en) * | 2008-12-25 | 2013-04-10 | 日産自動車株式会社 | Cooling abnormality detection device and cooling abnormality detection method |
| JP5636883B2 (en) * | 2010-11-05 | 2014-12-10 | 株式会社リコー | Cooling device and image forming apparatus |
| JP2011155301A (en) * | 2011-05-02 | 2011-08-11 | Hitachi Plant Technologies Ltd | Cooling system for electronic apparatus |
| JP5818131B2 (en) * | 2011-05-13 | 2015-11-18 | 株式会社リコー | Cooling device and image forming apparatus |
| JP2014035529A (en) * | 2012-08-10 | 2014-02-24 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Cooling device and image forming apparatus |
-
2014
- 2014-02-26 JP JP2014035955A patent/JP6270134B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2015161746A (en) | 2015-09-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6137613B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| US7715747B2 (en) | Image heating device with cooling air circulation | |
| US9285767B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP5223275B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP6270134B2 (en) | Cooling device and image forming apparatus | |
| US20140044462A1 (en) | Cooling device, image forming apparatus including same, and cooling method | |
| US20120282002A1 (en) | Image heating apparatus | |
| JP2015034970A (en) | Cooling device, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP5951118B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus and duct | |
| JP5686207B2 (en) | Recording material cooling apparatus and image forming apparatus | |
| JP6179808B2 (en) | Cooling device and image forming apparatus | |
| US7890002B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus with cooling device and controller permitting image heating during error occurrence | |
| JP6157401B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2008065146A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP6278257B2 (en) | Cooling device and image forming apparatus | |
| US10838338B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus including a chipped part to block the transmission of heat | |
| JP6269622B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP5818131B2 (en) | Cooling device and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2019215428A (en) | Image forming apparatus and fixing device | |
| JP2006267479A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP4397034B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus cooling apparatus and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2016090730A (en) | Conveying device, image forming apparatus, cooling means, and temperature control method | |
| JP6097680B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2019035790A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP7091730B2 (en) | Paper ejection device and image forming device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20161129 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20170207 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20170922 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20170920 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20171106 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20171208 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20171221 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 6270134 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |