JP2013023171A - Interior trim part for vehicle and method of manufacturing the same - Google Patents
Interior trim part for vehicle and method of manufacturing the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2013023171A JP2013023171A JP2011162925A JP2011162925A JP2013023171A JP 2013023171 A JP2013023171 A JP 2013023171A JP 2011162925 A JP2011162925 A JP 2011162925A JP 2011162925 A JP2011162925 A JP 2011162925A JP 2013023171 A JP2013023171 A JP 2013023171A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- composite film
- hot melt
- electromagnetic induction
- base material
- metal foil
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Vehicle Interior And Exterior Ornaments, Soundproofing, And Insulation (AREA)
- Lining Or Joining Of Plastics Or The Like (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、車両用内装部品およびその製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a vehicle interior part and a method for manufacturing the same.
従来から、車両室内の外観向上を図るために、各種の内装部品を装着することが行われている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。 2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, various interior parts are mounted in order to improve the appearance of a vehicle interior (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
この特許文献1に記載された内装部品であるクリップ取付用ブラケットは、裏面側に接着剤を貼着している。一方、内装材は、基材と該基材の表面に設けた低融点繊維ウェブ層とを有する。そして、クリップ取付用ブラケットを内装材の表面に載置した状態で電磁誘導加熱を施すと、前記接着剤、低融点繊維ウェブ層および基材が軟化することにより、クリップ取付用ブラケットが内装材に接合される。
The clip mounting bracket, which is an interior part described in
しかしながら、前記特許文献1においては、接着剤やクリップ取付用ブラケットの厚さが具体的に特定されていないため、クリップ取付用ブラケットと内装材との接合強度が必ずしも十分でないという問題があった。
However, in the said
そこで、本発明は、基材と溶着部材との接合強度を更に向上させる車両用内装部品およびその製造方法を提供することを目的とする。 Then, an object of this invention is to provide the interior component for vehicles which further improves the joint strength of a base material and a welding member, and its manufacturing method.
本発明に係る車両用内装部品の製造方法は、合成樹脂からなる基材に溶着部材を電磁誘導加熱を用いて取り付ける車両用内装部品の製造方法であって、前記基材と溶着部材との間に、20〜200μmの金属箔の両面に厚さが10〜50μmのホットメルトフィルムをそれぞれ貼り合わせた複合フィルムを配置する第1工程と、電磁誘導加熱装置本体部の下面と溶着部材の上面との距離を15mm以下に設定した状態で電磁誘導加熱装置を配置する第2工程と、前記電磁誘導加熱装置に高周波電流を流し、前記複合フィルムにおける金属箔部分を発熱させる第3工程と、前記金属箔部分の熱によって、前記複合フィルムにおけるホットメルトフィルム部分を溶融させ、基材と溶着部材とを複合フィルムを介して接合する第4工程と、を含んでなることを特徴とする。 A method for manufacturing an interior component for a vehicle according to the present invention is a method for manufacturing an interior component for a vehicle in which a welding member is attached to a base material made of a synthetic resin using electromagnetic induction heating. A first step of disposing a composite film in which a hot melt film having a thickness of 10 to 50 μm is bonded to both surfaces of a metal foil having a thickness of 20 to 200 μm, a lower surface of the electromagnetic induction heating device main body, and an upper surface of the welding member A second step of disposing the electromagnetic induction heating device in a state where the distance is set to 15 mm or less, a third step of supplying a high-frequency current to the electromagnetic induction heating device to generate heat in the metal foil portion of the composite film, and the metal And a fourth step of melting the hot melt film portion of the composite film by heat of the foil portion and joining the base material and the welding member through the composite film. It is characterized by that.
本発明では、複合フィルムにおける金属箔とホットメルトフィルムの厚さを適切な範囲に設定しているため、基材と溶着部材との接合強度を向上させることができる。 In the present invention, since the thickness of the metal foil and the hot melt film in the composite film is set in an appropriate range, the bonding strength between the base material and the welding member can be improved.
以下、本発明の実施形態を図面と共に詳述する。なお、本実施形態では、基材として熱可塑性樹脂からなる部材を用い、溶着部材として合成樹脂製のクリップやブラケット等を用いるが、本発明はこれらに限定されず、広く車両用内装部品全体に適用可能である。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. In the present embodiment, a member made of a thermoplastic resin is used as a base material, and a clip or bracket made of a synthetic resin is used as a welding member, but the present invention is not limited to these, and is widely applied to the entire interior part for a vehicle. Applicable.
本実施形態による車両用内装部品の製造方法は、合成樹脂からなる基材に溶着部材を電磁誘導加熱を用いて取り付ける製造方法である。 The vehicle interior part manufacturing method according to the present embodiment is a manufacturing method in which a welding member is attached to a base material made of synthetic resin using electromagnetic induction heating.
具体的には、前記基材と溶着部材との間に、金属箔とホットメルトフィルムとからなる複合フィルムを配置する第1工程と、電磁誘導加熱装置本体部の下面と基材の上面との距離を15mm以下に設定した状態で電磁誘導加熱装置を配置する第2工程と、前記電磁誘導加熱装置に高周波電流を流し、前記複合フィルムにおける金属箔部分を発熱させる第3工程と、前記金属箔部分の熱によって、前記複合フィルムにおけるホットメルトフィルム部分を溶融させ、基材と溶着部材とを複合フィルムを介して接合する第4工程と、を含んでいる。以下、各工程ごとの特徴を説明する。 Specifically, a first step of disposing a composite film composed of a metal foil and a hot melt film between the base material and the welding member, and a lower surface of the electromagnetic induction heating device main body and an upper surface of the base material A second step of disposing the electromagnetic induction heating device in a state where the distance is set to 15 mm or less; a third step of supplying a high-frequency current to the electromagnetic induction heating device to generate heat in the metal foil portion of the composite film; and the metal foil A fourth step of melting the hot melt film portion of the composite film by the heat of the portion and joining the base material and the welding member through the composite film. Hereinafter, characteristics of each process will be described.
[第1工程]
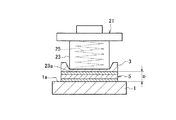
図1に示すように、第1工程では、下側に基材1を配置し、上側に溶着部材3を配置し、これらの基材1と溶着部材3との間に複合フィルム5を介在させる。
[First step]
As shown in FIG. 1, in the first step, the
前記基材1としては、熱可塑性樹脂からなり、ポリプロピレン(PP)、ポリエチレン(PE)、ポリエチレンテレフタレート(PET)、アクリロニトリル−スチレン−ブタジエン(ABS)、ポリカボネート(PC)、ポリ塩化ビニル(PVC)、高密度ポリスチレン(HPS)などの樹脂が可能である。前記熱可塑性樹脂のうちの1種のみでも良く、または、2種以上を選択して複合化した熱可塑性樹脂でも良い。
The
前記溶着部材3としては、一般の射出部品が適用可能であり、例えば、クリップ、ブラケット、リンフォース、ストライカー、ネット、クッション材(発泡体)などである。また、溶着部材3の材質は、例えば、熱可塑性樹脂からなり、ポリプロピレン(PP)、ポリエチレン(PE)、ポリエチレンテレフタレート(PET)、アクリロニトリル−スチレン−ブタジエン(ABS)、ポリカボネート(PC)、ポリ塩化ビニル(PVC)、高密度ポリスチレン(HPS)、エチレン酢酸ビニル(EVA)、ポリエステル、ポリアセタール(POM)、ポリアミド(PA)などを適用可能である。 As the welding member 3, a general injection part can be applied, and examples thereof include a clip, a bracket, a reinforcement, a striker, a net, and a cushion material (foam). The material of the welding member 3 is made of, for example, a thermoplastic resin, such as polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), acrylonitrile-styrene-butadiene (ABS), polycarbonate (PC), polyvinyl chloride. (PVC), high density polystyrene (HPS), ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), polyester, polyacetal (POM), polyamide (PA), and the like are applicable.
前記複合フィルム5は、金属箔7の両面にホットメルトフィルム9,11をそれぞれ貼り合わせて形成されている。金属箔7の厚さは、20〜200μmである。また、ホットメルトフィルム9,11の厚さは、10〜50μmである。
The
金属箔7としては、例えば、アルミニウムや鉄が好ましい。アルミニウムの場合は、厚さが20〜50μmが好ましく、鉄の場合は、厚さが80〜200μmが好ましい。
As the
アルミニウムの厚さが20μm未満になると薄くなりすぎて、電磁誘導による金属箔7の発熱量が不足するため、ホットメルトフィルム9,11が十分に溶融しない。その結果、ホットメルトフィルム9,11による接着力が低下するため、好ましくない。一方、50μmよりも厚くなると、発熱量が大きくなりすぎて焼けこげが発生するため、外観不良となって好ましくない。
When the thickness of aluminum is less than 20 μm, it becomes too thin and the heat generation amount of the
一方、鉄の厚さが80μm未満になると薄くなりすぎて、電磁誘導による金属箔7の発熱量が不足するため、ホットメルトフィルム9,11が十分に溶融しない。その結果、ホットメルトフィルム9,11による接着力が低下するため、好ましくない。一方、200μmよりも厚くなると、発熱量が大きくなりすぎて焼けこげが発生するため、外観不良となって好ましくない。
On the other hand, when the thickness of iron is less than 80 μm, the
また、ホットメルトフィルム9,11の厚さが10μm未満の場合、ホットメルトフィルム9,11の量が少なすぎて接着力が低下するため、好ましくない。ホットメルトフィルム9,11の厚さが50μmより厚い場合、ホットメルトフィルム9,11の量が多すぎてはみ出すために外観不良となると共に、コスト高となって好ましくない。
Moreover, when the thickness of the
ホットメルトフィルム9,11の材質は、ポリアミド系樹脂、ポリエステル系樹脂、PP系樹脂、PE系樹脂等を適用することが可能である。なお、基材1または溶着部材3のいずれかと同じ材質にすることが好ましい。また、前記金属箔7として、銅、亜鉛、錫、マグネシウム及びそれらの合金等を適用することも可能である。
As the material of the
[第2工程]
次いで、第2工程では、図2に示すように溶着部材3の上方に電磁誘導加熱装置21を配置する。
[Second step]
Next, in the second step, the electromagnetic
前記電磁誘導加熱装置21は、図2に示すように、下部に本体部23が配設されており、この本体部23内にコイル25が螺旋状に巻回されている。ここで、図3に示すように、本体部23の下面23aと基材1の上面1aとの距離Dを15mm以下に設定する。距離Dが15mmよりも大きい場合、コイル25に高周波電流を流しても複合フィルム5における金属箔部分7のジュール熱が小さくなりすぎ、ホットメルトフィルム9.11の溶融量も少なくなりすぎる。このため、複合フィルム5による接着力が低下するため、好ましくない。
As shown in FIG. 2, the electromagnetic
[第3工程、第4工程]
第3工程では、電磁誘導加熱装置21に設けたコイル25に高周波電流を流すと、コイル25の周りに磁力線が生じる。この磁力線によって、複合フィルム5における金属箔部分7に渦電流が流れ、ジュール熱によって金属箔部分7が加熱される。
[3rd process, 4th process]
In the third step, lines of magnetic force are generated around the
第4工程では、図3に示すように、前記金属箔部分7の熱によって、前記複合フィルム5におけるホットメルトフィルム部分9,11を溶融させ、基材1と溶着部材3とが複合フィルム5を介して接合される。そして、所定時間経過すると複合フィルム5が冷却されてホットメルトフィルム部分9,11が硬化し、図4に示すように基材1と溶着部材3とが複合フィルム5を介して接合された車両用内装部品31が完成する。
In the fourth step, as shown in FIG. 3, the hot
次に、本発明の実施例について説明する。 Next, examples of the present invention will be described.
[実施例1]
図5に示す試験片41を用いて引っ張りせん断試験を行った。縦70mmで横が20mmの板状のPP樹脂43,45(厚さ:2mm)を2枚準備し、これらのうち20×20mmの接合部分49を複合フィルム47を介して電磁誘導加熱によって接合させたものを試験片41とした。ここで、周波数を20kHz、接合時の加圧力を0.5MPa、通電時間を4秒、界面温度を140℃とした。その後、2枚の合成樹脂同士43,45を340Nで上下に引っ張り、破断するか否かを検証した。なお、実施例1では、複合フィルム47における金属箔はアルミニウムとした。また、電磁誘導加熱装置本体部の下面と下側に配置されたPP樹脂の上面との距離(図3参照)を5mmとした。
A tensile shear test was performed using the
表1では、○は340Nの引っ張り力で接合部分以外で破断した場合を示している。また、×は引っ張り時に接合部分で剥がれた場合や外観不良の場合を示している。具体的には、ホットメルトの厚さが5mmのときは、ホットメルトの量が少なすぎて接着力不足となった。ホットメルトの厚さが60mmのときは、ホットメルトの量が多すぎてはみ出したため、外観不良になった。アルミニウムからなる金属箔の厚さが10μmのときは、発熱量が不足してホットメルトが十分に溶融せず接着力不足となった。なお、金属箔の厚さが70μmのときは、発熱量が大きくなりすぎ焼けこげが発生して外観不良になった。 In Table 1, ◯ indicates a case where fracture occurred at a portion other than the joined portion with a pulling force of 340N. Moreover, x shows the case where it peeled off at the joint portion during pulling or the case of poor appearance. Specifically, when the thickness of the hot melt was 5 mm, the amount of hot melt was too small and the adhesive strength was insufficient. When the thickness of the hot melt was 60 mm, the amount of the hot melt was too large to protrude, resulting in poor appearance. When the thickness of the metal foil made of aluminum was 10 μm, the calorific value was insufficient, and the hot melt was not sufficiently melted, resulting in insufficient adhesion. When the thickness of the metal foil was 70 μm, the calorific value was too large, and burnt was generated, resulting in poor appearance.
[実施例2]
次いで、実施例2について説明する。実施例2は、ほぼ実施例1と同一の試験片を用いた。ただし、複合フィルムにおける金属箔は鉄とし、電磁誘導加熱装置本体部の下面と下側に配置されたPP樹脂の上面との距離を15mmとした点のみが異なる。
Next, Example 2 will be described. In Example 2, the same test piece as in Example 1 was used. However, the only difference is that the metal foil in the composite film is iron, and the distance between the lower surface of the electromagnetic induction heating device main body and the upper surface of the PP resin disposed on the lower side is 15 mm.
表2では、ホットメルトの厚さが5mmのときは、ホットメルトの量が少なすぎて接着力不足となった。ホットメルトの厚さが60mmのときは、ホットメルトの量が多すぎてはみ出したため、外観不良になった。鉄からなる金属箔の厚さが40μmのときは、発熱量が不足してホットメルトが十分に溶融せず接着力不足となった。なお、金属箔の厚さが240μmのときは、発熱量が大きくなりすぎ焼けこげが発生して外観不良になった。 In Table 2, when the thickness of the hot melt was 5 mm, the amount of the hot melt was too small and the adhesive strength was insufficient. When the thickness of the hot melt was 60 mm, the amount of the hot melt was too large to protrude, resulting in poor appearance. When the thickness of the metal foil made of iron was 40 μm, the calorific value was insufficient and the hot melt was not sufficiently melted, resulting in insufficient adhesion. When the thickness of the metal foil was 240 μm, the calorific value was too large, and burnt was generated, resulting in poor appearance.
以下に、本実施形態による作用効果を説明する。 Below, the effect by this embodiment is demonstrated.
(1)本実施形態による車両用内装部品の製造方法は、基材1と溶着部材3との間に、20〜200μmの金属箔7の両面に厚さが10〜50μmのホットメルトフィルム9,11をそれぞれ貼り合わせた複合フィルム5を配置する第1工程と、電磁誘導加熱装置本体部23の下面23aと基材1の上面1aとの距離を15mm以下に設定した状態で電磁誘導加熱装置21を配置する第2工程と、前記電磁誘導加熱装置21に高周波電流を流し、前記複合フィルム5における金属箔部分7を発熱させる第3工程と、前記金属箔部分7の熱によって、前記複合フィルム5におけるホットメルトフィルム部分9,11を溶融させ、基材1と溶着部材3とを複合フィルム5を介して接合する第4工程と、を含んでなる。
(1) The method for manufacturing an interior part for a vehicle according to the present embodiment includes a
このように、複合フィルム5における金属箔7とホットメルトフィルム9,11の厚さを適切な範囲に設定しているため、基材1と溶着部材3との接合強度を向上させることができる。
Thus, since the thickness of the
例えば、ホットメルトフィルム9,11の厚さが10μm未満の場合、ホットメルトフィルム9,11の量が少なすぎて接着力が低下するため、好ましくない。ホットメルトフィルム9,11の厚さが50μmより厚い場合、ホットメルトフィルム9,11の量が多すぎてはみ出すために外観不良となると共に、コスト高となって好ましくない。
For example, when the thickness of the
また、本体部23の下面23aと基材1の上面1aとの距離Dが15mmよりも大きい場合、コイル25に高周波電流を流しても複合フィルム5における金属箔部分7のジュール熱が小さくなりすぎ、ホットメルトフィルム9.11の溶融量も少なくなりすぎる。このため、複合フィルム5による接着力が低下するため、好ましくない。
Further, when the distance D between the
(2)前記複合フィルム5における金属箔部分7は、アルミニウムからなり、厚さが20〜50μmである。
(2) The
アルミニウムの厚さが20μm未満になると薄くなりすぎて、電磁誘導による金属箔7の発熱量が不足するため、ホットメルトフィルム9,11が十分に溶融しない。その結果、ホットメルトフィルム9,11による接着力が低下するため、好ましくない。一方、50μmよりも厚くなると、発熱量が大きくなりすぎて焼けこげが発生するため、外観不良となって好ましくない。
When the thickness of aluminum is less than 20 μm, it becomes too thin and the heat generation amount of the
(3)前記複合フィルムにおける金属箔部分は、鉄からなり、厚さが80〜200μmである。 (3) The metal foil part in the said composite film consists of iron, and thickness is 80-200 micrometers.
鉄の厚さが80μm未満になると薄くなりすぎて、電磁誘導による金属箔7の発熱量が不足するため、ホットメルトフィルム9,11が十分に溶融しない。その結果、ホットメルトフィルム9,11による接着力が低下するため、好ましくない。一方、200μmよりも厚くなると、発熱量が大きくなりすぎて焼けこげが発生するため、外観不良となって好ましくない。
When the thickness of iron is less than 80 μm, it becomes too thin and the heat generation amount of the
1…基材
1a…上面
3…溶着部材
5…複合フィルム
7…金属箔
9,11…ホットメルトフィルム
23…電磁誘導加熱装置本体部
23a…下面
31…車両用内装部品
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (4)
前記基材と溶着部材との間に、20〜200μmの金属箔の両面に厚さが10〜50μmのホットメルトフィルムをそれぞれ貼り合わせた複合フィルムを配置する第1工程と、
電磁誘導加熱装置本体部の下面と基材の上面との距離を15mm以下に設定した状態で電磁誘導加熱装置を配置する第2工程と、
前記電磁誘導加熱装置に高周波電流を流し、前記複合フィルムにおける金属箔部分を発熱させる第3工程と、
前記金属箔部分の熱によって、前記複合フィルムにおけるホットメルトフィルム部分を溶融させ、基材と溶着部材とを複合フィルムを介して接合する第4工程と、を含んでなる車両用内装部品の製造方法。 A method for manufacturing an interior part for a vehicle in which a welding member is attached to a base material made of synthetic resin using electromagnetic induction heating,
A first step of disposing a composite film in which a hot melt film having a thickness of 10 to 50 μm is bonded to both surfaces of a metal foil having a thickness of 20 to 200 μm between the base material and the welding member;
A second step of disposing the electromagnetic induction heating device in a state where the distance between the lower surface of the electromagnetic induction heating device main body and the upper surface of the substrate is set to 15 mm or less;
A third step of causing a high-frequency current to flow through the electromagnetic induction heating device to heat the metal foil portion in the composite film;
A fourth step of melting the hot melt film portion of the composite film by heat of the metal foil portion and joining the base material and the welding member via the composite film, .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011162925A JP2013023171A (en) | 2011-07-26 | 2011-07-26 | Interior trim part for vehicle and method of manufacturing the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011162925A JP2013023171A (en) | 2011-07-26 | 2011-07-26 | Interior trim part for vehicle and method of manufacturing the same |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013023171A true JP2013023171A (en) | 2013-02-04 |
| JP2013023171A5 JP2013023171A5 (en) | 2014-07-31 |
Family
ID=47781963
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011162925A Pending JP2013023171A (en) | 2011-07-26 | 2011-07-26 | Interior trim part for vehicle and method of manufacturing the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2013023171A (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106113484A (en) * | 2016-06-24 | 2016-11-16 | 武汉理工大学 | A kind of thermoplastic composite and the method for attachment of metal |
| CN112272610A (en) * | 2018-06-13 | 2021-01-26 | 杜凯恩Ias有限责任公司 | Method for determining a thickness of a molten layer associated with a predetermined welding strength based on a correlation between the predetermined welding strength and the thickness of the molten layer |
| CN115447151A (en) * | 2022-09-14 | 2022-12-09 | 浙江东洋佳嘉海绵制品有限公司 | Manufacturing method capable of completely compounding hot melt film and sponge |
| WO2023176964A1 (en) * | 2022-03-18 | 2023-09-21 | 藤森工業株式会社 | Adhesion method and hot-melt adhesive film for induction heating |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04364926A (en) * | 1991-06-11 | 1992-12-17 | Adoheya Sansho Kk | Method for bonding waterproof sheet and waterproof cloth |
| JPH07246657A (en) * | 1994-03-10 | 1995-09-26 | Kanto Auto Works Ltd | Method and apparatus for producing interior material |
| JPH0858030A (en) * | 1994-08-22 | 1996-03-05 | Inoac Corp | Three-layered hot-melt film and interior material using the same |
| JPH1016657A (en) * | 1996-06-29 | 1998-01-20 | Ikeda Bussan Co Ltd | Mounting structure of bracket for attaching clip of interior material of automobile |
| JP2010052638A (en) * | 2008-08-29 | 2010-03-11 | Meiwa Ind Co Ltd | Resin welding method, and resin component for vehicle interior |
-
2011
- 2011-07-26 JP JP2011162925A patent/JP2013023171A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04364926A (en) * | 1991-06-11 | 1992-12-17 | Adoheya Sansho Kk | Method for bonding waterproof sheet and waterproof cloth |
| JPH07246657A (en) * | 1994-03-10 | 1995-09-26 | Kanto Auto Works Ltd | Method and apparatus for producing interior material |
| JPH0858030A (en) * | 1994-08-22 | 1996-03-05 | Inoac Corp | Three-layered hot-melt film and interior material using the same |
| JPH1016657A (en) * | 1996-06-29 | 1998-01-20 | Ikeda Bussan Co Ltd | Mounting structure of bracket for attaching clip of interior material of automobile |
| JP2010052638A (en) * | 2008-08-29 | 2010-03-11 | Meiwa Ind Co Ltd | Resin welding method, and resin component for vehicle interior |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106113484A (en) * | 2016-06-24 | 2016-11-16 | 武汉理工大学 | A kind of thermoplastic composite and the method for attachment of metal |
| CN106113484B (en) * | 2016-06-24 | 2018-08-07 | 武汉理工大学 | A kind of connection method of thermoplastic composite and metal |
| CN112272610A (en) * | 2018-06-13 | 2021-01-26 | 杜凯恩Ias有限责任公司 | Method for determining a thickness of a molten layer associated with a predetermined welding strength based on a correlation between the predetermined welding strength and the thickness of the molten layer |
| US11633920B2 (en) | 2018-06-13 | 2023-04-25 | Dukane Ias, Llc | Methods for determining a melt layer thickness associated with a predetermined weld strength based on a correlation therebetween |
| WO2023176964A1 (en) * | 2022-03-18 | 2023-09-21 | 藤森工業株式会社 | Adhesion method and hot-melt adhesive film for induction heating |
| CN115447151A (en) * | 2022-09-14 | 2022-12-09 | 浙江东洋佳嘉海绵制品有限公司 | Manufacturing method capable of completely compounding hot melt film and sponge |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5639708B2 (en) | SMC multilayer component manufacturing method | |
| JP6341156B2 (en) | Resin bonded body, resin bonded body manufacturing method, and vehicle structure | |
| JP2013023171A (en) | Interior trim part for vehicle and method of manufacturing the same | |
| CN107116861B (en) | Method for manufacturing a lightweight laminate | |
| JP2017100319A (en) | Resin body and method for manufacturing resin body | |
| EP2117879B1 (en) | Resistive implant welding for structural bonds in automotive applications | |
| US20020122930A1 (en) | Formed lining for vehicle and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP5827505B2 (en) | Joining method of fiber reinforced thermoplastic resin | |
| JP2003252154A (en) | Energy managing system and welding method of it | |
| US9056426B2 (en) | Method for the thermal joining of two components, and a thermal joining strip | |
| JP2016036955A (en) | Dissimilar material joined body and method of manufacturing the same | |
| RU2635223C2 (en) | Vehicle structure element sealed with resin, method for manufacturing vehicle structure element sealed with resin, and vehicle structure element | |
| JP6585383B2 (en) | Non-woven fabric laminate and perforated film used therefor | |
| KR102299732B1 (en) | Welding method for aluminium sheet and carbon fiber reinforced plastics sheet | |
| US20190160759A1 (en) | Joining method for thermoplastic elements | |
| US20190176718A1 (en) | Automobile interior trim | |
| TW201934345A (en) | Vehicle interior material and manufacturing method of the same | |
| WO2021193828A1 (en) | Joining structure, joining method, exterior body for wire harness, and wire harness | |
| JP6348319B2 (en) | Method for producing metal resin composite | |
| JP7042423B2 (en) | Fixed structure of wiring member | |
| JPS63221032A (en) | Fixing method for bracket of interior parts in automobile | |
| CN203073154U (en) | Adhesive fastener tape for preventing crack propagation | |
| JP2683661B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing resin molded product having core member | |
| TW200946573A (en) | Foam product with an embedded accessory and method of making the same | |
| JP6098607B2 (en) | Method of joining metal member and resin member |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140612 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20140612 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150310 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20150312 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150420 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20151027 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20160308 |