JP5654288B2 - Optical module and high frequency module - Google Patents
Optical module and high frequency module Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5654288B2 JP5654288B2 JP2010187471A JP2010187471A JP5654288B2 JP 5654288 B2 JP5654288 B2 JP 5654288B2 JP 2010187471 A JP2010187471 A JP 2010187471A JP 2010187471 A JP2010187471 A JP 2010187471A JP 5654288 B2 JP5654288 B2 JP 5654288B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- substrate
- optical module
- conductor pattern
- conductor
- signal
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 title claims description 170
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 claims description 250
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 247
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 claims description 135
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 18
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 9
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 claims 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 claims 2
- 229920000106 Liquid crystal polymer Polymers 0.000 claims 1
- 239000004977 Liquid-crystal polymers (LCPs) Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 claims 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 30
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 30
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 30
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 17
- 238000001465 metallisation Methods 0.000 description 17
- 230000008054 signal transmission Effects 0.000 description 12
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 11
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 9
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 8
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 7
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 6
- 239000013307 optical fiber Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000005672 electromagnetic field Effects 0.000 description 5
- 235000011449 Rosa Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium oxide Inorganic materials [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Al+3] PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 3
- PMHQVHHXPFUNSP-UHFFFAOYSA-M copper(1+);methylsulfanylmethane;bromide Chemical compound Br[Cu].CSC PMHQVHHXPFUNSP-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 230000007257 malfunction Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005476 soldering Methods 0.000 description 3
- MCMNRKCIXSYSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zirconium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Zr]=O MCMNRKCIXSYSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000005219 brazing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007493 shaping process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004088 simulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 2
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silver Chemical compound [Ag] BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000003321 amplification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000013405 beer Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013039 cover film Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006355 external stress Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 1
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003199 nucleic acid amplification method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000149 penetrating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000644 propagated effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001902 propagating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000087 stabilizing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035882 stress Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002344 surface layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Optical Couplings Of Light Guides (AREA)
- Semiconductor Lasers (AREA)
- Light Receiving Elements (AREA)
- Optical Communication System (AREA)
Description
本発明は、セラミック基板を利用した光モジュールや高周波モジュールに係り、特に、光モジュールの高周波伝達特性に優れ、光モジュールからの電磁波放射の防止技術に関する。 The present invention relates to an optical module and a high-frequency module using a ceramic substrate, and more particularly to a technique for preventing electromagnetic wave radiation from the optical module, which is excellent in high-frequency transmission characteristics of the optical module.
光通信網は、光信号を伝播するための媒体として光ファイバと、光信号を送受信するための光モジュールによって構成されている。光モジュールは、その筐体内に、電気信号を光信号に、光信号を電気信号に変換するための光電変換部と、制御のための電子素子や電気コネクタ等が搭載されたプリント基板とによって構成される。これら光モジュールの形状は、各ベンダ間で共通化されていることが多く、たとえば10Gbpsを伝送するものでは、XFP、Xenpak、X2、300PINの通称で呼ばれたMSA(Multi Source Agreement)規格で知られ、数社より製品化されている。 The optical communication network includes an optical fiber as a medium for propagating an optical signal and an optical module for transmitting and receiving the optical signal. An optical module is composed of a photoelectric conversion unit for converting an electrical signal into an optical signal and an optical signal into an electrical signal, and a printed circuit board on which electronic elements and electrical connectors for control are mounted. Is done. The shapes of these optical modules are often shared by vendors. For example, in the case of transmitting 10 Gbps, it is known by the MSA (Multi Source Agreement) standard called XFP, Xenpak, X2, 300 PIN. It has been commercialized by several companies.
近年の光モジュールは、レーザ(発光素子)、フォトダイオード(受光素子)といった光電気変換を行う光素子を内部に搭載したパッケージと、パッケージ上の伝送線路と半田接続されたフレキシブル基板とを含んで成される。このフレキシブル基板が、プリント基板上の導体パターンと、半田固着される。一般的に、これら光モジュールのうち、パッケージとフレキシブル基板の結合体を、受光側ではROSA、送信側ではTOSAなどと呼ぶこともある。近年、これらのTOSA・ROSAのうち、10Gbps伝送クラスでは、XMDと呼ばれるMSA規格に対応した光モジュールが数社より製品化されている。なお、このTOSAとROSAを光モジュールと言い、TOSA・ROSAを、ICなどが搭載されたボードに取り付けたものを光トランシーバと指し示す場合もあるが、本特許では、光トランシーバも広義の光モジュールであるとして説明する。 2. Description of the Related Art Recent optical modules include a package in which an optical element that performs photoelectric conversion such as a laser (light emitting element) and a photodiode (light receiving element) is mounted, and a flexible substrate solder-connected to a transmission line on the package. Made. This flexible board is soldered to the conductor pattern on the printed board. In general, among these optical modules, a combination of a package and a flexible substrate may be called ROSA on the light receiving side and TOSA on the transmitting side. In recent years, among these TOSA / ROSA, in the 10 Gbps transmission class, optical modules corresponding to the MSA standard called XMD have been commercialized by several companies. The TOSA and ROSA are referred to as optical modules, and the TOSA / ROSA attached to a board on which an IC is mounted may be referred to as an optical transceiver. In this patent, the optical transceiver is also a broad optical module. It will be described as being.
10Gbpsを伝送する高周波パッケージでは、しばしば、光素子やICに、汚れや水分等が付着するのを防ぐために、気密封止されていることが多く、このようなパッケージには、パッケージ内部と外部の信号伝送にセラミック基板を用いた、パッケージがしばしば用いられる。これらのセラミック基板の代表的な材質として、アルミナやアルミナイトライド等が知られている。 High-frequency packages that transmit 10 Gbps are often hermetically sealed in order to prevent dirt and moisture from adhering to optical elements and ICs. Such packages often include internal and external packages. Packages using ceramic substrates for signal transmission are often used. As typical materials for these ceramic substrates, alumina, aluminum nitride and the like are known.
そして、パッケージ外部のセラミック基板上の信号、グランド、電源パターン等には、リードピンが固着されており、このリードピンはプリント基板やフレキシブル基板上の導体パターンと半田固着される。 A lead pin is fixed to a signal, ground, power supply pattern and the like on the ceramic substrate outside the package, and the lead pin is soldered to a conductor pattern on the printed circuit board or flexible substrate.
このような光モジュールの一例として、特許文献1が開示されている。 Patent Document 1 is disclosed as an example of such an optical module.
特許文献1では、パッケージ外部の積層セラミックス基板の表層に、高周波信号、電源、グランド等の伝送路がパターニングされている。このパターニング上に、リードピンが搭載接続されている。このリードピンの接続強度を高くするために、積層セラミックス端の側面にもメタライズが成されている。すなわち、リードピンを取り付けるために用いる半田金属は、リードピンが搭載されたパターン上だけでなく、側面のメタライズ上にも濡れ広がり、リードピンに外部から応力がかかった場合においても、剥離しづらいという利点を有している。 In Patent Document 1, a transmission path such as a high-frequency signal, a power source, and a ground is patterned on the surface layer of the multilayer ceramic substrate outside the package. On this patterning, lead pins are mounted and connected. In order to increase the connection strength of this lead pin, the side surface of the laminated ceramic end is also metallized. In other words, the solder metal used to attach the lead pin wets and spreads not only on the pattern on which the lead pin is mounted, but also on the metallization on the side surface, and has the advantage that it is difficult to peel off even when external stress is applied to the lead pin. Have.
しかしながら、前述の光モジュールでは、以下の(1)〜(3)が課題であった。
(1)10Gbpsを伝送する光モジュールでは、高周波信号用のパターンとグランドパターンは隣接しているのが一般的であり、これらのパターンにも、強度を保ちながらリードピンを取り付けようとした場合、この信号用の側面メタライズと、グランド用の側面メタライズとの間に、電磁界的な容量結合が起こり、特性インピーダンスが低下してしまう。特に、パッケージに用いているアルミナなどのセラミックは、比誘電率が8以上と大きいため、電気力線はパッケージ内に偏在しやすく容量結合は大きくなってしまう。
(2)側面メタライズはパターン端部(すなわちセラミック端部)にある。したがって、外部のプリント基板やフレキシブル基板上のパターンとリードピンを接続しようとした場合、基板上のパターンと側面メタライズ間にも容量結合が引き起こされ、更なる特性インピーダンスの低下が起きてしまう。
(3)以上の特性インピーダンス低下によって、高周波信号は、側面メタライズ周囲で反射もしくは放射を起こしてしまう。これらの反射、放射は、光モジュールの高周波伝達性能を劣化させてしまう。電磁界の放射に関しては、ボード上の能動電子素子(IC)の誤動作の原因となる。
However, in the above-described optical module, the following (1) to (3) are problems.
(1) In an optical module that transmits 10 Gbps, a high-frequency signal pattern and a ground pattern are generally adjacent to each other. When a lead pin is attached to these patterns while maintaining strength, An electromagnetic capacitive coupling occurs between the signal side metallization and the ground side metallization, and the characteristic impedance is lowered. In particular, ceramics such as alumina used in a package have a large relative dielectric constant of 8 or more, so that electric lines of force are likely to be unevenly distributed in the package, resulting in increased capacitive coupling.
(2) Side metallization is at the pattern edge (ie ceramic edge). Therefore, when an attempt is made to connect a lead pin to a pattern on an external printed board or flexible board, capacitive coupling is also caused between the pattern on the board and the side metallization, and the characteristic impedance is further lowered.
(3) Due to the above characteristic impedance reduction, the high-frequency signal is reflected or radiated around the side metallization. These reflections and radiations deteriorate the high-frequency transmission performance of the optical module. The electromagnetic field radiation causes malfunction of the active electronic device (IC) on the board.
従来の光モジュールは、10Gbps以下の伝送を目的としており、10GHz以下では、これらの反射や放射は問題にならないほど小さかった。しかしながら、近年、20Gbps、さらには40Gbps程度の伝送速度に対応した光モジュール、及び光トランシーバが必要となってきており、10GHz以上の高周波域においても、光モジュール自体の高周波伝達特性を高め、光モジュールからの電磁界放射を防ぐ必要性が出てきた。 The conventional optical module is intended for transmission of 10 Gbps or less, and at 10 GHz or less, these reflections and radiations are so small that they do not become a problem. However, in recent years, an optical module and an optical transceiver corresponding to a transmission speed of about 20 Gbps and further about 40 Gbps have been required, and the high frequency transmission characteristics of the optical module itself are improved even in a high frequency range of 10 GHz or more. There has been a need to prevent electromagnetic field radiation from.
そこで、本発明は、前記従来技術の問題点を解決するためになされたものであり、本発明の目的は、強度等の機械的信頼性を損なうことなく、高周波性能に優れ、セラミック基板を一部に具備した光モジュールと、それを適用した光トランシーバを提供することにある。 Therefore, the present invention has been made to solve the problems of the prior art, and an object of the present invention is to achieve excellent high frequency performance without compromising mechanical reliability such as strength, and to provide a ceramic substrate. An optical module provided in the unit and an optical transceiver to which the optical module is applied.
本発明の前記ならびにその他の目的と新規な特徴は、本明細書の記述及び添付図面によって明らかにする。 The above and other objects and novel features of the present invention will become apparent from the description of this specification and the accompanying drawings.
本願において開示される発明のうち、代表的なものの概要を簡単に説明すれば、下記の通りである。 Of the inventions disclosed in this application, the outline of typical ones will be briefly described as follows.
本発明の光モジュールでは、パッケージの一部が多層セラミック基板によって構成されており、さらに多層セラミック基板の内部または表層には信号が伝播する導体パターンやグランド導体がパターニングされている。この多層セラミック基板を第1の基板と指し示している。これらの光モジュール用のパッケージは、一般的に箱型もしくは同軸型形状を成しているが、目的に応じて形状が変わっても良い。なお、導体パターンとは、セラミック基板上にパターニングされたパターンだけでなく、セラミック基板内のパターン、セラミック基板を貫通するビアやスルーホールも含める。またグランド導体とは、接地導体などとも言われ、高周波信号が伝播する導体パターンの、特性インピーダンスが保つように、信号導体パターンに近接して配置される導体パターンのことを指し、グランド用導体の面積は、高周波信号が伝播する導体パターンの数十倍以上の広さを持つことが多い。またグランド用導体とは、必ずしも、パッケージ外部を覆う金属や金属パターン、もしくは、光モジュールおよび光トランシーバの筐体等と導通が取られている必要は無い。 In the optical module of the present invention, a part of the package is constituted by a multilayer ceramic substrate, and a conductor pattern for transmitting a signal and a ground conductor are patterned inside or on the surface of the multilayer ceramic substrate. This multilayer ceramic substrate is indicated as a first substrate. These packages for optical modules generally have a box shape or a coaxial shape, but the shape may be changed according to the purpose. The conductor pattern includes not only a pattern patterned on the ceramic substrate but also a pattern in the ceramic substrate, a via and a through hole penetrating the ceramic substrate. The ground conductor is also referred to as a ground conductor or the like, and refers to a conductor pattern arranged close to the signal conductor pattern so that the characteristic impedance of the conductor pattern through which a high-frequency signal propagates is maintained. The area often has a width of several tens of times the conductor pattern through which high-frequency signals propagate. The ground conductor does not necessarily need to be electrically connected to a metal or a metal pattern that covers the outside of the package, or the casing of the optical module and the optical transceiver.
さらに、本発明の光モジュールでは、第1の多層セラミック基板の導体パターンと、リードピンと半田等の導体を介して、導通がとられる導体パターンを有した第2の基板が取り付けられる。本発明の光モジュールとは、少なくとも、この第2の基板とパッケージを含めて指しているが、無論、パッケージ、第1、第2の基板と接続された部材等も指しても良い。 Furthermore, in the optical module of the present invention, a second substrate having a conductive pattern of the first multilayer ceramic substrate and a conductive pattern capable of conducting through a lead pin and a conductor such as solder is attached. The optical module of the present invention indicates at least the second substrate and the package, but of course, the package, a member connected to the first and second substrates, and the like may also be indicated.
本発明の光モジュールでは、第1の多層セラミック基板上の導体パターン端には、リードピンの取り付け強度を高めるために、ハーフビア、キャスタレーション等によって側面がメタライズされており、少なくとも一つのグランド用とシグナル用の側面メタライズの位置が信号伝送方向にずれて位置するべく、第1の多層セラミック基板自体に機構が設けられていることを特徴とする。 In the optical module of the present invention, side surfaces of the conductor pattern end on the first multilayer ceramic substrate are metallized by half vias, castellations, etc. in order to increase the mounting strength of the lead pins. The first multilayer ceramic substrate itself is provided with a mechanism so that the position of the side metallization for use is shifted in the signal transmission direction.
すなわち、本構成により効果が得られる原理を以下に述べる。本発明の光モジュールでは、セラミック基板端に設けられた、少なくとも1対の信号とグランドの側面メタライズが隣接することなく配置されており、信号とグランドの側面メタライズ間には比誘電率の低い空気層が多く位置している。また、信号とグランドの側面メタライズ間の距離も長くなる。容量結合とは、一般的に2平行平板間の容量で考えると、εsε0×S/d(εs:比誘電率、ε0:真空の誘電率、S:平板面積、d:距離)に比例する。信号とグランドの側面メタライズの形状は、2平行平板では無いが、本願によって開示される技術によって、2つの側面メタライズ間に空気層が多く位置することで実効的な比誘電率が下がり、また2つの側面メタライズ間の距離が長くなる。 That is, the principle on which the effect can be obtained by this configuration will be described below. In the optical module of the present invention, at least one pair of signals and ground side metallization provided at the end of the ceramic substrate are arranged without being adjacent to each other, and air having a low relative dielectric constant is provided between the signal and ground side metallization. There are many layers. Also, the distance between the signal and ground side metallization is increased. Capacitive coupling is generally considered as the capacitance between two parallel plates. Ε s ε 0 × S / d (ε s : relative permittivity, ε 0 : vacuum permittivity, S: plate area, d: distance ). The shape of the side metallization of the signal and the ground is not two parallel plates, but the effective relative dielectric constant is lowered by the presence of many air layers between the two side metallizations by the technique disclosed in the present application. The distance between the two side metallizations becomes longer.
以上により、2つの側面メタライズ間の容量結合が小さく、特性インピーダンスの低下がおきにくい。また、光モジュールのパッケージに、外部のプリント基板やフレキシブル基板等の第2の基板を接続した場合、信号の側面メタライズと第2の基板上のパターンとの間に容量結合が生じることがなく、特性インピーダンス低下が抑制されている。 As described above, the capacitive coupling between the two side surface metallizations is small, and the characteristic impedance is hardly lowered. In addition, when a second substrate such as an external printed circuit board or a flexible substrate is connected to the optical module package, capacitive coupling does not occur between the side metallization of the signal and the pattern on the second substrate, Reduction in characteristic impedance is suppressed.
本発明によれば、高周波信号の反射や放射の少ない、高周波伝達特性の高い光モジュールを提供することが可能となる。また、本光モジュールからの電磁界放射が抑制されているため、光モジュールおよび光トランシーバ自体の誤動作がなく、性能向上が可能となる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to provide an optical module having a high frequency transmission characteristic with less reflection and radiation of a high frequency signal. In addition, since electromagnetic field radiation from the present optical module is suppressed, there is no malfunction of the optical module and the optical transceiver itself, and performance can be improved.
以下、図面を参照して本発明の実施例を詳細に説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
なお、実施例を説明するための全図において、同一機能を有するものは、その繰り返しの説明は省略する。
<実施例1>
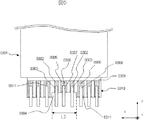
図1は、本発明の実施例1の光モジュール構成を示す斜視図であり、図2は、当該光モジュールの断面図である。また、便宜的に座標軸を図のように設定し、光信号の入出力方向をZ軸とした。なお、図示の都合上、同じ部材がある場合は、符号は代表する部材に付す場合がある。例えば、図1において、セラミック基板0115上の導体パターン0122や、図2においてフレキシブル基板0114上の導体パッド0148などは、代表して1つの部材に符号を付している。図1、2以外の図においても同様とする。
In all the drawings for explaining the embodiments, those having the same function are not described repeatedly.
<Example 1>
FIG. 1 is a perspective view showing an optical module configuration of Embodiment 1 of the present invention, and FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of the optical module. For convenience, the coordinate axes are set as shown in the figure, and the input / output direction of the optical signal is the Z axis. For convenience of illustration, when there are the same members, the reference numerals may be attached to the representative members. For example, in FIG. 1, the
図1において、パッケージの筐体0101は金属でできており、パッケージ内部と外部で、信号、グランド、電源を伝送するために、パッケージの筐体0101の一側面に多層セラミック基板0103が取り付けられている。セラミック基板0115は多層セラミック基板0103の一部である。このセラミック基板0103の材質としては、アルミナ、アルミナイトライド等が知られているが、無論、別材質でもよい。ここで多層セラミック基板0103とセラミック基板0115は本質的に同じであり、セラミック基板0115は、多層セラミック基板0103のうちの複数もしくは1つの層である。また多層セラミック基板0103とセラミック基板0115は、複数の単層セラミック基板が積み重ねられて構成されている。一般的に、単層セラミック基板は、XZ平面を主平面とし、厚さ数百ミクロン程度であることが多い。ここでは、多層セラミック基板0115の主平面上には、信号伝送用の導体パターン0106、電源や調整用の導体パターン0122、グランド用導体パターン0136等がパターニングされている。たとえば、信号用の導体パターン0106上には、リードピン0120が搭載接続されている。リードピン0120を接続する際に、銀ロウ等によってロウ付けされることが多いが、別材質でも構わない。以上は、他の導体パターンとリードピンにおいても同様である。セラミック基板0115上の導体パターン端にはハーフビア0104、0107、0108等があるが、これは、おおよそY軸を主軸とする円柱または多角柱状のビアを半分に割ったハーフビア構造となっている。これらのハーフビアは、例えば信号用の導体パターン0106にリードピン0120を取り付ける場合、接続用の銀ロウなどが導体パターン0106だけでなく、ハーフビア0107にも濡れ広がり、リードピン0120の接続強度を高めている。無論、必ずしも形状はハーフビアである必要はなく、セラミック基板0115側面にメタライズが施されていれば、その機能は同じである。
In FIG. 1, a
信号用のリードピン0120は、隣接して2本取り付けられており、さらに信号用のリードピン0120の両脇には、グランド用のリードピン0121が位置している。すなわち、信号入出力部は、GSSG(GND−SIGNAL−SIGNAL−GNDを略した表記である)配置となっており、これは図示した例が差動信号伝送用であることを示している。 Two signal lead pins 0120 are attached adjacent to each other, and ground lead pins 0121 are positioned on both sides of the signal lead pins 0120. That is, the signal input / output unit has a GSSG (GND-SIGNAL-SIGNAL-GND is abbreviated notation) arrangement, which indicates that the illustrated example is for differential signal transmission.
さて、本光モジュールのセラミック基板0115には、切り欠き部0105が設けられており、Z軸方向に、グランド用のハーフビア0104と、シグナル用のハーフビア0107の位置が、距離L1(図2を参照)だけ、Z軸方向にずらされて位置している。つまり、ハーフビア0104とハーフビア0107との間の一部には空気層が位置することになる。
The
さて、本実施例のフレキブル基板0114上の一つの主平面上には、導体パターン0113、0119や導体パッド0109、0116、0112がパターニングされおり、スルーホール0117、0118、0110、0111によって、フレキシブル基板0114裏面側の導体パターンや導体パッド(図示されず)と電気的コンタクトがなされている。なお、前述した導体パターンと導体パッドはつながっている限り、同一であり、便宜的に呼称を変えているに過ぎない。たとえば、信号伝送用の導体パッド0116と、導体パターン0119は、その基材は同一であり、導通がとられ、つながっている。
Now,
ただし、一般的に導体パッドは、半田等によって他の導体と接続するために設けられた部位を指すことが多く、その基材上面には、半田メッキや金メッキ等が施されることが多い。そして、導体パターンは、電源や信号を伝送するために、フレキシブル基板0114上に長く延在し、その基材上面にはカバー層などによって外気から保護されることが多い。
However, in general, a conductor pad often indicates a portion provided for connecting to another conductor by solder or the like, and the upper surface of the base material is often subjected to solder plating or gold plating. The conductor pattern extends long on the
スルーホール0118にはリードピン0120を挿入し、半田等によって両者を導通固着するために設けられている。以上によって信号は、フレキシブル基板0114上の導体パターン0119と、セラミック基板0115上の導体パターン0106を伝達することが可能となる。
A
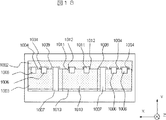
図2は、フレキシブル基板0114をセラミック基板0115に対して固定した時の断面図である。
筐体0101内には、導体パターン0130等がパターニングされ、平板コンデンサ0139、ドライバIC0132等が搭載された基板0127が搭載されている。基板0127上には、光素子0129が搭載された光素子搭載基板0128が搭載されている。
FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view when the
A
以上のように、基板0127は、様々な電子素子を搭載していてよく、様々なパターニングがなされることが多い。また光素子搭載基板0128は、温度コントローラ等の上に搭載されることもある。さらに、本実施例に記載されていなくても、筐体0101内の光素子0129の搭載法には様々な搭載法がある。筐体0101内のパターン、電子素子等の電気的導通には、半田、導電性接着剤のほか、ワイヤ0133等が使われている。
As described above, the
筐体0101には透光性窓0126が取り付けられており、筐体0101内部と外部の光信号の伝播が可能となっている。光ファイバ0124はスリーブ0125に取り付けられ、スリーブ0125は、ホルダ0123に取り付けられている。スリーブ0125は、ジルコニアなどのセラミックが使われることが多い。ホルダ0123自体は、筐体0101に、溶接、半田、接着剤などによって固定されている。ホルダ0123は外部から光ファイバコネクタが取り付けられるようになっている。レンズ0146はレンズホルダ0147に固定されており、光ファイバ0124を通る光信号と、光素子0129の光結合効率を高める役割を担っている。
A
多層セラミック基板0103は、筐体0101内部と外部の電気的な接続をする役割を担っている。多層セラミック基板0103のある層のセラミック基板0134の主平面上には導体パターン0122、0135、0137等がパターニングされているが、特に信号伝送用の導体パターン0137は導体パターン0106と同一主平面上にパターニングされていることが多い。ビア0138、0145によって、グランド用の導体パターン0135、0136は、多層セラミック基板0103内の他層にパターニングされたグランド用導体パターンと接続されている。また、グランドだけでなく、信号、電源、調整用の導体パターンもビアによってセラミック基板0103内もしくは表裏面にパターニングされた導体パターンと導通がとられることがある。
The multilayer
フレキシブル基板0114に設けられたスルーホール0110にリードピン0102が挿入され、半田0149によって固着されるが、他のスルーホールやリードピンも同様である。以上によって、フレキシブル基板0114が、セラミック基板0103に対して位置が固定されていることがわかる。
A
さて、切り欠き部0105が配置されることで、信号用のハーフビア0107とグランド用のハーフビア0104の距離が離間される。更に、自動的に2つのハーフビア中心間を結ぶ直線の間に空気層が位置することとなる。空気の比誘電率は1と、セラミック基板に対して低く、信号用のハーフビア0107とグランド用ハーフビア0104の間の容量結合が十分小さくなるという利点を有している。セラミック基板0103、0115に設ける切り欠き0105の、Z軸方向の距離L1とX軸方向の幅、そして形状によって、以上の容量結合の大きさは変化させることが可能である。
By arranging the
さらに、筐体0101とセラミック基板0103を基材とするパッケージと、フレキシブル基板0114との接続を行うと、もし切り欠き0105が無ければ、信号用のハーフビア0107と、グランド用導体パッド0112との間に大きな容量結合が形成され、特性を劣化させやすい。
Further, when the package having the
しかし、切り欠き部0105によって、信号用のハーフビア0107と、グランド用導体パッド0112との間が離間され、間に空気層が入ることによって、容量結合を小さくすることが可能となっている。セラミック基板0115に設ける切り欠き部0105の、Z軸方向の距離L1とX軸方向の幅、そして形状によって、以上の容量結合は変化させることが可能である。特に本実施例のようにフレキシブル基板0114に設けたスルーホールに、リードピンを挿して固定する場合、距離L1によって、ハーフビア0107とグランド用導体パッド0112との間にできる容量結合をコントロールすることが可能となる。つまり、他の新たな他部材を使用すること無く、フレキシブル基板0114上の導体パッドとハーフビア0106間の距離を規定することが出来、高周波性能をコントロールすることが出来るという利点を有している。
<実施例2>
図3は、本発明の実施例2の光モジュール構成を示す斜視図であり、図4は、該光モジュールの上面図である。
However, the
<Example 2>
FIG. 3 is a perspective view showing an optical module configuration according to the second embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 4 is a top view of the optical module.
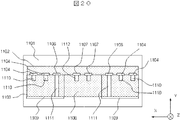
図3では、フレキシブル基板0216の主平面が、リードピン0203、0204、0205、0212、0213の主軸とおおよそ平行である。フレキシブル基板0216とセラミック基板0211の固定を行う場合、例えば、信号用のリードピン0205は、導体パターン0218上と、半田接続されるのが一般的である。このほか、導通接続の方法には、導電性接着剤等が用いられることがある。図3では、フレキシブル基板0216の表面側の導体パターンしか示していないが、実際は、裏面側にも導体パターンがパターニングされるのが普通である。スルーホール0220は表面側のグランド用導体パターン0220と裏面側の導体パターンとを導通させる役割を担っている。無論グランド用導体パターン0220以外の導体パターンにも、スルーホールを設けることは可能であり、これはパターン設計の範疇である。
In FIG. 3, the principal plane of the
図4は、図3に示された光モジュールにおいて、フレキシブル基板0216をセラミック基板0211、0202に対して固定した時の、Y軸正方向から見たときの上面図である。フレキシブル基板0216上の導体パターン0217、0218、0219、0217の上にリードピン0203、0204、0205、0213が配置されるように取り付けられているが、これは使用方法に応じて、逆でも構わず、リードピンがフレキシブル基板0216に対してY軸負方向に位置することもある。
FIG. 4 is a top view of the optical module shown in FIG. 3 when the
セラミック基板0211上の信号伝送用リードピン0205は隣接して配置されており、その隣にはグランド用リードピン0204が位置している。すなわち、セラミック基板0211とフレキシブル基板0216上の信号パターンの配置はGSSG(GND−SIGNAL−SIGNAL−GND)となっており、2本のシグナルラインには差動信号が伝播している。
The signal transmission lead pins 0205 on the
さて、セラミック基板0211には切り欠き部0215が設けられている。そのため、隣接したシグナル用ハーフビア0208とグランド用ハーフビア0209との間の電磁界結合は小さくなり、容量結合が小さくなる。また、シグナル用ハーフビア0208はフレキシブル基板0216に対して、Z軸正方向に後退しているため、シグナル用ハーフビア0208とフレキシブル基板上の導体パターン間の電磁界結合は小さくなる。
Now, the
したがって、フレキシブル基板0216とセラミック基板0211の接続部において、高周波伝送導体パターンの特性インピーダンスは低下することがなく、反射ロスが抑制される。さらに、この反射によって生じる電磁界放射も抑制されるため、本発明の光モジュールを適用した光トランシーバは、高周波ノイズによる誤動作が抑制されている。
Therefore, the characteristic impedance of the high-frequency transmission conductor pattern does not decrease at the connection portion between the
また、フレキシブル基板0216は、リードピン0205等に対してY軸負方向から接続している。すなわち、フレキシブル基板0216とセラミック基板0211はオーバーラップすること無く、フレキシブル基板0216の位置は、セラミック基板0211端面によって規定される。これは、シグナル用ハーフビア0208と、フレキシブル基板0216上の導体パターン間の容量結合を他部材を用いることなく制御することが可能であるとい利点を有している。
The
本実施例をモデリング化し、シミュレーションによる反射計算を行った。シミュレータにはAnsoft社のHFSSを用いている。計算に際しては、厚さ0.2mm、比誘電率5.0の基板に信号とグランド配線をパターニングした基板を、パッケージに使用されるセラミック基板のZ軸正方向に配置し、2つの基板のパターン同士はワイヤによって接続した。また、パッケージに使用されるセラミック基板としては、比誘電率を8.7、信号配線パターンから直下のグランドパターンまでの基板厚を0.75mmとした。セラミック基板上の導体パターンには、幅0.2mm、高さ0.1mmのリードピンを搭載し、リードピンをフレキブル基板上の導体パターンに接触させた。セラミック基板に設けるビアは0.2mmφ(径)の円柱状とした。すなわち、リードピン取り付けに際して、パターン端に配置するハーフビアは、Y軸方向から見ると半円状である。計算では、ハーフビアの高さをシグナル側は0.25mm、グランド側を0.75mmとした。フレキシブル基板は、厚さ50μm、比誘電率3程度のフィルム上下に、導体パターンをパターニングしたものである。また導体パターンの一部を保護するために、一部の導体パターン上にカバーフィルムを接着している。パッケージに使用されるセラミック基板に設ける切り欠き部の形状は直方体とし、そのX軸方向の幅は1.6mm、Y軸方向の高さは0.75mmである。 This example was modeled and reflection calculation was performed by simulation. An simulator HFSS is used for the simulator. In the calculation, a substrate obtained by patterning a signal and ground wiring on a substrate having a thickness of 0.2 mm and a relative dielectric constant of 5.0 is arranged in the positive direction of the Z axis of a ceramic substrate used for a package, and the pattern of two substrates They were connected by wires. Moreover, as a ceramic substrate used for the package, the relative dielectric constant was 8.7, and the substrate thickness from the signal wiring pattern to the ground pattern immediately below was 0.75 mm. A lead pin having a width of 0.2 mm and a height of 0.1 mm was mounted on the conductor pattern on the ceramic substrate, and the lead pin was brought into contact with the conductor pattern on the flexible substrate. The vias provided in the ceramic substrate were cylindrical with a diameter of 0.2 mmφ (diameter). That is, when the lead pin is attached, the half via disposed at the pattern end is semicircular when viewed from the Y-axis direction. In the calculation, the height of the half via is 0.25 mm on the signal side and 0.75 mm on the ground side. The flexible substrate is obtained by patterning a conductor pattern on the upper and lower sides of a film having a thickness of 50 μm and a relative dielectric constant of about 3. Moreover, in order to protect a part of conductor pattern, the cover film is adhere | attached on a part of conductor pattern. The shape of the notch provided in the ceramic substrate used for the package is a rectangular parallelepiped, the width in the X-axis direction is 1.6 mm, and the height in the Y-axis direction is 0.75 mm.
図24にフレキシブル基板側から見た40GHzまでの反射ロスのシミュレーション結果を示す。図の縦軸は、反射ロス(Return loss)を示し、横軸は入力周波数(Frequency)を示している。各グラフは、切り欠き部のZ軸方向深さ(すなわち図4のL1)をパラメータとして変化させた時の周波数と反射ロスとの関係を示している。例えば30GHzにおける反射ロスを見ると、切り欠き部のZ軸方向深さL1が0ミクロンの場合(すなわち切り欠き部がない場合)より、150μmとした場合において、反射ロスが13dB程度改善していることが分かる。但し300μmでは逆に劣化が見られるが、これは信号用リードピン0205が空気中に延在する長さが増え、インダクタンス成分が大きくなってしまい、50オーム系で設計した場合、リードピン周囲の特性インピーダンスが60オーム以上になってしまうためである。
FIG. 24 shows a simulation result of reflection loss up to 40 GHz viewed from the flexible substrate side. In the figure, the vertical axis indicates the return loss, and the horizontal axis indicates the input frequency (Frequency). Each graph shows the relationship between the frequency and the reflection loss when the depth of the notch in the Z-axis direction (that is, L1 in FIG. 4) is changed as a parameter. For example, looking at the reflection loss at 30 GHz, the reflection loss is improved by about 13 dB when the depth L1 of the notch is 0 μm (that is, when there is no notch) and 150 μm. I understand that. However, the degradation is seen at 300 μm, but this is because the length of the
これらの結果は、ハーフビア間の距離、形状、大きさによって変化するが、性能を鑑みるとL1の長さは100ミクロン以上300ミクロン以下が適当である。上限は、リードピン周囲の特性インピーダンスが、他の伝送線路の特性インピーダンスよりも20%以上増えない程度(即ち、120%以下)で規定するのが適当である。 These results vary depending on the distance, shape, and size between the half vias, but considering the performance, the length of L1 is suitably 100 microns or more and 300 microns or less. It is appropriate that the upper limit is defined so that the characteristic impedance around the lead pin does not increase by more than 20% (that is, 120% or less) than the characteristic impedance of other transmission lines.
以上より、本発明による効果が確認された。ここで、セラミック基板に設けた切り欠き部によって生じる、信号とグランド用ハーフビアの、信号伝播方向の位置ずれの大きさ(図4ではZ軸方向の位置ずれ)は、数百μm程度であり、これはセラミック基板のゆがみ、欠けによって生じる程度のものでは無いのは明らかである。
<実施例3>
図5は、本発明の実施例3の光モジュール構成の一部を示す上面図であり、図6は、Z軸負方向から光モジュールの一部を見た側面図であり、図7は、Y軸負方向からみた裏面図である。なお、以下の説明において、実施例1等での説明と重複する部分、例えば、パッケージの筐体やリードピンなどは、図中の符号は付してあるが、説明は省略している。
実施例4以降においても、図中の符号の付し方は、同様とする。
As mentioned above, the effect by this invention was confirmed. Here, the magnitude of the positional deviation in the signal propagation direction between the signal and the ground half via generated by the notch provided in the ceramic substrate (the positional deviation in the Z-axis direction in FIG. 4) is about several hundred μm. Clearly this is not to the extent caused by distortion or chipping of the ceramic substrate.
<Example 3>
FIG. 5 is a top view showing a part of the optical module configuration of Example 3 of the present invention, FIG. 6 is a side view of a part of the optical module viewed from the negative Z-axis direction, and FIG. It is the reverse view seen from the Y-axis negative direction. In the following description, parts that are the same as those described in the first embodiment, such as a package housing and lead pins, are given the reference numerals in the drawing, but the description is omitted.
In the fourth and subsequent embodiments, the same reference numerals are used in the drawings.
セラミック基板0310上には、高周波伝送路として、グランド用導体パターン0311、0305と、信号用導体パターン0302がパターニングされている。すなわち、信号線の並び方は、GSGSG(GND−SIGNAL−GND−SIGNAL−GNDを略した表記)構成となっている。切り欠き部0304によって、両脇のGND用ハーフビア0315とシグナル用のハーフビア0318の位置はZ軸方向にずれており、ハーフビア0315とハーフビア0318間に出来る容量結合を小さくする効果を持っている。
On the
ところで、真ん中のGND用ハーフビア0317は信号用ハーフビア0318とZ軸方向にズレは無い。無論、GND用ハーフビア0317と信号用ハーフビア0318の間に容量結合がつきやすい構成となるが、セラミック基板0310に切り欠き部0304の作成を考えた場合、L2(図5を参照)の幅を広く取ることが出来るため、加工性に優れるという利点を有している。このように加工性を鑑みて、全てのGND用ハーフビアと信号用ハーフビアの位置をずらす必要は必ずしも無く、必要とする性能を鑑み、一部のGND用ハーフビアと信号用ハーフビアの位置をずらす必要がある。
Incidentally, the GND half via 0317 in the middle is not displaced in the Z-axis direction from the signal half via 0318. Of course, capacitive coupling is likely to occur between the GND half via 0317 and the signal half via 0318. However, when creating the
ところで、GND用のハーフビア0315はGND用導体パターン0311とGND用導体パターン0316を接続している。これはセラミック基板0309、0310の表面または内部にパターニングされたGND用導体パターンの電位を安定にさせ、光モジュールが誤動作することが無いようにする効果を持っている。
Incidentally, the GND half via 0315 connects the
図7では、Y軸負方向からセラミック基板0310を見たものであるが、信号用リードピン0303直下付近のGND用導体パターン0316がパターニングされていない部分があり、セラミック基板0310が表出している。これは、ハーフビア0318とGND用導体パターン0316の容量結合を小さくするという効果を有している。
<実施例4>
図8は、本発明の実施例4の光モジュール構成の一部を示す上面図であり、図9は、Z軸負方向から光モジュールの一部を見た側面図である。
セラミック基板0411上には、グランド用の導体パターン0407、電源や調整端子用の導体パターン0403、信号用導体パターン0409等がパターニングされている。高周波信号が伝送する導体パターンは、GSGSG(GND−Signal−GND−Signal−GNDを略した表記)構造となっている。信号用導体パターン0409の端部に配置されたハーフビア0415は、切り欠き部0406によって、GND用ハーフビア0412より距離L3(図8を参照)だけ、Z軸正方向に配置されていることが分かる。これにより、信号用のハーフビア0415とGND用ハーフビア0412との間に出来る電磁界結合が大きくなるのを防いでいる。
In FIG. 7, the
<Example 4>
FIG. 8 is a top view illustrating a part of the configuration of the optical module according to the fourth embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 9 is a side view of a part of the optical module viewed from the negative Z-axis direction.
On the
なお、本実施例において、切り欠き部0406は幅L4(図8を参照)、深さL3の直方体形状になっているが、この形状は必ずしも直方体形状である必要は無い。ハーフビア0415とハーフビア0412とのZ軸方向距離が距離L3だけずれていれば、形状は問わない。
In this embodiment, the
また、切り欠き部0406を作成する方法としては、セラミック基板0402、0411を焼結する前に、セラミック基板を型によってプリフォームし、その後、セラミック基板0402、0411を焼結するのが一般的である。したがって、型の作製の容易さなどによって、L3の長さは100μm以上となることが多い。またL3が数百μm程度の時は、L4がL3以上の長さを有している方が、セラミック基板をプリフォームし易い。
<実施例5>
図10は、本発明の実施例5の光モジュール構成の一部を示す上面図である。
Further, as a method of creating the
<Example 5>
FIG. 10 is a top view illustrating a part of the configuration of the optical module according to the fifth embodiment of the present invention.
セラミック基板0503にはグランド用のリードピン0506、0508が固定されており、その真ん中に信号用のリードピン0507が固定されている。すなわち、信号入出力部は、GSG(GND−SIGNAL−GNDを略した表記)構造となっている。
Ground lead pins 0506 and 0508 are fixed to the
さて、ここで切り欠き部0509は、グランド側に形成されている。すなわち、グランド用導体パターン0512端に設けられたハーフビア(図示されず)は、信号用導体パターン0513端に設けられたハーフビア(図示されず)よりもZ軸正方向に位置している。
Now, the
以上のように、信号用とグランド用のハーフビアの位置がZ軸正方向にずれていれば、信号用導体パターン端に設けられたハーフビアがZ軸正方向にずれていても良い。ハーフビア間の容量結合を小さくするという効果は他実施例と同様にある。
<実施例6>
図11は、本発明の実施例6の光モジュール構成を示す斜視図である。
As described above, if the positions of the signal and ground half vias are shifted in the positive direction of the Z axis, the half vias provided at the signal conductor pattern ends may be shifted in the positive direction of the Z axis. The effect of reducing the capacitive coupling between the half vias is the same as in the other embodiments.
<Example 6>
FIG. 11 is a perspective view showing an optical module configuration according to the sixth embodiment of the present invention.
信号用のリードピンのY軸下方には、切り欠き部0610が設けられている。切り欠き部0610は、セラミック基板0605裏面につながっていない。しかしながら、この切り欠き部0610によって信号用導体パターン端に設けられたハーフビア0608と、グランド用導体パターン端に設けられたハーフビア0607の位置は、Z軸方向にずれている。
A
セラミック基板0605の上面の導体パターンには、それぞれ電源や調整端子用のリードピン0606と、信号用のリードピン0603が固定されている。セラミック基板0605の下面の導体パターンには、グランド用のリードピン0602が固定されている。このように、リードピンの取付位置はセラミック基板の同一面上である必要は必ずしもない。
セラミック基板0605とフレキシブル基板0613の固定は、リードピンをフレキシブル基板0613に設けられたスルーホールに挿入し、半田などによって固着することでなされる。例えば、スルーホール0611にリードピン0603を挿入し、グランド用のスルーホール0619にリードピン0602を挿入することとなる。
<実施例7>
図12は、本発明の実施例7の光モジュール構成を示す斜視図であり、図13は、Y軸正方向から光モジュールを構成するパッケージを見た上面図である。
A
The
<Example 7>
FIG. 12 is a perspective view showing the configuration of the optical module according to the seventh embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 13 is a top view of the package forming the optical module from the positive direction of the Y axis.
セラミック基板0713と0703は、セラミック基板0702の一部である。セラミック基板0713上に信号用導体パターン0712が形成されている。セラミック基板0703上にはグランド用導体パターン0708や、電源および調整端子用の導体パターン0711がパターニングされている。導体パターン0712の主平面は、導体パターン0708、0711の主平面よりも、Y軸方向に高い。無論、図示はしていないが、0708、0711のY軸方向の高さは、導体パターン0712と同等か、高くなるように、セラミック基板0702の形状が調整されていても良い。ただし、信号用の導体パターン0712の特性インピーダンスは、セラミック基板0702の表面および内部にて、おおよそ一定に保たれている。
さて、本実施例の光モジュール構成では、グランド用の導体パターン0708が信号用の導体パターン0712のY軸下方向に位置しているために、信号用導体パターン0712のY軸直下にグランド用導体パターンを配した、マイクロストリップ線路構造を構成しやすい。実際、本実施例では、セラミック基板0702内において、信号用の導体パターン0712のY軸方向直下にグランド用導体パターン0708が位置している部分がある。
In the optical module configuration of this embodiment, since the
信号用導体パターン0712端にあるハーフビア0709の位置は、グランド用導体パターン端0708端にあるハーフビア0707の位置より、Z軸方向正方向にある。これにより、ハーフビア0709と0707間の容量結合は低減されている。
The position of the half via 0709 at the end of the
図13から明らかなように、グランド用導体パターン0708の一部が後退し、セラミック表出部0724をなしている。すなわち、ハーフビア0709の直下には、グランド用導体パターン0708が来ていない構造となっている。これはハーフビア0709とグランド用導体パターン0708との容量結合を防ぐ役割を担っている。
As is clear from FIG. 13, a part of the
さて、本実施例では、フレキシブル基板0723を、セラミック基板0702、0703、0713に対して固定しようとした場合、リードピンを、フレキシブル基板0723に設けたスルーホールに貫通し、半田、導電性接着剤等によって接着する方法が一般的である。例えば、信号用のリードピン0706は、スルーホール0715に貫通し、半田によってリードピンと導体パッド0716とを導通固定する。その際、ハーフビア0709と、フレキシブル基板0723(もしくはフレキシブル基板0723上の導体パターン)との間に、おおよそL7(図13を参照)だけ間隙が出来る。すなわち、信号用の導体パターン0712と導体パッド0716の間に、信号用のリードピン0706が空気中を延在する部分が構成される。そのため、他部材を使用することなく、導体パターン0712と導体パッド0716の間にインダクタンス成分が付加することが可能となり、ハーフビア0709による容量成分増加をキャンセルすることが可能となる。
In this embodiment, when the
なお、本実施例とは逆に、グランド用の導体パターン0708端にあるハーフビア0707を、ハーフビア0709よりZ軸正方向に配することも可能である。しかしながら、グランドにインダクタンス成分を付加することは、グランド用導体パターンの共振などの原因になりやすく、光モジュール全体の安定性を損なう可能性がある。
<実施例8>
図14は、本発明の実施例8の光モジュール構成を示す上面図である。セラミック基板0806は、セラミック基板0802の一部である。セラミック基板0806上には、信号用の導体パターン0807、グランド用の導体パターン0810、電源、調整端子用の導体パターン0809がパターニングされている。これら各種導体パターン上に、リードピン0804、0805、0808等が固着されている。このリードピンのY軸上方からフレキシブル基板0816を搭載する。点線は、フレキシブル基板搭載位置0818である。切り欠き部0815によって、信号用導体パターン端にあるハーフビア(図示せず)の位置は、おおよそ距離L5+L6だけ、グランド用導体パターン端にあるハーフビア(図示せず)の位置よりも、Z軸正方向に位置している。
Contrary to the present embodiment, the half via 0707 at the end of the
<Example 8>
FIG. 14 is a top view showing an optical module configuration according to the eighth embodiment of the present invention. The
したがって、信号用ハーフビアとグランド用ハーフビア間に出来る容量結合は小さくなり、L5+L6によって、その大きさを制御することが可能である。ここで、フレキシブル基板搭載位置0818端は、距離L6だけ、セラミック基板0806端よりZ軸正方向にオーバーラップしている。すなわち、信号用導体パターン0807と導体パッド0819との間に出来るインダクタンス成分は距離L5によって制御することが可能である。
Therefore, the capacitive coupling between the signal half via and the ground half via is reduced, and the size can be controlled by L5 + L6. Here, the flexible
本実施例における光モジュールでは以下の利点がある。
(1)信号伝送用リードピン0805と導体パターン0807の接合長さはL8である。この接合部は一般的に、製造工程において特性インピーダンスばらつきが生じ易いため、特性確保のため、L8の長さは短いほど良く、一般的に数百ミクロン程度が良い。一方、リードピン0804、0808と、導体パターン0809、0810との接合長さはL5+L6+L8であり、その接合強度はL6の長さを長くすることによって強化することが可能となる。すなわち、性能向上を目的にL8を短くしても、L6の長さを調整することで、取り付けているフレキシブル基板0816を介して、リードピンに応力等が加わっても、リードピンが、セラミック基板から剥離するなどの恐れが少ないという利点を有している。つまり性能にも優れ、接続強度も強い光モジュール構成が可能となっている。
(2)グランド用導体パターン0810とフレキシブル基板0816上のグランド用導体パッド0814は、Y軸方向から見た場合、オーバーラップをしている。すなわち、この接続部において、グランドには、リードピンが空気中を延在することによるインダクタンス成分が付加されにくくなり、共振等がおきにくくなる。
(3)他実施例と比して、グランド用導体パターン0810端にあるハーフビア(図示せず)と、信号用導体パターン0807端のハーフビア(図示せず)の位置は、L6だけ多く離間されている。すなわち、信号とグランド用のハーフビア間の容量結合がより小さく抑制されていることがわかる。
The optical module in this embodiment has the following advantages.
(1) The joining length of the signal
(2) The
(3) Compared with the other embodiments, the positions of the half vias (not shown) at the end of the
切り欠き部0815の寸法、形状等は、その目的によって変わる。また、L5とL6の大きさは、その目的に応じて長さが変化する。ただし、切り欠き部0815は、セラミック基板を焼結する前に、型抜き等によって形作るのが一般的であり、型の作製精度を鑑みると、L5+L6は少なくとも100ミクロン以上はある。
<実施例9>
図15は、本発明の実施例9の光モジュール構成の一部を示す上面図であり、図16は、側面図である。
The size, shape, and the like of the
<Example 9>
FIG. 15 is a top view illustrating a part of the configuration of the optical module according to the ninth embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 16 is a side view thereof.
セラミック基板0903は、セラミック基板0902の一部であり、セラミック基板0902上には信号用の導体パターン0911、グランド用導体パターン0909、電源および調整端子用の導体パターン0904がパターニングされている。本実施例の光モジュールでは、これら導体パターン端にキャスタレーション0905、0906、0908が設けられている。キャスタレーションとはセラミック基板に形成された凹であり、その内壁がメタライズされている。すなわち、導体パターンにリードピン(図示せず)を、半田、銀ロウ付けなどによって接続する場合、ロウ材となる金属がキャスタレーション上にも濡れ広がり、リードピンの取り付け強度が強くなるというメリットを有している。
The
本実施例では、セラミック基板0903に切り欠き部0907が設けられることで、信号用のキャスタレーション0908と、グランド用のキャスタレーション0906の間に出来る容量結合が小さくなるという利点を有している。
In this embodiment, the
図16で示したとおり、グランド側のキャスタレーション0906は、上面のグランド導体パターン0909と、下面のグランド導体パターン0912を接続している。これによってセラミック基板0902、0903の内部、表面にパターニングされたグランド導体パターンの電位が揺らぐことが防がれている。図16では、グランド用の導体パターン0912がハーフビア0908の直下ではパターニングされていない。これは、信号用ハーフビア0908と導体パターン0912との間の容量結合を小さくするためである。
<実施例10>
図17は、本発明の実施例10の光モジュール構成の一部を示す上面図であり、図18は、側面図である。
As shown in FIG. 16, the
<Example 10>
FIG. 17 is a top view illustrating a part of the configuration of the optical module according to the tenth embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 18 is a side view thereof.
本実施例では、信号用導体パターン1012端にハーフビア1011、グランド用の導体パターン1009端にハーフビア1007、電源もしくは調整端子用の導体パターン1004端にハーフビア1006が配されている。ハーフビア1006、1007、1011の形状は、円柱を半分に切った形状をなしている。
In this embodiment, a half via 1011 is disposed at the end of the
信号用のハーフビア1011の直下には、グランド用の導体パターン1013が配されている。ハーフビア1011と導体パターン1013間で容量結合が生じやすいが、セラミック基板1003の厚さによって、その影響を小さくすることは可能である。
<実施例11>
図19は、本発明の実施例11の光モジュール構成の一部を示す上面図であり、図20は、側面図である。セラミック基板1103はセラミック基板1102の一部であり、セラミック基板1103上には導体パターン1104、1106、1107がパターニングされており、これらの導体パターン端のセラミック基板1103側面部には、メタライズ1110、1111、1112がパターニングされている。これは、リードピン(図示せず)を取り付ける場合において、接続強度を高めることが可能となる。
A
<Example 11>
FIG. 19 is a top view illustrating a part of the optical module configuration according to the eleventh embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 20 is a side view. The
セラミック基板1103には、切り欠き部1108が設けられており、信号用のメタライズ面1112とグランド用メタライズ面1111のZ軸方向の位置がずれて配置されている。これによって信号用のメタライズ面1112とグランド用のメタライズ面1111との間の容量結合が低減されるという利点を有している。
<実施例12>
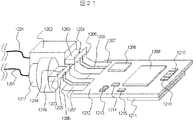
図21に、本発明の実施例12の光モジュールを示す斜視図である。光モジュールは、筐体1216がプリント基板1212に固定されることからなる光受信モジュールと、筐体1202とフレキシブル基板1207から構成される光送信モジュールによって構成されている。この光受信モジュール、光送信モジュール、プリント基板1212、およびそれらに接続された部材を含めて、光トランシーバという呼び方もあるが、本発明では光トランシーバを広義の光モジュールとして含めて扱っている。光受信モジュールの筐体1216は同軸型をなしている。筐体1216にはセラミック基板1203が取り付けられている。セラミック基板1203には切り欠き部1204が設けられており、プリント基板1212とセラミック基板1203の接続部において高周波信号の反射を低減する役割を担っている。
The
<Example 12>
FIG. 21 is a perspective view showing an optical module according to
一方、光送信モジュールにおいては、筐体1202の形状がボックス型を成しており、フレキシブル基板1207はリードピン1205を介して、セラミック基板1203に固定されている。フレキシブル基板1207上の導体パターンは、半田等によってプリント基板1212上の導体パターンに固着されている。さて、セラミック基板1203には切り欠き部1204が設けられているが、これはフレキシブル基板1207とセラミック基板1203接続部における高周波信号の反射を低減している。
On the other hand, in the optical transmission module, the
プリント基板1212上には、電子素子1208、1209、1210、1211、1213,1214,1215等が搭載されており、これらは、増幅作用、波形整形作用、調整機能を伴った能動素子がパッケージングされたものであるか、チップコンデンサ、インダクタ、抵抗などに代表される受動素子である。プリント基板1212の裏面には電気コネクタ1211が取り付けられている。この電気コネクタは、ルータ、サーバなどに代表される伝送装置のボードとの電気インターフェースをなしている。
On the printed
さて、本実施例では、光モジュールを構成するセラミック基板1203に切り欠き部1204を設けることで、接続部における高周波信号の反射を低減している。
高周波基板の反射は、例えば、フレキシブル基板1207の信号用導体パターンを往復し、共振することで、光トランシーバ内にノイズとして放出される。すなわち、高周波反射を引き起こすことになる。これらのノイズは、例えば、プリント基板1212上に搭載された電子素子1209の誤動作などを引き起こしてしまう。すなわち、切り欠き部1204を設けることは図21で示した光モジュール全体の性能を向上させるという利点を有している。
<実施例13>
In the present embodiment, the
The reflection of the high-frequency substrate is emitted as noise in the optical transceiver, for example, by reciprocating the signal conductor pattern of the
<Example 13>
図22に、本発明の実施例13の光モジュールと高周波モジュールを示す斜視図を示す。筐体1301などで構成される光モジュール1327とセラミック基板1322などによって構成される高周波モジュール1328は、フレキシブル基板1315によって接続されている。光モジュール1327は、送信または受信光モジュールであって、筐体1301内には、光素子と電子素子が内包されている。筐体にはファイバホルダ1302が取り付けられており、光信号の入出力は光ファイバ1303によって行われる。筐体1301はセラミックによって構成されており、材質はアルミナ、アルミナイトライド、LTCCなどが使われている。筐体1301にはセラミック基板1304が取り付けられており、表面または内装に導体パターンがパターニングされている。セラミック基板1304表面には、信号入出力用導体パターンとして、一つの信号用導体パターン1305と、両サイドに2つのグランド導体パターン1306がパターニングされ、リードピン1309、1310が固着されている。これらのリードピンは、フレキシブル基板1315上の導体パターンと半田、導電性接着剤、金属によって固着されている。
In FIG. 22, the perspective view which shows the optical module and high frequency module of Example 13 of this invention is shown. An
例えば、信号用の導体パターン1314は、リードピン1310に固着されている。セラミック基板1304には切り欠き部1308が設けられている。これによって信号用の導体パターン1305とグランド用導体パターン1309の端に配置されたハーフビアや側面メタライズ(図示されず)の位置は、おおよそ信号伝送方向にずれて配置されており、セラミック基板1304とフレキシブル基板1314との接続部において高周波伝送特性が優れるという利点を有している。
For example, the
一方、高周波モジュール1328はセラミック基板1322を筐体として使用している。セラミック基板の表裏面もしくは内部には導体パターンがパターニングされている。さらに目的によってセラミック基板1322内には電子素子が内包されており、例えば、ドライバ、増幅IC、波形整形IC、シリアルパラレル変換IC、コントロールIC等の能動素子の他、チップコンデンサ、チップインダクタ、チップ抵抗等などの受動素子が搭載されている。セラミック基板1322の表面には、導体パターンがパターニングされており、フレキシブル基板を接続にはリードピンが取り付けられている。例えば、信号用導体パターン1321上にはリードピン1316が取り付けられている。セラミック基板1322には切り欠き部1320が設けられている。そのため、信号用導体パターン1321端に設けられたハーフビア(図示されず)と、グランド用導体パターン1318端に設けられたハーフビア(図示されず)の位置は信号伝送方向にずれて配置されている。
On the other hand, the high frequency module 1328 uses a
セラミック基板1322の下面には導体パターンがパターニングされており、プリント基板1324との固着導通には半田のボールグリッドアレイ1323によって行われている。プリント基板1324には電子素子1325、1326等が搭載される。
A conductive pattern is patterned on the lower surface of the
以上で説明したように、本発明は、光モジュールおよび高周波モジュールに適用され、その高周波特性に優れるという利点を有している。
<実施例14>
As described above, the present invention is applied to an optical module and a high-frequency module, and has an advantage of excellent high-frequency characteristics.
<Example 14>
図23に本発明の実施例14の高周波モジュールを示す斜視図を示す。高周波モジュールはセラミック基板1401から成り、内部に電子素子を内包し、セラミック基板の表裏面および内部には導体パターンがパターニングされている。
セラミック基板裏面には、信号用導体パターン1405、グランド用導体パターン1407、電源や制御端子用導体パターン1406がパターニングされる。これらの導体パターン上には、リードピン1402、1403、1404、1412等が固着されている。これらリードピンの固着強度を高めるために、それぞれの導体パターン端にはハーフビアが配置されている。例えば、信号用導体パターン1405のパターン端にはハーフビア1408が配置されており、リードピン1404の取り付け強度を高めている。セラミック基板1401には切り欠き部1411が設けられており、信号用のハーフビア1408とグランド用のハーフビア1409の位置は信号伝送方向にずれて配置されている。これは、高周波伝送性能を高める役割を担っている。
FIG. 23 is a perspective view showing the high-frequency module according to Embodiment 14 of the present invention. The high-frequency module is composed of a
On the back surface of the ceramic substrate, a
プリント基板1413には信号用の導体パターン1418、グランド用の導体パターン1415、信号や制御用導体パターン1416がパターニングされており、セラミック基板1401をプリント基板1413に固着する際には、リードピン1402、1403、1404、1412等を半田もしくは導電性接着剤もしくは金属によって固着する。
The printed
プリント基板1413上には、ボールグリッドアレイ1420を用いて電子素子1419が搭載されている。また半田や導電性接着剤によって電子素子1421、1422等が、プリント基板1413上に搭載されている。
以上より、本発明は高周波モジュールに適用され、その高周波的特性を高めることが可能となる。
An electronic element 1419 is mounted on the printed
As described above, the present invention is applied to a high-frequency module, and its high-frequency characteristics can be improved.
0101,0201,0301,0401,0501,0601,0701,0801,0901,1001,1101,1202,1301…筐体、
0102,0120,0121,0203,0204,0205,0212,0213,0303,0307,0308,0312,0404,0405,0410,0504,0505,0506,0507,0508,0602,0603,0606,0706,0805,0808,1309,1310,1316,1317,1402,1403,1404,1412…リードピン、
0103,0115,0134,0202,0309,0310,0402,0411,0502,0503,0604,0605,0702,0703,0713,0802,0902,0903,1002,1003,1102,1103,1203,1205,1304,1322,1401…セラミック基板、
0104,0107,0108,0206,0208,0210,0211,0314,0315,0318,0413,0415,0607,0608,0609,0704,0705,0707,0710,1006,1007,1011,1408,1409,1410…ハーフビア、
0106,0113,0119,0122,0130,0131,0135,0136,0137,0138,0140,0141,0142,0144,0145,0207,0209,0214,0217,0218,0219,0222,0223,0302,0305,0306,0311,0313,0316,0317,0403,0407,0408、0511,0714,0811,0910,1008,1105…ビア、
0409,0412,0414,0510,0512,0513,0614,0618,0708,0709,0711,0712,0721,0722,0804,0806,0807,0809,0810,0817,0904,0909,0911,0912,1004,1009,1012,1013,1104,1106,1107,1109,1110,1206,1305,1306,1307,1314,1318,1319,1321,1405,1406,1407,1415,1416,1418…導体パターン、
0105,0215,0304,0406,0509,0610,0815,0907,1010,1108,1204,1308,1320,1411…切り欠き部、
0109,0112,0116,0148,0612,0615,0617,0716,0717,0719,0813,0814,0819,1312…導体パッド、
0110,0111,0117,0118,0220,0611,0616,0715,0718,0720,0812,1311,1313,1414,1417…スルーホール、
0114,0216,0613,0723,0816,1207,1315…フレキシブル基板、
0123,0221,0803…ホルダ、
0124,1303…光ファイバ、0149…半田、
0125…スリーブ、0126…透光性窓、0127…基板、0128…光素子搭載基板、0129…光素子、0132…ドライバIC、0133…ワイヤ、0139…平板コンデンサ、0143…チップサーミスタ、0146…レンズ、0147…レンズホルダ、
0724…セラミック表出部、0818…フレキシブル基板搭載位置、0905,0906,0908…キャスタレーション、1111,1112…メタライズ、1208,1209,1210,213,1214,1215,1325,1326,1419,1421,1422…電子素子、1211…電気コネクタ、1212,1324,1413…プリント基板、1、1216…ステム、1217,1302…ファイバホルダ、1323,1420…ボールグリッドアレイ、1327…光モジュール、1328…高周波モジュール。
0101, 0201, 0301, 0401, 0501, 0601, 0701, 0801, 0901, 1001, 1101, 1202, 1301 ... casing,
0102, 0120, 0121, 0203, 0204, 0205, 0212, 0213, 0303, 0307, 0308, 0312, 0404, 0405, 0410, 0504, 0505, 0506, 0507, 0508, 0602, 0603, 0606, 0706, 0805, 0808, 1309, 1310, 1316, 1317, 1402, 1403, 1404, 1412 ... lead pins,
0103, 0115, 0134, 0202, 0309, 0310, 0402, 0411, 0502, 0503, 0604, 0605, 0702, 0703, 0713, 0802, 0902, 0903, 1002, 1003, 1102, 1103, 1203, 1205, 1304, 1322, 1401 ... ceramic substrate,
0104,0107,0108,0206,0208,0210,0211,0314,0315,0318,0413,0415,0607,0608,0609,0704,0705,0707,0710,1006,1007,1011,1408,1409,1410 ... Half beer,
0106, 0113, 0119, 0122, 0130, 0131, 0135, 0136, 0137, 0138, 0140, 0141, 0142, 0144, 0145, 0207, 0209, 0214, 0217, 0218, 0219, 0222, 0223, 0302, 0305, 0306,0311,0313,0316,0317,0403,0407,0408, 0511,0714,0811,0910,1008,1105 ... via,
0409,0412,0414,0510,0512,0513,0614,0618,0708,0709,0711,0712,0721,0722,0804,0806,0807,0809,0810,0817,0904,0909,0911,0912,1004, 1009, 1012, 1013, 1104, 1106, 1107, 1109, 1110, 1206, 1305, 1306, 1307, 1314, 1318, 1319, 1321, 1405, 1406, 1407, 1415, 1416, 1418 ... conductor pattern,
0105,0215,0304,0406,0509,0610,0815,0907,1010,1108,1204,1308,1320,1411 ... notch,
0109,0112,0116,0148,0612,0615,0617,0716,0717,0719,0813,0814,0819,1312 ... conductor pads,
0110,0111,0117,0118,0220,0611,0616,0715,0718,0720,0812,1311,1313,1414,1417 ... through hole,
0114,0216,0613,0723,0816,1207,1315 ... flexible substrate,
0123,0221,0803 ... holder,
0124, 1303 ... Optical fiber, 0149 ... Solder,
0125 ... Sleeve, 0126 ... Translucent window, 0127 ... Substrate, 0128 ... Optical element mounting substrate, 0129 ... Optical element, 0132 ... Driver IC, 0133 ... Wire, 0139 ... Flat plate capacitor, 0143 ... Chip thermistor, 0146 ... Lens, 0147 ... Lens holder,
0724 ... Ceramic exposed part, 0818 ... Flexible substrate mounting position, 0905, 0906, 0908 ... Castellation, 1111, 1112 ... Metallization, 1208, 1209, 1210, 213, 1214, 1215, 1325, 1326, 1419, 1421, 1422 ... Electronic element, 1211 ... Electric connector, 1212,1324,1413 ... Printed circuit board, 1,1216 ... Stem, 1217,1302 ... Fiber holder, 1323,1420 ... Ball grid array, 1327 ... Optical module, 1328 ... High frequency module.
Claims (23)
前記パッケージ筐体の一端に設けられ積層絶縁体で構成された第1の基板と、
前記第1の基板に設けられた導体部と電気的に接続する接続部を一端に有する導体パターンが主表面に設けられてなる第2の基板と、を備え、
前記導体部は、前記第1の基板の主表面に設けられた信号用導体パターンと接地用導体パターンとを含み、
前記信号用導体パターンと接地用導体パターンのそれぞれに固着された第1のリードピンと第2のリードピンは、その一端が前記第1の基板の主表面より外側に突き出るように設けられ、
前記突き出た第1および第2のリードピンの概ね直下に位置する前記第1の基板の側面に第1および第2の導体層がそれぞれ設けられ、
前記第1の導体層が設けられた側面と、前記第2の導体層が設けられた側面との間で前記信号用導体パターンに沿った第1の方向に高低差を有する
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 A package housing containing an optical element for photoelectric conversion;
A first substrate provided at one end of the package housing and configured by a laminated insulator;
A second substrate in which a conductor pattern having one end of a connection portion electrically connected to a conductor portion provided on the first substrate is provided on the main surface;
The conductor portion includes a signal conductor pattern and a ground conductor pattern provided on the main surface of the first substrate,
The first lead pin and the second lead pin fixed to each of the signal conductor pattern and the ground conductor pattern are provided so that one end thereof protrudes outside the main surface of the first substrate,
First and second conductor layers are respectively provided on the side surfaces of the first substrate located almost immediately below the protruding first and second lead pins,
There is a difference in height in a first direction along the signal conductor pattern between a side surface on which the first conductor layer is provided and a side surface on which the second conductor layer is provided. Optical module.
前記第1の導体層が設けられた側面を、前記第1の方向に沿って前記パッケージ筐体方向に移動した位置に設けることにより、前記第2の導体層が設けられた側面との間で前記第1の方向に高低差を構成する
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 1,
By providing the side surface provided with the first conductor layer at a position moved in the package housing direction along the first direction, between the side surface provided with the second conductor layer. An optical module comprising a height difference in the first direction.
前記第1の基板の側面に切り欠き部を設けることにより、前記第1の導体層が設けられた側面を前記パッケージ筐体に向かって前記第1の方向へ後退させる
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 1,
An optical module characterized in that a side surface provided with the first conductor layer is retreated in the first direction toward the package housing by providing a notch in the side surface of the first substrate. .
前記切り欠き部は、前記高低差が概ね100ミクロン以上で300ミクロン以下となるように設定されている
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 3,
The optical module is characterized in that the notch is set so that the height difference is approximately 100 microns or more and 300 microns or less.
前記第2の導体層が設けられた側面の位置が、前記第1の導体層が設けられた側面の位置よりも、前記第2の基板の前記接続部に近接するように配置されている
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 1,
The position of the side surface on which the second conductor layer is provided is arranged closer to the connection portion of the second substrate than the position of the side surface on which the first conductor layer is provided. An optical module characterized by
前記突き出た第1および第2のリードピンは、前記信号用導体パターンおよび前記接地用導体パターンのそれぞれと固着されていない延在部を有し、その延在部の長さは前記第1のリードピンと前記第2のリードピンとで異なる
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 1,
The protruding first and second lead pins have extending portions that are not fixed to the signal conductor pattern and the grounding conductor pattern, and the length of the extending portions is the first lead. An optical module, wherein the pin and the second lead pin are different.
前記第1および第2の導体層は、前記第1の基板の側面に金属が塗布された層か、あるいは、前記第1の基板の側端に設けられたビアの一部であるか、あるいは、前記第1の基板の側端に設けられた導体層を有するキャスタレーションである
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 1,
The first and second conductor layers are layers in which a metal is applied to the side surface of the first substrate, or are a part of vias provided at side edges of the first substrate, or An optical module comprising a castellation having a conductor layer provided on a side end of the first substrate.
前記第1の基板は、多層セラミックで構成され、
前記第2の基板は、フレキシブル基板で構成されている
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 1,
The first substrate is made of a multilayer ceramic;
The optical module, wherein the second substrate is a flexible substrate.
前記第2の基板は、有機物質を基材とするプリント基板であるか、セラミックを基材とするプリント基板であるか、あるいは、液晶ポリマーやポリイミド系物質を基材としたフレキシブル基板である
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 1,
The second substrate is a printed board based on an organic substance, a printed board based on a ceramic, or a flexible board based on a liquid crystal polymer or a polyimide-based substance. An optical module characterized by
前記第2の基板上の前記接続部にはスルーホールが設けられ、
前記スルーホールに前記第1および第2のリードピンが挿入され、半田、導電性接着剤等によって固着されている
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 1,
A through hole is provided in the connection portion on the second substrate,
An optical module, wherein the first and second lead pins are inserted into the through-holes and fixed by solder, conductive adhesive or the like.
前記第1の基板上の導体パターンの上面と、前記第2の基板上の導体パターンの上面に、同一方向から前記リードピンが半田、導電性接着剤、金属によって固着されていること
を特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 1,
The lead pin is fixed to the upper surface of the conductor pattern on the first substrate and the upper surface of the conductor pattern on the second substrate from the same direction by solder, conductive adhesive, or metal. Optical module.
前記信号用導体パターンと接地用導体パターンのそれぞれの主表面に前記第1および第2のリードピンが配置固定され、
前記第2の基板上の導体パターンは、前記第1および第2のリードピンの上方向に配置され、該導体パターンと前記第1および第2のリードピンとが固着される
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 1,
The first and second lead pins are arranged and fixed on the main surfaces of the signal conductor pattern and the ground conductor pattern,
The conductor module on the second substrate is arranged above the first and second lead pins, and the conductor pattern and the first and second lead pins are fixed to each other. .
前記第1の基板の接地用導体パターンの一部と、前記第2の基板の接地用導体パターンの一部が、前記第1の方向と概ね垂直方向に、前記リードピンを介して重畳されていることを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 1,
A part of the grounding conductor pattern of the first substrate and a part of the grounding conductor pattern of the second substrate are overlapped via the lead pins in a direction substantially perpendicular to the first direction. An optical module characterized by that.
前記第1のリードピンが、前記信号用導体パターンと接続されずに概ね前記第1の方向に延在する部分を有している
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 12,
The optical module according to claim 1, wherein the first lead pin has a portion extending substantially in the first direction without being connected to the signal conductor pattern.
前記延在部の長さは、前記第1および第2の導体パターンのインピーダンスのそれぞれに対する前記第1および第2のリードピン周囲の特性インピーダンスの比が120%を超えないように設定されることを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 6,
The length of the extension is set so that the ratio of the characteristic impedance around the first and second lead pins to the impedance of the first and second conductor patterns does not exceed 120%. A featured optical module.
前記第1のリードピンが設けられた前記第1の基板上の面と、前記第2のリードピンが設けられた前記第1の基板上の面とが異なる
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 1,
An optical module, wherein a surface on the first substrate on which the first lead pin is provided and a surface on the first substrate on which the second lead pin is provided are different.
前記信号用導体パターンを2つ有し、
少なくとも前記信号用導体パターンと前記第1のリードピンとの固着領域において、前記2つの信号用導体パターンは並置され、
前記切り欠き部の側面に、前記2つの信号用導体パターンのそれぞれに接続する2つの前記第1の導体層が前記第1の方向に概ね同一位置となるように併設され、
前記第2の導体層が設けられた前記第1の基板の側面と、前記第1の導体層が設けられた前記切り欠き部の側面とは、前記第1の方向にずれて配置されている
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 3,
Having two signal conductor patterns,
At least in the fixing region between the signal conductor pattern and the first lead pin, the two signal conductor patterns are juxtaposed,
The two first conductor layers connected to each of the two signal conductor patterns are provided on the side surface of the notch so as to be substantially in the same position in the first direction,
The side surface of the first substrate on which the second conductor layer is provided and the side surface of the notch portion on which the first conductor layer is provided are shifted from each other in the first direction. An optical module characterized by that.
前記信号用導体パターンを2つ有し、
少なくとも前記信号用導体パターンと前記第1のリードピンとの固着領域において、前記接地用導電パターンの両側に前記信号用導体パターンが並置され、
前記切り欠き部の側面に、前記2つの信号用導体パターンのそれぞれに接続する2つの前記第1の導体層と前記接地用導電パターンに接続する前記第2の導体層が、前記第1の方向に概ね同一位置となるように併設され、
前記接地用導体パターン以外に接続する前記第2の導体層が設けられた前記第1の基板の側面と、前記切り欠き部の側面とは、前記第1の方向にずれて配置されている
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 3,
Having two signal conductor patterns,
At least in the fixed region between the signal conductor pattern and the first lead pin, the signal conductor pattern is juxtaposed on both sides of the ground conductive pattern,
Two first conductor layers connected to each of the two signal conductor patterns and the second conductor layer connected to the ground conductive pattern are formed on the side surface of the notch portion in the first direction. To be in the same position,
The side surface of the first substrate on which the second conductor layer connected to other than the grounding conductor pattern is provided and the side surface of the cutout portion are arranged so as to be shifted in the first direction. An optical module characterized by
前記信号用導体パターンを2つ有し、
少なくとも前記信号用導体パターンと前記第1のリードピンとの固着領域において、前記接地用導電パターンの両側に前記信号用導体パターンが並置され、
前記切り欠き部を複数有し、前記切り欠き部の一つと他の一つが前記第1の基板の側面を介して並置され、
前記切り欠き部の一つおよび他の一つの側面には、前記第1の導体層が設けれ、前記第1の基板の側面には、前記第2の導体層が設けられている
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 3,
Having two signal conductor patterns,
At least in the fixed region between the signal conductor pattern and the first lead pin, the signal conductor pattern is juxtaposed on both sides of the ground conductive pattern,
A plurality of the cutouts, one of the cutouts and the other of the cutouts being juxtaposed via the side surface of the first substrate;
The first conductor layer is provided on one of the notches and the other side surface, and the second conductor layer is provided on a side surface of the first substrate. And optical module.
