JP4714809B2 - Bullet ball machine - Google Patents
Bullet ball machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4714809B2 JP4714809B2 JP2000392369A JP2000392369A JP4714809B2 JP 4714809 B2 JP4714809 B2 JP 4714809B2 JP 2000392369 A JP2000392369 A JP 2000392369A JP 2000392369 A JP2000392369 A JP 2000392369A JP 4714809 B2 JP4714809 B2 JP 4714809B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- normal symbol
- special symbol
- symbol lottery
- special
- lottery
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Pinball Game Machines (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、弾球遊技機の技術分野に属する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
普通図柄抽選領域(例えば通過口)に遊技球が進入したことに起因して普通図柄抽選を行う普通図柄抽選手段と、普通図柄抽選の結果を普通図柄で表示する普通図柄表示手段と、普通図柄表示手段を制御して普通図柄を変動表示した後に確定表示させる普通図柄制御手段と、普通図柄抽選が当たりであると、開放状態では入賞が容易になる可変入賞装置(例えばチューリップ式の入賞装置)である特別図柄始動装置(普通電動役物)を、普通図柄の確定表示後に開放状態にさせる始動装置制御手段と、特別図柄始動装置への入賞に起因して特別図柄抽選を行う特別図柄抽選手段と、特別図柄抽選の結果を特別図柄で表示する特別図柄表示手段と、特別図柄抽選が当たりであったことを必須条件として遊技者に有利な特別遊技を実行する特別遊技実行手段とを備える弾球遊技機がある。
【0003】
この種の弾球遊技機においては、いわゆる確変や時短のとき(以下、これらをまとめて「特別状態」という。)に普通図柄抽選で当たりになる確率を高め、特別図柄始動装置の開放時間を長くすることがある。また、特別状態とそうでないとき(以下、「通常状態」という。)では普通図柄の変動時間を変更する(特別状態の方が短くなる)ものの、特別状態中はその変動時間は一定であり、通常状態においても同様であった。
【0004】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
特別図柄始動装置は普通図柄の確定表示(すなわち変動の終了)とほぼシンクロして開放されるので、遊技者には特別図柄始動装置が開放されるタイミングを予測でき、そのタイミングに合わせて遊技球を発射したり発射を止めたりする、いわゆる止め打ちを容易に行えた。
【0005】
止め打ちは、遊技者にしてみれば効率よく賞球を獲得するための手段であるが、遊技店にとっては弾球遊技機の稼働率の悪化、出球率の上昇となっていた。
【0006】
【課題を解決するための手段および発明の効果】
上記課題を解決するための請求項1記載の弾球遊技機は、
普通図柄抽選領域に遊技球が進入したことに起因して普通図柄抽選を行う普通図柄抽選手段と、該普通図柄抽選の結果を普通図柄で表示する普通図柄表示手段と、該普通図柄表示手段を制御して普通図柄を変動表示した後に確定表示させる普通図柄制御手段と、前記普通図柄抽選が当たりであると、開放状態では入賞が容易になる可変入賞装置である特別図柄始動装置を、前記普通図柄の確定表示後に開放状態にさせる始動装置制御手段と、前記特別図柄始動装置への入賞に起因して特別図柄抽選を行う特別図柄抽選手段と、該特別図柄抽選の結果を特別図柄で表示する特別図柄表示手段と、前記特別図柄抽選が当たりであったことを必須条件として遊技者に有利な特別遊技を実行する特別遊技実行手段とを備える弾球遊技機において、
前記普通図柄抽選領域への遊技球の進入が検出されたときから前記特別図柄始動装置の開放までの経過時間を各回毎に不一定に決定する時間決定手段を備え、
該時間決定手段は、前記抽選結果の表示動作を直ちに開始できない前記特別図柄抽選に関する記憶(特別図柄保留記憶)の有無又は個数に基づいて前記経過時間を選択することを特徴とする。
こうすることにより、普通図柄抽選領域(例えば通過口)に遊技球が進入してから特別図柄始動装置(普通電動役物)が開放されるまでの経過時間が一定せず、遊技者には特別図柄始動装置が開放されるタイミングを予測できない。
【0007】
その結果、特別図柄始動装置のタイミングに合わせて遊技球を発射したり発射を止めたりする止め打ちは容易でないばかりか、効率よく賞球を獲得するという止め打ちの効果は得られない。すなわち、止め打ちのメリットがないからこれを行う遊技者もなくなり、弾球遊技機の稼働率の悪化は防止され、出球率が特別に上昇することもない。
【0008】
普通図柄抽選領域への遊技球の進入が検出されたときから特別図柄始動装置の開放までの経過時間を各回毎に不一定にするに当たって、特別図柄始動装置の開放との関係で遊技者が明瞭に認識できるのは普通図柄の変動であるから、その変動時間、特に普通図柄の確定のタイミングを不一定にすればよい。
また、抽選結果の表示動作を直ちに開始できないというのは、例えば先行する抽選結果を表示するために特別図柄が変動表示中であるためにその確定を待たなければ表示動作を開始できない場合や、遊技状態との関係で(例えば特別遊技の実行中で)表示動作を行えない場合などである。特別図柄抽選に関する記憶とは、特別図柄抽選に用いる乱数値や抽選結果をいう。この特別図柄保留記憶の個数にも上限があるのが普通で(通常は4個まで)ある。
特別図柄保留記憶は特別図柄始動装置への入賞で増加するから、特別図柄保留記憶がある時にこれを更に増加すると特別図柄保留記憶がオーバーフローするおそれがある。したがって、特別図柄保留記憶があるときには、なるべくこれを増加させない、すなわち特別図柄始動装置を開放しないほうがよい。
これに対し、請求項1記載の弾球遊技機は、特別図柄保留記憶があるときには、実行中の或いはこれから実行する普通図柄の変動を長引かせることで特別図柄始動装置の開放を遅らせて、特別図柄保留記憶の増加を抑制でき、図柄保留記憶が無いときには、実行中の或いはこれから実行する普通図柄の変動を短時間にすることで、特別図柄始動装置の時間当たりの開放頻度を高めて、遊技者に特別図柄抽選の機会を与えることができる。
また、特別図柄保留記憶の個数に応じて経過時間を選択することで、普通図柄の変動時間をより細やかに選択することができる。
【0009】
この普通図柄の確定のタイミングを不一定にするに当たって、起算点は普通図柄の変動開始時点としてもよいし、普通図柄抽選領域への遊技球の進入が検出されたときとしてもよい。
また、請求項2記載の弾球遊技機は、前記時間決定手段は、前記特別図柄保留記憶の有無又は個数に基づいて前記経過時間の決定範囲を設定すると共に、前記普通図柄抽選領域への遊技球の進入が検出されたことに起因して抽出された乱数に基づき、該決定範囲内の時間を、前記経過時間として選択することを特徴とする。こうすることにより、比較的簡単な構成で経過時間をランダムに決めることができる。
【0010】
また、請求項3に記載の弾球遊技機は、前記普通図柄抽選手段による当たりの確率が相対的に低い又は前記普通図柄の変動時間が相対的に長い通常モードと、前記普通図柄抽選手段による当たりの確率が相対的に高い又は前記普通図柄の変動時間が相対的に短い特別モードとがあり、前記時間決定手段は、前記特別モードのときに作動することを特徴とする。
普通図柄抽選手段による普通図柄抽選に、当たりの確率が相対的に低い低確率抽選と当たりの確率が低確率抽選よりも高い高確率抽選とを用いるのは、従来の弾球遊技機でも行われている。普通は、特別図柄抽選における当たりの確率が通常時よりも高められている確率変動(確変)時や特別遊技の終了後に特別図柄の変動時間が短くされる時短のときに、普通図柄抽選が高確率抽選とされる。
【0011】
そして、特別図柄始動装置の開放時間は、低確率抽選が行われる期間中は短くて(例えば0.2〜0.3秒程度)、高確率抽選が行われる期間中は、例えば2〜3秒程度に長くされている。ただし、入賞個数にも上限が設定されているので、この時間に達する前に閉鎖状態に復帰することもある。
【0012】
したがって、特別図柄始動装置の開放時間がこのような設定であれば、低確率抽選が行われる期間中は特別図柄始動装置の開放のタイミングを狙って遊技球を発射することはまず不可能であるが、高確率抽選が行われる期間中には十分に行える。よって、特別図柄始動装置が開放されるタイミングを不一定にするのは高確率抽選が行われる期間中だけで十分である。つまり、請求項3の構成で十分に発明の目的を達成できる。また、このように時間決定手段の作動期間を限定することで、CPUの処理量を低減できるメリットもある。
【0014】
さらに、通常の弾球遊技機においては、特別図柄抽選における当たりの確率が通常時よりも高められている確率変動(確変)時や特別遊技の終了後に特別図柄の変動時間が短くされる時短のときには、普通図柄の変動時間が通常時(通常モード、変動時間は約28〜29秒)よりも短縮される(時短モード)のが普通である。
【0015】
そして、特別図柄始動装置の開放時間は、通常モードでは短くて(例えば0.2〜0.3秒程度)、時短モードでは例えば2〜3秒程度に長くされている。ただし、入賞個数にも上限が設定されているので、この時間に達する前に閉鎖状態に復帰することもある。
【0016】
したがって、特別図柄始動装置の開放時間がこのような設定であれば、通常モードでは特別図柄始動装置の開放のタイミングを狙って遊技球を発射することはまず不可能であるが、時短モードでなら十分に行える。よって、特別図柄始動装置が開放されるタイミングを不一定にするのは時短モードだけで十分である。つまり、請求項3の構成で十分に発明の目的を達成できる。また、このように時間決定手段の作動期間を限定することで、CPUの処理量を低減できるメリットもある。
【0027】
【発明の実施の形態】
次に、本発明の実施例により発明の実施の形態を説明する。
【0028】
【実施例】
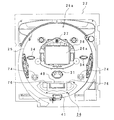
図1に示すように、弾球遊技機としてのパチンコ機10は、長方形の外枠11と前面枠12とからなる筐体にて構成の各部を保持する構造である。また、このパチンコ機10はいわゆるCR機であって、プリペイドカードの読み書き等を行うためのカードリーダユニット(以下、CRユニット)13が付属している。
【0029】
前面枠12は、左端上下のヒンジ14により外枠11に対し開閉可能に取り付けられており、通常は図示するように閉じた状態とされる。
前面枠12には、窓状のガラス枠20が前面枠12に対して開放可能に取り付けられている。このガラス枠20には板ガラス21が二重にはめ込まれ、板ガラス21の奥には前面枠12に保持された遊技盤22が収納されている。
【0030】
ガラス枠20の下方には上皿15が配され、前面枠12に対して開放可能に取り付けられている。上皿15には、プリペイドカードによる遊技球の貸出を指示するための貸出釦16、プリペイドカードの返却を指示するための精算釦17及びプリペイドカードの残高を表示するための残高表示部18が設けられている。CRユニット13のカード口19にプリペイドカードを挿入するとプリペイドカードの残高が残高表示部18に表示され、貸出釦16を押下するとその残高の範囲内で遊技球の貸出しが実行され上皿15に貸球としての遊技球が排出される。また、精算釦17押下するとプリペイドカードがカード口19から排出される。
【0031】
上皿15の下方にては下皿23が前面枠12に固定され、下皿23の右側には発射ハンドル24が取り付けられている。発射ハンドル24の外周にはダイヤル部24aが装着されており、これを時計回りに回動操作すれば発射装置(図示略)が稼働して、上皿15から供給された遊技球を遊技盤22に向けて発射する。この際、ダイヤル部24aの回動量によって発射力の強弱を調整できる。またダイヤル部24aに隣接して導電性のタッチセンサ24bが設けられている。
【0032】
図2に示すように、遊技盤22には、ガイドレール25によって囲まれた略円形の遊技領域25aが設けられ、その中央部には特別図柄表示手段に該当する液晶表示装置26が設置されている。また液晶表示装置26の枠の上部中央には7セグメントLEDが普通図柄表示器27として取り付けられている。普通図柄表示器27は普通図柄表示手段に該当する。
【0033】
遊技盤22には、液晶表示装置26の下方にチューリップ式の可変入賞装置31が設置されている。この可変入賞装置31は特別図柄始動装置に該当する。
液晶表示装置26の左右にはそれぞれゲート34が配されている。ゲート34は普通図柄抽選領域に該当し、遊技球がゲート34を通過すると普通図柄表示器27の表示が変動した後に静止され、それが当たり数値(例えば7)であると、可変入賞装置31は上限個数の入賞があるまで或いは設定時間までのいずれか短い方の時間だけ開放される。
【0034】
これらゲート34の下方に普通入賞口74が配され、可変入賞装置31の下方には大入賞口40と左右の普通入賞口76を備える大入賞装置36が配され、盤面最下部にはアウト口41が設けられている。
なお、遊技盤22には、多数の遊技釘が打ち付けられ風車等が備えられているが、これらは周知であるので図示と説明を省略する。
【0035】
このパチンコ機10は、図3に示すように、主制御基板70、表示制御基板90、払出制御基板92、ランプ制御基板96、発射制御基板94、音声制御基板98を備えている。
主制御基板70にはCPU70a、ROM70b、RAM70c、カウンタ70d、70e、70f、入出力ポート等が備わっており、主制御基板70(特にCPU70a)は、普通図柄抽選手段、始動装置制御手段、特別図柄抽選手段及び時間決定手段として機能し、大入賞装置36と共同して特別遊技実行手段としても機能する。
【0036】
この主制御基板70は、ゲート34(自体が通過センサである)、可変入賞装置31の入賞センサ31a、大入賞装置36の特別領域センサ36a及び非特別領域センサ36b、普通入賞口74、76の入賞センサ等からの検出信号、タッチセンサ24bの信号、その他遊技盤22やパチンコ機10の各部に設置されているセンサ類からの信号を取得し、それに基づいて遊技の進行に関わる各種のコマンドを、表示制御基板90、払出制御基板92、発射制御基板94、ランプ制御基板96、音声制御基板98に出力する。また、主制御基板70は、可変入賞装置31のソレノイド31b、大入賞装置36のソレノイド36cを制御することで、これらの開閉を制御する。
【0037】
表示制御基板90には、CPU90a、ROM90b、RAM90c、入出力ポート等が備わっており、主制御基板70から送られてくるコマンドに応じて液晶表示装置26の表示及び普通図柄表示器27を制御する。表示制御基板90(特にCPU90a)は普通図柄表示器27を制御する点で普通図柄制御手段に該当し、液晶表示装置26の表示を制御する点で特別図柄制御手段としても機能する。
【0038】
図示は省略するが、払出制御基板92、発射制御基板94、ランプ制御基板96及び音声制御基板98は、それぞれCPU、ROM、RAM、入出力ポート等を備え、音声制御基板98には音源LSIも備わっており、主制御基板70から送られてくるコマンドに応じてそれぞれの制御動作を行う。概略を説明すると、払出制御基板92は払出装置を、発射制御基板94は発射装置を、ランプ制御基板96は電飾(LEDや電球)の点滅と他の制御基板に制御されないモータやソレノイド類を、音声制御基板98はスピーカからの音声出力を、それぞれ制御する。
【0039】
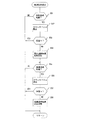
次に、主に普通図柄表示器27と液晶表示装置26の表示に関わる、主制御基板70(特にCPU70a)の処理と表示制御基板90(特にCPU90a)の処理を中心に、パチンコ機10の動作を説明する。なお、以下で説明するCPU70aの各処理は、いずれもメインルーチン(図示と説明は省略)のサブルーチンとして実行される。
【0040】
図4に示すのは特別図柄及び普通図柄の抽選乱数読込処理である。この処理では、CPU70aは、可変入賞装置31の入賞センサ31aからの遊技球検出信号(特別図柄始動信号)が入力されているか否か、すなわち遊技球が可変入賞装置31に入賞したか否かを判断する(S51)。
【0041】
肯定判断であれば、カウンタ70dの値を読み込み(S52)、RAM70cに設けられている特別図柄抽選乱数記憶エリアに4個の特別図柄抽選乱数が記憶されているか否か、つまり特別図柄保留が4個に達しているか否かを判断する(S53)。この保留が3個以下なら(S53:NO)、S52で読み込んだ値を特別図柄抽選乱数として特別図柄抽選乱数記憶エリアに記憶する(S54)。
【0042】
S51で否定判断のとき、S53で肯定判断のときまたはS54の後に、CPU70aは、ゲート34からの通過球検出信号(普通図柄始動信号)が入力されているか否か、すなわち遊技球がゲート34を通過したか否かを判断する(S55)。
【0043】
肯定判断であれば、カウンタ70eの値を読み込み(S56)、RAM70cに設けられている普通図柄抽選乱数記憶エリアに4個の普通図柄抽選乱数が記憶されているか否か、つまり普通図柄保留が4個に達しているか否かを判断する(S57)。この保留が3個以下なら(S57:NO)、S56で読み込んだ値を普通図柄抽選乱数として普通図柄抽選乱数記憶エリアに記憶する(S58)。
【0044】
S55で否定判断のとき、S57で肯定判断のときまたはS58の後に、本処理からリターンする。
次に、図5を参照して普通図柄抽選について説明する。
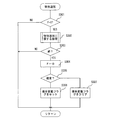
CPU70aは、この処理では、まず普通図柄表示器27において変動表示中か否かを判断する(S100)。肯定判断なら実質的な処理を行うことなく、本処理からリターンする。
【0045】
否定判断すなわち普通図柄の変動中でないときには、普通図柄抽選乱数記憶エリアに普通図柄抽選乱数が記憶されているか否かを判断する(S101)。否定判断なら本処理からリターンする。
肯定判断つまり上述のS58で記憶した普通図柄抽選乱数があれば、その中で最も古いものを読み込んで、これを普通図柄抽選乱数記憶エリアから抹消する(S102)。なお、この普通図柄抽選乱数はCPU70aが例えばレジスタに保持するので、抽選乱数自体が消滅するわけではない。
【0046】
次に、CPU70aは、高確率抽選モードか否かを判断する(S103)。本実施例の場合、特別図柄抽選が高確率で行われるとき(いわゆる確変中)が高確率抽選モードであり、このモードでは普通図柄抽選も高確率で行われる。言うまでもないが、特別図柄抽選の確率と普通図柄抽選の確率は同じではない。本実施例では、通常確率抽選モードでは特別図柄抽選の当たり確率は約1/300、普通図柄抽選の当たり確率は1/10であり、高確率抽選モードでは特別図柄抽選の当たり確率は約1/60、普通図柄抽選の当たり確率は9/10である。
【0047】
高確率抽選モードであれば(S103:YES)、普通図柄の変動時間を決めるための時間決定ルーチン(S104)を実行する。この処理にはさまざまなバリエーションがあるので、図8〜12を用いて代表的な例をいくつか説明する。なお、CPU70aは時間決定ルーチン1〜5を実行することで時間決定手段に該当する。
[時間決定ルーチン1]
この例は、普通図柄の保留個数(普通図柄抽選乱数記憶エリアに記憶されている普通図柄抽選乱数の個数)に応じて決定する例である。
【0048】
図8に示すように、この例では、まず普通図柄の保留個数が0以外(1〜3のいずれか)であるか否かを判断する(S120)。なお、S102において、今回の抽選対象となる普通図柄抽選乱数は普通図柄抽選乱数記憶エリアから抹消されているので、ここでは今回の抽選対象以外の普通図柄抽選乱数の個数を判断している。
【0049】
S120で否定判断すなわち普通図柄の保留個数が0なら7秒の変動時間を選択し(S121)、肯定判断であれば、普通図柄の保留個数が1以外(2または3)であるか否かを判断する(S122)。
S122で否定判断すなわち普通図柄の保留個数が1なら6秒の変動時間を選択し(S123)、肯定判断であれば普通図柄の保留個数が2以外(すなわち3)であるか否かを判断する(S124)。
【0050】
S124で否定判断すなわち普通図柄の保留個数が2なら5秒の変動時間を選択し(S125)、肯定判断であれば4秒の変動時間を選択する(S126)。
[時間決定ルーチン2]
この例は、特別図柄の保留個数(特別図柄抽選乱数記憶エリアに記憶されている特別図柄抽選乱数の個数)に応じて決定する例である。
【0051】
図9に示すように、この例では、まず特別図柄の保留個数が0以外(1〜4のいずれか)であるか否かを判断する(S130)。
S130で否定判断すなわち特別図柄の保留個数が0なら4秒の変動時間を選択し(S131)、肯定判断であれば、特別図柄の保留個数が1以外(2〜4のいずれか)であるか否かを判断する(S132)。
【0052】
S132で否定判断すなわち特別図柄の保留個数が1なら5秒の変動時間を選択し(S133)、肯定判断であれば特別図柄の保留個数が2以外(すなわち3または4)であるか否かを判断する(S134)。
S134で否定判断すなわち特別図柄の保留個数が2なら6秒の変動時間を選択し(S135)、肯定判断であれば特別図柄の保留個数が3以外(すなわち4)であるか否かを判断する(S136)。
【0053】
S136で否定判断すなわち特別図柄の保留個数が3なら7秒の変動時間を選択し(S137)、肯定判断であれば8秒の変動時間を選択する(S138)。
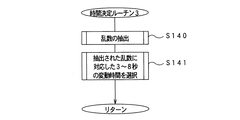
[時間決定ルーチン3]
この例は乱数値に基づいて決定する例である。
【0054】
図10に示すように、このルーチンでは、時間決定用のカウンタ70fの値を読み込み(S140)、その値に対応して(例えば乱数値と変動時間の対照テーブルに従って)、3〜8秒の範囲で変動時間を選択する(S141)。
[時間決定ルーチン4]
この例は、乱数値と普通図柄の保留個数とに応じて決定する例である。
【0055】
図11に示すように、このルーチンでは、まず時間決定用のカウンタ70fの値を読み込む(S150)。
次に、普通図柄の保留個数が0以外(1〜3のいずれか)であるか否かを判断する(S151)。
【0056】
S150で否定判断すなわち普通図柄の保留個数が0なら、カウンタ70fの値に対応して6〜7秒の範囲で変動時間を選択し(S152)、肯定判断であれば、普通図柄の保留個数が1以外(2または3)であるか否かを判断する(S153)。
【0057】
S153で否定判断すなわち普通図柄の保留個数が1なら、カウンタ70fの値に対応して5〜6秒の変動時間を選択し(S154)、肯定判断であれば普通図柄の保留個数が2以外(すなわち3)であるか否かを判断する(S155)。
S155で否定判断すなわち普通図柄の保留個数が2なら、カウンタ70fの値に対応して4〜5秒の変動時間を選択し(S156)、肯定判断であればカウンタ70fの値に対応して3〜4秒の変動時間を選択する(S157)。
[時間決定ルーチン5]
この例は、乱数値と特別図柄の保留個数とに応じて決定する例である。
【0058】
図12に示すように、このルーチンでは、まず時間決定用のカウンタ70fの値を読み込む(S160)。
次に、特別図柄の保留個数が0以外(1〜4のいずれか)であるか否かを判断する(S161)。
【0059】
S130で否定判断すなわち特別図柄の保留個数が0なら、カウンタ70fの値に対応して3〜4秒の範囲で変動時間を選択し(S162)、肯定判断であれば、特別図柄の保留個数が1以外(2〜4のいずれか)であるか否かを判断する(S163)。
【0060】
S163で否定判断すなわち特別図柄の保留個数が1なら、カウンタ70fの値に対応して4〜5秒の変動時間を選択し(S164)、肯定判断であれば特別図柄の保留個数が2以外(すなわち3または4)であるか否かを判断する(S165)。
【0061】
S165で否定判断すなわち特別図柄の保留個数が2なら、カウンタ70fの値に対応して5〜6秒の変動時間を選択し(S166)、肯定判断であれば特別図柄の保留個数が3以外(すなわち4)であるか否かを判断する(S167)。
S167で否定判断すなわち特別図柄の保留個数が3なら、カウンタ70fの値に対応して6〜7秒の変動時間を選択し(S168)、肯定判断であれば、カウンタ70fの値に対応して7〜8秒の変動時間を選択する(S169)。
【0062】
図5に示すとおり、これら時間決定ルーチン1〜5のいずれか或いはこれら以外の適宜の手法で普通図柄の変動時間を決めた(S104)後には、S102で読み込んでおいた普通図柄抽選乱数につき高確率抽選モードでの抽選を行う(S105)。また、S103で否定判断のときには、普通図柄の変動時間をデフォルト値(本実施例では約28秒)として(S106)、通常確率抽選モードでの抽選を行う(S107)。本実施例の場合、カウンタ70eは0〜9の整数値を昇順に繰り返してカウントする構成であり、通常確率抽選モードでは0が当たり値、高確率抽選モードでは0以外が当たり値で、普通図柄抽選乱数が当たり値のいずれかと一致すれば当たりである。
【0063】
抽選が当たりであれば(S108:YES)、当たりを表示させる普通図柄当たりコマンドを生成して表示制御基板90に送信する(S109)。このコマンドには、S104で決定した変動時間またはデフォルト値を指定する変動時間データが含まれている。
【0064】
表示制御基板90は、このコマンドを受け取ると、普通図柄表示器27に普通図柄を変動表示させ、変動時間データで指定されている時間後に当たり普通図柄を確定表示させる。
CPU70aは、普通図柄の確定を待って、可変入賞装置31を開閉制御する(S110)。可変入賞装置31の開放時間は、通常確率抽選モードでは約0.3秒、高確率抽選モードでは約2.3秒である。
【0065】
一方、抽選が外れであれば(S108:NO)、外れを表示させる普通図柄外れコマンドを生成して表示制御基板90に送信する(S111)。このコマンドにも変動時間データが含まれており、表示制御基板90は、このコマンドを受け取ると普通図柄表示器27に普通図柄を変動表示させ、変動時間データで指定されている時間後に外れ普通図柄を確定表示させる。
【0066】
なお、例えば特別図柄抽選が高確率で行われるとき(確変時)や特別図柄の変動時間が通常よりも短く設定されるとき(時短時)に、普通図柄抽選の確率を高確率に変更せずに、可変入賞装置31の開放時間だけを長くする場合がある。その場合には、図5の処理の一部を図13に例示するように変更すればよい。
【0067】
この例では、S100〜S102は図5と同様であるが、続いて特別図柄の変動時間が通常よりも短く設定されている時短状態であるか否か(本例では、時短状態では特別図柄抽選が高確率で行われる)を判断し(S103’)、肯定判断であれば、普通図柄の変動時間を決めるための時間決定ルーチン(S104)を実行する。この時間決定ルーチンの処理は図8〜12と同様である。また、S103’で否定判断のときには、普通図柄の変動時間をデフォルト値(例えば約28秒)とする(S106)。そして、S104またはS106の後に、S102で読み込んでおいた普通図柄抽選乱数につき抽選を行う(S107’)。その後の処理は図5と同様である。
【0068】
次に、図6を参照して特別図柄抽選について説明する。
CPU70aは、この処理では、まず特別図柄の変動表示を実行できるか否かを判断する(S200)。詳しくは、液晶表示装置26において変動表示中か又は特別遊技を実行中であるかを判断する。否定判断なら実質的な処理を行うことなく、本処理からリターンする。
【0069】
肯定判断すなわち特別図柄の変動表示が可能であれば、特別図柄抽選乱数記憶エリアに特別図柄抽選乱数が記憶されているか否かを判断する(S201)。否定判断なら本処理からリターンする。
肯定判断つまり上述のS54で記憶した特別図柄抽選乱数があれば、その中で最も古いものを読み込んで、これを特別図柄抽選乱数記憶エリアから抹消する(S201)。なお、この特別図柄抽選乱数はCPU70aが例えばレジスタに保持するので、抽選乱数自体が消滅するわけではない。
【0070】
次に、CPU70aは、高確率抽選モードか否かを判断する(S203)。
高確率抽選モードであれば(S203:YES)、読み込んでおいた特別図柄抽選乱数につき高確率抽選モードでの抽選を行う(S204)。また、S203で否定判断のときには、通常確率抽選モードでの低確率抽選を行う(S205)。
【0071】
抽選が当たりであれば(S206:YES)、当たりフラグFをセットして(S207)、当たりを表示させる特別図柄当たりコマンドを生成して表示制御基板90に送信する(S208)。
表示制御基板90は、このコマンドを受け取ると、液晶表示装置26を制御して特別図柄を変動表示させてから当たりの特別図柄を確定表示させる。
【0072】
抽選が外れであれば(S206:NO)、外れを表示させる特別図柄外れコマンドを生成して表示制御基板90に送信する(S209)。表示制御基板90は、このコマンドを受け取ると液晶表示装置26に特別図柄を変動表示させてから、外れの特別図柄を確定表示させる。
【0073】
ここで当たりの特別図柄が確定表示されると、これに続いて特別遊技が開始される。
本実施例で実行される特別遊技自体は、第一種と呼ばれる形式の公知のパチンコ機と同様であるが、図7を参照して簡単に説明する。CPU70aは、図7に示す特別遊技処理を実行することで、大入賞装置36と共同して特別遊技実行手段として機能する。
【0074】
特別遊技処理においては、主制御基板70は、当たりフラグFが1にセットされているか否かを判断し(S301)、否定判断なら実質的な処理は行わない(特別遊技は実行されない)。
S301で肯定判断であれば、表示制御基板90に大当たりオープニングコマンドを送って大当たりファンファーレ画面を表示させ、それに続いて大入賞口40を開閉し、表示制御基板90に対してラウンド数表示コマンドによる大入賞口40の開放回数(ラウンド数)の表示、大当たり図柄表示コマンドによる大当たり画面の表示、入賞個数コマンドによる大入賞口40への入賞個数(いわゆるカウント数)の表示、特定領域通過表示コマンドによる特定領域の通過表示、インターバルコマンドによるインターバル画面の表示などを指示するといった、特別遊技に関わる各種の処理を行う(S302)。そして、例えば規定のラウンド数が実行されて特別遊技の終了となれば(S303:YES)、大当たりエンディングコマンドにより大当たり終了画面の表示を指示し、当たりフラグFをリセットする(S304)。
【0075】
そして、高確率モードに設定(確率変動)するか否かを判断し(S305)、肯定判断なら確率変動フラグをセットし(S306)、否定判断なら確率変動フラグをクリア(S307)。ここで確率変動フラグがセットされると、以後は高確率モードとなって図6の特別図柄抽選が高確率で行われる。なお、高確率モードにするかしないかの決定は、例えば大当たり抽選が当たりであったときに(S206:YES)実行する確変抽選の結果による。すなわち、その確変抽選が当たりであるとS305で肯定判断となる設定である。
【0076】
本実施例では特別図柄抽選で当たりになるとこのような特別遊技が行われるが、この抽選で当たったことを条件として実行される特別遊技の形態はこれに限るわけではない。
以上の通り、このパチンコ機10は、高確率抽選モードでは普通図柄の変動時間を、その表示動作の各回毎に不一定に決定することにより、ゲート34を通過したことが検出されたときから可変入賞装置31の開放までの経過時間を各回毎に不一定にしているので、遊技者には可変入賞装置31が開放されるタイミングを予測できない。
【0077】
その結果、可変入賞装置31の開放のタイミングに合わせて遊技球を発射したり発射を止めたりする止め打ちは容易でないばかりか、効率よく賞球を獲得するという止め打ちの効果は得られない。すなわち、止め打ちのメリットがないからこれを行う遊技者もなくなり、パチンコ機10の稼働率の悪化は防止され、出球率が特別に上昇することもない。
【0078】
通常確率抽選モードでは可変入賞装置31の開放時間が短いので、その期間中は可変入賞装置31の開放のタイミングを狙って遊技球を発射することはまず不可能であるから、可変入賞装置31が開放されるタイミングを不一定にするのは高確率抽選モード中だけで十分であり、時間決定ルーチンの実行期間を高確率抽選モード時に限定することで、CPU70aの処理量を低減できる。
【0079】
普通図柄の変動時間を乱数に基づいて決定する(時間決定ルーチン3)のは、比較的簡単な構成で経過時間をランダムに決めることができる。
普通図柄保留記憶の有無で普通図柄の変動の決定範囲を異ならせ(時間決定ルーチン1、4)、普通図柄保留記憶の個数が多いほど変動時間を短くすることで普通図柄保留記憶のオーバーフローを防止して遊技者の利益を図ることができ、普通図柄保留記憶が無い或いは少数のときには、普通図柄の変動を長引かせることで普通図柄の変動が頻繁であると思わせることができる。
【0080】
また、特別図柄保留記憶の個数によって普通図柄の変動時間の決定範囲を異ならせ(時間決定ルーチン2、5)、特別図柄保留記憶の個数が多い場合には普通図柄の変動を長引かせることで可変入賞装置31の開放を遅らせて、特別図柄保留記憶の増加を抑制でき、特別図柄保留記憶が無いときには、普通図柄の変動を短時間にすることで、可変入賞装置31の時間当たりの開放頻度を高めて、遊技者に特別図柄抽選の機会をより多く与えることができる。
【0081】
以上、実施例に従って、本発明の実施の形態について説明したが、本発明はこのような実施例に限定されるものではなく、本発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲でさまざまに実施できることは言うまでもない。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 実施例のパチンコ機の斜視図。
【図2】 実施例のパチンコ機の遊技盤の正面図。
【図3】 実施例のパチンコ機の制御系のブロック図。
【図4】 実施例のパチンコ機において主制御基板のCPUが実行する抽選乱数読込処理のフローチャート。
【図5】 実施例のパチンコ機において主制御基板のCPUが実行する普通図柄抽選処理のフローチャート。
【図6】 実施例のパチンコ機において主制御基板のCPUが実行する特別図柄抽選処理のフローチャート。
【図7】 実施例のパチンコ機において主制御基板のCPUが実行する特別遊技処理のフローチャート。
【図8】 実施例で例示した時間決定ルーチン1のフローチャート。
【図9】 実施例で例示した時間決定ルーチン2のフローチャート。
【図10】 実施例で例示した時間決定ルーチン3のフローチャート。
【図11】 実施例で例示した時間決定ルーチン4のフローチャート。
【図12】 実施例で例示した時間決定ルーチン5のフローチャート。
【図13】 普通図柄抽選処理の変形例のフローチャート。
【符号の説明】
10 パチンコ機(弾球遊技機)
22 遊技盤
26 液晶表示装置(特別図柄表示手段)
27 普通図柄表示器(普通図柄表示手段)
31 可変入賞装置(特別図柄始動装置)
34 ゲート(普通図柄抽選領域)
36 大入賞装置(特別遊技実行手段)
40 大入賞口
70 主制御基板
70a CPU(普通図柄抽選手段、始動装置制御手段、特別遊技実行手段、時間決定手段)
90 表示制御基板(普通図柄制御手段)
98 音声制御基板[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention belongs to the technical field of ball game machines.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Normal symbol lottery means for performing normal symbol lottery due to a game ball entering the normal symbol lottery area (for example, a passage entrance), normal symbol display means for displaying the result of the normal symbol lottery as a normal symbol, and normal symbols Normal symbol control means for controlling the display means to display a fixed symbol after variably displaying it, and a variable winning device that makes it easy to win in an open state when the normal symbol lottery is won (for example, a tulip-type winning device) The special symbol starting device (ordinary electric accessory) which is a starting device control means for releasing the normal symbol after being displayed, and the special symbol lottery means for performing the special symbol lottery due to the winning of the special symbol starting device And a special symbol display means for displaying the result of the special symbol lottery as a special symbol, and a special game for executing a special game advantageous to the player on the condition that the special symbol lottery is a win. There are pinball game machine comprising an execution unit.
[0003]
In this type of ball game machine, the probability of winning in a normal symbol lottery is increased in the case of so-called probability change or short time (hereinafter collectively referred to as "special state"), and the opening time of the special symbol starter is reduced. May be longer. Also, when the special state and not (hereinafter referred to as “normal state”), the change time of the normal symbol is changed (the special state is shorter), but during the special state, the change time is constant, The same was true in the normal state.
[0004]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
Since the special symbol starter is released in synchronization with the normal symbol confirmation display (that is, the end of the fluctuation), the player can predict when the special symbol starter will be released, and the game ball will match the timing. It was easy to make a so-called “stop” that fired or stopped firing.
[0005]
Stopping is a means for efficiently obtaining a prize ball for the player, but for a game shop, the operation rate of the ball game machine has deteriorated and the rate of appearance has increased.
[0006]
[Means for Solving the Problems and Effects of the Invention]
A ball game machine according to
A normal symbol lottery means for performing a normal symbol lottery due to a game ball entering the normal symbol lottery area; a normal symbol display means for displaying the result of the normal symbol lottery in a normal symbol; and the normal symbol display means. A normal symbol control means for controlling and displaying a normal symbol after being controlled and a special symbol starting device which is a variable winning device that makes it easy to win in an open state when the normal symbol lottery is won. A starter control means for releasing the symbol after the symbol is displayed, a special symbol lottery means for performing a special symbol lottery due to winning in the special symbol starter, and a result of the special symbol lottery display as a special symbol In a ball game machine comprising special symbol display means and special game execution means for executing a special game advantageous to a player on the condition that the special symbol lottery was a win,
Time determining means for determining the elapsed time from the detection of the entry of the game ball to the normal symbol lottery area until the opening of the special symbol starting device is determined indefinitely each time.,
The time determination means selects the elapsed time based on whether or not there is a memory (special symbol hold memory) relating to the special symbol lottery that cannot immediately start the display operation of the lottery result.
By doing this,The elapsed time from when the game ball enters the normal symbol lottery area (for example, the passage opening) until the special symbol starter (normal electric accessory) is released is not constant, and the special symbol starter is open to the player. Cannot predict the timing.
[0007]
As a result, not only is it not easy to fire a game ball or stop firing in accordance with the timing of the special symbol starter, but it is also not possible to obtain the effect of efficiently winning a winning ball. That is, since there is no merit of stopping, there is no player who performs this, the deterioration of the operation rate of the ball game machine is prevented, and the pitch rate does not rise specially.
[0008]
When making the elapsed time from the detection of the entry of a game ball into the normal symbol lottery area until the release of the special symbol starter each time non-constant, the player is clearly related to the release of the special symbol starter Since it is possible to recognize the fluctuation of the normal symbol, it is only necessary to make the fluctuation time, particularly the timing of determining the normal symbol, indefinite.
Also, the fact that the lottery result display operation cannot be started immediately means that, for example, a special symbol is being displayed in a variable manner in order to display the preceding lottery result, and the display operation cannot be started without waiting for the confirmation. This is a case where the display operation cannot be performed in relation to the state (for example, during execution of a special game). The memory related to the special symbol lottery refers to a random value or a lottery result used for the special symbol lottery. Normally, there is an upper limit to the number of special symbol reservation memories (usually up to four).
Since the special symbol hold memory increases by winning the special symbol starting device, if the special symbol hold memory is further increased when there is a special symbol hold memory, the special symbol hold memory may overflow. Therefore, when there is a special symbol hold memory, it is better not to increase it as much as possible, that is, not to open the special symbol starter.
On the other hand, in the case of the ball game machine according to
In addition, by selecting the elapsed time according to the number of special symbol hold memories, it is possible to select the variation time of the normal symbol more finely.
[0009]
In order to make the timing of determining the normal symbol indefinite, the starting point may be the normal symbol change start time, or may be when the entry of a game ball into the normal symbol lottery area is detected.
Further, in the bullet ball game machine according to claim 2, the time determination means sets the determination range of the elapsed time based on the presence / absence or number of the special symbol hold memory, and the game to the normal symbol lottery area A time within the determination range is selected as the elapsed time based on a random number extracted due to the detection of the entry of a sphere. By doing so, the elapsed time can be determined randomly with a relatively simple configuration.
[0010]
According to a third aspect of the present invention, the ball game machine according to claim 3 is provided with a normal mode in which the probability of winning by the normal symbol lottery means is relatively low or the fluctuation time of the normal symbol is relatively long, and the normal symbol lottery means. There is a special mode in which the probability of winning is relatively high or the variation time of the normal symbol is relatively short, and the time determining means operates in the special mode.
The normal symbol lottery means using the low probability lottery with a relatively low probability of winning and the high probability lottery with a higher probability of winning than the low probability lottery are also used in conventional ball game machines. ing. Normally, when the probability variation (probability variation) in which the chance of winning in the special symbol lottery is higher than normal or when the special symbol variation time is shortened after the special game is finished, the normal symbol lottery has a high probability. It will be a lottery.
[0011]
The opening time of the special symbol starting device is short during the period when the low-probability lottery is performed (for example, about 0.2 to 0.3 seconds), and is 2-3 seconds during the period when the high-probability lottery is performed. It has been long to the extent. However, since there is also an upper limit for the number of winnings, it may return to the closed state before this time is reached.
[0012]
Therefore, if the opening time of the special symbol starting device is such a setting, it is impossible to launch a game ball aiming at the opening timing of the special symbol starting device during the period when the low probability lottery is performed. However, it can be performed sufficiently during the period when the high probability lottery is performed. Therefore, it is sufficient to make the timing at which the special symbol starting device is opened only during the period when the high probability lottery is performed. That is, the claim3The object of the invention can be sufficiently achieved with the configuration of. Moreover, there is an advantage that the processing amount of the CPU can be reduced by limiting the operation period of the time determining means in this way.
[0014]
further,In normal ball game machines, the probability of winning in the special symbol lottery is usually higher when the probability variation (probability variation) is higher than normal, or when the special symbol variation time is shortened after the special game ends Usually, the symbol variation time is shorter (normal mode, variation time is about 28 to 29 seconds) (time reduction mode).
[0015]
The opening time of the special symbol starting device is short in the normal mode (for example, about 0.2 to 0.3 seconds), and is long in the time reduction mode, for example, about 2 to 3 seconds. However, since there is also an upper limit for the number of winnings, it may return to the closed state before this time is reached.
[0016]
Therefore, if the opening time of the special symbol starter is set in this way, it is impossible to launch a game ball aiming at the opening timing of the special symbol starter in the normal mode. Can do enough. Therefore, only the short time mode is sufficient to make the timing at which the special symbol starting device is opened indefinite. In other words, the object of the invention can be sufficiently achieved with the structure of claim 3. Moreover, there is an advantage that the processing amount of the CPU can be reduced by limiting the operation period of the time determining means in this way..
[0027]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Next, embodiments of the present invention will be described by way of examples of the present invention.
[0028]
【Example】
As shown in FIG. 1, a
[0029]
The
A window-shaped
[0030]
An
[0031]
A
[0032]
As shown in FIG. 2, the
[0033]
In the
[0034]
Below these
Note that the
[0035]
As shown in FIG. 3, the
The main control board 70 is provided with a CPU 70a, ROM 70b, RAM 70c, counters 70d, 70e, 70f, input / output ports, etc., and the main control board 70 (particularly the CPU 70a) is a normal symbol lottery means, a starter control means, a special symbol. It functions as a lottery means and a time determination means, and also functions as a special game execution means in cooperation with the
[0036]
The main control board 70 includes a gate 34 (which itself is a passage sensor), a winning sensor 31a of the variable winning
[0037]
The display control board 90 includes a CPU 90a, a ROM 90b, a RAM 90c, an input / output port, and the like, and controls the display of the liquid
[0038]
Although not shown, the payout control board 92, the launch control board 94, the lamp control board 96, and the voice control board 98 are each provided with a CPU, ROM, RAM, input / output ports, etc., and the voice control board 98 also has a tone generator LSI. Each control operation is performed according to a command sent from the main control board 70. Briefly, the dispensing control board 92 is a dispensing apparatus, the firing control board 94 is a launching apparatus, the lamp control board 96 is a flash of electrical decorations (LEDs and light bulbs), and motors and solenoids that are not controlled by other control boards. The sound control board 98 controls sound output from the speakers.
[0039]
Next, the operation of the
[0040]
FIG. 4 shows a lottery random number reading process for special symbols and ordinary symbols. In this process, the CPU 70a determines whether or not a game ball detection signal (special symbol start signal) from the winning sensor 31a of the variable winning
[0041]
If the determination is affirmative, the value of the counter 70d is read (S52), and whether or not four special symbol lottery random numbers are stored in the special symbol lottery random number storage area provided in the RAM 70c, that is, the special symbol hold is four. It is determined whether or not the number has been reached (S53). If there are three or fewer holds (S53: NO), the value read in S52 is stored as a special symbol lottery random number in the special symbol lottery random number storage area (S54).
[0042]
When a negative determination is made at S51, when an affirmative determination is made at S53, or after S54, the CPU 70a determines whether or not a passing ball detection signal (ordinary symbol start signal) is input from the
[0043]
If the determination is affirmative, the value of the counter 70e is read (S56), and whether or not four normal symbol lottery random numbers are stored in the normal symbol lottery random number storage area provided in the RAM 70c, that is, the normal symbol hold is four. It is determined whether or not the number has been reached (S57). If there are three or less holds (S57: NO), the value read in S56 is stored in the normal symbol lottery random number storage area as a normal symbol lottery random number (S58).
[0044]
When a negative determination is made at S55, an affirmative determination is made at S57, or after S58, the process returns.
Next, the normal symbol lottery will be described with reference to FIG.
In this process, the CPU 70a first determines whether or not the
[0045]
When a negative determination, that is, when the normal symbol is not changing, it is determined whether or not the normal symbol lottery random number is stored in the normal symbol lottery random number storage area (S101). If the determination is negative, the process returns.
If there is an affirmative determination, that is, if there is the normal symbol lottery random number stored in S58, the oldest one is read and deleted from the normal symbol lottery random number storage area (S102). In addition, since the CPU 70a holds the normal symbol lottery random number in a register, for example, the lottery random number itself does not disappear.
[0046]
Next, the CPU 70a determines whether or not the high-probability lottery mode is set (S103). In the case of the present embodiment, when the special symbol lottery is performed with a high probability (during so-called probability change), the high-probability lottery mode is performed. In this mode, the normal symbol lottery is also performed with a high probability. Needless to say, the probability of the special symbol lottery and the probability of the normal symbol lottery are not the same. In this embodiment, in the normal probability lottery mode, the winning probability of the special symbol lottery is about 1/300, and the winning probability of the normal symbol lottery is 1/10. In the high probability lottery mode, the winning probability of the special symbol lottery is about 1/300. 60, the probability of winning the normal symbol lottery is 9/10.
[0047]
If it is the high probability lottery mode (S103: YES), a time determination routine (S104) for determining the fluctuation time of the normal symbol is executed. Since there are various variations in this process, some typical examples will be described with reference to FIGS. The CPU 70a corresponds to time determination means by executing
[Time determination routine 1]
This example is an example of determining according to the number of reserved normal symbols (the number of normal symbol lottery random numbers stored in the normal symbol lottery random number storage area).
[0048]
As shown in FIG. 8, in this example, it is first determined whether or not the number of normal symbols held is other than 0 (any one of 1 to 3) (S120). In S102, since the normal symbol lottery random numbers to be selected for the current lottery are deleted from the normal symbol lottery random number storage area, the number of the normal symbol lottery random numbers other than the target for the current lottery is determined.
[0049]
If negative determination is made in S120, that is, if the number of normal symbols held is 0, a change time of 7 seconds is selected (S121). If the determination is affirmative, whether or not the number of normal symbols held is other than 1 (2 or 3). Judgment is made (S122).
In S122, a negative determination is made, that is, if the number of held ordinary symbols is 1, a variation time of 6 seconds is selected (S123). If an affirmative determination is made, it is determined whether the number of retained ordinary symbols is other than 2 (ie 3). (S124).
[0050]
If a negative determination is made in S124, that is, if the number of normal symbols held is 2, then a change time of 5 seconds is selected (S125), and if a positive determination is made, a change time of 4 seconds is selected (S126).
[Time determination routine 2]
This example is an example of determining according to the number of reserved special symbols (the number of special symbol lottery random numbers stored in the special symbol lottery random number storage area).
[0051]
As shown in FIG. 9, in this example, it is first determined whether or not the number of reserved special symbols is other than 0 (any one of 1 to 4) (S130).
If the negative determination in S130, that is, if the number of reserved special symbols is 0, a variation time of 4 seconds is selected (S131). If the determination is affirmative, whether the number of reserved special symbols is other than 1 (any of 2 to 4). It is determined whether or not (S132).
[0052]
If negative determination is made in S132, that is, if the number of reserved special symbols is 1, 5 seconds is selected (S133). If the determination is affirmative, whether the number of reserved special symbols is other than 2 (that is, 3 or 4). Judgment is made (S134).
In S134, a negative determination is made, that is, if the number of reserved special symbols is 2, a 6-second fluctuation time is selected (S135). If an affirmative determination is made, it is determined whether the number of reserved special symbols is other than 3 (that is, 4). (S136).
[0053]
In S136, a negative determination is made, that is, if the number of special symbols to be held is 3, a change time of 7 seconds is selected (S137), and if a positive determination is made, a change time of 8 seconds is selected (S138).
[Time determination routine 3]
This example is an example of determination based on a random value.
[0054]
As shown in FIG. 10, in this routine, the value of the counter 70f for time determination is read (S140), and the range of 3 to 8 seconds corresponding to the value (for example, according to the random number value and variation time comparison table). The variation time is selected with (S141).
[Time determination routine 4]
In this example, the number is determined according to the random number value and the number of reserved ordinary symbols.
[0055]
As shown in FIG. 11, in this routine, first, the value of the time determination counter 70f is read (S150).
Next, it is determined whether or not the reserved number of normal symbols is other than 0 (any one of 1 to 3) (S151).
[0056]
If a negative determination is made in S150, that is, if the number of held ordinary symbols is 0, a variation time is selected in the range of 6 to 7 seconds corresponding to the value of the counter 70f (S152). It is determined whether it is other than 1 (2 or 3) (S153).
[0057]
If a negative determination is made in S153, that is, if the number of held ordinary symbols is 1, a fluctuation time of 5 to 6 seconds is selected corresponding to the value of the counter 70f (S154). That is, it is determined whether or not 3) (S155).
If a negative determination is made in S155, that is, if the number of ordinary symbols held is 2, a variation time of 4 to 5 seconds is selected corresponding to the value of the counter 70f (S156), and if an affirmative determination is made, 3 corresponding to the value of the counter 70f is selected. A variation time of ˜4 seconds is selected (S157).
[Time determination routine 5]
This example is an example of determining according to a random number value and the number of reserved special symbols.
[0058]
As shown in FIG. 12, in this routine, the value of the time determination counter 70f is first read (S160).
Next, it is determined whether the number of reserved special symbols is other than 0 (any one of 1 to 4) (S161).
[0059]
If the negative determination in S130, that is, if the number of reserved special symbols is 0, the variation time is selected in the range of 3 to 4 seconds corresponding to the value of the counter 70f (S162). It is determined whether it is other than 1 (any one of 2 to 4) (S163).
[0060]
If a negative determination is made in S163, that is, if the number of reserved special symbols is 1, a variation time of 4 to 5 seconds is selected corresponding to the value of the counter 70f (S164). If the determination is affirmative, the number of reserved special symbols is other than 2 ( That is, it is determined whether or not 3 or 4) (S165).
[0061]
If the negative determination is made in S165, that is, if the number of reserved special symbols is 2, a variation time of 5 to 6 seconds is selected corresponding to the value of the counter 70f (S166). That is, it is determined whether or not 4) (S167).
If negative determination is made in S167, that is, if the number of reserved special symbols is 3, a change time of 6 to 7 seconds is selected corresponding to the value of the counter 70f (S168), and if positive determination, the value corresponding to the value of the counter 70f is selected. A variation time of 7 to 8 seconds is selected (S169).
[0062]
As shown in FIG. 5, after the normal symbol variation time is determined by any one of these
[0063]
If the lottery is a win (S108: YES), a normal symbol hit command for displaying the win is generated and transmitted to the display control board 90 (S109). This command includes variation time data that specifies the variation time determined in S104 or a default value.
[0064]
When the display control board 90 receives this command, the normal
The CPU 70a waits for the normal symbol to be determined, and controls the variable winning
[0065]
On the other hand, if the lottery is out (S108: NO), a normal symbol out command for displaying the out is generated and transmitted to the display control board 90 (S111). This command also includes variable time data. When the display control board 90 receives this command, the
[0066]
For example, when the special symbol lottery is performed with a high probability (when the probability changes) or when the special symbol variation time is set shorter than usual (when the time is short), the probability of the normal symbol lottery is not changed to a high probability. In some cases, only the opening time of the variable winning
[0067]
In this example, S100 to S102 are the same as in FIG. 5, but subsequently whether or not the special symbol variation time is set shorter than usual is a short time state (in this example, the special symbol lottery in the short time state) Is determined with a high probability) (S103 ′), and if a positive determination is made, a time determination routine (S104) for determining the fluctuation time of the normal symbol is executed. The processing of this time determination routine is the same as in FIGS. When a negative determination is made in S103 ', the normal symbol change time is set to a default value (for example, about 28 seconds) (S106). Then, after S104 or S106, a lottery is performed for the normal symbol lottery random number read in S102 (S107 '). The subsequent processing is the same as in FIG.
[0068]
Next, the special symbol lottery will be described with reference to FIG.
In this process, the CPU 70a first determines whether or not the special symbol variation display can be executed (S200). Specifically, it is determined whether the liquid
[0069]
If an affirmative determination, that is, if the special symbol can be displayed in a variable manner, it is determined whether or not a special symbol lottery random number is stored in the special symbol lottery random number storage area (S201). If the determination is negative, the process returns.
If there is an affirmative determination, that is, if there is the special symbol lottery random number stored in S54, the oldest one is read and deleted from the special symbol lottery random number storage area (S201). Note that since the special symbol lottery random number is held in the register by the CPU 70a, for example, the lottery random number itself does not disappear.
[0070]
Next, the CPU 70a determines whether or not the high-probability lottery mode is set (S203).
If it is the high probability lottery mode (S203: YES), the lottery in the high probability lottery mode is performed for the special symbol lottery random number that has been read (S204). Further, when a negative determination is made in S203, a low probability lottery is performed in the normal probability lottery mode (S205).
[0071]
If the lottery is a win (S206: YES), a win flag F is set (S207), a special symbol hit command for displaying a win is generated and transmitted to the display control board 90 (S208).
When receiving this command, the display control board 90 controls the liquid
[0072]
If the lottery is out (S206: NO), a special symbol out command for displaying the out is generated and transmitted to the display control board 90 (S209). Upon receiving this command, the display control board 90 displays the special symbol on the liquid
[0073]
Here, when the winning special symbol is confirmed and displayed, a special game is started subsequently.
The special game itself executed in this embodiment is the same as a known pachinko machine of the type called the first type, but will be briefly described with reference to FIG. The CPU 70a functions as special game execution means in cooperation with the
[0074]
In the special game process, the main control board 70 determines whether or not the hit flag F is set to 1 (S301). If the determination is negative, no substantial process is performed (the special game is not executed).
If an affirmative determination is made in S301, a jackpot opening command is sent to the display control board 90 to display the jackpot fanfare screen, then the
[0075]
Then, it is determined whether or not the high probability mode is set (probability variation) (S305). If the determination is affirmative, the probability variation flag is set (S306). If the determination is negative, the probability variation flag is cleared (S307). Here, when the probability variation flag is set, the high probability mode is set thereafter, and the special symbol lottery of FIG. 6 is performed with high probability. The determination as to whether or not to enter the high probability mode is based on the result of the probability variation lottery executed when the jackpot lottery is a win (S206: YES). That is, if the probability variation lottery is a win, the determination is affirmative in S305.
[0076]
In this embodiment, such a special game is played when a special symbol lottery is won, but the form of the special game executed on condition that the lottery is won is not limited to this.
As described above, this
[0077]
As a result, not only is it easy to fire a game ball or stop firing in accordance with the opening timing of the variable
[0078]
In the normal probability lottery mode, since the opening time of the variable winning
[0079]
The change time of the normal symbol is determined based on random numbers (time determination routine 3), and the elapsed time can be determined randomly with a relatively simple configuration.
The normal symbol hold memory overflow is prevented by making the determination range of the normal symbol change different depending on the presence or absence of the normal symbol hold memory (
[0080]
Also, the variation range of the normal symbol change time is made different depending on the number of special symbol hold memories (time determination routines 2 and 5), and when the number of special symbol hold memories is large, it can be varied by prolonging the fluctuation of the normal symbols. Delaying the opening of the winning
[0081]
As mentioned above, although embodiment of this invention was described according to the Example, this invention is not limited to such an Example, and it cannot be overemphasized that it can implement variously in the range which does not deviate from the summary of this invention.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a pachinko machine according to an embodiment.
FIG. 2 is a front view of the game board of the pachinko machine according to the embodiment.
FIG. 3 is a block diagram of a control system of the pachinko machine according to the embodiment.
FIG. 4 is a flowchart of lottery random number reading processing executed by the CPU of the main control board in the pachinko machine according to the embodiment.
FIG. 5 is a flowchart of normal symbol lottery processing executed by the CPU of the main control board in the pachinko machine of the embodiment.
FIG. 6 is a flowchart of a special symbol lottery process executed by the CPU of the main control board in the pachinko machine of the embodiment.
FIG. 7 is a flowchart of special game processing executed by the CPU of the main control board in the pachinko machine according to the embodiment.
FIG. 8 is a flowchart of a
FIG. 9 is a flowchart of a time determination routine 2 exemplified in the embodiment.
FIG. 10 is a flowchart of a time determination routine 3 exemplified in the embodiment.
FIG. 11 is a flowchart of a
FIG. 12 is a flowchart of a time determination routine 5 exemplified in the embodiment.
FIG. 13 is a flowchart of a modified example of the normal symbol lottery process.
[Explanation of symbols]
10 Pachinko machine (ball game machine)
22 Game board
26 Liquid crystal display (special symbol display means)
27 Normal symbol display (normal symbol display means)
31 Variable winning device (special symbol starter)
34 Gate (normal symbol lottery area)
36 Grand Prize Winner (special game execution means)
40 grand prize opening
70 Main control board
70a CPU (normal symbol lottery means, starter control means, special game execution means, time determination means)
90 Display control board (Normal design control means)
98 Voice control board
Claims (3)
前記普通図柄抽選領域への遊技球の進入が検出されたときから前記特別図柄始動装置の開放までの経過時間を各回毎に不一定に決定する時間決定手段を備え、
該時間決定手段は、前記抽選結果の表示動作を直ちに開始できない前記特別図柄抽選に関する記憶(特別図柄保留記憶)の有無又は個数に基づいて前記経過時間を選択することを特徴とする弾球遊技機。A normal symbol lottery means for performing a normal symbol lottery due to a game ball entering the normal symbol lottery area; a normal symbol display means for displaying the result of the normal symbol lottery in a normal symbol; and the normal symbol display means. A normal symbol control means for controlling and displaying a normal symbol after being controlled and a special symbol starting device which is a variable winning device that makes it easy to win in an open state when the normal symbol lottery is won. A starter control means for releasing the symbol after the symbol is displayed, a special symbol lottery means for performing a special symbol lottery due to winning in the special symbol starter, and a result of the special symbol lottery display as a special symbol In a ball game machine comprising special symbol display means and special game execution means for executing a special game advantageous to a player on the condition that the special symbol lottery was a win,
A time determining means for determining the elapsed time from the time when the game ball enters the normal symbol lottery area until the opening of the special symbol starting device is determined in each case,
The time determining means selects the elapsed time based on the presence or absence or the number of the special symbol lottery that cannot immediately start the lottery result display operation (special symbol holding storage). .
前記時間決定手段は、前記特別図柄保留記憶の有無又は個数に基づいて前記経過時間の決定範囲を設定すると共に、前記普通図柄抽選領域への遊技球の進入が検出されたことに起因して抽出された乱数に基づき、該決定範囲内の時間を、前記経過時間として選択することを特徴とする弾球遊技機。In the ball game machine according to claim 1,
The time determination means sets the determination range of the elapsed time based on the presence / absence or number of the special symbol hold memory and extracts due to the detection of the entry of the game ball into the normal symbol lottery area A ball game machine characterized in that a time within the determined range is selected as the elapsed time based on the random number .
前記普通図柄抽選手段による当たりの確率が相対的に低い又は前記普通図柄の変動時間が相対的に長い通常モードと、
前記普通図柄抽選手段による当たりの確率が相対的に高い又は前記普通図柄の変動時間が相対的に短い特別モードとがあり、
前記時間決定手段は、前記特別モードのときに作動することを特徴とする弾球遊技機。In the bullet ball game machine according to claim 1 or claim 2 ,
A normal mode in which the probability of winning by the normal symbol lottery means is relatively low or the variation time of the normal symbol is relatively long ;
There is a special mode in which the probability of winning by the normal symbol lottery means is relatively high or the variation time of the normal symbol is relatively short,
The time determining means operates in the special mode.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000392369A JP4714809B2 (en) | 2000-12-25 | 2000-12-25 | Bullet ball machine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000392369A JP4714809B2 (en) | 2000-12-25 | 2000-12-25 | Bullet ball machine |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2002191831A JP2002191831A (en) | 2002-07-10 |
| JP2002191831A5 JP2002191831A5 (en) | 2008-02-07 |
| JP4714809B2 true JP4714809B2 (en) | 2011-06-29 |
Family
ID=18858370
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000392369A Expired - Lifetime JP4714809B2 (en) | 2000-12-25 | 2000-12-25 | Bullet ball machine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4714809B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5605820B2 (en) * | 2005-06-16 | 2014-10-15 | サミー株式会社 | Bullet ball machine |
| JP4987421B2 (en) * | 2006-10-24 | 2012-07-25 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP2008132145A (en) * | 2006-11-28 | 2008-06-12 | Fujishoji Co Ltd | Pinball game machine |
| JP4866450B2 (en) * | 2009-07-27 | 2012-02-01 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
| JP2011156082A (en) * | 2010-01-29 | 2011-08-18 | Sansei R&D:Kk | Pinball game machine |
| JP2011172743A (en) * | 2010-02-24 | 2011-09-08 | Sophia Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP5731162B2 (en) * | 2010-10-15 | 2015-06-10 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Pachinko machine |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3897834B2 (en) * | 1995-06-30 | 2007-03-28 | 株式会社三共 | Bullet ball machine |
| JPH09215828A (en) * | 1996-02-08 | 1997-08-19 | Sophia Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP2000037524A (en) * | 1998-07-21 | 2000-02-08 | Daiichi Shokai Co Ltd | Pachinko machine |
| JP2000334121A (en) * | 1999-05-31 | 2000-12-05 | Fuji Shoji:Kk | Pachinko machine |
-
2000
- 2000-12-25 JP JP2000392369A patent/JP4714809B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2002191831A (en) | 2002-07-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2007029262A (en) | Pachinko game machine | |
| JP2010035823A (en) | Pachinko game machine | |
| JP4714809B2 (en) | Bullet ball machine | |
| JP2010035824A (en) | Pachinko game machine | |
| JP2009291520A (en) | Pachinko game machine | |
| JP2007313160A (en) | Pinball game machine | |
| JP2010075302A (en) | Pachinko game machine | |
| JP2009232964A (en) | Pachinko game machine | |
| JP7097080B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP4428619B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP4656560B2 (en) | Bullet ball machine | |
| JP5695705B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP3875909B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP2010119489A (en) | Pachinko game machine | |
| JP2015163368A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP7097081B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP7097079B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP5313768B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP7097078B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP2002172225A (en) | Pinball game machine | |
| JP5247318B2 (en) | Pachinko machine | |
| JP5363039B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2016153045A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6356769B2 (en) | Bullet ball machine | |
| JP2007014584A (en) | Game machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20071214 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20071214 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20101014 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20101019 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20101208 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20110208 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20110214 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Ref document number: 4714809 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140408 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140408 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| EXPY | Cancellation because of completion of term |