JP5789446B2 - MOS type solid-state imaging device and imaging apparatus - Google Patents
MOS type solid-state imaging device and imaging apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5789446B2 JP5789446B2 JP2011174824A JP2011174824A JP5789446B2 JP 5789446 B2 JP5789446 B2 JP 5789446B2 JP 2011174824 A JP2011174824 A JP 2011174824A JP 2011174824 A JP2011174824 A JP 2011174824A JP 5789446 B2 JP5789446 B2 JP 5789446B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- pixels
- pixel
- floating diffusion
- imaging device
- pair
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 title claims description 63
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 claims description 37
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 claims description 27
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 15
- 230000000875 corresponding effect Effects 0.000 description 11
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 10
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003071 parasitic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000003705 background correction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002596 correlated effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006837 decompression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005070 sampling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Solid State Image Pick-Up Elements (AREA)
- Color Television Image Signal Generators (AREA)
Description
本発明は、信号読出回路としてMOSトランジスタ回路を搭載した固体撮像素子とこれを用いた撮像装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a solid-state image sensor on which a MOS transistor circuit is mounted as a signal readout circuit and an image pickup apparatus using the same.
デジタルカメラやカメラ付携帯電話機等の撮像装置に用いられる固体撮像素子は、多画素化が図られ、1000万画素以上を搭載するものも存在する。固体撮像素子の各画素(光電変換素子:フォトダイオード)には、各画素が検出した撮像画像信号を外部に読み出す信号読出回路が設けられる。撮像素子チップに占める信号読出回路の面積を小さくすることで、固体撮像素子の更なる多画素化を図ったり、撮像素子チップの小面積化,小型化を図ったりすることが可能となる。 A solid-state imaging device used in an imaging apparatus such as a digital camera or a camera-equipped mobile phone is increased in number of pixels, and some of them have 10 million pixels or more. Each pixel (photoelectric conversion element: photodiode) of the solid-state imaging device is provided with a signal readout circuit that reads out a captured image signal detected by each pixel to the outside. By reducing the area of the signal readout circuit occupying the image sensor chip, it is possible to further increase the number of pixels of the solid-state image sensor, and to reduce the area and size of the image sensor chip.
例えば、CMOS型の固体撮像素子では、特許文献1の図2に記載されている3トランジスタ構成の信号読出回路や、4トランジスタ構成の信号読出回路が1画素毎に設けられる。信号読出回路として垂直電荷転送路や水平電荷転送路が必要なCCD型固体撮像素子に比べて、CMOS型固体撮像素子は、トランジスタを小さく形成できるため、撮像素子チップに占めるフォトダイオードの面積を広く採れるという利点がある。しかし、特許文献1の図10に例示されている様に、フォトダイオードの脇に設けるトランジスタにも所要の面積が必要である。 For example, in a CMOS type solid-state imaging device, a signal readout circuit having a three-transistor configuration and a signal readout circuit having a four-transistor configuration described in FIG. 2 of Patent Document 1 are provided for each pixel. Compared to a CCD solid-state image sensor that requires a vertical charge transfer path or a horizontal charge transfer path as a signal readout circuit, a CMOS solid-state image sensor can form a smaller transistor, so that the area of the photodiode in the image sensor chip is widened. There is an advantage that it can be taken. However, as illustrated in FIG. 10 of Patent Document 1, the transistor provided on the side of the photodiode also requires a required area.
近年の固体撮像素子は、撮像素子チップの小型化と画素数の多画素化という相反する要求がある。CMOS型固体撮像素子に対しても、信号読出回路の占有面積を削減するために、そのトランジスタ数を減らすことが要求される。 In recent solid-state image sensors, there are conflicting demands for downsizing the image sensor chip and increasing the number of pixels. Also for the CMOS type solid-state imaging device, it is required to reduce the number of transistors in order to reduce the area occupied by the signal readout circuit.
そこで、下記の特許文献2に記載の従来技術では、2つの画素で1つの信号読出回路を共用し、1画素当たりのトランジスタ数の削減を図っている。しかし、2つの画素で1つの信号読出回路を共用する構成でも、まだ、トランジスタ数が多く、更なるトランジスタ数の削減が要求される。
Therefore, in the prior art described in
下記の特許文献3の図9(b)(d)に記載されている従来技術では、最隣接する4画素の中心部分に共通の信号読出部を設け、4画素で1つの信号読出回路を共用化している。4画素で1つの信号読出回路を共用できる構成にすれば、トランジスタ数の削減を図りフォトダイオードの面積を広くとることが可能となる。 In the prior art described in FIGS. 9B and 9D of Patent Document 3 below, a common signal readout unit is provided in the central portion of the four adjacent pixels, and one signal readout circuit is shared by the four pixels. It has become. If one signal readout circuit can be shared by four pixels, the number of transistors can be reduced and the area of the photodiode can be increased.
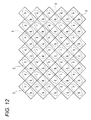
しかし、この特許文献3の技術を、そのまま適用できない画素配列,カラーフィルタ配列の固体撮像素子が存在する。図12に、その固体撮像素子の表面模式図を示す(例えば、特許文献4の図2)。 However, there is a solid-state imaging device having a pixel array and a color filter array to which the technique of Patent Document 3 cannot be applied as it is. FIG. 12 shows a schematic surface view of the solid-state imaging device (for example, FIG. 2 of Patent Document 4).
この固体撮像素子は、奇数行の画素行に対して偶数行の画素行が行方向に1/2画素ピッチずらして配列された所謂ハニカム画素配列となっている。更に、この固体撮像素子は、奇数行の画素で構成される正方格子配列の第1群画素に搭載される三原色のカラーフィルタがベイヤ配列(小文字のr(赤)g(緑)b(青)で示す。)となっている。また、偶数行の画素で構成される正方格子配列の第2群画素に搭載される三原色のカラーフィルタもベイヤ配列(大文字のR(赤)G(緑)B(青)で示す。)となっている。 This solid-state imaging device has a so-called honeycomb pixel arrangement in which even-numbered pixel rows are arranged with a 1/2 pixel pitch shifted in the row direction with respect to odd-numbered pixel rows. Further, in this solid-state imaging device, the three primary color filters mounted on the first group pixels in the square lattice arrangement composed of odd-numbered rows of pixels are arranged in a Bayer arrangement (lower case r (red) g (green) b (blue). It is indicated by.) In addition, the three primary color filters mounted on the second group of pixels in a square lattice array composed of pixels in even rows are also Bayer array (indicated by capital letters R (red) G (green) B (blue)). ing.
この固体撮像素子において、斜めに最隣接する同色のr画素とR画素,g画素とG画素,b画素とB画素が夫々ペア画素(図12の各楕円3で示す2画素)を構成する。そして、このペア画素間で信号電荷の混合読出を行うことで、撮像画像信号の高感度化を図ることができる。また、ペア画素の一方の露光時間と他方の露光時間を変えて混合読出を行うことで、撮像画像信号のダイナミックレンジ拡大を図ることが可能になる。 In this solid-state imaging device, r pixels and R pixels, g pixels and G pixels, and b pixels and B pixels that are diagonally closest to each other constitute a pair pixel (two pixels indicated by each ellipse 3 in FIG. 12). Then, by performing mixed readout of signal charges between the paired pixels, the sensitivity of the captured image signal can be increased. Further, by performing mixed readout while changing one exposure time and the other exposure time of the paired pixels, it is possible to expand the dynamic range of the captured image signal.
図12に示す固体撮像素子に特許文献3の図9(b)(d)の技術を、図12の点線枠4や斜め一行ずらした点線枠5で示す最隣接の4画素に1つの信号読出回路を適用した場合を考える。この場合は、ペア画素の関係が崩れてしまい、固体撮像素子内部での画素混合ができなくなってしまう。
9 (b) and 9 (d) of Patent Document 3 is applied to the solid-state imaging device shown in FIG. 12, and one signal is read out to the four adjacent pixels shown by the dotted line frame 4 and the
図12に示す画素配列及びカラーフィルタ配列の固体撮像素子では、上述した様に、高感度撮影及び広ダイナミックレンジ撮影を行うときに、素子内で画素混合して信号を高速読み出しすることができるため、特許文献3の技術をそのまま適用することはできない。このため、画素混合対象となるペア画素の関係を崩さずに、信号読出回路のトランジスタ数削減を図る必要が生じる。 In the solid-state imaging device having the pixel array and the color filter array shown in FIG. 12, as described above, when performing high-sensitivity imaging and wide dynamic range imaging, pixels can be mixed in the element and signals can be read at high speed. The technique of Patent Document 3 cannot be applied as it is. For this reason, it is necessary to reduce the number of transistors in the signal readout circuit without destroying the relationship of the paired pixels to be mixed with pixels.
本発明の目的は、ペア画素の関係を崩すことなく、信号読出回路のトランジスタ数削減を図ることができるMOS型固体撮像素子及びこの固体撮像素子を搭載した撮像装置を提供することにある。 An object of the present invention is to provide a MOS type solid-state imaging device capable of reducing the number of transistors in a signal readout circuit without destroying the relationship of paired pixels, and an imaging device equipped with the solid-state imaging device.
本発明のMOS型固体撮像素子は、三原色カラーフィルタがベイヤ配列された第1画素群と、前記第1画素群に対し水平方向,垂直方向共に1/2画素ピッチずつずれ三原色のカラーフィルタがベイヤ配列された第2画素群とを備えるMOS型固体撮像素子であって、前記第1画素群に属する1つの第1画素と該第1画素と同色のカラーフィルタを持ち、該第1画素と斜めに隣接する前記第2画素群に属する1つの第2画素との対から成る第1のペア画素と、該ペア画素に対して垂直方向に隣接する第2のペア画素との計4画素により読出単位が形成され、該4画素毎に、1つの共通のMOSトランジスタ回路で構成される信号読出回路が設けられ、前記画素のそれぞれの間には、各画素を分離する格子状の素子分離領域を有し、前記読出単位となる4画素の各々は読出トランジスタを有し、前記第1のペア画素を形成する2つの画素の間を分離する前記素子分離領域と、該第1のペア画素が含まれる前記読出単位の前記第2のペア画素と該第1のペア画素との間を分離する前記素子分離領域との交点位置に、前記2つの画素のそれぞれに設けられた前記読出トランジスタを介して該2つの画素が接続する第1のフローティングディフュージョンを有し、該2つの画素の前記読出トランジスタは、前記第1のフローティングディフュージョンが在る前記素子分離領域の交点位置に臨む角部に設けられ、前記第2のペア画素を形成する2つの画素の間を分離する前記素子分離領域と、該第2のペア画素が含まれる前記読出単位又は該読出単位に対し垂直方向に隣接する読出単位の前記第1のペア画素と該第2のペア画素との間を分離する前記素子分離領域との交点位置に、前記2つの画素のそれぞれに設けられた前記読出トランジスタを介して該2つの画素が接続する第2のフローティングディフュージョンを有し、該2つの画素の前記読出トランジスタは、前記第2のフローティングディフュージョンが在る前記素子分離領域の交点位置に臨む角部に設けられ、前記信号読出回路を構成するリセットトランジスタと出力トランジスタとが前記素子分離領域の異なる格子位置に設けられるものである。 The MOS type solid-state imaging device of the present invention includes a first pixel group in which three primary color filters are arranged in a Bayer array, and a three primary color color filter that is shifted by 1/2 pixel pitch in both the horizontal and vertical directions with respect to the first pixel group. A MOS type solid-state imaging device including a second pixel group arranged, having a first pixel belonging to the first pixel group, and a color filter of the same color as the first pixel, and oblique to the first pixel Is read out by a total of four pixels: a first pair pixel consisting of a pair with one second pixel belonging to the second pixel group adjacent to the second pixel group and a second pair pixel adjacent to the pair pixel in the vertical direction A unit is formed, and a signal readout circuit composed of one common MOS transistor circuit is provided for each of the four pixels. Between each of the pixels, a lattice-shaped element isolation region for separating each pixel is provided. The read unit Has 4 pixels each read transistor serving as said of said read unit and the device isolation region separating between two pixels for forming the first pair pixel, a pair of pixels of the first included The two pixels are connected via the readout transistor provided in each of the two pixels at the intersection of the element isolation region that separates the second pair pixel and the first pair pixel. The read transistor of the two pixels is provided at a corner facing the intersection of the element isolation region where the first floating diffusion exists, and the second pair of pixels the read units adjacent in a direction perpendicular to said read unit or said read out unit includes the element separation region, a pair of pixels of the second to separate between the two pixels forming the The intersection between the isolation region separating between the first pair pixel and the second pair of pixels, the two pixels that are connected to each other through said read transistor provided in each of the two pixels The readout transistor of the two pixels has a second floating diffusion, and is provided at a corner facing the intersection position of the element isolation region where the second floating diffusion exists, and constitutes the signal readout circuit. The reset transistor and the output transistor are provided at different lattice positions in the element isolation region.
また、本発明の撮像装置は、上記記載のMOS型固体撮像素子と、前記ペア画素の画素加算読出を行う制御部とを備えるものである。 An imaging apparatus according to the present invention includes the MOS solid-state imaging device described above and a control unit that performs pixel addition reading of the paired pixels.
本発明によれば、ペア画素の関係を崩すことなく、信号読出回路のトランジスタ数の削減を図ることができ、相対的に画素(フォトダイオード)の受光面積を広げることが可能となる。 According to the present invention, the number of transistors in the signal readout circuit can be reduced without destroying the relationship between the paired pixels, and the light receiving area of the pixel (photodiode) can be relatively widened.
以下、本発明の一実施形態について、図面を参照して説明する。 Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
図1は、本発明の一実施形態に係る固体撮像素子を搭載したデジタルカメラ(撮像装置)の機能ブロック構成図である。図1に示すデジタルカメラ10は、撮影レンズ21aや絞り21b等を備える撮影光学系21と、撮影光学系21の後段に配置された撮像素子チップ22とを備える。
FIG. 1 is a functional block configuration diagram of a digital camera (imaging apparatus) equipped with a solid-state imaging device according to an embodiment of the present invention. A
撮像素子チップ22は、MOSトランジスタ回路で構成された信号読出回路を持つカラー画像撮像用単板式の固体撮像素子22aと、固体撮像素子22aから出力されるアナログの画像データを自動利得調整(AGC)や相関二重サンプリング処理等のアナログ処理するアナログ信号処理部(AFE)22bと、アナログ信号処理部22bから出力されるアナログ画像データをデジタル画像データに変換するアナログデジタル変換部(A/D)22cとを備える。MOSトランジスタ回路は、例えば相補型MOS(CMOS)トランジスタ回路が好適である。
The image
このデジタルカメラ10は更に、後述のシステム制御部(CPU)29からの指示によって撮影光学系21,固体撮像素子22a,アナログ信号処理部22b,A/D22cの駆動制御を行う駆動部(タイミングジェネレータTGを含む)23と、CPU29からの指示によって発光するフラッシュ25とを備える。駆動部23を撮像素子チップ22内に一緒に搭載する場合もある。
The
デジタルカメラ10は更に、A/D22cから出力されるデジタル画像データを取り込み補間処理やホワイトバランス補正,RGB/YC変換処理等の周知の画像処理を行うデジタル信号処理部26と、画像データをJPEG形式などの画像データに圧縮したり逆に伸長したりする圧縮/伸長処理部27と、メニューなどを表示したりスルー画像や撮像画像を表示する表示部28と、デジタルカメラ全体を統括制御するシステム制御部(CPU)29と、フレームメモリ等の内部メモリ30と、JPEG画像データ等を格納する記録メディア32との間のインタフェース処理を行うメディアインタフェース(I/F)部31と、これらを相互に接続するバス34とを備える。システム制御部29には、ユーザからの指示入力を行う操作部33が接続されている。
The
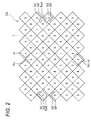
図2は、図1に示す固体撮像素子22aの表面模式図であり、画素配列とカラーフィルタ配列を示している。図2の例では、奇数行の画素行(45度傾けた正方形枠が各画素を示し、各画素上のr(赤),g(緑),b(青)がカラーフィルタの色を表している。)に対して偶数行の画素行を1/2画素ピッチずつずらして配置した、所謂ハニカム画素配列となっている。
FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of the surface of the solid-
奇数行の画素だけみると画素配列は正方格子配列となり、これに三原色カラーフィルタrgbがベイヤ配列されている。また、偶数行の画素だけみても画素配列は正方格子配列となり、これに三原色カラーフィルタRGBがベイヤ配列されている。R=赤,G=緑,B=青であり、斜めに隣接する同色画素がペア画素を形成する。各画素の上(カラーフィルタの上)には、全画素で同一形状のマイクロレンズが搭載される(図示は省略する)。 If only the pixels in the odd rows are viewed, the pixel arrangement is a square lattice arrangement, and the three primary color filters rgb are arranged in a Bayer arrangement. Further, even if only the pixels in even rows are viewed, the pixel arrangement is a square lattice arrangement, and the three primary color filters RGB are arranged in a Bayer arrangement. R = red, G = green, and B = blue, and the same color pixels diagonally adjacent form a pair pixel. On each pixel (on the color filter), microlenses having the same shape are mounted on all pixels (not shown).
本実施形態では、ペア画素2画素と、このペア画素に垂直方向に隣接するペア画素2画素の計4画素に対して1つの信号読出回路が設けられる。この4画素が読出単位画素群となり、読出単位画素群が垂直方向,水平方向に並ぶことになる。図2では、読出単位画素群の一例を点線枠7で囲って示してある。
In the present embodiment, one signal readout circuit is provided for a total of four pixels: two pair pixels and two pair pixels adjacent to the pair pixel in the vertical direction. These four pixels form a readout unit pixel group, and the readout unit pixel group is arranged in the vertical direction and the horizontal direction. In FIG. 2, an example of the readout unit pixel group is surrounded by a
固体撮像素子22aの左辺部分には、図示省略の垂直走査回路等が設けられている。そして、各画素行に対して読出信号やリセット信号を印加する制御信号線がこの垂直走査回路から画素行間を蛇行するように配線される。本実施形態では、4画素に対して1つの信号読出回路が設けられるため、制御信号線としては、4画素(行)夫々への読出信号線tg1,tg2,tg3,tg4と4画素共通のリセット信号線Rsetとが設けられる。
A vertical scanning circuit (not shown) is provided on the left side portion of the solid-
固体撮像素子22aの下辺部分には、図示省略の水平走査回路等が設けられている。この水平走査回路から各画素列に対して、信号出力線osや電源線Vccが画素列間を蛇行する様に配線される。
A horizontal scanning circuit (not shown) is provided on the lower side of the solid-
図3は、図2の読出単位画素群配列に対して信号読出回路を構成する各トランジスタを設けた平面概念図である。図が煩雑になるため、図4に、図3の1つの読出単位画素群(図3の左上のrRペア画素とその垂直方向直下のgGペア画素)とその信号読出回路とを例示する。また、図5は、図4の回路図を示す。 FIG. 3 is a conceptual plan view in which each transistor constituting a signal readout circuit is provided for the readout unit pixel group arrangement of FIG. Since the drawing becomes complicated, FIG. 4 illustrates one readout unit pixel group in FIG. 3 (the rR pair pixel in the upper left of FIG. 3 and the gG pair pixel in the vertical direction thereof) and its signal readout circuit. FIG. 5 shows a circuit diagram of FIG.
まず、図5から説明する。読出単位画素群の4つの画素(フォトダイオード:PD)はペア画素PD1,PD2とペア画素PD3,PD4で構成される。画素PD1は、読出トランジスタTr1を介してFD1(第1フローティングディフュージョン)に接続される。画素PD2は読出トランジスタTr2を介してFD1に接続される。画素PD3は、読出トランジスタTr3を介してFD2(第2フローティングディフュージョン)に接続される。画素PD4は読出トランジスタTr4を介してFD2に接続される。本実施形態の読出トランジスタTr1〜Tr4は、行読出トランジスタや行選択トランジスタとして機能する。 First, FIG. 5 will be described. The four pixels (photodiode: PD) of the readout unit pixel group are composed of paired pixels PD1 and PD2 and paired pixels PD3 and PD4. The pixel PD1 is connected to FD1 (first floating diffusion) via the read transistor Tr1. The pixel PD2 is connected to the FD1 through the readout transistor Tr2. The pixel PD3 is connected to FD2 (second floating diffusion) via the read transistor Tr3. Pixel PD4 is connected to FD2 via readout transistor Tr4. The read transistors Tr1 to Tr4 of this embodiment function as row read transistors and row select transistors.
FD1とFD2とは配線8を通して接続される。配線8で接続された2個のFD1,FD2はドライブトランジスタ(出力トランジスタ)Drのゲート電極OGに配線9で接続される。出力トランジスタDrのドレイン端子は電源(Vcc)接続端子ODに接続される。出力トランジスタDrのソース端子は撮像信号出力端子OSに接続される。
FD1 and FD2 are connected through
電源(Vcc)接続端子ODとFD1との間にはリセットトランジスタRTが設けられる。リセットトランジスタRTのリセットドレインRDが電源接続端子ODに接続される。リセットトランジスタRTのソース領域がFD1、即ち出力トランジスタDrのゲート電極OGに接続される。 A reset transistor RT is provided between the power supply (Vcc) connection terminal OD and FD1. The reset drain RD of the reset transistor RT is connected to the power supply connection terminal OD. The source region of the reset transistor RT is connected to FD1, that is, the gate electrode OG of the output transistor Dr.
リセットトランジスタRTのゲート電極RGが図2で説明したリセット信号線Rsetに接続される。出力トランジスタDrの信号出力端子OSが図2の出力信号線osに接続される。読出トランジスタTr1,Tr2,Tr3,Tr4の各ゲート電極TG1,TG2,TG3,TG4が、夫々図2の読出信号線tg1,tg2,tg3,tg4に接続される。電源接続端子ODが図示しない電源Vccに接続される。 The gate electrode RG of the reset transistor RT is connected to the reset signal line Rset described with reference to FIG. The signal output terminal OS of the output transistor Dr is connected to the output signal line os in FIG. The gate electrodes TG1, TG2, TG3, TG4 of the read transistors Tr1, Tr2, Tr3, Tr4 are connected to the read signal lines tg1, tg2, tg3, tg4 in FIG. A power connection terminal OD is connected to a power source Vcc (not shown).
図4において、PD1,PD2,PD3,PD4は、例えばn型半導体基板の表面pウェル層に、或いはp型半導体の表面部に二次元アレイ状に島状のn領域を形成することで構成される。各n領域間はp領域によって素子分離される。この素子分離領域に形成されるn領域により、図5で説明したFD1,FD2,リセットドレインRD,端子OD,OSが形成される。 In FIG. 4, PD1, PD2, PD3, and PD4 are configured, for example, by forming island-shaped n regions in a two-dimensional array on the surface p-well layer of the n-type semiconductor substrate or on the surface portion of the p-type semiconductor. The Each n region is separated by a p region. FD1, FD2, reset drain RD, and terminals OD, OS described in FIG. 5 are formed by the n region formed in the element isolation region.
図4に示すように、画素PD1,PD2の隣接部の画素PD3側の隅(各画素を格子状に分離する格子の交点部分)にはFD1を形成するn領域が設けられる。PD1のn領域とFD1のn領域との間はp型素子分離帯で分離される。この素子分離帯の上に絶縁膜を介して電極膜が積層されることで、ゲート電極TG1が形成される。PD2のn領域とFD1のn領域との間はp型素子分離帯で分離される。この素子分離帯の上に絶縁膜を介して電極膜が積層されることで、ゲート電極TG2が形成される。 As shown in FIG. 4, an n region for forming FD1 is provided at a corner on the pixel PD3 side of the adjacent portion of the pixels PD1 and PD2 (intersection portion of a lattice separating each pixel in a lattice shape). The n region of PD1 and the n region of FD1 are separated by a p-type element isolation band. A gate electrode TG1 is formed by laminating an electrode film on the element isolation band via an insulating film. The n region of PD2 and the n region of FD1 are separated by a p-type element isolation band. A gate electrode TG2 is formed by laminating an electrode film on the element isolation band via an insulating film.
画素PD3,PD4の隣接部の画素PD2と反対側の隅(上記同様に、格子の交点部分)にはFD2を形成するn領域が設けられる。PD3のn領域とFD2のn領域との間はp型素子分離帯で分離される。この素子分離帯の上に絶縁膜を介して電極膜が積層されることで、ゲート電極TG3が形成される。PD4のn領域とFD2のn領域との間はp型素子分離帯で分離される。この素子分離帯の上に絶縁膜を介して電極膜が積層されることで、ゲート電極TG4が形成される。 An n region for forming FD2 is provided at a corner on the opposite side of the pixel PD2 adjacent to the pixels PD3 and PD4 (similarly, at the intersection of the lattice). The n region of PD3 and the n region of FD2 are separated by a p-type element isolation band. A gate electrode TG3 is formed by laminating an electrode film on the element isolation band via an insulating film. The n region of PD4 and the n region of FD2 are separated by a p-type element isolation band. A gate electrode TG4 is formed by laminating an electrode film on the element isolation band via an insulating film.
画素PD1,PD2の境界部の延長線上の画素PD3の上辺に沿う位置には、リセットドレインRDを構成するn領域が形成される。リセットドレインRDのn領域とFD1のn領域との間のp型素子分離帯の上に絶縁膜を介して電極膜が積層されることで、ゲート電極RG(リセットゲート)が形成される。 An n region constituting the reset drain RD is formed at a position along the upper side of the pixel PD3 on the extension line of the boundary between the pixels PD1 and PD2. A gate electrode RG (reset gate) is formed by laminating an electrode film on the p-type element isolation band between the n region of the reset drain RD and the n region of the FD1 via an insulating film.
画素PD4の下辺(画素PD3と反対側の辺)に沿う部分にはOD端子(出力トランジスタのドレイン端子)となるn領域が形成される。更に、このOD端子のn領域に対して画素PD4の下隅を挟んだ位置に出力端子(出力トランジスタのソース端子)OSとなるn領域が形成される。OD端子とOS端子の両n領域間のp型素子分離帯の上に絶縁膜を介して電極膜が積層されることで、出力トランジスタDrのゲート電極OGが形成される。FD1とFD2とは画素境界部に沿って「く」の字状に形成された配線8で接続される。また、FD2と出力トランジスタDrのゲート電極OGとが配線9で接続される。
An n region serving as an OD terminal (drain terminal of the output transistor) is formed in a portion along the lower side of the pixel PD4 (side opposite to the pixel PD3). Further, an n region that becomes an output terminal (source terminal of the output transistor) OS is formed at a position sandwiching the lower corner of the pixel PD4 with respect to the n region of the OD terminal. A gate electrode OG of the output transistor Dr is formed by laminating an electrode film via an insulating film on the p-type element isolation band between the n regions of the OD terminal and the OS terminal. FD1 and FD2 are connected by a
図4に示す読出単位画素群の構成が、水平方向,垂直方向に繰り返されることで、図3の構成となる。同一水平線上に並ぶ読出単位画素群の各Tri(i=1〜4)のゲート電極TGiが同一読出信号線tgi(i=1〜4)に接続される。また、同一水平線上に並ぶ読出単位画素群のリセットトランジスタRTのゲート電極RGがリセット信号線Rsetに接続される。 The configuration of the readout unit pixel group shown in FIG. 4 is repeated in the horizontal direction and the vertical direction, so that the configuration of FIG. 3 is obtained. The gate electrodes TGi of the Tri (i = 1 to 4) of the readout unit pixel groups arranged on the same horizontal line are connected to the same readout signal line tgi (i = 1 to 4). Further, the gate electrode RG of the reset transistor RT of the readout unit pixel group arranged on the same horizontal line is connected to the reset signal line Rset.
同一垂直線上に並ぶ読出単位画素群の各信号出力端子OSが同一出力信号線osに接続され、同一垂直線上に並ぶ読出単位画素群の各電源接続端子ODが同一電源線Vccに接続される。 The signal output terminals OS of the readout unit pixel groups arranged on the same vertical line are connected to the same output signal line os, and the power connection terminals OD of the readout unit pixel groups arranged on the same vertical line are connected to the same power supply line Vcc.
斯かる構成の固体撮像素子22aにおいて、各読出単位画素群の画素PD1〜PD4には、入射光量に応じた電荷が蓄積される。各画素毎の撮像画像信号を外部に読み出す場合には、読出信号線tgiに読出パルスを印加する。これにより、該当の読出トランジスタTriが導通し、該当画素PDiの信号電荷がFDi(i=1,2)に読み出され、出力トランジスタDrのゲート電極OGに信号電荷が移動する。OD端子に電源電圧Vccを印加すると該当出力トランジスタDrがオン状態となり、出力トランジスタDrのゲート電極OGに印加された信号電荷量に応じた撮像画像信号が出力端子OSに出力される。
In the solid-
各読出トランジスタTr1,Tr2,Tr3,Tr4に印加する読出パルスの印加タイミングをずらすことで、各画素PD1,PD2,PD3,PD4の撮像画像信号を個別に読み出すことができる。 By shifting the application timing of the readout pulse applied to each readout transistor Tr1, Tr2, Tr3, Tr4, the captured image signal of each pixel PD1, PD2, PD3, PD4 can be individually read out.
画素PD1と画素PD2とは同色のカラーフィルタが積層され、画素PD3と画素PD4とにも同色のカラーフィルタが積層されている。このため、読出トランジスタTr1,Tr2に同タイミングで読出パルスを印加する。これにより、画素PD1と画素PD2の各信号電荷が同時にFD1に読み出されて画素混合される。画素混合された信号電荷量に応じた撮像画像信号を出力トランジスタDrから読み出すことで、短時間に画素加算した信号を得ることが可能となる。 The pixel PD1 and the pixel PD2 are stacked with the same color filter, and the pixel PD3 and the pixel PD4 are also stacked with the same color filter. Therefore, a read pulse is applied to the read transistors Tr1 and Tr2 at the same timing. As a result, the signal charges of the pixel PD1 and the pixel PD2 are simultaneously read out to the FD1 and mixed. By reading out the picked-up image signal corresponding to the signal charge amount mixed with the pixels from the output transistor Dr, it is possible to obtain a signal obtained by pixel addition in a short time.
次に、出力トランジスタDrのゲート電極OGに在る信号電荷を、リセットトランジスタRTをオンすることでリセットドレインRDに廃棄する。そして、次のタイミングで読出トランジスタTr3,Tr4に同タイミングで読出パルスを印加する。これにより、画素PD3,PD4の信号電荷を画素混合し、画素加算した撮像画像信号を読み出すことができ、高感度な画像を撮像することが可能となる。 Next, the signal charge in the gate electrode OG of the output transistor Dr is discarded to the reset drain RD by turning on the reset transistor RT. Then, a read pulse is applied to the read transistors Tr3 and Tr4 at the same timing. As a result, the signal charges of the pixels PD3 and PD4 are mixed, and the captured image signal obtained by adding the pixels can be read, and a highly sensitive image can be captured.
上記において、ペア画素の露光開始時点を同じとし、露光終了時点つまり読出トランジスタTr1,Tr2への読出パルスの印加タイミングをずらすことで、画素PD1,PD2の露光時間を変えることができる。これにより、ダイナミックレンジの広い画像を撮像することが可能となる。ペア画素の露光開始タイミングを変え、露光終了タイミングを同じとしても良い。 In the above description, the exposure time of the pixels PD1 and PD2 can be changed by setting the exposure start time of the paired pixels to be the same and shifting the exposure end time, that is, the application timing of the read pulse to the read transistors Tr1 and Tr2. As a result, it is possible to capture an image with a wide dynamic range. The exposure start timing of the paired pixels may be changed and the exposure end timing may be the same.
以上述べた実施形態によれば、読出単位画素群の4画素に6個のトランジスタを設けるだけ、即ち1画素当たり1.5個のトランジスタを設けるだけで、信号読出が可能となり、信号読出回路に要する面積を狭くできる。更に、水平方向のリセット信号線は、2画素行に1本設ければ良くなり、垂直方向の出力信号線,電源線は2画素列に1本ずつ設ければ良くなる。このため、それだけフォトダイオードの面積を広げることが可能となる。 According to the embodiment described above, it is possible to read a signal only by providing six transistors in four pixels of the readout unit pixel group, that is, by providing 1.5 transistors per pixel. The required area can be reduced. Further, it is only necessary to provide one horizontal reset signal line for two pixel rows, and one vertical output signal line and one power supply line for two pixel columns. Therefore, the area of the photodiode can be increased accordingly.
更に、本実施形態では、画素PD1,PD2のゲート電極TG1,TG2を設ける位置、即ち、各画素PD1,PD2の受光面が欠ける位置と、画素PD3,PD4のゲート電極TG3,TG4の位置とが同じとなる。このため、特に画素加算するときの画素〔PD1+PD2〕、〔PD3+PD4〕の光学特性を揃えることができ、シェーディング補正が容易になるという利点がある。 Furthermore, in the present embodiment, the positions where the gate electrodes TG1 and TG2 of the pixels PD1 and PD2 are provided, that is, the positions where the light receiving surfaces of the pixels PD1 and PD2 are missing, and the positions of the gate electrodes TG3 and TG4 of the pixels PD3 and PD4 are determined. It will be the same. For this reason, the optical characteristics of the pixels [PD1 + PD2] and [PD3 + PD4] at the time of pixel addition can be made uniform, and there is an advantage that shading correction becomes easy.
図6は、本発明の別実施形態に係る固体撮像素子の表面概念図である。また、図7は、図6における1つの読出単位画素群を抜き出した図である。図7の読出単位画素群の回路図は図5と同じである。 FIG. 6 is a conceptual diagram of the surface of a solid-state imaging device according to another embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 7 is a diagram in which one readout unit pixel group in FIG. 6 is extracted. The circuit diagram of the readout unit pixel group in FIG. 7 is the same as that in FIG.
本実施形態では、ゲート電極TG1,TG2、FD1、リセットゲートRG、及びリセットドレインRDの位置は、図4に示す実施形態と同じである。しかし、FD2、ゲート電極TG3,TG4、及び出力トランジスタDrの位置が図4とは異なる。図6の例では、FD2を、画素PD3,PD4の境界部の端部(格子の交点部分)において、図4の実施形態とは反対側の端部に設けている。これにより、FD1とFD2を結ぶ配線8の長さは、矩形の画素PD3の一辺の長さとなり、図4の実施形態に比べて半分となっている。
In the present embodiment, the positions of the gate electrodes TG1, TG2, FD1, the reset gate RG, and the reset drain RD are the same as those in the embodiment shown in FIG. However, the positions of FD2, gate electrodes TG3 and TG4, and output transistor Dr are different from those in FIG. In the example of FIG. 6, the FD2 is provided at the end of the boundary between the pixels PD3 and PD4 (intersection of the lattice) at the end opposite to the embodiment of FIG. Thereby, the length of the
更に、FD2の近傍となる各画素PD3,PD4の隅部にゲート電極TG3,TG4が設けられている。また、画素PD3と画素PD4の境界部におけるFD2の有る位置とは反対側の端部に出力トランジスタDrのゲート電極OGとドレインOD(電源端子)とソース端子(出力端子)OSが設けられている。 Furthermore, gate electrodes TG3 and TG4 are provided at the corners of the pixels PD3 and PD4 in the vicinity of the FD2. Further, a gate electrode OG, a drain OD (power supply terminal), and a source terminal (output terminal) OS of the output transistor Dr are provided at an end of the boundary portion between the pixel PD3 and the pixel PD4 opposite to the position where the FD2 is present. .
この実施形態によっても、読出単位画素群に対して設けるトランジスタ数を1画素当たり1.5個に減少でき、画素の受光面積を相対的に広げることが可能となる。更に、本実施形態では、配線8の長さを短くできるので配線8の抵抗分や寄生容量を低減できるため、電荷検出感度が向上して、撮像画像のS/Nが向上し、高感度化も図れる。
Also according to this embodiment, the number of transistors provided for the readout unit pixel group can be reduced to 1.5 per pixel, and the light receiving area of the pixel can be relatively widened. Furthermore, in this embodiment, since the length of the
図8は、本発明の更に別実施形態に係る固体撮像素子の表面概念図である。図9は、図8における1つの読出単位画素群を抜き出した図である。図9の読出単位画素群の回路図は図10となる。図5と図10の違いは、第3フローティングディフュージョンFD3を設けた点と、FD3にリセットトランジスタRT及び出力トランジスタDrを接続した点である。なお、図8の実施形態では、ドレインOD(電源端子)とリセットドレインRDとが兼用されている。 FIG. 8 is a conceptual diagram of the surface of a solid-state imaging device according to still another embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 9 is a diagram in which one readout unit pixel group in FIG. 8 is extracted. A circuit diagram of the readout unit pixel group in FIG. 9 is shown in FIG. The difference between FIG. 5 and FIG. 10 is that a third floating diffusion FD3 is provided and a reset transistor RT and an output transistor Dr are connected to FD3. In the embodiment of FIG. 8, the drain OD (power supply terminal) and the reset drain RD are also used.
本実施形態の読出単位画素群に設けるゲート電極TG1,TG2,TG3,TG4は図7の実施形態と同じであるが、図4の実施形態でFD2を設けた位置(画素PD3と画素PD4の隣接境界部であって画素PD2と反対側の隅部)にFD3を設け、FD1とFD2とFD3とを配線8で接続している。
The gate electrodes TG1, TG2, TG3, and TG4 provided in the readout unit pixel group of this embodiment are the same as those of the embodiment of FIG. 7, but the positions where the FD2 is provided in the embodiment of FIG. 4 (adjacent to the pixel PD3 and the pixel PD4). An FD 3 is provided at a boundary (a corner on the side opposite to the pixel PD 2), and FD 1,
そして、FD3に接続するリセットトランジスタRTのゲート電極RG及びリセットドレインRDを、FD2とFD3とを結ぶ画素境界部の延長線上に設けている。また、矩形の画素PD4のFD2を設けた隅と対角位置に来る隅に、出力トランジスタDrを設けている。そして、この出力トランジスタDrのゲート電極OGとFD3とを配線9で接続している。
Then, the gate electrode RG and the reset drain RD of the reset transistor RT connected to the FD3 are provided on the extension line of the pixel boundary portion connecting the FD2 and the FD3. Further, an output transistor Dr is provided at a corner that is diagonally opposite the corner where the FD2 of the rectangular pixel PD4 is provided. The gate electrode OG and the FD 3 of the output transistor Dr are connected by the
この構成であっても、読出単位画素群に対して設けるトランジスタ数を1画素当たり1.5個に減少でき、画素の受光面積を相対的に広げることが可能となる。FDの数が3箇所と増えるため寄生容量は増えるが、ゲート電極TG1,TG2,TG3,TG4に接続する読出信号線の配線位置と、リセットトランジスタRTに接続するリセット信号線の配置位置とをずらすことが容易となり、設計の自由度が増す。 Even with this configuration, the number of transistors provided for the readout unit pixel group can be reduced to 1.5 per pixel, and the light receiving area of the pixel can be relatively increased. Although the parasitic capacitance increases because the number of FDs increases to three, the position of the read signal line connected to the gate electrodes TG1, TG2, TG3, and TG4 is shifted from the position of the reset signal line connected to the reset transistor RT. And the degree of freedom of design increases.
尚、上述した実施形態では、図2の画素配列,カラーフィルタ配列の固体撮像素子に本発明を適用したが、図2において、偶数行の画素配列はそのままに、奇数行の画素配列における奇数行と偶数行を入れ替えた図11の画素配列,カラーフィルタ配列で構成される各読出単位画素群(一例を点線枠7’で示す。)であっても、これまでと同様に、図4,7,9において左右を反転すれば適用可能である。 In the above-described embodiment, the present invention is applied to the solid-state imaging device having the pixel array and the color filter array in FIG. 2, but in FIG. 2, the odd-numbered row in the odd-numbered pixel array is left unchanged. 4 and 7 in the same manner as before, even in each readout unit pixel group (an example is indicated by a dotted line frame 7 ') constituted by the pixel array and color filter array of FIG. , 9 can be applied if the left and right are reversed.
以上述べた様に、本明細書には以下の事項が開示されている。 As described above, the following items are disclosed in this specification.
開示されたMOS型固体撮像素子は、三原色カラーフィルタがベイヤ配列された第1画素群と、前記第1画素群に対し水平方向,垂直方向共に1/2画素ピッチずつずれ三原色のカラーフィルタがベイヤ配列された第2画素群とを備えるMOS型固体撮像素子であって、同色のカラーフィルタを持つ斜めに隣接した前記第1画素群に属する画素及び前記第2画素群に属する画素(以下、この2つの画素をペア画素という。)及び該ペア画素に対して垂直方向に隣接する前記ペア画素の計4画素を読出単位とし、該4画素毎に、1つの共通のMOSトランジスタ回路で構成される信号読出回路が設けられるものである。 The disclosed MOS type solid-state imaging device includes a first pixel group in which three primary color filters are arranged in a Bayer array, and a three-primary color filter that is shifted by 1/2 pixel pitch in both the horizontal and vertical directions with respect to the first pixel group. A MOS type solid-state imaging device having a second pixel group arranged, and a pixel belonging to the first pixel group and a pixel belonging to the second pixel group (hereinafter, referred to as this) having diagonally adjacent color filters having the same color filter Two pixels are referred to as a pair pixel.) And a total of four pixels, which are adjacent to the pair pixel in the vertical direction, are used as a readout unit, and each of the four pixels is configured by one common MOS transistor circuit. A signal readout circuit is provided.
開示されたMOS型固体撮像素子は、前記読出単位となる4画素に対して設けられる複数のフローティングディフュージョンを備え、前記各フローティングディフュージョンが、配線によって相互に接続されると共に、前記信号読出回路を構成する出力トランジスタのゲートに接続されるものである。 The disclosed MOS type solid-state imaging device includes a plurality of floating diffusions provided for the four pixels serving as the readout unit, and the floating diffusions are connected to each other by wiring and constitute the signal readout circuit Connected to the gate of the output transistor.
開示されたMOS型固体撮像素子は、前記読出単位となる4画素の各々に対して設けられる読出トランジスタと、前記読出単位となる4画素を構成する2つの前記ペア画素のうちの一方である第1のペア画素に対応して設けられる第1のフローティングディフュージョンと、前記読出単位となる4画素を構成する2つの前記ペア画素のうちの他方である第2のペア画素に対応して設けられる第2のフローティングディフュージョンとを備え、前記第1のペア画素は、前記第1のフローティングディフュージョンに、前記第1のペア画素に対応する2つの前記読出トランジスタを介して接続され、前記第2のペア画素は、前記第2のフローティングディフュージョンに、前記第2のペア画素に対応する2つの前記読出トランジスタを介して接続されているものである。 The disclosed MOS type solid-state imaging device is a readout transistor provided for each of the four pixels serving as the readout unit, and one of the two paired pixels constituting the four pixels serving as the readout unit. A first floating diffusion provided corresponding to one pair pixel and a second floating pixel provided corresponding to the other of the two pair pixels constituting the four pixels serving as the readout unit. The first pair of pixels is connected to the first floating diffusion via the two read transistors corresponding to the first pair of pixels, and the second pair of pixels Is connected to the second floating diffusion through the two readout transistors corresponding to the second pair of pixels. It is what is.
開示されたMOS型固体撮像素子は、前記第1のフローティングディフュージョンの前記第1のペア画素に対する位置と、前記第2のフローフィングディフュージョンの前記第2のペア画素に対する位置とが同じであるものを含む。 The disclosed MOS-type solid-state imaging device has the same position of the first floating diffusion with respect to the first pair of pixels and the position of the second floating diffusion with respect to the second pair of pixels. Including.
開示されたMOS型固体撮像素子は、前記信号読出回路を構成するリセットトランジスタは、前記信号読出回路を構成する出力トランジスタのゲートに接続される前記第1のフローティングディフュージョン及び前記第2のフローティングディフュージョンのうち、前記出力トランジスタに最も近いフローフィングディフュージョンとは別のフローティングディフュージョンをソース領域として形成されるものである。 In the disclosed MOS solid-state imaging device, the reset transistor that constitutes the signal readout circuit is configured such that the first floating diffusion and the second floating diffusion that are connected to the gate of the output transistor that constitutes the signal readout circuit. Among them, a floating diffusion different from the floating diffusion closest to the output transistor is formed as a source region.
開示されたMOS型固体撮像素子は、前記読出単位となる4画素に対応して設けられる第3のフローティングディフュージョンを備え、前記第3のフローティングディフュージョンをソース領域として前記信号読出回路のリセットトランジスタが形成されると共に、前記第3のフローティングディフュージョンが前記信号読出回路の出力トランジスタのゲートに接続されるものである。 The disclosed MOS type solid-state imaging device includes a third floating diffusion provided corresponding to the four pixels as the readout unit, and a reset transistor of the signal readout circuit is formed using the third floating diffusion as a source region. In addition, the third floating diffusion is connected to the gate of the output transistor of the signal readout circuit.
開示されたMOS型固体撮像素子は、前記信号読出回路を構成するリセットトランジスタと出力トランジスタとは、前記各画素間を分離する格子状の素子分離領域のうち別の格子位置に設けられるものである。 In the disclosed MOS type solid-state imaging device, the reset transistor and the output transistor constituting the signal readout circuit are provided at different grid positions in the grid-shaped element isolation region that separates the pixels. .
開示されたMOS型固体撮像素子は、前記画素毎に設けられる読出トランジスタは、フローティングディフュージョンが設けられた前記格子の交点位置に臨む該格子の角部に設けられるものである。 In the disclosed MOS type solid-state imaging device, the readout transistor provided for each pixel is provided at a corner of the grid facing the intersection of the grid provided with a floating diffusion.
また、開示された撮像装置は、上記記載のMOS型固体撮像素子と、前記ペア画素の画素加算読出を行う制御部とを備えるものである。 The disclosed imaging apparatus includes the MOS solid-state imaging device described above and a control unit that performs pixel addition reading of the paired pixels.
以上述べた実施形態によれば、4画素毎に1つの信号読出回路で4画素の撮像画像信号を個別に読み出したり、ペア画素の撮像画像信号を素子内で画素加算して読み出したりすることができ、1画素当たりのトランジスタ数を削減して画素(フォトダイオード)の受光面積を広くとることができる。このため、撮像素子チップの小型化と画素の微細化を図っても感度の高い撮像を行うことが可能となる。 According to the embodiment described above, the captured image signal of 4 pixels can be individually read out by one signal readout circuit for every 4 pixels, or the captured image signal of the paired pixels can be read out by adding the pixels within the element. In addition, the number of transistors per pixel can be reduced to increase the light receiving area of the pixel (photodiode). For this reason, it is possible to perform high-sensitivity imaging even if the imaging element chip is downsized and the pixels are miniaturized.
7,7’ 読出単位画素群
8,9 配線
10 デジタルカメラ
22a MOS型固体撮像素子
23 駆動部
29 システム制御部
PD1,PD2 フォトダイオード(読出単位画素群の半分の同色ペア画素)
PD3,PD4 フォトダイオード(読出単位画素群の半分の同色ペア画素)
FD1,FD2,FD3 フローティングディフュージョン
RG リセットトランジスタのリセットゲート
RD リセットトランジスタのリセットドレイン
Dr 出力トランジスタ
OS 出力端子
OD 電源端子
TG1,TG2,TG3,TG4 読出トランジスタ
tg1,tg2,tg3,tg4 読出信号線
Rset リセット信号線
os 出力信号線
Vcc 電源線
7, 7 'readout
PD3, PD4 Photodiode (same color pair pixel that is half of the readout unit pixel group)
FD1, FD2, FD3 Floating diffusion RG Reset transistor reset gate RD Reset transistor reset drain Dr Output transistor OS Output terminal OD Power supply terminal TG1, TG2, TG3, TG4 Read transistor tg1, tg2, tg3, tg4 Read signal line Rset Reset signal Line os Output signal line Vcc Power line
Claims (6)
前記第1画素群に属する1つの第1画素と該第1画素と同色のカラーフィルタを持ち、該第1画素と斜めに隣接する前記第2画素群に属する1つの第2画素との対から成る第1のペア画素と、該ペア画素に対して垂直方向に隣接する第2のペア画素との計4画素により読出単位が形成され、
該4画素毎に、1つの共通のMOSトランジスタ回路で構成される信号読出回路が設けられ、
前記画素のそれぞれの間には、各画素を分離する格子状の素子分離領域を有し、
前記読出単位となる4画素の各々は読出トランジスタを有し、
前記第1のペア画素を形成する2つの画素の間を分離する前記素子分離領域と、該第1のペア画素が含まれる前記読出単位の前記第2のペア画素と該第1のペア画素との間を分離する前記素子分離領域との交点位置に、前記2つの画素のそれぞれに設けられた前記読出トランジスタを介して該2つの画素が接続する第1のフローティングディフュージョンを有し、
該2つの画素の前記読出トランジスタは、前記第1のフローティングディフュージョンが在る前記素子分離領域の交点位置に臨む角部に設けられ、
前記第2のペア画素を形成する2つの画素の間を分離する前記素子分離領域と、該第2のペア画素が含まれる前記読出単位又は該読出単位に対し垂直方向に隣接する読出単位の前記第1のペア画素と該第2のペア画素との間を分離する前記素子分離領域との交点位置に、前記2つの画素のそれぞれに設けられた前記読出トランジスタを介して該2つの画素が接続する第2のフローティングディフュージョンを有し、
該2つの画素の前記読出トランジスタは、前記第2のフローティングディフュージョンが在る前記素子分離領域の交点位置に臨む角部に設けられ、
前記信号読出回路を構成するリセットトランジスタと出力トランジスタとが前記素子分離領域の異なる格子位置に設けられる、MOS型固体撮像素子。 A first pixel group in which three primary color filters are arranged in a Bayer array; and a second pixel group in which color filters of three primary colors are shifted by a ½ pixel pitch in both the horizontal and vertical directions with respect to the first pixel group. A MOS type solid-state imaging device,
From a pair of one first pixel belonging to the first pixel group and one second pixel belonging to the second pixel group having a color filter of the same color as the first pixel and obliquely adjacent to the first pixel A readout unit is formed by a total of four pixels, a first pair of pixels and a second pair of pixels adjacent to the pair of pixels in the vertical direction,
A signal readout circuit composed of one common MOS transistor circuit is provided for each of the four pixels,
Between each of the pixels, there is a lattice-shaped element isolation region that separates the pixels,
Each of the four pixels as the readout unit has a readout transistor,
The element isolation region that separates the two pixels forming the first pair pixel; the second pair pixel of the readout unit including the first pair pixel; and the first pair pixel; A first floating diffusion connected to the two pixels via the readout transistor provided in each of the two pixels, at the intersection position with the element isolation region that separates the two,
The read transistors of the two pixels are provided at corners facing the intersection position of the element isolation region where the first floating diffusion exists,
The element isolation region that separates the two pixels forming the second pair pixel, and the readout unit including the second pair pixel or the readout unit adjacent to the readout unit in the vertical direction The two pixels are connected via the readout transistor provided in each of the two pixels at the intersection of the element isolation region that separates the first pair pixel and the second pair pixel. Having a second floating diffusion
The read transistors of the two pixels are provided at corners facing an intersection position of the element isolation region where the second floating diffusion exists,
A MOS type solid-state imaging device, wherein a reset transistor and an output transistor constituting the signal readout circuit are provided at different lattice positions in the element isolation region.
前記第1のフローティングディフュージョンと前記第2のフローティングディフュージョンとが、配線によって相互に接続されると共に、前記出力トランジスタのゲートに接続されるMOS型固体撮像素子。 The MOS type solid-state imaging device according to claim 1,
The MOS type solid-state imaging device in which the first floating diffusion and the second floating diffusion are connected to each other by wiring and connected to the gate of the output transistor.
前記第1のフローティングディフュージョンの前記第1のペア画素に対する位置と、前記第2のフローティングディフュージョンの前記第2のペア画素に対する位置とが同じであるMOS型固体撮像素子。 The MOS type solid-state imaging device according to claim 1,
A MOS type solid-state imaging device, wherein a position of the first floating diffusion with respect to the first pair of pixels and a position of the second floating diffusion with respect to the second pair of pixels are the same.
前記リセットトランジスタは、前記出力トランジスタのゲートに接続される前記第1のフローティングディフュージョン及び前記第2のフローティングディフュージョンのうちの前記出力トランジスタに最も近いフローティングディフュージョンとは別のフローティングディフュージョンをソース領域として形成されるMOS型固体撮像素子。 The MOS type solid-state imaging device according to claim 1,
The reset transistor is formed with a floating diffusion different from the floating diffusion closest to the output transistor among the first floating diffusion and the second floating diffusion connected to the gate of the output transistor as a source region. MOS type solid-state imaging device.
前記読出単位となる4画素に対応して設けられる第3のフローティングディフュージョンを備え、
前記第3のフローティングディフュージョンをソース領域として前記リセットトランジスタが形成されると共に、前記第3のフローティングディフュージョンが前記出力トランジスタのゲートに接続されるMOS型固体撮像素子。 The MOS type solid-state imaging device according to claim 1,
A third floating diffusion provided corresponding to the four pixels serving as the readout unit;
A MOS type solid-state imaging device in which the reset transistor is formed using the third floating diffusion as a source region, and the third floating diffusion is connected to a gate of the output transistor.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011174824A JP5789446B2 (en) | 2011-08-10 | 2011-08-10 | MOS type solid-state imaging device and imaging apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011174824A JP5789446B2 (en) | 2011-08-10 | 2011-08-10 | MOS type solid-state imaging device and imaging apparatus |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013038312A JP2013038312A (en) | 2013-02-21 |
| JP2013038312A5 JP2013038312A5 (en) | 2014-02-20 |
| JP5789446B2 true JP5789446B2 (en) | 2015-10-07 |
Family
ID=47887613
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011174824A Expired - Fee Related JP5789446B2 (en) | 2011-08-10 | 2011-08-10 | MOS type solid-state imaging device and imaging apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5789446B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104319281B (en) * | 2014-10-28 | 2017-01-25 | 京东方科技集团股份有限公司 | Pixel display method and device |
| CN107529046B (en) * | 2017-02-23 | 2024-03-08 | 思特威(深圳)电子科技有限公司 | Color filter array and image sensor |
| JP2018160558A (en) * | 2017-03-23 | 2018-10-11 | ソニーセミコンダクタソリューションズ株式会社 | Solid-state imaging device and electronic apparatus |
| JP7543159B2 (en) | 2021-02-18 | 2024-09-02 | シャープセミコンダクターイノベーション株式会社 | Solid-state imaging device |
| JPWO2023032416A1 (en) * | 2021-08-31 | 2023-03-09 | ||
| WO2023243237A1 (en) * | 2022-06-15 | 2023-12-21 | ソニーセミコンダクタソリューションズ株式会社 | Solid-state imaging device |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5132102B2 (en) * | 2006-08-01 | 2013-01-30 | キヤノン株式会社 | Photoelectric conversion device and imaging system using photoelectric conversion device |
| JP4341664B2 (en) * | 2006-10-13 | 2009-10-07 | ソニー株式会社 | Solid-state imaging device and imaging device |
| JP2008099073A (en) * | 2006-10-13 | 2008-04-24 | Sony Corp | Solid imaging device and imaging device |
| JP4735702B2 (en) * | 2008-10-22 | 2011-07-27 | ソニー株式会社 | Solid-state imaging device, driving method of solid-state imaging device, and imaging device |
| JP2011015219A (en) * | 2009-07-02 | 2011-01-20 | Toshiba Corp | Solid-state imaging device |
| JP2011054832A (en) * | 2009-09-03 | 2011-03-17 | Panasonic Corp | Amplification type solid imaging element, and method of manufacturing the same |
-
2011
- 2011-08-10 JP JP2011174824A patent/JP5789446B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013038312A (en) | 2013-02-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5290923B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and imaging device | |
| JP5089017B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and solid-state imaging system | |
| JP4457326B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device | |
| JP5537172B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP5241454B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and imaging system using the same | |
| JP5026951B2 (en) | Imaging device driving device, imaging device driving method, imaging device, and imaging device | |
| KR102163310B1 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and camera system | |
| US20140184808A1 (en) | Photoelectric Conversion Device and Imaging Apparatus Having the Photoelectric Conversion Device | |
| US9257465B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and electronic apparatus with increased length of amplifying portion | |
| JP2009038263A (en) | Solid-state imaging element, and electronic information apparatus | |
| JP5789446B2 (en) | MOS type solid-state imaging device and imaging apparatus | |
| JP5526342B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device | |
| JP2012211942A (en) | Solid-state image sensor and image pickup apparatus | |
| JP4724414B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, digital camera, and color image data generation method | |
| JP5358747B2 (en) | Back-illuminated solid-state imaging device, manufacturing method thereof, and imaging apparatus | |
| JP6276297B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and electronic device | |
| TW201630174A (en) | Solid-state image pickup device | |
| WO2010090166A1 (en) | Solid-state image pickup device | |
| JP5874777B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and electronic device | |
| JP5124549B2 (en) | Moving image signal readout method and imaging apparatus for solid-state imaging device | |
| JP5619093B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and solid-state imaging system | |
| TWI795895B (en) | Solid-state imaging device, solid-state imaging device manufacturing method, and electronic apparatus | |
| JP2005175893A (en) | Two-plate type color solid-state image pickup device and digital camera | |
| JP4444990B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device | |
| JP2005210359A (en) | Two-ccd type color solid-state imaging apparatus and digital camera |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140106 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20140106 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20140924 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20140925 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20141125 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150507 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150622 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20150707 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20150803 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5789446 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |