JP5141222B2 - Imaging apparatus, imaging control method, and program - Google Patents
Imaging apparatus, imaging control method, and program Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5141222B2 JP5141222B2 JP2007315904A JP2007315904A JP5141222B2 JP 5141222 B2 JP5141222 B2 JP 5141222B2 JP 2007315904 A JP2007315904 A JP 2007315904A JP 2007315904 A JP2007315904 A JP 2007315904A JP 5141222 B2 JP5141222 B2 JP 5141222B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- photographing
- subject
- shooting
- unit
- scene
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Television Signal Processing For Recording (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
Description
本発明は、撮影装置、撮影制御方法及びプログラムに関する。 The present invention relates to a photographing apparatus, a photographing control method, and a program.
旅行や運動会等のイベントの際に写真を撮影することが多々ある。これらの写真を後で確認すると、たくさん撮影されている人物とほとんど撮影されていない人物がいる場合がある。ここで、従来、撮影の度に、撮影範囲にある複数の被写体に取り付けたICタグから、被写体IDを読み出すことで、ある撮影シーンにおける各被写体の撮影回数を把握できるデジタルカメラが知られている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。このデジタルカメラによれば、ユーザが各被写体の撮影回数を把握することで、ある撮影シーンでの各被写体の撮影回数の偏りをなくすことができる。
ところで、デジタルカメラにおいて、複数の撮影シーンにおける撮影シーンごとに各被写体の撮影量の偏りをなくしたいという要望がある。例えば、ある観光名所AAで撮影を行った後に別の観光名所BBで撮影を行う場合、観光名所AAでの各被写体の撮影量の偏りをなくし、観光名所BBでの被写体の撮影量の偏りもなくしたいというものである。 By the way, in a digital camera, there is a demand for eliminating a bias in the shooting amount of each subject for each shooting scene in a plurality of shooting scenes. For example, when shooting at one tourist attraction AA and then shooting at another tourist attraction BB, the bias of the shooting amount of each subject at the tourist attraction AA is eliminated, and the bias of the shooting amount of the subject at the tourist attraction BB is also eliminated. I want to lose it.
しかしながら、上記特許文献1記載のデジタルカメラでは、1つの撮影シーンにおける被写体の撮影回数を把握することしか開示されていない。そのため、複数の撮影シーンにおける撮影シーンごとに被写体の撮影量の偏りをなくすことができなかった。
However, the digital camera described in
本発明の課題は、複数の撮影シーンにおける撮影シーンごとに被写体の撮影量の偏りをなくすことである。 An object of the present invention is to eliminate bias in the amount of photographing of a subject for each photographing scene in a plurality of photographing scenes.
上記課題を解決するために、請求項1に記載の撮影装置は、被写体を撮影する撮影手段と、撮影シーンを検知する検知手段と、前記検知手段により検知された撮影シーンで撮影された画像の被写体別の撮影量を記憶する記憶手段と、前記記憶手段に記憶されている撮影量に基づいて、当該撮影量が所定下限値を下回る被写体を特定する特定手段と、前記特定手段により特定された被写体を撮影するよう前記撮影手段を制御する撮影制御手段と、を備えたことを特徴とする。
In order to solve the above problems, the imaging apparatus according to
また、請求項2に記載の発明は、請求項1に記載の撮影装置において、前記特定手段により特定された被写体に合焦する合焦手段と、を更に備え、前記撮影制御手段は、前記合焦手段により合焦された被写体を前記撮影手段に撮影させることを特徴とする。
The invention described in
また、請求項3に記載の発明は、請求項1に記載の撮影装置において、前記特定手段により特定された被写体の位置をズーム中心位置としてデジタルズームをするデジタルズーム手段とを更に備え、前記撮影制御手段は、前記特定された被写体の位置をズーム中心位置として前記デジタルズーム手段にデジタルズームさせ、前記撮影手段により前記特定された被写体を撮影させるよう制御することを特徴とする。
The invention described in
また、請求項4に記載の発明は、請求項1から3のいずれか一項に記載の撮影装置において、現在時刻情報を取得する第1の取得手段を更に備え、前記記憶手段は、前記被写体別の撮影量に対応付けて、更に、前記撮影シーンの撮影された時の時間帯情報を記憶し、前記検知手段は、前記第1の取得手段により取得された現在時刻情報と前記記憶手段により記憶された前記撮影シーンの時間帯情報とに基づき、現在の撮影シーンを検知することを特徴とする。
Further, the invention according to
また、請求項5に記載の発明は、請求項1から3のいずれか一項に記載の撮影装置において、本撮影装置の現在位置情報を取得する第2の取得手段を更に備え、前記記憶手段は、前記被写体別の撮影量に対応付けて、更に、前記撮影シーンの撮影された時の位置情報を記憶し、前記検知手段は、前記第2の取得手段により取得された現在位置情報と前記記憶手段により記憶された前記撮影シーンの位置情報とに基づき、現在の撮影シーンを検知することを特徴とする。
The invention described in claim 5 is the imaging device according to any one of
また、請求項6に記載の発明は、請求項5に記載の撮影装置において、前記第2の取得手段により取得された現在位置情報と前記記憶手段により記憶された撮影シーンの位置情報とに基づき、前記現在位置情報が前記撮影シーンを逸脱しているか否かを判別する判別手段と、前記判別手段により前記現在位置情報が前記撮影シーンを逸脱していると判別された場合に、前記現在位置情報に基づき、前記記憶手段に新たな撮影シーンを追加する撮影シーン追加手段と、を更に備えることを特徴とする。
The invention according to
また、請求項7に記載の発明は、請求項1から6のいずれか一項に記載の撮影装置において、前記特定手段により特定された被写体の撮影量が前記所定下限値を下回っているという旨を表示又は音の少なくとも一つにより報知する報知手段と、を更に備えることを特徴とする。
The invention described in
また、請求項8に記載の発明は、請求項2から7のいずれか一項に記載の撮影装置において、前記被写体の撮影量とは、撮影された被写体の撮影回数であることを特徴とする。
The invention according to
また、請求項9に記載の発明は、請求項2から7のいずれか一項に記載の撮影装置において、前記被写体の撮影量とは、撮影された被写体の記録時間であることを特徴とする。
The invention according to
また、請求項10に記載の発明は、被写体を撮影する撮影手段と、前撮影シーンを検知する検知手段と、前記検知手段により検知された撮影シーンで撮影された画像の被写体別の撮影量を記憶する記憶手段と、を備えた撮影装置の撮影制御方法であって、前記記憶手段に記憶されている撮影量に基づいて、当該撮影量が所定下限値を下回る被写体を特定する特定ステップと、前記特定ステップにて特定された被写体を撮影するよう前記撮影手段を制御する撮影制御ステップと、を含むことを特徴とする。 According to a tenth aspect of the present invention, there is provided a photographing means for photographing a subject, a detecting means for detecting a previous photographing scene, and a photographing amount for each subject photographed in the photographing scene detected by the detecting means. A storage unit for storing, and a specifying step of specifying a subject whose shooting amount is below a predetermined lower limit value based on the shooting amount stored in the storage unit, characterized in that it comprises a and a photographing control step of controlling the imaging means to photograph the object identified in the identifying step.
また、請求項11に記載の発明は、被写体を撮影する撮影手段、撮影シーンを検知する検知手段と、前記検知手段により検知された撮影シーンで撮影された画像の被写体別の撮影量を記憶する記憶手段と、を備えた撮影装置のコンピュータを、前記記憶手段に記憶されている撮影量に基づいて、当該撮影量が所定下限値を下回る被写体を特定する特定手段、前記特定手段により特定された被写体を撮影するよう前記撮影手段を制御する撮影制御手段、として機能させることを特徴とする。 According to an eleventh aspect of the present invention, a photographing means for photographing a subject, a detecting means for detecting a photographing scene, and a photographing amount for each subject of an image photographed in the photographing scene detected by the detecting means are stored. And a storage unit , on the basis of the shooting amount stored in the storage unit, a specifying unit for specifying a subject whose shooting amount is less than a predetermined lower limit, and the specifying unit characterized in that to the photographing control means for controlling the imaging means, and to function to photograph a subject.
本発明によれば、複数の撮影シーンにおける撮影シーンごとに被写体の撮影量の偏りをなくすことができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to eliminate unevenness in the shooting amount of a subject for each shooting scene in a plurality of shooting scenes.
以下、添付図面を参照して本発明に係る好適な実施の形態を詳細に説明する。なお、本発明は、図示例に限定されるものではない。 DESCRIPTION OF EMBODIMENTS Hereinafter, preferred embodiments according to the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. The present invention is not limited to the illustrated example.
先ず、図1〜図3を参照して、本実施の形態の装置構成を説明する。図1を参照して、本実施の形態の撮影装置としてのデジタルカメラ1の外観を説明する。図1(a)に、本実施の形態のデジタルカメラ1の主に前面の構成を示す。図1(b)に、デジタルカメラ1の主に背面の構成を示す。
First, the device configuration of the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. With reference to FIG. 1, the external appearance of a
図1(a)に示すように、デジタルカメラ1は、略矩形の薄板状ボディの前面に、撮影レンズ2、を配設し、上面には電源キー6及びシャッタキー7を配する。
As shown in FIG. 1A, the
撮影レンズ2は、合焦動作は行うためのフォーカスレンズを含む。電源キー6は、1回押圧操作する毎に電源をオン/オフするキーである。シャッタキー7は、撮影モード時にレリーズ(画像の記録)等を指示する一方で、メニュー選択等では設定/実行を指示するキーとしても機能するものとする。シャッタキー7は、撮影モード時に、半押しされることで、AF、AEの調整及びそのロックを指示し、全押しされることによりレリーズを指示する。
The taking
また、図1(b)に示すように、デジタルカメラ1の背面には、モードスイッチ(SW)8、メニューキー9、十字キー10、スピーカ12、及び表示部13を配する。
As shown in FIG. 1B, a mode switch (SW) 8, a
モードスイッチ8は、例えばスライドスイッチにより構成され、撮影モード「R」と再生モード「P」とを切換える。メニューキー9は、各種メニュー選択時に操作する。表示部13は、バックライト付きのカラー液晶パネルで構成されるもので、撮影モード時には電子ファインダとしてモニタ表示(スルー画像表示)を行なう一方で、再生モード時には選択した画像を再生表示する。なお、デジタルカメラ1のボディ下面には蓋付きのメモリカードスロット(図示略)が設けられ、このデジタルカメラ1の記録媒体であるメモリカードMが着脱自在に装着されるものとする。
The
次いで、図2を参照して、デジタルカメラ1の内部構成を説明する。図2に、デジタルカメラ1の内部構成を示す。
Next, the internal configuration of the
図2に示すように、デジタルカメラ1は、検知手段、計測手段、撮影制御手段、記憶制御手段、認識手段、認識制御手段、合焦制御手段、画像取り込み制御手段、判別手段、撮影シーン追加手段、報知制御手段としてのCPU(Central Processing Unit)21と、入力部22と、RAM(Random Access Memory)23と、報知手段としての表示部13と、撮影手段としての撮像部24と、第1の記憶手段及び第2の記憶手段としてのフラッシュメモリ25と、通信部26と、第1の取得手段及び第2の取得手段としてのGPS(Global Positioning System)部27と、記録部28と、RTC(Real Time Clock)29と、報知手段としての音出力部29aと、を備えて構成され、各部がバス30を介して接続される。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
CPU21は、デジタルカメラ1の各部を中央制御する。また、CPU21は、フラッシュメモリ25に記憶されたシステムプログラム及びアプリケーションプログラムの中から指定されたプログラムを読み出してRAM23に展開し、展開されたプログラムとの協働で各種処理を実行する。
The
CPU21は、フラッシュメモリ25に記憶された設定プログラムとの協働で、登録人物の顔登録を行って顔登録データ50を生成してフラッシュメモリ25に記憶し、スケジュールテーブル60の設定を行ってフラッシュメモリ25に記憶する。
In cooperation with the setting program stored in the
CPU21は、フラッシュメモリ25に記憶された撮影プログラムとの協働で、撮影シーンごとの各被写体の撮影において、シャッタキー7の半押しで、画角内の全ての被写体を認識してAF,AEを行い、又は撮影回数が下限値を下回る被写体があり残り時間が所定時間以下である場合に、その被写体のみを認識してAF,AEを行う。そして、CPU21は、シャッタキー7の全押しで、認識した被写体を撮像部24で撮影し、その被写体の撮影回数をインクリメントし、撮影回数が下限値を下回る被写体がある場合に、被写体の撮影に偏りがある旨を表示部13及び音出力部29aに接続されたスピーカ12に報知させる。
In cooperation with the shooting program stored in the
入力部22は、ユーザからの操作入力を受け付けて操作信号をCPU21に出力する。入力部22は、電源キー6、シャッタキー7、モードスイッチ8、メニューキー9、十字キー10等を含み、各種キー、スイッチ等の操作入力を受け付ける。
The
RAM23は、情報を一時的に格納する揮発性のメモリであり、各種プログラム及び各種データが展開されるワークエリアを有する。特に、RAM23は、撮像部24で撮像された画像データが一時的に格納される。
The
表示部13は、液晶ディスプレイであり、CPU21から入力される表示信号に基づいて各種情報を表示する。また、表示部13は、スルー画像、撮影画像、被写体撮影のスケジュール設定画面、被写体の撮影シーンの撮影回数、残り時間等の情報を表示する。また、表示部13は、液晶ディスプレイに限定されるものではなく、ELD(ElectroLuminescent Display)等としてもよい。
The
撮像部24は、被写体を撮像してデジタルの画像データを出力する。撮像部24は、撮影レンズ2などが含まれる。また、撮像部24の内部構成を後述する。
The
フラッシュメモリ25は、情報を読み込み及び書き込み可能な不揮発性の内部メモリである。フラッシュメモリ25は、後述する設定プログラム、撮影プログラム、顔登録データ50及びスケジュールテーブル60を記憶する。
The
通信部26は、PC(Personal Computer)等の外部機器とデータの送受信を行う。通信部26は、通信ケーブルを介して外部機器と有線通信を行うものとするが、これに限定されるものではなく、赤外線や無線等で通信を行う構成としてもよい。
The
GPS部27は、GPS衛星からのGPS信号を受信し、受信したGPS信号と予め記憶されるデータとに基づいて、デジタルカメラ1の現在の位置を示す現在位置情報(経度緯度情報)と現在の時刻を示す現在時刻情報とを算出してCPU21に出力する。
The
記録部28は、メモリカードMが着脱自在に接続(セット)され、CPU21から入力される制御信号に従い、接続されたメモリカードMに画像データ等のデータを書き込み、あるいは接続されたメモリカードMから画像データ等のデータを読み込んでCPU21に出力する。メモリカードMは、SD(Secure Digital)カード、メモリースティック等の記録媒体(記録メディア)である。
In the
RTC29は、計時部であり、日時指定割り込みやタイマ割り込みの情報をCPU21に出力する。CPU21により、RTC29から出力される割り込みの情報を用いた所定時間周期でGPS部27からデジタルカメラ1の現在位置情報及び現在時刻情報が取得される。
The
音出力部29aは、スピーカ等を備え、CPU21から入力される制御信号に従い、各種音出力を行う。また、音出力部29aは、シャッター音の出力や、均等撮影に偏りがある旨の警告を音声出力する。
The
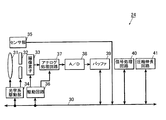
ここで、図3を参照して、撮像部24の詳細な内部構成を説明する。図3に、撮像部24の詳細な構成を示す。
Here, a detailed internal configuration of the
撮像部24は、レンズ光学系31、絞り機構32、撮像素子33、第1の駆動手段及び第2の駆動手段としての光学系駆動部34、センサ部35、駆動回路36、アナログ処理回路37、A/D(Analog to Digital)変換回路38、バッファレジスタ39、信号処理回路40、圧縮伸長回路41等を備えて構成される。
The
撮像部24は、CPU21の制御に従い動作する。具体的には、撮像部24は、撮影の際に、フォーカスレンズを含む撮影レンズ2を含むレンズ光学系31の光束の開口量が絞り機構32によって調整され、被写体像がレンズ光学系31によってCCD(Charge Coupled Devices)等の撮像素子33上に結像される。また、AF(Auto Focus)時に、合焦のためにフォーカスレンズが光学系駆動部34によって光軸に沿って移動され、AE(Automatic Exposure)時に、適切な露出となるように絞り機構32の開口量が光学系駆動部34によって制御される。
The
また、測距センサや光量センサを含むセンサ部35によって検出された検出値がバス30を介してCPU21に送られ、CPU21によって検出値に基づいて演算された移動量や開口量を示す信号が光学系駆動部34に送られることによって、光学系駆動部34によりレンズ光学系31の移動や絞り機構32の開口量を調整する。
A detection value detected by the
撮像素子33に被写体像が結像されることにより、撮像素子33には入射光量に応じた電荷が蓄積され、蓄積された電荷は駆動回路36から与えられる駆動パルス信号によって順次読み出されその信号がアナログ処理回路37に送られる。アナログ処理回路37では、入力された信号に対して色分離やゲイン調整、ホワイトバランスなどの各種処理が行われ、処理された信号がA/D変換回路38を介してデジタルのフレームデータ(撮像素子33の全画素領域の静止画データ)としてバッファレジスタ39に記憶される。
When the subject image is formed on the image sensor 33, charges corresponding to the amount of incident light are accumulated in the image sensor 33, and the accumulated charges are sequentially read out by a drive pulse signal supplied from the
バッファレジスタ39に記憶されたフレームデータは、信号処理回路40において輝度信号及び色差信号に変換されバス30を介してRAM23に順次記録される。このとき、順次記録されているフレームが表示部13にも表示され、撮影したスルー画像を確認できるようになっている。また、信号処理回路40は、フレームデータからデジタルズーム領域の画像データを取り込む画像取り込み手段としても用いられる。すなわち、信号処理回路40に、CPU21からズーム倍率およびズーム中心位置を制御する制御信号が入力されることで、フレームデータから該ズーム中心位置を中心とした画像データを切り出してデジタルズームする。これにより、1画面分の画像データを生成し、この画像をデジタルズーム領域の画像として取り込むことができる。さらに、信号処理回路40では、デジタルズーム処理後の画像データを撮影者に視覚的に示すため、取り込んだデジタルズーム領域の画像データを表示部13にて表示させることができる。なお、静止画の撮影の場合には、バッファレジスタ39に記憶されたフレームデータが圧縮伸長回路41によってJPEG(Joint Photographic Coding Experts Group)形式に圧縮され、バス30を介してRAM23に静止画データとして記録される。
The frame data stored in the
次に、図4及び図5を参照して、デジタルカメラ1で扱うデータを説明する。図4に、顔登録データ50を示す。図5に、スケジュールテーブル60を示す。
Next, data handled by the
フラッシュメモリ25には、被写体(人間)の顔登録データ50、撮影のスケジュールテーブル60が記憶される。図4に示すように、顔登録データ50は、被写体51と、認識用データ52と、を含んで構成される。被写体51は、被写体になりうる登録人物の識別情報であり、登録人物のID又は名称等である。
The
認識用データ52は、被写体51の各被写体(各登録人物)の顔認識をするための画像データである。また、認識用データ52は、各被写体につき1枚の画像データに限定されるものではなく、各被写体につき表情や撮影角度等を変えた複数の画像データとする構成としてもよい。また、認識用データ52は、画像データに限定されるものではなく、他の顔認識用のデータとして、被写体の顔の特徴を示すデータ等としてもよい。
The
図5に示すように、スケジュールテーブル60は、項目として、時間帯61、位置情報62、撮影シーン63、被写体64、撮影回数65を含み、各項目にデータを含んで構成される。また、全スケジュールは、少なくとも一つの撮影スケジュールからなるものとする。全スケジュールは、旅行、運動会、遠足等のイベントに対応する。各撮影スケジュールは、全スケジュール(イベント)を細分化したものであり、例えば、イベントが旅行である場合に、観光先の各観光地名等となる。
As shown in FIG. 5, the schedule table 60 includes a
時間帯61は、各撮影スケジュールの時間帯を示す。位置情報62は、各撮影スケジュールの撮影場所の経度緯度の範囲を示す。また、図5の位置情報62のa1,a2〜h1,h2は、それぞれ任意の数値とする。
A
撮影シーン63は、撮影シーン名を示し、背景名、撮影スケジュール名等である。被写体64は、各被写体(各登録人物)の識別情報であり、被写体51と対応する。撮影回数65は、各撮影スケジュールにおける各被写体の撮影回数である。
The
図5のスケジュールテーブル60は、各撮影スケジュールが、観光地名である金閣寺、銀閣寺、二条城、京都タワーの観光であり、各観光地を撮影シーン63とし、各撮影シーン63で被写体A〜Cの撮影を行うスケジュールテーブルの例である。
In the schedule table 60 of FIG. 5, each shooting schedule is a sightseeing spot name of Kinkakuji, Ginkakuji, Nijo Castle, and Kyoto Tower, and each sightseeing spot is set as a
次に、図6〜図12を参照して、デジタルカメラ1の動作を説明する。先ず、図6を参照して、デジタルカメラ1で実行される設定処理を説明する。図6に、設定処理の流れを示す。
Next, the operation of the
設定処理は、被写体となりうる人物の顔登録及びスケジュール設定を行う処理である。デジタルカメラ1において、例えば、入力部22を介して設定処理の実行開始が操作入力されたことをトリガとして、フラッシュメモリ25から読み出されて適宜RAM23に展開された設定プログラムと、CPU21との協働で設定処理が実行される。
The setting process is a process of registering a face of a person who can be a subject and setting a schedule. In the
