JP2016514007A - 強化された軸線方向疲労特性を有するポリマースキャフォールド - Google Patents
強化された軸線方向疲労特性を有するポリマースキャフォールド Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2016514007A JP2016514007A JP2016500108A JP2016500108A JP2016514007A JP 2016514007 A JP2016514007 A JP 2016514007A JP 2016500108 A JP2016500108 A JP 2016500108A JP 2016500108 A JP2016500108 A JP 2016500108A JP 2016514007 A JP2016514007 A JP 2016514007A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- scaffold
- radial
- tube
- diameter
- axial
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F2/00—Filters implantable into blood vessels; Prostheses, i.e. artificial substitutes or replacements for parts of the body; Appliances for connecting them with the body; Devices providing patency to, or preventing collapsing of, tubular structures of the body, e.g. stents
- A61F2/82—Devices providing patency to, or preventing collapsing of, tubular structures of the body, e.g. stents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F2/00—Filters implantable into blood vessels; Prostheses, i.e. artificial substitutes or replacements for parts of the body; Appliances for connecting them with the body; Devices providing patency to, or preventing collapsing of, tubular structures of the body, e.g. stents
- A61F2/82—Devices providing patency to, or preventing collapsing of, tubular structures of the body, e.g. stents
- A61F2/86—Stents in a form characterised by the wire-like elements; Stents in the form characterised by a net-like or mesh-like structure
- A61F2/90—Stents in a form characterised by the wire-like elements; Stents in the form characterised by a net-like or mesh-like structure characterised by a net-like or mesh-like structure
- A61F2/91—Stents in a form characterised by the wire-like elements; Stents in the form characterised by a net-like or mesh-like structure characterised by a net-like or mesh-like structure made from perforated sheet material or tubes, e.g. perforated by laser cuts or etched holes
- A61F2/915—Stents in a form characterised by the wire-like elements; Stents in the form characterised by a net-like or mesh-like structure characterised by a net-like or mesh-like structure made from perforated sheet material or tubes, e.g. perforated by laser cuts or etched holes with bands having a meander structure, adjacent bands being connected to each other
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C55/00—Shaping by stretching, e.g. drawing through a die; Apparatus therefor
- B29C55/22—Shaping by stretching, e.g. drawing through a die; Apparatus therefor of tubes
- B29C55/26—Shaping by stretching, e.g. drawing through a die; Apparatus therefor of tubes biaxial
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F2/00—Filters implantable into blood vessels; Prostheses, i.e. artificial substitutes or replacements for parts of the body; Appliances for connecting them with the body; Devices providing patency to, or preventing collapsing of, tubular structures of the body, e.g. stents
- A61F2/82—Devices providing patency to, or preventing collapsing of, tubular structures of the body, e.g. stents
- A61F2/86—Stents in a form characterised by the wire-like elements; Stents in the form characterised by a net-like or mesh-like structure
- A61F2/90—Stents in a form characterised by the wire-like elements; Stents in the form characterised by a net-like or mesh-like structure characterised by a net-like or mesh-like structure
- A61F2/91—Stents in a form characterised by the wire-like elements; Stents in the form characterised by a net-like or mesh-like structure characterised by a net-like or mesh-like structure made from perforated sheet material or tubes, e.g. perforated by laser cuts or etched holes
- A61F2/915—Stents in a form characterised by the wire-like elements; Stents in the form characterised by a net-like or mesh-like structure characterised by a net-like or mesh-like structure made from perforated sheet material or tubes, e.g. perforated by laser cuts or etched holes with bands having a meander structure, adjacent bands being connected to each other
- A61F2002/9155—Adjacent bands being connected to each other
- A61F2002/91575—Adjacent bands being connected to each other connected peak to trough
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C2793/00—Shaping techniques involving a cutting or machining operation
- B29C2793/0009—Cutting out
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C49/00—Blow-moulding, i.e. blowing a preform or parison to a desired shape within a mould; Apparatus therefor
- B29C49/08—Biaxial stretching during blow-moulding
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29L—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS B29C, RELATING TO PARTICULAR ARTICLES
- B29L2031/00—Other particular articles
- B29L2031/753—Medical equipment; Accessories therefor
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29L—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS B29C, RELATING TO PARTICULAR ARTICLES
- B29L2031/00—Other particular articles
- B29L2031/753—Medical equipment; Accessories therefor
- B29L2031/7542—Catheters
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T29/00—Metal working
- Y10T29/49—Method of mechanical manufacture
- Y10T29/49826—Assembling or joining
- Y10T29/49863—Assembling or joining with prestressing of part
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- Transplantation (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Prostheses (AREA)
- Materials For Medical Uses (AREA)
- Media Introduction/Drainage Providing Device (AREA)
Abstract
Description
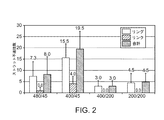
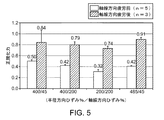
RE%=[(延伸チューブ内径)/(前駆体内径)−1]×100
AE%=[(延伸チューブ長さ)/(前駆体チューブ長さ)−1]×100
204 セル
207、209、210、307、309、310 冠部
212、312 リング
230、330 ストラット
234、334 リンク
363 ストラット幅、リンク幅
364 ストラット長
Claims (18)
- 末梢血管に埋め込まれる医療装置であって、
2軸延伸されるポリマーチューブから形成されるバルーン拡張スキャフォールドを備え、
前記チューブは、約2と1の間の半径方向延伸対軸線方向延伸の比に起因する好ましい配向を有するポリマー鎖を備えるモフォロジを有し;
リンクによって相互接続されるリングのネットワークを形成する前記スキャフォールドは、
リング当たり8又は12、又は8と12の間の冠部と、
隣接するリングの実質的にすべてのペアを接続する最大でも2つのリンクと、
を含み、
前記スキャフォールドのいずれのリングに対しても、リンクに接続される各冠部の各側部に、等しい数の支持されていない冠部が存在する、
医療装置。 - 前記スキャフォールドは前記バルーンにクリンプされる、
請求項1に記載の医療装置。 - 前記スキャフォールドは、前記バルーンの公称バルーン直径又は膨張後バルーン直径よりも2.0、2.5、又は3.0倍小さいクリンプ直径を有する、
請求項1又は請求項2による医療装置。 - 前記スキャフォールドは、前記バルーンの膨張直径よりも1.0、1.1、1.3、又は1.5倍大きい直径を有するチューブから形成される、
請求項1乃至請求項3のいずれか1項による医療装置。 - スキャフォールドのクリンプ前直径は5mmを超え、壁厚は0.2〜0.3mm(0.008インチと0.012インチの間)である、
請求項1乃至請求項4のいずれか1項による医療装置。 - 前記スキャフォールドの外径は5と7mmの間であり、壁厚は0.2〜0.3mm(0.008インチと0.012インチの間)である、
請求項1乃至請求項5のいずれか1項による医療装置。 - 前記スキャフォールドはクリンプ前直径を有し、前記スキャフォールドは、そのクリンプ前直径の少なくとも75%まで押し潰された後、そのクリンプ前直径の90%超を達成する、
請求項1乃至請求項6のいずれか1項による医療装置。 - 前記半径方向延伸量は約400であり、前記軸線方向延伸量は約200である、
請求項1乃至請求項7のいずれか1項による医療装置。 - 前記スキャフォールドの材料は、前記スキャフォールドの材料のための破損時における半径方向の伸び及び破損時における軸線方向の伸びの比が約1又は1未満であるようなものである、
請求項1乃至請求項8のいずれか1項による医療装置。 - 前記スキャフォールドはPLLAからできている、
請求項1乃至請求項9のいずれか1項による医療装置。 - 末梢血管に埋め込まれるスキャフォールドを製造する方法であって、
400/200と200/200の間のRE/AEの比に従ってポリマーチューブを2軸延伸することによって前記スキャフォールドのリコイルを低減するステップと;
リンクによって相互接続されるリングのネットワークを形成することを含む、前記2軸延伸チューブからスキャフォールドを形成するステップとを備える;
方法。 - 前記スキャフォールドは、そのクリンプ前直径の70%まで押し潰された後、そのクリンプ前直径の少なくとも80%、又は少なくとも90%を達成する、
請求項11に記載の方法。 - 末梢血管に埋め込まれるスキャフォールドを製造する方法であって:
チューブを2軸延伸するステップであって、前記チューブの半径方向対軸線方向延伸の量は、前記2軸延伸チューブ材料の前記半径方向での破損時における伸び及び前記軸線方向での破損時における伸びが約1又は1未満であるような量であるステップと;
リンクによって相互接続されるリングのネットワークを形成することを含む、前記2軸延伸チューブからスキャフォールドを形成するステップとを備える;
方法。 - 末梢血管に埋め込まれる医療装置であって:
2軸延伸されたポリマーチューブから形成されるバルーン拡張スキャフォールドを備え、前記2軸延伸チューブ材料が、約1又は1未満の破損時における半径方向の伸びと破損時における軸線方向の伸びの比を有し、
リンクによって相互接続されるリングのネットワークを形成する前記スキャフォールドは、
リング当たり8又は12の冠部と、
隣接するリングの実質的にすべてのペアを接続する最大でも2つのリンクと、を含み、前記スキャフォールドのいずれのリングに対しても、リンクに接続される各冠部の各側部に、等しい数の支持されていない冠部が存在する、
医療装置。 - 前記スキャフォールドのいずれのリングに対しても、リンクに接続される各冠部の各側部に、等しい数の支持されていない冠部が存在する、
請求項11に記載の方法。 - 請求項1乃至請求項10のいずれか1項と組み合わされる請求項14に記載の機器。
- 請求項1乃至請求項10のいずれか1項と組み合わされる請求項13に記載の方法。
- 請求項1乃至請求項15のいずれか1項で見出されるいずれかの特徴のいずれかの組み合わせ。
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/840,257 | 2013-03-15 | ||
| US13/840,257 US9662231B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2013-03-15 | Polymer scaffolds having enhanced axial fatigue properties |
| PCT/US2013/070947 WO2014149083A1 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2013-11-20 | Polymer scaffolds having enhanced axial fatigue properties |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2016514007A true JP2016514007A (ja) | 2016-05-19 |
| JP2016514007A5 JP2016514007A5 (ja) | 2017-01-19 |
Family
ID=49681238
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016500108A Pending JP2016514007A (ja) | 2013-03-15 | 2013-11-20 | 強化された軸線方向疲労特性を有するポリマースキャフォールド |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9662231B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2967940A1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP2016514007A (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN105188618B (ja) |
| HK (1) | HK1216497A1 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2014149083A1 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022107629A (ja) * | 2017-09-08 | 2022-07-22 | ゼウス カンパニー インコーポレイテッド | 制御された配向を有するポリマーチューブ |
Families Citing this family (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8128677B2 (en) | 2007-12-12 | 2012-03-06 | Intact Vascular LLC | Device and method for tacking plaque to a blood vessel wall |
| US9517150B2 (en) | 2012-10-23 | 2016-12-13 | Abbott Cardiovascular Systems Inc. | Time-dependent polymer scaffolds |
| EP3062832B1 (en) | 2013-10-29 | 2017-09-27 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Bioerodible magnesium alloy microstructures for endoprostheses |
| US9795497B2 (en) | 2014-09-18 | 2017-10-24 | Abbott Cardiovascular Systems Inc. | Thermal processing of polymer scaffolds |
| US9375336B1 (en) | 2015-01-29 | 2016-06-28 | Intact Vascular, Inc. | Delivery device and method of delivery |
| US9433520B2 (en) | 2015-01-29 | 2016-09-06 | Intact Vascular, Inc. | Delivery device and method of delivery |
| CA2973155A1 (en) * | 2015-03-11 | 2016-09-15 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Bioerodible magnesium alloy microstructures for endoprostheses |
| US10993824B2 (en) | 2016-01-01 | 2021-05-04 | Intact Vascular, Inc. | Delivery device and method of delivery |
| CN105902331A (zh) * | 2016-04-08 | 2016-08-31 | 南京永明医疗器械有限公司 | 一种血管支架及其制备方法 |
| WO2018226991A1 (en) | 2017-06-07 | 2018-12-13 | Shifamed Holdings, Llc | Intravascular fluid movement devices, systems, and methods of use |
| US11660218B2 (en) | 2017-07-26 | 2023-05-30 | Intact Vascular, Inc. | Delivery device and method of delivery |
| CN111556763B (zh) | 2017-11-13 | 2023-09-01 | 施菲姆德控股有限责任公司 | 血管内流体运动装置、系统 |
| EP4085965A1 (en) | 2018-02-01 | 2022-11-09 | Shifamed Holdings, LLC | Intravascular blood pumps and methods of use and manufacture |
| JP2022540616A (ja) | 2019-07-12 | 2022-09-16 | シファメド・ホールディングス・エルエルシー | 血管内血液ポンプならびに製造および使用の方法 |
| US11654275B2 (en) | 2019-07-22 | 2023-05-23 | Shifamed Holdings, Llc | Intravascular blood pumps with struts and methods of use and manufacture |
| CN112426612B (zh) * | 2019-08-26 | 2022-12-06 | 上海康德莱医疗器械股份有限公司 | 一种球囊及其制备和应用 |
| EP4034192A4 (en) | 2019-09-25 | 2023-11-29 | Shifamed Holdings, LLC | INTRAVASCULAR BLOOD PUMP SYSTEMS AND METHODS OF USE AND CONTROL THEREOF |
| WO2021062270A1 (en) | 2019-09-25 | 2021-04-01 | Shifamed Holdings, Llc | Catheter blood pumps and collapsible pump housings |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007313327A (ja) * | 2006-05-25 | 2007-12-06 | Cordis Corp | フープの選定された領域に、改変された分子構造を有するポリマーステント、および、破断点伸びを増大させる方法 |
| US20110073733A1 (en) * | 2010-07-29 | 2011-03-31 | John Hartelius | Slider clip and photovoltaic structure mounting system |
| US20110190871A1 (en) * | 2010-01-30 | 2011-08-04 | Abbott Cardiovascular Systems Inc. | Crush Recoverable Polymer Scaffolds |
| JP2011525137A (ja) * | 2008-06-20 | 2011-09-15 | アマランス メディカル プライベイト | チューブ鋳造プロセスによるステント作製 |
| JP2012517247A (ja) * | 2009-02-09 | 2012-08-02 | エビーシオ・メディカル・デバイセズ・ユーエルシー | ステント |
| WO2013003644A1 (en) * | 2011-06-30 | 2013-01-03 | Elixir Medical Corporation | Biodegradable endoprostheses and methods for their fabrication |
| JP2013504459A (ja) * | 2009-09-14 | 2013-02-07 | アボット カルディオバスキュラー システムズ インコーポレーテッド | 生体吸収性ステントの結晶モルフォロジの制御 |
Family Cites Families (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA2079417C (en) | 1991-10-28 | 2003-01-07 | Lilip Lau | Expandable stents and method of making same |
| US20070073384A1 (en) | 1995-03-01 | 2007-03-29 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Longitudinally flexible expandable stent |
| US20110066222A1 (en) | 2009-09-11 | 2011-03-17 | Yunbing Wang | Polymeric Stent and Method of Making Same |
| US7875233B2 (en) | 2004-09-30 | 2011-01-25 | Advanced Cardiovascular Systems, Inc. | Method of fabricating a biaxially oriented implantable medical device |
| US20100010622A1 (en) * | 2006-03-13 | 2010-01-14 | Abbott Laboratories | Hybrid segmented endoprosthesis |
| WO2007105067A1 (en) | 2006-03-14 | 2007-09-20 | Arterial Remodeling Technologies, S.A. | Method of monitoring positioning of polymeric stents |
| US8388673B2 (en) | 2008-05-02 | 2013-03-05 | Abbott Cardiovascular Systems Inc. | Polymeric stent |
| US7972373B2 (en) | 2007-12-19 | 2011-07-05 | Advanced Technologies And Regenerative Medicine, Llc | Balloon expandable bioabsorbable stent with a single stress concentration region interconnecting adjacent struts |
| US8808353B2 (en) | 2010-01-30 | 2014-08-19 | Abbott Cardiovascular Systems Inc. | Crush recoverable polymer scaffolds having a low crossing profile |
| US8261423B2 (en) * | 2010-04-30 | 2012-09-11 | Abbott Cardiovascular Systems Inc. | Methods for crimping a polymeric stent onto a delivery balloon |
| US20120059451A1 (en) | 2010-09-08 | 2012-03-08 | Qiang Zhang | Method of Manufacturing a Polymeric Stent Having Reduced Recoil |
| US9345602B2 (en) | 2010-09-23 | 2016-05-24 | Abbott Cardiovascular Systems Inc. | Processes for making crush recoverable polymer scaffolds |
| JP2014507196A (ja) * | 2010-12-28 | 2014-03-27 | ボストン サイエンティフィック サイムド,インコーポレイテッド | ステント |
| US8414528B2 (en) | 2011-05-27 | 2013-04-09 | Abbott Cardiovascular Systems Inc. | Polymer scaffold sheaths |
| US8726483B2 (en) | 2011-07-29 | 2014-05-20 | Abbott Cardiovascular Systems Inc. | Methods for uniform crimping and deployment of a polymer scaffold |
| US8841412B2 (en) | 2011-08-11 | 2014-09-23 | Abbott Cardiovascular Systems Inc. | Controlling moisture in and plasticization of bioresorbable polymer for melt processing |
| US8968387B2 (en) | 2012-07-23 | 2015-03-03 | Abbott Cardiovascular Systems Inc. | Shape memory bioresorbable polymer peripheral scaffolds |
| US9517150B2 (en) * | 2012-10-23 | 2016-12-13 | Abbott Cardiovascular Systems Inc. | Time-dependent polymer scaffolds |
-
2013
- 2013-03-15 US US13/840,257 patent/US9662231B2/en active Active
- 2013-11-20 EP EP13798898.6A patent/EP2967940A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2013-11-20 JP JP2016500108A patent/JP2016514007A/ja active Pending
- 2013-11-20 CN CN201380074488.6A patent/CN105188618B/zh active Active
- 2013-11-20 WO PCT/US2013/070947 patent/WO2014149083A1/en active Application Filing
-
2016
- 2016-04-21 HK HK16104604.2A patent/HK1216497A1/zh unknown
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007313327A (ja) * | 2006-05-25 | 2007-12-06 | Cordis Corp | フープの選定された領域に、改変された分子構造を有するポリマーステント、および、破断点伸びを増大させる方法 |
| JP2011525137A (ja) * | 2008-06-20 | 2011-09-15 | アマランス メディカル プライベイト | チューブ鋳造プロセスによるステント作製 |
| JP2012517247A (ja) * | 2009-02-09 | 2012-08-02 | エビーシオ・メディカル・デバイセズ・ユーエルシー | ステント |
| JP2013504459A (ja) * | 2009-09-14 | 2013-02-07 | アボット カルディオバスキュラー システムズ インコーポレーテッド | 生体吸収性ステントの結晶モルフォロジの制御 |
| US20110190871A1 (en) * | 2010-01-30 | 2011-08-04 | Abbott Cardiovascular Systems Inc. | Crush Recoverable Polymer Scaffolds |
| US20110073733A1 (en) * | 2010-07-29 | 2011-03-31 | John Hartelius | Slider clip and photovoltaic structure mounting system |
| WO2013003644A1 (en) * | 2011-06-30 | 2013-01-03 | Elixir Medical Corporation | Biodegradable endoprostheses and methods for their fabrication |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022107629A (ja) * | 2017-09-08 | 2022-07-22 | ゼウス カンパニー インコーポレイテッド | 制御された配向を有するポリマーチューブ |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2967940A1 (en) | 2016-01-20 |
| HK1216497A1 (zh) | 2016-11-18 |
| CN105188618B (zh) | 2017-09-22 |
| WO2014149083A1 (en) | 2014-09-25 |
| US9662231B2 (en) | 2017-05-30 |
| US20140277372A1 (en) | 2014-09-18 |
| CN105188618A (zh) | 2015-12-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2016514007A (ja) | 強化された軸線方向疲労特性を有するポリマースキャフォールド | |
| JP6344727B2 (ja) | 圧潰復元可能なポリマースキャフォールドの作製方法 | |
| JP6258340B2 (ja) | Pllaで作られたバルーン膨張ステント | |
| JP6267196B2 (ja) | 末梢血管のための高分子スキャフォールド | |
| JP5175277B2 (ja) | 遅発型炎症反応の確率を低減する植込型医療装置の製作方法 | |
| JP5914938B2 (ja) | 圧縮復元可能な高分子スキャフォールド | |
| US20110066222A1 (en) | Polymeric Stent and Method of Making Same | |
| US10022906B2 (en) | Methods for solid phase processing of tubes and medical devices made from the processed tubes | |
| KR20150141956A (ko) | 말초-이식되는 스캐폴드에서 리코일의 감소 | |
| JP2015525104A (ja) | ポリ(l−ラクチド)と親水性ポリマーとのブロックコポリマーでできている生体吸収性ポリマーに関連したスキャフォールド |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20161117 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20161117 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20161129 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20170831 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20171003 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20171206 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20180105 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20180515 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20180810 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20180926 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20181016 |