JP4758564B2 - paint - Google Patents
paint Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4758564B2 JP4758564B2 JP2001152824A JP2001152824A JP4758564B2 JP 4758564 B2 JP4758564 B2 JP 4758564B2 JP 2001152824 A JP2001152824 A JP 2001152824A JP 2001152824 A JP2001152824 A JP 2001152824A JP 4758564 B2 JP4758564 B2 JP 4758564B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- meth
- acrylate
- metal
- coating film
- acid
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Landscapes
- Paints Or Removers (AREA)
- Addition Polymer Or Copolymer, Post-Treatments, Or Chemical Modifications (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、塗料等の被覆材料に使用される金属含有共重合体に関するものであり、詳しくは、長期にわたって光沢を保持し、かつ耐汚染性、耐溶剤性、耐熱黄変性といった塗膜性能に優れた塗膜を提供でき、金属被覆用塗料として特に有用な金属含有共重体に関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
プレコートメタルは、屋根材、壁材、エアコン室外機等に用いられ、予め塗膜が形成された状態で折り曲げ等の加工が施されるため、その塗膜としては光沢や加工性が長期間保持される特性が要求され、その要求は年々厳しくなっている。
プレコートメタルに用いられる金属被覆用塗料には、耐候性、耐汚染性、耐食性等に優れていることから、ポリフッ化ビニリデンが広く利用されているが、基材との密着性、外観、硬度等に劣るという問題点を有しているため、これを単独で使用することは少ない。例えば、特公昭43−10363号公報に記載されているように、ポリフッ化ビニリデンをアクリル系共重合体とブレンドする等の方法によって、基材との密着性の改善が図られており、一般的には、アクリル系共重合体の溶解した高沸点溶剤に、ポリフッ化ビニリデンの微粉末を分散させたものが使用されている。また、特公昭58−32183号公報には、耐溶剤性、屈曲性等の塗膜性能を改善するため、N−アルコキシアルキルアミド基含有熱硬化性重合体および熱可塑性アクリル系共重合体からなる樹脂組成物をポリフッ化ビニリデンとブレンドしたものが開示されている。
【0003】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、特公昭43−10363号公報に開示されている塗膜は、屋外暴露等のように長時間高温にさらされると、ポリフッ化ビニリデンとアクリル系共重合体との相分離が進行し、塗膜の光沢が失われるとともに、塗膜の伸度が低下するため、予め折り曲げ等の加工を施された塗膜は、剥離やクラック等が発生しやすくなるという問題点を有している。また、特公昭58−32183号公報に開示されている塗膜は、成膜時の焼付炉内の温度ムラやラインスピード向上のためと称し焼付温度を上げ、その分焼付時間を短くするいわゆる高温短時間焼付が行われているため、高熱によって黄変が生じやすいという耐熱黄変性の問題を有している。また、特開平5−171066号公報および特開平10−158547号公報には、金属含有共重合体を使った防汚塗料組成物が開示されているが、プレコートメタル用に使用されるものではない。
【0004】
本発明は、前記課題を解決するためになされたものであって、金属含有共重合体を含有することを特徴とする塗料を用いて、長期にわたって光沢を保持し、かつ耐溶剤性、耐熱黄変性といった塗膜性能に優れた塗膜を提供することにある。
【0005】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明者らは、上記従来技術の問題点に鑑み、金属被覆用塗料に用いられる共重合体について鋭意検討した結果、金属含有重合性単量体(a)0.1〜10質量%と該(a)成分と共重合可能なα、β−モノエチレン性不飽和基含有重合性単量体(b)90〜99.9質量%とを共重合させた金属含有共重合体を用いて、光沢の保持および優れた塗膜の提供が可能であることを見いだした。
具体的には、前記金属含有重合性単量体(a)としては、下記(I)で示される金属含有重合性単量体(a1)、または2個の不飽和基を有する金属含有重合性単量体(a2)、または下記(I)で示される該金属含有重合性単量体(a1)と2個の不飽和基を有する該金属含有重合性単量体(a2)との混合物であることが望ましい。
【化3】
(式中、R1は水素原子またはメチル基、MはMg、ZnまたはCa、R2は有機酸残基を示す)
【0006】
本発明の塗料は、上記金属含有共重合体を含有することを特徴とするもので、ポリフッ化ビニリデンを含有する塗料に特に好適なものである。
【0007】
【発明の実施の形態】
本発明の金属含有共重合体は、金属含有重合性単量体(a)0.1〜10質量%、(a)成分と共重合可能なα、β−モノエチレン性不飽和基含有重合性単量体(b)90〜99.9質量%を共重合して得られることを特徴とする。
本発明の金属含有共重合体に使用される金属含有重合性単量体(a)は金属含有重合性単量体(a1)及びまたは(a2)からなるものが望ましい。金属含有重合性単量体(a1)は、上記の一般式(I)で表わされるものである。上記の一般式(I)で表される化合物の具体例としては、モノクロル酢酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート((メタ)アクリレートは、アクリレートまたはメタクリレートを意味する。以下、同じ。)、モノクロル酢酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、モノクロル酢酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、モノフルオロ酢酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、モノフルオロ酢酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、モノフルオロ酢酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、プロピオン酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、プロピオン酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、プロピオン酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、オクチル酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、オクチル酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、オクチル酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、バーサチック酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、バーサチック酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、バーサチック酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、オレイン酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、オレイン酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、オレイン酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、イソステアリン酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、イソステアリン酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、イソステアリン酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、パルミチン酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、パルミチン酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、パルミチン酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、クレソチン酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、クレソチン酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、クレソチン酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、α−ナフトエ酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、α−ナフトエ酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、α−ナフトエ酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、β−ナフトエ酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、β−ナフトエ酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、β−ナフトエ酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、安息香酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、安息香酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、安息香酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、2,4,5−トリクロロフェノキシ酢酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、2,4,5−トリクロロフェノキシ酢酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、2,4,5−トリクロロフェノキシ酢酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、2,4−ジクロロフェノキシ酢酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、2,4−ジクロロフェノキシ酢酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、2,4−ジクロロフェノキシ酢酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、キノリンカルボン酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、キノリンカルボン酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、キノリンカルボン酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、ニトロ安息香酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、ニトロ安息香酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、ニトロ安息香酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、ニトロナフタレンカルボン酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、ニトロナフタレンカルボン酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、ニトロナフタレンカルボン酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート、プルビン酸マグネシウム(メタ)アクリレート、プルビン酸亜鉛(メタ)アクリレート、プルビン酸カルシウム(メタ)アクリレート等が挙げられる。これら金属含有重合性単量体(a1)は、1種または2種以上を必要に応じて適宜選択して使用することができるが、特に、亜鉛含有重合性単量体が好ましい。
【0008】
上記の一般式(I)において、R1は水素原子またはメチル基、MはMg、ZnまたはCaの金属を表し、R2は有機酸残基を示す。有機酸残基としては、モノクロル酢酸、モノフルオロ酢酸、プロピオン酸、オクチル酸、バーサチック酸、オレイン酸、イソステアリン酸、パルミチン酸、クレソチン酸、α−ナフトエ酸、β−ナフトエ酸、安息香酸、2,4,5−トリクロロフェノキシ酢酸、2,4−ジクロロフェノキシ酢酸、キノリンカルボン酸、ニトロ安息香酸、ニトロナフタレンカルボン酸、プルビン酸等の一価の有機酸から誘導されるものが例示される。これらの有機酸残基の中でも本発明の金属含有共重合体としては脂肪酸系のものが特に好ましく、それにより長期にわたりクラックや剥離のない塗膜を維持することができる。
【0009】
前記金属含有重合性単量体(a1)は、後述するα、β−モノエチレン性不飽和基含有重合性単量体(b)との溶解性において、無機金属化合物とカルボキシル基含有ラジカル重合性単量体の反応物と、少なくともアルコール系化合物を含む有機溶剤と、非重合性有機酸残基とからなり、無機金属化合物のモル数に対して非重合性有機酸を等モル含有する金属含有モノマー混合物として使用することが、工業生産上好ましい。これらは、必要に応じて単独であるいは2種以上を併用して使用することができる。
【0010】
本発明の金属含有共重合体に使用される金属含有重合性単量体(a)のうち、金属含有重合性単量体(a2)は2個の不飽和基を有する金属含有重合性単量体であり、例えば、ジアクリル酸マグネシウム[(CH2=CHCOO)2Mg]、ジメタクリル酸マグネシウム[(CH2=C(CH3)COO)2Mg]、ジアクリル酸亜鉛[(CH2=CHCOO)2Zn]、ジメタクリル酸亜鉛[(CH2=C(CH3)COO)2Zn]、ジアクリル酸カルシウム[(CH2=CHCOO)2Ca]、ジメタクリル酸カルシウム[(CH2=C(CH3)COO)2Ca]等を挙げることができる。これら金属含有重合性単量体(a2)は、1種または2種以上を必要に応じて適宜選択して用いることができるが、特にジ(メタ)アクリル酸亜鉛が好ましい(なお、(メタ)アクリルとは、アクリルまたはメタクリルのことを意味する。以下、同じ)。
【0011】
上記2個の不飽和基を有する金属含有重合性単量体(a2)は通常粉末であり、粉末のまま使用すると一般的な有機溶剤やアクリルモノマーと相溶性が悪く溶解しないため、重合が難しく、例えば単量体混合物を送液する配管内で析出し、重合溶液中に不溶解物が多量生成する傾向が見られる。しかしながら、金属含有重合性単量体(a2)を無機金属化合物とカルボキシル基含有ラジカル重合性単量体の反応物と、少なくともアルコール系溶剤合物を有機溶剤と、水とからなり、水の含有量が0.01〜30質量%である金属含有モノマー混合物として使用すると、上記問題が解決され工業生産上好ましい。
金属含有重合性単量体(a)として、上記の一般式()で示される金属含有重合性単量体(a1)と2個の不飽和基を有する金属含有重合性単量体(a2)とを併用することもできるが、金属含有重合性単量体同士の相溶性の観点から同種金属が好ましく、ジ(メタ)アクリル酸亜鉛と、脂肪酸系亜鉛(メタ)アクリレートの組み合わせが特に好ましい。
【0012】
本発明の金属含有共重合体に使用される金属含有重合性単量体(a)は、耐溶剤性、耐汚染性、下地との付着性及びそれによる加工性の低下を抑制するための成分であり、金属含有共重合体の単量体の総計に対して、0.1〜10質量%の範囲で用いられる。これは、金属含有重合性単量体(a)が0.1質量%以上で、塗膜の耐溶剤性、耐汚染性、加工性が良好となり、10質量%以下であると、塗膜の光沢等の美粧性が良好となるからである。より好ましくは、0.5〜5質量%の範囲である。
【0013】
本発明の金属含有共重合体に使用されるα、β−モノエチレン性不飽和基含有重合性単量体(b)は、塗膜を形成するための成分であり、金属含有共重合体の単量体の総計に対して、90〜99.9質量%の範囲で用いられる。本発明の金属含有共重合体に使用されるα、β−モノエチレン性不飽和基含有重合性単量体(b)としては、例えば、メタクリル酸、アクリル酸、クロトン酸、ビニル安息香酸、フマール酸、イタコン酸、マレイン酸、シトラコン酸等の一塩基酸または二塩基酸単量体類、マレイン酸モノメチル、マレイン酸モノエチル、マレイン酸モノブチル、マレイン酸モノオクチル、イタコン酸モノメチル、イタコン酸モノエチル、イタコン酸モノブチル、イタコン酸モノオクチル、フマル酸モノメチル、フマル酸モノエチル、フマル酸モノブチル、フマル酸モノオクチル、シトラコン酸モノエチル等に代表される二塩基酸または酸無水物単量体のモノエステル類等のカルボキシル基含有単量体を挙げられる。これらカルボキシル基含有単量体は、必要に応じて単独であるいは二種以上を併用して使用することができる。
【0014】
さらに本発明の金属含有共重合体に使用されるα、β−モノエチレン性不飽和基含有重合性単量体(b)としては(メタ)アクリル酸エステルを挙げることができ、例えば、メチル(メタ)アクリレート、エチル(メタ)アクリレート、n−プロピル(メタ)アクリレート、i−プロピル(メタ)アクリレート、n−ブチル(メタ)アクリレート、i−ブチル(メタ)アクリレート、t−ブチル(メタ)アクリレート、2−エチルヘキシル(メタ)アクリレート、デシル(メタ)アクリレート、トリデシル(メタ)アクリレート、シクロヘキシル(メタ)アクリレート、イソボルニル(メタ)アクリレート、トリフルオロエチル(メタ)アクリレート、ヘプタデカフルオロデシル(メタ)アクリレート、2−メトキシエチル(メタ)アクリレート、2−エトキシエチル(メタ)アクリレート、2−ヒドロキシエチル(メタ)アクリレート、2−ヒドロキシプロピル(メタ)アクリレート、4−ヒドロキシブチル(メタ)アクリレート、6−ヒドロキシヘキシル(メタ)アクリレート、グリシジル(メタ)アクリレート、テトラヒドロフルフリル(メタ)アクリレート、アリル(メタ)アクリレート、ジメチルアミノエチル(メタ)アクリレート、ジエチルアミノエチル(メタ)アクリレート、エチレングリコールジ(メタ)アクリレート、トリメチロールプロパントリ(メタ)アクリレート、2−ヒドロキシエチル(メタ)アクリレートとε−カプロラクトンとの開環反応生成物(例えば、ダイセル化学工業(株)製プラクセルFA及びFMシリーズ)、γ−(メタ)アクリロキシプロピルメチルジメトキシシラン、γ−(メタ)アクリロキシプロピルメチルジエトキシシラン、γ−(メタ)アクリロキシプロピルトリメトキシシラン等のシラン化合物、(メタ)アクリルアミドおよびそのメチロール化物、さらにそれらを低級アルコール化合物で変性した末端アルコキシ化メチル(メタ)アクリルアミド類、2−アクリルアミド2−メチルプロパンスルホン酸及びその金属塩やアミン塩、(メタ)アクリロニトリルが挙げられる。これら(メタ)アクリル酸エステルは、単独であるいは2種以上を併用して使用することができる。これらは共重合可能なものであれば特に限定されるものではなく、目的に応じて適宜選択することができ、溶液重合法、塊状重合法、乳化重合法等の公知の重合法により製造することができる。また、α、β−モノエチレン性不飽和基含有重合性単量体(b)の使用量は金属含有共重合体の単量体の総計に対して、85〜99.9重量%の範囲で用いられる。これは(メタ)アクリル酸エステルが、85質量%以上であると、塗膜の光沢等の美粧性が良好であり、99.9質量%以下で塗膜の耐溶剤ラビング性が良好となるためである。また、α、β−モノエチレン性不飽和基含有重合性単量体(b)が、90質量%以上で、塗膜の耐溶剤ラビング性、下地への付着性が良好であり、99.9質量%以下で、塗膜の光沢等の美粧性が良好であるためである。より好ましくは、95〜99.5質量%の範囲である。
【0015】
本発明の金属被覆用塗料に用いる金属含有共重合体は、前記の単量体(a)および(b)を特定の比率で共重合させて得られるものであり、酸価(フェノールフタレインの変色点を基準にして、共重合体溶液に、エタノールに溶解したKOHを滴下して滴定し、共重合体1gを中和するのに必要なKOHのmg数)は、0.5〜50mgKOH/g、重量平均分子量は8000〜150000、ガラス転移温度(Tg)は0〜110℃の範囲であることが好ましい。
【0016】
本発明の金属含有共重合体の酸価については0.5mgKOH/g以上であると、塗膜の金属への密着性が良好にあり、50mgKOH/g以下にてポリフッ化ビニリデンとの相溶性が良く塗膜の外観など美粧性が良好となるからである。より好ましくは、2〜30mgKOH/gの範囲である。
本発明の金属含有共重合体の重量平均分子量については8000以上であると、塗膜の硬度、耐溶剤ラビング性が良好となり、150000以下にて、ポリフッ化ビニリデンとの相溶性や塗膜の外観が良好である。より好ましくは、20000〜100000の範囲である。
本発明の金属含有共重合体のガラス転移温度(以下Tgと略記する)についてはTgが0℃以上であると、塗膜の硬度が良好で有り、110℃以下にて、折り曲げ等の加工性が良好となる。より好ましくは、30〜80℃の範囲である。金属含有共重合体のTgは、例えば金属含有重合性単量体(a)及びα、β−モノエチレン性不飽和基含有重合性単量体(b)のそれぞれのホモポリマーのTgが既知であればT.G.Foxの式から計算にて求めることができ、また、DSC(示差熱質量分析)法などにより実測することもできる。
【0017】
本発明の金属含有共重合体は単独で金属被覆用塗料として使用することができるが、耐候性、耐汚染性、耐食性等に優れていることから、ポリフッ化ビニリデンを併用することが特に好ましい。ポリフッ化ビニリデンとしては、フッ化ビニリデンのホモポリマーあるいはフッ化ビニリデンを70質量%以上含有する共重合体を使用することができ、それ以外の他の単量体としては、エチレン、塩化ビニル、テトラフルオロエチレン、ジクロロフルオロエチレン、1,1,2−トリフルオロ−2−クロロエチレン等が挙げられる。
【0018】
本発明の金属含有共重合体とポリフッ化ビニリデンの配合割合は、質量比で10/90≦(金属含有共重合体/ポリフッ化ビニリデン)≦80/20の範囲が好ましい。これは、金属含有共重合体/ポリフッ化ビニリデンが10/90以上では、形成される塗膜の基材密着性、外観、硬度等が良好であり、80/20以下では、形成される塗膜の耐候性が良好となるからである。より好ましくは、20/80≦(金属含有共重合体/ポリフッ化ビニリデン)≦70/30の範囲である。本発明の金属含有共重合体に併用されるポリフッ化ビニリデンとしては、重量平均分子量が、50000〜400000の範囲であることが好ましい。これはポリフッ化ビニリデンの重量平均分子量が50000以上であると、塗膜の耐候性が良好であり、400000以下で、塗膜の平滑性が良好であり塗膜形成が容易であるためである。より好ましくは、100000〜300000の範囲である。
【0019】
本発明の金属含有共重合体、および併用されるポリフッ化ビニリデンに対しては高沸点溶剤を主体に用いることが特に好ましく、沸点が120〜250℃程度である有機溶剤が好ましい。高沸点溶剤の具体例としては、イソホロン、キシレン、シクロヘキサノン、ソルベッソ150(エクソン化学(株)商品名;炭化水素系溶剤)、スーパーゾール1500(日石三菱(株)商品名;炭化水素系溶剤)エトキシエチルプロピオネート、酢酸n−ブチル、エチレングリコールモノブチルエーテル、エチレングリコールモノブチルエーテルアセテート、ジエチレングリコールモノブチルエーテル、ジエチレングリコールモノブチルエーテルアセテート、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル、プロピレングリコールメチルエーテルアセテート、プロピレングリコールモノブチルエーテル、プロピレングリコールブチルエーテルアセテート、ジプロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル、ジプロピレングリコールメチルエーテルアセテートあるいはこれらの混合物を挙げることができる。高沸点溶剤を使用する理由としてはポリフッ化ビニリデンを高温では溶解し、室温では微粒子状で高沸点溶剤中に分散しており、金属含有共重合体は高沸点溶剤中に溶解した状態が好ましいからである。
【0020】
本発明の金属含有共重合体を塗料化する際には、ポリエステル樹脂、ポリエーテル樹脂等の柔軟性付与材、エポキシ樹脂、ウレタン樹脂等の密着性向上剤、メラミン樹脂等の塗膜硬度向上剤、顔料、希釈剤、表面調製剤、紫外線吸収剤、光安定剤、酸化防止剤、垂れ止め剤等を必要に応じて添加することができる。
【0021】
本発明の金属含有共重合体からなる塗料は、例えば、各種基材に直接あるいはプライマー、中塗り塗料等を塗布した塗膜上に、吹き付け塗り、ローラー塗り等の方法で塗布し、180℃以上で1〜30分間焼き付けた後、冷水、空気圧送等により急冷することにより塗膜を形成することができる。
【0022】
【実施例】
以下、本発明を実施例により具体的に説明する。 例中の部および%は、全て質量基準である。
[金属含有共重合体および非金属含有共重合体の物性の定義]
加熱残分:重合体溶液0.5gをアルミ製皿に取り、少量のキシレンを加えてウオーターバス上で均一に溶解・分散し、次に熱風乾燥機で200℃×2時間乾燥し、乾燥質量から算出した。
ガードナー粘度:重合体溶液をガードナー粘度管に入れJISK5400に準じて溶液粘度を測定した。
酸価:金属含有共重合体溶液1gを中和するのに要する水酸化カリウムのmg数を測定し、酸価(mgKOH/g)とした。
重量平均分子量:ゲルパーミエーションクロマトグラフ(HLC−8020型、東ソー製)にて測定した。
【0023】
[塗膜性能の定義]
初期外観:リン酸亜鉛処理された鋼鈑上に形成させた塗膜を目視判定した。
耐汚染性:リン酸亜鉛処理された鋼鈑上に形成させた塗膜上に赤マジックインキにて2cm角の正方形になるよう描き、5分経過後直ちにn−ブタノールを染み込ませたガーゼにてよく拭き取り、拭き取り部分とそれ以外の部分とを目視比較し、全く赤マジックインキの痕跡が無い塗膜を◎、極僅かに赤マジックインキの痕跡が見られる塗膜を○、処理後僅かに赤マジックインキの痕跡が見られる塗膜を△、著しい赤マジックインキの痕跡が見られる塗膜を×とした。
耐溶剤性:リン酸亜鉛処理された鋼板上に形成させた塗膜にメチルエチルケトンをしみこませたガーゼをラビングテスター(大栄科学精機製作所(株)製)に取りつけ、荷重1kgにて300回ラビングし、この塗膜の外観を目視判定した。
耐熱黄変性:リン酸亜鉛処理された鋼板上に形成させた塗膜を沸騰水中に浸漬し5時間後取り出して、処理後に黄変のない塗膜を◎、処理後極僅かに黄変が見られる塗膜を○、処理後僅かに黄変が見られる塗膜を△、著しい黄変が見られる塗膜を×とした。
耐候性:リン酸亜鉛処理された鋼鈑上に形成させた塗膜をJISK5400に従い、サンシャインウエザオメーターにて3000時間経過後の60度光沢保持率にて比較した。
【0024】
[目視判定の基準]
◎:良好な光沢を持ち、塗膜の曇りもない場合。
○:極僅かに光沢が低く、塗膜の曇りもない場合。
△:僅かに光沢が低く、塗膜の曇りが発生している場合。
×:著しく光沢が低く、塗膜の曇りが著しい場合。
【0025】
製造例1
[金属含有共重合体(A−1)の製造]
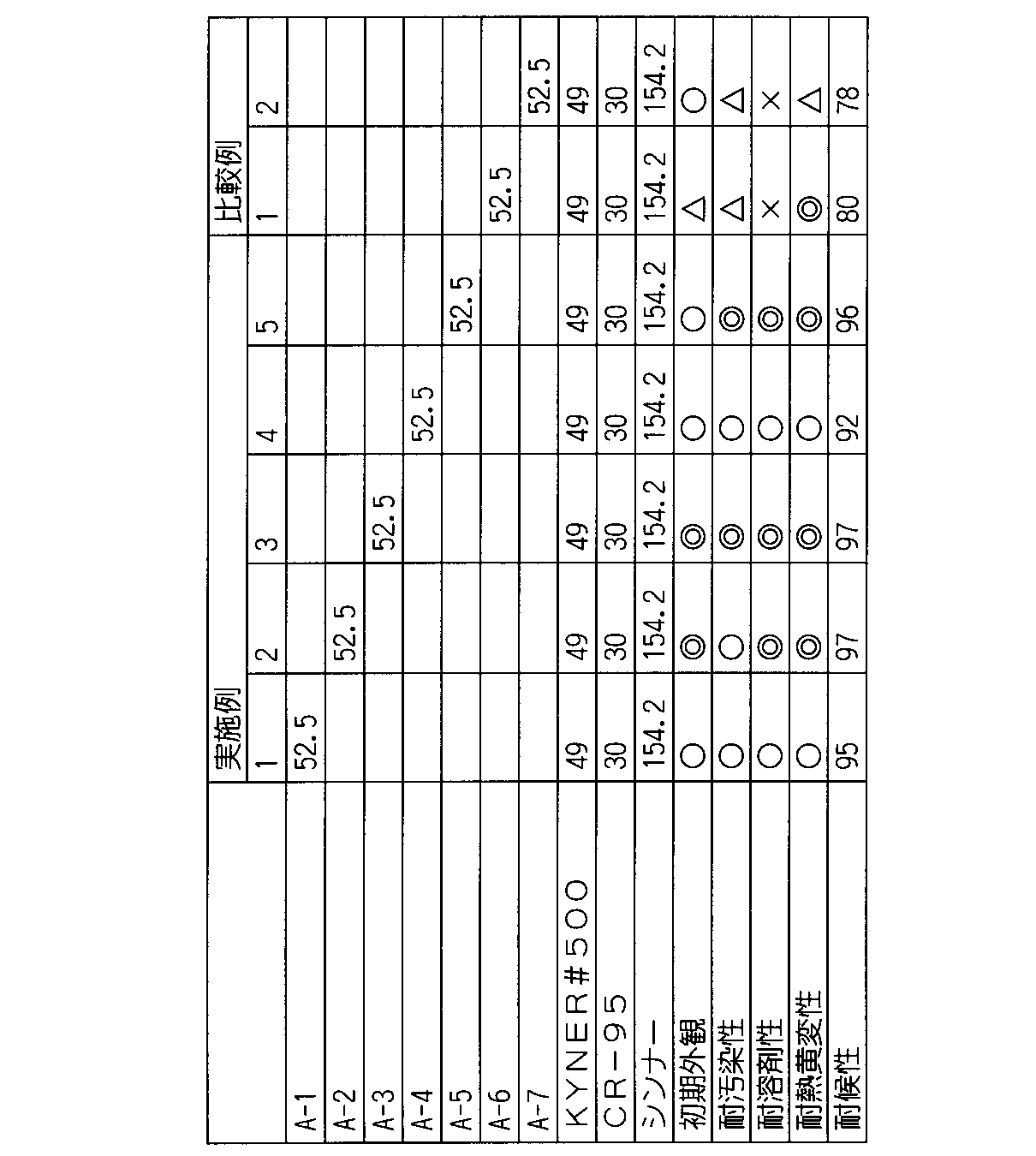
攪拌機、温度制御装置、窒素導入管、コンデンサー、滴下ロートを備えた四つ口フラスコに酢酸n−ブチル55部、キシレン45部を仕込み攪拌しながら90℃に加熱し、この温度を維持した。次に、メチルメタクリレート51部、t−ブチルメタクリレート10部、エチルアクリレート30部、オレイン酸亜鉛メタクリレート8.5部、プロピオン酸亜鉛メタクリレート0.5部、t−ブチルパーオクトエート0.8部を添加した混合物を滴下ロートから5時間かけて四つ口フラスコ中の溶液に滴下した。滴下終了後1時間後に、キシレン30部、t−ブチルパーオクトエート0.3部との混合物を2時間かけて滴下した。滴下終了後30分かけて溶液の温度を100℃に昇温した後、この状態を1時間保持した。この後、冷却しながら酢酸n−ブチル20部を添加して反応を終了させ、加熱残分が40.3%の金属含有共重合体(A−1)を得た。得られた金属含有共重合体のガードナー粘度は+V、酸価5.7mgKOH/g、重量平均分子量(Mw)は31000であった。得られた値を表1に示した。
【0026】
【表1】
【0027】
製造例2〜7
[金属含有共重合体(A−2)〜(A−6)、および非金属含有共重合体(A−7)の製造]
金属含有共重合体(A−1)の製造方法と同様な操作で表1に示す金属含有重合性単量体およびα、β−モノエチレン性不飽和基含有重合性単量体を用いてそれぞれ重合し、金属含有共重合体(A−2)〜(A−6)、および非金属含有共重合体(A−7)を得た。得られた金属含有共重合体(A−2)〜(A−6)、および非金属含有共重合体(A−7)の加熱残分およびガードナー粘度、酸価、重量平均分子量(Mw)を表1に示した。
【0028】
[実施例1〜5、比較例1〜2]
上記製造例で得た金属含有共重合体溶液および非金属含有共重合体溶液と、酸化チタン(石原産業(株)製CR−95))、KYNER#500(ペンウォルト社製、フッ化ビニリデンホモポリマー、重量平均分子量:270000)と、シンナー(キシレン/イソホロン=66.7/33.3(質量比))を表2の割合で配合し、遊星ボールミルで攪拌混合して、金属含有共重合体溶液および非金属含有共重合体溶液とポリフッ化ビニリデンの質量比が30/70であり、固形分35%である塗料組成物を得た。次いで、リン酸亜鉛処理された鋼板に塗料組成物を乾燥膜厚が40μmになるように塗装し、250℃で3分間焼き付けた後冷水で急冷して塗膜を得た。得られた塗膜の試験結果を表2に示した。
【0029】
【表2】
【0030】
本発明の金属含有共重合体を含有する塗膜は、実施例1〜5に示されているように、外観、塗膜性能に優れていた。これに対して、本発明が規定する条件を満たさない金属含有共重合体および非金属含有共重合体は、比較例1〜2に示されているように、塗膜の外観、塗膜性能等の点で満足な特性を示さなかった。
【0031】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように、本発明の金属含有共重合体を含有した塗膜は、長期にわたって光沢を保持し、かつ耐汚染性、耐溶剤性、耐熱黄変性といった塗膜性能に優れ、工業上非常に有益なものである。[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a metal-containing copolymer used for a coating material such as a paint, and more specifically, it retains gloss over a long period of time and has a coating performance such as contamination resistance, solvent resistance, and heat yellowing resistance. The present invention relates to a metal-containing copolymer that can provide an excellent coating film and is particularly useful as a coating material for metal coating.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Pre-coated metal is used for roofing materials, wall materials, air conditioner outdoor units, etc., and since it is subjected to processing such as bending with a coating film formed in advance, the coating film retains gloss and workability for a long period of time. The required properties are required, and the requirements are becoming stricter year by year.
Polyvinylidene fluoride is widely used for metal coatings used for pre-coated metal because of its excellent weather resistance, stain resistance, corrosion resistance, etc., but adhesion to the base material, appearance, hardness, etc. Therefore, it is rarely used alone. For example, as described in Japanese Examined Patent Publication No. 43-10363, adhesion to a base material is improved by a method such as blending polyvinylidene fluoride with an acrylic copolymer. For example, a dispersion of a fine powder of polyvinylidene fluoride in a high boiling point solvent in which an acrylic copolymer is dissolved is used. Japanese Patent Publication No. 58-32183 includes an N-alkoxyalkylamide group-containing thermosetting polymer and a thermoplastic acrylic copolymer in order to improve the coating performance such as solvent resistance and flexibility. A resin composition blended with polyvinylidene fluoride is disclosed.
[0003]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, when the coating film disclosed in Japanese Patent Publication No. 43-10363 is exposed to a high temperature for a long time such as outdoor exposure, the phase separation between the polyvinylidene fluoride and the acrylic copolymer proceeds. Since the gloss of the film is lost and the elongation of the coating film is reduced, the coating film that has been subjected to processing such as bending in advance has a problem that peeling or cracking is likely to occur. In addition, the coating film disclosed in Japanese Patent Publication No. 58-32183 is a so-called high temperature that raises the baking temperature and shortens the baking time by increasing the temperature in the baking furnace during film formation and improving the line speed. Since baking is performed for a short time, there is a problem of heat-resistant yellowing that yellowing is likely to occur due to high heat. In addition, Japanese Patent Laid-Open Nos. H5-171066 and H10-158547 disclose antifouling paint compositions using metal-containing copolymers, but they are not used for precoated metals. .
[0004]
The present invention has been made in order to solve the above-mentioned problems, and uses a paint characterized by containing a metal-containing copolymer. The object is to provide a coating film excellent in coating film performance such as modification.
[0005]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In view of the above-mentioned problems of the prior art, the present inventors have conducted extensive studies on the copolymer used in the coating material for metal coating. As a result, the metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a) is 0.1 to 10% by mass and (A) Using a metal-containing copolymer obtained by copolymerizing an α, β-monoethylenically unsaturated group-containing polymerizable monomer (b) 90 to 99.9% by mass, which is copolymerizable with the component, It has been found that it is possible to maintain gloss and provide an excellent coating film.
Specifically, the metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a) includes a metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a) represented by the following (I): 1 ) Or a metal-containing polymerizable monomer having two unsaturated groups (a 2 ) Or the metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a) represented by the following (I) 1 ) And the metal-containing polymerizable monomer having two unsaturated groups (a 2 ).
[Chemical 3]
(Wherein R 1 Is a hydrogen atom or a methyl group, M is Mg, Zn or Ca, R 2 Represents an organic acid residue)
[0006]
The coating material of the present invention is characterized by containing the above metal-containing copolymer, and is particularly suitable for a coating material containing polyvinylidene fluoride.
[0007]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The metal-containing copolymer of the present invention has a metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a) of 0.1 to 10% by mass and an α, β-monoethylenically unsaturated group-containing polymerizability copolymerizable with the component (a). It is obtained by copolymerizing 90 to 99.9% by mass of the monomer (b).
The metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a) used in the metal-containing copolymer of the present invention is a metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a 1 And / or (a 2 ) Is desirable. Metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a 1 ) Is represented by the above general formula (I). Specific examples of the compound represented by the general formula (I) include monochloromagnesium acetate (meth) acrylate ((meth) acrylate means acrylate or methacrylate; the same shall apply hereinafter), monochlorozinc acetate (meta ) Acrylate, monochloro calcium acetate (meth) acrylate, magnesium monofluoroacetate (meth) acrylate, zinc monofluoroacetate (meth) acrylate, calcium monofluoroacetate (meth) acrylate, magnesium propionate (meth) acrylate, zinc propionate ( (Meth) acrylate, calcium propionate (meth) acrylate, magnesium octylate (meth) acrylate, zinc octylate (meth) acrylate, calcium octylate (meth) acrylate, versa Magnesium oxalate (meth) acrylate, zinc versatate (meth) acrylate, calcium versatate (meth) acrylate, magnesium oleate (meth) acrylate, zinc oleate (meth) acrylate, calcium oleate (meth) acrylate, isostearin Magnesium (meth) acrylate, zinc isostearate (meth) acrylate, calcium isostearate (meth) acrylate, magnesium palmitate (meth) acrylate, zinc palmitate (meth) acrylate, calcium palmitate (meth) acrylate, magnesium cresotate (Meth) acrylate, zinc cresotate (meth) acrylate, calcium cresotate (meth) acrylate, α-naphthoic acid magnesi Um (meth) acrylate, α-naphthoic acid zinc (meth) acrylate, α-calcium naphthoic acid (meth) acrylate, β-naphthoic acid magnesium (meth) acrylate, β-naphthoic acid zinc (meth) acrylate, β-naphthoic acid Calcium (meth) acrylate, magnesium benzoate (meth) acrylate, zinc benzoate (meth) acrylate, calcium benzoate (meth) acrylate, 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxymagnesium acetate (meth) acrylate, 2,4,5 -Zinc trichlorophenoxyacetate (meth) acrylate, 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetate calcium (meth) acrylate, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate magnesium (meth) acrylate, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate zinc (meth) acrylate Chryrate, calcium 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate (meth) acrylate, magnesium quinolinecarboxylate (meth) acrylate, zinc quinolinecarboxylate (meth) acrylate, calcium quinolinecarboxylate (meth) acrylate, magnesium nitrobenzoate (meth) acrylate , Zinc nitrobenzoate (meth) acrylate, calcium nitrobenzoate (meth) acrylate, magnesium nitronaphthalenecarboxylate (meth) acrylate, zinc nitronaphthalenecarboxylate (meth) acrylate, calcium nitronaphthalenecarboxylate (meth) acrylate, purvin Examples include magnesium oxide (meth) acrylate, zinc puruvate (meth) acrylate, and calcium (meth) acrylate puruvate. These metal-containing polymerizable monomers (a 1 1) or 2 or more types can be appropriately selected and used as necessary, and a zinc-containing polymerizable monomer is particularly preferable.
[0008]
In the above general formula (I), R 1 Represents a hydrogen atom or a methyl group, M represents a metal of Mg, Zn or Ca, R 2 Represents an organic acid residue. Examples of organic acid residues include monochloroacetic acid, monofluoroacetic acid, propionic acid, octylic acid, versatic acid, oleic acid, isostearic acid, palmitic acid, cresotic acid, α-naphthoic acid, β-naphthoic acid, benzoic acid, 2, Examples thereof include those derived from monovalent organic acids such as 4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, quinolinecarboxylic acid, nitrobenzoic acid, nitronaphthalenecarboxylic acid, and puruvic acid. Among these organic acid residues, fatty acid-based copolymers are particularly preferable as the metal-containing copolymer of the present invention, whereby a coating film free from cracks or peeling can be maintained over a long period of time.
[0009]
The metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a 1 ) Is a solubility of an α, β-monoethylenically unsaturated group-containing polymerizable monomer (b) described later, and a reaction product of an inorganic metal compound and a carboxyl group-containing radical polymerizable monomer, and at least an alcohol. An industrial production comprising a metal-containing monomer mixture comprising an organic solvent containing an organic compound and a non-polymerizable organic acid residue, and containing an equimolar amount of the non-polymerizable organic acid relative to the number of moles of the inorganic metal compound Above preferred. These may be used alone or in combination of two or more as required.
[0010]
Of the metal-containing polymerizable monomers (a) used in the metal-containing copolymer of the present invention, a metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a 2 ) Is a metal-containing polymerizable monomer having two unsaturated groups, for example, magnesium diacrylate [(CH 2 = CHCOO) 2 Mg], magnesium dimethacrylate [(CH 2 = C (CH Three ) COO) 2 Mg], zinc diacrylate [(CH 2 = CHCOO) 2 Zn], zinc dimethacrylate [(CH 2 = C (CH Three ) COO) 2 Zn], calcium diacrylate [(CH 2 = CHCOO) 2 Ca], calcium dimethacrylate [(CH 2 = C (CH Three ) COO) 2 Ca] and the like. These metal-containing polymerizable monomers (a 2 ) Can be used by appropriately selecting one or two or more kinds as required, and particularly preferred is zinc di (meth) acrylate (note that (meth) acryl is acrylic or methacrylic). Means the same).
[0011]
Metal-containing polymerizable monomer having two unsaturated groups (a 2 ) Is usually a powder, and if used as a powder, it is not compatible with common organic solvents and acrylic monomers and does not dissolve, making it difficult to polymerize, for example, depositing in a pipe that feeds the monomer mixture, resulting in a polymerization solution There is a tendency to produce a large amount of insoluble matter. However, the metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a 2 ) Comprising a reaction product of an inorganic metal compound and a carboxyl group-containing radical polymerizable monomer, and at least an alcohol solvent mixture comprising an organic solvent and water, and the water content is 0.01 to 30% by mass. When used as a metal-containing monomer mixture, the above problems are solved, which is preferable for industrial production.
As the metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a), the metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a) represented by the above general formula () 1 ) And two metal-containing polymerizable monomers having two unsaturated groups (a 2 ) May be used in combination, but the same metal is preferable from the viewpoint of the compatibility between the metal-containing polymerizable monomers, and a combination of zinc di (meth) acrylate and zinc fatty acid (meth) acrylate is particularly preferable. .
[0012]
The metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a) used in the metal-containing copolymer of the present invention is a component for suppressing solvent resistance, contamination resistance, adhesion to the base and processability deterioration thereby. It is used in the range of 0.1 to 10% by mass with respect to the total amount of monomers of the metal-containing copolymer. This is because when the metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a) is 0.1% by mass or more, the solvent resistance, stain resistance and processability of the coating film are good, and when it is 10% by mass or less, This is because cosmetic properties such as gloss are improved. More preferably, it is the range of 0.5-5 mass%.
[0013]
The α, β-monoethylenically unsaturated group-containing polymerizable monomer (b) used in the metal-containing copolymer of the present invention is a component for forming a coating film, It is used in the range of 90 to 99.9% by mass with respect to the total amount of monomers. Examples of the α, β-monoethylenically unsaturated group-containing polymerizable monomer (b) used in the metal-containing copolymer of the present invention include methacrylic acid, acrylic acid, crotonic acid, vinyl benzoic acid, and fumar. Monobasic acid or dibasic acid monomers such as acid, itaconic acid, maleic acid, citraconic acid, monomethyl maleate, monoethyl maleate, monobutyl maleate, monooctyl maleate, monomethyl itaconate, monoethyl itaconate, itacone Carboxyl such as monoesters of dibasic acids or acid anhydride monomers represented by monobutyl acid, monooctyl itaconate, monomethyl fumarate, monoethyl fumarate, monobutyl fumarate, monooctyl fumarate, monoethyl citraconic acid, etc. And group-containing monomers. These carboxyl group-containing monomers can be used alone or in combination of two or more as required.
[0014]
Furthermore, (alpha), (beta) -monoethylenically unsaturated group containing polymerizable monomer (b) used for the metal containing copolymer of this invention can mention (meth) acrylic acid ester, for example, methyl ( (Meth) acrylate, ethyl (meth) acrylate, n-propyl (meth) acrylate, i-propyl (meth) acrylate, n-butyl (meth) acrylate, i-butyl (meth) acrylate, t-butyl (meth) acrylate, 2-ethylhexyl (meth) acrylate, decyl (meth) acrylate, tridecyl (meth) acrylate, cyclohexyl (meth) acrylate, isobornyl (meth) acrylate, trifluoroethyl (meth) acrylate, heptadecafluorodecyl (meth) acrylate, 2 -Methoxyethyl (meth) acrylate 2-ethoxyethyl (meth) acrylate, 2-hydroxyethyl (meth) acrylate, 2-hydroxypropyl (meth) acrylate, 4-hydroxybutyl (meth) acrylate, 6-hydroxyhexyl (meth) acrylate, glycidyl (meta ) Acrylate, tetrahydrofurfuryl (meth) acrylate, allyl (meth) acrylate, dimethylaminoethyl (meth) acrylate, diethylaminoethyl (meth) acrylate, ethylene glycol di (meth) acrylate, trimethylolpropane tri (meth) acrylate, 2 -Ring-opening reaction product of hydroxyethyl (meth) acrylate and ε-caprolactone (for example, Plaxel FA and FM series manufactured by Daicel Chemical Industries, Ltd.), γ- (meth) acryloxypro Silane compounds such as pyrmethyldimethoxysilane, γ- (meth) acryloxypropylmethyldiethoxysilane, γ- (meth) acryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane, (meth) acrylamide and methylolated products thereof, and further lower alcohol compounds. Examples thereof include modified terminal alkoxylated methyl (meth) acrylamides, 2-acrylamido 2-methylpropanesulfonic acid, metal salts and amine salts thereof, and (meth) acrylonitrile. These (meth) acrylic acid esters can be used alone or in combination of two or more. These are not particularly limited as long as they are copolymerizable, and can be appropriately selected according to the purpose, and can be produced by a known polymerization method such as a solution polymerization method, a bulk polymerization method, an emulsion polymerization method, or the like. Can do. The amount of the α, β-monoethylenically unsaturated group-containing polymerizable monomer (b) used is in the range of 85 to 99.9% by weight based on the total amount of monomers of the metal-containing copolymer. Used. If the (meth) acrylic acid ester is 85% by mass or more, the cosmetic properties such as gloss of the coating film are good, and if it is 99.9% by mass or less, the solvent rubbing resistance of the coating film is good. It is. Further, the α, β-monoethylenically unsaturated group-containing polymerizable monomer (b) is 90% by mass or more, the solvent rubbing resistance of the coating film and the adhesion to the base are good, and 99.9 This is because the cosmetic properties such as gloss of the coating film are good at a mass% or less. More preferably, it is the range of 95-99.5 mass%.
[0015]
The metal-containing copolymer used in the coating material for metal coating according to the present invention is obtained by copolymerizing the monomers (a) and (b) at a specific ratio, and has an acid value (of phenolphthalein). Based on the color change point, KOH dissolved in ethanol was added dropwise to the copolymer solution and titrated, and the number of mg of KOH required to neutralize 1 g of the copolymer) was 0.5 to 50 mg KOH / g, weight average molecular weight is preferably 8000 to 150,000, and glass transition temperature (Tg) is preferably in the range of 0 to 110 ° C.
[0016]
When the acid value of the metal-containing copolymer of the present invention is 0.5 mgKOH / g or more, the adhesion of the coating film to the metal is good, and the compatibility with polyvinylidene fluoride is 50 mgKOH / g or less. This is because the cosmetic properties such as the appearance of the coating film are good. More preferably, it is the range of 2-30 mgKOH / g.
When the weight average molecular weight of the metal-containing copolymer of the present invention is 8000 or more, the hardness of the coating film and the solvent rubbing resistance are good. When the weight average molecular weight is 150,000 or less, the compatibility with polyvinylidene fluoride and the appearance of the coating film are obtained. Is good. More preferably, it is the range of 20000-100,000.
Regarding the glass transition temperature (hereinafter abbreviated as Tg) of the metal-containing copolymer of the present invention, if the Tg is 0 ° C. or higher, the hardness of the coating film is good. Becomes better. More preferably, it is the range of 30-80 degreeC. The Tg of the metal-containing copolymer is, for example, the Tg of each homopolymer of the metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a) and the α, β-monoethylenically unsaturated group-containing polymerizable monomer (b). If there is T. G. It can be obtained by calculation from the Fox equation, and can also be measured by DSC (differential thermal mass spectrometry) method or the like.
[0017]
The metal-containing copolymer of the present invention can be used alone as a coating material for metal coating, but it is particularly preferable to use polyvinylidene fluoride in combination because of excellent weather resistance, stain resistance, corrosion resistance and the like. As the polyvinylidene fluoride, a homopolymer of vinylidene fluoride or a copolymer containing 70% by mass or more of vinylidene fluoride can be used, and other monomers include ethylene, vinyl chloride, tetra Examples include fluoroethylene, dichlorofluoroethylene, 1,1,2-trifluoro-2-chloroethylene, and the like.
[0018]
The blending ratio of the metal-containing copolymer of the present invention to polyvinylidene fluoride is preferably in the range of 10/90 ≦ (metal-containing copolymer / polyvinylidene fluoride) ≦ 80/20 by mass ratio. This is because when the metal-containing copolymer / polyvinylidene fluoride is 10/90 or more, the substrate adhesion, appearance, hardness, etc. of the formed coating film are good, and when it is 80/20 or less, the coating film is formed. This is because the weather resistance of the is improved. More preferably, the range is 20/80 ≦ (metal-containing copolymer / polyvinylidene fluoride) ≦ 70/30. The polyvinylidene fluoride used in combination with the metal-containing copolymer of the present invention preferably has a weight average molecular weight in the range of 50,000 to 400,000. This is because when the weight average molecular weight of polyvinylidene fluoride is 50000 or more, the weather resistance of the coating film is good, and when it is 400000 or less, the smoothness of the coating film is good and the coating film can be easily formed. More preferably, it is the range of 100,000-300000.
[0019]
For the metal-containing copolymer of the present invention and the polyvinylidene fluoride used in combination, it is particularly preferable to use a high-boiling solvent mainly, and an organic solvent having a boiling point of about 120 to 250 ° C. is preferable. Specific examples of the high boiling point solvent include isophorone, xylene, cyclohexanone, Solvesso 150 (trade name of Exxon Chemical Co., Ltd .; hydrocarbon solvent), Supersol 1500 (trade name of Mitsubishi Oil Corporation, hydrocarbon solvent) Ethoxyethyl propionate, n-butyl acetate, ethylene glycol monobutyl ether, ethylene glycol monobutyl ether acetate, diethylene glycol monobutyl ether, diethylene glycol monobutyl ether acetate, propylene glycol monomethyl ether, propylene glycol methyl ether acetate, propylene glycol monobutyl ether, propylene glycol butyl ether Acetate, dipropylene glycol monomethyl ether, dipropylene glycol methyl ether Tate or can mixtures thereof. The reason for using a high-boiling solvent is that polyvinylidene fluoride is dissolved at a high temperature, is finely dispersed at room temperature in a high-boiling solvent, and the metal-containing copolymer is preferably dissolved in the high-boiling solvent. It is.
[0020]
When coating the metal-containing copolymer of the present invention, flexibility imparting materials such as polyester resins and polyether resins, adhesion improvers such as epoxy resins and urethane resins, and coating film hardness improvers such as melamine resins , Pigments, diluents, surface preparation agents, ultraviolet absorbers, light stabilizers, antioxidants, anti-sagging agents and the like can be added as necessary.
[0021]
The coating material comprising the metal-containing copolymer of the present invention is applied, for example, by spray coating, roller coating, or the like directly on various substrates or on a coating film on which a primer, intermediate coating or the like is applied, and is 180 ° C. or higher. After baking for 1 to 30 minutes, the coating film can be formed by quenching with cold water, pneumatic feeding or the like.
[0022]
【Example】
Hereinafter, the present invention will be specifically described by way of examples. All parts and percentages in the examples are based on mass.
[Definition of physical properties of metal-containing copolymer and non-metal-containing copolymer]
Residue on heating: 0.5 g of the polymer solution is placed in an aluminum dish, a small amount of xylene is added, and the mixture is uniformly dissolved and dispersed on a water bath, then dried in a hot air dryer at 200 ° C. for 2 hours, and the dry mass Calculated from
Gardner viscosity: The polymer solution was put into a Gardner viscosity tube, and the solution viscosity was measured according to JISK5400.
Acid value: The number of mg of potassium hydroxide required to neutralize 1 g of the metal-containing copolymer solution was measured and used as the acid value (mgKOH / g).
Weight average molecular weight: Measured with a gel permeation chromatograph (HLC-8020, manufactured by Tosoh Corporation).
[0023]
[Definition of coating film performance]
Initial appearance: The coating film formed on the steel plate treated with zinc phosphate was visually judged.
Contamination resistance: Draw a 2 cm square with red magic ink on a coating film formed on a zinc phosphate-treated steel plate. After 5 minutes, immediately with a gauze soaked with n-butanol. Wipe well, visually compare the wiped area with the other areas, ◎ for the film without any red magic ink traces, ○ for the film with very slight red magic ink traces, slightly red after processing A coating film in which a trace of magic ink was seen was indicated by Δ, and a coating film in which a marked trace of red magic ink was seen was marked by x.
Solvent resistance: Gauze with methyl ethyl ketone soaked in a coating film formed on a zinc phosphate-treated steel plate was attached to a rubbing tester (manufactured by Daiei Kagaku Seisakusho Co., Ltd.) and rubbed 300 times with a load of 1 kg. The appearance of this coating film was visually determined.
Heat-resistant yellowing: A coating formed on a zinc phosphate-treated steel plate is immersed in boiling water and taken out after 5 hours. The coating film to be obtained was marked with ◯, the coating film with slight yellowing after treatment was marked with Δ, and the coating film with marked yellowing was marked with ×.
Weather resistance: The coating film formed on the steel plate treated with zinc phosphate was compared in accordance with JISK5400 with 60 degree gloss retention after 3000 hours with a sunshine weatherometer.
[0024]
[Standard for visual judgment]
(Double-circle): It has favorable gloss and there is no cloudiness of a coating film.
○: When the gloss is slightly low and the coating film is not cloudy.
Δ: When the gloss is slightly low and the coating film is cloudy.
X: When gloss is remarkably low and cloudiness of a coating film is remarkable.
[0025]
Production Example 1
[Production of metal-containing copolymer (A-1)]
A four-necked flask equipped with a stirrer, a temperature controller, a nitrogen inlet tube, a condenser, and a dropping funnel was charged with 55 parts of n-butyl acetate and 45 parts of xylene and heated to 90 ° C. while stirring to maintain this temperature. Next, 51 parts of methyl methacrylate, 10 parts of t-butyl methacrylate, 30 parts of ethyl acrylate, 8.5 parts of zinc oleate, 0.5 parts of zinc propionate, and 0.8 parts of t-butyl peroctoate are added. The resulting mixture was added dropwise from the dropping funnel to the solution in the four-necked flask over 5 hours. One hour after the completion of dropping, a mixture of 30 parts of xylene and 0.3 part of t-butyl peroctoate was dropped over 2 hours. After the completion of dropping, the temperature of the solution was raised to 100 ° C. over 30 minutes, and this state was maintained for 1 hour. Thereafter, 20 parts of n-butyl acetate was added while cooling to terminate the reaction, and a metal-containing copolymer (A-1) having a heating residue of 40.3% was obtained. The obtained metal-containing copolymer had a Gardner viscosity of + V, an acid value of 5.7 mgKOH / g, and a weight average molecular weight (Mw) of 31,000. The obtained values are shown in Table 1.
[0026]
[Table 1]
[0027]
Production Examples 2-7
[Production of metal-containing copolymers (A-2) to (A-6) and non-metal-containing copolymers (A-7)]
Using the metal-containing polymerizable monomer and the α, β-monoethylenically unsaturated group-containing polymerizable monomer shown in Table 1 in the same manner as in the method for producing the metal-containing copolymer (A-1), respectively. Polymerization was performed to obtain metal-containing copolymers (A-2) to (A-6) and a non-metal-containing copolymer (A-7). The heating residue and Gardner viscosity, acid value, and weight average molecular weight (Mw) of the obtained metal-containing copolymers (A-2) to (A-6) and nonmetal-containing copolymer (A-7) It is shown in Table 1.
[0028]
[Examples 1-5, Comparative Examples 1-2]
Metal-containing copolymer solution and non-metal-containing copolymer solution obtained in the above production example, titanium oxide (CR-95 manufactured by Ishihara Sangyo Co., Ltd.), KYNER # 500 (manufactured by Penwald, vinylidene fluoride homo) Polymer, weight average molecular weight: 270000) and thinner (xylene / isophorone = 66.7 / 33.3 (mass ratio)) are blended in the ratios shown in Table 2, and stirred and mixed with a planetary ball mill to obtain a metal-containing copolymer. A coating composition having a mass ratio of the solution and the non-metal-containing copolymer solution to polyvinylidene fluoride of 30/70 and a solid content of 35% was obtained. Next, the coating composition was applied to a steel sheet treated with zinc phosphate so that the dry film thickness was 40 μm, baked at 250 ° C. for 3 minutes, and then rapidly cooled with cold water to obtain a coating film. The test results of the obtained coating film are shown in Table 2.
[0029]
[Table 2]
[0030]
As shown in Examples 1 to 5, the coating film containing the metal-containing copolymer of the present invention was excellent in appearance and coating film performance. On the other hand, the metal-containing copolymer and the non-metal-containing copolymer that do not satisfy the conditions specified by the present invention are, as shown in Comparative Examples 1 and 2, the appearance of the coating film, the coating film performance, etc. However, satisfactory characteristics were not exhibited.
[0031]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, the coating film containing the metal-containing copolymer of the present invention retains gloss over a long period of time and has excellent coating performance such as contamination resistance, solvent resistance, and heat-resistant yellowing, and is extremely industrially It is useful for.
Claims (1)
ポリフッ化ビニリデンとを含有することを特徴とする塗料。 0.1 to 10% by mass of a metal-containing polymerizable monomer (a) composed of a fatty acid zinc (meth) acrylate and / or zinc di (meth) acrylate and α and β copolymerizable with the component (a) A metal-containing copolymer obtained by copolymerization of 90 to 99.9% by mass of a monoethylenically unsaturated group-containing polymerizable monomer (b) ,
A paint comprising polyvinylidene fluoride.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001152824A JP4758564B2 (en) | 2001-05-22 | 2001-05-22 | paint |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001152824A JP4758564B2 (en) | 2001-05-22 | 2001-05-22 | paint |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2002338632A JP2002338632A (en) | 2002-11-27 |
| JP4758564B2 true JP4758564B2 (en) | 2011-08-31 |
Family
ID=18997439
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001152824A Expired - Fee Related JP4758564B2 (en) | 2001-05-22 | 2001-05-22 | paint |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4758564B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4522656B2 (en) * | 2003-01-20 | 2010-08-11 | 三菱レイヨン株式会社 | Water-based low-contamination coating material |
| JP4564236B2 (en) * | 2003-03-13 | 2010-10-20 | 三菱レイヨン株式会社 | Water-based low-contamination coating material |
| JP4522659B2 (en) * | 2003-03-13 | 2010-08-11 | 三菱レイヨン株式会社 | Water-based low-contamination coating material |
| JP5424575B2 (en) * | 2008-04-17 | 2014-02-26 | 三菱レイヨン株式会社 | Coating composition and copolymer |
| JP5513451B2 (en) * | 2010-08-13 | 2014-06-04 | ローム アンド ハース カンパニー | Aqueous coating composition |
| US9139741B2 (en) * | 2010-11-25 | 2015-09-22 | Mitsubishi Rayon Co., Ltd. | Antifouling paint composition and antifouling paint |
| JP6365812B2 (en) * | 2013-09-25 | 2018-08-01 | 三菱ケミカル株式会社 | Fluorine resin composition and film |
| CN116925602B (en) * | 2023-03-01 | 2024-03-26 | 格林斯达(北京)环保科技股份有限公司 | Modified ETFE powder coating resistant to chemical medium permeation and electrostatic spraying process thereof |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH02174977A (en) * | 1988-12-28 | 1990-07-06 | Nippon Oil & Fats Co Ltd | Formation of coating film on coated metallic sheet |
| JPH10168350A (en) * | 1996-12-10 | 1998-06-23 | Mitsubishi Rayon Co Ltd | Antifouling paint composition |
| JP2000351815A (en) * | 1999-06-09 | 2000-12-19 | Nippon Shokubai Co Ltd | Crosslinked vinyl polymer, preparation thereof and damping material |
-
2001
- 2001-05-22 JP JP2001152824A patent/JP4758564B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2002338632A (en) | 2002-11-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3779375B2 (en) | Latex binders and paints without volatile flocculants and freeze-thaw additives | |
| US9574105B2 (en) | Coating composition comprising autoxidisable component | |
| CN102089458B (en) | Aqueous metal-surface-treating agent and surface-treated metal material | |
| CN1303151C (en) | Aqueous copolymer composition and method for preparing a coating therefrom | |
| CN108727530A (en) | High acid value carboxy acrylic matting resin and epoxy polyester type powdery paints containing it | |
| JP4758564B2 (en) | paint | |
| EP2271678B1 (en) | Coating composition comprising autoxidisable component | |
| JPH08120214A (en) | Thermosetting coating composition | |
| JP2649559B2 (en) | Non-aqueous dispersion type resin composition | |
| JPH0853598A (en) | Water-dispersible acrylic graft copolymer,its production andwater-based coating material | |
| EP2271679A1 (en) | Coating composition comprising autoxidisable component | |
| JP4818533B2 (en) | Thermosetting coating composition and paint | |
| JP2000080324A (en) | Resin composition for coating | |
| JP7706912B2 (en) | Coatings and paint compositions | |
| JP3279773B2 (en) | Room temperature crosslinkable resin composition and method for producing the same | |
| JPS629264B2 (en) | ||
| JP2001254020A (en) | Non-aqueous dispersion type resin composition and use thereof | |
| JPH05214290A (en) | Resin composition for water-base coating material | |
| JPS6197367A (en) | Solvent-borne coating composition | |
| JPS627956B2 (en) | ||
| JPS62138513A (en) | Method for producing non-aqueous dispersion resin composition | |
| JP3629579B2 (en) | Resin composition for powder coating | |
| JP4351856B2 (en) | Coating composition and method for producing the same | |
| CN119306875A (en) | A hydroxy acrylic resin and its preparation method, coating and coating | |
| JPS6220229B2 (en) |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20080513 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20101104 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20101109 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20101227 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20110524 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20110603 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140610 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140610 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140610 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |