EP3733348B1 - Procédé et dispositif pour lisser la surface d'une pièce - Google Patents
Procédé et dispositif pour lisser la surface d'une pièce Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP3733348B1 EP3733348B1 EP20156017.4A EP20156017A EP3733348B1 EP 3733348 B1 EP3733348 B1 EP 3733348B1 EP 20156017 A EP20156017 A EP 20156017A EP 3733348 B1 EP3733348 B1 EP 3733348B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- component
- liquid
- guide
- solids mixture
- guide surface
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 23
- 238000009499 grossing Methods 0.000 title claims description 14
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 32
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 claims description 25
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 11
- 239000008247 solid mixture Substances 0.000 description 10
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 8
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 8
- 238000002485 combustion reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 3
- MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen peroxide Chemical compound OO MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003350 kerosene Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000004760 silicates Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005054 agglomeration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002776 aggregation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001427 coherent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000567 combustion gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000265 homogenisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005096 rolling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B24—GRINDING; POLISHING
- B24B—MACHINES, DEVICES, OR PROCESSES FOR GRINDING OR POLISHING; DRESSING OR CONDITIONING OF ABRADING SURFACES; FEEDING OF GRINDING, POLISHING, OR LAPPING AGENTS
- B24B31/00—Machines or devices designed for polishing or abrading surfaces on work by means of tumbling apparatus or other apparatus in which the work and/or the abrasive material is loose; Accessories therefor
- B24B31/10—Machines or devices designed for polishing or abrading surfaces on work by means of tumbling apparatus or other apparatus in which the work and/or the abrasive material is loose; Accessories therefor involving other means for tumbling of work
- B24B31/116—Machines or devices designed for polishing or abrading surfaces on work by means of tumbling apparatus or other apparatus in which the work and/or the abrasive material is loose; Accessories therefor involving other means for tumbling of work using plastically deformable grinding compound, moved relatively to the workpiece under the influence of pressure
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B24—GRINDING; POLISHING
- B24B—MACHINES, DEVICES, OR PROCESSES FOR GRINDING OR POLISHING; DRESSING OR CONDITIONING OF ABRADING SURFACES; FEEDING OF GRINDING, POLISHING, OR LAPPING AGENTS
- B24B31/00—Machines or devices designed for polishing or abrading surfaces on work by means of tumbling apparatus or other apparatus in which the work and/or the abrasive material is loose; Accessories therefor
- B24B31/12—Accessories; Protective equipment or safety devices; Installations for exhaustion of dust or for sound absorption specially adapted for machines covered by group B24B31/00
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B24—GRINDING; POLISHING
- B24B—MACHINES, DEVICES, OR PROCESSES FOR GRINDING OR POLISHING; DRESSING OR CONDITIONING OF ABRADING SURFACES; FEEDING OF GRINDING, POLISHING, OR LAPPING AGENTS
- B24B19/00—Single-purpose machines or devices for particular grinding operations not covered by any other main group
- B24B19/14—Single-purpose machines or devices for particular grinding operations not covered by any other main group for grinding turbine blades, propeller blades or the like
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B24—GRINDING; POLISHING
- B24B—MACHINES, DEVICES, OR PROCESSES FOR GRINDING OR POLISHING; DRESSING OR CONDITIONING OF ABRADING SURFACES; FEEDING OF GRINDING, POLISHING, OR LAPPING AGENTS
- B24B31/00—Machines or devices designed for polishing or abrading surfaces on work by means of tumbling apparatus or other apparatus in which the work and/or the abrasive material is loose; Accessories therefor
- B24B31/003—Machines or devices designed for polishing or abrading surfaces on work by means of tumbling apparatus or other apparatus in which the work and/or the abrasive material is loose; Accessories therefor whereby the workpieces are mounted on a holder and are immersed in the abrasive material
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B24—GRINDING; POLISHING
- B24B—MACHINES, DEVICES, OR PROCESSES FOR GRINDING OR POLISHING; DRESSING OR CONDITIONING OF ABRADING SURFACES; FEEDING OF GRINDING, POLISHING, OR LAPPING AGENTS
- B24B31/00—Machines or devices designed for polishing or abrading surfaces on work by means of tumbling apparatus or other apparatus in which the work and/or the abrasive material is loose; Accessories therefor
- B24B31/12—Accessories; Protective equipment or safety devices; Installations for exhaustion of dust or for sound absorption specially adapted for machines covered by group B24B31/00
- B24B31/14—Abrading-bodies specially designed for tumbling apparatus, e.g. abrading-balls
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B24—GRINDING; POLISHING
- B24B—MACHINES, DEVICES, OR PROCESSES FOR GRINDING OR POLISHING; DRESSING OR CONDITIONING OF ABRADING SURFACES; FEEDING OF GRINDING, POLISHING, OR LAPPING AGENTS
- B24B37/00—Lapping machines or devices; Accessories
- B24B37/02—Lapping machines or devices; Accessories designed for working surfaces of revolution
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01D—NON-POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES, e.g. STEAM TURBINES
- F01D5/00—Blades; Blade-carrying members; Heating, heat-insulating, cooling or antivibration means on the blades or the members
- F01D5/12—Blades
- F01D5/14—Form or construction
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01D—NON-POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES, e.g. STEAM TURBINES
- F01D9/00—Stators
- F01D9/02—Nozzles; Nozzle boxes; Stator blades; Guide conduits, e.g. individual nozzles
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F05—INDEXING SCHEMES RELATING TO ENGINES OR PUMPS IN VARIOUS SUBCLASSES OF CLASSES F01-F04
- F05D—INDEXING SCHEME FOR ASPECTS RELATING TO NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES, GAS-TURBINES OR JET-PROPULSION PLANTS
- F05D2230/00—Manufacture
- F05D2230/10—Manufacture by removing material
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a method and a device for smoothing a component surface.
- a turbomachine can be functionally divided into a compressor, combustion chamber and turbine.
- air drawn in is compressed in the compressor and burned in the downstream combustion chamber with added kerosene.
- the resulting hot gas a mixture of combustion gas and air, flows through the downstream turbine and is expanded in the process.
- the turbine and compressor are usually constructed in several stages, with each stage comprising a guide vane and a rotor blade ring.
- Each blade ring is made up of a plurality of blades arranged in a rotating sequence, around which the compressor or hot gas flows depending on the application. Smoothing these component surfaces can be aerodynamically advantageous, for example.
- the present invention is based on the technical problem of specifying an advantageous method for smoothing a surface of a component.
- the component is placed in a container (bath) with a liquid-solid mixture, and a relative movement is generated between the mixture and the component.
- the mixture flows along the surface to be smoothed, which allows a combined chemical-mechanical removal of material to be achieved, and the component is polished chemically and mechanically.
- a guide surface is provided in the bath or container with the mixture, along which the mixture flows. The guide surface guides the flow and in particular presses the solid component towards the component surface, thus superimposing a directional component towards the component surface.
- the guide surface guides the mixture, and in particular the solid portion, onto the surface so that sufficient pressure is achieved there to remove material.
- the solid portion can, for example, be in the form of particles, in particular spheres, with the balls then rolling along the component surface with sufficient pressure due to the guide to achieve the desired polishing effect.
- the solid portion in the mixture can, in particular, be so high that a coherent agglomeration of particles or balls is present between the guide surface and the surface of the component; a force chain is thus formed between the guide surface and the component so that the particles/balls are reliably pressed against the component surface.
- the guide surface can, for example, create or help to set a more uniform pressure across the component surface, which can improve the homogeneity of the smoothing result.
- the component can preferably be a blade of a turbomachine, which is arranged in the gas channel and has hot gas flowing around it.
- a turbine area is also conceivable, i.e. the blade can be arranged in the hot gas channel and hot gas can flow around it.
- An application in the compressor area is preferred, i.e. the blade can have compressor gas flowing around it in the compressor gas channel.
- the guide surface is a side surface of a guide body around which the bath flows.
- the latter means that the liquid-solid mixture flows not only along the guide surface, but also along a side surface of the guide body opposite the guide surface.
- the guide body is preferably made of metal, in particular it can be a guide plate (simple and flexible production).
- the component surface has a curved profile when viewed in a cutting plane and the guide surface is complementarily curved when viewed in the same cutting plane. If the surface is convex, for example, the guide surface extends concavely, and in the case of a concave component surface, it extends convexly.
- the cutting plane in question is preferably parallel to the direction of flow; in the case of the blade, for example, it can be a tangential cutting plane (in this, the blade profile is viewed, the cutting plane is tangential to a revolution around the longitudinal or rotational axis of the turbomachine).
- the guide surface is arranged in relation to the component surface in such a way that a distance between them decreases in the direction of flow.
- the distance is viewed in section (see the previous paragraph regarding the cutting plane) perpendicular to the streamlines between the surface and the guide surface.
- a distance that decreases continuously (without jumps/steps) in the direction of flow can be used, which can offer advantages with regard to the desired homogenization.
- a further guide surface is provided in the bath, which can also be formed by a guide body, in particular a guide plate.
- the component is or will be arranged between the guide surfaces in a direction perpendicular to the direction of flow.
- the flow is then guided by one guide surface to a surface area of the component and by the other guide surface to an opposite surface area.
- one guide surface can be assigned to the suction side surface and the other to the pressure side surface.
- the guide surfaces between which the component is placed are arranged relative to one another in such a way that a distance between them decreases in the direction of flow.
- this guide surface distance is taken in section perpendicular to the streamlines between the guide surfaces, see also the above comments. So, for example, if an airfoil is smoothed and the flow is directed at the leading edge, the distance between the guide surfaces arranged on either side of it decreases from the leading to the trailing edge.
- the distance between the guide surface and the respective surface area also decreases, see above.
- the component can generally also be a fairing , for example.
- Channel plates ( panels ) can also be smoothed and thus optimized with regard to the flow around the gas channel.
- the component is preferably an airfoil.
- a nozzle could generally also be provided in the bath, through which the mixture is pumped and thus accelerated onto the component. In this case, the latter would be viewed in a fixed coordinate system, i.e. in the processing machine and therefore also in the assembly or production hall, for example.
- the relative movement is achieved by moving the component through the liquid-solid mixture.
- the component is then moved; it is pulled or pushed through the mixture.
- the guide surfaces or guide bodies/guide plates are moved through the bath together with the component.
- they can be arranged on a holder into which the component is placed and which is then moved through the mixture together with the component.
- the liquid-solid mixture can be water-based, for example. Depending on the material of the component, it can contain an acid, e.g. hydrogen peroxide.
- the liquid component can also contain silicates, for example.
- the solid component is preferably provided in particle or spherical form, in particular in the form of glass or metal spheres. These can have a diameter in the micro- or millimeter range, for example of at least 200 ⁇ m and a maximum of 2 mm, for example of around 0.5 mm.
- the invention also relates to a device for smoothing a component surface according to claim 9.
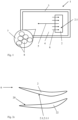
- Fig.1 shows a device 1 for smoothing a component 2, specifically a surface 2.1 of the component 2.
- the component 2 is a blade or a vane of an aircraft engine, see also Fig.3 for illustration.
- the component 2 is placed in a container 3 that is filled with a liquid-solid mixture 4.
- the component 2 is then moved in the liquid-solid mixture 4, thus generating a relative movement 5 between the liquid-solid mixture 4 and the component 2.
- the mixture 4 is made up of a liquid component 7 (in this case, e.g. water, H 2 O 2 , silicates) and spherical solids 8 with a diameter of e.g. 0.5 mm.
- a liquid component 7 in this case, e.g. water, H 2 O 2 , silicates
- spherical solids 8 with a diameter of e.g. 0.5 mm.
- a guide surface 20 is arranged in the mixture 4, which imposes a directional component 21 on the flow 6 towards the surface 2.1 of the component 2.
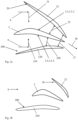
- Fig. 2a -c illustrates (especially in Fig. 2a ), each in one cut (based on Fig.1 the cutting plane is perpendicular to the drawing surface and horizontal).
- the profile shape of component 2 e.g. the blade, can be seen.
- a further guide surface 200 is provided, which also imposes a directional component 210 on the flow 6 towards the component surface 2.1.
- a guide surface 20,200 is thus assigned to both a suction side surface 2.1.1 and a pressure side surface 2.1.2 of the blade.
- Each of the guide surfaces 20,200 is formed by a guide body 22,220, namely a guide plate around which the mixture 5 flows.
- the guide surfaces 20,200 are arranged relative to the component 2 or its surface 2.1 such that a respective distance 25,250 to the surface 2.1 decreases in the flow direction 26. Furthermore, a guide surface distance 27 between the guide surfaces 20,200 also decreases in the flow direction 26.
- the component 2 i.e. the blade
- the component 2 is not flown at its leading edge, but at its trailing edge during smoothing.
- only a single guide body 22 with the guide surface 20 is used, which is assigned to the suction side surface 2.1.1 of the component 2.
- the Fig. 2a-c illustrate different possibilities and options.
- Fig.3 shows a turbomachine 30, specifically a turbofan engine, in an axial section (the section plane includes the longitudinal axis 31).
- the turbomachine 30 is divided into a compressor 32, a combustion chamber 33 and a turbine 34, whereby air drawn in is compressed in the compressor 32.
- the combustion chamber 33 it is burned with kerosene mixed in, and the resulting hot gas is expanded in the turbine 34.
- Both the compressor 32 and the turbine 34 are constructed in several stages.
- the component 2 (the blade smoothed as described above) can be used in both the turbine 34 and the compressor 32, the latter being preferred (due to the high aerodynamic requirements there).
- Component 2 Surface (component surface) 2.1 Suction side surface 2.1.1 Print side area 2.1.2 container 3 Liquid-solid mixture 4 Relative motion 5 flow 6 Liquid component 7 Solids 8th Guide surface 20
- Directional component (to the component surface) 21
- Guide body 22 Distance 25
- Flow direction 26 Guide surface distance 27
- Turbomachine 30 Longitudinal axis 31
- compressor 32 Combustion chamber 33
- turbine 34 Guide surface (other) 200
- Directional component (of the further guide surface) 210 Guide body (further) 220 Distance (of the further guide surface) 250
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Structures Of Non-Positive Displacement Pumps (AREA)
Claims (9)
- Procédé permettant le lissage d'une surface (2.1) d'une pièce (2) qui est conçue pour être disposée dans un canal de gaz d'une turbomachine (30) et la pièce (2) est de préférence une pale d'aube pour une turbomachine (30), dans lequel la surface (2.1) est une surface (2.1) tournée vers le canal de gaz, dans lequel procédé- la pièce (2) est placée dans un récipient (3) comportant un mélange liquide-solides (4) ;- un déplacement relatif (5) est généré entre le mélange liquide-solides (4) et la pièce (2), c'est-à-dire un écoulement (6) du mélange liquide-solides (4) le long de la surface (2.1) ;dans lequel une surface de guidage (20) est prévue dans le mélange liquide-solides (4), le long de laquelle s'écoule le mélange liquide-solides (4), dans lequel une composante directionnelle (21) est imposée à l'écoulement (6) en direction de la surface (2.1) etdans lequel une autre surface de guidage (200) est prévue dans le mélange liquide-solides (4), le long de laquelle s'écoule le mélange liquide-solides (4), caractérisé en ce quela pièce (2) est disposée entre les surfaces de guidage (20, 200) et dans lequel les surfaces de guidage (20, 200) sont disposées l'une par rapport à l'autre de telle sorte qu'une distance entre les surfaces de guidage (27), laquelle est prise, vue dans un plan de coupe, perpendiculairement à un profil de lignes de courant entre les surfaces de guidage (20, 200), diminue dans le sens d'écoulement (26).
- Procédé selon la revendication 1, dans lequel la surface de guidage (20) est une surface latérale d'un corps de guidage (22) autour duquel s'écoule le mélange liquide-solides (4), dans lequel le mélange liquide-solides (4) s'écoule donc également le long d'une surface latérale opposée à la surface de guidage (20).
- Procédé selon la revendication 1 ou 2, dans lequel la surface (2.1) de la pièce (2), vue dans un plan de coupe, a un tracé courbe et la surface de guidage (20), vue dans le même plan de coupe, a un tracé courbe complémentaire.
- Procédé selon l'une des revendications précédentes, dans lequel la surface de guidage (20) est disposée par rapport à la surface (2.1) de telle sorte qu'une distance (25) prise, vue dans un plan de coupe, perpendiculairement à un profil de lignes de courant entre la surface (2.1) et la surface de guidage (20), diminue dans le sens d'écoulement (26).
- Procédé selon la revendication 1, dans lequel la surface (2.1) de la pièce (2) comprend une surface latérale d'aspiration et une surface latérale de pression, dans lequel respectivement une surface de guidage (20, 200) dans le mélange liquide-solides (4) est associée à la fois à la surface latérale d'aspiration et à la surface latérale de pression.
- Procédé selon l'une des revendications précédentes, dans lequel la pièce (2) est déplacée dans un système de coordonnées fixe pour générer le déplacement relatif (5), c'est-à-dire que la pièce (2) est déplacée par le mélange liquide-solides (4).
- Procédé selon la revendication 6, dans lequel la surface de guidage (20) ou les surfaces de guidage (20, 200) sont déplacées conjointement avec la pièce (2) par le mélange liquide-solides (4).
- Procédé selon l'une des revendications précédentes, dans lequel le mélange liquide-solides (4) est prévu à base d'eau avec des solides sphériques (8).
- Dispositif permettant le lissage d'une surface (2.1) de la pièce (2) pour la mise en oeuvre d'un procédé selon l'une des revendications précédentes, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif présente :- un récipient (3) permettant de recevoir le mélange liquide-solides (4) et permettant de disposer la pièce (2) ;- un appareil de déplacement permettant de générer le déplacement relatif (5) entre le mélange liquide-solides (4) et la pièce (2) ;- une surface de guidage (20) dans le récipient (3) pour imposer à l'écoulement (6) la composante directionnelle (21) vers la surface (2.1) et dans lequel une autre surface de guidage (200) est prévue dans le mélange liquide-solides (4), le long de laquelle s'écoule le mélange liquide-solides (4), pour disposer la pièce (2) entre les surfaces de guidage (20, 200),caractérisé en ce que les surfaces de guidage (20, 200) sont disposées l'une par rapport à l'autre de telle sorte qu'une distance entre les surfaces de guidage (27), laquelle est prise, vue dans un plan de coupe, perpendiculairement à un profil de lignes de courant entre les surfaces de guidage (20, 200), diminue dans le sens d'écoulement (26).
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102019201656.1A DE102019201656A1 (de) | 2019-02-08 | 2019-02-08 | Verfahren zum glätten einer oberfläche eines bauteils |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP3733348A1 EP3733348A1 (fr) | 2020-11-04 |
| EP3733348B1 true EP3733348B1 (fr) | 2024-06-26 |
Family
ID=69526148
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP20156017.4A Active EP3733348B1 (fr) | 2019-02-08 | 2020-02-07 | Procédé et dispositif pour lisser la surface d'une pièce |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11612977B2 (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP3733348B1 (fr) |
| DE (1) | DE102019201656A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114453990B (zh) * | 2022-04-12 | 2022-08-19 | 徐州中顺尚奕机械制造有限公司 | 混合清洁型热膨胀式金属表面全方位无损除锈加工装置 |
| DE102022209051A1 (de) | 2022-08-31 | 2024-02-29 | Zf Friedrichshafen Ag | Verfahren und Steuergerät zum Betreiben eines Antriebsstrangs eines Fahrzeugs |
Family Cites Families (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5216098A (en) * | 1975-07-28 | 1977-02-07 | Sumitomo Electric Ind Ltd | Scraping device of scal on wire |
| US5341602A (en) * | 1993-04-14 | 1994-08-30 | Williams International Corporation | Apparatus for improved slurry polishing |
| FR2713974B1 (fr) | 1993-12-22 | 1996-01-19 | Snecma | Dispositif de grenaillage de surfaces non accessibles par une canalisation droite. |
| EP0922530B1 (fr) * | 1997-12-10 | 2005-03-23 | Shuji Kawasaki | Dispositif de tribofinition |
| DE59901771D1 (de) * | 1998-11-14 | 2002-07-18 | Mtu Aero Engines Gmbh | Anordnung zur feinbearbeitung von rotationssymmetrischen bauteilen |
| JP4059421B2 (ja) | 2000-10-31 | 2008-03-12 | 新東工業株式会社 | ショットピ−ニング装置 |
| US6464570B1 (en) | 2001-07-17 | 2002-10-15 | General Electric Company | Omnidirectional shot nozzle |
| JP3997315B2 (ja) * | 2002-06-14 | 2007-10-24 | 株式会社Ihi | ブレード表面研摩装置のブレード固定治具 |
| US6962522B1 (en) * | 2004-05-12 | 2005-11-08 | Bbf Yamate Corporation | Barrel polishing device |
| JP5066430B2 (ja) | 2007-11-20 | 2012-11-07 | 日本発條株式会社 | ショットピーニング用反射部材およびそれを用いたショットピーニング方法 |
| DE102008017475A1 (de) * | 2008-04-03 | 2009-10-08 | Siegrid Peggy Seltmann | Verfahren zur Oberflächenbehandlung von metallischen Werkstücken |
| US20110244770A1 (en) * | 2010-04-05 | 2011-10-06 | Boutaghou Llc | Abrasive slurry formulations containing nano and micro spheres additives or self-assembled monolayers |
| US9421661B2 (en) * | 2013-04-30 | 2016-08-23 | United Technologies Corporation | Airfoil edge form transfer grinding tool |
| SI24359A (sl) * | 2013-05-14 | 2014-11-28 | Univerza V Ljubljani | Priprave in postopki poliranja z abrazivnim tokom |
| EP2848367B1 (fr) | 2013-09-11 | 2016-03-23 | Rolls-Royce Deutschland Ltd & Co KG | Appareil et procédé pour le grenaillage de surfaces de montage de lame sur le disque d'un agencement de rotor |
| JP6264347B2 (ja) | 2015-09-10 | 2018-01-24 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | 空調室内機 |
| GB201805763D0 (en) * | 2018-04-06 | 2018-05-23 | Rolls Royce Plc | A method and apparatus for finishing an internal channel of a component |
-
2019
- 2019-02-08 DE DE102019201656.1A patent/DE102019201656A1/de active Pending
-
2020
- 2020-02-07 US US16/784,704 patent/US11612977B2/en active Active
- 2020-02-07 EP EP20156017.4A patent/EP3733348B1/fr active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3733348A1 (fr) | 2020-11-04 |
| US20200254581A1 (en) | 2020-08-13 |
| DE102019201656A1 (de) | 2020-08-13 |
| US11612977B2 (en) | 2023-03-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE69718514T2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum gasdynamischen beschichten | |
| EP2093021B1 (fr) | Produit de plaque d'alliage d'aluminium doté de faibles niveaux de contrainte résiduelle et son procédé de fabrication | |
| EP3733348B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour lisser la surface d'une pièce | |
| EP2353772B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif destinés à la fixation de surfaces de pales de blisk | |
| EP2158381B1 (fr) | Aube directrice pour turbine à gaz | |
| DE3728946C2 (fr) | ||
| EP2308646A1 (fr) | Procédé de traitement de pièces usinées à l'aide d'un jet d'eau contenant un agent abrasif sortant d'une buse sous haute pression, installation de jet d'eau destiné à exécuter et à appliquer le procédé | |
| EP2099585B1 (fr) | Dispositif et procédé pour grenailler la surface d'une pièce de turbine à gaz | |
| EP1624192A1 (fr) | Aube de rouet pour compresseur axial | |
| EP2125292B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour grenailler la surface d'un élément d'une pièce de turbine à gaz | |
| DE102014222530A1 (de) | Bandabweiser und Walzenanordnung | |
| DE102016213075A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Oberflächenbearbeitung, Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Motorblockes, Vorrichtung zur Oberflächenbearbeitung und Kraftfahrzeug | |
| EP1617972B1 (fr) | Procede pour arrondir des aretes de pieces | |
| DE3444847C1 (de) | Verfahren zum Vergleichmaessigen der Teilchengroesse feinteiligen Pulvers,Vorrichtung zur Durchfuehrung des Verfahrens und Verwendung des Pulvers | |
| DE10348805B4 (de) | Verfahren zur Erzeugung eines Wasserabrasivstrahls | |
| EP3235593B1 (fr) | Outil de façonnage pour la coupe de materiaux | |
| EP2808124A1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif destinés au traitement d'aubes de turbine | |
| EP1954421A1 (fr) | Procede de fabrication de pieces metalliques, en particulier pour des turbomachines, a petits rayons d'aretes, et piece ainsi fabriquee | |
| WO2007036203A1 (fr) | Aube mobile pour une turbomachine axiale | |
| WO2019105672A1 (fr) | Aube directrice d'une turbomachine et procédé de fabrication de celle-ci | |
| EP3486494B1 (fr) | Boîtier de ventilateur radial et ventilateur radial | |
| DE102023108350A1 (de) | Zweistoffsprühventil und Zweistoffsprühvorrichtung sowie deren Verwendungen und Maschine zum Bearbeiten eines plattenförmigen Werkstücks | |
| WO2024165356A1 (fr) | Dispositif d'enlèvement électrochimique de matériau | |
| EP4431234A1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif d'usinage d'une surface de pièce usinée revêtue de matériau dur d'une pièce à symétrie de rotation | |
| DE202020002587U1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum federnden Lagern eines Düsenkopfes einer Auftragsdüse für pastenförmige Klebstoffe |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION HAS BEEN PUBLISHED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20210416 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20240117 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240626 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240626 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240626 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG9D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240927 |