JP5522191B2 - Vehicle shock absorption structure - Google Patents
Vehicle shock absorption structure Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5522191B2 JP5522191B2 JP2012071191A JP2012071191A JP5522191B2 JP 5522191 B2 JP5522191 B2 JP 5522191B2 JP 2012071191 A JP2012071191 A JP 2012071191A JP 2012071191 A JP2012071191 A JP 2012071191A JP 5522191 B2 JP5522191 B2 JP 5522191B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- absorbing member
- shock absorbing
- impact
- bumper
- vehicle
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000035939 shock Effects 0.000 title claims description 158
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 title claims description 11
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 claims description 31
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 claims description 31
- 239000002023 wood Substances 0.000 claims description 30
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 claims description 18
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000006096 absorbing agent Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 13
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 11
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 11
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 230000009191 jumping Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000011148 porous material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 4
- 241000218645 Cedrus Species 0.000 description 3
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 3
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000008331 Pinus X rigitaeda Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 235000011613 Pinus brutia Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 241000018646 Pinus brutia Species 0.000 description 2
- 210000002421 cell wall Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000011056 performance test Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910000838 Al alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 241000218631 Coniferophyta Species 0.000 description 1
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000218691 Cupressaceae Species 0.000 description 1
- 240000000731 Fagus sylvatica Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000010099 Fagus sylvatica Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 241000190021 Zelkova Species 0.000 description 1
- 230000004323 axial length Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005336 cracking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Vibration Dampers (AREA)
Description
本発明は、車両の衝撃吸収構造に関する。 The present invention relates to a shock absorbing structure for a vehicle.
従来、一般に、車両前部においては、バンパリンインホースとサイドメンバとの間に金属製で中空筒状の衝撃吸収部材(クラッシュボックス)が介装されている。この種の車両の衝撃吸収構造では、衝撃吸収部材が軸方向に潰れることで衝突時の衝撃荷重を吸収することができる。このような衝撃吸収構造は、例えば、特許文献1に開示されている。 Conventionally, generally, in the front part of a vehicle, a metal-made hollow cylindrical shock absorbing member (crash box) is interposed between the bumper-in hose and the side member. In this type of vehicle impact absorbing structure, the impact absorbing member can be crushed in the axial direction to absorb the impact load at the time of collision. Such a shock absorbing structure is disclosed in Patent Document 1, for example.
衝撃吸収性能は、衝撃吸収部材の変位に対する反力としての圧縮荷重によって指標される。そして、車両の衝撃吸収構造では、歩行者等の衝突対照を保護する観点から、急激に力が加わることで衝突初期に一時的に圧縮荷重が跳ね上がるのは好ましくなく、圧縮荷重が衝突開始時からできるだけ一定に保たれることが望ましい。 The shock absorbing performance is indicated by a compressive load as a reaction force against the displacement of the shock absorbing member. And, in the shock absorbing structure of the vehicle, it is not preferable that the compressive load jumps temporarily at the beginning of the collision by applying a sudden force from the viewpoint of protecting the collision control of the pedestrian or the like. It is desirable to keep it as constant as possible.
そこで、衝突開始時の圧縮荷重の跳ね上がりを防ぐために、特許文献1では、次の構成とされている。すなわち、図12に示されるように、衝撃吸収部材311は中空四角筒状であり、その後側の端面は、軸方向に直交して平坦であり、平板状の第2のプレート313で塞がれて、該第2のプレート313を介してサイドメンバ321に対して全面で接地している。一方、前側の端面は、軸方向に直交する平坦面の一部が斜めに欠けた形状とされて、屈曲した板状の第1のプレート315で塞がれている。そして、第1のプレート315を介し、端面の一部(接触面部311a)のみがバンパリインホースと連結され、傾斜面部311bはバンパリインホースから離反した状態とされている。特許文献1によれば、衝撃吸収部材311の前側の端部にバンパリインホース323から離反した傾斜面部311bを設け、バンパリインホースから衝撃吸収部材への衝突荷重の伝達面積を小さくさせることで、衝突初期の圧縮荷重が特に大きくなるのを防ぎ、更に衝撃吸収部材の先端から潰れるように生じる変形が順に後方へと安定して進行するとされている。
Therefore, in order to prevent the compression load from jumping up at the start of the collision, Patent Document 1 has the following configuration. That is, as shown in FIG. 12, the
一方、特許文献2では、中空筒状の衝撃吸収部材を、その前後の端面でバンパリインホース又はサイドメンバに対して全面で接地させているが、その内部に柱状の木材を嵌め込むことにより、衝突初期の圧縮荷重の跳ね上がりを抑制するとともに、その後の圧縮荷重の変動を抑制することができるとされている。 On the other hand, in Patent Document 2, the hollow cylindrical impact absorbing member is grounded to the bumper inn hose or the side member at the front and rear end surfaces thereof, but by inserting columnar wood therein In addition, it is said that it is possible to suppress the jump of the compression load at the initial stage of the collision and to suppress the subsequent fluctuation of the compression load.
木材は、空洞化した細胞壁が一方向に整列しており、細孔が一方向に整列する多孔質であるとともに、該一方向に繊維補強されている。そのため、繊維方向を圧縮方向に一致させると、細孔が軸方向に順番に潰れる。したがって、衝撃吸収部材を中空筒体のみで構成する場合に比べて、木材を用いることで圧縮荷重の変動を小さく抑えることができ、衝撃吸収効率に優れた衝撃吸収部材を得ることができる。しかし、ブロック状の木材で衝撃を吸収する場合、中空筒体に比べて断面積が大きいため、急激に力が加わり木材が潰れ始める衝突初期に圧縮荷重が跳ね上がりやすい。そのため、圧縮荷重は、衝突初期に一時的に高くなり、ある程度下がった後に安定して推移する。 Wood has a porous cell wall that is aligned in one direction, and is porous with pores aligned in one direction, and is reinforced with fibers in the one direction. Therefore, if the fiber direction is matched with the compression direction, the pores are crushed sequentially in the axial direction. Therefore, as compared with the case where the shock absorbing member is composed only of the hollow cylindrical body, the use of wood makes it possible to suppress the fluctuation of the compressive load and to obtain the shock absorbing member having excellent shock absorbing efficiency. However, when the impact is absorbed by the block-shaped wood, since the cross-sectional area is larger than that of the hollow cylinder, the compressive load is likely to jump up at the beginning of the collision when a force is suddenly applied and the wood starts to collapse. For this reason, the compressive load temporarily becomes high at the beginning of the collision, and changes stably after being lowered to some extent.
一方、中空筒体のみの衝撃吸収部材でも、軸方向に真っ直ぐ蛇腹状に潰すことができれば、ある程度衝撃を吸収することができる。しかし、荷重の重心がずれると座屈して中折れし、その機能を的確に発揮することができない。そのため、特許文献1では、衝撃吸収部材311の前側の端部にバンパリインホースから離反した傾斜面部311bを形成することで、衝撃荷重がバンパリインホース323から衝撃吸収部材311に直接的に伝達される面積を小さくしてはいるものの、傾斜面部311bまで第1のプレート315を延ばすことで、第1のプレート315を介して傾斜面部311bを含む端面全体に均等に衝撃荷重が作用する構成となっている。したがって、このような中空筒状の衝撃吸収部材の構成を、木材からなる衝撃吸収部材に適用したとしても、特に、ブロック状の木材を用いる場合は中空筒体よりも断面積が大きいため、傾斜面部までもが第1のプレート315を介して荷重を受けることで衝突初期に圧縮荷重が跳ね上がりやすい。つまり、衝撃吸収部材の前側の端面の全体に衝撃加重が作用する以上、バンパリインホースに全面接地させる場合と実質的な差異はなく、衝突開始時の圧縮荷重の跳ね上がりを低減することはできない。
On the other hand, even a shock absorbing member having only a hollow cylindrical body can absorb a certain amount of shock if it can be crushed in a bellows shape straight in the axial direction. However, if the center of gravity of the load is deviated, it will buckle and bend, and its function cannot be exhibited accurately. Therefore, in Patent Document 1, by forming the
そこで、本発明は、衝突開始時に圧縮荷重が跳ね上がるのを抑え、圧縮荷重の変動がより小さい車両の衝撃吸収構造を提供することを目的とする。 Accordingly, an object of the present invention is to provide a shock absorbing structure for a vehicle in which the compression load is prevented from jumping up at the start of a collision and the fluctuation of the compression load is smaller.
本発明は、バンパ部材と、車両骨格部材との間に、車両衝突時の衝撃を軸方向の圧縮荷重として受ける衝撃吸収部材を備えた車両の衝撃吸収構造であって、前記衝撃吸収部材は、柱状の木材であり、その繊維方向が軸方向と平行であり、前記衝撃吸収部材の一方の端面は、前記バンパ部材又は前記車両骨格部材の一方にその一部分のみが連接されており、前記衝撃吸収部材の他方の端面は、前記バンパ部材又は前記車両骨格部材の他方にその全体を支持可能に連接されており、前記衝撃吸収部材は、衝突開始時は、前記一方の端面が一部分のみで圧縮荷重を受けて局所的に圧縮変形し、該局所的な圧縮変形を経て最終的には前記一方の端面が全体で圧縮荷重を受けることを特徴とする車両の衝撃吸収構造である。ここで、前記バンパ部材又は前記車両骨格部材の一方に対して衝撃吸収部材の“一方の端面の一部分” が連接されていることにおいて、一方の端面とは、柱状の衝撃吸収部材の一方の端が一平面で構成されている場合はその一平面のことであり、柱状の衝撃吸収部材の一方の端が二平面以上の面にカットされている場合は、その二平面以上の全ての面を併せて一方の端面とする概念である。また、連接していることは、直接的に連なって接続している場合と、間接的に連なって接続している場合の双方を含む。また、衝撃吸収部材が衝撃を軸方向の圧縮荷重として受けることは、軸方向と圧縮方向とがちょうど一致する場合だけでなく、若干ずれている場合も含む。また、衝撃吸収部材を構成する木材の繊維方向が軸方向と平行であるとは、ちょうど平行である場合だけでなく、若干ずれた略平行な状態も含む。 The present invention is a vehicle impact absorbing structure including an impact absorbing member that receives an impact at the time of a vehicle collision as a compressive load in an axial direction between a bumper member and a vehicle skeleton member, and the impact absorbing member includes: Columnar wood, the fiber direction of which is parallel to the axial direction, and one end surface of the shock absorbing member is connected to only one of the bumper member or the vehicle skeleton member, and the shock absorbing member The other end surface of the member is connected to the other of the bumper member or the other vehicle skeleton member so as to be able to support the whole, and the impact absorbing member has a compressive load with only a part of the one end surface at the start of the collision. The shock absorbing structure of the vehicle is characterized in that it is locally compressed and deformed, and finally undergoes the local compressive deformation and finally the one end surface receives a compressive load as a whole. Here, “a part of one end face” of the shock absorbing member is connected to one of the bumper member or the vehicle skeleton member, and one end face is one end of the columnar shock absorbing member. Is composed of one plane, it means that one plane, and when one end of a columnar shock absorbing member is cut into two or more planes, all the planes of two or more planes are It is also the concept of using one end face. Further, being connected includes both a case where they are directly connected and a case where they are connected indirectly. Further, the impact absorbing member receiving an impact as an axial compressive load includes not only the case where the axial direction and the compressing direction are exactly the same, but also a case where they are slightly shifted. Further, the fiber direction of the wood constituting the shock absorbing member being parallel to the axial direction includes not only a case where the fiber is just parallel, but also a substantially parallel state with a slight deviation.
かかる構成の車両の衝撃吸収構造によれば、バンパ部材に衝撃が加わると、木材からなる衝撃吸収部材が軸方向に圧縮変形して衝撃を吸収する。その際、先ず、衝突開始時には、衝撃吸収部材において、バンパ部材又は車両骨格部材にその一部分のみが連接している一方の端面の、その連接している一部分に圧縮荷重が集中する。その結果、衝撃吸収部材は、圧縮荷重の集中した一方の端面の一部分から軸方向に局所的に圧縮変形する。そのため、軸方向に直交する断面の一部分のみで衝撃を吸収する。このように衝撃吸収部材が局所的に圧縮変形するのは、木材が、元来、繊維と直交する方向(横方向)に比べて繊維方向(縦方向)の結合が極端に強く、柱状の木材を、その繊維方向に押圧する場合、端面の一部分のみを押圧すると、その一部分だけが軸方向に圧縮変形するためである。そして、衝撃吸収部材は、局所的な圧縮変形を経た後、最終的には、全体で圧縮荷重を受けて軸方向に直交する断面の全体で効率よく衝撃を吸収する。本発明の衝撃吸収構造によれば、このように、圧縮荷重が跳ね上がりやすい衝突開始時に衝撃吸収部材が局所的に圧縮変形することで、その後の全体が圧縮変形する際と同程度にまで圧縮荷重を下げて圧縮荷重の変動をより小さくすることができる。 According to the impact absorbing structure for a vehicle having such a configuration, when an impact is applied to the bumper member, the impact absorbing member made of wood compresses and deforms in the axial direction to absorb the impact. At that time, first, at the start of the collision, in the impact absorbing member, the compressive load is concentrated on a part of the end face where only a part of the shock absorbing member is connected to the bumper member or the vehicle frame member. As a result, the shock absorbing member is locally compressed and deformed in the axial direction from a part of one end face where the compressive load is concentrated. Therefore, the impact is absorbed only by a part of the cross section orthogonal to the axial direction. In this way, the shock absorbing member is locally compressed and deformed because the wood originally has an extremely strong bond in the fiber direction (longitudinal direction) compared to the direction orthogonal to the fiber (lateral direction), and columnar wood. This is because if only a part of the end face is pressed in the fiber direction, only that part is compressed and deformed in the axial direction. The impact absorbing member, after undergoing local compressive deformation, finally receives the compressive load as a whole and efficiently absorbs the impact across the entire cross section perpendicular to the axial direction. According to the shock absorbing structure of the present invention, the compressive load is reduced to the same level as when the entire subsequent compressive deformation is caused by the compressive deformation of the shock absorbing member locally at the start of the collision, in which the compressive load is likely to jump up. To reduce the fluctuation of the compression load.
前記衝撃吸収部材の前記一方の端面は、前記バンパ部材又は前記車両骨格部材の一方に当接する接続面部と、前記バンパ部材又は前記車両骨格部材の一方から離間した離間面部とを備えているのが好ましい。この場合、衝撃吸収部材の一方の端面をバンパ部材又は車両骨格部材とを直接的に連結するため、少ない部品点数での連結が可能である。 The one end surface of the shock absorbing member includes a connection surface portion that comes into contact with one of the bumper member or the vehicle skeleton member, and a separation surface portion spaced from one of the bumper member or the vehicle skeleton member. preferable. In this case, since one end surface of the shock absorbing member is directly connected to the bumper member or the vehicle frame member, connection with a small number of parts is possible.
また、前記衝撃吸収部材の前記一方の端面は、介装物を介して前記バンパ部材又は前記車両骨格部材の一方に連接されており、前記介装物は、前記衝撃吸収部材よりも剛性の高い衝撃伝達部を有し、該衝撃伝達部が前記衝撃吸収部材の前記一方の端面の一部分のみと重複して配されているのも好ましい。この場合、衝撃吸収部材の一方の端面を単純形状とすることが可能であり、加工が容易になるのと同時に、裁断加工時の木材の割れを低減し得る。特に、衝撃吸収部材の一方の端面が、軸方向に直交する一平面のみで形成されている場合、つまり、繊維方向に直交する裁断面で形成されている場合、木材を裁断加工する際だけでなく圧縮変形する際にも割れにくく、衝撃吸収性能を安定させることができる。 In addition, the one end face of the shock absorbing member is connected to one of the bumper member or the vehicle skeleton member via an interposed member, and the interposed member is higher in rigidity than the shock absorbing member. It is also preferable that an impact transmitting portion is provided, and the impact transmitting portion is disposed so as to overlap with only a part of the one end face of the impact absorbing member. In this case, it is possible to make one end surface of the impact absorbing member into a simple shape, and processing can be facilitated, and at the same time, cracking of wood during cutting can be reduced. In particular, when one end face of the shock absorbing member is formed by only one plane orthogonal to the axial direction, that is, when it is formed by a cut surface orthogonal to the fiber direction, only when cutting wood. Even when compressively deformed, it is difficult to break, and the shock absorbing performance can be stabilized.
本発明の車両の衝撃吸収構造において、前記衝撃吸収部材は、前記一方の端面が前記バンパ部材に連接されており、前記他方の端面が前記車両骨格部材に連接されているのが好ましい。この場合、衝撃吸収部材の衝撃が入力されるバンパ部材側の端面とは反対側の基端側の端面が、その全体で車両骨格部材に連接しており、圧縮変形時に衝撃吸収部材が転倒しにくい。したがって、より確実に衝撃吸収部材を軸方向に圧縮変形させることができ、衝撃吸収性能をより的確に発揮させやすい。 In the vehicle impact absorbing structure of the present invention, it is preferable that the one end face of the shock absorbing member is connected to the bumper member, and the other end face is connected to the vehicle skeleton member. In this case, the end surface on the base end side opposite to the end surface on the bumper member side where the impact of the impact absorbing member is input is connected to the vehicle skeleton member as a whole, and the impact absorbing member falls over during compression deformation. Hateful. Therefore, the shock absorbing member can be more reliably compressed and deformed in the axial direction, and the shock absorbing performance can be more easily exhibited.
本発明によれば、初期の圧縮荷重が跳ね上がるのを抑え、圧縮荷重の変動をより小さい車両の衝撃吸収構造を提供することができる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, it can suppress that the initial compressive load jumps up, and can provide the impact-absorbing structure of a vehicle with smaller fluctuation | variation of a compressive load.
<実施形態1>
図1〜図3を参照しながら、本発明の一実施形態について説明する。本実施形態の車両の衝撃吸収構造では、バンパリインホース11とサイドメンバ13との間に衝撃吸収部材21が配されている。先ず、この衝撃吸収構造の構成について説明する。なお、図中に矢印で示されるF,Rは車両の前方,後方を示し、Cは車両の幅方向(車幅方向)を示す。
<Embodiment 1>
An embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. In the impact absorbing structure for a vehicle according to the present embodiment, an
バンパリインホース11は、アルミニウム合金の押出材や鉄鋼等からなる筒状の剛体であり、車体の前部において車幅方向に沿って配設されている。その長手方向の中央は車幅方向に沿って真っ直ぐに延びており、両端は後方へ傾斜している。このバンパリインホース11が本発明のバンパ部材に相当する。本実施形態では、バンパリインホース11の車幅方向に沿って真っ直ぐに延びている部分11aの後方に衝撃吸収部材21が配されている。
The bumper-in
サイドメンバ13は、鉄鋼等からなる筒状の剛体であり、車両前後方向に沿って、幅方向に離間して対で配され、車両の骨格を構成する。
The
衝撃吸収部材21は、柱状の木材Wからなる。木材Wは、その繊維方向が軸方向と平行になるように製材されている。木材Wの種類は特に限定されず、例えば、スギ、ヒノキ、マツ等の針葉樹や、ケヤキやブナ等の広葉樹を用いることができる。比重が高い木材は強度に優れ、比重が低い木材は気孔率が高いため、クラッシュストローク(圧縮による変位量)が長くなる特徴がある。この点を考慮し、車両の設置位置に合わせて適宜の比重の木材を選択するのが望ましい。比重が0.2〜0.4の木材を用いると、クラッシュストロークを十分に確保しつつ、ある程度の強度を有することで、衝撃エネルギーの吸収量をより高めることができ好ましい。比重が0.2〜0.4の木材としては、例えば、スギ、ヒノキ、マツ等が挙げられる。
The
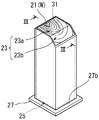
本実施形態の衝撃吸収部材21は、図2、図3(A)に示されるように、軸方向に直交する平断面が正四角形の四角柱において、その軸方向の一方の端部が一部斜めに欠かれた形状である。衝撃吸収部材21の一方の端面23は、軸方向に直交する四角形の面からなる接触面部23aと、軸方向に対して斜めに傾いた四角形の面からなる離間面部23bとで構成されている。衝撃吸収部材21の他方の端面25は、軸方向に直交する正四角形の一平面で構成されている。
As shown in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3A, the
衝撃吸収部材21の外側には、中空四角筒状の枠体31が嵌っている。言い換えれば、衝撃吸収部材21は枠体31に収容されている。枠体31は、衝撃吸収部材21を支持することができ、且つ、車両の衝突時に衝撃吸収部材21とともに軸方向に潰れることができるものであり、例えば、アルミニウムや銅、鉄などの金属からなる。
A hollow rectangular
衝撃吸収部材21は、接触面部23aと離間面部23bとを有する一方の端面23がバンパリインホース11側に、他方の端面25がサイドメンバ13側となるように配されている。衝撃吸収部材21のバンパリインホース11側の端面23は、バンパリインホース11の平らな後面に対して接触面部23aのみが接触した状態で保持され、離間面部23bはバンパリインホース11から離れた状態となっている。衝撃吸収部材21のバンパリインホース11に対する固定方法は特に限定されない。例えば、枠体31を溶接や接着等によってバンパリインホース11に固定することができる。この他、取付金具を介して枠体31をバンパリインホース11にビス止めしたりすることによって、バンパリインホース11に対して衝撃吸収部材21を固定することもできる。
The
衝撃吸収部材21は、サイドメンバ13と同軸で配されている。衝撃吸収部材21のサイドメンバ13側の端面25とサイドメンバ13との間には、支持プレート27が介装されており、衝撃吸収部材21の端面25は、その全体が支持プレート27に当接した状態で保持されている。支持プレート27は、車両衝突時に容易に変形せずに衝撃吸収部材21の荷重を受け止めることのできる剛体であり、鋼板等からなる。支持プレート27は、衝撃吸収部材21の端面25よりも面積の大きい平板状であり、図3(A)に示されるように、中央は衝撃吸収部材21の他方の端面25全体を覆う支持部27aを構成し、その全周にサイドメンバ13との接続部27bとしての余白を残している。支持プレート27に対する衝撃吸収部材21の固定方法は特に限定されないが、例えば、枠体31を溶接や接着等によって支持プレート27に接合することによって固定するができる。この他、取付金具を介して枠体31を支持プレート27にビス止めしたりすることによって、支持プレート27に対して衝撃吸収部材21を固定することもできる。そして、支持プレート27とサイドメンバ13との連結方法も特に限定されないが、支持プレート27の接続部27bとサイドメンバ13の先端に設けられたフランジ13fを突き合わせて締結、あるいは溶接又は接着により接合することができる。
The
次に、この衝撃吸収構造の衝撃吸収機構について説明する。車両の前方衝突時、図1に白抜き矢印で示されるように、バンパリインホース11に前方からの衝撃が加わると、より剛性の高いバンパリインホース11とサイドメンバ13とに挟まれた衝撃吸収部材21が潰れることで衝撃を吸収する。その際、図3(A)に示されるように、衝突開始時は、衝撃吸収部材21には、バンパリインホース11側の端面23において、衝突前からバンパリインホース11と接触している接触面部23aに圧縮荷重が集中する。すると、衝撃吸収部材21は、圧縮荷重が集中した接触面部23aから軸方向に潰れ、軸方向に直交する断面の一部分のみで衝撃を吸収する。これは、衝撃吸収部材21が木材Wからなり、その繊維方向が軸方向(荷重方向)と平行になっているためである。というのも、木材Wは、元来、空洞化した細胞壁が一方向に整列しており、細孔が一方向に整列する多孔質であるとともに、該一方向に繊維補強されている。そのため、繊維方向と軸方向とが平行なとき、軸方向の一方の端面23が、その一部分(接触面部23a)のみで圧縮荷重を受けると、その圧縮荷重を受けた部分(接触面部23a)から繊維方向(軸方向)に順に細孔が潰れて部分的に緻密化するのである。図3(B)には、緻密化部分に網掛けを付して模式的に示す。このように、衝撃吸収部材21は、衝突開始時に、先ず、集中的に圧縮荷重を受けた接触面部23aから局所的に圧縮変形するため、圧縮変形が進むに従いバンパリインホース11から離れていた離間面部23bもバンパリインホース11に接触し、図3(C)に示されるように端面23全体で衝撃を受けるようになる。そうして、衝撃吸収部材21の軸方向に直交する断面における圧縮変形領域が徐々に増え、最終的には軸方向に直交する断面全体が圧縮変形する。
Next, the shock absorbing mechanism of this shock absorbing structure will be described. At the time of a frontal collision of the vehicle, as indicated by the white arrow in FIG. 1, when an impact from the front is applied to the
このような衝撃吸収構造によれば、衝突開始時は、軸方向に直交する断面の一部のみで衝撃を吸収し、最終的には、全体で衝撃を吸収するため、衝撃吸収部材21の圧縮荷重が衝突開始時に跳ね上がるのを防ぐことができ、圧縮荷重の変動を小さく抑えながらも、効率よく衝撃を吸収することができる。 According to such a shock absorbing structure, at the start of the collision, the shock is absorbed by only a part of the cross section orthogonal to the axial direction, and finally the shock is absorbed as a whole. The load can be prevented from jumping up at the start of the collision, and the impact can be absorbed efficiently while suppressing the fluctuation of the compression load.
<実施形態2>
図4〜図6を参照しながら本発明の別の実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、図4に示されるように、衝撃吸収部材41がバンパリインホース11の両端の後方へ傾斜している部分11bの後方に配されている点が実施形態1とは相違している。以下、相違点を中心に説明し、実施形態1と同様の構成については図中に同じ符号で示し、その詳細な説明は省略する。
<Embodiment 2>
Another embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. As shown in FIG. 4, the present embodiment is different from the first embodiment in that the
本実施形態の衝撃吸収部材41も柱状の木材Wからなる。その形状は、図5に示されるように、軸方向に直交する平断面が正四角形の四角柱において、バンパリインホース11側の端面43が軸方向に対して傾斜した二平面からなる山型となっている。バンパリインホース11側の端面43を構成する二平面のうち、一方がバンパリインホース11に対して接触状態で配される接触面部43aを構成し、バンパリインホース11から離間して配される離間面部43bを構成する。なお、衝撃吸収部材41のサイドメンバ13側の端面45は本実施形態でも軸方向に直交する一平面で構成されており、サイドメンバ13への接続形態は実施形態1と同様である。
The
このように、衝撃吸収部材41の軸方向に対して接触面部43aが傾斜している場合でも、その基本的な衝撃吸収機構は実施形態1と同様である。すなわち、衝撃吸収部材41は、図6(A)に示されるように、衝突開始時にはバンパリインホース11と接触している接触面部43aで集中的に圧縮荷重を受け、その圧縮荷重が集中した部分(接触面部43a)から軸方向に順次圧縮変形し、軸方向に直交する断面の一部分のみで衝撃を吸収する。そして、圧縮変形が進むに従い、圧縮変形領域が増え、最終的には軸方向に直交する断面が圧縮変形して全体で衝撃を吸収する。
Thus, even when the
<実施形態3>
図7、図8を参照しながら本発明の別の実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、衝撃吸収部材51がバンパリインホース11の車幅方向に沿って真っ直ぐに延びている部分11aの後方に配されている点は上記実施形態1と同様であるが、衝撃吸収部材51とバンパリインホース11との間にブラケット61が介在している点が相違している。以下、相違点を中心に説明し、実施形態1と同様の構成については図中に同じ符号で示し、その詳細な説明は省略する。
<Embodiment 3>
Another embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. Although the present embodiment is the same as the first embodiment in that the
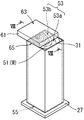
本実施形態の衝撃吸収部材51も柱状の木材Wからなる。その形状は、図7に示されるように、軸方向に直交する平断面が正四角形の四角柱であり、バンパリインホース11側の端面53が軸方向に直交する一平面で構成されている。また、サイドメンバ13側の端面55も軸方向に直交する一平面で構成されており、そのサイドメンバ13への接続形態は実施形態1と同様である。
The
バンパリインホース11側の端面53とバンパリインホース11とは、両者の間に介装されたブラケット61を介して連結されている。ブラケット61は、図示されている本体部は、車両衝突時に容易に変形しない剛体であり、鋼材等からなる。このブラケット61が本発明の介装物に相当し、図示されている部分が衝撃伝達部に相当する。本実施形態のブラケット61の形状は、扁平な直方体であり、図8(A)に示されるように、相対する一面63がバンパリインホース11に連結されており、他面65が衝撃吸収部材51のバンパリインホース11側の端面53と接触している。ブラケット61は、衝撃吸収部材51のバンパリインホース11側の端面53に対し、その一部分にだけ重複するように配されている。したがって、衝撃吸収部材51の端面53には、ブラケット61と接触している接触面部53aと接触していない離間面部53bとが形成されている。ブラケット61のバンパリインホース11に対する固定方法は特に限定されないが、例えば、溶接や接着により接合したり、ビス止めしたりして固定することができる。また、ブラケット61に対する衝撃吸収部材51の固定方法も特に限定されず、例えば、枠体31をブラケット61に対して溶接や接着により接合したり、ビス止めしたりして固定することができる。
The
このような衝撃吸収構造でも、基本的な衝撃吸収機構は上記実施形態と同様であり、衝撃吸収部材51は、衝突開始時には、圧縮荷重の集中するバンパリインホース11側の端面53の一部分(接触面部53a)から局所的に変形して軸方向に直交する断面の一部分のみで衝撃を吸収し、最終的には、端面53の全体で圧縮荷重を受けて直交する断面の全体で衝撃を吸収する。すなわち、衝突開始時には、バンパリインホース11に衝撃が加わると、衝撃がブラケット61を通じて衝撃吸収部材51に衝撃が伝達される。このとき、衝撃吸収部材51は、バンパリインホース11側の端面53のうちブラケット61に接触している接触面部53aにのみで圧縮荷重を受け、その圧縮荷重を受けた部分から軸方向に順次圧縮変形する。そのため、図8(B)に示されるように、ブラケット61が衝撃吸収部材51に対して接触面部53aから軸方向にめり込む。そして、ブラケット61の厚み全体が衝撃吸収部材51にめり込むと、図8(C)に示されるように、バンパリインホース11が衝撃吸収部材51に当接し、バンパリインホース11とブラケット61とでバンパリインホース11側の端面53全体が押される。そのため、衝撃吸収部材51は、軸方向に直交する断面全体が圧縮変形する。
Even in such a shock absorbing structure, the basic shock absorbing mechanism is the same as that of the above embodiment, and the
このように、衝撃吸収部材51の形状が単純な四角柱であって、両端面が繊維方向に直交する一平面からなる場合、その木材Wの裁断加工が容易であるとともに、繊維方向に対して斜めに裁断する場合に比べて加工時に割れ等の不具合が生じにくい。また、圧縮変形時にも割れにくく、衝撃吸収性能を安定して発揮することができる。
Thus, when the shape of the
<実施形態4>
図9、図10を参照しながら、本発明の別の実施形態について説明する。本実施形態では、実施形態3のように単純な四角柱形状の木材Wからなる衝撃吸収部材51を用い、該衝撃吸収部材51を実施形態2のように衝撃吸収部材51がバンパリインホース11の両端の後方へ傾斜している部分11bの後方を配している。
<Embodiment 4>
Another embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. In the present embodiment, the
本実施形態でも、バンパリインホース11と衝撃吸収部材51との間に剛体からなるブラケット71が介装されている。ブラケット71は、バンパリインホース11側の面73はバンパリインホース11に沿って傾斜しており、この面73に対向して衝撃吸収部材51との当接面75が設定されている。そして、衝撃吸収部材51に対する当接面75は、衝撃吸収部材51の端面53の一部分にのみ当接している。
Also in this embodiment, a
本実施形態のブラケット71は、衝撃吸収部材51との当接面75に沿って衝撃吸収部材51の端面53を覆う保護カバー77を付帯している。保護カバー77は、ブラケット71の衝撃吸収部材51に対する当接面75から張り出し、衝撃吸収部材51の端面53のブラケット71とは接触していない離間面部53bを覆う。保護カバー77は、車両の通常使用時において衝撃吸収部材51を保護するものであり、車両衝突時に衝撃吸収部材51を変形させない程度に柔らかいもの、あるいは脆弱なものである。例えば、アルミ等の柔らかい金属製の薄板で構成することができる。この場合、車両衝突時には、図10(B)、(C)に示されるように、柔らかい保護カバー77からは衝撃吸収部材51に衝撃が伝達されず、衝撃吸収部材51の端面53は、始めはブラケット71により部分的に押され、その後ブラケット71とバンパリインホース11と押される。したがって、本実施形態の衝撃吸収構造も、実施形態3と同様の作用機能を発揮する。
The
なお、保護カバー77は、例えば、樹脂板等で形成し、ブラケット71が衝撃吸収部材51にめり込み始めて衝撃吸収部材51に強く押し当てられることで破断してブラケット71から分離するようなものとしてもよい。
The
<その他の実施形態>
実施形態3または実施形態4のように、バンパリインホース11と衝撃吸収部材51との間にブラケット61(71)を介装する場合において、図11に示されるように、離間面部53bを傾斜させてもよい。この場合、ブラケット61が衝撃吸収部材51に完全にめり込んだ後に11が衝撃吸収部材51に当接する際、徐々に当接面積が増えるため、圧縮荷重の変動をよりなだらかにしやすい。
<Other embodiments>
As shown in FIG. 11, when the bracket 61 (71) is interposed between the bumper-in
また、ブラケット61は、衝撃吸収部材51の端面53の一部に対して重複していれば、端面53からはみ出さない大きさとしてもよい。ただし、衝撃吸収部材51からブラケット61がはみ出している場合は、ブラケット61のバンパリインホース11に対する接触面積が大きいため、衝撃吸収部材51を介してサイドメンバ13に支持されているバンパリインホース11がぐらつき難く、安定して連結されるため好ましい。
Further, the
なお、上記各実施形態では、衝撃吸収部材のバンパリインホース11側の端面が、その一部分でバンパリインホース11に連接する構成を示したが、衝撃吸収部材を反転させてサイドメンバ13側の端面が、その一部分でサイドメンバ13に連接する構成としてもよい。
In each of the above-described embodiments, the end surface of the impact absorbing member on the
以下に、本発明の衝撃吸収構造による衝撃吸収性能を評価した結果について説明する。各試験では、衝撃吸収部材として、スギを繊維方向が軸方向と平行になるように四角柱状に製材したものを用い、これをアルミニウム(A5052)製の四角筒状の枠体に収容して試験に供した。 Below, the result of having evaluated the shock absorption performance by the shock absorption structure of this invention is demonstrated. In each test, as a shock absorbing member, a cedar made of a square columnar shape so that the fiber direction is parallel to the axial direction was used, and this was accommodated in a square cylindrical frame made of aluminum (A5052). It was used for.
(試験1)
試験1では、図13に示されるように、模擬バンパ部材111として、厚み35mmのアルミニウムA5052製中空四角筒体の左右の両端部が内側へ10°傾斜した剛体バンパリインホースを用意した。そして、この模擬バンパ111の端部の傾斜部111bに対して衝撃吸収部材41,41を配したときの衝撃吸収性能を評価した。衝撃吸収部材は、実施例1と比較例1とで、模擬バンパ111側の面の形状の異なるものをそれぞれ対で用意した。
(Test 1)
In Test 1, as shown in FIG. 13, a rigid bumper-in hose was prepared as a
[実施例1]
実施例1では、衝撃吸収部材として、図5に示される衝撃吸収部材41と同じ形状の具体的な試料を用いた。実施例1の衝撃吸収部材は、14.7mm角×軸方向長さ70mmの角材を、長さを変えずに軸方向の一端を山切りカットして模擬バンパ111への接触面部43aと離間面部43bとを形成したものである。接触面部43aは10°傾斜しており、離間面部43bは15°傾斜している。
[Example 1]
In Example 1, a specific sample having the same shape as the
[比較例1]
実施例1の衝撃吸収部材としては、14.7mm角×軸方向長さ70mmの角材を、長さを変えずに軸方向の一端を10°傾斜するように斜めカットして、端面全体で模擬バンパ部材111に接触する衝撃吸収部材を用意した。
[Comparative Example 1]
As the impact absorbing member of Example 1, a square material of 14.7 mm square × 70 mm in the axial direction is cut obliquely so that one end in the axial direction is inclined by 10 ° without changing the length, and the entire end face is simulated. An impact absorbing member that contacts the
用意した衝撃吸収部材を、それぞれ、肉厚0.5mmで外寸16mm角の四角筒状の枠体に収容した。そして、図13に示されるように、剛体からなる平らな試験台Sに実施例1または比較例1の対の衝撃吸収部材41,41を離間して立設し、その上に左右対称になるように模擬バンパ111を載置して接着固定して模擬バンパ111の両斜面部111bを衝撃吸収部材で支持させた。そして、株式会社島津製作所製の圧縮試験機(オートグラフAG−100kNE型)を用い、模擬バンパ111の中央を2mm/minの速度で衝撃吸収部材の軸方向と平行に押圧した。すると、両衝撃吸収部材が軸方向に真っ直ぐに圧縮変形した。このときの変位と圧縮荷重の関係を測定した。その結果を、実施例1については図14に、比較例1については図15に示す。
Each of the prepared shock absorbing members was accommodated in a square cylindrical frame having a thickness of 0.5 mm and an outer dimension of 16 mm square. Then, as shown in FIG. 13, the pair of
その結果から明らかなように、模擬バンパに対して端面全体が接触した状態で接続されている比較例1では、圧縮し始めた直後に一端圧縮荷重が高まった後に少し下がって、その後は多少の上下はあるものの概ね安定した(図15)。それに対し、模擬バンパに対して一部分のみで接触した状態で接続されている実施例1では、圧縮し始めた直後に一時的に圧縮荷重が高まることはなく、圧縮開始直後からこれ以上圧縮できなくなるまで圧縮荷重が極めて安定していた(図14)。 As is clear from the results, in Comparative Example 1 in which the entire end face is in contact with the simulated bumper, the compression load slightly decreases after the compression load increases immediately after starting to compress, and then a little. Although there was up and down, it was almost stable (Fig. 15). On the other hand, in Example 1, which is connected to the simulated bumper in a state where it is in contact with only a part, the compression load does not increase temporarily immediately after starting to compress, and it becomes impossible to compress any more immediately after starting compression. The compression load was extremely stable until (FIG. 14).
(試験2)
試験2では、バンパ部材の車幅方向に真っ直ぐに延びる部分に衝撃吸収部材を配したときの衝撃吸収性能を評価した。図16に示されるように、模擬バンパ部材211として、厚み35mmのアルミニウムA5052製のストレートなブロックからなる剛体バンパリインホースを用意した。また、衝撃吸収部材として、実施例2と比較例2とで共通して、図7に示される衝撃吸収部材51と同じ形状の具体的な試料を用意した。用意した衝撃吸収部材は、29.4mm角×軸方向長さ70mmの角材であり、肉厚0.8mmで外寸31.6mm角の四角筒状枠体に収容して試験に供した。
(Test 2)
In Test 2, the impact absorbing performance was evaluated when the impact absorbing member was disposed in a portion of the bumper member extending straight in the vehicle width direction. As shown in FIG. 16, a rigid bumper-in hose made of a straight block made of aluminum A5052 having a thickness of 35 mm was prepared as the
[実施例2]
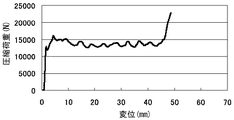
実施例2では、図16に示されるように、模擬バンパ211と衝撃吸収部材との間に介装する模擬ブラケットとして、アルミニウムA5052製のロの字型剛体リング213を用意した。なお、模擬ブラケットの形状をロの字型としたのは、バンパ部材と衝撃吸収部材との間にブラケットを介装した衝撃吸収構造の衝撃吸収性能を評価するにあたり、圧縮試験機に負荷される荷重の重心がずれることで、試験機が試験を中止するのを回避するためである。ロの字型剛体リング213の寸法は、内寸24mm角、外寸33mm角、厚み3mmである。平らな試験台Sに衝撃吸収部材を立設し、衝撃吸収部材の上に、互いに軸芯が一致するようにロの字型剛体リング213を載置した。それにより、衝撃吸収部材の端面において、四周の各辺が2.7mm幅でロの字型剛体リング213と接触している状態となった。さらに、その上に模擬バンパ部材211を載置した。そして、IMATEK社製衝撃圧縮試験機(IM10T−20HV)を用い、模擬バンパ211の中央を5.41m/secの速度で衝撃吸収部材の軸方向と平行に押圧した。すると、衝撃吸収部材が真っ直ぐに圧縮変形した。このときの変位と圧縮荷重の関係を測定した。その結果を、図17に示す。
[Example 2]
In Example 2, as shown in FIG. 16, a square-shaped
[比較例2]
比較例2では、模擬ブラケットとして、ロの字型剛体リングに替えて、33mm角、厚み3mmの中央に穴のないアルミニウムA5052製の剛体厚板を用い、衝撃吸収部材の端面全体がアルミニウムA5052製の剛体厚板と接触している状態として、実施例2と同様に試験した。すると、比較例2衝撃吸収部材が真っ直ぐに圧縮変形した。このときの変位と圧縮荷重の関係を測定した結果を図18に示す。
[Comparative Example 2]
In Comparative Example 2, a rigid thick plate made of aluminum A5052 without a hole in the center of a 33 mm square and a thickness of 3 mm is used as a simulated bracket instead of the square-shaped rigid ring, and the entire end face of the shock absorbing member is made of aluminum A5052. The test was conducted in the same manner as in Example 2 in a state where the plate was in contact with the rigid board. As a result, the impact absorbing member of Comparative Example 2 was directly compressed and deformed. The result of measuring the relationship between the displacement and the compressive load at this time is shown in FIG.
その結果から明らかなように、模擬ブラケットが衝撃吸収部材の端面全体に接触した状態で配されている比較例2では、圧縮し始めた直後に一端急激に圧縮荷重が高まった後に急激に下がって安定した(図18)。それに対し、模擬ブラケットが衝撃吸収部材の端面の一部のみに接触した状態で配されている実施例2では、圧縮し始めた直後に一時的に圧縮荷重が高まることはなく、圧縮開始直後からこれ以上圧縮できなくなるまで圧縮荷重が非常に安定していた(図17)。 As is apparent from the results, in Comparative Example 2 in which the simulated bracket is arranged in contact with the entire end face of the shock absorbing member, immediately after the compression starts, the compression load suddenly increases and then rapidly decreases. Stable (Figure 18). On the other hand, in Example 2 where the simulated bracket is arranged in contact with only a part of the end surface of the shock absorbing member, the compression load does not increase temporarily immediately after the compression starts, and immediately after the compression starts. The compression load was very stable until no further compression was possible (FIG. 17).
11 バンパリインホース
13 サイドメンバ
21 衝撃吸収部材
23 (バンパリインホース側の)端面
23a 接触面部
23b 離間面部
25 (サイドメンバ側の)端面
27 支持プレート
41 衝撃吸収部材
43 (バンパリインホース側の)端面
43a 接触面部
45 (サイドメンバ側の)端面
51 衝撃吸収部材
53 (バンパリインホース側の)端面
53a 接触面部
53b 離間面部
55 (サイドメンバ側の)端面
61 ブラケット
71 ブラケット
W 木材
11
Claims (1)
前記衝撃吸収部材が柱状の木材であり、その繊維方向が軸方向と平行であり、
前記衝撃吸収部材の一方の端面が前記バンパ部材又は前記車両骨格部材の一方にその一部分のみで面接触を介して連接されており、
前記衝撃吸収部材の他方の端面が前記バンパ部材又は前記車両骨格部材の他方にその全体で面接触を介して支持可能に連接されており、
前記衝撃吸収部材が、衝突開始時には前記一方の端面の一部分のみで圧縮荷重を受けて局所的に圧縮変形し、該局所的な圧縮変形を経て最終的には前記一方の端面の全体で圧縮荷重を受け、
前記衝撃吸収部材の前記一方の端面が軸方向に直交する一平面のみで形成され、介装物を介して前記バンパ部材又は前記車両骨格部材の一方に連接されており、
前記介装物が前記衝撃吸収部材よりも剛性の高い衝撃伝達部を有し、この衝撃伝達部が前記衝撃吸収部材の前記一方の端面の一部分のみと重複して配されていることを特徴とする車両の衝撃吸収構造。
Between the bumper member and the vehicle both skeletal members, a shock absorber for a vehicle equipped with a shock absorbing member for receiving the impact of a vehicle collision as a compression load in the axial direction,
The shock absorbing member is a columnar wood, the fiber direction is parallel to the axial direction,
Wherein one end face of the shock absorbing member is connected via only surface contact portion thereof to one of said bumper member and the vehicle frame member,
Wherein is supported capable connected via a surface contact the other end surface of the impact absorbing member on the other hand the whole of the bumper member or the vehicle frame member,
The impact absorbing member is locally deformed by compression under compressive load only a portion of the one end face at the start collision, ultimately through said local compression deformation in the entire end face of the one Under compressive load ,
The one end face of the shock absorbing member is formed by only one plane orthogonal to the axial direction, and is connected to one of the bumper member or the vehicle skeleton member via an interposed object,
The intervening object has an impact transmission portion having rigidity higher than that of the impact absorbing member, and the impact transmitting portion is arranged to overlap with only a part of the one end surface of the impact absorbing member. Vehicle shock absorption structure.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012071191A JP5522191B2 (en) | 2012-03-27 | 2012-03-27 | Vehicle shock absorption structure |
| PCT/JP2012/080223 WO2013080864A1 (en) | 2011-11-29 | 2012-11-21 | Shock-absorbing structure for vehicle |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012071191A JP5522191B2 (en) | 2012-03-27 | 2012-03-27 | Vehicle shock absorption structure |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013203106A JP2013203106A (en) | 2013-10-07 |
| JP2013203106A5 JP2013203106A5 (en) | 2013-12-05 |
| JP5522191B2 true JP5522191B2 (en) | 2014-06-18 |
Family
ID=49522706
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012071191A Active JP5522191B2 (en) | 2011-11-29 | 2012-03-27 | Vehicle shock absorption structure |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5522191B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6398853B2 (en) * | 2015-04-13 | 2018-10-03 | トヨタ車体株式会社 | Shock absorbing member |
| JP6354677B2 (en) * | 2015-06-25 | 2018-07-11 | トヨタ車体株式会社 | Vehicle shock absorption structure |
| JP6796244B2 (en) * | 2017-11-15 | 2020-12-09 | トヨタ車体株式会社 | Vehicle shock absorber |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001182769A (en) * | 1999-12-27 | 2001-07-06 | Showa Alum Corp | Shock absorbing member |
| JP2003054442A (en) * | 2001-08-16 | 2003-02-26 | Nippon Light Metal Co Ltd | Shock absorber |
| JP4852624B2 (en) * | 2009-03-31 | 2012-01-11 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Rail vehicle with collision mitigation device |
-
2012
- 2012-03-27 JP JP2012071191A patent/JP5522191B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013203106A (en) | 2013-10-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5545259B2 (en) | Shock absorbing member | |
| JP5945992B2 (en) | Shock absorption mechanism | |
| JP6677201B2 (en) | Vehicle shock absorber | |
| EP2202118B1 (en) | Impact absorbing member for vehicle | |
| WO2013150671A1 (en) | Impact-absorbing member for vehicle | |
| CN109774634B (en) | Vehicle shock absorbing member | |
| JP5776537B2 (en) | Shock absorber for vehicle | |
| WO2013164931A1 (en) | Impact absorption mechanism | |
| JP5522191B2 (en) | Vehicle shock absorption structure | |
| KR102346877B1 (en) | Skeletal members and vehicles for vehicles | |
| KR20110128650A (en) | Assembly Method of Bumper Beam for Vehicle | |
| WO2013080863A1 (en) | Shock-absorbing member for vehicle | |
| JP2012035691A (en) | Towing hook mounting structure of vehicle | |
| US20200406844A1 (en) | Structural member for vehicle | |
| JP6034729B2 (en) | Shock absorption mechanism for vehicles | |
| JP2013141936A (en) | Impact absorbing structure for vehicle | |
| KR20180136815A (en) | Vibro-impact energy absorbing device using composite crush tube and Vibration Damping Device for Building having the same | |
| JP6225800B2 (en) | Vehicle energy absorption structure | |
| JP5729274B2 (en) | Vehicle shock absorption structure | |
| WO2013080864A1 (en) | Shock-absorbing structure for vehicle | |
| JP2015182560A (en) | Vehicle shock absorption structure | |
| KR101603147B1 (en) | A stay for bumper beam | |
| KR101603143B1 (en) | Bumper stay unit for vehicle | |
| KR20120075026A (en) | A bumper beam unit for vehicles | |
| KR101551959B1 (en) | Rear roll rod for improving collision performance |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20131022 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20131022 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20131022 |
|
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20131119 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20131203 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140128 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20140311 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140324 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5522191 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |