JP3601056B2 - Monitoring apparatus and method, and recording medium - Google Patents
Monitoring apparatus and method, and recording medium Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3601056B2 JP3601056B2 JP2001063389A JP2001063389A JP3601056B2 JP 3601056 B2 JP3601056 B2 JP 3601056B2 JP 2001063389 A JP2001063389 A JP 2001063389A JP 2001063389 A JP2001063389 A JP 2001063389A JP 3601056 B2 JP3601056 B2 JP 3601056B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- mobile terminal
- warning area
- setting
- monitoring target
- processing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
- Telephonic Communication Services (AREA)
- Emergency Alarm Devices (AREA)
- Alarm Systems (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、監視装置および方法、並びに記録媒体に関し、特に、監視対象者が危険なエリアに進入していることを、容易に、かつ確実に監視者が確認できるようにした監視装置および方法、並びに記録媒体に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
近年、通信技術の発達に伴い、PHS(Personal Handy Phone)端末を保持している、例えば、子供や老人などの監視対象者の位置情報を、その保護者に通知するサービスが行われている。
【0003】
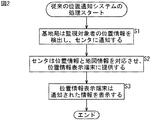
図1は、従来の位置通知システムの構成例を示すブロック図である。このシステムの動作について、図2のフローチャートを参照して説明する。PHS端末1は、例えば、監視対象者である子供により保持されており、基地局2は、ステップS1において、受信される電波に基づいて、PHS端末1(子供)の位置を検出する。
【0004】
検出された子供の位置情報は、センタ3に通知され、ステップS2において、センタ3は、地図情報と対応づけて、監視者が有する位置情報表示端末4に提供する。この位置情報表示端末4は、例えば、パーソナルコンピュータやファクシミリなどであり、ステップS3において、地図上に、子供の現在位置がポインタなどにより示される。これにより保護者は、子供の現在位置を確認することができ、危険な場所に近づいていないかなどを判断することができる。
【0005】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、上述したシステムにおいては、位置情報が通知されるものの、その位置が危険な場所であるか否かの判断は、保護者がしなければならない。そのため、実際に危険な場所に進入しているにも関わらず、それに気付かないということがあった。
【0006】
また、監視対象の子供などの位置は、刻々と変化するため、それを監視するためには、常時、または所定の時間毎に、このサービスを利用して監視対象者の位置を確認しなければならない。
【0007】
本発明はこのような状況に鑑みてなされたものであり、監視対象者が危険な場所に進入していることを、容易に、かつ、確実に監視者が確認できるようにしたものである。
【0008】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明の監視装置は、監視者により通信網を介して行われる設定に応じて警告エリアを設定する設定手段と、携帯端末を有するそれぞれの監視対象者の ID に対応付けて、設定手段により設定された警告エリアを記憶する第1の記憶手段と、監視対象としての携帯端末の位置を取得する取得手段と、取得手段により取得された携帯端末の位置が、設定手段により設定された警告エリア内であるか否かを判定する判定手段と、判定手段により携帯端末の位置が警告エリア内であると判定された場合の通知先を指定する通知先指定情報を記憶する第2の記憶手段と、第2の記憶手段により記憶されている通知先指定情報により指定される通知先に、携帯端末の位置が警告エリア内であることを通知する第1の通知手段とを備えることを特徴とする。
【0009】
設定手段は、例えば、図12のステップS45の処理を実行する図5のセンタ制御装置21により構成され、取得手段は、例えば、図16のステップS91の処理を実行する図5のセンタ制御装置21により構成され、判定手段は、例えば、図16のステップS95の処理を実行する図5のセンタ制御装置21により構成される。また、第2の記憶手段は、例えば、図5の記憶装置42により構成され、第1の通知手段は、例えば、図16のステップS97の処理を実行する図5のセンタ制御装置21により構成される。
【0010】
警告エリアは、監視対象者がそのエリアに進入したとき監視者に対して警告するエリアであり、監視者により、監視対象者が進入禁止である危険エリアとして設定される。
【0011】
取得手段は、監視対象としての携帯端末の位置を取得する。この携帯端末は、例えば、PHS端末、携帯電話機、GPS(Global Positioning System)端末などとされる。取得手段は、携帯端末がPHS端末、携帯電話機である場合、携帯端末から送信される電波を受信してその位置を特定し、GPS端末である場合、送信される位置情報によりその位置を特定する。
【0012】
通報先指定情報は、監視者が通報先として設定する情報であり、例えば、携帯電話機やパーソナルコンピュータなどのメールアドレスなどとされる。監視者は、通報先指定情報を複数設定することができる。
【0013】
第1の通知手段は、監視者が有する携帯電話機やパーソナルコンピュータなどに監視対象者が警告エリアに進入していることを通知する。監視者に対しては、警告するメッセージの他に、監視対象者が存在する地点を含む地図なども提示される。
【0014】
警告エリア内であることを携帯端末に対して通知する第2の通知手段をさらに備えるようにすることができる。
【0015】
第2の通知手段は、例えば、図16のステップS96の処理を実行する図5のセンタ制御装置21により構成される。
【0016】
これにより、監視対象者も警告エリアに進入していることを確認することができ、警告エリアから出ることができる。
監視対象者を監視する監視者が有する携帯端末に対して、監視対象者を監視状態とするか否かを選択する機能を提供する提供手段をさらに備えるようにすることができる。
判定手段は、IDに基づいて、監視対象者の警告エリアが設定されている地図情報を読み出し、監視対象者の携帯端末の位置が警告エリア内であるか否かを判定するようにすることができる。
【0017】
本発明の監視装置の監視方法は、監視者により通信網を介して行われる設定に応じて警告エリアを設定する設定ステップと、携帯端末を有するそれぞれの監視対象者の ID に対応付けて、前記設定ステップの処理により設定された前記警告エリアを記憶する第1の記憶ステップと、監視対象としての携帯端末の位置を取得する取得ステップと、取得ステップの処理により取得された携帯端末の位置が、設定ステップの処理により設定された警告エリア内であるか否かを判定する判定ステップと、判定ステップの処理により携帯端末の位置が警告エリア内であると判定された場合の通知先を指定する通知先指定情報を記憶する第2の記憶ステップと、第2の記憶ステップの処理により記憶されている通知先指定情報により指定される通知先に、携帯端末の位置が警告エリア内であることを通知する通知ステップとを含むことを特徴とする。
【0018】
設定ステップは、例えば、図12のステップS45の危険エリアを設定する処理により構成され、取得ステップは、例えば、図16のステップS91により構成され、判定ステップは、例えば、図16のステップS95により構成される。また、第2の記憶ステップは、例えば、図16のステップS97の処理の前に、監視者により予め実行される処理により構成され、通知ステップは、例えば、図16のステップS97により構成される。
本発明の記録媒体は、監視者により通信網を介して行われる設定に応じて警告エリアを設定する設定ステップと、携帯端末を有するそれぞれの監視対象者の ID に対応付けて、設定ステップの処理により設定された警告エリアの記憶を制御する第1の記憶制御ステップと、監視対象としての携帯端末の位置の取得を制御する取得制御ステップと、取得制御ステップの処理により取得された携帯端末の位置が、設定ステップの処理により設定された警告エリア内であるか否かを判定する判定ステップと、判定ステップの処理により携帯端末の位置が警告エリア内であると判定された場合の通知先を指定する通知先指定情報の記憶を制御する第2の記憶制御ステップと、第2の記憶制御ステップの処理により記憶されている通知先指定情報により指定される通知先に対する、携帯端末の位置が警告エリア内であることの通知を制御する通知制御ステップとを含むコンピュータが読み取り可能なプログラムが記録されていることを特徴とする。
【0019】
本発明の監視装置および方法においては、警告エリアが設定され、監視対象としての携帯端末の位置が取得され、取得された携帯端末の位置が、設定された警告エリア内であるか否かが判定される。そして、携帯端末の位置が警告エリア内であると判定された場合の通知先を指定する通知先指定情報が記憶され、記憶されている通知先指定情報により指定される通知先に、携帯端末の位置が警告エリア内であることが通知される。
【0020】
これにより、監視者は、監視対象者が危険な場所に進入していることを、容易に、かつ、確実に確認することができる。また、監視対象者の位置も通知されるため、監視対象者を確認しに行くなどして、監視対象者が危険な場所に進入していることに対処することができる。
【0021】
【発明の実施の形態】
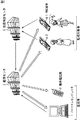
図3は、本発明を適用した監視システムの概念を示す図である。
【0022】
図3において、パーソナルコンピュータ1、および携帯電話機2は、監視者が有するものであり、PHS端末4−1,4−2(以下、PHS端末4−1,4−2のそれぞれを個々に区別する必要がない場合、まとめてPHS端末4と称する)は、監視対象者が有するものである。そして、監視対象者は、例えば、図に示すように子供や老人などであり、監視者は、その保護者である。
【0023】
位置検出センタ5は、PHS端末4から送信される電波を図示せぬ受信端末において受信し、その受信端末の位置に基づいて、監視対象者の位置を特定する。位置検出センタ5により検出された位置情報は、監視センタ3に通知される。
【0024】
監視センタ3は、監視者(パーソナルコンピュータ1)により予め設定された危険エリア(警告エリア)に関する情報を保持しており、位置検出センタ5から通知された位置情報に基づいて、監視対象者が危険エリアに進入しているか否かを判定する。そして、監視センタ3は、監視対象者が危険エリアに進入していると判定した場合、その場合の通知先として予め登録されている、監視者が有するパーソナルコンピュータ1および携帯電話機2に電子メールなどにより通知する。また、監視センタ3は、監視対象者が有するPHS端末4に対しても、危険エリアに進入していることを電子メールで通知する。すなわち、図3において、白抜き矢印は、警告情報(監視対象者が危険エリア内に進入していることを通知する情報)の流れを示している。
【0025】
上述したように、監視者は、警告を受けるために、パーソナルコンピュータ1を利用して、監視センタ3の所定のページにアクセスし、危険エリアを設定するとともに、監視対象者が危険エリアに進入した場合の通知先を設定する必要がある。この通知先は、複数個設定することもできる。
【0026】
図4は、図3の監視システムの構成例を示すブロック図である。
【0027】
図3において、センタ装置11は、監視センタ3により管理され、基本的に、センタ制御装置21、およびセンタ通信装置22から構成される。センタ制御装置21は、センタ通信装置22を制御し、通信網13を介して、様々な情報を送受信する。
【0028】
位置情報検出装置12は、位置検出センタ5により管理され、PHS端末4の現在位置を取得する。取得された位置情報は、通信網13を介してセンタ装置11に送信される。
【0029】
パーソナルコンピュータ1は、監視者により管理され、基本的に、監視対象者の位置情報を表示するCRT(Cathode Ray Tube)やLCD(Liquid Crystal Display)などよりなる位置情報表示部31、センタ装置11にアクセスし、地図上に危険エリアを設定するとき起動するプログラムである属性情報設定部32、および通信部33により構成される。
【0030】
図5は、図4のセンタ装置11の詳細な構成例を示すブロック図である。センタ制御装置21は、入出力バス41を介して、センタ装置11の全体の動作を制御する。記憶装置42は、監視者により設定される危険エリアなどの地図上における属性情報を、ユーザID(監視対象者のID)に対応させて記憶する。CRT43は、センタ制御装置21からの指示に基づいて、例えば、設定されている危険エリアに監視対象者が進入したとき、それをセンタ装置11の管理者に提示する。キーボード44、およびマウス45は、センタ装置11の管理者により操作され、操作内容に対応する信号を入出力バス41を介してセンタ制御装置21に出力する。
【0031】
図6は、図4のパーソナルコンピュータ1の詳細な構成例を示すブロック図である。制御部61は、入出力バス62を介して、パーソナルコンピュータ1の全体の動作を制御する。記憶装置63は、制御部61により実行されるプログラムを記憶する。キーボード64、およびマウス65は、監視者により操作され、操作内容に対応する信号を入出力バス62を介して制御部61に出力する。
【0032】
図7は、図4の携帯電話機2の構成例を示すブロック図である。制御部71は、入出力バス73を介して各部を制御し、携帯電話機2の全体の動作を制御する。通信部72は、通信網13を介して様々な装置と通信し、受信したパケットを制御部71に出力する。メモリ74は、不揮発性のフラッシュメモリよりなり、登録された電話番号などの情報を記憶するとともに、例えば、センタ装置11から送信されてきた、監視対象者が危険エリアに進入していることを通知するメッセージを含む電子メールなどを記憶する。LCD75は、制御部71からの指示に基づいて、各種の情報を表示する。例えば、LCD75には、監視対象者が危険エリアに進入していることを監視者に通知するメッセージなどが表示される。入力部76は、テンキーや十字キーなどよりなり、携帯電話機2のユーザ(監視者)からの入力を受け付ける。スピーカ77およびマイクロフォン78は、制御部71が通話モードを実行しているとき動作し、スピーカ77は、他の電話機などから送信されてきた音声を入出力バス73を介して制御部71から受信したとき、それを出力し、マイクロフォン78は、携帯電話機2のユーザの発話を集音して入出力バス73を介して制御部71に出力する。
【0033】
なお、PHS端末4の構成は、基本的に、携帯電話機2の構成と同様の構成である。
【0034】
次に、図4の監視システムの動作について説明する。まず、図8のフローチャートを参照して、危険エリアを設定するパーソナルコンピュータ1の設定処理について説明する。
【0035】
ステップS11において、制御部61は、監視者からキーボード64などが操作され、危険エリアを設定することが指示された場合、センタ装置11にアクセスし、監視者により入力された監視対象者のIDを送信する。すなわち、この監視システムを利用するに先立ち、監視者は、監視対象者に関する情報をセンタ装置11に登録しておく必要がある。センタ装置11は、発行したIDに対応させて、監視者(パーソナルコンピュータ1)により設定された危険エリアを記憶する。
【0036】
ステップS12において、制御部61は、センタ装置11から送信されてきたメニューページをCRTなどよりなる位置情報表示部31に表示する。
【0037】
図9は、ステップS12で表示されるメニューページの例を示す図である。図に示すように、例えば、属性情報(危険エリア)を初めて設定するとき操作されるボタン91、既に設定している属性情報の設定を変更するとき操作されるボタン92が表示され、監視者は、カーソル93を移動させて選択する。
【0038】
ステップS13において、制御部61は、属性情報を初期設定することが選択されたか(図9においてボタン91が選択されたか)否かを判定し、属性情報を初期設定することが選択されたと判定した場合、ステップS14に進み、属性情報設定処理を実行する。また、制御部61は、ステップS13において、属性情報を設定することが選択されていない、すなわち、設定の変更が選択された(図9においてボタン92が選択された)と判定した場合、ステップS15に進み、属性情報設定変更処理を実行する。そして、ステップS14、またはステップS15の処理の後、処理は終了される。
【0039】
次に、図10のフローチャートを参照して、図8のステップS14において実行されるパーソナルコンピュータ1の属性情報設定処理の詳細な処理について説明する。
【0040】
ステップS31において、制御部61は、センタ装置11に格納される属性情報の設定ページにアクセスし、監視者により選択されたエリアの地図情報を位置情報表示部31に表示する。
【0041】
図11は、ステップS31において表示される地図情報の例を示す図である。例えば、図に示すように、地図が表示され、監視者は、マウス65でカーソル93を操作し、ドラックなどをすることにより危険エリアEを設定することができる。また、所定の区画毎に、1区画ずつ監視者がクリックして危険エリアEを設定するようにしてもよい。
【0042】
制御部61は、ステップS32において、監視者から危険エリアが入力されたか否かを判定し、上述したように、ドラックなどにより危険エリアが入力されたと判定するまで、ステップS31に戻り、それ以降の処理を繰り返し実行する。そして、制御部61は、危険エリアが入力されたと判定した場合、ステップS33に進み、入力されたエリアを危険エリアとして設定することを監視装置11に指示する。入力された危険エリアに関する情報は、IDとともに、通信部33から通信網13を介して、センタ装置11に送信される。
【0043】
ステップS34において、制御部61は、属性情報(危険エリア)の設定を終了することが指示されたか否かを判定し、指示されていないと判定した場合、ステップS31に戻り、それ以降の処理を繰り返し実行する。一方、制御部61は、ステップS34で、設定を終了することが指示されたと判定した場合、図8のステップS14以降の処理を実行する。
【0044】
以上においては、図8のステップS14において実行される処理について説明したが、ステップS15においても、図10と同様の処理により、危険エリアが設定される。すなわち、センタ装置11においては、送信されてきたIDに対応する、既に危険エリアが設定されている地図情報が読み出され、それがパーソナルコンピュータ1の位置情報表示部31に表示される。監視者は、表示されている地図情報に対してマウス65などを操作して危険エリアを設定し、センタ装置11に送信する。センタ装置11においては、変更した危険エリアにより更新登録される。このように、監視者は、容易に危険エリアを設定することができる。また、携帯電話機2からセンタ装置11にアクセスし、上述したような処理により危険エリアを設定するようにしてもよい。
【0045】
次に、図12のフローチャートを参照して、センタ装置11の属性情報(危険エリア)の登録処理について説明する。
【0046】
ステップS41において、センタ制御装置21は、パーソナルコンピュータ1からIDが送信されてきたか否かを判定し、送信されてきたと判定するまで待機する。そして、センタ制御装置21は、IDが送信されてきたと判定した場合、ステップS42に進み、メニューページを送信する。メニューページは、通信網13を介してパーソナルコンピュータ1に送信され、図9に示した画面がパーソナルコンピュータ1の位置情報表示部31に表示される。
【0047】
そして、センタ制御装置21は、ステップS43において、危険エリアの新規登録、または危険エリアの設定変更が選択されることに応じて、IDに対応させて記憶装置42に登録している設定情報(地図情報)を読み出し、センタ通信装置22から送信する。地図情報は、通信網13を介してパーソナルコンピュータ1に送信される。これにより、パーソナルコンピュータ1においては、例えば、図11に示したような地図情報が表示され、監視者が危険エリアを設定できるようになる。
【0048】
ステップS44において、センタ制御装置21は、危険エリアの設定が指示されたか否かを判定し、指示されるまで待機する。そして、センタ制御装置21は、設定が指示されたと判定した場合、ステップS45に進み、危険エリアを設定し、IDに対応づけて記憶装置42に登録する。これにより、新規登録の場合、指示されたエリアが危険エリアとして登録され、設定変更の場合、危険エリアが、指示されたエリアにより更新登録される。
【0049】
ステップS46において、センタ制御装置21は、パーソナルコンピュータ1において、設定が終了されたか否かを判定し、終了されるまでステップS44に戻り、それ以降の処理を繰り返し実行する。一方、パーソナルコンピュータ1において、属性情報の設定が終了されたとき、処理は終了される。
【0050】
この監視システムにおいては、監視者は、セキュリティモードを携帯電話機2からセンタ装置11の所定のページにアクセスして変更することができる。例えば、監視対象者の位置を監視するとき、セキュリティモードがオン状態であるとし、監視をしないとき、セキュリティモードがオフ状態であるとする。次に、図13のフローチャートを参照して、セキュリティモードを変更する携帯電話機2の処理について説明する。
【0051】
ステップS71において、制御部71は、監視者が入力部76を操作し、セキュリティモードを変更することを指示したとき、それに応じて、センタ装置11に格納される所定のページにアクセスする。
【0052】
制御部71は、ステップS72において、入力部76から監視者により入力された監視対象者のIDを通信部72を制御し、センタ装置11に送信する。IDを受信したセンタ装置11は、監視対象者のIDに基づいて、現在のモードの状態を確認し、監視者が設定を選択するページを携帯電話機2に対して送信する。
【0053】
ステップS73において、センタ装置11から送信されてきた設定ページを受信した制御部71は、セキュリティモードの設定ページをLCD75に表示する。
【0054】
図14は、LCD75に表示される設定ページの例を示す図である。図に示すように、監視者は、例えば、入力部76を構成するテンキーの1番のボタンを操作してセキュリティモードをオンとし、2番のボタンを操作してオフとすることができる。
【0055】
図14に示すような設定ページにおいて、監視者からセキュリティモードが入力されたとき、制御部71は、ステップS74において、入力されたセキュリティモードをセンタ装置11に送信する。以上のような処理により、監視者は、容易にセキュリティモードを変更することができる。当然、監視者は、上述したものと同様に、パーソナルコンピュータ1からセンタ装置11にアクセスして、セキュリティモードを変更することができる。
【0056】
次に、図15乃至図17、および図18のフローチャートを参照して、図4の監視システムの一連の処理について説明する。まず、図15のフローチャートを参照して、位置検出装置12の位置検出処理について説明する。
【0057】
ステップS81において、位置検出装置12は、PHS端末4から出力される電波を受信している受信端末の位置情報に基づいて、監視対象者の現在位置を検出する。すなわち、PHS端末4の電波を受信する受信端末が様々な位置に設置されており、その複数の受信端末は、有線により位置検出装置12に接続されている。そして、ステップS82において、位置検出装置12は、検出した監視対象者の位置情報を通信網13を介してセンタ装置11に送信する。
【0058】
次に、図16のフローチャートを参照して、センタ装置11の監視処理について説明する。
【0059】
ステップS91において、センタ制御装置21は、位置検出装置12から送信されてきた位置情報が、セキュリティモードがオンである監視対象者に関する情報であるか否かを判定する。センタ制御装置21は、セキュリティモードがオンである監視対象者に関する情報であると判定するまで待機し、セキュリティモードがオンである監視対象者に関する情報であると判定した場合、ステップS92に進み、それを受信する(取り込む)。
【0060】
センタ制御装置21は、ステップS93において、登録されている設定情報(危険エリアが設定されている地図情報)を読み出す。そして、センタ制御装置21は、ステップS94において、通知された監視対象者の現在の位置情報と、危険エリアが設定されている地図情報とをマッチングする。
【0061】
センタ制御装置21は、ステップS95において、ステップS94で実行したマッチングの結果、監視対象者が危険エリアに存在するか否かを判定し、危険エリアに存在しないと判定した場合、ステップS91に戻り、それ以降の処理を繰り返し実行する。一方、ステップS95において、センタ制御装置21は、監視対象者が危険エリアに存在すると判定した場合、警告モードとなり、ステップS96において、監視対象者が有しているPHS端末4に、危険エリアに入っていることを通知する警告情報を送信する。
【0062】
また、センタ制御装置21は、ステップS97において、通知先として予め登録されている監視者の携帯電話機2の電話番号やメールアドレスなどを記憶装置42から読み出し、監視対象者が危険エリアに進入していることを通知する警告情報を、通信網13を介して携帯電話機2に送信する。
【0063】
さらに、センタ制御装置21は、ステップS98において、監視者が有するパーソナルコンピュータ1に対して、監視対象者が危険エリアに進入していることを通知する警告情報を、通信網13を介して通知する。このステップS97、およびステップS98で通知する通知先が複数登録されている場合、センタ制御装置21は、その全ての通知先に対して、監視対象者が危険エリアに存在することを通知する。
【0064】
ステップS99において、センタ制御装置21は、警告モードを解除することがパーソナルコンピュータ1、または携帯電話機2から指示されたか否かを判定し、解除することが指示されたと判定するまで、ステップS96に戻り、それ以降の処理を繰り返し実行する。すなわち、警告モードが解除されるまで、PHS端末4、携帯電話機2、およびパーソナルコンピュータ1に対して、所定時間毎に、警告情報が送信される。
【0065】
そして、センタ制御装置21は、ステップS99において、パーソナルコンピュータ1、または携帯電話機2から警告モードを解除することが指示されたと判定した場合、ステップS100に進み、警告モードを解除する。例えば、監視者が、通知された監視対象者の位置情報に基づいて、監視対象者の安全を確認した場合、携帯電話機2からセンタ装置11に警告モードを解除することが指示される。
【0066】
次に、図17のフローチャートを参照して、PHS端末4の警告出力処理について説明する。ステップS111において、PHS端末4の制御部は、センタ装置11から警告情報が送信されてきたか否かを判定し、送信されてきたと判定するまで待機する。そして、制御部は、警告情報が送信されてきたと判定した場合、ステップS112に進み、それを表示する。
【0067】
図18は、監視対象者が有するPHS端末4に表示される警告情報の例を示す図である。図に示すように、例えば、監視対象者が子供の場合、「学校で決められた行動地域から出ようとしています。すぐに戻って下さい。」などのメッセージが表示される。また、監視対象者が、老人である場合、例えば、「ここから先に入ってはいけません。」などのメッセージとされる。このようなメッセージを確認した監視対象者は、危険エリアに入っていることを確認し、危険エリアから出る。
【0068】
そして、処理はステップS111に戻り、例えば、センタ装置11において警告モードが解除されるまで、所定時間毎に、警告情報が繰り返し表示される。
【0069】
次に、図19のフローチャートを参照して、携帯電話機2の警告情報の出力処理について説明する。
【0070】
ステップS121、およびS122の処理は、図17のフローチャートを参照して説明したPHS端末4の処理(ステップS111、およびS112の処理)と同様の処理である。すなわち、ステップS121において、制御部71は、警告情報がセンタ装置11から送信されてきたか否かを判定し、送信されてきたと判定するまで待機する。制御部71は、警告情報がセンタ装置11から送信されてきたと判定した場合、ステップS122に進み、それをLCD75に表示する。
【0071】
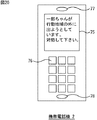
図20は、携帯電話機2に表示される警告情報の例を示す図である。図に示すように、監視対象者が子供である場合、例えば、「一郎ちゃんが行動地域の外に出ようとしています。対処して下さい。」などのメッセージが表示される。また、監視対象者の位置も表示されるため、このメッセージを確認した監視者は、外出中であっても、監視対象者がいる場所に確認しに行ったり、監視対象者が有するPHS端末4に電話するなどの対策をとることができる。
【0072】
監視対象者の安全を確認したとき、監視者は、警告モードを解除することをセンタ装置11に指示する。そして、制御部71は、ステップS123において、警告モードを解除することが入力部76から入力されたか否かを判定する。制御部71は、警告モードを解除することが入力されたと判定するまでステップS122に戻り、警告情報を表示し続ける。
【0073】
一方、ステップS123において、制御部71は、監視者が監視対象者の安全を確認し、入力部76から警告モードを解除することを入力したと判定した場合、ステップS124に進み、警告情報の表示を消し、警告モードを解除することをセンタ装置11に対して指示する。
【0074】
以上においては、図19のフローチャートを参照して、携帯電話機2の警告情報の出力処理について説明したが、パーソナルコンピュータ1においても同様の処理が実行され、警告情報が表示される。そして、パーソナルコンピュータ1の位置情報表示部31には、例えば、図21に示すような警告情報が表示される。
【0075】
図21においては、位置情報表示部31のほぼ中央に、監視対象者がいる地点の周辺のエリアの地図が表示され、監視対象者の位置が位置表示ポインタ101で指定される。また、地図の下方には、「一郎ちゃんが危険エリアに入っています。対処してください。」などのメッセージが表示される。
【0076】
以上においては、監視対象者が有する端末をPHS端末であるとしたが、位置を検出することができるものであれば、いずれの端末であってもよい。例えば、監視対象者が携帯電話機を有している場合、いわゆる三角測量の原理により、その位置を特定することができる。また、監視対象者がGPS端末を有している場合も、位置検出装置12は、GPS端末から送信される位置情報を受信し、位置を特定することができる。
【0077】
【発明の効果】
以上のように、本発明によれば、監視者は、容易に、かつ確実に監視対象者が危険エリアに進入したことを確認することができる。また、移動する監視対象者を、常時監視する必要が無くなるため、監視者の労力を軽減することができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】従来の監視システムの構成を示すブロック図である。
【図2】図1の監視システムの処理を説明するフローチャートである。
【図3】本発明を適用した監視システムの概念を示す図である。
【図4】図3の監視システムの構成例を示すブロック図である。
【図5】図4のセンタ装置の詳細な構成例を示すブロック図である。
【図6】図4のパーソナルコンピュータの詳細な構成例を示すブロック図である。
【図7】図4の携帯電話機の詳細な構成例を示すブロック図である。
【図8】図4のパーソナルコンピュータの処理を説明するフローチャートである。
【図9】パーソナルコンピュータの表示例を示す図である。
【図10】図4のパーソナルコンピュータの他の処理を説明するフローチャートである。
【図11】パーソナルコンピュータの他の表示例を示す図である。
【図12】図4のセンタ装置の処理を説明するフローチャートである。
【図13】図4の携帯電話機の処理を説明するフローチャートである。
【図14】携帯電話機の表示例を示す図である。
【図15】図4の位置検出装置の処理を説明するフローチャートである。
【図16】図4のセンタ装置の他の処理を説明するフローチャートである。
【図17】図4のPHS端末の処理を説明するフローチャートである。
【図18】PHS端末の表示例を示す図である。
【図19】図4の携帯電話機の他の処理を説明するフローチャートである。
【図20】携帯電話機の他の表示例を示す図である。
【図21】パーソナルコンピュータのさらに他の表示例を示す図である。
【符号の説明】
1 パーソナルコンピュータ
2 携帯電話機
4 PHS端末
11 センタ装置
12 位置検出装置
21 センタ制御装置
22 センタ通信装置
31 位置情報表示部
32 属性情報設定部[0001]
TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a monitoring device and method.And recording mediaIn particular, a monitoring device and method enabling a monitor to easily and surely confirm that a monitor target has entered a dangerous areaAnd recording mediaAbout.
[0002]
[Prior art]
2. Description of the Related Art In recent years, with the development of communication technology, a service of notifying a guardian of the position information of a monitoring target such as a child or an elderly person holding a PHS (Personal Handy Phone) terminal has been provided.
[0003]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of a conventional position notification system. The operation of this system will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. The PHS terminal 1 is held, for example, by a child who is a monitoring target, and the
[0004]
The detected position information of the child is notified to the center 3, and in step S2, the center 3 provides the information to the position information display terminal 4 of the monitor in association with the map information. The position information display terminal 4 is, for example, a personal computer or a facsimile, and the current position of the child is indicated on the map by a pointer or the like in step S3. As a result, the guardian can check the current position of the child and determine whether or not the child is approaching a dangerous place.
[0005]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, in the above-described system, although the position information is notified, the parent must determine whether or not the position is a dangerous place. As a result, people sometimes entered a dangerous place but did not notice it.
[0006]
In addition, since the position of a monitored child or the like changes every moment, in order to monitor it, the position of the monitored person must be confirmed using this service at all times or at predetermined intervals. No.
[0007]
The present invention has been made in view of such a situation, and is intended to allow an observer to easily and surely confirm that a monitored person has entered a dangerous place.
[0008]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The monitoring device of the present inventionDepending on the settings made by the observer over the communication networkSetting means for setting a warning area;For each monitored person with a mobile terminal ID First storage means for storing the warning area set by the setting means in association withObtaining means for obtaining the position of the mobile terminal as a monitoring target; determining means for determining whether the position of the mobile terminal obtained by the obtaining means is within a warning area set by the setting means; Notification destination specification information for specifying a notification destination when the position of the mobile terminal is determined to be within the warning area bySecondStorage means;SecondA first notification unit that notifies the notification destination specified by the notification destination specification information stored in the storage unit that the position of the mobile terminal is within the warning area is provided.
[0009]
The setting unit is configured by, for example, the
[0010]
The warning area is an area that warns the monitoring person when the monitoring target enters the area, and is set by the monitoring person as a dangerous area where the monitoring target is prohibited from entering.
[0011]
The obtaining means obtains the position of the mobile terminal to be monitored. The mobile terminal is, for example, a PHS terminal, a mobile phone, a GPS (Global Positioning System) terminal, or the like. When the mobile terminal is a PHS terminal or a mobile phone, the acquisition unit receives a radio wave transmitted from the mobile terminal to specify the position, and when the mobile terminal is a GPS terminal, specifies the position based on the transmitted position information. .
[0012]
The report destination designation information is information set by the monitor as a report destination, and is, for example, a mail address of a mobile phone, a personal computer, or the like. The monitor can set a plurality of report destination designation information.
[0013]
The first notifying unit notifies a mobile phone, a personal computer, or the like of the monitor that the monitor target has entered the warning area. For the monitoring person, a map including a point where the monitoring target exists is presented in addition to the warning message.
[0014]
It is possible to further include a second notification unit that notifies the mobile terminal that the mobile terminal is in the warning area.
[0015]
The second notification unit is configured by, for example, the
[0016]
Accordingly, it is possible to confirm that the monitored person has also entered the warning area, and to exit the warning area.
It is possible to further include providing means for providing a function of selecting whether or not the monitoring target is in a monitoring state to a portable terminal of the monitoring target who monitors the monitoring target.
The determining means may read map information in which a warning area of the monitoring target is set based on the ID, and determine whether or not the position of the mobile terminal of the monitoring target is within the warning area. it can.
[0017]
The monitoring method of the monitoring device of the present invention,Depending on the settings made by the observer over the communication networkA setting step for setting a warning area;For each monitored person with a mobile terminal ID A first storage step of storing the warning area set by the processing of the setting step in association withAn obtaining step of obtaining the position of the mobile terminal as a monitoring target; and a determining step of determining whether the position of the mobile terminal obtained by the processing of the obtaining step is within the warning area set by the processing of the setting step. And notification destination specifying information for specifying a notification destination when the position of the mobile terminal is determined to be within the warning area by the processing of the determination step.SecondA memory step;SecondThe notification destination specified by the notification destination specification information stored in the storage step includes a notification step of notifying that the position of the mobile terminal is within the warning area.
[0018]
The setting step is configured by, for example, the process of setting a dangerous area in step S45 of FIG. 12, the acquisition step is configured by, for example, step S91 of FIG. 16, and the determination step is configured by, for example, step S95 of FIG. Is done. Also,SecondThe storage step is configured by, for example, a process executed in advance by the monitor before the process of step S97 in FIG. 16, and the notification step is configured by, for example, step S97 in FIG.
The recording medium of the present inventionDepending on the settings made by the observer over the communication networkA setting step for setting a warning area;For each monitored person with a mobile terminal ID A first storage control step of controlling storage of the warning area set by the processing of the setting step in association withAn acquisition control step of controlling the acquisition of the position of the mobile terminal as a monitoring target, and whether or not the position of the mobile terminal acquired by the processing of the acquisition control step is within the warning area set by the processing of the setting step. A determination step of determining and controlling storage of notification destination specification information for specifying a notification destination when the position of the mobile terminal is determined to be within the warning area by the processing of the determination step.SecondA memory control step;SecondA notification control step of controlling the notification that the position of the mobile terminal is within the warning area for the notification destination specified by the notification destination specification information stored by the processing of the storage control step. Is recorded.
[0019]
In the monitoring device and method of the present invention, a warning area is set, the position of the mobile terminal as a monitoring target is obtained, and it is determined whether the obtained position of the mobile terminal is within the set warning area. Is done. Then, notification destination specification information for specifying a notification destination when the position of the mobile terminal is determined to be within the warning area is stored, and the notification destination specified by the stored notification destination specification information includes It is notified that the position is within the warning area.
[0020]
Thus, the monitor can easily and surely confirm that the monitor target has entered a dangerous place. In addition, since the position of the monitoring target is also notified, it is possible to deal with the case where the monitoring target enters a dangerous place by going to check the monitoring target or the like..
[0021]
BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing a concept of a monitoring system to which the present invention is applied.
[0022]
In FIG. 3, a personal computer 1 and a
[0023]
The position detection center 5 receives a radio wave transmitted from the PHS terminal 4 at a receiving terminal (not shown), and specifies the position of the monitoring target based on the position of the receiving terminal. The position information detected by the position detection center 5 is notified to the monitoring center 3.
[0024]
The monitoring center 3 holds information on a danger area (warning area) set in advance by a monitor (personal computer 1), and based on the position information notified from the position detection center 5, the monitoring target 3 It is determined whether the vehicle has entered the area. When the monitoring center 3 determines that the monitoring target has entered the dangerous area, the monitoring center 3 sends an e-mail or the like to the personal computer 1 and the
[0025]
As described above, the monitor accesses the predetermined page of the monitoring center 3 using the personal computer 1 to set a dangerous area using the personal computer 1 to receive a warning, and the monitored person enters the dangerous area. It is necessary to set the notification destination in the case. A plurality of notification destinations can be set.
[0026]
FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of the monitoring system of FIG.
[0027]
In FIG. 3, the
[0028]
The position
[0029]
The personal computer 1 is managed by a monitor, and basically includes a position
[0030]
FIG. 5 is a block diagram showing a detailed configuration example of the
[0031]
FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing a detailed configuration example of the personal computer 1 of FIG. The
[0032]
FIG. 7 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of the
[0033]
The configuration of the PHS terminal 4 is basically the same as the configuration of the
[0034]
Next, the operation of the monitoring system of FIG. 4 will be described. First, a setting process of the personal computer 1 for setting a dangerous area will be described with reference to a flowchart of FIG.
[0035]
In step S11, when the
[0036]
In step S12, the
[0037]
FIG. 9 is a diagram showing an example of the menu page displayed in step S12. As shown in the figure, for example, a
[0038]
In step S13, the
[0039]
Next, a detailed process of the attribute information setting process of the personal computer 1 executed in step S14 of FIG. 8 will be described with reference to a flowchart of FIG.
[0040]
In step S31, the
[0041]
FIG. 11 is a diagram illustrating an example of the map information displayed in step S31. For example, as shown in the figure, a map is displayed, and the observer can set the danger area E by operating the
[0042]
In step S32, the
[0043]
In step S34, the
[0044]
Although the processing executed in step S14 in FIG. 8 has been described above, the dangerous area is also set in step S15 by the same processing as in FIG. That is, in the
[0045]
Next, a registration process of the attribute information (dangerous area) of the
[0046]
In step S41, the
[0047]
In step S43, the
[0048]
In step S44, the
[0049]
In step S46, the
[0050]
In this monitoring system, the supervisor can change the security mode by accessing a predetermined page of the
[0051]
In step S71, when the monitor operates the
[0052]
The
[0053]
In step S73, the
[0054]
FIG. 14 is a diagram showing an example of a setting page displayed on the
[0055]
When the security mode is input from the monitor on the setting page as shown in FIG. 14, the
[0056]
Next, a series of processes of the monitoring system in FIG. 4 will be described with reference to FIGS. 15 to 17 and a flowchart in FIG. First, the position detection process of the
[0057]
In step S81, the
[0058]
Next, a monitoring process of the
[0059]
In step S91, the
[0060]
In step S93, the
[0061]
In step S95, as a result of the matching executed in step S94, the
[0062]
Further, in step S97, the
[0063]
Further, in step S98, the
[0064]
In step S99, the
[0065]
If the
[0066]
Next, the warning output process of the PHS terminal 4 will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. In step S111, the control unit of the PHS terminal 4 determines whether or not warning information has been transmitted from the
[0067]
FIG. 18 is a diagram illustrating an example of warning information displayed on the PHS terminal 4 of the monitoring target. As shown in the figure, for example, when the monitoring target is a child, a message such as "I am about to leave the action area decided at the school. Please return immediately" is displayed. If the monitoring target is an elderly person, the message is, for example, "Do not enter from here." The monitoring subject who confirms such a message confirms that he / she is in the dangerous area, and leaves the dangerous area.
[0068]
Then, the process returns to step S111, and the warning information is repeatedly displayed at predetermined time intervals, for example, until the warning mode is canceled in the
[0069]
Next, an output process of the warning information of the
[0070]
The processing of steps S121 and S122 is the same as the processing of the PHS terminal 4 (the processing of steps S111 and S112) described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. That is, in step S121, the
[0071]
FIG. 20 is a diagram illustrating an example of warning information displayed on the
[0072]
When confirming the safety of the monitoring target person, the monitoring person instructs the
[0073]
On the other hand, in step S123, the
[0074]
In the above, the output processing of the warning information of the
[0075]
In FIG. 21, a map of the area around the point where the monitoring target is located is displayed substantially at the center of the position
[0076]
In the above description, the terminal owned by the person to be monitored is a PHS terminal. However, any terminal can be used as long as its position can be detected. For example, when the person to be monitored has a mobile phone, its position can be specified by the so-called triangulation principle. Also, when the monitoring target has a GPS terminal, the
[0077]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, the observer can easily and surely confirm that the monitoring target has entered the dangerous area. Further, since it is not necessary to constantly monitor the moving monitoring target person, the labor of the monitoring person can be reduced.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a conventional monitoring system.
FIG. 2 is a flowchart illustrating a process of the monitoring system of FIG. 1;
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing a concept of a monitoring system to which the present invention is applied.
FIG. 4 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration example of the monitoring system of FIG. 3;
FIG. 5 is a block diagram showing a detailed configuration example of the center device of FIG. 4;
6 is a block diagram illustrating a detailed configuration example of the personal computer in FIG.
FIG. 7 is a block diagram showing a detailed configuration example of the mobile phone of FIG. 4;
FIG. 8 is a flowchart illustrating processing of the personal computer of FIG. 4;
FIG. 9 is a diagram illustrating a display example of a personal computer.
FIG. 10 is a flowchart illustrating another process of the personal computer in FIG. 4;
FIG. 11 is a diagram showing another display example of the personal computer.
FIG. 12 is a flowchart illustrating a process of the center device of FIG. 4;
FIG. 13 is a flowchart illustrating processing of the mobile phone of FIG. 4;
FIG. 14 is a diagram illustrating a display example of a mobile phone.
FIG. 15 is a flowchart illustrating a process of the position detection device in FIG. 4;
FIG. 16 is a flowchart illustrating another process of the center device in FIG. 4;
FIG. 17 is a flowchart illustrating a process of the PHS terminal in FIG. 4;
FIG. 18 is a diagram illustrating a display example of a PHS terminal.
FIG. 19 is a flowchart illustrating another process of the mobile phone in FIG. 4;
FIG. 20 is a diagram illustrating another display example of the mobile phone.
FIG. 21 is a diagram showing still another display example of the personal computer.
[Explanation of symbols]
1 Personal computer
2 Mobile phone
4 PHS terminal
11 Center equipment
12 Position detection device
21 Center control device
22 center communication equipment
31 Position information display
32 Attribute information setting section
Claims (6)
携帯端末を有するそれぞれの監視対象者のIDに対応付けて、前記設定手段により設定された前記警告エリアを記憶する第1の記憶手段と、
監視対象としての前記携帯端末の位置を取得する取得手段と、
前記取得手段により取得された前記携帯端末の位置が、前記設定手段により設定された前記警告エリア内であるか否かを判定する判定手段と、
前記判定手段により前記携帯端末の位置が前記警告エリア内であると判定された場合の通知先を指定する通知先指定情報を記憶する第2の記憶手段と、
前記第2の記憶手段により記憶されている前記通知先指定情報により指定される前記通知先に、前記携帯端末の位置が前記警告エリア内であることを通知する第1の通知手段と
を備えることを特徴とする監視装置。Setting means for setting a warning area according to a setting performed by a monitor via a communication network;
First storage means for storing the warning area set by the setting means in association with the ID of each monitoring target having a mobile terminal;
Acquisition means for acquiring the position of the mobile terminal as a monitoring target,
Determining means for determining whether or not the position of the mobile terminal obtained by the obtaining means is within the warning area set by the setting means;
Second storage means for storing notification destination designation information for specifying a notification destination when the position of the portable terminal is determined to be within the warning area by the determination means;
A first notification unit that notifies the notification destination specified by the notification destination specification information stored in the second storage unit that the position of the mobile terminal is within the warning area. A monitoring device characterized by the above-mentioned.
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の監視装置。The monitoring device according to claim 1, further comprising a second notification unit that notifies the portable terminal that the mobile terminal is in the warning area.
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の監視装置。2. The mobile terminal according to claim 1, further comprising: a providing unit configured to provide a function of selecting whether or not the monitoring target is in a monitoring state to a portable terminal of the monitoring target that monitors the monitoring target. 3. The monitoring device as described.
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の監視装置。The determining unit reads out map information in which the warning area of the monitoring target is set based on the ID, and determines whether the position of the mobile terminal of the monitoring target is within the warning area. The monitoring device according to claim 1, wherein:
携帯端末を有するそれぞれの監視対象者のIDに対応付けて、前記設定ステップの処理により設定された前記警告エリアを記憶する第1の記憶ステップと、
監視対象としての前記携帯端末の位置を取得する取得ステップと、
前記取得ステップの処理により取得された前記携帯端末の位置が、前記設定ステップの処理により設定された前記警告エリア内であるか否かを判定する判定ステップと、
前記判定ステップの処理により前記携帯端末の位置が前記警告エリア内であると判定された場合の通知先を指定する通知先指定情報を記憶する第2の記憶ステップと、
前記第2の記憶ステップの処理により記憶されている前記通知先指定情報により指定される前記通知先に、前記携帯端末の位置が前記警告エリア内であることを通知する通知ステップと
を含むことを特徴とする監視方法。A setting step of setting a warning area according to settings performed by a monitor via a communication network;
A first storage step of storing the warning area set by the processing of the setting step in association with the ID of each monitoring target person having a mobile terminal;
An acquisition step of acquiring a position of the mobile terminal as a monitoring target,
A determining step of determining whether or not the position of the mobile terminal obtained by the processing of the obtaining step is within the warning area set by the processing of the setting step;
A second storage step of storing notification destination specification information for specifying a notification destination when the position of the mobile terminal is determined to be within the warning area by the processing of the determination step;
A notification step of notifying that the location of the portable terminal is within the warning area to the notification destination specified by the notification destination specification information stored by the processing of the second storage step. Characteristic monitoring method.
携帯端末を有するそれぞれの監視対象者のIDに対応付けて、前記設定ステップの処理により設定された前記警告エリアの記憶を制御する第1の記憶制御ステップと、
監視対象としての前記携帯端末の位置の取得を制御する取得制御ステップと、
前記取得制御ステップの処理により取得された前記携帯端末の位置が、前記設定ステップの処理により設定された前記警告エリア内であるか否かを判定する判定ステップと、
前記判定ステップの処理により前記携帯端末の位置が前記警告エリア内であると判定された場合の通知先を指定する通知先指定情報の記憶を制御する第2の記憶制御ステップと、
前記第2の記憶制御ステップの処理により記憶されている前記通知先指定情報により指定される前記通知先に対する、前記携帯端末の位置が前記警告エリア内であることの通知を制御する通知制御ステップと
を含むことを特徴とするコンピュータが読み取り可能なプログラムが記録されている記録媒体。 A setting step of setting a warning area according to settings performed by a monitor via a communication network;
A first storage control step of controlling storage of the warning area set by the processing of the setting step in association with the ID of each monitoring target having a mobile terminal;
An acquisition control step of controlling acquisition of the position of the mobile terminal as a monitoring target,
A determining step of determining whether or not the position of the mobile terminal obtained by the processing of the obtaining control step is within the warning area set by the processing of the setting step;
A second storage control step of controlling storage of notification destination specification information for specifying a notification destination when the position of the mobile terminal is determined to be within the warning area by the processing of the determination step;
A notification control step of controlling a notification that the position of the portable terminal is within the warning area with respect to the notification destination specified by the notification destination specification information stored by the processing of the second storage control step; A recording medium on which a computer-readable program is recorded .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001063389A JP3601056B2 (en) | 2001-03-07 | 2001-03-07 | Monitoring apparatus and method, and recording medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001063389A JP3601056B2 (en) | 2001-03-07 | 2001-03-07 | Monitoring apparatus and method, and recording medium |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004192595A Division JP4081685B2 (en) | 2004-06-30 | 2004-06-30 | Monitoring device and method, and recording medium |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2002269653A JP2002269653A (en) | 2002-09-20 |
| JP3601056B2 true JP3601056B2 (en) | 2004-12-15 |
| JP2002269653A5 JP2002269653A5 (en) | 2005-01-27 |
Family
ID=18922389
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001063389A Expired - Fee Related JP3601056B2 (en) | 2001-03-07 | 2001-03-07 | Monitoring apparatus and method, and recording medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3601056B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013088500A (en) * | 2011-10-14 | 2013-05-13 | Omron Corp | Map creation system, map creation device, and portable terminal |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4062148B2 (en) | 2003-03-27 | 2008-03-19 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Mobile terminal and information providing system using the same |
| KR100692803B1 (en) | 2004-10-27 | 2007-03-12 | 에스케이 텔레콤주식회사 | Method and system for providing location based health care service |
| JP4609067B2 (en) * | 2004-12-22 | 2011-01-12 | 日本電気株式会社 | Specific area entry / exit detection system, location information control server, and location information control program |
| JP2006277422A (en) * | 2005-03-30 | 2006-10-12 | Nec Corp | Moving body monitoring guidance system and monitoring guidance method therefor |
| JP4702129B2 (en) * | 2006-03-22 | 2011-06-15 | 株式会社デンソー | Route guidance device for vehicles |
| US8035526B2 (en) * | 2008-09-19 | 2011-10-11 | Intel-GE Care Innovations, LLC. | Remotely configurable assisted-living notification system with gradient proximity sensitivity |
| JP4911478B2 (en) * | 2008-10-01 | 2012-04-04 | リンクハートコミュニケーションズ株式会社 | Area access information notification system and system server |
| JP2012238068A (en) * | 2011-05-10 | 2012-12-06 | Nec Corp | Information processor, portable terminal, attention calling system, attention calling method and program |
| WO2013147867A1 (en) * | 2012-03-30 | 2013-10-03 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | Defining a perimeter to monitor a wireless device for a violation of the perimeter |
| JP6273157B2 (en) * | 2014-02-21 | 2018-01-31 | 京セラ株式会社 | Route guidance system, route guidance program, and route guidance method |
| JP6363633B2 (en) * | 2016-01-15 | 2018-07-25 | キャプテン山形株式会社 | ネ ッ ト ワ ー ク Missing person prevention network system and its control method |
| JP7035525B2 (en) * | 2017-12-27 | 2022-03-15 | オムロンヘルスケア株式会社 | Attention system, information processing device, information processing method, and program |
| CN113711281A (en) * | 2019-04-01 | 2021-11-26 | 比赛斯株式会社 | Monitoring system, monitoring method, and program |
-
2001
- 2001-03-07 JP JP2001063389A patent/JP3601056B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013088500A (en) * | 2011-10-14 | 2013-05-13 | Omron Corp | Map creation system, map creation device, and portable terminal |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2002269653A (en) | 2002-09-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3601056B2 (en) | Monitoring apparatus and method, and recording medium | |
| JP4796587B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for managing ringtones in portable devices | |
| JP4552366B2 (en) | Mobile portable terminal, position search system, position search method and program thereof | |
| KR100735421B1 (en) | Mobile communication terminal for outputting schedule information based on location of the user and method thereof | |
| JP4479697B2 (en) | Information notification system, information notification method, information device, and program | |
| JP2007087139A (en) | System and method for collecting/managing disaster safety information, mobile terminal, and program | |
| US20070054688A1 (en) | Mobile terminal for transmitting emergency message and method thereof | |
| JP2003224674A (en) | Health management service system by portable telephone terminal | |
| JP5603606B2 (en) | Communication system and portable communication device | |
| JP2003087436A (en) | Emergency notice system and emergency notice device | |
| KR101767474B1 (en) | Emergency rescue system and emergency rescue method using the same | |
| US20030119494A1 (en) | Wireless terminal having a scanner for issuing an alert when within the range of a target wireless terminal | |
| JP2002099971A (en) | Emergency reporting system and emergency reporting device | |
| JP3278645B2 (en) | Wireless emergency rescue system | |
| WO2006135120A1 (en) | Mobile terminal for transmitting emergency message and method thereof | |
| JP5360405B2 (en) | Disaster safety confirmation system and method | |
| JP4081685B2 (en) | Monitoring device and method, and recording medium | |
| JP2013021435A (en) | Wireless communication terminal device and wireless communication method | |
| JP2007164486A (en) | Information report unit | |
| JP6505168B2 (en) | Notification system | |
| JP5122413B2 (en) | Safety confirmation system and monitoring center device | |
| JP3806642B2 (en) | Mobile communication device and communication method | |
| JP3927558B2 (en) | Wireless communication system | |
| JP4448285B2 (en) | Mobile phone | |
| JP2019191856A (en) | Security system and security method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040223 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20040223 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20040223 |
|
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20040315 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20040317 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040517 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20040611 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040726 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20040830 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20040912 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 3601056 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20071001 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20081001 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20091001 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20101001 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20101001 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111001 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111001 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121001 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121001 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131001 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |