JP2005512236A - タイミンググラフ縮小によるタイミングモデル抽出 - Google Patents
タイミンググラフ縮小によるタイミングモデル抽出 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2005512236A JP2005512236A JP2003551710A JP2003551710A JP2005512236A JP 2005512236 A JP2005512236 A JP 2005512236A JP 2003551710 A JP2003551710 A JP 2003551710A JP 2003551710 A JP2003551710 A JP 2003551710A JP 2005512236 A JP2005512236 A JP 2005512236A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- timing
- model
- graph
- pin
- arc
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 title description 38
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 title description 29
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 86
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims description 37
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 24
- 230000002441 reversible effect Effects 0.000 claims description 9
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000003638 chemical reducing agent Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 abstract description 41
- 230000006399 behavior Effects 0.000 description 14
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 11
- 230000001934 delay Effects 0.000 description 10
- 101100537937 Caenorhabditis elegans arc-1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 9
- 230000003111 delayed effect Effects 0.000 description 9
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 9
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 8
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000011946 reduction process Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 7
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000013507 mapping Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000002459 sustained effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000012512 characterization method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000006837 decompression Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000007717 exclusion Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000005457 optimization Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002688 persistence Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002085 persistent effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000013138 pruning Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000009419 refurbishment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013500 data storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012634 fragment Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012886 linear function Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003362 replicative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005477 standard model Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012795 verification Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F30/00—Computer-aided design [CAD]
- G06F30/30—Circuit design
- G06F30/32—Circuit design at the digital level
- G06F30/33—Design verification, e.g. functional simulation or model checking
- G06F30/3308—Design verification, e.g. functional simulation or model checking using simulation
- G06F30/3312—Timing analysis
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F2115/00—Details relating to the type of the circuit
- G06F2115/08—Intellectual property [IP] blocks or IP cores
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Design And Manufacture Of Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Test And Diagnosis Of Digital Computers (AREA)
- Stored Programmes (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本願は、2001年12月7日に出願された米国仮出願番号第60/339,235号の優先権を主張し、その全体において参考として援用される。
(著作権表示)
本発明文書の一部の開示には、著作権保護の対象になる資料を含む。著作権所有者は、特許商標局の特許ファイルおよび記録に記載されるように特許文書および特許開示の、誰かによる複製に反対はないが、さもなければ、全ての他の著作権を確保する。
本発明の開示される実施形態は、タイミンググラフを縮小することによってタイミングモデルを生成するための方法およびシステムに向けられる。本方法は、明確な許容内にある正確さがあり、かつ極めて効率的であるモデルを生成し得る。タイミング制約/アサーションをモデルに対して持続し、適用するためのアプローチがさらに開示される。ある実施形態において、タイミング制約/アサーションは、一部のモデルとして観測され、新しいタイミング制約のセットは、一部のモデル抽出プロセスとして自動的に生成され得る。オリジナルアサーションのアプリケーションに対するラッチタイム借用およびサポートは、いくつかの中間ピンによって達成され得る。
(モデルグラフビルダ)
このセクションは、モデルグラフを構築するためのプロセスおよびメカニズムの実施形態を記載する。このアプローチでは、オリジナルタイミンググラフにおける全てのチェックアークは、新しいモデルグラフに追加される。オリジナルタイミンググラフにおける遅延アークのほとんどまたは全ては、モデルグラフに複製される。例えば、(a)ラッチD−>Qフラッシュアーク、および(b)クロックゲーティングアーク(クロックゲート入力ピンからクロックゲート出力ピンまでの全てのアーク)。この実施形態において、例えば、set_disable_timingといった遅延アークおよびチェックアークは、モデルグラフに含まれない。
(モデルグラフリデューサ)
図4aは、グラフ縮小を実行するためのプロセスおよびメカニズムの実施形態について擬似コードを示す。このアプローチにおいて、タイミンググラフは、幅優先検索(BFS)順序において各中間ピンにアクセスすることによって時間におけるあるピンを縮小させる。縮小は、さらなる変化が可能にならなくなるまで繰り返される。BFSトラバーサルを用いるための理由は、ピンが取り除かれる以前に、ピンに遅延アークを入来することがすでに処理されたこと、および遅延アークが入力スルー値の最小数に関して特徴付けられることを保証することを含む。removePin()は、マージ動作を実行するメインルーチンである。postProcess()ルーチンは、初期入力ピン(または持続された中間ピン)から始まり、かつ初期出力ピン(または持続された中間ピン)で終端する遅延アークまたはチェックアークを管理する。このようなアークについて、値rン計算ルーチンは、ピンの移動がこのようなアークに対して実行されないので、明白になり得る。
(縮小するか、縮小から排他するためのタイミンググラフエレメントを識別すること)
このセクションは、特定のタイミンググラフエレメントがモデル縮小プロセスに含まれるか、またはモデル縮小プロセスから排他されるかどうかを決定するためのプロセスおよび機構の実施形態を記載する。
ゲイン=(#入来遅延アークの数 × #出て行く遅延アークの数)−#入来遅延アークの数−#出て行く遅延アークの数
この値は、ピンが移動される場合、遅延アークの数において増大を表す。ある実施形態において、ポジティブゲインを有し、かつ、観察可能である任意のピンは、アンカーポイントに対する候補である。ピンから初期の出力または持続されたピンへのパスがある場合、ピンは観察可能である。このアプローチにおいて、可観測性により、アンカーポイントは、最終的に移動されるピンの推移的ファンイン(fanin)錐体に形成されることが防止される。例えば、レジスタ入力ピンは、観測されず、最終的に移動され得る。
(組み合わせモデルの縮小)
このセクションは、組み合わせモードを処理するために図4bのセクション474を実施するためのアプローチの実施形態を記載する。タイミンググラフを縮小するためのこのアプローチにおける2つの操作は、シリアル−マージ(「sマージ」)およびパラレル−マージ(「pマージ」)操作である。
(シーケンシャルモデル)
このセクションは、シーケンシャルモデルを処理するために、図4bのセクション476および478をインプリメントするためのアプローチの実施形態を記載する。チェックアークは、少なくとも2つのメイングループに分類化され得る。あるグループは、「セットアップ」グループと呼ばれる、ここではデータ信号が基準またはクロック信号より以前に到達するように予測される。「セットアップ」グループの例は、セットアップ、リカバリ、スキュー、クロック分離などである。他のグループは、「ホールド」グループと呼ばれ、ここでは、基準信号がデータ信号より以前に到達するように予測される。「ホールド」グループの例は、ホールド、および移動である。
(セルフループチェックアーク)
信号端および基準端が共に同様のピンを差す場合、ある「セルフループ」チェックアークがある。このようなタイミングチェックは、限定されないが、クロック上に最小パルス幅(MPW)および最小周期(MP)チェックを含む。前方および後進sマージ操作を用いることによって、このようなセルフ−ループチェックアークは、正確なクロックパス遅延(非対称の起伏/落ち込みを含む)およびスルー伝播を用いてかたどられ得る。
(遅延計算およびロード特徴付け)
一実施形態において、遅延計算は、sマージおよびpマージ操作の間に実行される。この操作中に、スルー、ロード、および/またはデータ値の固定レンジを越えて計算される。例えば、ロードレンジは、出力ポートで終端する遅延アークに利用され得る。レンジは、ある遅延アークまたはチェックアークから他のものへ変化し得る。
(Splin
(Input_Slew_Axis
0.0500,0.3000,0.5500,0.8000,1.0500)
(Load_Axis
0.0820,0.1639,0.3279,0.6557.1.3115,2.6230,5.2459)
data()
)
)
このテンプレートの初期のロードレンジは、以下の7つの値、0.0820、0.1639、0.3279、0.6557、1.3115、2.6230、5.2459からなる。
(複数のファンインおよびファンアウトの考慮)
入力ポートは、再改装パスにつながり得、これは、pマージにおいて問題を生じ得、再改装パスが異なるスルー値と共に関連付けられる。同様に、出力ポートは、マルチプレクサを含む設計から生じる複数のファンインパスを有し得る。この理由のため、全ての遅延アークおよび入力ポートから発散するチェックアークに対して同様のスルーレンジおよび出力ポートを終端する全ての遅延アークに対する同様の出力ロードレンジを用いることは適切である。レンジは、入力/出力ポートによって異なり得る。これを適応させるために、スルー(ロード)範囲は、入力ポートから発散する(出力ポートで終端する)全ての遅延アークおよびチェックアークに対して特徴付けられる。その後、全てのスルー/ロード値は、各入力/出力ポートに対するリストにマージされる。
(チェックアークの考慮)
本発明の実施形態のBFSトラバーサルアプローチは、ピンへの遅延アークの入力が全て、ピンが移動される前に処理されることを確実にする。しかし、チェックアークは、時として、特別な考慮を必要とする。なぜなら、完全にチェックアークを特徴付けるために、スルー値のレンジが信号端および基準端において共に利用可能にされるからである。いくつかの場合において、BFSトラバーサルは、全てのチェックアークの信号端および基準端が共に、前方sマージまたは後進sマージ操作以前に処理されることを保証しない。
(挿入遅延)
挿入遅延は、クロックソースポートからレジスタおよびラッチに属する内部クロックピンまでの遅延について言う。挿入遅延は、セル内に組み込まれるクロックツリーを介するファースト(早い)パスおよびスロー(遅い)パスの特徴付けをイネーブルにする。挿入遅延を計算するために、さらなる計算が、内部クロックピンにおいて実行され得る。一実施形態において、プロセスがレジスタまたはラッチにおいてクロックピンに遭遇するときに、挿入遅延は計算される。下記は、本発明の一実施形態において挿入遅延を計算するための擬似コードである。
computeInsertionDelay(pin){
Paths=tracePathsToClockSourcePin(pin);
for each path in paths{
addInsertionDelay(src pin of path,path);
}
}
パスは、遅延アークのリストである。addInsertionDelay()の手続は、パス遅延を計算し、かつ、クロックソースポートであるパス発生ピンにそのパス遅延を格納する。前述したsマージおよびpマージ操作は、このルーチンにおいて用いられ得る。実質的に、ラッチまたはレジスタのクロックピンに遭遇するとき、プロセスは、オリジナルクロックソースまでさかのぼってパスをトレースし、かつ、最悪の挙動を有するあるピンをトラッキングする。
(縮小の例示)
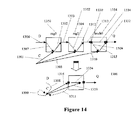
図14は、2つのレジスタ1350、1352、および1つのラッチ1354を有する回路上のグラフ縮小の例示を示す。この例示おいて、アーク1306および1307は、後進sマージ操作を用いてチェックアーク1308にマージされる。アーク1301、1302、1303、1304、および1305は、sマージ、後進sマージ、および前方sマージ操作の組み合わせを用いてセルフループチェックアーク1300にマージされる。アーク1309および1310は、前方sマージ操作を用いてアーク1311にマージされる。アーク1305、1312、および1313は、sマージ操作を用いてアーク1314にマージされる。アーク1305が、最終タイミングモデルにおいて、結果としてアーク1300および1314を共に生じる、2つの個々の操作のセットにかかわることに留意されたい。アーク1310および1313は、sマージ操作を用いてアーク1319にマージされる。
(モデルライタ)
このセクションは、タイミングモデルを書き込むためのプロセスおよびメカニズムの実施形態を記載する。モデルライタは、所望のフォーマットにおけるピン、遅延アーク、およびチェックアークを外へ放出するために縮小したモデルグラフを越えるか、または渡る。
(アサーションハンドラ)
このセクションは、本発明の一実施形態においてどのようにアサーションがモデル抽出に対して処理されるかを記載する。説明のため、アサーションの扱いは、モデル抽出のグラフ縮小のコンテキストおよび内部ピンのコンテキストに記載される。しかし、アサーションを扱うための本発明のコンセプトは、他のモデル抽出アプローチおよび非内部ピンに対して等しく利用可能であり(例えば、ブラックボックスモデルのパストレーシングに対するアサーションを扱う)、故に、説明のため、かつ、データの異なるソースからの抽出(例えば、ネットリスト、タイミンググラフなどからのタイミングモデルの抽出)のために本明細書中に開示される特定の実施形態に限定されるべきでないことに留意されたい。
・クロック到達時刻
・クロック必要時間
・データ到達時刻
・データ必要時間
・スルー時間
・一定のタイミング
・駆動抵抗
・駆動セル
・入力遅延
・出力(外部)遅延
を含む。ユーザによるアサーションのセットである「ユーザアサーション」の例は、誤ったパス、マルチサイクルパス、またはディセーブルタイミングを含む。
回路内に見られるピンには少なくとも2つのタイプがあり得る。インスタンスピンおよび階層ピンがある。階層ピンは、階層境界を確立する。信号が階層ピンを交差する場合、ある階層から他の階層へと移動する。階層ピンは、境界交差情報のプレースホルダーであり、基礎となる物理的なピン表現を有さない。
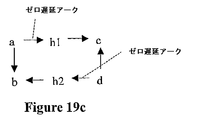
抽出されたモデルにおいてこのアサーションを捕捉するため、2つの新たな内部ピンがモデルに導入される。これらの新たなピンは、「ダミー」内部ピンと考えることができる。この例において、a−>bおよびa−>c遅延がd−>bおよびd−>c遅延とは異なるので、2つのピンが用いられる。新たな内部ピン「h1」および「h2」を用いて伸長されたタイミンググラフを、図19cに示す。新たなピンh1およびh2が導入される場合、新たなアークa−>h1およびd−>h2も導入される。この例において、a−>h1およびd−>h2は、ゼロ遅延アークを表すことに留意されたい。h1−>cおよびh2−>b遅延は、それぞれ、元のタイミンググラフにおけるa−>cおよびd−>b遅延と同じである。
set_false_path−from a-through h2−to c
階層ピンアサーションのサポートに関わる2つのアクションは、1)タイミンググラフ伸長、および2)モデルアサーションライターである。
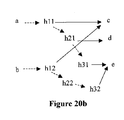
h2:h21,h22
h3:h31,h32
モデルアサーションライターは、モデルデータを変換し、モデル内のピンに関連付けられたアサーション情報を書き込むメカニズムのことを指す。階層ピンアサーションがサポートされていない場合、アサーションライターは、所与の階層の全てを単純に横切り、全てのモジュールポートおよび全てのインスタンスピンにおいてアサーションを書き出す。ある実施形態において、クロック定義のようなグローバルアサーションは、例えば、ある特定の状況において、モデルの構築の間このようなアサーションが有限ループにつながり得るので、書き込まれない。また、ある実施形態において、電気的ポートアサーションが書き込まれる。
アサーションライターは、このアサーションを以下のアサーションにマッピングする。
set_false_path−from a2−to b
(ポートアサーション)
空間的な考慮がI/Oポートのアサーションに対して為され得る。しばしば、モデルに関連付けられたアサーションが、モデルが用いられる場合に自動的に手に入れられ、モデルが取り除かれるか、または、交換される場合に自動的に取り除かれることが所望される。ある特定の状況において、I/Oポートのアサーションは、取り除くプロセスを困難にする。このため、ある実施形態において、I/Oポートのアサーションは、以前のセクションの類似のグラフ伸長技術を用いて内部ピンに移動される。これによって、モデルが、入力および出力ポートに直接付けられたアサーションを有さないことを可能にし、モデルをより自己充足的にする。
Claims (40)
- タイミングモデルを抽出する方法であって、
タイミンググラフを受け取るステップと、
該タイミンググラフを縮小することによって縮小されたモデルグラフを生成するステップと、
該縮小されたモデルグラフから該タイミングモデルを抽出するステップと
を包含する、方法。 - タイミンググラフ要素が保持のために識別される、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記タイミンググラフ要素はタイミングピンを含む、請求項2に記載の方法。
- アンカー点の識別は、前記タイミンググラフ要素が保持されるか否かを判定する基準を含む、請求項2に記載の方法。
- アンカー点は、該アンカー点が取り除かれる場合、利得値によって規定される、請求項4に記載の方法。
- 前記利得値は、
Gain=(#入来遅延アークx#出て行く遅延アーク)−#入来遅延アーク−#出て行く遅延アーク
として規定される、請求項5に記載の方法。 - アンカー点が任意の正の利得値に関連付けられている、請求項5に記載の方法。
- 利得値の閾値は、パフォーマンス予測を変動させるように調節可能である、請求項5に記載の方法。
- 前記タイミンググラフ要素が保持されるか否かを判定する基準は、ラッチ入力ピン、ラッチ出力ピン、ゲーテッドクロック出力ピン、ゲーテッドクロック入力ピン、アサーションに関連付けられているピン、ラッチイネーブルピン、ラッチクリアピン、ラッチプリセットピン、出力から出力へのパスに関連付けられているピン、取り除かれる場合モデルサイズの増大と関連付けられているピンからなる群から選択される、請求項2に記載の方法。
- 前記タイミンググラフにおけるピンは、BFS順序で処理されて、前記縮小されたモデルグラフが生成される、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記タイミンググラフにおける組み合わせ回路部分が縮小される、請求項1に記載の方法。
- シリアルマージ動作は、前記組み合わせ回路部分に対して行われる、請求項11に記載の方法。
- パラレルマージ動作は、前記組み合わせ回路部分に対して行われる、請求項11に記載の方法。
- パラレルマージ動作は、シリアルマージ動作の直後に続く、請求項11に記載の方法。
- 前記タイミンググラフにおける連続的回路部分が縮小される、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前進sマージ動作は、前記連続的回路部分に対して行われる、請求項15に記載の方法。
- 後進sマージ動作は、前記連続的回路部分に対して行われる、請求項15に記載の方法。
- 自己ループチェックアークが前記タイミンググラフにおいて処理される、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記タイミングモデルを抽出する行動は、前記タイミングモデルを書き込むステップを含む、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記タイミングモデルを抽出するため、ピンが反復的に取り除かれる、請求項1に記載の方法。
- チェックアークが可能なスルー値全てに対して特徴付けられている、請求項1に記載の方法。
- チェックアークは推定されたスルー値に対して特徴付けられている、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 挿入遅延はクロックソースポートへのパスをトレーシングすることによって計算される、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記タイミングモデルを抽出する行動は、モデル構成要素を識別するように、前記縮小されたモデルグラフをウォーキングさせる行動を含む、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記タイミングモデルを抽出する行動の間、遅延テーブルがソートされ、縮小される、請求項24に記載の方法。
- 前記モデル構成要素は、ピン、遅延アーク、およびチェックアークを含む、請求項24に記載の方法。
- アサーションに関連付けられている前記タイミンググラフにおけるピンは、前記縮小されたモデルグラフ内に保持される、請求項1に記載の方法。
- アサーションは、前記タイミングモデル内の対応するピンに自動的に関連付けられている、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記タイミングモデルは、前記タイミンググラフ内のピンに対応するアサーション情報を含む、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 階層アサーションは前記タイミングモデル内に自動的に含まれる、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 新たな内部ピンが、前記階層アサーションに関連付けられている前記縮小されたモデルグラフにおいて作製される、請求項30に記載の方法。
- 前記新たな内部ピンは、前記縮小されたモデルグラフ内に保持される、請求項30に記載の方法。
- ゼロ遅延アークが前記新たな内部ピンに対して作製される、請求項30に記載の方法。
- ポートアサーションが前記タイミングモデルに自動的に含まれる、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 新たな内部ピンは、前記ポートアサーションに関連付けられている前記縮小されたモデルグラフにおいて作製される、請求項34に記載の方法。
- ゼロ遅延アークが前記新たな内部ピンに対して作製される、請求項34に記載の方法。
- タイミングモデルを抽出するシステムであって、
タイミンググラフを受け取る手段と、
該タイミンググラフを縮小することによって縮小されたモデルグラフを生成する手段と、
該縮小されたモデルグラフから該タイミングモデルを抽出する手段と
を備える、システム。 - タイミングモデルを抽出するプロセスを実行する実行可能なコードを有するコンピュータ使用可能媒体を含むコンピュータプログラム製品であって、該プロセスは、
タイミンググラフを受け取るステップと、
該タイミンググラフを縮小することによって縮小されたモデルグラフを生成するステップと、
該縮小されたモデルグラフから該タイミングモデルを抽出するステップと
を含む、コンピュータプログラム製品。 - タイミング解析のシステムであって、
タイミンググラフに基づいて、モデルグラフを生成するモデルグラフビルダと、
タイミングモデルを書くモデルライタと、
該モデルグラフを減少させるモデルグラフリデューサと
を含む、システム。 - アサーションハンドラをさらに含み、該アサーションハンドラは、前記タイミングモデルのアサーションを処理する、請求項39に記載のシステム。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US33923501P | 2001-12-07 | 2001-12-07 | |
| PCT/US2002/038799 WO2003050724A2 (en) | 2001-12-07 | 2002-12-06 | Timing model extraction by timing graph reduction |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005512236A true JP2005512236A (ja) | 2005-04-28 |
| JP2005512236A5 JP2005512236A5 (ja) | 2005-12-22 |
Family
ID=23328095
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003551711A Pending JP2005512237A (ja) | 2001-12-07 | 2002-12-06 | タイミングモデル抽出のためのアサーションハンドリング |
| JP2003551710A Pending JP2005512236A (ja) | 2001-12-07 | 2002-12-06 | タイミンググラフ縮小によるタイミングモデル抽出 |
Family Applications Before (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003551711A Pending JP2005512237A (ja) | 2001-12-07 | 2002-12-06 | タイミングモデル抽出のためのアサーションハンドリング |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US7356451B2 (ja) |
| EP (2) | EP1451730A2 (ja) |
| JP (2) | JP2005512237A (ja) |
| AU (2) | AU2002351253A1 (ja) |
| WO (2) | WO2003050725A2 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008146142A (ja) * | 2006-12-06 | 2008-06-26 | Nec Corp | 電子回路用プリント基板の設計方法とシステム |
Families Citing this family (47)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6857116B1 (en) * | 2000-11-15 | 2005-02-15 | Reshape, Inc. | Optimization of abutted-pin hierarchical physical design |
| US7356451B2 (en) * | 2001-12-07 | 2008-04-08 | Cadence Design Systems, Inc. | Assertion handling for timing model extraction |
| US6763507B2 (en) * | 2002-01-30 | 2004-07-13 | Agilent Technologies, Inc. | System and method for testing abstracted timing models |
| US6763505B2 (en) * | 2002-04-04 | 2004-07-13 | International Business Machines Corporation | Apparatus and method for automated use of phase abstraction for enhanced verification of circuit designs |
| US6745377B2 (en) * | 2002-04-04 | 2004-06-01 | International Business Machines Corporation | Apparatus and method for representing gated-clock latches for phase abstraction |
| US6925621B2 (en) * | 2002-06-24 | 2005-08-02 | Agilent Technologies, Inc. | System and method for applying timing models in a static-timing analysis of a hierarchical integrated circuit design |
| US6836874B2 (en) * | 2002-06-26 | 2004-12-28 | Agilent Technologies, Inc. | Systems and methods for time-budgeting a complex hierarchical integrated circuit |
| US7096442B2 (en) * | 2003-07-10 | 2006-08-22 | Lsi Logic Corporation | Optimizing IC clock structures by minimizing clock uncertainty |
| US7983891B1 (en) * | 2003-08-19 | 2011-07-19 | Cadence Design Systems, Inc. | Receiver dependent selection of a worst-case timing event for static timing analysis |
| US20050091555A1 (en) * | 2003-10-27 | 2005-04-28 | Tong Xiao | Abstraction generation for hierarchical timing analysis using implicity connectivity graph derived from domain propagation |
| US7243313B1 (en) * | 2003-11-24 | 2007-07-10 | Cadence Design Systems, Inc. | System and method for reducing the size of RC circuits |
| US7076753B2 (en) * | 2003-12-18 | 2006-07-11 | Synopsys, Inc. | Method and apparatus for solving sequential constraints |
| US7606692B2 (en) * | 2004-04-26 | 2009-10-20 | Lsi Corporation | Gate-level netlist reduction for simulating target modules of a design |
| US7089143B2 (en) * | 2004-04-29 | 2006-08-08 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method and system for evaluating timing in an integrated circuit |
| JP2006039621A (ja) * | 2004-07-22 | 2006-02-09 | Nec Electronics Corp | タイミング制約ライブラリの作成方法及び作成システム |
| US20060190235A1 (en) * | 2005-02-22 | 2006-08-24 | Faraday Technology Corp. | Verilog HDL simulation model for retain time |
| US20080115099A1 (en) * | 2006-11-15 | 2008-05-15 | Priyadarsan Patra | Spatial curvature for multiple objective routing |
| US7926011B1 (en) * | 2007-01-10 | 2011-04-12 | Cadence Design Systems, Inc. | System and method of generating hierarchical block-level timing constraints from chip-level timing constraints |
| US8365113B1 (en) * | 2007-01-10 | 2013-01-29 | Cadence Design Systems, Inc. | Flow methodology for single pass parallel hierarchical timing closure of integrated circuit designs |
| US8640066B1 (en) | 2007-01-10 | 2014-01-28 | Cadence Design Systems, Inc. | Multi-phase models for timing closure of integrated circuit designs |
| US8977995B1 (en) * | 2007-01-10 | 2015-03-10 | Cadence Design Systems, Inc. | Timing budgeting of nested partitions for hierarchical integrated circuit designs |
| JP2009037278A (ja) * | 2007-07-31 | 2009-02-19 | Nec Corp | 動作タイミング検証装置、方法、及び、プログラム |
| US8239798B1 (en) * | 2007-08-03 | 2012-08-07 | Cadence Design Systems, Inc. | Methods, systems, and apparatus for variation aware extracted timing models |
| US7962872B2 (en) * | 2007-12-04 | 2011-06-14 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Timing analysis when integrating multiple circuit blocks while balancing resource requirements and accuracy |
| US8499230B2 (en) * | 2008-05-07 | 2013-07-30 | Lsi Corporation | Critical path monitor for an integrated circuit and method of operation thereof |
| US8122404B2 (en) * | 2009-02-19 | 2012-02-21 | International Business Machines Corporation | Performing a statistical timing abstraction for a hierarchical timing analysis of VLSI circuits |
| US8239805B2 (en) | 2009-07-27 | 2012-08-07 | Lsi Corporation | Method for designing integrated circuits employing a partitioned hierarchical design flow and an apparatus employing the method |
| US8341573B2 (en) * | 2010-10-15 | 2012-12-25 | Lsi Corporation | Modeling approach for timing closure in hierarchical designs leveraging the separation of horizontal and vertical aspects of the design flow |
| US8458637B2 (en) * | 2010-10-22 | 2013-06-04 | International Business Machines Corporation | Implementing enhanced RLM connectivity on a hierarchical design with top level pipeline registers |
| US8589846B2 (en) * | 2011-12-02 | 2013-11-19 | Synopsys, Inc. | Modeling transition effects for circuit optimization |
| US8522179B1 (en) * | 2012-02-06 | 2013-08-27 | Lsi Corporation | System and method for managing timing margin in a hierarchical integrated circuit design process |
| US8990445B2 (en) * | 2012-03-05 | 2015-03-24 | Mediatek Inc. | Control chip for communicating with wired connection interface by using one configurable pin selectively serving as input pin or output pin |
| US8578304B1 (en) * | 2012-07-26 | 2013-11-05 | International Business Machines Corporation | Implementing mulitple mask lithography timing variation mitigation |
| US20140156233A1 (en) * | 2012-12-03 | 2014-06-05 | Can Wang | Method and apparatus for electronic circuit simulation |
| US8977998B1 (en) * | 2013-02-21 | 2015-03-10 | Altera Corporation | Timing analysis with end-of-life pessimism removal |
| US8713502B1 (en) | 2013-02-26 | 2014-04-29 | International Business Machines Corporation | Methods and systems to reduce a number of simulations in a timing analysis |
| WO2015035144A1 (en) * | 2013-09-06 | 2015-03-12 | Blue Pearl Software, Inc. | User grey cell |
| US9940431B2 (en) | 2016-01-07 | 2018-04-10 | International Business Machines Corporation | Accurate statistical timing for boundary gates of hierarchical timing models |
| JP2017167732A (ja) * | 2016-03-15 | 2017-09-21 | 株式会社東芝 | 回路設計検証装置およびプログラム |
| US10223493B1 (en) | 2016-06-28 | 2019-03-05 | Altera Corporation | Dynamic tag allocation for clock reconvergence pessimism removal |
| US9977850B2 (en) * | 2016-07-12 | 2018-05-22 | International Business Machines Corporation | Callback based constraint processing for clock domain independence |
| US10394987B2 (en) * | 2017-03-21 | 2019-08-27 | International Business Machines Corporation | Adaptive bug-search depth for simple and deep counterexamples |
| US11176293B1 (en) * | 2018-03-07 | 2021-11-16 | Synopsys, Inc. | Method and system for emulation clock tree reduction |
| US10747925B1 (en) * | 2019-01-25 | 2020-08-18 | International Business Machines Corporation | Variable accuracy incremental timing analysis |
| US11188696B1 (en) | 2019-04-15 | 2021-11-30 | Cadence Design Systems, Inc. | Method, system, and product for deferred merge based method for graph based analysis pessimism reduction |
| US10831954B1 (en) | 2019-10-29 | 2020-11-10 | International Business Machines Corporation | Technology lookup table-based default assertion generation and consumption for timing closure of VLSI designs |
| US10891412B1 (en) | 2020-02-13 | 2021-01-12 | International Business Machines Corporation | Offline analysis of hierarchical electronic design automation derived data |
Family Cites Families (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5657239A (en) * | 1992-10-30 | 1997-08-12 | Digital Equipment Corporation | Timing verification using synchronizers and timing constraints |
| US5508937A (en) * | 1993-04-16 | 1996-04-16 | International Business Machines Corporation | Incremental timing analysis |
| US5581473A (en) * | 1993-06-30 | 1996-12-03 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Method and apparatus for managing timing requirement specifications and confirmations and generating timing models and constraints for a VLSI circuit |
| US5469367A (en) | 1994-06-06 | 1995-11-21 | University Technologies International Inc. | Methodology and apparatus for modular partitioning for the machine design of asynchronous circuits |
| US5535145A (en) | 1995-02-03 | 1996-07-09 | International Business Machines Corporation | Delay model abstraction |
| US5740347A (en) | 1995-05-01 | 1998-04-14 | Synopsys, Inc. | Circuit analyzer of black, gray and transparent elements |
| US5778216A (en) * | 1995-06-30 | 1998-07-07 | Cadence Design Systems, Inc. | Method for hierarchical time drive circuit layout by rebudgeting timing constraints of plurality of logical blocks after placement |
| US5790830A (en) | 1995-12-29 | 1998-08-04 | Synopsys, Incorporated | Extracting accurate and efficient timing models of latch-based designs |
| US5796621A (en) | 1996-07-31 | 1998-08-18 | International Business Machines Corporation | Circuit delay abstraction tool |
| US5923564A (en) | 1996-08-12 | 1999-07-13 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | Performance analysis including half-path joining |
| US5946475A (en) * | 1997-01-21 | 1999-08-31 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method for performing transistor-level static timing analysis of a logic circuit |
| US6421818B1 (en) * | 1998-02-20 | 2002-07-16 | Lsi Logic Corporation | Efficient top-down characterization method |
| US6212665B1 (en) * | 1998-03-27 | 2001-04-03 | Synopsys, Inc. | Efficient power analysis method for logic cells with many output switchings |
| US6247165B1 (en) * | 1998-03-31 | 2001-06-12 | Synopsys, Inc. | System and process of extracting gate-level descriptions from simulation tables for formal verification |
| US6321362B1 (en) | 1999-04-06 | 2001-11-20 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method of reformulating static circuit optimization problems for reduced size, degeneracy and redundancy |
| WO2001008028A2 (en) | 1999-07-23 | 2001-02-01 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics Nv | Timing shell automation for hardware macro-cell modeling |
| US6539536B1 (en) | 2000-02-02 | 2003-03-25 | Synopsys, Inc. | Electronic design automation system and methods utilizing groups of multiple cells having loop-back connections for modeling port electrical characteristics |
| US6591407B1 (en) * | 2000-03-01 | 2003-07-08 | Sequence Design, Inc. | Method and apparatus for interconnect-driven optimization of integrated circuit design |
| EP1402426A2 (en) * | 2001-06-08 | 2004-03-31 | Magma Design Automation, Inc. | Method for generating design constraints for modulates in a hierarchical integrated circuit design system |
| US7103863B2 (en) | 2001-06-08 | 2006-09-05 | Magma Design Automation, Inc. | Representing the design of a sub-module in a hierarchical integrated circuit design and analysis system |
| US6609233B1 (en) * | 2001-08-10 | 2003-08-19 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | Load sensitivity modeling in a minimal level sensitive timing abstraction model |
| US7356451B2 (en) * | 2001-12-07 | 2008-04-08 | Cadence Design Systems, Inc. | Assertion handling for timing model extraction |
-
2002
- 2002-12-06 US US10/313,247 patent/US7356451B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2002-12-06 US US10/313,774 patent/US6928630B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-12-06 AU AU2002351253A patent/AU2002351253A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2002-12-06 WO PCT/US2002/038941 patent/WO2003050725A2/en active Application Filing
- 2002-12-06 JP JP2003551711A patent/JP2005512237A/ja active Pending
- 2002-12-06 EP EP02786901A patent/EP1451730A2/en not_active Ceased
- 2002-12-06 JP JP2003551710A patent/JP2005512236A/ja active Pending
- 2002-12-06 EP EP02794153A patent/EP1451731A2/en not_active Ceased
- 2002-12-06 WO PCT/US2002/038799 patent/WO2003050724A2/en active Application Filing
- 2002-12-06 AU AU2002359605A patent/AU2002359605A1/en not_active Abandoned
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008146142A (ja) * | 2006-12-06 | 2008-06-26 | Nec Corp | 電子回路用プリント基板の設計方法とシステム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2003050725A2 (en) | 2003-06-19 |
| AU2002359605A1 (en) | 2003-06-23 |
| EP1451730A2 (en) | 2004-09-01 |
| JP2005512237A (ja) | 2005-04-28 |
| WO2003050724A2 (en) | 2003-06-19 |
| US7356451B2 (en) | 2008-04-08 |
| AU2002351253A1 (en) | 2003-06-23 |
| WO2003050725A3 (en) | 2004-04-08 |
| WO2003050724A3 (en) | 2004-06-10 |
| US20030120474A1 (en) | 2003-06-26 |
| US6928630B2 (en) | 2005-08-09 |
| EP1451731A2 (en) | 2004-09-01 |
| US20030121013A1 (en) | 2003-06-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2005512236A (ja) | タイミンググラフ縮小によるタイミングモデル抽出 | |
| US9165098B1 (en) | Machine readable products for single pass parallel hierarchical timing closure of integrated circuit designs | |
| US6530073B2 (en) | RTL annotation tool for layout induced netlist changes | |
| US10776547B1 (en) | Infinite-depth path-based analysis of operational timing for circuit design | |
| US20050091025A1 (en) | Methods and systems for improved integrated circuit functional simulation | |
| US7840931B2 (en) | Loop manipulation if a behavioral synthesis tool | |
| US10467365B1 (en) | Systems and methods for calculating common clock path pessimism for hierarchical timing analysis in an electronic design | |
| Ju et al. | Incremental techniques for the identification of statically sensitizable critical paths | |
| US7707530B2 (en) | Incremental timing-driven, physical-synthesis using discrete optimization | |
| US9953120B2 (en) | Relative timing characterization | |
| US20080201671A1 (en) | Method for generating timing exceptions | |
| US7882483B2 (en) | Method for checking constraints equivalence of an integrated circuit design | |
| Hua et al. | Cyclone: A static timing and power engine for asynchronous circuits | |
| US6834379B2 (en) | Timing path detailer | |
| Moon et al. | Timing model extraction of hierarchical blocks by graph reduction | |
| US8302049B2 (en) | Method for enabling multiple incompatible or costly timing environment for efficient timing closure | |
| Kukimoto et al. | Hierarchical functional timing analysis | |
| Bommu et al. | Retiming-based factorization for sequential logic optimization | |
| JPH1091651A (ja) | 論理合成方法および論理合成装置 | |
| JP4139236B2 (ja) | タイミング解析プログラム | |
| JP2010257003A (ja) | 論理等価性検証システム、論理等価性検証方法、半導体集積回路の製造方法、制御プログラムおよび可読記憶媒体 | |
| US20070083350A1 (en) | Estimation of average-case activity for a digital circuit using activity sequences | |
| Krishna et al. | Timing Model Extraction of Hierarchical Block!; by Graph Reduction |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20051201 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080806 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20081105 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20081112 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20081208 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20081215 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20081229 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090204 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20090501 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20090513 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20090603 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20090604 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20090610 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20090611 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20091030 |