JP4053558B2 - Heat resistant fabric, clothing and heat resistant gloves using the same - Google Patents
Heat resistant fabric, clothing and heat resistant gloves using the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4053558B2 JP4053558B2 JP2005310420A JP2005310420A JP4053558B2 JP 4053558 B2 JP4053558 B2 JP 4053558B2 JP 2005310420 A JP2005310420 A JP 2005310420A JP 2005310420 A JP2005310420 A JP 2005310420A JP 4053558 B2 JP4053558 B2 JP 4053558B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- yarn
- heat
- fiber
- resistant
- fabric
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Description
本発明は、断熱性、耐熱性、防炎性、難燃性の高い耐熱性布帛とこれを用いた衣類及び耐熱手袋に関する。 The present invention relates to a heat-resistant fabric having high heat insulation, heat resistance, flame resistance, and flame retardancy, and clothing and heat-resistant gloves using the same.
アーク溶接などの溶接作業、溶鉱炉などの炉前作業、加熱調理などの高熱物体を扱う作業には、安全の面から耐熱手袋が必要である。熱的に過酷な作業における耐熱手袋の材料は、一般的に動物の皮を使用している。また、消防服も耐熱性を要求される。さらに、自動車、電車等の車両内装材も耐熱性、防炎性、難燃性は要求される。 Heat-resistant gloves are required from the viewpoint of safety in welding work such as arc welding, pre-furnace work such as a blast furnace, and work involving high-heat objects such as cooking. The material of heat-resistant gloves in heat-intensive operations generally uses animal skins. Fire fighting clothing is also required to have heat resistance. Furthermore, vehicle interior materials such as automobiles and trains are also required to have heat resistance, flame resistance, and flame resistance.
従来から、アラミド繊維、ポリベンズイミダゾール繊維、ポリベンズオキサゾール繊維、ポリベンズアゾール繊維、ポリアミドイミド繊維、メラミン繊維及びポリイミド繊維などの耐熱性繊維を用いて耐熱手袋や消防服を作成することは提案されている(例えば非特許文献1、特許文献1)。非特許文献1には、消防服は防炎性と作業性のためメタ型アラミド繊維を95%、寸法安定性、収縮率防止のためパラ型アラミド繊維を5%使用することが記載されている。また特許文献1には、アラミド繊維糸単体を用いて手袋を編成し、手のひら部分に合成樹脂を加熱融着することが記載されている。
従来の動物の皮を用いた耐熱手袋は、指が動かしにくく、作業性に問題があり、かつ汗を吸水する機能もなく、洗濯もできず、使用勝手の悪い材料であった。また、従来の耐熱性繊維糸単体の布帛を用いた手袋は、断熱性に問題があり、例えばアーク溶接でアークが前記手袋に降りかかったとき、肌が火傷するという問題があった。布帛の厚さを大きくすればこの問題は解消されるが、今度は指が動かしにくく作業性に問題が生じ、かつコストが高くなる問題がある。さらに、耐熱性繊維を用いた消防服は、最外層にアルミ箔(コーティングを含む)を形成し、その内部に前記耐熱性繊維単体の布帛を形成し、その内部に断熱のために不織布を配置しており、全体として重量が重くなり、作業に支障が出たり、人体が故障する問題があった。さらに近年は耐熱性及び防護性を備えた衣類も要請されている。 Conventional heat-resistant gloves using animal skin are difficult to use because they are difficult to move fingers, have problems in workability, do not function to absorb sweat, cannot be washed, and are not easy to use. Moreover, the conventional glove using the cloth of a heat-resistant fiber yarn single-piece | unit has a problem in heat insulation, for example, when the arc fell on the said glove by arc welding, there existed a problem that a skin was burned. Increasing the thickness of the fabric solves this problem, but this time there is a problem that it is difficult to move the finger, causing problems in workability and increasing the cost. Furthermore, fire-fighting clothing using heat-resistant fibers is formed with aluminum foil (including coating) in the outermost layer, the fabric of the heat-resistant fibers alone is formed inside, and a non-woven fabric is placed inside for heat insulation As a result, the weight is increased as a whole, and there are problems that work is hindered and the human body breaks down. In recent years, clothing with heat resistance and protective properties has been demanded.
本発明は、前記従来の問題を解決するため、耐熱性繊維と意匠撚糸と含む編物又は織物とし、表面に耐熱性糸を配置し、組織内に意匠撚糸を配置して多くの空気を含ませることにより、断熱性、耐熱性、防炎性、難燃性、防護性の高い耐熱性布帛とこれを用いた衣類及び耐熱手袋を提供する。 In order to solve the above-mentioned conventional problems, the present invention is a knitted or woven fabric including heat-resistant fibers and design twisted yarns, the heat-resistant yarns are arranged on the surface, and the design twist yarns are arranged in the structure so as to contain a lot of air. Thus, a heat-resistant fabric having high heat insulating properties, heat resistance, flameproof properties, flame retardancy, and protective properties, and clothing and heat-resistant gloves using the same are provided.
本発明の耐熱性布帛は、耐熱性繊維糸と意匠撚糸を含む編物又は織物であって、一方の面に前記耐熱性繊維糸が多く存在し、他方の面に前記意匠撚糸が多く存在し、前記意匠撚糸は、芯糸とループヤーンと押さえ糸で構成され、前記ループヤーンは木綿、レーヨン、麻、羊毛及びアクリル繊維から選ばれる少なくとも一つであることを特徴とする。
The heat resistant fabric of the present invention is a knitted or woven fabric containing a heat resistant fiber yarn and a design twist yarn, wherein the heat resistant fiber yarn is present on one side in a large amount, and the design twist yarn is present on the other side in many ways . The design twisted yarn is composed of a core yarn, a loop yarn, and a presser yarn, and the loop yarn is at least one selected from cotton, rayon, hemp, wool, and acrylic fiber .
本発明の衣類は前記耐熱性布帛を一部又は全部に含むものである。 The garment of the present invention includes the heat-resistant fabric in part or in whole.
本発明の耐熱性手袋は、耐熱性繊維糸と意匠撚糸を含む編物で構成され、前記編物はニットであり、外面に耐熱性繊維糸が多く存在し、内面に意匠撚糸が多く存在し、前記意匠撚糸は、芯糸とループヤーンと押さえ糸で構成され、前記ループヤーンは木綿、レーヨン、麻、羊毛及びアクリル繊維から選ばれる少なくとも一つであることを特徴とする。
Heat resistant gloves of the present invention is constituted by knitted fabric containing heat-resistant fiber yarn and the design twisting, the knitted fabric is knitted, heat-resistant fiber yarn is often present on the outer surface, and there are many design twist yarn on the inner surface, the The design twisted yarn is composed of a core yarn, a loop yarn, and a presser yarn, and the loop yarn is at least one selected from cotton, rayon, hemp, wool, and acrylic fiber .
本発明の別の耐熱性手袋は、耐熱性繊維糸と意匠撚糸を含む編物で構成され、前記編物はニットであり、外面に耐熱性繊維糸が多く存在し、内面に意匠撚糸が多く存在し、前記意匠撚糸は、芯糸とループヤーンと押さえ糸で構成され、前記ループヤーンは木綿、レーヨン、麻、羊毛及びアクリル繊維から選ばれる少なくとも一つである耐熱性手袋を内面に配置し、外側に耐熱性繊維糸で構成される手袋を配置し、両手袋を指先で固定した複層構造であることを特徴とする。 Another heat-resistant glove of the present invention is constituted by knitted fabric containing heat-resistant fiber yarn and the design twisting, the knitted fabric is knitted, present in many heat-resistant fiber yarn outer surface, there are many and are design twisting the inner surface The design twisted yarn is composed of a core yarn, a loop yarn, and a presser yarn, and the loop yarn is arranged on the inner surface with a heat-resistant glove that is at least one selected from cotton, rayon, hemp, wool, and acrylic fiber on the inner surface. It is characterized by having a multilayer structure in which gloves composed of heat-resistant fiber yarns are arranged and both gloves are fixed with fingertips.
本発明の耐熱性布帛及び耐熱性手袋は、耐熱性繊維と意匠撚糸とを用いて、一方の面に前記耐熱性繊維を多く存在させ、他方の面に前記意匠撚糸を多く存在させるようにして編物又は織物を形成したことにより、組織内に多くの空気を含ませることができ、これにより、断熱性、耐熱性、防炎性、難燃性及び防護性の高い耐熱性布帛を提供できる。すなわち、意匠撚糸には多数のループが存在するため、これを用いた編物及び織物は、組織内に多くの空気を含ませることができる。空気は断熱性が高いため前記編物及び織物も断熱性が高いものとなる。さらに、一方の面には前記耐熱性繊維が多く存在しているため、この部分で耐熱性、防炎性、難燃性、防護性を発揮する。加えて本発明の耐熱性布帛とこれを用いた衣類及び耐熱性手袋は、通気性があり、作業性も良好で、洗濯することもできる。 The heat-resistant fabric and heat-resistant gloves of the present invention use heat-resistant fibers and design twisted yarns so that one side has a large amount of the heat-resistant fibers and the other side has a lot of the design twisted yarns. By forming a knitted fabric or a woven fabric, a large amount of air can be included in the tissue, and thus a heat-resistant fabric having high heat insulation, heat resistance, flame resistance, flame retardancy, and protection can be provided. That is, since many loops exist in the design twisted yarn, a knitted fabric and a fabric using the loop can contain a lot of air in the structure. Since air has high heat insulating properties, the knitted fabric and the fabric also have high heat insulating properties. Furthermore, since there are many heat-resistant fibers on one surface, this portion exhibits heat resistance, flame resistance, flame retardancy, and protection. In addition, the heat-resistant fabric of the present invention, clothing and heat-resistant gloves using the fabric are breathable, have good workability, and can be washed.
本発明において耐熱性繊維は、融点又は分解点が約350℃以上、好ましくは400℃以上であれば、無機繊維又は有機繊維のいかなるものであってもよい。好ましくはアラミド繊維(パラ系アラミドの融点又は分解点:480〜570℃、メタ系同:400〜430℃)、ポリベンズイミダゾール繊維(ガラス転移温度:400℃以上)、ポリベンズオキサゾール繊維(融点又は分解温度:650℃)、ポリベンズチアゾール繊維(融点又は分解温度:650℃)、ポリアミドイミド繊維(融点又は分解温度:350℃以上)、メラミン繊維(融点又は分解温度:400℃以上)、ポリイミド繊維(融点又は分解温度:350℃以上)、ポリアリレート繊維(融点又は分解温度:400℃以上)及び炭素繊維(融点又は分解温度:2000〜3500℃)から選ばれる少なくとも一つである。これらの繊維は編物又は織物に加工しやすい。繊度は綿番手で1〜50番程度が好ましい。単糸で使用することもできるし、複数本引き揃えるか、あるいは合撚して使用できる。 In the present invention, the heat resistant fiber may be any inorganic fiber or organic fiber as long as it has a melting point or decomposition point of about 350 ° C. or higher, preferably 400 ° C. or higher. Preferably, aramid fiber (melting point or decomposition point of para-aramid: 480 to 570 ° C., meta-type: 400 to 430 ° C.), polybenzimidazole fiber (glass transition temperature: 400 ° C. or higher), polybenzoxazole fiber (melting point or Decomposition temperature: 650 ° C), polybenzthiazole fiber (melting point or decomposition temperature: 650 ° C), polyamideimide fiber (melting point or decomposition temperature: 350 ° C or higher), melamine fiber (melting point or decomposition temperature: 400 ° C or higher), polyimide fiber (Melting point or decomposition temperature: 350 ° C. or higher), polyarylate fiber (melting point or decomposition temperature: 400 ° C. or higher) and carbon fiber (melting point or decomposition temperature: 2000 to 3500 ° C.). These fibers are easy to process into knitted or woven fabrics. The fineness is preferably about 1 to 50 in cotton count. A single yarn can be used, or a plurality of yarns can be aligned or twisted.
前記意匠撚糸は、一例として芯糸とループヤーンと押さえ糸で構成され、ループヤーンは木綿、レーヨン、麻、羊毛及びアクリル繊維から選ばれる少なくとも一つであることが好ましい。芯糸と押さえ糸は例えばポリエステルフィラメント糸を使用できる。芯糸に対してループヤーンは2〜6倍オーバーフィードして作成すると、芯糸の周囲にあらゆる方向にランダムにループが形成できる。意匠撚糸の繊度は綿番手で0.5〜50番程度が好ましい。単糸で使用することもできるし、複数本引き揃えるか、あるいは合撚して使用できる。 The design twisted yarn is composed of, for example, a core yarn, a loop yarn, and a presser yarn, and the loop yarn is preferably at least one selected from cotton, rayon, hemp, wool, and acrylic fiber. For example, a polyester filament yarn can be used as the core yarn and the holding yarn. If the loop yarn is formed by overfeeding the core yarn by 2 to 6 times, a loop can be formed randomly in any direction around the core yarn. The fineness of the design twisted yarn is preferably about 0.5 to 50 in cotton count. A single yarn can be used, or a plurality of yarns can be aligned or twisted.
前記耐熱性布帛は、多層構造にし、一方の面に耐熱性繊維を多く存在させ、他方の面に意匠撚糸を多く存在させるようにして編物又は織物を形成する。このような編物又は織物の組織としては、ダブルニット、ダブルジャージ、両面編地、ダブルラッシェル、二重編物、二重織物、シングルジャージ及びスムース編物から選ばれる少なくとも一つの組織がある。 The heat-resistant fabric has a multilayer structure, and a knitted fabric or a woven fabric is formed so that a large amount of heat-resistant fibers are present on one surface and a large amount of design twist yarn is present on the other surface. Examples of such a knitted or woven structure include at least one structure selected from double knit, double jersey, double-sided knitted fabric, double raschel, double knitted fabric, double woven fabric, single jersey, and smooth knitted fabric.
前記のような組織においては、ループヤーンの一部のループが、耐熱性繊維のリッチな面に突出することがあるので、この場合は外表面に現れるループをカットしてカットパイルとするのが好ましい。このようにすると耐熱手袋を作業手袋として使用した場合、ループが機械部品等に引っ掛かることがなく、作業の安全性が高くなる。 In the structure as described above, some loops of the loop yarn may protrude on the rich surface of the heat resistant fiber. In this case, the loop appearing on the outer surface is cut into a cut pile. preferable. In this case, when the heat resistant glove is used as a work glove, the loop does not get caught on a machine part or the like, and the work safety is increased.
本発明の耐熱性布帛、衣類及び耐熱性手袋の厚さは0.3mm以上3mm以下が好ましく、さらに0.5mm以上2mm以下が好ましい。前記耐熱性手袋の単位面積あたりの重量は0.09g/cm2以上であることが好ましく、さらに0.1g/cm2以上が好ましい。厚さ及び単位面積あたりの重量が前記の範囲であると、熱遮断性に加えて耐燃焼性も向上する。衣類は手袋ほど耐熱性を要求されず、また軽量であるほうが着心地も良いので、目付けは300〜700g/m2の範囲が好ましい。 The thickness of the heat-resistant fabric, clothing, and heat-resistant gloves of the present invention is preferably from 0.3 mm to 3 mm, more preferably from 0.5 mm to 2 mm. The weight per unit area of the heat-resistant gloves is preferably 0.09 g / cm 2 or more, more preferably 0.1 g / cm 2 or more. When the thickness and the weight per unit area are in the above ranges, the flame resistance is improved in addition to the thermal barrier properties. Since clothing is not required to have heat resistance as much as gloves and is lighter and more comfortable to wear, the basis weight is preferably in the range of 300 to 700 g / m 2 .
本発明の布帛は例えばパーカー、ジャンパー、コート、ベスト等の外衣類、腕カバー、前掛け、防護頭巾、消防服、防護服、作業服、防火布、自動車、電車等の車両内装材に有用である。また、アーク溶接などの溶接作業、溶鉱炉などの炉前作業、加熱調理などの高熱物体を扱う作業に使用する耐熱手袋としても有用である。 The fabric of the present invention is useful, for example, for outer clothing such as parkers, jumpers, coats, vests, arm covers, aprons, protective hoods, fire clothes, protective clothes, work clothes, fire cloths, automobile interior materials such as automobiles and trains. . It is also useful as a heat-resistant glove for use in welding work such as arc welding, pre-furnace work such as a blast furnace, and work involving high heat objects such as cooking.
以下図面を用いて説明する。 This will be described below with reference to the drawings.
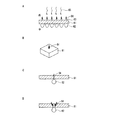
図1Aは本発明で使用する一実施例の意匠撚糸1の側面図、図1Bは同断面図である。この意匠撚糸1は、芯糸2とループヤーン3とその上からの押さえ糸4で構成され、ループヤーン3は木綿の例である。
FIG. 1A is a side view of a design twisted yarn 1 of one embodiment used in the present invention, and FIG. 1B is a sectional view thereof. The design twisted yarn 1 includes a core yarn 2, a
図2A−Bは本発明の一実施例で使用する両面編物10の組織図である。図2Aに示すように、耐熱性繊維糸11と意匠撚糸12とが引き揃えられ、耐熱性繊維糸11が表面に配置され、意匠撚糸12が裏面に配置される。意匠撚糸12には多数のループ13が突出しており、両面編物10の内面から裏面に多く存在している。これにより空隙を多く含むことになり、断熱作用を発揮する。表面には耐熱性繊維糸11が多く存在するので、耐熱性、防炎性、難燃性を発揮する。
2A-B are organization diagrams of the double-sided knitted
耐熱性繊維糸11側表面にも多少のループ13は突出するが、耐熱性にはあまり影響しない。むしろ炎を受けたり、高温の物体を触ったとき、耐熱性繊維糸11側表面のループ13は焦げるので、作業者は危険を感ずることができる。前記したとおり耐熱性繊維糸11側表面のループ13はカットしてカットパイルの状態としても良い。
Although some
前記の編物は耐熱手袋として好適である。手袋編み機は、例えば島精機社製の全自動手袋編み機を使用してニット手袋に編成する。 The knitted fabric is suitable as a heat-resistant glove. The glove knitting machine is knitted into knit gloves using, for example, a fully automatic glove knitting machine manufactured by Shima Seiki Co., Ltd.
図3A−Bは本発明の他の実施例の二重織の例である。図3Aは経二重織の組織図、図3Bは緯二重織の組織図である。このような織物の表面側に耐熱性繊維を配置し、裏面側に意匠撚糸を配置する。 3A-B are examples of a double weave according to another embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 3A is a structure diagram of warp double weave, and FIG. 3B is a structure diagram of weft double weave. Heat resistant fibers are arranged on the front side of such a woven fabric, and design twisted yarns are arranged on the back side.
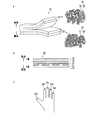
図11は本発明の一実施例の袖部の長いロングタイプの耐熱手袋71の使用例である。この手袋はキッチンなどの調理用に好適であり、オーブン72の加熱部に腕があたっても火傷を防ぐことができる。
FIG. 11 shows an example of using a long-type heat-
以下実施例を用いて、さらに本発明を具体的に説明する。 Hereinafter, the present invention will be described more specifically with reference to examples.
(実施例1)
(1)意匠撚糸の製造
芯糸及び押さえ糸としてポリエステルマルチフィラメント加工糸(東レ製)、トータル繊度75デニール、フィラメント数48本を使用し、ループヤーンとして木綿糸30番(綿番手)を使用した。木綿糸の単糸を3本使用し、芯糸1本に対してオーバーフィード率5〜7倍で供給して絡み付け、絡みつけと同時にその上から押さえ糸を撚り数約1000回/mで実撚を掛けた。得られた意匠撚糸は、図1A−Bに示すとおりであり、ループの平均突出長さ3mm、1インチあたり平均70個のループが360°の角度であらゆる角度に突出していた。この意匠撚糸の繊度は2.3530番(綿番手、2260デニール)であった。
(2)耐熱性繊維糸の準備
市販の帝人社製商品名“コーネックス”(メタ系アラミド繊維)の紡績糸20番(綿番手)を8本又は9本使用した。
(3)手袋の編成
島精機社製の全自動手袋編み機を使用してニット手袋に編成した。耐熱性繊維を60重量%、意匠撚糸を40重量%の割合で編成した。編み物構造は図2A−Bに示すとおりである。この両面編み物10の模式的断面図を図4に示す。耐熱性繊維糸11は表面側に配置され、意匠撚糸12は裏面側に配置され、ループ13は裏面側に主として存在しているが、一部は表面側にも露出していた。得られた手袋の片方の重量は70.3gであった。この重量は市販の“コーネックス”(メタ系アラミド繊維)100%使いの耐熱手袋とほぼ同一である。
(4)耐熱性試験
得られた耐熱作業軍手を手にはめてライターの火を当てたところ、表面はうっすらと焦げるが内部に熱は感じなかった。このことから難燃性と耐熱性を確認できた。
Example 1
(1) Manufacture of design twist yarn Polyester multifilament processed yarn (manufactured by Toray), total fineness 75 denier, 48 filaments were used as the core yarn and presser yarn, and cotton yarn No. 30 (cotton count) was used as the loop yarn. . Three cotton yarns are used, and entangled by supplying an overfeed rate of 5 to 7 times to one core yarn. At the same time as entanglement, a presser yarn is twisted at about 1000 turns / m. A real twist was applied. The obtained design twisted yarn was as shown in FIGS. 1A-B. The average protruding length of the loop was 3 mm, and an average of 70 loops per inch protruded at an angle of 360 ° at every angle. The fineness of this design twisted yarn was 2.3530 (cotton count, 2260 denier).
(2) Preparation of heat-resistant fiber yarn Eight or nine spun yarn No. 20 (cotton count) of a commercial name “Conex” (meta-aramid fiber) manufactured by Teijin Limited was used.
(3) Knitting of gloves Knitted gloves were knitted using a fully automatic glove knitting machine manufactured by Shima Seiki. The heat resistant fiber was knitted at a ratio of 60% by weight and the design twisted yarn was knitted at a ratio of 40% by weight. The knitted structure is as shown in FIGS. 2A-B. A schematic sectional view of the double-sided
(4) Heat resistance test When the obtained heat-resistant work gloves were used and the lighter was lit, the surface burned slightly but no heat was felt inside. This confirmed the flame retardancy and heat resistance.
また、アーク溶接作業に使用したところ、熱さは感じず、溶接の火花(約1200℃)がかかっても熱くなく、薄くて作業動作を損なうことがなく、通気性もあり、作業性はきわめて良かった。作業後の洗濯もすることができ、繰り返し使用ができた。 Also, when used for arc welding work, it does not feel heat, it does not heat even when welding sparks (approx. 1200 ° C) are applied, it is thin and does not impair work operation, it has air permeability, and workability is very good. It was. It could be washed after work and used repeatedly.
また、燃焼炉でピザパイを焼く加熱調理作業に使用したところ、同様に断熱性が高く、耐熱性、防炎性、難燃性、通気性があり、作業性も良好で、洗濯もできることから、衛生性も良好であった。 In addition, when used for cooking cooking to bake pizza pie in a combustion furnace, it also has high heat insulation, heat resistance, flame resistance, flame resistance, breathability, good workability, and washing is also possible, Hygiene was also good.
(実施例2)
図5A−Cは4層構造の耐熱手袋の例である。図5Aに示すように、裏面(肌側)には実施例1と同様の2層構造手袋22を配置し、表面側の外層には表面糸及び裏面糸共にアラミド繊維糸からなる2層構造の手袋21を配置した。24は手袋21の表面に位置するアラミド繊維糸、25は手袋21の裏面に位置するアラミド繊維糸である。26はアラミド繊維糸24と25で構成される編組織である。アラミド繊維糸24と25は、市販の帝人社製商品名“コーネックス”(メタ系アラミド繊維)の紡績糸20番(綿番手)を7本使用した。アラミド繊維糸24はループのない通常の紡績糸とし、アラミド繊維糸25は平均1.5mmのループを有する紡績糸とした。裏面(肌側)の2層構造手袋22の編組織は実施例1と同一であるが、木綿糸からなる意匠撚糸28の繊度は2.3530番(綿番手、2260デニール)、メタ系アラミド繊維の紡績糸27は20番(綿番手)を5本使用した。29は意匠撚糸27とアラミド繊維糸28で構成される編組織である。
(Example 2)
5A-C are examples of heat-resistant gloves having a four-layer structure. As shown in FIG. 5A, the same two-layered
以上の手袋2枚を重ね、図5Cに示す指先5点32a〜32eに耐熱接着剤(スリーボンド社製製品名“スリーボンド1212”)を塗布して接着した。この手袋1枚(片手)の重量は95gであった。
Two gloves as described above were stacked, and a heat resistant adhesive (product name “ThreeBond 1212” manufactured by ThreeBond Co., Ltd.) was applied and adhered to the five
得られた4層構造の耐熱手袋20の断面図を図5Bに示す。表面側からアラミド繊維糸26、アラミド繊維で形成されている小さなループの層30、空気層23、アラミド繊維層31、木綿糸からなる意匠撚糸で構成される大きなループ層29がこの順番で形成されていた。アラミド繊維層(表面)と木綿層(裏面)の厚さの比は、約2:1であった。
A cross-sectional view of the resulting heat-resistant glove 20 having a four-layer structure is shown in FIG. 5B. From the surface side, an
この4層構造の耐熱手袋は実施例1の手袋より耐熱性は高かった。また、手袋の表面にはループがまったく出なくなり、作業安全性が向上した。 This four-layer heat-resistant glove had higher heat resistance than the glove of Example 1. In addition, no loops appear on the surface of the glove, improving work safety.
(実施例3)
図6A−Cは3層構造の耐熱手袋の例である。図6Aに示すように、裏面(肌側)には実施例1と同様の2層構造手袋42を配置し、表面側の外層にはアラミド繊維糸からなる単層構造の手袋41を配置した。手袋41は前記メタ系アラミド繊維糸20/1番手を10本使い(綿番手5番)、通常の紡績糸として用いた。裏面(肌側)の2層構造手袋42の編組織は実施例1と同一であるが、木綿糸からなる意匠撚糸42の繊度は2.35番(綿番手)、前記メタ系アラミド繊維の紡績糸27は10番(綿番手)を2本使用した。
(Example 3)
6A-C are examples of heat-resistant gloves having a three-layer structure. As shown in FIG. 6A, a double-layered
以上の手袋2枚を重ね、図6Cに示す指先5点46a〜46eに耐熱接着剤(スリーボンド社製製品名“スリーボンド1212”)を塗布して接着した。
Two gloves as described above were stacked, and a heat-resistant adhesive (product name “3Bond 1212” manufactured by ThreeBond Co., Ltd.) was applied and adhered to the five
得られた3層構造の耐熱手袋の断面図を図6Bに示す。表面側からアラミド繊維糸41、空気層45、アラミド繊維層43、木綿糸からなる意匠撚糸で構成される大きなループ層44がこの順番で形成されていた。この手袋1枚(片手)の重量は65gであった。アラミド繊維層(表面)と木綿層(裏面)の厚さの比は、約3:2であった。
A cross-sectional view of the resulting heat-resistant glove having a three-layer structure is shown in FIG. 6B. A
この3層構造の耐熱手袋は実施例1と実施例3の手袋の中間の耐熱性を示した。この手袋も実施例2の手袋と同様、表面にはループがまったく出なくなり、作業安全性が向上した。 This heat-resistant glove having a three-layer structure exhibited intermediate heat resistance between the gloves of Example 1 and Example 3. Similarly to the glove of Example 2, this glove was completely free of loops on the surface, improving work safety.
(実施例4)
図7A−Bは炭素繊維とアラミド繊維を表層に配置した2層構造の耐熱手袋50の例である。図7Aに示すように、表層には前記メタ系アラミド繊維20番(綿番手)の紡績糸51と、炭素繊維5番(綿番手)(東邦レーヨン社製製品名“パイロメックス”)の紡績糸52を2.5回/インチで実撚をかけ撚糸53とした。裏面(肌側)には木綿糸からなる意匠撚糸54を配置して編み立てた。意匠撚糸の繊度は2.35番(綿番手)である。
Example 4
FIGS. 7A and 7B are examples of a heat-resistant glove 50 having a two-layer structure in which carbon fibers and aramid fibers are arranged on the surface layer. As shown in FIG. 7A, on the surface layer, the spun
得られた耐熱手袋50の断面図を図7Bに示す。表面側にアラミド繊維糸51と炭素繊維52が配置され、裏面側に木綿糸からなる意匠撚糸54で構成される大きなループ層が形成されていた。この手袋1枚(片手)の重量は86gであった。アラミド繊維と炭素繊維からなる表面層と木綿ループ裏面層の厚さの比は、約3:2であった。
A cross-sectional view of the resulting heat-resistant glove 50 is shown in FIG. 7B. An
この耐熱手袋は炭素繊維糸とアラミド繊維糸を撚って表面に配置しているため、耐火性と切創性が向上し、全体的に硬い風合いで使い勝手がよいものとなった。 Since this heat-resistant glove has a carbon fiber yarn and an aramid fiber yarn twisted and arranged on the surface, the fire resistance and the cutability are improved, and the overall is hard and easy to use.
(実施例5)
本実施例で得られた耐熱手袋を用いて、燃焼試験をさらに詳細に実験した。耐熱手袋は実施例1と同様にして製造した。図8A−Dは水平燃焼試験、図9A−Cは斜め燃焼試験を示す。燃焼試験に使用した編地は、手袋の「手のひら」部分(面積:72cm2)を切り取りって使用した。まず図8Aに示すように、編地61のループを有する木綿意匠撚糸62を下側に、アラミド繊維糸を上側に配置した。このとき木綿の小ループ64が上側表面にわずかに突出している。上側からJIS−1091−1999に規定されている「繊維製品の燃焼性試験」に準じて、ニッケルバーナー66の約800℃の炎65を当てると木綿の小ループ64は燃焼又は焦げる。アラミド繊維糸は短時間炎を当てるだけでは変化しない。木綿の小ループ64が燃焼又は焦げる状態は図8B〜D及び図9A〜Cに示す。炎を当てていくと、編地61の編密度が密な場合は図8C,図9Bのように火は中に入っていかない。これは燃焼を維持し続けるのに必要な最低酸素体積分率(LOI)が約30のアラミド繊維糸を用いているために、燃焼又は焦げが断ち切られるためである。これに対して編地61の編密度が粗な場合は図8D,図9Cのように火は中に入っていく。
(Example 5)
Using the heat-resistant gloves obtained in this example, the combustion test was performed in more detail. Heat resistant gloves were produced in the same manner as in Example 1. 8A-D show a horizontal combustion test, and FIGS. 9A-C show an oblique combustion test. The knitted fabric used for the combustion test was cut out from the “palm” part (area: 72 cm 2 ) of the glove. First, as shown in FIG. 8A, the cotton
そこで編密度が異なる編地を使用して燃焼試験をした結果を表1に示す。燃焼試験は大阪府立産業技術総合研究所において、JIS−1091に規定されている「繊維製品の燃焼性試験」に準じて行った。 Accordingly, Table 1 shows the results of a combustion test using knitted fabrics having different knitting densities. The combustion test was conducted at the Osaka Prefectural Industrial Technology Research Institute in accordance with “Flammability test of textile products” defined in JIS-1091.
以上燃焼試験の結果から、実施例1に示す2層構造の編み物の平方センチメートルあたりの重量は0.090g/cm2以上が耐燃焼性が好適であることがわかった。ただし、これ以下の単位面積あたりの重量であっても熱遮断性は良好であった。 From the results of the above-described combustion test, it was found that the weight per square centimeter of the knitted fabric having the two-layer structure shown in Example 1 is preferably 0.090 g / cm 2 or more in terms of combustion resistance. However, even if the weight per unit area was less than this, the thermal barrier property was good.
さらに実施例2の4層構造の手袋は、表面に導火線となる木綿のループが出ていないので、ニッケルバーナーの約800℃の炎を2分当てても燃焼しないことが確認できた。 Furthermore, since the four-layered gloves of Example 2 did not have a cotton loop serving as a conducting wire on the surface, it was confirmed that even when a flame of about 800 ° C. of nickel burner was applied for 2 minutes, it did not burn.
(実施例6)
本実施例では熱遮断性及び切創性について説明する。図10A−Bは本発明の布帛の耐熱性を説明する断面図である。図10Aの2層構造の耐熱手袋(実施例1)の場合、肌側に木綿のループヤーン62を配置し、外側に耐熱性繊維61を配置しているので、熱は耐熱性繊維61の部分で遮断され、内部には入ってこない。これは、ループヤーン62は多くの空気を含んでいるためである。実際に他の物質との熱伝導率を測定すると表2のとおりとなった。熱伝導率は大阪府立産業技術総合研究所のKES−F7(サーモラボ)装置で測定した。
(Example 6)
In the present embodiment, the heat blocking property and the cutting property will be described. 10A-B are cross-sectional views illustrating the heat resistance of the fabric of the present invention. In the case of the two-layer heat resistant glove (Example 1) of FIG. 10A, the
表2から明らかなとおり、本発明の実施例1の耐熱手袋は熱伝導率が低かった。 As is clear from Table 2, the heat-resistant gloves of Example 1 of the present invention had low thermal conductivity.
さらに図10Bに示す耐熱手袋は4層構造の断面図であり、外側からアラミド繊維26、アラミド繊維の小さなループの層30、アラミド繊維層31、木綿糸からなる意匠撚糸で構成される大きなループ層62がこの順番で形成されており、熱は耐熱性繊維26の部分で遮断され、内部には入らないため、図10Aの2層構造に比べてさらに熱遮断性が高かった。
Further, the heat-resistant glove shown in FIG. 10B is a cross-sectional view of a four-layer structure. From the outside, a large loop layer composed of
次に本発明の実施例1の耐熱手袋を用いて切創強さを測定した。切創強さは大阪府立産業技術総合研究所において、JIS−1096破裂強さB法に規定されている「定速伸長計法試験」に準じ、押し棒先端にナイフ(OLFA SDS-7)を取り付け、ナイフ速度2cm/minでナイフがサンプルを突き切る時の強さを測定した。比較例として切創性が良いといわれている市販の耐熱用皮手袋を測定した。結果を表3に示す。 Next, the cutting strength was measured using the heat-resistant gloves of Example 1 of the present invention. The cutting strength is determined by the Osaka Prefectural Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology in accordance with the “Constant Speed Extensometer Test” prescribed in the JIS-1096 Burst Strength B Method. The strength when the knife cuts through the sample at a knife speed of 2 cm / min was measured. As a comparative example, a commercially available heat-resistant leather glove that is said to have good cutting properties was measured. The results are shown in Table 3.
表3に示すように本発明の実施例1の耐熱手袋の切創強さは、市販の耐熱用皮手袋より高かった。これはアラミド繊維を使用しているからである。 As shown in Table 3, the cut strength of the heat-resistant gloves of Example 1 of the present invention was higher than that of commercially available heat-resistant leather gloves. This is because aramid fibers are used.
(実施例7)
(1)意匠撚糸の製造
芯糸及び押さえ糸としてポリエステルマルチフィラメント加工糸(東レ製)、トータル繊度150デニール、フィラメント数75本を使用し、ループヤーンとして木綿糸30番(綿番手)を使用した。木綿糸の単糸を2本から3本使用し、芯糸1本に対してオーバーフィード率5〜7倍で供給して絡み付け、絡みつけと同時にその上から押さえ糸を撚り数約1000回/mで実撚を掛けた。得られた意匠撚糸は、図1A−Bに示すとおりであり、ループの平均突出長さ3mm、1インチあたり平均70個のループが360°の角度であらゆる角度に突出していた。この意匠撚糸の繊度は2.3530番(綿番手、2260デニール)であった。
(2)耐熱性繊維糸の準備
市販の帝人社製商品名“コーネックス”(メタ系アラミド繊維)の紡績糸20番(綿番手)を8本又は9本使用した。
(3)編み物の編成と衣類の縫製
フライス横編機を用いて図12A−Bに示す基本組織にしたがって編み物を編成した。図12A−Bはフライス柄を示している。アラミド繊維糸は編目の全部を構成する糸11とし、意匠撚糸12は1ループおきに沿わせた。得られた編み物の目付けは650g/m2であった。この編み物の表目を衣類の裏面にし、裏目を衣類の表面にして紳士用パーカーに縫製した。
(4)試験
前記パーカーの着用試験をしたところ、暖かく着心地は良かった。このパーカーの耐熱性は実施例1と同等であった。また、カッターナイフで切りつけても切断されず、防護性も高かった。
(Example 7)
(1) Manufacture of design twisted yarn Polyester multifilament processed yarn (manufactured by Toray), total fineness of 150 denier and 75 filaments were used as the core yarn and presser yarn, and cotton yarn No. 30 (cotton count) was used as the loop yarn. . Two to three cotton yarns are used, and the core yarn is fed at an overfeed rate of 5 to 7 times and entangled. At the same time, the presser yarn is twisted about 1000 times. Real twist was applied at / m. The obtained design twisted yarn was as shown in FIGS. 1A-B. The average protruding length of the loop was 3 mm, and an average of 70 loops per inch protruded at an angle of 360 ° at every angle. The fineness of this design twisted yarn was 2.3530 (cotton count, 2260 denier).
(2) Preparation of heat-resistant fiber yarn Eight or nine spun yarn No. 20 (cotton count) of a commercial name “Conex” (meta-aramid fiber) manufactured by Teijin Limited was used.
(3) Knitting of knitting and sewing of clothing Knitting was knitted according to the basic structure shown in FIGS. 12A and 12B using a milling flat knitting machine. 12A-B show a milling pattern. The aramid fiber yarn was the
(4) Test When the Parker was tested for wear, it was warm and comfortable. The heat resistance of this parker was equivalent to that of Example 1. Moreover, even if it cut with a cutter knife, it was not cut | disconnected and the protection property was also high.
(実施例8)
意匠撚糸の木綿糸をウール糸(毛番手64番)に替えた以外は実施例7と同様に意匠撚糸と耐熱性繊維糸を準備し、図13に示す編組織でシングル3とび裏毛ニットを編成した。図13において、上の図は編み組織図、下の図は各々の構成糸の動きを示している。11a,11bはアラミド繊維糸、12は意匠撚糸である。得られた編み物の目付けは530g/m2であった。この編み物を使用してブルゾンジャンパーを縫製した。着用試験をしたところ、暖かく着心地は良かった。このジャンパーの耐熱性は実施例1と同等であった。また、カッターナイフで切りつけても切断されず、防護性も高かった。
(Example 8)
A design twist yarn and a heat-resistant fiber yarn were prepared in the same manner as in Example 7 except that the cotton yarn of the design twist yarn was changed to a wool yarn (hair count of 64), and a single three-line back knit was prepared with the knitting structure shown in FIG. Organized. In FIG. 13, the upper figure shows the knitting structure, and the lower figure shows the movement of each constituent yarn. 11a and 11b are aramid fiber yarns, and 12 is a design twist yarn. The basis weight of the obtained knitted fabric was 530 g / m 2 . A blouson jumper was sewn using this knitting. As a result of the wearing test, it was warm and comfortable. The heat resistance of this jumper was equivalent to that in Example 1. Moreover, even if it cut with a cutter knife, it was not cut | disconnected and the protection property was also high.
(実施例9)
意匠撚糸の木綿糸をウール糸(毛番手48番)に替えた以外は実施例7と同様に意匠撚糸と耐熱性繊維糸を準備し、図14に示す編組織でシングル2とび裏毛ニットを編成した。図14において、上の図は編み組織図、下の(1)〜(3)の図は各々の柄と構成糸の動きを示している。11a,11bはアラミド繊維糸、12は意匠撚糸である。得られた編み物の目付けは450g/m2であった。この編み物を使用してジャケットを縫製した。着用試験をしたところ、暖かく着心地は良かった。このベストの耐熱性は実施例1と同等であった。また、カッターナイフで切りつけても切断されず、防護性も高かった。
Example 9
A design twist yarn and a heat-resistant fiber yarn were prepared in the same manner as in Example 7 except that the cotton yarn of the design twist yarn was changed to a wool yarn (hair count No. 48). Organized. In FIG. 14, the upper diagram shows the knitting structure, and the lower diagrams (1) to (3) show the movements of the respective patterns and constituent yarns. 11a and 11b are aramid fiber yarns, and 12 is a design twist yarn. The basis weight of the obtained knitted fabric was 450 g / m 2 . A jacket was sewn using this knitting. As a result of the wearing test, it was warm and comfortable. The heat resistance of this vest was equivalent to that of Example 1. Moreover, even if it cut with a cutter knife, it was not cut | disconnected and the protection property was also high.
1 意匠撚糸
2 芯糸
3 ループヤーン
4 押さえ糸
10 両面編物
11,11a,11b 耐熱性繊維糸
12 意匠撚糸
13 ループ
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1 Design twist yarn 2
Claims (9)
前記意匠撚糸は、芯糸とループヤーンと押さえ糸で構成され、前記ループヤーンは木綿、レーヨン、麻、羊毛及びアクリル繊維から選ばれる少なくとも一つであることを特徴とする耐熱性布帛。 A knitted fabric or a woven fabric containing a heat-resistant fiber yarn and a design twisted yarn, where there are many heat-resistant fiber yarns on one side, and many design twist yarns on the other side ,
The design twisted yarn is composed of a core yarn, a loop yarn, and a presser yarn, and the loop yarn is at least one selected from cotton, rayon, hemp, wool, and acrylic fiber .
前記意匠撚糸は、芯糸とループヤーンと押さえ糸で構成され、前記ループヤーンは木綿、レーヨン、麻、羊毛及びアクリル繊維から選ばれる少なくとも一つであることを特徴とする耐熱性手袋。 Consists of a knitted fabric including heat-resistant fiber yarn and design twist yarn, the knitted fabric is a knit, there are many heat-resistant fiber yarns on the outer surface, there are many design twist yarns on the inner surface ,
The design twisted yarn is composed of a core yarn, a loop yarn, and a presser yarn, and the loop yarn is at least one selected from cotton, rayon, hemp, wool, and acrylic fiber .
外側に耐熱性繊維糸で構成される手袋を配置し、
両手袋を指先で固定した複層構造の耐熱性手袋。 Consists of a knitted fabric including heat-resistant fiber yarn and design twist yarn, the knitted fabric is knit, there are many heat-resistant fiber yarns on the outer surface, there are many design twist yarns on the inner surface, and the design twist yarn is a core yarn and a loop It is composed of yarn and presser yarn, and the loop yarn is arranged on the inner surface with heat-resistant gloves that are at least one selected from cotton, rayon, hemp, wool and acrylic fiber ,
Place gloves composed of heat-resistant fiber threads on the outside,
A heat-resistant glove with a multi-layer structure in which both gloves are fixed with fingertips.
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005310420A JP4053558B2 (en) | 2005-02-03 | 2005-10-25 | Heat resistant fabric, clothing and heat resistant gloves using the same |
| CN2006800216029A CN101198732B (en) | 2005-06-17 | 2006-05-18 | Heat resistant cloth and clothing and heat resistant glove employing it |
| PCT/JP2006/309926 WO2006134748A1 (en) | 2005-06-17 | 2006-05-18 | Heat resistant cloth and clothing and heat resistant glove employing it |
| EP20060756341 EP1914333B1 (en) | 2005-06-17 | 2006-05-18 | Heat resistant cloth and clothing and heat resistant glove employing it |
| US11/922,272 US7681417B2 (en) | 2005-06-17 | 2006-05-18 | Heat-resistant fabric and garment and heat-resistant glove using the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005028060 | 2005-02-03 | ||
| JP2005178165 | 2005-06-17 | ||
| JP2005310420A JP4053558B2 (en) | 2005-02-03 | 2005-10-25 | Heat resistant fabric, clothing and heat resistant gloves using the same |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2007023463A JP2007023463A (en) | 2007-02-01 |
| JP2007023463A5 JP2007023463A5 (en) | 2007-12-06 |
| JP4053558B2 true JP4053558B2 (en) | 2008-02-27 |
Family
ID=37784606
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005310420A Active JP4053558B2 (en) | 2005-02-03 | 2005-10-25 | Heat resistant fabric, clothing and heat resistant gloves using the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4053558B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104125784B (en) * | 2012-02-20 | 2017-08-11 | 安塞尔有限公司 | The method of gloves and knitted gloves |
| JP5993617B2 (en) * | 2012-05-28 | 2016-09-14 | アキレス株式会社 | Synthetic leather |
| PL3140120T3 (en) * | 2014-05-08 | 2023-12-11 | Southern Mills, Inc. | Flame resistant fabric having wool blends |
| FR3053702B1 (en) * | 2016-07-05 | 2019-09-13 | Saint-Gobain Adfors | HYBRID WOVEN TEXTILE FOR COMPOSITE REINFORCEMENT |
| US20200199790A1 (en) | 2017-07-10 | 2020-06-25 | Hayashi Yarn Twisting Co., Ltd. | Covering yarn, twisted yarn, and fiber structure using the same |
-
2005
- 2005-10-25 JP JP2005310420A patent/JP4053558B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2007023463A (en) | 2007-02-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7681417B2 (en) | Heat-resistant fabric and garment and heat-resistant glove using the same | |
| AU2018247356B2 (en) | Frame resistant fabric having wool blends | |
| US20160237594A1 (en) | Flame Resistant Fiber Blends and Flame Resistant Yarns, Fabrics, and Garments Formed Thereof | |
| US20170067192A1 (en) | Flame Resistant Composite Fabrics | |
| CA2881104C (en) | Flame resistant fiber blends and flame resistant yarns, fabrics, and garments formed thereof | |
| TWI381075B (en) | Double layer fabric and the use of its heat-resistant protective clothing | |
| JP5378505B2 (en) | Fireproof fabric and fireproof clothing using the same | |
| JP6037837B2 (en) | Laminated heat-resistant protective clothing | |
| US20140187113A1 (en) | Fiber blends for dual hazard and comfort properties | |
| ES2437339T3 (en) | A multi-use non-woven fabric structure for arc lightning protection | |
| US20090209155A1 (en) | Layered thermally-insulating fabric with thin heat reflective and heat distributing core | |
| JP7128365B2 (en) | flame retardant fabric | |
| JPWO2008075505A1 (en) | Heat-resistant double woven fabric and clothing and heat-resistant gloves using the same | |
| WO2012121759A2 (en) | Flame resistant composite fabrics | |
| TW201237229A (en) | Flame resistant fabric for protective clothing | |
| JP6170814B2 (en) | Fabrics and textile products | |
| WO2000057738A2 (en) | Heat-resistant garment | |
| JP4053558B2 (en) | Heat resistant fabric, clothing and heat resistant gloves using the same | |
| CN115210421A (en) | Flame resistant fabrics formed from long staple yarns and filament yarns | |
| KR20090040977A (en) | Antifire fabrics using clothes of extinguish a fire | |
| CN214710679U (en) | Fire-fighting gloves with composite multilayer structure | |
| JP2018087397A (en) | Heat insulation glove and sock | |
| KR20220153775A (en) | High heat resistance firefighting gloves containing ceramic fiber and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2020084347A (en) | Heat resistant protective wear |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20061227 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20061227 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20071023 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20071023 |
|
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20071108 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20071127 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20071205 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20101214 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4053558 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20101214 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131214 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |