JP4751908B2 - 能動ディスプレイ装置におけるミキシング型ピクセル駆動方法 - Google Patents
能動ディスプレイ装置におけるミキシング型ピクセル駆動方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4751908B2 JP4751908B2 JP2008079745A JP2008079745A JP4751908B2 JP 4751908 B2 JP4751908 B2 JP 4751908B2 JP 2008079745 A JP2008079745 A JP 2008079745A JP 2008079745 A JP2008079745 A JP 2008079745A JP 4751908 B2 JP4751908 B2 JP 4751908B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- light emission
- digital data
- intensity
- driving method
- light
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 46
- 238000013507 mapping Methods 0.000 claims description 19
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 7
- 101150099000 EXPA1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 102100029095 Exportin-1 Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 101100119348 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) EXP1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 101100269618 Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 4 (strain ATCC BAA-334 / TIGR4) aliA gene Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 108700002148 exportin 1 Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 229920001621 AMOLED Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 102000018252 Tumor Protein p73 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010091356 Tumor Protein p73 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09G—ARRANGEMENTS OR CIRCUITS FOR CONTROL OF INDICATING DEVICES USING STATIC MEANS TO PRESENT VARIABLE INFORMATION
- G09G3/00—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes
- G09G3/20—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09G—ARRANGEMENTS OR CIRCUITS FOR CONTROL OF INDICATING DEVICES USING STATIC MEANS TO PRESENT VARIABLE INFORMATION
- G09G3/00—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes
- G09G3/20—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters
- G09G3/2007—Display of intermediate tones
- G09G3/2077—Display of intermediate tones by a combination of two or more gradation control methods
- G09G3/2081—Display of intermediate tones by a combination of two or more gradation control methods with combination of amplitude modulation and time modulation
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09G—ARRANGEMENTS OR CIRCUITS FOR CONTROL OF INDICATING DEVICES USING STATIC MEANS TO PRESENT VARIABLE INFORMATION
- G09G3/00—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes
- G09G3/20—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters
- G09G3/22—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters using controlled light sources
- G09G3/30—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters using controlled light sources using electroluminescent panels
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09G—ARRANGEMENTS OR CIRCUITS FOR CONTROL OF INDICATING DEVICES USING STATIC MEANS TO PRESENT VARIABLE INFORMATION
- G09G3/00—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes
- G09G3/20—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters
- G09G3/22—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters using controlled light sources
- G09G3/30—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters using controlled light sources using electroluminescent panels
- G09G3/32—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters using controlled light sources using electroluminescent panels semiconductive, e.g. using light-emitting diodes [LED]
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09G—ARRANGEMENTS OR CIRCUITS FOR CONTROL OF INDICATING DEVICES USING STATIC MEANS TO PRESENT VARIABLE INFORMATION
- G09G3/00—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes
- G09G3/20—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters
- G09G3/22—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters using controlled light sources
- G09G3/30—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters using controlled light sources using electroluminescent panels
- G09G3/32—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters using controlled light sources using electroluminescent panels semiconductive, e.g. using light-emitting diodes [LED]
- G09G3/3208—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters using controlled light sources using electroluminescent panels semiconductive, e.g. using light-emitting diodes [LED] organic, e.g. using organic light-emitting diodes [OLED]
- G09G3/3225—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters using controlled light sources using electroluminescent panels semiconductive, e.g. using light-emitting diodes [LED] organic, e.g. using organic light-emitting diodes [OLED] using an active matrix
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09G—ARRANGEMENTS OR CIRCUITS FOR CONTROL OF INDICATING DEVICES USING STATIC MEANS TO PRESENT VARIABLE INFORMATION
- G09G3/00—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes
- G09G3/20—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters
- G09G3/34—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters by control of light from an independent source
- G09G3/36—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters by control of light from an independent source using liquid crystals
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09G—ARRANGEMENTS OR CIRCUITS FOR CONTROL OF INDICATING DEVICES USING STATIC MEANS TO PRESENT VARIABLE INFORMATION
- G09G2300/00—Aspects of the constitution of display devices
- G09G2300/08—Active matrix structure, i.e. with use of active elements, inclusive of non-linear two terminal elements, in the pixels together with light emitting or modulating elements
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09G—ARRANGEMENTS OR CIRCUITS FOR CONTROL OF INDICATING DEVICES USING STATIC MEANS TO PRESENT VARIABLE INFORMATION
- G09G2330/00—Aspects of power supply; Aspects of display protection and defect management
- G09G2330/02—Details of power systems and of start or stop of display operation
- G09G2330/021—Power management, e.g. power saving
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09G—ARRANGEMENTS OR CIRCUITS FOR CONTROL OF INDICATING DEVICES USING STATIC MEANS TO PRESENT VARIABLE INFORMATION
- G09G2340/00—Aspects of display data processing
- G09G2340/04—Changes in size, position or resolution of an image
- G09G2340/0407—Resolution change, inclusive of the use of different resolutions for different screen areas
- G09G2340/0435—Change or adaptation of the frame rate of the video stream
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09G—ARRANGEMENTS OR CIRCUITS FOR CONTROL OF INDICATING DEVICES USING STATIC MEANS TO PRESENT VARIABLE INFORMATION
- G09G2360/00—Aspects of the architecture of display systems
- G09G2360/16—Calculation or use of calculated indices related to luminance levels in display data
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Control Of Indicators Other Than Cathode Ray Tubes (AREA)
- Electroluminescent Light Sources (AREA)
- Control Of El Displays (AREA)
- Liquid Crystal Display Device Control (AREA)
Description
230 駆動部
231 ゲートドライバー部
233 ソースドライバー部
235 コントローラー
Claims (3)
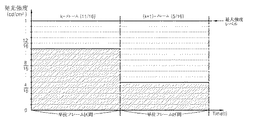
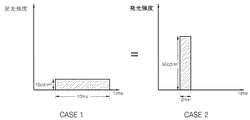
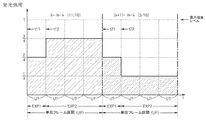
- 能動ディスプレイ装置の映像駆動方法において、
A)選択されたピクセルのデジタルデータを生成する段階;
B)第1発光区間で第1発光強度で前記選択されたピクセルを発光させる段階であって、前記第1発光区間及び前記第1発光強度はマッピングテーブルにマッピングされる前記デジタルデータの値によって決定される段階;及び
C)第2発光区間で第2発光強度で前記選択されたピクセルを発光させる段階であって、前記第2発光区間及び前記第2発光強度は前記マッピングテーブルにマッピングされる前記デジタルデータの値によって決定される段階;を含み、
前記第1発光区間と前記第2発光区間は単位フレーム区間内で実行され、
前記第1発光区間と前記第2発光区間の長さは前記デジタルデータに関係なく、前記第1発光強度と前記第2発光強度との間の相対比が前記デジタルデータの値によって可変し、
前記第2発光区間の長さは、前記第1発光区間の長さと異なり、
前記デジタルデータはn(nは2以上の自然数)ビットであり、
前記マッピングテーブルは、前記単位フレーム区間を形成する2 i (iは自然数)個の単位時間が配列される時間軸と2 j (jは自然数、j=n−i)個の強度レベルが配列される強度軸でなり、
前記第1発光区間の長さは、一つの前記単位時間と同一であり、
前記第2発光区間の長さは、(2 i −1)個の前記単位時間と同一である
ことを特徴とする、能動ディスプレイ装置の映像駆動方法。 - 前記jは前記iと同一であることを特徴とする、請求項1に記載の能動ディスプレイ装置の映像駆動方法。
- 前記jは前記iと異なることを特徴とする、請求項1に記載の能動ディスプレイ装置の映像駆動方法。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR10-2007-0083328 | 2007-08-20 | ||
| KR1020070083328A KR100789654B1 (ko) | 2007-08-20 | 2007-08-20 | 능동 디스플레이 장치에서의 믹싱형 픽셀 구동 방법 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009048161A JP2009048161A (ja) | 2009-03-05 |
| JP4751908B2 true JP4751908B2 (ja) | 2011-08-17 |
Family
ID=38689166
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008079745A Expired - Fee Related JP4751908B2 (ja) | 2007-08-20 | 2008-03-26 | 能動ディスプレイ装置におけるミキシング型ピクセル駆動方法 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8044979B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP4751908B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR100789654B1 (ja) |
| TW (1) | TWI391893B (ja) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2610846A3 (en) | 2011-12-28 | 2014-07-09 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Device and method for displaying image, device and method for supplying power, and method for adjusting brightness of contents |
| KR102264163B1 (ko) | 2014-10-21 | 2021-06-11 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 텍스쳐를 처리하는 방법 및 장치 |
| CN110570810B (zh) | 2019-09-11 | 2021-05-04 | 成都辰显光电有限公司 | 一种显示面板的驱动装置和驱动方法 |
| EP4182915A4 (en) * | 2020-08-05 | 2023-08-16 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | DIGITAL ANALOG MULTIPLICATION DRIVE METHOD FOR A DISPLAY DEVICE |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6094187A (en) * | 1996-12-16 | 2000-07-25 | Sharp Kabushiki Kaisha | Light modulating devices having grey scale levels using multiple state selection in combination with temporal and/or spatial dithering |
| JP2003058120A (ja) * | 2001-08-09 | 2003-02-28 | Sharp Corp | 表示装置およびその駆動方法 |
| JP2003330422A (ja) * | 2002-05-17 | 2003-11-19 | Hitachi Ltd | 画像表示装置 |
| US7551258B2 (en) * | 2002-07-04 | 2009-06-23 | Zbd Displays Limited | Patterned light modulating device |
| KR100872713B1 (ko) * | 2002-08-30 | 2008-12-05 | 엘지디스플레이 주식회사 | 강유전성 액정표시장치의 전계 배향 방법 및 이를 이용한강유전성 액정표시장치의 구동방법 및 장치 |
| EP1455337A1 (en) * | 2003-03-05 | 2004-09-08 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Control method for a backlight arrangement, display controller using this method and display apparatus |
| GB0319963D0 (en) | 2003-08-27 | 2003-09-24 | Koninkl Philips Electronics Nv | Display device |
| JP2004233969A (ja) * | 2003-10-22 | 2004-08-19 | Seiko Epson Corp | 電気光学装置の駆動方法、電気光学装置および電子機器 |
| TWI284231B (en) * | 2004-02-17 | 2007-07-21 | Au Optronics Corp | Method for driving a backlight of a liquid crystal display device |
| KR100818013B1 (ko) * | 2004-02-19 | 2008-03-31 | 샤프 가부시키가이샤 | 영상 표시 장치 및 영상 표시 방법 |
| KR100588755B1 (ko) | 2004-09-01 | 2006-06-12 | 매그나칩 반도체 유한회사 | 능동 매트릭스 유기 발광 다이오드 패널을 시분할 제어방식으로 구동하기 위한 데이터 처리 회로 및 방법 |
| KR101446340B1 (ko) * | 2005-08-11 | 2014-10-01 | 엘지디스플레이 주식회사 | 일렉트로-루미네센스 표시장치 |
| TWI345741B (en) * | 2006-04-13 | 2011-07-21 | Chimei Innolux Corp | Circuit and method for driving backlight module |
-
2007
- 2007-08-20 KR KR1020070083328A patent/KR100789654B1/ko not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2008
- 2008-02-21 US US12/034,795 patent/US8044979B2/en active Active
- 2008-03-04 TW TW097107569A patent/TWI391893B/zh not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2008-03-26 JP JP2008079745A patent/JP4751908B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR100789654B1 (ko) | 2008-01-02 |
| US8044979B2 (en) | 2011-10-25 |
| TW200910296A (en) | 2009-03-01 |
| KR20070091253A (ko) | 2007-09-10 |
| US20090051708A1 (en) | 2009-02-26 |
| TWI391893B (zh) | 2013-04-01 |
| JP2009048161A (ja) | 2009-03-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TWI636448B (zh) | 有機發光顯示裝置、資料驅動器及其驅動方法與顯示裝置及其驅動方法 | |
| CN1202503C (zh) | 液晶驱动装置以及灰度显示方法 | |
| KR101857809B1 (ko) | RGB-to-RGBW 변환방법과 이를 이용한 표시장치 | |
| JP6694989B2 (ja) | 発光装置、表示装置、およびled表示装置 | |
| WO2017191714A1 (ja) | バックライト装置およびそれを備えた表示装置 | |
| JP6960026B2 (ja) | 表示装置 | |
| KR101158868B1 (ko) | 다수의 분할 영역별로 휘도 레벨을 조절할 수 있는 액정표시 장치 및 그의 구동 방법 | |
| US10019939B2 (en) | Organic light emitting display device and driving method thereof | |
| CN101221308A (zh) | 背光单元及液晶显示器 | |
| JP4751908B2 (ja) | 能動ディスプレイ装置におけるミキシング型ピクセル駆動方法 | |
| WO2012124646A1 (ja) | 映像表示装置 | |
| WO2017098676A1 (ja) | 表示装置およびバックライトの制御方法 | |
| US10043437B2 (en) | Display device and method for driving backlight thereof | |
| WO2016189997A1 (ja) | バックライト装置およびそれを備えた液晶表示装置 | |
| WO2015174144A1 (ja) | バックライト装置およびそれを備えた液晶表示装置 | |
| JPWO2014192148A1 (ja) | 表示装置、表示システム、映像出力装置、および表示装置の制御方法 | |
| KR102679100B1 (ko) | 디스플레이 장치, 데이터 구동 회로 및 구동 방법 | |
| CN1698084A (zh) | 数字驱动型显示装置 | |
| KR101791865B1 (ko) | 데이터 처리 방법 및 이를 수행하는 표시 장치 | |
| KR102044133B1 (ko) | 유기발광소자표시장치 및 그 구동방법 | |
| JP2011138673A (ja) | バックライト装置および画像表示装置 | |
| JP5078690B2 (ja) | 画像表示装置の階調制御方法 | |
| US10283041B2 (en) | Display device | |
| CN1225720C (zh) | 点阵显示设备及确定像素的新亮度值的方法 | |
| JP2005301176A (ja) | 表示装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110118 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110411 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20110517 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20110523 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140527 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |