JP2005533254A - Assembly for electrically connecting a device under test to a test machine for testing an electrical circuit on the device under test - Google Patents
Assembly for electrically connecting a device under test to a test machine for testing an electrical circuit on the device under test Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2005533254A JP2005533254A JP2004521866A JP2004521866A JP2005533254A JP 2005533254 A JP2005533254 A JP 2005533254A JP 2004521866 A JP2004521866 A JP 2004521866A JP 2004521866 A JP2004521866 A JP 2004521866A JP 2005533254 A JP2005533254 A JP 2005533254A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- contactor
- electrical
- interposer
- assembly
- test
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 97
- 239000000523 sample Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 36
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 33
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 claims description 24
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 23
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 14
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000012858 resilient material Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910000760 Hardened steel Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 229920002379 silicone rubber Polymers 0.000 claims 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 14
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002950 deficient Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005489 elastic deformation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000015654 memory Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- NJPPVKZQTLUDBO-UHFFFAOYSA-N novaluron Chemical compound C1=C(Cl)C(OC(F)(F)C(OC(F)(F)F)F)=CC=C1NC(=O)NC(=O)C1=C(F)C=CC=C1F NJPPVKZQTLUDBO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01R—MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES
- G01R1/00—Details of instruments or arrangements of the types included in groups G01R5/00 - G01R13/00 and G01R31/00
- G01R1/02—General constructional details
- G01R1/06—Measuring leads; Measuring probes
- G01R1/067—Measuring probes
- G01R1/073—Multiple probes
- G01R1/07307—Multiple probes with individual probe elements, e.g. needles, cantilever beams or bump contacts, fixed in relation to each other, e.g. bed of nails fixture or probe card
- G01R1/07364—Multiple probes with individual probe elements, e.g. needles, cantilever beams or bump contacts, fixed in relation to each other, e.g. bed of nails fixture or probe card with provisions for altering position, number or connection of probe tips; Adapting to differences in pitch
- G01R1/07378—Multiple probes with individual probe elements, e.g. needles, cantilever beams or bump contacts, fixed in relation to each other, e.g. bed of nails fixture or probe card with provisions for altering position, number or connection of probe tips; Adapting to differences in pitch using an intermediate adapter, e.g. space transformers
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01R—MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES
- G01R1/00—Details of instruments or arrangements of the types included in groups G01R5/00 - G01R13/00 and G01R31/00
- G01R1/02—General constructional details
- G01R1/06—Measuring leads; Measuring probes
- G01R1/067—Measuring probes
- G01R1/073—Multiple probes
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01R—MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES
- G01R31/00—Arrangements for testing electric properties; Arrangements for locating electric faults; Arrangements for electrical testing characterised by what is being tested not provided for elsewhere
- G01R31/28—Testing of electronic circuits, e.g. by signal tracer
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01R—MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES
- G01R31/00—Arrangements for testing electric properties; Arrangements for locating electric faults; Arrangements for electrical testing characterised by what is being tested not provided for elsewhere
- G01R31/28—Testing of electronic circuits, e.g. by signal tracer
- G01R31/2851—Testing of integrated circuits [IC]
- G01R31/2886—Features relating to contacting the IC under test, e.g. probe heads; chucks
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01R—MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES
- G01R31/00—Arrangements for testing electric properties; Arrangements for locating electric faults; Arrangements for electrical testing characterised by what is being tested not provided for elsewhere
- G01R31/28—Testing of electronic circuits, e.g. by signal tracer
- G01R31/2851—Testing of integrated circuits [IC]
- G01R31/2855—Environmental, reliability or burn-in testing
- G01R31/286—External aspects, e.g. related to chambers, contacting devices or handlers
- G01R31/2863—Contacting devices, e.g. sockets, burn-in boards or mounting fixtures
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Testing Or Measuring Of Semiconductors Or The Like (AREA)
- Measuring Leads Or Probes (AREA)
- Testing Of Individual Semiconductor Devices (AREA)
- Tests Of Electronic Circuits (AREA)
Abstract
一実施の形態において本発明は、被試験部品上の電気回路を試験するために、被試験部品を試験機械に電気的に接続するための試験組立体を提供する。本組立体は、被試験部品と相互接続されるコンタクタ組立体と、コンタクタ組立体を機械的に支持し、コンタクタ組立体を試験機械に電気的に接続するプローブ組立体と、第1のクランピング部材及び第2のクランピング部材を含むクランピングメカニズムとを備え、両クランピング部材は、プローブ組立体とコンタクタ組立体との間の電気的接続の導電性バンプを変形させるクランピング力を加えるように押し付けられる。In one embodiment, the present invention provides a test assembly for electrically connecting a part under test to a test machine for testing an electrical circuit on the part under test. The assembly includes a contactor assembly interconnected with a part under test, a probe assembly that mechanically supports the contactor assembly and electrically connects the contactor assembly to the test machine, and a first clamping A clamping mechanism including a member and a second clamping member, wherein both clamping members apply a clamping force that deforms the conductive bumps of the electrical connection between the probe assembly and the contactor assembly. Pressed against.
Description
本発明は試験機器に関する。特定的には、本発明は集積回路を含む電気回路を試験するための試験機器に関する。 The present invention relates to test equipment. In particular, the invention relates to test equipment for testing electrical circuits including integrated circuits.
コンピュータプロセッサ及びメモリのような電子デバイスの製造が完了すると、それらを出荷する前に欠陥デバイスを識別して排除するために、これらの電子デバイスに対してバーンイン及び電気試験を遂行する。“バーンイン”という用語は、所定の温度または温度プロファイル(典型的には炉内の高温)における集積回路の動作に関係付けられている。電子デバイスを高温に保ちながら、ある動作電気バイアスレベル及び/または信号を電子デバイスに印加する。高温を使用するとバーンイン中にデバイスが受ける応力が加速されるので、そのようにしなければサービスのために実装されてから短時間内に障害を起こしてしまうような境界上にあるデバイスはバーンイン中に障害を起こすから出荷されなくなる。 When the manufacture of electronic devices such as computer processors and memories is complete, burn-in and electrical tests are performed on these electronic devices to identify and eliminate defective devices before shipping them. The term “burn-in” relates to the operation of an integrated circuit at a given temperature or temperature profile (typically high temperature in a furnace). An operating electrical bias level and / or signal is applied to the electronic device while keeping the electronic device at an elevated temperature. The use of high temperatures accelerates the stress experienced by the device during burn-in, so devices on the boundary that would otherwise fail within a short time after being installed for service during burn-in It will not be shipped because it causes trouble.
電気回路のバーンイン試験のための試験機器は、一般的に、ウェーハまたは被試験基体上の集積回路のような被試験電気回路を試験プローブ回路に電気的に接続するための接続配列を含んでいる。 Test equipment for burn-in testing of electrical circuits generally includes a connection arrangement for electrically connecting an electrical circuit under test, such as an integrated circuit on a wafer or substrate under test, to a test probe circuit. .
一実施の形態において本発明は、被試験部品上の電気回路を試験するために、被試験部品を試験機械に電気的に接続するための試験組立体を提供する。組立体は、被試験部品と相互接続されるコンタクタ組立体と、コンタクタ組立体を機械的に支持してコンタクタ組立体を試験機械に電気的に接続するプローブ組立体と、第1のクランピング部材及び第2のクランピング部材を含むクランピングメカニズムとを備え、両クランピング部材は、プローブ組立体とコンタクタ組立体との間の電気的接続の導電性バンプを変形させるクランピング力を加えるように押し付けられる。 In one embodiment, the present invention provides a test assembly for electrically connecting a part under test to a test machine for testing an electrical circuit on the part under test. The assembly includes a contactor assembly interconnected with the part under test, a probe assembly that mechanically supports the contactor assembly and electrically connects the contactor assembly to the test machine, and a first clamping member And a clamping mechanism including a second clamping member, wherein both clamping members apply a clamping force that deforms the conductive bumps of the electrical connection between the probe assembly and the contactor assembly. Pressed.
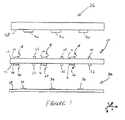
図1は、インタポーザ10及び電気的コンタクタ26を示しており、これらは、例えばウェーハ32上の電気回路を試験するために使用される本発明の一実施の形態によるコンタクタ組立体を形成している。
FIG. 1 shows an
図1に示すように、インタポーザ10は、第1の側12及び第2の側14を有する基体を含む。インタポーザ10は、第1の側12上に複数の電気端子16を含む。インタポーザ10は更に、相互接続用ばね要素18の形状の弾力性相互接続要素を含む。各相互接続ばね要素18は、側12上の電気端子から伸びて自由端において終端している。各相互接続ばね要素18の目的は、電気コンタクタ26上の対応する電気端子と良好な電気的接触を得ることである。他の実施の形態における弾力性相互接続要素は、ポーゴーピン及び順応し易い導電性バンプを含む。
As shown in FIG. 1, the
インタポーザ10は更に、側14上の各電気端子上に相互接続ばね要素20を有している。相互接続ばね要素20は相互接続ばね要素18と類似しているが、相互接続ばね要素20がウェーハ32上の対応する電気端子と電気的に接触する点が異なっている。
The
インタポーザ10は更に、その側12及び14上に、相互接続ばね要素18の過走行を防ぎ、且つインタポーザがウェーハ32のある領域に接触するのを防ぐための機械的位置合わせストップ22を含んでいる。
電気コンタクタ26は、側28を含むコンタクタ基体を含む。電気コンタクタ26は更に、側28上に電気端子30を含む。
The
ウェーハ32は被試験電気回路を有する側34を含むように図示されている。ウェーハ32は側34上に電気端子36を有し、それによって電気回路への電気接続を行うことができるようになっている。
Wafer 32 is shown to include a side 34 having an electrical circuit under test. Wafer 32 has
図2に、本発明の一実施の形態によるコンタクタ組立体40を示す。組立体40は、インタポーザ10、及びリング42の形状の保持部品を含んでいる。インタポーザ10は、リング42によって電気コンタクタ26に対する所定の、即ち位置合わせされた位置に確保、または保持される。所定の、即ち位置合わせされた位置においては、各相互接続ばね要素18がそのばね力に対抗して変形し、電気コンタクタ26の対応する電気端子30と電気的に接触することが理解されよう。この所定の位置には、リング42及びその中に座しているインタポーザ10を、位置合わせストップ22が電気コンタクタ26の側28と接触するまで運動させることによって到達する。他の実施の形態においては、所定の位置には、コンタクタ26を定位置に保持するために相互接続ばね要素18(他の実施の形態においては、ポーゴーピンまたは順応し易い導電性バンプ)によって十分な圧力を加えた時に到達するようになっている。従って、ストップ22はオプションである。インタポーザ10と電気コンタクタ26との間隔は、各相互接続ばね要素18が圧縮されるような間隔である。
FIG. 2 shows a
リング42には、インタポーザ10のための座を限定している凹み付き表面44が形成されている。リング42は、電気コンタクタ26の側28に載るフラットなフランジ状の面46を有している。リング42は、例えばねじ孔48を通って伸びるねじのような締め具43(図4参照)によって、電気コンタクタ26に固定される。孔48は、インタポーザ10及びコンタクタ26上のそれぞれの基準マーキングに位置合わせできるようにするために、ある程度の遊びをもって締め具43を受入れるような寸法である。
The
図3に、コンタクタ組立体40の形成の最初の段階を示す。図3に示すように、真空板50がリング42の面46とは反対の側に固定され、サブ組立体51が形成される。真空板50は、継ぎ手54及びこの継ぎ手54に接続されるホース52によってポンプ(図示せず)に接続することができる。使用中、ポンプは真空板50とインタポーザ10との間の領域56内を真空にする。真空が、インタポーザ10を凹み付き表面44に対して保持する。図4及び5から理解されるように、真空板50は、締め具43へのアクセスを与えるような形状及び寸法である。
FIG. 3 shows the first stage of formation of the
サブ組立体51の断面図である図6(図5の6−6矢視)から理解されるように、インタポーザ10はリング42内にぴったりと着座している。
As can be understood from FIG. 6, which is a cross-sectional view of the subassembly 51 (see arrow 6-6 in FIG. 5), the
図7は、どのようにしてインタポーザ10と電気コンタクタ26との位置合わせが達成されるかを示すブロック図である。リング42内に着座しているインタポーザ10は、インタポーザ10の側12の上の基準マーキング58と、電気コンタクタ26の側28の上の基準マーキング60の位置が合うようにx、y、またはθ方向に運動する。基準マーキング58と基準マーキング60とを位置合わせした後に、リング42が電気コンタクタ26と接触するようにリング42をインタポーザ10と一緒にz方向に変位させる。次いで孔48内に位置するねじ43を、電気コンタクタ26内に形成されている相補的なねじ付きの孔68内にねじ込む。基準マーキング58、60によって、相互接続ばね要素18のイメージを取る必要なく、電気コンタクタ26上の電気端子30と、相互接続ばね要素18の端とを位置合わせすることが可能になっている。各相互接続ばね要素のx−y面における位置、またはそれがx−y面から投射する角度の公差は、位置合わせプロセスに影響しない。インタポーザ10の側18上の機械的ストップ22は、組立体40を形成する時に、電気コンタクタ26に向かうインタポーザ10の運動を制限する(各相互接続ばね要素18が所望の圧縮状態にあるようにする)ために使用することができる。
FIG. 7 is a block diagram illustrating how alignment between the
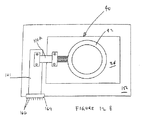
図8は、本発明の一実施の形態による位置合わせ機械70の斜視図であって、この機械70は、リング42及びインタポーザ10の組合わせと、電気コンタクタ26とを位置合わせするために使用することができる。位置合わせ機械70は、プローブ板152(図10参照)上に載るような形状及び寸法のベース72を含む。プローブ板152は、使用中に電気コンタクタ26を収容する。位置合わせ機械70は更に、小高くされたプラットフォームまたは板74を含む。プラットフォーム74は、取付け用ブラケット76によってベース72に固定されている。プラットフォーム74は、キャリッジ78を支持している。位置合わせ機械70の側面図である図9に、キャリッジ78が示されている。キャリッジ78は、アングルブラケット88及び水平ばね90からなる取付け配列によってプラットフォーム74の下側に固定されている。アングルブラケット88はプラットフォーム74に固定されていてばね90の一方の端のためのアンカーになっており、ばね90の他方の端は図9に示すようにキャリッジ78の浮動板80に固定されている。
FIG. 8 is a perspective view of an
キャリッジ78は更に、リングホールダ82を含んでいる。リングホールダ82は、リングホールダ取付け板82と浮動板80との間に伸びる垂直部材84に固定されている。
The
プラットフォーム74と浮動板80との間に配置されているローラ軸受94が、浮動板80をプラットフォーム74に対して滑り変位可能にしている。垂直ばね95が、浮動板80をローラ軸受94に接触させている。浮動板80とプラットフォーム74とがばね取付け配列によって結合されているために、浮動板80はx−y面内で運動することができる。x−y面内におけるこのような運動は、調整メカニズムによって制御される。調整メカニズムは、一実施の形態においては、マイクロメータ96、98、及び100を含む。各マイクロメータは、そのチップを浮動板80の縁に係合させるように動作可能であり、それによって浮動板80に変位を生じさせることができる。例えば、図9に示すように、マイクロメータ98のチップ98.1を浮動板80の縁に係合させてy方向に変位させ、それによって浮動板80をy方向に変位させることができる。リングホールダ82は浮動板80に堅固に接続されているので、浮動板80が変位するとリングホールダ82も対応して変位する。
A roller bearing 94 disposed between the
使用中、真空板50及びポンプ(図示せず)の援助によって生ずる吸引力によってリング42内に着座しているインタポーザ10は、キャリッジ78のリングホールダ82に機械的に接続される。次いで、図10に示すように、位置合わせ機械70がプローブ板152上に位置決めされる。この位置においては、リング42及びリング42内に着座しているインタポーザ10は、プローブ板152内に着座している電気コンタクタ26の直上に位置決めされる。
During use, the
図9に示すように、スコープ部分104及びベース106を含む顕微鏡102からなる拡大システムが、プラットフォーム74上に固定されている。
As shown in FIG. 9, a magnification system consisting of a microscope 102 including a scope portion 104 and a
顕微鏡102は、インタポーザ10及び電気コンタクタ26上の基準マーキング58、60を拡大する。マイクロメータ96、98、及び100を操作してキャリッジ78を運動させることができる。キャリッジ78はリング42及びインタポーザ10を担持しているので、インタポーザ10を電気コンタクタ26上の所定の、即ち位置合わせされた位置(即ち、インタポーザ10及び電気コンタクタ26上の基準マーキング58、60が位置合わせされた位置)に位置決めすることができる。
The microscope 102 magnifies the reference markings 58, 60 on the
位置合わせ機械70は更に、マイクロメータヘッド108を含む。マイクロメータヘッド108は、キャリッジ78をz方向に運動させるように動作可能であり、それによってインタポーザ及びリングの組合わせを電気コンタクタ26に向かってz方向に変位させる。使用中、z方向の変位は、位置合わせストップ22が電気コンタクタ26の側28と接触するまで、または所望のz位置に到達するまで続行される。この位置に到達した時にねじ43を電気コンタクタ26内のソケット68にねじ込み、それによってリング及びその中に着座しているインタポーザ10を電気コンタクタ26に固定する。
The
リング42及びインタポーザ10を電気コンタクタ26に固定した後に、真空板50及び位置合わせ機械70を取り外す。図12Aに示すように、プローブ板152は、電気ピン166の形状の複数の電気コネクタからなる外部インタフェース部品164を含む。フレキシブルコネクタ110がコンタクタ組立体40をインタフェース部品164に電気的に接続し、インタフェース部品164自体はピン166を介して試験機械(図示せず)のバーンインチャンバに電気的に接続されている。
After fixing the
図13Aに示すように、フレキシブルコネクタ110は、側112.1及び112.2を有するフレキシブル基体112を含む。更に、フレキシブル基体112は、第1の端115及び第2の端116を有する。図13A及び13Bに示すように、フレキシブルライン導体114.1及び114.2が、それぞれ側112.1及び112.2上に形成されている。各フレキシブルライン導体114は、インタフェース部品164に電気的に接続されている第1の端と、第1の端とは反対側の第2の端とを有している。図13Bに示すように、各フレキシブルライン導体114.1はその第2の端に、2つの導電性バンプ118.1からなる端子を含んでいる。同様に、各フレキシブルライン導体114.2は、インタフェース部品164に電気的に接続されている第1の端と、第1の端とは反対側の第2の端とを有している。各フレキシブルライン導体114.2の第2の端は、基体112を通って伸びるバイア113によって側112.1上の2つの導電性バンプ118.2からなる端子に接続されている。基体112の各側112.1及び112.2上にフレキシブルライン導体を設けることによって、基体112がより多くのライン導体114.1及び114.2を担持できることが理解されよう。
As shown in FIG. 13A, the
フレキシブルコネクタ110はフレキシブル基体112に損傷を与えることなくそれ自体の上に折り曲げることができるように十分にフレキシブルであり、典型的には、ポリイミドのような材料で作られる。幾つかの実施の形態によれば、フレキシブル基体112は25.4ミクロン、または49ミクロンの厚みを有することができるが、フレキシブル基体112に損傷を与えることなくそれ自体の上に折り曲げることができるという点からは、125ミクロンまでの厚みでも未だフレキシブルである。
The
典型的には、バンプ118.1、118.2は金で形成され、約100マイクロメートルの幅と約60マイクロメートルの高さとを有している。金は酸化することがなく、150℃乃至350℃の温度に耐えるので、バンプ118のための材料として好ましい。更に、金は180℃乃至240℃の温度範囲内においてその弾性を維持する。フレキシブルコネクタ110はライン導体114.1及び114.2をカバーする層119を含む。図15に示すように、層119は非導電性フレキシブル材料で作られる。
Typically, the bumps 118.1, 118.2 are made of gold and have a width of about 100 micrometers and a height of about 60 micrometers. Gold is preferred as a material for the bump 118 because it does not oxidize and can withstand temperatures of 150 to 350 ° C. In addition, gold maintains its elasticity within the temperature range of 180 ° C to 240 ° C. The
フレキシブルコネクタ110は、コンタクタ組立体40の堅固で実質的に折り曲げることができない電気コンタクタ26に電気的に接続される。この目的のために、電気コンタクタ26は、フレキシブルコネクタ110の導電性バンプ118.1及び118.2への電気接続に匹敵する複数の電気コンタクタ(接点)要素120を有している。図14に、電気コンタクタ26上の電気コンタクタ要素のレイアウトを示す。図14に明示されているように、電気コンタクタ要素120は概ね矩形であり、2つの列125に配列されている。各要素120は、平坦な接点表面120.1を有している(図15参照)。全ての電気コンタクタ要素120は同一面内にある。一実施の形態においては、各電気コンタクタ要素120は、500ミクロンの横方向寸法と、30ミクロンの高さを有している。この実施の形態においては、電気コンタクタ要素120は、100ミクロンのピッチで離間している。電気コンタクタ要素120は、典型的には金で形成され、導体バンプ118.1及び118.2との間にかなり強固な接続が得られる。フレキシブルコネクタ110と電気コンタクタ26との間の電気的接続のプロファイルは低く、一実施の形態においては、約6ミリメートルの高さにしか過ぎない。
The
図15は、フレキシブルコネクタ110と電気コンタクタ要素120との間の電気的接続を形成させる一段階のブロック図である。
FIG. 15 is a block diagram of one stage for forming an electrical connection between the
基本的には、フレキシブルコネクタ110と電気コンタクタ要素120との間に電気的接続を形成させるために、フレキシブル電気コネクタ110の第2の端116を、クランプを用いて電気コンタクタ26上にクランプする。クランプは、加工硬化した金属の細長いバー122の形状の第1のクランピング部材と、電気コンタクタ26によって限定される第2のクランピング部材とからなる。金属バー122の熱膨張係数は、電気コンタクタ26の熱膨張係数と整合している。一実施の形態においては、金属バー122の熱膨張係数は、電気コンタクタ26の熱膨張係数の0.5ppm/℃以内である。
Basically, the second end 116 of the flexible
細長い金属バー122、フレキシブルコネクタ110、及び電気コンタクタ26は、締付け用ボルト124を受入れるための軸方向に伸びる孔を有している。図16に示すようにナット126がボルト124にねじ込まれ、導電性バンプ118.1及び118.2と電気コンタクタ要素120とを接触させる位置に締め付ける。締付け用ボルト124によって加えられるクランピング力によって導電性バンプ118.1及び118.2は電気コンタクタ要素120に押し付けられ、導電性バンプ118.1及び118.2は弾性変形及び塑性変形を受ける。これにより、導電性バンプ118.1及び118.2と電気コンタクタ要素120との間に良好な電気的接触が得られる。
The
締付け用ボルト124、金属バー122、及び導電性バンプ118.1及び118.2は異なる熱係数を有し得るので、またバーンイン試験が高温で行われることから、バーンイン試験中に締付け用ボルト124は伸び得る。これは、締付け用ボルト124の頭124.1と金属バー122との間に間隙を生じさせる。
Because the
このような間隙が生ずると、締付け用ボルト124によってフレキシブルコネクタ110に加えられるクランピング力が解放されることが理解されよう。このような間隙を生ずる傾向を補償するために、図16に示すように、細長い金属バー122とフレキシブルコネクタ110との間に弾力性材料のエキスパンダ部材128を挿入、またはサンドウィッチすることができる。エキスパンダ部材128は、締付け用ボルト124の締付けによって生ずるクランピング力の下では圧縮され、またもし締付けボルト124に伸びが発生すれば弛緩、または膨張する。従って、エキスパンダ部材128は頭124.1と金属バー122との間の何等かの間隙を吸収し、それによって締付け用ボルト124のクランピング力を維持する。エキスパンダ部材は、バーンインチャンバ内の高温に耐えることができる材料である。更に、導電性バンプ118.1及び118.2の高さが変化し得るから、エキスパンダ部材128はフレキシブル基体112を変形させて導電性バンプ118.1及び118.2の高さの変動を個々に補償する。
It will be appreciated that when such a gap occurs, the clamping force applied to the
図12Aに、フレキシブルコネクタの別の実施の形態110Aを示す。フレキシブルコネクタ110Aはフレキシブルコネクタ110に類似しているが、バンプ118.1及び118.2に類似した導電性バンプをその各端に有している点が異なる。フレキシブルコネクタ110Aの一方の端は上述したように電気コンタクタ26にクランプされており、フレキシブルコネクタ110Aの反対端は同じような手法でコネクタ121(外部インタフェース164へ、及びそれから電気信号を伝える)にクランプされる。
FIG. 12A shows another embodiment 110A of the flexible connector. Flexible connector 110A is similar to
コンタクタ26は、クランプする前に導電性バンプ118と電気コンタクタ要素120との位置合わせを容易にするための基準マーキング130(図17参照)を含んでいる。これらの基準マーキング130は、フレキシブルコネクタ110を通して見ることができる。フレキシブルコネクタ110は、コンタクタ26上の基準マーキング130と位置合わせすることができる相補的な基準マーキング132(図13B参照)を有しており、それによって導電性バンプ118とコンタクタ要素120とを位置合わせ可能にしている。
図18に、本発明の一実施の形態による試験プローブ組立体150の部品を示す。試験プローブ組立体150は、プローブ板152及びチャック板154を含む。これらは、これらの間に図2に示したコンタクタ組立体40のようなコンタクタ組立体を受入れるための空間を限定している。
FIG. 18 shows the components of a
チャック板154は、ウェーハ32を支持するペデスタル156を有している。プローブ板152は、ピストン158を含んでいる。ピストン158は、シリンダ160に取り外し可能なように接続できるホース162を通して使用中にシリンダ160内に導入される水圧流体によってシリンダ160内において変位可能である。ピストン158は、コンタクタ組立体40の電気コンタクタ26に接続されている。
The
使用中、ホース162を通して空気がチャンバ160内に導入されてピストン158をz方向に駆動すると、コンタクタ組立体40はインタポーザ10の側14の上の機械的位置合わせストップ22がウェーハ32の側34と接触するまでチャック板154に向かって変位させられる。リング42とチャック板154との間に位置決めされているOリング163のような弾力的に変形可能な部材は、ピストン158の運動によって生ずるコンタクタ組立体40の変位の大きさを制限、または制御するのに役立つ。従って、ピストン158の運動を精密に制御する必要はない。更に、Oリング163は、リング42とチャック板154との間のシールとして役立つ。Oリング163は、リング42がチャック板154に向かって変位する際にリング42の面46が同一z面をなさなくなる変動を、リング42をクッショニングすることによって受入れる。一実施の形態においては、Oリング163はピストン158の運動に対して反応するばねに置換することができる。インタポーザ10の側14の機械的ストップ22がウェーハ32の側34に接触すると相互接続ばね要素が圧縮され、それによってインタポーザ10の相互接続ばね要素20とウェーハ32の電気端子36との間に良好な電気接触が得られる。次いでホース162が取り外される。プローブ組立体152は更に、チャック板154をプローブ板152に取り外し可能なように確保、または締付ける確保メカニズムを含んでいる。図12には確保メカニズムは示されていないが、米国特許第6,340,895号の運動継ぎ手のような何等かの適当なクランピング配列を含んでいる。次いで、試験プローブ組立体150が試験バーンインチャンバ内へ挿入され、電気接続ピン166が相補的な電気ソケット内に受入れられる。
In use, when air is introduced through the hose 162 into the
以上に、本発明を特定の実施の形態に関して説明したが、これらの実施の形態に対して本発明の思想から逸脱することなく種々に変更及び変化させ得ることは明白である。従って、以上の説明は本発明を限定するものではなく、単なる例示に過ぎないことを理解されたい。 Although the invention has been described with reference to particular embodiments, it will be apparent that various changes and modifications can be made to these embodiments without departing from the spirit of the invention. Accordingly, it is to be understood that the above description is not intended to limit the invention but is merely exemplary.
Claims (62)
複数の第1の導体、各々が前記第1の導体のそれぞれに接続されている複数の第1の端子、及び各々が前記第1の導体のそれぞれに接続されていて前記被試験部品と電気的に接触する端を有する弾力性相互接続要素、及びコンタクタ組立体を支持する支持部品を含むコンタクタ組立体と、
前記支持部品上にあって、前記試験機械に電気的接続を行うための電気コネクタを含む外部インタフェース部品と、
フレキシブル基体と、
前記フレキシブル基体上にあって、前記外部インタフェース部品に電気的に接続されているフレキシブルな第2の導体と、
前記フレキシブル基体上にあって、前記フレキシブルな第2の導体に電気的に接続されている複数の第2の端子と、
前記第1の端子と前記第2の端子との間に配置されている複数の導電性バンプと、
前記第1の端子及び前記第2の端子を互いに他方に向かって押し付けて前記導電性バンプを変形させる第1及び第2のクランピング部材を含むクランプと、
を備えていることを特徴とする組立体。 An assembly for electrically connecting the device under test to a test machine for testing an electrical circuit on the device under test;
A plurality of first conductors, a plurality of first terminals each connected to each of the first conductors, and each connected to each of the first conductors and electrically connected to the component under test A contactor assembly including a resilient interconnection element having an end in contact with the contactor and a support component supporting the contactor assembly
An external interface component on the support component and including an electrical connector for making an electrical connection to the test machine;
A flexible substrate;
A flexible second conductor on the flexible substrate and electrically connected to the external interface component;
A plurality of second terminals on the flexible substrate and electrically connected to the flexible second conductor;
A plurality of conductive bumps disposed between the first terminal and the second terminal;
A clamp including first and second clamping members for pressing the first terminal and the second terminal toward each other to deform the conductive bump;
An assembly comprising:
第1の電気導体、前記第1の電気導体の第1の端に接続されている複数の第1の端子、前記第1の電気導体の第2の端に接続されている複数の第2の端子、及び前記第1の端子を前記被試験部品に電気的に相互接続する弾力性相互接続要素を含むコンタクタ組立体と、
前記コンタクタ組立体を支持している板部品、前記板部品上にあって前記試験機械に電気的に接続するための複数の外部電気コネクタからなるインタフェース部品、前記インタフェース部品に接続されている第1の端及び前記第1の端とは反対側の第2の端を有するフレキシブル基体、前記フレキシブル基体上のフレキシブル導体を含むプローブ組立体と、
を備え、
前記フレキシブル導体は、前記インタフェース部品に接続されている第1の部分、及び前記フレキシブル基体の第2の端にある端子部分を有し、前記端子部分は前記第2の端子と位置合わせされている複数の第3の端子を含み、
前記試験組立体は更に、
前記第2の端子と前記第3の端子との間の複数の電気コンタクタバンプと、
第1のクランピング部材及び第2のクランピング部材からなるクランピングメカニズムと、
を備え、
前記両クランピング部材は、前記第2及び第3の端子を運動させて前記コンタクタバンプを前記両端子の間で変形させるようなクランピング力を加えるように押し付けられる、
ことを特徴とする試験組立体。 A test assembly for electrically connecting the part under test to a test machine for testing an electrical circuit on the part under test,
A first electrical conductor, a plurality of first terminals connected to a first end of the first electrical conductor, and a plurality of second terminals connected to a second end of the first electrical conductor. A contactor assembly including a terminal and a resilient interconnection element that electrically interconnects the first terminal to the part under test;
A plate component supporting the contactor assembly, an interface component comprising a plurality of external electrical connectors on the plate component and electrically connected to the test machine, and a first connected to the interface component A flexible substrate having a second end opposite to the first end, a probe assembly including a flexible conductor on the flexible substrate;
With
The flexible conductor has a first portion connected to the interface component and a terminal portion at a second end of the flexible base, and the terminal portion is aligned with the second terminal. Including a plurality of third terminals;
The test assembly further includes
A plurality of electrical contactor bumps between the second terminal and the third terminal;
A clamping mechanism comprising a first clamping member and a second clamping member;
With
The clamping members are pressed to apply a clamping force that moves the second and third terminals to deform the contactor bumps between the terminals.
A test assembly characterized by that.
コンタクタ組立体を支持して前記被試験部品と電気的に接触させる支持部品と、
前記支持部品上にあって、前記試験機械に電気的に接続するための複数の電気コネクタを含む外部インタフェース部品と、
前記インタフェース部品に電気的に接続されている第1の端、及び前記第1の端とは反対側の第2の端を有するフレキシブル基体と、
前記フレキシブル基体上のフレキシブル導体と、
を備え、
前記フレキシブル導体は、前記インタフェース部品に電気的に接続されている第1の部分及び前記フレキシブル基体の第2の端にある端子部分を有し、前記端子部分は複数の端子を含み、前記フレキシブル導体は更に、前記端子のそれぞれに接続されている複数の導電性バンプを有し、前記端子部分は前記コンタクタ組立体に接続可能であって前記コンタクタ組立体と前記試験機械との間の電気信号を伝えるようになっている、
ことを特徴とするユニット。 A unit for interfacing the device under test and a test machine to test an electrical circuit on the device under test;
A support component that supports the contactor assembly and is in electrical contact with the component under test;
An external interface component on the support component and including a plurality of electrical connectors for electrical connection to the test machine;
A flexible substrate having a first end electrically connected to the interface component and a second end opposite to the first end;
A flexible conductor on the flexible substrate;
With
The flexible conductor has a first portion electrically connected to the interface component and a terminal portion at a second end of the flexible base, and the terminal portion includes a plurality of terminals, and the flexible conductor Further includes a plurality of conductive bumps connected to each of the terminals, the terminal portion being connectable to the contactor assembly for transmitting electrical signals between the contactor assembly and the test machine. To communicate,
A unit characterized by that.
試験構造と、
前記試験構造上の複数の電気端子と、
前記電気端子に接続されている第1の端、及び前記第1の端とは反対側にあって前記被試験部品に接続される自由端を各々が有している複数の弾力性相互接続要素と、
前記電気端子から離れた前記試験構造上の複数の電気接点要素と、
前記各電気端子を前記電気接点要素のそれぞれとブリッジする電気経路と、
を備え、
前記各電気接点要素は、対応コンタクタ要素がクランピング力の下で変形した時に前記対応コンタクタを支持する平坦な表面を限定している、
ことを特徴とするコンタクタ組立体。 A contactor assembly for electrically connecting the device under test to a test machine for testing the device under test comprising:
Test structure and
A plurality of electrical terminals on the test structure;
A plurality of resilient interconnection elements each having a first end connected to the electrical terminal and a free end opposite the first end and connected to the part under test When,
A plurality of electrical contact elements on the test structure remote from the electrical terminals;
An electrical path that bridges each electrical terminal with each of the electrical contact elements;
With
Each electrical contact element defines a flat surface that supports the corresponding contactor when the corresponding contactor element deforms under clamping force;
A contactor assembly characterized by that.
コンタクタ基体及び前記コンタクタ基体上の複数の電気端子を含む電気コンタクタと、
第1及び第2の側を有するインタポーザ基体、及び前記インタポーザ基体の第1及び第2の側からそれぞれ伸びている複数の第1及び第2の弾力性相互接続要素を含むインタポーザと、
を備え、
前記インタポーザは前記電気コンタクタに対する所定の位置に位置決めされ、前記所定の位置においては、前記インタポーザ基体が前記第1の弾力性相互接続要素を弾力的に変形させるように前記コンタクタ基体に向かって相対的に運動して前記各第1の弾力性相互接続要素を前記電気コンタクタの電気端子に電気的に接触させ、
前記コンタクタ組立体は更に、
前記電気コンタクタに固定される第1の位置、及び前記インタポーザと接触して前記インタポーザを前記電気コンタクタに対する所定の位置に保持する第2の位置を有する保持部品、
を備えていることを特徴とするコンタクタ組立体。 A contactor assembly for use in testing an electrical circuit comprising:
An electrical contactor including a contactor base and a plurality of electrical terminals on the contactor base;
An interposer including an interposer substrate having first and second sides, and a plurality of first and second resilient interconnection elements extending respectively from the first and second sides of the interposer substrate;
With
The interposer is positioned at a predetermined position relative to the electrical contactor, wherein the interposer base is relative to the contactor base such that the interposer base elastically deforms the first resilient interconnection element. Moving each first resilient interconnection element in electrical contact with an electrical terminal of the electrical contactor;
The contactor assembly further includes:
A holding part having a first position fixed to the electric contactor and a second position for contacting the interposer and holding the interposer in a predetermined position with respect to the electric contactor;
A contactor assembly comprising:
第1の部材を有するフレーム部材と、
前記第1の部材に固定されているコンタクタ組立体と、
を備え、
前記コンタクタ組立体は、
コンタクタ基体、及び前記コンタクタ基体上の複数の電気端子を含む電気コンタクタと、
第1及び第2の側、及び前記第1及び第2の側からそれぞれ伸びている複数の第1及び第2の弾力性相互接続要素を有する導電性インタポーザ基体を含むインタポーザと、
を含み、
前記インタポーザは前記電気コネクタに対する所定の位置に位置決めされ、前記所定の位置においては、前記各第1の弾力性相互接続要素が前記電気コンタクタの電気端子と電気的に接触し、前記第2の弾力性相互接続要素が被試験電気回路が形成されている基体と電気的に接触し、
前記コンタクタ組立体は更に、
前記電気コンタクタに固定される第1の位置、及び前記インタポーザに固定されて前記インタポーザを前記電気コンタクタに対する所定の位置に保持する第2の位置を有する保持部品、
を備えていることを特徴とする試験プローブ組立体。 A test probe assembly for testing an electrical circuit comprising:
A frame member having a first member;
A contactor assembly secured to the first member;
With
The contactor assembly includes:
An electrical contactor including a contactor base and a plurality of electrical terminals on the contactor base;
An interposer including a conductive interposer substrate having first and second sides and a plurality of first and second resilient interconnecting elements extending from the first and second sides, respectively.
Including
The interposer is positioned at a predetermined position with respect to the electrical connector, wherein each first resilient interconnecting element is in electrical contact with an electrical terminal of the electrical contactor and the second resilient The electrical interconnection element is in electrical contact with the substrate on which the electrical circuit under test is formed;
The contactor assembly further includes:
A holding part having a first position fixed to the electric contactor and a second position fixed to the interposer to hold the interposer in a predetermined position with respect to the electric contactor;
A test probe assembly comprising:
電気コンタクタ上に位置決め可能なフレームと、
x−y面内において、及び前記x−y面に垂直なz方向に変位するように前記フレームに取付けられているキャリッジと、
前記フレーム上にあって、前記キャリッジを前記x−y面内において、及び前記z方向に変位させるように動作可能な変位メカニズムと、
前記キャリッジ上にあって、前記インタポーザを前記キャリッジ上に取付けるための取付け配列と、
を備えていることを特徴とする位置合わせ機械。 An alignment machine for aligning an electrical contactor with an interposer,
A frame that can be positioned on the electrical contactor;
a carriage attached to the frame so as to be displaced in the xy plane and in a z direction perpendicular to the xy plane;
A displacement mechanism on the frame and operable to displace the carriage in the xy plane and in the z direction;
A mounting arrangement on the carriage for mounting the interposer on the carriage;
An alignment machine characterized by comprising:
インタポーザと電気コンタクタとを位置合わせするステップを含み、
前記インタポーザの弾力性相互接続要素が弾力的に変形して電気接点を前記電気コンタクタ上の対応する電気端子に接触させ、
前記方法は更に、
前記位置合わせされたインタポーザ及び電気コンタクタを一緒に固定するステップ、
を含むことを特徴とする方法。 A method of assembling a test contactor,
Aligning the interposer and the electrical contactor,
The resilient interconnecting elements of the interposer elastically deform to bring electrical contacts into contact with corresponding electrical terminals on the electrical contactor;
The method further comprises:
Securing the aligned interposer and electrical contactor together;
A method comprising the steps of:
インタポーザをそれのためのマウント内に着座させるステップと、
前記マウントを位置合わせ機械に結合するステップと、
前記インタポーザの弾力性相互接続要素が前記電気コンタクタ上の対応する電気端子に接触して弾力的に変形するような位置合わせされた位置まで前記マウントを電気コンタクタに対して変位させるように前記位置合わせ機械の設定を調整するステップと、
前記位置合わせされた位置において前記マウントを前記電気コンタクタに固定するステップと、
を含むことを特徴とする方法。 A method of assembling a test contactor for testing an integrated circuit comprising:
Sitting the interposer in the mount for it;
Coupling the mount to an alignment machine;
The alignment to displace the mount relative to the electrical contactor to an aligned position such that the resilient interconnecting element of the interposer contacts a corresponding electrical terminal on the electrical contactor and elastically deforms. Adjusting machine settings;
Securing the mount to the electrical contactor in the aligned position;
A method comprising the steps of:
インタポーザの第1の弾力性相互接続要素が電気コンタクタ上の対応する電気端子に接触して弾力的に変形するように前記インタポーザ及び前記電気コンタクタを位置合わせするステップと、
位置合わせされた前記インタポーザ及び前記電気コンタクタを一緒に固定してサブ組立体を形成するステップと、
前記サブ組立体を試験基体に向かって運動させ、前記インタポーザ上の第2の弾力性相互接続要素を前記試験基体に電気的に接触させるステップと、
前記電気コンタクタを、試験プローブ回路に接続するステップと、
を含むことを特徴とする方法。 A method of assembling a test contactor,
Aligning the interposer and the electrical contactor such that a first resilient interconnection element of the interposer contacts and flexibly deforms a corresponding electrical terminal on the electrical contactor;
Securing the aligned interposer and the electrical contactor together to form a subassembly;
Moving the subassembly toward a test substrate to electrically contact a second resilient interconnection element on the interposer to the test substrate;
Connecting the electrical contactor to a test probe circuit;
A method comprising the steps of:
インタポーザ及び電気コンタクタ上のそれぞれの基準マーキングが位置合わせされる第1の位置に前記インタポーザを前記電気コンタクタ上のx−y面内において位置決めするステップと、
前記インタポーザの複数の弾力性相互接続要素のそれぞれが前記電気コンタクタ上の複数の電気端子のそれぞれに電気的に接触する第2の位置まで前記インタポーザをz方向に変位させるステップと、
前記インタポーザの各弾力性相互接続要素が圧縮される第3の位置まで前記インタポーザをz方向に変位させるステップと、
を含むことを特徴とする方法。 A method of assembling a test contactor,
Positioning the interposer in an xy plane on the electrical contactor at a first position where respective reference markings on the interposer and electrical contactor are aligned;
Displacing the interposer in the z-direction to a second position where each of the plurality of resilient interconnection elements of the interposer is in electrical contact with each of a plurality of electrical terminals on the electrical contactor;
Displacing the interposer in the z-direction to a third position where each resilient interconnection element of the interposer is compressed;
A method comprising the steps of:
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US10/197,133 US6853209B1 (en) | 2002-07-16 | 2002-07-16 | Contactor assembly for testing electrical circuits |
| US10/197,104 US6867608B2 (en) | 2002-07-16 | 2002-07-16 | Assembly for electrically connecting a test component to a testing machine for testing electrical circuits on the test component |
| PCT/US2003/022125 WO2004008163A2 (en) | 2002-07-16 | 2003-07-15 | Assembly for connecting a test device to an object to be tested |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005533254A true JP2005533254A (en) | 2005-11-04 |
| JP2005533254A5 JP2005533254A5 (en) | 2006-08-17 |
Family
ID=30117843
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004521866A Pending JP2005533254A (en) | 2002-07-16 | 2003-07-15 | Assembly for electrically connecting a device under test to a test machine for testing an electrical circuit on the device under test |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1523685A2 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2005533254A (en) |
| KR (1) | KR20050029215A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN100523826C (en) |
| AU (1) | AU2003249276A1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2004008163A2 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020505584A (en) * | 2017-01-09 | 2020-02-20 | デルタ・デザイン・インコーポレイテッドDelta Design, Inc. | Socket side surface heat system |
| US11774486B2 (en) | 2021-06-30 | 2023-10-03 | Delta Design Inc. | Temperature control system including contactor assembly |
Families Citing this family (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1894027A1 (en) | 2005-04-27 | 2008-03-05 | Aehr Test Systems, Inc. | Apparatus for testing electronic devices |
| CN101051067B (en) * | 2006-04-03 | 2010-08-11 | 航天科工防御技术研究试验中心 | Comprehensive detection control device design method for electric connector |
| MY152599A (en) | 2007-02-14 | 2014-10-31 | Eles Semiconductor Equipment S P A | Test of electronic devices at package level using test boards without sockets |
| EP1959265A1 (en) | 2007-02-16 | 2008-08-20 | Eles Semiconductor Equipment S.P.A. | Testing integrated circuits on a wafer with a cartridge leaving exposed a surface thereof |
| US7557594B2 (en) * | 2007-08-14 | 2009-07-07 | Electro Scientific Industries, Inc. | Automated contact alignment tool |
| US7800382B2 (en) | 2007-12-19 | 2010-09-21 | AEHR Test Ststems | System for testing an integrated circuit of a device and its method of use |
| CN101545926B (en) * | 2008-03-25 | 2011-05-11 | 旺矽科技股份有限公司 | Probe testing device |
| DE102009012021B4 (en) * | 2009-03-10 | 2011-02-03 | Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der angewandten Forschung e.V. | Measuring device for the electrical measurement of a measurement structure that can be electrically contacted on one side of a measurement side |
| US8030957B2 (en) | 2009-03-25 | 2011-10-04 | Aehr Test Systems | System for testing an integrated circuit of a device and its method of use |
| TWI440412B (en) * | 2011-12-28 | 2014-06-01 | Princo Corp | Package method of thin multi-layer substrate |
| CN103808969A (en) * | 2012-11-08 | 2014-05-21 | 富泰华工业(深圳)有限公司 | Tool for bearing to-be-tested electronic device |
| CN103808979A (en) * | 2012-11-08 | 2014-05-21 | 富泰华工业(深圳)有限公司 | Tool for bearing to-be-tested electronic device |
| CN105548859A (en) * | 2015-12-09 | 2016-05-04 | 上海精密计量测试研究所 | Testing equipment and method for environment testing |
| CN108780114B (en) | 2016-01-08 | 2021-11-16 | 雅赫测试系统公司 | Method and system for temperature control of devices in an electronic tester |
| CN106200239B (en) * | 2016-09-14 | 2019-03-15 | 海信集团有限公司 | Ray machine lighting system |
| EP3589965B1 (en) | 2017-03-03 | 2023-12-06 | AEHR Test Systems | Electronics tester |
| EP4226165A4 (en) | 2020-10-07 | 2024-10-30 | Aehr Test Systems | Electronics tester |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5148103A (en) * | 1990-10-31 | 1992-09-15 | Hughes Aircraft Company | Apparatus for testing integrated circuits |
| JPH0763788A (en) * | 1993-08-21 | 1995-03-10 | Hewlett Packard Co <Hp> | Probe, electrical part / circuit inspecting device and electrical part / method of circuit inspection |
| US6028437A (en) * | 1997-05-19 | 2000-02-22 | Si Diamond Technology, Inc. | Probe head assembly |
| US6137297A (en) * | 1999-01-06 | 2000-10-24 | Vertest Systemsn Corp. | Electronic test probe interface assembly and method of manufacture |
| JP2001013208A (en) * | 1999-06-30 | 2001-01-19 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Semiconductor-testing tool |
-
2003
- 2003-07-15 JP JP2004521866A patent/JP2005533254A/en active Pending
- 2003-07-15 WO PCT/US2003/022125 patent/WO2004008163A2/en active Application Filing
- 2003-07-15 KR KR1020057000799A patent/KR20050029215A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2003-07-15 CN CNB038166755A patent/CN100523826C/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2003-07-15 AU AU2003249276A patent/AU2003249276A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2003-07-15 EP EP03764698A patent/EP1523685A2/en not_active Withdrawn
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020505584A (en) * | 2017-01-09 | 2020-02-20 | デルタ・デザイン・インコーポレイテッドDelta Design, Inc. | Socket side surface heat system |
| JP2022188088A (en) * | 2017-01-09 | 2022-12-20 | デルタ・デザイン・インコーポレイテッド | Socket side surface heat system |
| US11879910B2 (en) | 2017-01-09 | 2024-01-23 | Delta Design, Inc. | Socket side thermal system |
| US11774486B2 (en) | 2021-06-30 | 2023-10-03 | Delta Design Inc. | Temperature control system including contactor assembly |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2004008163A3 (en) | 2004-06-10 |
| AU2003249276A1 (en) | 2004-02-02 |
| WO2004008163A2 (en) | 2004-01-22 |
| CN1668929A (en) | 2005-09-14 |
| CN100523826C (en) | 2009-08-05 |
| AU2003249276A8 (en) | 2004-02-02 |
| EP1523685A2 (en) | 2005-04-20 |
| KR20050029215A (en) | 2005-03-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7511521B2 (en) | Assembly for electrically connecting a test component to a testing machine for testing electrical circuits on the test component | |
| JP2005533254A (en) | Assembly for electrically connecting a device under test to a test machine for testing an electrical circuit on the device under test | |
| JP4704426B2 (en) | Electrical connection device, method of manufacturing the same, and electrical connection device | |
| US5739050A (en) | Method and apparatus for assembling a semiconductor package for testing | |
| KR101258101B1 (en) | Probe card | |
| US7872482B2 (en) | High density interconnect system having rapid fabrication cycle | |
| EP1364221B1 (en) | Planarizing interposer | |
| US7471096B2 (en) | Contactor for electronic parts and a contact method | |
| US6853209B1 (en) | Contactor assembly for testing electrical circuits | |
| KR20080076992A (en) | Apparatus and method for adjusting an orientation of probes | |
| WO2008015962A1 (en) | Parallelism adjusting mechanism of probe card | |
| WO2005069019A1 (en) | Probe guard | |
| US20080030211A1 (en) | Active probe contact array management | |
| US7282934B2 (en) | Flexible microcircuit space transformer assembly | |
| JPWO2008114464A1 (en) | Electrical connection device | |
| KR101181639B1 (en) | Apparatus for planarizing a probe card and method using same | |
| WO2008114973A1 (en) | Probe card having planarization means | |
| JPH08227769A (en) | Ic socket | |
| JP2000055983A (en) | Carrier board for test of ic-device | |
| KR100906345B1 (en) | Probe card of semiconductor device test apparatus and method for positioning correction of probe block in the probe card | |
| JP3500834B2 (en) | Semiconductor test equipment | |
| KR100920790B1 (en) | Probe Assembly, Method of Producing the Probe Assembly, and Electrical Connection Device | |
| US20240302411A1 (en) | Semiconductor wafer testing apparatus, semiconductor wafer testing system, flatness measuring device, and method of adjusting flatness of wiring board | |
| KR100906344B1 (en) | Probe card |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20060703 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20060703 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20090220 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090302 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20090803 |