JP3773510B2 - Discharge plasma processing method and discharge plasma processing apparatus - Google Patents
Discharge plasma processing method and discharge plasma processing apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3773510B2 JP3773510B2 JP2003315932A JP2003315932A JP3773510B2 JP 3773510 B2 JP3773510 B2 JP 3773510B2 JP 2003315932 A JP2003315932 A JP 2003315932A JP 2003315932 A JP2003315932 A JP 2003315932A JP 3773510 B2 JP3773510 B2 JP 3773510B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- discharge
- voltage
- plasma
- electrodes
- treatment
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Plasma Technology (AREA)
- Physical Or Chemical Processes And Apparatus (AREA)
- Chemical Vapour Deposition (AREA)
Description
本発明は、プラスチックシート等に例えば親水性処理等の表面改質、エッチングまたはCVD等の表面処理を行う放電プラズマ処理方法に係り、特に、大気圧近傍の圧力条件下におけるグロー放電によりプラズマを発生させて被処理物の表面をプラズマ処理する放電プラズマ処理方法および放電プラズマ処理装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a discharge plasma processing method in which a plastic sheet or the like is subjected to surface modification such as hydrophilic treatment, surface treatment such as etching or CVD, and in particular, plasma is generated by glow discharge under pressure conditions near atmospheric pressure. The present invention relates to a discharge plasma processing method and a discharge plasma processing apparatus for performing plasma processing on a surface of an object to be processed.
従来、この種の放電処理を行う装置として、特許文献1に記載のグロー放電プラズマ処理装置は、対向電極、該対向電極の少なくとも一方の対向面に設置された固体誘電体、当該一対の電極間にパルス化された電界を印加するようになされている高電圧パルス電源からなり、高電圧パルス電源が高電圧直流を供給可能な直流電圧供給部、並びに、ターンオン時間及びターンオフ時間が500ns以下である半導体素子により当該高電圧直流を高電圧パルスに変換するパルス制御部から構成されるものである。これにより、電界強度が1〜100kV/cmであり、かつ、パルスの立ち上がり時間及び立ち下がり時間が100μS以下であるような高電圧かつ高速のパルス電圧を実現することができる装置である。
ところで、前記構造のグロー放電プラズマ処理装置は、大気圧近傍の圧力下で均一なグロー放電プラズマを継続して発生させ、安定して基材の表面処理を行うことができるものであるが、処理が終了し放電を停止した際に、印加電圧を0Vにしていた。そして、次の処理のために放電を立てるとき、0Vから放電処理電圧にいきなり昇圧して印加するため、その際には通常の放電中ではあり得ない電圧や電流が流れ、電極や電源に負荷がかかり、固体誘電体の絶縁破壊や素子の破壊を誘発するため、連続処理に比べて電極の寿命が短くなる問題点があった。 By the way, the glow discharge plasma processing apparatus having the above structure is capable of continuously generating uniform glow discharge plasma under a pressure in the vicinity of atmospheric pressure and stably performing the surface treatment of the substrate. The voltage applied was 0 V when the discharge was terminated and the discharge was stopped. When a discharge is generated for the next treatment, the voltage is suddenly increased from 0 V to the discharge treatment voltage, and at that time, a voltage or current that cannot be obtained during normal discharge flows, and a load is applied to the electrode or power source. As a result, the dielectric breakdown of the solid dielectric and the breakdown of the element are induced, so that there is a problem that the life of the electrode is shortened as compared with the continuous treatment.
すなわち、放電を立てるために、スイッチをONした瞬間、対向する電極間には0Vから約15000Vの電圧がかかり、それに伴い大電流がいきなり電子回路や放電部を流れようとする。この電流の流れには、慣性的な力が働き、通常では流れない電流が流れるのである。さらに、その負荷は、電源素子の電気的に弱くなっているところや、電極間距離の局所的に小さいところ、電子が存在するところ、誘電体の厚みや誘電率のバラツキのあるところに電界が局所集中し、その部分が絶縁破壊を起こし、異常放電になるといった問題があった。 That is, the voltage from 0V to about 15000V is applied between the opposing electrodes at the moment when the switch is turned on in order to establish a discharge, and a large current suddenly tries to flow through the electronic circuit or the discharge part. An inertial force acts on the current flow, and a current that does not normally flow flows. Furthermore, the electric field is generated where the load is electrically weak in the power supply element, where the distance between the electrodes is locally small, where electrons are present, where there is variation in the thickness of the dielectric or in the dielectric constant. There was a problem of local concentration, causing dielectric breakdown in that part, and abnormal discharge.
本発明は、このような問題に鑑みてなされたものであって、その目的とするところは、放電プラズマ処理を行う対向する電極の長寿命化を図ることができると共に、電極に電圧を印加する電気回路に異常電流が流れるのを防止できると共に、複数の被処理物を効率良くプラズマ処理できる放電プラズマ処理方法を提供することにある。また、電極の長寿命化を図ることができると共に、電極に放電処理電圧を印加する電気回路の故障を防止できる放電プラズマ処理方法および放電プラズマ処理装置を提供することにある。 The present invention has been made in view of such problems, and an object of the present invention is to extend the life of the opposing electrodes that perform discharge plasma treatment and to apply a voltage to the electrodes. An object of the present invention is to provide a discharge plasma processing method capable of preventing abnormal current from flowing through an electric circuit and capable of efficiently plasma-processing a plurality of objects to be processed. It is another object of the present invention to provide a discharge plasma processing method and a discharge plasma processing apparatus capable of extending the life of an electrode and preventing failure of an electric circuit that applies a discharge processing voltage to the electrode.
前記目的を達成すべく、本発明に係る放電プラズマ処理方法は、少なくとも一方の電極対向面が固体誘電体で被覆された一対の対向する電極を備え、該電極間に放電処理電圧を印加して放電させ、プラズマを発生させて被処理物をプラズマ処理する方法であって、放
電処理電圧を印加するプラズマ処理工程の前工程および/または後工程として、放電処理電圧より低く電極間で放電が立たない放電準備電圧を電極間に印加することを特徴とする。すなわち、プラズマ処理工程では、電極間に高電圧を印加するが、その前工程として低い電圧を印加した待機状態を作っておく。この放電プラズマ処理方法は、大気圧近傍の圧力下で行うことが好ましく、印加される放電処理電圧はパルス状電圧が好ましい。
In order to achieve the above object, a discharge plasma processing method according to the present invention comprises a pair of opposing electrodes whose at least one electrode facing surface is coated with a solid dielectric, and a discharge processing voltage is applied between the electrodes. A method of performing plasma processing on an object to be processed by discharging and generating plasma, wherein a discharge is generated between electrodes lower than the discharge processing voltage as a pre-process and / or a post-process of a plasma processing process for applying a discharge processing voltage. No discharge preparation voltage is applied between the electrodes. That is, in the plasma treatment process, a high voltage is applied between the electrodes, but a standby state in which a low voltage is applied is created as a previous process. This discharge plasma treatment method is preferably performed under a pressure near atmospheric pressure, and the applied discharge treatment voltage is preferably a pulsed voltage.
前記のごとく構成された本発明の放電プラズマ処理方法は、表面処理等を行う被処理物を対向する電極間、または電極間外におけるプラズマ吹き出し口近傍などに設置して位置させ、電極間に放電処理電圧を印加して被処理物に対して放電を立たせるときに、放電電圧制御手段により放電開始前に放電処理電圧より低く電極間で放電が立たない放電準備電圧を印加して待機状態としたあと、放電処理電圧を印加して放電を開始させるため、プラズマ処理前に電子の飛びやすい状態、すなわち予めチャネルを作っておくことができ、固体誘電体の絶縁破壊等を防止して電極の消耗を防止することができ、装置の耐久性を向上できると共に、電極間に電圧を印加する電気回路に異常電流が流れるのを防止できる。 In the discharge plasma processing method of the present invention configured as described above, the object to be processed is subjected to surface treatment or the like between the electrodes facing each other or in the vicinity of the plasma outlet near the outside of the electrodes. When a treatment voltage is applied to cause discharge on the workpiece, the discharge voltage control means applies a discharge preparation voltage that is lower than the discharge treatment voltage and does not cause a discharge between the electrodes before starting discharge, and enters a standby state. After that, since the discharge treatment voltage is applied to start the discharge, a state in which electrons can easily fly before the plasma treatment, that is, a channel can be formed in advance to prevent dielectric breakdown of the solid dielectric and the like of the electrode. Consumption can be prevented, the durability of the apparatus can be improved, and abnormal current can be prevented from flowing in an electric circuit that applies a voltage between the electrodes.
また、放電処理工程の後工程として放電処理電圧より低い放電準備電圧を電極間に印加し、放電処理後に放電の立たない低い電圧を印加した状態とする。この構成によれば、放電処理を行った高電圧から、一気に0Vまで電圧を降下させず、放電処理電圧より低い放電準備電圧とするため、固体誘電体の絶縁破壊等を防止して電極の耐久性を向上でき、電気回路の電気素子の破壊を防止でき、装置の耐久性を向上できる。 In addition, a discharge preparation voltage lower than the discharge treatment voltage is applied between the electrodes as a subsequent step of the discharge treatment step, and a low voltage that does not cause a discharge after the discharge treatment is applied. According to this configuration, since the discharge preparation voltage is lower than the discharge treatment voltage without dropping the voltage from the high voltage subjected to the discharge treatment to 0 V at a stretch, the dielectric breakdown of the solid dielectric is prevented and the durability of the electrode is reduced. Performance can be improved, the electrical elements of the electrical circuit can be prevented from being destroyed, and the durability of the apparatus can be improved.
本発明に係る放電プラズマ処理方法の他の態様としては、前記の放電プラズマ処理方法により、複数の被処理物をプラズマ処理する方法であって、被処理物を、前工程として電極間に順次設置する工程と、電極間に設置された被処理物をプラズマ処理する工程と、後工程としてプラズマ処理後の被処理物を撤去する工程とを備え、設置工程および/または撤去工程では、放電準備電圧を電極間に印加する。この構成によれば、前記と同様に効果の他に、特に、複数の被処理物に対して、同様のプラズマ処理を連続して行うようなバッチ処理の場合は、電極の消耗の少ない効率良い放電プラズマ処理が可能となる。 Another aspect of the discharge plasma processing method according to the present invention is a method of plasma processing a plurality of objects to be processed by the above-described discharge plasma processing method, wherein the objects to be processed are sequentially installed between electrodes as a pre-process. A process of plasma-treating a workpiece placed between the electrodes, and a step of removing the workpiece after the plasma treatment as a post-process. In the installation step and / or the removal step, a discharge preparation voltage is provided. Is applied between the electrodes. According to this configuration, in addition to the effects similar to the above, particularly in the case of batch processing in which the same plasma processing is continuously performed on a plurality of objects to be processed, the electrode consumption is low and the efficiency is high. Discharge plasma treatment is possible.
また、本発明に係る放電プラズマ処理方法の好ましい具体的な態様としては、前記放電準備電圧は、放電処理電圧の10〜99.9%に設定することを特徴としている。10%未満では待機電圧としての効果が低く、放電開始時に大きな電流が流れてしまい、99.9%を超えると放電が立ってしまい、待機状態とすることができない。特に、放電準備電圧を放電処理電圧の70〜95%の電圧に設定することが好ましい。このように放電準備電圧を設定することで電極の消耗を防止することができると共に、電気回路の異常電流を防止でき、装置の耐久性を向上できる。 Moreover, as a preferable specific aspect of the discharge plasma processing method according to the present invention, the discharge preparation voltage is set to 10 to 99.9% of the discharge processing voltage. If it is less than 10%, the effect as a standby voltage is low, and a large current flows at the start of discharge, and if it exceeds 99.9%, a discharge is generated and the standby state cannot be established. In particular, it is preferable to set the discharge preparation voltage to a voltage of 70 to 95% of the discharge processing voltage. By setting the discharge preparation voltage in this way, it is possible to prevent the electrode from being consumed, to prevent an abnormal current in the electric circuit, and to improve the durability of the apparatus.
さらに、本発明に係る放電プラズマ処理装置は、少なくとも一方の電極対向面が固体誘電体で被覆された一対の対向する電極を備え、該電極間に放電処理電圧を印加して放電させ、プラズマを発生させて被処理物をプラズマ処理する装置であって、この装置は放電電圧制御手段を備え、この制御手段は放電処理電圧印加前および/または放電処理電圧印加後に、放電処理電圧より低く電極間で放電が立たない放電準備電圧を印加制御することを特徴としている。 Furthermore, the discharge plasma processing apparatus according to the present invention includes a pair of opposing electrodes in which at least one electrode facing surface is coated with a solid dielectric, and a discharge processing voltage is applied between the electrodes to discharge the plasma. An apparatus for generating a plasma treatment of an object to be processed, the apparatus comprising a discharge voltage control means, the control means being lower than the discharge treatment voltage before and / or after applying the discharge treatment voltage. It is characterized by controlling the application of a discharge preparation voltage at which no discharge occurs.
この構成によれば、放電を開始してプラズマ処理する前に、あるいは放電プラズマ処理後に電極間に放電の立たない低い電圧の放電準備電圧を印加しておくことにより、電子を飛びやすい状態にしておくことができ、すなわちチャネルを予め作っておくことにより、急激な電圧、電流の変化が抑えられるため、固体誘電体の絶縁破壊や素子の破壊を抑えられ、結果的に異常放電等を抑えられ、寿命も長くなる。これにより、安定した放電プラズマ処理が行えるため被処理物の表面改質が均一になり、ランニングコストも低減すること
ができる。
According to this structure, before starting the discharge and performing the plasma treatment, or after applying the discharge plasma treatment, by applying a low voltage discharge preparation voltage that does not cause a discharge between the electrodes, the electrons can be made to fly easily. In other words, by making the channel in advance, rapid changes in voltage and current can be suppressed, so that dielectric breakdown of the solid dielectric and element breakdown can be suppressed, resulting in suppression of abnormal discharge and the like. , Life is also prolonged. Thereby, since stable discharge plasma processing can be performed, the surface modification of the object to be processed becomes uniform, and the running cost can be reduced.
本発明の放電プラズマ処理方法及び放電プラズマ処理装置によれば、放電プラズマ処理を行う際に放電処理電圧より低く放電が立たない放電準備電圧を印加してから処理用の高電圧を印加するため、電極の消耗を少なくすることができ、放電プラズマ処理装置の耐久性を高めることができる。また、放電プラズマ処理後に一端低い電圧の放電準備電圧に戻すため電流の急激な遮断を防止でき、電極の消耗を抑えることができると共に、再度プラズマ処理を連続して均一に行うことができるため、少ない電極の消耗でプラズマ処理を行え、特にバッチ処理を効率良く行うことができる。 According to the discharge plasma processing method and the discharge plasma processing apparatus of the present invention, in order to apply a high voltage for processing after applying a discharge preparation voltage lower than the discharge processing voltage and causing no discharge when performing the discharge plasma processing, Electrode consumption can be reduced, and durability of the discharge plasma processing apparatus can be improved. In addition, since the discharge preparatory voltage is returned to the low discharge preparatory voltage after the discharge plasma treatment, it is possible to prevent a sudden interruption of the current, to suppress the consumption of the electrode, and to perform the plasma treatment continuously and uniformly again. Plasma processing can be performed with little electrode consumption, and batch processing can be performed particularly efficiently.
以下、本発明に係る放電プラズマ処理方法を実施する装置の一実施形態として、グロー放電プラズマ処理装置の例を図面に基づき詳細に説明する。図1は、本実施形態に係るグロー放電プラズマ処理装置の要部構成図である。図1において、グロー放電プラズマ処理装置(以下、プラズマ処理装置という)10は、例えば樹脂シート等の被処理物の表面に、親水性や撥水性等を付与する改質処理を行う装置であり、平行平板型の一対の電極11,12が上下方向に対向して配置されている。電極11,12は、例えば銅、アルミニウム等の金属単体、ステンレス、黄銅等の合金、金属間化合物等から構成され、その対向面は電界集中によるアーク放電の発生を抑えるため、電極間距離が略一定となるように構成されている。電極11,12の少なくとも一方の電極対向面は、アルミナ等の固体誘電体で被覆され、本実施形態では両方の電極の対向面に固体誘電体13,14が形成され、これらの間の空間が放電空間15として構成されている。
Hereinafter, an example of a glow discharge plasma processing apparatus will be described in detail with reference to the drawings as an embodiment of an apparatus for performing the discharge plasma processing method according to the present invention. FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram of a main part of a glow discharge plasma processing apparatus according to the present embodiment. In FIG. 1, a glow discharge plasma processing apparatus (hereinafter referred to as a plasma processing apparatus) 10 is an apparatus that performs a modification process that imparts hydrophilicity, water repellency, etc. to the surface of an object to be processed such as a resin sheet. A pair of parallel
固体誘電体13,14は設置される電極11,12と密着し、電極を完全に覆うように被覆される。本実施形態では、固体誘電体としてアルミナのコーティング層を用いている、固体誘電体13,14の厚さは0.01〜4mm程度が好ましく、厚すぎると放電を立たせるのに高電圧を要し、薄すぎると電圧印加時に絶縁破壊が起こり、アーク放電が発生する虞がある。固体誘電体としては、セラミックスや樹脂等の板状物、シート状物でもよく、フィルム状のものでもよい。電極11,12間の間隔は、固体誘電体の厚さ、印加電圧の大きさ、処理ガスの種類、プラズマを利用する目的等を考慮して設定されるが、1〜20mm程度が好ましい。1mm未満では、間隔内に被処理物を設置しにくく、20mmを超えると均一な放電プラズマを発生しにくくなる。
The
固体誘電体の材質としては、前記のアルミナの他に、例えばポリテトラフルオロエチレン、ポリエチレンテレフタレート等のプラスチックや、ガラス、二酸化珪素、二酸化ジルコニウム、二酸化チタン等の金属酸化物、チタン酸バリウム等の複酸化物や、これらを複層化したもの等、種々のものを用いることができる。固体誘電体は、比誘電率が2以上(25°C環境下、以下同じ)であることが好ましい。 As the material of the solid dielectric, in addition to the above-mentioned alumina, for example, plastics such as polytetrafluoroethylene and polyethylene terephthalate, metal oxides such as glass, silicon dioxide, zirconium dioxide, and titanium dioxide, and composites such as barium titanate are used. Various oxides such as oxides and multilayers thereof can be used. The solid dielectric preferably has a relative dielectric constant of 2 or more (in the environment of 25 ° C., the same shall apply hereinafter).
比誘電率が2以上の誘電体の具体例としては、ポリテトラフルオロエチレン、ガラス、金属酸化膜等を挙げることができる。さらに高密度の放電プラズマを安定して発生させるためには、比誘電率が10以上の固定誘電体を用いことが好ましい。比誘電率の上限は特に限定されるものではないが、現実の材料では18500程度のものが知られている。比誘電率が10以上の固体誘電体としては、酸化チタニウム5〜50重量%、酸化アルミニウム50〜95重量%で混合された金属酸化物被膜、または、酸化ジルコニウムを含有する金属酸化物被膜からなり、その被膜の厚みが10〜1000μmであるものを用いることが好ましい。 Specific examples of the dielectric having a relative dielectric constant of 2 or more include polytetrafluoroethylene, glass, and metal oxide film. In order to stably generate a high-density discharge plasma, it is preferable to use a fixed dielectric having a relative dielectric constant of 10 or more. The upper limit of the relative dielectric constant is not particularly limited, but an actual material of about 18500 is known. The solid dielectric having a relative dielectric constant of 10 or more is composed of a metal oxide film mixed with 5 to 50% by weight of titanium oxide and 50 to 95% by weight of aluminum oxide, or a metal oxide film containing zirconium oxide. It is preferable to use a film having a thickness of 10 to 1000 μm.
上部電極11の固体誘電体13と、下部電極12の固体誘電体14との間の放電空間1
5は、処理ガスが流される構成となっている。すなわち、放電空間の左方にはガス導入容器16が設置され、右方にはガス排出容器17が設置されている。ガス導入容器16には、例えば窒素ガスを含む処理ガスのボンベ(図示せず)が接続され、容器の吹き出し口が放電空間15に向けられている。ガス排出容器17は放電空間15に向けて吸い込み口が位置しており、放電空間15に供給された処理ガスを吸入して、廃棄用ボンベや排ガス処理装置(図示せず)に廃棄するように構成されている。
Discharge space 1 between the
No. 5 has a configuration in which a processing gas flows. That is, the
上下の電極11,12及びガス導入容器16、ガス排出容器17を容器18で覆うように構成してもよい。この容器18の材質は樹脂やガラスが好ましいが、電極と絶縁がとれていれば金属を用いることができる。処理ガスは放電空間15に均一に供給されることが好ましく、複数種の処理用ガスを用いる場合、又は処理用ガスと希釈ガスの混合気体中で処理を行う場合、供給時に不均一にならないようにされることが好ましい。また、処理ガスの吹き出し口、吸い込み口はスリットまたは多孔のものが好ましい。なお、処理ガスは高圧で吹き付けて供給する構成でもよい。
The upper and
放電空間15には、被処理物として樹脂シート19が下方の電極12の固体誘電体14に接触する状態で供給される。すなわち、樹脂シート19は巻き出しロール19aから供給され、処理装置10内でプラズマ処理された後、巻き取りロール19bで巻き取られるように構成されている。ガス導入容器16から処理ガスを流して、上下の電極11、12間に放電処理電圧が印加されると放電空間15にはグロー放電が発生し、この空間は放電プラズマが発生して電極間に位置する樹脂シート19の表面に、改質処理を行うことができる。
The
プラズマ処理装置10においては、樹脂シート19は発生した放電プラズマに接触した部位が処理されるので、図1の例では被処理物である樹脂シート19の上面がプラズマ処理される。樹脂シートの両面に処理を施したい場合は、下方の電極12から樹脂シート19を浮かせて位置させればよい。本実施形態のグロー放電プラズマ処理は、樹脂シート19を加熱または冷却して行ってもよいが、常温で行うことも可能である。グロー放電プラズマ処理に要する時間は、印加電圧、処理ガスの種類および混合気体中の割合等を考慮して適宜決定される。
In the
本実施形態のプラズマ処理装置10においては、例えば図2に示す電源回路20により電極11,12間にパルス化された電圧が印加される。電源回路20は、所定の周波数のパルス信号を作るパルス発振回路21、パルス信号が入力されるスイッチングインバータ回路22、このスイッチングインバータ回路にプラス電源とマイナス電源を供給する+DC電源回路23、および−DC電源回路24とを備え、スイッチングインバータ回路22からの出力信号が昇圧トランス25で増幅されて出力端子26から放電処理電圧VHとして出力され、昇圧トランスの他端は接地される。
In the
電源回路20より出力されたパルス状の放電処理電圧は、図1に示されるように、電極11,12間に印加する電圧を制御する手段としてコントローラ27を介して、例えばプラズマ処理装置10の上部電極11に印加され、下部電極12は接地される。コントローラ27はパルス信号の電圧を調整するもので、Vppを任意に設定することができる。本実施形態では、Vppを10〜99.9%の範囲で電圧を下げて放電準備電圧VLとすることができ、調整された電圧を放電処理工程の前工程として電極11,12間に印加制御すると共に、放電処理工程の後工程として電極11,12間に印加する。このような電圧範囲に設定するのは、電圧を10%以下にすると準備段階の待機電圧としては効果が乏しく、99.9%以上では待機状態にはならずに放電が開始してしまうからである。放電準備電圧VLは、より好ましくは、放電処理電圧VHの70〜95%の電圧に設定する。
As shown in FIG. 1, the pulsed discharge processing voltage output from the
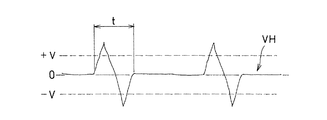
図3に、電源回路20から出力されるパルス状の放電処理電圧VHを示す。なお、破線で示す正負の電圧±vは、この範囲以上の電圧Vppが印加されると放電が始まる電圧を示している。電源回路20で形成されるパルス状の電圧は、図3に示すような電圧立ち上がり時間が100μs以下、電界強度が1〜100kV/cm程度で、周波数が0.5kHz〜100kHzのインパルス型が使用されている。パルス状の電圧波形は、図示のインパルス型の他に、方形波型、変調型等の適宜の波形を用いることができる。また、図3では、電圧印加が正負の繰り返しであるものを挙げたが、正又は負のいずれかの極性側に電圧を印加する、いわゆる片波状の波形を用いてもよい。また、バイポーラ型の波形を用いてもよい。
FIG. 3 shows the pulsed discharge processing voltage VH output from the
電源回路20から出力されるパルス状の電圧波形は、ここで挙げた波形に限定されないが、パルスの立ち上がり時間が短いほどプラズマ発生の際のガスの電離が効率よく行われる。パルスの立ち上がり時間が100μsを超えると放電状態がアークに移行しやすく不安定なものとなり、パルス電圧による高密度プラズマ状態を期待できなくなる。また、立ち上がり時間は早いほうがよいが、常圧でプラズマが発生する程度の大きさの電界強度を有し、かつ、立ち上がり時間が早い電界を発生させる装置には制約があり、現実的には40ns未満の立ち上がり時間のパルス電圧を実現することは困難である。より好ましくは立ち上がり時間が50ns〜5μsである。なお、ここでいう立ち上がり時間とは、電圧変化が連続して正である時間を指す。
Although the pulsed voltage waveform output from the
また、パルス状の電圧の立ち下がり時間も急峻であることが好ましく、立ち上がり時間と同様の100μs以下であることが好ましく、本実施形態で使用した電源回路20では、立ち上がり時間と立ち上がり時間が略同じ時間に設定されている。さらに、パルス波形、立ち上がり時間、周波数の異なるパルスを用いて変調を行ってもよい。パルス状の電圧の周波数は、0.5kHz〜100kHzであることが好ましい。0.5kHz未満であるとプラズマ密度が低いため処理に時間がかかりすぎ、100kHzを超えるとアーク放電が発生しやすくなる。より好ましくは、1kHz以上であり、このような高周波数のパルス電圧を印加することにより、プラズマ処理の処理速度を大きく向上させることができる。
Further, the fall time of the pulse voltage is preferably steep, and is preferably 100 μs or less, which is the same as the rise time. In the
また、パルス状の電圧におけるパルス継続時間は、1〜1000μsであることが好ましい。1μs未満であると放電が不安定なものとなり、1000μsを超えるとアーク放電に移行しやすくなる。より好ましくは、3μs〜200μsである。ここで、1つのパルス継続時間とは、図3中にtとして示してあるが、ON、OFFの繰り返しからなるパルス電圧における、パルスが連続する時間をいう。 Moreover, it is preferable that the pulse duration in a pulse-form voltage is 1-1000 microseconds. If it is less than 1 μs, the discharge becomes unstable, and if it exceeds 1000 μs, it tends to shift to arc discharge. More preferably, it is 3 μs to 200 μs. Here, although one pulse duration is indicated as t in FIG. 3, it means the time for which pulses continue in a pulse voltage consisting of repetition of ON and OFF.
図3に示されるパルス状の放電処理電圧VHのピーク電圧Vppの大きさは適宜決められるが、本実施形態においては、電極間の電界強度が1〜100kV/cmとなる範囲にしている。1kV/cm未満であると処理に時間がかかりすぎ、100kV/cmを超えるとアーク放電が発生しやすくなる。また、パルス状の電圧の印加において、直流を重畳してもよい。本発明では、パルス状の放電処理電圧VHは、前記したコントローラ27により、そのピーク電圧Vppを10〜99.9%の範囲で調整することができ、プラズマ処理の前工程、後工程として電極11,12間に印加する。図4aは、電極間に電圧を印加しない無通電状態を示し、図4bは電圧を50%程度とした放電準備電圧VLを印加した待機状態を示し、図4cは、100%の放電処理電圧VHを印加した処理状態を示している。
The magnitude of the peak voltage Vpp of the pulsed discharge processing voltage VH shown in FIG. 3 is determined as appropriate, but in the present embodiment, the electric field strength between the electrodes is in the range of 1 to 100 kV / cm. If it is less than 1 kV / cm, the process takes too much time, and if it exceeds 100 kV / cm, arc discharge tends to occur. In addition, direct current may be superimposed when applying a pulsed voltage. In the present invention, the pulsed discharge processing voltage VH can be adjusted by the
前記のように構成されたプラズマ処理装置10による放電プラズマ処理の動作について、図4を参照して以下に説明する。図4aは第1状態で電極間には電界が印加されていない状態で、電源回路20は出力していない状態である。プラズマ処理を行うときには、電
極11,12間に被処理物である樹脂シート19を位置させ、放電処理電圧VHより低く放電の立たない、例えば放電処理電圧VHの50%程度の放電準備電圧VL(図4b)を、プラズマ処理の前工程として電極11,12間に印加する。この状態では上部電極11と樹脂シート19との間に放電が立たず、電子が飛びやすい状態、すなわちチャネルが形成された状態である。この待機状態は0.1〜5秒程度、継続させることが好ましい。
The operation of the discharge plasma processing by the
この待機状態の後、電極11,12間に放電処理電圧VH(図4c)を印加すると、樹脂シート19と上部電極11との間に放電が立ち、樹脂シート19のプラズマ処理による改質処理が行われる。プラズマ処理時間は、前記のとおり種々の条件により異なるが、1〜5秒程度が好ましい。処理を途中で停止する場合や、処理が完了した場合には、プラズマ処理の後工程として低電圧印加工程で、例えば放電処理電圧VHの50%程度の放電準備電圧VL(図4b)を電極間に印加して待機状態とし、プラズマ処理済の樹脂シート19を搬送する。樹脂シート19搬送後に、次の樹脂シートを電極間に位置させて放電プラズマ処理を行うが、このときも電極間は放電が立たずにチャネルが形成された状態であるため、次のプラズマ処理時に電極間に異常電流が流れることがなく、電極の消耗を防止できる。
After this standby state, when a discharge treatment voltage VH (FIG. 4c) is applied between the
本発明の放電プラズマ処理方法でプラズマ処理した実施例と、従来の放電プラズマ処理方法でプラズマ処理した比較例について述べる。 An example in which plasma processing is performed by the discharge plasma processing method of the present invention and a comparative example in which plasma processing is performed by a conventional discharge plasma processing method will be described.
電極サイズを印加側、接地側とも長さ150mm、幅150mm、厚さ20mmとし、対向する面の4辺をR=10mmで面取りした。電極内部に温度調節用の媒体の流路(図示せず)を形成し、35℃となるように設定した。電極の基材はステンレス鋼(SUS430J2)を使用し、誘電体としてアルミナコーティング(t=1mm)を使用し、電極間距離を2mmに設定した。処理ガスとして、窒素ガスを30slmで流した。放電条件は周波数15kHz、放電処理電圧VHは15.0kVpp(放電開始14.5kVpp)、放電待機時の放電準備電圧VLは13.5kVppで、放電処理電圧VHの約93%とした。前記の条件で5秒間放電処理電圧VHを印加して放電させ、放電プラズマ処理を行った後、5秒間放電準備電圧VLを印加して待機状態とした結果、放電は終始良好であり、10万サイクル終了後の誘電体の絶縁抵抗を測定したところ、絶縁抵抗の低下を確認することはできなかった。 The electrode size was 150 mm long, 150 mm wide, and 20 mm thick on both the application side and the ground side, and four sides of the opposing surface were chamfered with R = 10 mm. A temperature control medium flow path (not shown) was formed inside the electrode and set to 35 ° C. Stainless steel (SUS430J2) was used as the electrode substrate, alumina coating (t = 1 mm) was used as the dielectric, and the distance between the electrodes was set to 2 mm. Nitrogen gas was flowed at 30 slm as the processing gas. The discharge conditions were a frequency of 15 kHz, a discharge treatment voltage VH of 15.0 kVpp (discharge start 14.5 kVpp), a discharge preparation voltage VL during discharge standby of 13.5 kVpp, and about 93% of the discharge treatment voltage VH. Under the above conditions, the discharge treatment voltage VH was applied for 5 seconds to discharge, the discharge plasma treatment was performed, and then the discharge preparation voltage VL was applied for 5 seconds to enter a standby state. When the insulation resistance of the dielectric after the end of the cycle was measured, a decrease in insulation resistance could not be confirmed.
比較例として、無放電時の電圧を0kVppとし、放電準備状態、すなわち待機状態を設けずに、いきなり周波数15kHz、放電処理電圧VH,15.0kVppを印加して放電プラズマ処理を開始した。この条件で処理した結果は、5万サイクルくらいから異常放電が発生し始め、10万サイクル後の、固体誘電体の絶縁抵抗は初期の抵抗値の2%まで低下していた。この状態では、グロー放電は安定せず、アーク放電等の異常放電が発生することがあり、均一なプラズマ処理は不可能であった。 As a comparative example, the discharge plasma treatment was started by applying a voltage of 15 kHz, a discharge treatment voltage VH, and 15.0 kVpp suddenly without providing a discharge ready state, i.e., a standby state, with a non-discharge voltage of 0 kVpp. As a result of processing under these conditions, abnormal discharge began to occur from about 50,000 cycles, and after 100,000 cycles, the insulation resistance of the solid dielectric decreased to 2% of the initial resistance value. In this state, glow discharge is not stable, and abnormal discharge such as arc discharge may occur, and uniform plasma treatment is impossible.
本発明の他の実施形態を図5に基づき詳細に説明する。図5は本発明に係る放電プラズマ処理方法の他の実施形態の処理動作説明図である。なお、この実施形態は前記した実施形態に対し、前記の放電プラズマ処理方法により、複数の被処理物を連続してバッチ処理することを特徴とする。 Another embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to FIG. FIG. 5 is an explanatory view of the processing operation of another embodiment of the discharge plasma processing method according to the present invention. In addition, this embodiment is characterized in that a plurality of objects to be processed are batch-processed continuously by the above-described discharge plasma processing method as compared with the above-described embodiment.
図5において、放電プラズマ処理装置30は、下方の電極31と、その上方に位置し電極31上を、間隔をあけて移動する電極32とを備えている。電極31,32の間が放電空間となっており、被処理物であるワーク35は下方の電極31上に載置されて設置され、上方の電極32が移動して電極31,32間の放電空間でプラズマ処理される。電極間には電源回路からパルス状の電圧が印加され、グロー放電が発生する構成となっている。
この実施形態では、上部の電極32の移動に伴ってプラズマ空間が移動するように構成されている。放電空間には、図示していないが処理ガスが流れるようにガス導入口、ガス排出口が設置される。
In FIG. 5, the discharge
In this embodiment, the plasma space is configured to move as the upper electrode 32 moves. Although not shown, a gas inlet and a gas outlet are installed in the discharge space so that the processing gas flows.
プラズマ処理装置30の左側には、処理前の樹脂製のワーク35がベース36上に積層されて置かれており、ワークは1枚ずつ搬送装置40によりプラズマ処理装置30の電極31上に載置して設置される。放電プラズマ処理装置30上で放電処理電圧VHを電極間に印加してプラズマ処理を行い、例えば表面の撥水処理や親水性処理が行われた後、右側の搬送装置41により電極31上から撤去され、処理物載置台37上に積層される。このようなバッチ処理を行う際に、プラズマ処理装置30は放電準備電圧VLを印加した待機状態でワーク35の搬送、設置を行い、処理後の搬送、撤去時にも放電準備電圧VLを印加した待機状態としている。搬送装置40,41は、ワーク35を負圧で吸着して搬送するものや、アームで挟んで搬送するもの等、適宜の形態のものを適用できる。
On the left side of the
すなわち、この実施形態の放電プラズマ処理方法は、プラズマ処理工程の前工程としてワーク35を電極間に順次設置する工程と、電極間に設置されたワーク35をプラズマ処理する工程と、後工程としてプラズマ処理後のワーク35を撤去する工程とを備え、ワーク35の設置工程および撤去工程では電極間には放電準備電圧VLを印加している。この放電準備電圧VLも、前記の実施形態と同様に放電処理電圧VHより低く電極間で放電が立たないような10〜99.9%の電圧に設定され、特に、放電処理電圧の70〜95%の電圧に設定することが好ましい。
That is, the discharge plasma processing method of this embodiment includes a step of sequentially placing the
この実施形態の動作は、第1の工程として搬送装置40でワーク35を持ち上げ、旋回して下部電極31上にワーク35を設置し、搬送装置40は復帰する。ワーク35が設置されたあと、電極31,32間に放電準備電圧VLを印加し、第2の工程として放電処理電圧VHを印加して放電状態とし、上部電極32を移動してワーク35の全表面をプラズマ処理して上部電極32を元の位置に戻してプラズマ処理を終了し、第3の工程として処理された下部電極31上のワーク35を搬送装置41で持ち上げて旋回して撤去し、処理物載置台37上に積み重ねる。前記の第1〜3の工程を繰り返して、複数のワーク35の処理を連続して行うことができる。
In the operation of this embodiment, as a first step, the
この実施形態においては、ワーク35を搬送する第1と第3の工程の間、すなわち設置工程および撤去工程では放電を停止し、放電準備電圧VL(図4b)を印加した待機状態としており、第2の工程で放電処理電圧VH(図4c)を印加してプラズマ処理する際に、電子が飛びやすい状態にしておくことができる。このように、プラズマ処理工程で放電処理電圧VHを印加するときに、前工程の設置工程で放電準備電圧VLが印加された待機状態で予めチャネルが形成されているため、急激な電圧、電流の変化が抑えられ、従来の0Vからいきなり高電圧を印加する場合のように、オーバーシュートした過大な電流が流れることを防止でき、電極の固体誘電体の絶縁破壊や電気素子の破壊を防止できる。
In this embodiment, during the first and third steps for conveying the
また、プラズマ処理後の後工程の撤去工程で放電準備電圧VLを印加するため、従来のように高電圧からいきなり0Vとしないため、電極の消耗を防止できると共に、電源回路の故障を防止できる。そして、つぎに搬送されてきたワークのプラズマ処理が連続して効率良く行えるため、プラズマ処理によるワークの表面改質の効率良い処理が可能となる。なお、本実施形態では、対向する一方の電極が移動する構成としたが、電極が移動しない場合には、設置工程はワークを電極間に挿入するように設置して行う。 In addition, since the discharge preparation voltage VL is applied in the subsequent removal step after the plasma treatment, the voltage is not suddenly changed from 0 V as in the conventional case, so that the consumption of the electrodes can be prevented and the failure of the power supply circuit can be prevented. And since the plasma processing of the workpiece | work conveyed next can be performed efficiently continuously, the efficient process of the surface modification of the workpiece | work by plasma processing is attained. In addition, in this embodiment, it was set as the structure which one electrode which opposes moved, However, When an electrode does not move, an installation process is performed by installing so that a workpiece | work may be inserted between electrodes.
以上、本発明の一実施形態について詳述したが、本発明は、前記の実施形態に限定されるものではなく、特許請求の範囲に記載された本発明の精神を逸脱しない範囲で、種々の設計変更を行うことができるものである。例えば、電極に印加されるパルス電圧のピーク
電圧Vppを調整するコントローラは、スイッチングインバータ回路、または+DC電源回路や−DC電源回路で機能させてもよい。また、放電処理工程の前工程、後工程で印加する放電準備電圧は、前工程と後工程で同じ電圧の例を示したが、前後の工程で異なる電圧を用いてもよい。さらに、電極間に印加する電圧としてパルス状の電圧の例を示したが、連続波でもよい。
Although one embodiment of the present invention has been described in detail above, the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and various modifications can be made without departing from the spirit of the present invention described in the claims. Design changes can be made. For example, the controller that adjusts the peak voltage Vpp of the pulse voltage applied to the electrodes may function in a switching inverter circuit, a + DC power supply circuit, or a −DC power supply circuit. Moreover, although the example of the same voltage was shown by the pre-process and a post process as the discharge preparatory voltage applied by the pre process of a discharge treatment process, and a post process, you may use a different voltage by the process before and behind. Furthermore, although the example of the pulse-shaped voltage was shown as a voltage applied between electrodes, a continuous wave may be sufficient.
10,30:グロー放電プラズマ処理装置、11,12,31,32:電極、13,14:固体誘電体、15:放電空間、16:ガス導入容器、17:ガス排出容器、19:樹脂シート(被処理物)、20:電源回路(電気回路)、27:コントローラ(電圧制御手段)、30:ワーク(被処理物)、40,41:搬送装置、VL:放電準備電圧、VH:放電処理電圧 10, 30: glow discharge plasma processing apparatus, 11, 12, 31, 32: electrode, 13, 14: solid dielectric, 15: discharge space, 16: gas introduction container, 17: gas discharge container, 19: resin sheet ( Processing object), 20: power supply circuit (electric circuit), 27: controller (voltage control means), 30: work (processing object), 40, 41: transfer device, VL: discharge preparation voltage, VH: discharge processing voltage
Claims (5)
前記放電処理電圧を間欠的ないし連続的に印加するプラズマ処理工程の前工程として、前記放電処理電圧より低くグロー放電に至らない放電準備電圧を前記電極間に間欠的ないし連続的に印加することを特徴とする放電プラズマ処理方法。 At least one electrode facing surface is provided with a pair of facing electrodes coated with a solid dielectric, and a discharge treatment voltage is applied between the electrodes under a pressure near atmospheric pressure to generate glow discharge and generate plasma. A discharge plasma treatment method for plasma-treating an object to be treated,
As a pre-process of the plasma treatment step of intermittently or continuously applying the discharge treatment voltage, a discharge preparation voltage lower than the discharge treatment voltage and not resulting in a glow discharge is intermittently or continuously applied between the electrodes. A characteristic discharge plasma treatment method.
前記被処理物を、前記前工程として電極間に順次設置する工程と、前記電極間に設置された被処理物をプラズマ処理する工程と、前記後工程としてプラズマ処理後の被処理物を撤去する工程とを備え、前記設置工程では、前記放電準備電圧を前記電極間に印加することを特徴とする放電プラズマ処理方法。 A method of plasma processing a plurality of objects to be processed by the discharge plasma processing method according to claim 1,
The step of sequentially placing the object to be treated between the electrodes as the pre-process, the step of plasma-treating the object to be treated disposed between the electrodes, and removing the object to be treated after the plasma treatment as the post-process A discharge plasma treatment method, wherein, in the installation step, the discharge preparation voltage is applied between the electrodes.
該処理装置は、前記電極に印加する電圧を制御する手段を備え、該電圧制御手段は、前記放電処理電圧の間欠的ないし連続的な印加前に、該放電処理電圧より低くグロー放電に至らない放電準備電圧の間欠的ないし連続的な印加制御を行なうことを特徴とする放電プラズマ処理装置。 At least one electrode facing surface is provided with a pair of facing electrodes coated with a solid dielectric, and a discharge treatment voltage is applied between the electrodes under a pressure near atmospheric pressure to generate glow discharge and generate plasma. A discharge plasma processing apparatus for plasma processing an object to be processed,
The processing apparatus includes means for controlling a voltage applied to the electrode, and the voltage control means does not reach a glow discharge lower than the discharge processing voltage before intermittent or continuous application of the discharge processing voltage. A discharge plasma processing apparatus that performs intermittent or continuous application control of a discharge preparation voltage.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003315932A JP3773510B2 (en) | 2003-09-08 | 2003-09-08 | Discharge plasma processing method and discharge plasma processing apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003315932A JP3773510B2 (en) | 2003-09-08 | 2003-09-08 | Discharge plasma processing method and discharge plasma processing apparatus |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005085586A JP2005085586A (en) | 2005-03-31 |
| JP2005085586A5 JP2005085586A5 (en) | 2005-07-14 |
| JP3773510B2 true JP3773510B2 (en) | 2006-05-10 |
Family
ID=34416030
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003315932A Expired - Fee Related JP3773510B2 (en) | 2003-09-08 | 2003-09-08 | Discharge plasma processing method and discharge plasma processing apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3773510B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5336691B2 (en) * | 2005-09-16 | 2013-11-06 | 国立大学法人東北大学 | Plasma generator, surface treatment apparatus, light source, plasma generation method, surface treatment method, and light irradiation method |
| US7914692B2 (en) | 2006-08-29 | 2011-03-29 | Ngk Insulators, Ltd. | Methods of generating plasma, of etching an organic material film, of generating minus ions, of oxidation and nitriding |
| JP6376685B2 (en) * | 2014-05-16 | 2018-08-22 | 東レエンジニアリング株式会社 | Thin film forming apparatus and thin film forming method |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5864030A (en) * | 1981-10-13 | 1983-04-16 | Nec Kyushu Ltd | Plasma etching device |
| JPS63102318A (en) * | 1986-10-20 | 1988-05-07 | Tokyo Electron Ltd | Plasma etching method |
| JPH04199816A (en) * | 1990-11-29 | 1992-07-21 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Plasma cvd equipment |
| JP4378592B2 (en) * | 2000-11-13 | 2009-12-09 | 株式会社安川電機 | Control method of discharge generator |
| JP2002217168A (en) * | 2001-01-15 | 2002-08-02 | Nec Corp | Method of plasma treatment |
-
2003
- 2003-09-08 JP JP2003315932A patent/JP3773510B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2005085586A (en) | 2005-03-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4414765B2 (en) | Plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method | |
| JP4092937B2 (en) | Plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method | |
| EP3219176B1 (en) | Balanced barrier discharge neutralization in variable pressure environments | |
| WO2020121819A1 (en) | Substrate processing apparatus and substrate processing method | |
| JP3516305B2 (en) | Arc prevention device for vacuum sputtering equipment | |
| WO2013099133A1 (en) | Plasma treatment apparatus | |
| JP2010238881A (en) | Plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method | |
| JP2006302625A (en) | Plasma treatment device and method | |
| KR20070040747A (en) | Deposition by magnetron cathodic pulverization in a pulsed mode with preionization | |
| JP2003502831A (en) | Apparatus and method for minimizing semiconductor wafer arcing during semiconductor wafer processing | |
| TW202126122A (en) | Plasma processing method and plasma processing apparatus | |
| US20220139672A1 (en) | Plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method | |
| JP3773510B2 (en) | Discharge plasma processing method and discharge plasma processing apparatus | |
| JP2010182553A (en) | Plasma processing apparatus | |
| JP2006302624A (en) | Plasma treatment device and method | |
| JP2003318000A (en) | Discharge plasma treatment apparatus | |
| JP2002151480A (en) | Processing method for semiconductor element and device therefor | |
| JP2002094221A (en) | Normal pressure pulse plasma treatment method and its device | |
| JP2003133291A (en) | Discharge plasma treatment apparatus and discharge plasma treatment method using it | |
| KR20020071694A (en) | Method and apparatus for removing contaminants from the surface of a substrate with atmospheric-pressure plasma | |
| JPH07142453A (en) | Plasma etching system | |
| JP2002008895A (en) | Plasma treatment device and plasma treatment method | |
| JP5485619B2 (en) | Surface treatment apparatus and surface treatment method | |
| WO2022124334A1 (en) | Plasma processing method and plasma processing device | |
| JP2003100733A (en) | Discharge plasma treatment system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050117 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20050117 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20050117 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20050117 |
|
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20050217 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20050329 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050428 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20050906 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20060117 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20060214 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100224 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100224 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110224 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120224 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130224 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140224 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |