JP2018167576A - Piezoelectric device, liquid injection head, and liquid injection device - Google Patents
Piezoelectric device, liquid injection head, and liquid injection device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2018167576A JP2018167576A JP2017247345A JP2017247345A JP2018167576A JP 2018167576 A JP2018167576 A JP 2018167576A JP 2017247345 A JP2017247345 A JP 2017247345A JP 2017247345 A JP2017247345 A JP 2017247345A JP 2018167576 A JP2018167576 A JP 2018167576A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- pressure chamber
- substrate
- piezoelectric
- piezoelectric device
- partition member
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Particle Formation And Scattering Control In Inkjet Printers (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、複数の空間が壁で隔てて形成された基板と、基板の一方の面において空間の一部を区画する区画部材と、を備えた圧電デバイス、液体噴射ヘッド、及び、液体噴射装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a piezoelectric device, a liquid ejecting head, and a liquid ejecting apparatus, each including a substrate having a plurality of spaces separated by walls and a partition member that partitions a part of the space on one surface of the substrate. It is about.
複数の空間が壁で隔てて形成された基板と、当該基板の一方の面において空間の一部を区画する区画部材と、を備え、当該区画部材における空間に対応する部分が可動領域として機能する圧電デバイスは、各種の装置(液体噴射装置やセンサー等)に応用されている。例えば、液体噴射装置においては、基板の空間に液体が導入され、この空間の一部を区画する可撓性を有する区画部材(弾性膜)が駆動素子としての圧電素子により変位される圧電デバイスが、液体噴射ヘッドに組み込まれている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。このような液体噴射ヘッドでは、圧電素子を駆動することにより区画部材が変位して空間内の液体に圧力変動が生じ、この圧力変動により空間に連通するノズルから液体が噴射される。また、例えば、可動領域の圧力変化、振動、あるいは変位等を検出するセンサー等にも上記の構成の圧電デバイスが採用される場合がある。 A substrate having a plurality of spaces separated by walls and a partition member that partitions a part of the space on one surface of the substrate, and a portion corresponding to the space in the partition member functions as a movable region. Piezoelectric devices are applied to various devices (liquid ejecting devices, sensors, etc.). For example, in a liquid ejecting apparatus, there is a piezoelectric device in which a liquid is introduced into a space of a substrate, and a flexible partition member (elastic film) that partitions a part of this space is displaced by a piezoelectric element as a drive element. The liquid jet head is incorporated (for example, see Patent Document 1). In such a liquid ejecting head, the partition member is displaced by driving the piezoelectric element to cause a pressure fluctuation in the liquid in the space, and the liquid is ejected from a nozzle communicating with the space by the pressure fluctuation. In addition, for example, the piezoelectric device having the above-described configuration may be employed for a sensor that detects pressure change, vibration, displacement, or the like of the movable region.
ところで、上記の圧電デバイスでは、複数の材料が積層されて構成されており、それぞれの材料が持つ応力(残留応力)によっては、製造工程で基板に変形や歪みを生じさせる場合がある。これにより、上記のように空間を区画している壁に他の部材を接着剤により接合しようとした場合、複数の当該壁の接合面の位置にばらつきが生じて接合不良が生じるおそれがあった。また、このような接合不良を抑制するべく、接合面のばらつきを考慮して接着剤の厚さをより厚くした場合、接合領域から上記の空間側に接着剤がはみ出す可能性がある。そして、はみ出した接着剤が可動領域に付着すると、可動領域の変位時の変位量が付着前の状態から変わってしまう場合がある。その結果、可動領域の変位量が空間毎にばらつくおそれがあった。 By the way, the above-described piezoelectric device is configured by laminating a plurality of materials, and depending on the stress (residual stress) of each material, the substrate may be deformed or distorted in the manufacturing process. Thereby, when trying to join another member to the wall partitioning the space as described above with an adhesive, there is a possibility that the position of the joining surface of the plurality of walls varies and a joining failure may occur. . In addition, in order to suppress such bonding failure, when the thickness of the adhesive is increased in consideration of the variation of the bonding surface, the adhesive may protrude from the bonding region to the space side. When the protruding adhesive adheres to the movable region, the displacement amount when the movable region is displaced may change from the state before the adhesion. As a result, the displacement amount of the movable region may vary from space to space.
本発明は、このような事情に鑑みてなされたものであり、その目的は、残留応力に基づく基板の変形を抑制して基板の接着信頼性を向上することが可能な圧電デバイス、液体噴射ヘッド、及び、液体噴射装置を提供することにある。 The present invention has been made in view of such circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to provide a piezoelectric device and a liquid ejecting head capable of improving the adhesion reliability of the substrate by suppressing the deformation of the substrate based on the residual stress. And providing a liquid ejecting apparatus.
本発明の圧電デバイスは、上記目的を達成するために提案されたものであり、複数の空間が壁で隔てて並設された基板と、
前記基板の一方の面において隣り合う前記壁を跨いで前記空間の一部を区画する区画部材と、
前記区画部材の前記空間側とは反対側に形成された圧電素子と、
を備え、
前記空間の並設方向における前記壁の幅をa、前記一方の面から当該一方の面とは反対側の他方の面までの前記壁の高さをb、前記区画部材の厚さをt、前記区画部材における変位可能な可動領域の長手方向の寸法をLとして、
t×L4/(a×b3)≦5×105
を満たすことを特徴とする。
The piezoelectric device of the present invention has been proposed in order to achieve the above-mentioned object, and a substrate in which a plurality of spaces are arranged in parallel with a wall,
A partition member that partitions a part of the space across the adjacent walls on one surface of the substrate;
A piezoelectric element formed on the side opposite to the space side of the partition member;
With
The width of the wall in the parallel arrangement direction of the space is a, the height of the wall from the one surface to the other surface opposite to the one surface is b, the thickness of the partition member is t, The dimension in the longitudinal direction of the movable region that can be displaced in the partition member is L,
t × L 4 / (a × b 3 ) ≦ 5 × 10 5
It is characterized by satisfying.
この構成によれば、壁の高さ方向(縦方向)の強度が確保されるので、基板の変形が抑制される。これにより、他の部材に接合される壁の端面の位置のばらつきが抑制されるので、基板の他方の面に他の部材が接着剤により接合される際の接合不良が低減される。また、接合不良を抑制するための接着剤の厚みを抑えることができるので、接合部分から空間側への接着剤のはみ出し(流れ出し)を低減することが可能となる。これにより、空間側へ流れ出した接着剤が可動領域に付着することによる当該可動領域の変位特性に悪影響を及ぼすことが抑制される。 According to this configuration, the strength in the height direction (vertical direction) of the wall is ensured, so that deformation of the substrate is suppressed. Thereby, since the dispersion | variation in the position of the end surface of the wall joined to another member is suppressed, the joining defect at the time of another member joining to the other surface of a board | substrate with an adhesive agent is reduced. Moreover, since the thickness of the adhesive for suppressing poor bonding can be suppressed, it is possible to reduce the protrusion (flow out) of the adhesive from the bonded portion to the space. Thus, adverse effects on the displacement characteristics of the movable region due to the adhesive flowing out to the space side adhering to the movable region are suppressed.
また、上記各構成において、さらに、1.2×105≦t×L4/(a×b3)≦1.6×105
を満たすことがより望ましい。
In each of the above configurations, 1.2 × 10 5 ≦ t × L 4 / (a × b 3 ) ≦ 1.6 × 10 5
It is more desirable to satisfy.
この構成によれば、基板の歪み等の抑制と、隣接する空間において可動領域が駆動した際の駆動特性について影響し合ういわゆるクロストークの抑制とを両立させることが可能となる。 According to this configuration, it is possible to achieve both suppression of substrate distortion and the like and suppression of so-called crosstalk that affects driving characteristics when the movable region is driven in an adjacent space.
上記構成において、t×b4/(a×L3)≦1.2×10−3
を満たすことがさらに望ましい。
In the above configuration, t × b 4 / (a × L 3 ) ≦ 1.2 × 10 −3
It is further desirable to satisfy.
この構成によれば、隔壁の空間並設方向(横方向)の強度が確保されるので、クロストークがより確実に抑制される。 According to this configuration, the strength in the direction in which the partitions are arranged in the space (lateral direction) is ensured, so that crosstalk is more reliably suppressed.
また、本発明は、前記区画部材が残留応力を有している構成に好適である。 Further, the present invention is suitable for a configuration in which the partition member has a residual stress.
この構成によれば、区画部材の残留応力による基板の変形を抑制することができる。 According to this configuration, the deformation of the substrate due to the residual stress of the partition member can be suppressed.
上記構成において、前記壁の母材がシリコンであり、
前記区画部材が、前記母材の熱酸化により形成されたシリコン酸化膜である構成を採用することができる。
In the above configuration, the base material of the wall is silicon,
The partition member may be a silicon oxide film formed by thermal oxidation of the base material.
この構成によれば、熱酸化の工程で母材であるシリコンに酸素が結合する結果、区画部材が圧縮応力(残留応力)を有する。このような構成においても区画部材の圧縮応力による基板の変形を抑制することができる。 According to this configuration, as a result of oxygen bonding to silicon as a base material in the thermal oxidation process, the partition member has compressive stress (residual stress). Even in such a configuration, the deformation of the substrate due to the compressive stress of the partition member can be suppressed.
また、本発明の液体噴射ヘッドは、上記何れかの一の構成の圧電デバイスを備えたことを特徴とする。 According to another aspect of the invention, there is provided a liquid jet head including the piezoelectric device having any one of the configurations described above.
本発明によれば、接合不良が抑制された圧電デバイスを備えるので、接着が不十分な箇所からの液体の漏出リスクが低減される。 According to the present invention, since the piezoelectric device in which poor bonding is suppressed is provided, the risk of leakage of liquid from a location where adhesion is insufficient is reduced.
そして、本発明の液体噴射装置は、上記各構成の液体噴射ヘッドを備えたことを特徴とする。 According to another aspect of the invention, a liquid ejecting apparatus includes the liquid ejecting head having the above-described configuration.
本発明によれば、液体の漏出リスクが低減された液体噴射ヘッドを備えるので、信頼性が向上する。 According to the aspect of the invention, since the liquid ejecting head in which the risk of liquid leakage is reduced is provided, the reliability is improved.
以下、本発明を実施するための形態を、添付図面を参照して説明する。なお、以下に述べる実施の形態では、本発明の好適な具体例として種々の限定がされているが、本発明の範囲は、以下の説明において特に本発明を限定する旨の記載がない限り、これらの態様に限られるものではない。また、以下においては、本発明に係る圧電デバイスを備えた液体噴射ヘッドの一形態であるインクジェット式記録ヘッド(以下、記録ヘッド)、及び、これを搭載した液体噴射装置の一形態であるインクジェット式プリンター(以下、プリンター)を例に挙げて説明する。 DESCRIPTION OF EMBODIMENTS Hereinafter, embodiments for carrying out the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings. In the embodiments described below, various limitations are made as preferred specific examples of the present invention. However, the scope of the present invention is not limited to the following description unless otherwise specified. However, the present invention is not limited to these embodiments. In the following, an ink jet recording head (hereinafter referred to as a recording head) that is one form of a liquid ejecting head including the piezoelectric device according to the present invention, and an ink jet type that is one form of a liquid ejecting apparatus equipped with the same. A printer (hereinafter referred to as a printer) will be described as an example.
プリンター1の構成について、図1を参照して説明する。プリンター1は、記録紙等の記録媒体2の表面に対して記録ヘッド3のノズル27(図2参照)からインクを噴射して画像等の記録を行う装置である。このプリンター1は、記録ヘッド3、当該記録ヘッド3が取り付けられたキャリッジ4、当該キャリッジ4を主走査方向に移動させるキャリッジ移動機構5、記録媒体2を副走査方向に移送するプラテンローラー6等を備えている。液体の一種であるインクは、液体供給源としてのインクカートリッジ7に貯留されている。このインクカートリッジ7は、キャリッジ4に対して着脱可能に装着されると、内部に貯留されているインクを記録ヘッド3に供給する。なお、インクカートリッジ7がプリンター1の本体側に配置され、当該インクカートリッジ7からインク供給チューブを通じて記録ヘッド3に供給される構成を採用することもできる。
The configuration of the printer 1 will be described with reference to FIG. The printer 1 is a device that records an image or the like by ejecting ink from a nozzle 27 (see FIG. 2) of the
上記のキャリッジ移動機構5はタイミングベルト8を備えている。そして、このタイミングベルト8はDCモーター等のパルスモーター9により駆動される。従ってパルスモーター9が作動すると、キャリッジ4は、プリンター1に架設されたガイドロッド10に案内されて、主走査方向(記録媒体2の幅方向)に往復移動する。
The
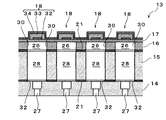
図2は、記録ヘッド3の構成の一例を示す断面図である。また、図3は、記録ヘッド3が備える圧電デバイス13の圧力室長手方向の断面図であり、図4は、圧電デバイス13の圧力室並設方向の断面図である。図5は、圧力室形成基板16における圧力室26の上部開口周辺の平面図である。なお、便宜上、各部材の積層方向を上下方向として説明する。本実施形態における記録ヘッド3は、本発明の圧電デバイスの一形態である圧電デバイス13を備えている。この圧電デバイス13は、複数の基板、具体的には、ノズルプレート14、連通基板15、及び圧力室形成基板16(本発明における基板の一種)が、この順で積層されて互いに接着剤21により接合されてユニット化されている。また、この圧電デバイス13における圧力室形成基板16の連通基板15側とは反対側の面には、弾性膜17(本発明における区画部材の一種)、圧電素子18(駆動素子の一種)、及び、当該圧電素子18を保護する保護基板19が積層されている。そして、このような構成の圧電デバイス13がケース20に取り付けられて記録ヘッド3が構成されている。
FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view showing an example of the configuration of the
ケース20は、底面側に圧電デバイス13が固定される合成樹脂製の箱体状部材である。このケース20の下面側には、当該下面からケース20の高さ方向の途中まで直方体状に窪んだ収容空部22が形成されており、圧電デバイス13が下面に接合されると、圧電デバイス13における圧力室形成基板16、弾性膜17、圧電素子18、及び保護基板19が、収容空部22内に収容される。また、ケース20には、インク導入路23が形成されている。上記インクカートリッジ7側からのインクは、インク導入路23を通じて圧電デバイス13の共通液室24に導入される。
The
本実施形態における圧力室形成基板16は、シリコン単結晶基板(本発明における母材に相当。以下、単にシリコン基板とも言う。)から作製されている。この圧力室形成基板16には、圧力室26(本発明における空間の一種)を区画する複数の圧力室空部が隔壁30(本発明における壁の一種)で隔てられて並設されている。各圧力室空部は、圧力室形成基板16の連通基板15側の面から異方性エッチングが施されて形成されている。このように、シリコン基板に対して異方性エッチングによって圧力室等の流路となる空間が形成されることで、より高い寸法・形状精度を確保することができる。圧力室形成基板16の一方の面(連通基板15側とは反対側の面)における圧力室空部の開口(以下、上部開口)は、弾性膜17によって封止されている。また、圧力室形成基板16における弾性膜17とは反対側の他方の面には、連通基板15(他の部材の一種)が接合され、当該連通基板15によって圧力室空部の他方の開口が封止される。これにより、圧力室26が区画形成される。すなわち、弾性膜17は、隣り合う隔壁30を跨いで圧力室26の一部を区画している。
The pressure
本実施形態において、圧力室形成基板16と弾性膜17とは一体的に形成されている。より具体的には、圧力室形成基板16の母材であるシリコン基板の一方の面が熱酸化されることによりシリコン酸化膜(SiO2)が形成され、また、当該シリコン基板の他方の面からシリコン酸化膜に至るまで異方性エッチング処理が施されて圧力室空部が形成され、残ったシリコン酸化膜が弾性膜17として機能する。なお、弾性膜17には、図示しない二酸化ジルコニウム(ZrO2)からなる絶縁体膜が積層されている。そして、この絶縁体膜上(弾性膜17の圧力室26側とは反対側の面)における圧力室26に対応する位置に圧電素子18がそれぞれ形成されている。ここで、弾性膜17において圧力室26の上部開口を封止する部分は、圧電素子18の駆動により変位可能な可動領域の一部として機能する。一方、弾性膜17において圧力室26の上部開口から外れた領域であって、以下において説明する錘層35が形成された領域、及び、これよりも外側の領域は、弾性膜17の撓み変形が阻害される非可動領域となる。可動領域の詳細については後述する。
In the present embodiment, the pressure
本実施形態における圧力室26は、ノズル27の並設方向に直交する方向に長尺な空部である。この圧力室26の長手方向における一端部は、連通基板15のノズル連通口28を介してノズル27と連通する。また、圧力室26の長手方向における他端部は、連通基板15の個別連通口29を介して共通液室24と連通する。そして、圧力室26は、ノズル27毎に対応してノズル列方向に沿って隔壁30により隔てられて複数並設されている。
The
本実施形態における圧電素子18は、所謂撓みモードの圧電素子である。この圧電素子18は、弾性膜17上に、下電極層32(第1の電極層)、誘電体の一種である圧電体層33、上電極層34(第2の電極層)が順次積層されて構成されている。本実施形態では、下電極層32が圧電素子18毎に独立してパターニングされている。図5に示されるように、本実施形態における下電極層32は、圧力室26のノズル列方向(圧力室並設方向)における幅wよりも狭い幅で圧力室26の長手方向に沿って延在している。この下電極層32の延在方向(長手方向)における両端部は、圧力室26の上部開口内から当該上部開口よりも外側の非可動領域まで延設されている。一方、上電極層34は、圧力室並設方向に沿って各圧力室26に亘って連続して形成されている。そして、上電極層34、圧電体層33、及び下電極層32がこれらの積層方向で見て互いにオーバーラップする部分が、両電極層32,34への電圧の印加により圧電歪みが生じる圧電体能動部である。すなわち、上電極層34は複数の圧電素子18に共通に設けられた共通電極となっており、下電極層32は圧電素子18毎に個別に設けられた個別電極となっている。なお、下電極層32及び上電極層34としては、イリジウム(Ir)、白金(Pt)、チタン(Ti)、タングステン(W)、ニッケル(Ni)、パラジウム(Pd)、金(Au)等の各種金属、及び、これらの合金やLaNiO3等の導電性酸化物等が用いられる。
The
本実施形態における圧電体層33は、下電極層32を覆う状態で弾性膜17の上に形成されている。この圧電体層33としては、鉛(Pb)、チタン(Ti)及びジルコニウム(Zr)を含むもの、例えば、チタン酸ジルコン酸鉛(PZT)等の強誘電性圧電材料や、これに酸化ニオブ、酸化ニッケル又は酸化マグネシウム等の金属酸化物を添加したもの等を用いることができる。図5に示されるように、この圧電体層33において隣り合う圧力室26の間の領域に対応する部分には、開口36が形成されている。この開口36は、圧電体層33が部分的に除去されて形成された凹部或いは貫通穴から構成されており、圧力室26の開口の辺(開口縁)に沿って延在している。要するに、この開口36は、圧電体層33における他の部分の厚さよりも相対的に薄くなった或いは圧電体層33を貫通した部分である。この開口36の圧力室長手方向の両端部は、圧力室並設方向の幅が次第に狭くなる先細り形状となっている。
The
そして、隣り合う開口36の間の領域における圧力室26の上部開口の位置には、開口36の部分よりも厚い圧電体層33が梁状に設けられている。この当該梁状の圧電体層33は、圧電体能動部に対応する部分に設けられている。この梁状部分の圧電体層33の圧力室並設方向における幅は、同方向における圧力室26の幅wよりも少し狭くなっている。この梁状の圧電体層33の圧力室並設方向の両側に上記の開口36が設けられることにより、圧電体能動部に対応する圧電体層33を円滑に変位させることができる。
A
図3及び図5に示されるように、本実施形態における圧電素子18の上電極層34上には、錘層35が積層されている。本実施形態では、圧力室26の一側の端部に対応する位置と、圧力室26の他側の端部に対応する位置にそれぞれ錘層35a及び錘層35bが形成されている。なお、錘層35としては、金(Au)、銅(Cu)、アルミ(Al)及び、これらの合金等が用いられる。また、錘層35が金(Au)等からなる場合には、チタン(Ti)、ニッケル(Ni)、クロム(Cr)、タングステン(W)、及び、これらの合金等からなる密着層が上電極層34との間に設けても良い。
As shown in FIGS. 3 and 5, a
錘層35a,35bは、それぞれ圧力室26の長手方向における一側の端部及び他側の端部の近傍において上電極層34に積層されて当該上電極層34と導通している。本実施形態における錘層35a,35bは、圧力室26の長手方向において当該圧力室26の上部開口より少し外側に外れた位置に設けられている。これらの錘層35a,35bが設けられていることにより、圧電素子18の駆動時において、圧力室26の上部開口の縁付近における圧電素子18及び弾性膜17の不規則な変形が抑制され、当該部分における圧電素子18及び弾性膜17の損傷が抑制される。本実施形態における弾性膜17において、圧力室26の幅wの範囲内(より厳密には、圧力室並設方向において隣り合う開口36の間の範囲内)であって一側の錘層35aと他側の錘層35bとの間の領域が、圧電素子18の駆動時において実質的に変位可能な可動領域となる。すなわち、本実施形態においては、両側の錘層35a,35bの間の領域であって、圧力室26の上部開口よりも外側に外れた領域も圧電素子18の駆動に応じて多少動くことができ、可動領域の一部として機能する。これらの錘層35a,35bのノズル列方向における両端は、上電極層34と同様に、一群の圧力室26が形成された領域よりも外側まで延設されている。なお、錘層35a,35bに関し、圧力室26の長手方向において当該圧力室26の上部開口の端部に平面視で一部が重なる位置に設けられてもよい。また、錘層35は、必ずしも設けられていなくてもよい。この場合、圧電素子18の駆動時において実質的に変位する領域が可動領域となる。
The weight layers 35 a and 35 b are stacked on the
連通基板15は、圧力室形成基板16と同様にシリコン基板から作製された板材である。この連通基板15には、圧力室形成基板16の複数の圧力室26に共通に設けられる共通液室24(リザーバーあるいはマニホールドとも呼ばれる)となる空部が、異方性エッチングによって形成されている。この共通液室24は、各圧力室26の並設方向に沿って長尺な空部である。図2に示されるように、本実施形態における共通液室24は、連通基板15の板厚方向を貫通した第1液室24aと、連通基板15の下面側から上面側に向けて当該連通基板15の板厚方向の途中まで上面側に薄肉部を残した状態で形成された第2液室24bと、から構成される。この第2液室24bの圧力室長手方向における一端部(ノズル27から遠い側の端部)は、第1液室24aと連通する一方、同方向の他端部は、平面視において圧力室26と重なる位置に形成されている。この第2液室24bの他端部、すなわち、第1液室24a側とは反対側には、薄肉部を貫通する個別連通口29が、圧力室形成基板16の各圧力室26にそれぞれ対応して複数形成されている。この個別連通口29の一端は、第2液室24bと連通し、個別連通口29の他端は、圧力室形成基板16の圧力室26と連通する。
The
上記のノズルプレート14は、複数のノズル27が列状に開設された板材である。本実施形態では、ドット形成密度に対応した形成ピッチでノズル27が複数列設されてノズル列が構成されている。本実施形態におけるノズルプレート14は、シリコン基板から作製され、当該基板に対してドライエッチングにより円筒形状のノズル27が形成されている。そして、本実施形態における圧電デバイス13には、上記の共通液室24から個別連通口29、圧力室26、及びノズル連通口28を通ってノズル27に至るまでのインク流路が形成されている。
The
そして、上記構成の圧電デバイス13を備える記録ヘッド3では、圧電素子18に印加される駆動信号の電圧の変化に応じて圧電能動部が撓み変形することにより、弾性膜17の可動領域が、ノズル27に近づく側又はノズル27から遠ざかる方向に変位する。これにより、圧力室26内のインクに圧力変動が生じ、この圧力変動を利用してノズル27からインクが噴射される。
In the
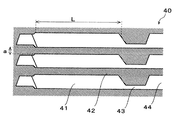
図6は、圧力室26を区画している隔壁30と弾性膜17(可動領域)の形状及び寸法について説明する模式図である。以下、圧力室26の並設方向(本実施形態においてはノズル列方向)における隔壁30の幅(厚さ)をa、隔壁30の高さ(弾性膜17側の基端から連通基板15側の先端までの長さ)をb、また、圧力室26の長手方向(可動領域の長手方向)における弾性膜17の可動領域の長さをLとする。近年、高解像度化や小型化の要請に応じて記録ヘッド3においてはノズル27の形成ピッチがより狭小化し、これに伴って圧力室26の形成ピッチもより狭小化している。これにより、隔壁30の幅(厚さ)aはより薄くなり、圧力室26の幅wもより狭くなる傾向にある。圧力室26の長手方向の寸法が一定であると仮定して圧力室26の幅wが狭くなると、その分だけ、圧力室26の容積が減少することになる。所定の電圧を圧電素子18に印加して駆動したときにノズル27から噴射されるインクの重量(排除堆積)を所定の値に維持するためには、圧力室26の長手方向の寸法をより長くすることにより、上記の可動領域の長さLをより長くする必要がある。ところが、可動領域の長さLを長くすることによって隔壁30の高さ方向の強度が低下する。これにより、記録ヘッド3(圧電デバイス13)の製造工程において以下のような不具合が生じるおそれがある。
FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram for explaining the shapes and dimensions of the
図7から図9は、記録ヘッド3(圧電デバイス13)の製造工程における不具合について説明する模式図である。なお、各図において、弾性膜17上に形成された圧電素子18等の他の構成部材の図示は省略されている。また、図8及び図9において、圧力室形成基板16の歪みは実際よりも誇張されて図示されている。例えば、本実施形態における圧電デバイス13の製造工程では、図7に示されるように、シリコン基板からなる圧力室形成基板16の一方の面が熱酸化されることにより、シリコン酸化膜からなる弾性膜17が形成される。この工程で母材であるシリコンに酸素が結合する結果、膨張しようとするため、弾性膜17は圧縮応力(残留応力の一種)を有することになる。この状態で、図8において矢印で示されるように、圧力室形成基板16の他方の面から水酸化カリウム(KOH)等のエッチング用液による異方性エッチングによって圧力室26となる空部が形成されていくと、これに伴って弾性膜17を支えている圧力室形成基板16の強度が低下することにより、弾性膜17の圧縮応力が次第に開放されて圧力室形成基板16に変形(歪み)が生じる。そして、図9に示されるように、エッチングストップとして機能する弾性膜17に到達するまで異方性エッチングが施されると、圧力室形成基板16において圧力室26に対応する部分では、弾性膜17を支える部分が無くなるため、隔壁30の高さ方向(縦方向)の強度によっては、圧力室形成基板16の歪みがより大きくなり、隔壁30の先端面、すなわち、後の工程において他の部材である連通基板15と接合される面の位置が大きくばらついてしまう。このような状態では、連通基板15との接合の際、隔壁30の先端面に接着剤21を転写等により均一に塗布することが難しく、これにより、接合不良が生じるおそれがあった。
7 to 9 are schematic views for explaining problems in the manufacturing process of the recording head 3 (piezoelectric device 13). In addition, in each figure, illustration of other structural members, such as the
また、接合される面の位置がばらつくと上記のように接着剤によっては転写自体ができなくなる(接合できない箇所が生じる)ほか、転写できたとしても、接合箇所からのインクの漏洩を防ぐためには接着剤の厚さを厚くする必要があり、この状態で接合すると流路側(圧力室26側)への接着剤のはみ出し量がばらつくことになる。このように流路側にはみ出した接着剤は、例えば圧力室26の隔壁等を毛細管現象により伝って弾性膜17まで到達して硬化すると、可動領域の駆動時の変位量を変化させてしまう場合がある。そして、接着剤のはみ出し量がばらつくと、弾性膜17まで這い上がる接着剤の量もばらつくため、その結果として可動領域の変位量が各圧力室26でばらついてしまうという問題がある。
In addition, if the positions of the surfaces to be joined vary, the transfer itself cannot be performed depending on the adhesive as described above (a part that cannot be joined occurs), and even if it can be transferred, in order to prevent ink leakage from the joint part It is necessary to increase the thickness of the adhesive, and if it is joined in this state, the amount of adhesive protruding to the flow path side (
上記の問題に鑑み、本発明に係るプリンター1においては、上記の各寸法を適切に設定することにより圧力室形成基板16の変形の発生が抑制されている。より具体的には、隔壁30の幅a、隔壁30の高さb、弾性膜17の可動領域の長さL、及び、弾性膜17の膜厚tについて、以下の条件(1)を満たすように各寸法が設定されている。
t×L4/(a×b3)≦5×105 …(1)
上記条件(1)において、「t×L4/(a×b3)」は、圧力室形成基板16において両端が固定された梁として機能する隔壁30の高さ方向(縦方向)の強度を表す式(以下、適宜、縦強度計算式と称する)である。この縦強度計算式において、隔壁30の高さbが3乗、可動領域の長さLが4乗であるため、隔壁30の縦方向の強度を確保する上では、特に、可動領域の長さLをより短く、隔壁30の高さbをより低くすることが有効である。
In view of the above problems, in the printer 1 according to the present invention, the occurrence of deformation of the pressure
t × L 4 / (a × b 3 ) ≦ 5 × 10 5 (1)
In the above condition (1), “t × L 4 / (a × b 3 )” indicates the strength in the height direction (longitudinal direction) of the
図10は、上記寸法及び形状が異なる複数の記録ヘッド(圧電デバイス)についての隔壁30の縦方向の強度と隔壁30の先端面のばらつき(以下、適宜、隔壁段差と称する)との関係について説明するグラフである。同図において横軸が、隔壁30の縦方向の強度を表す上記縦強度計算式の算出値を示し、縦軸が、隔壁段差〔nm〕を示している。なお、隔壁段差は、図9に示されるように、圧力室形成基板16の圧力室並設方向における両端を通る仮想面(図9においてPvで示される高さの面)から各隔壁30の先端面までの高さ(仮想面Pvの法線方向の距離)の最大値と最小値の差Δdで表される。
FIG. 10 illustrates the relationship between the vertical strength of the
図10に示されるように、縦強度計算式の値がある一定の値を超えると、隔壁30の縦方向の強度が低下して隔壁段差が著しく大きくなる。ここで、隔壁30の先端面に接着剤21が転写により塗布されて連通基板15が接合される場合において、接着剤21の厚みを極端に厚くすることなく、すなわち、圧力室26等の流路側への接着剤21のはみ出しを抑えつつ、接合不良の発生を抑制するためには、隔壁段差が200〔nm〕以下であることが望ましい。そして、隔壁段差が200〔nm〕以下となるためには、縦強度の値が5×105以下である必要がある。同図に示されるように、縦強度の値が5×105を超えると、隔壁段差が200〔nm〕よりも大きくなり、これにより接合不良が発生する可能性が高くなる。
As shown in FIG. 10, when the value of the longitudinal strength calculation formula exceeds a certain value, the strength in the longitudinal direction of the
上記条件(1)が成立するように各寸法を設定することにより、隔壁30の縦方向の強度が確保されるので、圧力室形成基板16の変形が抑制される。これにより、隔壁30の先端面の位置のばらつきが抑制されるので、圧力室形成基板16の他方の面に連通基板15が接着剤21により接合される際の接合不良が低減される。その結果、圧電デバイス13の歩留まりが向上し、また、信頼性も向上する。特に、本実施形態においては、弾性膜17がシリコンの熱酸化により形成されているため圧縮応力(残留応力)を有しており、この状態で異方性エッチングにより圧力室26が形成された際においても、弾性膜17の圧縮応力が開放されることによる圧力室形成基板16の変形を抑制することができるので、好適である。そして、接合不良を抑制するための接着剤21の厚みを抑えることができるので、圧力室26等の流路への接着剤21のはみ出し(流れ出し)を低減することが可能となる。これにより、流路側へ流れ出した接着剤21が弾性膜17の可動領域に付着することによる当該可動領域の変位特性に悪影響を及ぼすことが抑制される。
このような圧電デバイス13を採用する記録ヘッド3では、接着が不十分な箇所からのインクの漏出リスクが低減される。また、接着剤21の流れ出しに起因する可動領域の変位特性のばらつきが抑制されるので、各ノズル27の噴射特性のばらつきを抑制することが可能となる。さらに、このような記録ヘッド3を備えるプリンター1では、信頼性が向上する。
By setting the dimensions so that the above condition (1) is satisfied, the vertical strength of the
In the
ところで、条件(1)が成立する場合においても、圧力室並設方向における隔壁30の強度(横方向の強度)によっては、インクの噴射の際に圧力室26内に生じる圧力変動によって隔壁30が変形することによりノズル27から噴射されるインクの量や飛翔速度などの噴射特性が変動する、つまり、隣接する空間において可動領域が駆動した際の駆動特性について影響し合ういわゆるクロストークが発生するおそれがある。
この観点から、本発明に係るプリンター1においては、さらに以下の条件(2)を満たすように各寸法が設定されている。
t×b4/(a×L3)≦1.2×10−3…(2)
上記条件(2)において、「t×b4/(a×L3)」は、圧力室形成基板16において両端が固定された梁として機能する隔壁30の横方向(圧力室並設方向)の強度を表す式(以下、適宜、横強度計算式と称する)である。
By the way, even when the condition (1) is satisfied, depending on the strength (lateral strength) of the
From this viewpoint, in the printer 1 according to the present invention, the dimensions are set so as to further satisfy the following condition (2).
t × b 4 / (a × L 3 ) ≦ 1.2 × 10 −3 (2)
In the above condition (2), “t × b 4 / (a × L 3 )” is the horizontal direction (pressure chamber side-by-side direction) of the
図11は、隔壁30の横方向における強度と、クロストーク率との関係を示すグラフである。ここで、クロストーク率とは、同一ノズル列に属する複数の隣接するノズル27からインクを同時に噴射させた場合(全ON時)のインクの飛翔速度Vmaと、1つのノズル27から単独でインクを噴射させた場合(1ON時)のインク飛翔速度Vmsとの比率で表される噴射特性の変化の度合いであり、以下の式(CT)で表される。
クロストーク率=1−Vms/Vma …(CT)
例えば、Vma=10〔m/s〕、Vms=8〔m/s〕であったとき、クロストーク率は0.2となる。プリンター1において、記録媒体2に画像等を記録する場合、特に、より高解像度の画像を記録する場合、このクロストーク率が0.15未満であることが求められる。クロストーク率が0.15を超えると、ノズル27から噴射されたインクの記録媒体2における目標とする位置からの着弾位置ずれが顕著になり、記録画像等においていわゆる粒状感などのように視覚的な粗さが目立ってしまうからである。
FIG. 11 is a graph showing the relationship between the strength in the lateral direction of the
Crosstalk rate = 1−Vms / Vma (CT)
For example, when Vma = 10 [m / s] and Vms = 8 [m / s], the crosstalk rate is 0.2. When the printer 1 records an image or the like on the
したがって、上記条件(2)が成立するように各寸法を設定することにより、隔壁30の横方向(圧力室並設方向)の強度が確保されるので、ノズル27からインクを噴射させるべく圧電素子18が駆動されて圧力室26内に圧力変動が生じたときに、隔壁30が変位することが抑制される。その結果、上記クロストークが抑制される。すなわち、噴射特性(ノズル27から噴射されるインクの量や飛翔速度)の変動が抑制される。
Therefore, by setting the dimensions so that the above condition (2) is satisfied, the strength in the lateral direction of the partition wall 30 (the direction in which the pressure chambers are arranged side by side) is secured. Displacement of the
図12は、縦強度及び横強度に応じた隔壁段差及びクロストーク(CT)の発生について示した表である。同図において太枠で囲まれた部分は、縦強度及び横強度がそれぞれ上記条件(1)及び条件(2)を満たす範囲を示している。また、隔壁段差について「〇」は隔壁段差が殆ど生じていないことを示し、「△」は200〔nm〕以下の段差が生じていることを示し、「×」は200〔nm〕を超える段差が生じていることを示している。さらに、クロストークについて「〇」はクロストークが殆ど生じていない(例えば、クロストーク率が0.1未満である)ことを示し、「△」はクロストークが生じているが許容範囲内である(例えば、クロストーク率が0.1以上、0.15以下である)ことを示している。そして、隔壁30の幅a、可動領域の長さL、及び、弾性膜17の膜厚tについては上記排除堆積が所定値となるような値で固定され、隔壁30の高さbのみが変更されることで縦強度及び横強度の値が変えられている。
FIG. 12 is a table showing the partition wall level difference and the occurrence of crosstalk (CT) according to the vertical strength and the horizontal strength. In the figure, the portion surrounded by a thick frame indicates a range in which the longitudinal strength and the lateral strength satisfy the above condition (1) and the condition (2), respectively. In addition, “◯” indicates that there is almost no partition wall level difference, “Δ” indicates that a level difference of 200 nm or less is generated, and “X” indicates a level difference exceeding 200 nm. Indicates that this has occurred. Further, for crosstalk, “◯” indicates that almost no crosstalk has occurred (for example, the crosstalk rate is less than 0.1), and “Δ” indicates that crosstalk has occurred but is within an allowable range. (For example, the crosstalk rate is 0.1 or more and 0.15 or less). The width a of the
図12に示されるように、条件(1)が成立すれば、隔壁段差及びクロストークのいずれも「△」又は「〇」となり、隔壁段差の抑制とクロストークの抑制を概ね両立させることができるが、隔壁段差及びクロストークの両方が「〇」となるようにするには、さらに以下の条件(3)又は条件(4)を満たせばよい。
1.2×105≦t×L4/(a×b3)≦1.6×105 …(3)
5.9×10−4≦t×b4/(a×L3)≦8.6×10−3…(4)
これにより、隔壁段差の抑制とクロストークの抑制とをより効果的に両立させることが可能となる。
As shown in FIG. 12, when the condition (1) is satisfied, both the partition wall step and the crosstalk are “Δ” or “◯”, and both the suppression of the partition wall step and the suppression of the crosstalk can be achieved. However, the following condition (3) or condition (4) may be further satisfied so that both of the partition wall step and the crosstalk become “◯”.
1.2 × 10 5 ≦ t × L 4 / (a × b 3 ) ≦ 1.6 × 10 5 (3)
5.9 × 10 −4 ≦ t × b 4 / (a × L 3 ) ≦ 8.6 × 10 −3 (4)
As a result, it is possible to more effectively achieve both the suppression of the partition wall step and the suppression of crosstalk.
ところで、本発明は、上記した実施形態に限定されるものではなく、特許請求の範囲の記載に基づいて種々の変形が可能である。 By the way, the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and various modifications can be made based on the description of the scope of claims.
図13は、本発明の第2の実施形態における圧力室形成基板40の平面図である。上記第1の実施形態においては、圧力室26の上部開口の周囲が圧力室形成基板16の隔壁30を含む構造壁により途切れることなく囲まれた構成を例示したが、これには限られない。本実施形態における圧力室形成基板40には、本発明における空間に相当する圧力室41が本発明における壁に相当する隔壁42で隔てられて複数並設されている他、各圧力室41に共通な共通液室44、及び、当該共通液室44と各圧力室41とを連通させる個別連通口43が形成されている。このため、圧力室41の上部開口は、隔壁42を含む圧力室形成基板40の構造壁により全周を閉じられておらず、個別連通口43に対応する部分で開いている。このような構成においても上記第1の実施形態の構成と同様に本発明を適用することができる。すなわち、圧力室41の並設方向における隔壁42の幅をa、隔壁42の高さをb、圧力室形成基板40の一方の面に設けられた弾性膜(区画部材)の可動領域の長さをL、弾性膜の厚さをtとして、上記各条件(1)〜(4)が成立するように各寸法を設定すれば、上記第1の実施形態の構成と同様の作用効果を奏し得る。なお、他の構成については第1の実施形態と同様である。
FIG. 13 is a plan view of the pressure
図14は、第3の実施形態における電子デバイスの一種である超音波センサー60を備える超音波診断装置51の構成を示す図である。また、図15は、本実施形態に係る超音波センサー60の一例を示す平面図、図16は超音波センサー60の行方向(図15における横方向)における要部断面図である。上記各実施形態においては、可動領域が変位することでノズルから液体の一種であるインクを噴射させる構成を例示したが、これには限られず、本実施形態における超音波センサー60のように、可動領域の振動(変位)等を検出するセンサー等にも本発明を適用することができる。このため、本発明における空間は、液体が流通するものには限られない。
FIG. 14 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of an ultrasonic
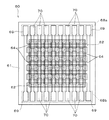
図14に示される超音波診断装置51は、装置端末52と超音波プローブ53とを備える。装置端末52と超音波プローブ53とはケーブル54で相互に接続されている。装置端末52と超音波プローブ53とはケーブル54を通じて電気信号を送受する。超音波プローブ53は、本体部55と、この本体部55に着脱可能に取り付けられたプローブヘッド56と、を備えている。そして、プローブヘッド56に超音波センサー60が設けられている。超音波センサー60は、表面(図15に示される面)から音波(超音波)を測定対象に向けて発信するとともに、測定対象からの反射波を受信することにより、測定対象までの距離や測定対象の形状等の検知を行う。本実施形態における超音波センサー60は、基体61に素子アレイ62が形成されて構成されている。素子アレイ62は、圧電素子64の配列で構成されている。配列は複数行・複数列のマトリクス状に形成されている。図16に示されるように、圧電素子64は、上部電極65、下部電極66、及び圧電体膜67で構成され、上部電極65と下部電極66との間に圧電体膜67が挟み込まれている。本実施形態においては上部電極65が各圧電素子64に共通の共通電極として機能し、下部電極66が各圧電素子64のそれぞれの個別電極として機能する。なお、上部電極65及び下部電極66の機能は入れ替えられてもよい。すなわち、マトリクス全体の圧電素子64に下部電極が共通に設けられる一方、各圧電素子64に上部電極が個別に設けられてもよい。また、素子アレイ62の配列に関し、例えば、隣り合う列の圧電素子64の列方向の位置が互い違いとなるような構成を採用することもできる。この場合、偶数列の圧電素子64群は、奇数列の圧電素子64群に対して行ピッチの2分の1で列方向にずらされて配置される構成とすることができる。
An ultrasonic
基体61において、圧電素子64の列方向における一端側と他端側であって、素子アレイ62から外れた位置に、それぞれ第1端子アレイ68a及び第2端子アレイ68bが形成されている。各端子アレイ68a,68bは、それぞれ、行方向の両側に配置された1対の共通電極端子69と、両側の共通電極端子69の間に配置された複数の個別電極端子70とで構成されている。共通電極端子69は、圧電素子64の上部電極65に導通され、個別電極端子70は、圧電素子64の下部電極66にそれぞれ導通されている。各端子アレイ68a,68bには、一端が超音波診断装置51の図示しない制御回路と接続された図示しないフレキシブル配線基板が電気的に接続される。当該フレキシブル配線基板を通じて制御回路と超音波センサー60との間で、後述するように駆動信号VDR及び受信信号VRの送受信が行われる。
In the
図16に示されるように、基体61は、基板72及び可撓膜73(本発明における区画部材の一種)を互いに積層した状態で備えている。より具体的には、基板72の一方の面に可撓膜73が一面に形成される。この基板72には、各圧電素子64にそれぞれ対応して複数の空部74(本発明における空間の一種)が隔壁75(本発明における壁の一種)により区画形成されている。すなわち、空部74は、基板72に対してアレイ状に配置されており、隣接する2つの空部74の間に隔壁75が配置されている。そして、可撓膜73における空部74の上部開口に対応する部分が、可動領域78として機能する。可動領域78は、可撓膜73のうち、空部74の一部(天井面)を区画して基板72の厚み方向に振動(変位)することができる部分である。本実施形態において、基板72と可撓膜73とは一体的に形成されている。より具体的には、基板72の母材であるシリコン基板の一方の面が熱酸化されることによりシリコン酸化膜(SiO2)が形成され、また、当該シリコン基板の他方の面からシリコン酸化膜に至るまで異方性エッチング処理が施されて空部74が形成され、残ったシリコン酸化膜が可撓膜73として機能する。なお、可撓膜73には、図示しない絶縁体膜が積層されている。そして、この可動領域78の表面(空部74側の面とは反対側の面)に下部電極66、圧電体膜67及び上部電極65が順番に積層されて圧電素子64が配設されている。
As shown in FIG. 16, the
基体61の裏面(可撓膜73側とは反対側の面)には、補強板76が接着剤80により接合されている。補強板76は超音波センサー60の裏面で空部74を閉じている。この補強板76としては、例えばシリコン基板を用いることができる。
A reinforcing
上記超音波センサー60において、超音波を発信する発信期間(振動期間)には、制御回路が出力する駆動信号VDRが、個別電極端子70を介して各圧電素子64の下部電極66に供給(印加)される。また、超音波の反射波(エコー)を受信する受信期間(振動期間)には、圧電素子64からの受信信号VRが、下部電極66及び個別電極端子70を介して出力される。また、共通電極端子69を介して各圧電素子64の上部電極65には、共通電圧VCOMが供給される。この共通電圧VCOMは一定の直流電圧である。駆動信号VDRと共通電圧VCOMとの差の電圧が各圧電素子64に印加されると、当該圧電素子64からは所定の周波数の超音波が発信される。そして、全圧電素子64からそれぞれ放射される超音波が合成されて、超音波センサー60の素子アレイ面から放射される超音波が形成される。この超音波は、測定対象(例えば人体の内部)に向けて発信される。また、超音波が発信された後、測定対象から反射されてきた反射波が圧電素子64に入力されると、これに応じて当該圧電素子64が検知用振動部として振動することにより起電力が生じる。この起電力は受信信号VRとして制御回路に出力される。本実施形態において、検知用振動部として機能する圧電素子群は、音波の発信と反射波の受信とを、時間を異ならせて交互に行う。
In the
上記第1の実施形態と同様に、製造工程において基板72に変形や歪みが生じた場合、接合される面(基板72の補強板76との接合面)の位置がばらついて、接合不良や可動領域78の変位量のばらつきが生じるおそれがある。このため、本実施形態における隔壁75の幅をa、隔壁75の高さをb、可動領域78の可動領域の長尺方向の長さをL、及び、可動領域78の膜厚tとして、上記各条件(1)〜(4)が成立するように各寸法を設定すれば、上記第1の実施形態の構成と同様の作用効果を奏し得る。すなわち、基板72の変形が抑制されるので、基板72の他方の面に補強板76が接着剤80により接合される際の接合不良が低減される。その結果、圧電デバイスである超音波センサー60の歩留まりが向上し、また、信頼性も向上する。そして、接合不良を抑制するための接着剤80の厚みを抑えることができるので、空部74側への接着剤80のはみ出し(流れ出し)を低減することが可能となる。これにより、空部74側へ流れ出した接着剤80が可動領域78に付着することによる当該可動領域78の変位特性(振動特性)に悪影響を及ぼすことが抑制される。さらに、隔壁75の強度が確保されるので、圧電素子64及び可動領域78の振動の際に、隔壁75が変位することが抑制される。その結果、いわゆる隣接クロストークによる可動領域78の振動特性(発信特性・受信特性)の変動が抑制される。
As in the first embodiment, when deformation or distortion occurs in the
なお、区画部材が有する残留応力としては圧縮応力に限られず、成膜方法によっては区画部材が引張応力を有する場合もあり、このような構成においても本発明を適用することができる。これにより、引張応力に起因する基板の変形を抑制することが可能となる。 The residual stress of the partition member is not limited to compressive stress, and the partition member may have tensile stress depending on the film forming method, and the present invention can be applied to such a configuration. Thereby, it becomes possible to suppress the deformation | transformation of the board | substrate resulting from a tensile stress.
さらに、本発明によれば、基板とこれに接合される他の部材(他の基材)とがそれぞれ残留応力(圧縮応力又は引張応力を問わず)を有する構成においても適用することができる。これにより、これらの残留応力の相違に起因する基板の変形を抑制することが可能となる。 Furthermore, according to the present invention, the present invention can also be applied to a configuration in which a substrate and other members (other base materials) bonded thereto have residual stresses (regardless of compressive stress or tensile stress). Thereby, it is possible to suppress the deformation of the substrate due to the difference in these residual stresses.
そして、上記第1の実施形態においては、液体噴射ヘッドとしてインクジェット式記録ヘッド3を例に挙げて説明したが、本発明は、複数の基板が接着剤により接合されることで空間が壁を隔てて複数形成され、空間の一部が可動領域を有する区画部材により区画された構成を採用する他の液体噴射ヘッドにも適用することができる。例えば、液晶ディスプレイ等のカラーフィルターの製造に用いられる色材噴射ヘッド、有機EL(Electro Luminescence)ディスプレイ、FED(面発光ディスプレイ)等の電極形成に用いられる電極材噴射ヘッド、バイオチップ(生物化学素子)の製造に用いられる生体有機物噴射ヘッド等にも本発明を適用することができる。ディスプレイ製造装置用の色材噴射ヘッドでは液体の一種としてR(Red)・G(Green)・B(Blue)の各色材の溶液を噴射する。また、電極形成装置用の電極材噴射ヘッドでは液体の一種として液状の電極材料を噴射し、チップ製造装置用の生体有機物噴射ヘッドでは液体の一種として生体有機物の溶液を噴射する。
In the first embodiment, the ink
1…プリンター,2…記録媒体,3…記録ヘッド,4…キャリッジ,5…キャリッジ移動機構,6…プラテンローラー,7…インクカートリッジ,8…タイミングベルト,9…パルスモーター,10…ガイドロッド,13…圧電デバイス,14…ノズルプレート,15…連通基板,16…圧力室形成基板,17…弾性膜,18…圧電素子,19…保護基板,20…ケース,21…接着剤,22…収容空部,23…インク導入路,24…共通液室,26…圧力室,27…ノズル,28…ノズル連通口,29…個別連通口,30…隔壁,32…下電極層,33…圧電体層,34…上電極層,35…錘層,36…開口,40…圧力室形成基板,41…圧力室,42…隔壁,43…個別連通口,44…共通液室,51…超音波診断装置,52…端末装置,53…超音波プローブ,54…ケーブル,55…本体部,56…プローブヘッド,60…超音波センサー,61…基体,62…素子アレイ,64…圧電素子,65…上部電極,66…下部電極,67…圧電体膜,68…端子アレイ,69…共通電極端子,70…個別電極端子,72…基板,73…可撓膜,74…空部,75…隔壁,76…補強板,78…可動領域,80…接着剤 DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1 ... Printer, 2 ... Recording medium, 3 ... Recording head, 4 ... Carriage, 5 ... Carriage moving mechanism, 6 ... Platen roller, 7 ... Ink cartridge, 8 ... Timing belt, 9 ... Pulse motor, 10 ... Guide rod, 13 DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS ... Piezoelectric device, 14 ... Nozzle plate, 15 ... Communication substrate, 16 ... Pressure chamber forming substrate, 17 ... Elastic film, 18 ... Piezoelectric element, 19 ... Protective substrate, 20 ... Case, 21 ... Adhesive, 22 ... Housing space , 23 ... Ink introduction path, 24 ... Common liquid chamber, 26 ... Pressure chamber, 27 ... Nozzle, 28 ... Nozzle communication port, 29 ... Individual communication port, 30 ... Bulkhead, 32 ... Lower electrode layer, 33 ... Piezoelectric layer, 34 ... upper electrode layer, 35 ... weight layer, 36 ... opening, 40 ... pressure chamber forming substrate, 41 ... pressure chamber, 42 ... partition wall, 43 ... individual communication port, 44 ... common liquid chamber, 51 ... ultrasonic diagnostic device, 52 ... Terminal equipment , 53 ... ultrasonic probe, 54 ... cable, 55 ... main body, 56 ... probe head, 60 ... ultrasonic sensor, 61 ... substrate, 62 ... element array, 64 ... piezoelectric element, 65 ... upper electrode, 66 ... lower electrode , 67 ... Piezoelectric film, 68 ... Terminal array, 69 ... Common electrode terminal, 70 ... Individual electrode terminal, 72 ... Substrate, 73 ... Flexible film, 74 ... Empty part, 75 ... Bulkhead, 76 ... Reinforcing plate, 78 ... Movable region, 80 ... adhesive
Claims (7)
前記基板の一方の面において隣り合う前記壁を跨いで前記空間の一部を区画する区画部材と、
前記区画部材の前記空間側とは反対側に、前記空間毎に対応させて形成された圧電素子と、
を備え、
前記空間の並設方向における前記壁の幅をa、前記一方の面から当該一方の面とは反対側の他方の面までの前記壁の高さをb、前記区画部材の厚さをt、前記区画部材における変位可能な可動領域の長手方向の寸法をLとして、
t×L4/(a×b3)≦5×105
を満たすことを特徴とする圧電デバイス。 A substrate in which a plurality of spaces are arranged side by side with a wall;
A partition member that partitions a part of the space across the adjacent walls on one surface of the substrate;
A piezoelectric element formed corresponding to each space on the side opposite to the space side of the partition member;
With
The width of the wall in the parallel arrangement direction of the space is a, the height of the wall from the one surface to the other surface opposite to the one surface is b, the thickness of the partition member is t, The dimension in the longitudinal direction of the movable region that can be displaced in the partition member is L,
t × L 4 / (a × b 3 ) ≦ 5 × 10 5
A piezoelectric device characterized by satisfying
を満たすことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の圧電デバイス。 Furthermore, 1.2 × 10 5 ≦ t × L 4 / (a × b 3 ) ≦ 1.6 × 10 5
The piezoelectric device according to claim 1, wherein:
を満たすことを特徴とする請求項1又は請求項2に記載の圧電デバイス。 t × b 4 / (a × L 3 ) ≦ 1.2 × 10 −3
The piezoelectric device according to claim 1 or 2, wherein:
前記区画部材が、前記母材の熱酸化により形成されたシリコン酸化膜であることを特徴とする請求項4に記載の圧電デバイス。 The base material of the wall is silicon;
The piezoelectric device according to claim 4, wherein the partition member is a silicon oxide film formed by thermal oxidation of the base material.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/923,891 US20180287046A1 (en) | 2017-03-29 | 2018-03-16 | Piezoelectric device, liquid ejecting head, and liquid ejecting apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017064532 | 2017-03-29 | ||
| JP2017064532 | 2017-03-29 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2018167576A true JP2018167576A (en) | 2018-11-01 |
| JP2018167576A5 JP2018167576A5 (en) | 2021-01-07 |
Family
ID=64018351
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017247345A Withdrawn JP2018167576A (en) | 2017-03-29 | 2017-12-25 | Piezoelectric device, liquid injection head, and liquid injection device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2018167576A (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11427000B2 (en) | 2020-04-22 | 2022-08-30 | Brother Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Liquid discharge head |
| US11485138B2 (en) | 2020-04-22 | 2022-11-01 | Brother Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Liquid discharge head |
| US11535033B2 (en) | 2019-12-26 | 2022-12-27 | Brother Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Liquid discharge head having a common flow channel and a plurality of individual flow channels, and liquid discharge device having the liquid discharge head |
| US11565526B2 (en) | 2020-04-30 | 2023-01-31 | Brother Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Liquid discharging head |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1998018632A1 (en) * | 1996-10-28 | 1998-05-07 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Ink jet recording head |
| JPH10181010A (en) * | 1995-11-24 | 1998-07-07 | Seiko Epson Corp | Ink-jet printer head and its manufacture |
| WO2001074590A1 (en) * | 2000-03-31 | 2001-10-11 | Fujitsu Limited | Multinozzle ink-jet head |
| JP2008087471A (en) * | 2006-09-08 | 2008-04-17 | Canon Inc | Liquid discharge head and its manufacturing method |
| JP2015157395A (en) * | 2014-02-24 | 2015-09-03 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Liquid ejection head and liquid ejection device |
| EP3072693A1 (en) * | 2015-03-23 | 2016-09-28 | Brother Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Piezoelectric actuator and recording head |
-
2017
- 2017-12-25 JP JP2017247345A patent/JP2018167576A/en not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH10181010A (en) * | 1995-11-24 | 1998-07-07 | Seiko Epson Corp | Ink-jet printer head and its manufacture |
| WO1998018632A1 (en) * | 1996-10-28 | 1998-05-07 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Ink jet recording head |
| WO2001074590A1 (en) * | 2000-03-31 | 2001-10-11 | Fujitsu Limited | Multinozzle ink-jet head |
| JP2008087471A (en) * | 2006-09-08 | 2008-04-17 | Canon Inc | Liquid discharge head and its manufacturing method |
| JP2015157395A (en) * | 2014-02-24 | 2015-09-03 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Liquid ejection head and liquid ejection device |
| EP3072693A1 (en) * | 2015-03-23 | 2016-09-28 | Brother Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Piezoelectric actuator and recording head |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11535033B2 (en) | 2019-12-26 | 2022-12-27 | Brother Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Liquid discharge head having a common flow channel and a plurality of individual flow channels, and liquid discharge device having the liquid discharge head |
| US11427000B2 (en) | 2020-04-22 | 2022-08-30 | Brother Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Liquid discharge head |
| US11485138B2 (en) | 2020-04-22 | 2022-11-01 | Brother Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Liquid discharge head |
| US11565526B2 (en) | 2020-04-30 | 2023-01-31 | Brother Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Liquid discharging head |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4258668B2 (en) | Liquid ejecting head and liquid ejecting apparatus | |
| US20180287046A1 (en) | Piezoelectric device, liquid ejecting head, and liquid ejecting apparatus | |
| JP4450238B2 (en) | Liquid ejecting head and liquid ejecting apparatus | |
| US11390079B2 (en) | MEMS device, liquid ejecting head, liquid ejecting apparatus, manufacturing method of MEMS device, manufacturing method of liquid ejecting head, and manufacturing method of liquid ejecting apparatus | |
| JP2018167576A (en) | Piezoelectric device, liquid injection head, and liquid injection device | |
| JP5115330B2 (en) | Liquid ejecting head and liquid ejecting apparatus including the same | |
| JP2015150713A (en) | Liquid ejection head and liquid ejection device | |
| US10964877B2 (en) | Piezoelectric element, piezoelectric actuator, ultrasonic probe, ultrasonic apparatus, electronic apparatus, liquid jet head, and liquid jet apparatus | |
| JP4594262B2 (en) | Dispensing device | |
| JP6728718B2 (en) | MEMS device and liquid jet head | |
| JP2011029305A (en) | Piezoelectric actuator and liquid ejecting head | |
| JP2016185600A (en) | Ink jet head and ink jet printer | |
| JP2012179785A (en) | Liquid ejecting head and liquid ejecting device | |
| JP2009018551A (en) | Actuator, liquid jet head and liquid jet apparatus | |
| JP6418311B2 (en) | Actuators and sensors | |
| JP6273893B2 (en) | Liquid ejecting head and liquid ejecting apparatus | |
| JP6417740B2 (en) | Liquid ejecting head and manufacturing method of liquid ejecting head | |
| JP6256101B2 (en) | Liquid ejecting head and liquid ejecting apparatus | |
| JP6152679B2 (en) | Liquid ejecting head and liquid ejecting apparatus | |
| JP7059656B2 (en) | Liquid discharge heads, liquid discharge devices, and piezoelectric devices | |
| JP6172437B2 (en) | Liquid ejecting head and liquid ejecting apparatus | |
| JP2010069688A (en) | Liquid jetting head and liquid jetting apparatus | |
| JP5151844B2 (en) | Droplet ejection head, droplet discharge device, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2012218251A (en) | Liquid jet head, and liquid jet apparatus | |
| JP2012218186A (en) | Liquid jetting head and liquid jetting device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD05 | Notification of revocation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7425 Effective date: 20180906 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20181119 |
|
| RD07 | Notification of extinguishment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7427 Effective date: 20200803 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20201119 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20201119 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20210915 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20211014 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20211019 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20211108 |
|
| A761 | Written withdrawal of application |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A761 Effective date: 20211220 |