EP2292818B1 - Verfahren zur Herstellung einer elastischen Schnur und eine so hergestellte elastische Schnur - Google Patents
Verfahren zur Herstellung einer elastischen Schnur und eine so hergestellte elastische Schnur Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2292818B1 EP2292818B1 EP10290472A EP10290472A EP2292818B1 EP 2292818 B1 EP2292818 B1 EP 2292818B1 EP 10290472 A EP10290472 A EP 10290472A EP 10290472 A EP10290472 A EP 10290472A EP 2292818 B1 EP2292818 B1 EP 2292818B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- string
- core yarns
- core
- longitudinal axis
- yarns
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Not-in-force
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D02—YARNS; MECHANICAL FINISHING OF YARNS OR ROPES; WARPING OR BEAMING
- D02G—CRIMPING OR CURLING FIBRES, FILAMENTS, THREADS, OR YARNS; YARNS OR THREADS
- D02G3/00—Yarns or threads, e.g. fancy yarns; Processes or apparatus for the production thereof, not otherwise provided for
- D02G3/22—Yarns or threads characterised by constructional features, e.g. blending, filament/fibre
- D02G3/32—Elastic yarns or threads ; Production of plied or cored yarns, one of which is elastic
- D02G3/326—Elastic yarns or threads ; Production of plied or cored yarns, one of which is elastic the elastic properties due to the construction rather than to the use of elastic material
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04C—BRAIDING OR MANUFACTURE OF LACE, INCLUDING BOBBIN-NET OR CARBONISED LACE; BRAIDING MACHINES; BRAID; LACE
- D04C1/00—Braid or lace, e.g. pillow-lace; Processes for the manufacture thereof
- D04C1/06—Braid or lace serving particular purposes
- D04C1/12—Cords, lines, or tows
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a method for manufacturing an elastic string or the like, from an assembly of at least two basic threads made of fibers and / or filaments.
- string is not limiting and refers to any linear textile product, of any size or title (from a millimeter to a few centimeters), obtained from an assembly of at least two basic yarns made of fibers and / or filaments, in any natural material (animal and / or vegetable and / or mineral) and / or chemical (synthetic and / or artificial), called according to the applications: thread, string, cord, rope, etc. ., and used in any type of application such as industry, furniture, boating, agri-food, medical, etc.
- Elasticity is defined in the following way: it is the quality of an object to be deformable while resuming its original form when the constraint applied to it disappears.
- the final elasticity of the product depends on the elasticity of the yarn used and its manufacturing process. Some synthetic or artificial fibers have their own elasticity. But for natural fibers, the elasticity is limited or even zero.
- the present invention provides a solution for providing elasticity to the final product made from any type of fibers and / or filaments, including from natural fibers.
- publications are known BE 621 724 A and DE 29 28 692 A an elastic string obtained by twisting together at least two base yarns previously over-twisted in one direction "S" for one and in the other direction "Z” for the other, and then subjecting them to a heat treatment for to stabilize their torsion.
- Some elastic strings are also manufactured by wrapping, an example of which is illustrated in the publication EP 1 746 189 A1 .
- Grape wrapping is a method of assembling a core wire with a wire wrapped around the core wire which is called a wire wrapper.
- the core wire is a spandex, latex or similar yarn, of fairly large size (about 2 mm in diameter), and is coated with one or more cotton or polyester threads. .
- This manufacturing process is controlled and the production yield is high. Thus, the product obtained is cheap.
- wrapping has major disadvantages.
- the core wire is not integral with the coating wire. In fact, when the elastic gimped string is cut, it is common that the ends fray or loosen, leaving apparent the core thread.
- a particular case concerns the use of a gimped elastic string in the food industry, particularly for tying meat pieces, such as paupiettes, roasts, poultry, etc., to ensure the maintenance of different pieces of meat, decoration, stuffing, etc. during cooking.
- meat pieces such as paupiettes, roasts, poultry, etc.
- the meat can shrink and the string used must be able to follow the retraction of the piece of meat while keeping it tight.
- the elastic gimped string retracts rapidly and causes splashes of cooking juices, sauce and the like, in its environment.
- This disadvantage does not exist with a traditional non-elastic string. But in this case, the traditional non-elastic string does not ensure effective maintenance of the piece of meat throughout its cooking and is difficult to mechanize. It must be placed manually to avoid cutting the meat in case of automatic break.
- the present invention aims to provide a solution to the problems mentioned above by proposing a method of manufacturing an elastic string without elastane or latex, having a high power of retraction and whose elasticity is controllable and can be stabilized or even neutralized under certain conditions to avoid the disadvantages mentioned above.
- the invention relates to a method of manufacture of the kind indicated in the preamble, in which one applies an over-twist in a direction S to a first basic thread and an over-twist in the other direction Z to a second base yarn, such that the fibers and / or filaments form an angle ⁇ between 30 ° and 90 ° with the longitudinal axis of said first base yarn and said second base yarn is fixed the over-twist of said yarns
- said overwired basic threads are assembled by a braiding process to form said twine so that, when said twine is in the free state without traction, said over-twisted basic threads have a tendency to away from the longitudinal axis of the string and to orient itself in the direction of an axis perpendicular to said longitudinal axis of the string by forming an angle ⁇ with the longitudinal axis of the string between 30 ° and 90 °.
- this manufacturing process makes it possible to impart great elasticity to the twine made by combining an over-twist of the base yarns with a particular assembly of these basic yarns, without the addition of elastane or latex, the elongation at the rupture obtained which may be at least between 20% and 150%.
- base wires whose title is relatively thin and at least between Nm150 and Nm17 (or between 6 tex and 60 tex).
- T k ⁇ Nm, where T is the value of the twist in r / m and Nm is the metric number of the yarn, a high torsion coefficient k is advantageously chosen between at least 200 and 600 .
- More than two basic threads can be used to make said string.
- the over-twist on said base yarns may be fixed by a vaporizing process or any other equivalent method.
- At least four basic yarns and a braiding machine are used, and the over-twisted basic yarns are arranged in a first direction S on the spindles of the braiding machine going into counterclockwise and the over-twisted basic yarns in the other direction Z on the spindles of the braiding machine going clockwise.
- the basic son is arranged on at least one spindle out of two.
- the invention also relates to an elastic string obtained by the manufacturing method as described above, characterized in that it comprises a braided assembly of at least four basic threads made of fibers and / or filaments, two first base yarns with one S-direction over-torsion and two second base yarns with Z-direction over-twisting, the fibers and / or filaments of the base yarns forming an angle B included in less between 30 ° and 90 ° with the longitudinal axis of each base wire; and the base yarns deviating from the longitudinal axis of the braided string and orienting towards an axis perpendicular to that longitudinal axis of the string at an angle ⁇ with the longitudinal axis of the twine included between 30 ° and 90 °.
- the process according to the invention makes it possible to manufacture a string 10 or any similar product such as thread, cord, rope, etc., from an assembly of at least two base yarns 20 and 30, themselves made of fibers and / or filaments 40, the twine 10 obtained having high elastic properties, moreover controllable, without using elastane, latex or the like.
- the number of basic threads is not limited to two and it is of course possible to manufacture a string according to the invention from an assembly of several basic threads.
- an even number of base yarns are preferred and split into two equal parts to balance the number of over-twisted S-baseline yarns and the number of basic yarns.
- the over-twist value applied to each of the basic threads may be the same or different depending on the desired results. Of course, any combination of basic threads in quality, number, value of torsion, etc. is possible.
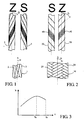
- the twist of the wire can be carried out in the S direction or in the Z direction (cf. Fig. 1 and 2 ).
- the value of the torsion expressed in revolutions / meter is calculated with the Koechlin formula: T towers / m ⁇ k ⁇ nm where k corresponds to the torsion coefficient and Nm corresponds to the title of the wire.
- the figure 3 illustrates the curve of the tensile strength (R) of the yarn as a function of its torsion value (T). There is a saturating twist (Ts) where the tensile strength is the highest. Beyond this, the tensile strength of the wire drops to the critical twist (Tc) where the wire breaks.
- Ts saturating twist
- twisting the resulting yarn is called twisted yarn or double-stranded or stranded or multi-stranded wire or ends.
- the main effect of the twisting is to obtain a wire of larger diameter whose fibers are parallel and oriented along the longitudinal axis of the wire.
- the final twist value is calculated from the same Koechlin formula given previously.
- the spinner selects a torsion coefficient (k) so that the yarn obtained is balanced and has no tendency to twist.
- k torsion coefficient
- twisted twisted yarns 20, 30 are made on conventional twists capable of working on fine threads or small titles. Indeed, if the over-twisted yarn is large, especially greater than about 100 tex, the twist will be only superficial and will not reach the fibers in the heart of the yarn.
- the torsion should preferably apply to fine threads, especially less than about 100 tex, and for example son having a metric number (Nm) of 50 which equals 20 tex.
- Nm metric number
- a torsion coefficient k of 425 would be a good compromise and would give good elasticity.
- a twist of 2100tr / m is obtained for a twisted yarn at two ends, each of Nm50 is 20 tex, to finally obtain a thread of Nm 25 or 40tex, and a twist of 1750tr. / m for a twisted yarn with three ends each of Nm50 to finally obtain a thread of Nm16 or 60 tex.
- This torsion can correspond to the saturating torsion Ts which is the optimal torsion (cf. Fig. 3 ) or approaching it.
- the values mentioned above are not limiting and may vary depending on the title of the wire or the material used, or even depending on the application with a wire having the same or similar characteristics.
- the over-twisted base yarns are nervous and tend to twist.
- the over-torsion of the basic threads 20, 30 is fixed by any known method.
- a steaming method will be chosen in an autoclave at a temperature of 90 ° C. for a determined time equal, for example, to 20 minutes.
- these values are not limiting and are only mentioned by way of example.
- step 2 when the over-twist of the base wires is fixed, they are assembled by a braiding process to make a braided string.
- the spindles of the braiding machine being clockwise are equipped with S-shaped bobbins 3 and the counter-clockwise bobbins are equipped with Z-twisted yarn bobbins 2.
- the braided string 1 obtained by the method classic has little or no elasticity.
- the base yarns 20, 30 have a tendency to deviate from the longitudinal axis A of the braided twine and to orient towards an axis perpendicular to this axis, forming an angle ⁇ with the longitudinal axis A braided twine 10 greater than that of a conventional braided twine, for example beyond 30 ° and between 30 ° and 90 °.
- This phenomenon is visible on Figures 4 and 5 which make it possible to compare the same braided string by a traditional braiding process at the place and by the process of the invention in reverse.
- the same string we mean the same nature of base son, the same value of torsion, the same speed of braiding, the same number of crosses per centimeter, the same speed of traction of the braid.
- the base yarns 20 and 30 and the fibers and / or filaments 40 will tend to regain their preferred orientation, that given by the over-torsion for the fibers and / or filaments 40 and that given by the inverted braiding, resulting in a high elasticity, which can reach at least between 20% and 150% elongation at break and for example 100% elongation.
- the braiding angle or the number of centimeter crossings can be varied while maintaining the elasticity characteristics of the braided twine obtained.
- Additional elasticity can be achieved by releasing the over-twisting of the basic yarns 20, 30. Depending on the needs of the end user, this release may be revealed at the end of the process or during use (see example given below).
- base yarns made of twisted cotton fibers are used at two ends of Nm50 each with an over-twist of 2100 rpm.
- Half of the base wires are applied with an S-twist and at the other half with Z-over-torsion.
- the over-torsion is fixed on all of the base wires with steam at 90 ° C. in an autoclave for 20 minutes.
- Braided basic threads are then assembled on a conventional small-diameter braiding machine with a capacity of sixteen reels, thus provided with sixteen spindles.
- One spindle out of two is used.
- the four S-coils are installed on the spindles of the braiding machine which rotate counter-clockwise and the four Z-coils are installed on the spindles in a clockwise direction - cf. fig.2 and 5 .
- the braided twine thus obtained has a natural elasticity of 120%, in particular allowing it to be used on automatic machines to tie the pieces of meat.
- This string has a good cohesion and can be cut without fray. The ends can be knotted easily by hand or by automatic machine.
- the string When the string is wrapped around the piece of meat, she marries and firmly holds the piece of meat without cutting it.
- the water vapor present in the oven releases the remaining voltage contained in the over-twisted base wires 20, 30.
- the string 10 retracts and thus accompanies the narrowing of the piece of meat.
- the string 10 loses its nervousness, so its elasticity. When cut, it behaves like ordinary string without elasticity and causes no splashing.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Yarns And Mechanical Finishing Of Yarns Or Ropes (AREA)
- Ropes Or Cables (AREA)
- Decoration Of Textiles (AREA)
Claims (11)
- Verfahren zur Herstellung einer elastischen Schnur (10) oder ähnlich, durch Zusammenfügen von mindestens zwei Grundfäden (20, 30) bestehend aus Fasern und/oder Filamenten (40), dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass man einen ersten Grundfaden (20) in die eine Richtung S überzwirnt und den zweiten Grundfaden (30) in die andere Richtung Z überzwirnt, so dass die Fasern und/oder Filamente (40) mit der Längsachse des besagten ersten Grundfadens (20) und des besagten zweiten Grundfadens (30) einen Winkel β zwischen 30° und 90° bilden, man die Überzwirnung der besagten Grundfäden (20, 30) fixiert um sie zu stabilisieren, man die besagten überzwirnten Grundfäden mit einem Flechtverfahren zusammenfügt um die besagte Schnur (10) so herzustellen dass, wenn die besagte Schnur im unbelasteten Zustand ist, ohne Zug, die besagten überzwirnten Grundfäden dazu neigen, sich von der Längsachse (A) der Schnur zu entfernen und sich in Richtung einer zur Längsachse (A) der Schnur senkrechten Achse auszurichten und dabei einen Winkel α zwischen 30° und 90° mit der Längsachse (A) der Schnur (10) bilden.
- Verfahren nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass man relativ feintitrige Grundfäden verwendet, zwischen mindestens Nm150 et Nm17 (also zwischen 6 Tex und 60 Tex).
- Verfahren nach einem beliebigen der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass, in der Formel, die die Zwirnung festlegt: T = k√Nm, wobei T der Wert der Zwirnung in Drehungen/m ist und Nm die metrische Nummer des Fadens ist, man einen hohen Zwirnkoeffizienten k wählt, zwischen mindestens 200 und 600, um einen Überzwirn-Wert zu erhalten, mit dem die Fasern und/oder Filamente (40) den besagten Winkel β bilden.
- Verfahren nach einem beliebigen der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, in dem mehr als zwei Grundfäden (20, 30) verwendet werden um die besagte Schnur herzustellen, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass ein Teil der Grundfäden in eine S-Richtung überzwirnt wird und der andere Teil der Grundfäden in die andere Richtung Z überzwirnt wird.
- Verfahren nach Anspruch 4, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass eine gerade Anzahl Grundfäden verwendet und in zwei gleiche Teile aufgeteilt wird.
- Verfahren nach einem beliebigen der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Überzwirnung der besagte Grundfäden mit einem Dämpf-Verfahren fixiert wird.
- Verfahren nach einem beliebigen der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass mindestens vier Grundfäden (20, 30) verwendet werden.
- Verfahren nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass eine Flechtmaschine eingesetzt wird, und man die besagten in Richtung S überzwirnten Grundfäden (20) auf den Spindeln der Flechtmaschine anordnet, die sich entgegen dem Uhrzeigersinn bewegen und die in der anderen Richtung Z überzwirnten Grundfäden (30) auf den Spindeln der Flechtmaschine anordnet, die sich im Uhrzeigersinn bewegen.
- Verfahren nach Anspruch 8, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die eingesetzte Flechtmaschine mehr Spindeln aufweist, als die Anzahl der zusammen zu fügenden Grundfäden (20, 30), und dadurch, dass die besagten Grundfäden mindestens auf jeder zweiten Spindel angeordnet werden.
- Mit dem Herstellungsverfahren nach mindestens Anspruch 7 erhaltene elastische Schnur (10), dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass sie aus dem Zusammenflechten von mindestens vier aus Fasern und/oder Filamenten (40) bestehenden Grundfäden (20, 30) besteht, wobei zwei erste Grundfäden (20) in S-Richtung überzwirnt sind und zwei zweite Grundfäden (30) in die andere Z-Richtung überzwirnt sind, wobei die Fasern und/oder Filamente (40) der besagten Grundfäden (20, 30) mit der Längsache jedes Grundfadens einen Winkel (β) zwischen mindestens 30° und 90° bilden; und wobei die besagten Grundfäden (20, 30) sich von der Längsachse (A) der geflochtenen Schnur (10) entfernen und sich in Richtung einer zur Längsachse (A) der Schnur senkrechten Achse ausrichten und dabei mit der Längsachse (A) der Schnur (10) einen Winkel α zwischen 30° und 90° bilden.
- Schnur nach Anspruch 10, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass ihre Bruchdehnung mindestens zwischen 20% und 150% liegt.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR0956033A FR2949790B1 (fr) | 2009-09-04 | 2009-09-04 | Procede de fabrication d'une ficelle elastique ou similaire et ficelle elastique obtenue |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2292818A1 EP2292818A1 (de) | 2011-03-09 |
| EP2292818B1 true EP2292818B1 (de) | 2012-05-09 |
Family
ID=42237170
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP10290472A Not-in-force EP2292818B1 (de) | 2009-09-04 | 2010-09-03 | Verfahren zur Herstellung einer elastischen Schnur und eine so hergestellte elastische Schnur |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2292818B1 (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE557123T1 (de) |
| DK (1) | DK2292818T3 (de) |
| FR (1) | FR2949790B1 (de) |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE621724A (de) * | ||||
| DE1138669B (de) * | 1960-10-15 | 1962-10-25 | Klaus Uhlmann | Verfahren zur Erzeugung von hochelastischen Baumwollgarnen und -zwirnen |
| DE2633903A1 (de) * | 1975-08-27 | 1977-03-10 | Duersteler & Co | Mischzwirn, verfahren zu seiner herstellung und seine verwendung |
| DE2928692A1 (de) * | 1979-07-16 | 1981-02-12 | Klaus Uhlmann | Verfahren zum herstellen eines wenigstens in einer richtung stark elastisch dehnbaren gewebes aus naturfasern |
| FR2888855B1 (fr) | 2005-07-19 | 2007-08-31 | Cognon Morin Soc Par Actions S | Fil guipe destine a constituer au moins une partie d'un article de contention, et article de contention associe |
-
2009
- 2009-09-04 FR FR0956033A patent/FR2949790B1/fr not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2010
- 2010-09-03 EP EP10290472A patent/EP2292818B1/de not_active Not-in-force
- 2010-09-03 AT AT10290472T patent/ATE557123T1/de active
- 2010-09-03 DK DK10290472.9T patent/DK2292818T3/da active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| ATE557123T1 (de) | 2012-05-15 |
| EP2292818A1 (de) | 2011-03-09 |
| FR2949790A1 (fr) | 2011-03-11 |
| FR2949790B1 (fr) | 2011-08-19 |
| DK2292818T3 (da) | 2012-08-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CH361881A (fr) | Filé élastique | |
| EP0126659A1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Herstellen eines Zwirns | |
| FR2488513A1 (fr) | Fil pour sutures chirurgicales et procede pour sa fabrication | |
| EP0078753B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung umsponnenen Elasthan-Garns | |
| EP2807296A1 (de) | Hybrides elastisches kabel und verfahren zur herstellung eines solchen kabels | |
| EP1746189B1 (de) | Coregarn zur Verwendung im Kompressionsartikel sowie Kompressionsartikel | |
| FR2488512A1 (fr) | Fil pour sutures chirurgicales | |
| EP1753315B1 (de) | Gewebtes band mit variabler breite und produkte, für die besagtes band verwendet wird | |
| EP2292818B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung einer elastischen Schnur und eine so hergestellte elastische Schnur | |
| FR2507634A1 (fr) | Procede et appareil pour le filage de fils a ame | |
| FR2576045A1 (fr) | Cordage tresse a ame et procede de fabrication d'un tel cordage | |
| EP0070210A1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung eines Hülle-Kern-Garns | |
| FR2808697A1 (fr) | Corde synthetique composite pour raquette de tennis | |
| BE646976A (de) | ||
| CH188297A (fr) | Fil élastique et procédé pour le fabriquer. | |
| BE412683A (de) | ||
| FR2738579A1 (fr) | Procede de fabrication de brides elastiques | |
| BE683479A (de) | ||
| FR2920787A1 (fr) | Procede de fabrication d'un fil hybride | |
| EP2130957A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Kabelherstellung aus synthetischen Fäden durch gegenseitiges Verdrehen | |
| BE540261A (de) | ||
| FR2749859A1 (fr) | Procede de realisation d'un fil mixte extensible et machine pour sa mise en oeuvre | |
| FR2580675A1 (fr) | Procede de fabrication d'un fil par projection de fibres sur un element perfore | |
| BE551829A (de) | ||
| CH185908A (fr) | Procédé pour transformer des filaments continus directement en un fil contenant des fibres en mèche, appareil pour la mise en oeuvre de ce procédé, et fil obtenu au moyen de ce procédé. |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME RS |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20110907 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: A22C 13/00 20060101ALI20111018BHEP Ipc: D02G 3/32 20060101AFI20111018BHEP Ipc: D04C 1/12 20060101ALI20111018BHEP |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 557123 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20120515 Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: FRENCH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602010001494 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20120712 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: VDEP Effective date: 20120509 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D Effective date: 20120509 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120909 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120809 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MK05 Ref document number: 557123 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20120509 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120810 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120910 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: CORDERIE MEYER SANSBOEUF S.A.S. Effective date: 20120930 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20130212 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120930 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120820 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 602010001494 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20130212 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120809 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120903 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120930 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120903 Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20100903 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Payment date: 20140916 Year of fee payment: 5 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20140917 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20140905 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20140925 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20140930 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20140930 Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120509 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 602010001494 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: EBP Effective date: 20150930 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20150903 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20160531 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20160401 Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150903 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150930 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150930 |