前記パッケージ筐体の一端に設けられ積層絶縁体で構成された第1の基板と、
前記第1の基板に設けられた導体部と電気的に接続する接続部を一端に有する導体パターンが主表面に設けられてなる第2の基板と、を備え、
前記導体部は、前記第1の基板の主表面に設けられた信号用導体パターンと接地用導体パターンとを含み、
前記第1の基板上に設けられ前記信号用導体パターンを配置する信号用導体パターン配置基板を有し、
前記信号用導体パターンに固着された第1のリードピンは、その一端が前記信号用導体パターン配置基板の主表面より外側に突き出るように設けられ、
前記接地用導体パターンに固着された第2のリードピンは、その一端が前記第1の基板の主表面より外側に突き出るように設けられ、
前記突き出た第1および第2のリードピンの概ね直下に位置する前記信号用導体パターン配置基板の側面および前記第1の基板の側面のそれぞれに第1および第2の導体層が設けられ、
前記信号用導体パターン配置基板の主表面と前記第1の基板の主表面との間に前記第1の基板の主表面に垂直な方向に高低差を設け、
前記第1の導体層と、前記第2の導体層との間で前記信号用導体パターンに沿った第1の方向に垂直な方向に高低差を有する
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 A package housing containing an optical element for photoelectric conversion;
A first substrate provided at one end of the package housing and configured by a laminated insulator;
A second substrate in which a conductor pattern having one end of a connection portion electrically connected to a conductor portion provided on the first substrate is provided on the main surface;
The conductor portion includes a signal conductor pattern and a ground conductor pattern provided on the main surface of the first substrate,
A signal conductor pattern arrangement substrate disposed on the first substrate and arranging the signal conductor pattern;
The first lead pin fixed to the signal conductor pattern is provided so that one end of the first lead pin protrudes outside the main surface of the signal conductor pattern arrangement substrate,
The second lead pin fixed to the grounding conductor pattern is provided so that one end of the second lead pin protrudes outside the main surface of the first substrate,
A first conductor layer and a second conductor layer are respectively provided on a side surface of the signal conductor pattern placement substrate and a side surface of the first substrate located substantially immediately below the protruding first and second lead pins;
Providing a height difference in a direction perpendicular to the main surface of the first substrate between the main surface of the signal conductor pattern arrangement substrate and the main surface of the first substrate;
An optical module having a height difference between the first conductor layer and the second conductor layer in a direction perpendicular to the first direction along the signal conductor pattern.
前記信号用導体パターン配置基板の側面を、前記第1の基板の側面に対して前記第1の方向に沿って前記パッケージ筺体方向に後退した位置に設けることにより、
前記第1の導体層と、前記第2の導体層との間で前記第1の方向および前記第1の方向に垂直な方向のいずれにも高低差を有する
ことを特徴とする光モジュール。 The optical module according to claim 20,
By providing the side surface of the signal conductor pattern arrangement substrate at a position retracted in the package housing direction along the first direction with respect to the side surface of the first substrate,
An optical module having a height difference between the first conductor layer and the second conductor layer in both the first direction and a direction perpendicular to the first direction.
前記第1の基板の一端に設けられた導体部と電気的に接続する接続部を一端に有する導体パターンが、主表面に設けられてなる第2の基板と、を備え、
前記導体部は、前記第1の基板の主表面に設けられた信号用導体パターンと接地用導体パターンとを含み、
前記信号用導体パターンと接地用導体パターンのそれぞれに固着された第1のリードピンと第2のリードピンは、その一端が前記第1の基板の主表面より外側に突き出るように設けられ、
前記突き出た第1および第2のリードピンの概ね直下に位置する前記第1の基板の側面に第1および第2の導体層がそれぞれ設けられ、
前記第1の導体層が設けられた側面と、前記第2の導体層が設けられた側面との間で前記信号用導体パターンに沿った第1の方向に高低差を有する
ことを特徴とする高周波モジュール。 A first substrate containing an electronic element;
A conductor pattern having at one end a connection portion electrically connected to a conductor portion provided at one end of the first substrate, and a second substrate provided on the main surface;
The conductor portion includes a signal conductor pattern and a ground conductor pattern provided on the main surface of the first substrate,
The first lead pin and the second lead pin fixed to each of the signal conductor pattern and the ground conductor pattern are provided so that one end thereof protrudes outside the main surface of the first substrate,
First and second conductor layers are respectively provided on the side surfaces of the first substrate located almost immediately below the protruding first and second lead pins,
There is a difference in height in a first direction along the signal conductor pattern between a side surface on which the first conductor layer is provided and a side surface on which the second conductor layer is provided. High frequency module.
請求項1に記載の光モジュールと前記第2の基板を介して電気的に接続されていること
を特徴とする高周波モジュール。 The high frequency module according to claim 22,
A high-frequency module, wherein the optical module according to claim 1 is electrically connected to the optical module via the second substrate.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010187471A JP5654288B2 (en) | 2010-08-24 | 2010-08-24 | Optical module and high frequency module |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010187471A JP5654288B2 (en) | 2010-08-24 | 2010-08-24 | Optical module and high frequency module |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2012047823A JP2012047823A (en) | 2012-03-08 |
| JP2012047823A5 JP2012047823A5 (en) | 2013-08-01 |
| JP5654288B2 true JP5654288B2 (en) | 2015-01-14 |
Family
ID=45902808
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010187471A Active JP5654288B2 (en) | 2010-08-24 | 2010-08-24 | Optical module and high frequency module |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5654288B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013201473A (en) * | 2012-03-23 | 2013-10-03 | Sumitomo Electric Ind Ltd | Optica receiver module |
| US9775245B2 (en) | 2014-03-24 | 2017-09-26 | Photonics Electronics Technology Research Association | Pad-array structure on substrate for mounting IC chip on substrate, and optical module having said pad-array structure |
| JP6229649B2 (en) | 2014-12-08 | 2017-11-15 | 富士通オプティカルコンポーネンツ株式会社 | Optical module |
| WO2016129277A1 (en) * | 2015-02-12 | 2016-08-18 | 古河電気工業株式会社 | Flexible substrate and optical module |
| JP6430296B2 (en) | 2015-03-06 | 2018-11-28 | 日本オクラロ株式会社 | Optical module |
| JP6430312B2 (en) * | 2015-03-24 | 2018-11-28 | 日本オクラロ株式会社 | Optical module |
| JP6540417B2 (en) | 2015-09-18 | 2019-07-10 | 富士通オプティカルコンポーネンツ株式会社 | Optical transmission apparatus and optical module |
| JP6958098B2 (en) * | 2017-08-10 | 2021-11-02 | 住友電気工業株式会社 | Optical module |
| JP6939603B2 (en) * | 2018-01-26 | 2021-09-22 | 住友電気工業株式会社 | Package for optical receiver module |
| JP7166874B2 (en) * | 2018-10-25 | 2022-11-08 | 古河電気工業株式会社 | Optical module mounting board and container mounting board |
| JP7474145B2 (en) * | 2020-07-29 | 2024-04-24 | CIG Photonics Japan株式会社 | Optical Modules |
| CN114217390B (en) * | 2021-12-24 | 2024-02-23 | 苏州浪潮智能科技有限公司 | Optical switch design method, optical switch, electronic device, and storage medium |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002184888A (en) * | 2000-12-13 | 2002-06-28 | Kyocera Corp | Input/output terminal and semiconductor element housing package |
| JP2003224324A (en) * | 2002-01-30 | 2003-08-08 | Kyocera Corp | Package for housing optical semiconductor element and optical semiconductor device |
| JP2004356340A (en) * | 2003-05-28 | 2004-12-16 | Kyocera Corp | Package for housing semiconductor element, and semiconductor device |
| JP2005222003A (en) * | 2004-02-09 | 2005-08-18 | Fujikura Ltd | Mount, optical component, optical transmission/reception module, and bidirectional optical communication module |
| JP2007207803A (en) * | 2006-01-31 | 2007-08-16 | Opnext Japan Inc | Optical transmitting module |
| JP2008166730A (en) * | 2006-12-04 | 2008-07-17 | Nec Corp | Optical module and optical transceiver |
| JP2009004460A (en) * | 2007-06-19 | 2009-01-08 | Opnext Japan Inc | Optical communication module and forming method of wiring pattern |
-
2010
- 2010-08-24 JP JP2010187471A patent/JP5654288B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2012047823A (en) | 2012-03-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5654288B2 (en) | Optical module and high frequency module | |
| JP5580994B2 (en) | Optical module | |
| JP6929113B2 (en) | Optical assemblies, optical modules, and optical transmission equipment | |
| US9980379B2 (en) | Optical module | |
| JP6430160B2 (en) | Optical module and optical module manufacturing method | |
| JP4662986B2 (en) | Opto-electric interface, flexible optoelectronic interconnection, optical transponder | |
| US20090135864A1 (en) | Optical module | |
| US8552304B2 (en) | High-frequency circuit package and high-frequency circuit device | |
| JP6654364B2 (en) | Optical module | |
| US10042133B2 (en) | Optical module | |
| JP6445268B2 (en) | Optical module, optical transceiver module, and flexible substrate | |
| JP2019046922A (en) | Optical module and optical transmission device | |
| JP2021027136A (en) | Optical module | |
| JP7063695B2 (en) | Optical module | |
| JP2022132918A (en) | optical module | |
| US20220173571A1 (en) | Optical module | |
| JP2007287767A (en) | Optical subassembly | |
| JP2022143754A (en) | optical module | |
| JP2004093606A (en) | Optical module and optical transmitter | |
| JP2010034386A (en) | Optical semiconductor device | |
| US11653442B2 (en) | Optical module and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP2002043460A (en) | Package for high frequency | |
| JP2019175939A (en) | Package for semiconductor element and semiconductor device | |
| JP2004048617A (en) | Transmission line substrate for high frequency | |
| JP6671567B1 (en) | Optical module |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20130412 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20130418 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130614 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20130614 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20131227 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20140603 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140725 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20140812 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20141002 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20141021 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20141120 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5654288 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |