JP2009537507A - アテローム性動脈硬化症に対して保護的な自己抗体を誘導するIL−1α免疫法 - Google Patents
アテローム性動脈硬化症に対して保護的な自己抗体を誘導するIL−1α免疫法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2009537507A JP2009537507A JP2009510567A JP2009510567A JP2009537507A JP 2009537507 A JP2009537507 A JP 2009537507A JP 2009510567 A JP2009510567 A JP 2009510567A JP 2009510567 A JP2009510567 A JP 2009510567A JP 2009537507 A JP2009537507 A JP 2009537507A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- atherosclerosis
- mammal
- disease
- mice
- use according
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 201000001320 Atherosclerosis Diseases 0.000 title claims abstract description 37
- 230000003053 immunization Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 15
- 238000002649 immunization Methods 0.000 title abstract description 13
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 title description 3
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 22
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 20
- 208000005764 Peripheral Arterial Disease Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 208000030831 Peripheral arterial occlusive disease Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 208000026106 cerebrovascular disease Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 208000029078 coronary artery disease Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 208000031225 myocardial ischemia Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 241000124008 Mammalia Species 0.000 claims abstract 17
- 241000699670 Mus sp. Species 0.000 claims description 69
- 102000013918 Apolipoproteins E Human genes 0.000 claims description 28
- 108010025628 Apolipoproteins E Proteins 0.000 claims description 28
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 24
- 241000699666 Mus <mouse, genus> Species 0.000 claims description 13
- WNROFYMDJYEPJX-UHFFFAOYSA-K aluminium hydroxide Chemical group [OH-].[OH-].[OH-].[Al+3] WNROFYMDJYEPJX-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 claims description 8
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 claims description 6
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 claims description 6
- 241000283707 Capra Species 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 241000282326 Felis catus Species 0.000 claims description 3
- 241001494479 Pecora Species 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229960001005 tuberculin Drugs 0.000 claims description 3
- 241000282898 Sus scrofa Species 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000002671 adjuvant Substances 0.000 claims 4
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 claims 3
- 241000282472 Canis lupus familiaris Species 0.000 claims 2
- 241000700605 Viruses Species 0.000 claims 2
- 241000282887 Suidae Species 0.000 claims 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 abstract description 6
- 210000002966 serum Anatomy 0.000 description 27
- HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N cholesterol Chemical compound C1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CCCC(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N 0.000 description 16
- 230000003902 lesion Effects 0.000 description 16
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 description 12
- 229940037003 alum Drugs 0.000 description 11
- 210000000709 aorta Anatomy 0.000 description 11
- 238000002965 ELISA Methods 0.000 description 10
- 230000003143 atherosclerotic effect Effects 0.000 description 9
- 210000001744 T-lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 7
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 7
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 7
- 235000012000 cholesterol Nutrition 0.000 description 7
- 235000005911 diet Nutrition 0.000 description 7
- 230000037213 diet Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000013258 ApoE Receptor knockout mouse model Methods 0.000 description 5
- 108091003079 Bovine Serum Albumin Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 description 5
- 101001002629 Mus musculus Interleukin-1 alpha Proteins 0.000 description 5
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 210000003719 b-lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 5
- 229940098773 bovine serum albumin Drugs 0.000 description 5
- 230000003472 neutralizing effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000008188 pellet Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000003442 weekly effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- BHQCQFFYRZLCQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N (3alpha,5alpha,7alpha,12alpha)-3,7,12-trihydroxy-cholan-24-oic acid Natural products OC1CC2CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(CCC(O)=O)C)C1(C)C(O)C2 BHQCQFFYRZLCQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 208000037260 Atherosclerotic Plaque Diseases 0.000 description 4
- 101100404912 Caenorhabditis elegans nob-1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 239000004380 Cholic acid Substances 0.000 description 4
- WZUVPPKBWHMQCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Haematoxylin Chemical compound C12=CC(O)=C(O)C=C2CC2(O)C1C1=CC=C(O)C(O)=C1OC2 WZUVPPKBWHMQCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 241000282412 Homo Species 0.000 description 4
- 238000010171 animal model Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000005875 antibody response Effects 0.000 description 4
- 210000001367 artery Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 230000000923 atherogenic effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 210000004369 blood Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 239000008280 blood Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 description 4
- 235000019416 cholic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- BHQCQFFYRZLCQQ-OELDTZBJSA-N cholic acid Chemical compound C([C@H]1C[C@H]2O)[C@H](O)CC[C@]1(C)[C@@H]1[C@@H]2[C@@H]2CC[C@H]([C@@H](CCC(O)=O)C)[C@@]2(C)[C@@H](O)C1 BHQCQFFYRZLCQQ-OELDTZBJSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229960002471 cholic acid Drugs 0.000 description 4
- KXGVEGMKQFWNSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N deoxycholic acid Natural products C1CC2CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(CCC(O)=O)C)C1(C)C(O)C2 KXGVEGMKQFWNSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- LOKCTEFSRHRXRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-I dipotassium trisodium dihydrogen phosphate hydrogen phosphate dichloride Chemical compound P(=O)(O)(O)[O-].[K+].P(=O)(O)([O-])[O-].[Na+].[Na+].[Cl-].[K+].[Cl-].[Na+] LOKCTEFSRHRXRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-I 0.000 description 4
- 235000013305 food Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 230000036039 immunity Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000011534 incubation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 150000002632 lipids Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 239000002953 phosphate buffered saline Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000007929 subcutaneous injection Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000010254 subcutaneous injection Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 4
- 108010001336 Horseradish Peroxidase Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 206010061218 Inflammation Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 102000004889 Interleukin-6 Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108090001005 Interleukin-6 Proteins 0.000 description 3
- MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oxalic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)=O MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229920001213 Polysorbate 20 Polymers 0.000 description 3
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- OHDRQQURAXLVGJ-HLVWOLMTSA-N azane;(2e)-3-ethyl-2-[(e)-(3-ethyl-6-sulfo-1,3-benzothiazol-2-ylidene)hydrazinylidene]-1,3-benzothiazole-6-sulfonic acid Chemical compound [NH4+].[NH4+].S/1C2=CC(S([O-])(=O)=O)=CC=C2N(CC)C\1=N/N=C1/SC2=CC(S([O-])(=O)=O)=CC=C2N1CC OHDRQQURAXLVGJ-HLVWOLMTSA-N 0.000 description 3
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N citric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000001727 in vivo Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000006698 induction Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000004054 inflammatory process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000011081 inoculation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000001404 mediated effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 235000010486 polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000000256 polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000010186 staining Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000002255 vaccination Methods 0.000 description 3
- 108700031361 Brachyury Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 108090000695 Cytokines Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102000004127 Cytokines Human genes 0.000 description 2
- SXRSQZLOMIGNAQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glutaraldehyde Chemical compound O=CCCCC=O SXRSQZLOMIGNAQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 108010063738 Interleukins Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102000015696 Interleukins Human genes 0.000 description 2
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium chloride Chemical compound [Na+].[Cl-] FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 206010048215 Xanthomatosis Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 210000002376 aorta thoracic Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 238000003556 assay Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012512 characterization method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002950 deficient Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 description 2
- 208000035475 disorder Diseases 0.000 description 2
- YQGOJNYOYNNSMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N eosin Chemical compound [Na+].OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1C1=C2C=C(Br)C(=O)C(Br)=C2OC2=C(Br)C(O)=C(Br)C=C21 YQGOJNYOYNNSMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000036541 health Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007490 hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007431 microscopic evaluation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000035772 mutation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000013642 negative control Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000006386 neutralization reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 102000005962 receptors Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108020003175 receptors Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000013207 serial dilution Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007920 subcutaneous administration Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 2
- 210000003462 vein Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- HQFLTUZKIRYQSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-ethyl-2h-1,3-benzothiazole-6-sulfonic acid Chemical compound OS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C2N(CC)CSC2=C1 HQFLTUZKIRYQSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 101150037123 APOE gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100216294 Danio rerio apoeb gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000010834 Extracellular Matrix Proteins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010037362 Extracellular Matrix Proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101001002634 Homo sapiens Interleukin-1 alpha Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000934372 Homo sapiens Macrosialin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010002352 Interleukin-1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100025136 Macrosialin Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 101100055876 Mus musculus Apoe gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000187479 Mycobacterium tuberculosis Species 0.000 description 1
- 208000034827 Neointima Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000009328 Perro Species 0.000 description 1
- 238000011579 SCID mouse model Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920005654 Sephadex Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000012507 Sephadex™ Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002684 Sepharose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 208000019802 Sexually transmitted disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 101710120037 Toxin CcdB Proteins 0.000 description 1
- GLNADSQYFUSGOU-GPTZEZBUSA-J Trypan blue Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].C1=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C=C2C=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C(/N=N/C3=CC=C(C=C3C)C=3C=C(C(=CC=3)\N=N\C=3C(=CC4=CC(=CC(N)=C4C=3O)S([O-])(=O)=O)S([O-])(=O)=O)C)=C(O)C2=C1N GLNADSQYFUSGOU-GPTZEZBUSA-J 0.000 description 1
- 206010048214 Xanthoma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000008064 anhydrides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 210000000702 aorta abdominal Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000004556 brain Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000001364 causal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000006285 cell suspension Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000002987 choroid plexus Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000004351 coronary vessel Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006735 deficit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003989 endothelium vascular Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000002744 extracellular matrix Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000000497 foam cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002068 genetic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000019622 heart disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 235000009200 high fat diet Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000000260 hypercholesteremic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000000987 immune system Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000006058 immune tolerance Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000016784 immunoglobulin production Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001939 inductive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008595 infiltration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001764 infiltration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002757 inflammatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005764 inhibitory process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007689 inspection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011813 knockout mouse model Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000027928 long-term synaptic potentiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000002540 macrophage Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000013011 mating Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001338 necrotic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000006408 oxalic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000013641 positive control Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003938 response to stress Effects 0.000 description 1
- 206010039073 rheumatoid arthritis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 210000000329 smooth muscle myocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000001179 sorption measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006886 spatial memory Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010561 standard procedure Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000638 stimulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000004697 synapse damage Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000001541 thymus gland Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- UFTFJSFQGQCHQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N triformin Chemical compound O=COCC(OC=O)COC=O UFTFJSFQGQCHQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 201000008827 tuberculosis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 210000004881 tumor cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229960005486 vaccine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000002792 vascular Effects 0.000 description 1
- 231100000216 vascular lesion Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000031836 visual learning Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K39/0005—Vertebrate antigens
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K38/00—Medicinal preparations containing peptides
- A61K38/16—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof
- A61K38/17—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof from animals; from humans
- A61K38/19—Cytokines; Lymphokines; Interferons
- A61K38/20—Interleukins [IL]
- A61K38/2006—IL-1
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
- A61P37/02—Immunomodulators
- A61P37/04—Immunostimulants
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P43/00—Drugs for specific purposes, not provided for in groups A61P1/00-A61P41/00
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/10—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system for treating ischaemic or atherosclerotic diseases, e.g. antianginal drugs, coronary vasodilators, drugs for myocardial infarction, retinopathy, cerebrovascula insufficiency, renal arteriosclerosis
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K16/00—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies
- C07K16/18—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans
- C07K16/24—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans against cytokines, lymphokines or interferons
- C07K16/244—Interleukins [IL]
- C07K16/245—IL-1
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K2039/505—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies comprising antibodies
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K2039/51—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies comprising whole cells, viruses or DNA/RNA
- A61K2039/525—Virus
- A61K2039/5258—Virus-like particles
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K2039/60—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies characteristics by the carrier linked to the antigen
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K2039/60—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies characteristics by the carrier linked to the antigen
- A61K2039/6031—Proteins
- A61K2039/6075—Viral proteins
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Mycology (AREA)
- Gastroenterology & Hepatology (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
- Peptides Or Proteins (AREA)
- Compositions Of Oxide Ceramics (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Material From Animals Or Micro-Organisms (AREA)
Abstract
Description
IL-1αは炎症の基本的な調節因子として十分に特徴決定されており、炎症関連疾患におけるその役割はいくつかの動物モデルにおいて示唆されている。インターロイキン(IL)-1αに対するヒトIgG自己抗体(aAb)は一般の集団において比較的高頻度で検出されている。実際に、表面上は健常なヒトの20%よりも多くが高度に特異的なIL-1αaAbを有することが報告されている。天然IL-1α aAbを有する男性の所見により、アテローム性動脈硬化症または関節リウマチなどの炎症関連疾患の進行のリスクの減少における内因性IL-1αの中和に関する役割が示唆されてきたが、これらの研究は上記個体における他の自己抗体の存在を排除しておらず、因果関係を確立することは難しく、これらの抗IL-1a抗体の生理学的役割ははっきりと確立されていない。
ApoE-/-マウスは、主要動脈においてアテローム性動脈硬化症様プラークの急速な進行をもたらす、操作された脂質輸送欠損を有する。これらのマウスは高コレステロール血症であり、かつ動脈性病変を自発的に発症するため、ヒトアテローム性動脈硬化症の最も説得力のあるモデルと考えられている。したがって、ApoE-/-マウスは、アテローム性動脈硬化症および処置を研究するためのモデル系として広範に使用されている。
ApoEノックアウトマウス
ApoE-/-マウスはJackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, MEより取得する。血管病変の発症に対する性別の潜在的な影響を回避するために、雄の動物のみを使用する;さらに、アテローム性動脈硬化症の進行におけるIL-1α aAbの保護的役割を観察する臨床研究は、この時点で男性においてのみ行われてきた。10週齢のマウスを使用し、高コレステロール含量(1.25%コレステロール、0%コレート;Research Diets, New Brunswick, NJ)の食餌を与える。マウスに10週間食餌を与え、その後屠殺する。標準的な方法にしたがって、血液を採取し、かつ大動脈を灌流して、部分に切断し、固定するかまたは凍結する。
マウスIL-1αによる免疫
Svenson et al., J Immunol Methods. 2000 Mar 6;236(1-2):1-8により記載された方法にしたがって、0.41(w/w)の割合でツベルクリンの精製タンパク質誘導体(PPD)と接合したマウスIL-1αでマウスを免疫する。マウスの尾の付け根に皮下注射で接種する。接種は3週間間隔で3回繰り返す。IL-1α aAbを解析するため、各注射の2週間後にマウスの後眼窩叢から採血する。対照動物は、IL-1αを含まないPPD溶液を用いた同一の接種スケジュールを受ける。
アッセイ
IL-1αに対するマウスIgGの応答は、Svenson et al., 2000により記載されたように測定する。IgGへのIL-1αの飽和結合解析は、記載されたように(Svenson et al., J Clin Invest. 1993 Nov;92(5):2533-9)行う。血清IgGに結合した125I-IL-1αを血清への全結合と比較するために、同一の試料を並行してプロテインG SepharoseカラムおよびSephadex G-75 superfineを含むカラムに流す(Svenson et al., Cytokine. 1992 Mar;4(2):125-33)。
ApoE-/-マウスにおける天然の抗IL-1α aAbの欠如
10週齢〜10ヶ月齢の15匹のApoE-/-マウス由来の血清は、IgG抗IL-1α aAbについてすべて陰性である。
ApoE-/-マウスにおけるIL-1α aAbの産生
PPDと接合したIL-1αを4回接種した後、すべてのマウスは高いIL-1αIgG aAb力価を有する。PPDのみを接種された対照マウスの血清においてaAbは見出されない。ワクチン投与から3ヶ月後の群の間で有意な重量の差異は無い。
誘導されたIL-1α aAbの特徴決定
陽性マウスのワクチン投与から2週間後および6週間後に採取された血清を試験する。血清への全IL-1αの結合およびIgGへの結合の間に差異は見られない。Kdは0.1 nM〜1.3 nMの範囲(例えば、0.1、0.15、0.2、0.25、0.3、0.4、0.5、0.6、0.7、0.8、0.9、1.0、1.1、1.2、1.3 nM)にわたる。
誘導された抗IL-1α aAbの特徴決定
IL-1α aAbはRIAを用いて試験する。抗血清はSvenson et al., 2000において開示されたものと同様に機能する。
受容体結合の抑制
マウス細胞株NOB-1への125I-IL-1αの結合は、ワクチン投与から2週間後に採取されてSvenson et al., 2000に記載されたように試験されるすべてのaAb陽性血清によって、少なくとも10%(例えば、少なくとも10、15、20、25、30、35、40、45、50、55、60、65、70、75、80、85、90、または95%)抑制される。aAb陰性対照は陰性である。
IL-1αのインビボ中和
代表的な抗血清の中和活性をSvenson et al., 2000に記載されたように試験する。データは、IL-1α aAbがNOB-1細胞においてIL-1α活性を中和することを示す。
アテローム性動脈硬化性病変の解析
マウスを様々な時点で屠殺し、アテローム性動脈硬化症の程度を評価する。プラーク沈着およびアテローム性動脈硬化性病変は、標準化された方法にしたがって(例えば、Trogan et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Feb 19;99(4):2234-9; Chaabane et al., Invest Radiol. 2003 Aug;38(8):532-8)、大動脈基部および胸腹部大動脈において評価し、定量する。IL-1αで免疫したApoE-/-マウスにおける大動脈基部アテローム性動脈硬化性病変領域は、ApoE-/-対照マウスと比較して有意に(例えば、少なくとも10、15、20、25、30、35、40、45、50、55、60、65、70、75、80、85、90、または95%)減少している。アテローム性動脈硬化性病変の発症はまた、スダンIVで染色された下行大動脈の標本において検査する。IL-1αで免疫されたApoE-/-マウスの腹部大動脈におけるスダン親和性の脂質に富む病変の形成は、その同腹仔対照群と比較して有意に(例えば、少なくとも10、15、20、25、30、35、40、45、50、55、60、65、70、75、80、85、90、または95%)減少している。同様に、ヘマトキシリン‐エオシンで染色した後に現れる大動脈弓切片におけるアテローム性動脈硬化性病変の形成は、IL-1αで免疫された動物において、対照と比較して有意に(例えば、少なくとも10、15、20、25、30、35、40、45、50、55、60、65、70、75、80、85、90、または95%)減少している。
材料および方法
ELISAによる抗IL-1α抗体力価の測定
ヒトまたはマウスIL-1αをそれぞれ、1ウェルあたり100μlの容量で0.5μg/mlを用いて、96ウェルELISAプレート上で一晩インキュベーションする。その後プレートをリン酸緩衝生理食塩水(PBS)+0,05% Tween 20で4回洗浄し、その後PBS中の1%ウシ血清アルブミン(BSA)+0.05% Tween 20を含むブロッキング溶液で飽和させる。1ウェルあたり200μlの本ブロッキング緩衝液を1〜2時間室温で使用する。その後プレートを再びPBS+0.05% Tween 20(PBST)で4回洗浄する。その後、100 mlの連続希釈した血清試料(PBST+1% BSA中で1:2希釈)を添加し、室温で1時間、または4℃で一晩インキュベーションする。その後プレートを再びPBSTで4回洗浄する。その後、西洋ワサビペルオキシダーゼ(HRP)結合抗Fc抗体を二次抗体として添加する(1% BSAを含むPBST中で1:2000希釈、1ウェルあたり100μl、1時間、室温)。ヒト:400μl PBST+1% BSA中、0.2μlヤギ抗ヒトIgG-HRP。マウス:0.5μl HRPヤギ抗マウスIgG(H+L)。その後プレートを再びPBSTで4回洗浄する。着色反応はABTS緩衝液を用いて行う。ABTS緩衝液(500 ml中、3-エチルベンズチアゾリン-6-スルホン酸、Sigma カタログ番号A-1888、150 mg、0.1 Mクエン酸、Fisher無水物、カタログ番号A-940;pHをNaOHペレットで4.35に調整し、11 mlのアリコートを−20℃で保存する、40% SDS(200 ml dd H2O中、80 g SDS)、200 ml DMF(N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド)を添加)。100μl のABTS緩衝液を各ウェルに添加する。良好なコントラストが見えたら、100μlの2%シュウ酸溶液を添加することによって反応を停止する。その後、ELISAリーダーを用いて波長405 nmで光学濃度を測定する。
ApoE-/-マウスはJackson Laboratory(Bar Harbor, Maine、B6.129P2-Apoetm1Unc/J系統)から取得した。Apoetm1Unc変異について同型接合であるマウスは、年齢や性別に影響を受けない著しい総血漿コレステロールレベル増加を示す。近位大動脈における脂肪線条は3ヶ月齢で認められる。病変は年齢と共に増加し、脂質がより少ないがより伸長した細胞を有する、プレアテローム性動脈硬化性病変のより進んだ段階に典型的な病変へと進行する。穏やかに増加したトリグリセリドレベルが、C57BL/6×129交配の遺伝的背景上で本変異を有するマウスにおいて報告されている。高齢ApoE欠損マウス(>17ヶ月)は、主として結晶性コレステロール裂、脂質小滴、および泡沫細胞からなる黄色腫性病変を脳において発症することが示されている。より小さな黄色腫が、脈絡叢および腹側脳弓において見られた。最近の研究は、ApoE欠損マウスが、ストレス応答の変化、空間学習および記憶の減退、長期増強の変化、およびシナプス損傷を有することを示す。C57BL/6およびSCIDマウスはHarlan(Horst, the Netherlands)から取得した。
IL-1αおよびIL-1βはeBioscience(San Diego, CA)から取得した。PPDはStatens Serum Institute(Copenhagen, Denmark)から取得した。接合法はSvensonら(Svenson M. 2000)から適合させた。IL-1αまたはIL-1bを4℃で48時間、0.41(w/w)の割合のPPDと0.1%グルタルアルデヒドの存在下でインキュベーションした(IL-1/PPD=0.41)。対照として、PPDをIL-1αまたはIL-1β無しで並行して処置した。その後、最終容量において1.5% Al(OH)3になるように、接合体をAl(OH)3(Rehydragel; Reheis Chemical, Dublin, Ireland)に吸着させた。
C57BL/6マウスにおける抗IL-1α抗体応答の産生
免疫系はサイトカインなどの自己タンパク質に対して寛容であるため、能動ワクチン投与は自己寛容を破壊する必要がある。大部分の自己タンパク質の場合、免疫寛容は、胸腺におけるネガティブ選択の結果としての特異的T細胞の欠如によって引き起こされる。対照的に、潜在的に自己反応性のB細胞は通常存在する。IL-1αのような自己タンパク質のみを注射する場合、T細胞ヘルプがないためにこれらのB細胞は応答しない。PPDなどの外来性タンパク質を自己抗原IL-1αに結合させると、T細胞がPPDを認識するので、B細胞刺激のためのT細胞ヘルプが提供され、これは、IL-1αおよびPPDに対する刺激されたB細胞の抗体産生をもたらす。
アテローム性動脈硬化症の形成を予防する、IL-1αに対する能動免疫
ApoEノックアウトマウス(6週齢)を、水酸化アルミニウム中の10μg PPD(結核菌(M. tuberculosis)由来の精製タンパク質誘導体)と接合した15μgのマウスIL-1αで、0、14、および28日目に首領域への皮下投与によって能動免疫した。注射容量は100μlであり、水酸化アルミニウムの量は約1 mgであった。対照マウスを同様に、しかし、同じ量のPPDおよび水酸化アルミニウムを含むがIL-1αを含まない調製物で処置した。ELISAにより抗IL1α抗体応答を測定するために、0、28、42、および56日目に尾静脈から血液を採取した。最初の免疫の4週間後に、アテローム性動脈硬化症を加速することが公知の食餌である、16%脂肪、1.16%コレステロール、および0.5%コール酸を含む食物ペレットによるアテローム発生性食餌をマウスに与え始めた。その後、18週齢でマウスを安楽死させた。肉眼的および顕微鏡的解析のために大動脈を取り出した。組織学的切片を、ヘマトキシリンおよびエオシン(HE)、ならびにスダンを用いて染色した。
アテローム性動脈硬化症の形成を予防する、IL-1αに対する受動免疫
C57BL/6マウスを、アラム中のIL-1α-PPD接合体の3回の皮下注射により、IL-1αに対して能動的に免疫した。56日後に血清を収集して、抗IL-1α自己抗体力価の生成をELISAにより確認した。そのような血清200μlを、6週齢のApoEノックアウトマウスに受動的に導入した。これらの受動血清導入を毎週繰り返した。対照ApoE-/-マウスには、未処理のC57BL/6マウス由来の血清の受動導入を毎週行った。アテローム性動脈硬化症の形成を加速するため、これらの受動血清導入と共に、16%脂肪、1.16%コレステロール、および0.5%コール酸を含む食物ペレットによるアテローム発生性食餌をApoE-/-マウスに与え始めた。対照ApoE-/-マウスには未処理のC57BL/6マウス由来の血清200 mlを1週間間隔で受動的に導入した。大動脈の肉眼的および組織学的な解析のためにマウスを6週間後に安楽死させた。組織学的解析は、横断面のヘマトキシリンおよびエオシン染色、ならびにスダン染色を含んだ。
アテローム性動脈硬化症に対する効果が無いままであった、IL-1αに対する能動免疫
ApoEノックアウトマウス(6週齢)を、水酸化アルミニウム中の10μg PPD(結核菌由来精製タンパク質誘導体)と接合した15μgのマウスIL-1αで、0、14、および28日目に首領域への皮下投与によって能動的に免疫した。注射容量は100μlであり、水酸化アルミニウムの量は約1 mgであった。対照マウスを、同様に、しかし、同じ量のPPDおよび水酸化アルミニウムを含むがIL-1αは含まない調製物で処置した。ELISAにより抗IL1α抗体応答を測定するために、0、28、42、および56日目に尾静脈から血液を採取した。初回免疫の4週間後に、アテローム性動脈硬化症を加速することが公知の食餌である、16%脂肪、1.16%コレステロール、および0.5%コール酸を含む食物ペレットによるアテローム発生性食餌をマウスに与え始めた。その後、18週齢でマウスを安楽死させた。肉眼的および顕微鏡的な解析のために大動脈を除去した。組織学切片は、ヘマトキシリンおよびエオシン(HE)、ならびにスダンを用いて染色した。
アテローム性動脈硬化症に対する効果が無いままであった、IL-1αに対する受動免疫
C57BL/6マウスを、アラム中のIL-1α-PPD接合体の3回の皮下注射によりIL-1αに対して能動的に免疫した。56日後にその血清を採取して、抗IL-1α自己抗体力価の生成をELISAにより確認した。そのような血清200μlを、6週齢のApoEノックアウトマウスに受動的に導入した。これらの受動血清導入を毎週繰り返した。対照ApoE-/-マウスには未処理のC57BL/6マウスから200μlの血清導入を行った。アテローム性動脈硬化症の形成を加速するため、これらの受動血清導入と共に、16%脂肪、1.16%コレステロール、および0.5%コール酸を含む食物ペレットによるアテローム発生性食餌をApoE-/-マウスに与え始めた。対照ApoE-/-マウスには未処理のC57BL/6マウス由来の血清200 mlを1週間間隔で受動的に導入した。大動脈の肉眼的および組織学的な解析のためにマウスを6週間後に安楽死させた。組織学的解析には、断面のヘマトキシリンおよびエオシン染色、ならびにスダン染色が含まれた。
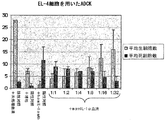
ADCK―抗体依存性補体媒介性殺傷
C57BL/6マウスを、アラム中のIL-1α-PPD接合体の3回の皮下注射によりIL-1αに対して能動的に免疫した。56日目にその血清を採取して、抗IL-1α自己抗体力価の生成をELISAにより確認した。血清を熱不活性化した。50μlのEL-4細胞懸濁液を96ウェルプレート中に播種した。これらのウェル各々に熱不活性化血清の1:2連続希釈物15μlを添加した。その後、プレートを20分間37℃でインキュベーションした。その後、25mlのマウス血清を各ウェルに添加した。37℃でのインキュベーションをさらに5時間行った後、ウェルの写真撮影を行い、その後、死細胞を生細胞から識別するためにトリパンブルーを用いて血球計算盤中で細胞を計数した。
Claims (36)
- 哺乳動物においてアテローム性動脈硬化症関連疾患のリスクおよび重症度を減少させるための薬物の調製における、IL-1αの使用。
- 哺乳動物においてアテローム性動脈硬化症関連疾患のリスクおよび重症度を減少させるための薬物の調製における、IL-1αをコードする組換えウイルスの使用。
- 哺乳動物においてアテローム性動脈硬化症関連疾患のリスクおよび重症度を減少させるための薬物の調製における、IL-1αに化学的に結合したウイルス様粒子の使用。
- 哺乳動物が、マウス、ブタ、ヤギ、イヌ、ネコ、およびヒツジからなる群より選択される、請求項1〜3のいずれか一項記載の使用。
- 哺乳動物がマウスであり、かつマウスがApoE-/-である、請求項3記載の使用。
- 哺乳動物がヒトである、請求項1〜3のいずれか一項記載の使用。
- アテローム性動脈硬化症関連疾患が末梢動脈疾患である、請求項1〜3のいずれか一項記載の使用。
- アテローム性動脈硬化症関連疾患が末梢虚血性心疾患である、請求項1〜3のいずれか一項記載の使用。
- アテローム性動脈硬化症関連疾患が冠動脈疾患である、請求項1〜3のいずれか一項記載の使用。
- アテローム性動脈硬化症関連疾患が脳血管疾患である、請求項1〜3のいずれか一項記載の使用。
- アテローム性動脈硬化症関連疾患が末梢動脈性疾患である、請求項1〜3のいずれか一項記載の使用。
- IL-1αが組換えIL-1αである、請求項1または3記載の使用。
- 組換えIL-1αがマウスまたはヒトである、請求項2または12記載の使用。
- IL-1αが担体に結合している、請求項1記載の使用。
- 担体がツベルクリンの精製タンパク質誘導体(PPD)である、請求項14記載の使用。
- IL-1αがアジュバントの存在下で使用される、請求項1〜3のいずれか一項記載の使用。
- アジュバントが水酸化アルミニウムである、請求項16記載の使用。
- IL-1αで免疫されたApoE-/-マウス。
- IL-1α自己抗体を含むApoE-/-マウス。
- 哺乳動物をIL-1αで免疫する段階を含む、アテローム性動脈硬化症関連疾患のリスクおよび重症度を減少させるために哺乳動物を処置する方法。
- 哺乳動物が、マウス、ブタ、ヤギ、イヌ、ネコ、およびヒツジからなる群より選択される、請求項20記載の方法。
- 哺乳動物がマウスであり、かつマウスがApoE-/-である、請求項21記載の方法。
- 哺乳動物がヒトである、請求項20記載の方法。
- アテローム性動脈硬化症関連疾患が末梢動脈疾患である、請求項20記載の方法。
- アテローム性動脈硬化症関連疾患が末梢虚血性心疾患である、請求項20記載の方法。
- アテローム性動脈硬化症関連疾患が冠動脈疾患である、請求項20記載の方法。
- アテローム性動脈硬化症関連疾患が脳血管疾患である、請求項20記載の方法。
- アテローム性動脈硬化症関連疾患が末梢動脈性疾患である、請求項20記載の方法。
- 哺乳動物が組換えIL-1αで免疫される、請求項20記載の方法。
- 組換えIL-1αがマウスまたはヒトである、請求項20記載の方法。
- 哺乳動物が、担体に結合したIL-1αで免疫される、請求項20記載の方法。
- 担体がツベルクリンの精製タンパク質誘導体(PPD)である、請求項31記載の方法。
- 哺乳動物がアジュバントの存在下でIL-1αで免疫される、請求項20記載の方法。
- アジュバントが水酸化アルミニウムである、請求項33記載の方法。
- 哺乳動物がIL-1αをコードする組換えウイルスを用いて免疫される、請求項20記載の方法。
- 哺乳動物がIL-1αに化学的に結合したウイルス様粒子を用いて免疫される、請求項20記載の方法。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US80002906P | 2006-05-15 | 2006-05-15 | |
| PCT/IB2007/001264 WO2007132338A2 (en) | 2006-05-15 | 2007-05-15 | IL-1α IMMUNIZATION INDUCES AUTOANTIBODIES PROTECTIVE AGAINST ATHEROSCLEROSIS |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009537507A true JP2009537507A (ja) | 2009-10-29 |
| JP2009537507A5 JP2009537507A5 (ja) | 2010-07-01 |
Family
ID=38694276
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009510567A Pending JP2009537507A (ja) | 2006-05-15 | 2007-05-15 | アテローム性動脈硬化症に対して保護的な自己抗体を誘導するIL−1α免疫法 |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20090191149A1 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2021033B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP2009537507A (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN101448528A (ja) |
| AT (1) | ATE551365T1 (ja) |
| AU (1) | AU2007251239B2 (ja) |
| CA (1) | CA2652274A1 (ja) |
| ES (1) | ES2384278T3 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2007132338A2 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015019617A (ja) * | 2013-07-19 | 2015-02-02 | 国立大学法人三重大学 | 閉塞性動脈硬化症モデル動物、るい痩研究用モデル動物、及び全身性アミロイドーシスモデル動物としての非ヒト哺乳動物 |
Families Citing this family (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA2617637C (en) * | 2005-08-02 | 2017-07-18 | Xbiotech Inc. | Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of vascular disorders using il-1.alpha. autoantibodies |
| US20110008282A1 (en) * | 2006-05-15 | 2011-01-13 | Xbiotech, Inc. | IL-1alpha immunization induces autoantibodies protective against atherosclerosis |
| PL2109623T3 (pl) * | 2006-05-22 | 2012-03-30 | Xbiotech Inc | Leczenie nowotworu przeciwciałami przeciw il-1 |
| EP3085773B1 (en) | 2008-05-30 | 2020-03-18 | XBiotech, Inc | Uses of il-1 alpha antibodies |
| US8242074B2 (en) | 2008-09-12 | 2012-08-14 | Xbiotech, Inc. | Modulation of the amount or function of pathogenic CD14+CD16+ monocytes |
| EP2569640A1 (en) | 2010-05-12 | 2013-03-20 | The University of Birmingham | Biomarker |
| US20110311547A1 (en) | 2010-06-18 | 2011-12-22 | Xbiotech, Inc. | Arthritis Treatment |
| KR20130108305A (ko) | 2010-08-23 | 2013-10-02 | 엑스바이오테크, 인크. | 종양성 질병들에 대한 치료 |
| US9724409B2 (en) | 2011-04-01 | 2017-08-08 | Xbiotech, Inc. | Treatment of inflammatory skin disease |
| US9809649B2 (en) | 2011-09-23 | 2017-11-07 | Xbiotech, Inc. | Cachexia treatment |
| US9545441B2 (en) | 2012-09-18 | 2017-01-17 | Xbiotech, Inc. | Treatment of diabetes |
| CN105175503A (zh) * | 2015-09-08 | 2015-12-23 | 苏州普罗达生物科技有限公司 | 因子viii抑制多肽及其应用 |
| CN105175504A (zh) * | 2015-09-08 | 2015-12-23 | 苏州普罗达生物科技有限公司 | 血管性血友病因子抑制多肽及其应用 |
| CA3053231A1 (en) | 2017-02-16 | 2018-08-23 | Xbiotech Inc. | Treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa |
| US10975146B2 (en) | 2018-06-29 | 2021-04-13 | Cedars-Sinai Medical Center | Interleukin-1 inhibition for combination treatment of pancreatic cancer |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2004100987A2 (en) * | 2003-05-06 | 2004-11-25 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Methods of using il-1 antagonists to treat neointimal hyperplasia |
| JP2009503529A (ja) * | 2005-08-02 | 2009-01-29 | エクスバイオテク インコーポレーティッド | IL−1α自己抗体を用いた血管障害の診断、処置、および予防 |
| JP2009510025A (ja) * | 2005-09-28 | 2009-03-12 | サイトス バイオテクノロジー アーゲー | インターロイキン−1コンジュゲート及びその使用 |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE9802402D0 (sv) * | 1998-07-03 | 1998-07-03 | Karolinska Innovations Ab | Method of diagnosing cardiovascular disease and early atherosclerosis |
| AU5561999A (en) * | 1998-08-13 | 2000-03-06 | Wistar Institute, The | Methods for reducing atherosclerotic plaques |
| US20030040617A9 (en) * | 1999-03-12 | 2003-02-27 | Rosen Craig A. | Nucleic acids, proteins and antibodies |
| US20030232054A1 (en) * | 2000-01-25 | 2003-12-18 | Tang Y. Tom | Novel nucleic acids and polypeptides |
| US20030026806A1 (en) * | 2000-10-27 | 2003-02-06 | Amgen Inc. | Antibodies and other selective IL-1 binding agents that allow binding to IL-1 receptor but not activation thereof |
| HN2004000285A (es) * | 2003-08-04 | 2006-04-27 | Pfizer Prod Inc | ANTICUERPOS DIRIGIDOS A c-MET |
| EP3085773B1 (en) * | 2008-05-30 | 2020-03-18 | XBiotech, Inc | Uses of il-1 alpha antibodies |
| US8242074B2 (en) * | 2008-09-12 | 2012-08-14 | Xbiotech, Inc. | Modulation of the amount or function of pathogenic CD14+CD16+ monocytes |
-
2007
- 2007-05-15 WO PCT/IB2007/001264 patent/WO2007132338A2/en active Application Filing
- 2007-05-15 CN CNA2007800186140A patent/CN101448528A/zh active Pending
- 2007-05-15 EP EP07734572A patent/EP2021033B1/en active Active
- 2007-05-15 ES ES07734572T patent/ES2384278T3/es active Active
- 2007-05-15 AT AT07734572T patent/ATE551365T1/de active
- 2007-05-15 CA CA002652274A patent/CA2652274A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2007-05-15 AU AU2007251239A patent/AU2007251239B2/en active Active
- 2007-05-15 US US12/300,712 patent/US20090191149A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2007-05-15 JP JP2009510567A patent/JP2009537507A/ja active Pending
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2004100987A2 (en) * | 2003-05-06 | 2004-11-25 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Methods of using il-1 antagonists to treat neointimal hyperplasia |
| JP2009503529A (ja) * | 2005-08-02 | 2009-01-29 | エクスバイオテク インコーポレーティッド | IL−1α自己抗体を用いた血管障害の診断、処置、および予防 |
| JP2009510025A (ja) * | 2005-09-28 | 2009-03-12 | サイトス バイオテクノロジー アーゲー | インターロイキン−1コンジュゲート及びその使用 |
Non-Patent Citations (4)
| Title |
|---|
| JPN5008011508; Dardik A, et al.: 'Shear stress-stimulated endothelial cells induce smooth muscle cell chemotaxis via platelet-derived' Journal of Vascular Surgery Vol. 41, No. 2, 200502, p. 321-331 * |
| JPN5008011515; Garrone P, et al.: 'Generation and characterization of a human monoclonal autoantibody that acts as a high affinity inte' Molecular Immunology Vol. 33, No. 7-8, 199605, p. 649-658 * |
| JPN6012002566; Journal of Immunological Methods Vol.236,No.1-2, 2000, p1-8 * |
| JPN6012028876; Cardiovascular Research Vol.66, 2005, p.583-593 * |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015019617A (ja) * | 2013-07-19 | 2015-02-02 | 国立大学法人三重大学 | 閉塞性動脈硬化症モデル動物、るい痩研究用モデル動物、及び全身性アミロイドーシスモデル動物としての非ヒト哺乳動物 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2007132338A3 (en) | 2008-06-12 |
| CA2652274A1 (en) | 2007-11-22 |
| EP2021033B1 (en) | 2012-03-28 |
| AU2007251239B2 (en) | 2013-08-22 |
| EP2021033A4 (en) | 2010-02-24 |
| EP2021033A2 (en) | 2009-02-11 |
| US20090191149A1 (en) | 2009-07-30 |
| AU2007251239A1 (en) | 2007-11-22 |
| CN101448528A (zh) | 2009-06-03 |
| WO2007132338A2 (en) | 2007-11-22 |
| ATE551365T1 (de) | 2012-04-15 |
| ES2384278T3 (es) | 2012-07-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2009537507A (ja) | アテローム性動脈硬化症に対して保護的な自己抗体を誘導するIL−1α免疫法 | |
| US20120114598A1 (en) | IL-1alpha immunization induces autoantibodies protective against atherosclerosis | |
| Movsesyan et al. | Reducing AD-like pathology in 3xTg-AD mouse model by DNA epitope vaccine—a novel immunotherapeutic strategy | |
| Castellino et al. | Chemokines enhance immunity by guiding naive CD8+ T cells to sites of CD4+ T cell–dendritic cell interaction | |
| Klinman et al. | DNA vaccines: safety and efficacy issues | |
| Regan et al. | Characterization of cytokines associated with Th17 cells in the eyes of horses with recurrent uveitis | |
| US9078843B2 (en) | Immunogenic fragments of T-cell receptor constant domains and peptides derived therefrom | |
| Wu et al. | Pathogenic IL‐23 signaling is required to initiate GM‐CSF‐driven autoimmune myocarditis in mice | |
| Bates et al. | Mucosal adjuvant activity of flagellin in aged mice | |
| Halliday et al. | Parasite loss and inhibited development of Teladorsagia circumcincta in relation to the kinetics of the local IgA response in sheep | |
| US20140227304A1 (en) | Vaccines for preventing and treating alzheimer's disease | |
| JP2016214240A (ja) | 医薬化合物を評価するための新規動物モデル | |
| Austin et al. | Short-term β-amyloid vaccinations do not improve cognitive performance in cognitively impaired APP+ PS1 mice. | |
| Constantinescu et al. | Modulation of susceptibility and resistance to an autoimmune model of multiple sclerosis in prototypically susceptible and resistant strains by neutralization of interleukin-12 and interleukin-4, respectively | |
| Babai et al. | Depletion of peritoneal CD5+ B cells has no effect on the course of Leishmania major infection in susceptible and resistant mice | |
| Wildbaum et al. | Augmentation of natural immunity to a pro-inflammatory cytokine (TNF-alpha) by targeted DNA vaccine confers long-lasting resistance to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis | |
| JP5068505B2 (ja) | 乳アレルギーモデル動物 | |
| JP2010510986A (ja) | Th2媒介炎症症状治療のためのtslpワクチン | |
| Beal et al. | Antibody response to Salmonella: its induction and role in protection against avian enteric salmonellosis | |
| Facincone et al. | A novel murine model of late‐phase reaction of immediate hypersensitivity | |
| Alderuccio et al. | Organ-specific autoimmunity in granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) deficient mice | |
| Bungiro Jr et al. | Interleukin-12 as an adjuvant for an antischistosome vaccine consisting of adult worm antigens: protection of rats from cercarial challenge | |
| Bakela et al. | Rescue of autoimmune hepatitis by soluble MHC class II molecules in an altered concanavalin A‐induced experimental model | |
| JP7411970B2 (ja) | 乳汁中のIgA抗体含有量の増加剤 | |
| JP2018118960A (ja) | 1型糖尿病の予防又は治療剤 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100513 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100513 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110413 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120606 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120905 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130508 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20130806 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20130813 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20140108 |