JP4807855B2 - Anti-vibration device, anti-vibration method and program - Google Patents
Anti-vibration device, anti-vibration method and program Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4807855B2 JP4807855B2 JP2007199813A JP2007199813A JP4807855B2 JP 4807855 B2 JP4807855 B2 JP 4807855B2 JP 2007199813 A JP2007199813 A JP 2007199813A JP 2007199813 A JP2007199813 A JP 2007199813A JP 4807855 B2 JP4807855 B2 JP 4807855B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- vibration
- turning operation
- information detected
- correction
- angular velocity
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Adjustment Of Camera Lenses (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
Description
本発明は、カメラ装置(レンズシステム)の防振機能に関する。 The present invention relates to an image stabilization function of a camera device (lens system).
従来、レンズとカメラ、ズームデマンド、フォーカスデマンド、三脚装置で構成されるレンズシステム(カメラ装置)は、CCD等の撮像素子からなる撮像素子部を有するカメラと、ズーム機能とフォーカス機能を有したレンズと、フォーカスレンズを移動させるためのフォーカスレンズ移動モータと、ズーム時にズームレンズを移動させるためのズームレンズモータとを有する。さらに、レンズシステムは、各モータの移動および回転位置をそれぞれ検出する位置センサを有する。 2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, a lens system (camera device) composed of a lens and a camera, a zoom demand, a focus demand, and a tripod device is a camera having an image sensor unit composed of an image sensor such as a CCD, and a lens having a zoom function and a focus function. And a focus lens moving motor for moving the focus lens and a zoom lens motor for moving the zoom lens during zooming. Furthermore, the lens system has a position sensor that detects the movement and rotation position of each motor.
また、レンズシステムは、レンズの外部に取り付けられズーム機能を操作するズームデマンドと、フォーカス機能を操作するフォーカスデマンドと、三脚装置とを有する。なお、三脚装置は、カメラ、レンズ、デマンド全体を保持し、カメラマンの操作によりカメラ装置の向きを上下左右に変更可能とするものである。 The lens system includes a zoom demand that is attached to the outside of the lens and operates a zoom function, a focus demand that operates a focus function, and a tripod device. The tripod device holds the entire camera, lens, and demand, and can change the orientation of the camera device up, down, left, and right by the operation of the cameraman.
さらに、近年のレンズシステムでは、上記構成要素に加えて、レンズシステムを設置する環境において発生する振動を除去し、視覚上良好な画像を得るために、振動を検知する振動検出センサ、即ち圧電振動ジャイロ等による角速度センサと、レンズから入光される光学信号の光軸補正を行う光路補正光学系と光路補正光学系を制御する光路補正制御部と、フォーカスレンズ移動モータ、ズームレンズ移動モータと、光路補正制御部全体を制御するマイクロコンピュータ(CPU)とを有する。 Furthermore, in recent lens systems, in addition to the above components, a vibration detection sensor that detects vibrations, that is, piezoelectric vibrations, in order to remove vibrations generated in the environment where the lens system is installed and obtain a visually good image. An angular velocity sensor such as a gyro, an optical path correction optical system that performs optical axis correction of an optical signal incident from the lens, an optical path correction control unit that controls the optical path correction optical system, a focus lens movement motor, a zoom lens movement motor, And a microcomputer (CPU) for controlling the entire optical path correction control unit.
以下、このように構成された従来のレンズシステムの防振制御について説明する。 Hereinafter, the image stabilization control of the conventional lens system configured as described above will be described.
図10は、従来のレンズシステムにおける防振制御処理手順の一例を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing an example of the image stabilization control processing procedure in the conventional lens system.
防振制御処理が開始するとまず、レンズシステムのCPUは、防振スイッチの状態を読み込み(S101)、防振スイッチがON状態か否かを判定する(S102)。 When the image stabilization control process starts, first, the CPU of the lens system reads the state of the image stabilization switch (S101) and determines whether the image stabilization switch is in the ON state (S102).
そして、ステップS102において、防振スイッチがOFF状態であると判定した場合、CPUは、防振制御を実行しないため、そのまま防振制御処理を終了する。 If it is determined in step S102 that the image stabilization switch is in the OFF state, the CPU does not execute image stabilization control, and thus ends the image stabilization control process as it is.
一方、ステップS102において、防振スイッチがON状態であると判定した場合、CPUは、レンズのズーム位置を読み込み(S103)、レンズのズーム位置が所定値よりテレ側にあるか否かを判定する(S104)。 On the other hand, if it is determined in step S102 that the image stabilization switch is in the ON state, the CPU reads the zoom position of the lens (S103), and determines whether or not the zoom position of the lens is on the tele side from a predetermined value. (S104).
そして、ステップS104において、レンズのズーム位置が所定値よりテレ側にないと判定した場合、CPUは、振れ補正の必要がない、即ち撮影画角が広いため画面に占める振動の割合が微量であり振れ補正を実施しても効果がないと判断して、そのまま防振制御処理を終了する。 If it is determined in step S104 that the zoom position of the lens is not on the telephoto side from the predetermined value, the CPU does not need to perform shake correction, that is, since the shooting angle of view is wide, the vibration ratio in the screen is very small. If it is determined that there is no effect even if the shake correction is performed, the image stabilization control process is ended as it is.
一方、ステップS104において、レンズのズーム位置が所定値よりテレ側にあると判定した場合、CPUは、角速度センサからの電圧値を読み込み(S105)、振れの向きと量を認識する。 On the other hand, if it is determined in step S104 that the zoom position of the lens is on the tele side from the predetermined value, the CPU reads the voltage value from the angular velocity sensor (S105) and recognizes the direction and amount of shake.
次に、CPUは、角速度センサから得られた電圧値から光軸補正量を演算する(S106)。さらに、CPUは、光路補正装置に対して所定の電圧値を出力し、光軸を振れとは逆方向に移動させ振れを補正し(S107)、防振制御処理を終了する。 Next, the CPU calculates the optical axis correction amount from the voltage value obtained from the angular velocity sensor (S106). Further, the CPU outputs a predetermined voltage value to the optical path correction device, moves the optical axis in the direction opposite to the shake to correct the shake (S107), and ends the image stabilization control process.
図11は、従来のレンズシステムにおける防振制御についての解説を図示したものである。 FIG. 11 illustrates a description of image stabilization control in a conventional lens system.
図11において、(a)の図は、レンズシステムに振動がない場合で、撮影したい被写体がCCDの中央に位置している。(b)の図は、振動があり防振制御を実施しない場合で、振動によりレンズシステムの撮影方向が傾くと被写体がCCDの中央から中央以外の場所にずれしてしまう。 In FIG. 11, (a) shows the case where the lens system is not vibrated, and the subject to be photographed is located at the center of the CCD. FIG. 5B shows a case where vibration is present and image stabilization control is not performed. If the photographing direction of the lens system is tilted due to vibration, the subject is shifted from the center of the CCD to a place other than the center.
(c)の図は、光路補正光学系を使用して防振制御を実施する場合で、振動によりレンズシステムが傾いてしまったずれ量を角速度センサで検知し、ずれに対し逆方向に光路補正光学系を移動させる事で光の屈折を変え、撮影したい被写体をCCDの中央に移動させている。 The figure in (c) shows the case where vibration control is performed using an optical path correction optical system, and the amount of deviation in which the lens system is tilted due to vibration is detected by an angular velocity sensor, and the optical path is corrected in the opposite direction to the deviation. By moving the optical system, the refraction of light is changed, and the subject to be photographed is moved to the center of the CCD.
又、特許文献1では、グリップ部にテレビカメラのパン・チルト動作を検出する検出部(例えば圧電素子)を設け、検出部からパン・チルト動作を示す信号が防振装置の演算部に出力されると、演算部が防振装置の駆動部を制御して補正レンズの移動を停止させることにより、カメラマンのパン・チルト操作では像ぶれを補正せず、外乱振動による像ぶれのみを補正するテレビカメラの防振装置が開示されている。
しかしながら、上記従来のレンズシステムにおける防振制御では、以下に掲げる問題点があり、その改善が要望されていた。 However, the image stabilization control in the above-described conventional lens system has the following problems, and improvement has been demanded.
即ち、カメラマンがレンズシステムの方向を作為的に左右にふる操作、即ちパンニング操作する場合、レンズに取り付けられた角速度センサはパンニング操作を振動と判断してしまい、その振動情報をCPUに出力する。 That is, when the cameraman performs a panning operation in which the direction of the lens system is intentionally moved to the left or right, that is, the angular velocity sensor attached to the lens determines that the panning operation is vibration, and outputs the vibration information to the CPU.
この振動情報を受けたCPUは、この振動情報に応じた振れ量に相当する光軸補正量を演算し、光路補正を実施する。 The CPU that has received the vibration information calculates an optical axis correction amount corresponding to the shake amount corresponding to the vibration information, and performs optical path correction.
従って、この光路補正により、パンニング直後は、パンニングの反対方向に光軸が移動し、パンニング中はそのまま張り付き、パンニング操作が終了すると、光軸が元に戻るといった動きをしてしまう場合がある。 Therefore, due to this optical path correction, the optical axis may move in the opposite direction of panning immediately after panning, sticking as it is during panning, and the optical axis may return to its original state when the panning operation is completed.
なお、従来では、この問題を解決するために、以下の対策を実施しているのが現状である。 Conventionally, in order to solve this problem, the following measures are currently taken.
振動情報を所定時間メモリに格納し、1秒間以上、同じ向きの振動が継続した場合はパンニング操作であると判断し、防振制御を停止している。 The vibration information is stored in the memory for a predetermined time, and if the vibration in the same direction continues for one second or more, it is determined that the operation is a panning operation, and the image stabilization control is stopped.
しかしパンニング操作であると判断し防振制御を停止するするまで少なくとも1秒間かかってしまうため、レスポンスの低下が問題視される。また、パンニング終了の検知についても同様の手法を取っているため時間がかり、パンニング操作終了直後の振動については補正できない状況にある。 However, since it takes at least one second to determine that the operation is a panning operation and to stop the image stabilization control, a reduction in response is regarded as a problem. Further, since the same method is used for detecting the end of panning, it takes time, and the vibration immediately after the end of the panning operation cannot be corrected.
その一方で、放送用途におけるズームレンズは、高付加価値化を実現するため、年々ズーム倍率の高倍率化が進んでいる。これに伴い、長焦点側の焦点距離が大きな数値になってくると、撮影画角が狭くなるため、カメラシステム撮影環境下の振動が画面の大きな振れとなって現れてしまう。このような背景から近年、防振装置の高精度制御が求められるようになってきている。 On the other hand, zoom lenses for broadcasting use have been increasing year by year in order to realize high added value. Along with this, when the focal length on the long focal point side becomes a large numerical value, the shooting angle of view becomes narrow, and thus vibration under the camera system shooting environment appears as a large shake of the screen. From such a background, in recent years, high-precision control of the vibration isolator has been demanded.
また、特許文献1のように、パンチルト操作棒のグリップ部に圧電素子を組み込んで、カメラマンがグリップを握ったか否かでパンニングと非パンニングを判断し、パンニングと判断した場合、振動補正動作を停止させる手法が提案されている。 In addition, as in Patent Document 1, a piezoelectric element is incorporated in the grip portion of the pan / tilt operating rod, and panning and non-panning are determined based on whether or not the cameraman has gripped the grip. A technique to make it has been proposed.
しかしながら、この手法だとカメラマンが、グリップを握っただけで防振制御が停止してしまうため、動作させたいシーンで防振機能が働かない場合があるといった問題点がある。 However, this method has a problem that the image stabilization function may not work in a scene to be operated because the image stabilization control is stopped only by the cameraman holding the grip.
本発明は、上記の問題点を解決するためになされたものである。本発明の目的は、カメラ装置に掛かる振動とカメラマンによる作為的な旋回操作(パンニング操作,チルティング操作等)を瞬時に判定して、カメラマンによる作為的な旋回操作時でない場合にはカメラ装置に掛かる振動を従来通り除去しながら、カメラマンによる作為的な旋回操作時は、旋回操作による振動を除いた振動に対して防振制御させて、旋回操作時の動作不具合を抑えることができる仕組みを提供することである。 The present invention has been made to solve the above problems. An object of the present invention is to instantaneously determine the vibration applied to the camera device and the artificial turning operation (panning operation, tilting operation, etc.) by the cameraman, and to the camera device when it is not at the time of the artificial turning operation by the cameraman. while vibration applied was removed conventionally, when intentional turning operation by the cameraman, and anti Fusei by us against excluding the vibration caused by the turning operation vibration mechanism can be suppressed malfunction during turning operations Is to provide.
本発明は、所定の軸を中心に回動して撮影方向を変更する旋回操作が可能なカメラ装置の防振装置であって、前記回動の中心から前記カメラ装置の撮像方向側の前記回動する部位に設けられた第1の振動検出手段と、前記回動の中心から前記カメラ装置の撮像方向の逆側の前記回動する部位に設けられた第2の振動検出手段と、振動による撮像のブレを補正する振動補正を行う振動補正手段と、前記第1の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報と前記第2の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報とを用いて前記旋回操作中か否かを判定する判定手段と、前記判定手段により前記旋回操作中でないと判定された場合、前記第1の振動検出手段又は前記第2の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報を用いて前記振動補正手段に前記振動補正を実行させ、一方、前記判定手段により前記旋回操作中であると判定された場合、前記第1の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報と前記第2の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報との差分に従った前記旋回操作中の振動情報を用いて前記振動補正手段に前記振動補正を実行させるように制御する制御手段と、を有することを特徴とする。 The present invention provides a vibration isolator for a camera device that is capable of a turning operation that rotates around a predetermined axis to change a shooting direction, and the rotation of the camera device in the imaging direction side from the center of rotation. A first vibration detecting means provided at a moving part; a second vibration detecting means provided at the rotating part opposite to the imaging direction of the camera device from the center of rotation; During the turning operation using vibration correction means for performing vibration correction for correcting image blurring, vibration information detected by the first vibration detection means, and vibration information detected by the second vibration detection means And determining means for determining whether or not the turning operation is being performed by the determining means, using the vibration information detected by the first vibration detecting means or the second vibration detecting means. Causing the vibration correction means to execute the vibration correction; Write the case where it is determined that the turning operation, according to difference between the first vibration information detected by the detected vibration information second vibration detection means by the vibration detecting means by said determining means Control means for controlling the vibration correction means to execute the vibration correction using vibration information during the turning operation .
本発明によれば、カメラ装置に掛かる振動とカメラマンによる作為的な旋回操作(パンニング操作,チルティング操作等)を判断できるので、カメラマンによる作為的な旋回操作時でない場合にはカメラ装置に掛かる振動を従来通り除去しながら、カメラマンによる作為的な旋回操作時は、旋回操作による振動を除いた振動に対して防振制御させることにより、旋回操作時の動作不具合を抑えることができる等の効果を奏する。 According to the present invention, the vibration applied to the camera device and the artificial turning operation (panning operation, tilting operation, etc.) by the cameraman can be determined. Therefore, the vibration applied to the camera device is not during the artificial turning operation by the cameraman. while removed conventionally, when intentional turning operation by the cameraman, by explosion Fusei your respect except for vibration by turning operation vibrations, etc. can be suppressed malfunction during turning operations There is an effect.
以下、図面を参照して、レンズとカメラ、ズームデマンド、フォーカスデマンド、三脚装置で構成されるレンズシステム(カメラ装置)の防振機能について説明する。 Hereinafter, with reference to the drawings, an image stabilization function of a lens system (camera device) including a lens and a camera, a zoom demand, a focus demand, and a tripod device will be described.
〔第1実施形態〕
まず、図1,図2を参照して、本発明の実施形態を示すレンズシステムの構成について説明する。
[First Embodiment]
First, with reference to FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, the structure of the lens system which shows embodiment of this invention is demonstrated.
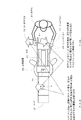
図1は、本発明の実施形態を示すレンズシステムの制御構成を示すブロック図である。 FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a control configuration of a lens system showing an embodiment of the present invention.
図2は、本発明の実施形態を示すレンズシステムを説明する側面図である。 FIG. 2 is a side view for explaining a lens system showing an embodiment of the present invention.
図1において、1はピントを可変するフォーカスレンズ群、2は画角を可変するズームレンズ群、4はその他のレンズ群である。 In FIG. 1, reference numeral 1 denotes a focus lens group that changes focus, 2 denotes a zoom lens group that changes the angle of view, and 4 denotes other lens groups.
3は光路補正光学系であり、フォーカスレンズ群1、ズームレンズ群2を介して入光される光学信号の光軸を補正する。 An optical path correction optical system 3 corrects the optical axis of an optical signal incident through the focus lens group 1 and the zoom lens group 2.
5は角速度センサであり、レンズシステムの振動の向きと大きさ(振動情報)を検出する。6は光路補正制御部であり、光路補正光学系3を駆動する。
Reference numeral 5 denotes an angular velocity sensor, which detects the direction and magnitude of vibration (vibration information) of the lens system. An optical path
8はフォーカスレンズ移動モータであり、フォーカスレンズを移動させるためのものである。9はズームレンズ移動モータであり、ズーム時にズームレンズを移動させるためのものである。
10及び11は位置センサであり、各モータの移動位置をそれぞれ検出する。また、12および13はモータ駆動回路であり、各モータをそれぞれ駆動する。
14はCPU(マイクロコンピュータ)であり、ズーム及びフォーカスモータ制御、角速度センサからの振動情報読み出し、ズーム位置読み出し、光路補正制御、防振スイッチ25の状態読み出し等レンズ全体を制御する。
A CPU (microcomputer) 14 controls the entire lens, such as zoom and focus motor control, readout of vibration information from the angular velocity sensor, readout of zoom position, optical path correction control, and readout of the state of the
このCPU14は、ROM、RAMなどを内蔵する、いわゆるワンチップマイコンタイプであるがROMやRAMを外付けにした構成であっても良い。
The
25は防振スイッチで、防振制御のON/OFFを切り換えるためのものである。カメラマン24(図2)は、防振スイッチ25を操作して、防振制御のON/OFFを切り換え可能である。
15は撮像素子部であり、3枚のCCDから構成される。16は信号処理部であり、カメラ装置の映像信号を出力する。17はズームデマンドであり、レンズのズーム機能を外部から操作する。
18はフォーカスデマンドであり、レンズのフォーカス機能を外部から操作するためのものである。19は角速度センサであり、フォーカスデマンド18に内蔵されている。
20は三脚装置であり、上述のレンズシステムを保持し、レンズシステムの撮影方向を前後左右することができる。
なお、図2に示すように、カメラマン24は、ズームデマンド17とフォーカスデマンド18を握り、ビューファインダー23の映像を見ながらレンズシステムを操作する。26は三脚20の支持点であり、パンニング時の回動中心となる。即ち、カメラマン24は、この支持点26を中心にカメラ装置を回動させて撮影方向を変更する旋回操作(パンニング操作)を行うことができる。また、カメラマン24は、図示しない軸を中心にカメラ装置を上下(天地)回動させて撮影方向を変更するチルティング操作を行うことも可能である。
As shown in FIG. 2, the cameraman 24 holds the
図1に示したように、角速度センサ5,19は、レンズ21とフォーカスデマンド18に各々取り付けられており、同一種類又は同一出力特性の角速度センサが用いられる。
As shown in FIG. 1, the
また、角速度センサ19は、三脚20の支持点26を中心として反時計回りの回転を正の角速度、時計回りの回転を負の角速度となるように取り付けられている。即ち、角速度センサ5,19はいずれも、レンズシステムが三脚20の支持点26を中心として反時計回りに回動する場合には正の角速度として検出し、一方、レンズシステムが三脚20の支持点26を中心として時計回りに回動する場合には負の角速度として検出する。即ち、角速度センサ5,角速度センサ19は、パンニング軌道を含む平面(即ち水平)に略平行で且つレンズシステムの撮像方向に略直交する方向(即ち図2の表裏方向(カメラマン24にとって左右方向))の振動を検出可能である。
Further, the
なお、角速度センサ5,19は、レンズ筐体やフォーカスデマンド18内に内蔵しても良いし外側に取り付けても良い。
The
角速度センサ5は、パンニング中心となる支点26からレンズシステムの撮像方向側に設けられ、角速度センサ19は、パンニング中心となる支点26からレンズシステムの撮像方向側の逆側に設けられる。即ち、角速度センサ19は、ズームデマンド17に設けても、他のパンニング操作を行うことが可能な操作部等に設けてもよい。
The angular velocity sensor 5 is provided on the imaging direction side of the lens system from the fulcrum 26 that is the center of panning, and the
以下、図3,図4を参照して、パンニングと振動の判断について説明する。 Hereinafter, panning and vibration determination will be described with reference to FIGS.
図3は、角速度センサ5,19の角速度と出力電圧の関係の一例を示した図である。
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing an example of the relationship between the angular velocity of the
角速度センサ5,19は、物体の回転角速度ω(°/S)を検出さるためのセンサであり、センサがある角速度で回転すると、角速度に応じて例えば図4に示すような電圧を出力する。
The
図3では振動のない状態(角速度=0の状態)では基準電圧である2.0Vが出力されるが、振動が発生すると出力電圧が0.5V〜3.5Vに可変する。つまり正の角速度では2.0Vより大きな電圧を出力し、負の角速度では2.0Vより小さな電圧を出力する。よって、CPU14は、この角速度センサの出力電圧を読み取ることで振動の向きと大きさを判断することができる。
In FIG. 3, a reference voltage of 2.0 V is output in a state where there is no vibration (state where angular velocity = 0), but when vibration occurs, the output voltage varies from 0.5 V to 3.5 V. That is, a voltage greater than 2.0V is output at a positive angular velocity, and a voltage smaller than 2.0V is output at a negative angular velocity. Therefore, the
図4は、パンニングと振動の判断を説明するための図である。 FIG. 4 is a diagram for explaining determination of panning and vibration.
レンズシステム全体に図4のようなカメラマンから見て左方向から右方向への振動が加わった場合、レンズ21にもフォーカスデマンド18にもカメラマンから見て左方向から右方向への力が加わる。そこで三脚20の支持点26を中心とすると、レンズ21に取り付けられた角速度センサ5は負の角速度を検知し、フォーカスデマンド18の角速度センサ19は正の角速度を検知する。このようにレンズシステム全体に振動が加わった場合2つの角速度センサが異なる向きの略同一の角速度に対応する電圧を出力する。つまり片方は基準電圧より低い電圧を出力し、片方は基準電圧より高い電圧を出力し、かつ基準電圧からのずれは略同一になる(ケース1)。
When vibration from the left to the right as viewed from the cameraman as shown in FIG. 4 is applied to the entire lens system, a force from the left to the right as viewed from the cameraman is applied to the lens 21 and the
また、角速度センサがノンリニアな出力電圧特性の場合は、特定の正の角速度に対応する出力電圧と該特定の正の角速度と略同一な絶対値の負の角速度に対応する出力電圧を各々出力する(ケース2)。 When the angular velocity sensor has non-linear output voltage characteristics, an output voltage corresponding to a specific positive angular velocity and an output voltage corresponding to a negative angular velocity having an absolute value substantially the same as the specific positive angular velocity are output. (Case 2).
そこで2つの角速度センサ5,19の出力電圧をそれぞれAD変換してCPU14で比較することにより、上記ケース1やケース2においてはレンズシステム全体に振動が加わったと判定することができる。
Therefore, the output voltages of the two
また、カメラマン24が、カメラ22を三脚装置20の支点を中心にして反時計周りにパンニングさせた場合、レンズ21に取り付けられた角速度センサ5もフォーカスデマンド18の角速度センサ19も略同一の正の角速度を検知する。即ち、パンニングさせた場合2つの角速度センサは略同一の出力電圧を出力する(ケース3)。
When the cameraman 24 pans the camera 22 counterclockwise around the fulcrum of the
なお、角速度センサ5,1の取り付け方向によって、角速度センサ5,1の出力電圧は異なり、それに応じてパンニングの判定も異なってくる。 Note that the output voltage of the angular velocity sensors 5 and 1 varies depending on the mounting direction of the angular velocity sensors 5 and 1, and the panning determination varies accordingly.
ただし、CPU14は、角速度センサ5で検出された振動情報が示す振動方向と角速度センサ19で検出された振動情報が示す振動方向とが支点26を中心(基準)として同一回転方向を示す場合、パンニング操作中であると判定する。
However, the
一方、CPU14は、角速度センサ5で検出された振動情報が示す振動方向と角速度センサ19で検出された振動情報が示す振動方向とが支点26を中心(基準)として逆回転方向を示す場合、パンニング操作中でないと判定する、
以下、図5を参照して、本発明の第1実施形態における防振制御処理について説明する。
On the other hand, when the vibration direction indicated by the vibration information detected by the angular velocity sensor 5 and the vibration direction indicated by the vibration information detected by the
Hereinafter, the image stabilization control process according to the first embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG.
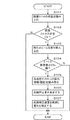
図5は、本発明における第1の制御処理手順の一例を示すフローチャートであり、本発明の第1実施形態における防振制御処理に対応する。なお、このフローチャートの処理は、CPU14が内蔵するROMに格納されたプログラムを実行することにより実現する機能に対応する。
FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing an example of a first control processing procedure in the present invention, and corresponds to the image stabilization control processing in the first embodiment of the present invention. Note that the processing of this flowchart corresponds to a function realized by executing a program stored in a ROM built in the
まず、防振処理が開始されると、ステップS201において、CPU14は、レンズ本体に取り付けられた防振スイッチ25の状態(ON又はOFF)を読み込む。
First, when the image stabilization process is started, in step S201, the
そして、ステップS202において、CPU14は、防振スイッチ25がON状態にあるか否かを判定し、防振スイッチ25がOFF状態であると判定した場合、そのまま防振処理を終了する。
In step S202, the
一方、ステップS202において、防振スイッチ25がON状態と判定した場合、CPU14は、ステップS203に処理を進める。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S202 that the
ステップS203では、CPU14は、ズームモータ位置センサ10からレンズのズーム位置を読み込み、ステップS204に処理を進める。
In step S203, the
ステップS204では、CPU14は、レンズのズーム位置が所定値よりテレ側にあるか否かを判定する。
In step S204, the
そして、ステップS204において、レンズのズーム位置が所定値よりテレ側にない(所定値よりワイド側にある)と判定した場合、CPU14は、振れ補正の必要がない、即ち撮影画角が広いため画面に占める振動の割合が微量であると判定し、振れ補正を実施しても効果がないと判断して、そのまま防振制御処理を終了する。
In step S204, if it is determined that the zoom position of the lens is not on the tele side from the predetermined value (the side is on the wide side from the predetermined value), the
一方、ステップS204において、レンズのズーム位置が所定値よりテレ側にあると判定した場合、CPU14は、ステップS205において、レンズ筐体に取り付けられた角速度センサ5からの電圧値を読み込み、テップS206に処理を進める。
On the other hand, when it is determined in step S204 that the zoom position of the lens is on the tele side from the predetermined value, the
ステップS206では、CPU14は、フォーカスデマンド18に取り付けられた角速度センサ19からの電圧値を読み込み、振れの向きと量を認識する。
In step S206, the
次にステップS207において、CPU14は、パンニング中か否かを判定する。ここでは、CPU14は、双方の角速度センサからの振動情報すなわち出力電圧値から判定される角速度が同じ向き(支持点26を中心とした同一回転方向)で、且つ、基準電圧(2.0V)と双方の角速度センサの出力電圧値との差異が略同等の場合、レンズシステムに回転方向の力がかかっている、即ちレンズシステムがパンニング操作中であると判定する。一方、CPU14は、双方の角速度センサ(5及び19)の出力電圧値から判定される角速度が同じ向きでない(支持点26を中心とした同一回転方向でない(逆回転方向))、又は、基準電圧(2.0V)と双方の角速度センサの出力電圧値との差異が略同等でない場合、レンズシステムに振動が加わった、即ちレンズシステムがパンニング中でないと判定する。
Next, in step S207, the
そして、ステップS207において、CPU14が、パンニング中であると判定した場合には、そのまま防振制御処理を終了する。
If the
一方、ステップS207において、CPU14が、パンニング中でないと判定した場合には、ステップS208に処理を進める。
On the other hand, if the
次にステップS208では、CPU14は、レンズ筐体に取り付けられた角速度センサの出力電圧値を基に、光路補正光学系3を移動させれば光軸ズレが補正できるかを演算する。
Next, in step S208, the
そして、ステップS209において、CPU14は、ステップS208の演算結果を用いて、光路補正制御部6を介して光路補正光学系3を移動させて、防振制御処理を終了する。
In step S209, the
なお、パンニング操作の終了時は回転運動が停止するため、双方の角速度センサからの出力電圧が基準電圧に近くなる。よって、CPU14は、パンニング操作中であると判定した後、双方の角速度センサ(5及び19)の出力電圧値と基準電圧(2.0V)との差分が所定値未満になった場合、パンニング操作が終了したと判定することができる。よって、CPU14は、ステップS207において、パンニング操作の終了がリアルタイムに検知できる。このため、CPU14は、パンニング操作の終了直後に光路補正を実施することになる。これにより、パンニング終了直後に発生した振動についても補正が可能になる。従来はパンニング操作の終了検知についても1秒程度かかっていたため応答性の向上が図れる。
At the end of the panning operation, the rotary motion stops, so that the output voltages from both angular velocity sensors are close to the reference voltage. Therefore, after determining that the panning operation is being performed, the
なお、本発明のレンズシステムが撮影可能な間、CPU14は、この図5のフローチャートに示した処理を繰り返し実行しているものとする。即ち、CPU14は、この図5のフローチャートに示した処理を、終了後、また直ぐにS201から開始するように制御している。
It is assumed that the
〔第2実施形態〕
第2実施形態のレンズシステムは、上記第1実施形態と同一のハードウェア構成を有し、レンズ筐体21に取り付けた角速度センサ5(第1の角速度センサ)からの振動情報とフォーカスデマンド18に取り付けられた角速度センサ19(第2の角速度センサ)からの振動情報を使用して作為的な振れ、即ちパンニング操作中に発生した振動を抽出し、振れ補正する事に特徴がある。
[Second Embodiment]
The lens system of the second embodiment has the same hardware configuration as that of the first embodiment, and includes vibration information from the angular velocity sensor 5 (first angular velocity sensor) attached to the lens housing 21 and the
このように、第2実施形態では、上記第1実施形態と同様のハードウェア構成をとりながらパンニング中に発生した振動を除去するものである。即ち、角速度センサ5をレンズ筐体21に取り付けると共に、レンズを外部から操作するフォーカスデマンド18にも同一種類又は同一出力特性の角速度センサ19を取り付ける。各角速度センサは、レンズ筐体21やフォーカスデマンド18内に内蔵しても良いし外側に取り付ける構成であっても良い。
As described above, in the second embodiment, vibrations generated during panning are removed while adopting the same hardware configuration as that of the first embodiment. That is, the angular velocity sensor 5 is attached to the lens casing 21 and the
取り付けられた各角速度センサは、振動を検出する。 Each attached angular velocity sensor detects vibration.
CPU14は、レンズ筐体21内の角速度センサ5とフォーカスデマンド18の角速度センサ19の双方のセンサの出力電圧をAD変換したデジタルの出力電圧値から角速度情報を読み取る。
The
この時、パンニング操作の場合は三脚装置の回転中心を中心とした回転運動になるため、双方の角速度センサからの出力電圧で判定される角速度の符号が同じでかつ角速度の絶対値もほぼ同値になる。しかしながらパンニング中に振動が発生した場合は、双方の角速度センサからの出力が振動の寄与分については角速度の符号が逆でかつ角速度の絶対値がほぼ同値になる。 At this time, in the case of the panning operation, since the rotation motion is centered on the rotation center of the tripod device, the signs of the angular velocities determined by the output voltages from both angular velocity sensors are the same, and the absolute values of the angular velocities are almost the same. Become. However, if vibration occurs during panning, the output from both angular velocity sensors has the opposite sign of the angular velocity and the absolute value of the angular velocity is almost the same for the contribution of vibration.
この点に注目し、双方の出力電圧差を1/2倍した数値はレンズシステムにかかる振動の大きさであると判断でき、光路補正量を演算し光路補正を実施する事によりパンニング中に発生した振動についても除去する事が可能となる。これにより請求項1の発明では除去できなかったパンニング中に発生した振動を除去する。 Paying attention to this point, it can be determined that the value obtained by halving the output voltage difference between the two is the magnitude of vibration applied to the lens system, and occurs during panning by calculating the optical path correction amount and performing optical path correction. It is also possible to remove the vibrations that have occurred. As a result, the vibration generated during panning that could not be removed by the invention of claim 1 is removed.
以下、図6を参照して、本発明の第2実施形態における防振制御処理について説明する。 Hereinafter, with reference to FIG. 6, the image stabilization control process according to the second embodiment of the present invention will be described.
図6は、本発明における第2の制御処理手順の一例を示すフローチャートであり、本発明の第2実施形態における防振制御処理に対応する。なお、このフローチャートの処理は、CPU14が内蔵するROMに格納されたプログラムを実行することにより実現する機能に対応する。
FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing an example of the second control processing procedure in the present invention, and corresponds to the image stabilization control processing in the second embodiment of the present invention. Note that the processing of this flowchart corresponds to a function realized by executing a program stored in a ROM built in the
まず、防振処理が開始されると、ステップS401において、CPU14は、レンズ本体に取り付けられた防振スイッチ25の状態(ON又はOFF)を読み込む。
First, when the image stabilization process is started, in step S401, the
そして、ステップS402において、CPU14は、防振スイッチ25がON状態にあるか否かを判定し、防振スイッチ25がOFF状態であると判定した場合、そのまま防振処理を終了する。
In step S402, the
一方、ステップS402において、防振スイッチ25がON状態と判定した場合、CPU14は、ステップS403に処理を進める。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S402 that the
ステップS403では、CPU14は、ズームモータ位置センサ10からレンズのズーム位置を読み込み、ステップS404に処理を進める。
In step S403, the
ステップS404では、CPU14は、レンズのズーム位置が所定値よりテレ側にあるか否かを判定する。
In step S404, the
そして、ステップS404において、レンズのズーム位置が所定値よりテレ側にない(所定値よりワイド側にある)と判定した場合、CPU14は、振れ補正の必要がない、即ち撮影画角が広いため画面に占める振動の割合が微量であると判定し、振れ補正を実施しても効果がないと判断して、そのまま防振制御処理を終了する。
In step S404, if it is determined that the zoom position of the lens is not on the tele side from the predetermined value (the side is on the wide side from the predetermined value), the
一方、ステップS404において、レンズのズーム位置が所定値よりテレ側にあると判定した場合、CPU14は、ステップS405において、レンズ筐体に取り付けられた角速度センサ5からの電圧値を読み込み、テップS406に処理を進める。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S404 that the zoom position of the lens is on the tele side from the predetermined value, the
ステップS406では、CPU14は、フォーカスデマンド18に取り付けられた角速度センサ19からの電圧値を読み込み、振れの向きと量を認識する。
In step S406, the
次にステップS407において、CPU14は、パンニング中か否かを判定する。ここでは、CPU14は、双方の角速度センサからの振動情報すなわち出力電圧値から判定される角速度が同じ向きで、且つ、基準電圧(2.0V)と双方の角速度センサの出力電圧値との差異が略同等の場合、レンズシステムに回転方向の力がかかっている、即ちレンズシステムがパンニング操作中であると判定する。一方、CPU14は、双方の角速度センサの出力電圧値から判定される角速度が同じ向きでない、又は、基準電圧(2.0V)と双方の角速度センサの出力電圧値との差異が略同等でない場合、レンズシステムに振動が加わった、即ちレンズシステムがパンニング中でないと判定する。
In step S407, the
そして、ステップS407において、CPU14が、パンニング中でないと判定した場合には、ステップS408に処理を進める。
In step S407, if the
次にステップS408では、CPU14は、レンズ筐体に取り付けられた角速度センサの出力電圧値を基に、光路補正光学系3をどれだけ移動させれば光軸ズレが補正できるかを演算する。
In step S408, the
そして、ステップS409において、CPU14は、ステップS408の演算結果を用いて、光路補正制御部6を介して光路補正光学系3を移動させて、防振制御処理を終了する。
In step S409, the
一方、ステップS407において、CPU14が、パンニング中であると判定した場合には、ステップS410に処理を進める。
On the other hand, if the
ステップS410において、CPU14は、パンニング中の振動量として「((レンズ21の角速度センサ5の電圧値)−(フォーカスデマンド18の角速度センサの電圧値))÷2」を演算する。なお、この演算値は、レンズシステムにかかる振動と同値になるため、これを用いてCPU14はパンニング中の振動の有無と振動の向きと振動量を把握できる。ここで、図7を用いてパンニング中の出力波形について説明する。
In step S410, the
図7は、パンニング中の出力波形に関して説明する図である。 FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating an output waveform during panning.
図7において、(a)はパンニングした際のレンズ筐体21に内蔵された角速度センサ5の出力波形を示す。 7A shows an output waveform of the angular velocity sensor 5 built in the lens housing 21 when panning.
(b)はパンニングした際のフォーカスデマンド18に内蔵された角速度センサ19の出力波形を示す。
(B) shows the output waveform of the
(c)は「((レンズの振れ電圧)−(デマンドの振れ電圧))÷2」の波形、即ちパンニング中の振動波形を示す。 (C) shows a waveform of “((lens shake voltage) − (demand shake voltage)) ÷ 2”, that is, a vibration waveform during panning.
以下、図6のフローチャートの説明に戻る。 Returning to the flowchart of FIG.
次に、ステップS411において、CPU14は、ステップS410の演算結果を用いて、パンニング中に振動があった(S410の演算したパンニング中の振動量が所定値より大きい)か否かを判定し、パンニング中に振動がなかった(S410の演算したパンニング中の振動量が所定値以下)と判定した場合、そのまま防振制御処理を終了する。
Next, in step S411, the
一方、ステップS411において、パンニング中に振動があった(S410の演算したパンニング中の振動量が所定値より大きい)と判定した場合、CPU14は、ステップS408に処理を進め、ステップS410で演算したパンニング中の振動量に基づき光路補正光学系3をどれだけ移動させれば光軸ズレが補正できるかを演算し、S408の演算結果を用いて光路補正光学系3を移動させて(S409)、防振制御処理を終了する。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S411 that there is vibration during panning (the amount of vibration during panning calculated in S410 is greater than a predetermined value), the
なお、本実施形態においても、レンズシステムが撮影可能な間、CPU14は、この図6のフローチャートに示した処理を繰り返し実行しているものとする。即ち、CPU14は、この図6のフローチャートに示した処理を、終了後、また直ぐにS401から開始するように制御している。
Also in this embodiment, it is assumed that the
以上示したように、本発明の第1実施形態によれば、レンズとカメラ、ズームデマンド、フォーカスデマンド、三脚装置で構成されるレンズシステムにおいて、振動とカメラマンによる作為的なパンニング操作を瞬時で判断できるので、レンズシステムに掛かる振動を従来通り除去しながら、カメラマンによる作為的なパンニング操作時は、防振制御を停止させる事で、パンニング時の動作不具合を抑圧する事ができる。 As described above, according to the first embodiment of the present invention, in a lens system including a lens, a camera, a zoom demand, a focus demand, and a tripod device, vibrations and an artificial panning operation by a cameraman can be instantaneously determined. Therefore, while removing the vibration applied to the lens system as usual, the camera shake can be suppressed by stopping the image stabilization control during the artificial panning operation by the photographer.
また、カメラマンによる作為的なパンニング操作が終了した時点を把握できるので、従来以上にすばやく防振制御が開始できる。 In addition, since it is possible to grasp the point at which the artificial panning operation by the photographer is completed, the image stabilization control can be started more quickly than before.
また、本発明の第2実施形態によれば、レンズとカメラ、ズームデマンド、フォーカスデマンド、三脚装置で構成されるレンズシステムにおいて、カメラマンによる作為的なパンニング操作中に発生した、レンズシステムに掛かる振動を除去できるので、パンニング操作中においてもブレのない安定した映像を提供する事ができる。 According to the second embodiment of the present invention, in a lens system including a lens and a camera, a zoom demand, a focus demand, and a tripod device, vibrations applied to the lens system that occur during an artificial panning operation by a cameraman. Therefore, it is possible to provide a stable image without blurring during the panning operation.
〔第3実施形態〕
角速度センサ5,19の代りに加速度センサを設ける実施形態であり、例えば反時計周りにパンニングした場合に両方のセンサが正の加速度を検出し、時計周りにパンニングした場合に両方のセンサが負の加速度を検出するように設置する。パンニング操作では、パンニング開始後の加速時やパンニング終了前の減速時に加速度センサは回転分の同符号の加速度を検出し、振動分については逆符号の加速度を検出する。
[Third Embodiment]
An embodiment in which an acceleration sensor is provided instead of the
従って2つのセンサの加速度の差の1/2を振動分の寄与として防振制御を行なう。又一定の速度でパンニングしている場合は、加速度センサは基準電圧(オフセット電圧)を出力し振動分については同様に逆符号の加速度を検出する。 Accordingly, the image stabilization control is performed with 1/2 of the difference in acceleration between the two sensors as a contribution of vibration. When panning at a constant speed, the acceleration sensor outputs a reference voltage (offset voltage) and similarly detects an acceleration with an opposite sign for vibration.
〔第4の実施形態〕
第4の実施形態のレンズシステムは、前記第1の実施形態と同一のハードウェア構成を有し、レンズ筐体に取付けた第1の角速度センサからの振動情報とフォーカスデマンドに取付けられた第2の角速度センサからの振動情報が異なる場合の振動発生時において、所定量抑圧させて防振制御させる事に特徴がある。
[Fourth Embodiment]
The lens system of the fourth embodiment has the same hardware configuration as that of the first embodiment, and the vibration information from the first angular velocity sensor attached to the lens housing and the second attached to the focus demand. When vibration information is generated when the vibration information from the angular velocity sensors is different, the vibration suppression control is performed by suppressing a predetermined amount.
第4の実施形態は、請求項5の発明に対応し、請求項1と同様のハードウェア構成をとりながら前記第1の実施形態で誤動作してしまうケースにおいて有効で、振動が第1の角速度センサと第2の角速度センサに同時に伝わらず、時間を置いて他方の角速度センサに振動が伝わるような斜め方向からの振動や特殊な振動の場合、前記第1の実施形態では防振制御を停止させてしまうため振動が除去できない。第4の実施形態は、カメラマンによるパンニング操作と判定した場合において、一定期間のみ1/2の防振制御を実施させる事で上記の振動においても防振効果を発揮するものである。 The fourth embodiment corresponds to the invention of claim 5 and is effective in a case where malfunction occurs in the first embodiment while adopting the same hardware configuration as that of claim 1, and the vibration is the first angular velocity. In the case of a vibration from an oblique direction or a special vibration that is not transmitted to the sensor and the second angular velocity sensor at the same time but is transmitted to the other angular velocity sensor over time, the vibration proof control is stopped in the first embodiment. Vibrations cannot be removed. In the fourth embodiment, when it is determined that the panning operation is performed by a cameraman, the anti-vibration effect is exhibited even in the above-described vibration by performing the anti-vibration control of 1/2 for a certain period.
図8、は第4の実施形態におけるCPU14によって実行される光軸ズレ補正処理プログラムの処理手順を示すフローチャートである。
FIG. 8 is a flowchart illustrating a processing procedure of an optical axis misalignment correction processing program executed by the
まず、CPUはレンズ本体に取り付けられた防振スイッチがONかOFFを読み込み(ステップS501)、防振スイッチがON状態にあるか否かを判定し(ステップS502)、防振スイッチがOFF状態の場合、何もしないで終了する。防振スイッチがONの場合、レンズのズーム位置を読み込む(ステップS503)。 First, the CPU reads whether the image stabilization switch attached to the lens body is ON or OFF (step S501), determines whether the image stabilization switch is in the ON state (step S502), and the image stabilization switch is in the OFF state. If so, exit without doing anything. If the image stabilization switch is ON, the zoom position of the lens is read (step S503).
ズーム位置が所定値よりテレ側にあるか否かを判定し、所定値よりワイド側にあると判断した場合、振れ補正の必要がない、すなわち撮影画角が広いため画面に占める振動の割合が微量であると判定し、振れ補正を実施しても効果がないので何もしないで終了する(ステップS504)。 When it is determined whether or not the zoom position is on the tele side from the predetermined value, and it is determined that the zoom position is on the wide side from the predetermined value, there is no need for shake correction, i.e., the ratio of vibration to the screen is large because the shooting angle of view is wide. Even if it is determined that the amount is very small and there is no effect even if the shake correction is performed, the process ends without doing anything (step S504).
次にCPUはレンズ筐体に取付けられた角速度センサからの電圧値を読み込み(ステップS505)振れの向きと量を認識する。次にCPUはフォーカスデマンドに取付けられた角速度センサからの電圧値を読み込み(ステップS506)振れの向きと量を認識する。双方の角速度センサからの振動情報すなわち電圧値が同じ向きでかつ基準電圧からの差異が同等の場合は、レンズシステムに回転方向の力がかかっている、すなわちレンズシステムがパンニング操作中であると判断し、ステップS510に進む(ステップS507)。 Next, the CPU reads the voltage value from the angular velocity sensor attached to the lens housing (step S505) and recognizes the direction and amount of shake. Next, the CPU reads the voltage value from the angular velocity sensor attached to the focus demand (step S506) and recognizes the direction and amount of shake. If the vibration information from both angular velocity sensors, that is, the voltage values are in the same direction and the difference from the reference voltage is the same, it is determined that a rotational force is applied to the lens system, that is, the lens system is performing a panning operation. Then, the process proceeds to step S510 (step S507).
双方の角速度からの振動情報すなわち電圧値が異なる向きの場合は、レンズシステム全体が振動を受けていると判断し、レンズ筐体に取付けられた角速度センサの電圧値を基に、光路補正光学系3を移動させれば光軸ズレが補正できるかを演算(ステップS508)し、光路補正制御部6を介して、光路補正光学系3を移動させて(ステップS509)終了する。 If the vibration information from both angular velocities, that is, the voltage values are in different directions, it is determined that the entire lens system is receiving vibration, and the optical path correction optical system is based on the voltage value of the angular velocity sensor attached to the lens housing. It is calculated whether the optical axis deviation can be corrected by moving 3 (step S508), the optical path correction optical system 3 is moved via the optical path correction control unit 6 (step S509), and the process ends.
一方レンズシステムがパンニング操作中であると判断した場合でも、双方の角速度センサに伝わる振動が同時でないケースが想定できるため、パンニング開始後0.1秒以内であるか否かを判別し(ステップS510)パンニング開始後0.1秒以内の場合ステップS511へ進み、パンニング直後でない場合終了する。次に角速度センサからの振動情報に対応する電圧値を1/2する演算(ステップS511)を実施して、ステップS508へ進み、半分の振動量で振動補正量を演算させ振動補正する。 On the other hand, even when it is determined that the lens system is performing a panning operation, it can be assumed that vibrations transmitted to both angular velocity sensors are not simultaneous, so it is determined whether or not it is within 0.1 seconds after the start of panning (step S510). ) If within 0.1 seconds after the start of panning, the process proceeds to step S511, and if not immediately after panning, the process ends. Next, calculation (step S511) to halve the voltage value corresponding to the vibration information from the angular velocity sensor is performed (step S511), the process proceeds to step S508, and the vibration correction amount is calculated with half the vibration amount to correct the vibration.
〔第5の実施形態〕
上記第4の実施形態では、ステップS511において、角速度センサの出力電圧を1/2にする演算を実行したが、第5の実施形態では振動補正割合を一定とはせず、角速度センサの速度に応じて補正割合を変化させる点が異なる。
[Fifth Embodiment]
In the fourth embodiment, the calculation for reducing the output voltage of the angular velocity sensor to ½ is performed in step S511. However, in the fifth embodiment, the vibration correction ratio is not constant, and the speed of the angular velocity sensor is increased. The difference is that the correction ratio is changed accordingly.
すなわち、RAM内に経過時間と補正割合を記憶するテーブルを更に備え、ステップS511において、パンニング開始からの経過時間に応じた補正割合を適用する。例えばパンニング開始から0.05秒以内では角速度センサからの振動情報に対応する電圧値を1/2する演算を行い、パンニング開始から0.05秒以降0.1秒以内では角速度センサからの振動情報に対応する電圧値を1/3する演算を行う。さらに対象時間内で連続的に変化させても良く、このように制御することでさらにスムーズな振動補正を実行することができる。 In other words, the RAM further includes a table for storing the elapsed time and the correction ratio, and the correction ratio corresponding to the elapsed time from the start of panning is applied in step S511. For example, the calculation is performed to halve the voltage value corresponding to the vibration information from the angular velocity sensor within 0.05 seconds from the start of panning, and the vibration information from the angular velocity sensor is within 0.05 seconds after 0.05 seconds from the start of panning. An operation is performed to reduce the voltage value corresponding to 1/3. Further, it may be changed continuously within the target time, and smoother vibration correction can be executed by such control.
以上、第1実施形態乃至第5実施形態について示したが、本発明は、例えば、システム、装置、方法、プログラムもしくは記録媒体等としての実施態様をとることが可能であり、具体的には、複数の機器から構成されるシステムに適用しても良いし、また、一つの機器からなる装置に適用しても良い。 また、以上の説明では、本発明をパンニング操作時の防振制御に用いる場合について説明したが、チルティング操作等の他の旋回操作時の防振制御にも同様に用いることが可能である。 As described above, the first to fifth embodiments have been described. However, the present invention can take an embodiment as, for example, a system, apparatus, method, program, or recording medium. Specifically, You may apply to the system comprised from a some apparatus, and may apply to the apparatus which consists of one apparatus. In the above description, the case where the present invention is used for the image stabilization control during the panning operation has been described. However, the present invention can be similarly used for the image stabilization control during other turning operations such as the tilting operation.
チルティング操作時の防振制御を行う場合、角速度センサ5,19を、三脚20の支持点26を中心として図2において反時計回りの回転(図2の左上から左下方向への回転)を正の角速度、時計回りの回転(図2の左下から左上方向への回転)を負の角速度となる等のように取り付ける。即ち、角速度センサ5,19はいずれも、レンズシステムが、三脚装置20の上方に設けられた図示しないチルティング用の軸を中心として反時計回り(図2の左上から左下方向へ)に回動する場合には正の角速度として検出し、一方、レンズシステムが上記チルティング用の軸を中心として時計回り(図2の左下から左上方向へ)に回動する場合には負の角速度として検出する。即ち、角速度センサ5,角速度センサ19は、チルティング軌道を含む平面(即ち垂直)に略平行で且つレンズシステムの撮像方向に略直交する方向(即ち図2の上下(天地)方向(カメラマン24にとって上下方向))の振動を検出可能な構成する。
When performing anti-vibration control during tilting operation, the
このような構成により、上述のパンニング操作の場合と同様に、チルティング操作と振動とを判別可能となる。 With such a configuration, the tilting operation and the vibration can be discriminated as in the case of the panning operation described above.
即ち、本発明は、パンニング操作であってもチルティング操作であっても、所定の軸を中心に回動して撮影方向を変更する旋回操作であれば、該旋回操作と振動とを判別可能に構成できる。 That is, the present invention can discriminate between the turning operation and the vibration as long as it is a turning operation that rotates around a predetermined axis to change the photographing direction, whether it is a panning operation or a tilting operation. Can be configured.
なお、上述したパンニング操作の防振機能とチルティング操作の防振機能とを双方備えるように構成してもよい。 In addition, you may comprise so that both the anti-vibration function of panning operation mentioned above and the anti-vibration function of tilting operation may be provided.
即ち、本発明では、レンズシステムにかかる振動とカメラマンによる旋回操作(パンニング操作やチルティング操作)を的確に判別し、精度良く防振制御可能である。 In other words, according to the present invention, it is possible to accurately discriminate between the vibration applied to the lens system and the turning operation (panning operation and tilting operation) by the cameraman, and to perform the vibration control with high accuracy.
なお、上記実施形態では、振動補正方法として、角速度センサからの振動情報に用いて光路補正光学系をシフト移動させて、レンズシステムにレンズを介して入光した光学信号の光路を変更して振動補正する方法を示した。しかし、バリアングルプリズムを用いて光学信号の光路を変更して振動補正するように構成してもよい。 In the above embodiment, as the vibration correction method, the optical path correction optical system is shifted by using the vibration information from the angular velocity sensor, and the optical path of the optical signal incident on the lens system via the lens is changed to vibrate. The method of correction was shown. However, the vari-angle prism may be used to correct the vibration by changing the optical path of the optical signal.
また、光路を変更する代わりに、角速度センサからの振動情報に用いてCCD15の位置を変更して振動補正するように構成してもよい。
Further, instead of changing the optical path, the position of the
また、CCD15として通常の撮像領域より広い領域を撮像可能なものを採用し、角速度センサからの振動情報に用いてCCD15における撮像領域を変更して振動補正するように構成してもよい。即ち、CCD15の全領域で撮像した画像をバッファメモリに読み込み、角速度センサからの振動情報に用いてCPU14が採用する撮影領域を変更制御する。
In addition, a
さらに、その他の振動補正方法を用いる構成であってもよい。 Furthermore, the structure using another vibration correction method may be sufficient.
以上説明したように、本発明では、角速度センサをレンズ筐体及びレンズシステムを操作するフォーカスデマンド等に内蔵させ振動を検出させる。CPU14は、レンズ筐体内の角速度センサとフォーカスデマンド内の角速度センサの出力電圧をAD変換したデジタルの出力電圧値を振動情報として読み取る。この時、パンニング(チルティング)操作の場合は三脚装置の回転中心を中心とした回転運動になるため、双方の角速度センサからの出力電圧で判定される角速度の符号が同じでかつ角速度の絶対値もほぼ同値になる。一方、振動の場合は双方の角速度センサからの出力電圧で判定される角速度の符号が逆、又は、角速度の絶対値が略同一とはならなくなる。これを利用して、CPU14は、レンズシステムにかかる振動とカメラマンによるパンニング等の旋回操作を判別する。そして、CPU14は、パンニング操作等の旋回操作の場合、防振機能を動作させないことにより、従来のパンニング中等の動作不具合を回避することができる。なお、チルティングの場合も同様である。
As described above, in the present invention, the angular velocity sensor is built in the focus demand or the like for operating the lens housing and the lens system to detect vibration. CPU14 reads the digital output voltage value which AD-converted the output voltage of the angular velocity sensor in a lens housing | casing, and the angular velocity sensor in a focus demand as vibration information. At this time, in the case of panning (tilting) operation, the rotational motion is centered on the center of rotation of the tripod device. Therefore, the signs of the angular velocities determined by the output voltages from both angular velocity sensors are the same, and the absolute value of the angular velocity. Is almost equivalent. On the other hand, in the case of vibration, the signs of the angular velocities determined by the output voltages from both angular velocity sensors are reversed, or the absolute values of the angular velocities are not substantially the same. Using this, the
なお、パンニング中に振動が発生した場合は、双方の角速度センサからの出力が振動の寄与分については角速度の符号が逆でかつ角速度の絶対値がほぼ同値になる。これを利用して、CPU14は、パンニング中と判別した場合、双方の角速度センサからの出力電圧の差分を1/2した数値を、レンズシステムにかかる振動の大きさであると判断し、光路補正量を演算し光路補正を実施する。これにより、パンニング中に発生した振動についても除去する事が可能となる。なお、チルティングの場合も同様である。
When vibration occurs during panning, the output from both angular velocity sensors has the opposite sign of the angular velocity and the absolute value of the angular velocity is substantially the same for the contribution of vibration. Using this, if the
このように、本発明によれば、振動とカメラマンによる作為的な旋回操作(パンニング操作,チルティング操作等)を瞬時で判断できるので、カメラ装置(レンズシステム)に掛かる振動を従来通り除去しながら、カメラマンによる作為的な旋回操作時は、防振制御を停止させることにより、旋回操作時の動作不具合を抑えることができる。 As described above, according to the present invention, since vibration and an artificial turning operation (panning operation, tilting operation, etc.) by a cameraman can be determined instantaneously, vibration applied to the camera device (lens system) is removed as usual. When an intentional turning operation is performed by the cameraman, it is possible to suppress malfunctions during the turning operation by stopping the image stabilization control.
また、カメラマンによる作為的な旋回操作が終了した時点を把握でき、従来以上にすばやく防振制御が開始できる。 In addition, it is possible to grasp the point in time when the intentional turning operation by the photographer is completed, and to start the image stabilization control more quickly than before.
さらに、カメラマンによる作為的なパンニング操作中に発生した、レンズシステムに掛かる振動を除去できるので、パンニング操作中においてもブレのない安定した映像を提供することができる。 Furthermore, since the vibration applied to the lens system that occurred during the artificial panning operation by the cameraman can be removed, a stable image without blurring can be provided even during the panning operation.
また、本発明の第4の実施形態に記載の防振装置によれば、レンズとカメラ、ズームデマンド、フォーカスデマンド、三脚装置で構成されるレンズシステムにおいて、斜め方向からの振動やうねる振動のような振動が発生し、第1の角速度センサと第2の角速度センサに同時に伝わらないケースにおいても、防振制御を停止させずに、振動量を1/2にした防振制御させる事で、多種多様な振動に対し、防振効果を上げることができる。 Further, according to the vibration isolator described in the fourth embodiment of the present invention, in a lens system including a lens and a camera, a zoom demand, a focus demand, and a tripod device, vibrations from an oblique direction and undulating vibrations are observed. Even in the case where a large amount of vibration is generated and is not transmitted to the first angular velocity sensor and the second angular velocity sensor at the same time, various types of vibration isolation control can be performed by halving the vibration amount without stopping the vibration isolation control. Anti-vibration effect can be improved against various vibrations.
以下、図9に示すメモリマップを参照して本発明に係るレンズシステムのCPU14で読み取り可能な制御プログラムの構成について説明する。
The configuration of the control program that can be read by the
図9は、本発明に係るレンズシステムのCPU14で読み取り可能な制御プログラムを格納する記録媒体(記憶媒体)のメモリマップを説明する図である。
FIG. 9 is a diagram illustrating a memory map of a recording medium (storage medium) that stores a control program readable by the
なお、特に図示しないが、記録媒体に記憶されるプログラム群を管理する情報、例えばバージョン情報,作成者等も記憶され、かつ、プログラム読み出し側のOS等に依存する情報、例えばプログラムを識別表示するアイコン等も記憶される場合もある。 Although not specifically shown, information for managing a program group stored in the recording medium, for example, version information, creator, etc. is also stored, and information depending on the OS on the program reading side, for example, a program is identified and displayed. Icons may also be stored.
さらに、各種プログラムに従属するデータも上記ディレクトリに管理されている。また、インストールするプログラムやデータが圧縮されている場合に、解凍するプログラム等も記憶される場合もある。 Further, data depending on various programs is also managed in the directory. In addition, when a program or data to be installed is compressed, a program to be decompressed may be stored.
本実施形態における図5,図6,図8に示す機能が外部からインストールされるプログラムによって、ホストコンピュータにより遂行されていてもよい。そして、その場合、CD−ROMやフラッシュメモリやFD等の記録媒体により、あるいはネットワークを介して外部の記録媒体から、プログラムを含む情報群を出力装置に供給される場合でも本発明は適用されるものである。 The functions shown in FIGS. 5, 6, and 8 in this embodiment may be performed by a host computer by a program installed from the outside. In this case, the present invention is applied even when an information group including a program is supplied to the output device from a recording medium such as a CD-ROM, a flash memory, or an FD, or from an external recording medium via a network. Is.
以上のように、前述した実施形態の機能を実現するソフトウェアのプログラムコードを記録した記録媒体を、システムあるいは装置に供給し、そのシステムあるいは装置のコンピュータ(またはCPUやMPU)が記録媒体に格納されたプログラムコードを読出し実行することによっても、本発明の目的が達成されることは言うまでもない。 As described above, a recording medium in which a program code of software for realizing the functions of the above-described embodiments is recorded is supplied to the system or apparatus, and the computer (or CPU or MPU) of the system or apparatus is stored in the recording medium. It goes without saying that the object of the present invention can also be achieved by reading and executing the program code.
この場合、記録媒体から読み出されたプログラムコード自体が本発明の新規な機能を実現することになり、そのプログラムコードを記憶した記録媒体は本発明を構成することになる。 In this case, the program code itself read from the recording medium realizes the novel function of the present invention, and the recording medium storing the program code constitutes the present invention.
プログラムコードを供給するための記録媒体としては、例えば、フレキシブルディスク,ハードディスク,光ディスク,光磁気ディスク,CD−ROM,CD−R,DVD−ROM,磁気テープ,不揮発性のメモリカード,ROM,EEPROM,シリコンディスク等を用いることができる。 As a recording medium for supplying the program code, for example, a flexible disk, hard disk, optical disk, magneto-optical disk, CD-ROM, CD-R, DVD-ROM, magnetic tape, nonvolatile memory card, ROM, EEPROM, A silicon disk or the like can be used.
また、コンピュータが読み出したプログラムコードを実行することにより、前述した実施形態の機能が実現されるだけでなく、そのプログラムコードの指示に基づき、コンピュータ上で稼働しているOS(オペレーティングシステム)等が実際の処理の一部または全部を行い、その処理によって前述した実施形態の機能が実現される場合も含まれることは言うまでもない。 Further, by executing the program code read by the computer, not only the functions of the above-described embodiments are realized, but also an OS (operating system) or the like running on the computer based on the instruction of the program code. It goes without saying that a case where the function of the above-described embodiment is realized by performing part or all of the actual processing and the processing is included.
さらに、記録媒体から読み出されたプログラムコードが、コンピュータに挿入された機能拡張ボードやコンピュータに接続された機能拡張ユニットに備わるメモリに書き込まれた後、そのプログラムコードの指示に基づき、その機能拡張ボードや機能拡張ユニットに備わるCPU等が実際の処理の一部または全部を行い、その処理によって前述した実施形態の機能が実現される場合も含まれることは言うまでもない。 Furthermore, after the program code read from the recording medium is written in a memory provided in a function expansion board inserted in the computer or a function expansion unit connected to the computer, the function expansion is performed based on the instruction of the program code. It goes without saying that the case where the CPU or the like provided in the board or the function expansion unit performs part or all of the actual processing and the functions of the above-described embodiments are realized by the processing.
また、本発明は、複数の機器から構成されるシステムに適用しても、1つの機器からなる装置に適用してもよい。また、本発明は、システムあるいは装置にプログラムを供給することによって達成される場合にも適応できることは言うまでもない。この場合、本発明を達成するためのソフトウェアによって表されるプログラムを格納した記録媒体を該システムあるいは装置に読み出すことによって、そのシステムあるいは装置が、本発明の効果を享受することが可能となる。 Further, the present invention may be applied to a system composed of a plurality of devices or an apparatus composed of a single device. Needless to say, the present invention can be applied to a case where the present invention is achieved by supplying a program to a system or apparatus. In this case, by reading a recording medium storing a program represented by software for achieving the present invention into the system or apparatus, the system or apparatus can enjoy the effects of the present invention.
さらに、本発明を達成するためのソフトウェアによって表されるプログラムをネットワーク上のサーバ,データベース等から通信プログラムによりダウンロードして読み出すことによって、そのシステムあるいは装置が、本発明の効果を享受することが可能となる。 Furthermore, by downloading and reading out a program represented by software for achieving the present invention from a server, database, etc. on a network using a communication program, the system or apparatus can enjoy the effects of the present invention. It becomes.
なお、上述した各実施形態およびその変形例を組み合わせた構成も全て本発明に含まれるものである。 In addition, all the structures which combined each embodiment mentioned above and its modification are also included in this invention.
1 フォーカスレンズ群
2 ズームレンズ群
3 光路補正光学系
4 その他のレンズ群
5 角速度センサ
6 光路補正光学系制御部
8 フォーカスモータ
9 ズームモータ
10 フォーカスモータ位置センサ
11 ズームモータ位置センサ
12 フォーカスモータ駆動回路
13 ズームモータ駆動回路
14 CPU(マイクロコンピュータ)
15 CCD(撮像素子)
16 信号処理部
17 ズームデマンド
18 フォーカスデマンド
19 角速度センサ
20 三脚装置
21 レンズ
22 カメラ
23 ビューファインダー
24 カメラマン
25 防振スイッチ
26 三脚の支持点(パンニング時の回転中心)
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1 Focus lens group 2 Zoom lens group 3 Optical path correction | amendment
15 CCD (imaging device)
16
Claims (13)
前記回動の中心から前記カメラ装置の撮像方向側の前記回動する部位に設けられた第1の振動検出手段と、
前記回動の中心から前記カメラ装置の撮像方向の逆側の前記回動する部位に設けられた第2の振動検出手段と、
振動による撮像のブレを補正する振動補正を行う振動補正手段と、
前記第1の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報と前記第2の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報とを用いて前記旋回操作中か否かを判定する判定手段と、
前記判定手段により前記旋回操作中でないと判定された場合、前記第1の振動検出手段又は前記第2の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報を用いて前記振動補正手段に前記振動補正を実行させ、一方、前記判定手段により前記旋回操作中であると判定された場合、前記第1の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報と前記第2の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報との差分に従った前記旋回操作中の振動情報を用いて前記振動補正手段に前記振動補正を実行させるように制御する制御手段と、
を有することを特徴とする防振装置。 An anti-vibration device for a camera device capable of turning operation that rotates around a predetermined axis to change a shooting direction,
First vibration detecting means provided at the rotating portion on the imaging direction side of the camera device from the center of rotation;
A second vibration detecting means provided at the rotating portion on the opposite side of the imaging direction of the camera device from the center of rotation;
Vibration correcting means for performing vibration correction for correcting image blur due to vibration;
Determining means for determining whether or not the turning operation is being performed using vibration information detected by the first vibration detecting means and vibration information detected by the second vibration detecting means;
When it is determined by the determination means that the turning operation is not being performed, the vibration correction means is caused to execute the vibration correction using vibration information detected by the first vibration detection means or the second vibration detection means. On the other hand, if the determination means determines that the turning operation is being performed, the difference between the vibration information detected by the first vibration detection means and the vibration information detected by the second vibration detection means Control means for controlling the vibration correction means to execute the vibration correction using vibration information during the turning operation according to the above ;
An anti-vibration device comprising:
前記判定手段は、前記第1の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報が示す振動方向と前記第2の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報が示す振動方向とが同一方向を示す場合には前記旋回操作中であると判定し、一方、前記第1の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報が示す振動方向と前記第2の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報が示す振動方向とが逆方向を示す場合には前記旋回操作中でないと判定する、ことを特徴とする請求項1又は2に記載の防振装置。 The first vibration detection means and the second vibration detection means simultaneously detect vibrations in a direction substantially parallel to a plane including the rotation trajectory and substantially perpendicular to the imaging direction of the camera device,
In the case where the vibration direction indicated by the vibration information detected by the first vibration detection means and the vibration direction indicated by the vibration information detected by the second vibration detection means indicate the same direction, the determination means On the other hand, it is determined that the turning operation is being performed. On the other hand, the vibration direction indicated by the vibration information detected by the first vibration detection unit is opposite to the vibration direction indicated by the vibration information detected by the second vibration detection unit. The anti-vibration device according to claim 1, wherein it is determined that the turning operation is not being performed.
前記判定手段は、前記第1の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報が示す振動方向と前記第2の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報が示す振動方向とが逆方向を示す場合には前記旋回操作中であると判定し、一方、前記第1の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報が示す振動方向と前記第2の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報が示す振動方向とが同一方向を示す場合には前記旋回操作中でないと判定する、ことを特徴とする請求項1又は2に記載の防振装置。 The first vibration detection means and the second vibration detection means detect vibrations in a direction substantially parallel to a plane including the rotation trajectory and substantially perpendicular to the imaging direction of the camera device,
When the vibration direction indicated by the vibration information detected by the first vibration detection means and the vibration direction indicated by the vibration information detected by the second vibration detection means indicate opposite directions, On the other hand, it is determined that the turning operation is being performed. On the other hand, the vibration direction indicated by the vibration information detected by the first vibration detection unit and the vibration direction indicated by the vibration information detected by the second vibration detection unit are the same direction. The anti-vibration device according to claim 1, wherein it is determined that the turning operation is not being performed.
を有することを特徴とする請求項2記載の防振装置。 The determination means is further configured to be able to measure a time from the start of the turning operation. When the determination means is within a predetermined time from the start of the turning operation, the vibration information further corresponds to a certain rate or an elapsed time from the start of the turning operation. Control means for multiplying the variable ratio to obtain vibration information during the turning operation, and controlling the vibration correction means to execute the vibration correction using the vibration information during the turning operation;
The vibration isolator according to claim 2, wherein:
前記第2の振動検出手段は、前記旋回操作を行うことが可能な操作部に設置される、ことを特徴とする請求項1乃至7のいずれか1項に記載の防振装置。 The first vibration detection means is installed in a lens housing of the camera device,
The vibration isolator according to any one of claims 1 to 7, wherein the second vibration detection unit is installed in an operation unit capable of performing the turning operation.
前記第2の振動検出手段は、前記カメラ装置のレンズ筐体外に設置されるフォーカス又はズームを操作するデマンド筐体に設置される、ことを特徴とする請求項1乃至7のいずれか1項に記載の防振装置。 The first vibration detection means is installed in a lens housing of the camera device,
The said 2nd vibration detection means is installed in the demand housing | casing which operates the focus or zoom installed outside the lens housing | casing of the said camera apparatus, The any one of Claim 1 thru | or 7 characterized by the above-mentioned. The vibration isolator as described.
前記回動の中心から前記カメラ装置の撮像方向側の前記回動する部位に設けられた第1の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報と、前記回動の中心から前記カメラ装置の撮像方向の逆側の前記回動する部位に設けられた第2の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報とを用いて前記旋回操作中か否かを判定する判定ステップと、
前記判定ステップにより前記旋回操作中でないと判定された場合、前記第1の振動検出手段又は前記第2の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報を用いて振動補正手段に振動補正を実行させ、一方、前記判定ステップにより前記旋回操作中であると判定された場合、前記第1の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報と前記第2の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報との差分に従った前記旋回操作中の振動情報を用いて前記振動補正手段に前記振動補正を実行させるように制御する制御ステップと、
を有することを特徴とする防振方法。 A camera device anti-vibration method capable of turning around a predetermined axis to change a shooting direction,
The vibration information detected by the first vibration detecting means provided at the rotating portion on the imaging direction side of the camera device from the center of rotation, and the imaging direction of the camera device from the center of rotation. A determination step of determining whether or not the turning operation is being performed using vibration information detected by second vibration detection means provided in the rotating part on the opposite side;
When it is determined by the determination step that the turning operation is not being performed, the vibration correction unit is caused to execute vibration correction using the vibration information detected by the first vibration detection unit or the second vibration detection unit, When it is determined by the determination step that the turning operation is being performed, the difference between the vibration information detected by the first vibration detection unit and the vibration information detected by the second vibration detection unit is followed. a control step of controlling so as to execute the vibration correction to the vibration correcting means using the vibration information in the turning operation,
An anti-vibration method comprising:
前記判定ステップにより前記旋回操作中でないと判定された場合、前記第1の振動検出手段又は前記第2の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報を用いて振動補正手段に振動補正を実行させ、一方、前記判定ステップにより前記旋回操作中であると判定された場合、前記第1の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報と前記第2の振動検出手段で検出された振動情報との差分に従った前記旋回操作中の振動情報を用いて前記振動補正手段に前記振動補正を実行させるように制御する制御ステップ、
を実行させるためのプログラム。 A computer in the camera device capable of turning operation that rotates around a predetermined axis to change the shooting direction is provided at the rotating portion on the imaging direction side of the camera device from the rotation center. Vibration information detected by the first vibration detection means and vibration detected by the second vibration detection means provided on the rotating portion on the opposite side of the imaging direction of the camera device from the center of rotation. A determination step of determining whether or not the turning operation is being performed using information;
When it is determined by the determination step that the turning operation is not being performed, the vibration correction unit is caused to execute vibration correction using the vibration information detected by the first vibration detection unit or the second vibration detection unit, When it is determined by the determination step that the turning operation is being performed, the difference between the vibration information detected by the first vibration detection unit and the vibration information detected by the second vibration detection unit is followed. control step of controlling so as to execute the vibration correction to the vibration correcting means using the vibration information in the turning operation,
A program for running
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007199813A JP4807855B2 (en) | 2007-07-31 | 2007-07-31 | Anti-vibration device, anti-vibration method and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007199813A JP4807855B2 (en) | 2007-07-31 | 2007-07-31 | Anti-vibration device, anti-vibration method and program |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009038515A JP2009038515A (en) | 2009-02-19 |
| JP2009038515A5 JP2009038515A5 (en) | 2010-01-21 |
| JP4807855B2 true JP4807855B2 (en) | 2011-11-02 |
Family
ID=40440071
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007199813A Expired - Fee Related JP4807855B2 (en) | 2007-07-31 | 2007-07-31 | Anti-vibration device, anti-vibration method and program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4807855B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5599039B2 (en) * | 2010-06-01 | 2014-10-01 | キヤノン株式会社 | Optical device with image blur correction function |
| JP6291726B2 (en) * | 2013-05-29 | 2018-03-14 | 株式会社ニコン | Blur correction device, lens barrel |
| JP6250446B2 (en) * | 2014-03-19 | 2017-12-20 | 日本テレビ放送網株式会社 | Image processing system, image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program |
| JP6205073B2 (en) | 2014-09-10 | 2017-09-27 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, and program |
| JP6746972B2 (en) * | 2016-03-11 | 2020-08-26 | リコーイメージング株式会社 | Imaging device and imaging method |
| CN106461727B (en) * | 2016-10-31 | 2019-11-15 | 北京小米移动软件有限公司 | Control method and device, the electronic equipment of motor vibrations |
| JP2018109776A (en) * | 2018-02-15 | 2018-07-12 | 株式会社ニコン | Blurring correction device |
| JP7423270B2 (en) * | 2019-11-14 | 2024-01-29 | キヤノン株式会社 | display device |
| JP7252419B2 (en) * | 2020-05-29 | 2023-04-04 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Vibration isolator, optical device, binoculars, vibration isolator control method, and program |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3557573B2 (en) * | 1995-09-28 | 2004-08-25 | 富士写真光機株式会社 | TV camera anti-vibration device |
| JP3783296B2 (en) * | 1996-09-26 | 2006-06-07 | ソニー株式会社 | Image pickup apparatus having a camera shake correction function |
| JP3442000B2 (en) * | 1999-05-11 | 2003-09-02 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | Optical disk information recording / reproducing device |
| JP2005303492A (en) * | 2004-04-08 | 2005-10-27 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Imaging apparatus |
| JP2005316294A (en) * | 2004-04-30 | 2005-11-10 | Olympus Corp | Photographing device and single lens reflex camera |
-
2007
- 2007-07-31 JP JP2007199813A patent/JP4807855B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2009038515A (en) | 2009-02-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4807855B2 (en) | Anti-vibration device, anti-vibration method and program | |
| CN101236307B (en) | Hand shake correction method and device for camera module used in mobile device | |
| JP6071545B2 (en) | IMAGING DEVICE, IMAGE PROCESSING DEVICE AND ITS CONTROL METHOD, PROGRAM, AND STORAGE MEDIUM | |
| JP2013017165A (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP6642971B2 (en) | Image blur correction device, optical device, imaging device, and control method | |
| JPH10254007A (en) | Shake preventing device and image pickup device provided therewith | |
| JP4878320B2 (en) | Imaging device and portable device | |
| JP4973219B2 (en) | Optical equipment | |
| JP2012163824A (en) | Shake correction apparatus and optical device | |
| JP2008124763A (en) | Imaging apparatus, control method, and program | |
| JP5724057B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP4314176B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP2012013778A (en) | Imaging apparatus | |
| JP2002207232A (en) | Method and apparatus for correcting image blur of image pickup device | |
| JP5458521B2 (en) | Lens barrel, lens barrel adjustment method, optical device, and optical device adjustment method | |
| JP2006220758A (en) | Shake correction device, optical equipment, control method for shake correction device | |
| JP5957796B2 (en) | Blur correction device and optical apparatus | |
| JP6737307B2 (en) | Image stabilization device and photographing device | |
| JP2000081646A (en) | Camera with camera-shake correction function | |
| JP6851172B2 (en) | Imaging device and its control method | |
| JP2012173302A (en) | Shake correcting device and optical apparatus | |
| WO2007023663A1 (en) | Imaging device, image processing program, information recording medium containing the image processing program, image processing apparatus, and image processing method | |
| JP2016080892A (en) | Image blur correction device, focus adjustment device, control unit, and optical instrument | |
| JP2015119299A (en) | Imaging apparatus | |
| JPH0690398A (en) | Image blur correction device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20091201 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20091201 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20110421 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110426 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110621 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20110726 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20110812 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140826 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4807855 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |