JP2008008997A - Composite sound absorbing structural body - Google Patents
Composite sound absorbing structural body Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2008008997A JP2008008997A JP2006177348A JP2006177348A JP2008008997A JP 2008008997 A JP2008008997 A JP 2008008997A JP 2006177348 A JP2006177348 A JP 2006177348A JP 2006177348 A JP2006177348 A JP 2006177348A JP 2008008997 A JP2008008997 A JP 2008008997A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- sound
- nonwoven fabric
- sound absorbing
- base material
- absorbing structure
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
本発明は、騒音低減や音場コントロールのキーテクノロジーの一つである吸音技術を構成する複合吸音構造体に関する。 The present invention relates to a composite sound absorbing structure constituting a sound absorbing technique which is one of key technologies for noise reduction and sound field control.
従来の吸音材料や吸音構造体には、多孔質材料系、膜状・板状材料系、又は共鳴構造体系のものがある。膜状・板状材料系や共鳴構造体系については、一般に、その適用周波数帯域は、中・低周波数帯域であり、チューニング周波数も狭く、吸音率も余り高くない。又、材料(構造体)を厚くするか背後に空気層等のスペースを必要とすることが多く、特に、産業機械、家電製品、自動車、車両等の分野では余り取り扱いやすいものとはいえない。 Conventional sound-absorbing materials and sound-absorbing structures include porous materials, film / plate-like materials, and resonance structures. In general, the applied frequency band of the film / plate material system and the resonance structure system is a medium / low frequency band, the tuning frequency is narrow, and the sound absorption coefficient is not so high. In addition, the material (structure) is often thick or requires a space such as an air layer behind it, and it cannot be said that it is particularly easy to handle in the fields of industrial machinery, home appliances, automobiles, vehicles and the like.
これに対して、グラスウール、ロックウール等の無機繊維系のもの、ポリエステル等高分子繊維系のもの等の多孔質材料系、軟質ウレタンフォ−ム等の樹脂発泡系のもの、アルミニウム等金属発泡系等の発泡材料系ものがあり、いずれも、中・高音域用の吸音材としては優れた材料である。 On the other hand, inorganic fiber type such as glass wool and rock wool, porous material type such as polymer fiber type such as polyester, resin foam type such as soft urethane foam, metal foam type such as aluminum These are excellent materials as sound-absorbing materials for medium and high sounds.
しかしながら、中・高音域に加え、低音域の吸音率を大きくするためには、前記した膜状、板状、共鳴構造体と同じように、材料を厚くするか或いは空気層を備える必要があり、かなりのスペースが必要となる。更に、このために高音域の吸音特性の低下を余儀なくされることも多く、前記の例と同じく、産業機械、家電製品、自動車や車両の分野においては、吸音特性面、構造設計面、重量面、費用面等で適用が難しくなるケースがよく見られる。 However, in order to increase the sound absorption coefficient in the low range in addition to the mid / high range, it is necessary to increase the thickness of the material or provide an air layer as in the case of the film, plate, and resonance structure described above. , Requires considerable space. Furthermore, for this reason, it is often necessary to lower the sound absorption characteristics in the high sound range, and in the fields of industrial machines, household appliances, automobiles and vehicles, as in the above examples, the sound absorption characteristics, structural design, and weight In many cases, it is difficult to apply due to costs.
一方、多孔質材料は中・高音域用吸音材として優れた吸音材料であるが、スペースの関係で厚さがとれない場合には、中・低音域では吸音率が不足することがよくある。しかるに、騒音でよく問題になる周波数帯域は500〜2kHzであるが、厚さの面から言えば、例えばポリエステル繊維系(密度44kg/m3 )で、吸音特性(垂直入射法)は厚さ35mmの場合、500Hzで20%、1kHzで40%程度の吸音率しかない。グラスウ−ルや軟質ウレタンフォーム等では、35〜50mmで同程度の吸音率である。このため、吸音母材の厚さを厚くする、空気層を設ける等の処置が取られるが、これでは、スペース、重量、経済性等問題が出てくる。 On the other hand, the porous material is an excellent sound absorbing material as a sound absorbing material for the middle / high range, but if the thickness cannot be taken due to space, the sound absorption rate is often insufficient in the middle / low range. However, the frequency band that is often a problem with noise is 500 to 2 kHz. From the viewpoint of thickness, for example, a polyester fiber system (density 44 kg / m 3), and the sound absorption characteristic (normal incidence method) is 35 mm thick. In this case, the sound absorption coefficient is only about 20% at 500 Hz and about 40% at 1 kHz. For glass wool, flexible urethane foam, etc., the sound absorption coefficient is about the same at 35-50 mm. For this reason, measures such as increasing the thickness of the sound-absorbing base material and providing an air layer are taken, but this causes problems such as space, weight, and economy.
しかるに、多孔質材料の一つとして、最近広く使われるようになったポリエステル繊維系吸音材は、音の入射エネルギーが密集した材料内に入り、その材料の中を空気が出入りするときに粘性抵抗が生じること、繊維間のフリクションを生じること、或いは織維を振動させること等により、入射する音響エネルギーを熱エネルギーに変換することで吸音性能を発揮する。この吸音性能は吸音体の流れ抵抗と密接な関係にあり、流れ抵抗を調整することで吸音特性を制御することができる。ポリエステル繊維系吸音材は不織布を表面に貼り付けて複合化することで、この流れ抵抗を調整することにより、実用的な厚さで高い吸音特性を得ている。 However, as one of the porous materials, the polyester fiber-based sound absorbing material, which has been widely used recently, has a viscous resistance when the incident energy of sound enters a dense material and air enters and exits the material. The sound absorbing performance is exhibited by converting incident acoustic energy into thermal energy by generating friction, causing friction between fibers, or vibrating the fabric. This sound absorption performance is closely related to the flow resistance of the sound absorber, and the sound absorption characteristics can be controlled by adjusting the flow resistance. The polyester fiber-based sound absorbing material is obtained by combining a non-woven fabric with a non-woven fabric to adjust the flow resistance, thereby obtaining high sound absorption characteristics with a practical thickness.
しかし、更に中・低音域の吸音特性を向上するためには、ポリエステル繊維からなる吸音母材を厚くする方法、密度を増やす方法、背後に空気層を設ける方法等が考えられるが、スペース等の面から実行できない場合も多い。このことは、他の多孔質材料であるグラスウールやロックウールでも同様なことがいえる。 However, in order to further improve the sound absorption characteristics in the middle and low frequencies, methods such as thickening the sound absorbing matrix material made of polyester fiber, increasing the density, and providing an air layer behind can be considered. There are many cases that cannot be executed from the aspect. The same is true for glass wool and rock wool, which are other porous materials.
そこで、吸音母材の多孔質材料の嵩密度、厚さを増やさず、又、母材に加えて、空気層を備えることなく、広い周波帯域の吸音特性を改善する方法があれば大変有用であり、本発明はそれを可能にする吸音構造体を提供しようとするものである。 Therefore, it would be very useful if there was a method to improve the sound absorption characteristics in a wide frequency band without increasing the bulk density and thickness of the porous material of the sound absorbing base material, and without providing an air layer in addition to the base material. The present invention seeks to provide a sound absorbing structure that enables this.
本発明の要旨は、多孔質材料或いは発泡材料を吸音母材とし、少なくとも音波が入射する側に不織布を通気抵抗を阻害しないホットメルト材で前記吸音母材の表面に、一又は複数層熱融着したことを特徴とする複合吸音構造体にかかるものである。 The gist of the present invention is that a porous material or foamed material is used as a sound-absorbing base material, and a nonwoven fabric is used at least on the side on which sound waves are incident. The present invention relates to a composite sound absorbing structure characterized by being worn.
本発明の複合吸音構造体によれば、吸音母材の厚さを変えることなく、音波が入射する面に不織布を通気抵抗を阻害しないホットメルト材で複数層積層することで、例えば、ポリエステル繊維系吸音材では実現が難しい高周波数帯域の吸音特性を低下させずに、中・低音域でも優れた吸音性能を発揮することができることとなったものである。 According to the composite sound-absorbing structure of the present invention, a non-woven fabric is laminated on a surface on which sound waves are incident without changing the thickness of the sound-absorbing base material, and a plurality of layers are laminated with a hot-melt material that does not inhibit the airflow resistance. This makes it possible to exhibit excellent sound absorbing performance even in the mid- and low-frequency range without deteriorating the sound absorption characteristics in the high frequency band, which is difficult to realize with a system sound absorbing material.
又、本発明の複合吸音構造体によれば、優れた吸音性能を示すだけでなく、音波入射側の最外層の不織布に、耐候性、耐久性、防水性、耐薬品性等の処理を施し、種々の素因に対するプロテクトになり、その他、表面強度、難燃性(金属系複層構造体にすればより高まる)の向上にも有効であることも大きな利点であり、実用面でのメリットも大きい。又、ダクト等気流が伴う部位に適用する場合に繊維の一部等を持ち去られることもなく、空気清浄の面でも安心である。 Further, according to the composite sound absorbing structure of the present invention, not only excellent sound absorbing performance is shown, but also the outermost nonwoven fabric on the sound wave incident side is subjected to treatment such as weather resistance, durability, waterproofness, chemical resistance and the like. Protects against various predisposing factors, and is also a great advantage in improving surface strength and flame retardancy (more enhanced with a metal-based multi-layer structure). large. In addition, when applied to a part with an air flow such as a duct, a part of the fiber is not taken away, and it is safe in terms of air cleaning.
本発明の複合吸音構造体は、多孔質材料よりなる吸音母材の音波入射側に少なくとも一層以上の不織布/ホットメルト材を配し、これを熱融着し一体・複合化したもので、要求吸音性能に適合するように通気抵抗をコントロールし、広い周波帯域の吸音特性を改善した複合吸音構造体を提供したものである。 The composite sound-absorbing structure of the present invention comprises at least one non-woven fabric / hot melt material disposed on the sound wave incident side of a sound-absorbing base material made of a porous material, and is heat-fused to be integrated and combined. The present invention provides a composite sound absorbing structure in which ventilation resistance is controlled so as to match the sound absorbing performance and the sound absorbing characteristics in a wide frequency band are improved.
この複合吸音構造体によれば、高周波数帯域の吸音特性を低下させることなく、又、吸音母材の厚さや嵩密度等を増やすことなく、中低周波数帯域の吸音特性を向上することが出来るのである。これは、吸音母材の少なくとも音波入射側に少なくとも一層以上、好ましくは複数層の不織布/ホットメルトを積層、熱融着することで、複合構造体としての通気抵抗をコントロールすることができるためであり、音響入射エネルギーが複合構造体に侵入することにより、先ず積層された不織布間での粘性抵抗が増大し、更に吸音母材を含めた複合構造としての粘性抵抗が高まり、それらに加えて、積層された不織布間や吸音母材の繊維間のフリクション、繊維の共振等が加わり、総合的に音響エネルギーから熱エネルギーヘの変換効率を高められることにより、高周波数帯域の吸音特性を低下させずに中低周波数帯域の吸音特性を向上させることができるのである。 According to this composite sound absorbing structure, it is possible to improve the sound absorbing characteristics in the middle and low frequency bands without deteriorating the sound absorbing characteristics in the high frequency band and without increasing the thickness, bulk density, etc. of the sound absorbing base material. It is. This is because the ventilation resistance of the composite structure can be controlled by laminating and heat-sealing at least one layer, preferably a plurality of layers of non-woven fabric / hot melt, on at least the sound wave incident side of the sound-absorbing base material. Yes, when the acoustic incident energy penetrates into the composite structure, first, the viscous resistance between the laminated nonwoven fabrics is increased, and further, the viscous resistance as a composite structure including the sound-absorbing base material is increased. Friction between laminated nonwoven fabrics and fibers of the sound-absorbing base material, resonance of the fibers, etc. are added, so that the conversion efficiency from acoustic energy to thermal energy can be improved overall, so that the sound absorption characteristics in the high frequency band are not deteriorated In addition, the sound absorption characteristics in the middle and low frequency band can be improved.
先ず、上記複合吸音構造体において、構成している吸音母材の代表例は、ポリエステル系等の高分子系、グラスウールやロックウール等の無機繊維系、金属繊維系等の多孔質材料系、軟質ウレタンフォーム等の高分子発泡系、アルミ等の金属発泡系等の多孔質材料或いは発泡材料が挙げられる。そして、吸音母材の通気抵抗が3×103 〜7×104 N・sec/m4 が好ましい範囲である。中でも最近では吸音性能がよく、地球環境や作業環境に優しい、リサクルができる、耐侯・耐久性がある等の優れた性能を有するポリエステル繊維系の多孔質材料が好んで用いられる。ポリエステル繊維系を吸音母材とする場合、実用的な範囲では、嵩密度が20〜80kg/m3 、通気抵抗が4×103 〜2×104 N・sec/m4 の範囲ものが良く用いられる。尚、ホットメルト材による不織布の熱融着・積層体の構成によっては、上記の吸音母材の代わりに空気層を構成するだけでも十分に吸音特性が発揮される場合がある。
First, in the above composite sound absorbing structure, typical examples of the sound absorbing base material are polymer materials such as polyester, inorganic fibers such as glass wool and rock wool, porous materials such as metal fibers, and soft materials. Examples thereof include porous materials such as polymer foams such as urethane foam and metal foams such as aluminum, or foam materials. And the ventilation resistance of the sound-absorbing base material is in a preferable range of 3 × 10 3 to 7 × 10 4 N · sec / m 4. Among them, recently, a polyester fiber-based porous material having excellent performance such as good sound absorption performance, friendly to the global environment and working environment, can be recycled, and has weather resistance and durability, is preferably used. When a polyester fiber system is used as the sound-absorbing base material, those having a bulk density of 20 to 80 kg /
通気抵抗についていえば、通気抵抗が小さすぎると音圧加振されて母材の中で空気が動きやすくなり粘性抵抗が小さくなり、逆に、通気抵抗が大きすぎると母材の中で空気が動きにくくなり、この場合も粘性抵抗が小さくなり、吸音率は低い方に移行してしまうという知見から、吸音体として最適な通気抵抗の範囲を特定したものである。 Regarding airflow resistance, if the airflow resistance is too small, the sound pressure is vibrated and air moves easily in the base material, reducing the viscous resistance. Conversely, if the airflow resistance is too high, air is generated in the base material. The range of the airflow resistance optimum as the sound absorber is specified from the knowledge that the viscous resistance becomes small and the sound absorption rate shifts to the lower side in this case.
吸音母材に一体化される不織布は、ホットメルト材を介して一層或いは複数層が熱融着にて積層されるが、かかる不織布は高分子系、例えばポリエステル系、ポリエチレン系、ナイロン系の、紙系としては和紙や壁紙等の不織布であり、好ましくはポリエステル繊維からなる不織布が好適である。そして、不織布として、面重量が20〜200g/m2 、通気抵抗が0.5〜5×104 N・sec/m4 のものが良い。目標の吸音特性に対して、同じ特性のもの、異種の特性のものを適宜組み合わせることができる。 The nonwoven fabric integrated with the sound-absorbing matrix is laminated by hot fusion with one or more layers through a hot melt material, but such nonwoven fabrics are polymer-based, for example polyester-based, polyethylene-based, nylon-based, The paper type is a non-woven fabric such as Japanese paper or wallpaper, and preferably a non-woven fabric made of polyester fibers. A nonwoven fabric having a surface weight of 20 to 200 g / m 2 and a ventilation resistance of 0.5 to 5 × 10 4 N · sec / m 4 is preferable. With respect to the target sound absorption characteristics, those having the same characteristics or different characteristics can be appropriately combined.
付言すれば、例えばスパンボンド不織布にあっては、通気抵抗が0.7×104 N・sec/m4 前後のものが多く、母材の通気抵抗と合わせて複合的な通気抵抗とするものであり、ある厚さの中で吸音特性を最適化するものである。本発明では、表面の不織布(ポリエステル繊維系の場合はスパンボンド不織布が多い)を多層に重ねることで、通気抵抗をコントロールしようとする点にねらいがある。 In addition, for example, many spunbond nonwoven fabrics have a ventilation resistance of around 0.7 × 10 4 N · sec / m 4, and are combined with the ventilation resistance of the base material to provide a composite ventilation resistance. The sound absorption characteristics are optimized within a certain thickness. In the present invention, the aim is to control the airflow resistance by superimposing a nonwoven fabric on the surface (in the case of polyester fiber, many spunbond nonwoven fabrics) in multiple layers.
更にいえば、本発明の最大のポイントは、不織布(例えばスパンボンド不織布)を多層にパウダー状のホットメルトで母材と熱融着で複合することにあり、場合により母材の代わりに空気層を設けることで、特性を出すこともできる点にある。この場合も多層の不織布の中や表と裏(空気層)の間の空気の出入りで粘性抵抗が大きくなり、音響エネルギ−が熱エネルギ−に変換され、吸音特性が向上することになり、勿論、母材を用いた場合にはこの母材の中でも当然熱エネルギ−に変換され、その分だけ吸音特性はよくなることは言うまでもない。 Furthermore, the most important point of the present invention is that a non-woven fabric (for example, spunbond non-woven fabric) is composited with a base material by heat fusion with powdery hot melt in multiple layers, and an air layer may be used instead of the base material. It is in the point which can also show a characteristic by providing. Also in this case, the viscous resistance increases due to the flow of air in and out of the multilayer nonwoven fabric and between the front and back (air layers), acoustic energy is converted into thermal energy, and sound absorption characteristics are improved, of course. Needless to say, when a base material is used, the base material is naturally converted into thermal energy, and the sound absorption characteristics are improved accordingly.
不織布と不織布、不織布と吸音母材を熱融着し複合化するためのホットメルト材は、ポリエステル系、ナイロン系、ポリプロピレン系、オレフィン系等の高分子系で、通気抵抗を阻害しないように、パウダー状、網目状或いは繊維状で融点が70〜180℃のものが好適である。 Non-woven fabrics and non-woven fabrics, hot melt materials for thermal fusion and composite of non-woven fabrics and sound-absorbing base materials are polyester-based, nylon-based, polypropylene-based, olefin-based polymer systems, etc. A powder, mesh, or fiber having a melting point of 70 to 180 ° C. is preferred.
上記複合吸音構造体において、吸音母材に不織布/ホットメルト材を積層してあるので、音波入射側の最外層に必要に応じて撥水処理、難燃処理、耐候・光処理、防汚処理等を施し、通気抵抗を阻害しないように留意し、各種の特性を付与することで、経済的に実用性を高めることができることは言うまでもない。 In the above composite sound absorbing structure, since the nonwoven fabric / hot melt material is laminated on the sound absorbing base material, water repellent treatment, flame retardant treatment, weather resistance / light treatment, antifouling treatment are applied to the outermost layer on the sound wave incident side as required. It goes without saying that practicality can be enhanced economically by applying the above and the like so as not to disturb the airflow resistance and imparting various characteristics.
以下、本発明による吸音構造体の実施形態について、代表的な構成例を断面図と立体図に基づいて説明する。又、以下の実施例では、垂直入射法を用いた実験例で本発明の効果について述べる。 Hereinafter, an exemplary configuration of a sound absorbing structure according to the present invention will be described based on a cross-sectional view and a three-dimensional view. In the following examples, the effects of the present invention will be described with experimental examples using the normal incidence method.
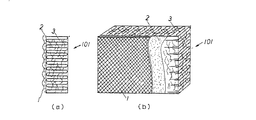
図1に本発明による複合吸音構造体の第1実施例の構造を示す。図1(a)は断面図、図1(b)は一部を破断して示す立体図である。図1に示す複合吸音構造体101は、一層の不織布1をホットメルト材2で吸音母材3に熱融着した本発明の基本構造を示す。使用された吸音母材3はポリエステル繊維系の多孔質材料であり、嵩密度は44kg/m3 であった。不織布1及び後述する不織布はスパンボンド不織布であり、面重量が100g/m2 、通気抵抗が0.7N・sec/m4 のものを用いた。ホットメルト材2及び後述するホットメルト材5はナイロン系であり、通気抵抗を阻害しないようにパウダ−状であり、融点が150℃のものを用いた。
FIG. 1 shows the structure of a first embodiment of a composite sound absorbing structure according to the present invention. 1A is a cross-sectional view, and FIG. 1B is a three-dimensional view with a part broken away. A composite
図2に、図1の基本構造をベースに更に通気・粘性抵抗を不織布を積層した第2実施例の構造を示す。図2(a)は断面図、図2(b)は立体図である。図2に示す複合吸音構造体102は、101の不織布1の上に、更に、不織布1/ホットメルト材2と積層・融着し、不織布を二層(1、1)積層することで、通気・粘性抵抗を効果的に増し、高周波数帯域を殆ど低下させずに、低・中周波数帯域を向上した構造例を示すものである。
FIG. 2 shows the structure of a second embodiment in which a nonwoven fabric is laminated on the basis of the basic structure of FIG. 2A is a cross-sectional view, and FIG. 2B is a three-dimensional view. The composite sound-absorbing
本発明によれば、吸音母材はそのままで不織布を積層することで粘性抵抗を増大し、更に通気抵抗を複合的にコントロールするので、厚さ等ほとんどスペースを変更せずに、広い周波数帯域に渡って、吸音特性を大将に向上できることとなったものである。 According to the present invention, the non-woven fabric is laminated as it is to increase the viscous resistance, and the ventilation resistance is controlled in a complex manner. Over time, the sound absorption characteristics can be improved to general.
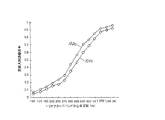
図3は、本発明の有効性を示したグラフである。吸音母材として、ポリエステル繊維系(嵩密度:44kg/m3 、厚さ:35mm)を選び、吸音母材のみの場合(比較例:100)に比べて、本発明である不織布(ポリエステル繊維系のスパンボンド不織布の面密度:100g/m2 、通気抵抗:0.7×104 N・sec/m4 )をパウダー状のホットメルト処理したもの一層を吸音母材に熱融着した場合(第1実施例:101)、同じ不織布を二層にして吸音母材に熱融着した場合(第2実施例:102)を示している。不織布が一層の第1実施例でかなり吸音性能が向上するが、不織布を二層にした第2実施例では、更に吸音性能が向上することが分かり、本発明の有効性が認められる。
FIG. 3 is a graph showing the effectiveness of the present invention. As a sound absorbing base material, a polyester fiber type (bulk density: 44 kg /
図4は、別の性状をもつ不織布を二層用いた効果を示す図であり、互いに、更には吸音母材と熱融着により積層・複合化した複合吸音構造体(第2実施例:102a)と、単層の不織布を吸音母材に熱融着した面重量及び通気抵抗をほぼ第2実施例と同じとした複合吸音構造体(第1実施例:101a)とを比較したグラフである。不織布を二層用いた102aの方が、一層の場合の101aより有効であることが証明されている。 FIG. 4 is a diagram showing the effect of using two layers of non-woven fabric having different properties, and a composite sound absorbing structure (second embodiment: 102a) laminated and composited with each other and with a heat absorbing base material. ) And a composite sound absorbing structure (first example: 101a) in which the surface weight and the airflow resistance obtained by heat-sealing a single-layer nonwoven fabric to the sound absorbing base material are substantially the same as those of the second example. . It has been proved that 102a using two layers of nonwoven fabric is more effective than 101a in the case of one layer.
これは、多層にする方が粘性抵抗が有効に働き、吸音母材も含めた総合的な通気・粘性抵抗が増し、音響エネルギーが熱エネルギーに効率よく変換され、吸音性能が大幅に向上するのである。尚、図4における第1実施例(101a)の構成は、不織布をポリエステル繊維系のスパンボンド不織布(面密度:200g/m2 、通気抵抗:1.5×104 N・sec/m4 )とし、第2実施例(102a)は図3のそれと同様であり、夫々、面密度及び通気抵抗は全体としてほぼ同じ数値となっている。 This is because the multilayer resistance is more effective in the multilayer, the overall ventilation and viscosity resistance including the sound-absorbing base material is increased, the acoustic energy is efficiently converted into thermal energy, and the sound-absorbing performance is greatly improved. is there. In addition, the structure of 1st Example (101a) in FIG. 4 made the nonwoven fabric into the polyester fiber type spunbonded nonwoven fabric (Area density: 200 g / m <2>, Ventilation resistance: 1.5 * 104 N * sec / m <4>), The second embodiment (102a) is the same as that of FIG. 3, and the surface density and the ventilation resistance are almost the same as each other.
図5は更に不織布を複数層とした例を示すものであり、図中、Eは三層としたもの(実施例3:103)、Fは五層としたもの(実施例4:104)の効果を示すグラフである。いずれも実施例1に使用した吸音母材、不織布、ホットメルト材を用いた。 FIG. 5 shows an example in which the nonwoven fabric is further composed of a plurality of layers. In the figure, E is a three-layered (Example 3: 103), and F is a five-layered (Example 4: 104). It is a graph which shows an effect. All used the sound-absorbing base material, nonwoven fabric, and hot melt material used in Example 1.
図6はパウダー状ホットメルト材にて不織布を複数積層して熱融着・複合化し、母材を空気層で置換した第5実施例105の構造を示す。不織布1は前例と同様にスパンボンド不織布であり、パウダー状ホットメルト材2はナイロン系であり、いずれも不織布は五層構造とした。又、空気層6の構成は任意手段であるが、例えば図6(a)に示すようにハニカム7で支持・構成(105a)してもよいし、図6(b)に示すように、膜のない高分子系不織布、例えばサランネット8(105b)や膜のない高分子系発泡材で支持・構成してもよい。
FIG. 6 shows the structure of a fifth embodiment 105 in which a plurality of non-woven fabrics are laminated with a powdered hot melt material, heat-sealed and composited, and the base material is replaced with an air layer. The
図7は図6に示す第5実施例の効果を示すグラフである。即ち、スパンボンド不織布をパウダー状ホットメルトで五層の複合構造体とし、空気層6を0mm(100a)、25mm(105c)、35mm(105d)とした場合を例示しているが、この例では空気層をハニカム7にて設けた例(105a)であるが、吸音特性が飛躍的に向上することが分かる。このように、本発明によれば、母材3を空気層6に置換しても優れた吸音特性が得られることが分かった。
FIG. 7 is a graph showing the effect of the fifth embodiment shown in FIG. That is, the case where the spunbonded nonwoven fabric is made into a five-layer composite structure with powdered hot melt and the air layer 6 is 0 mm (100a), 25 mm (105c), and 35 mm (105d) is illustrated. In the example (105a) in which the air layer is provided by the
本発明による複合吸音構造体の適用対象は、建機、農機、圧縮機等の各種産業機械、家電製品等のケーシングやその開口部の吸音処理、吸音ダクト、自動車、車両の内部の吸音処理、鉄道、道路分野の遮音壁等の吸音構造部位、建築分野の騒音低減や室内の音響コントロール用等の吸音材として、幅広く利用できるものである。 The object of application of the composite sound absorbing structure according to the present invention is various industrial machines such as construction machinery, agricultural machinery, and compressors, sound absorption processing of casings and openings of household electrical appliances, sound absorption ducts, automobiles, sound absorption processing inside vehicles, It can be widely used as a sound-absorbing structure such as a sound-insulating wall in the railway and road fields, and as a sound-absorbing material for noise reduction in the building field and indoor acoustic control.
1‥不織布、
2‥ホットメルト材、
3‥吸音母材、
6‥空気層、
7‥ハニカム、
8‥サランネット、
101、102、103、104、105‥複合吸音構造体。
1. Nonwoven fabric,
2. Hot melt material
3. Sound absorbing base material
6. Air layer,
7. Honeycomb
8 ... Saran Net,
101, 102, 103, 104, 105... Composite sound absorbing structure.
Claims (11)
The composite sound absorbing structure according to any one of claims 1 to 10, wherein an air layer is used as the sound absorbing base material.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006177348A JP2008008997A (en) | 2006-06-27 | 2006-06-27 | Composite sound absorbing structural body |
| CNA2006101722551A CN101097715A (en) | 2006-06-27 | 2006-12-30 | Compound sound-absorption structural body |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006177348A JP2008008997A (en) | 2006-06-27 | 2006-06-27 | Composite sound absorbing structural body |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008008997A true JP2008008997A (en) | 2008-01-17 |
| JP2008008997A5 JP2008008997A5 (en) | 2008-05-01 |
Family
ID=39011488
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006177348A Pending JP2008008997A (en) | 2006-06-27 | 2006-06-27 | Composite sound absorbing structural body |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2008008997A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN101097715A (en) |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2009125742A1 (en) * | 2008-04-10 | 2009-10-15 | ブリヂストンケービージー株式会社 | Sound-absorbing composite structure |
| JP2010079164A (en) * | 2008-09-29 | 2010-04-08 | Hitachi Ltd | Compound sound absorbing structure and storage structure using the same |
| JP2010281131A (en) * | 2009-06-05 | 2010-12-16 | Bridgestone Kbg Co Ltd | Sound absorbing panel |
| CN102275346A (en) * | 2011-05-16 | 2011-12-14 | 东华大学 | Sound absorption composite structural material and preparation method thereof |
| CN102347024A (en) * | 2011-07-21 | 2012-02-08 | 昆明理工大学 | Anechoic tile based on combinatorial materials |
| JP2014527478A (en) * | 2011-07-28 | 2014-10-16 | サン−ゴバン アドフォル | Wall covering sound absorbing material |
| JP2014529524A (en) * | 2011-08-25 | 2014-11-13 | サン−ゴバンアドフォル | Wall covering for thermal and acoustic comfort |
| CN104989939A (en) * | 2015-07-02 | 2015-10-21 | 辽宁融达新材料科技有限公司 | Punched foamed aluminum panel and manufacturing method thereof |
| CN106626570A (en) * | 2016-09-13 | 2017-05-10 | 天津工业大学 | Preparation method of resistant gradually changed sound-absorbing and noise-reducing composite functional material |
| JP2018092131A (en) * | 2016-11-28 | 2018-06-14 | Jxtgエネルギー株式会社 | Sound absorbing nonwoven fabric and sound absorbing material including the same |
| CN108257589A (en) * | 2018-03-11 | 2018-07-06 | 西北工业大学 | A kind of exoskeletal lightweight air bag with high acoustic absorption performance |
| JP2019196640A (en) * | 2018-05-10 | 2019-11-14 | 三井化学株式会社 | Foldable screen and space partition method |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104118177B (en) * | 2014-07-29 | 2016-01-20 | 宁波华乐特汽车装饰布有限公司 | A kind of vehicle inside decoration fabric |
| WO2019035192A1 (en) * | 2017-08-16 | 2019-02-21 | 日産自動車株式会社 | Antifouling structure |
| JP6923796B2 (en) * | 2017-08-25 | 2021-08-25 | キョーラク株式会社 | Structures, vehicle structures and vehicle air conditioning ducts |
| CN109263157B (en) * | 2018-08-30 | 2021-01-26 | 无锡吉兴汽车部件有限公司 | Acoustic functional component and application thereof |
| KR102604135B1 (en) * | 2018-12-13 | 2023-11-17 | 아사히 가세이 가부시키가이샤 | Nonwoven fabric, laminated nonwoven fabric of this nonwoven fabric, and composite sound-absorbing material using them as a skin material |
| WO2020213139A1 (en) * | 2019-04-18 | 2020-10-22 | 日立化成株式会社 | Sound-absorbing material |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH10205352A (en) * | 1997-01-24 | 1998-08-04 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | Engine cover |
| JP2004107605A (en) * | 2002-09-20 | 2004-04-08 | Jfe Chemical Corp | Powdery adhesive for acoustical material, and adhesive surface skin material, acoustic material and automobile interior material containing the same |
| JP2004163510A (en) * | 2002-11-11 | 2004-06-10 | Daicel Chem Ind Ltd | Sound absorptive molded body |
| JP2006098890A (en) * | 2004-09-30 | 2006-04-13 | Toray Ind Inc | Sound-deadening material and manufacturing method thereof |
-
2006
- 2006-06-27 JP JP2006177348A patent/JP2008008997A/en active Pending
- 2006-12-30 CN CNA2006101722551A patent/CN101097715A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH10205352A (en) * | 1997-01-24 | 1998-08-04 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | Engine cover |
| JP2004107605A (en) * | 2002-09-20 | 2004-04-08 | Jfe Chemical Corp | Powdery adhesive for acoustical material, and adhesive surface skin material, acoustic material and automobile interior material containing the same |
| JP2004163510A (en) * | 2002-11-11 | 2004-06-10 | Daicel Chem Ind Ltd | Sound absorptive molded body |
| JP2006098890A (en) * | 2004-09-30 | 2006-04-13 | Toray Ind Inc | Sound-deadening material and manufacturing method thereof |
Cited By (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5501959B2 (en) * | 2008-04-10 | 2014-05-28 | ブリヂストンケービージー株式会社 | Composite sound absorbing structure |
| WO2009125742A1 (en) * | 2008-04-10 | 2009-10-15 | ブリヂストンケービージー株式会社 | Sound-absorbing composite structure |
| JPWO2009125742A1 (en) * | 2008-04-10 | 2011-08-04 | ブリヂストンケービージー株式会社 | Composite sound absorbing structure |
| JP2010079164A (en) * | 2008-09-29 | 2010-04-08 | Hitachi Ltd | Compound sound absorbing structure and storage structure using the same |
| JP2010281131A (en) * | 2009-06-05 | 2010-12-16 | Bridgestone Kbg Co Ltd | Sound absorbing panel |
| CN102275346A (en) * | 2011-05-16 | 2011-12-14 | 东华大学 | Sound absorption composite structural material and preparation method thereof |
| CN102347024A (en) * | 2011-07-21 | 2012-02-08 | 昆明理工大学 | Anechoic tile based on combinatorial materials |
| JP2014527478A (en) * | 2011-07-28 | 2014-10-16 | サン−ゴバン アドフォル | Wall covering sound absorbing material |
| JP2014529524A (en) * | 2011-08-25 | 2014-11-13 | サン−ゴバンアドフォル | Wall covering for thermal and acoustic comfort |
| CN104989939A (en) * | 2015-07-02 | 2015-10-21 | 辽宁融达新材料科技有限公司 | Punched foamed aluminum panel and manufacturing method thereof |
| CN106626570A (en) * | 2016-09-13 | 2017-05-10 | 天津工业大学 | Preparation method of resistant gradually changed sound-absorbing and noise-reducing composite functional material |
| JP2018092131A (en) * | 2016-11-28 | 2018-06-14 | Jxtgエネルギー株式会社 | Sound absorbing nonwoven fabric and sound absorbing material including the same |
| CN108257589A (en) * | 2018-03-11 | 2018-07-06 | 西北工业大学 | A kind of exoskeletal lightweight air bag with high acoustic absorption performance |
| JP2019196640A (en) * | 2018-05-10 | 2019-11-14 | 三井化学株式会社 | Foldable screen and space partition method |
| JP7081975B2 (en) | 2018-05-10 | 2022-06-07 | 三井化学株式会社 | Folding tsuitate and space partitioning method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101097715A (en) | 2008-01-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2008008997A (en) | Composite sound absorbing structural body | |
| JP2008008997A5 (en) | ||
| KR101544622B1 (en) | Sound absorbing cover, method of manufacturing thereof and method of sound absorbing | |
| US8950548B2 (en) | Broadband sound absorber | |
| JP5501959B2 (en) | Composite sound absorbing structure | |
| JP6510653B2 (en) | Soundproof structure | |
| JP2009235761A (en) | Flexible soundproof/sound-absorbing sheet | |
| JP6570641B2 (en) | Soundproof structure | |
| JP2007334285A (en) | Sound absorbing structure and rail vehicle | |
| JP2007034254A (en) | Porous material-based sound absorbing material with improved sound absorbing performance | |
| WO2021049224A1 (en) | Sound absorbing/insulating material | |
| JP2006323204A (en) | Double sound absorption structure | |
| JP2006098966A (en) | Sound insulation cover | |
| JP2008076871A (en) | Sound absorber and sound absorbing structure using thr same | |
| JP5320002B2 (en) | Storage structure for composite sound absorbing structure and composite sound absorbing structure disposed in the storage structure | |
| WO2019004151A1 (en) | Cover material for acoustic insulation, and engine unit | |
| JP2006153926A (en) | Compound sound absorbing structure body | |
| RU2583438C1 (en) | Kochetov sound-absorbing element | |
| JP2018194649A (en) | Composite sound absorbing material | |
| JP2005263118A (en) | Sound absorbing material for vehicle | |
| JP6944057B2 (en) | Laminate | |
| RU2576264C1 (en) | Kochetov(s noise absorber with sound reflecting layer | |
| JP2003211574A (en) | Sound absorption material | |
| JP5813290B2 (en) | Sound absorption structure | |
| JP2021138143A (en) | Laminate |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080314 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20090626 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20090810 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20090810 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20110425 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110524 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110704 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20111213 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120110 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20121002 |