EP2176552B1 - Eccentric worm pump with split stator - Google Patents
Eccentric worm pump with split stator Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2176552B1 EP2176552B1 EP08785517A EP08785517A EP2176552B1 EP 2176552 B1 EP2176552 B1 EP 2176552B1 EP 08785517 A EP08785517 A EP 08785517A EP 08785517 A EP08785517 A EP 08785517A EP 2176552 B1 EP2176552 B1 EP 2176552B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- stator
- progressive cavity
- cavity pump
- pump according
- jacket
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04C—ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; ROTARY-PISTON, OR OSCILLATING-PISTON, POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04C2/00—Rotary-piston machines or pumps
- F04C2/08—Rotary-piston machines or pumps of intermeshing-engagement type, i.e. with engagement of co-operating members similar to that of toothed gearing
- F04C2/10—Rotary-piston machines or pumps of intermeshing-engagement type, i.e. with engagement of co-operating members similar to that of toothed gearing of internal-axis type with the outer member having more teeth or tooth-equivalents, e.g. rollers, than the inner member
- F04C2/107—Rotary-piston machines or pumps of intermeshing-engagement type, i.e. with engagement of co-operating members similar to that of toothed gearing of internal-axis type with the outer member having more teeth or tooth-equivalents, e.g. rollers, than the inner member with helical teeth
- F04C2/1071—Rotary-piston machines or pumps of intermeshing-engagement type, i.e. with engagement of co-operating members similar to that of toothed gearing of internal-axis type with the outer member having more teeth or tooth-equivalents, e.g. rollers, than the inner member with helical teeth the inner and outer member having a different number of threads and one of the two being made of elastic materials, e.g. Moineau type
- F04C2/1073—Rotary-piston machines or pumps of intermeshing-engagement type, i.e. with engagement of co-operating members similar to that of toothed gearing of internal-axis type with the outer member having more teeth or tooth-equivalents, e.g. rollers, than the inner member with helical teeth the inner and outer member having a different number of threads and one of the two being made of elastic materials, e.g. Moineau type where one member is stationary while the other member rotates and orbits
- F04C2/1075—Construction of the stationary member
Definitions
- the invention relates to an eccentric screw pump with at least one stator made of an elastic material and a rotor mounted in the stator, wherein the stator is at least partially surrounded by a stator casing or stator housing.
- the rotor is regularly connected to the drive or the drive shaft via at least one coupling rod, which is also referred to as a cardan shaft.
- the pump has a suction housing and a connection piece, wherein the stator is connected at one end to a connection flange of the suction housing and the other end to a connection flange of the connection piece.
- Elastic material in the context of the invention means in particular an elastomer, e.g. a (synthetic) rubber or a rubber mixture.
- composites of an elastomer or other material, e.g. Metal includes.
- the elastic stator is formed into a stator jacket of e.g. Metal is vulcanised.
- the elastomeric stators are subject to wear during operation, so that at regular intervals maintenance or a stator replacement is required.
- the stators are often replaced with their molded stator covers.
- stator For cost reasons and also for reasons of environmental protection, it has therefore been proposed in practice to manufacture the elastomeric stator on the one hand and the stator jacket or stator housing made of metal on the other as separate components.
- the stator can then be inserted in the course of assembly in the cylindrical stator shell made of metal, so that after appropriate wear only the stator replaced and used the stator case again can be.
- stators are also referred to as a push-in.
- the assembly of such a slide-in stator is often expensive in practice and associated with extensive disassembly of the eccentric screw pump.
- the invention has for its object to provide an eccentric screw pump of the type described above, which allows replacement of the elastic stator in a cost effective and simple assembly technique.
- the stator consists of a longitudinally divided stator of at least two stator sub-shells. It is preferably two stator shells, which are thus designed as half shells and each cover an angle of 180 °.
- the invention also includes split stators with three, four or more sub-shells, which then each cover an angle of 120 ° or 90 ° or less.
- the invention is initially based on the recognition that it is expedient to produce the elastomeric stator as a separate component from the stator shell or stator housing to ensure replacement of only the elastomeric component and a reusability of the stator shell.
- the exchange can be done without a costly disassembly of the pump is necessary.
- the pump can remain mounted in its basic structure on eg a base plate or mounting plate.
- the suction housing on the one hand and the connection piece on the other as well as the rotor can remain mounted.
- the two half shells or the plurality of partial shells can then be mounted as it were around the rotor.
- the stator is connected with its ends, on the one hand, to a connection flange of the suction housing and, on the other hand, to a connecting flange of the connecting piece, wherein the separate partial shells - as explained - can be mounted individually, without disassembly of the pump being required.
- the partial shells are elastically deformable and therefore are kinkable or bendable for insertion. It may be expedient not to mount the stator or the stator shells directly to the connection flanges, but to provide adapter pieces which are connected to the one or more connection flanges.
- annular adapter pieces are adapted to the geometry of the stator or the stator partial shells, so that with the help of the adapter pieces in principle also has the possibility of using the longitudinally divided stator according to the invention in connection with conventional pump housings or suction housings and connecting pieces.
- the adapters can also be referred to as centering rings.
- stator or the stator partial shells with end sealing surfaces can each be plugged into a stator receptacle of the corresponding connection flange or of the corresponding adapter piece or can be plugged onto such.
- the stator at the end has conical, preferably outer-conical or inner-conical sealing surfaces, while the described stator receptacles of the connecting flanges or adapter pieces have conical, preferably inner-conical or outer-conical sealing counter surfaces.
- the end-side sealing surfaces of the stator are formed externally conical and they then abut against the inner-conical sealing mating surfaces of the stator.
- the stator has end-to-end conical sealing surfaces, and the stator receptacles on the connection flange or on the adapter piece have outer-conical sealing opposing surfaces.
- stator receptacle protrudes, as it were, in the axial or axially parallel direction from the connection flange or the adapter piece, so that the stator receptacle engages in the stator end or the stator is plugged onto the stator receptacle.
- the cone angle of the sealing surfaces or the sealing counter surfaces may be 10 ° to 50 °, preferably 20 ° to 30 °.
- stator casing is designed as a longitudinally divided casing and has for this purpose at least two, preferably at least four casing segments.
- This also contributes to the fact that the wearing part forming elastomeric stator can be replaced without major disassembly, because even the multi-part stator jacket can now be dismantled without the suction housing, discharge nozzle and / or rotor must be removed from its installed position.
- a longitudinally divided stator jacket with its several shell segments at the same time forms a stator-clamping device or stator adjustment device with which the stator can be tensioned against the rotor, in particular in the radial direction.
- the invention is based on the recognition that the elastomeric stator is usually mounted with respect to the rotatably driven rotor with a bias, wherein the function of the eccentric screw pump depends substantially on this bias.
- the simple structure and in particular the simple replacement of the stator can now be the desired Vorspannure set excellent and in particular set up a post-tension with appropriate wear.
- the tightness of the longitudinally divided stator is ensured by the multi-part clamping device.
- the stator clamping device ensures not only a sufficient tightness or connection of the two stator sub-shells to each other, but also a tight connection or a tight engagement of the stator ends in the corresponding stator receptacles of the connecting flanges or adapters.
- the invention proposes that the outer side abutting against the stator shroud segments have, for example, end mounting flanges for attachment to the flange or adapter piece. These mounting flanges can be connected to the connection flange or the adapter piece with clamping devices for the purpose of clamping the stator.
- the clamping means can be designed as screw devices, so that can be adjusted in a simple manner, the desired bias or adjusted.
- the shroud segments are adapted with their mounting flanges to the geometry of the stator and the connecting flanges or adapter pieces, that the fastening of the mounting flanges on the connecting flanges or adapter pieces to form an adjustable annular gap.
- This can be a gap width of up to 10 mm, preferably up to 5 mm. It may therefore be expedient to mount the mounting flanges first with a gap width of, for example, 5 mm, so that then a residual tension of a total of 5 mm clamping path can take place when wear occurs.
- the mounting flanges can overlap or engage in the connection flange or the adapter piece.
- stator subshells each have at least one antirotation protruding on the outside.
- an anti-rotation can be connected as a longitudinal ridge on the outside of the stator subshells, for example.
- the geometry of the stator shells with their longitudinal webs is preferably adapted to the geometry of the plurality of shroud segments, so that engage in the invention, the longitudinal webs forming the rotation in corresponding spaces between two adjacent shroud segments.
- these webs may also have end stops, which serve as axial securing and abut against the adapter pieces or connecting flanges.
- stator according to the invention can be easily mounted and replaced, without, e.g. Pressure nozzle or pressure lines must be solved.
- the required rotor-stator clamp can be easily adjusted.
- the stator can be easily manufactured in relation to the dimensions of the stator geometry, since exact dimensional accuracy is no longer required.
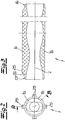
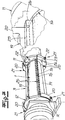
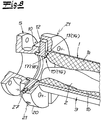
- an eccentric screw pump which in its basic structure has a stator 1 made of an elastic material and a rotor 2 mounted in the stator 1, wherein the stator 1 is surrounded at least in regions by a stator shell 3. Furthermore, the pump has a suction housing 4 and a connection piece 5, which is also referred to as a discharge nozzle. Not shown is also provided drive, wherein the drive operates on the rotor 2 via a merely indicated coupling rod 6. The coupling rod is connected via coupling joints on the one hand to the rotor 2 and on the other hand to the drive shaft, not shown, wherein of the coupling joints only the rotor-side hinge 7 is shown.
- the pump is usually mounted on a merely indicated base plate 8, which may be a base plate supplied with the pump or a base plate provided by the user.
- the stator 1 is connected in a conventional manner with its one end to a connecting flange 9 of the suction housing 4 and with its other end to a connecting flange 10 of the connecting piece 5.
- the connection in the illustrated embodiment is not directly to these connection flanges 9, 10, but with the interposition of an adapter piece 11, 12, whose structure will be explained in more detail below.
- These adapters are also referred to as centering rings.
- stator 1 is now formed as a longitudinally divided stator and consists of two stator-part shells 1 a, 1 b, which form half-shells in the embodiment, each covering an angle of 180 °.
- Longitudinal means means along the stator longitudinal axis L or parallel to this. The separating cut between the partial shells consequently runs along or parallel to the longitudinal axis L.
- This longitudinally divided configuration of the elastomeric stator makes it possible to disassemble and mount the stator 1 with the suction housing 4, discharge nozzle 5 and rotor 2 mounted, since the stator 1 does not, as in the prior art, e.g. must be pushed from one side onto the rotor 2 after removing the pressure port 5.
- stator 1 and its stator shells 1 a, 1 b end sealing surfaces 13, 14 (or 13 ', 14') on.
- the stator partial shells 1a, 1b are then (successively) with their end-side sealing surfaces 13, 14 in Statorfactn 15, 16 inserted or with sealing surfaces 13 ', 14' on such Statorabilityn 15 ', 16' attachable, said Statorfactn in the here illustrated embodiment with adapter pieces on these adapter pieces 11, 12 are provided.
- the adapter pieces 11, 12 themselves can be used in known receptacles on the one hand suction housing 4 and the other pressure port 5, so that suction housing 4 on the one hand and pressure port 5 on the other hand can be formed in a conventional construction and consequently can be used with conventional one-piece stators.
- the end-side sealing surfaces 13, 14 (or 13 ', 14') of the stator 1 are conical or designed as a conical surface, in the embodiment according to Fig. 1 to 7 "Outside-conical".
- the Statorchantn 15, 16 (or 15 ', 16') also have corresponding conical sealing mating surfaces 17, 18 (17 ', 18') according to Fig. 1 to 7 can be formed internally-conical.
- stator jacket 3 is provided.
- This is inventively designed as a longitudinally divided shell and has several, in the exemplary embodiment four, shell segments 19. Consequently, this stator jacket 3 forms, with its jacket segments 19, a stator clamping device or stator adjusting device with which the longitudinally divided stator 1 can be fixed and sealed on the one hand and a desired voltage or bias voltage can be introduced into the stator 1 on the other hand.
- This succeeds within the scope of the invention in a particularly uniform manner, since four or more shell segments 19 are used. In Fig. 1 only one of these shell segments is shown.
- the outer side of the stator 1 adjacent jacket segments 19 have end mounting flanges 20 for attaching the shell segments 19 to the adapter pieces 11, 12. These mounting flanges 20 engage over the adapter piece 11, 12.
- the mounting flanges 20 are connected to the shell segment 19 by means of welded joints.
- the shroud segments 20 can also be made in one piece, including mounting flange.
- a plurality of stud bolts are connected as screw bolts 22 to the connecting flanges 9, 10 or in the exemplary embodiment adapter pieces 11, 12.
- the desired voltages can be adjusted via suitable nuts 23.
- the end attachment flanges thus have openings for the studs 22 or suitable screws on.
- the figures show that the attachment takes place with an adjustable annular gap R between the mounting flanges of the shell segments 19 and the adapter pieces. By adjusting this annular gap R, the desired preload can then be adjusted or re-tensioned.
- the shell segments 19 can then be fixed by means of screw 24 in the longitudinal direction of the adapter pieces or flanges.
- stator partial shells 1 a, 1 b each have at least one torsion protection 25 projecting on the outside, which in the exemplary embodiment are designed as longitudinal webs 25 extending over almost the entire stator length, which are integrally formed on the outside of the stator, for example vulcanized.
- Fig. 6 shows that these longitudinal webs 25 engage in the course of assembly in intermediate spaces between the individual maneseat segments 19, so that the longitudinal webs are as it were clamped between two adjacent shell segments 19 and thus form an anti-rotation.
- the longitudinal webs 25 but also the axial securing, because they are placed in their length to the distance between the adapter pieces, so that stops 26 are provided, which rest against the adapter pieces 11, 12.
- the longitudinally divided stator 1 according to the invention is preferably first manufactured as a one-piece stator 1 and then separated, for example in the way of water jet cutting. This allows a simple and cost-effective production.
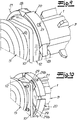
- Fig. 1 to 7 show a possible embodiment in which stator 1 is inserted into corresponding receptacles 15, 16. This ensures a good seal in the course of clamping.
- Fig. 8 to 10 show embodiments, in which the stator 1 with its partial shells 1 a, 1 b on suitable "projecting" receptacles 15 ', 16' can be plugged.
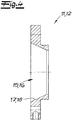
- Fig. 8 shows a preferred embodiment of the invention, which in its basic structure of the embodiment according to Fig. 1 to 7 equivalent. It differs from this embodiment essentially in that the stator 1 is not inserted with its ends in a receptacle, but on recordings 15 ', 16' is attached.
- the stator 1 therefore has end-side sealing surfaces 13 ', 14', which are formed inside-conical.
- the Statorfactn 15 ', 16' have accordingly outer-conical sealing mating surfaces 17 ', 18'.
- the Statorfactn 15 ', 16' are therefore each formed by a projecting axially outwardly sealing collar, which is formed in the embodiment of the adapter piece.
- stator receivers 15 ', 16' engage, as it were, in the interior of the stator end of the stator 1.
- Fig. 8 Strictly shows only the one end of the arrangement with the reference numerals 13 ', 15' and 17 '.
- the reference numerals 14 ', 16' and 18 ', which refer to the opposite, not shown end, are therefore provided in parentheses for the sake of completeness.
- the stator 1 is also formed in several parts in this embodiment. In detail, the structure - apart from the configuration of the stator receptacles and the sealing surfaces - the structure according to Fig. 1 to 7 ,
- Fig. 8 recognizable that means for receiving Kipp beyond or radial forces can be provided on the connecting flanges and / or adapter pieces.
- Fig. 8 Radially projecting from the adapter pieces threaded pins 27 can be seen, which engage in corresponding recesses on the stator casing or on the mounting flanges 20.
- These setscrews 27 are thus provided in addition to the clamping means 21 provided anyway. While on the clamping means 21, the adjustment the segments can take place, the set screws 27 serve to receive the tilting forces or radial forces.
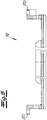
- Fig. 9 shows an example of an alternative way to accommodate the tilting forces or radial forces.
- the in Fig. 8 Grub screws 27 omitted.
- spacers are used between the individual shell segments or their mounting flanges, which are wedge-shaped in the embodiment as guide wedges 28.
- FIG. 10 Another way to absorb tilting forces or radial forces.
- a quasi-positive connection between the connecting flanges or adapter pieces on the one hand and the shell segments or their mounting flanges on the other hand is provided.
- claw-like projections 29 are provided, which engage in corresponding receptacles or recesses 29b on the respective shell segment or its mounting flange.
- axial and radial securing via these form-locking elements, eg, claws, on the centering ring on the one hand and the stator adjustment segment on the other hand are possible.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Rotary Pumps (AREA)
- Details And Applications Of Rotary Liquid Pumps (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft eine Exzenterschneckenpumpe mit zumindest einem Stator aus einem elastischen Material und einem in dem Stator gelagerten Rotor, wobei der Stator zumindest bereichsweise von einem Statormantel bzw. Statorgehäuse umgeben ist. - Bei einer solchen Exzenterschneckenpumpe ist der Rotor regelmäßig über zumindest eine Kupplungsstange, welche auch als Gelenkwelle bezeichnet wird, mit dem Antrieb bzw. der Antriebswelle verbunden. Die Pumpe weist ein Sauggehäuse sowie einen Anschlussstutzen auf, wobei der Stator mit seinem einen Ende an einen Anschlussflansch des Sauggehäuses und seinem anderen Ende an einen Anschlussflansch des Anschlussstutzens angeschlossen ist. Elastisches Material meint im Rahmen der Erfindung insbesondere einen Elastomer, z.B. einen (Synthese-)Kautschuk oder eine Kautschukmischung. Es werden im Übrigen auch Verbundwerkstoffe aus einem Elastomer oder einem anderen Material, z.B. Metall, umfasst.The invention relates to an eccentric screw pump with at least one stator made of an elastic material and a rotor mounted in the stator, wherein the stator is at least partially surrounded by a stator casing or stator housing. In such an eccentric screw pump, the rotor is regularly connected to the drive or the drive shaft via at least one coupling rod, which is also referred to as a cardan shaft. The pump has a suction housing and a connection piece, wherein the stator is connected at one end to a connection flange of the suction housing and the other end to a connection flange of the connection piece. Elastic material in the context of the invention means in particular an elastomer, e.g. a (synthetic) rubber or a rubber mixture. Incidentally, composites of an elastomer or other material, e.g. Metal, includes.
Aus der Praxis sind Exzenterschneckenpumpen bekannt, bei welchen der elastische Stator in einen Statormantel aus z.B. Metall einvulkanisiert ist. Die elastomeren Statoren unterliegen während des Betriebes einem Verschleiß, so dass in regelmäßigen Abständen Wartungsarbeiten bzw. ein Stator-Austausch erforderlich ist. In der Praxis werden dazu häufig die Statoren mit ihren angeformten Statormänteln ausgetauscht.Progressive cavity pumps are known in practice in which the elastic stator is formed into a stator jacket of e.g. Metal is vulcanised. The elastomeric stators are subject to wear during operation, so that at regular intervals maintenance or a stator replacement is required. In practice, the stators are often replaced with their molded stator covers.
Aus Kostengründen und auch aus Gründen des Umweltschutzes wurde daher in der Praxis vorgeschlagen, den elastomeren Stator einerseits und den Statormantel bzw. Statorgehäuse aus Metall andererseits als separate Bauteile zu fertigen. Der Stator kann dann im Zuge der Montage in den zylindrischen Statormantel aus Metall eingeschoben werden, so dass nach entsprechendem Verschleiß lediglich der Stator ausgetauscht und der Statormantel wieder verwendet werden kann. Derartige Statoren werden auch als Einschubstator bezeichnet. Die Montage eines derartigen Einschubstators ist jedoch in der Praxis häufig aufwendig und mit einer umfangreichen Zerlegung der Exzenterschneckenpumpe verbunden.For cost reasons and also for reasons of environmental protection, it has therefore been proposed in practice to manufacture the elastomeric stator on the one hand and the stator jacket or stator housing made of metal on the other as separate components. The stator can then be inserted in the course of assembly in the cylindrical stator shell made of metal, so that after appropriate wear only the stator replaced and used the stator case again can be. Such stators are also referred to as a push-in. However, the assembly of such a slide-in stator is often expensive in practice and associated with extensive disassembly of the eccentric screw pump.
Außerdem kennt man aus der
Aus der
Der Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, eine Exzenterschneckenpumpe der eingangs beschriebenen Art zu schaffen, welche einen Austausch des elastischen Stators auf kostengünstige und montagetechnisch einfache Weise ermöglicht.The invention has for its object to provide an eccentric screw pump of the type described above, which allows replacement of the elastic stator in a cost effective and simple assembly technique.
Zur Lösung dieser Aufgabe lehrt die Erfindung eine Exzenterschneckenpumpe mit den Merkmalen des Anspruchs 1. Der Stator besteht als längsgeteilter Stator aus zumindest zwei Stator-Teilschalen. Es handelt sich vorzugsweise um zwei Stator-Teilschalen, die folglich als Halbschalen ausgeführt sind und jeweils einen Winkel von 180° überdecken. Die Erfindung umfasst jedoch auch geteilte Statoren mit drei, vier oder auch mehr Teilschalen, die dann jeweils einen Winkel von 120° bzw. 90° oder auch weniger überdecken.To solve this problem, the invention teaches an eccentric screw pump with the features of
Dabei geht die Erfindung zunächst einmal von der Erkenntnis aus, dass es zweckmäßig ist, den elastomeren Stator als von dem Statormantel bzw. Statorgehäuse separat austauschbares Bauteil herzustellen, um einen Austausch lediglich des elastomeren Bauteils und eine Wiederverwertbarkeit des Statormantels zu gewährleisten. Im Rahmen der Erfindung wird darüber hinaus jedoch eine besonders einfache Montage erreicht, denn durch die längsgeteilte Bauweise des elastomeren Stators kann der Austausch erfolgen, ohne dass eine aufwendige Zerlegung der Pumpe notwendig ist. Die Pumpe kann in ihrem grundsätzlichen Aufbau auf z.B. einer Grundplatte bzw. Montageplatte montiert bleiben. Sauggehäuse einerseits und Anschlussstutzen andererseits sowie der Rotor können montiert bleiben. Die beiden Halbschalen bzw. die mehreren Teilschalen können dann gleichsam um den Rotor herum montiert werden. Dazu wird der Stator mit seinen Enden einerseits an einen Anschlussflansch des Sauggehäuses und andererseits an einen Anschlussflansch des Anschlussstutzens angeschlossen, wobei die separaten Teilschalen - wie erläutert - einzeln montiert werden können, ohne dass eine Demontage der Pumpe erforderlich ist. Dieses gelingt auch deshalb, weil die Teilschalen elastisch verformbar sind und daher zum Einsetzen knickbar bzw. biegbar sind. Es kann zweckmäßig sein, den Stator bzw. die Stator-Teilschalen nicht unmittelbar an den Anschlussflanschen zu montieren, sondern Adapterstücke vorzusehen, welche an den oder die Anschlussflansche angeschlossen sind. Diese z.B. ringförmigen Adapterstücke sind an die Geometrie des Stators bzw. die Stator-Teilschalen angepasst, so dass mit Hilfe der Adapterstücke grundsätzlich auch die Möglichkeit besteht, den erfindungsgemäßen längsgeteilten Stator im Zusammenhang mit herkömmlichen Pumpengehäusen bzw. Sauggehäusen und Anschlussstutzen zu verwenden. Die Adapterstücke können auch als Zentrierringe bezeichnet werden.The invention is initially based on the recognition that it is expedient to produce the elastomeric stator as a separate component from the stator shell or stator housing to ensure replacement of only the elastomeric component and a reusability of the stator shell. In the context of the invention, however, beyond a particularly simple assembly is achieved because the longitudinally divided construction of the elastomeric stator, the exchange can be done without a costly disassembly of the pump is necessary. The pump can remain mounted in its basic structure on eg a base plate or mounting plate. The suction housing on the one hand and the connection piece on the other as well as the rotor can remain mounted. The two half shells or the plurality of partial shells can then be mounted as it were around the rotor. For this purpose, the stator is connected with its ends, on the one hand, to a connection flange of the suction housing and, on the other hand, to a connecting flange of the connecting piece, wherein the separate partial shells - as explained - can be mounted individually, without disassembly of the pump being required. This also succeeds because the partial shells are elastically deformable and therefore are kinkable or bendable for insertion. It may be expedient not to mount the stator or the stator shells directly to the connection flanges, but to provide adapter pieces which are connected to the one or more connection flanges. These, for example, annular adapter pieces are adapted to the geometry of the stator or the stator partial shells, so that with the help of the adapter pieces in principle also has the possibility of using the longitudinally divided stator according to the invention in connection with conventional pump housings or suction housings and connecting pieces. The adapters can also be referred to as centering rings.
Die Erfindung sieht vor, dass der Stator bzw. die Stator-Teilschalen mit endseitigen Dichtungsflächen jeweils in eine Statoraufnahme des entsprechenden Anschlussflansches bzw. des entsprechenden Adapterstückes einsteckbar oder auf eine solche aufsteckbar sind. Durch dieses Einstecken der Statorenden in geeignete Statoraufnahmen oder ein Aufstecken auf geeignete vorkragende Statoraufnahmen wird insbesondere im Zuge des Montierens des Statorgehäuses eine einwandfreie Dichtigkeit gewährleistet, da im Zuge der Montage des Statorgehäuses bzw. Statormantels die endseitigen Dichtungsflächen in die Dichtungsaufnahmen eingreifen oder (umgekehrt) die vorkragenden Statoraufnahmen in die Dichtflächen des Stators eingreifen.The invention provides that the stator or the stator partial shells with end sealing surfaces can each be plugged into a stator receptacle of the corresponding connection flange or of the corresponding adapter piece or can be plugged onto such. By inserting the Statorenden in suitable Statoraufnahmen or plugging on suitable projecting Statoraufnahmen perfect sealing is ensured in particular in the course of mounting the stator housing, as in the course of assembly of the stator housing or stator shell engage the end-side sealing surfaces in the seal receptacles or (conversely) the projecting stator recordings engage in the sealing surfaces of the stator.
Dabei weist der Stator endseitig konische, vorzugsweise außen-konische oder innen-konische Dichtungsflächen auf, während die beschriebenen Statoraufnahmen der Anschlussflansche bzw. Adapterstücke konische, vorzugsweise innen-konische bzw. außen-konische Dichtungsgegenflächen aufweisen. In einer ersten Ausführungsform sind die endseitigen Dichtungs-flächen des Stators auβen konisch ausgebildet und diese liegen dann gegen die innen-konischen Dichtungsgegenflächen der Statoraufnahme an. In einer abgewandelten, bevorzugten Ausführungsform weist der Stator endseitig innen-konische Dichtungsflächen auf und die Statoraufnahmen am Anschlussflansch oder am Adapterstück weisen außen-konische Dichtungsgegenflächen auf. Bei dieser Ausführungsform kragt die Statoraufnahme gleichsam in axialer bzw. achsparalleler Richtung aus dem Anschlussflansch bzw. dem Adapterstück vor, so dass die Statoraufnahme in das Statorende eingreift bzw. der Stator auf die Statoraufnahme aufgesteckt wird. Auf diese Weise lässt sich eine besonders gute Dichtigkeit erzeugen. Insgesamt wird durch die Konizität bzw. kegelförmige Ausgestaltung eine hervorragende Dichtigkeit gewährleistet. Der Konuswinkel der Dichtungsflächen bzw. der Dichtungsgegenflächen kann 10° bis 50°, vorzugsweise 20° bis 30° betragen.In this case, the stator at the end has conical, preferably outer-conical or inner-conical sealing surfaces, while the described stator receptacles of the connecting flanges or adapter pieces have conical, preferably inner-conical or outer-conical sealing counter surfaces. In a first embodiment, the end-side sealing surfaces of the stator are formed externally conical and they then abut against the inner-conical sealing mating surfaces of the stator. In a modified preferred embodiment, the stator has end-to-end conical sealing surfaces, and the stator receptacles on the connection flange or on the adapter piece have outer-conical sealing opposing surfaces. In this embodiment, the stator receptacle protrudes, as it were, in the axial or axially parallel direction from the connection flange or the adapter piece, so that the stator receptacle engages in the stator end or the stator is plugged onto the stator receptacle. In this way, a particularly good tightness can be generated. Overall, an excellent tightness is ensured by the conicity or conical configuration. The cone angle of the sealing surfaces or the sealing counter surfaces may be 10 ° to 50 °, preferably 20 ° to 30 °.
Erfindungsgemäß ist nicht nur der Stator selbst als längsgeteilter Stator ausgebildet, sondern auch der Statormantel ist als längsgeteilter Mantel ausgebildet und weist dazu zumindest zwei, vorzugsweise zumindest vier Mantelsegmente auf. Auch dieses trägt dazu bei, dass der ein Verschleißteil bildende elastomere Stator ohne größere Demontage ausgetauscht werden kann, denn auch der mehrteilige Statormantel lässt sich nun demontieren, ohne dass Sauggehäuse, Druckstutzen und/oder Rotor aus ihrer Einbauposition entfernt werden müssen. Darüber hinaus bildet ein solcher längsgeteilter Statormantel mit seinen mehreren Mantelsegmenten zugleich eine Stator-Spannvorrichtung bzw. Stator-Einstellvorrichtung, mit welcher der Stator insbesondere in radialer Richtung gegen den Rotor spannbar ist. Dabei geht die Erfindung von der Erkenntnis aus, dass der elastomere Stator gegenüber dem drehbar angetriebenen Rotor üblicherweise mit einer Vorspannung montiert wird, wobei die Funktion der Exzenterschneckenpumpe wesentlich von dieser Vorspannung abhängt. Trotz des einfachen Aufbaus und insbesondere des einfachen Austausches des Stators lässt sich nun das gewünschte Vorspannmaß hervorragend einstellen und insbesondere auch eine Nachspannung bei entsprechendem Verschleiß einrichten. Zugleich wird über die mehrteilige Spannvorrichtung die Dichtheit des längsgeteilten Stators gewährleistet. Dabei gewährleistet die Stator-Spannvorrichtung nicht nur eine ausreichende Dichtheit bzw. Verbindung der beiden Stator-Teilschalen zueinander, sondern auch eine dichte Verbindung bzw. ein dichtes Eingreifen der Statorenden in die entsprechenden Stator-Aufnahmen der Anschlussflansche bzw. Adapterstücke.According to the invention, not only the stator itself is designed as a longitudinally divided stator, but also the stator casing is designed as a longitudinally divided casing and has for this purpose at least two, preferably at least four casing segments. This also contributes to the fact that the wearing part forming elastomeric stator can be replaced without major disassembly, because even the multi-part stator jacket can now be dismantled without the suction housing, discharge nozzle and / or rotor must be removed from its installed position. In addition, such a longitudinally divided stator jacket with its several shell segments at the same time forms a stator-clamping device or stator adjustment device with which the stator can be tensioned against the rotor, in particular in the radial direction. The invention is based on the recognition that the elastomeric stator is usually mounted with respect to the rotatably driven rotor with a bias, wherein the function of the eccentric screw pump depends substantially on this bias. Despite the simple structure and in particular the simple replacement of the stator can now be the desired Vorspannmaß set excellent and in particular set up a post-tension with appropriate wear. At the same time the tightness of the longitudinally divided stator is ensured by the multi-part clamping device. In this case, the stator clamping device ensures not only a sufficient tightness or connection of the two stator sub-shells to each other, but also a tight connection or a tight engagement of the stator ends in the corresponding stator receptacles of the connecting flanges or adapters.
In diesem Zusammenhang schlägt die Erfindung vor, dass die außenseitig gegen den Stator anliegenden Mantelsegmente z.B. endseitig Befestigungsflansche für die Befestigung an dem Anschlussflansch oder Adapterstück aufweisen. Diese Befestigungsflansche können zum Zwecke des Spannens des Stators mit Spannmitteln an den Anschlussflansch bzw. das Adapterstück angeschlossen werden. Die Spannmittel können dabei als Schraubvorrichtungen ausgebildet sein, so dass auf einfache Weise die gewünschte Vorspannung eingestellt oder auch nachgestellt werden kann. Die Mantelsegmente sind mit ihren Befestigungsflanschen so an die Geometrie des Stators und der Anschlussflansche bzw. Adapterstücke angepasst, dass die Befestigung der Befestigungsflansche an den Anschlussflanschen bzw. Adapterstücken unter Bildung eines einstellbaren Ringspaltes erfolgt. Dieser kann eine Spaltweite von bis zu 10 mm, vorzugsweise bis zu 5 mm betragen. Es kann folglich zweckmäßig sein, die Befestigungsflansche zunächst mit einer Spaltweite von z.B. 5 mm zu montieren, so dass dann bei auftretendem Verschleiß eine Nachspannung von insgesamt 5 mm Spannweg erfolgen kann.In this context, the invention proposes that the outer side abutting against the stator shroud segments have, for example, end mounting flanges for attachment to the flange or adapter piece. These mounting flanges can be connected to the connection flange or the adapter piece with clamping devices for the purpose of clamping the stator. The clamping means can be designed as screw devices, so that can be adjusted in a simple manner, the desired bias or adjusted. The shroud segments are adapted with their mounting flanges to the geometry of the stator and the connecting flanges or adapter pieces, that the fastening of the mounting flanges on the connecting flanges or adapter pieces to form an adjustable annular gap. This can be a gap width of up to 10 mm, preferably up to 5 mm. It may therefore be expedient to mount the mounting flanges first with a gap width of, for example, 5 mm, so that then a residual tension of a total of 5 mm clamping path can take place when wear occurs.
Dabei können die Befestigungsflansche in den Anschlussflansch oder das Adapterstück übergreifen bzw. umgreifen. Dazu wird auf die Figuren und die Figurenbeschreibung verwiesen.The mounting flanges can overlap or engage in the connection flange or the adapter piece. Reference is made to the figures and the description of the figures.
Ferner schlägt die Erfindung in einer Weiterentwicklung vor, dass eine oder mehrere, vorzugsweise alle, Stator-Teilschalen jeweils zumindest eine außenseitig vorkragende Verdrehsicherung aufweisen. Eine solche Verdrehsicherung kann z.B. als Längssteg außenseitig an die Stator-Teilschalen angeschlossen sein. Die Geometrie der Stator-Teilschalen mit ihren Längsstegen ist dabei vorzugsweise an die Geometrie der mehreren Mantelsegmente angepasst, so dass im Rahmen der Erfindung die Längsstege unter Bildung der Verdrehsicherung in entsprechende Zwischenräume zwischen zwei benachbarten Mantelsegmenten eingreifen. Darüber hinaus können diese Stege auch endseitige Anschläge aufweisen, welche als Axialsicherung dienen und dazu gegen die Adapterstücke bzw. Anschlussflansche anliegen.Furthermore, the invention proposes, in a further development, that one or more, preferably all, stator subshells each have at least one antirotation protruding on the outside. Such an anti-rotation can be connected as a longitudinal ridge on the outside of the stator subshells, for example. The geometry of the stator shells with their longitudinal webs is preferably adapted to the geometry of the plurality of shroud segments, so that engage in the invention, the longitudinal webs forming the rotation in corresponding spaces between two adjacent shroud segments. In addition, these webs may also have end stops, which serve as axial securing and abut against the adapter pieces or connecting flanges.
Insgesamt lässt sich der erfindungsgemäße Stator einfach montieren und austauschen, ohne dass z.B. Druckstutzen oder Druckleitungen gelöst werden müssen. Die erforderliche Rotor-Stator-Klemmung lässt sich gut einstellen. Der Stator lässt sich bezogen auf die Statorgeometriemaße einfach herstellen, da keine exakte Maßgenauigkeit mehr erforderlich ist.Overall, the stator according to the invention can be easily mounted and replaced, without, e.g. Pressure nozzle or pressure lines must be solved. The required rotor-stator clamp can be easily adjusted. The stator can be easily manufactured in relation to the dimensions of the stator geometry, since exact dimensional accuracy is no longer required.
Im Folgenden wird die Erfindung anhand einer lediglich ein Ausführungsbeispiel darstellenden Zeichnung näher erläutert. Es zeigen
- Fig. 1
- eine vereinfachten Längsschnitt durch eine erfindungsgemäße Exzenterschneckenpumpe,
- Fig. 2
- einen erfindungsgemäßen längsgeteilten Stator in einer Stirnansicht,
- Fig. 3
- einen Schnitt A-B durch den Gegenstand nach
Fig. 2 , - Fig. 4
- ein erfindungsgemäßes Adapterstück für den Gegenstand nach
Fig. 1 , - Fig. 5
- ein erfindungsgemäßes Mantelsegment für den Gegenstand nach
Fig. 1 in einem Längsschnitt, - Fig. 6
- einen Ausschnitt aus dem Gegenstand nach
Fig. 1 in perspektivischer Ansicht, - Fig. 7
- den Gegenstand nach
Fig. 6 in einer anderen Ansicht in teilweise demontiertem Zustand,
- Fig. 8
- eine weitere Ausführungsform der Erfindung,
- Fig. 9
- eine abgewandelte Ausführungsform der Erfindung und
- Fig. 10
- eine andere Ausführungsform der Erfindung.
- Fig. 1
- a simplified longitudinal section through an eccentric screw pump according to the invention,
- Fig. 2
- a longitudinally divided stator according to the invention in an end view,
- Fig. 3
- cut AB through the object
Fig. 2 . - Fig. 4
- an inventive adapter piece for the object
Fig. 1 . - Fig. 5
- an inventive shell segment for the object
Fig. 1 in a longitudinal section, - Fig. 6
- a section of the object after
Fig. 1 in perspective view, - Fig. 7
- the object after
Fig. 6 in another view partially disassembled,
- Fig. 8
- a further embodiment of the invention,
- Fig. 9
- a modified embodiment of the invention and
- Fig. 10
- another embodiment of the invention.
In den Figuren ist eine Exzenterschneckenpumpe dargestellt, welche in ihrem grundsätzlichen Aufbau einen Stator 1 aus einem elastischen Material und einen in dem Stator 1 gelagerten Rotor 2 aufweist, wobei der Stator 1 zumindest bereichsweise von einem Statormantel 3 umgeben ist. Ferner weist die Pumpe ein Sauggehäuse 4 sowie einen Anschlussstutzen 5 auf, welcher auch als Druckstutzen bezeichnet wird. Nicht dargestellt ist ein ebenfalls vorgesehener Antrieb, wobei der Antrieb über eine lediglich angedeutete Kupplungsstange 6 auf den Rotor 2 arbeitet. Die Kupplungsstange ist über Kupplungsgelenke einerseits an den Rotor 2 und andererseits an die nicht dargestellte Antriebeswelle angeschlossen, wobei von den Kupplungsgelenken lediglich das rotorseitige Gelenk 7 dargestellt ist. Die Pumpe ist üblicherweise auf einer lediglich angedeuteten Grundplatte 8 montiert, wobei es sich insoweit um eine mit der Pumpe ausgelieferte Grundplatte oder auch eine anwenderseitig vorhandene Grundplatte handeln kann. Der Stator 1 ist in an sich bekannter Weise mit seinem einen Ende an einem Anschlussflansch 9 des Sauggehäuses 4 und mit seinem anderen Ende an einen Anschlussflansch 10 des Anschlussstutzens 5 angeschlossen. Dabei erfolgt der Anschluss bei dem dargestellten Ausführungsbeispiel nicht unmittelbar an diese Anschlussflansche 9, 10, sondern unter Zwischenschaltung jeweils eines Adapterstückes 11, 12, dessen Aufbau im Folgenden noch näher erläutert wird. Diese Adapterstücke werden auch als Zentrierringe bezeichnet.In the figures, an eccentric screw pump is shown, which in its basic structure has a
Erfindungsgemäß ist der Stator 1 nun als längsgeteilter Stator ausgebildet und besteht dazu aus zwei Stator-Teilschalen 1 a, 1 b, welche im Ausführungsbeispiel Halbschalen bilden, die jeweils einen Winkel von 180° überdecken. Längsgeteilt meint, entlang der Statorlängsachse L bzw. parallel zu dieser. Der Trennschnitt zwischen den Teilschalen verläuft folglich entlang bzw. parallel zu der Längsachse L.According to the
Diese längsgeteilte Ausgestaltung des elastomeren Stators ermöglicht es, den Stator 1 bei montiertem Sauggehäuse 4, Druckstutzen 5 und Rotor 2 zu demontieren und zu montieren, da der Stator 1 nicht - wie beim Stand der Technik - z.B. nach Entfernen des Druckstutzens 5 von einer Seite auf den Rotor 2 aufgeschoben werden muss.This longitudinally divided configuration of the elastomeric stator makes it possible to disassemble and mount the
Um trotz dieser geteilten Bauweise eine ausreichende Dichtigkeit des Stators zu gewährleisten, weist der Stator 1 bzw. dessen Stator-Teilschalen 1 a, 1 b endseitig Dichtungsflächen 13, 14 (bzw. 13', 14') auf. Die Stator-Teilschalen 1a, 1 b sind dann (nacheinander) mit ihren endseitigen Dichtungsflächen 13, 14 in Statoraufnahmen 15, 16 einsteckbar oder mit Dichtungsflächen 13', 14' auf solche Statoraufnahmen 15', 16' aufsteckbar, wobei diese Statoraufnahmen bei dem hier dargestellten Ausführungsbeispiel mit Adapterstücken an diesen Adapterstücken 11, 12 vorgesehen sind. Die Adapterstücke 11, 12 selbst sind in an sich bekannte Aufnahmen von einerseits Sauggehäuse 4 und andererseits Druckstutzen 5 einsetzbar, so dass Sauggehäuse 4 einerseits und Druckstutzen 5 andererseits in herkömmlicher Bauweise ausgebildet sein können und folglich auch mit herkömmlichen einteiligen Statoren verwendet werden können. Die endseitigen Dichtungsflächen 13, 14 (bzw. 13', 14') des Stators 1 sind konisch bzw. als Kegelmantelflächen ausgebildet, und zwar bei der Ausführungsform nach
Die außenseitig an den Stator 1 anliegende Mantelsegmente 19 weisen endseitig Befestigungsflansche 20 für die Befestigung der Mantelsegmente 19 an den Adapterstücken 11, 12 auf. Diese Befestigungsflansche 20 übergreifen das Adapterstück 11, 12. In
Ferner weisen die Stator-Teilschalen 1a, 1 b jeweils zumindest eine außenseitig vorkragende Verdrehsicherung 25 auf, welche im Ausführungsbeispiel als sich über nahezu die gesamte Statorlänge erstreckende Längs-Stege 25 ausgebildet sind, welche außenseitig an den Stator angeformt, z.B. anvulkanisiert sind. Insbesondere
Im Zuge der Fertigung wird der erfindungsgemäße längsgeteilte Stator 1 vorzugsweise zunächst als einteiliger Stator 1 gefertigt und anschließend aufgetrennt, z.B. im Wege des Wasserstrahlschneidens. Dieses ermöglicht eine einfache und kostengünstige Fertigung.In the course of production, the longitudinally divided
Die
Ergänzend ist in
Schließlich zeigt
Claims (11)
- A progressive cavity pump having at least one stator (1) made of an elastic material and a rotor (2), which is mounted in the stator (1),
having a suction housing (4) and a connecting part (5), the stator being attached at one end to an attachment flange (9) of the suction housing (4) and being attached at its other end to an attachment flange (10) of the connecting part,
wherein the stator (1) is at least partially enclosed by a stator jacket (3), the stator (1), as a longitudinally-divided stator, comprises at least two stator partial shells (1, 1 b),
terminal sealing surfaces (13, 14, 13', 14') of the stator (1) or the stator partial shells (1a, 1 b) can each be plugged into a stator receptacle (15, 16, 15', 16') of the attachment flange (9, 10) or an adapter part (11, 12) or can be plugged thereon,
the stator (1) has terminal conical, e.g., external conical or internal conical, sealing surfaces (13, 14, 13', 14'),
the stator receptacles (15, 16, 15', 16') of the attachment flanges or adapter parts have conical, e.g., external conical or internal conical, sealing collar surfaces (17, 18, 17', 18'),
the stator jacket (3) is implemented as a longitudinally-divided jacket and has at least two, preferably four jacket segments (19), and
the jacket segments (19) of the stator jacket (3) form a stator clamping device, using which the stator (1) can be clamped in the radial direction against the rotor (2). - The progressive cavity pump according to Claim 1, characterized in that the stator (1) or the partial shells (1a, 1 b) are attached to the attachment flange or flanges (9, 10) with one or more adapter parts (11, 12) interposed.
- The progressive cavity pump according to Claim 1 or 2, characterized in that the cone angle (α) of the sealing surfaces (13, 14) and/or the sealing counter surfaces (17, 18, 17', 18') is approximately 10° to 50°, preferably 20° to 30°.
- The progressive cavity pump according to one of Claims 1 to 3, characterized in that the jacket segments (19) which press externally against the stator (1) have, e.g., terminal fastening flanges (20) for the fastening on the attachment flange (9, 10) or the adapter part (11, 12).
- The progressive cavity pump according to Claim 4, characterized in that the fastening flanges (20) are attached to the attachment flange (9, 10) or the adapter part (11, 12) using clamping means (21) for the purpose of clamping the stator.
- The progressive cavity pump according to Claim 5, characterized in that the clamping means (21) are implemented as clamping screw devices (22, 23).
- The progressive cavity pump according to one of Claims 4 to 6, characterized in that the fastening flanges are attached to the attachment flange (9, 10) or the adapter part (11, 12) with an adjustable ring gap (R).
- The progressive cavity pump according to one of Claims 4 to 7, characterized in that the fastening flanges (20) overlap or encompass the attachment flange (9, 10) or the adapter part (11, 12).
- The progressive cavity pump according to one of Claims 1 to 8, characterized in that one or more, preferably all stator partial shells (1a, 1 b) each have at least one externally protruding twist lock (25).
- The progressive cavity pump according to Claim 9, characterized in that the twist lock (25) is implemented as a longitudinal web (25) which is externally attached, e.g., molded onto, the stator partial shells.
- The progressive cavity pump according to Claim 10, characterized in that the longitudinal web (25) has terminal stops (26) as an axial safeguard.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PL08785517T PL2176552T3 (en) | 2007-08-17 | 2008-08-13 | Eccentric worm pump with split stator |
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102007039062 | 2007-08-17 | ||
| DE102008011690 | 2008-02-28 | ||
| DE102008021920A DE102008021920A1 (en) | 2007-08-17 | 2008-05-02 | Eccentric spiral pump has stator of flexible material and rotor supported in stator, where stator is area wise surrounded by stator core having two stator fitting lines |
| PCT/EP2008/006641 WO2009024279A1 (en) | 2007-08-17 | 2008-08-13 | Eccentric worm pump with split stator |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2176552A1 EP2176552A1 (en) | 2010-04-21 |
| EP2176552B1 true EP2176552B1 (en) | 2012-05-16 |
Family
ID=39942685
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP08785517A Active EP2176552B1 (en) | 2007-08-17 | 2008-08-13 | Eccentric worm pump with split stator |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8439659B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP2176552B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2010537095A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN101796301B (en) |
| BR (1) | BRPI0815403A2 (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2387834T3 (en) |
| PL (1) | PL2176552T3 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2009024279A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US12152588B1 (en) | 2023-05-26 | 2024-11-26 | Grant Prideco, Inc. | Free-mold stator for a progressing cavity pump |
Families Citing this family (37)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8182252B2 (en) | 2007-10-30 | 2012-05-22 | Moyno, Inc. | Progressing cavity pump with split stator |
| US8215014B2 (en) | 2007-10-31 | 2012-07-10 | Moyno, Inc. | Method for making a stator |
| FR2948424B1 (en) * | 2009-07-23 | 2017-07-21 | Pcm | PROGRESSIVE CAVITY PUMP AND ASSOCIATED PUMPING DEVICE |
| CN101892982B (en) * | 2010-06-28 | 2012-06-20 | 中国石油大学(北京) | Single-screw metal screw pump stator and processing method for inner helical surface thereof |
| JP5331253B2 (en) * | 2010-08-25 | 2013-10-30 | 古河産機システムズ株式会社 | Stator seal structure in uniaxial eccentric screw pump |
| DE102010037440B4 (en) | 2010-09-09 | 2014-11-27 | Seepex Gmbh | Cavity Pump |
| CN102062089A (en) * | 2010-12-24 | 2011-05-18 | 新疆华易石油工程技术有限公司 | Method for machining full metal screw pump stator |
| DE102012112044B4 (en) * | 2012-05-04 | 2015-10-08 | Netzsch Pumpen & Systeme Gmbh | Self-fixing stator housing |
| US8967985B2 (en) | 2012-11-13 | 2015-03-03 | Roper Pump Company | Metal disk stacked stator with circular rigid support rings |
| KR101864972B1 (en) * | 2013-10-29 | 2018-06-05 | 헤이신 엘티디. | Uniaxial eccentric screw pump |
| JP6349565B2 (en) | 2014-01-28 | 2018-07-04 | 兵神装備株式会社 | Uniaxial eccentric screw pump |
| JP6349566B2 (en) * | 2014-01-28 | 2018-07-04 | 兵神装備株式会社 | Uniaxial eccentric screw pump |
| DE102014112552B4 (en) * | 2014-09-01 | 2016-06-30 | Seepex Gmbh | Cavity Pump |
| DE102014112550B4 (en) * | 2014-09-01 | 2016-06-16 | Seepex Gmbh | Cavity Pump |
| DE102015112248A1 (en) * | 2015-01-29 | 2016-08-04 | Netzsch Pumpen & Systeme Gmbh | Eccentric screw pump and method for adjusting the operating state of an eccentric screw pump |
| CN105351184A (en) * | 2015-11-23 | 2016-02-24 | 重庆高研泵业有限公司 | Safety screw pump |
| CZ306826B6 (en) * | 2016-04-01 | 2017-07-26 | Petr Havránek | A device for pumping liquids and a replacement part for it |
| DE102017100540B4 (en) | 2017-01-12 | 2018-09-06 | Seepex Gmbh | Cavity Pump |
| EP3382203B1 (en) * | 2017-03-30 | 2024-05-15 | Roper Pump Company LLC | Progressive cavity pump with integrated heating jacket |
| EP3473856B1 (en) * | 2017-10-20 | 2020-12-30 | Circor Pumps North America, Llc. | Dismounting device for progressive cavity pumps |
| DE102018102640A1 (en) | 2018-02-06 | 2019-08-08 | Seepex Gmbh | Cavity Pump |
| DE102018106228A1 (en) | 2018-03-16 | 2019-09-19 | Seepex Gmbh | Plant for conveying pasty material |
| DE102018113347A1 (en) | 2018-06-05 | 2019-12-05 | Seepex Gmbh | Method for determining or monitoring the condition of an eccentric screw pump |
| CN110410316B (en) * | 2019-09-05 | 2024-06-11 | 无锡恒信北石科技有限公司 | Novel driving and lifting device of high-stability all-metal conical screw pump |
| JP6824537B1 (en) * | 2019-09-24 | 2021-02-03 | 兵神装備株式会社 | Uniaxial eccentric screw pump |
| DE102019130981A1 (en) | 2019-11-15 | 2021-05-20 | Seepex Gmbh | Eccentric screw pump |
| EP3825552B1 (en) * | 2019-11-22 | 2025-03-12 | Grundfos Holding A/S | Eccentric screw pump |
| DE102021112419A1 (en) | 2021-05-12 | 2022-11-17 | Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Körperschaft des öffentlichen Rechts | Pump for conveying a medium and monitoring method |
| DE102021112422A1 (en) | 2021-05-12 | 2022-11-17 | Seepex Gmbh | Pump for conveying a medium and monitoring method |
| DE102021132549A1 (en) | 2021-12-09 | 2023-06-15 | Seepex Gmbh | Articulated joint, rotating unit and progressive cavity pump |
| DE102021132561A1 (en) | 2021-12-09 | 2023-06-15 | Seepex Gmbh | Articulated joint, rotating unit and progressive cavity pump |
| DE102022118485B3 (en) * | 2022-07-25 | 2023-12-21 | Netzsch Pumpen & Systeme Gmbh | System for clamping a dip tube of a tank pump in an end connection |
| DE102022119147A1 (en) | 2022-07-29 | 2024-02-01 | Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Körperschaft des öffentlichen Rechts | Method for determining or monitoring the flow rate of an eccentric screw pump |
| DE102022134734A1 (en) | 2022-12-23 | 2024-07-04 | Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Körperschaft des öffentlichen Rechts | Method for controlling an eccentric screw pump |
| AU2024280427A1 (en) * | 2023-05-26 | 2026-01-15 | Grant Prideco, Inc. | Progressive cavity pump |
| FR3153383A1 (en) * | 2023-09-22 | 2025-03-28 | Pcm Technologies | Pumping device |
| FR3164507A1 (en) | 2024-07-09 | 2026-01-16 | Pcm Technologies | Stator jacketing, stator, and method for manufacturing a stator jacket |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1995352U (en) * | 1965-04-09 | 1968-10-24 | Oskar Seidl | HOUSING FOR ECCENTRIC SCREW PUMPS. |
| DE2754913A1 (en) * | 1977-12-09 | 1979-06-13 | Streicher Foerdertech | Stages near stator discs of eccentric disc pump - are coupled at angle half that between rotor discs of same stages |
| DE2817280A1 (en) * | 1978-04-20 | 1979-10-25 | Streicher Foerdertech | STATOR FOR ECCENTRIC SCREW PUMPS |
Family Cites Families (29)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR1488652A (en) * | 1967-10-25 | |||
| US2527670A (en) * | 1946-04-04 | 1950-10-31 | Robbins & Myers | Helical pump |
| US3354537A (en) * | 1965-12-01 | 1967-11-28 | Walter J O'connor | Renewable moineau-type pumping mechanism |
| US3512904A (en) * | 1968-05-24 | 1970-05-19 | Clifford H Allen | Progressing cavity helical pump |
| US3603407A (en) * | 1969-12-29 | 1971-09-07 | Wallace Clark | Well drilling apparatus |
| US3643877A (en) * | 1970-01-28 | 1972-02-22 | Robbins & Myers | Pump with macerator |
| DE2313261C3 (en) * | 1973-03-16 | 1980-08-14 | Sumitomo Heavy Industries, Ltd., Tokio | Eccentric screw pump |
| SU1012647A1 (en) * | 1980-09-12 | 1984-02-23 | Пермский Филиал Всесоюзного Ордена Трудового Красного Знамени Научно-Исследовательского Института Буровой Техники | Pivotal clutch (modifications) |
| US4499561A (en) * | 1982-12-06 | 1985-02-12 | Hoge, Warren, Zimmerman Company | Apparatus for continuously producing a dry material and liquid slurry |
| US5615801A (en) * | 1990-06-06 | 1997-04-01 | The Coca-Cola Company | Juice concentrate package for postmix dispenser |
| FR2683001B1 (en) * | 1991-10-23 | 1994-02-04 | Andre Leroy | AXIAL VOLUMETRIC MACHINE. |
| GB9303507D0 (en) * | 1993-02-22 | 1993-04-07 | Mono Pumps Ltd | Progressive cavity pump or motors |
| JPH0777172A (en) | 1993-09-03 | 1995-03-20 | Heishin Sobi Kk | Uniaxial eccentric screw pump |
| DE4413818A1 (en) * | 1994-04-20 | 1995-10-26 | Artemis Kautschuk Kunststoff | Eccentric worm gear pump |
| US5769618A (en) * | 1995-09-25 | 1998-06-23 | Heishin Sobi Kabushiki Kaisha | Uniaxial eccentric screw pump having a flexible plastic shaft |
| US5688114A (en) * | 1996-03-20 | 1997-11-18 | Robbins & Myers, Inc. | Progressing cavity pumps with split extension tubes |
| DE19804259A1 (en) * | 1998-02-04 | 1999-08-12 | Artemis Kautschuk Kunststoff | Elastomer stator for eccentric screw pumps |
| DE19811889A1 (en) * | 1998-03-18 | 1999-09-30 | Usd Formteiltechnik Gmbh | Clamp |
| DE19847406C2 (en) * | 1998-10-14 | 2001-02-08 | Usd Formteiltechnik Gmbh | Stator for progressing cavity pumps |
| JP2001034054A (en) * | 1999-07-23 | 2001-02-09 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Powder transfer pump, toner supply device comprising the same, reused toner classification device, and image forming device |
| DE10207483C1 (en) * | 2002-02-22 | 2003-06-18 | Netzsch Mohnopumpen Gmbh | Eccentric peristaltic pump for viscous fluids has curved shaft connected between rotor and drive shaft with latter coaxial |
| DE10241753C1 (en) * | 2002-09-10 | 2003-11-13 | Netzsch Mohnopumpen Gmbh | Stator for eccentric screw pump has outside of hollow body defining rotor space enclosed by manrle assembled from linked segments |
| US7192260B2 (en) * | 2003-10-09 | 2007-03-20 | Lehr Precision, Inc. | Progressive cavity pump/motor stator, and apparatus and method to manufacture same by electrochemical machining |
| DE102004038477B3 (en) * | 2004-08-07 | 2005-10-06 | Netzsch-Mohnopumpen Gmbh | Cavity Pump |
| FR2876755B1 (en) * | 2004-10-20 | 2007-01-26 | Pcm Pompes Sa | PUMPING DEVICE WITH PROGRESSIVE CAVITY PUMP |
| DE102004060222A1 (en) * | 2004-12-15 | 2006-06-29 | Netzsch-Mohnopumpen Gmbh | Progressive cavity pump in compact design |
| US7396220B2 (en) * | 2005-02-11 | 2008-07-08 | Dyna-Drill Technologies, Inc. | Progressing cavity stator including at least one cast longitudinal section |
| DE102005013466B3 (en) * | 2005-03-21 | 2006-10-05 | Netzsch-Mohnopumpen Gmbh | jig |
| US7553139B2 (en) * | 2006-10-06 | 2009-06-30 | Moyno, Inc. | Progressing cavity pump with wobble stator and magnetic drive |
-
2008
- 2008-08-13 PL PL08785517T patent/PL2176552T3/en unknown
- 2008-08-13 US US12/671,508 patent/US8439659B2/en active Active
- 2008-08-13 ES ES08785517T patent/ES2387834T3/en active Active
- 2008-08-13 BR BRPI0815403-1A2A patent/BRPI0815403A2/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2008-08-13 WO PCT/EP2008/006641 patent/WO2009024279A1/en not_active Ceased
- 2008-08-13 JP JP2010520483A patent/JP2010537095A/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2008-08-13 CN CN2008801030280A patent/CN101796301B/en active Active
- 2008-08-13 EP EP08785517A patent/EP2176552B1/en active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1995352U (en) * | 1965-04-09 | 1968-10-24 | Oskar Seidl | HOUSING FOR ECCENTRIC SCREW PUMPS. |
| DE2754913A1 (en) * | 1977-12-09 | 1979-06-13 | Streicher Foerdertech | Stages near stator discs of eccentric disc pump - are coupled at angle half that between rotor discs of same stages |
| DE2817280A1 (en) * | 1978-04-20 | 1979-10-25 | Streicher Foerdertech | STATOR FOR ECCENTRIC SCREW PUMPS |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US12152588B1 (en) | 2023-05-26 | 2024-11-26 | Grant Prideco, Inc. | Free-mold stator for a progressing cavity pump |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| HK1144457A1 (en) | 2011-02-18 |
| JP2010537095A (en) | 2010-12-02 |
| US20100196182A1 (en) | 2010-08-05 |
| WO2009024279A1 (en) | 2009-02-26 |
| US8439659B2 (en) | 2013-05-14 |
| ES2387834T3 (en) | 2012-10-02 |
| CN101796301B (en) | 2013-05-15 |
| CN101796301A (en) | 2010-08-04 |
| BRPI0815403A2 (en) | 2015-02-03 |
| EP2176552A1 (en) | 2010-04-21 |
| PL2176552T3 (en) | 2012-10-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2176552B1 (en) | Eccentric worm pump with split stator | |
| DE102008021920A1 (en) | Eccentric spiral pump has stator of flexible material and rotor supported in stator, where stator is area wise surrounded by stator core having two stator fitting lines | |
| EP2428680B1 (en) | Eccentric screw pump | |
| EP3538766B1 (en) | Eccentric screw pump | |
| DE102014112550B4 (en) | Cavity Pump | |
| EP3749861B2 (en) | Eccentric screw pump | |
| DE102008021919A1 (en) | Eccentric screw pump, has spacer ring arranged between stator and connection piece, where spacer ring is detachable for disassembly of stator and attached under interconnection of flat seals to stator and/or to connection piece | |
| WO2010051870A1 (en) | Immersion motor | |
| DE102012008761A1 (en) | Divided stator jacket | |
| EP1233215A2 (en) | Ready to fit mechanical seal for the shaft of a pump | |
| WO2000068588A1 (en) | Receiving element for at least one shaft that is sealingly received in a housing | |
| DE102012112044B4 (en) | Self-fixing stator housing | |
| EP3266343B1 (en) | Brush unit for a brush roller for an abrasive blasting installation | |
| DE102004012396A1 (en) | Elastic shaft coupling | |
| DE102017100540B4 (en) | Cavity Pump | |
| DE202010012138U1 (en) | rotary | |
| DE968718C (en) | Vibrating screen | |
| DE102004040720A1 (en) | Eccentric screw pump for conveying e.g. liquid, has pump housing consisting of different housing units such as stator and suction housing, and separate fastening unit is supported at peripheral side of stator in axial direction | |
| DE202023100839U1 (en) | Lubricating ring, sealing device and extrusion device | |
| EP2535591B1 (en) | Centrifugal pump | |
| DE9101893U1 (en) | Split lid | |
| DD291939A5 (en) | ARRANGEMENT FOR CONNECTING AND SEALING THE SEPARATOR PROVIDED BETWEEN PIPING AND HOUSING COMPONENTS | |
| DE20205206U1 (en) | Arrangement of a filter cartridge |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20091028 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA MK RS |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20101108 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 558236 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20120615 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502008007227 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20120719 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2387834 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20121002 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D Effective date: 20120516 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120916 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120816 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: PL Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120817 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120917 Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120831 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20130219 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120831 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120831 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502008007227 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20130219 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120816 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120813 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120516 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120813 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080813 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 558236 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20130813 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130813 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20210819 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20220901 |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230524 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220901 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 502008007227 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: MURGITROYD GERMANY PATENTANWALTSGESELLSCHAFT M, DE |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20250902 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20250828 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Payment date: 20250729 Year of fee payment: 18 Ref country code: TR Payment date: 20250811 Year of fee payment: 18 Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20250826 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20250829 Year of fee payment: 18 Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20250825 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20250828 Year of fee payment: 18 |