図6に示すように、先ず、顔登録が実行される(ステップS1)。ステップS1では、先ず、撮像部24等を介する登録対象の被写体の撮影により被写体の顔の画像データが取得され、撮影した被写体の識別情報が入力部22を介して入力され、その画像データと登録人物の識別情報が認識用データ52、被写体51として、顔登録データ50がフラッシュメモリ25に記憶される。なお、登録対象の被写体の顔の画像データを取得する方法としては、メモリカードMに記録された撮影済の被写体の顔の画像データが記録部28を介して読み出されて取得されたり、又は通信部26を介して外部機器から被写体の顔の画像データを受信して取得することとしてもよい。登録したい人物の顔登録データ50がフラッシュメモリ25に記憶されていない場合に、ステップS1の顔登録を実行することとしてもよい。また、ステップS1において、現在の撮影シーンに対応する各被写体の撮影回数(全スケジュールの始まりでは撮影回数=0)がRAM23に格納される。
As shown in FIG. 6, first, face registration is executed (step S1). In step S1, first, image data of the face of the subject is acquired by photographing the subject to be registered via the
そして、スケジュール設定画面が表示部13に表示され、スケジュール設定が実行され(ステップS2)、設定処理が終了する。ステップS2では、スケジュール設定画面に応じて、入力部22を介して撮影スケジュールの各項目(時間帯、位置情報、撮影シーン、被写体、撮影回数)の操作入力が受け付けられ、入力された各項目を含むスケジュールテーブル60が生成されてフラッシュメモリ25に記憶され、又はフラッシュメモリ25に記憶されたスケジュールテーブル60が更新される。なお、スケジュールテーブル60のうち、不要又は不明な項目は省略可能な構成としてもよい。
Then, a schedule setting screen is displayed on the
次いで、図7〜図12を参照して撮影処理を説明する。図7に、撮影処理の流れを示す。図8に、図7の続きの撮影処理の流れを示す。図9に、仮想シーンの挿入時のスケジュールテーブルの変更の一例を示す。図10に、被写体Aを認識した画面70aを示す。図11に、被写体A,B,Cを認識した画面70bを示す。図12に、位置情報が同じであるスケジュールテーブル60cを示す。
Next, the photographing process will be described with reference to FIGS. FIG. 7 shows the flow of the photographing process. FIG. 8 shows a flow of the photographing process continued from FIG. FIG. 9 shows an example of changing the schedule table when a virtual scene is inserted. FIG. 10 shows a
撮影処理は、設定処理の実行後に実行され、被写体の撮影回数の偏りを検出し撮影者に報知するとともに撮影を行う処理である。デジタルカメラ1において、例えば、入力部22を介して撮影処理の実行開始が操作入力されたことをトリガとして、フラッシュメモリ25から読み出されて適宜RAM23に展開された撮影プログラムと、CPU21との協働で撮影処理が実行される。
The imaging process is a process that is executed after the setting process is executed, detects a deviation in the number of times the subject is captured, notifies the photographer, and performs imaging. In the
図7、図8に示すように、先ず、GPS部27の起動(現在位置、現在時刻計測開始)等の初期動作が実行される(ステップS11)。ステップS11以後、RTC29から出力される割り込みの情報に応じてGPS部27で所定周期でデジタルカメラ1の現在位置情報及び現在時刻情報が取得されるが、ステップS1において、スケジュールテーブル60の各撮影スケジュールの撮影シーンが密集している場合(各撮影スケジュールの時間帯61が短い場合等)には、GPS部27での現在位置情報及び現在時刻情報の取得周期が小さく初期設定されるものとする。これによれば、精度よく撮影シーンの切り替わりを検知できる。
As shown in FIGS. 7 and 8, first, initial operations such as activation of the GPS unit 27 (current position, current time measurement start) and the like are executed (step S11). After step S11, the
なお、GPS部27からの現在位置情報及び現在時刻情報の取得について、撮影スケジュールの進行状況に応じて、GPS部27での現在位置情報及び現在時刻情報の取得周期を適宜変更する構成としてもよい。以下、現在位置情報及び現在時刻情報とは、GPS部27から取得された最新のものとする。
The acquisition of the current position information and the current time information from the
そして、フラッシュメモリ25に記憶されたスケジュールテーブル60が参照され、ステップS11で取得された現在時刻情報に対応する時間帯61において、現在の撮影シーン63における各被写体の撮影回数65と、現在時刻情報及び時間帯61から算出される現在の撮影シーン63の残り時間と、が表示部13に表示される(ステップS12)。
Then, the schedule table 60 stored in the
そして、スケジュールテーブル60が参照され、GPS部27で取得された現在の位置情報が、現在の撮影シーン63に対応する位置情報から逸脱したか否かにより、撮影シーンを逸脱したか否かが判別される(ステップS13)。撮影シーンを逸脱していない場合(ステップS13;NO)、スケジュールテーブル60が参照され、GPS部27から取得された現在時刻情報が次の時間帯61に移行されたか否かにより、撮影スケジュールが進行したか否かが判別される(ステップS14)。
Then, the schedule table 60 is referred to, and it is determined whether or not the current position information acquired by the
撮影スケジュールが次の時間帯に移行された場合(ステップS14;YES)、現在の撮影シーン(撮影スケジュール)が次の撮影シーンに変更され、スケジュールテーブル60の読み出し、書き込み対象のレコードが次のレコードに移行される(ステップS15)。なお、イベントがスケジュールどおりに進むとは限らないので、ステップS14;YESの場合に、現在の撮影シーン等を表示部13に表示して撮影者に確認させ、スケジュールどおりでない場合に、撮影者の入力部22を介した操作入力に基づいてスケジュールテーブル60の再設定を行う構成としてもよい。そして、スケジュールテーブル60において、ステップS15で変更された撮影シーンに対応して、RAM23に格納された現在の撮影シーンに対応する各被写体の撮影回数が0にリセットされる(ステップS16)。
When the shooting schedule is shifted to the next time zone (step S14; YES), the current shooting scene (shooting schedule) is changed to the next shooting scene, and the record to be read and written to the schedule table 60 is the next record. (Step S15). Since the event does not always proceed according to the schedule, in the case of step S14; YES, the current shooting scene or the like is displayed on the
そして、入力部22のシャッタキー7が半押しされたか否かが判別される(ステップS17)。シャッタキー7が半押しされていない場合(ステップS17;NO)、ステップS17に移行される。撮影スケジュールが次の時間帯に移行されていない場合(ステップS14;NO)、ステップS17に移行される。
Then, it is determined whether or not the
撮影シーンを逸脱した場合(ステップS13;YES)、GPS27から取得される現在位置情報及び現在時刻情報に基づいて、現在位置(所定の経度緯度範囲)にデジタルカメラ1が所定時間以上あるか否かが判別される(ステップS18)。現在位置に所定時間以上いる場合(ステップS18;YES)、現在位置(所定の緯度、経度範囲)が仮想シーンに決定される(ステップS19)。そして、現在の撮影シーンが仮想シーンに変更され、これに伴いスケジュールテーブル60が変更され、RAM23に格納された各被写体の撮影回数がリセットされ(ステップS20)、ステップS17に移行される。
If the shooting scene has been deviated (step S13; YES), based on the current position information and current time information acquired from the
ここで、図9を参照して、ステップS20におけるスケジュールテーブル60の変更の一例を示す。図9に示すように、スケジュールテーブル60の一例としてのスケジュールテーブル60aは、時間帯61が11:00〜12:00の撮影シーン63(銀閣寺)のレコードR1を有する。スケジュールテーブル60aにおいて、撮影シーンの逸脱(ステップS15;YES)が発生し、ステップS18において、所定時間その位置にいたものとする。
Here, with reference to FIG. 9, an example of the change of the schedule table 60 in step S20 is shown. As shown in FIG. 9, the schedule table 60a as an example of the schedule table 60 includes a record R1 of a shooting scene 63 (Ginkakuji) whose
すると、ステップS20において、スケジュールテーブル60aのレコードR1がレコードR11,R12に分割されてスケジュールテーブル60bに変更される。スケジュールテーブル60aのレコードR1の時間帯61の終了時間が、位置を移動した時刻11:15に設定されてレコードR11とされ、現在時刻〜レコードR1の時間帯61の終了時間を時間帯61とし、現在位置(経度x1〜x2、緯度y1〜y2)が位置情報62に設定されたレコードR12が追加される。
Then, in step S20, the record R1 of the schedule table 60a is divided into records R11 and R12 and changed to the schedule table 60b. The end time of the
ステップS20の時点では、レコードR12において、撮影シーン63が空いている。その撮影シーン名の操作入力を、例えば、仮想シーン決定時又はそれ以後に入力部22を介して受け付けてレコードR12の撮影シーン63に設定する。
At step S20, the
図7に戻り、現在位置に所定時間以上いない場合(ステップS18;NO)、RAM23に格納された撮影回数のインクリメントが禁止に設定され(ステップS21)、ステップS17に移行される。
Returning to FIG. 7, when the current position is not longer than the predetermined time (step S18; NO), the increment of the number of photographing stored in the
シャッタキー7が半押しされた場合(ステップS17;YES)、RAM23に格納された撮影回数の下限値が算出され、RAM23に格納された現在の撮影回数が下限値を下回る被写体がいるか否かが判別される(ステップS22)。下限値は、次式(1)により算出されるものとする。
下限値=max(0,平均値×重み付け係数−1) …(1)
When the
Lower limit value = max (0, average value × weighting coefficient−1) (1)
式(1)において、平均値とは、現在の撮影シーン63の撮影回数65の合計値を全被写体数で割った値とする。式(1)において、重み係数とは、所定の固定値とするが、現在の撮影シーンの撮影回数の合計値に応じた値としてもよい。式(1)により、撮影回数の平均値が小さいうちは、撮影回数の少ない被写体を認識しないようにしている。
In Equation (1), the average value is a value obtained by dividing the total value of the number of
現在の撮影回数が下限値を下回る被写体がいる場合(ステップS22;YES)、現在の撮影シーンの残り時間が所定値以下であるか否かが判別される(ステップS23)。現在の撮影シーンの残り時間が所定値以下である場合(ステップS23;YES)、フラッシュメモリ25に記憶された顔登録データ50を用いて、撮影範囲である画角内において、ステップS22で判別された現在の撮影回数が下限値を下回る被写体が認識され、光学系駆動部34、駆動回路36を介してレンズ光学系31、絞り機構32、撮像素子33が駆動されて、その認識された被写体に対してのみAF及びAEが実行されてロックされる(ステップS24)。
When there is a subject whose current number of photographing is below the lower limit (step S22; YES), it is determined whether or not the remaining time of the current photographing scene is equal to or less than a predetermined value (step S23). If the remaining time of the current shooting scene is equal to or less than the predetermined value (step S23; YES), the
ここで、図10を参照して、ステップS24における被写体の認識の様子を示す。図10に示すように、ステップS24において、表示部13に、画面70aが表示されているものとする。画面70aは、現在の撮影シーンにおける各被写体の撮影回数71、残り時間72とを含む。ステップS24で認識された被写体を印73で示す。ステップS24では、例えば、スルー画像データから顔画像データが切り出され、顔登録データ50の被写体51が被写体Aである認識用データ52が読み出されて、その顔画像データと認識用データとが比較され、一致する場合に被写体Aである顔画像データが認識される。認識用データが顔の特徴を示すデータである場合は、前記顔画像データから顔の特徴を示すデータが抽出され、顔画像データの顔の特徴を示すデータと認識用データとが比較される。
Here, with reference to FIG. 10, the state of recognition of the subject in step S24 is shown. As shown in FIG. 10, it is assumed that the
画面70aにおいて、撮影回数71の被写体Aの撮影回数が下限値よりも少なく、残り時間72が所定値以下であるので、被写体Aのみに対してAF及びAEが実行される。
In the
現在の撮影回数が下限値を下回る被写体がない場合(ステップS22;NO)、又は現在の撮影シーンの残り時間が所定値以下でない場合(ステップS23;NO)、フラッシュメモリ25に記憶された顔登録データ50を用いて、スルー画像データの画角内の全ての被写体が認識され、光学系駆動部34、駆動回路36を介してレンズ光学系31、絞り機構32、撮像素子33が駆動されて、その認識された被写体に対してAF及びAEが実行されてロックされる(ステップS25)。
When there is no subject whose current number of photographing is below the lower limit (step S22; NO), or when the remaining time of the current photographing scene is not less than a predetermined value (step S23; NO), the face registration stored in the
ここで、図11を参照して、ステップS24における被写体の認識の様子を示す。図11に示すように、ステップS25において、表示部13に、画面70bが表示されているものとする。画面70bは、現在の撮影シーンにおける各被写体の撮影回数71、残り時間72とを含む。ステップS25では、例えば、スルー画像データから各顔画像データが切り出され、顔登録データ50の被写体51が被写体A,B,Cである認識用データ52が読み出されて、その顔画像データと認識用データとが比較され、一致する被写体A,B,Cの顔画像データが認識される。
Here, with reference to FIG. 11, how the subject is recognized in step S24 is shown. As shown in FIG. 11, it is assumed that the
ステップS25で認識された被写体を印73で示す。画面70bにおいて、全ての被写体A,B,Cが認識され、被写体A,B,Cに対してAF及びAEが実行される。
The subject recognized in step S25 is indicated by a
そして、ステップS24又はS25の実行後、入力部22のシャッタキー7が全押しされたか否かが判別される(ステップS26)。シャッタキー7が全押しされていない場合(ステップS26;NO)、ステップS26に移行される。シャッタキー7が全押しされた場合(ステップS26;YES)、ステップS24又はS25の状態で、撮像部24により被写体が撮影されてその画像データが取得され、その取得された画像データが記録部28を介してメモリカードMに記録される(ステップS27)。
Then, after step S24 or S25 is executed, it is determined whether or not the
そして、RAM23に格納された現在の撮影シーンの各被写体の撮影回数のうち、ステップS24,S25で認識された各被写体の撮影回数が+1インクリメントされる(ステップS28)。そして、ステップS28でインクリメントされた撮影回数に応じて、スケジュールテーブル60の現在の撮影シーン63に対応する撮影回数65が更新される(ステップS29)。
Then, out of the number of times of shooting of each subject in the current shooting scene stored in the
そして、RAM23に格納された撮影回数の下限値が算出され、RAM23に格納された現在の撮影回数が下限値を下回る被写体がいるか否かが判別される(ステップS30)。下限値は、式(1)により算出されるものとする。現在の撮影回数が下限値を下回る被写体がいる場合(ステップS30;YES)、その被写体の撮影回数が少なく被写体の撮影に偏りがある旨の警告が、表示部13による警告情報の表示と、音出力部29aによる警告音の出力とで報知される(ステップS31)。例えば、現在の撮影シーンの撮影回数が下限値を下回る被写体64がサムネイル表示及び音声出力される。
Then, the lower limit value of the number of times of photographing stored in the
そして、スケジュールテーブル60の時間帯61と、GPS部27から取得された現在時刻情報とが参照され、全スケジュールが終了したか否かが判別される(ステップS32)。全スケジュールが終了していない場合(ステップS32;NO)、ステップS13に移行される。全スケジュールが終了した場合(ステップS32;YES)、撮影処理が終了する。
Then, the
上記説明では、図5、図9に示したスケジュールテーブル60として、各撮影シーンの位置情報62が異なる例を説明したが、これに限定されるものではない。例えば、スケジュールテーブル60として、図12に示すスケジュールテーブル60cのように、ある学校の校庭で運動会を撮影する場合のように、同じ位置情報62で各撮影シーン63(100M走等)の被写体を撮影する構成としてもよい。
In the above description, an example in which the
本実施の形態によれば、各被写体の撮影シーンごとの撮影回数をインクリメントして撮影回数65を更新するため、複数の撮影シーン(撮影スケジュール)における撮影シーンごとに各被写体の撮影回数を把握できる。更に、撮影回数65が下限値を下回った被写体があるか否かを判別して当該被写体のみを認識し、若しくは後述するデジタルズーム処理をして、撮影回数65が少ない被写体を優先的に撮影対象とする。このため、複数の撮影シーンにおける撮影シーンごとに被写体の撮影回数の偏りをなくすことができ、複数の撮影シーンにおける撮影シーンごとに被写体の均等撮影を行うことができる。 According to the present embodiment, the number of times of photographing for each subject is incremented and the number of times of photographing 65 is updated, so that the number of times of photographing of each subject can be grasped for each photographing scene in a plurality of photographing scenes (shooting schedules). . Further, it is determined whether or not there is a subject whose number of photographing 65 is below the lower limit value, and only the subject is recognized, or a digital zoom process described later is performed, and a subject with a small number of photographing 65 is preferentially designated as a subject to be photographed. To do. For this reason, it is possible to eliminate bias in the number of times the subject is shot for each shooting scene in a plurality of shooting scenes, and it is possible to perform equal shooting of the subject for each shooting scene in a plurality of shooting scenes.
つまり、シャッタキー7半押しで、RAM23上の撮影回数が下限値を下回った被写体があるか否かを判別し、撮影回数が下限値を下回った被写体がある場合に、その撮影回数65が下限値を下回った被写体のみを認識する。そして、認識された被写体のみに対しAF、AEが実行されてロックされるので、認識された被写体のみにピントが合う。一方、認識されていない被写体にはピントが合わない、即ち、ボケることとなる。すると、画角内に、撮影回数65が下限値を下回る被写体、及び下回らない被写体の両方が存在していても、撮影回数65が下限値を下回る被写体のみが実質的に撮影されたこととなる。その結果、撮影者は、撮影回数65が下限値を下回る被写体のみを画角内に収めるようにデジタルカメラ1を振るといった面倒な操作を行うことなく当該被写体のみを実質的に撮影でき、各被写体の撮影回数の偏りを容易になくすことができる。
That is, when the
また、シャッタキー7半押しで、RAM23上の撮影回数が下限値を下回った被写体がある場合に、撮影スケジュールの残り時間が所定値以下か否かを判別し、残り時間が所定値以下である場合に、その撮影回数65が下限値を下回った被写体のみを認識する。これによっても、撮影者は、撮影回数65が下限値を下回る被写体のみを画角内に収めるようにデジタルカメラ1を振るといった面倒な操作を行うことなく当該被写体のみを実質的に撮影でき、各被写体の撮影回数の偏りを容易になくすことができる。さらに、残り時間が所定値以下である場合にのみ、撮影回数65が下限値を下回る被写体のみを認識するため、残り時間が多い場合には、ユーザの操作により当該被写体のみが画角内に収まるよう調整でき、利便性が向上する。
If there is a subject whose number of shootings on the
また、デジタルカメラ1が現在位置が現在の撮影シーン63から逸脱して且つ所定時間以上経過した場合に、撮影シーンとして仮想シーンを決定しスケジュールテーブル60に追加して変更する。このため、スケジュールが変更になり新たな撮影シーンを撮影する場合にも、その撮影シーンを仮想シーンとして撮影スケジュールに加えて被写体の均等撮影を行うことができる。
When the
また、撮影回数65が下限値を下回った被写体がある場合に、その被写体の撮影回数が少なく被写体の撮影に偏りがある旨を表示部13及び音出力部29aにより撮影者に報知する。この報知によって、撮影者は画角を調整して複数の被写体の撮影回数の偏りをなくすことができ、被写体の均等撮影を行うことができる。
In addition, when there is a subject whose number of
なお、上記実施の形態における記述は、本発明に係る撮影装置、撮影方法及びプログラムの一例であり、これに限定されるものではない。 The description in the above embodiment is an example of a photographing apparatus, a photographing method, and a program according to the present invention, and the present invention is not limited to this.
例えば、上記実施の形態では、静止画の撮影において、被写体の撮影回数の偏りを防ぐ構成であったが、これに限定されるものではない。動画の撮影において、被写体の撮影量の偏りをなくす構成としてもよい。図13に、ムービーカメラ1aの外観を示す。
For example, in the above-described embodiment, the configuration is configured to prevent deviation in the number of times the subject is captured in still image capturing. However, the present invention is not limited to this. In moving image shooting, it is possible to eliminate the bias of the shooting amount of the subject. FIG. 13 shows the appearance of the
図13に示すようなムービーカメラ1aが、撮影シーンごとに被写体を撮影時間の偏りなく撮影する機能を有する構成としてもよい。より具体的には、ムービーカメラ1aにおいて、動画撮影時に被写体を認識し、認識した被写体毎に撮影量としての撮影時間をカウントしていき、ある被写体の撮影時間が下限値を下回る場合に、その被写体の撮影時間が少なく被写体の撮影に偏りがある旨の警告を表示及び音声出力して撮影者に報知する構成としてもよい。
The
また、上記実施の形態では、認識した被写体に対してAF及びAEを行う構成としたが、これに限定されるものではない。シャッタキー7半押しで、RAM23上の撮影回数が下限値を下回った被写体があるか否かを判別し、撮影回数65が下限値を下回った被写体がある場合に、当該被写体が画角の中心に位置するように、デジタルズームを自動的に行う構成としてもよい。この場合、CPU21から信号処理回路40に、撮影回数65が下限値を下回る被写体が画角の中心に位置するよう制御する制御信号が出力される。そして、信号処理回路40にて、フレームデータに対しデジタルズーム領域の画像データを取り込むデジタルズーム処理(フレームデータから、撮影回数65が下限値を下回る被写体を中心とした所定量のズーム倍率の画像データを切り出して、1画面分の画像データを生成する)が行われる。また、デジタルズーム処理された画像データは、表示部13一杯に拡大して表示される。なお、このデジタルズーム領域の画像データには、撮影回数65が下限値以上である被写体の一部が含まれていてもよい。これによれば、撮影者は、撮影回数65が下限値を下回る被写体のみを画角内に収めるようにデジタルカメラ1を振るといった面倒な操作を行うことなく当該被写体のみを撮影でき、各被写体の撮影回数の偏りを容易になくすことができる。
In the above embodiment, AF and AE are performed on the recognized subject. However, the present invention is not limited to this. When the
また、シャッタキー7半押しで、RAM23上の撮影回数65が下限値を下回った被写体がある場合に、撮影スケジュールの残り時間が所定値以下か否かを判別し、残り時間が所定値以下である場合に、当該被写体が画角の中心に位置するように、デジタルズームを自動的に行う構成としてもよい。これによっても、撮影者は、撮影回数65が下限値を下回る被写体のみを画角内に収めるようにデジタルカメラ1を振るといった面倒な操作を行うことなく当該被写体のみを撮影でき、各被写体の撮影回数の偏りを容易になくすことができる。さらに、残り時間が所定値以下である場合にのみ、撮影回数65が下限値を下回る被写体のみを認識してズームするため、残り時間が多い場合には、撮影者の操作により当該被写体のみが画角内に収まるよう調整でき、利便性が向上する。
Further, when there is an object whose number of
また、上記実施の形態におけるデジタルカメラ1の各構成要素の細部構成及び細部動作に関しては、本発明の趣旨を逸脱することのない範囲で適宜変更可能であることは勿論である。
Of course, the detailed configuration and detailed operation of each component of the
1 デジタルカメラ
2 撮影レンズ
6 電源キー
7 シャッタキー
8 モードスイッチ
9 メニューキー
10 十字キー
12 スピーカー
13 表示部
21 CPU
22 入力部
23 RAM
24 撮像部
25 フラッシュメモリ
26 通信部
27 GPS部
28 記録部
29 RTC
29a 音出力部
30 バス
M メモリカード
1a ムービーカメラ
1
22
24
29a
Claims (11)
撮影シーンを検知する検知手段と、
前記検知手段により検知された撮影シーンで撮影された画像の被写体別の撮影量を記憶する記憶手段と、
前記記憶手段に記憶されている撮影量に基づいて、当該撮影量が所定下限値を下回る被写体を特定する特定手段と、
前記特定手段により特定された被写体を撮影するよう前記撮影手段を制御する撮影制御手段と、
を備えたことを特徴とする撮影装置。 An imaging means you shoot the Utsushitai,
Detection means for detecting a shooting scene ;
Storage means for storing a photographing amount for each subject of an image photographed in a photographing scene detected by the detecting means ;
A specifying unit for specifying a subject whose shooting amount is below a predetermined lower limit based on the shooting amount stored in the storage unit;
And imaging control means for controlling the photographing means to photograph the object specified by the specifying means,
An imaging apparatus comprising:
前記撮影制御手段は、前記合焦手段により合焦された被写体を前記撮影手段に撮影させることを特徴とする請求項1記載の撮影装置。 Focusing means for focusing on the subject specified by the specifying means,
The photographing apparatus according to claim 1 , wherein the photographing control unit causes the photographing unit to photograph the subject focused by the focusing unit.
前記撮影制御手段は、前記特定された被写体の位置をズーム中心位置として前記デジタルズーム手段にデジタルズームさせ、前記撮影手段により前記特定された被写体を撮影させるよう制御することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の撮影装置。 Anda digital zoom means for digital zoom position of the object specified by the specifying means as the zoom center position,
2. The control unit according to claim 1, wherein the photographing control unit controls the digital zoom unit to digitally zoom the position of the identified subject as a zoom center position and causes the photographing unit to photograph the identified subject. Shooting device.
前記記憶手段は、前記被写体別の撮影量に対応付けて、更に、前記撮影シーンの撮影された時の時間帯情報を記憶し、
前記検知手段は、前記第1の取得手段により取得された現在時刻情報と前記記憶手段により記憶された前記撮影シーンの時間帯情報とに基づき、現在の撮影シーンを検知することを特徴とする請求項1から3のいずれか一項に記載の撮影装置。 A first acquisition means for acquiring current time information;
Wherein the storage unit, in association with the object by the imaging volume further stores the time zone information when photographing the photographic scene,
Said sensing means, wherein said first based on the current time information acquired by the acquisition means and the time zone information of the photographic scene stored by the storage means, and detecting the current shooting scene Item 4. The photographing device according to any one of Items 1 to 3.
前記記憶手段は、前記被写体別の撮影量に対応付けて、更に、前記撮影シーンの撮影された時の位置情報を記憶し、
前記検知手段は、前記第2の取得手段により取得された現在位置情報と前記記憶手段により記憶された前記撮影シーンの位置情報とに基づき、現在の撮影シーンを検知することを特徴とする請求項1から3のいずれか一項に記載の撮影装置。 A second acquisition means for acquiring current position information of the photographing apparatus;
Wherein the storage unit, in association with the object by the imaging volume, further, the position information of the time taken for the photographic scene remembers,
Said sensing means, wherein said based on has been the current position information acquired by the second acquisition means and the position information of the photographic scene stored by the storage means and the detection child the current shooting scene Item 4. The photographing device according to any one of Items 1 to 3.
前記判別手段により前記現在位置情報が前記撮影シーンを逸脱していると判別された場合に、前記現在位置情報に基づき、前記記憶手段に新たな撮影シーンを追加する撮影シーン追加手段と、
を更に備えることを特徴とする請求項5に記載の撮影装置。 Based on the position information before Symbol photographic scene stored by the current position information and the storage means is acquired by the second acquisition unit, determines whether the current position information is out of the photographic scene determination Means,
When the current position information Ri by said determining means is determined to deviate the photographic scene, based on the current position information, the photographic scene addition means for adding a new photographic scene in the storage means ,
The imaging apparatus according to claim 5, further comprising:
を更に備えることを特徴とする請求項1から6のいずれか一項に記載の撮影装置。 And distribution Shitte stage for notifying at least one display or sound effect that is captured of the object identified is below the predetermined lower limit value by the pre-Symbol specifying means,
The imaging device according to claim 1, further comprising:
前記記憶手段に記憶されている撮影量に基づいて、当該撮影量が所定下限値を下回る被写体を特定する特定ステップと、
前記特定ステップにて特定された被写体を撮影するよう前記撮影手段を制御する撮影制御ステップと、
を含むことを特徴とする撮影制御方法。 An imaging apparatus comprising: an imaging unit that captures a subject; a detection unit that detects a previous shooting scene; and a storage unit that stores a shooting amount of each image captured in the shooting scene detected by the detection unit. The shooting control method of
A specifying step of specifying a subject whose shooting amount is below a predetermined lower limit based on the shooting amount stored in the storage unit;
A photographing control step of controlling the imaging means to photograph the subject identified by said identification step,
Photographing control method, which comprises a.
前記記憶手段に記憶されている撮影量に基づいて、当該撮影量が所定下限値を下回る被写体を特定する特定手段、
前記特定手段により特定された被写体を撮影するよう前記撮影手段を制御する撮影制御手段、
として機能させることを特徴とするプログラム A computer of a photographing apparatus comprising photographing means for photographing a subject, detecting means for detecting a photographing scene, and storage means for storing a photographing amount for each subject of an image photographed in the photographing scene detected by the detecting means. The
A specifying unit for specifying a subject whose shooting amount is below a predetermined lower limit based on the shooting amount stored in the storage unit;
Photographing control means for controlling the photographing means to photograph the object specified by the specifying means,
Program for causing to function as an
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007315904A JP5141222B2 (en) | 2007-12-06 | 2007-12-06 | Imaging apparatus, imaging control method, and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007315904A JP5141222B2 (en) | 2007-12-06 | 2007-12-06 | Imaging apparatus, imaging control method, and program |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009141669A JP2009141669A (en) | 2009-06-25 |
| JP2009141669A5 JP2009141669A5 (en) | 2011-01-20 |
| JP5141222B2 true JP5141222B2 (en) | 2013-02-13 |
Family
ID=40871844
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007315904A Expired - Fee Related JP5141222B2 (en) | 2007-12-06 | 2007-12-06 | Imaging apparatus, imaging control method, and program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5141222B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5359754B2 (en) * | 2009-10-05 | 2013-12-04 | 株式会社Jvcケンウッド | Imaging control device and program |
| JP6028549B2 (en) * | 2012-11-30 | 2016-11-16 | キヤノンマーケティングジャパン株式会社 | Information processing apparatus, information processing system, control method thereof, and program |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005086237A (en) * | 2003-09-04 | 2005-03-31 | Casio Comput Co Ltd | Imaging apparatus and program |
| JP4661413B2 (en) * | 2005-07-11 | 2011-03-30 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Imaging apparatus, number of shots management method and number of shots management program |
| JP4678843B2 (en) * | 2005-09-15 | 2011-04-27 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging apparatus and control method thereof |
| JP4724890B2 (en) * | 2006-04-24 | 2011-07-13 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Image reproduction apparatus, image reproduction method, image reproduction program, and imaging apparatus |
-
2007
- 2007-12-06 JP JP2007315904A patent/JP5141222B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2009141669A (en) | 2009-06-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4463792B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| US7693406B2 (en) | Image capturing apparatus, method of controlling the same, and storage medium | |
| JP5713055B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, and program | |
| US7978254B2 (en) | Image capturing apparatus, its controlling method, and program | |
| JP4315212B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging control program, and imaging control method | |
| JP5402341B2 (en) | Automatic imaging apparatus and automatic imaging method | |
| JP2010245607A (en) | Image recording device and electronic camera | |
| JP2011175281A (en) | Imaging apparatus and program therefor | |
| JP2007166420A (en) | Camera system and digital camera | |
| JP2006246354A (en) | Imaging unit and imaging program | |
| JP4914688B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP2006308813A (en) | Imaging apparatus with focus bracket function | |
| JP5141222B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging control method, and program | |
| JP2012235393A (en) | Controller, imaging system, and program | |
| JP2010087598A (en) | Photographic apparatus, photographic control method and program therefor, image display apparatus, image display method and program therefor, and photographic system, control method therefor and program therefor | |
| JP2007267309A (en) | Electronic camera | |
| JP5962974B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, and program | |
| JP3913046B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP2006174010A (en) | Imaging apparatus | |
| JP5612934B2 (en) | Portable device and playback display method | |
| JP2008104070A (en) | Portable apparatus with camera and program for portable apparatus with camera | |
| JP2008048152A (en) | Moving picture processing apparatus, moving picture photographing apparatus and moving picture photographing program | |
| JP2010183565A (en) | Image capturing apparatus, image retrieval device, and program | |
| JP2005107358A (en) | Camera and camera system | |
| JP2013211719A (en) | Digital camera |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20101129 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20101129 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20101129 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120308 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120313 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20121023 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20121105 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20151130 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5141222 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |