JP2012166350A - Resin laminate, and resin laminated sheet - Google Patents
Resin laminate, and resin laminated sheet Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2012166350A JP2012166350A JP2011026468A JP2011026468A JP2012166350A JP 2012166350 A JP2012166350 A JP 2012166350A JP 2011026468 A JP2011026468 A JP 2011026468A JP 2011026468 A JP2011026468 A JP 2011026468A JP 2012166350 A JP2012166350 A JP 2012166350A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- resin
- resin layer
- metal compound
- foaming agent
- containing resin
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Landscapes
- Synthetic Leather, Interior Materials Or Flexible Sheet Materials (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
Abstract
【課題】発泡樹脂層の樹脂成分としてエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を用いた場合に、発泡樹脂層の樹脂製膜性を良好に維持しながら、発泡壁紙等の表面強度を更に向上させることができ、そして、生産性を良好に維持できる樹脂積層体及び樹脂積層シートを提供する。
【解決手段】発泡剤含有樹脂層の片面又は両面に金属化合物含有樹脂層が積層された層構成を有する未発泡中間体を熱処理し、前記発泡剤含有樹脂層を発泡樹脂層にすることにより得られる樹脂積層体であって、
(1)前記発泡剤含有樹脂層が、樹脂成分としてエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含み、
(2)前記金属化合物含有樹脂層の樹脂成分は、水素結合が含まれないモノマーからなる共重合体であり、
(3)前記熱処理又は別途の熱処理により、前記発泡剤含有樹脂層と前記金属化合物含有樹脂層とが複合化されている、
ことを特徴とする樹脂積層体。
【選択図】なしWhen an ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin is used as a resin component of a foamed resin layer, the surface strength of foamed wallpaper and the like is further increased while maintaining the resin film formability of the foamed resin layer. Provided are a resin laminate and a resin laminate sheet that can be improved and maintain good productivity.
An unfoamed intermediate having a layer structure in which a metal compound-containing resin layer is laminated on one side or both sides of a foaming agent-containing resin layer is heat-treated, and the foaming agent-containing resin layer is obtained as a foamed resin layer. A resin laminate,
(1) The foaming agent-containing resin layer contains an ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin as a resin component,
(2) The resin component of the metal compound-containing resin layer is a copolymer composed of monomers that do not contain hydrogen bonds,
(3) The foaming agent-containing resin layer and the metal compound-containing resin layer are combined by the heat treatment or a separate heat treatment,
The resin laminated body characterized by the above-mentioned.
[Selection figure] None
Description
本発明は、発泡壁紙、各種装飾材等として有用な、発泡樹脂層を有する樹脂積層体及び樹脂積層シートに関する。 The present invention relates to a resin laminate and a resin laminate sheet having a foamed resin layer, which are useful as foamed wallpaper, various decorative materials, and the like.
従来、発泡壁紙としては、繊維質シートに塩化ビニル樹脂の発泡樹脂層を形成し、更に絵柄模様層を形成したもの知られている。近年では、環境に配慮し、発泡樹脂層にはエチレン−酢酸ビニル共重合体、アクリル樹脂、オレフィン系樹脂等の、ハロゲン非含有樹脂が用いられてきている(特許文献1〜3等)。 Conventionally, foamed wallpaper is known in which a foamed resin layer of vinyl chloride resin is formed on a fibrous sheet and a pattern layer is further formed. In recent years, in consideration of the environment, halogen-free resins such as ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer, acrylic resin, and olefin resin have been used for the foamed resin layer (Patent Documents 1 to 3, etc.).
発泡壁紙の発泡樹脂層の表面強度(耐スクラッチ性等)を向上させる目的で、発泡樹脂層の発泡樹脂としてエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を用いることが知られている。また、発泡壁紙の物性を向上させる目的で、発泡樹脂層上に非発泡樹脂層を設けることも知られている。 In order to improve the surface strength (scratch resistance, etc.) of the foamed resin layer of the foamed wallpaper, it is known to use an ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin as the foamed resin of the foamed resin layer. It is also known to provide a non-foamed resin layer on the foamed resin layer for the purpose of improving the physical properties of the foamed wallpaper.
しかしながら、発泡壁紙の更なる表面強度向上を目指し、発泡樹脂層を形成する樹脂を硬くすると(重合度等を調整)、発泡樹脂層の製膜性が悪く(発泡剤が発泡しない温度領域で製膜できない等)、生産性が劣ることに繋がる問題があった。また、たとえ製膜できたとしても、発泡体形成が難しい(発泡し難い等)という問題があった。 However, if the resin forming the foamed resin layer is hardened (adjusting the degree of polymerization, etc.) with the aim of further improving the surface strength of the foam wallpaper, the film-forming property of the foamed resin layer is poor (manufactured in a temperature range where the foaming agent does not foam). There is a problem that leads to inferior productivity. In addition, even if the film can be formed, there is a problem that it is difficult to form a foam (it is difficult to foam).
従って、発泡樹脂層の発泡樹脂としてエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を用いた場合に、発泡樹脂層の樹脂製膜性を良好に維持しながら、発泡壁紙等の表面強度を更に向上させることができ、そして、生産性を良好に維持できる樹脂積層体及び樹脂積層シートの開発が望まれている。 Therefore, when ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin is used as the foamed resin for the foamed resin layer, the surface strength of foamed wallpaper and the like is further improved while maintaining the resin film formability of the foamed resin layer. Development of a resin laminate and a resin laminate sheet that can be maintained and can maintain good productivity is desired.
本発明は、発泡樹脂層の樹脂成分としてエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を用いた場合に、発泡樹脂層の樹脂製膜性を良好に維持しながら、発泡壁紙等の表面強度を更に向上させることができ、そして、生産性を良好に維持できる樹脂積層体及び樹脂積層シートを提供することを目的とする。 In the present invention, when ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin is used as the resin component of the foamed resin layer, the surface strength of the foamed wallpaper and the like is improved while maintaining the resin film formability of the foamed resin layer. It is another object of the present invention to provide a resin laminate and a resin laminate sheet that can be further improved and can maintain good productivity.
本発明者は、鋭意研究を重ねた結果、樹脂成分としてエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含む発泡剤含有樹脂層及び金属化合物含有樹脂層が複合化した樹脂積層体によれば上記目的を達成できることを見出し、本発明を完成するに至った。これは、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含む発泡剤含有樹脂層と金属化合物含有樹脂層が接しているため、熱処理時に両樹脂層が複合化して、発泡樹脂層の強靭性が増加するためである。 As a result of intensive studies, the present inventors have found that the resin laminate in which the foaming agent-containing resin layer containing the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin as the resin component and the metal compound-containing resin layer are combined is the above. The inventors have found that the object can be achieved and have completed the present invention. This is because the foaming agent-containing resin layer containing the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin is in contact with the metal compound-containing resin layer, so that both resin layers are combined during heat treatment, and the toughness of the foamed resin layer is reduced. This is because it increases.
即ち、本発明は、下記の樹脂積層体及び樹脂積層シートに関する。
項1. 発泡剤含有樹脂層の片面又は両面に金属化合物含有樹脂層が積層された層構成を有する未発泡中間体を熱処理し、前記発泡剤含有樹脂層を発泡樹脂層にすることにより得られる樹脂積層体であって、
(1)前記発泡剤含有樹脂層が、樹脂成分としてエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含み、
(2)前記金属化合物含有樹脂層の樹脂成分は、水素結合が含まれないモノマーからなる共重合体であり、
(3)前記熱処理又は別途の熱処理により、前記発泡剤含有樹脂層と前記金属化合物含有樹脂層とが複合化されている、
ことを特徴とする樹脂積層体。
項2. 前記金属化合物が、酸化マグネシウム、酸化亜鉛、酸化アルミニウム、酸化ジルコニウム、酸化アンチモン、酸化チタン、酸化ケイ素、窒化ホウ素、窒化アルミニウム及び金属石鹸からなる群から選択される少なくとも1種である、請求項1に記載の樹脂積層体。
項3. 前記金属化合物含有樹脂層が、前記金属化合物を5重量%以上含有する、請求項1又は2に記載の樹脂積層体。
項4. 繊維質シート上に、請求項1〜3のいずれかに記載の樹脂積層体を積層してなる樹脂積層シート。
That is, this invention relates to the following resin laminated body and resin laminated sheet.
Item 1. A resin laminate obtained by heat-treating an unfoamed intermediate having a layer structure in which a metal compound-containing resin layer is laminated on one side or both sides of a foaming agent-containing resin layer, and making the foaming agent-containing resin layer a foamed resin layer Because
(1) The foaming agent-containing resin layer contains an ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin as a resin component,
(2) The resin component of the metal compound-containing resin layer is a copolymer composed of monomers that do not contain hydrogen bonds,
(3) The foaming agent-containing resin layer and the metal compound-containing resin layer are combined by the heat treatment or a separate heat treatment,
The resin laminated body characterized by the above-mentioned.
Item 2. The metal compound is at least one selected from the group consisting of magnesium oxide, zinc oxide, aluminum oxide, zirconium oxide, antimony oxide, titanium oxide, silicon oxide, boron nitride, aluminum nitride, and metal soap. The resin laminate according to 1.
Item 3. The resin laminate according to claim 1 or 2, wherein the metal compound-containing resin layer contains 5% by weight or more of the metal compound.
Item 4. The resin laminated sheet formed by laminating | stacking the resin laminated body in any one of Claims 1-3 on a fibrous sheet.
以下、本発明の樹脂積層体及び樹脂積層シートについて詳細に説明する。
≪樹脂積層体≫
本発明の樹脂積層体は、
発泡剤含有樹脂層の片面又は両面に金属化合物含有樹脂層が積層された層構成を有する未発泡中間体を熱処理し、前記発泡剤含有樹脂層を発泡樹脂層にすることにより得られる樹脂積層体であって、
(1)前記発泡剤含有樹脂層が、樹脂成分としてエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含み、
(2)前記金属化合物含有樹脂層の樹脂成分は、水素結合が含まれないモノマーからなる共重合体であり、
(3)前記熱処理又は別途の熱処理により、前記発泡剤含有樹脂層と前記金属化合物含有樹脂層とが複合化されている、
ことを特徴とする。
Hereinafter, the resin laminate and the resin laminate sheet of the present invention will be described in detail.
≪Resin laminate≫
The resin laminate of the present invention is
A resin laminate obtained by heat-treating an unfoamed intermediate having a layer structure in which a metal compound-containing resin layer is laminated on one side or both sides of a foaming agent-containing resin layer, and making the foaming agent-containing resin layer a foamed resin layer Because
(1) The foaming agent-containing resin layer contains an ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin as a resin component,
(2) The resin component of the metal compound-containing resin layer is a copolymer composed of monomers that do not contain hydrogen bonds,
(3) The foaming agent-containing resin layer and the metal compound-containing resin layer are combined by the heat treatment or a separate heat treatment,
It is characterized by that.
上記特徴を有する本発明の樹脂積層体は、樹脂成分としてエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含む発泡剤含有樹脂層及び金属化合物含有樹脂層を、熱処理により複合化して得られるので、発泡樹脂層の樹脂製膜性を良好に維持しながら、発泡壁紙等の表面強度を更に向上させることができ、そして、生産性を良好に維持できる。この効果は、熱処理により、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂が溶融し、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂に起因するイオン性基(−COO−等)が隣接する金属化合物含有樹脂層中の金属化合物とイオン性の架橋構造(擬似架橋構造)を形成すること(複合化)により表面強度が向上することに基づくと考えられている。 Since the resin laminate of the present invention having the above characteristics is obtained by combining a foaming agent-containing resin layer containing an ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin as a resin component and a metal compound-containing resin layer by heat treatment, While maintaining the resin film-forming property of the foamed resin layer, the surface strength of the foamed wallpaper and the like can be further improved, and the productivity can be maintained well. This effect, by heat treatment, ethylene - (meth) melted acrylic acid copolymer resin, an ethylene - (meth) ionic group due to the acrylic acid copolymer resin (-COO -, etc.) is adjacent metal compound It is considered that the surface strength is improved by forming (compositing) an ionic cross-linked structure (pseudo cross-linked structure) with the metal compound in the containing resin layer.
未発泡中間体
本発明の樹脂積層体では、熱処理により発泡剤含有樹脂層を発泡樹脂層にする前に、発泡剤含有樹脂層の片面又は両面に金属化合物含有樹脂層を積層させた層構成を有する未発泡中間体を形成する。そして、その未発泡中間体を熱処理して、発泡剤含有樹脂層を発泡樹脂層にすることにより、本発明の樹脂積層体を得る。
Unfoamed intermediate The resin laminate of the present invention has a layer structure in which a metal compound-containing resin layer is laminated on one or both sides of a foaming agent-containing resin layer before the foaming agent-containing resin layer is made into a foamed resin layer by heat treatment. Having an unfoamed intermediate. And the resin laminated body of this invention is obtained by heat-processing the unfoamed intermediate body and making a foaming agent containing resin layer into a foamed resin layer.
発泡剤含有樹脂層
発泡剤含有樹脂層とは、熱処理する前の未発泡状態の発泡樹脂層である。
Foaming agent-containing resin layer The foaming agent-containing resin layer is an unfoamed foamed resin layer before heat treatment.
樹脂成分として、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を用いる。これは、アクリル酸(CH2=CHCOOH)及びメタクリル酸(CH2=C(CH3)COOH)の少なくとも1種をモノマーとして得られる重合体であり、例えばアクリル酸及びメタクリル酸の少なくとも1種をモノマーとエチレンとの組み合わせにより得られる共重合体である。このような樹脂成分を用いることで、樹脂中の水素結合等に起因する強固な層を形成することができるので、優れた耐スクラッチ性、耐摩耗性等を得ることができる。 As the resin component, ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin is used. This is a polymer obtained using at least one of acrylic acid (CH 2 ═CHCOOH) and methacrylic acid (CH 2 ═C (CH 3 ) COOH) as a monomer, for example, at least one of acrylic acid and methacrylic acid. It is a copolymer obtained by a combination of a monomer and ethylene. By using such a resin component, it is possible to form a strong layer resulting from hydrogen bonding in the resin, and thus excellent scratch resistance, wear resistance, and the like can be obtained.
なお、本発明では、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂と表記するとき、エチレン−アクリル酸共重合体樹脂及びエチレン−メタクリル酸共重合体樹脂の両方を意味する。 In the present invention, when expressed as an ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin, it means both an ethylene-acrylic acid copolymer resin and an ethylene-methacrylic acid copolymer resin.
上記エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂以外の樹脂を併用してもよい。例えば、ポリプロピレン、ポリスチレン及びエチレン−酢酸ビニル共重合体樹脂(EVA)等のポリオレフィン系樹脂、アクリロニトリルーブタジエンースチレン共重合体樹脂(ABS)、アクリロニトリル−スチレン系共重合体樹脂、ナイロン、ポリアセタール系樹脂、アクリル系樹脂、ポリカーボネート系樹脂、ポリエステル系樹脂、ポリ酢酸ビニル系樹脂、ポリビニルアルコール系樹脂、ポリウレタン系樹脂及びポリ塩化ビニル系樹脂等の少なくとも1種が挙げられる。 A resin other than the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin may be used in combination. For example, polyolefin resin such as polypropylene, polystyrene and ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer resin (EVA), acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer resin (ABS), acrylonitrile-styrene copolymer resin, nylon, polyacetal resin And at least one of acrylic resins, polycarbonate resins, polyester resins, polyvinyl acetate resins, polyvinyl alcohol resins, polyurethane resins, and polyvinyl chloride resins.
上記の他の樹脂を併用する場合には、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂含有樹脂層の樹脂成分中のエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂の含有量は、60質量%以上が好ましく、70質量%以上がより好ましく、100質量%であっても良い。エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂含有樹脂層の樹脂成分として、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を主成分として用いることで、発泡壁紙の発泡樹脂層の表面強度を向上させることができる。 When the other resin is used in combination, the content of the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin in the resin component of the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin-containing resin layer is 60% by mass. The above is preferable, 70 mass% or more is more preferable, and 100 mass% may be sufficient. By using ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin as a main component as a resin component of the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin-containing resin layer, the surface strength of the foamed resin layer of the foam wallpaper is improved. be able to.
エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体のメルトフローレート値(MFR)(JIS K7210:190℃,2.16kg)は、用いる重合体の種類等によるが、通常は100g/10分以下とすることが好ましい。加工性及び以下に説明する発泡樹脂層とした場合の発泡状態を考慮すると10〜60g/10分の範囲に設定することが好ましい。このような数値範囲のものを使用することにより、より優れた耐スクラッチ性、摩耗性等を得ることができる。MFRが上記範囲内の場合には、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂含有樹脂層を押出し製膜により形成する際の温度上昇が少なく、非発泡状態で製膜できるため、後に絵柄模様層を形成する際に平滑な面に印刷処理をすることができて柄抜け等が少ない。また、MFRが大きすぎる場合は、樹脂が軟らかすぎることにより、発泡樹脂層として形成した場合の耐傷性が不十分となるおそれがある。 The melt flow rate value (MFR) of the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer (JIS K7210: 190 ° C., 2.16 kg) depends on the type of polymer used, but is usually 100 g / 10 min or less. Is preferred. Considering the workability and the foamed state when the foamed resin layer described below is taken into consideration, it is preferable to set it in the range of 10 to 60 g / 10 minutes. By using a material having such a numerical range, more excellent scratch resistance, wear resistance and the like can be obtained. When the MFR is within the above range, there is little increase in temperature when the resin layer containing the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin is formed by extrusion film formation, and the film can be formed in a non-foamed state. When a layer is formed, a printing process can be performed on a smooth surface, and pattern loss or the like is small. Moreover, when MFR is too large, there exists a possibility that the flaw resistance at the time of forming as a foamed resin layer may become inadequate because resin is too soft.
発泡剤含有樹脂層は発泡剤を含有する。 The foaming agent-containing resin layer contains a foaming agent.
発泡剤としては熱分解型発泡剤を用いることが好ましい。熱分解型発泡剤としては、例えば、アゾジカルボンアミド(ADCA)、アゾビスホルムアミド等のアゾ系;オキシベンゼンスルホニルヒドラジド(OBSH)、パラトルエンスルホニルヒドラジド等のヒドラジド系などが挙げられる。熱分解型発泡剤の含有量は、発泡剤の種類、発泡倍率等に応じて適宜設定できる。発泡倍率の観点からは、1.5倍以上、好ましくは3〜7倍程度であり、熱分解型発泡剤は、樹脂成分100重量部に対して、1〜20重量部程度とすることが好ましい。 It is preferable to use a pyrolytic foaming agent as the foaming agent. Examples of the thermally decomposable foaming agent include azo series such as azodicarbonamide (ADCA) and azobisformamide; hydrazide series such as oxybenzenesulfonyl hydrazide (OBSH) and paratoluenesulfonyl hydrazide. The content of the pyrolytic foaming agent can be appropriately set according to the type of foaming agent, the expansion ratio, and the like. From the viewpoint of the expansion ratio, it is 1.5 times or more, preferably about 3 to 7 times, and the pyrolytic foaming agent is preferably about 1 to 20 parts by weight with respect to 100 parts by weight of the resin component. .
発泡剤含有樹脂層を形成する樹脂組成物には、更に、発泡助剤を使用することができる。発泡助剤は、例えばヒドラジド系化合物が好適に用いられる。 A foaming aid can be further used for the resin composition forming the foaming agent-containing resin layer. As the foaming aid, for example, a hydrazide compound is preferably used.
ヒドラジド系化合物として、一般式(1):
R−CO−NHNH2 (1)
に示されるモノヒドラジド化合物、及び一般式(2):
H2NHN−X−NHNH2 (2)
に示されるジヒドラジド化合物を好適に使用することができる。
As a hydrazide compound, general formula (1):
R—CO—NHNH 2 (1)
And a monohydrazide compound represented by formula (2):
H 2 NHN-X-NHNH 2 (2)
The dihydrazide compound shown by can be used suitably.
前記一般式(1)のヒドラジド化合物としては、より具体的には、ラウリル酸ヒドラジド、サリチル酸ヒドラジド、ホルムヒドラジド、アセトヒドラジド、プロピオン酸ヒドラジド、p−ヒドロキシ安息香酸ヒドラジド、ナフトエ酸ヒドラジド、3−ヒドロキシ−2−ナフトエ酸ヒドラジド等を例示できる。 More specific examples of the hydrazide compound of the general formula (1) include lauric acid hydrazide, salicylic acid hydrazide, form hydrazide, acetohydrazide, propionic acid hydrazide, p-hydroxybenzoic acid hydrazide, naphthoic acid hydrazide, 3-hydroxy- Examples include 2-naphthoic acid hydrazide.
前記一般式(2)のジヒドラジド化合物は、具体的には、例えば、シュウ酸ジヒドラジド、マロン酸ジヒドラジド、コハク酸ジヒドラジド、アジピン酸ジヒドラジド、アゼライン酸ジヒドラジド、セバシン酸ジヒドラジド、ドデカン−2酸ジヒドラジド、マレイン酸ジヒドラジド、フマル酸ジヒドラジド、ジグリコール酸ジヒドラジド、酒石酸ジヒドラジド、リンゴ酸ジヒドラジド、イソフタル酸ジヒドラジド、テレフタル酸ジヒドラジド、ダイマー酸ジヒドラジド、2,6−ナフトエ酸ジヒドラジド等の2塩基酸ジヒドラジド等が挙げられる。更に、特公平2−4607号公報に記載の各種2塩基酸ジヒドラジド化合物、2,4−ジヒドラジノ−6−メチルアミノ−sym−トリアジン等も本発明のジヒドラジドとして用いることができる。 Specific examples of the dihydrazide compound of the general formula (2) include oxalic acid dihydrazide, malonic acid dihydrazide, succinic acid dihydrazide, adipic acid dihydrazide, azelaic acid dihydrazide, sebacic acid dihydrazide, dodecane-2-acid dihydrazide, and maleic acid. Examples include dihydrazide, fumaric acid dihydrazide, diglycolic acid dihydrazide, tartaric acid dihydrazide, malic acid dihydrazide, isophthalic acid dihydrazide, terephthalic acid dihydrazide, dimer acid dihydrazide, and dibasic acid dihydrazide such as 2,6-naphthoic acid dihydrazide. Furthermore, various dibasic acid dihydrazide compounds described in Japanese Patent Publication No. 2-4607, 2,4-dihydrazino-6-methylamino-sym-triazine, and the like can also be used as the dihydrazide of the present invention.
発泡助剤の含有量は、樹脂成分100重量部に対して、0.3〜10重量部程度が好ましく、1〜6重量部程度がより好ましい。 The content of the foaming aid is preferably about 0.3 to 10 parts by weight and more preferably about 1 to 6 parts by weight with respect to 100 parts by weight of the resin component.
発泡剤含有樹脂層を形成する樹脂組成物には、上記エチレン−メタクリル酸共重合体を主成分とする樹脂成分、発泡剤及び発泡助剤以外にも、例えば、無機充填剤、顔料、架橋助剤、安定剤及び滑剤等を使用することができる。 The resin composition forming the foaming agent-containing resin layer includes, for example, an inorganic filler, a pigment, a crosslinking aid, in addition to the resin component, the foaming agent and the foaming aid mainly composed of the ethylene-methacrylic acid copolymer. Agents, stabilizers, lubricants and the like can be used.
無機充填剤としては、例えば、炭酸カルシウム、水酸化アルミニウム、水酸化マグネシウム、三酸化アンチモン、モリブデン化合物等が挙げられる。無機充填剤を含むことにより、目透き抑制効果、表面特性向上効果等が得られる。無機充填剤の含有量は、樹脂成分100重量部に対して0〜100重量部程度が好ましく、20〜70重量部程度がより好ましい。 Examples of the inorganic filler include calcium carbonate, aluminum hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, antimony trioxide, and a molybdenum compound. By including an inorganic filler, an effect of suppressing see-through, an effect of improving surface characteristics, and the like are obtained. About 0-100 weight part is preferable with respect to 100 weight part of resin components, and, as for content of an inorganic filler, about 20-70 weight part is more preferable.
顔料については、無機顔料として、例えば、酸化チタン、カーボンブラック、黒色酸化鉄、黄色酸化鉄、黄鉛、モリブデートオレンジ、カドミウムイエロー、ニッケルチタンイエロー、クロムチタンイエロー、酸化鉄(弁柄)、カドミウムレッド、群青、紺青、コバルトブルー、酸化クロム、コバルトグリーン、アルミニウム粉、ブロンズ粉、雲母チタン等が挙げられる。また、有機顔料として、例えば、アニリンブラック、ペリレンブラック、アゾ系(アゾレーキ、不溶性アゾ、縮合アゾ)、多環式(イソインドリノン、イソインドリン、キノフタロン、ペリノン、フラバントロン、アントラピリミジン、アントラキノン、キナクリドン、ペリレン、ジケトピロロピロール、ジブロムアンザントロン、ジオキサジン、チオインジゴ、フタロシアニン、インダントロン、ハロゲン化フタロシアニン)等が挙げられる。顔料の含有量は、樹脂成分100重量部に対して3〜50重量部程度が好ましく、15〜30重量部程度がより好ましい。 Regarding pigments, examples of inorganic pigments include titanium oxide, carbon black, black iron oxide, yellow iron oxide, yellow lead, molybdate orange, cadmium yellow, nickel titanium yellow, chrome titanium yellow, iron oxide (valve), and cadmium. Examples include red, ultramarine blue, bitumen, cobalt blue, chromium oxide, cobalt green, aluminum powder, bronze powder, and mica titanium. Examples of organic pigments include aniline black, perylene black, azo (azo lake, insoluble azo, condensed azo), polycyclic (isoindolinone, isoindoline, quinophthalone, perinone, flavantron, anthrapyrimidine, anthraquinone, quinacridone. Perylene, diketopyrrolopyrrole, dibromoanthanthrone, dioxazine, thioindigo, phthalocyanine, indanthrone, halogenated phthalocyanine). The content of the pigment is preferably about 3 to 50 parts by weight and more preferably about 15 to 30 parts by weight with respect to 100 parts by weight of the resin component.
発泡剤含有樹脂層に対して電子線を照射してもよい。その方法としては、後記の製造方法に記載された方法に従って実施すればよい。 You may irradiate an electron beam with respect to a foaming agent containing resin layer. What is necessary is just to implement according to the method described in the manufacturing method of the postscript as the method.
なお、発泡剤含有樹脂層の厚さは40〜100μm程度が好ましい。 In addition, as for the thickness of a foaming agent containing resin layer, about 40-100 micrometers is preferable.
金属化合物含有樹脂層
本発明の樹脂積層体は、前記発泡剤含有樹脂層の片面又は両面に、金属化合物含有樹脂層が形成されている。
Metal compound-containing resin layer In the resin laminate of the present invention, a metal compound-containing resin layer is formed on one side or both sides of the foaming agent-containing resin layer.
本発明では、該金属化合物含有樹脂層は、非発泡樹脂層を形成する。 In the present invention, the metal compound-containing resin layer forms a non-foamed resin layer.
金属化合物含有樹脂層を構成する樹脂成分は、添加される金属化合物がイオン系架橋構造形成に寄与しないという理由から、当該樹脂層に水素結合が含まれないようなモノマーの組み合わせから得られる樹脂を用いる。 The resin component constituting the metal compound-containing resin layer is a resin obtained from a combination of monomers that does not contain hydrogen bonds in the resin layer because the added metal compound does not contribute to the formation of an ionic crosslinked structure. Use.
従って、例えばエチレンとOH基又はCOOH基を有しないモノマーとの組み合わせから得られるエチレン共重合体樹脂を好適に用いることができる。前記エチレン共重合体樹脂としては、例えばエチレン−酢酸ビニル共重合体樹脂(EVA)、エチレン−メチルメタクリレート共重合体樹脂(EMMA)、エチレン−エチルアクリレート共重合体樹脂(EEA)、エチレン−メチルアクリレート共重合体樹脂(EMA)、エチレン−αオレフィン共重合体を用いることができる。また、ポリエチレン、ポリプロピレン、ポリブテン、ポリブタジエン、ポリイソプレン等の樹脂単体からなるポリオレフィン系樹脂を用いることもできる。エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂含有樹脂層(特に、発泡剤含有樹脂層)との共押出し性を考慮して、融点・流動特性を合せ易いという理由から、この中でも、特にポリエチレン、EVA及びEMMA樹脂を用いることが好ましい。 Therefore, for example, an ethylene copolymer resin obtained from a combination of ethylene and a monomer having no OH group or COOH group can be suitably used. Examples of the ethylene copolymer resin include ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer resin (EVA), ethylene-methyl methacrylate copolymer resin (EMMA), ethylene-ethyl acrylate copolymer resin (EEA), and ethylene-methyl acrylate. A copolymer resin (EMA) or an ethylene-α olefin copolymer can be used. In addition, a polyolefin-based resin composed of a resin simple substance such as polyethylene, polypropylene, polybutene, polybutadiene, polyisoprene can also be used. In view of coextrusion with an ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin-containing resin layer (particularly, a foaming agent-containing resin layer), the melting point and flow characteristics are easy to match. It is preferable to use EVA and EMMA resins.
金属化合物含有樹脂層は、金属化合物を含有する。 The metal compound-containing resin layer contains a metal compound.
金属化合物としては、前述のエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂含有樹脂層の樹脂成分として用いられるエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂に起因するイオン性基(−COO−等)とイオン性の架橋構造(擬似架橋構造)を形成し得るものであればよく、例えば、酸化マグネシウム、酸化亜鉛、酸化アルミニウム、酸化ジルコニウム、酸化アンチモン、酸化チタン、酸化ケイ素、窒化ホウ素、窒化アルミニウム及び金属石鹸からなる群から選択される少なくとも1種が挙げられる。 As the metal compound, the above-mentioned ethylene - (meth) ethylene is used as the resin component of the acrylic acid copolymer resin containing resin layer - (meth) ionic group due to the acrylic acid copolymer resin (-COO -, etc.) And an ionic crosslinked structure (pseudo-crosslinked structure) may be used, for example, magnesium oxide, zinc oxide, aluminum oxide, zirconium oxide, antimony oxide, titanium oxide, silicon oxide, boron nitride, aluminum nitride and There may be mentioned at least one selected from the group consisting of metal soaps.
金属石鹸としては、ステアリン酸亜鉛、ステアリン酸マグネシウム、及び、ラウリン酸亜鉛、リシノール酸亜鉛、オクチル酸亜鉛等の脂肪酸金属塩が好ましい。 As the metal soap, fatty acid metal salts such as zinc stearate, magnesium stearate, zinc laurate, zinc ricinoleate and zinc octylate are preferable.
この中でも、酸化マグネシウム及び酸化亜鉛の少なくとも1種が好ましい。 Among these, at least one of magnesium oxide and zinc oxide is preferable.
金属化合物の粒子径は限定されないが、3.5μm以下が好ましく、イオン性の観点からは0.6μm以下がより好ましい。下限値としては0.02μm程度である。ただし、金属石鹸の場合は、層形成時または複合時に溶融状態となるため、粒径の下限値としては特に制限されない。 Although the particle diameter of a metal compound is not limited, 3.5 micrometers or less are preferable and 0.6 micrometers or less are more preferable from an ionic viewpoint. The lower limit is about 0.02 μm. However, in the case of metal soap, it is in a molten state at the time of layer formation or at the time of compounding, so the lower limit of particle size is not particularly limited.
また、金属化合物含有樹脂層中の金属化合物の含有量は、5重量%以上が好ましく、10重量%以上がより好ましく、上限値としては40重量%程度である。 Further, the content of the metal compound in the metal compound-containing resin layer is preferably 5% by weight or more, more preferably 10% by weight or more, and the upper limit is about 40% by weight.
金属化合物含有樹脂層の厚さは限定的ではないが、5〜50μm程度が好ましい。 Although the thickness of a metal compound containing resin layer is not limited, About 5-50 micrometers is preferable.
接着樹脂層
更に、発泡樹脂層の裏面(後記の繊維質シートが積層される面)には、繊維質シートとの接着力を向上させる目的で接着樹脂層を有してもよい。
Further, an adhesive resin layer may be provided on the back surface of the foamed resin layer (the surface on which the fibrous sheet described later is laminated) for the purpose of improving the adhesive force with the fibrous sheet.
接着樹脂層の樹脂成分としては、エチレン−酢酸ビニル共重合体(EVA)が好ましい。EVAは特に限定されず、公知又は市販のものを使用することができる。特に、酢酸ビニル成分(VA成分)が10〜30重量%であるものが好ましく、15〜30質量%であるものがより好ましい。 As the resin component of the adhesive resin layer, an ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA) is preferable. EVA is not particularly limited, and known or commercially available EVA can be used. In particular, the vinyl acetate component (VA component) is preferably 10 to 30% by weight, and more preferably 15 to 30% by weight.
接着樹脂層の厚さは限定的ではないが、5〜50μm程度が好ましい。 The thickness of the adhesive resin layer is not limited, but is preferably about 5 to 50 μm.
絵柄模様層
エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含む発泡剤含有樹脂層と金属化合物含有樹脂層の間、若しくは金属化合物含有樹脂層の上には、絵柄模様層が形成されていてもよい。なお、絵柄模様層をエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含む発泡剤含有樹脂層と金属化合物含有樹脂層の間に形成する場合は、上記金属化合物含有樹脂層に含有する金属化合物と同様の金属化合物を結着材樹脂中に添加することが好ましい。
Even if a pattern layer is formed between the foaming agent-containing resin layer containing the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin and the metal compound-containing resin layer or on the metal compound-containing resin layer Good. When the pattern layer is formed between the foaming agent-containing resin layer containing the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin and the metal compound-containing resin layer, the metal compound contained in the metal compound-containing resin layer and It is preferable to add the same metal compound to the binder resin.
絵柄模様層は、樹脂積層体に意匠性を付与する。絵柄模様としては、例えば木目模様、石目模様、砂目模様、タイル貼模様、煉瓦積模様、布目模様、皮絞模様、幾何学図形、文字、記号、抽象模様等が挙げられる。絵柄模様は、発泡壁紙の種類に応じて選択できる。 The design pattern layer imparts design properties to the resin laminate. Examples of the design pattern include a wood grain pattern, a stone pattern, a grain pattern, a tiled pattern, a brickwork pattern, a cloth pattern, a leather pattern, a geometric figure, a character, a symbol, and an abstract pattern. The pattern can be selected according to the type of foam wallpaper.
絵柄模様層は、例えば、絵柄模様を印刷することで形成できる。印刷手法としては、グラビア印刷、フレキソ印刷、シルクスクリーン印刷、オフセット印刷等が挙げられる。印刷インキとしては、着色剤、結着材樹脂、溶剤を含む印刷インキが使用できる。これらのインキは公知又は市販のものを使用してもよい。 The pattern pattern layer can be formed, for example, by printing a pattern pattern. Examples of printing methods include gravure printing, flexographic printing, silk screen printing, offset printing, and the like. As the printing ink, a printing ink containing a colorant, a binder resin, and a solvent can be used. These inks may be known or commercially available.
着色剤としては、例えば、前記の発泡剤含有樹脂層で使用されるような顔料を適宜使用することができる。 As the colorant, for example, a pigment used in the above-described foaming agent-containing resin layer can be appropriately used.
結着材樹脂は、基材シートの種類に応じて設定できる。例えば、アクリル系樹脂、スチレン系樹脂、ポリエステル系樹脂、ウレタン系樹脂、塩素化ポリオレフィン系樹脂、塩化ビニル−酢酸ビニル共重合体系樹脂、ポリビニルブチラール樹脂、アルキド系樹脂、石油系樹脂、ケトン樹脂、エポキシ系樹脂、メラミン系樹脂、フッ素系樹脂、シリコーン系樹脂、繊維素誘導体、ゴム系樹脂等が挙げられる。 The binder resin can be set according to the type of the base sheet. For example, acrylic resin, styrene resin, polyester resin, urethane resin, chlorinated polyolefin resin, vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate copolymer resin, polyvinyl butyral resin, alkyd resin, petroleum resin, ketone resin, epoxy Resin, melamine resin, fluorine resin, silicone resin, fiber derivative, rubber resin and the like.
溶剤(又は分散媒)としては、例えば、ヘキサン、ヘプタン、オクタン、トルエン、キシレン、エチルベンゼン、シクロヘキサン、メチルシクロヘキサン等の石油系有機溶剤;酢酸エチル、酢酸ブチル、酢酸−2−メトキシエチル、酢酸−2−エトキシエチル等のエステル系有機溶剤;メチルアルコール、エチルアルコール、ノルマルプロピルアルコール、イソプロピルアルコール、イソブチルアルコール、エチレングリコール、プロピレングリコール等のアルコール系有機溶剤;アセトン、メチルエチルケトン、メチルイソブチルケトン、シクロヘキサノン等のケトン系有機溶剤;ジエチルエーテル、ジオキサン、テトラヒドロフラン等のエーテル系有機溶剤、;ジクロロメタン、四塩化炭素、トリクロロエチレン、テトラクロロエチレン等の塩素系有機溶剤;水などが挙げられる。これらの溶剤は単独、又は混合物として用いられる。 Examples of the solvent (or dispersion medium) include petroleum organic solvents such as hexane, heptane, octane, toluene, xylene, ethylbenzene, cyclohexane, and methylcyclohexane; ethyl acetate, butyl acetate, acetic acid-2-methoxyethyl, acetic acid-2 -Ester-based organic solvents such as ethoxyethyl; alcohol-based organic solvents such as methyl alcohol, ethyl alcohol, normal propyl alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, isobutyl alcohol, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol; ketones such as acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, methyl isobutyl ketone, and cyclohexanone Organic solvents; ether organic solvents such as diethyl ether, dioxane, tetrahydrofuran; dichloromethane, carbon tetrachloride, trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene, etc. Chlorinated organic solvents; and water. These solvents are used alone or as a mixture.
絵柄模様層の厚みは、絵柄模様の種類より異なるが、一般には0.1〜10μm程度とすることが好ましい。 The thickness of the design pattern layer is different from the type of design pattern, but is generally preferably about 0.1 to 10 μm.
エンボス
本発明の樹脂積層体は、おもて面からエンボス加工されていてもよい。エンボス加工は、エンボス版等の公知の手段により実施することができる。例えば、複合型表面樹脂層のおもて面を加熱軟化後、エンボス版を押圧することにより所望のエンボス模様を賦型できる。エンボス模様としては、例えば、木目板導管溝、石板表面凹凸、布表面テクスチャア、梨地、砂目、ヘアライン、万線条溝等がある。
Embossing The resin laminate of the present invention may be embossed from the front surface. Embossing can be performed by known means such as an embossed plate. For example, a desired embossed pattern can be formed by pressing the embossed plate after heating and softening the front surface of the composite surface resin layer. Examples of the embossed pattern include a wood grain plate conduit groove, a stone plate surface unevenness, a cloth surface texture, a satin texture, a grain texture, a hairline, and a multiline groove.
≪樹脂積層シート≫
本発明の樹脂積層体を繊維質シート上に積層することにより樹脂積層シートとすることができる。
≪Resin laminated sheet≫
A resin laminate sheet can be obtained by laminating the resin laminate of the present invention on a fibrous sheet.
繊維質シートとしては限定されず、公知の壁紙基材(裏打紙)などが利用できる。 The fiber sheet is not limited, and a known wallpaper base material (backing paper) can be used.
具体的には、壁紙用一般紙(パルプ主体のシートを既知のサイズ剤でサイズ処理したもの);難燃紙(パルプ主体のシートをスルファミン酸グアニジン、リン酸グアジニン等の難燃剤で処理したもの);水酸化アルミニウム、水酸化マグネシウム等の無機添加剤を含む無機質紙;上質紙;薄用紙などが挙げられる。 Specifically, wallpaper general paper (pulp-based sheet sized with a known sizing agent); flame-retardant paper (pulp-based sheet treated with a flame retardant such as guanidine sulfamate or guanidine phosphate) ); Inorganic paper containing inorganic additives such as aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide; fine paper; thin paper.
紙質基材の坪量は限定的ではないが、50〜300g/m2程度が好ましく、50〜120g/m2程度がより好ましい。 The basis weight of the paper quality substrate is not limited, but preferably about 50 to 300 g / m 2, about 50 to 120 / m 2 is more preferable.
≪樹脂積層体の製造方法≫
本発明の樹脂積層体は、(i)樹脂成分としてエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含む発泡剤含有樹脂層の片面又は両面に、樹脂成分が水素結合が含まれないモノマーからなる共重合体である金属化合物含有樹脂層を積層させ、(ii)この様に層構成を有する未発泡中間体を熱処理し、前記発泡剤含有樹脂層を発泡樹脂層にし、(iii)前記熱処理又は別途の熱処理により、前記発泡剤含有樹脂層と前記金属化合物含有樹脂層を複合化することにより、製造できる。
≪Method for producing resin laminate≫
The resin laminate of the present invention comprises (i) a monomer in which the resin component does not contain hydrogen bonds on one or both sides of a foaming agent-containing resin layer containing an ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin as a resin component. Laminating a metal compound-containing resin layer that is a copolymer, (ii) heat-treating the unfoamed intermediate having a layer structure in this way, and making the foaming agent-containing resin layer a foamed resin layer, and (iii) the heat treatment or It can be manufactured by combining the foaming agent-containing resin layer and the metal compound-containing resin layer by separate heat treatment.
この様に、発泡剤含有樹脂層を熱処理し発泡させることにより、発泡樹脂層を得ることができる。発泡樹脂層の発泡状態(例えば、発泡セルの大きさ、発泡セル密度等)は限定されず、樹脂積層体及び樹脂積層シートの種類、用途等に応じて適宜設計できる。 Thus, a foamed resin layer can be obtained by heat-treating and foaming the foaming agent-containing resin layer. The foamed state of the foamed resin layer (for example, the size of the foamed cell, the foamed cell density, etc.) is not limited, and can be appropriately designed according to the type and use of the resin laminate and the resin laminate sheet.
発泡剤含有樹脂層を熱処理した後の発泡後の発泡樹脂層の厚さは、300〜700μm程度が好ましい。 The thickness of the foamed resin layer after foaming after heat-treating the foaming agent-containing resin layer is preferably about 300 to 700 μm.
この複合化のための熱処理は、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含む発泡剤含有樹脂層が溶融する条件であればよい。従って、発泡剤含有樹脂層を発泡樹脂層にする(発泡させる)ための熱処理により、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含む発泡剤含有樹脂層が溶融するのであれば、発泡のための熱処理を複合化のための熱処理として利用することができる。 The heat treatment for the composite may be performed under the condition that the foaming agent-containing resin layer containing the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin is melted. Therefore, if the foaming agent-containing resin layer containing the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin is melted by the heat treatment for forming (foaming) the foaming agent-containing resin layer, the foaming agent-containing resin layer is foamed. This heat treatment can be used as a heat treatment for compounding.
本発明では、この様な熱処理により、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含む発泡剤含有樹脂層が溶融し、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂に起因するイオン性基(−COO−等)が、隣接する金属化合物含有樹脂層中の金属化合物とイオン性の架橋構造(擬似架橋構造)を形成することにより表面強度が向上すると考えられる。 In the present invention, by such heat treatment, the foaming agent-containing resin layer containing the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin is melted, and the ionic group ( -COO -, etc.) is believed to surface strength by forming metal compound and an ionic cross-linking structure (pseudo crosslinking structure) of adjacent metal compound-containing resin layer is improved.
樹脂積層体の製造方法としては、前述の通り、例えば、繊維質シート上に、(I)エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含む発泡剤含有樹脂層と金属化合物含有樹脂層を同時に形成した後、或いは、(II)エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含む発泡剤含有樹脂層及び金属化合物含有樹脂層を順に形成した後、この樹脂層を熱処理(加熱溶融)させること(溶融押出し製膜)により製造できる。この様に、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含む発泡剤含有樹脂層及び金属化合物含有樹脂層は別々に積層してもよく、同時押出し製膜により積層してもよい。同時押出し製膜の場合には、例えば、両面に金属化合物含有樹脂層を有する場合には、3つの層に対応する溶融樹脂を同時に押出すことにより3層の同時製膜(3層同時押出し製膜)が可能なマルチマニホールドタイプのTダイを用いることができる。 As a manufacturing method of the resin laminate, as described above, for example, a foaming agent-containing resin layer containing a (I) ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin and a metal compound-containing resin layer are simultaneously formed on a fibrous sheet. After forming, or (II) after sequentially forming a foaming agent-containing resin layer and a metal compound-containing resin layer containing an ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin, the resin layer is heat-treated (heated and melted). It can be produced by (melt extrusion film formation). Thus, the foaming agent-containing resin layer containing the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin and the metal compound-containing resin layer may be laminated separately or by coextrusion film formation. In the case of coextrusion film formation, for example, in the case of having a metal compound-containing resin layer on both sides, three layers of simultaneous film formation (three-layer coextrusion production) are performed by simultaneously extruding molten resin corresponding to the three layers. A multi-manifold type T die capable of forming a film) can be used.
前記エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含む発泡剤含有樹脂層を製膜後、発泡前に電子線照射を行うことができる。これにより樹脂成分を架橋して発泡樹脂層の表面強度、発泡特性等を調整することができる。電子線のエネルギーは、150〜250kV程度が好ましく、175〜200kV程度がより好ましい。照射量は、10〜100kGy程度が好ましく、10〜50kGy程度がより好ましい。電子線源としては、公知の電子線照射装置が使用できる。この電子線照射は、後述の絵柄模様層の形成後でもよい。 After forming the foaming agent-containing resin layer containing the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin, electron beam irradiation can be performed before foaming. Thereby, the resin component can be cross-linked to adjust the surface strength, foaming characteristics, etc. of the foamed resin layer. The energy of the electron beam is preferably about 150 to 250 kV, more preferably about 175 to 200 kV. The irradiation amount is preferably about 10 to 100 kGy, and more preferably about 10 to 50 kGy. A known electron beam irradiation apparatus can be used as the electron beam source. This electron beam irradiation may be performed after the formation of a pattern layer to be described later.
次に金属化合物含有樹脂層上に、絵柄模様層を形成する。 Next, a pattern layer is formed on the metal compound-containing resin layer.
次いで、発泡剤含有樹脂層を加熱することにより発泡樹脂層を形成する。加熱条件は、熱分解型発泡剤の分解により発泡樹脂層が形成される条件ならば限定されない。加熱温度は210〜240℃程度が好ましく、加熱時間は20〜80秒程度が好ましい。また、この熱処理により、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂含有樹脂層と金属化合物含有樹脂層とが複合化する。 Next, the foamed resin layer is formed by heating the foaming agent-containing resin layer. The heating conditions are not limited as long as the foamed resin layer is formed by the decomposition of the pyrolytic foaming agent. The heating temperature is preferably about 210 to 240 ° C., and the heating time is preferably about 20 to 80 seconds. In addition, the heat treatment makes the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin-containing resin layer and the metal compound-containing resin layer complex.
本発明の樹脂積層体は、樹脂成分としてエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含む発泡剤含有樹脂層及び金属化合物含有樹脂層を、熱処理により複合化しているため、発泡樹脂層の樹脂製膜性を良好に維持しながら、発泡壁紙等の表面強度を更に向上させることができ、そして、生産性を良好に維持できる。この効果は、熱処理により、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂が溶融し、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂に起因するイオン性基(−COO−等)が隣接する金属化合物含有樹脂層中の金属化合物とイオン性の架橋構造(擬似架橋構造)を形成することにより表面強度が向上することに基づくと考えられている。 Since the resin laminate of the present invention is a composite of a foaming agent-containing resin layer and a metal compound-containing resin layer containing an ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin as a resin component by heat treatment, the resin of the foamed resin layer The surface strength of foamed wallpaper and the like can be further improved while maintaining the film forming property, and the productivity can be maintained well. This effect, by heat treatment, ethylene - (meth) melted acrylic acid copolymer resin, an ethylene - (meth) ionic group due to the acrylic acid copolymer resin (-COO -, etc.) is adjacent metal compound It is considered that the surface strength is improved by forming an ionic cross-linked structure (pseudo cross-linked structure) with the metal compound in the containing resin layer.
以下に実施例及び比較例を示して本発明を具体的に説明する。但し、本発明は実施例に限定されない。 The present invention will be specifically described below with reference to examples and comparative examples. However, the present invention is not limited to the examples.
実施例1
3種3層マルチマニホールドTダイ押出し機を用いて、以下の表1の配合にて、i)非発泡樹脂層(金属化合物含有樹脂層)/ii)発泡剤含有樹脂層/iii)非発泡樹脂層の順に厚み10μm/70μm/10μmになるように製膜した。
Example 1
Using a three-type, three-layer multi-manifold T-die extruder, i) non-foamed resin layer (metal compound-containing resin layer) / ii) foaming agent-containing resin layer / iii) non-foamed resin The layers were formed in the order of the layers so as to have a thickness of 10 μm / 70 μm / 10 μm.
製膜後、90℃に加熱した裏打紙(WK−665DO、興人製)に前記iii)層の面を積層し、i)層上から電子線(195kV,30kGy)を照射して、積層樹脂層を樹脂架橋した。これにより、積層樹脂シート原反を作製した。 After the film formation, the surface of the iii) layer is laminated on a backing paper (WK-665DO, manufactured by Kojin Co., Ltd.) heated to 90 ° C., and i) an electron beam (195 kV, 30 kGy) is irradiated from above the layer to obtain a laminated resin The layer was resin cross-linked. Thereby, the laminated resin sheet original fabric was produced.
次いで、i)層上にコロナ放電処理を行い、グラビア印刷機により絵柄印刷として水性インキ(「ハイドリック」、大日精化工業製)を用いて布目絵柄を印刷した。 Next, a corona discharge treatment was performed on the i) layer, and a texture pattern was printed using a water-based ink (“Hydric”, manufactured by Dainichi Seika Kogyo Co., Ltd.) as a pattern print by a gravure printing machine.
次に、オーブンにて加熱(220℃×35秒)し、樹脂層を溶融させると同時に、発泡剤含有樹脂層に含有する発泡剤を発泡させ発泡樹脂層にするとともに、前記発泡剤含有樹脂層及び金属化合物含有樹脂層を複合化して、樹脂積層シートを形成した。 Next, it is heated in an oven (220 ° C. × 35 seconds) to melt the resin layer, and at the same time, the foaming agent contained in the foaming agent-containing resin layer is foamed into a foamed resin layer, and the foaming agent-containing resin layer And the metal compound containing resin layer was compounded and the resin laminated sheet was formed.
次に、その発泡体に対して布目パターンの凹凸エンボスを施し樹脂積層シートを得た。 Next, the foam was embossed with a textured pattern to obtain a resin laminated sheet.
各層は、それぞれ以下の成分を用いて形成した。 Each layer was formed using the following components.
実施例2
実施例1のi)非発泡樹脂層(金属化合物含有樹脂層)の金属化合物を、酸化亜鉛(粒子径0.6μm)に替えた以外は、実施例1と同様にして作製した。
Example 2
Example 1 i) A non-foamed resin layer (metal compound-containing resin layer) was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the metal compound was changed to zinc oxide (particle diameter 0.6 μm).
実施例3
実施例1のiii)非発泡樹脂層のエチレン−酢酸ビニル共重合樹脂100部に酸化マグネシウム(粒子径0.5μm)30部を添加し、金属化合物含有樹脂層とした以外は、実施例1と同様にして作製した。
Example 3
Iii of Example 1) Example 1 except that 30 parts of magnesium oxide (particle diameter 0.5 μm) was added to 100 parts of the ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer resin of the non-foamed resin layer to obtain a metal compound-containing resin layer. It produced similarly.
比較例1
実施例1のi)非発泡樹脂層(金属化合物含有樹脂層)に金属化合物を、含まない以外は、実施例1と同様にして作製した。
Comparative Example 1
Example 1 i) A non-foamed resin layer (metal compound-containing resin layer) was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the metal compound was not included.
比較例2
実施例1のii)発泡剤含有樹脂層のエチレン−メタクリル酸共重合樹脂を、「ポリエチレン樹脂(ペトロセン208 東ソー製)」に替えた以外は、実施例1と同様にして作製した。
Comparative Example 2
It was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the ethylene-methacrylic acid copolymer resin in the ii) foaming agent-containing resin layer of Example 1 was replaced with “polyethylene resin (Petrocene 208 manufactured by Tosoh Corporation)”.
比較例3
実施例1のi)非発泡樹脂層(金属化合物含有樹脂層)のポリエチレン樹脂を「エチレン−メタクリル酸共重合樹脂(ニュクレルN1560 三井・デュポン ポリケミカル製)」層にして作製した。他は同じである。
Comparative Example 3
In Example 1, i) a non-foamed resin layer (metal compound-containing resin layer) polyethylene resin was prepared as an “ethylene-methacrylic acid copolymer resin (Nucrel N1560, Mitsui / DuPont Polychemical)” layer. Others are the same.
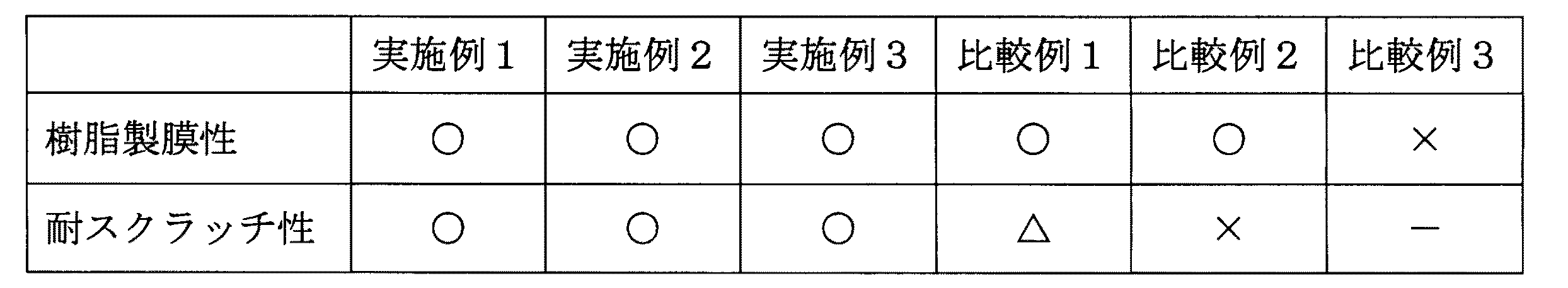
試験例1
実施例及び比較例で得られた樹脂積層シートについて、耐スクラッチ性及び樹脂製膜性を調べた。
Test example 1
About the resin lamination sheet obtained by the Example and the comparative example, the scratch resistance and resin film-forming property were investigated.
各試験方法及び評価基準は次の通りである。
(樹脂製膜性)
壁紙の最表層の樹脂層(単層または2層)の押出し製膜形成時の製膜状態を観察した。評価基準は次のとおり。○:樹脂切れ、穴開きなし。 ×:樹脂切れ、穴開きで製膜できない。
Each test method and evaluation criteria are as follows.
(Resin film-forming properties)
The state of film formation during extrusion film formation of the outermost resin layer (single layer or two layers) of the wallpaper was observed. The evaluation criteria are as follows. ○: Resin cut, no hole. X: The film could not be formed due to the resin being cut or perforated.
(耐スクラッチ性)
壁紙工業会制定の表面強化壁紙の性能評価方法に準じて行った。評価基準としては次のとおり。○:表面に変化なし。 △:表層のみ傷付く。 ×:傷が発泡樹脂層まで達する。
(Scratch resistance)
This was performed in accordance with the performance evaluation method for surface-enhanced wallpaper established by the Wallpaper Industry Association. The evaluation criteria are as follows. ○: No change on the surface. Δ: Only the surface layer is damaged. X: Scratches reach the foamed resin layer.
評価結果は下記表2の通りである。 The evaluation results are as shown in Table 2 below.
実施例1〜3は、発泡樹脂層としてエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂含有樹脂層を使用し、非発泡樹脂層として金属化合物含有樹脂層を使用したものである。このため、実施例1〜3では、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂含有樹脂層と金属化合物含有樹脂層が、熱処理(加熱溶融)により複合化(一体化)して、エチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂と金属化合物含有非発泡樹脂層が反応して発泡樹脂層が硬くなり、従来のエチレン−メタクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含む発泡樹脂層よりも強靭な樹脂層が形成された。その結果、耐スクラッチ性が優れた樹脂積層シートを作成することができ、また、押出し製膜時にも不具合なく製膜できた。
In Examples 1 to 3, an ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin-containing resin layer is used as the foamed resin layer, and a metal compound-containing resin layer is used as the non-foamed resin layer. For this reason, in Examples 1-3, the ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin-containing resin layer and the metal compound-containing resin layer are combined (integrated) by heat treatment (heating and melting), and ethylene- ( The (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin and the metal compound-containing non-foamed resin layer react to harden the foamed resin layer, forming a tougher resin layer than the conventional foamed resin layer containing ethylene-methacrylic acid copolymer resin. It was done. As a result, a resin laminated sheet having excellent scratch resistance could be produced, and the film could be formed without any trouble during extrusion film formation.
Claims (4)
(1)前記発泡剤含有樹脂層が、樹脂成分としてエチレン−(メタ)アクリル酸共重合体樹脂を含み、
(2)前記金属化合物含有樹脂層の樹脂成分は、水素結合が含まれないモノマーからなる共重合体であり、
(3)前記熱処理又は別途の熱処理により、前記発泡剤含有樹脂層と前記金属化合物含有樹脂層とが複合化されている、
ことを特徴とする樹脂積層体。 A resin laminate obtained by heat-treating an unfoamed intermediate having a layer structure in which a metal compound-containing resin layer is laminated on one side or both sides of a foaming agent-containing resin layer, and making the foaming agent-containing resin layer a foamed resin layer Because
(1) The foaming agent-containing resin layer contains an ethylene- (meth) acrylic acid copolymer resin as a resin component,
(2) The resin component of the metal compound-containing resin layer is a copolymer composed of monomers that do not contain hydrogen bonds,
(3) The foaming agent-containing resin layer and the metal compound-containing resin layer are combined by the heat treatment or a separate heat treatment,
The resin laminated body characterized by the above-mentioned.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011026468A JP5760472B2 (en) | 2011-02-09 | 2011-02-09 | Resin laminate and resin laminate sheet |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011026468A JP5760472B2 (en) | 2011-02-09 | 2011-02-09 | Resin laminate and resin laminate sheet |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2012166350A true JP2012166350A (en) | 2012-09-06 |
| JP5760472B2 JP5760472B2 (en) | 2015-08-12 |
Family
ID=46971006
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011026468A Expired - Fee Related JP5760472B2 (en) | 2011-02-09 | 2011-02-09 | Resin laminate and resin laminate sheet |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5760472B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012166349A (en) * | 2011-02-09 | 2012-09-06 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Resin laminate, and resin laminated sheet |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007270386A (en) * | 2006-03-31 | 2007-10-18 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Method and system for producing foam wallpaper |
-
2011
- 2011-02-09 JP JP2011026468A patent/JP5760472B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007270386A (en) * | 2006-03-31 | 2007-10-18 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Method and system for producing foam wallpaper |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012166349A (en) * | 2011-02-09 | 2012-09-06 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Resin laminate, and resin laminated sheet |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5760472B2 (en) | 2015-08-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4807269B2 (en) | Raw material for foam wallpaper and foam wallpaper | |
| JP4006603B2 (en) | Method for producing foam wallpaper | |
| JP5569290B2 (en) | Foam laminated sheet | |
| JP5760471B2 (en) | Resin laminate and resin laminate sheet | |
| JP4667151B2 (en) | Foam wallpaper | |
| JP5703810B2 (en) | Resin laminate and resin laminate sheet | |
| JP5760472B2 (en) | Resin laminate and resin laminate sheet | |
| JP4810951B2 (en) | Wall decoration sheet | |
| JP2008081886A (en) | Foam wallpaper | |
| JP4748014B2 (en) | Foam wallpaper | |
| JP5725696B2 (en) | Foam wallpaper | |
| JP5195960B2 (en) | Foam wallpaper | |
| JP2012213940A (en) | Laminated sheet and foamed laminated sheet | |
| JP4962457B2 (en) | Method for producing a raw material for foam wallpaper | |
| JP5974783B2 (en) | Laminated sheet and foam laminated sheet | |
| JP2007046207A (en) | Foam wallpaper | |
| JP5786560B2 (en) | Method for producing foamed laminated sheet | |
| JP5240351B2 (en) | Foam wallpaper | |
| JP5817352B2 (en) | Method for producing foamed laminated sheet | |
| JP5899753B2 (en) | LAMINATED SHEET AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING FOAM LAMINATED SHEET | |
| JP2007291598A (en) | Foam wallpaper | |
| JP2007270412A (en) | Foam wallpaper | |
| JP2007270413A (en) | Foam wallpaper | |
| JP2011144494A (en) | Decorative sheet for wall covering | |
| JP2008081885A (en) | Foam wallpaper |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20131216 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20140918 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20140924 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20141120 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20150512 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20150525 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5760472 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |