JP4598416B2 - Plasma processing method - Google Patents
Plasma processing method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4598416B2 JP4598416B2 JP2004069155A JP2004069155A JP4598416B2 JP 4598416 B2 JP4598416 B2 JP 4598416B2 JP 2004069155 A JP2004069155 A JP 2004069155A JP 2004069155 A JP2004069155 A JP 2004069155A JP 4598416 B2 JP4598416 B2 JP 4598416B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- substrate
- processed
- plasma processing
- plasma
- container
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Drying Of Semiconductors (AREA)
Description
本発明は、半導体および薄膜ディスプレイ産業における、薄膜回路形成方法に利用できるものであり、特に絶縁性の高い基板であるガラスや石英、化合物半導体等の上にトランジスター素子形成可能なプラズマ処理方法に関し、プラズマ処理前の被処理基板は既に電価が蓄積した状態にあり、この状態の前記被処理基板をプラズマ処理すると、デバイスダメージやデバイス破壊を発生させる事に対して、効率的に軽減することのできるプラズマ処理方法に関する。 The present invention, in the semiconductor and thin-film display industry, which can be used in thin-film circuit forming method, in particular glass or quartz having a high substrate insulating property, the transistor element can be formed plasma treatment how on such compound semiconductor In this regard, the substrate to be processed before plasma processing is already in a state where the electric charge has accumulated, and if the substrate to be processed in this state is plasma-processed, device damage and device destruction can be effectively reduced. about the plasma processing how that can be.
近年、薄膜素子製造分野において、製造コスト削減や環境保護の観点から、工程簡略や製造方法の環境負荷の少ない製造方法に変更を望む声が高まっており、従来の薬液による工法から、プラズマを応用した薄膜加工する工法及び、装置が望まれている。 In recent years, in the field of thin-film device manufacturing, there has been an increasing demand for a simplified manufacturing process and a manufacturing method with a low environmental impact from the viewpoint of manufacturing cost reduction and environmental protection. A thin film processing method and apparatus are desired.
しかしながら、上記薄膜素子デバイスでは、多岐にわたる製造工程を経て製造されており、たとえば熱処理であり、水洗処理であり、プラズマを応用した処理であったりすることから、常に様々な要因により、被処理基板の表裏に電荷の蓄積が発生することになる。 However, the thin film element device is manufactured through a variety of manufacturing processes, such as heat treatment, water washing treatment, and plasma treatment, so that the substrate to be treated is always caused by various factors. Accumulation of charge occurs on the front and back of the film.
プラズマを応用した薄膜加工および装置はプラズマを真空中にて発生させ、プロセスガスを乖離させ、イオンやラジカルにより物理的、化学的な反応を組み合わせた加工を行うため、被処理基板上にますます多量な電荷を発生させることになる。 Thin film processing and equipment using plasma generates plasma in a vacuum, dissociates process gases, and performs processing that combines physical and chemical reactions with ions and radicals, so it is on the substrate to be processed. A large amount of charge is generated.
多量に発生した電荷は、薄膜回路の構成上、金属膜と金属膜の間を絶縁する為の絶縁膜が薄膜形成されているが、耐電圧には閾値を持つことになり、その閾値を超えるような電荷を被処理基板が帯び、帯電した場合には絶縁膜の破壊が発生し、薄膜回路を形成しえなくなる。この為、なるべく被処理基板上にチャージしないようなプラズマにするか、チャージした電荷をプラズマプロセス上の工夫で低減する取り組みを実施してきた。 Due to the structure of the thin film circuit, a large amount of generated charge has a thin insulating film that insulates between the metal film, but the withstand voltage has a threshold value that exceeds the threshold value. When the substrate to be processed has such a charge and is charged, the insulating film is broken and a thin film circuit cannot be formed. For this reason, efforts have been made to reduce the charged charge by means of a plasma process, or to make the plasma as low as possible on the substrate to be processed.
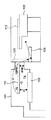
以下、図3に代表的なドライエッチング装置形態について説明する。 Hereinafter, a typical dry etching apparatus will be described with reference to FIG.
101はドライエッチ処理するためのプラズマ処理容器、101aはプロセスガスおよび、不活性ガス導入装置、102は被処理基板112を載置するためのプラズマを発生させる機能を具備した電極、103は真空排気装置、104はプラズマ処理容器へ被処理基板112を真空圧力の状態で出し入れする真空移載容器、104aは真空排気装置、104bは不活性ガス導入装置、105はプラズマ処理容器101と真空移載容器104の隔壁となり開閉機構を有するゲート扉、106は真空搬送機構、106aは真空搬送機構106と連動し、被処理基板112を電極102上へ載置するために動作するリフトピン、107は大気状態から真空状態へ容器内を減圧する動作やその逆に、真空状態から大気状態へ加圧する動作ができる機能を有するロードロック容器、107aは真空排気装置、107bは不活性ガス導入装置、108は真空移載容器104とロードロック容器107の隔壁となり開閉機構を有するゲート扉、109はロードロック容器107を真空に保持するためのゲート扉、110は被処理基板112を収納している基板収納装置、111は基板収納装置110より被処理基板112を取り出し、前記ロードロック容器107へ移載するための大気搬送機構である。
101 is a plasma processing vessel for performing a dry etching process, 101a is a process gas and inert gas introducing device, 102 is an electrode having a function of generating plasma for placing a substrate to be processed 112, and 103 is evacuated. 104, a vacuum transfer container for transferring the
以上のように構成されたドライエッチング装置について、以下にその動作について説明する。 The operation of the dry etching apparatus configured as described above will be described below.
まず、被処理基板112を、基板収納装置110より大気搬送機構111にて取り出し、ロードロック容器107に不活性ガス導入装置107bより不活性ガスをパージして大気状態にし、ゲート扉109を開き、大気搬送機構111によって、被処理基板112をロードロック容器107へと搬送する。
First, the
続いて、ゲート扉109を閉じて、ロードロック容器107において、不活性ガス導入装置107bの動作を止め、排気装置107aより排気し、一定の圧力にまで真空排気が完了した後、ゲート扉108を開く。真空移載容器104は排気装置104aが常時真空排気動作しており常に真空状態を保持した状態となっている。真空搬送機構106によりロードロック容器107に載置されている被処理基板112を取り出し、真空移載容器104へと移載して、ゲート扉108を閉じる。
Subsequently, the
プラズマ処理容器101にある真空排気装置103は常時真空排気動作しており容器内は常に真空状態を保持している。ゲート扉105が開き、真空移載容器104内の真空搬送機構106にある被処理基板112はプラズマ処理容器101の電極102へ移載され、リフトピン106a上に被処理基板112を載置後、ゲート扉105が閉まり、リフトピン106aが下降し電極102上に被処理基板が載置され、その後、プラズマ処理が行われる。
The
プラズマ処理終了後、N2やO2等のガスによる除電プロセスといわれる、プラズマの発生領域を圧力やパワーにより変化させて、被処理基板112上に帯電した電荷を除去するプロセス処理後、またはプロセス処理中にリフトピン106aが上昇し、被処理基板112を上昇させる。
After the plasma treatment is completed, a process of removing a charge on the substrate to be treated 112 by changing a plasma generation region by pressure or power, which is called a static elimination process with a gas such as N 2 or O 2 , or a process During the processing, the
その後、ゲート扉105が開き、真空搬送機構106により、プラズマ処理容器101内のリフトピン106a上にある被処理基板112は、プラズマ処理容器101内より取り出され、真空移載容器104内に移載される。
Thereafter, the
このとき、プラズマ処理容器101の真空排気装置103はプラズマ処理後の反応生成物が前記真空移載容器104へ流入しないように排気動作をしている。ゲート扉105が閉じ、次に、ゲート扉108が開き、真空移載機構106により被処理基板112はロードロック容器107へと移載され、ゲート扉108が閉まる。ロードロック容器107内の真空排気装置107aが停止し、不活性ガス導入装置107bより不活性ガスがパージされ、ロードロック容器107内は真空圧状態から大気圧状態へとなり、ゲート扉109が開き、大気搬送機構111により、ロードロック容器107内にある被処理基板112が取り出され、基板収納装置110へと収められる。特許文献1〜3参照。
At this time, the
しかしながら、プラズマ処理容器101内にて被処理基板112がプラズマ処理終了後、除電プロセス終了後、ゲート扉105が開き、真空搬送機構106により、プラズマ処理容器101内の電極102上にある被処理基板112が、プラズマ処理容器101内より取り出され、真空移載容器104内に移載される時に、被処理基板112の表面に残留帯電した電荷の電位値は図4(b)に示すような挙動を示す。
However, after the plasma processing of the
プラズマ処理後の被処理基板112の表面に帯電した電荷は、前記ゲート扉105を通過する時に最大電位値を示し、その後も高い電位を保持した状態で被処理基板112が真空移載容器104に載置される。被処理基板112が真空中において移載される際に変化する帯電位が被処理基板112上に成膜された絶縁膜の耐電圧閾値102aを超えた時に、絶縁破壊を起こす問題点がある。
The electric charge charged on the surface of the substrate to be processed 112 after the plasma treatment shows a maximum potential value when passing through the
これは、図5に示すように、前記被処理基板112が移載する際に、前記被処理基板112の表面に帯電した電荷−Qが対向して分極している前記電極102表面の電荷+Q(この時点では、前記被処理基板112の裏面と前記電極102の表面との間の距離dが限りなく大きいため、(式1)の公式には当てはまらない)から、前記プラズマ処理容器の底面、ゲート扉105の底面、真空移載容器104の底面へと移り変わる時に、下記の公式(式1)に当てはまる距離dが存在している場合に限る。
As shown in FIG. 5, when the substrate to be processed 112 is transferred, the charge −Q charged on the surface of the substrate to be processed 112 is polarized oppositely to the charge + Q on the surface of the
前記(式1)から分かるように、d(距離)に影響される領域(dmin)に達した時に、Vgが上昇する可能性があるためと考えられる。
As can be seen from the above (Equation 1), it is considered that V g may increase when the region (dmin) affected by d (distance) is reached.
無論、被処理基板112の表面電位が最も上昇するのは、電極102より被処理基板112が離れる瞬間であることは、容易に想像がつくが、そのとき、絶縁破壊を免れても、被処理基板112の一部が、ゲート扉105を通過しているため、被処理基板112の一部分のみ表面の電位が異常に上昇する可能性があり、その部分で絶縁破壊が起こると想像されている。
Of course, it can be easily imagined that the surface potential of the substrate to be processed 112 rises the most at the moment when the substrate to be processed 112 is separated from the
また、絶縁破壊が起こらなくても、一般的にダメージといわれる、被処理基板112上に形成される活性な状態を保った薄膜は、電荷の局所的な上昇で、薄膜内部の組成を変化させ、薄膜が持つ特性、性能を劣化させる要因ともなる。 In addition, even if dielectric breakdown does not occur, a thin film that remains active and is formed on the substrate to be processed 112, which is generally referred to as damage, changes the composition inside the thin film due to local increase in charge. It also becomes a factor that degrades the characteristics and performance of the thin film.
一般的な真空量産設備は、ゲート扉開閉時の圧力損失を小さくするため、ゲート扉を限りなく小さく製作している。被処理基板112がゲート扉105を通過する地点での、被処理基板112とゲート扉105の距離は、限りなく被処理基板112とゲート扉105が近くなり静電容量の基本公式の影響を受ける範囲となることになる。被処理基板112上の一部分で電位Vgが、電極102上にあるときよりも高い値を示すこととなる。
In general vacuum mass production equipment, the gate door is made as small as possible to reduce the pressure loss when the gate door is opened and closed. The distance between the substrate to be processed 112 and the
上記内容は、真空中にて被処理基板112を移載する限り、蓄積された電荷は放電される場所がないため、大気状態になるまでは、非常に高いレベルで電荷を保った状態のままとなるため、量産設備の形態によっては、ゲート扉105だけではなく、他の部分においても、(式1)の影響を受けやすいこともありえる。
As long as the substrate to be processed 112 is transferred in a vacuum, there is no place where the accumulated charge is discharged, so that the charge remains at a very high level until the atmospheric condition. Therefore, depending on the form of mass production equipment, not only the
本発明は、このような従来の問題点に鑑み、プラズマ処理後に被処理基板を移載する際に変化する被処理基板上の電荷量を軽減する事が可能なプラズマ処理方法を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention is, that such light of the conventional problems, to provide a plasma processing how that can reduce the amount of charge to be treated on a substrate which changes in transferring a substrate to be processed after the plasma treatment With the goal.
上記目的を達成するために、本発明は以下のように構成する。 In order to achieve the above object, the present invention is configured as follows.
本発明の第1態様によれば、減圧下で被処理基板を載置する電極に電力を印加することで前記被処理基板に薄膜回路を形成するプラズマ処理方法において、
前記被処理基板にプラズマ処理を施す以前に、前記被処理基板を前記電極から離した状態で、前記被処理基板の表面及び裏面を不活性ガスを主体とするガス中で帯電電荷除去用プラズマに曝し、前記被処理基板の前記表面及び裏面に帯電した電荷を取り除くことを特徴とするプラズマ処理方法を提供する。
本発明の第2態様によれば、上記帯電電荷除去用プラズマはプラズマ処理時の高周波電力の1/3以下であることを特徴とする第1の態様に記載のプラズマ処理方法を提供する。
本発明の第3態様によれば、上記帯電電荷除去用プラズマは0.1〜1.0W/cm2であることを特徴とする第1又は2の態様に記載のプラズマ処理方法を提供する。
本発明の第4態様によれば、上記帯電電荷除去用プラズマに前記被処理基板を曝し、前記被処理基板の前記表面及び裏面に帯電した電荷を取り除くことにより、上記被処理基板の表裏両面と上記電極の表面とを同電位とすることを特徴とする第1〜3のいずれか1つの態様に記載のプラズマ処理方法を提供する。
According to the first aspect of the present invention, in the plasma processing method of forming a thin film circuit on the substrate to be processed by applying power to the electrode on which the substrate to be processed is placed under reduced pressure,
Wherein the plasma treatment is applied to a previously treated substrate, wherein in a state where the target substrate is released from the electrode, the front and back surfaces of the substrate to be processed charge removal plasma in a gas mainly containing inert gas and 曝, to provide a plasma processing method characterized by removing the charges on the surface and the back surface of the substrate to be treated.
According to a second aspect of the present invention, there is provided the plasma processing method according to the first aspect, wherein the charged charge removing plasma is 1/3 or less of the high frequency power during the plasma processing.
According to a third aspect of the present invention, there is provided the plasma processing method according to the first or second aspect, wherein the charged charge removing plasma is 0.1 to 1.0 W / cm 2 .
According to a fourth aspect of the present invention, the above charge removing plasma exposure of the substrate to be processed, by removing the charged charges on the surface and the back surface of the substrate to be processed, and the front and back surfaces of the substrate to be processed The plasma processing method according to any one of the first to third aspects, wherein the surface of the electrode has the same potential.
本発明によれば、前記被処理基板にプラズマ処理を施す以前に、不活性ガスを主体とするガス中で帯電電荷除去用プラズマに被処理基板をすることにより、被処理基板の持つ初期電荷をプラズマ処理直前に除去して被処理基板の表裏両面と電極の表面とを同電位として、プラズマ処理後に発生するプラズマダメージを防止できるプラズマ処理方法を提供することができる。
According to the present invention, before performing the plasma treatment on the substrate to be processed, the initial charge of the substrate to be processed is obtained by applying the substrate to be charged to the plasma for removing charged charges in a gas mainly composed of an inert gas. was removed in the plasma treatment immediately before the surface of the front and back surfaces and the electrodes of the substrate as the same potential, it is possible to provide a plasma treatment how that can prevent plasma damage that occurs after the plasma treatment.
従来、一般的には、プラズマ処理前には、プラズマ処理室の壁面に付着した反応性生物などが舞って被処理基板に付着してパーティクル不良となる可能性があるため、プラズマ放電することは考えられていなかった。しかしながら、近年、パーティクル不良の比率よりも、被処理基板が搬送中に帯電し、帯電した被処理基板を、別の電位で帯電している電極に載置するときに生じる不良の比率の方が多くなる傾向がある。そこで、本発明は、パーティクル不良とならないようにプラズマ処理室の壁面に付着した反応性生物などが舞うのを極力抑えつつ、最低限のプラズマを生じさせて、被処理基板の表裏両面と電極の表面とを同電位にするようにしたものである。言い換えれば、処理基板の表裏両面と電極の表面とを同電位とすることができるような最低限のプラズマすなわち帯電電荷除去用プラズマを生じさせることにより、プラズマ処理後に発生するプラズマダメージをより効果的に防止することができる。 Conventionally, in general, before plasma processing, there is a possibility that reactive organisms attached to the wall of the plasma processing chamber may fly and adhere to the substrate to be processed, resulting in particle failure. It was not thought. However, in recent years, the ratio of defects that occur when a substrate to be processed is charged during transportation and the charged substrate to be processed is placed on an electrode that is charged at a different potential than the ratio of particle defects. There is a tendency to increase. Therefore, the present invention generates a minimum amount of plasma while minimizing the influence of reactive organisms attached to the wall of the plasma processing chamber so as not to cause particle defects, while generating both surfaces of the substrate to be processed and the electrodes. The surface is set to the same potential. In other words, plasma damage that occurs after plasma processing is more effective by generating a minimum plasma that can make the front and back surfaces of the processing substrate and the surface of the electrode have the same potential, that is, plasma for removing charged charges. Can be prevented.
以下に、本発明にかかる実施の形態を図面に基づいて詳細に説明する。 Embodiments according to the present invention will be described below in detail with reference to the drawings.
本発明の第1実施形態にかかるプラズマ処理方法および装置について、図面を参照しつつ説明する。 A plasma processing method and apparatus according to a first embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
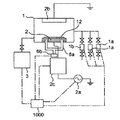
以下、図1A及び図1B及び図2に第1実施形態プラズマ処理方法および装置についての代表的なドライエッチング装置及び方法について説明する。1はドライエッチ処理するためのプラズマ処理容器(プラズマ処理室の一例)、1aはプラズマ処理前の帯電電荷除去時にプラズマ処理容器1内に不活性ガスを導入する不活性ガス導入装置、1bはプラズマ処理時にプラズマ処理容器1内にプロセスガスを導入するプロセスガス導入装置である。また、2は被処理基板12を載置する為のプラズマを発生させる機能を具備する電極、2aは高周波電源、2bは接地された対向電極、2cは高周波電源2aと電極2との間介在させられたインピーダンス整合回路であるマッチングボックスである。また、3はプラズマ処理容器1内を減圧するポンプなどの真空排気装置、4はプラズマ処理容器1との間で被処理基板12を真空圧力の状態で出し入れするためにプラズマ処理容器1に隣接された真空移載容器(真空移載室の一例)、4aは真空移載容器4内をプラズマ処理容器1と同様に減圧するポンプなどの真空排気装置、4bは真空移載容器4内にN2ガスを導入するN2ガス導入装置、5はプラズマ処理容器1と真空移載容器4の隔壁となり開閉機構を有するゲート扉、6は共に真空状態のプラズマ処理容器1と真空移載容器4との間で被処理基板12を搬送する真空搬送機構である。また、6aはプラズマ処理容器1内で被処理基板12と電極2を分離するために使われるリフトピン、6bはリフトピン6aを昇降させるモータやエアシリンダなどのリフトピン昇降装置、7は大気状態から真空状態へ容器内を減圧する動作やその逆に、真空状態から大気状態へ加圧する動作ができる機能を有するロードロック容器(ロードロック室の一例)、7aは前記ロードロック容器7での前記減圧動作を行うポンプなどの真空排気装置、7bはN2ガス導入装置である。また、8は真空移載容器4とロードロック容器7の隔壁となり開閉機構を有するゲート扉、9はロードロック容器7を真空に保持するためのゲート扉、10は被処理基板12を収納する基板収納装置である。また、11は基板収納装置10より被処理基板12を取り出し、前記ロードロック容器7へ移載するためのロボットアームなどの大気搬送機構である。また、1000は不活性ガス導入装置1aとプロセスガス導入装置1bと高周波電源2aとマッチングボックス2cと真空排気装置3と真空排気装置4aとN2ガス導入装置4bとゲート扉5と真空搬送機構6とリフトピン昇降装置6bと真空排気装置7aとN2ガス導入装置7bとゲート扉8とゲート扉9と基板収納装置10と大気搬送機構11との動作をそれぞれ制御する制御装置である。
A typical dry etching apparatus and method for the plasma processing method and apparatus according to the first embodiment will be described below with reference to FIGS. 1A, 1B, and 2. FIG. 1 is a plasma processing container for dry etching (an example of a plasma processing chamber), 1a is an inert gas introduction device that introduces an inert gas into the plasma processing container 1 when charged charges are removed before plasma processing, and 1b is plasma. It is a process gas introduction device that introduces a process gas into the plasma processing container 1 during processing. 2 is an electrode having a function of generating plasma for placing the
以上のように構成されたドライエッチング装置について、以下にその動作について説明する。以下の動作は制御装置1000で動作制御される。
The operation of the dry etching apparatus configured as described above will be described below. The following operations are controlled by the
まず、被処理基板12を、基板収納装置10より大気搬送機構11にて取り出し、ロードロック容器7に不活性ガス導入装置7bよりN2ガスをパージして大気状態にし、ゲート扉9を開き、大気搬送機構11によって、被処理基板12をロードロック容器7へと搬送する。続いて、ゲート扉9を閉じて、ロードロック容器7において、不活性ガス導入装置7bの動作を止め、排気装置7aより排気し、一定の圧力にまで真空排気が完了した後、ゲート扉8を開く。
First, the
真空移載容器4は排気装置4aが常時真空排気動作しており常に真空状態を保持した状態となっている。真空搬送機構6によりロードロック容器7に載置されている被処理基板12を取り出し、真空移載容器4へと移載して、ゲート扉8を閉じる。プラズマ処理容器1にある真空排気装置3は常時真空排気動作しておりプラズマ処理容器1内は常に真空常置を保持した状態となっている。ゲート扉5が開き、真空移載容器4内の真空搬送機構6にある被処理基板12はプラズマ処理容器1のリフトピン6a上に移載され、ゲート扉5が閉まる。
In the
リフトピン6a上に被処理基板12が保持された状態において、不活性ガス導入装置1aから不活性ガスをプラズマ処理容器1内に導入して、高周波電源2aから高周波電力を電極2へ印加して、不活性ガスが主体とするガス中で被処理基板12がエッチングされたり薄膜が形成されたりしない程度の微弱な帯電電荷除去用プラズマを発生させる。すなわち、ここでは、N2ガスなどの不活性ガスを不活性ガス導入装置1aより導入し、真空排気装置3にて、プラズマ処理容器1内を40Pa程度に調圧し、高周波電源2aより0.1W/cm2の高周波電力を電極2へ印加した微弱な帯電電荷除去用プラズマを5秒間発生させ、被処理基板12の表裏両面と電極2の表面の前処理除電を行って被処理基板12の表裏両面と電極2の表面とを同電位とする。その後、リフトピン6aがリフトピン昇降装置6bの駆動により下降し、電極2上へ被処理基板12が載置され、不活性ガス導入装置1aからの不活性ガスの導入を停止するとともに、プロセスガスをプロセスガス導入装置1bより導入し、被処理基板12の一例として8インチのウェハに対して所望のプラズマ処理が、例えば100〜150W/cm2の高周波電力を高周波電源2aより電極2へ印加して、行われる。所望のプラズマ処理を行うとき、被処理基板12のメタル系薄膜に対しては塩素系のガスをプロセスガスとして導入し、シリコンの被処理基板12に対してはフッ素系のガスをプロセスガスとして導入し、被処理基板12のレジストなどのプラズマ処理に対しては酸素系のガスをプロセスガスとして導入して、所望のプラズマ処理、例えば、エッチングや薄膜形成やレジスト除去などの処理を行う。
In a state where the
ここで、前記不活性ガスが主体とするガス中で被処理基板12がエッチングされたり薄膜が形成されたりしない程度の微弱なプラズマを発生させるときに使用する高周波電力は、プラズマ処理時の高周波電力の1/3以下、又は、0.1〜1.0W/cm2が好ましい。時間は10秒以下が好ましい。
Here, the high-frequency power used when generating the weak plasma that does not etch the
不活性ガスは、Ar、He、N2、H2、気化したH2Oガスの少なくとも1つのガスである。 The inert gas is at least one of Ar, He, N 2 , H 2 , and vaporized H 2 O gas.
また、被処理基板12と電極2の前処理除電を行ったのちにリフトピン6aが下降するものに限られず、被処理基板12と電極2の前処理除電を行いながらリフトピン6aが下降するようにしてもよい。
Further, the
前述するように微弱プラズマによる前処理を行った場合と、行わない場合において、プラズマ処理容器1内において真空中で非接触表面電位計にて、被処理基板12上の帯電位を測定した。その結果、被処理基板12の表面に蓄積される電荷は、表1のようになる。
As described above, the charged potential on the
しかしながら、本発明の元となる上記評価結果より、処理前に蓄積された、被処理基板12の表裏にある電荷に、所望のプラズマ処理で被処理基板12の表側だけに帯電される電荷が加わることで、被処理基板12の表裏の電荷バランスを乱し、薄膜回路上のデバイスに悪影響を及ぼし、プラズマダメージや絶縁破壊を発生させていると考えられる。
However, from the above evaluation results that form the basis of the present invention, the electric charge charged only on the front side of the substrate to be processed 12 in the desired plasma treatment is added to the charges on the front and back of the substrate to be processed 12 accumulated before the processing. Thus, it is considered that the charge balance between the front and back surfaces of the
被処理基板12が初期から持つ電荷は、前工程での熱処理や水洗処理、或いは被処理基板12を大気中で搬送している過程での摩擦帯電、また基板収納装置10よりロードロック容器7へ移載され、大気圧から真空状態へ排気されるときに、摩擦帯電される電荷であると推測される。
The charge of the substrate to be processed 12 from the beginning is the heat treatment or washing treatment in the previous process, or frictional charging in the process of transporting the substrate to be processed 12 in the atmosphere, or from the
よって、所望のプラズマ処理を行う直前に、前処理として微弱プラズマにより被処理基板12の表裏及び電極2の表面を同時に除電処理を行うことで、被処理基板12の表裏両面と電極2の表面とをプラズマという媒体を通じて同電位とすることにより被処理基板12の表裏両面と電極2の表面とを除電して、プラズマ処理後に発生するプラズマダメージ、例えば、薄膜回路上のデバイスにプラズマダメージや絶縁破壊を発生させることを効果的に防止できる。
Therefore, immediately before performing the desired plasma treatment, the front and back surfaces of the substrate to be processed 12 and the surface of the
その後、リフトピン昇降装置6bの駆動によりリフトピン6aが上昇し、電極2上から被処理基板12が離される。次いで、ゲート扉5が開き、真空搬送機構6により、プラズマ処理容器1内のリフトピン6a上にある被処理基板12は、プラズマ処理容器1内より取り出され、真空移載容器4内に移載される。
Thereafter, the
また、プラズマ処理終了後、N2やO2などのガスによる除電プロセスにて、被処理基板12の表裏両面及び電極2の表面上に帯電した電荷を除去するプロセス処理を行うことで、一層、ダメージの抑制効果が発揮される。
Further, after the plasma treatment is completed, by performing a process treatment for removing charges charged on both the front and back surfaces of the
その後、N2ガス導入装置4bを停止させ、ゲート扉5を閉じ、真空排気装置4aを動作させ、真空移載容器4内を所定の圧力以下まで排気し、真空排気装置3にて、プラズマ処理容器1内も所定の圧力以下まで排気する。次に、前記ゲート扉8が開き、真空移載機構6により被処理基板12はロードロック容器7へと移載され、ゲート扉8が閉まる。ロードロック容器7内の真空排気装置7aが停止し、不活性ガス導入装置7bより不活性ガスがパージされ、ロードロック容器7内は真空圧状態から大気圧状態へとなり、ゲート扉9が開き、大気搬送機構11により、ロードロック容器7内にある被処理基板12が取り出され、基板収納装置10へと収められる。
Thereafter, the N 2
なお、本発明の実施形態として、平行平板型RIEプラズマ処理方式で述べたが、これが、ICP方式やECR方式、PE方式などのプラズマ処理方式であっても、同様の効果が得られる。 Although the parallel plate RIE plasma processing method has been described as an embodiment of the present invention, the same effect can be obtained even if this is a plasma processing method such as an ICP method, an ECR method, or a PE method.
また、プラズマ処理容器1とは別に、帯電電荷除去用プラズマを発生させる前処理専用の処理容器を別途配置することや、真空移載容器4のような容器で前処理をしても、同様の効果が得られる。
In addition to the plasma processing container 1, the same processing can be performed by separately arranging a processing container dedicated to pretreatment for generating a plasma for removing charged charges, or by preprocessing with a container such as the
なお、前記様々な実施形態のうちの任意の実施形態を適宜組み合わせることにより、それぞれの有する効果を奏するようにすることができる。 It is to be noted that, by appropriately combining any of the various embodiments, the effects possessed by them can be produced.
1 プラズマ処理容器
1a 不活性ガス導入装置
1b プロセスガス導入装置
2 電極
2a 高周波電源
2b 対向電極
2c マッチングボックス
3 真空排気装置
4 真空移載容器
4a 真空排気装置
4b 不活性ガス導入装置
5 ゲート扉
6 真空搬送機構
6a リフトピン
6b リフトピン昇降装置
7 ロードロック容器
7a 真空排気装置
7b 不活性ガス導入装置
8 ゲート扉
9 ゲート扉
10 基板収納装置
11 大気搬送機構
12 被処理基板
1000 制御装置
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1
Claims (4)
前記被処理基板にプラズマ処理を施す以前に、前記被処理基板を前記電極から離した状態で、前記被処理基板の表面及び裏面を不活性ガスを主体とするガス中で帯電電荷除去用プラズマに曝し、前記被処理基板の前記表面及び裏面に帯電した電荷を取り除くことを特徴とするプラズマ処理方法。 In the plasma processing method of forming a thin film circuit on the substrate to be processed by applying electric power to an electrode on which the substrate to be processed is placed under reduced pressure,
Wherein the plasma treatment is applied to a previously treated substrate, wherein in a state where the target substrate is released from the electrode, the front and back surfaces of the substrate to be processed charge removal plasma in a gas mainly containing inert gas 曝 and, a plasma processing method characterized by removing the charged charges on the surface and the back surface of the substrate to be treated.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004069155A JP4598416B2 (en) | 2003-03-18 | 2004-03-11 | Plasma processing method |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003073861 | 2003-03-18 | ||
| JP2004069155A JP4598416B2 (en) | 2003-03-18 | 2004-03-11 | Plasma processing method |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009033349A Division JP4697315B2 (en) | 2003-03-18 | 2009-02-17 | Plasma processing method |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004304169A JP2004304169A (en) | 2004-10-28 |
| JP2004304169A5 JP2004304169A5 (en) | 2007-04-05 |
| JP4598416B2 true JP4598416B2 (en) | 2010-12-15 |
Family
ID=33421807
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004069155A Expired - Fee Related JP4598416B2 (en) | 2003-03-18 | 2004-03-11 | Plasma processing method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4598416B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100683110B1 (en) | 2005-06-13 | 2007-02-15 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method of generating plasma and method of forming a layer using the same |
| JP6333302B2 (en) * | 2016-03-30 | 2018-05-30 | 株式会社日立国際電気 | Semiconductor device manufacturing method, substrate processing apparatus, and program |
-
2004
- 2004-03-11 JP JP2004069155A patent/JP4598416B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2004304169A (en) | 2004-10-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9396962B2 (en) | Etching method | |
| US10115614B2 (en) | Transfer chamber and method for preventing adhesion of particle | |
| CN107078050B (en) | Etching method | |
| TWI791540B (en) | Etching method and etching device | |
| US8057603B2 (en) | Method of cleaning substrate processing chamber, storage medium, and substrate processing chamber | |
| KR100662959B1 (en) | Plasma processing machine and method thereof | |
| US20150024603A1 (en) | Plasma etching method and plasma etching apparatus | |
| TW201635382A (en) | Integrated etch/clean for dielectric etch applications | |
| JP4143684B2 (en) | Plasma doping method and apparatus | |
| JP4697315B2 (en) | Plasma processing method | |
| WO2011056484A2 (en) | Method and apparatus of halogen removal | |
| JP2021021950A (en) | Cleaning apparatus of reflection-type mask, and cleaning method of reflection-type mask | |
| US10053773B2 (en) | Method of cleaning plasma processing apparatus | |
| US11784054B2 (en) | Etching method and substrate processing system | |
| KR20150069514A (en) | Etching method | |
| US20080216957A1 (en) | Plasma processing apparatus, cleaning method thereof, control program and computer storage medium | |
| JP4656364B2 (en) | Plasma processing method | |
| KR100745153B1 (en) | Plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method | |
| JP4598416B2 (en) | Plasma processing method | |
| JP3649797B2 (en) | Semiconductor device manufacturing method | |
| KR100743275B1 (en) | Plasma processing method and post-processing method | |
| JPH11340208A (en) | Plasma treatment method | |
| KR0175073B1 (en) | Plasma etching method fo silicon containing layer | |
| JP3649798B2 (en) | Semiconductor device manufacturing method | |
| JP4134671B2 (en) | Plasma processing method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20061206 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070220 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070220 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20080929 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20081224 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090121 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20090217 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090309 |
|
| A911 | Transfer of reconsideration by examiner before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20090423 |
|
| A912 | Removal of reconsideration by examiner before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A912 Effective date: 20090828 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20100924 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131001 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |