JP2006220758A - Shake correction device, optical equipment, control method for shake correction device - Google Patents
Shake correction device, optical equipment, control method for shake correction device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2006220758A JP2006220758A JP2005032047A JP2005032047A JP2006220758A JP 2006220758 A JP2006220758 A JP 2006220758A JP 2005032047 A JP2005032047 A JP 2005032047A JP 2005032047 A JP2005032047 A JP 2005032047A JP 2006220758 A JP2006220758 A JP 2006220758A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- correction
- information
- shake
- shake correction
- correcting
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Adjustment Of Camera Lenses (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、手ぶれ等のぶれを補正する機能を備えたぶれ補正装置、光学機器およびぶれ補正装置の制御方法に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a shake correction apparatus, an optical apparatus, and a control method for a shake correction apparatus having a function of correcting a shake such as a camera shake.
カメラによる画像撮影時に、手ぶれやカメラ載置台のぶれ(揺れ)等によるぶれが原因によって画像劣化が生じることがある。この画像劣化を防止するために光学的にぶれを補正するぶれ補正装置が開発されている。この種のぶれ補正装置は、ぶれを検出する角速度センサ等からなるぶれ検出部と、ぶれ検出情報を駆動位置信号へ変換する積分器などからなるぶれ補正演算部と、ぶれを補正するための補正レンズを駆動するアクチュエータや駆動回路からなる補正レンズ駆動部とによって構成される。角速度センサとしては、振動ジャイロセンサ等が使用される。速度情報であるジャイロセンサの出力信号を積分演算することにより位置情報に変換することができる。この位置情報に補正レンズを追従させることによってぶれ補正(防振)動作を実現することが可能である。 When an image is captured by a camera, image degradation may occur due to camera shake or camera shake (blurring). In order to prevent the image deterioration, a shake correction apparatus that optically corrects the shake has been developed. This type of shake correction apparatus includes a shake detection unit that includes an angular velocity sensor that detects shake, a shake correction calculation unit that includes an integrator that converts shake detection information into a drive position signal, and correction for correcting shake. It is comprised by the correction lens drive part which consists of the actuator which drives a lens, and a drive circuit. A vibration gyro sensor or the like is used as the angular velocity sensor. The output signal of the gyro sensor, which is speed information, can be converted into position information by integrating. By making the correction lens follow the position information, it is possible to realize a shake correction (anti-vibration) operation.
上記の補正装置においては、ぶれを補正するための補正レンズはバネなどの部材によりレンズ鏡筒内で支持されている。したがって、バネの弾性力が補正レンズの自重による力よりも弱い場合、補正レンズの光軸と撮像面にずれが生じてしまい、その結果、撮影画像の上部の隅のみ光量(輝度)落ちすることがある。 In the above correction device, the correction lens for correcting the shake is supported in the lens barrel by a member such as a spring. Therefore, when the elastic force of the spring is weaker than the force due to the weight of the correction lens, a deviation occurs between the optical axis of the correction lens and the imaging surface, and as a result, the amount of light (luminance) drops only at the upper corner of the captured image. There is.
撮影画像の光量落ちに関し、撮像レンズにおいて、レンズ周辺部にいくに従い通過する光量が減少する周辺光量落ちにより、撮影画像の周辺部が低輝度な画像として生成されることが知られている。この周辺光量落ちの課題に対して、従来、光量落ちした画素を画像処理によって補正する方法(特許文献1、特許文献2)や、絞り開放径を制限することによって補正する方法(特許文献2)などが提案されている。
しかしながら、バネの弾性力が補正レンズの自重による力よりも弱いために、撮影画像の上部隅のみ光量落ちする問題に対し、上記の各提案のような技術を具備することは、ぶれ補正装置等が高価になってしまうものであった。 However, since the elastic force of the spring is weaker than the force due to the weight of the correction lens, the problem that the amount of light falls only at the upper corner of the photographed image is provided with the techniques as described in the above proposals such as a shake correction device or the like. Would be expensive.
一方、バネの弾力性を補正レンズの自重による力よりも強くし、補正レンズの光軸と撮像面(撮像素子の中心)のずれが生じないようにして、撮影画像の上部隅の光量落ちといった問題をなくすことも考えられるが、この場合、ぶれを補正する際には補正レンズの駆動力を増す必要があり、その結果、ぶれ補正装置の大型化、駆動電力の増大を招くことになり、好ましくない。 On the other hand, the elasticity of the spring is made stronger than the force due to the weight of the correction lens so that the optical axis of the correction lens and the imaging surface (center of the image sensor) do not shift, and the amount of light at the upper corner of the captured image is reduced. Although it is conceivable to eliminate the problem, in this case, it is necessary to increase the driving force of the correction lens when correcting the blur, resulting in an increase in the size of the blur correction device and an increase in driving power. It is not preferable.
(発明の目的)
本発明の目的は、簡単な構成により、ぶれ補正手段の自重に起因する周辺光量落ちを軽減させることのできるぶれ補正装置、光学機器およびぶれ補正装置の制御方法を提供しようとするものである。
(Object of invention)
An object of the present invention is to provide a shake correction apparatus, an optical apparatus, and a control method for the shake correction apparatus that can reduce a peripheral light amount drop caused by the weight of the shake correction unit with a simple configuration.
上記目的を達成するために、請求項1に記載の発明は、ぶれを検出するぶれ検出手段と、ぶれを補正するためのぶれ補正手段と、前記ぶれ検出手段からのぶれ検出情報に基づいて前記ぶれ補正手段を駆動するためのぶれ補正情報を算出する演算手段と、当該ぶれ補正装置の姿勢を検出する姿勢検出手段とを有するぶれ補正装置であって、画像の周辺光量落ちを補正するための補正情報と前記姿勢情報の対応関係をあらかじめ記憶した記憶手段と、実使用時の前記姿勢情報と周辺落ちを補正するための前記補正情報から重力補正情報を取得し、該重力補正情報により、前記ぶれ補正情報を補正し、該補正したぶれ補正情報により前記ぶれ補正手段を駆動するぶれ補正制御手段とを有するぶれ補正装置とするものである。
In order to achieve the above object, the invention described in
同じく上記目的を達成するために、請求項2に記載の発明は、撮像手段と、ぶれを検出するぶれ検出手段と、ぶれを補正するためのぶれ補正手段と、前記ぶれ検出手段からのぶれ検出情報に基づいて前記ぶれ補正手段を駆動するためのぶれ補正情報を算出する演算手段と、当該光学機器の姿勢を検出する姿勢検出手段とを有する光学機器であって、前記撮像素子により撮像される画像の周辺光量落ちを補正するための補正情報と前記姿勢情報の対応関係をあらかじめ記憶した記憶手段と、実使用時の前記姿勢情報と周辺落ちを補正するための前記補正情報から前記重力補正情報を取得し、該重力補正情報により、前記ぶれ補正情報を補正し、前記ぶれ補正手段を駆動するぶれ補正制御手段とを有する光学機器とするものである。 In order to achieve the above object, the invention described in claim 2 is directed to an image pickup means, a shake detection means for detecting a shake, a shake correction means for correcting a shake, and a shake detection from the shake detection means. An optical device having calculation means for calculating shake correction information for driving the shake correction means based on information, and posture detection means for detecting the posture of the optical device, and is imaged by the imaging device Gravity correction information based on the correction information for correcting the peripheral light loss of the image and the correspondence information of the posture information in advance, the posture information at the time of actual use and the correction information for correcting the peripheral drop , The shake correction information is corrected by the gravity correction information, and the shake correction control means for driving the shake correction means is used.
同じく上記目的を達成するために、請求項3に記載の発明は、画像の周辺光量落ちを補正する補正情報とぶれ補正装置の姿勢を検出する姿勢情報の対応関係をあらかじめ記憶した記憶手段を有するぶれ補正装置の制御方法であって、実使用の際の姿勢情報と周辺落ちを補正する前記補正情報から重力補正情報を取得し、該重力補正情報により前記ぶれ補正装置を駆動するためのぶれ補正情報を補正し、該補正したぶれ補正情報によりぶれ補正手段を駆動するぶれ補正装置の制御方法とするものである。 Similarly, in order to achieve the above object, the invention described in claim 3 includes a storage unit that stores in advance a correspondence relationship between correction information for correcting a peripheral light amount drop in an image and posture information for detecting the posture of a shake correction device. A method for controlling a shake correction apparatus, wherein gravity correction information is acquired from posture information in actual use and the correction information for correcting peripheral fall, and shake correction for driving the shake correction apparatus based on the gravity correction information The control method of the shake correction apparatus that corrects information and drives the shake correction means based on the corrected shake correction information.
本発明によれば、簡単な構成により、ぶれ補正手段の自重に起因する周辺光量落ちを軽減させることができるぶれ補正装置、光学機器またはぶれ補正装置の制御方法を提供できるものである。 According to the present invention, it is possible to provide a shake correction device, an optical apparatus, or a control method for a shake correction device that can reduce a peripheral light amount drop due to the weight of the shake correction unit with a simple configuration.
本発明を実施するための最良の形態は、以下に記載する実施例1および実施例2に示す通りである。 The best mode for carrying out the present invention is as shown in Example 1 and Example 2 described below.
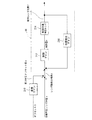
図1は本発明の実施例1に係るデジタルカメラ等のカメラ(撮像装置)の回路構成を示すブロック図である。鏡筒10の内部には、アクチュエータにより光軸に対して垂直方向に駆動される手ぶれ等のぶれを補正するための補正レンズ12、不図示のモータにより光軸方向に駆動されるズームレンズ14やフォーカスレンズ16、さらには絞り機能を備えたシャッタ18を有している。撮影素子20は鏡筒10を通過して入射する光学像をアナログ信号に変換するものであり、アナログ信号はA/D変換部28によりデジタル信号に変換され、後段に出力される。タイミング発生器22は、撮像素子20、D/A変換部24、A/D変換部28にクロック信号や制御信号を供給するものである。
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a circuit configuration of a camera (imaging device) such as a digital camera according to
薄膜トランジスタ駆動型液晶表示器(TFT LCD)等により構成される画像表示部26は、メモリ制御部30の制御にしたがってD/A変換部24を介して入力される画像表示記憶部32に保存された画像データ等を表示する。撮像された画像データを画像表示部26に逐次表示することにより、電子ファインダ機能を実現することが可能である。メモリ制御部30は、カメラシステム制御部46により制御され、上記のタイミング発生器22、D/A変換部24、A/D変換部28、画像表示記憶部32、後述の画像処理部34に対するデータの入出力制御を行う。画像処理部34は、A/D変換部28、あるいはメモリ制御部30からのデータに対して所定の画素補間処理や色変換処理を行う。
An
カメラシステム制御部46は、操作部56にて行われる操作に応じて、鏡筒制御部36、露光制御部38、測距制御部40、ズーム制御部42を制御する。鏡筒制御部36は、カメラの再生撮影状態によって、補正レンズ12、ズームレンズ14、フォーカスレンズ16、絞り機能を備えたシャッタ18を、撮影可能な状態や収納状態に駆動する。露光制御部38は、画像処理部34によって測光された情報をもとに、絞り機能を備えたシャッタ18を制御することによってAE(自動露出)制御を行う。測距制御部40は、画像処理部34によって得られた被写体距離をもとに、フォーカスレンズ16を駆動制御してAF(オートフォーカス)制御などを行う。ズーム制御部42は、操作部56のズームレバーまたはズームボタンなどの操作部材の操作量に応じてズームレンズ14を駆動制御する。また、カメラシステム制御部46は、手ぶれ等のぶれを検出するぶれ検出部58によって検出されたぶれ量からレンズ補正量を算出し、ぶれ補正制御部44に補正量を伝達する。ぶれ補正制御部44は、補正レンズ12を垂直方向および水平方向の2方向に駆動制御することで2次元画像上のぶれ補正を行うことが可能である。さらに、カメラシステム制御部46は、姿勢検出部60よって検出されたカメラの姿勢情報を取得し、画像再生時に最適な表示方向に画像を表示するように制御する。
The camera
メモリ48には、カメラシステム制御部46の作業領域や撮影した静止画像や動画像の一時的な格納領域として使用される揮発領域と、カメラ駆動に必要な設計値などを記憶しておく不揮発領域とがある。このメモリ48の記憶容量は、所定枚数の静止画像や所定時間の動画像を格納するのに十分な容量となっており、複数枚の静止画像を連続して撮影する連続撮影やパノラマ撮影の場合にも、高速かつ大量の画像書き込みを可能にしている。電源50は、不図示の、電池検出回路、DC−DCコンバータおよび通電する回路ブロックを切り替えるスイッチ回路等により構成され、電池の装着の有無、電池の種類、電池残量等の検出を行い、これらの検出結果およびカメラシステム制御部46からの指示に基づいて、上記DC−DCコンバータを制御し、必要な電源を必要な期間だけ記録媒体を含む各部へ電圧や電流を供給する。
The
インターフェース(I/F)52は、メモリーカードやハードディスク等の記録媒体とのインターフェースである。記録部54は、記録媒体に対して画像データ等を格納するためのものであり、インターフェース50を介してカメラシステム制御部46とアクセスすることが可能である。
An interface (I / F) 52 is an interface with a recording medium such as a memory card or a hard disk. The
姿勢検知部60は、重力方向を検出する例えば傾斜センサなどによって構成される。図2に、傾斜センサにより構成される姿勢検知部60について説明する。動作原理としては、検知部材60aと該検知部材60a上を転がるボール部材60c、および、検知部材60bと該検知部材60b上を転がるボール部材60cとがそれぞれスイッチSW1,SW2として働き、検知部材60a,60bとボール部材60cが接地するときにはスイッチSW1,SW2がON状態に、非接地のときにはスイッチSW1,SW2がOFF状態となる。所定の傾きを越えるとスイッチ状態が変化することで被計測物であるカメラの傾きを検知することができる。例えば、カメラの姿勢が横向き(正位置)の時が図2(b)の状態であるとした場合、スイッチSW1,SW2は共にONになり、カメラの姿勢が縦向き(グリップ側が下)であった場合は、スイッチSW1がONになり、スイッチSW2がOFFになる。また、上記とはカメラの姿勢が反対の縦向き(グリップ側が上)であった場合は、スイッチSW1がOFFになり、スイッチSW2がONになる。したがって、カメラシステム制御部46は、上記スイッチSW1,SW2の状態をカメラの姿勢情報として認識することが可能となる。
The
図3は、撮影画像の上部隅の光量(輝度)落ちが生じた撮影画像を示す図であり、図3(a)はカメラを横向きに構えて撮影した場合、図3(b)はカメラを縦向きに構えて撮影した場合に、それぞれ生じる光量落ちする場所を黒点領域で示している。 FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating a captured image in which a light amount (brightness) drop occurs in the upper corner of the captured image. FIG. 3A illustrates a case where the camera is photographed while holding the camera sideways, and FIG. A black spot region indicates a place where the amount of light that occurs when shooting is taken in the vertical direction.
ここで、上記補正レンズ12はバネなどの弾性部材により鏡筒10内で支持されている。上記バネの弾力性を該補正レンズ12の自重による力よりも強くすると、既に述べたように、該補正レンズ12の駆動力を増す必要があり、鏡筒10、さらにはカメラの大型化等を招くという不都合がある。そのため、上記バネの弾性力は補正レンズ12の自重による力よりも弱く設定されており、よって、補正レンズ12の光軸と撮像面(詳しくは、補正レンズ以外のレンズの光軸(撮影光軸))にずれが生じてしまい、図3(a)のカメラの横向き姿勢では、長辺の上部両端に光量落ちが生じ、図3(b)のカメラの縦向き姿勢では、短辺の上部両端に光量落ちが生じてしまう。
Here, the
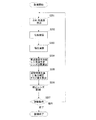
次に、上記構成におけるカメラにおいて、カメラシステム制御部46にて行われる手ぶれ等のぶれ補正(防振)時の動作について、図4のフローチャートを用いて説明する。
Next, in the camera having the above-described configuration, an operation at the time of camera shake correction (anti-shake) performed by the camera
カメラシステム制御部46は、まず、ステップS101にて、ぶれ検出部58にて検出されるぶれ角速度情報の検出を行う。ぶれ検出部58としては、例えばジャイロセンサなどの角速度検出センサが用いられ、該ジャイロセンサのアナログ出力はA/D変換部によって量子化、標本化され、カメラシステム制御部46で以後の演算処理に供される。次のステップS102では、位相補償フィルタ演算を行うことで制御系全体にて生じる位相遅れを補償する。続くステップS103では、ローパスフィルタ積分演算により上記角速度情報を位置(変位)情報に変換する。続くステップS104では、ズーム制御部42によって駆動制御されているズームレンズ14の位置により変更される焦点距離情報を取得し、補正レンズ12の制御量(位置情報)に適切なゲイン(利得)をかける。焦点距離が長くなるほどぶれ補正の制御量は大きくなり、逆に焦点距離が短くなるほどぶれ補正の制御量は小さくなる。これにより、カメラの姿勢を考慮していないときの目標予定レンズ位置が得られる。
First, in step S101, the camera
次のステップS105では、姿勢検知部60にて検知されたカメラの姿勢情報(図2に示したスイッチSW1,SW2の状態信号)とオフセットb(後述)を基にあらかじめカメラに保存されている重力補正オフセット値を導出し、この重力補正オフセット値に上記目標予定レンズ位置を加算して、姿勢情報を考慮した最終的なレンズ駆動目標値が算出される。上記オフセットbは、あらかじめ同一輝度のチャート画像を撮影し、取得した輝度データから画像中心部の輝度と周辺部の輝度差を算出することで得られる周辺光量落ちを補正するための補正情報であり、カメラの姿勢情報(後述の姿勢ゲインに相当)との対応を示すテーブルがメモリ48の不揮発領域に保存されている。重力補正オフセット値は、実使用時のカメラの姿勢情報に基づいてこのテーブルより導出される情報である。そして、次のステップS106にて、上記重力補正オフセット値に目標予定レンズ位置を加算したレンズ駆動目標値をぶれ補正制御部44の制御入力とし、続くステップS107にて、ぶれ補正制御部44に補正レンズ12の駆動を行わせる。これにより、ぶれ補正制御部44にて図5により後述するようにして補正レンズ12の駆動制御が行われ、その結果、補正レンズ12の自重を含んだぶれ補正がなされ、図2に示した上部隅の光量落ちのない撮影画像を得ることができる。
In the next step S105, the gravity previously stored in the camera based on the camera posture information (state signals of the switches SW1 and SW2 shown in FIG. 2) and the offset b (described later) detected by the
次のステップS108では、ぶれ補正(防振)動作を継続する状態に設定されているかの判定を例えば操作部56の状態を確認することにより行い、継続する状態に設定されていればステップS101へ戻り、上記の同様の動作を繰り返す。また、ぶれ補正動作を終了する状態にあればこのぶれ補正動作を終了する。
In the next step S108, it is determined whether or not the state of continuing the shake correction (anti-vibration) operation is set, for example, by confirming the state of the
図5は、上記ぶれ補正制御部44の制御系を示すブロック図である。同図において、目標予定レンズ位置aは、図5のステップS101〜S104の処理によって求められたものであり、オフセットbは、上記のようにして予め測定されている周辺光量落ちを補正するための、カメラの姿勢が考慮されていない(換言すれば、補正レンズ12の自重による光軸ずれを考慮していない)情報であり、重力補正オフセット値cは、(オフセットb)×(姿勢ゲイン)により得られる、カメラの姿勢を考慮した重力補正情報であり、レンズ駆動目標値dは、(目標予定レンズ位置a)+(オフセットd)×(姿勢ゲイン)により得られた情報である。そして、レンズ駆動目標値dがぶれ補正制御部44の制御入力となる。なお、上記の重力補正オフセット値cは、前述したように、周辺光量落ちを補正するための情報(オフセットb)と姿勢情報(姿勢ゲイン)の対応関係を示すメモリ48に予め保存されているテーブルより導出される値であり、図5では、模式的に(オフセットb)×(姿勢ゲイン)により得られる情報として示している。
FIG. 5 is a block diagram showing a control system of the shake
ぶれ補正制御部44では、制御ゲイン212に従い導出した制御量eによって、制御対象214である補正レンズ12を制御する。制御ゲイン212は、例えば、PID制御(比例/微分/積分制御)などの制御手法に基づくゲインである。駆動制御されている現在の補正レンズ12の位置、つまり制御レンズ位置fは例えばホール素子などの位置センサにより計測されており、この制御レンズ位置fに位置検出ゲイン216がかけられてぶれ補正制御部44の制御入力へとフィードバックされる。位置検出ゲイン216は、位置センサの計測レンジを決定するゲインである。このとき、位置検出ゲイン216は、計測レンジ内で検出位置が制御量eに対して線形性を得られるゲインを設定する必要がある。
The shake
ここで、例えば姿勢検知部60がカメラの姿勢を横向き(正位置)であると検知した場合、補正レンズ12を垂直方向および水平方向の2方向に駆動制御するうちの一方の、水平(左右)方向の制御系における姿勢ゲイン210は0であり、このときの制御入力は目標予定レンズ位置aの情報のみで、通常のぶれ補正制御が行われる。一方、垂直(上下)方向の制御系における姿勢ゲインは1であり、このときの制御入力は、(目標予定レンズ位置a+重力補正オフセット値c)となり、重力補正オフセット値cの分だけ制御量eが増大し、補正レンズ12を上方向に押し上げる制御がぶれ補正制御部44にて行われる。このことで上部に発生する周辺光量落ちが補正されることになる。
Here, for example, when the
同様に、グリップを下もしくは上としたカメラの姿勢を縦向きに傾けた場合にも、重力方向と逆向きに制御量eを増大させることで、カメラの姿勢によらず、周辺光量落ちを補正することが可能となる。 Similarly, even when the camera is tilted vertically with the grip down or up, the control amount e is increased in the direction opposite to the gravitational direction to compensate for the loss of peripheral light regardless of the camera posture. It becomes possible to do.
上記の実施例1によれば、撮影画像の周辺光量落ちを補正するための補正情報(オフセットb)とカメラの姿勢情報(姿勢ゲイン)の対応関係をあらかじめカメラに保存しておき、カメラの実使用時には、そのときのカメラの姿勢情報を検出し、この姿勢情報から得られる重力補正情報(重力補正オフセット値c)を得、この重力補正情報により、ぶれ検出部58からの情報により算出される補正レンズ12のぶれ補正制御量(目標予定レンズ位置a)を変化させる(補正を加える)ようにしている。
According to the first embodiment, the correspondence relationship between the correction information (offset b) and the camera posture information (posture gain) for correcting the peripheral light amount drop in the captured image is stored in the camera in advance, and At the time of use, the posture information of the camera at that time is detected, gravity correction information (gravity correction offset value c) obtained from the posture information is obtained, and the gravity correction information is calculated from information from the
よって、従来の周辺光量落ちを補正するための高価かつ複雑な回路を備えることなしに、簡単な構成により、補正レンズ12の自重に起因する光軸ずれ(補正レンズ12と撮像素子20の中心との光軸のずれ)を適正に補正し、撮影画像の周辺光量落ちを軽減させることが可能となる。さらに、カメラの姿勢が横位置であっても、グリップを下もしくは上とした縦向きであったとしても、補正レンズ12と撮像素子20の中心との光軸のずれを適正に補正することができ、カメラの姿勢によらず、撮影画像の周辺光量落ちを軽減させることが可能となる。
Therefore, without providing a conventional expensive and complicated circuit for correcting the peripheral light loss, the optical axis shift (the center of the
次に、本発明の実施例2に係わるカメラについて説明する。なお、カメラの回路構成は図1と同様であるので、その説明は省略する。 Next, a camera according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described. Since the circuit configuration of the camera is the same as that in FIG. 1, the description thereof is omitted.
図6は本発明の実施例2に係わるカメラに具備されるぶれ補正制御部44の制御系を示すブロック図である。
FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing a control system of the shake
上記実施例1では、目標予定レンズ位置aに、姿勢情報と周辺光量落ちを補正するため情報とにより得られる重力補正情報(オフセットb×姿勢ゲイン)を加算して、これをぶれ補正制御部44の制御入力としていた。これに対し、本発明の実施例2では、図6に示すように、ぶれ補正制御部44のフィードバック入力である位置検出系に重力補正オフセット値cを入力し、位置検出系の信号から重力補正オフセット値cを減算するようにしたものである。この構成においても、上記実施例1と同様の制御量eを導出することが可能である。
In the first embodiment, the gravity correction information (offset b × posture gain) obtained from the posture information and the information for correcting the peripheral light amount drop is added to the target planned lens position a, and this is added to the shake
図7は、図6のような制御系にした場合における、本発明の実施例2に係わるカメラシステム制御部46でのぶれ補正(防振)時の動作を示すフローチャートである。
FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing an operation at the time of shake correction (anti-vibration) in the camera
カメラシステム制御部46は、まず、ステップS201にて、ぶれ検出部58にて検出されるぶれ角速度情報の検出を行う。次のステップS202では、位相補償フィルタ演算を行うことで制御系全体にて生じる位相遅れを補償する。続くステップS203では、ローパスフィルタ積分演算により上記角速度情報を位置(変位)情報に変換する。続くステップS204では、ズーム制御部42によって駆動制御されているズームレンズ14の位置により変更される焦点距離情報を取得し、補正レンズ12の制御量(位置情報)に適切なゲイン(利得)をかける。これにより、カメラの姿勢を考慮していないときの目標予定レンズ位置aが得られる。そして、この目標予定レンズ位置aの情報をぶれ補正制御部44の制御入力の一つとする。
The camera
次のステップS205では、姿勢検知部60にて検知されたカメラの姿勢情報(図2に示したスイッチSW1,SW2の状態信号)とオフセットbを基にあらかじめカメラに保存されている重力補正オフセット値cを導出し、この重力補正オフセット値cをぶれ補正制御部44の制御入力の一つとする。これにより、ぶれ補正制御部44内にて、図6に示すような動作(目標予定レンズ位置a−(位置検出系の信号−重力補正オフセット値c))が行われ、姿勢情報を考慮した最終的な補正レンズ12の駆動目標値が算出される。このときのオフセットbは、上記実施例1と同様、あらかじめ同一輝度のチャート画像を撮影し、取得した輝度データから画像中心部の輝度と周辺部の輝度差を算出することで得られる周辺光量落ちを補正するための補正情報であり、カメラの姿勢情報(姿勢ゲインに相当)との対応を示すテーブルがメモリ48の不揮発領域に保存されている。重力補正オフセット値cは、実使用時のカメラの姿勢情報に基づいてこのテーブルより導出される情報である。そして、次のステップS206にて、ぶれ補正制御部44に補正レンズ12の駆動を行わせる。これにより、ぶれ補正制御部44にて補正レンズ12の駆動制御が行われ、その結果、補正レンズ12の自重を含んだぶれ補正がなされ、図3に示した上部隅の光量落ちのない撮影画像を得ることができる。
In the next step S205, the gravity correction offset value stored in the camera in advance based on the camera posture information (state signals of the switches SW1 and SW2 shown in FIG. 2) detected by the
次のステップS207では、ぶれ補正(防振)動作を継続する状態に設定されているかの判定を例えば操作部56の状態を確認することにより行い、継続する状態に設定されていればステップS201へ戻り、上記の同様の動作を繰り返す。また、ぶれ補正動作を終了する状態にあればこのぶれ補正動作を終了する。
In the next step S207, it is determined whether or not the state of continuing the shake correction (anti-vibration) operation is set, for example, by checking the state of the
上記の実施例2によれば、上記実施例1と同様、撮影画像の周辺光量落ちを補正するため補正情報(オフセットb)とカメラの姿勢情報(姿勢ゲイン)の対応関係をあらかじめカメラに保存しておき、カメラの実使用時には、そのときのカメラの姿勢情報を検出し、この姿勢情報から得られる重力補正情報を得、この重力補正情報により、ぶれ検出情報に基づいて算出される補正レンズ12のぶれ補正制御量(目標予定レンズ位置a)を変化させるようにしている。
According to the second embodiment, as in the first embodiment, the correspondence relationship between the correction information (offset b) and the camera posture information (posture gain) is stored in the camera in advance in order to correct the peripheral light amount drop in the captured image. When the camera is actually used, the posture information of the camera at that time is detected, gravity correction information obtained from the posture information is obtained, and the
よって、従来の周辺光量落ちを補正するための高価かつ複雑な回路を備えることなしに、簡単な構成により、補正レンズ12の自重に起因する光軸ずれ(補正レンズ12と撮像素子20の中心との光軸のずれ)を適正に補正し、撮影画像の周辺光量落ちを軽減させることが可能となる。さらに、カメラの姿勢が横位置であっても、グリップを下もしくは上とした縦向きであったとしても、補正レンズ12と撮像素子20の中心との光軸のずれを適正に補正することができ、カメラの姿勢によらず、撮影画像の周辺光量落ちを軽減させることが可能となる。
Therefore, without providing a conventional expensive and complicated circuit for correcting the peripheral light loss, the optical axis shift (the center of the
本発明は、カード型を含むデジタルカメラ等の撮像装置に好適である。さらには、撮影機能を内蔵した携帯電話等の光学機器にも好適である。 The present invention is suitable for an imaging apparatus such as a digital camera including a card type. Furthermore, it is also suitable for an optical device such as a mobile phone with a built-in photographing function.
12 補正レンズ
20 撮像素子
26 画像表示部
30 メモリ制御部
42 ズーム制御部
44 ぶれ補正制御部(ぶれ補正制御手段)
46 カメラシステム制御部(演算手段、ぶれ補正制御手段)
48 メモリ(記憶手段)
56 操作部
58 ぶれ検出部(ぶれ検出手段)
60 姿勢検出部(姿勢検出手段)
DESCRIPTION OF
46 Camera system control unit (calculation means, shake correction control means)
48 memory (memory means)
56
60 Posture detection unit (posture detection means)
Claims (3)
ぶれを補正するためのぶれ補正手段と、
前記ぶれ検出手段からのぶれ検出情報に基づいて前記ぶれ補正手段を駆動するためのぶれ補正情報を算出する演算手段と、
当該ぶれ補正装置の姿勢を検出する姿勢検出手段と、
を有するぶれ補正装置であって、
画像の周辺光量落ちを補正する補正情報と前記姿勢情報の対応関係をあらかじめ記憶した記憶手段と、
実使用の際の前記姿勢情報と周辺落ちを補正する前記補正情報から重力補正情報を取得し、該重力補正情報により、前記ぶれ補正情報を補正し、該補正したぶれ補正情報により前記ぶれ補正手段を駆動するぶれ補正制御手段と、
を有することを特徴とするぶれ補正装置。 Blur detection means for detecting blur;
Blur correction means for correcting blur;
Calculation means for calculating shake correction information for driving the shake correction means based on shake detection information from the shake detection means;
Posture detection means for detecting the posture of the shake correction device;
A shake correction device comprising:
Storage means for preliminarily storing the correspondence between the correction information for correcting the peripheral light loss of the image and the posture information;
Gravity correction information is acquired from the posture information in actual use and the correction information for correcting peripheral fall, the shake correction information is corrected by the gravity correction information, and the shake correction unit is corrected by the corrected shake correction information. Blur correction control means for driving
A shake correction apparatus comprising:
ぶれを検出するぶれ検出手段と、
ぶれを補正するためのぶれ補正手段と、
前記ぶれ検出手段からのぶれ検出情報に基づいて前記ぶれ補正手段を駆動するためのぶれ補正情報を算出する演算手段と、
当該光学機器の姿勢を検出する姿勢検出手段と、
を有する光学機器であって、
前記撮像素子により撮像される画像の周辺光量落ちを補正する補正情報と前記姿勢情報の対応関係をあらかじめ記憶した記憶手段と、
実使用の際の前記姿勢情報と周辺落ちを補正する前記補正情報から重力補正情報を取得し、該重力補正情報により、前記ぶれ補正情報を補正し、前記ぶれ補正手段を駆動するぶれ補正制御手段と、
を有することを特徴とする光学機器。 Imaging means;
Blur detection means for detecting blur;
Blur correction means for correcting blur;
Calculation means for calculating shake correction information for driving the shake correction means based on shake detection information from the shake detection means;
Attitude detection means for detecting the attitude of the optical device;
An optical instrument comprising:
Storage means for storing in advance a correspondence relationship between correction information for correcting a decrease in peripheral light amount of an image captured by the image sensor and the posture information;
Gravity correction information is acquired from the posture information in actual use and the correction information for correcting peripheral fall, the blur correction information is corrected by the gravity correction information, and the shake correction control unit drives the shake correction unit. When,
An optical apparatus comprising:
実使用の際の姿勢情報と周辺落ちを補正する前記補正情報から重力補正情報を取得し、該重力補正情報により前記ぶれ補正装置を駆動するためのぶれ補正情報を補正し、該補正したぶれ補正情報によりぶれ補正手段を駆動することを特徴とするぶれ補正装置の制御方法。
A method for controlling a shake correction apparatus having storage means that stores in advance a correspondence relationship between correction information for correcting a peripheral light amount drop in an image and attitude information for detecting the attitude of the shake correction apparatus,
Gravity correction information is acquired from the posture information in actual use and the correction information for correcting peripheral fall, and the shake correction information for driving the shake correction device is corrected based on the gravity correction information, and the corrected shake correction is performed. A control method for a shake correction apparatus, wherein the shake correction means is driven by information.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005032047A JP2006220758A (en) | 2005-02-08 | 2005-02-08 | Shake correction device, optical equipment, control method for shake correction device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005032047A JP2006220758A (en) | 2005-02-08 | 2005-02-08 | Shake correction device, optical equipment, control method for shake correction device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006220758A true JP2006220758A (en) | 2006-08-24 |
| JP2006220758A5 JP2006220758A5 (en) | 2008-03-27 |
Family
ID=36983145
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005032047A Pending JP2006220758A (en) | 2005-02-08 | 2005-02-08 | Shake correction device, optical equipment, control method for shake correction device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2006220758A (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2040118A1 (en) * | 2007-09-21 | 2009-03-25 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Lens apparatus and camera |
| JP2010026172A (en) * | 2008-07-17 | 2010-02-04 | Nikon Corp | Lens barrel, method of adjusting lens barrel, optical device, and method of adjusting optical device |
| JP2010152168A (en) * | 2008-12-25 | 2010-07-08 | Nikon Corp | Optical device, method of manufacturing the optical device, method of adjusting the optical device, and imaging device |
| JP2010237250A (en) * | 2009-03-30 | 2010-10-21 | Canon Inc | Imaging apparatus |
| JP2016014750A (en) * | 2014-07-02 | 2016-01-28 | リコーイメージング株式会社 | Imaging apparatus and imaging method, and drive control device and drive control method |
| JP2018106051A (en) * | 2016-12-27 | 2018-07-05 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | Camera controller and method for calibrating correction lens |
| JP2019102884A (en) * | 2017-11-29 | 2019-06-24 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging apparatus and control method of the same |
| JP2020184027A (en) * | 2019-05-08 | 2020-11-12 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image tremor correction device and method, and imaging device |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04328531A (en) * | 1991-04-26 | 1992-11-17 | Canon Inc | Image blurring correction device |
| JPH0990456A (en) * | 1995-09-25 | 1997-04-04 | Canon Inc | Optical device and camera |
| JPH1184455A (en) * | 1997-09-09 | 1999-03-26 | Minolta Co Ltd | Camera |
| JP2000221557A (en) * | 1999-01-29 | 2000-08-11 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Image blur correcting device and photographing device using the same |
| JP2003091028A (en) * | 2001-09-19 | 2003-03-28 | Canon Inc | Controller for positioning correcting means |
| JP2005173160A (en) * | 2003-12-10 | 2005-06-30 | Canon Inc | Image blurring correcting apparatus and optical device |
-
2005
- 2005-02-08 JP JP2005032047A patent/JP2006220758A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04328531A (en) * | 1991-04-26 | 1992-11-17 | Canon Inc | Image blurring correction device |
| JPH0990456A (en) * | 1995-09-25 | 1997-04-04 | Canon Inc | Optical device and camera |
| JPH1184455A (en) * | 1997-09-09 | 1999-03-26 | Minolta Co Ltd | Camera |
| JP2000221557A (en) * | 1999-01-29 | 2000-08-11 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Image blur correcting device and photographing device using the same |
| JP2003091028A (en) * | 2001-09-19 | 2003-03-28 | Canon Inc | Controller for positioning correcting means |
| JP2005173160A (en) * | 2003-12-10 | 2005-06-30 | Canon Inc | Image blurring correcting apparatus and optical device |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2040118A1 (en) * | 2007-09-21 | 2009-03-25 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Lens apparatus and camera |
| US7856177B2 (en) | 2007-09-21 | 2010-12-21 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Lens apparatus and camera |
| JP2010026172A (en) * | 2008-07-17 | 2010-02-04 | Nikon Corp | Lens barrel, method of adjusting lens barrel, optical device, and method of adjusting optical device |
| JP2010152168A (en) * | 2008-12-25 | 2010-07-08 | Nikon Corp | Optical device, method of manufacturing the optical device, method of adjusting the optical device, and imaging device |
| JP2010237250A (en) * | 2009-03-30 | 2010-10-21 | Canon Inc | Imaging apparatus |
| JP2016014750A (en) * | 2014-07-02 | 2016-01-28 | リコーイメージング株式会社 | Imaging apparatus and imaging method, and drive control device and drive control method |
| JP2018106051A (en) * | 2016-12-27 | 2018-07-05 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | Camera controller and method for calibrating correction lens |
| JP2019102884A (en) * | 2017-11-29 | 2019-06-24 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging apparatus and control method of the same |
| JP7073081B2 (en) | 2017-11-29 | 2022-05-23 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image pickup device and its control method |
| JP2020184027A (en) * | 2019-05-08 | 2020-11-12 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image tremor correction device and method, and imaging device |
| JP7328788B2 (en) | 2019-05-08 | 2023-08-17 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image blur correction device and method, and imaging device |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4717748B2 (en) | Camera body and camera system having the same | |
| JP4671705B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| US7385632B2 (en) | Lens, camera body and camera system | |
| US7672578B2 (en) | Image capturing apparatus | |
| KR101728590B1 (en) | An image pickup apparatus and control method | |
| US7885523B2 (en) | Image pickup apparatus | |
| JP6472176B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, image shake correction apparatus, image pickup apparatus control method, and image shake correction method | |
| US7907205B2 (en) | Optical apparatus with unit for correcting blur of captured image caused by displacement of optical apparatus in optical-axis direction | |
| JP2006220758A (en) | Shake correction device, optical equipment, control method for shake correction device | |
| JP4724493B2 (en) | Optical apparatus, imaging apparatus, and attitude detection method of optical apparatus | |
| JP2009105784A (en) | Imaging apparatus | |
| US8866917B2 (en) | Optical apparatus and control method therefor | |
| JP2007043584A (en) | Image pickup device and control method thereof | |
| JP4732148B2 (en) | Optical apparatus and imaging system | |
| JP5939768B2 (en) | Image blur correction apparatus, imaging system, and image blur correction apparatus control method | |
| JP4876550B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, control method, and control program | |
| JP4594004B2 (en) | IMAGING DEVICE, ITS CONTROL METHOD, PROGRAM, AND STORAGE MEDIUM | |
| JP2012013778A (en) | Imaging apparatus | |
| JP5001014B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and imaging method | |
| JP5318078B2 (en) | Optical apparatus and control method thereof | |
| JP2006203493A (en) | Image movement correction device | |
| JP2008233156A (en) | Method for controlling imaging apparatus and imaging apparatus | |
| JP2004252486A (en) | Image blurring correction device for imaging apparatus | |
| JP2007194813A (en) | Imaging apparatus, control method, and control program | |
| JP2008257033A (en) | Camera, lens barrel, manufacturing method for camera, and manufacturing method for lens barrel |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080207 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20080207 |
|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date: 20100520 |
|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date: 20100630 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20101012 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20101207 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110125 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110303 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20110419 |