JP3969907B2 - Plasma processing equipment - Google Patents
Plasma processing equipment Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3969907B2 JP3969907B2 JP25962799A JP25962799A JP3969907B2 JP 3969907 B2 JP3969907 B2 JP 3969907B2 JP 25962799 A JP25962799 A JP 25962799A JP 25962799 A JP25962799 A JP 25962799A JP 3969907 B2 JP3969907 B2 JP 3969907B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- gas supply
- substrate
- gas
- vacuum chamber
- plasma processing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Drying Of Semiconductors (AREA)
- Plasma Technology (AREA)
- Chemical Vapour Deposition (AREA)
- ing And Chemical Polishing (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、ガス供給部を有した真空室に処理ガスを供給するとともに高周波電圧を印加して前記真空室内にプラズマを発生させて基板を処理するプラズマ処理装置に関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来より、半導体素子や液晶表示素子の製造過程におけるドライエッチング装置やCVD装置等には、高周波誘導結合を利用したプラズマ処理装置が使用されている。
図3と図4は、従来のプラズマ処理装置を示す。
【0003】
図3に示すように、プラズマ処理装置は、真空室4に配置された基板7に真空室4に配設されたガス供給部より処理ガスを供給して、真空室4の外部より高周波電圧を印加して真空室4の内部にプラズマを発生させて基板7を処理するよう構成されている。
真空室4の上側には誘電板3を介してプラズマを発生させる高周波誘導用コイル2とこれに繋がる第1高周波電源1が設けられ、下側には真空室4内を真空排気するポンプ10が配設されている。
【0004】
真空室4の内部には、第2高周波電源9より高周波電圧が印加される電極8が配置され、この電極8に基板7が載置される。
ガス供給部は、真空室4の側壁に設けられたガス供給口5と、このガス供給口5に繋がる真空室4の内面側に接続されたガス供給部品13とから構成される。
ガス供給部品13の構成を図4に示す。図4(a)は、ガス供給部品13の平面図、図4(b)はガス供給部品13の側面図である。
【0005】
ガス供給部品13は、ガス供給口5より処理ガスを導入するガス導入管13aと、これに繋がる基板7の外形よりも大きい環状管のガス供給管13bとからなり、ガス供給管13bの内周壁には基板7と平行になるように多数のガス吹出し孔12が形成されている。
このように構成されたプラズマ処理装置では、電極8に基板7が載置されると、ポンプ10によって真空室4が排気され、ガス供給口5よりガス導入管13aを介して処理ガスが供給され、ガス導入管13aのガス吹出し孔12より真空室4内が低圧力(10mTorr〜1000mTorr程度)状態になるまで任意の処理ガスが供給される。
【0006】
次いで、高周波誘導用コイル2と第1高周波電源1によって、高密度プラズマが発生し、基板7にエッチングや成膜などの処理が施される。
【0007】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、上記従来のプラズマ処理装置では、ガス供給管13bの内部で圧力損失が発生し、ガス導入管13aから遠いガス吹出し孔12ではかなりの流量減少が発生する。
これは、基板7の大きさが半導体ウエハ(直径8インチ)ほどの大きさでは問題にならないが、液晶表示装置に使用する基板のように基板サイズが大きくなると、ガス供給管13bがリング状になっていることも影響してガス導入管13aから遠い部分ではガス流量が小さくなり、基板7の中央部分ではガス供給量のばらつきが顕著になって基板面内の処理速度の均一性に大きな影響を及ぼすようになる。
【0008】
例えば、このプラズマ処理装置を550mm×670mmサイズの液晶表示装置用の基板に対応するドライエッチング装置として、アルミニウム膜のエッチングに適用した場合には、エッチング速度にばらつきが生じ、基板面内のエッチング速度の均一性が確保されないという問題が生じる。
本発明は前記問題点を解決し、面積の大きい基板を処理する場合でもその全面に均一に処理ガスを供給できるプラズマ処理装置を提供することを目的とする。
【0009】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明のプラズマ処理装置は、ガス供給部の構成を特殊にしたことを特徴とする。
この本発明によると、面積の大きい基板を用いた場合でも基板の全面に処理ガスを均一に供給して、基板面内における処理速度の均一性を確保できる。
【0010】
【発明の実施の形態】
本発明の請求項1記載のプラズマ処理装置は、真空室にガスを供給するガス供給部と、前記真空室に配置され基板を載置する電極と、前記電極に対向して配置されたコイルと、前記コイルに高周波電圧を印加する高周波電源とを有するプラズマ処理装置において、前記ガス供給部は、前記基板の中心点上から先端部が外周部に向かって放射状に延びる複数のガス供給管で構成され、前記ガス供給管に設けられた2個以上のガス吹出しのうち少なくとも1個は前記基板の外側に形成されたことを特徴とする。
【0011】
この構成によると、前記基板の中心点上から先端部が外周部に向かって放射状に延びる複数のガス供給管で構成され、前記ガス供給管に設けられた2個以上のガス吹出しのうち少なくとも1個は前記基板の外側に形成されたことによって、ガス供給部へのガス導入が基板の中心点上から行われるとともに、基板の中心点上から放射状に複数のガス供給管が設置されているため、ガス吹出し孔から供給される処理ガスの流量のばらつきを抑え、基板の全面に均一性の高いガス供給を行える。
以下、本発明のプラズマ処理装置を具体的な実施の形態に基づいて説明する。
【0012】
なお、上記従来例を示す図3,図4と同様をなすものについては、同一の符号をつけて説明する。
(実施の形態)
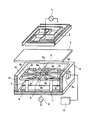
図1と図2は、本発明のプラズマ処理装置を示す。
この実施の形態では、従来のプラズマ処理装置よりも基板の加工均一性を高めるために、特殊な構成としたガス供給部を設けた点で上記従来例と異なる。
【0013】
真空室4の上部には誘電板3を介してプラズマを発生させる高周波誘導用コイル2とこれに繋がる第1高周波電源1が設けられ、下側には、真空排気するためのポンプ10が設けられている。
真空室4の内部には、第2高周波電源9より高周波電圧が印加される電極8が配置され、この電極8に基板7が載置されている。
【0014】
真空室4の側壁には、ガス供給口5が設けられており、ガス供給部として、このガス供給口5に真空室4の内側からガス供給部品6が接続され、金属もしくはセラミックスにより構成されたブラケット11にて真空室4に固定されている。
ガス供給部品6は、ガス供給口5から基板7の中心点上まで延びさらに基板面側に直角に屈折したガス導入管6aと、この先端に接続された基板7の中心点上から先端部が基板7の外周部に向かって放射状に延びる複数のガス供給管6b〜6mと、ガス供給管6b〜6mの先端部を固定する基板7の外形よりも大きい固定用リング6nとからなり、これらは一体化されている。ガス供給管6b〜6mには、それぞれ複数のガス吹出し孔12が設けられ、ガス導入管6aよりガス供給管6b〜6mの基端部に処理ガスが供給される。
【0015】
ガス供給部品6の詳細を図2に示す。図2(a)はガス供給部品6を基板7との対向面側から見た平面図であり、図2(b)はガス供給部品6の側面図である。
ガス供給管6b〜6mは、その内径が1/8〜3/8インチ程度で、長さは先端部が基板7よりも外側にくる長さであることが好ましい。それぞれのガス供給管6b〜6mには少なくとも2個以上のガス吹出し孔12が等ピッチであけられており、ガス吹出し孔12のうち少なくとも1個以上は基板7の外側にあることが好ましい。ガス吹出し孔12はすべて同一方向にあけられており、その孔径は0.5〜3mm程度である。
【0016】
固定用リング6nは、ガス供給管6b〜6mの先端を固定して一体化しており、ブラケット11を介して固定用リング6nが真空室4に固定されている。
このようにしてガス供給部品6が真空室4に固定されることで、放射状に配置されたそれぞれのガス供給管6b〜6mの位置およびガス供給部品6と真空室4との位置が固定され、基板7に対するパイプの孔の位置や向きがしっかりと固定される。なお、ガス供給部品6をガス供給口5に接続するときには、ガス吹出し孔12と基板7とが対向するように配置する。
【0017】
このように構成されたガス供給部品6では、ガス供給口5より導入された処理ガスは、ガス導入管6aによって基板7の中心点上まで導かれさらに基板7の面側に向かって直角に供給されるため、放射状に設置されたガス供給管6b〜6mに均等にガスを分配できる。
以上のように構成されたプラズマ処理装置では、電極8に基板7が載置されると、ポンプ10によって真空室4が排気され、ガス供給口5よりガス導入管6aを介してガス供給管6b〜6mのガス吹出し孔12より、真空室4内を適当な圧力(10mTorr〜1000mTorr程度)になるまで任意の処理ガスが供給される。
【0018】
真空室4内が一定の圧力に保たれると、第1高周波電源1により高周波誘導用コイル2に高周波電力が印加され、高密度プラズマが発生し、第2高周波電源9により電極8に高周波電源が印加され、基板7に入射するイオンのエネルギーが制御される。
高密度プラズマが発生すると、電極8に載置された基板7は反応ガスにより処理される。
【0019】
基板7に供給される反応ガスは、上述のようにガス供給部品6によって一旦ガス導入管6aより基板7の中心点上まで導入された後、放射状のガス供給管6b〜6mに供給されるため、従来よりもガス吹出し孔12から吹出されるガス流量のばらつきを抑えることができ、大面積の基板7を用いた場合でも基板7の全面に均一性の高いガスを供給できる。
【0020】
例えば、このプラズマ処理装置を、550mm×670mmサイズの液晶表示装置用の基板に対応するドライエッチング装置としてアルミニウム膜のエッチングに適用し、反応ガスとしてCl2とBCl3を使用した場合には、従来よりもエッチング速度の均一性を高められる。
なお、上記説明では、ガス導入管6a,ガス供給管6b〜6m,固定用リング6nをそれぞれ一体化したガス供給部品6を例に挙げたが、各部を構成する材質は同一であっても、また異なる材質の複合体であってもよい。
【0021】
ガス供給部品6を構成する材質としては、SUS316などの金属が好ましいが、本発明はこれに限定されるものではなく、例えば石英、アルミナ、窒化硅素、窒化アルミなどのセラミックスによる構成も可能である。
また、ガス供給管の本数や管の径、ガス吹出し孔の孔径,孔の位置,孔の方向などは上記のものに限定されるものではなく、処理ガスの圧力損失や真空室4の大きさ、処理すべき基板7の大きさ等を考慮して決めればよく、例えば、パイプの本数を4本にしたり、パイプの外側端部に近づくにしたがい孔径を大きくしたり、孔と孔の間隔を狭くしたり、パイプ径を徐々に太くしたり、孔の向きを処理すべき基板7に対して平行に向けて一体化してもかまわない。
【0022】
また、処理する基板7として矩形状のものを用い、真空室4,ガス供給部品6,電極8などの形状を矩形状とした場合を例に挙げたが、本発明はこれに限定されるものではなく、例えば半導体素子を製造する際のように円形の基板を処理する場合には、真空室,ガス供給部品,電極などの形状を円形に構成する方が装置の構成から容易である。
【0023】
【発明の効果】
以上のように本発明のプラズマ処理装置によれば、ガス供給部は、基板の中心点上から先端部が外周部に向かって放射状に延びる複数のガス供給管で構成され、前記ガス供給管に設けられた2個以上のガス吹出しのうち少なくとも1個は前記基板の外側に形成された構成であるため、それぞれのガス吹出し孔から出るガス流量のばらつきを抑えて大面積の基板であっても全体に均一性の高いガスを供給でき、基板面内の処理速度の均一性の高いプラズマ処理が実現できる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の実施の形態におけるプラズマ処理装置の構成を示す図
【図2】本発明の実施の形態におけるガス供給部品を下側から見た平面図および側面図
【図3】従来例のプラズマ処理装置の構成を示す図
【図4】従来例のプラズマ処理装置におけるガス供給部品の下側からみた平面図および側面図
【符号の説明】
4 真空室
5 ガス供給口
6 ガス供給部品
6a ガス導入経路
6b〜6m ガス導入管
6n 固定用リング
7 基板
12 ガス吹出し孔[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a plasma processing apparatus for processing a substrate by supplying a processing gas to a vacuum chamber having a gas supply unit and applying a high frequency voltage to generate plasma in the vacuum chamber.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Conventionally, plasma processing apparatuses using high-frequency inductive coupling have been used in dry etching apparatuses, CVD apparatuses, and the like in the process of manufacturing semiconductor elements and liquid crystal display elements.
3 and 4 show a conventional plasma processing apparatus.
[0003]
As shown in FIG. 3, the plasma processing apparatus supplies a processing gas from a gas supply unit disposed in the
A high-
[0004]
Inside the
The gas supply unit includes a gas supply port 5 provided on the side wall of the
The configuration of the
[0005]
The
In the plasma processing apparatus configured as described above, when the
[0006]
Next, high-frequency plasma is generated by the high-
[0007]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, in the above-described conventional plasma processing apparatus, a pressure loss occurs inside the
This is not a problem when the size of the
[0008]
For example, when this plasma processing apparatus is applied to the etching of an aluminum film as a dry etching apparatus corresponding to a substrate for a liquid crystal display device having a size of 550 mm × 670 mm, the etching rate varies, and the etching rate within the substrate surface occurs. There arises a problem that the uniformity is not ensured.
An object of the present invention is to solve the above problems and to provide a plasma processing apparatus capable of supplying a processing gas uniformly over the entire surface even when processing a substrate having a large area.
[0009]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The plasma processing apparatus of the present invention is characterized by a special configuration of the gas supply unit.
According to the present invention, even when a substrate having a large area is used, the processing gas can be uniformly supplied to the entire surface of the substrate, and the uniformity of the processing speed within the substrate surface can be secured.
[0010]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The plasma processing apparatus according to
[0011]
According to this configuration, the front end portion is configured by the plurality of gas supply pipes extending radially from the center point of the substrate toward the outer peripheral portion, and at least one of the two or more gas outlets provided in the gas supply pipe. Since the individual is formed outside the substrate, gas introduction into the gas supply unit is performed from above the center point of the substrate, and a plurality of gas supply pipes are installed radially from the center point of the substrate. Further, it is possible to suppress a variation in the flow rate of the processing gas supplied from the gas blowing holes and to supply a highly uniform gas over the entire surface of the substrate.
Hereinafter, the plasma processing apparatus of the present invention will be described based on specific embodiments.
[0012]
Components similar to those in FIGS. 3 and 4 showing the conventional example will be described with the same reference numerals.
(Embodiment)
1 and 2 show a plasma processing apparatus of the present invention.
This embodiment is different from the conventional example in that a gas supply unit having a special configuration is provided in order to improve the processing uniformity of the substrate as compared with the conventional plasma processing apparatus.
[0013]
A high
Inside the
[0014]
A gas supply port 5 is provided on the side wall of the
The
[0015]
Details of the
The
[0016]
The fixing
By fixing the
[0017]
In the
In the plasma processing apparatus configured as described above, when the
[0018]
When the inside of the
When high-density plasma is generated, the
[0019]
Since the reaction gas supplied to the
[0020]
For example, when this plasma processing apparatus is applied to the etching of an aluminum film as a dry etching apparatus corresponding to a substrate for a liquid crystal display device having a size of 550 mm × 670 mm, and Cl 2 and BCl 3 are used as reaction gases, Therefore, the uniformity of the etching rate can be improved.
In the above description, the
[0021]
The material constituting the
Further, the number of gas supply pipes, the diameter of the pipe, the diameter of the gas blowing hole, the position of the hole, the direction of the hole, etc. are not limited to the above, but the pressure loss of the processing gas and the size of the
[0022]
Moreover, although the case where the rectangular-shaped thing was used as the board |
[0023]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the plasma processing apparatus of the present invention, the gas supply unit is composed of a plurality of gas supply pipes whose front end portions extend radially from the center point of the substrate toward the outer peripheral portion. Since at least one of the two or more gas outlets provided is formed on the outside of the substrate, even if the substrate has a large area while suppressing variation in the gas flow rate from each gas outlet hole. Gas with high uniformity can be supplied to the whole, and plasma processing with high uniformity of processing speed within the substrate surface can be realized.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a configuration of a plasma processing apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a plan view and a side view of a gas supply component viewed from below according to an embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 4 is a plan view and a side view as seen from the lower side of a gas supply component in a conventional plasma processing apparatus.
4 Vacuum chamber 5
Claims (1)
前記真空室に配置され基板を載置する電極と、
前記電極に対向して配置されたコイルと、
前記コイルに高周波電圧を印加する高周波電源と
を有するプラズマ処理装置において、
前記ガス供給部は、前記基板の中心点上から先端部が外周部に向かって放射状に延びる複数のガス供給管で構成され、前記ガス供給管に設けられた2個以上のガス吹出しのうち少なくとも1個は前記基板の外側に形成された
プラズマ処理装置。A gas supply unit for supplying gas to the vacuum chamber;
An electrode disposed in the vacuum chamber and mounting a substrate;
A coil disposed opposite the electrode;
In a plasma processing apparatus having a high frequency power source for applying a high frequency voltage to the coil,
The gas supply part is composed of a plurality of gas supply pipes whose tip ends extend radially from the center point of the substrate toward the outer peripheral part, and at least of two or more gas outlets provided in the gas supply pipe One is a plasma processing apparatus formed outside the substrate .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP25962799A JP3969907B2 (en) | 1999-09-14 | 1999-09-14 | Plasma processing equipment |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP25962799A JP3969907B2 (en) | 1999-09-14 | 1999-09-14 | Plasma processing equipment |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2001085409A JP2001085409A (en) | 2001-03-30 |
| JP2001085409A5 JP2001085409A5 (en) | 2005-09-02 |
| JP3969907B2 true JP3969907B2 (en) | 2007-09-05 |
Family
ID=17336714
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP25962799A Expired - Lifetime JP3969907B2 (en) | 1999-09-14 | 1999-09-14 | Plasma processing equipment |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3969907B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20020080014A (en) * | 2001-04-10 | 2002-10-23 | 주식회사 에이티씨 | plasma processing apparatus |
| JP4185483B2 (en) | 2004-10-22 | 2008-11-26 | シャープ株式会社 | Plasma processing equipment |
| JP4584722B2 (en) | 2005-01-13 | 2010-11-24 | シャープ株式会社 | Plasma processing apparatus and semiconductor device manufactured by the same |
| JP2006196681A (en) | 2005-01-13 | 2006-07-27 | Sharp Corp | Plasma processing device and semiconductor element manufactured by the same |
| US20090130335A1 (en) * | 2005-09-01 | 2009-05-21 | Tomohiro Okumura | Plasma processing apparatus, plasma processing method, dielectric window used therein, and manufacturing method of such a dielectric window |
-
1999
- 1999-09-14 JP JP25962799A patent/JP3969907B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2001085409A (en) | 2001-03-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5185251B2 (en) | Gas injection system with reduced contamination and method of use thereof | |
| JP6948822B2 (en) | Board processing device and board removal method | |
| JP4869610B2 (en) | Substrate holding member and substrate processing apparatus | |
| JP4935143B2 (en) | Mounting table and vacuum processing apparatus | |
| WO2002065531A1 (en) | Focus ring for semiconductor treatment and plasma treatment device | |
| JP2007250967A (en) | Plasma treating apparatus and method, and focus ring | |
| JPH1041281A (en) | Plasma treating apparatus | |
| JP2009224441A (en) | Showerhead and substrate processing apparatus | |
| KR20210008725A (en) | Unit for supporting substrate and system for treating substrate with the unit | |
| JP3969907B2 (en) | Plasma processing equipment | |
| TWI809007B (en) | Focus ring for semiconductor manufacturing apparatus and semiconductor manufacturing apparatus | |
| JP2004022822A (en) | Plasma processing method and device | |
| WO2020116248A1 (en) | Plasma processing device | |
| JP2005209885A (en) | Plasma etching apparatus | |
| TWI278953B (en) | Apparatus for manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| JP2021097102A (en) | Edge ring and substrate processing apparatus | |
| JP2002009065A (en) | Plasma cvd device | |
| JPH11233292A (en) | Plasma processing device | |
| JP6085106B2 (en) | Plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method | |
| JP2020092034A (en) | Plasma processing apparatus | |
| JP5302813B2 (en) | Deposit control cover and plasma processing apparatus | |
| TWI744657B (en) | Wafer holding apparatus, system and method | |
| JP6348321B2 (en) | Etching device | |
| JPH08158073A (en) | Chemical dry etching device | |
| JPS5943880A (en) | Dry etching device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050307 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20050307 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20061115 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20061121 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070115 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20070508 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20070605 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 3969907 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100615 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100615 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110615 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120615 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120615 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130615 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| EXPY | Cancellation because of completion of term |