JP5354255B2 - Imaging apparatus, photographing angle of view correction method, and program - Google Patents
Imaging apparatus, photographing angle of view correction method, and program Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5354255B2 JP5354255B2 JP2008251124A JP2008251124A JP5354255B2 JP 5354255 B2 JP5354255 B2 JP 5354255B2 JP 2008251124 A JP2008251124 A JP 2008251124A JP 2008251124 A JP2008251124 A JP 2008251124A JP 5354255 B2 JP5354255 B2 JP 5354255B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- view
- information
- angle
- subject
- imaging
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Description
本発明は、スチルカメラやビデオカメラまたはテレビカメラ等の撮像装置における撮影画角補正技術に関する。 The present invention relates to a photographing field angle correction technique in an imaging apparatus such as a still camera, a video camera, or a television camera.
撮像装置の撮影画角は使用する撮影レンズの焦点距離で決まるため、固定焦点レンズの場合、撮影対象によっては画角からはみ出したり、小さく写り過ぎたりするので、撮影位置(カメラポジション)を前後に移動しなければならないという面倒がある。ズームレンズを用いた光学的ズームや、画像処理によって電子的に行われるデジタルズーム(及びそれらの組み合わせ型ズーム)はこの欠点を解消したものであり、スチルカメラやビデオカメラまたはテレビカメラ等の撮像装置に多用されている。 Since the shooting angle of view of the imaging device is determined by the focal length of the shooting lens used, a fixed focus lens may protrude from the angle of view or be too small depending on the shooting target. There is the hassle of having to move. Optical zoom using a zoom lens and digital zoom (and their combination zoom) electronically performed by image processing have solved this drawback, and can be applied to imaging devices such as still cameras, video cameras, and television cameras. It is used a lot.
光学的ズームを代表にして説明すると、ズームレンズの操作方式は、機械的なものと電子的なものの二つがある。機械的な操作方式は、レンズ鏡筒の周囲に設けられた操作リングとズームレンズとを機械的に連結し、リングの動きに合わせてズームレンズを動かす(光軸に沿って前後に移動する)というものである。この方式の欠点は、構造が複雑になり、また、重量が増すことにある。一方、電子的な操作方式は、上記の操作リング等の操作手段の動きを電子的に検出し、その検出信号に基づいてズームレンズの駆動制御信号を生成するというものである。操作手段の設計自由度が高い(上記の操作リングだけでなくダイヤル式やシーソー式など自由に設計できる)うえ、機械的な連結機構が不要なため、構造を簡素化でき、しかも重量も軽減できるという利点があることから、今日、多くの撮像装置に用いられている方式である。 If the optical zoom is described as a representative, there are two methods of operating the zoom lens: mechanical and electronic. The mechanical operation system mechanically connects an operation ring and a zoom lens provided around the lens barrel, and moves the zoom lens according to the movement of the ring (moves back and forth along the optical axis). That's it. The disadvantage of this method is that the structure is complicated and the weight is increased. On the other hand, the electronic operation method is to electronically detect the movement of the operation means such as the operation ring and generate a zoom lens drive control signal based on the detection signal. There is a high degree of freedom in design of the operating means (it can be designed freely such as the dial type and seesaw type as well as the above operating ring), and since no mechanical coupling mechanism is required, the structure can be simplified and the weight can be reduced. Therefore, this system is used in many imaging apparatuses today.
かかるズームレンズの電子的な操作方式の従来技術としては、たとえば、下記の特許文献1に記載のものが知られている。この従来技術では、操作リングの内周面に等間隔に形成した反射部に向けて光を発射し、反射部からの反射光を受光部で受光して、その反射光の単位時間あたりの数を計数し、その計数結果に基づいてズームレンズの駆動制御信号を生成するようにしている。 As a prior art of an electronic operation method of such a zoom lens, for example, the one described in Patent Document 1 below is known. In this prior art, light is emitted toward the reflecting portion formed at equal intervals on the inner peripheral surface of the operation ring, the reflected light from the reflecting portion is received by the light receiving portion, and the number of the reflected light per unit time And a zoom lens drive control signal is generated based on the counting result.
この従来技術によれば、操作リングを大きく動かすと反射光の単位時間あたりの数が多くなってズームレンズを大きく駆動することができる一方、その逆に、操作リングを小さく動かすと反射光の単位時間あたりの数が少なくなってズームレンズを微細に駆動することができる。 According to this prior art, if the operation ring is moved greatly, the number of reflected light per unit time increases and the zoom lens can be driven greatly. Conversely, if the operation ring is moved small, the unit of reflected light is increased. The number per time is reduced and the zoom lens can be finely driven.
ところで、ズームレンズの画角を広角側から望遠側へ又はその逆へと一気に変更する場合、操作リングを大きく動かす必要がある。とりわけ、倍率が大きいズームレンズの場合、操作リングを相当大きく動かさなければならないが、人間の手首の動きには限界があるので、操作リングを動かしている途中で持ち直すなどの手間が生じることがある。この不都合を解消するためには、操作リングの動き検出値である前記の「光の計数結果」を増加すればよく、それには、「光の計数結果」に所要の係数を乗じればよい。たとえば、係数2を乗じれば、「光の計数結果」を2倍にすることができ、操作リングの必要な動き量を半減(1/2)してズーム操作の応答性を改善できる。
By the way, when changing the angle of view of the zoom lens from the wide-angle side to the telephoto side or vice versa, it is necessary to move the operation ring greatly. In particular, in the case of a zoom lens with a high magnification, the operation ring must be moved considerably. However, there is a limit to the movement of the human wrist, which may require troublesome operations such as holding the operation ring while moving the operation ring. . In order to eliminate this inconvenience, the “light counting result”, which is the motion detection value of the operation ring, may be increased, and the “light counting result” may be multiplied by a required coefficient. For example, if the
しかし、そのようにすると、今度は、所望の画角を微調整する際に不都合を生じる(きめ細かな動きが得られない)ので、従来技術では、要するに、操作リングの操作速度に対応させて前記の係数を増減変化させるようにしていると思われる。つまり、ズームレンズの画角を広角側から望遠側へ又はその逆へと一気に変更する場合は操作リングを素早く動かし、これに対して、所望画角付近で画角の微調整を行う場合は操作リングをゆっくり動かす、という一般的な操作傾向に着目し、操作リングを素早く動かしたときは「大きな係数」を、また、操作リングをゆっくりと動かしたときは「小さな係数」を採用するようにしていると推認される。 However, if this is done, then inconvenience will occur when finely adjusting the desired angle of view (a fine movement cannot be obtained). It seems that the coefficient of change is increased or decreased. In other words, when changing the zoom lens angle of view from the wide-angle side to the telephoto side or vice versa, move the operating ring quickly, while to fine-tune the angle of view near the desired angle of view. Paying attention to the general operation tendency of moving the ring slowly, adopt a “large coefficient” when moving the operation ring quickly, and adopt a “small coefficient” when moving the operation ring slowly. It is inferred that
しかしながら、前記の従来技術にあっては、下記の点で、必ずしも撮影者の操作傾向に従うものではなく、とりわけ、所望画角付近で画角の微調整を行う際に不都合を生じるという問題点がある。 However, the above-described prior art does not always follow the photographer's operation tendency in the following points, and in particular, there is a problem that inconvenience occurs when finely adjusting the angle of view near the desired angle of view. is there.
このことについて詳述すると、まず、従来技術における第一の前提(ズームレンズの画角を広角側から望遠側へ又はその逆へと一気に変更する場合は操作リングを素早く動かす)については異論がないが、第二の前提(所望画角付近で画角の微調整を行う場合は操作リングをゆっくり動かす)については、必ずしもそうとは言い切れない。 This will be described in detail. First, there is no objection to the first premise in the prior art (when the angle of view of the zoom lens is changed from the wide angle side to the telephoto side or vice versa, the operation ring is moved quickly). However, the second premise (when the angle of view is finely adjusted near the desired angle of view, the operating ring is moved slowly) is not necessarily the case.
撮影者によっては、素早く小刻みに操作リングを動かすことがあるからであり、特にズーム操作に手慣れた撮影者にその傾向が見られるからである。 This is because, depending on the photographer, the operation ring may be moved quickly and in small increments, and this tendency is especially seen by photographers who are familiar with zoom operations.
したがって、従来技術にあっては、所望画角付近で画角の微調整を行う際に、素早く小刻みに操作リングを動かしたときにも「大きな係数」が設定されてしまうことがあるから、画角の微調整を行い難くなるという問題点がある。 Therefore, in the prior art, when performing fine adjustment of the angle of view near the desired angle of view, a “large coefficient” may be set even when the operation ring is moved quickly in small increments. There is a problem that it becomes difficult to finely adjust the corners.
そこで、本発明の目的は、ズーム操作の応答性を改善した撮像装置、撮影画角補正方法及びプログラムを提供することにある。 Therefore, an object of the present invention is to provide an imaging apparatus, a shooting angle of view correction method, and a program that improve the responsiveness of a zoom operation.
請求項1記載の発明は、撮影画角の変更が可能な撮像手段と、前記撮像手段の撮影画角を変更するための操作手段と、被写体に対する前記操作手段による撮影画角の変更を伴う構図調整から前記撮像手段への撮像指示に至る間に検出される被写体に関するイベント情報を収集する収集手段と、前記収集手段によって収集された前記被写体に関するイベント情報に基づいて、前記操作手段による前記撮像手段の撮影画角の変更速度を制御する画角制御手段とを備え、前記被写体に関するイベント情報は、AF合焦情報、手振れ情報、ハーフシャッタ情報、被写体の顔が検出されたか否かの顔検出情報、または被写体の検出された顔の数の情報のいずれかであり、複数のイベント情報のそれぞれに対応して評価点数を付与し、前記画角制御手段は、前記評価点数を組み合わせて用いて前記撮像手段の撮影画角の変更速度を制御することを特徴とする撮像装置である。
請求項2記載の発明は、撮像手段の撮影画角の変更が可能な撮像ステップと、前記撮像手段の撮影画角を変更するための操作ステップと、被写体に対する前記操作ステップによる撮影画角の変更を伴う構図調整から前記撮像手段への撮像指示に至る間に検出される被写体に関するイベント情報を収集する収集ステップと、前記収集ステップにて収集された前記被写体に関するイベント情報に基づいて、前記操作ステップによる前記撮像手段の撮影画角の変更速度を制御する画角制御ステップとを含み、前記被写体に関するイベント情報は、AF合焦情報、手振れ情報、ハーフシャッタ情報、被写体の顔が検出されたか否かの顔検出情報、または被写体の検出された顔の数の情報のいずれかであり、複数のイベント情報のそれぞれに対応して評価点数を付与し、前記画角制御ステップは、前記評価点数を組み合わせて用いて前記撮像手段の撮影画角の変更速度を制御することを特徴とする撮影画角補正方法である。
請求項3記載の発明は、撮影画角の変更が可能な撮像手段とその撮影画角を変更するための操作手段とを備えた撮像装置が具備するコンピュータを、被写体に対する前記操作手段による撮影画角の変更を伴う構図調整から前記撮像手段への撮像指示に至る間に検出される被写体に関するイベント情報を収集する収集手段、前記収集手段によって収集された前記被写体に関するイベント情報に基づいて、前記操作手段による前記撮像手段の撮影画角の変更速度を制御する画角制御手段として機能させるとともに、前記被写体に関するイベント情報は、AF合焦情報、手振れ情報、ハーフシャッタ情報、被写体の顔が検出されたか否かの顔検出情報、または被写体の検出された顔の数の情報のいずれかであり、複数のイベント情報のそれぞれに対応して評価点数を付与し、前記画角制御手段は、前記評価点数を組み合わせて用いて前記撮像手段の撮影画角の変更速度を制御することを特徴とするプログラムである。
According to the first aspect of the present invention, there is provided an imaging means capable of changing a shooting angle of view, an operation means for changing a shooting angle of view of the imaging means, and a composition involving a change of the shooting angle of view by the operating means for a subject. Collecting means for collecting event information relating to a subject detected during the period from adjustment to an imaging instruction to the imaging means, and the imaging means by the operating means based on event information relating to the subject collected by the collecting means Angle-of-view control means for controlling the change speed of the shooting angle of view, and the event information relating to the subject includes AF focus information, camera shake information, half-shutter information, and face detection information as to whether or not the face of the subject has been detected. or Ri der any number of information of detected face of the subject, for each of the plurality of event information to grant merit, the view angle control means An imaging apparatus characterized by controlling the change rate of the imaging angle of the imaging means by using a combination of the evaluation scores.
According to a second aspect of the present invention, an imaging step capable of changing a shooting field angle of the imaging unit, an operation step for changing the shooting field angle of the imaging unit, and a change of the shooting field angle by the operation step for a subject. A collection step for collecting event information relating to a subject detected during a period from composition adjustment involving imaging to an imaging instruction to the imaging means, and the operation step based on the event information relating to the subject collected in the collection step And an angle-of-view control step for controlling a change speed of a shooting angle of view of the imaging means according to the above, and the event information regarding the subject includes AF focus information, camera shake information, half-shutter information, and whether or not the face of the subject is detected. face detection information or Ri der either detected number information of the face of the subject, criticism in correspondence with each of the plurality of event information, Grant points, the field angle control step, a photographing field angle correction method characterized by controlling the change rate of the imaging angle of the imaging means by using a combination of the evaluation scores.
According to a third aspect of the present invention, there is provided a computer having an imaging device including an imaging unit capable of changing a shooting angle of view and an operation unit for changing the shooting angle of view. Collecting means for collecting event information relating to a subject detected during composition adjustment accompanied by a change in angle and imaging instructions to the imaging means, and based on the event information relating to the subject collected by the collecting means, the operation Function as an angle of view control means for controlling the change speed of the imaging angle of view of the imaging means by the means, and the event information relating to the subject includes AF focus information, camera shake information, half shutter information, whether the subject's face has been detected. whether the face detection information or Ri der any number of information of the detected face of the subject, pairs with each of the plurality of event information The evaluation score assigned by the angle control means is a program characterized by controlling the change rate of the imaging angle of the imaging means by using a combination of the evaluation scores.
本発明によれば、ズーム操作の応答性を改善した撮像装置、撮影画角補正方法及びプログラムを提供することができる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, the imaging device which improved the responsiveness of zoom operation, the imaging | photography angle-of-view correction method, and a program can be provided.
以下、本発明の実施形態を、デジタルカメラへの適用を例にして、図面を参照しながら説明する。なお、以下の説明における様々な細部の特定ないし実例および数値や文字列その他の記号の例示は、本発明の思想を明瞭にするための、あくまでも参考であって、それらのすべてまたは一部によって本発明の思想が限定されないことは明らかである。また、周知の手法、周知の手順、周知のアーキテクチャおよび周知の回路構成等(以下「周知事項」)についてはその細部にわたる説明を避けるが、これも説明を簡潔にするためであって、これら周知事項のすべてまたは一部を意図的に排除するものではない。かかる周知事項は本発明の出願時点で当業者の知り得るところであるので、以下の説明に当然含まれている。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings, taking application to a digital camera as an example. It should be noted that the specific details or examples in the following description and the illustrations of numerical values, character strings, and other symbols are only for reference in order to clarify the idea of the present invention, and the present invention may be used in whole or in part. Obviously, the idea of the invention is not limited. In addition, a well-known technique, a well-known procedure, a well-known architecture, a well-known circuit configuration, and the like (hereinafter, “well-known matter”) are not described in detail, but this is also to simplify the description. Not all or part of the matter is intentionally excluded. Such well-known matters are known to those skilled in the art at the time of filing of the present invention, and are naturally included in the following description.
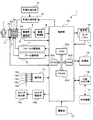
図1は、デジタルカメラの概念構成図である。この図において、デジタルカメラ1は、撮影レンズ2aやズームレンズ2b及びフォーカスレンズ2c並びに手振れ補正レンズ2dなどを含む光学系2と、この光学系2を介して取り込まれた被写体3の像を撮像するCCDやCMOS等の二次元イメージセンサを含む撮像部4と、被写体3までの距離を測定するコンティニアスAF(一度、合焦すると構図を変えても合焦を追従するAF方式)の測距部5と、撮像部4で撮像された画像信号に所要の画像処理(ガンマ補正等)を施す画像処理部6と、フォーカスレンズ2cを駆動するフォーカス駆動部7と、ズームレンズ2bを駆動するズーム駆動部8と、加速度センサ等によってデジタルカメラ1の動き(つまり手振れ)を検出する手振れ検出部9及びその手振れ検出部9の検出結果を打ち消すように手振れ補正レンズ2dを撮影レンズ2aの光軸の直交方向に駆動する手振れ補正部10と、光学系2のレンズ鏡筒の周囲に回動自在に取り付けられたズーム操作用の操作リング11と、各種ボタン類(撮影動作と再生動作とのモード切り換えボタン12aやメニューボタン12b、カーソルキー12c及びシャッタボタン12d、音声収録ボタン12eなど)を含む操作部12と、ストロボ発光部13a及びストロボ駆動部13bと、液晶ディスプレイ等からなる表示部14と、この表示部14の表示面上に併設されたタッチパネル15と、固定式又は着脱式の大容量記憶デバイスで構成された記憶部16と、パーソナルコンピュータ等の外部機器17との間のデータ入出力を必要に応じて仲介する外部入出力部18と、バッテリ等を含む電源部19と、制御部20とを備える。
FIG. 1 is a conceptual configuration diagram of a digital camera. In this figure, a digital camera 1 captures an image of an
制御部20は、コンピュータ(以下、CPU)20a、不揮発性メモリ(以下、ROM)20b、揮発性メモリ(以下、RAM)20c及び書き換え可能型不揮発性メモリ(以下、PROM)20dを備えており、ROM20bに予め格納されている制御プログラムやPROM20dに予め又は任意に書き込まれるデータをRAM20cにロードしてCPU20aで実行することにより、つまり、プログラム制御方式によって、このデジタルカメラ1の撮影機能や再生機能などを統括制御するものであるが、これに限らず、その機能の全て又は一部をハードロジックで実現してもよいことはもちろんである。
The
図示のデジタルカメラ1は、操作部12のモード切り換えボタン12aが「撮影」位置にあるときに撮影モード(静止画又は動画撮影モード)で動作し、「再生」位置にあるときに再生モードで動作する。
The illustrated digital camera 1 operates in the shooting mode (still image or moving image shooting mode) when the
静止画又は動画撮影モードを選択した場合、撮像部4から周期的(毎秒数十フレーム)に出力される画像信号が、画像処理部6と制御部20を経て表示部14に出力され、構図確認用のスルー画像として継続的に表示される。撮影者は、スルー画像を見ながら所望の構図になるように撮影方向や撮像部4の画角(ズーム倍率)などを調節し、所望の画角と構図が得られたときにハーフシャッタ操作(シャッタボタン12dの半押し操作)を行う。
When the still image or moving image shooting mode is selected, an image signal output periodically (several tens of frames per second) from the
そして、ハーフシャッタ操作に応答して、AF(自動焦点)やAE(自動露出)及び手振れ補正などの事前処理が実行され、その後のシャッタレリーズ操作(シャッタボタン12dの全押し操作)に応答して、撮像部4から高画質の画像信号が取り出される。この画像信号は、画像処理部6と制御部20を経て記憶部16に送られ、撮影済み画像として記憶部16に記録保存される。この撮影済み画像は、撮像部4から取り出された高画質の画像信号に相当する生画像であってもよいが、生画像はサイズが大きく、記憶部16の記憶容量を圧迫するので、たとえば、JPEG(Joint Photographic Experts Group)等の汎用圧縮技術を用いて圧縮した画像を撮影済み画像として記録することが望ましい。
In response to the half shutter operation, pre-processing such as AF (auto focus), AE (auto exposure) and camera shake correction is executed, and in response to the subsequent shutter release operation (full pressing operation of the
再生モードを選択した場合、直近に撮影された画像を記憶部16から読み出し、表示部14に拡大表示する。あるいは、撮影済み画像の縮小画像を記憶部16から読み出して表示部14に一覧表示し、その一覧の中から再生を希望する画像を選択して、その元画像を記憶部16から読み出して表示部14に拡大表示する。
When the reproduction mode is selected, the most recently captured image is read from the
以上の撮影モードと再生モードの動作は、従来公知のものであるが、本実施形態においては、それに加えて、以下の特徴的事項を含む。 The above-described operations in the shooting mode and the playback mode are conventionally known, but in the present embodiment, the following characteristic items are included in addition thereto.
図2は、本実施形態の操作リング11の構成を示す図である。この図において、操作リング11は、デジタルカメラ1のボディ21の前面から突出するレンズ鏡筒22の周囲に回動自在に取り付けられた環状部材であり、被写体に向かって時計回り方向に回動させると望遠側、反時計回り方向に回動させると広角側へのズーム操作となる。図において、Tは望遠、Wは広角の略である。
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of the
操作リング11の外表面は、たとえば、細かな凹凸を形成するなどして滑り止め加工が施されており、また、その内表面には、その周方向に沿って等間隔に配列された多数の反射部材(ミラーまたは鏡面仕上げされたもの)23が取り付けられている。
The outer surface of the
操作リング11に対向するレンズ鏡筒22の外表面には発光素子部24と受光素子25が近接して取り付けられており、発光素子部24は、発光駆動部26からの駆動信号を受けて発光し、その光で操作リング11の内周面をスポット照明する。操作リング11の内周面には多数の反射部材23が等間隔で配列されているので、スポット光が任意の反射部材23に照射されると、その反射部材23でスポット光が反射する。この反射光は受光素子25に受光され、受光信号生成部27によって信号成形された後、信号計数部28に取り込まれる。そして、この信号計数部28によって、単位時間あたりの受光数が計数された後、この計数結果が、操作リング11の回動量を示すズーム操作検出信号としてズーム制御部29に出力される。また、この受光素子部24は、複数の受光素子からなり、時間の経過に伴う各受光素子の受光量の遷移から、操作リング11は、W方向へ回転しているのか、T方向へ回転しているのか、を判別する。
A light emitting
ズーム制御部29は、図1の制御部21において、プログラム制御方式により機能的に実現されたブロック部であり、本実施形態に特有の構成要素である。このズーム制御部29は、要するに、信号計数部28から出力されたズーム操作検出信号(操作リング11の回動量に比例したもの)に所要の補正を加えることにより、ズーム操作の応答性改善と、所望画角付近での画角微調整の性能向上とを共に達成するための信号特性を与えるものである。この“信号特性”の詳細については、以降の説明でも明らかになるが、その概要を説明すれば、以下のとおりである。
The
すなわち、ズームレンズの画角を広角側から望遠側へ又はその逆へと一気に変更する場合、操作リングを大きく動かす必要があり、とりわけ、倍率が大きいズームレンズの場合、操作リングを相当大きく動かさなければならないが、人間の手首の動きには限界があるので、操作リングを動かしている途中で持ち直すなどの手間が生じることがある。この欠点を解消するには、操作リングの動き検出値である「光の計数結果」(本実施形態の信号計数部28から出力されたズーム操作検出信号に相当)に所要の係数を乗じればよい。たとえば、係数2を乗じれば、「光の計数結果」を2倍にすることができ、操作リングの動き量を半減(1/2)してズーム操作の応答性を改善できるが、そうすると今度は、所望の画角を微調整する際に不都合を生じるので、冒頭で説明した従来技術では、要するに、操作リングの操作速度に対応させて前記の係数を増減変化させるようにしている。つまり、ズームレンズの画角を広角側から望遠側へ又はその逆へと一気に変更する場合は操作リングを素早く動かし、これに対して、所望画角付近で画角の微調整を行う場合は操作リングをゆっくり動かす、という一般的な操作傾向に着目し、操作リングを素早く動かしたときは「大きな係数」を、また、操作リングをゆっくりと動かしたときは「小さな係数」を採用するようにしている。
In other words, when changing the angle of view of the zoom lens from the wide-angle side to the telephoto side or vice versa, it is necessary to move the operation ring greatly, especially in the case of a zoom lens with a large magnification, the operation ring must be moved considerably. However, since there is a limit to the movement of the human wrist, there are cases where troubles such as re-handling the operation ring while moving it. In order to eliminate this drawback, the “light counting result” (corresponding to the zoom operation detection signal output from the
しかしながら、この方法にあっては、「所望画角付近で画角の微調整を行う場合は操作リングをゆっくり動かす」という前提の元で、操作リングをゆっくりと動かしたときは「小さな係数」を採用するようにしているが、そもそも、この前提が成立しないことがある。撮影者によっては、素早く小刻みに操作リングを動かすことがあるからであり、特にズーム操作に手慣れた撮影者にその傾向が見られるからである。したがって、従来技術にあっては、所望画角付近で画角の微調整を行う際に、素早く小刻みに操作リングを動かしたときにも「大きな係数」が設定されてしまうことがあるから、画角の微調整を行い難くなるという問題点があった。 However, with this method, under the premise that “if the angle of view is finely adjusted near the desired angle of view, the operating ring is moved slowly”, when the operating ring is moved slowly, a “small coefficient” is set. In the first place, this premise may not be established. This is because, depending on the photographer, the operation ring may be moved quickly and in small increments, and this tendency is especially seen by photographers who are familiar with zoom operations. Therefore, in the prior art, when performing fine adjustment of the angle of view near the desired angle of view, a “large coefficient” may be set even when the operation ring is moved quickly in small increments. There was a problem that it was difficult to finely adjust the corners.
そこで、本実施形態では、従来技術のように、操作リングの操作速度に対応させてズームレンズの駆動特性を制御するのではなく、ズーム操作に伴って被写体がだんだんと特定されるにつれて上がってくる各種の“イベント情報”に基づいて、ズームレンズの駆動特性を制御するようにしたものであり、これによって、ズーム操作の応答性改善を図ると共に、所望画角付近での画角微調整の性能向上を達成したズーム制御装置、ズーム制御方法及びプログラムを提供することを意図したものである。 Therefore, in this embodiment, unlike the conventional technique, the driving characteristics of the zoom lens are not controlled in accordance with the operation speed of the operation ring, and the subject is gradually increased as the subject is specified as the zoom operation is performed. The drive characteristics of the zoom lens are controlled based on various types of “event information”. This improves the responsiveness of the zoom operation and also makes fine adjustments to the angle of view near the desired angle of view. It is intended to provide a zoom control device, a zoom control method, and a program that achieve improvement.
ここで、上記のイベント情報とは、画角調整からシャッタレリーズ操作までの間においてデジタルカメラ1の内部で発生する様々な処理イベント情報のことをいい、具体的には、AF合焦情報や手振れ情報、顔検出情報またはハーフシャッタ情報などを指す。AF合焦情報は被写体へのピントの合い具合を示す情報であり、手振れ情報はデジタルカメラ1に加えられる手振れの大小及びその方向を示す情報である。また、顔検出情報は撮影画角内に人間の顔があるか否か及びある場合にはその顔の数を示す情報であり、さらに、ハーフシャッタ情報は撮影者によるシャッタボタン12dの「半押し操作」、つまり、シャッタレリーズ操作直前のAF確定及びAE確定操作の情報である。これらの情報から、画角調整のためのズーム操作なのか、または、シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のためのズーム操作なのかを判別することができる。たとえば、AF合焦情報が非合焦状態(ピント外れ状態)を示していたり、あるいは、手振れ情報が手振れありを示していれば、画角調整のためのズーム操作であると判定でき、一方、AF合焦情報が合焦状態を示していたり、あるいは、手振れ情報が手振れなしを示していれば、シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のためのズーム操作であると判定できる。
Here, the above event information refers to various processing event information that occurs inside the digital camera 1 from the angle of view adjustment to the shutter release operation, and specifically, AF focusing information and camera shake. Information, face detection information, or half shutter information. The AF focusing information is information indicating the degree of focus on the subject, and the camera shake information is information indicating the magnitude and direction of camera shake applied to the digital camera 1. The face detection information is information indicating whether or not there is a human face within the shooting angle of view and, if there is, the number of faces, and the half shutter information is “half-pressed” of the
この判定は、ハーフシャッタ情報においても同様である。ハーフシャッタ情報が非ハーフシャッタ状態(シャッタボタン12dが押されていない状態)を示していた場合は、まだ、シャッタレリーズ操作直前のAF確定やAE確定の操作が行われていないので、この場合は、画角調整のためのズーム操作である可能性が高いと判定でき、一方、ハーフシャッタ状態(シャッタボタン12dが半押しされている状態)を示していた場合は、シャッタレリーズ操作直前のAF確定やAE確定の操作が行われたことを示しているので、この場合は、シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のためのズーム操作であると判定することができるからである。
This determination is the same for the half shutter information. If the half-shutter information indicates a non-half-shutter state (a state where the
なお、顔検出情報については、この情報だけで上記の判定は行えない。風景撮影などのように、被写体を人間としない場合もあるからである。顔検出情報は、上記のAF合焦情報や手振れ情報及びハーフシャッタ情報などと併用すべき情報である。これらの情報(AF合焦情報や手振れ情報及びハーフシャッタ情報)によってシャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のためのズーム操作であると判定された際に、さらに、顔検出情報を考慮して再判定することが望ましい。顔検出ありを検出した場合は上記の判定を補強(その判定結果をより確かにする)することができるからである。 For face detection information, the above determination cannot be made with this information alone. This is because the subject may not be a human being, such as in landscape photography. The face detection information is information that should be used in combination with the above AF focusing information, camera shake information, half shutter information, and the like. When it is determined by these pieces of information (AF focusing information, camera shake information, and half shutter information) that the zoom operation is for fine composition adjustment just before the shutter release, the determination is further performed in consideration of the face detection information. It is desirable. This is because when the presence of face detection is detected, the above determination can be reinforced (the determination result is made more reliable).
次に、本実施形態の具体的な制御動作の一例を説明する。
図3は、制御部20のCPU20aで実行される制御プログラムの要部フローを示す図である。このフローは、制御プログラムのうちのズーム制御に係わる部分を抜き出して概略的に示しており、この要部フローは、操作リング11が動かされたときに実行されるものである。この要部フローにおいては、まず、カメラ情報を収集して所要のテーブル(図4のカメラ情報テーブル30参照)に格納する(ステップS1)。カメラ情報とは、前記の“イベント情報”、つまり、画角調整からシャッタレリーズ操作までの間においてデジタルカメラ1の内部で発生する様々な処理イベントの情報のことであり、具体的には、AF合焦情報や手振れ情報、顔検出情報またはハーフシャッタ情報などである。
Next, an example of a specific control operation of this embodiment will be described.
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing a main part flow of a control program executed by the
カメラ情報の収集を完了すると、次に、収集したカメラ情報に基づいて、ズーム補正係数を演算する(ステップS2)。ズーム補正係数とは、図2の信号計数部28から出力されたズーム操作検出信号(操作リング11の回動量に比例したもの)に適用する係数のことである。このズーム補正係数を1にするとズーム操作検出信号は無補正になるが、1を越える値(>1)にすればズーム操作検出信号が増加し、1未満(<1)にすればズーム操作検出信号が減少するように補正される。なお、「増加」または「減少」とは、単位時間あたりの信号数の増減のことをいう。具体的には、操作リング11をXだけ回動させたときの受光素子25の受光パルス数をYとしたとき、ズーム補正係数=1であれば、このYは変わらない(無補正)が、ズーム補正係数>1にすると実質的にYが増加し、また、ズーム補正係数<1にすると実質的にYが減少する。
When the collection of camera information is completed, a zoom correction coefficient is then calculated based on the collected camera information (step S2). The zoom correction coefficient is a coefficient applied to the zoom operation detection signal (proportional to the rotation amount of the operation ring 11) output from the
図4は、ズーム補正係数を演算する際に参照されるカメラ情報テーブルを示す図である。この図において、カメラ情報テーブル30は、AF合焦情報や手振れ情報及び顔検出情報並びにハーフシャッタ情報などを格納したカメラ情報フィールド30aと、それらの情報に対応した評価点数を格納した評価点数フィールド30bとによって構成されている。ここで、図中の評価点数A、B、C、Dは説明の便宜上のものである。ズーム補正係数は、これらの評価点数A、B、C、Dを単独で用いまたは組み合わせて用いることによって得られる。このズーム補正係数は、画角調整のためのズーム操作なのか、シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のためのズーム操作なのかを判別することができるものであればよく、たとえば、以下のようなものであってもよい。
FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating a camera information table referred to when calculating the zoom correction coefficient. In this figure, the camera information table 30 includes a
図5は、評価点数の実際例を示す図である。この図において、カメラ情報テーブル31は、状態フィールド31aと、項目フィールド31bと、評価点数フィールド31cとから構成されている。状態フィールド31aには、カメラ情報(ここでは撮影画像とカメラに関する情報)が格納されており、項目フィールド31bには、カメラ情報ごとの詳細項目、たとえば、撮影画像について、顔検出1つ、顔検出2つ、顔検出それ以上、顔の大きさ「大」、顔の大きさ「小」、画像類似設定ON:検出大、画像類似設定ON:検出小、画像類似設定OFF、AF合焦、などが、また、カメラについて、コンティニアスAF:ON、手振れ:大、手振れ:中、手振れ:小、などが格納されており、評価点数フィールド31cには、各項目ごとの評価点数が格納されている。
FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating an actual example of the evaluation score. In this figure, the camera information table 31 includes a
ここで、顔検出1つの評価点数は「50」、顔検出2つの評価点数は「20」、顔検出それ以上の評価点数は「10」、顔の大きさ「大」の評価点数は「50」、顔の大きさ「小」の評価点数は「10」である。評価点数が大きいほど、シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のためのズーム操作であることを示す。図示の例では、顔検出1つと顔の大きさ「大」の評価点数が最大の「50」となっており、顔検出2つの評価点数「20」がそれに次ぎ、顔検出それ以上(2つ以上)と、顔の大きさ「小」の評価点数が最小の「10」となっている。これは、顔検出が1つのとき、または、顔の大きさが「大」のときは、シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のためのズーム操作であると判断して差し支えないからであり、これに対して、顔検出が2つのときは、被写体振れに伴う顔の誤検出の可能性があるために、シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のためのズーム操作であると判断し切れないからである。さらに、顔検出それ以上(2つ以上)と、顔の大きさ「小」のときは、より一層、シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のためのズーム操作であると判断し切れないからである。このような考え方に基づいて、顔検出情報に対する評価点数を適切に設定すればよい。 Here, the evaluation score for one face detection is “50”, the evaluation score for two face detections is “20”, the evaluation score for face detection is “10”, and the evaluation score for the face size “large” is “50”. The evaluation score for the face size “small” is “10”. A larger evaluation score indicates a zoom operation for composition fine adjustment just before the shutter release. In the example shown in the figure, the evaluation score for one face detection and the face size “Large” is “50” which is the maximum, and the two evaluation scores “20” are next, followed by more than two face detection (two As described above, the evaluation score for the face size “small” is the smallest “10”. This is because when there is one face detection or when the face size is “large”, it may be determined that the zoom operation is for fine composition adjustment just before the shutter release. On the other hand, when there are two face detections, there is a possibility that the face is erroneously detected due to the subject shake, so that it cannot be determined that the zoom operation is for fine composition adjustment just before the shutter release. Further, when the face is detected more than two (two or more) and the face size is “small”, it cannot be determined that the zoom operation is for fine composition adjustment just before the shutter release. Based on this concept, the evaluation score for the face detection information may be set appropriately.
また、画像類似設定ON:検出大の評価点数が「100」、画像類似設定ON:検出小の評価点数が「30」、画像類似設定OFFの評価点数が「0」となっているが、これは、画像類似設定、つまり、顔検出を特定の人物画像に基づいて行う場合(ONの場合)に、その類似度合いが大であるときには、シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のためのズーム操作であると判断して差し支えないからであり、一方、画像類似設定ON:検出小のときには、多少の疑いはあるものの、やはり、シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のためのズーム操作であると判断して差し支えないからである。これに対して、画像類似設定OFFのときには、その類似判定結果を無視するために、その評価点数を「0」としたものである。 Also, the image similarity setting ON: the evaluation score of large detection is “100”, the image similarity setting ON: the evaluation score of small detection is “30”, and the evaluation score of the image similarity setting OFF is “0”. Is a zoom operation for fine composition adjustment immediately before the shutter release when the image similarity setting, that is, when face detection is performed based on a specific person image (when ON) and the degree of similarity is large. On the other hand, when the image similarity setting is ON: the detection is small, it may be determined that the zoom operation is for fine composition adjustment just before the shutter release, although there is some doubt. Because there is no. On the other hand, when the image similarity setting is OFF, the evaluation score is set to “0” in order to ignore the similarity determination result.
また、AF合焦の評価点数が「100」、コンティニアスAF:ONの評価点数が「50」、手振れ:大の評価点数が「10」、手振れ:中の評価点数が「30」、手振れ:小の評価点数が「50」となっているが、これは、AF合焦の場合は、シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のためのズーム操作であると判断して差し支えないからであり、さらに、コンティニアスAF:ONの場合も、一度、合焦すると、構図をずらしてもその合焦動作が継続(コンティニアスAF)されるため、やはり、シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のためのズーム操作であると判断して差し支えないからである。また、手振れの大きさが小さくなるほど、シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のためのズーム操作であると判断して差し支えないからである。 Also, the AF in-focus evaluation score is “100”, the continuous AF: ON evaluation score is “50”, hand shake: large evaluation score is “10”, hand shake: middle evaluation score is “30”, hand shake: The small evaluation score is “50”. This is because, in the case of AF in-focus, it may be determined that the zoom operation is for fine composition adjustment just before the shutter release. Even in the case of continuous AF: ON, once in-focus, the in-focus operation continues even if the composition is shifted (continuous AF). Therefore, the zoom operation for fine composition adjustment just before the shutter release is also performed. This is because it can be judged that there is. Moreover, it is because it may be judged that it is a zoom operation for composition fine adjustment just before a shutter release, so that the magnitude | size of camera shake becomes small.
なお、図5の評価点数は、最小値の0から最大値の100までであるが、これは説明上の便宜値に過ぎない。前記例示の係数(1、>1、<1)に対応させるのであれば、それぞれを割合(%)で表してもよい。つまり、最小値の0を0%、最大値の100を100%と読み替えてもよい。そのようにすれば、0%は前記例示の係数1に相当し、100%は前記例示の係数2に相当することとなり、これらの評価点数を総合的に加味することによって、1〜2までのズーム補正係数を演算することができる。
The number of evaluation points in FIG. 5 is from a minimum value of 0 to a maximum value of 100, but this is merely a convenient value for explanation. If they correspond to the exemplified coefficients (1,> 1, <1), each may be expressed as a percentage (%). That is, the minimum value 0 may be read as 0%, and the
以上のようにして、ズーム補正係数を演算すると、次に、ズーム制御量を演算する(ステップS3)。このズーム制御量は、たとえば、ズームリング操作量に、ステップS2で演算したズーム補正係数を乗じた結果で得ることができる。つまり、「ズーム制御量=ズームリング操作量×ズーム補正係数」である。ズームリング操作量とは、操作リング11の回動量と回動方向(WまたはT)を示す値であり、ズーム操作検出信号(操作リング11の回動量に比例したもの)から与えられる。
Once the zoom correction coefficient is calculated as described above, the zoom control amount is then calculated (step S3). This zoom control amount can be obtained, for example, as a result of multiplying the zoom ring operation amount by the zoom correction coefficient calculated in step S2. That is, “zoom control amount = zoom ring operation amount × zoom correction coefficient”. The zoom ring operation amount is a value indicating the rotation amount and rotation direction (W or T) of the
ズーム制御量は、ズーム駆動部8に与える制御量のことであり、ズーム駆動部8は、このズーム制御量に従ってズームレンズ2bを駆動するための駆動信号を生成出力する。このようにして、ズーム制御量を用いてズームレンズ2bを駆動制御(ステップS4)すると、次に、ズーム操作の完了(操作リング11の回動操作完了)を判定し(ステップS5)、完了を判定しなければ、再び、ステップS1以降を繰り返し、完了を判定すると、プログラムを終了する。
The zoom control amount is a control amount given to the
以上のとおり、本実施形態によれば、従来技術のように、操作リングの操作速度に対応させてズームレンズの駆動特性を制御するのではなく、ズーム操作に伴って被写体がだんだんと特定されるにつれて上がってくる各種の“イベント情報”(AF合焦情報や手振れ情報、顔検出情報またはハーフシャッタ情報など)に基づいて、ズームレンズの駆動特性を制御するようにしたので、操作リング11の回動操作が「画角調整のため」か、それとも、「シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のため」かを確実に判別することができる。
As described above, according to the present embodiment, the subject is gradually identified as the zoom operation is performed, instead of controlling the driving characteristics of the zoom lens in accordance with the operation speed of the operation ring as in the conventional technique. Since the driving characteristics of the zoom lens are controlled based on various “event information” (AF focusing information, camera shake information, face detection information, half shutter information, etc.) that rises as the
そして、その判定結果に基づいて、ズーム操作が「画角調整のため」の場合にはズーム制御速度特性を“速め”にする一方、「シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のため」の場合にはズーム制御速度特性を“遅め”にすることにより、たとえば、ズームレンズの画角を広角側から望遠側へ又はその逆へと一気に変更する場合には速やかにズームして応答性の向上を図りつつ、所望の画角を微調整する際にはゆっくりとズームして画角微調整の性能向上を図ることができるのである。 Based on the determination result, when the zoom operation is “for angle of view adjustment”, the zoom control speed characteristic is set to “fast”, while when “for fine composition adjustment immediately before the shutter release” is set. By making the zoom control speed characteristic “slow”, for example, when the angle of view of the zoom lens is changed from the wide angle side to the telephoto side or vice versa, the zoom is quickly zoomed in to improve responsiveness. On the other hand, when finely adjusting a desired angle of view, it is possible to zoom slowly to improve the performance of fine adjustment of the angle of view.
図6は、イベント情報とズーム制御速度特性の対比図である。この図において、(イ)のAF合焦なし、手振れあり、顔検出なし、ハーフシャッタなし、の場合、ズーム制御速度特性はシステム上最も高速の「最高速」に設定される。これらのイベント情報の場合は、間違いなく「画角調整のため」のズーム操作と判断されるからであり、たとえば、ズームレンズの画角を広角側から望遠側へ又はその逆へと一気に変更する際の応答性向上を図るためにも最も高速にズームレンズ2bを動かすべきであるからである。
FIG. 6 is a comparison diagram of event information and zoom control speed characteristics. In this figure, in the case of (i) no AF focus, camera shake, face detection, no half shutter, the zoom control speed characteristic is set to the “highest speed”, which is the fastest in the system. In the case of these event information, it is definitely determined that the zoom operation is “for angle of view adjustment”. For example, the angle of view of the zoom lens is changed from the wide angle side to the telephoto side or vice versa. This is because the
次に、(ロ)のAF合焦あり、手振れあり、顔検出なし、ハーフシャッタなし、の場合は、(イ)に比べて「AF合焦あり」になっているが、未だに手振れあり、顔検出なし、ハーフシャッタなし、であるので、「画角調整のため」のズーム操作と判断して差し支えないからであり、同様に、たとえば、ズームレンズの画角を広角側から望遠側へ又はその逆へと一気に変更する際の応答性向上を図るためにも高速にズームレンズ2bを動かすべきであるからである。ただし、この(ロ)は(イ)に比べて「AF合焦あり」になっている分だけ被写体が少し特定されているといえるので、(イ)の「最高速」よりも若干遅い「高速」にすることが望ましい。
Next, in the case of (b) AF in focus, camera shake, no face detection, and no half shutter, it is “AF in focus” compared to (A), but still has camera shake and face This is because there is no detection and no half-shutter, so it can be determined that the zoom operation is “for angle of view adjustment”. Similarly, for example, the angle of view of the zoom lens is changed from the wide angle side to the telephoto side. This is because the
次の(ハ)のAF合焦なし、手振れあり、顔検出あり、ハーフシャッタなし、の場合も(ロ)と同様である。(イ)に比べて「顔検出あり」になっているが、未だにAF合焦なし、手振れあり、ハーフシャッタなし、であるので、「画角調整のため」のズーム操作と判断して差し支えないからであり、同様に、たとえば、ズームレンズの画角を広角側から望遠側へ又はその逆へと一気に変更する際の応答性向上を図るためにも高速にズームレンズ2bを動かすべきであるからである。ただし、この(ハ)も(イ)に比べて「顔検出あり」になっている分だけ被写体が少し特定されているといえるので、(イ)の「最高速」よりも若干遅い「高速」にすることが望ましい。
The following (C) is also the same as (B) in the case of no AF focusing, camera shake, face detection, and no half shutter. Compared to (a), “Face detection is present”, but since there is still no AF focus, no camera shake, and no half shutter, it can be determined that the zoom operation is “for angle of view adjustment”. Similarly, for example, the
次に、(ニ)のAF合焦あり、手振れあり、顔検出あり、ハーフシャッタなし、の場合は、(ハ)や(ロ)に比べて「AF合焦あり」及び「顔検出あり」になっている分だけさらに被写体が特定されているといえるので、(ハ)や(ロ)の「高速」よりも遅い「中速」にすることが望ましい。 Next, in the case of (d) with AF in-focus, camera shake, face detection, and no half shutter, compared to (c) and (b), “with AF in focus” and “with face detection”. Since it can be said that the subject is further specified as much as it is, it is desirable to set the “medium speed” slower than the “high speed” in (c) and (b).
次に、(ホ)のAF合焦あり、手振れなし、顔検出あり、ハーフシャッタなし、の場合は、(ニ)に比べて「AF合焦あり」及び「手振れなし」並びに「顔検出あり」になっている分だけさらに被写体が特定されているといえるので、(ニ)の「中高速」よりも遅い「低速」にすることが望ましく、最後の(ヘ)のAF合焦あり、手振れなし、顔検出あり、ハーフシャッタあり、の場合は、全ての情報が「シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のためのズーム操作である」ことを明らかに示しているので、この場合は、システム上最も遅い速度である「極低速」にすることが望ましい。 Next, in the case of (e) AF in-focus, no camera shake, face detection, and no half-shutter, “with AF focus”, “no camera shake” and “with face detection” compared to (D). Since it can be said that the subject is further specified by the amount of, it is desirable to set the “low speed” slower than the “medium high speed” in (d), the last (f) AF in focus, and no camera shake In the case of face detection and half shutter, all the information clearly indicates that “the zoom operation is just for the composition fine adjustment just before the shutter release”. It is desirable to set the speed to “very low speed”.
このようにすることにより、画角調整のためのズーム操作を行う場合と、シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のためのズーム操作行う場合との各々に適合したズーム制御速度特性とすることができる。その結果、ズーム操作の応答性改善を図ると共に、所望画角付近での画角微調整の性能向上を達成したズーム制御装置、ズーム制御方法及びプログラムを提供するという、本件発明の課題を達成できるのである。 By doing so, it is possible to achieve zoom control speed characteristics suitable for each of a case where a zoom operation for adjusting the angle of view is performed and a case where a zoom operation is performed for composition fine adjustment immediately before the shutter release. As a result, it is possible to achieve the object of the present invention, which is to provide a zoom control device, a zoom control method, and a program that improve the responsiveness of the zoom operation and improve the performance of fine adjustment of the view angle near the desired view angle. It is.
なお、以上の実施形態は、本件発明の技術的思想を具現化した一例に過ぎない。当該思想には、以上の実施形態の変形例や発展例などの様々な態様を含むことは当然であり、たとえば、以下のようにしてもよい。 In addition, the above embodiment is only an example which actualized the technical idea of this invention. The idea naturally includes various aspects such as modifications and developments of the above-described embodiment. For example, it may be as follows.
まず、実施形態のズーム操作手段は、光学系2のレンズ鏡筒の周囲に回動自在に取り付けられた操作リング11としているが、これに限定されない。撮影者によって操作され、且つ、その操作に応答してズーム操作信号を生成出力できるものであればよく、たとえば、ダイヤル式のものや、シーソーボタン式のもの、または、2ボタン式のものであってもよい。ここで、ダイヤル式のズーム操作手段とは、デジタルカメラ1のボディ21の任意位置に設けられた円盤状の自在回転ボタンであり、ボタンを正逆回転させることにより、WまたはTへのズーム操作を行うことができるもののことをいう。また、シーソーボタン式のズーム操作手段とは、デジタルカメラ1のボディ21の任意位置に設けられたシーソー型のボタンであって、一端側をT、他端側をWとし、いずれか一方端を押すことにより、WまたはTへのズーム操作を行うことができるもののことをいう。また、2ボタン式のズーム操作手段とは、デジタルカメラ1のボディ21の任意位置に設けられたTボタン及びWボタンであって、いずれか一方のボタンを押すことにより、WまたはTへのズーム操作を行うことができるもののことをいう。これらいずれの方式のズーム操作手段であっても構わない。
First, the zoom operation means of the embodiment is the
次に、実施形態では、ズーム操作が「画角調整のため」のものであるか、または、「シャッタレリーズ寸前の構図微調整のため」のものであるかの判定をAF合焦情報、手振れ情報、顔検出情報、ハーフシャッタ情報といったイベント情報に基づいて行うようにしているが、これに限定されない。他の望ましい情報があれば、これに加えてもよく、あるいは、上記のイベント情報のいずれかと入れ替えてもよい。 Next, in the embodiment, it is determined whether the zoom operation is “for adjusting the angle of view” or “for adjusting the composition just before the shutter release”. Although it is performed based on event information such as information, face detection information, and half shutter information, the present invention is not limited to this. If there is other desirable information, it may be added to it, or may be replaced with any of the above event information.
また、実施形態では、図6に示すように、ズーム制御速度を「最高速」、「中速」、「低速」及び「極低速」の4段階に分けているが、これに限らない。4段よりも少なくてもよく、または、4段以上の多段にしてもよい。あるいは、ズーム制御速度を段階的に変えるのではなく線形的に変えるようにしてもよい。
また、各イベント情報を「あり」「なし」の2値で判断しているが、これに限らず、図5のような点数表を用いて複数段階に管理制御しても構わない。
In the embodiment, as shown in FIG. 6, the zoom control speed is divided into four stages of “highest speed”, “medium speed”, “low speed”, and “very low speed”, but is not limited thereto. There may be fewer than four stages, or four or more stages. Alternatively, the zoom control speed may be changed linearly instead of stepwise.
Further, each event information is determined by binary values of “Yes” and “No”. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and management control may be performed in a plurality of stages using a score table as shown in FIG.
また、以上の実施形態では、デジタルカメラ1への適用を例にしたが、これに限定されない。ズームを備えた撮像装置一般であればよく、たとえば、銀塩カメラを含むスチルカメラやビデオカメラまたはテレビカメラであってもよい。 In the above embodiment, application to the digital camera 1 has been described as an example, but the present invention is not limited to this. The image pickup apparatus generally includes a zoom, and may be, for example, a still camera including a silver salt camera, a video camera, or a television camera.
また、以上の実施形態では、光学的ズーム(ズームレンズを用いたもの)を例にしているが、デジタルズームであっても、あるいは、光学的ズームとデジタルズームの混在型であってもよい。デジタルズームや混在型のズームの場合も倍率が大きくなるほど、ズームレンズの画角を広角側から望遠側へ又はその逆へと一気に変更する場合の操作量が大きくなり、一方、所望の画角を微調整する際には微妙な操作が求められるからである。 In the above embodiment, an optical zoom (using a zoom lens) is taken as an example. However, a digital zoom or a mixed type of optical zoom and digital zoom may be used. Also in the case of digital zoom and mixed zoom, the larger the magnification, the greater the amount of operation when changing the zoom lens angle of view from the wide angle side to the telephoto side or vice versa, while the desired angle of view becomes smaller. This is because a delicate operation is required for adjustment.
2b ズームレンズ
4 撮像部
8 ズーム駆動部
11 操作リング
20 制御部)
23 反射部材
24 発光素子
25 受光素子
26 発光駆動部
27 受光信号生成部
28 信号計数部
29 ズーム制御部
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (3)
前記撮像手段の撮影画角を変更するための操作手段と、
被写体に対する前記操作手段による撮影画角の変更を伴う構図調整から前記撮像手段への撮像指示に至る間に検出される被写体に関するイベント情報を収集する収集手段と、
前記収集手段によって収集された前記被写体に関するイベント情報に基づいて、前記操作手段による前記撮像手段の撮影画角の変更速度を制御する画角制御手段と
を備え、
前記被写体に関するイベント情報は、AF合焦情報、手振れ情報、ハーフシャッタ情報、被写体の顔が検出されたか否かの顔検出情報、または被写体の検出された顔の数の情報のいずれかであり、
複数のイベント情報のそれぞれに対応して評価点数を付与し、前記画角制御手段は、前記評価点数を組み合わせて用いて前記撮像手段の撮影画角の変更速度を制御することを特徴とする撮像装置。 Imaging means capable of changing the shooting angle of view;
Operating means for changing the shooting angle of view of the imaging means;
A collection unit that collects event information about a subject that is detected during a period from a composition adjustment involving a change in a field of view by the operation unit to the subject to an imaging instruction to the imaging unit;
An angle-of-view control means for controlling a change speed of a shooting angle of view of the imaging means by the operation means based on event information on the subject collected by the collecting means,
Event information on the subject, AF focusing information, camera shake information, half shutter information state, and are any number of information whether or not the face detection information face of a subject is detected or the detected face of the subject, ,
An evaluation score is assigned to each of a plurality of pieces of event information, and the angle-of-view control means controls a change speed of a shooting angle of view of the imaging means using a combination of the evaluation scores. apparatus.
前記撮像手段の撮影画角を変更するための操作ステップと、
被写体に対する前記操作ステップによる撮影画角の変更を伴う構図調整から前記撮像手段への撮像指示に至る間に検出される被写体に関するイベント情報を収集する収集ステップと、
前記収集ステップにて収集された前記被写体に関するイベント情報に基づいて、前記操作ステップによる前記撮像手段の撮影画角の変更速度を制御する画角制御ステップと
を含み、
前記被写体に関するイベント情報は、AF合焦情報、手振れ情報、ハーフシャッタ情報、被写体の顔が検出されたか否かの顔検出情報、または被写体の検出された顔の数の情報のいずれかであり、
複数のイベント情報のそれぞれに対応して評価点数を付与し、前記画角制御ステップは、前記評価点数を組み合わせて用いて前記撮像手段の撮影画角の変更速度を制御することを特徴とする撮影画角補正方法。 An imaging step capable of changing the field of view of the imaging means ;
An operation step for changing the photographing field angle of the imaging means,
A collection step of collecting event information relating to a subject detected during a period from composition adjustment accompanied by a change in a shooting angle of view by the operation step on the subject to an imaging instruction to the imaging unit;
An angle-of-view control step for controlling a change speed of a shooting angle of view of the imaging means based on the operation step based on event information about the subject collected in the collecting step;
Event information on the subject, AF focusing information, camera shake information, half shutter information state, and are any number of information whether or not the face detection information face of a subject is detected or the detected face of the subject, ,
An evaluation score is assigned to each of a plurality of pieces of event information, and the angle-of-view control step uses the combination of the evaluation scores to control a change speed of a shooting angle of view of the imaging unit. Angle of view correction method.
被写体に対する前記操作手段による撮影画角の変更を伴う構図調整から前記撮像手段への撮像指示に至る間に検出される被写体に関するイベント情報を収集する収集手段、
前記収集手段によって収集された前記被写体に関するイベント情報に基づいて、前記操作手段による前記撮像手段の撮影画角の変更速度を制御する画角制御手段
として機能させるとともに、
前記被写体に関するイベント情報は、AF合焦情報、手振れ情報、ハーフシャッタ情報、被写体の顔が検出されたか否かの顔検出情報、または被写体の検出された顔の数の情報のいずれかであり、
複数のイベント情報のそれぞれに対応して評価点数を付与し、前記画角制御手段は、前記評価点数を組み合わせて用いて前記撮像手段の撮影画角の変更速度を制御することを特徴とするプログラム。 A computer provided in an imaging apparatus having an imaging means capable of changing a shooting angle of view and an operation means for changing the shooting angle of view;
A collecting unit that collects event information related to a subject that is detected during a period from a composition adjustment involving a change in a field of view by the operation unit to the subject to an imaging instruction to the imaging unit;
Based on the event information about the subject collected by the collecting means, and functioning as an angle-of-view control means for controlling the changing speed of the photographing angle of the imaging means by the operating means,
Event information on the subject, AF focusing information, camera shake information, half shutter information state, and are any number of information whether or not the face detection information face of a subject is detected or the detected face of the subject, ,
An evaluation score is assigned corresponding to each of a plurality of event information, and the angle-of-view control means controls a change speed of a shooting angle of view of the imaging means using a combination of the evaluation scores. .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008251124A JP5354255B2 (en) | 2008-09-29 | 2008-09-29 | Imaging apparatus, photographing angle of view correction method, and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008251124A JP5354255B2 (en) | 2008-09-29 | 2008-09-29 | Imaging apparatus, photographing angle of view correction method, and program |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010087564A JP2010087564A (en) | 2010-04-15 |
| JP2010087564A5 JP2010087564A5 (en) | 2011-11-10 |
| JP5354255B2 true JP5354255B2 (en) | 2013-11-27 |
Family
ID=42251124
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008251124A Expired - Fee Related JP5354255B2 (en) | 2008-09-29 | 2008-09-29 | Imaging apparatus, photographing angle of view correction method, and program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5354255B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11949984B2 (en) | 2021-03-12 | 2024-04-02 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Electronic device that performs a driving operation of a second camera based on a determination that a tracked object is leaving the field of view of a moveable first camera having a lesser angle of view than the second camera, method for controlling the same, and recording medium of recording program |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6020583B2 (en) * | 2012-10-11 | 2016-11-02 | ソニー株式会社 | Position detection device, lens barrel, imaging device |
| EP3250997A1 (en) * | 2015-03-08 | 2017-12-06 | Apple Inc. | User interface using a rotatable input mechanism |
| JP6632441B2 (en) * | 2016-03-22 | 2020-01-22 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging device and control method thereof |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04311909A (en) * | 1991-04-10 | 1992-11-04 | Canon Inc | Camera system |
| JP2008211401A (en) * | 2007-02-23 | 2008-09-11 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Imaging device |
| JP5164721B2 (en) * | 2007-08-22 | 2013-03-21 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging apparatus and zoom control method |
-
2008
- 2008-09-29 JP JP2008251124A patent/JP5354255B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11949984B2 (en) | 2021-03-12 | 2024-04-02 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Electronic device that performs a driving operation of a second camera based on a determination that a tracked object is leaving the field of view of a moveable first camera having a lesser angle of view than the second camera, method for controlling the same, and recording medium of recording program |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2010087564A (en) | 2010-04-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4408001B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and imaging system | |
| JP4003742B2 (en) | Electronic camera | |
| JP4727534B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| US20090128640A1 (en) | Image device and lens barrel | |
| JP2007072252A (en) | Lens device, imaging apparatus and imaging system | |
| JP2008271132A (en) | Imaging apparatus and imaging method | |
| JP2011248159A (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging system, imaging apparatus control method and program | |
| JP2007072254A (en) | Imaging apparatus and its program | |
| JP5363621B2 (en) | Image display device and imaging device | |
| JP5197532B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and imaging system | |
| JP5354255B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, photographing angle of view correction method, and program | |
| KR20110001655A (en) | Digital image signal processing apparatus, method for controlling the apparatus, and medium for recording the method | |
| JP5465224B2 (en) | Lens apparatus and imaging system | |
| JPWO2020158008A1 (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP2006109196A (en) | Imaging apparatus and mobile communication apparatus | |
| JP4975247B2 (en) | Electronic camera, electronic camera control method, and program | |
| JP2009036832A (en) | Photographing device | |
| JP5586215B2 (en) | camera | |
| JP2003322788A (en) | Camera | |
| JP2010190913A (en) | Imaging device with automatic focus function | |
| WO2004021064A1 (en) | Camera | |
| JP2008245129A (en) | Electronic camera and control method thereof | |
| JP2007334242A (en) | Digital camera | |
| JP2004069783A (en) | Electronic camera | |
| JP5385428B2 (en) | Imaging device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110926 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110926 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120827 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120911 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20121106 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130204 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130325 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130801 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130814 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5354255 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |